- 1Key Laboratory of Biodiversity Conservation and Characteristic Resource Utilization in Southwest Anhui, Anqing Forestry Technology Innovation Research Institute, School of Life Sciences, Anqing Normal University, Anqing, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
- 3Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shenzhen University General Hospital, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Candidiasis, a prevalent class of human infections caused by fungi belonging to the Candida genus, is garnering increasing attention due to its pathogenicity and the emergence of drug resistance. The advancement of genomics technologies has offered powerful tools for investigating the pathogenic mechanisms and drug resistance characteristics of Candida. This comprehensive review provides an overview of the applications of genomics in candidiasis research, encompassing genome sequencing, comparative genomics, and functional genomics, along with the pathogenic features and core virulence factors of Candida. Moreover, this review highlights the role of genomic variations in the emergence of drug resistance, further elucidating the evolutionary and adaptive mechanisms of Candida. In conclusion, the review underscores the current state of research and prospective avenues for exploration of candidiasis, providing a theoretical basis for clinical treatments and public health strategies.
1 Introduction
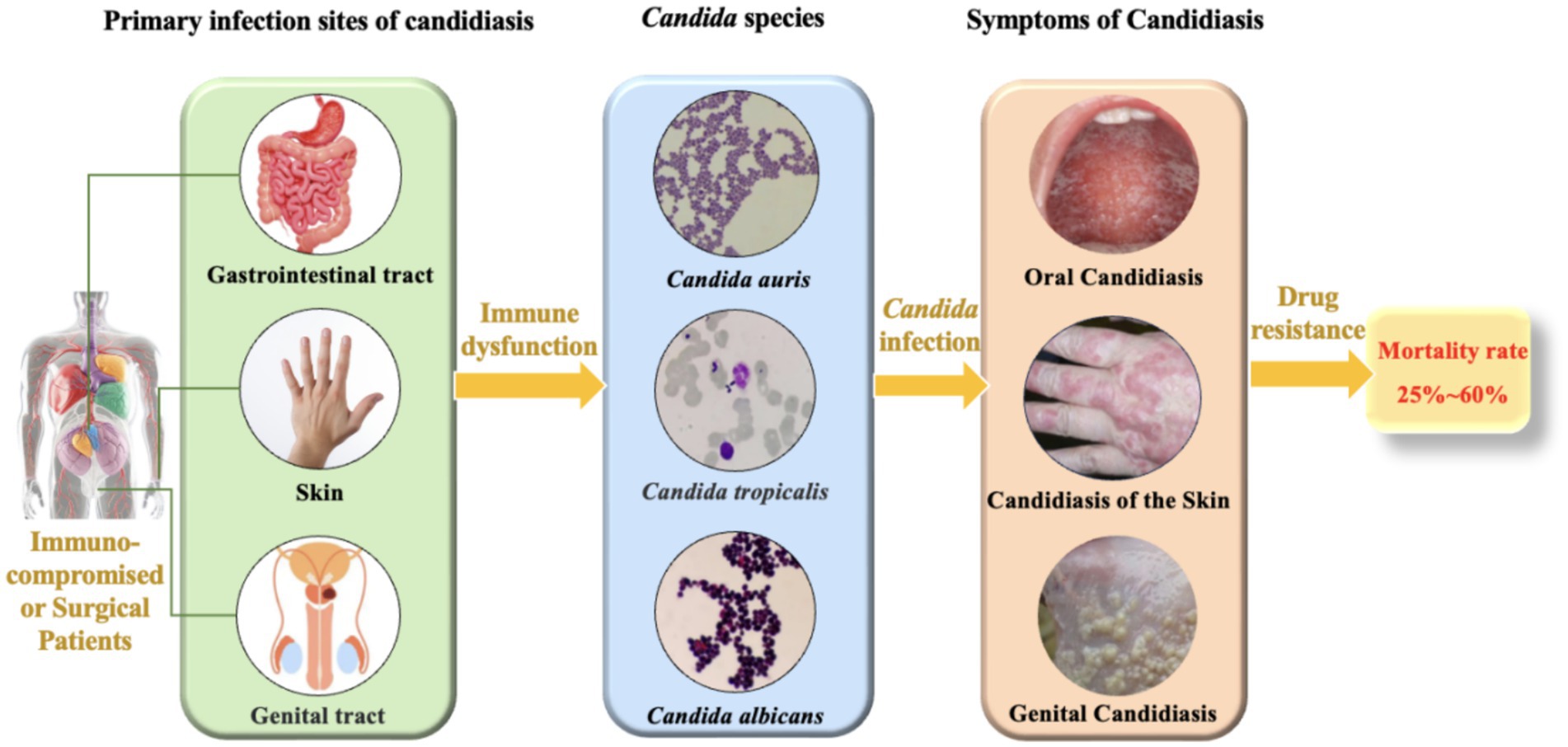
Candidiasis is a prevalent fungal infection caused by pathogenic fungi belonging to the Candida genus. Candida is a commensal fungus and an integral member of the human normal microbiota, predominantly colonizing the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and genital tract (Shiyadeh et al., 2024). Despite their normal presence, Candida can cause a spectrum of infections, ranging from superficial skin and mucosal infections to invasive systemic infections (Figure 1). These infections are particularly common in immunocompromised patients, such as those with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), organ transplant recipients, and patients undergoing chemotherapy (Bhattacharya et al., 2020; Fisher et al., 2022). Although C. albicans is the most prevalent pathogenic species in the genus, constituting approximately 37% of reported cases (Henriques and Williams, 2020; Marquez et al., 2023), recent studies have shown an increasing frequency of infections caused by non-albicans Candida. These non-albicans Candida species (e.g., C. auris, C. krusei, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis) are associated with higher mortality rates compared to C. albicans (Mandras et al., 2021; Husni et al., 2023) and frequently exhibit resistance to commonly used antifungal drugs (Seyoum et al., 2020; Kitaya et al., 2023), which poses significant challenges for clinical treatment. According to the 2019 Antibiotic Resistance Threats Report by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 34,000 cases and 1,700 deaths annually are attributed to drug-resistant Candida species (Kadri, 2020). Additionally, 323 cases of emerging multidrug-resistant Candida infections have been reported (Lyman et al., 2023). Given the significant impact of Candida infections on human health and the clinical challenges posed by antifungal resistance, Candida infections have become a serious threat to global public health. Consequently, a deeper understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms and resistance characteristics of Candida is imperative. Such knowledge is vital for devising efficacious therapeutic strategies and curbing the escalating epidemic of candidiasis.
A multitude of factors contribute to the escalating drug resistance observed in Candida species. The overexpression of genes encoding efflux pump proteins such as CDR1 and CDR2 in C. albicans (Rocha et al., 2017; Prasad and Rawal, 2014) and MDR1 in C. tropicalis (Jin et al., 2018), facilitates the efflux of antifungal drugs like fluconazole, thereby reducing intracellular drug levels and augmenting resistance. Additionally, the ability of Candida to form biofilms significantly hinders drug penetration (Pereira et al., 2021). Furthermore, the prolonged use of broad-spectrum antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole and itraconazole, during hospital treatment can create selective pressure, which encourages the emergence of resistant strains in pathogens with high mutation rates (Cai et al., 2023). This can lead to the unnecessary utilization of antifungal drugs, thereby promoting resistance in patients with non-invasive candidiasis or delaying effective antifungal treatment in infected patients. Consequently, the development of drug resistance is multifaceted, encompassing genetic mechanisms such as mutations, gene expression, and alterations in cell membrane permeability (Sanglard and Odds, 2002; Czajka et al., 2023).This review endeavors to underscore the latest breakthroughs in the genomics of candidiasis, encompassing the utilization of genome sequencing, comparative genomics, and functional genomics to elucidate the pathogenic mechanisms and drug resistance. The review further expounds on the impact of genomic variations in the development of drug resistance, as well as the evolutionary and adaptive mechanisms of Candida, providing a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment and prevention of candidiasis.
2 Epidemiological trends of candidiasis and genomic response strategies
2.1 Epidemiological trends and basic characteristics of candidiasis
The epidemiological landscape of candidiasis is undergoing a transformation, with a global shift observed from the historically predominant C. albicans to drug-resistant non-albicans Candida species (Quindós et al., 2018). The emergence of multidrug-resistant Candida species, notably C. auris, has been identified in over 40 countries worldwide and has diverged into four distinct genetic lineages (Rhodes and Fisher, 2019), revealing their global transmission patterns and diversity. Hospital environments are pivotal in the propagation of candidiasis, where Candida can survive and resist routine cleaning and disinfection measures (Erganis et al., 2024). Nevertheless, the prevalence of Candida in special environments or workplaces, such as farms, livestock, and slaughterhouses, requires further investigation.
Candida species primarily inhabit the human body (Fidel, 2011), with different species predominating in various infection sites. Oral and esophageal candidiasis are mainly caused by C. albicans, and vaginal candidiasis is also predominantly attributed to C. albicans, although it can also be linked to C. tropicalis and C. glabrata (Dabas, 2013). Skin and bloodstream candidiasis can be caused by multiple Candida species, including C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, and C. krusei (Williams et al., 2013; Fidel, 2011). Additionally, C. auris, an emerging pathogen, has been reported to cause infections in hospital settings and is capable of colonizing the skin of patients (Proctor et al., 2021).Candidiasis poses a significant challenge to public health, with clinical studies indicating that the mortality rate associated with Candida infections of the bloodstream, peritoneum, and other sites is alarmingly high (Figure 1), typically ranging from 25 to 60% within 30 days of diagnosis (Rajendran et al., 2016; Hirano et al., 2015; Bassetti et al., 2015). In the United States, the incidence of invasive candidiasis is as high as about 90 cases per 100,000 people, with a rising trend in non-bloodstream infections (Ricotta et al., 2021). This situation not only increases the hospitalization burden but also leads to a significant rise in the use of antifungal drugs, exacerbating the development of antifungal resistance (Parslow and Thornton, 2022; Oliva et al., 2023). From an economic perspective, the cost of hospitalization for candidiasis is high, accompanied by longer hospital stays and higher readmission rates, further straining the healthcare system (Ricotta et al., 2021).
In clinical practice, the diagnosis of candidiasis generally relies on clinical symptoms and laboratory examination results. Candidal vaginitis, the most common form of Candida infection, is mainly an inflammatory change in the vagina and vulva caused by Candida species, especially Candida albicans (Jeanmonod et al., 2025). For invasive candidiasis, the diagnosis is more challenging and requires a comprehensive assessment integrating clinical manifestations and laboratory tests such as Candida antigen detection (Barantsevich and Barantsevich, 2022). Currently, the diagnosis is typically carried out by first evaluating the patient’s symptoms related to the suspected candidiasis site. Then, relevant laboratory tests are conducted to confirm the presence and type of Candida. However, there are limitations in the existing diagnostic methods. Clinicians often rely on empirical treatment, such as the overuse of antibiotics like fluconazole, potentially overlooking critical diagnostic steps, including the detection of C. glabrata infections (C. glabrata has developed a resistance rate of up to 14.3% to fluconazole and is continuously rising) and conducting drug susceptibility testing (Poves-Alvarez et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2024), which may in turn affect the overall treatment efficacy. This can lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment (Benedict et al., 2022; Huang et al., 2023). Additionally, detecting and identifying certain Candida species, like C. glabrata and C. parapsilosis, present difficulties (Sobel, 2022). These challenges in diagnosis can potentially affect the treatment outcome. In summary, current diagnostic methods for candidiasis have limitations, necessitating urgent exploration of new approaches. Genomics research may revolutionize diagnosis by enhancing accuracy and timeliness.
2.2 Application of genomics in candidiasis research
The genome of Candida is primarily composed of linear chromosomes, with the specific number and size varying among species. For instance, C. albicans possesses eight pairs of homologous chromosomes, whereas other species such as C. glabrata have 13 chromosomes (Selmecki et al., 2010; Helmstetter et al., 2022; Butler et al., 2009). Generally, the Candida genome contains numerous repetitive sequences and transposable elements, which may play crucial roles in gene regulation and evolution (Selmecki et al., 2010; Braun et al., 2005). The Candida genome also includes several gene families associated with pathogenicity, such as the ALS (adhesin) family and SAP (secreted aspartyl protease) family. These genes play a crucial role in the infection process of Candida (Ruiz-Herrera et al., 2006; Arnaud et al., 2009; Kabir et al., 2012). Moreover, the Candida genome exhibits a high degree of plasticity because of genomic instability, prone to chromosomal rearrangements, gene amplifications, and horizontal gene transfers, attributes closely associated with environmental adaptation and drug resistance (Butler et al., 2009; Selmecki et al., 2010; Helmstetter et al., 2022). Comparative genomics studies have unveiled the genomic instability among various Candida species, such as C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis, which are associated with their pathogenic mechanisms and ecological adaptability (Butler et al., 2009; Desjardins et al., 2011). The genomic instability of Candida is primarily caused by multiple internal and external factors. Firstly, the genome is rich in repetitive sequences and active transposable elements that can easily trigger homologous recombination, leading to chromosomal rearrangements, deletions, or amplifications. Meanwhile, the dynamic changes in telomeres also increase the risk of chromosome fusion or breakage (Aguilera and García-Muse, 2013). Secondly, the alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction in Candida increases the possibility of genomic recombination, while the emergence of aneuploidy can rapidly alter gene dosage to adapt to environmental stress (Mba et al., 2022; Marton, 2020). Furthermore, environmental stresses such as temperature, pH, nutrient deficiency, and the use of antifungal drugs can also induce genomic instability (Aguilera and Gómez-González, 2008; Pais et al., 2019; Mba et al., 2022). Additionally, Candida can acquire exogenous genes from other microorganisms through horizontal gene transfer, further altering the genomic structure and acquiring new functions (Bezerra et al., 2013). Finally, defects in DNA repair mechanisms exacerbate genomic instability (Aguilera and Gómez-González, 2008). These factors collectively enable Candida to rapidly respond to environmental stress, enhance pathogenicity, and become a significant driving force for its environmental adaptation and evolution (Pais et al., 2019).Candidiasis poses a significant global health challenge, with the increasing prevalence of multidrug resistance and the emergence of novel pathogens complicating therapeutic interventions. Traditional research methods have limitations in accurately identifying Candida species, elucidating resistance mechanisms, and facilitating rapid diagnostics. In this context, genomic technologies have emerged as pivotal tools in the study of candidiasis, particularly through genome sequencing, comparative genomics, and functional genomics, which enable researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms and resistance characteristics of Candida (Figure 2). In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of genomics in the study of candidiasis, allowing researchers to analyze the genetic features of Candida in detail and elucidate the complex relationships between its genetics, pathogenicity, and resistance. For example, Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón (2022) emphasized the central role of genomic sequencing studies in revealing the pathogenic mechanisms of Candida, providing important guidance for research in this field (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2022). Recently, Mathur et al. (2024) made new breakthroughs in this area. They utilized high-throughput genomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis to successfully identify long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in C. auris. These lncRNAs exhibit a distinct chromosomal distribution, with GC content concentrated between 40 and 45%, and most are predicted to be localized in the nucleus (Mathur et al., 2024). These findings suggest that lncRNAs may play important roles in regulating gene expression and maintaining genome stability. Furthermore, Mathur et al. (2024) observed differential expression patterns of lncRNAs at different infection stages, which could be intricately linked to the pathogenicity and drug resistance of C. auris, shedding new light on Candida’s pathogenic mechanisms. Additionally, through protein interaction network analysis, the researchers revealed potential interactions between lncRNAs and proteins, offering scientific evidence and potential targets for further exploring the development of drug resistance in Candida and the development of new therapies.
