- 1Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of In-forest Resource, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 2Southwest Research Center for Engineering Technology of Landscape Architecture (State Forestry and Grassland Administration), Kunming, Yunnan, China
Introduction: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (NFB) have a pivotal impact on the nitrogen cycle within agroforestry systems. The organic management of the Panax notoginseng (sanqi)-Pinus armandii agroforestry (SPA) system resulted in nitrogen deficiency because of the lack of application of chemical fertilizers. Therefore, assessing the variability in NFB due to the cultivation of sanqi in the SPA system becomes crucial.
Methods: The seasonal dynamics in the abundance, diversity, and community structure of NFB in the soil of monocropping pine (MP) and SPA systems were assessed using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and high-throughput sequencing technology.
Results and discussion: Sanqi cultivation triggered a decrease in the abundance of NFB but increased α diversity. Additionally, significant differences in the community structure of NFB were noted between the MP and SPA systems. Moreover, the abundance of Bradyrhizobium and Azospirillum increased in the soil after sanqi was cultivated. Furthermore, the cultivation of sanqi broadened the ecological niche breadth of NFB and increased the stochasticity in its community structure assembly (i.e., dispersal limitation). Additionally, the SPA system increased the network complexity but not the stability of NFB. The structural equation model (SEM) revealed that pH directly impacted the network complexity and stability of NFB in the SPA system. Sanqi cultivation positively influences the community characteristics of NFB in the soil in the SPA system. Our study provides new insights into nitrogen cycling and utilization in the SPA system.
Highlights
• Sanqi cultivation triggered a decrease in the abundance of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
• Sanqi cultivation increased the assembly stochasticity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
• The network complexity but not the stability of nitrogen-fixing bacteria was increased following Sanqi planting.
• pH directly impacted the network complexity and stability of nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
1 Introduction
Biological nitrogen fixation is an essential step of the nitrogen cycle (Levy-Booth et al., 2014) as it is the largest source of biologically-available nitrogen (Canfield et al., 2010) and the biggest contributor to the global reservoir of nitrogen of most terrestrial ecosystems (Galloway et al., 2004). Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (NFB) utilize nitrogenase to reduce atmospheric gaseous nitrogen (N2) to ammonia that is easily absorbed and utilized by plants (Rilling et al., 2018). The nifH gene encodes the ferritin subunit of nitrogenase, it is therefore essential for nitrogen fixation (Ininbergs et al., 2011) and serves as a marker gene for NFB in terrestrial ecosystems (Chen et al., 2019). Agriculture, forest, and agroforestry systems have the potential to annually fix 40–70, 55, and 246.4 Tg N (Cleveland et al., 1999; Vitousek et al., 2013; Kim and Isaac, 2022), respectively, via the activity of NFB. The elevated rate of nitrogen fixation in the agroforestry system is attributed to the enhanced utilization of nitrogen owing to the introduction of plants, which subsequently affects NFB (Dang et al., 2024). Therefore, the alterations in the abundance and community structure of NFB can be utilized as a reliable indicator for evaluating nitrogen cycling in different agroforestry systems (Wang S. S. et al., 2023) and reflect the status of nitrogen utilization in these systems (Zhong et al., 2022).
An agroforestry system combines trees and crops within the same land unit (Kwak et al., 2019), which notably impacts the NFB community (Solanki et al., 2017). Due to the introduction of different plant species, the abundance and diversity of NFB in the soil varied across the agroforestry systems. For instance, some agroforestry systems such as the red oak–soybean (Graungaard, 2015), poplar–wheat/sweet potato (Kong et al., 2015), and Hippophae rhamnoides–Pinus tabuliformis/Platycladus orientalis/Robinia pseudoacacia (Yang et al., 2015) systems can significantly enhance the abundance of NFB. By contrast, other agroforestry systems such as Macadamia ternifolia/Populus euphratica–Hordeum vulgare (Beule and Karlovsky, 2021; Wang R. L. et al., 2023) can either reduce or not exert any effect on the abundance of NFB. Moreover, the sugarcane–peanut/soybean agroforestry system remarkably enriched the diversity of NFB (Liu et al., 2021; Pang et al., 2022). Mulberry–alfalfa (Zhang et al., 2018), citrus–poplar (Gopal et al., 2021), tea–mung bean/adzuki bean (Wang D. L. et al., 2023), and tea–soybean/canola (Zhong et al., 2022) agroforestry systems notably altered the community composition of NFB concomitantly with an increase in the abundance of Proteobacteria, Rhizobium, and Burkholderia. These different findings can be attributable to alterations in environmental factors among the agroforestry systems, including soil metabolites (Qiao et al., 2024), edaphic factors (Kerfahi et al., 2016), plant species (Arafat et al., 2017), microbiome (Hayden et al., 2010), and enzyme activity (Xie et al., 2022). Additionally, seasonal dynamics had a notable influence on the abundance and diversity of NFB (Li H. P. et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2021). The seasonal dynamics directly/indirectly impact the communities of NFB in the soil by regulating energy influx, carbon source availability, and carbon source quality via variations in temperature and moisture (Pereira et al., 2013; Che et al., 2018). Briefly, a comprehensive assessment of the abundance and community structure of NFB in agroforestry systems and of the influencing factors establishes a theoretical foundation for improving nitrogen utilization through improved management practices in agroforestry systems.
Co-occurrence networks are critical for understanding the community structure of NFB, as they offer new insights beyond diversity and community composition, elucidating intricate interactions among community members (Wu et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2021). It has been established that plant introduction positively impacts the network properties of NFB in soil. For instance, a study on Alternanthera philoxeroides showed that demonstrated that its introduction substantially enhanced the network complexity and stability of NFB in soil (Li C. C. et al., 2022), potentially due to heightened nutrient effectiveness (Cao et al., 2020) and ecological niche differentiation (Zhang and Okabe, 2020). Furthermore, investigations into community assembly mechanisms can illuminate the shaping process of microbial communities (Zhou and Ning, 2017). It is widely acknowledged that both stochasticity (neutral theory) and determinism (ecological niche theory) jointly shape the community structure of NFB (Zhou et al., 2014), yet this balance can be affected by external factors such as pH (Fan et al., 2018b), fertilizer application (Feng et al., 2018), altitude (Wang et al., 2019), etc. However, the specific impact of Sanqi introduction on the co-occurrence network of NFB in SPA system and its underlying assembly mechanisms remain unclear.
Panax notoginseng (sanqi), mainly found in the Yunnan and Guangxi Provinces (Hei et al., 2024), is a precious perennial medicinal herb known for its antitumor (Leung et al., 2007), immunity–boosting (Liu et al., 1995), anti–inflammatory (Jiao D. L. et al., 2022), and blood pressure–lowering (Loh et al., 2019) effects. Compared to conventionally managed sanqi, the cultivation of sanqi under the forest understory in the Yunnan Province has been widely popularized (Hei et al., 2023) owing to the advantages it offers with respect to the alleviation of continuous cropping obstacles (Rui et al., 2024), quality enhancement of sanqi (Li et al., 2024), and the delivery of beneficial microorganisms for pine tree growth (Jia et al., 2022). The introduction of plants into agroforestry systems results in the consumption of a large quantity of nitrogen (Wakelin et al., 2010). However, the organic management of the sanqi-pine agroforestry (SPA) system without the application of chemical pesticides and fertilizers resulted in nitrogen deprivation. Moreover, the subtropical forests in the Yunnan Province, especially the monoculture pine (MP) forests, are subjected to significant nitrogen limitation (Luo et al., 2020). Presently, the impact of converting the MP forests to SPA systems on the community characteristics of the NFB remains uncertain. Therefore, we established MP and SPA systems and analyzed the seasonal dynamics in the abundance and community of NFB using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and high-throughput sequencing technology. Furthermore, we conducted an analysis on the association between NFB and edaphic factors. The research objectives of the current study include the following: (1) exploring the effects of sanqi cultivation on the abundance, diversity, and community structure of NFB, and (2) exploring the main factors that affect the NFB.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area and soil collection
The study site includes sanqi from the forest understory base located in Xundian County, Kunming (China) at an elevation of 2,199 meters (103°12′45″ E, 25°28′18″ N). The region experiences a monsoon climate, with an annual rainfall and average temperature of 1,900 mm and 14.5°C, respectively. Pinus armandii, the main species of tree that is predominantly found in this region, has a lifespan of 30 years, a canopy density ranging from 0.7 to 0.9, an average trunk diameter of 18 cm, and a height of 9.5 m. The plant-row spacing of sanqi planted in P. armandii forests is maintained at 10 to 15 cm by 10 to 15 cm. Furthermore, the planting density of sanqi in these pine forests is set at 14,000 plants per 667 m2. The method of cultivation and daily management practices for the sanqi from the forest understory were based on the findings reported by Hei et al. (2024).
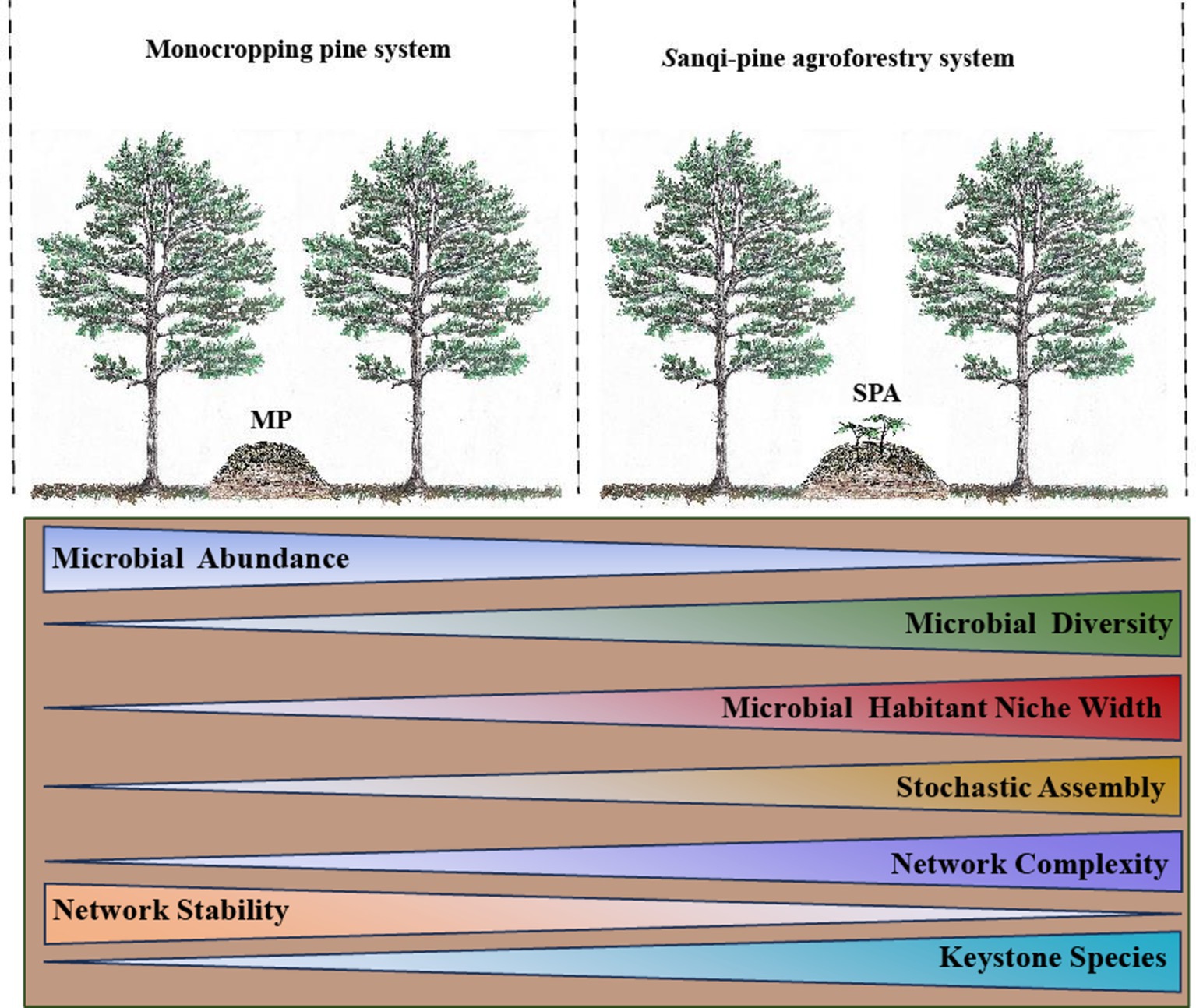
Tillage and ridging were carried out in the P. armandii forest followed by the establishment of control (MP) and treatment (SPA) systems without and with sanqi plantation, respectively (Supplementary Figure S1). Each treatment consisted of three 20 m × 20 m plots, totaling six plots. The soil samples were collected on the 10th and 20th of each month from September 2020 to August 2021, resulting in a total of 144 samples (6 plots × 12 months × 2 times/month). All soil samples were meticulously analyzed for their physicochemical properties and the abundance of NFB. Furthermore, we collected soil samples across four distinct sampling periods—10th October 2020 (autumn), 10th January 2021 (winter), 10th April 2021 (spring), and 10th July 2021 (summer)—for high-throughput sequencing analysis. Five soil cores, each ranging from 0 to 20 cm in depth, were collected from each plot utilizing the five-point sampling technique and then blended together to create a composite sample (Jia et al., 2024). Aliquots of the soil samples were rapidly transferred to the laboratory and stored at −4°C and − 80°C for subsequent analysis.