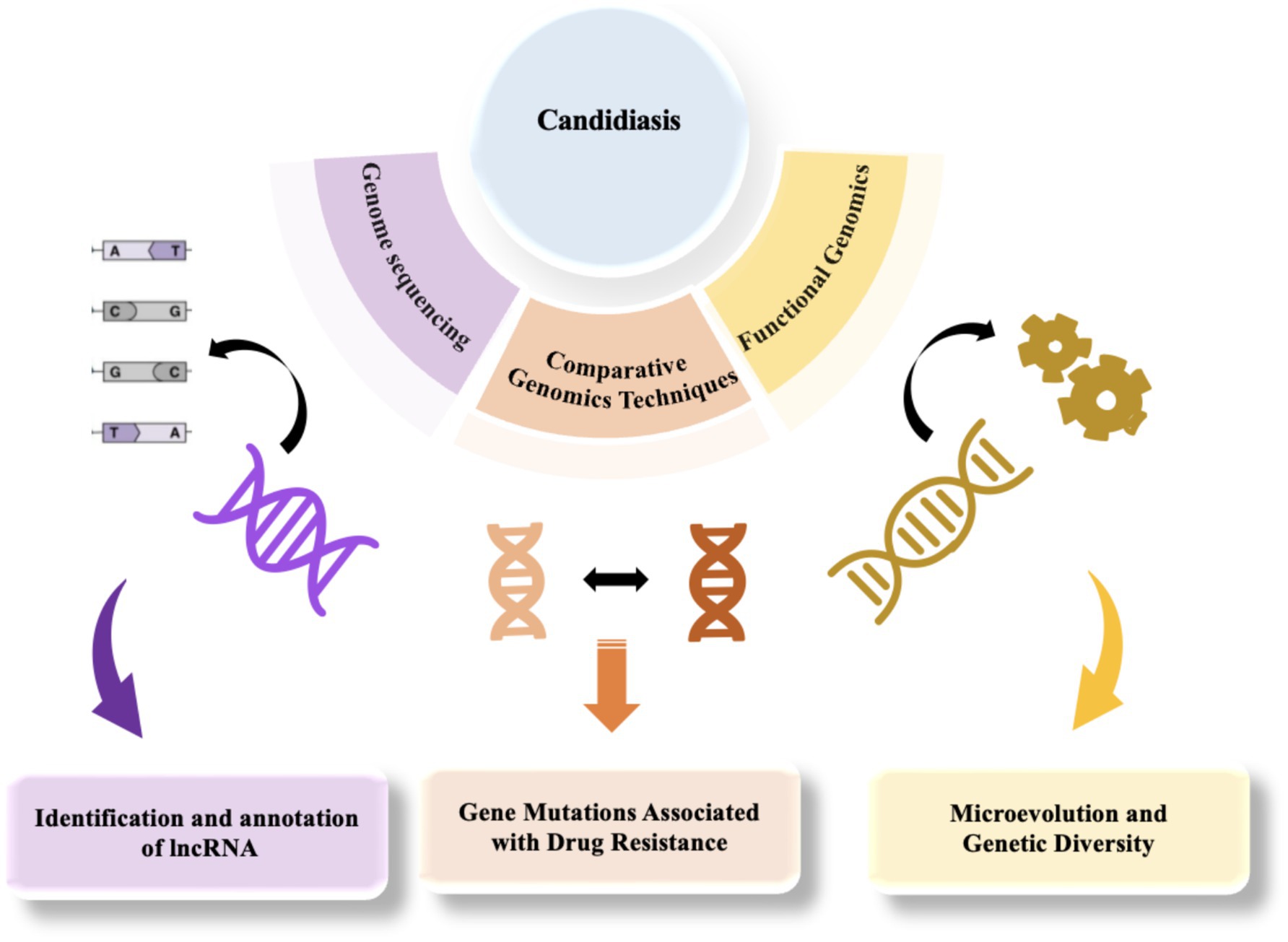
Figure 2. The application of genomics in the study of candidiasis, from sequencing to functional analysis.
In terms of drug resistance, researchers have identified multiple gene mutations and mechanisms associated with resistance. Kannan et al. (2019) discovered 18 non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with multidrug resistance through comparative genomic analysis, with six SNPs being particularly implicated in resistance to various antifungal agents (Kannan et al., 2019). These findings indicate that genomic analysis not only provides clues to resistance mechanisms but also helps identify specific resistance genes. Czajka et al. (2023) summarized the antifungal drug resistance mechanisms of Candida species, pointing out that the development of resistance is primarily attributed to three factors: gene mutations, transcriptional regulation, and biofilm formation (Czajka et al., 2023). Moreover, Helmstetter et al. (2022) conducted an in-depth investigation into the microevolution of C. glabrata in clinical settings, revealing high levels of variation and recombination in mitochondrial genomes, pathogenic genes, and drug targets. This not only highlights the significant genetic diversity of C. glabrata but also demonstrates its capacity for rapid adaptability. It emphasizes that the inherent genetic diversity within C. glabrata populations may have a significant impact on its pathogenicity and drug resistance, with microevolution and genetic exchange/recombination being the two key primary drivers of this diversity (Helmstetter et al., 2022). Chow et al. (2020) traced the global spread history of the multidrug-resistant C. auris by comparing the genomes of 304 isolates, revealing its population structure and evolutionary relationships across different geographic regions (Chow et al., 2020). The results corroborate the hypothesis that C. auris may have spread to different countries through multiple independent introductions and provide insights into its global transmission patterns, which encompass multiple origins, geographic admixture, rapid evolutionary changes, and the maintenance of population structure. These findings are pivotal for public health surveillance, hospital infection control, and the development of personalized treatment strategies. However, the research did not extensively discuss the drug resistance characteristics of different lineages of C. auris and their relationship with genomic variations, thus necessitating the application of comparative genomics and further exploration.
Comparative genomics allows scientists to systematically compare the genomes of different Candida species, thereby identifying specific genes associated with pathogenicity and drug resistance. For example, Kannan et al. (2019) utilized comparative genomics to elucidate the genetic basis of multidrug resistance (MDR) mechanisms within the Candida genus, demonstrating that genomic analysis can identify important mutations (e.g., MRR1, FKS1, ERG3, and ERG4 gene) related to drug resistance (Kannan et al., 2019). Additionally, Maphanga et al. (2021) revealed the genetic basis of multidrug resistance in C. auris isolates from bloodstream infections through genomic analysis, identifying a suite of gene mutations associated with antifungal drug resistance, including ERG11, FKS1, UPC2, and FKS2 (Maphanga et al., 2021). These genes are also widely present in other Candida species (such as C. albicans, C. glabrata, and C. parapsilosis.), constituting a critical genetic basis for the multidrug resistance of Candida (Ibe et al., 2025; Boyce, 2023; Bédard et al., 2024; ElFeky et al., 2025). This provides new insights into the mechanisms of antifungal resistance in Candida and offers important reference data for clinical antifungal therapy.
In terms of virulence and resistance genes, significant differences and similarities exist among Candida species. For instance, in C. albicans, virulence is primarily regulated by adhesin genes (ALS family), hydrolase genes (SAP family), and morphogenesis-related genes such as EFG1 and CPH1 (Davari et al., 2019; Bras et al., 2024). In contrast, virulence of C. glabrata relies on the EPA family of adhesin genes and drug resistance-related genes such as CDR1 and PDH1 (Caudle et al., 2011). Notably, C. tropicalis and C. krusei exhibit unique virulence and resistance mechanisms, with C. tropicalis depending on the SAP family, which degrades host proteins to facilitate invasion and evasion of the host immune response, and also enables nutrient acquisition from the host, and BCR1 genes, which regulate cell wall remodeling, promote hyphal formation, assist Candida in adapting to different environments, resist host immune responses, and invade host tissues to initiate infection, while C. krusei demonstrates intrinsic resistance to fluconazole, potentially linked to mutations in the ERG11 gene (Pais et al., 2016; Modrzewska and Kurnatowski, 2015). Despite these differences, conserved mechanisms such as efflux pump genes and biofilm formation genes are shared across Candida species (Frías-De-León et al., 2021). However, variations in genome size and structure, gene family expansion, horizontal gene transfer, and specific virulence or resistance mechanisms highlight the diversity within the Candida genus (Zhou et al., 2021).
While the above studies have identified drug resistance-related gene mutations in pathogenic fungi at the genomic level, they lack further functional validation and mechanistic investigation, which limits a deeper understanding of resistance mechanisms. Consequently, there is an imperative for comprehensive research in functional genomics to elucidate the adaptive significance of these genes across different Candida species.
In the study of Candida functional genomics, to comprehensively explore the molecular basis of Candida drug resistance and pathogenic mechanisms, it is necessary to adopt various experimental methods for the validation of gene functions. Firstly, gene function validation experiments are one of the core methodologies. Through gene knockout or overexpression experiments, we can directly verify the roles that specific genes play in drug resistance and virulence of Candida species, such as C. glabrata and C. tropicalis (Gale et al., 2023; Paul et al., 2022). This method provides us with intuitive evidence demonstrating the impact of gene function on the biological characteristics of Candida. Secondly, expression analysis is also an indispensable part. Advanced technologies such as RNA sequencing can be utilized to deeply analyze the gene expression changes of Candida under different environmental conditions (e.g., antifungal drug treatment; Zuber et al., 2023; Helmstetter et al., 2022). By comparing the gene expression differences between resistant strains and sensitive strains, key genes related to drug resistance can be identified, providing important clues for subsequent research. Moreover, the application of genome sequencing technology has greatly advanced the development of Candida functional genomics. Through whole-genome sequencing, we are able to unveil the genetic variations between resistant and susceptible strains of Candida, which may involve critical aspects of the resistance mechanisms (Helmstetter et al., 2022; Burrack et al., 2022). Based on these findings, we can further explore the molecular mechanisms of drug resistance, providing a theoretical foundation for the development of novel antifungal agents. Finally, functional genomics analysis, as a systematic research approach, integrates data from multiple aspects including gene expression and genetic variation (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2022; Helmstetter et al., 2022; Burrack et al., 2022). Using this method, a more comprehensive understanding can be gained of how Candida regulates its genome to adapt to the host environment during the infection process. These comprehensive verifications and analyses not only contribute to unveiling the complex mechanisms of Candida resistance but also provide a scientific basis for formulating effective treatment regimens.
In functional genomics, researchers have explored how Candida species regulates its genome to adapt to the host environment during infection by analyzing gene expression and gene function. Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón (2022) highlighted that the study of genomic sequences is fundamental for identifying pathogenic and drug-resistant characteristics, emphasizing the importance of comparative genomics and population genomics in elucidating these traits (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2022). Building on the foundation of comparative genomics, studies using improved annotation tools, CRISPR-Cas9 technology, and long-read sequencing have shown that genomic alterations, such as gene expansion and horizontal gene transfer, are intimately linked to the emergence of fungal pathogenicity and drug resistance. Population genomics research has revealed the genetic structure of fungal pathogen populations, identifying genetic variants associated with these traits through genome-wide association studies. Moreover, directed evolution experiments have detected phenotypic mutations under controlled conditions, further simplifying the identification of mutations related to pathogenicity and drug resistance (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2022). Other studies, such as the Candida Comparative Genomics Project that sequenced and annotated multiple Candida species including C. albicans (WO-1), C. tropicalis, C. guilliermondii, and C. lusitaniae (Butler et al., 2009), population genomics research on C. albicans revealing evidence of gene flow and (para) sexuality in nature (Ropars et al., 2018), recent investigations on gene selection and drug resistance analyzing the genomes and phenotypes of 2,000 Candida strains (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2024), and studies utilizing direct RNA sequencing technology to examine the mitochondrial transcriptome of C. albicans (Piątkowski et al., 2024), have also made significant contributions to the understanding of this field.
In addition to direct whole genome sequencing for comparative genomics, transposon mutagenesis and transposon insertion site sequencing (Tn-seq) technologies play crucial roles in understanding Candida’s pathogenic mechanisms. Transposon mutagenesis technology is not only applicable for large-scale screening of genes affecting Candida virulence and identification of virulence factors but also for investigating the functions of genes that play a pivotal role during infection processes, thereby uncovering the functions of previously unknown genes and deepening our understanding of Candida biology (Kim et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). Moreover, Tn-seq facilitates precise localization of transposon insertion sites, identifies affected genes, and promotes accurate studies of gene function, aiding functional genomics research to comprehensively elucidate the roles of genes in Candida virulence and adaptability (Nickels et al., 2024; Xiong et al., 2024). For instance, utilizing Tn-seq technology, researchers have identified multiple known virulence factors and novel genes critical for virulence and adaptability across the entire genome of C. glabrata, providing new insights into its pathogenic mechanisms (Nickels et al., 2024). Researchers have also employed functional genomics analysis using transposon mutant libraries to study the adaptability of C. albicans under various environmental conditions, discovering several important genes related to adaptability, including novel genes involved in cell wall synthesis, metabolism, and stress response (Xiong et al., 2024).
These above studies contribute significantly to understanding candidiasis by elucidating how genetic variations and mutations in Candida species affect their adaptability to host environments, virulence, and resistance to antifungal treatments, and by providing a solid foundation for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies and personalized treatment regimens (Jacobs et al., 2024; Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2024).