2.2 Analysis of edaphic factors
Soil temperature (ST) was determined at a depth of 0–20 cm with a chromium-plated soil thermometer (WNG-11, Tianjin Jixing Instrument Factory, China). Soil moisture (SM) was calculated by the difference between the wet and dry weights of the soil, while soil bulk density (BD) and water-filled pore space (WFPS) were obtained using the ring-knife technique. Soil pH was determined with a pH meter (AB23 PH-F, OHAUS, United States). The continuous flow analyzer (Auto Analyzer AA3, Seal, Germany) was used for determining the content of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+–N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−–N), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP). The soil was treated with hydrofluoric and perchloric acids for digestion, followed by the determination of total potassium (TK) using atomic emission spectroscopy with an AA-6300C flame photometer (SHIMADZU, Japan). The potassium dichromate oxidation method was used for estimating soil organic carbon (SOC).
2.3 qPCR analysis
DNA from the soil microbes was extracted from fresh soil samples (0.5 g) using the Fast DNA® SPIN Kit (MP Biomedical, United States) as per the manufacturer’s protocol. The concentration and quality of the isolated DNA were estimated according to standard methods (Jia et al., 2024). The quantification of NFB was conducted using the LightCycler® 480 II System (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The primer sequences and reaction conditions are specified in Supplementary Table S1. The target product containing nifH gene was isolated with a plasmid extraction kit (Takara), and its concentration was determined. The plasmid was then subjected to a tenfold serial dilution (10−1–10−7) to construct a standard curve with an amplification efficiency of 93.94% and a slope of −3.48. The initial copy number in the samples was established by comparing the Cp values of the amplified samples to that of the standard curve; the experiment was repeated thrice for each sample.
2.4 DNA extraction and sequencing
The procedure for DNA extraction and the primer sequences were consistent with those used for qPCR analysis, and the amplification conditions are recorded in Supplementary Table S1. After purification and quantification with the Gel Recovery Kit (Axygen Biosciences, USA) and QuantiFluor TMST (Promega, United States), respectively, the purified products were combined in an equimolar ratio as per the protocol provided and subsequently subjected to sequencing analysis.
Following the removal of the primers and barcode sequences, the raw data were subjected to quality control and assembly with fastp v.0.20.0 and FLASH v.1.2.11 software (Magoč and Salzberg, 2011; Chen et al., 2018), respectively. The sequences were grouped into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at a similarity threshold of 97% using UPARSE 7.1 software, followed by the removal of chimeras (Edgar, 2013). Subsequently, species classification for the sequences was performed in the nifH database with the RDP v 2.13 classifier (Gaby and Buckley, 2014), with the exclusion of OTUs from chloroplasts and mitochondria. The “VEGAN” package was utilized for the standardization of all samples (Dixon, 2003). The original sequence was deposited to the sequence read archive database (accession number: PRJNA1173392).
2.5 Statistical analysis
Pairwise Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed on the OTUs using the “psych” package, OTUs with |R| > 0.6 and p < 0.05 were retained (Zheng et al., 2021). The visualization of the co-occurrence network was conducted using Gephi v 0.9.2 software (Bastian et al., 2009). The approach suggested by Xu et al. (2023) was followed to evaluate the network complexity and stability (Wu et al., 2023). The critical nodes in the network (with Zi > 2.5 or Pi >0.62) were identified as their removal may lead to network collapse (Yuan et al., 2021).
The Chao1 and Shannon’s indices was calculated with Mothur v1.30.2 software. The “vegan” and “ggplot2” packages were employed to generate PCoA plots and stacked bar graphs for visualizing community structure and composition, respectively. SPSS 19.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States) was used for statistical analysis of soil characteristics, nifH gene abundance, α diversity (including Chao1 and Shannon index), and the relative abundance of major genera of NFB. To investigate the effect of soil properties on the community structure of NFB, we used the top 10 genera and soil physicochemical properties for redundancy analysis (RDA). The ecological niche breadth of the NFB was determined using the methodology detailed in Li et al. (2021). The neutral (Sloan et al., 2006) and null (RCBray index, Ning et al., 2020) models were utilized for inferring the mechanisms underlying the variation in community structure. The collinear clustering analysis of soil physical and chemical factors was carried out, and 9 key factors were found out from 11 factors. Random forest algorithms were performed using the packages “rfPermute” (Archer, 2016) and “A3” (Fortmann-Roe, 2015) to assess the variables (key factors) of network stability and model significance, respectively. The nutrient elements included TK, NH4+-N, and NO3−-N. Network complexity included node number and edge number, average degree, average path length, graph diameter, graph density and clustering coefficient. Network stability refers to the absolute value of negative/positive cohesion. Structural equation model (SEM) was constructed using Amos 28.0 (AMOS IBM) to determine the effects of pH, nutrient elements, α diversity, and network complexity on network stability. The model’s reliability was evaluated using the R2-value, Chi-square test, degrees of freedom, and p-value, root-mean-square error of approximation (RMSEA), and goodness-of-fit index (GFI).
3 Results
3.1 Edaphic properties of the soil
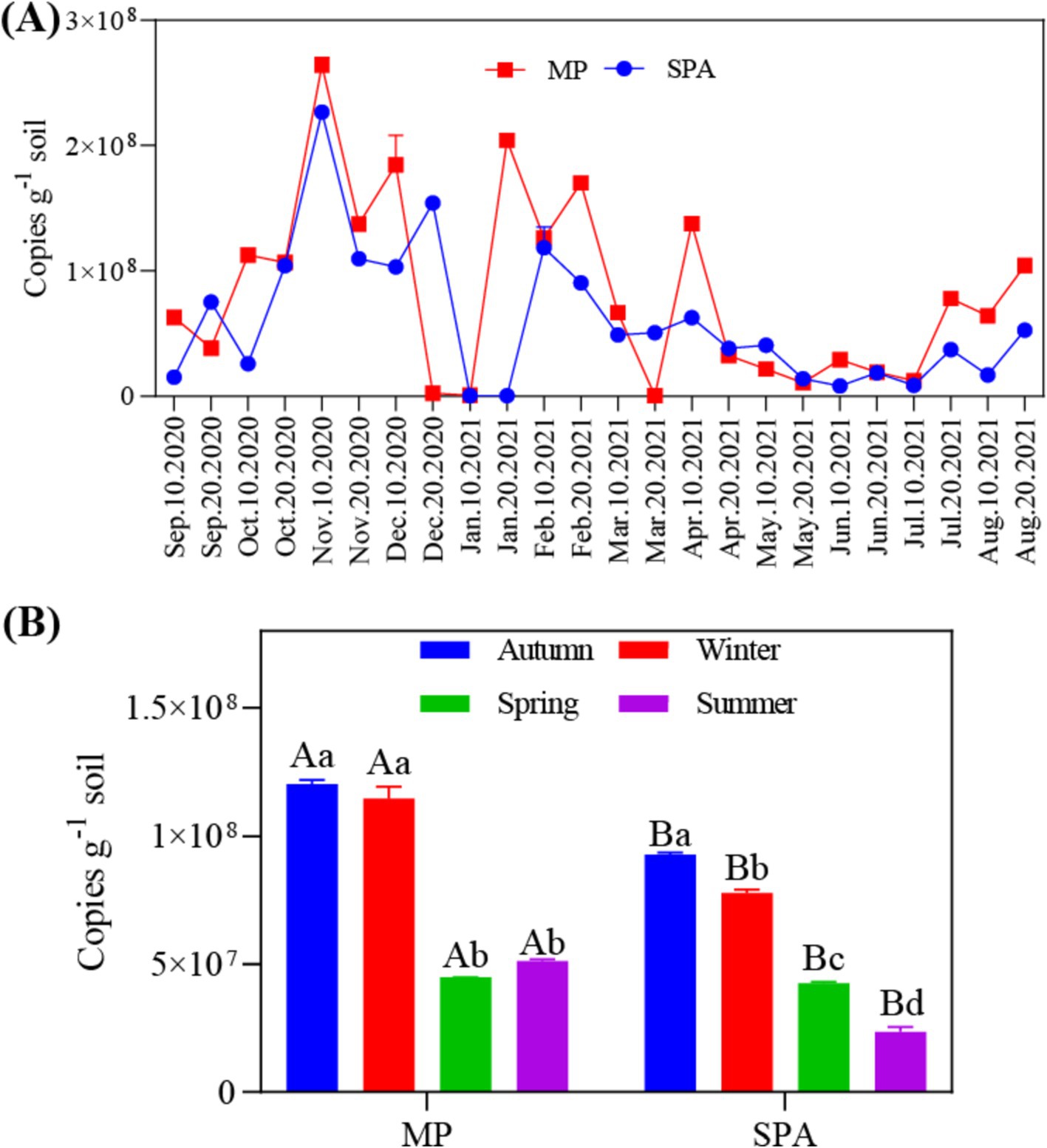
The average edaphic factors in the MP and SPA systems over the year was listed in Supplementary Table S2 and Figure S2. The ST, SM, BD, TN and WFPS as well as the contents of TK, NO3−–N, and SOC were significantly elevated in the soil of the SPA system compared to that of the MP system, while the pH and contents of TP, and NH4+–N were noticeably reduced (p < 0.05; Supplementary Table S2). In the MP system, the SM, WFPS, and the contents of TP and NH4+–N were the highest during autumn and lowest during spring (Supplementary Table S3). In the SPA system, soil pH and the contents of TN and NO3−–N were the highest during spring and lowest during summer (Supplementary Table S3).