In the study of candidiasis, to optimize treatment strategies and facilitate the creation of innovative antifungal drugs and diagnostic technologies, we should pay more attention to the following comparative genomics and functional genomics techniques. In the field of comparative genomics technology, noteworthy aspects include genome sequencing and alignment, evolutionary analysis, and genome collinearity analysis. These techniques can unveil the genomic diversity, evolutionary relationships, and structural similarities of Candida genomes, providing crucial information for understanding the adaptability and pathogenicity of Candida. Specifically, genome sequencing and alignment technologies can identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions/deletions (InDels), and structural variations (SVs) (Arafa et al., 2023). Evolutionary analysis aids in elucidating the evolutionary history of Candida and the mechanisms underlying the evolution of traits such as drug resistance (Morschhäuser, 2024). Meanwhile, genome collinearity analysis can detect events such as genome rearrangements and gene duplications (Arafa et al., 2023), which are closely related to the adaptability and pathogenicity of Candida. In the field of functional genomics technology, transcriptomics, gene knockout and knock-in technologies, as well as proteomics and metabolomics, all hold significant value. Transcriptomics can identify differentially expressed genes of Candida under various conditions (Xiong et al., 2024), providing clues for drug target prediction (Xiong et al., 2024). Gene knockout and knock-in technologies (e.g., CRISPR-Cas9) can directly elucidate the functions of specific genes in Candida growth, pathogenicity, and drug resistance, while also identifying potential drug targets (Wang et al., 2022). Proteomics and metabolomics further unveil the expression and regulatory mechanisms of functional genes in Candida (Xiong et al., 2024). In the study of candidiasis, these aforementioned techniques each have their own characteristics and complement each other. For instance, genome sequencing and alignment can pinpoint specific genetic variations that may confer drug resistance or enhance virulence (Gaston et al., 2025), while transcriptomics can reveal how these genetic changes impact gene expression patterns under different environmental conditions (Zhang et al., 2025). Gene knockout and knock-in technologies allow for the functional validation of these genes, confirming their roles in pathogenicity and drug resistance (Hou et al., 2025). Meanwhile, proteomics and metabolomics provide insights into the downstream effects of these genetic and transcriptional changes on cellular processes and metabolic pathways. Therefore, the research on candidiasis should comprehensively integrate these technologies to jointly promote the optimization of treatment strategies and the development of innovative antifungal drugs and diagnostic techniques.
In summary, the application of genomics technologies has markedly advanced in-depth research on candidiasis, providing a theoretical framework for clinical management and guiding the development of future antifungal drug development (Figure 2). However, considering the global challenge of candidiasis, it is still necessary to delve into the molecular mechanisms and evolutionary pathways of drug resistance. This exploration should be complemented by optimizing treatment strategies through comparative and functional genomics, as well as by fostering the creation of innovative antifungal drugs and diagnostic techniques. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and ongoing innovation, both greater breakthroughs in the research and treatment of candidiasis are anticipated.
3 Pathogenic mechanisms of Candida
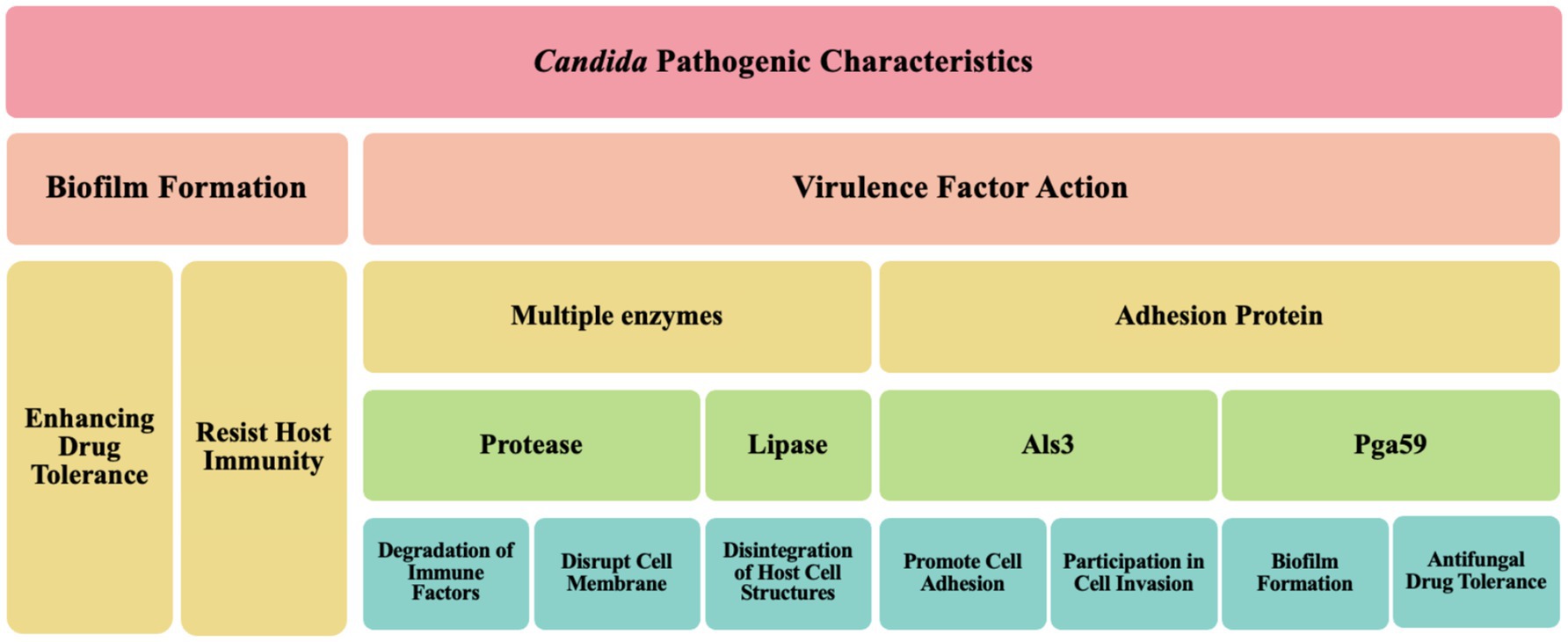
3.1 Pathogenic characteristics of Candida species
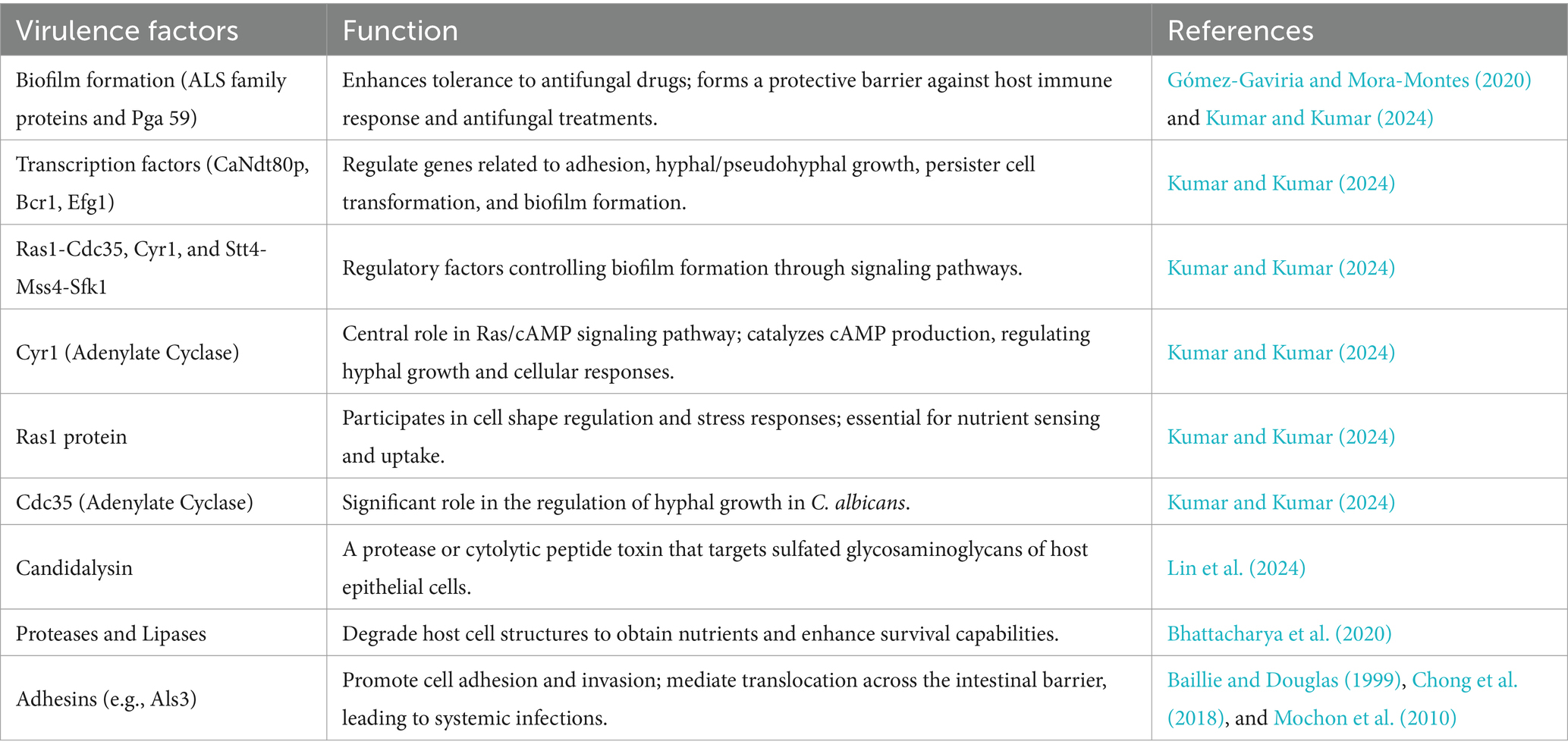
Candida, a significant human pathogenic fungus, its pathogenic characteristics are primarily manifested in biofilm formation and the action of virulence factors (Figure 3). Biofilm formation is a key feature of Candida infections, significantly enhancing its tolerance to antifungal drugs. These biofilms are typically complex structures composed of fungal cells, extracellular matrix, and other microbial symbionts, forming a protective barrier that shields Candida from both the host’s immune response and antifungal treatment attacks (Gómez-Gaviria and Mora-Montes, 2020). Further research, such as that revealed by Kumar and Kumar (2024), indicates that the biofilm formation mechanism in C. albicans involves multiple molecular determinants, including the precise regulation by transcription factors (e.g., CaNdt80p, Bcr1, and Efg1) and regulatory factors (e.g., Ras1-Cdc35, Cyr1, and Stt4-Mss4-Sfk1). These factors work in concert to control the expression of genes related to adhesion, hyphal/pseudohyphal growth, persister cell transformation, and overall biofilm formation. Notably, Cyr1, as an adenylate cyclase, plays a central role in the Ras/cAMP signaling pathway, catalyzing the production of cAMP, which serves as a crucial second messenger in regulating hyphal growth and various other cellular responses. Additionally, the Ras1 protein, a key component of the Ras/cAMP signaling pathway, not only participates in the regulation of cell shape but also exerts precise control over various stress responses, which is essential for nutrient sensing and uptake in C. albicans. Moreover, Cdc35, another adenylate cyclase, plays a significant role in the regulation of hyphal growth in C. albicans. The complex gene expression differences and regulation within the biofilm not only lead to adaptive changes in the morphology and metabolism of Candida but also enable it to form a robust protective barrier composed of fungal cells, an extracellular matrix, and other microbial symbionts. This barrier effectively resists attacks from the host immune system and exhibits significant resistance to antifungal treatments (Kumar and Kumar, 2024). Furthermore, previous studies have indicated that Candida promotes its colonization and infection capabilities by forming biofilms on host tissues and medical implants (Villard et al., 2015; Shinde et al., 2012; Gao et al., 2013), corroborating the latest findings on C. albicans biofilm formation mechanisms by Kumar and Kumar (2024). This highlights the critical role and complexity of Candida biofilms in their pathogenic processes. According to a recent study by Zeng et al. (2023), Rubiginosin C can effectively inhibit the biofilm formation and morphological transitions of C. auris and C. albicans, thereby exerting an inhibitory effect without causing lethal effects on host cells (Zeng et al., 2023). This finding underscores the importance of biofilms in the challenges of antifungal therapy and provides strong support for the development of novel antifungal drugs.
The pathogenicity of Candida is closely related to its multiple virulence factors. On one hand, Candida can produce various enzymes, such as proteases and lipases, which are instrumental in the invasion and damage of host tissues. For example, Lin et al. (2024) demonstrated that C. albicans can secrete candidalysin, a protease or cytolytic peptide toxin, which targets the sulfated glycosaminoglycans of host epithelial cells (Lin et al., 2024). This indicates that Candida can degrade host cell structures by releasing enzymes to obtain nutrients and enhance its survival capabilities (Bhattacharya et al., 2020). On the other hand, the adhesins on the surface of Candida also significantly influence its pathogenicity. These adhesins, such as Als3, are multifunctional, not only promoting cell adhesion but also participating in cell invasion, thereby helping Candida effectively attach to host cells (Baillie and Douglas, 1999). Additionally, these adhesins can mediate the translocation of Candida across the intestinal barrier, leading to systemic infections (Chong et al., 2018; Mochon et al., 2010).
Collectively, the pathogenic characteristics of Candida are primarily achieved through the formation of biofilms and the action of multiple virulence factors (Table 1), which enable it to successfully survive and cause infections in various host environments.
In the pathogenic mechanisms of Candida, core virulence factors (Table 1) play a vital role. Key virulence factors encompass a spectrum of enzymes and adhesion proteins that synergistically target the host to facilitate infection onset and progression.
3.1.1 Crucial factors in biofilm formation and pathogenicity of Candida
Candida species, especially C. albicans, are significant pathogens causing diverse infections. Their ability to form drug- and immune-resistant biofilms is crucial for pathogenicity, necessitating an understanding of biofilm formation mechanisms for effective treatment.
Adhesins of Candida are also central to their pathogenicity, binding to specific receptors on the surface of host cells to promote adhesion and colonization. Studies have shown that adhesins such as the ALS family proteins not only enhance the adhesion of Candida to epithelial cells (Muñoz et al., 2018; Nishimoto et al., 2020), but also participate in biofilm formation, significantly increasing its survival and drug resistance within biofilms. These biofilms are closely associated with antifungal drug tolerance and host immune evasion, making them a major challenge in clinical settings.