3.2 Copy number of the nifH gene
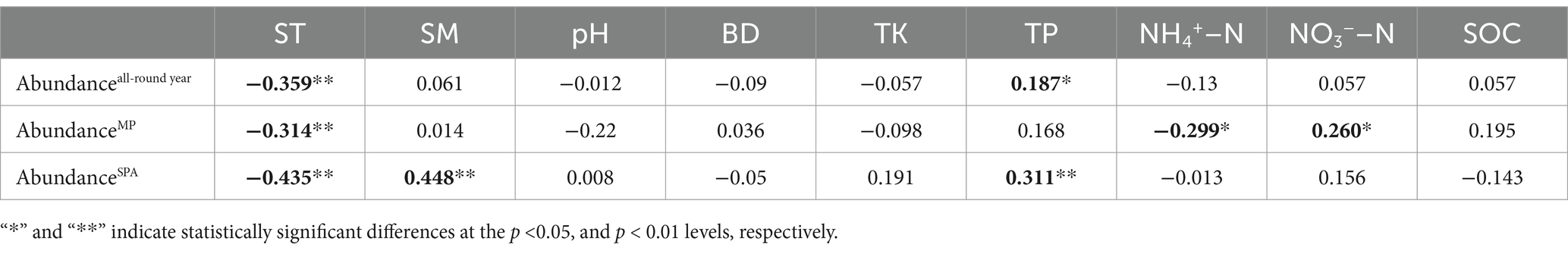
The data collected over the year revealed that the abundance of the nifH gene ranged from 4.22 × 105 to 2.70 × 108 and 4.03 × 105 to 2.28 × 108 copies g−1 soil in the MP and SPA systems, respectively (Figure 1A). The soil from the MP system exhibited significantly higher abundance of nifH than that of the SPA system (p < 0.01), with peak abundance of nifH recorded during autumn and winter (Figure 1B). Correlation analysis indicated that ST and TP were the essential factors that exhibited negative and positive correlation, respectively, with the abundance of NFB (p < 0.05; Table 1).
3.3 Analysis of diversity and community structure of NFB
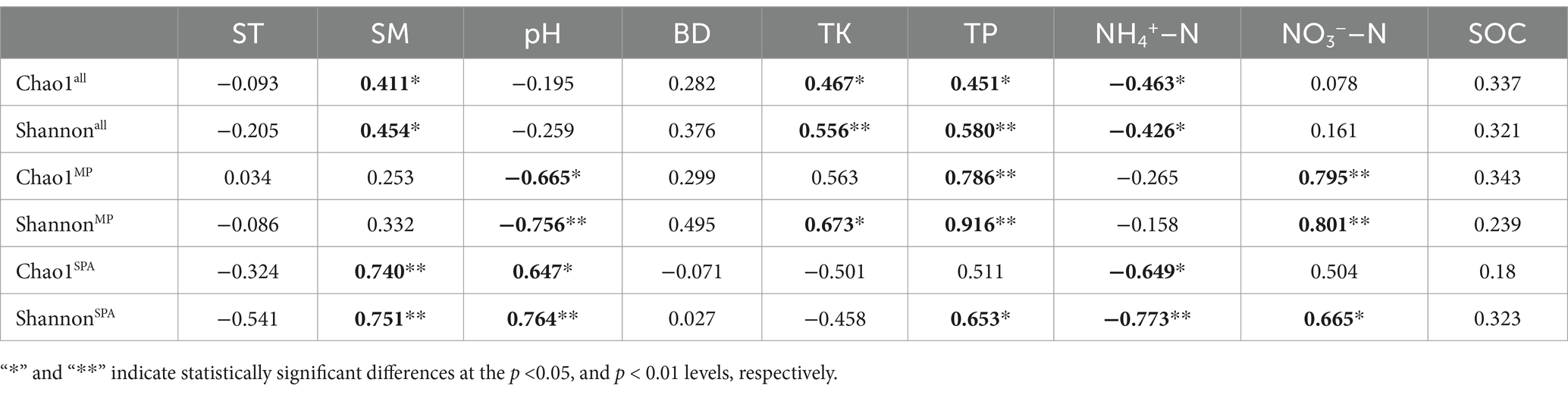
High-throughput sequencing was carried out using the microbial DNA isolated from soil sampled from the two systems in October 10th 2020, January 10th 2021, April 10th 2021, and July 10th 2021. The dilution curve demonstrated that the sequencing depth adequately encompassed most species of the nifH microbial community (Supplementary Figure S3). The α diversity (Chao1 and Shannon’s indices) was notably elevated in the SPA system compared to the MP system (p < 0.01; Figures 2A,B) and was lowest in summer (Figures 2C,D). Correlation analysis revealed that SM and the contents of TK, TP, and NH4+–N were the crucial factors regulating the α diversity of NFB (Table 2).
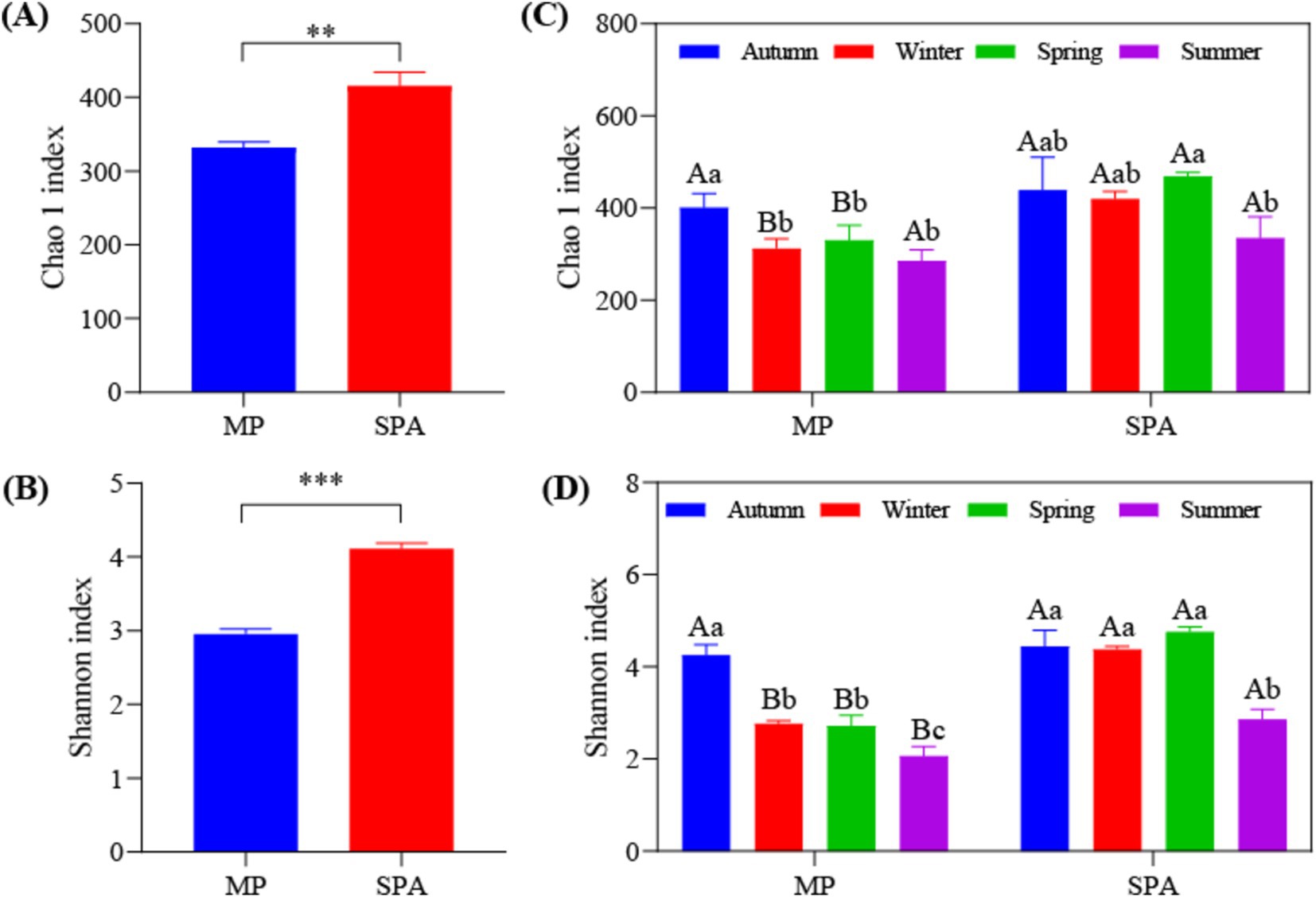
Figure 2. Analysis of α diversity of NFB in MP and SPA systems. Average of Chao1 (A) and Shannon (B) index; Seasonal changes of Chao1 (C) and Shannon (D) index.
The components PCoA1 and PCoA2 of the PCoA contributed to 43.65 and 19.40%, respectively, of the variability within the community structure of NFB. This finding suggests a substantial distinction between the two systems with respect to the component PCoA1. Permutation multivariate analysis of variance indicated that system exerted a more pronounced influence on community structure (R2 = 0.310, p < 0.01), followed by the season (R2 = 0.277, p < 0.01, Figure 3A; Supplementary Table S4). Redundancy analysis (RDA) demonstrated that SM, TP and NH4+–N were essential factors that shaped the community structure of NFB (p < 0.01; Supplementary Figure S4).
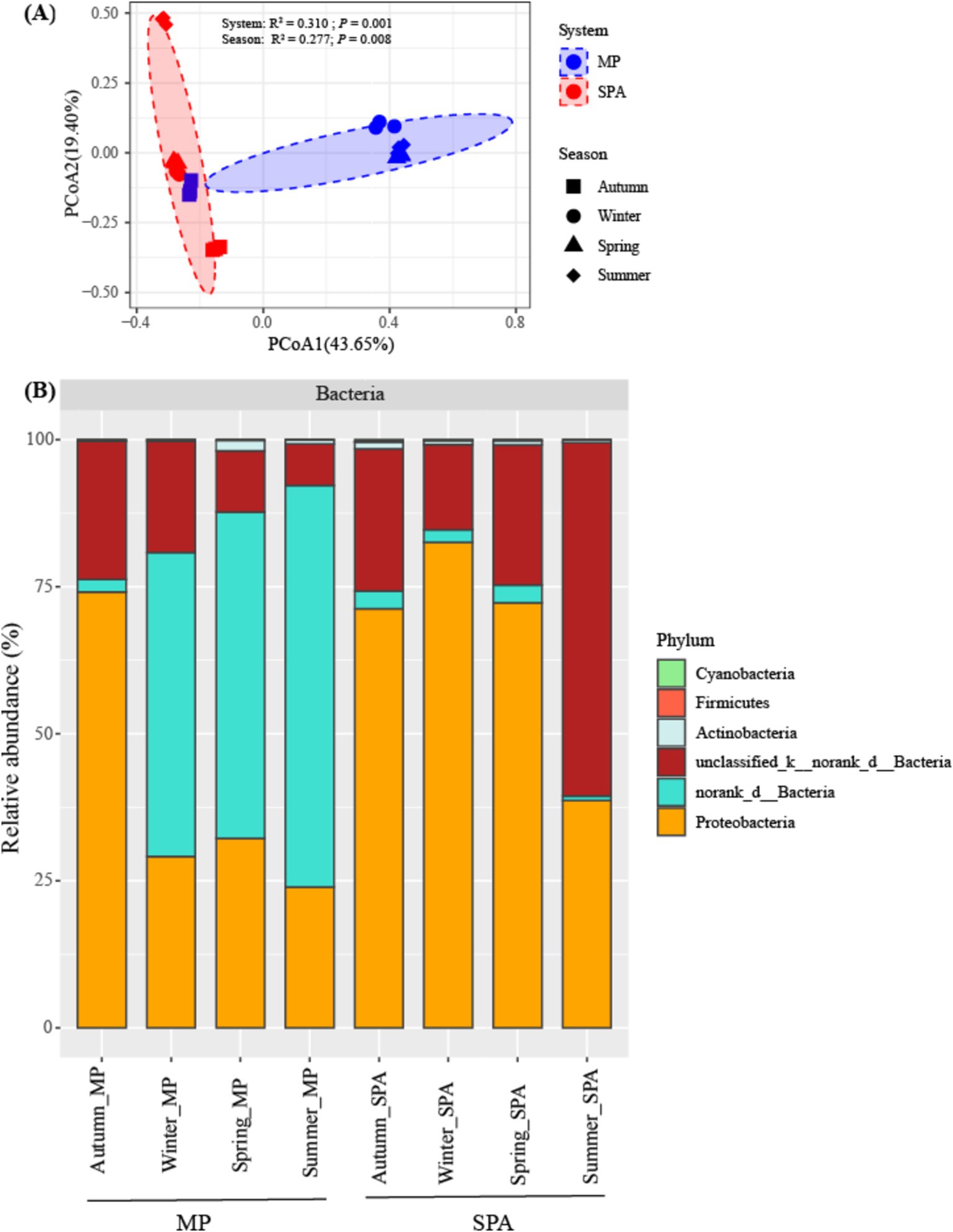
Figure 3. Analysis of the community structure (A), and composition (B) of the NFB at a phylum level.
The community composition of NFB was subsequently analyzed at the levels of phylum and genus. Six NFB phyla were identified, with the combined abundance of the top three dominant phyla (norank_d__Bacteria, unclassified_k__norank_d__Bacteria, and Proteobacteria) ranging from 98.08 to 99.70% (Figure 3B). Moreover, the relative abundance of five bacterial genera, namely Bradyrhizobium, Azospirillum, Anaeromyxobacter, Beijerinckia, and Xanthobacter, was dramatically higher in the SPA system compared to the MP system. By contrast, norank_d__Bacteria exhibited an opposite trend. Paraburkholderia, Frankia, and Sphingomonas did not display substantial variations between the two systems (Supplementary Table S5).
3.4 Evaluation of NFB assembly
The adaptability of the NFB to the environment was assessed by calculating the ecological niche breadth in the two systems. The results indicated significantly greater ecological niche breadth for the NFB in the SPA system compared to those in the MP system (p < 0.05, Figure 4A). Moreover, the neutral model accounted for 27.5 and 36.6% of the variation of NFB in the MP and SPA systems, respectively, suggesting that the cultivation of sanqi increased the assembly stochasticity of the community structure of NFB (Supplementary Figures S5A,B). The βNTI and RCBray indices further confirmed that drift and dispersal limitation were the main factors that shaped NFB communities in the MP and SPA systems, respectively (Figures 4B,C). In conclusion, the cultivation of sanqi significantly impacts the community structure of NFB.
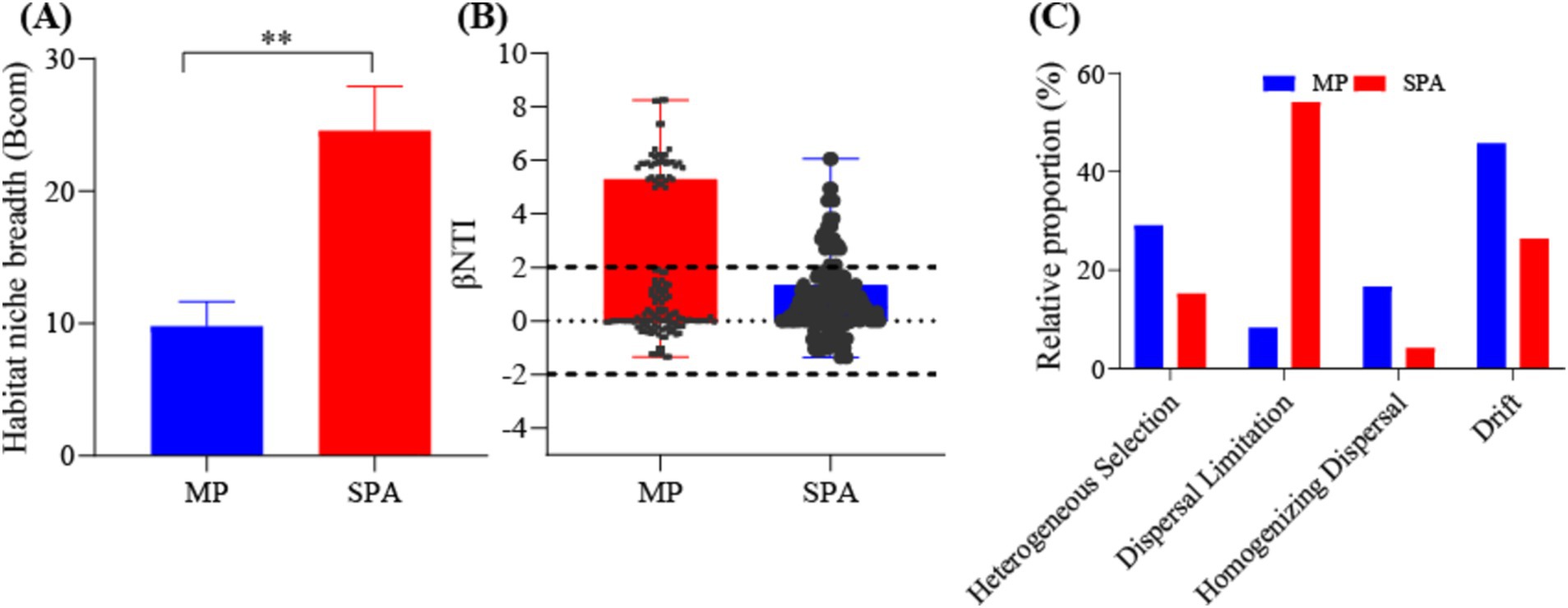
Figure 4. Analysis of the ecological niche breadth (A), βNTI index (B), and null-model (C) of NFB in the MP and SPA systems.
3.5 Co-occurrence network analysis of NFB communities
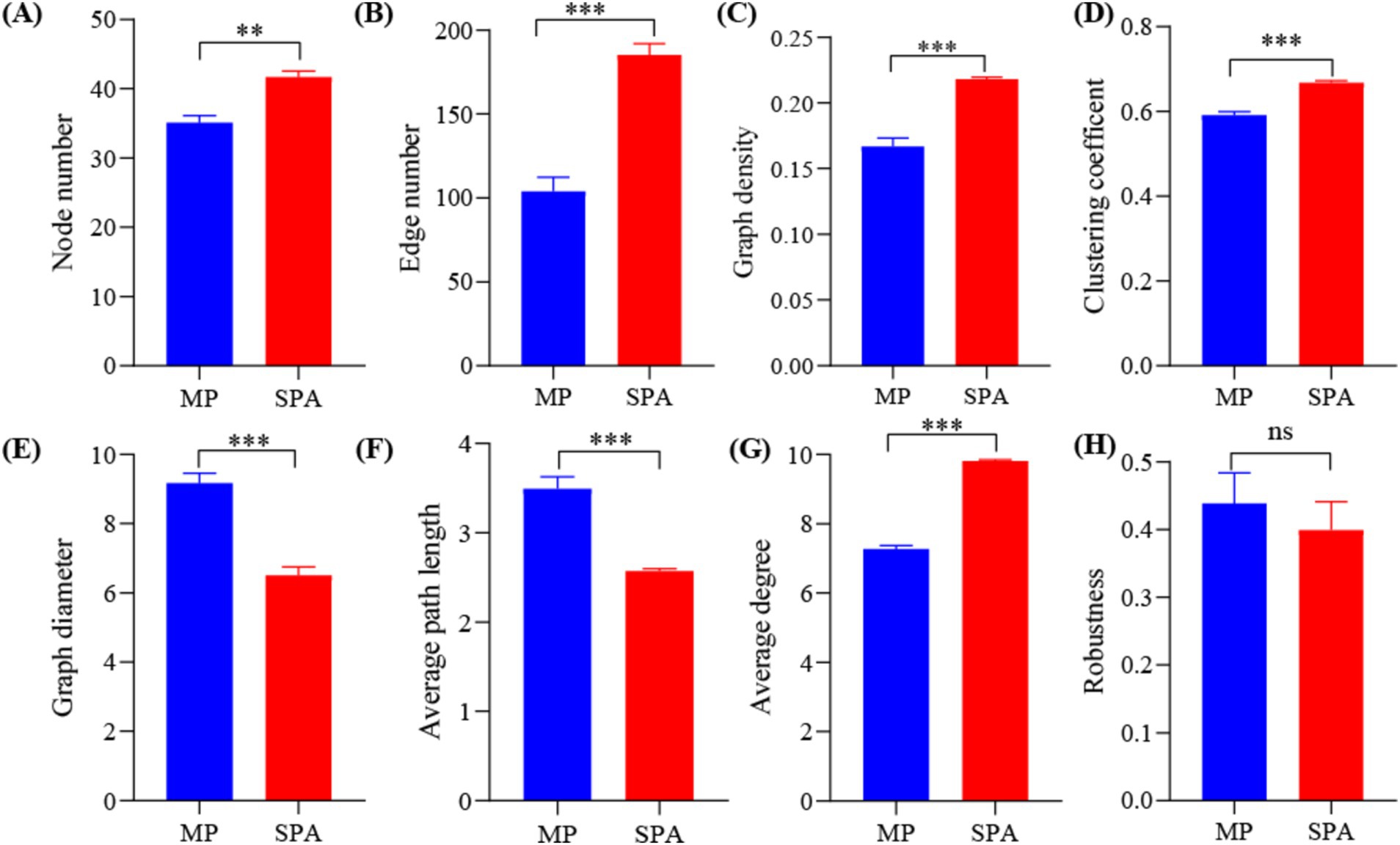
A NFB network based on the top 50 OTUs was constructed to describe the associations within the communities of both MP and SPA systems (Figure 5). The network complexity of NFB was found to be greater in the SPA system compared to the MP system (p < 0.05; Figures 6A–G), with no substantial impact on network stability (Figure 6H).