In addition to the ALS family proteins, another key component in biofilm formation is Pga59. Pga59 is an amyloid protein in the cell wall of C. albicans, and X-ray diffraction measurements have revealed its critical role in adhesion and biofilm establishment (Mourer et al., 2023). Given that biofilms are closely associated with antifungal drug tolerance and host immune evasion, Pga59 plays a significant role in the pathogenic mechanisms of C. albicans, with recent studies highlighting its major contribution to biofilm structural stability (Mourer et al., 2023).
In summary, the adhesins of Candida, particularly the ALS family proteins and Pga59, are key in biofilm formation and pathogenicity, enhancing adhesion, stability, and drug resistance. Future research may offer new strategies to combat Candida infections.
3.1.2 Other important virulence factors of Candida
Candida proteases, such as the SAP family proteases, act as virulence factors by effectively degrading host immune factors and extracellular matrix components, thereby enabling the fungus to evade host immune surveillance and promote its invasiveness (Nishimoto et al., 2020). Specifically, the Sap2 protease not only degrades host immunoglobulins but also promotes fungal growth by compromising the integrity of host cell membranes. Additionally, recent studies have confirmed the critical role of Sap2 in immune evasion (Lin et al., 2023).
Additionally, the virulence factors of Candida also include specific cell wall components (e.g., β-glucan). These components provide structural stability and modulate immune responses by interacting with the host’s immune system, thereby promoting the pathogenicity of Candida (Yoo et al., 2020). β-glucan can be recognized by the Dectin-1 receptor on the surface of host cells, thereby activating the host’s immune response (Netea et al., 2006). This process not only inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone resorption (Zhu et al., 2017) but also suppresses inflammation and bone destruction by producing calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) (Maruyama et al., 2017). These findings also explain the phenomenon previously observed by Amanai et al. (2008), where Candida-infected rats in an experimental osteoarthritis model exhibited irregular new bone formation and significant bone resorption, leading to severe joint bone deformities (Amanai et al., 2008). Therefore, specific cell wall components of Candida can significantly augment its pathogenicity by influencing host immune response and bone resorption processes.
In summary, the core virulence factors of Candida, including various enzymes and adhesion proteins, significantly augment its pathogenicity by disrupting host cells and their immune responses, making it a dangerous pathogen.
4 Mechanisms of antifungal resistance in Candida
4.1 Overview of major drug resistance types and their mechanisms
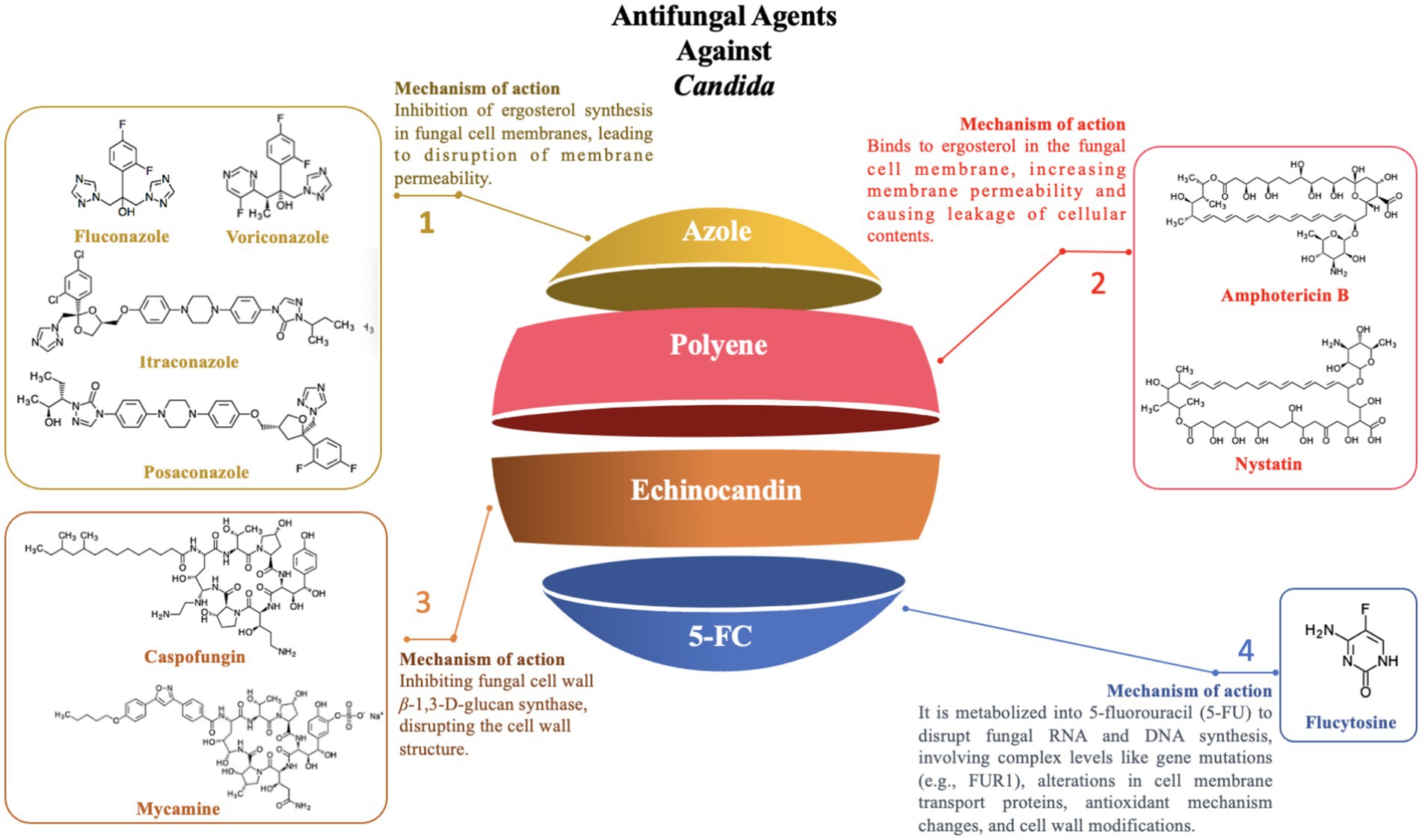
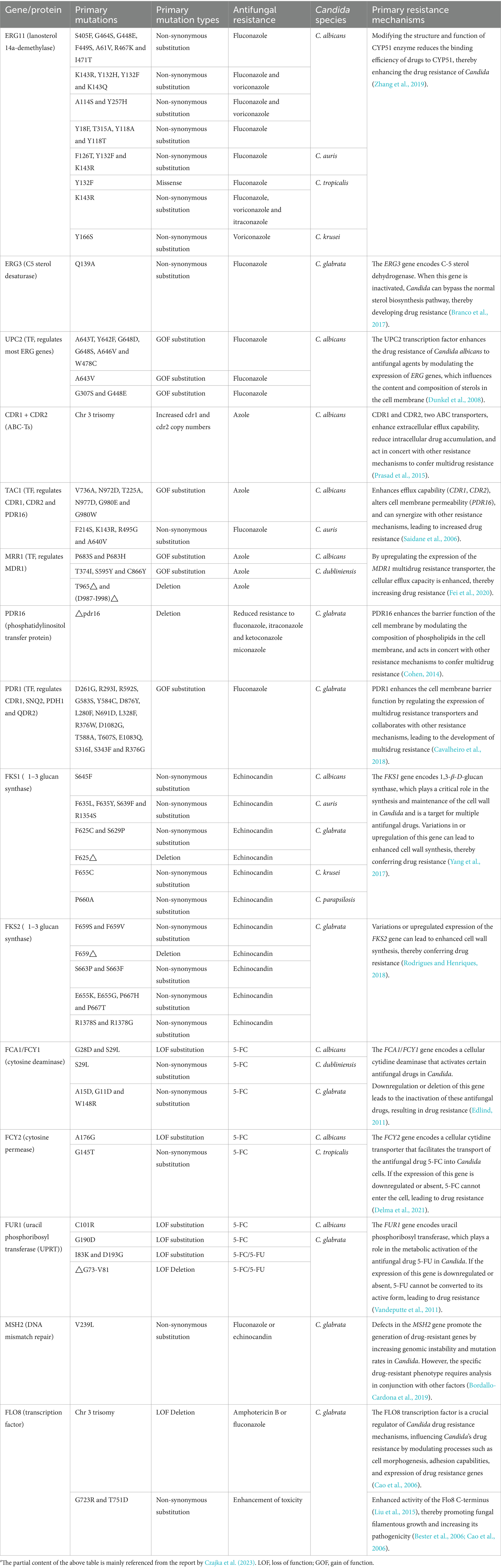
With the widespread use of antifungal agents, antifungal resistance in Candida species has become an increasingly severe issue. This resistance issue is mediated by a variety of mechanisms that are species-specific and can be categorized as follows (Figure 4):
4.1.1 Azole resistance
Azole drugs, including fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole, primarily target the sterol-14-α-demethylase (CYP51) enzyme, which is pivotal in ergosterol synthesis, thereby disrupting the formation of the fungal cell membrane. Among these, the mechanism of fluconazole resistance in Candida primarily involves mutations in the ERG11 gene and the overexpression of specific transporters (e.g., CDR1 and CDR2). The ERG11 gene encodes CYP51 in Candida and is the primary target of fluconazole. Studies have shown that specific mutations in the ERG11 gene, particularly the Y132F and Y132H variants, significantly alter the structure and function of the CYP51 enzyme, reducing the binding efficiency of fluconazole to the enzyme, thereby enhancing the resistance of Candida to fluconazole. Additionally, molecular docking and simulation techniques have revealed that variations or conformational changes in other key residues of the CYP51 enzyme (e.g., I304, G308, I379) also affect the binding affinity, further weakening the antimicrobial efficacy (Medeiros et al., 2022). In addition to ERG11 mutations, overexpression of transporters like CDR1 and CDR2 has been confirmed to contribute to fluconazole resistance through real-time PCR and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, as it augments Candida’s efflux capacity, expelling fluconazole before it can exert its intracellular effects (Maenchantrarath et al., 2022). However, mutations in the ERG11 gene and overexpression of specific transporters are not the sole mechanisms of azole resistance. In addition to these two mechanisms, other resistance mechanisms exist, including genomic amplification of the ERG11 gene (Hu et al., 2023), mutations in transcription factors (such as TAC1, leading to overexpression of both the ERG11 gene and efflux pump genes) (Fan et al., 2023), biofilm formation (Siqueira et al., 2025), and mutations in other genes (such as MRR1) that may also be associated with azole resistance (Branco et al., 2022). In summary, the resistance of Candida to azole drugs is the result of the synergistic action of the aforementioned multiple molecular mechanisms, which makes its treatment challenging.
4.1.2 Polyene resistance
Polyene antifungals primarily include Amphotericin B and Nystatin, which mainly act by binding to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, leading to increased membrane permeability and subsequent leakage of cellular contents, ultimately resulting in cell death (Wang et al., 2021). Although Amphotericin B is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent, it has faced a significant challenge in clinical practice due to the emergence of resistance among Candida species.
The resistance mechanism of Candida to amphotericin B involves not only changes in cell membrane components but is also closely related to biofilm formation. In particular, biofilm formation can significantly enhance the drug resistance of Candida. Moreover, the FLO8 gene, a key transcription factor in biofilm formation, plays a pivotal role in this process. Mutations in the FLO8 gene promote biofilm formation, thus significantly enhancing Candida’s resistance to amphotericin B (Misas et al., 2019). Therefore, in species such as C. auris and C. albicans, FLO8 gene mutations play a pivotal role in the development of amphotericin B resistance (Fenton and John, 2024; Jin et al., 2023).
Beyond biofilm formation, variations in multiple genes associated with the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway, such as ERG1, ERG2, ERG3, ERG5, ERG6, ERG11, and ERG13, greatly influence Candida’s resistance to amphotericin B. Overexpression or functional alterations in these genes can lead to adjustments in the lipid composition of the cell membrane, thereby affecting the binding capacity of amphotericin B to the cell membrane (Chybowska et al., 2020; Sarma and Upadhyay, 2017; Iguchi et al., 2019; Chatterjee et al., 2015; Arendrup et al., 2017; Kean and Ramage, 2019). These processes involve changes in multiple genes and cellular structures, which collectively enable Candida to effectively resist the antimicrobial effects of amphotericin B (Bohner et al., 2022; Chaabane et al., 2019).
4.1.3 Echinocandin resistance
Echinocandins, a class of antifungal agents that target the synthesis of β-1,3-D-glucan in the fungal cell wall (Szymański et al., 2022), inhibit the synthesis of the fungal cell wall, leading to cell death. In recent years, echinocandins have shown significant therapeutic potential in clinical treatment. These drugs are not only used independently for antifungal therapy but are also frequently combined with other antifungal or non-antifungal drugs to enhance therapeutic outcomes (Dos Reis et al., 2023). However, with the widespread use of echinocandins, resistance among Candida species has become a growing concern, posing a major challenge in clinical treatment.
Studies have shown that Candida resistance to echinocandins is predominantly mediated through mutations in the FKS1 gene, which encodes a key enzyme in β-1,3-D-glucan synthesis (Frías-De-León et al., 2020; Lara-Aguilar et al., 2021; Kordalewska et al., 2023). As early as 2018, Kordalewska et al. reported that four Candida isolates from India exhibited resistance to all echinocandins tested, with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values reaching or exceeding 4 mg/L within 24 h. Further analysis through PCR amplification and sequencing revealed specific mutations (e.g., S639F) in the FKS1 gene of these resistant strains, which were absent in sensitive strains and aligned with known echinocandin resistance mechanisms. Mouse model experiments corroborated these findings, showing that strains carrying specific FKS1 gene mutations exhibited resistance to echinocandins in vivo, whereas wild-type strains did not (Kordalewska et al., 2018).
Although the role of the FKS2 gene in Candida drug resistance is relatively minor, studies have revealed that its mutations may also lead to partial echinocandin resistance (Asadzadeh et al., 2022). It is important to note that research on specific types, frequencies, and contributions of FKS2 gene mutations to drug resistance remains limited and requires further in-depth investigation. Candida resistance to echinocandins not only complicates treatment but also significantly increases its pathogenicity and risk of infection, particularly in immunosuppressed patients (Lakshmi et al., 2018).