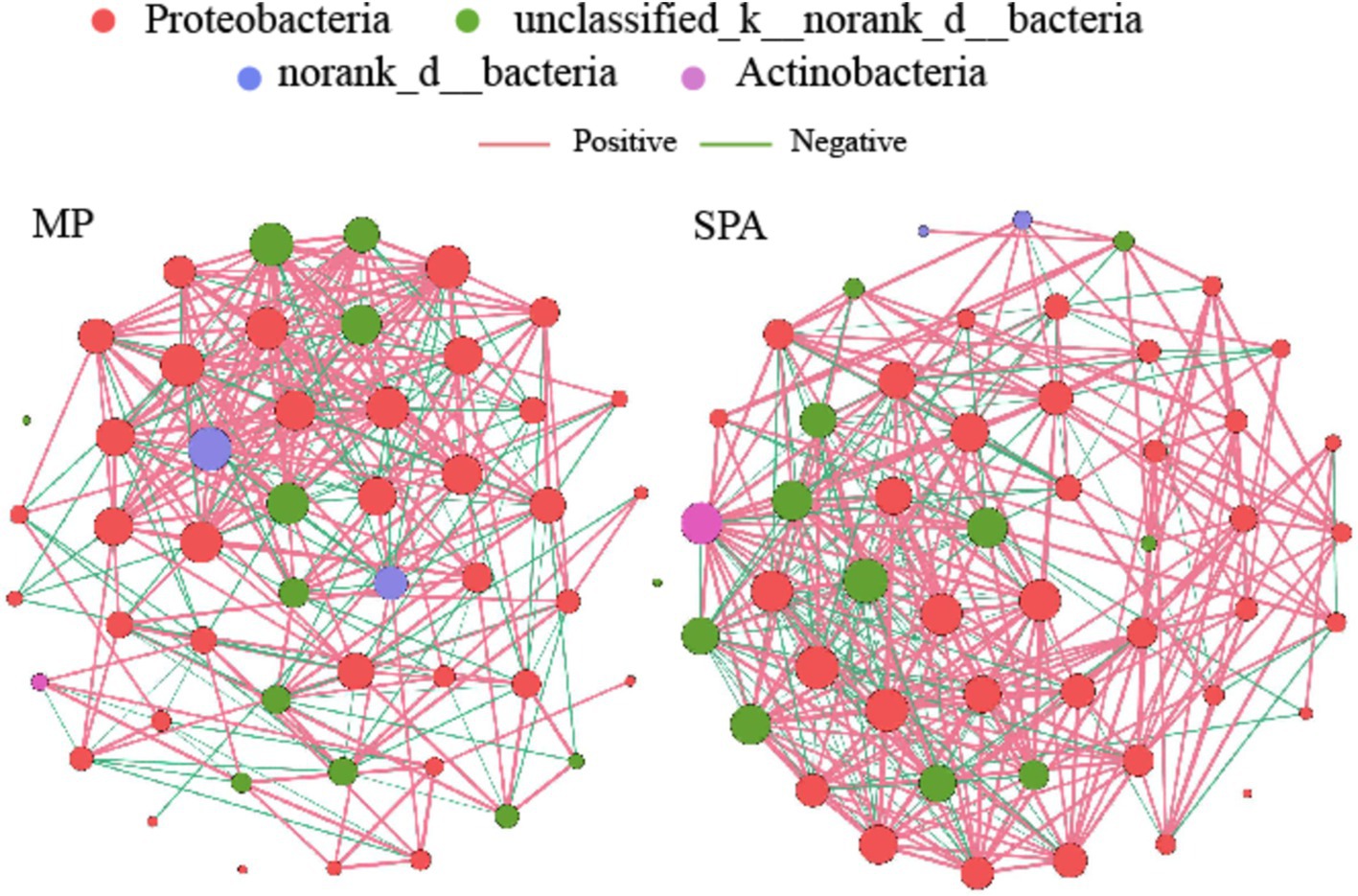
Figure 5. Co-occurrence networks of soil NFB communities in MP and SPA systems. Red and green lines represent positive and negative correlations, respectively.
The crucial nodes (OTU) in the network were determined through analysis of within-module (Zi) and between-module (Pi) interactions. Eleven connectors were detected in the two systems (Figures 7A,B; Supplementary Table S6). The three connectors (OTU1217, OTU1227, and OTU584) in the MP system were annotated as Rhizobiales, unclassified_k__norank_d__Bacteria, and norank_d__Bacteria, respectively. Additionally, the eight connectors (OTU1312, OTU1332, OTU1373, OTU510, OTU512, OTU532, OTU599, and OTU766) in the SPA system were assigned to the Rhizobiales (4), Burkholderiales (1), unclassified_p__Proteobacteria (2), and unclassified_k__norank_d__Bacteria (1), respectively.
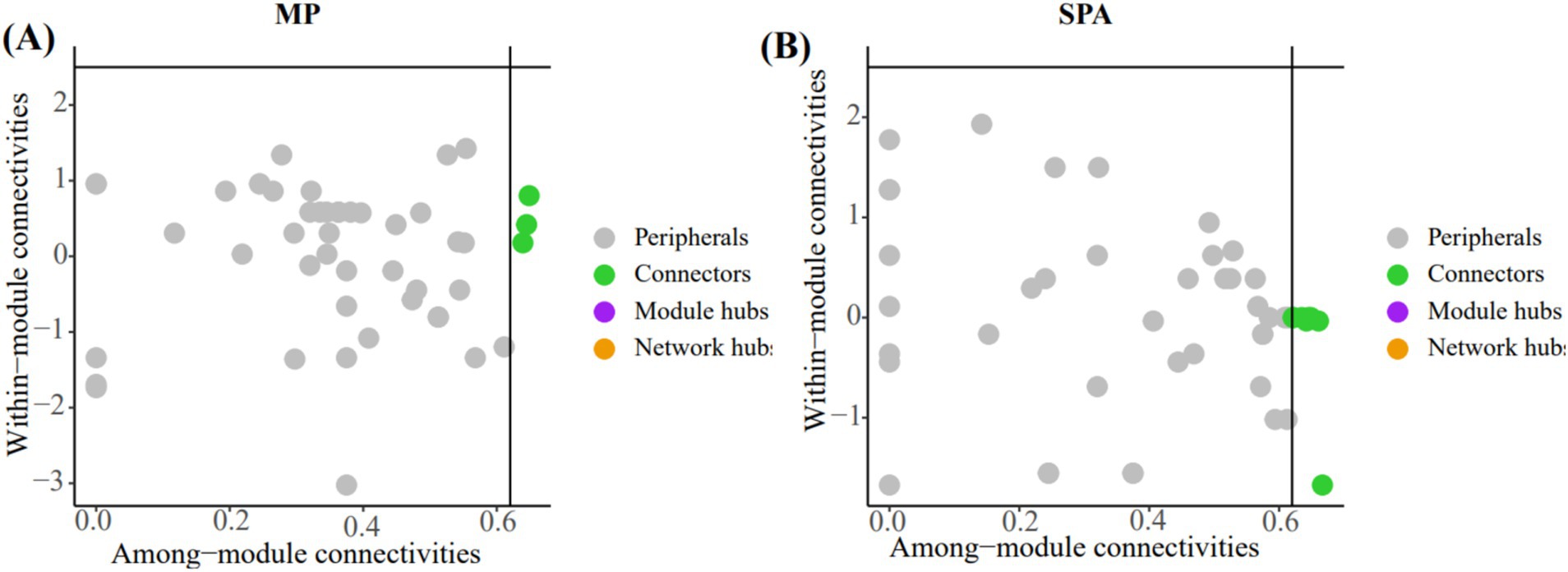
Figure 7. In analyzing the key OTUs in the soil NFB network of MP system (A) and SPA system (B) using the Zi-Pi method, the nodes (OTUs) in the green solid circles are defined as connectors.
3.6 SEM analysis
Random forest analysis indicated that pH, nutrient elements, α diversity, and network complexity significantly influenced network stability (p < 0.05; Supplementary Figure S6). The nutrient elements and network complexity directly enhanced network stability in the MP system, whereas α diversity exhibited the opposite effect. SEM analysis showed that pH negatively regulated α diversity in an indirect manner, which subsequently affected network stability (Figure 8A). By contrast, the soil pH and nutrient elements directly impacted network stability in a positive manner in the SPA system (Figure 8B). Moreover, pH negatively regulated nutrient elements in an indirect manner, thereby affecting network stability positively. According to the normalized total effect, pH and network complexity have positive effects on network stability in MP systems, while nutrient elements and α diversity have negative effects on network stability (Figure 8C). In SPA systems, pH, nutrient elements, α diversity, and network complexity all contribute positively to network stability (Figure 8D).
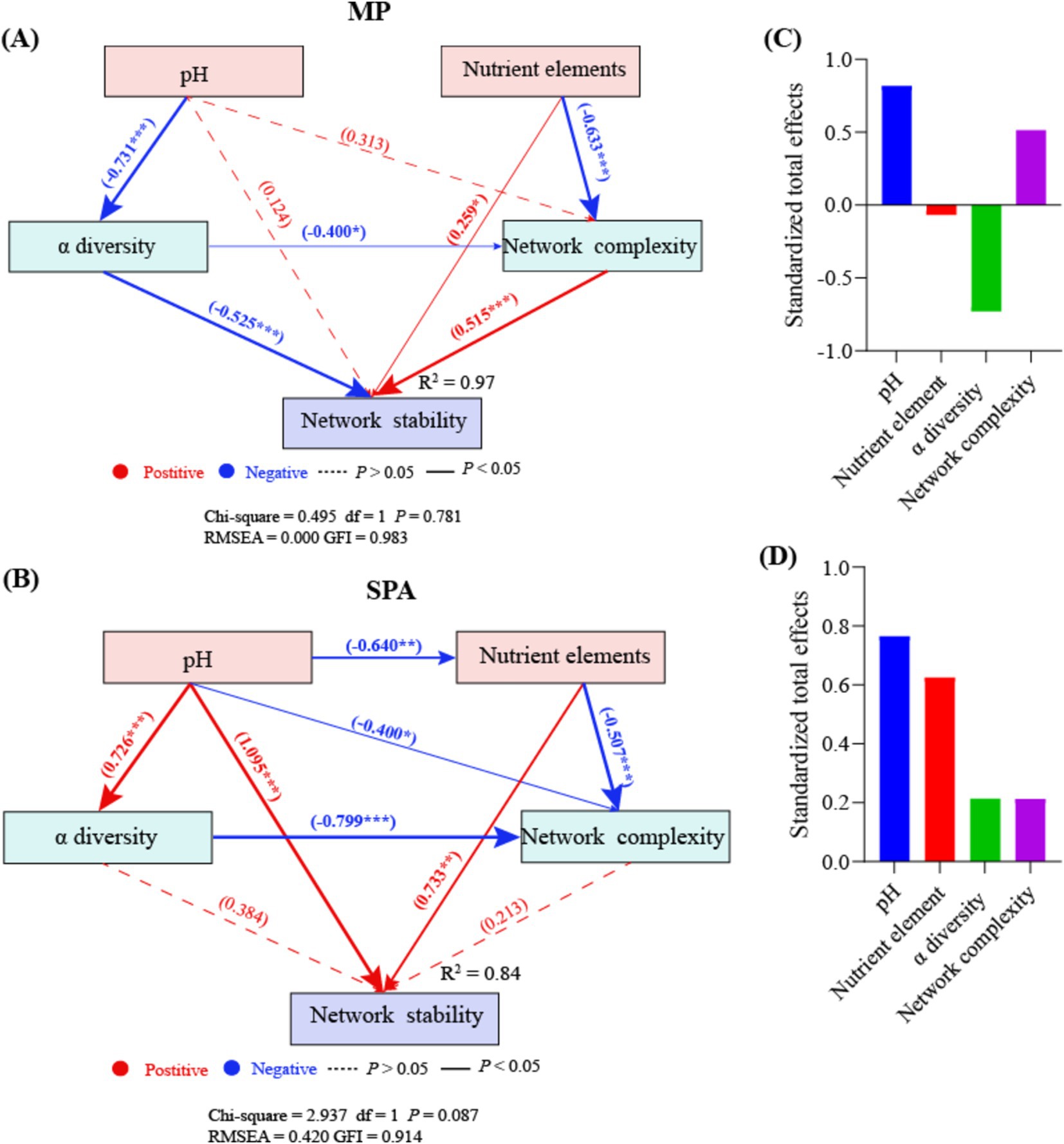
Figure 8. SEM analysis of the direct and indirect effects on the network stability of NFB in MP (A) and SPA (B) systems. The standardized total effects of each indicator in the SEM of the MP (C) and the SPA system (D).
4 Discussion
4.1 Introduction of sanqi significantly increases α diversity but not abundance of NFB
Agroforestry systems serve as model systems for sustainable development and play a vital function in regulating tree growth (Tadesse et al., 2021), soil microbiomes (Wang et al., 2022), and soil nutrients (Manasa et al., 2024). Prior researches have verified that the introduction of plants can lead either to a substantial boost or no change in the abundance of NFB in the soils of agroforestry management systems (Beule and Karlovsky, 2021; do Rego Barros et al., 2021). However, the decrease in the abundance of NFB in the soil due to sanqi cultivation (p < 0.01) may be attributable to variations in plant species (Graungaard, 2015), root exudates (Strugstad and Despotovski, 2012; Na et al., 2018), and soil characteristics (Reed et al., 2011) across different agroforestry systems. Tillage has been reported to significantly affect the abundance and community structure of soil microorganisms (Hu et al., 2020); therefore, tillage was performed in both the systems to avoid any tillage-based effects on the NFB. The correlation analysis suggested that ST and TP were important factors that exhibited negative and positive correlation, respectively, with the abundance of NFB. Previous research has shown that the content of phosphorus may positively impact the abundance of NFB in the soil (Yang et al., 2019). Artificial pine forests are deficient in phosphorus (Fan et al., 2018), and the cultivation of sanqi further exacerbates the decrease in the soil phosphorus content, potentially resulting in a reduced abundance of NFB. In addition, the seasonal variations in SM and ST can affect the abundance of NFB in the soil (Mergel et al., 2001; Gao et al., 2021). We speculate that the highest abundance of NFB is found during autumn and winter, possibly due to the lower temperatures experienced during these seasons compared to spring and summer.
4.2 Sanqi cultivation alters the diversity, community structure, and composition of NFB
Interestingly, the cultivation of sanqi has been found to considerably improve the α diversity of NFB in the soil, which aligns with similar findings in other agroforestry systems such as the sugarcane–peanut and sugarcane–soybean systems (Liu et al., 2021; Pang et al., 2022). Sugars, amino acids, and hormones are released by plants introduced into the agroforestry systems, these can serve as additional substrates and energy sources for soil microbiomes, resulting in a rise in the α diversity of soil microbiomes (Zhang et al., 2004; Qian et al., 2017). The root exudates of sanqi primarily include sugars, saponins, flavonoids amino and organic acids (Liu et al., 2020), which may serve as the primary sources of carbon and nitrogen for NFB and lead to a further increase in α diversity. Moreover, the α diversity of NFB was the lowest in summer due to the seasonal regulation of energy input, availability and quality of the carbon source, and the community of NFB in the soil due to changes in ST and SM (Pereira et al., 2013; Che et al., 2018). Correlation analysis indicated that the α diversity of NFB was primarily influenced by SM and the contents of TK, TP, and NH4+–N. The potassium present in the soil may regulate the diversity of NFB by directly competing for NH4+–N-binding sites (Nieder et al., 2011) or indirectly by influencing nitrogen uptake by plants (Hou et al., 2019). Prior study has verified that NH4+–N exerts a detrimental effect on the α diversity of NFB (Herold et al., 2014). Therefore, the reduction in NH4+–N content in the soil along with the elevation in that of potassium and phosphorus after planting sanqi may be responsible for the increase in the α diversity of NFB.
The PERMANOVA analysis revealed that the system rather than the season significantly affected the community structure of NFB, which is inconsistent with a previous study on the cucumber-rapeseed system, wherein the community structure of NFB was found to be dramatically affected by sampling season rather than the treatment type (Gao et al., 2021). The variation may be attributable to the influence of plant species and seasonal dynamics on edaphic factors, which consequently impacts the composition of NFB (Huang et al., 2014; Hu et al., 2019). RDA analysis indicated that SM and the content of TK, TP, and NH4+–N notably affected the community structure of NFB as well. Sources of nitrogen play a regulatory role in the growth and reproduction of NFB (Mergel et al., 2001). Moreover, moisture may shape these NFB communities by regulating available nitrogen (Williams and Rice, 2007).
Intercropping has been demonstrated to influence the community composition of NFB in the soil (Gopal et al., 2021). For instance, the abundance of Bradyrhizobium, Rhizobium, and Pseudomonas significantly differed in the mulberry–alfalfa system compared to the monocropping mulberry system (Zhang et al., 2018), contributing to the enhancement of biological nitrogen fixation in the soil (VanInsberghe et al., 2015). Notably, the conversion from MP to SPA system triggered a noteworthy rise in the abundance of Bradyrhizobium and Azospirillum. Bradyrhizobium is recognized for its vital contribution to the N cycle in soil, particularly in nitrogen fixation in root nodules (VanInsberghe et al., 2015), while Azospirillum is recognized for its effective nitrogen-fixing capabilities (Miao et al., 2020). We hypothesize that the cultivation of sanqi may lead to an improvement in soil nutrient content and subsequently selective recruit certain microbial taxa involved in biological nitrogen fixation, thereby enhancing the plants’ ability to absorb and utilize nitrogen (Liu et al., 2021).
4.3 Sanqi cultivation enhances the ecological niche breadth and stochastic assembly of NFB
Ecological niche breadth is determined by the balance between intra- and inter-specific competition among microorganisms (Zhang and Okabe, 2020). In our research, the niche breadth of NFB in the soil was found to be wider in the SPA system compared to the MP system, which aligns with prior results reported by Li C. C. et al. (2022). The ecological niche breadth is inversely related to environmental stress (Jiao S. et al., 2022), which has been elucidated in the “ecological release” theory (Herrmann et al., 2021). The introduction of sanqi enhances the content of carbon and other nutrients (e.g., N and P) in the soil, alleviating the competition for resources among the NFB to facilitate their growth and reproduction (Gao et al., 2021), thereby expanding their niche breadth.
Deterministic and stochastic processes jointly shape the structure and functioning of the microbiome (Zhou and Ning, 2017). In alignment with the results of Li C. C. et al. (2022), the introduction of sanqi into the pine forests increased stochasticity in the community structure of NFB by reducing heterogeneous selection and increasing dispersal limitation while decreasing the prominent dependence on deterministic processes. This result is also supported by neutral models owing to the reduction in interspecific competition and increase in substrate availability (Jia et al., 2018). In conclusion, the cultivation of sanqi enhances the SOC content in the soil to facilitate the growth of NFB and reduces interspecific competition (Li C. C. et al., 2022), thereby enhancing the stochastic processes in establishing the community structure of NFB.
4.4 Sanqi cultivation increases the community complexity rather than stability of NFB
Microbial visualization networks can reveal the intricate interactions among species, offering an avenue for understanding the network complexity of microbiome (Faust and Raes, 2012). The network complexity of microbiomes can be measured using various topological characteristics (Xu et al., 2023). Compared to the MP system, the SPA system increased the network complexity but not the stability of NFB. The network complexity of microbiome regulates the network stability of the microbiome (Wagg et al., 2019), in fact, increased complexity was found to reduce network stability (Fan et al., 2018a), which contradicts the findings of this study. Network modularity is positively correlated with network stability, as this modular structure effectively isolates local perturbations, preventing their spread across the entire network and thereby maintaining overall stability (Li et al., 2023). Additionally, an increase in microbial cooperation tends to reduce network stability due to the high interdependence among species involved in cooperation. This interdependence can lead to a decline in other species when one species decreases, thus reducing stability (Coyte et al., 2015). In this study, both network modularity and microbial cooperation were observed to be higher in the SPA system compared to the MP system. This dual increase may counterbalance the respective effects on network stability, resulting in the network stability remaining unchanged. SEM analysis suggested that pH is a direct factor that increases the network complexity and stability of NFB in soil of the SPA systems. Previous studies revealed that the bacterial networks in an alpine grassland exhibited higher network complexity at a pH range of 5.17–8.92 (Chen et al., 2021). However, soil acidification may reduce the network stability of bacteria in desert grasslands (Liu et al., 2022). This difference arises because pH regulates the topological characteristics of bacterial networks by modifying both the community composition (Cho et al., 2019) and substrate availability (Pande and Kost, 2017). Therefore, the lower soil pH following the plantation of sanqi may indirectly impact the network complexity and stability of NFB by altering soil nutrient availability and diversity of NFB.
5 Conclusion
In the SPA system, Sanqi cultivation notably reduced the abundance of NFB and increased α diversity. The community structure of NFB exhibited notable disparities between the MP and SPA systems, with notable enrichment of Bradyrhizobium and Azospirillum in the SPA system. Moreover, the cultivation of sanqi broadened the ecological niche breadth of NFB and increased the stochasticity in community assembly (i.e., dispersal limitation) of NFB. Additionally, the SPA system increased the network complexity but not the stability of NFB. SEM analysis indicated that pH directly impacted the network complexity and stability of the NFB in the SPA system. To sum up, regulating the pH of the soil and supplementation with nitrogen can create a more favorable environment for cultivating sanqi.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1173392.
Author contributions
XZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. JH: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. SW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (grant no. 202401BD070001-122), Yunnan Ten Thousand People Plan Youth Top Talent Project (YNWR-QNBJ-2019-028), Major Science and Technology Project of Yunnan (202102AE090042, 2019ZG0901, and 2021Y250), and Major Science and Technology Project of Kunming (2021JH002).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the members of our group for their joint efforts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531875/full#supplementary-material
References
Arafat, Y., Wei, X. Y., Jiang, Y. H., Chen, T., Saqib, H. S. A., Lin, S., et al. (2017). Spatial distribution patterns of root-associated bacterial communities mediated by root exudates in different aged ratooning tea monoculture systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:1727. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081727
Archer, E. (2016). rfPermute: estimate permutation p-values for random forest importance metrics. R package version. 1, 1–22. Available at: http://github.com/EricArcher/rfPermute (Accessed July 30, 2024).