4.1.4 5-Fluorocytosine
5-Fluorocytosine (5-FC) can be utilized to target and disrupt nucleic acid biosynthesis within cells, functioning as a nucleoside analog. When combined with polyene antifungal agents such as amphotericin B, it is a reliable option for the treatment of refractory Candida infections and Cryptococcus meningitis. This drug demonstrates good efficacy against several major Candida species, including C. albicans, C. parapsilosis, and C. dubliniensis.
The mechanisms of Candida resistance to 5-FC involve multiple complex levels (Czajka et al., 2023; Delma et al., 2021). Specifically, 5-FC must be metabolized intracellularly to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) to interfere with fungal RNA and DNA synthesis. However, mutations in 5-FC metabolism-related genes (e.g., the FUR1 gene) can impede this effective conversion, leading to resistance (Edlind Thomas and Katiyar Santosh, 2010). Additionally, alterations in cell membrane transporters, including (e.g., FCY2 and AFR1), can reduce intracellular 5-FC concentrations, while enhanced intracellular antioxidant mechanisms can better counteract the oxidative stress generated by 5-FU (Billmyre et al., 2020; Chang et al., 2021), both of which contribute to resistance development. Furthermore, changes in cell wall components, acting as the first barrier for 5-FC entry, can decrease 5-FC permeability, further contributing to resistance (Czajka et al., 2023).
In summary, the resistance mechanisms of Candida to antifungal drugs are multifaceted, involving gene mutations, drug transport, and cell wall synthesis (Table 1). These mechanisms not only complicate treatment but also enhance the pathogenicity and infection risk of Candida, posing significant challenges to clinical therapy. In this context, whole-genome studies, as a powerful tool, play an invaluable role in advancing the understanding of Candida resistance mechanisms, the development of novel antifungal drugs, and the innovation of therapeutic strategies. By conducting in-depth whole-genome studies and integrating advanced technologies such as high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, it is crucial for elucidating Candida resistance mechanisms, developing new antifungal drugs and therapeutic strategies, and ultimately controlling Candida infections. This will equip clinicians and researchers with more powerful tools to confront the growing challenges posed by Candida infections and improve patient outcomes.
4.2 Mechanisms of drug resistance based on genomic variation and evolution
4.2.1 Evolution and genomic variation of Candida
Candida has undergone complex evolutionary mechanisms in diverse environments, including gene flow, hybridization, and microevolution. Gene flow is a critical evolutionary force in populations of the Candida genus, significantly shaping the diversity and adaptability of these fungi. Specifically, Candida species have the ability to acquire new traits through the biological process of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) (Chakrabarti and Sood, 2021; Sekizuka et al., 2019). This genetic exchange across strains or species not only provides Candida with valuable genetic resources but also greatly enhances its survival and reproduction under varying environmental conditions. HGT enables Candida to rapidly adapt to environmental shifts, including adjustments in metabolic pathways and morphological transformations, thereby allowing Candida to thrive in a variety of ecological niches, including those that were not part of its original habitats (Santana et al., 2024; Rhodes et al., 2024; Santana and O'Meara, 2021). For example, Candida species may have initially evolved in an intermediate host, such as birds, and later acquired traits through HGT that enabled them to adapt to human habitats (Chakrabarti and Sood, 2021), thereby facilitating their spread into human populations. Additionally, due to restricted gene flow within populations, Candida may have developed unique adaptive traits in different regions (Chow et al., 2020). This interplay between geographic isolation and restricted gene flow further drives the diversity and geographical specialization of the Candida genus. Therefore, horizontal gene transfer not only provides Candida with a rich source of genetic variation but also promotes its rapid adaptation and dissemination in different environments, making it a globally emerging multidrug-resistant fungal pathogen (Santana et al., 2024; Yue et al., 2018; Santana and O'Meara, 2021). In recent years, genomic sequencing, comparative analysis, and gene mutation detection have enabled scientists to identify the primary sources of Candida drug resistance. Ksiezopolska and Gabaldón, (2018) identified that the causes of resistance to major antifungal drugs, such as fluconazole and amphotericin B, are often due to mutations in specific genes (Ksiezopolska and Gabaldón, 2018). These mutated genes, such as Erg11, Upc2p, Mrr1p, Tac1p, CDR1, and CDR2, are particularly prevalent in specific Candida populations (Lohberger et al., 2014; Znaidi et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2015). The distribution of these genetic variations among different populations is closely related to the genetic background of the populations, the environmental pressures, and the selective pressures for drug resistance.
Microevolutionary processes also play a critical role in the evolution of Candida. Selective pressures in different environments drive genetic mutations and selective amplification in Candida, leading to significant changes in its survival and pathogenic capabilities. Studies have shown that Candida can rapidly develop drug resistance through microevolution when exposed to antifungal drugs, an adaptive mechanism that enhances its survival in clinical settings (Kannan et al., 2019). For example, research on C. glabrata has revealed that this species achieves adaptation to antifungal drugs through small-scale genomic changes, such as copy number variations (CNVs) (Ropars et al., 2018). Further studies indicate a close link between drug resistance and adaptability in Candida. Research on C. albicans has shown that certain drug-resistant mutations not only enhance the survival of Candida in drug-exposed environments but are also associated with increased virulence traits. This association may involve multiple levels of biological processes, including genomic instability, altered metabolic activity, and gene recombination. These processes are driven not only by genetic mutations but may also be influenced by the interaction of environmental and genetic factors (Priest et al., 2020). These physiological and biochemical changes, whether acting independently or synergistically, significantly enhance the adaptability and pathogenicity of Candida, making it more difficult to control infections.
Collectively, the evolutionary mechanisms of Candida in different environments are multifaceted and complex, with gene flow, hybridization, and microevolution collectively driving the development of its adaptability and pathogenicity. The variations resulting from these evolutionary mechanisms, such as point mutations, insertions/deletions, and CNVs, are pivotal in the development of antifungal resistance in Candida, providing valuable biological insights for the control of Candida infections.
4.2.2 Point mutations
During the process of Candida developing resistance to antifungal drugs, point mutations serve as a core mechanism, playing a crucial role (Table 2). Specifically, regarding the antifungal drug fluconazole, studies have revealed that point mutations in the ERG11 gene are one of the key factors leading to resistance. These genetic alterations modify the drug’s binding site, diminishing the affinity between fluconazole and its molecular target, thereby enabling Candida to circumvent the drug’s antimicrobial action (Medeiros et al., 2022). Similarly, echinocandin resistance has been widely reported as being associated with mutations in the FKS1 gene, which are recognized as an important resistance mechanism. These mutations not only affect the interaction between echinocandins and the target enzyme but may also induce functional changes in the enzyme, endowing Candida with resistance to echinocandins (Lara-Aguilar et al., 2021; Kordalewska et al., 2023). Drug resistance in Candida is not only due to genetic mutations but can also spread through genetic recombination and gene flow among distinct species. Research by Märtson et al. (2021) has shown that certain Candida species, such as C. albicans and C. glabrata, can develop resistance to multiple antifungal drugs. These resistance genes can be transmitted through genetic recombination and gene flow among different species, leading to an increase in resistant strains (Märtson et al., 2021). Moreover, some non-Candida albicans species, such as C. krusei and C. tropicalis, are inherently more resistant to certain antifungal drugs, which also complicates therapeutic strategies.
Therefore, point mutations play a crucial role in the development of antifungal drug resistance in Candida, whether against fluconazole or echinocandins. Mutations in key genes like ERG11 and FKS1 are critical in leading to treatment failure. Currently, point mutations at the gene level primarily include non-synonymous substitutions, missense mutations, and deletions; at the amino acid level, they can be categorized into gain-of-function (GOF) substitutions and loss-of-function (LOF) substitutions (Chaabane et al., 2019; Frías-De-León et al., 2020; Table 1).
4.2.3 Copy number variation
Copy Number Variation (CNVs) refers to changes in the copy number of certain genes within the genome, a mechanism that is also commonly observed in the development of antifungal resistance in Candida (Table 2). Specifically, studies have found that upon exposure to antifungal drugs, the copy number of genes associated with drug transporters in Candida’s genome significantly increases (Maenchantrarath et al., 2022). This increase in copy number directly enhances the capacity of Candida to expel the drug, thereby reducing the effective intracellular drug concentration and enhancing the organism’s resistance. Furthermore, as Candida continuously adapts to antifungal drug pressure, its genome undergoes a series of changes, including the emergence of numerous new high-copy-number genes (Todd and Selmecki, 2020). These newly emerged CNVs not only endow Candida with the ability to rapidly adapt to drug environments but also enable it to survive and reproduce under drug pressure. Therefore, CNVs play a significant role in the development and maintenance of antifungal resistance in Candida.
4.2.4 Microevolution
Due to the limited gene flow between different geographic regions, unique resistant genotypes can emerge in localized areas (Chow et al., 2020). This genetic differentiation, driven by geographic isolation, forms a complex foundation for the evolution of antifungal resistance in Candida. Additionally, Candida also has the ability to acquire novel resistance genes through horizontal gene transfer (HGT). This process is further enhanced by the hybridization between different genotypes of Candida, significantly facilitating the rapid formation and extensive dissemination of genetic diversity (Chakrabarti and Sood, 2021; Gifford et al., 2024). The rapid diversification of its genome, particularly linked to the rapid development of resistance (Bravo Ruiz et al., 2019; Wang and Xu, 2022), highlighting the high adaptability and flexibility of Candida in response to various clinical treatment challenges. In light of the growing challenge of antifungal treatment for Candida, it is important to enhance the monitoring and management of its resistance to curb further spread (Ionescu et al., 2024). To address this global issue, researchers are vigorously exploring new therapeutic approaches, including the development of monoclonal antibodies targeting Candida (Singh et al., 2023), aiming to break the limitations of traditional treatments. Effectively addressing the multidrug resistance of Candida is crucial for enhancing the efficacy of clinical treatment and protecting patients from the threat posed by these pathogens.
In conclusion, the drug resistance of Candida is a complex and multifactorial process involving genomic variations, evolutionary mechanisms, and microevolutionary processes. Genetic variations such as point mutations, CNVs, and gene flow play pivotal roles in the development and dissemination of resistance. These mechanisms not only affect the sensitivity of Candida to existing antifungal drugs but also pose challenges for the development of novel drugs and therapeutic strategies. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms of Candida drug resistance is essential for developing effective preventive measures and innovative treatment methods. In the future, it is essential to further strengthen resistance surveillance, explore new therapeutic targets, and promote interdisciplinary collaboration to effectively address this growing global health issue.
5 Future directions
In summary, the field of genomics has witnessed remarkable advancements in understanding Candida infections over recent years. These findings have provided new insights into the complex biological behavior of Candida, enhancing our understanding of its virulence and resistance to antifungal agents, and informing the development of novel therapeutics and public health strategies. However, the pathogenicity and drug resistance of Candida remain complex and dynamic issues that require ongoing research and exploration. Future research should delve into the genomic resources and genetic diversity of Candida to uncover additional genes and novel mechanisms related to pathogenicity and drug resistance. Moreover, integrating clinical data with experimental validation is imperative for devising innovative treatment modalities and preventive measures to counter the public health threat posed by Candida infections.
Collectively, future research on Candida infections should prioritize the following key issues and research directions (Figure 5).
5.1 New approaches to candidiasis treatment: the significance of genomics research
Currently, the treatment strategies for candidiasis predominantly focus on the use of antifungal drugs, but the issue of drug resistance is becoming increasingly severe, which imposes a significant medical and economic burden. Therefore, it is crucial to explore new treatment methods and preventive measures. Genomics has shown broad application prospects in candidiasis research and offers new avenues and methods for its research and treatment (Lass-Flörl et al., 2024; Rhodes and Fisher, 2019). By conducting in-depth analysis of the Candida genome, researchers can uncover resistance mechanisms, achieve a better understanding of their virulence factors and regulatory mechanisms, providing a theoretical foundation for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies (Rhodes and Fisher, 2019; Fidel, 2011; Rybak et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2024). These research findings not only enhance the overall understanding of candidiasis but also promote the development of precision medicine, which could help alleviate and address the pressures and challenges of related public health issues. These research advances provide theoretical support for developing new therapeutic strategies, while specific treatment methods are continually being explored.
Based on the achievements of genomic research, investigators are exploring a multitude of novel therapeutic strategies. Alternative therapies for Candida infections and biofilm disruption strategies offer new perspectives for clinical treatment. Research has found that natural plants such as sesame, sesame leaves, and honeysuckle contain antifungal components that can be used to treat oral candidiasis. They are being explored as alternative options for antifungal drugs, capable of inhibiting the growth of oral Candida (Contaldo et al., 2023). Meanwhile, probiotic therapy, particularly strains such as Lactobacillus sp. and Bifidobacterium sp., effectively prevents the recurrence of Candida infections on oral mucosa and skin surfaces by restoring microbial balance at the infection sites. With low toxicity, it offers a safer treatment option in clinical settings (Contaldo, 2023; Fusco et al., 2023; Ricci et al., 2022). Moreover, photodynamic therapy utilizes photosensitizers and specific wavelengths of light to selectively destroy Candida cells. This method offers advantages such as non-induction of drug resistance, high selectivity, and low toxicity, introducing a novel physical approach for the treatment of Candida infections (Contaldo et al., 2023). Additionally, biofilm degradation strategies employ methods such as enzymes (like DNase) and metal chelators to break down fungal biofilms associated with Candida infections. This indirectly inhibits fungal growth and is particularly suitable for cases of recurrent or refractory Candida infections, providing a new approach to enhance the efficacy of antifungal drugs and reduce infection recurrence rates (Contaldo et al., 2023; Contaldo, 2023; Fusco et al., 2023; Chanda et al., 2017). These strategies and research prospects have opened new avenues for the clinical treatment of candidiasis infections, warranting further in-depth investigation and exploration.