Bastian, M., Heymann, S., and Jacomy, M. (2009). Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. ICWSM. 3, 361–362. doi: 10.1609/icwsm.v3i1.13937
Beule, L., and Karlovsky, P. (2021). Tree rows in temperate agroforestry croplands alter the composition of soil bacterial communities. PLoS One 16:e0246919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246919
Canfield, D. E., Glazer, A. N., and Falkowski, P. G. (2010). The evolution and future of Earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science 330, 192–196. doi: 10.1126/science.1186120
Cao, Q., Zhang, H., Ma, W., Wang, R., and Liu, J. (2020). Composition characteristics of organic matter and bacterial communities under the Alternanthera philoxeroide invasion in wetlands. Appl. Sci. 10:5571. doi: 10.3390/app10165571
Che, R. X., Deng, Y. C., Wang, F., Wang, W. J., Xu, Z. H., Hao, Y. B., et al. (2018). Autotrophic and symbiotic diazotrophs dominate nitrogen-fixing communities in Tibetan grassland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 639, 997–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.238
Chen, B. B., Jiao, S., Luo, S. W., Ma, B. B., Qi, W., et al. (2021). High soil pH enhances the network interactions among bacterial and archaeal microbiota in alpine grasslands of the Tibetan plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 23, 464–477. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15333
Chen, J., Wang, P. F., Wang, C., Wang, X., Miao, L. Z., Liu, S., et al. (2019). Dam construction alters function and community composition of diazotrophs in riparian soils across an environmental gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 132, 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.01.020
Chen, S. F., Zhou, Y. Q., Chen, Y. R., and Gu, J. (2018). Fastp: an ultrafast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Cho, H., Tripathi, B. M., Moroenyane, I., Takahashi, K., Kerfahi, D., Dong, K., et al. (2019). Soil pH rather than elevation determines bacterial phylogenetic community assembly on Mt. Norikura. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 95:fiy216. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy216
Cleveland, C. C., Townsend, A. R., Schimel, D. S., Fisher, H., Howarth, R. W., Hedin, L. O., et al. (1999). Global patterns of terrestrial biological nitrogen (N2) fixation in natural ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 13, 623–645. doi: 10.1029/1999GB900014
Coyte, K. Z., Schluter, J., and Foster, K. R. (2015). The ecology of the microbiome: networks, competition, and stability. Science 350, 663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2602
Dang, P. F., Lu, C., Huang, T. T., Zhang, M. M., Yang, N., Han, X. Q., et al. (2024). Enhancing intercropping sustainability: manipulating soybean rhizosphere microbiome through cropping patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 931:172714. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172714
Dixon, P. (2003). VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 14, 927–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1654-1103.2003.tb02228.x
do Rego Barros, F. M., Fracetto, F. J. C., Junior, M. A. L., Bertini, S. C. B., and Fracetto, G. G. M. (2021). Spatial and seasonal responses of diazotrophs and ammonium-oxidizing bacteria to legume-based silvopastoral systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 158:103797. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103797
Edgar, R. C. (2013). UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 10, 996–998. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2604
Fan, Y., Lin, F., Yang, L., Zhong, X., Wang, M., Zhou, J., et al. (2018). Decreased soil organic P fraction associated with ectomycorrhizal fungal activity to meet increased P demand under N application in a subtropical forest ecosystem. Biol. Fertil. 54, 149–161. doi: 10.1007/s00374-017-1251-8
Fan, K., Weisenhorn, P., Gilbert, J. A., and Chu, H. (2018a). Wheat rhizosphere harbors a less complex and more stable microbial co-occurrence pattern than bulk soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 125, 251–260. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.07.022
Fan, K., Weisenhorn, P., Gilbert, J. A., Shi, Y., Bai, Y., and Chu, H. (2018b). Soil pH correlates with the co-occurrence and assemblage process of diazotrophic communities in rhizosphere and bulk soils of wheat fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 121, 185–192. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.03.017
Faust, K., and Raes, J. (2012). Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 538–550. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2832
Feng, M., Adams, J. M., Fan, K., Shi, Y., Sun, R., Wang, D., et al. (2018). Long-term fertilization influences community assembly processes of soil diazotrophs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 126, 151–158. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.08.021
Fortmann-Roe, S. (2015). Consistent and clear reporting of results from diverse modeling techniques: the A3 method. J. Stat. Softw. 66, 1–23. doi: 10.18637/jss.v066.i07
Gaby, J. C., and Buckley, D. H. (2014). A comprehensive aligned nifH gene database: a multipurpose tool for studies of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Database 2014, 2–3. doi: 10.1093/database/bau001
Galloway, J. N., Dentener, F. J., Capone, D. G., Boyer, E. W., Howarth, R. W., Seitzinger, S. P., et al. (2004). Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 70, 153–226. doi: 10.1007/s10533-004-0370-0
Gao, H., Li, S., and Wu, F. Z. (2021). Impact of intercropping on the diazotrophic community in the soils of continuous cucumber cropping systems. Front. Microbiol. 12:630302. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.630302
Gopal, A. V., Gosal, S. K., and Kaur, J. (2021). Diversity of nitrogen fixing bacteria in rhizospheric soils of citrusâ poplar cropping system of Punjab. Indian j. agrofor. 23, 5–12.
Graungaard, K. C. (2015). Bacterial communities associated with the cycling of nitrogen in a tree-based intercropping system ([dissertation's thesis]. [Canada]: University of Guelph).
Hayden, H. L., Drake, J., Imhof, M., Oxley, A. P., Norng, S., and Mele, P. M. (2010). The abundance of nitrogen cycle genes amoA and nifH depends on land-uses and soil types in south-eastern Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42, 1774–1783. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.06.015
Hei, J. Y., Li, Y., Wang, Q., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2024). Effects of exogenous organic acids on the soil metabolites and microbial communities of Panax notoginseng from the Forest understory. Agronomy 14:601. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14030601
Hei, J. Y., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2023). Effects of exogenous organic acids on the growth, edaphic factors, soil extracellular enzymes, and microbiomes predict continuous cropping obstacles of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Plant Soil 503, 105–122. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06044-0
Herold, N., Schöning, I., Gutknecht, J., Alt, F., Boch, S., Müller, J., et al. (2014). Soil property and management effects on grassland microbial communities across a latitudinal gradient in Germany. Appl. Soil Ecol. 73, 41–50. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.07.009
Herrmann, N. C., Stroud, J. T., and Losos, J. B. (2021). The evolution of ‘ecological release’ into the 21st century. Trends Ecol. Evol. 36, 206–215. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2020.10.019
Hou, W. F., Xue, X. X., Li, X. H., Khan, M. R., Yan, J. Y., Ren, T., et al. (2019). Interactive effects of nitrogen and potassium on: grain yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen use efficiency of rice in low potassium fertility soil in China. Field Crop Res. 236, 14–23. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.03.006
Hu, X. J., Liang, A. Z., Yao, Q., Liu, Z. X., Yu, Z. H., Wang, G. H., et al. (2020). Ridge tillage improves soil properties, sustains diazotrophic communities, and enhances extensively cooperative interactions among diazotrophs in a clay loam soil. Front. Microbiol. 11:1333. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01333
Hu, X. J., Liu, J. J., Wei, D., Zhou, B. K., Chen, X. L., Jin, J., et al. (2019). Long-term application of nitrogen, not phosphate or potassium, significantly alters the diazotrophic community compositions and structures in a Mollisol in Northeast China. Res. Microbiol. 170, 147–155. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.02.002
Huang, X. M., Liu, S. R., Wang, H., Hu, Z. D., Li, Z. G., and You, Y. M. (2014). Changes of soil microbial biomass carbon and community composition through mixing nitrogen-fixing species with Eucalyptus urophylla in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 73, 42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.01.021
Ininbergs, K., Bay, G., Rasmussen, U., Wardle, D. A., and Nilsson, M. C. (2011). Composition and diversity of nifH genes of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria associated with boreal forest feather mosses. New Phytol. 192, 507–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03809.x
Jia, X., Dini-Andreote, F., and Salles, J. F. (2018). Community assembly processes of the microbial rare biosphere. Trends Microbiol. 26, 738–747. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2018.02.011
Jia, W. J., Hei, J. Y., He, X. H., and Wang, S. (2024). Altitude rather than season and slope aspect has the greatest effect on the bacterial communities in subtropical forests in Yunnan. China. Plant Soil. 501, 57–74. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-06319-6
Jia, W. J., Wang, S., He, X. H., and Zhao, X. Y. (2022). Different factors drive the assembly of pine and Panax notoginseng-associated microbiomes in Panax notoginseng-pine agroforestry systems. Front. Microbiol. 13:1018989. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1018989
Jiao, S., Chen, W. M., and Wei, G. H. (2022). Core microbiota drive functional stability of soil microbiome in reforestation ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 28, 1038–1047. doi: 10.1111/gcb.16024
Jiao, D. L., Liu, Y., Hou, T., Xu, H., Wang, X. Y., Shi, Q., et al. (2022). Notoginsenoside R1 (NG-R1) promoted lymphatic drainage function to ameliorating rheumatoid arthritis in TNF-Tg mice by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 12:730579. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.730579
Kerfahi, D., Tripathi, B. M., Dong, K., Go, R., and Adams, J. M. (2016). Rainforest conversion to rubber plantation may not result in lower soil diversity of bacteria, fungi, and nematodes. Microb. Ecol. 72, 359–371. doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0790-0
Kim, D. G., and Isaac, M. E. (2022). Nitrogen dynamics in agroforestry systems. A review. Agronomy for Sustain. Develop. 42:60. doi: 10.1007/s13593-022-00791-7
Kong, L. G., Kuang, X. X., Dong, Y. F., and Han, X. Y. (2015). The rhizosphere effect of soil microbes on Populus agroforestry ecosystems. Shandong Forestry Sci. Technol. 45, 16–19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2724.2015.04.004
Kwak, J. H., Lim, S. S., Baah-Acheamfour, M., Choi, W. J., Fatemi, F., Carlyle, C. N., et al. (2019). Introducing trees to agricultural lands increases greenhouse gas emission during spring thaw in Canadian agroforestry systems. Sci. Total Environ. 652, 800–809. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.241
Leung, K. W., Cheung, L. W. T., Pon, Y. L., Wong, R. N. S., Mak, N. K., Fan, T. P., et al. (2007). Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits tube-like structure formation of endothelial cells by regulating pigment epithelium-derived factor through the oestrogen β receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 152, 207–215. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707359
Levy-Booth, D. J., Prescott, C. E., and Grayston, S. J. (2014). Microbial functional genes involved in nitrogen fixation, nitrification and denitrification in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 75, 11–25. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2014.03.021
Li, C. C., Bo, H. Z., Song, B. Z., Chen, X. C., Cao, Q. Q., Yang, R. R., et al. (2022). Reshaping of the soil microbiome by the expansion of invasive plants: shifts in structure, diversity, co-occurrence, niche breadth, and assembly processes. Plant Soil 477, 629–646. doi: 10.1007/s11104-022-05445-x
Li, Y., Hei, J. Y., Wang, B., Wang, S., and He, X. H. (2024). Unraveling the molecular mechanisms of flavonoid biosynthesis in Panax notoginseng flowers across planting patterns and developmental stages using integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses. Sci. Hortic. 335:113362. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113362
Li, H. P., Jia, W. J., Li, Y., He, X. H., and Wang, S. (2022). Responses of nitrogen-fixing bacteria communities to elevation, season, and slope aspect variations in subtropical forests of Yunnan, China. Forests. 13:681. doi: 10.3390/f13050681
Li, C., Jin, L., Zhang, C., Li, S., Zhou, T., Hua, Z., et al. (2023). Destabilized microbial networks with distinct performances of abundant and rare biospheres in maintaining networks under increasing salinity stress. iMeta 2:e79. doi: 10.1002/imt2.79
Li, C. C., Wang, L. F., Ji, S. P., Chang, M. J., Wang, L. F., Gan, Y. D., et al. (2021). The ecology of the plastisphere: microbial composition, function, assembly, and network in the freshwater and seawater ecosystems. Water Res. 202:117428. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117428
Liu, K., Liu, Z., Zhou, N., Shi, X., Lock, T. R., Kallenbach, R. L., et al. (2022). Diversity-stability relationships in temperate grasslands as a function of soil pH. Land Degrad. Dev. 33, 1704–1717. doi: 10.1002/ldr.4259