5.2 In-depth research on mechanisms of antifungal resistance
Despite considerable research on antifungal resistance, further exploration is needed to understand how different Candida species develop resistance in various environments. Particularly, the complexity and severity of resistance in emerging species or strains, such as C. auris, have garnered significant attention (Rybak et al., 2022). C. auris exhibits multidrug resistance, showing resistance to commonly used antifungal agents like polyenes, echinocandins, and 5-FC (Bhattacharya et al., 2020; Rybak et al., 2022). Therefore, in-depth investigation into the specific changes in resistant genes during the mutation process and the transmission of these mutant genes within Candida populations has become a current research focus. However, existing research still faces some challenges and limitations. For example, in-depth studies on the Candida resistance mechanisms require high-precision experimental techniques and complex data analysis methods (Branco et al., 2023), demanding high levels of expertise and experimental conditions. Additionally, Candida resistance mechanisms may be influenced by multiple factors, including environmental factors and host immune status (Costa-de-Oliveira and Rodrigues, 2020; Czajka et al., 2023), and the interactions between these factors make the research even more complicated. To address these challenges, future research could explore the following aspects: First, continue to deepen the fundamental research on the mechanisms of Candida drug resistance mechanisms to uncover additional unknown resistance mechanisms; Second, strengthen interdisciplinary collaboration and utilize advanced technologies, such as bioinformatics and genomics, to conduct more comprehensive analysis and prediction of Candida drug resistance; Finally, foster the innovative development of antifungal drugs and therapeutic strategies to provide more effective solutions for combating the threat of emerging drug-resistant Candida. In particular, systematic research on the variation and transmission mechanisms of resistance genes in emerging drug-resistant species or strains, such as C. auris, and the formulation of targeted treatment strategies will be the top priority for future research (Jangir et al., 2023). Only through in-depth research and continuous exploration can we better understand and address the challenges of Candida drug resistance, ensuring the safeguarding of human health.
5.3 Integration of genomics and personalized therapy
With the rapid advancement of genomics technology, we are entering a new era where personalized treatment of Candida infections based on individual genomic characteristics is becoming feasible. Currently, in-depth analysis of the genomic data of approximately 2,000 primary Candida species (Schikora-Tamarit and Gabaldón, 2024), alongside genomic studies of emerging pathogens such as C. albicans (Bruno et al., 2021), has shed light on the genetic diversity and resistance mechanisms of Candida. Additionally, the integration of transcriptomic analysis and functional genomics approaches has provided new insights into the interactions between Candida and host defense mechanisms, offering new perspectives for personalized therapy. In the future, further exploration of the relationship between Candida resistance genomics and clinical treatment responses is expected to provide a scientific basis for personalized medicine (Stalder et al., 2023). However, achieving personalized treatment for Candida infections necessitates a holistic examination of pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenomics, and other pertinent factors (Daneshnia et al., 2023). Interdisciplinary collaboration and resource integration will be key to advancing this field.
5.4 Development of novel therapeutic strategies
Attention should be focused on the development of new antifungal drugs, particularly those targeting multidrug-resistant Candida strains, which is essential for improving treatment outcomes. With the continuous advancement of genomics technology, personalized treatment based on the individual genomic characteristics of Candida may become a reality, laying the foundation for personalized medicine. To effectively address the challenge of multidrug-resistant Candida, researchers are actively employing strategies such as drug repositioning, identification of novel targets, and the discovery or synthesis of novel compounds to explore novel antifungal drugs that can effectively inhibit these resistant strains. Meanwhile, by integrating multi-omics research methods, including transcriptomics and metabolomics, new drug targets and combination therapy strategies are being further explored to enhance treatment efficacy (Brackin et al., 2021). For example, Candida biofilms have been identified as a promising target (Kovács et al., 2021; Jamiu et al., 2021), and combination therapies may potentially overcome their resistance in the future. Collectively, the development of new antifungal drugs in combination with multi-omics research methods will be an important and effective strategy for improving the treatment outcomes of multidrug-resistant Candida.
5.5 Optimization of public health strategies
Considering the transmission characteristics of Candida, comprehensive and in-depth measures are imperative to address the public health challenges posed by Candida infections. Strengthening public health surveillance, particularly infection control in hospital environments, should be a priority. This includes implementing strict contact isolation policies, ensuring thorough environmental cleaning and disinfection to curb the spread of Candida within hospitals. Additionally, promoting international cooperation to facilitate information sharing and coordinated responses on a global scale is crucial for this cross-border challenge (Rhodes and Fisher, 2019). Close collaboration between public health departments and healthcare institutions is also indispensable, as each brings its own expertise in areas such as surveillance and early warning, the development of prevention and control strategies, and patient diagnosis and treatment. Such collaborative efforts can markedly enhance the effectiveness of control measures (Borman and Johnson, 2020). The development of new drugs targeting drug-resistant Candida is urgent, utilizing multi-omics research methods to explore new drug targets and combination therapy strategies will open new avenues for treating drug-resistant Candida infections (Janniger and Kapila, 2021).
In summary, comprehensive strengthening of surveillance, international cooperation, hospital infection control, inter-departmental collaboration, and new drug development are key strategies for addressing the public health issue of Candida infections. Through in-depth exploration of these research directions, a better understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms and drug resistance of Candida infections can be achieved, ultimately facilitating the development of more effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Author contributions
XH: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QD: Writing – review & editing. QZ: Writing – review & editing. SF: Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – review & editing. HL: Writing – review & editing. JC: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing. HQ: Writing – review & editing. DM: Writing – review & editing. XC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Authors were supported by the University Research Projects of Anhui Provincial (no. 2024AH051076), the Open Project of Key Lab. of Provincial Key Laboratory (no. Wxn202403), Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (no. 202410372016 and 202410372004S), the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (no. JCYJ20230808105208017).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguilera, A., and García-Muse, T. (2013). Causes of genome instability. Annu. Rev. Genet. 47, 1–32. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133232
Aguilera, A., and Gómez-González, B. (2008). Genome instability: a mechanistic view of its causes and consequences. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 204–217. doi: 10.1038/nrg2268
Amanai, T., Nakamura, Y., Aoki, S., and Mataga, I. (2008). Micro-CT analysis of experimental Candida osteoarthritis in rats. Mycopathologia 166, 133–141. doi: 10.1007/s11046-008-9134-z
Arafa, S. H., Elbanna, K., Osman, G. E. H., and Abulreesh, H. H. (2023). Candida diagnostic techniques: a review. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 9, 360–377. doi: 10.1007/s43994-023-00049-2
Arendrup, M. C., Prakash, A., Meletiadis, J., Sharma, C., and Chowdhary, A. (2017). Comparison of EUCAST and CLSI reference microdilution MICs of eight antifungal compounds for Candida auris and associated tentative epidemiological cutoff values. Antimicrob. Agents. Ch. 61, e00485–e00417. doi: 10.1128/aac.00485-17
Arnaud, M. B., Costanzo, M. C., Shah, P., Skrzypek, M. S., and Sherlock, G. (2009). Gene ontology and the annotation of pathogen genomes: the case of Candida albicans. Trends Microbiol. 17, 295–303. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.04.007
Asadzadeh, M., Mokaddas, E., Ahmad, S., Abdullah, A. A., de Groot, T., Meis, J. F., et al. (2022). Molecular characterisation of Candida auris isolates from immunocompromised patients in a tertiary-care hospital in Kuwait reveals a novel mutation in FKS1 conferring reduced susceptibility to echinocandins. Mycoses 65, 331–343. doi: 10.1111/myc.13419
Baillie, G. S., and Douglas, L. J. (1999). Role of dimorphism in the development of Candida albicans biofilms. J. Med. Microbiol. 48, 671–679. doi: 10.1099/00222615-48-7-671
Barantsevich, N., and Barantsevich, E. (2022). Diagnosis and treatment of invasive candidiasis. Antibiotics 11:718. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11060718
Bassetti, M., Righi, E., Ansaldi, F., Merelli, M., Scarparo, C., Antonelli, M., et al. (2015). A multicenter multinational study of abdominal candidiasis: epidemiology, outcomes and predictors of mortality. Intensive Care Med. 41, 1601–1610. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3866-2
Bédard, C., Gagnon-Arsenault, I., Boisvert, J., Plante, S., Dubé, A. K., Pageau, A., et al. (2024). Most azole resistance mutations in the Candida albicans drug target confer cross-resistance without intrinsic fitness cost. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 3025–3040. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01819-2
Benedict, K., Lyman, M., and Jackson, B. R. (2022). Possible misdiagnosis, inappropriate empiric treatment, and opportunities for increased diagnostic testing for patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis—United States, 2018. PLoS One 17:e0267866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267866
Bester, M. C., Pretorius, I. S., and Bauer, F. F. (2006). The regulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae FLO gene expression and Ca2+ −dependent flocculation by Flo8p and Mss11p. Curr. Genet. 49, 375–383. doi: 10.1007/s00294-006-0068-z
Bezerra, A. R., Simões, J., Lee, W., Rung, J., Weil, T., Gut, I. G., et al. (2013). Reversion of a fungal genetic code alteration links proteome instability with genomic and phenotypic diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110, 11079–11084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302094110
Bhattacharya, S., Sae-Tia, S., and Fries, B. C. (2020). Candidiasis and mechanisms of antifungal resistance. Antibiotics. 9:312. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9060312
Billmyre, R. B., Applen Clancey, S., Li, L. X., Doering, T. L., and Heitman, J. (2020). 5-fluorocytosine resistance is associated with hypermutation and alterations in capsule biosynthesis in Cryptococcus. Nat. Commun. 11:127. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13890-z
Bohner, F., Papp, C., and Gácser, A. (2022). The effect of antifungal resistance development on the virulence of Candida species. FEMS Yeast Res. 22:foac019. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foac019
Bordallo-Cardona, M., Agnelli, C., Gómez-Nuñez, A., Sánchez-Carrillo, C., Bouza, E., Muñoz, P., et al. (2019). MSH2 gene point mutations are not antifungal resistance markers in Candida glabrata. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63:18. doi: 10.1128/aac.01876-18
Borman, A. M., and Johnson, E. M. (2020). Candida auris in the UK: introduction, dissemination, and control. PLoS Pathog. 16:e1008563. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008563
Boyce, K. J. (2023). The microevolution of antifungal drug resistance in pathogenic Fungi. Microorganisms 11:2757. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112757
Brackin, A. P., Hemmings, S. J., Fisher, M. C., and Rhodes, J. (2021). Fungal genomics in respiratory medicine: what, how and when? Mycopathologia 186, 589–608. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00573-x
Branco, J., Miranda, I. M., and Rodrigues, A. G. (2023). Candida parapsilosis virulence and antifungal resistance mechanisms: a comprehensive review of key determinants. J. Fungi. 9:80. doi: 10.3390/jof9010080
Branco, J., Ola, M., Silva, R. M., Fonseca, E., Gomes, N. C., Martins-Cruz, C., et al. (2017). Impact of ERG3 mutations and expression of ergosterol genes controlled by UPC2 and NDT80 in Candida parapsilosis azole resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 23, 575.e1–75.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.02.002
Branco, J., Ryan, A. P., Pinto e Silva, A., Butler, G., Miranda, I. M., and Rodrigues, A. G. (2022). Clinical azole cross-resistance in Candida parapsilosis is related to a novel MRR1 gain-of-function mutation. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 28, 1655.e5–55.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.08.014
Bras, G., Satala, D., Juszczak, M., Kulig, K., Wronowska, E., Bednarek, A., et al. (2024). Secreted aspartic proteinases: key factors in Candida infections and host-pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:4775. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094775
Braun, B. R., van het Hoog, M., d’Enfert, C., Martchenko, M., Dungan, J., Kuo, A., et al. (2005). A human-curated annotation of the Candida albicans genome. PLoS Genet. 1:e1. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010001
Bravo Ruiz, G., Ross, Z. K., Holmes, E., Schelenz, S., Gow, N. A. R., and Lorenz, A. (2019). Rapid and extensive karyotype diversification in haploid clinical Candida auris isolates. Curr. Genet. 65, 1217–1228. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00976-w
Bruno, M., Matzaraki, V., van de Veerdonk, F. L., Kumar, V., and Netea, M. G. (2021). Challenges and opportunities in understanding genetics of fungal diseases: towards a functional genomics approach. Infect. Immun. 89:e0000521. doi: 10.1128/iai.00005-21
Burrack, L. S., Todd, R. T., Soisangwan, N., Wiederhold, N. P., and Selmecki, A. (2022). Genomic diversity across Candida auris clinical isolates shapes rapid development of antifungal resistance in vitro and in vivo. MBio 13, e00842–e00822. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00842-22
Butler, G., Rasmussen, M. D., Lin, M. F., Santos, M. A., Sakthikumar, S., Munro, C. A., et al. (2009). Evolution of pathogenicity and sexual reproduction in eight Candida genomes. Nature 459, 657–662. doi: 10.1038/nature08064
Cai, W., Ruan, Q., Li, J., Lin, L., Xi, L., Sun, J., et al. (2023). Fungal spectrum and susceptibility against nine antifungal agents in 525 deep fungal infected cases. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 4687–4696. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S403863
Cao, F., Lane, S., Raniga, P. P., Lu, Y., Zhou, Z., Ramon, K., et al. (2006). The Flo8 transcription factor is essential for hyphal development and virulence in Candida albicans. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 295–307. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-06-0502
Caudle, K. E., Barker, K. S., Wiederhold, N. P., Xu, L., Homayouni, R., and Rogers, P. D. (2011). Genomewide expression profile analysis of the Candida glabrata Pdr1 regulon. Eukaryot. Cell 10, 373–383. doi: 10.1128/ec.00073-10
Cavalheiro, M., Pais, P., Galocha, M., and Teixeira, M. C. (2018). Host-pathogen interactions mediated by MDR transporters in fungi: as pleiotropic as it gets! Genes (Basel) 9:332. doi: 10.3390/genes9070332
Chaabane, F., Graf, A., Jequier, L., and Coste, A. T. (2019). Review on antifungal resistance mechanisms in the emerging pathogen Candida auris. Front. Microbiol. 10:2788. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02788
Chakrabarti, A., and Sood, P. (2021). On the emergence, spread and resistance of Candida auris: host, pathogen and environmental tipping points. J. Med. Microbiol. 70:001318. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001318
Chanda, W., Joseph, T. P., Wang, W., Padhiar, A. A., and Zhong, M. (2017). The potential management of oral candidiasis using anti-biofilm therapies. Med. Hypotheses 106, 15–18. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2017.06.029
Chang, Y. C., Lamichhane, A. K., Cai, H., Walter, P. J., Bennett, J. E., and Kwon-Chung, K. J. (2021). Moderate levels of 5-fluorocytosine cause the emergence of high frequency resistance in cryptococci. Nat. Commun. 12:3418. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23745-1
Chatterjee, S., Alampalli, S. V., Nageshan, R. K., Chettiar, S. T., Joshi, S., and Tatu, U. S. (2015). Draft genome of a commonly misdiagnosed multidrug resistant pathogen Candida auris. BMC Genomics 16:686. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1863-z
Chen, X.-F., Zhang, H., Liu, L.-L., Guo, L.-N., Liu, W.-J., Liu, Y. L., et al. (2024). Genome-wide analysis of in vivo-evolved Candida auris reveals multidrug-resistance mechanisms. Mycopathologia 189:35. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00832-7
Chong, P. P., Chin, V. K., Wong, W. F., Madhavan, P., Yong, V. C., and Looi, C. (2018). Transcriptomic and genomic approaches for unravelling Candida albicans biofilm formation and drug resistance-an update. Genes Basel 9:540. doi: 10.3390/genes9110540
Chow, N., Muñoz, J. F., Gade, L., Berkow, E., Li, X., Welsh, R. M., et al. (2020). Tracing the evolutionary history and global expansion of Candida auris using population genomic analyses. MBio 11, e03364–e03319. doi: 10.1101/2020.01.06.896548
Chybowska, A. D., Childers, D. S., and Farrer, R. A. (2020). Nine things genomics can tell us about Candida auris. Front. Genet. 11:351. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00351
Cohen, B. E. (2014). Functional linkage between genes that regulate osmotic stress responses and multidrug resistance transporters: challenges and opportunities for antibiotic discovery. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 640–646. doi: 10.1128/aac.02095-13
Contaldo, M. (2023). Use of probiotics for oral candidiasis: state of the art and perspective. A further step toward personalized medicine? Front. Biosci. 15:6. doi: 10.31083/j.fbe1501006
Contaldo, M., Di Stasio, D., Romano, A., Fiori, F., Della Vella, F., Rupe, C., et al. (2023). Oral candidiasis and novel therapeutic strategies: antifungals, phytotherapy, probiotics, and photodynamic therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 20, 441–456. doi: 10.2174/1567201819666220418104042
Costa-de-Oliveira, S., and Rodrigues, A. G. (2020). Candida albicans antifungal resistance and tolerance in bloodstream infections: the triad yeast-host-antifungal. Microorganisms 8:154. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020154
Czajka, K. M., Venkataraman, K., Brabant-Kirwan, D., Santi, S. A., Verschoor, C., Appanna, V. D., et al. (2023). Molecular mechanisms associated with antifungal resistance in pathogenic Candida species. Cells 12:2655. doi: 10.3390/cells12222655
Dabas, P. S. (2013). An approach to etiology, diagnosis and management of different types of candidiasis. J. Yeast Fungal Res. 4, 63–74. doi: 10.5897/JYFR2013.0113
Daneshnia, F., Hilmioğlu-Polat, S., Ilkit, M., Fuentes, D., Lombardi, L., Binder, U., et al. (2023). Whole-genome sequencing confirms a persistent candidaemia clonal outbreak due to multidrug-resistant Candida parapsilosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemoth. 78, 1488–1494. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad112
Davari, A., Ahmadkhani, F., Jafarzadeh, J., Mirzakhani, R., Roodgari, S., Bagheri, S., et al. (2019). A new approach to virulence factors of Candida albicans: from gene to function. J. Mazandaran Univ. Med. Sci. 29, 181–196.
Delma, F. Z., Al-Hatmi, A. M. S., Brüggemann, R. J. M., Melchers, W. J. G., De Hoog, S., Verweij, P. E., et al. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of 5-fluorocytosine resistance in yeasts and filamentous fungi. J. Fungi. 7:909. doi: 10.3390/jof7110909
Desjardins, C. A., Champion, M. D., Holder, J. W., Muszewska, A., Goldberg, J., Bailão, A. M., et al. (2011). Comparative genomic analysis of human fungal pathogens causing paracoccidioidomycosis. Plos Geneti. 7:e1002345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002345
Dos Reis, T. F., De, C. P. A., Bastos, R. W., Pinzan, C. F., Souza, P. F., and Ackloo, S. (2023). A host defense peptide mimetic, brilacidin, potentiates caspofungin antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi. Nat. Commun. 14:2052. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37573-y
Dunkel, N., Liu, T. T., Barker, K. S., Homayouni, R., Morschhäuser, J., and Rogers, P. D. (2008). A gain-of-function mutation in the transcription factor Upc2p causes upregulation of ergosterol biosynthesis genes and increased fluconazole resistance in a clinical Candida albicans isolate. Eukaryot. Cell 7, 1180–1190. doi: 10.1128/ec.00103-08
Edlind, T. D. (2011). Molecular detection of antifungal resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 11, 677–684. doi: 10.1128/9781555816834.ch44
Edlind Thomas, D., and Katiyar Santosh, K. (2010). Mutational analysis of flucytosine resistance in Candida glabrata. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 4733–4738. doi: 10.1128/aac.00605-10
ElFeky, D. S., El-Wakil, D. M., Mwafy, M. M., Atia, M. M. A., and Gohar, N. M. (2025). Comparative evaluation of antifungal susceptibility testing methods of invasive Candida species and detection of FKS genes mutations in caspofungin intermediate and resistant isolates. BMC Infect. Dis. 25:114. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10435-8
Erganis, S., Ozturk, A., Uzuntas, S. T., Kirca, F., Dogan, A., Dinc, B., et al. (2024). Variable sensitivity of clinical Candida auris strains to biocides: implications for infection control in healthcare settings. BMC Microbiol. 24:447. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03605-w
Fan, X., Dai, R.-C., Zhang, S., Geng, Y.-Y., Kang, M., Guo, D. W., et al. (2023). Tandem gene duplications contributed to high-level azole resistance in a rapidly expanding Candida tropicalis population. Nat. Commun. 14:8369. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43380-2
Fei, Z., Hu, M., Baum, L., Kwan, P., Hong, T., and Zhang, C. (2020). The potential role of human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) in the transport of Huperzine a in vitro. Xenobiotica 50, 354–362. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2019.1623935
Fenton, A., and John, G. K. (2024). Candida auris resistance mechanisms to amphotericin B alternative treatments development. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. 11, 166–176. doi: 10.1007/s40588-024-00233-w
Fidel, P. L. (2011). Candida-host interactions in HIV disease: implications for oropharyngeal candidiasis. Adv. Dent. Res. 23, 45–49. doi: 10.1177/0022034511399284
Fisher, M., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A., Berman, J., Bicanic, T., Bignell, E., Bowyer, P., et al. (2022). Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 557–571. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00720-1
Frías-De-León, M. G., Hernández-Castro, R., Conde-Cuevas, E., García-Coronel, I. H., Vázquez-Aceituno, V. A., Soriano-Ursúa, M. A., et al. (2021). Candida glabrata antifungal resistance and virulence factors, a perfect pathogenic combination. Pharmaceutics 13:1529. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101529
Frías-De-León, M. G., Hernández-Castro, R., Vite-Garín, T., Arenas, R., Bonifaz, A., Castañón-Olivares, L., et al. (2020). Antifungal resistance in Candida auris: molecular determinants. Antibiotics 9:568. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090568
Fusco, A., Contaldo, M., Savio, V., Baroni, A., Ferraro, G. A., di Stasio, D., et al. (2023). An unconventional oral Candidiasis in an immunocompetent patient. J. Fungi. 9:295. doi: 10.3390/jof9030295
Gale, A. N., Pavesic, M. W., Nickels, T. J., Xu, Z., Cormack, B. P., and Cunningham, K. W. (2023). Redefining pleiotropic drug resistance in a pathogenic yeast: Pdr1 functions as a sensor of cellular stresses in Candida glabrata. mSphere 8, e00254–e00223. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00254-23
Gao, Y., Zhang, C., Lu, C., Liu, P., Li, Y., Li, H., et al. (2013). Synergistic effect of doxycycline and fluconazole against Candida albicans biofilms and the impact of calcium channel blockers. FEMS Yeast Res. 13, 453–462. doi: 10.1111/1567-1364.12048
Gaston, J. M., Alm, E. J., and Zhang, A.-N. (2025). X-mapper: fast and accurate sequence alignment via gapped x-mers. Genome Biol. 26:15. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03473-7
Gifford, H., Rhodes, J., and Farrer, R. A. (2024). The diverse genomes of Candida auris. Lancet Microbe. 5:100903. doi: 10.1016/s2666-5247(24)00135-6
Gómez-Gaviria, M., and Mora-Montes, H. M. (2020). Current aspects in the biology, pathogeny, and treatment of Candida krusei, a neglected fungal pathogen. Infec. Drug Resist. 13, 1673–1689. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S247944
Helmstetter, N., Chybowska, A. D., Delaney, C., Da Silva Dantas, A., Gifford, H., Wacker, T., et al. (2022). Population genetics and microevolution of clinical Candida glabrata reveals recombinant sequence types and hyper-variation within mitochondrial genomes, virulence genes, and drug targets. Genetics 221:31. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac031
Henriques, M., and Williams, D. (2020). Pathogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Pathogens 9:752. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9090752
Hirano, R., Sakamoto, Y., Kudo, K., and Ohnishi, M. (2015). Retrospective analysis of mortality and Candida isolates of 75 patients with candidemia: a single hospital experience. Infect. Drug Resist. 8, 199–205. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S80677
Hou, Z.-J., Lai, H.-M., Cao, C.-Y., Xu, Q.-M., and Cheng, J.-S. (2025). Targeted knockout and plasmid-based transfer of NRPS/PKS for improving lipopeptide iturin a synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 302:140610. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140610
Hu, T., Wang, S., Bing, J., Zheng, Q., Du, H., Li, C., et al. (2023). Hotspot mutations and genomic expansion of ERG11 are major mechanisms of azole resistance in environmental and human commensal isolates of Candida tropicalis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 62:107010. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.107010
Huang, S.-H., Hsu, H.-C., Lee, T.-F., Fan, H.-M., Tseng, C.-W., Chen, I. H., et al. (2023). Prevalence, associated factors, and appropriateness of empirical treatment of Trichomoniasis, bacterial vaginosis, and vulvovaginal candidiasis among women with vaginitis, microbiology. Spectrum 11, e00161–e00123. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00161-23
Husni, R., Bou Zerdan, M., Samaha, N., Helou, M., Mahfouz, Y., Saniour, R., et al. (2023). Characterization and susceptibility of non-albicans Candida isolated from various clinical specimens in Lebanese hospitals. Front. Public Health 11:1115055. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1115055
Ibe, C., Otu, A., and Pohl, C. H. (2025). Mechanisms of resistance to cell wall and plasma membrane targeting antifungal drugs in Candida species isolated in Africa. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 23, 91–104. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2448844
Iguchi, S., Itakura, Y., Yoshida, A., Kamada, K., Mizushima, R., Arai, Y., et al. (2019). Candida auris: a pathogen difficult to identify, treat, and eradicate and its characteristics in Japanese strains. J. Infect. Chemother. 25, 743–749. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.05.034
Ionescu, S., Luchian, I., Damian, C., Goriuc, A., Porumb-Andrese, E., Popa, C. G., et al. (2024). Candida auris updates: outbreak evaluation through molecular assays and antifungal stewardship-a narrative review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 46, 6069–6084. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060362
Jacobs, S., Boccarella, G., van den Berg, P., Van Dijck, P., and Carolus, H. (2024). Unlocking the potential of experimental evolution to study drug resistance in pathogenic fungi. NPJ Antimicrob. Resist. 2:48. doi: 10.1038/s44259-024-00064-1
Jamiu, A. T., Albertyn, J., Sebolai, O. M., and Pohl, C. H. (2021). Update on Candida krusei, a potential multidrug-resistant pathogen. Med. Mycol. 59, 14–30. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa031
Jangir, P., Kalra, S., Tanwar, S., and Bari, V. K. (2023). Azole resistance in Candida auris: mechanisms and combinatorial therapy. APMIS 131, 442–462. doi: 10.1111/apm.13336
Janniger, E. J., and Kapila, R. (2021). Public health issues with Candida auris in COVID-19 patients. World Med. Health Policy 13, 766–772. doi: 10.1002/wmh3.472
Jeanmonod, R., Chippa, V., and Jeanmonod, D. (2025). Vaginal Candidiasis. StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL.