Liu, Y., Ma, W. Q., He, H. L., Wang, Z. T., and Cao, Y. H. (2021). Effects of sugarcane and soybean intercropping on the nitrogen-fixing bacterial community in the rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 12:713349. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.713349
Liu, J. D., Wang, S., Liu, H. T., Yang, L. P., and Nan, G. Z. (1995). Stimulatory effect of saponin from Panax ginseng on immune function of lymphocytes in the elderly. Mech. Ageing Dev. 83, 43–53. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(95)01618-A
Liu, H. J., Zhao, X. Q., Han, X. P., Xu, S. X., Zhao, L., Hu, L. Y., et al. (2020). Comparative study of gut microbiota in Tibetan wild asses (Equus kiang) and domestic donkeys (Equus asinus) on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. PeerJ. 8:e9032. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9032
Loh, Y. C., Tan, C. S., Chng, Y. S., Ng, C. H., Yeap, Z. Q., and Yam, M. F. (2019). Mechanisms of action of Panax notoginseng ethanolic extract for its vasodilatory effects and partial characterization of vasoactive compounds. Hypertens. Res. 42, 182–194. doi: 10.1038/s41440-018-0139-9
Luo, X. Z., Hou, E. Q., Chen, J. Q., Li, J., Zhang, L. L., Zang, X. W., et al. (2020). Dynamics of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stocks and stoichiometry resulting from conversion of primary broadleaf forest to plantation and secondary forest in subtropical China. Catena 193:104606. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104606
Magoč, T., and Salzberg, S. L. (2011). FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27, 2957–2963. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507
Manasa, P. A., Hegde, R., Salimath, S. K., and Maheswarappa, V. (2024). Intercropping performance and its influence on soil nutrient status in bamboo-based agroforestry practice. Agrofor. Syst. 98, 1803–1816. doi: 10.1007/s10457-024-00992-x
Mergel, A., Kloos, K., and Bothe, H. (2001). Seasonal fluctuations in the population of denitrifying and N2-fixing bacteria in an acid soil of a Norway spruce forest. Plant Soil 230, 145–160. doi: 10.1023/A:1004826116981
Miao, L., Feng, W., Zhang, Y. Q., Bai, Y. X., Sun, Y. F., She, W. W., et al. (2020). Chemoheterotrophic diazotrophs contribute to nitrogen incorporation in a semi-arid desert. Biol. Fertil. 56, 1165–1176. doi: 10.1007/s00374-020-01492-7
Na, X. F., Li, X. R., Zhang, Z. Y., Li, M., Kardol, P., Xu, T. T., et al. (2018). Bacterial community dynamics in the rhizosphere of a long-lived, leguminous shrub across a 40-year age sequence. J. Soils Sediments 18, 76–84. doi: 10.1007/s11368-017-1745-x
Nieder, R., Benbi, D. K., and Scherer, H. W. (2011). Fixation and defixation of ammonium in soils: a review. Biol. Fertil. 47, 1–14. doi: 10.1007/s00374-010-0506-4
Ning, D., Yuan, M., Wu, L., Zhang, Y., Guo, X., Zhou, X., et al. (2020). A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat. Commun. 11:4717. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18560-z
Pande, S., and Kost, C. (2017). Bacterial unculturability and the formation of intercellular metabolic networks. Trends Microbiol. 25, 349–361. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.02.015
Pang, Z., Fallah, N., Weng, P., Zhou, Y., Tang, X., Tayyab, M., et al. (2022). Sugarcane-peanut intercropping system enhances bacteria abundance, diversity, and sugarcane parameters in rhizospheric and bulk soils. Front. Microbiol. 12:815129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.815129
Pereira, E., Silva, M. C., Schloter-Hai, B., Schloter, M., van Elsas, J. D., and Salles, J. F. (2013). Temporal dynamics of abundance and composition of nitrogen-fixing communities across agricultural soils. PLoS One 8:e74500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074500
Qian, J. Q., Yu, X., Liang, X. J., Liu, Y. F., Borriss, R., and Liu, Y. Z. (2017). Addition of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus subtilis PTS-394 on tomato rhizosphere has no durable impact on composition of root microbiome. BMC Microbiol. 17, 131–112. doi: 10.1186/s12866-017-1039-x
Qiao, M. G., Sun, R. B., Wang, Z. X., Dumack, K., Xie, X. G., Dai, C. C., et al. (2024). Legume rhizodeposition promotes nitrogen fixation by soil microbiota under crop diversification. Nat. Commun. 15:2924. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47159-x
Reed, S. C., Cleveland, C. C., and Townsend, A. R. (2011). Functional ecology of free-living nitrogen fixation: a contemporary perspective. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 42, 489–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-102710-145034
Rilling, J. I., Acuña, J. J., Sadowsky, M. J., and Jorquera, M. A. (2018). Putative nitrogen-fixing bacteria associated with the rhizosphere and root endosphere of wheat plants grown in an andisol from southern Chile. Front. Microbiol. 9:2710. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02710
Rui, R., Hei, J. Y., Li, Y., Al Farraj, D. A., Noor, F., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Effects of humic acid fertilizer on the growth and microbial network stability of Panax notoginseng from the forest understorey. Sci. Rep. 14:17816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68949-9
Sloan, W. T., Lunn, M., Woodcock, S., Head, I. M., Nee, S., and Curtis, T. P. (2006). Quantifying the roles of immigration and chance in shaping prokaryote community structure. Environ. Microbiol. 8, 732–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00956.x
Solanki, M. K., Wang, Z., Wang, F. Y., Li, C. N., Lan, T. J., Singh, R. K., et al. (2017). Intercropping in sugarcane cultivation influenced the soil properties and enhanced the diversity of vital diazotrophic bacteria. Sugar Tech. 19, 136–147. doi: 10.1007/s12355-016-0445-y
Strugstad, M., and Despotovski, S. (2012). A summary of extraction, synthesis, properties, and potential uses of juglone: A literature review. JEMS 13, 1–16. doi: 10.22230/jem.2012v13n3a119
Tadesse, S., Gebretsadik, W., Muthuri, C., Derero, A., Hadgu, K., Said, H., et al. (2021). Crop productivity and tree growth in intercropped agroforestry systems in semi-arid and sub-humid regions of Ethiopia. Agrofor. Syst. 95, 487–498. doi: 10.1007/s10457-021-00596-9
VanInsberghe, D., Maas, K. R., Cardenas, E., Strachan, C. R., Hallam, S. J., and Mohn, W. W. (2015). Non-symbiotic Bradyrhizobium ecotypes dominate north American forest soils. ISME J. 9, 2435–2441. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.54
Vitousek, P. M., Menge, D. N., Reed, S. C., and Cleveland, C. C. (2013). Biological nitrogen fixation: rates, patterns and ecological controls in terrestrial ecosystems. Philos T R Soc B. 368:20130119. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0119
Wagg, C., Schlaeppi, K., Banerjee, S., Kuramae, E. E., and van der Heijden, M. G. (2019). Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 10:4841. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12798-y
Wakelin, S. A., Gupta, V. V., and Forrester, S. T. (2010). Regional and local factors affecting diversity, abundance and activity of free-living, N2-fixing bacteria in Australian agricultural soils. Pedobiologia 53, 391–399. doi: 10.1016/j.pedobi.2010.08.001
Wang, H. L., Cao, X. Q., Fan, W., Deng, P. F., and Xu, X. N. (2023). Effects of intercropping systems of Phyllostachys edulis and Bletilla striata on soil bacterial community composition and function. Agrofor. Syst. 97, 617–630. doi: 10.1007/s10457-023-00814-6
Wang, Y., Li, C., Shen, Z., Rui, J., Jin, D., and Li, J. (2019). Community assemblage of free-living diazotrophs along the elevational gradient of mount Gongga. Soil Ecol. Lett. 1, 136–146. doi: 10.1007/s42832-019-0013-y
Wang, R. L., Shi, R., Lei, E., Li, D. Y., Bao, S. J., and Xiong, Z. (2023). The structure and diversity of nitrogen-fixing microbiomes in Macadamia integrifolia plantations in Australia. Jiangsu Agricul. Sci. 51, 211–217. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2023.08.030
Wang, W. J., Wen, J., Xiang, W. Q., Malabrigo, J. P. L., and Ren, M. X. (2022). Soil bacterial and fungal communities respond differently to Bombax ceiba (Malvaceae) during reproductive stages of rice in a traditional agroforestry system. Plant Soil 479, 543–558. doi: 10.1007/s11104-022-05542-x
Wang, S. S., Zhang, X. J., Li, X. J., Shen, J. Z., Sun, L. T., Zaman, S., et al. (2023). Different changes of bacterial diversity and soil metabolites in tea plants-legume intercropping systems. Front. Plant Sci. 14:1110623. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1110623
Williams, M. A., and Rice, C. W. (2007). Seven years of enhanced water availability influences the physiological, structural, and functional attributes of a soil microbial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 35, 535–545. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2006.09.014
Wu, D. M., Dai, Q. P., Liu, X. Z., Fan, Y. P., and Wang, J. X. (2019). Comparison of bacterial community structure and potential functions in hypoxic and non-hypoxic zones of the Changjiang estuary. PLoS One 14:e0217431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217431
Wu, H., Yang, J. J., Fu, W., Rillig, M. C., Cao, Z. J., Zhao, A. H., et al. (2023). Identifying thresholds of nitrogen enrichment for substantial shifts in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community metrics in a temperate grassland of northern China. New Phytol. 237, 279–294. doi: 10.1111/nph.18516
Xie, Y. A., Ouyang, Y., Han, S., Se, J., Tang, S., Yang, Y. F., et al. (2022). Crop rotation stage has a greater effect than fertilisation on soil microbiome assembly and enzymatic stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 815:152956. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.152956
Xu, Z. Y., Hu, Z. H., Jiao, S., Bell, S. M., Xu, Q., Ma, L. L., et al. (2023). Depth-dependent effects of tree species identity on soil microbial community characteristics and multifunctionality. Sci. Total Environ. 878:162972. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162972
Yang, L., Bai, J. S., Zeng, N. H., Zhou, X., Liao, Y. L., Lu, Y. H., et al. (2019). Diazotroph abundance and community structure are reshaped by straw return and mineral fertilizer in rice-rice-green manure rotation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 136, 11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2018.12.015
Yang, D., Xu, X., Liu, X., Liu, J. L., Zhang, S. X., and Yu, Z. Q. (2015). Effect of afforestation modes on soil microbial community and nitrogen functional genes in Hippophae rhamnoides plantation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 26, 3634–3640. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.20150929.01
Yuan, M. M., Guo, X., Wu, L., Zhang, Y. A., Xiao, N., Ning, D., et al. (2021). Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 11, 343–348. doi: 10.1038/s41558-021-00989-9
Zhang, X., Hu, W., Jin, X. T., Chen, T., and Niu, Y. H. (2021). Diversity of soil nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the rhizosphere and non-rhizophere soils of Ebinur Lake wetland. Arch. Microbiol. 203, 3919–3932. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02363-x
Zhang, L., and Okabe, S. (2020). Ecological niche differentiation among anammox bacteria. Water Res. 171:115468. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115468
Zhang, F., Shen, J., Li, L., and Liu, X. (2004). An overview of rhizosphere processes related with plant nutrition in major cropping systems in China. Plant Soil 260, 89–99. doi: 10.1023/b:plso.0000030192.15621.20
Zhang, M. M., Wang, N., Hu, Y. B., and Sun, G. Y. (2018). Changes in soil physicochemical properties and soil bacterial community in mulberry (Morus alba L.)/alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) intercropping system. Microbiol. Open. 7:e00555. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.555
Zheng, H. P., Yang, T. J., Bao, Y. Z., He, P. P., Yang, K. M., Mei, X. L., et al. (2021). Network analysis and subsequent culturing reveal keystone taxa involved in microbial litter decomposition dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 157:108230. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108230
Zhong, Y. J., Liang, L. N., Xu, R. N., Xu, H. Y., Sun, L. L., and Liao, H. (2022). Intercropping tea plantations with soybean and rapeseed enhances nitrogen fixation through shifts in soil microbial communities. Front Agric Sci Eng. 9:355. doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2022451
Zhou, J., Deng, Y., Zhang, P., Xue, K., Liang, Y., Van Nostrand, J. D., et al. (2014). Stochasticity, succession, and environmental perturbations in a fluidic ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 111, E836–E845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1324044111
Keywords: Panax notoginseng, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, nifH gene, high-throughput sequencing, structural equation model
Citation: Zhao X, He S, Rui R, Hei J, He X and Wang S (2025) Introduction of Panax notoginseng into pine forests significantly enhances the diversity, stochastic processes, and network complexity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil. Front. Microbiol. 16:1531875. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531875
Edited by:
Tofazzal Islam, Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Agricultural University, BangladeshReviewed by:
Shuaimin Chen, Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaQian Lyu, Sichuan University of Science and Engineering, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, He, Rui, Hei, He and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiahong He, aHhoQHN3ZnUuZWR1LmNu; Shu Wang, d2FuZ3NodUBzd2Z1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaoyan Zhao
Xiaoyan Zhao Shu He1†
Shu He1† Shu Wang
Shu Wang