Jin, L., Cao, Z., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Chen, H., et al. (2018). MDR1 overexpression combined with ERG11 mutations induce high-level fluconazole resistance in Candida tropicalis clinical isolates. BMC Infec. Dis. 18:162. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3082-0
Jin, X., Luan, X., Xie, F., Chang, W., and Lou, H. (2023). Erg6 acts as a downstream effector of the transcription factor Flo8 to regulate biofilm formation in Candida albicans. Microbiol. Spectr. 11:e0039323. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00393-23
Kabir, M. A., Hussain, M. A., and Ahmad, Z. (2012). Candida albicans: a model organism for studying fungal pathogens. ISRN Microbiol. 2012:538694, 1–15. doi: 10.5402/2012/538694
Kadri, S. S. (2020). Key takeaways from the US CDC's 2019 antibiotic resistance threats report for frontline providers. Crit. Care Med. 48, 939–945. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004371
Kannan, A., Asner, S. A., Trachsel, E., Kelly, S., Parker, D., and Sanglard, J. (2019). Comparative genomics for the elucidation of multidrug resistance in Candida lusitaniae. MBio 10, e02512–e02519. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02512-19
Kean, R., and Ramage, G. (2019). Combined antifungal resistance and biofilm tolerance: the global threat of Candida auris. mSphere 4:e00458. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00458-19
Kim, M.-J., White, A. M., and Mitchell, A. P. (2024). Strain variation in Candida albicans glycolytic gene regulation. mSphere 9:579. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00579-24
Kitaya, S., Kanamori, H., Katori, Y., and Tokuda, K. (2023). Clinical features and outcomes of persistent Candidemia caused by Candida albicans versus non-albicans Candida species: a focus on antifungal resistance and follow-up blood cultures. Microorganisms 11:928. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11040928
Kordalewska, M., Cancino-Prado, G., de Almeida, N., Júnior, J., Brasil Brandão, I., de Souza, T., et al. (2023). Novel non-hot spot modification in Fks1 of Candida auris confers echinocandin resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 67:e00423. doi: 10.1128/aac.00423-23
Kordalewska, M., Lee, A., Park, S., Berrio, I., Chowdhary, A., Zhao, Y., et al. (2018). Understanding echinocandin resistance in the emerging pathogen Candida auris. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e00238–e00218. doi: 10.1128/aac.00238-18
Kovács, R., Nagy, F., Tóth, Z., Forgács, L., Tóth, L., Váradi, G., et al. (2021). The Neosartorya fischeri antifungal protein 2 (NFAP2): a new potential weapon against multidrug-resistant Candida auris biofilms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:771. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020771
Ksiezopolska, E., and Gabaldón, T. (2018). Evolutionary emergence of drug resistance in Candida opportunistic pathogens. Genes 9:461. doi: 10.3390/genes9090461
Kumar, D., and Kumar, A. (2024). Molecular determinants involved in Candida albicans biofilm formation and regulation. Mol. Biotechnol. 66, 1640–1659. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00796-x
Lakshmi, K., Sharanya, K., Govindasamy, K., and Chitralekha, S. (2018). Molecular mechanisms of antifungal drug resistance in Candida species. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 12, 3390–3411. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/36218.11961
Lara-Aguilar, V., Rueda, C., García-Barbazán, I., Varona, S., Monzón, S., Jiménez, P., et al. (2021). Adaptation of the emerging pathogenic yeast Candida auris to high caspofungin concentrations correlates with cell wall changes. Virulence 12, 1400–1417. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1927609
Lass-Flörl, C., Kanj, S. S., Govender, N. P., Thompson, G. R., Ostrosky-Zeichner, L., and Govrins, MA. (2024). Invasive candidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 10:20. doi: 10.1038/s41572-024-00503-3
Lin, J., Miao, J., Schaefer, K. G., Russell, C. M., Pyron, R. J., Zhang, F., et al. (2024). Sulfated glycosaminoglycans are host epithelial cell targets of the Candida albicans toxin candidalysin. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 2553–2569. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01794-8
Lin, L., Wang, M., Zeng, J., Mao, Y.-h., Qin, R.-j., Deng, J., et al. (2023). Sequence variation of Candida albicans Sap2 enhances fungal pathogenicity via complement evasion and macrophage M2-like hhenotype induction. Adv. Sci. 10:e2206713. doi: 10.1002/advs.202206713
Liu, J. Y., Li, W. J., Shi, C., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., and Xiang, M. J. (2015). Mutations in the Flo8 transcription factor contribute to virulence and phenotypic traits in Candida albicans strains. Microbiol. Res. 178, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2015.05.007
Lohberger, A., Coste, A. T., and Sanglard, D. (2014). Distinct roles of Candida albicans drug resistance transcription factors TAC1, MRR1, and UPC2 in virulence. Eukaryot. Cell 13, 127–142. doi: 10.1128/ec.00245-13
Lyman, M., Forsberg, K., Sexton, D. J., Chow, N. A., Lockhart, S. R., Jackson, B. R., et al. (2023). Worsening spread of Candida auris in the United States, 2019 to 2021. Ann. Intern. Med. 176, 489–495. doi: 10.7326/M22-3469
Maenchantrarath, C., Khumdee, P., Samosornsuk, S., Mungkornkaew, N., and Samosornsuk, W. (2022). Investigation of fluconazole susceptibility to Candida albicans by MALDI-TOF MS and real-time PCR for CDR1, CDR2, MDR1 and ERG11. BMC Microbiol. 22:153. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02564-4
Mandras, N., Roana, J., Scalas, D., Del Re, S., Cavallo, L., Ghisetti, V., et al. (2021). The inhibition of non-albicans Candida species and uncommon yeast pathogens by selected essential oils and their major compounds. Molecules 26:4937. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164937
Maphanga, T. G., Naicker, S. D., Kwenda, S., Muñoz, J. F., van Schalkwyk, E., Wadula, J., et al. (2021). In vitro antifungal resistance of Candida auris isolates from bloodstream infections, South Africa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65:e0051721. doi: 10.1128/aac.00517-21
Marquez, L., Lee, Y., Duncan, D., Whitesell, L., Cowen, L. E., and Quave, C. (2023). Potent antifungal activity of penta-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose against drug-resistant Candida albicans, Candida auris, and other non-albicans Candida species. ACS Infect. Dis. 9, 1685–1694. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00113
Marton, T. B. (2020). Loss of heterozygosity: Its impact on generating and shaping genetic variations in human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Paris: Université Paris Cité.
Märtson, A. G., Alffenaar, J. C., Brüggemann, R. J., and Hope, W. (2021). Precision therapy for invasive fungal diseases. J. Fungi. 8:18. doi: 10.3390/jof8010018
Maruyama, K., Takayama, Y., Kondo, T., Ishibashi, K. I., Sahoo, B. R., Kanemaru, H., et al. (2017). Nociceptors boost the resolution of fungal osteoinflammation via the TRP Channel-CGRP-Jdp2 axis. Cell Rep. 19, 2730–2742. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.002
Mathur, K., Singh, B., Puria, R., and Nain, V. (2024). In silico genome wide identification of long non-coding RNAs differentially expressed during Candida auris host pathogenesis. Arch. Microbiol. 206:253. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03969-7
Mba, I. E., Nweze, E. I., Eze, E. A., and Anyaegbunam, Z. K. G. (2022). Genome plasticity in Candida albicans: a cutting-edge strategy for evolution, adaptation, and survival. Infect. Genet. Evol. 99:105256. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105256
Medeiros, C. I. S., de Sousa, M. N. A., Filho, G. G. A., Freitas, F. O. R., Uchoa, D. P. L., Nobre, M. S. C., et al. (2022). Antifungal activity of linalool against fluconazole-resistant clinical strains of vulvovaginal Candida albicans and its predictive mechanism of action. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 55:e11831. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e11831
Misas, E., Escandón, P., McEwen, J. G., and Clay, O. K. (2019). The LUFS domain, its transcriptional regulator proteins, and drug resistance in the fungal pathogen Candida auris. Protein Sci. 28, 2024–2029. doi: 10.1002/pro.3727
Mochon, A. B., Jin, Y., Kayala, M. A., Wingard, J. R., Clancy, C. J., Nguyen, M. H., et al. (2010). Serological profiling of a Candida albicans protein microarray reveals permanent host-pathogen interplay and stage-specific responses during candidemia. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1000827. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000827
Modrzewska, B., and Kurnatowski, P. (2015). Adherence of Candida sp. to host tissues and cells as one of its pathogenicity features. Ann. Parasitol. 61, 3–9
Morschhäuser, J. (2024). Adaptation of Candida albicans to specific host environments by gain-of-function mutations in transcription factors. PLoS Pathog. 20:e1012643. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012643
Mourer, T., El Ghalid, M., Pehau-Arnaudet, G., Kauffmann, B., Loquet, A., Brûlé, S., et al. (2023). The Pga59 cell wall protein is an amyloid forming protein involved in adhesion and biofilm establishment in the pathogenic yeast Candida albicans. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 9:6. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00371-x
Muñoz, J. F., Gade, L., Chow, N. A., Loparev, V. N., Juieng, P., Berkow, E. L., et al. (2018). Genomic insights into multidrug-resistance, mating and virulence in Candida auris and related emerging species. Nat. Commun. 9:5346. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07779-6
Netea, M. G., Gow, N. A., Munro, C. A., Bates, S., Collins, C., Ferwerda, G., et al. (2006). Immune sensing of Candida albicans requires cooperative recognition of mannans and glucans by lectin and toll-like receptors. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1642–1650. doi: 10.1172/jci27114
Nickels, T. J., Gale, A. N., Harrington, A. A., Timp, W., and Cunningham, K. W. (2024). Transposon-sequencing (Tn-seq) of the Candida glabrata reference strain CBS138 reveals epigenetic plasticity, structural variation, and intrinsic mechanisms of resistance to micafungin, G3-genes Genom. Genet 14:173. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkae173
Nishimoto, A. T., Sharma, C., and Rogers, P. D. (2020). Molecular and genetic basis of azole antifungal resistance in the opportunistic pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 75, 257–270. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkz400
Oliva, A., De Rosa, F. G., Mikulska, M., Pea, F., Sanguinetti, M., Tascini, C., et al. (2023). Invasive Candida infection: epidemiology, clinical and therapeutic aspects of an evolving disease and the role of rezafungin. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 21, 957–975. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2023.2240956
Pais, P., Costa, C., Cavalheiro, M., Romão, D., and Teixeira, M. C. (2016). Transcriptional control of drug resistance, virulence and immune system evasion in pathogenic fungi: a cross-species comparison. Front. Cell. Infect. Mi. 6:131. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00131
Pais, P., Galocha, M., Viana, R., Cavalheiro, M., Pereira, D., and Teixeira, M. C. (2019). Microevolution of the pathogenic yeasts Candida albicans and Candida glabrata during antifungal therapy and host infection. Microb. Cell 6, 142–159. doi: 10.15698/mic2019.03.670
Parslow, B. Y., and Thornton, C. R. (2022). Continuing shifts in epidemiology and antifungal susceptibility highlight the need for improved disease management of invasive candidiasis. Microorganisms 10:1208. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061208
Paul, S., Shaw, D., Joshi, H., Singh, S., Chakrabarti, A., Rudramurthy, S. M., et al. (2022). Mechanisms of azole antifungal resistance in clinical isolates of Candida tropicalis. PLoS One 17:e0269721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269721
Pereira, R., dos Santos Fontenelle, R. O., de Brito, E. H. S., and de Morais, S. M. (2021). Biofilm of Candida albicans: formation, regulation and resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 131, 11–22. doi: 10.1111/jam.14949
Piątkowski, J., Koźluk, K., and Golik, P. (2024). Mitochondrial transcriptome of Candida albicans in flagranti — direct RNA sequencing reveals a new layer of information. BMC Genomics 25:860. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10791-4
Poves-Alvarez, R., Cano-Hernández, B., Muñoz-Moreno, M. F., Balbás-Alvarez, S., Román-García, P., Gómez-Sánchez, E., et al. (2019). Impact of empirical treatment with antifungal agents on survival of patients with candidemia. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 32, 6–14
Prasad, R., Banerjee, A., Khandelwal, N. K., and Dhamgaye, S. (2015). The ABCs of Candida albicans multidrug transporter Cdr1. Eukaryot. Cell 14, 1154–1164. doi: 10.1128/ec.00137-15
Prasad, R., and Rawal, M. K. (2014). Efflux pump proteins in antifungal resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 5:202. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00202
Priest, S. J., Yadav, V., and Heitman, J. (2020). Advances in understanding the evolution of fungal genome architecture. F1000 Faculty Rev 9:776. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25424.1
Proctor, D. M., Dangana, T., Sexton, D. J., Fukuda, C., Yelin, R. D., Stanley, M., et al. (2021). Integrated genomic, epidemiologic investigation of Candida auris skin colonization in a skilled nursing facility. Nat. Med. 27, 1401–1409. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01383-w
Quindós, G., Marcos-Arias, C., San-Millán, R., Mateo, E., and Eraso, E. (2018). The continuous changes in the aetiology and epidemiology of invasive candidiasis: from familiar Candida albicans to multiresistant Candida auris. Int. Microbiol. 21, 107–119. doi: 10.1007/s10123-018-0014-1
Rajendran, R., Sherry, L., Nile, C. J., Sherriff, A., Johnson, E. M., Hanson, M. F., et al. (2016). Biofilm formation is a risk factor for mortality in patients with Candida albicans bloodstream infection-Scotland, 2012-2013. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22, 87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.09.018
Rhodes, J., and Fisher, M. C. (2019). Global epidemiology of emerging Candida auris. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 52, 84–89. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2019.05.008
Rhodes, J., Jacobs, J., Dennis, E. K., Manjari, S. R., Banavali, N., Marlow, R., et al. (2024). What makes Candida auris pan-drug resistant? Integrative insights from genomic, transcriptomic, and phenomic analysis of clinical strains resistant to all four major classes of antifungal drugs. bioRxiv 68:548. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.18.599548
Ricci, L., Mackie, J., Donachie, G. E., Chapuis, A., Mezerová, K., Lenardon, M. D., et al. (2022). Human gut bifidobacteria inhibit the growth of the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 98:95. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiac095
Ricotta, E. E., Lai, Y. L., Babiker, A., Strich, J. R., Kadri, S. S., Lionakis, M. S., et al. (2021). Invasive candidiasis species distribution and trends, United States, 2009-2017. J. Infect. Dis. 223, 1295–1302. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa502
Rocha, M. F. G., Bandeira, S. P., de Alencar, L. P., Melo, L. M., Sales, J. A., Paiva, M. A. N., et al. (2017). Azole resistance in Candida albicans from animals: highlights on efflux pump activity and gene overexpression. Mycoses 60, 462–468. doi: 10.1111/myc.12611
Rodrigues, C. F., and Henriques, M. (2018). Portrait of matrix gene expression in Candida glabrata biofilms with stress induced by different drugs. Genes (Basel) 9:205. doi: 10.3390/genes9040205
Ropars, J., Maufrais, C., Diogo, D., Marcet-Houben, M., Perin, A., Sertour, N., et al. (2018). Gene flow contributes to diversification of the major fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Nat. Commun. 9:2253. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04787-4
Ruiz-Herrera, J., Victoria Elorza, M., Valentín, E., and Sentandreu, R. (2006). Molecular organization of the cell wall of Candida albicans and its relation to pathogenicity. FEMS Yeast Res. 6, 14–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2005.00017.x
Rybak, J. M., Cuomo, C. A., and Rogers, P. D. (2022). The molecular and genetic basis of antifungal resistance in the emerging fungal pathogen Candida auris. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 70:102208. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2022.102208
Saidane, S., Weber, S., De Deken, X., St-Germain, G., and Raymond, M. (2006). PDR16-mediated azole resistance in Candida albicans. Mol. Microbiol. 60, 1546–1562. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05196.x
Sanglard, D., and Odds, F. C. (2002). Resistance of Candida species to antifungal agents: molecular mechanisms and clinical consequences. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2, 73–85. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(02)00181-0
Santana, D. J., and O'Meara, T. R. (2021). Forward and reverse genetic dissection of morphogenesis identifies filament-competent Candida auris strains. Nat. Commun. 12:7197. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27545-5
Santana, D. J., Zhao, G., and O'Meara, T. R. (2024). The many faces of Candida auris: phenotypic and strain variation in an emerging pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 20:e1012011. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012011
Sarma, S., and Upadhyay, S. (2017). Current perspective on emergence, diagnosis and drug resistance in Candida auris. Infect. Drug Resist. 10, 155–165. doi: 10.2147/idr.S116229
Schikora-Tamarit, M., and Gabaldón, T. (2022). Using genomics to understand the mechanisms of virulence and drug resistance in fungal pathogens. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 50, 1259–1268. doi: 10.1042/bst20211123
Schikora-Tamarit, M., and Gabaldón, T. (2024). Recent gene selection and drug resistance underscore clinical adaptation across Candida species. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 284–307. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01547-z
Sekizuka, T., Iguchi, S., Umeyama, T., Inamine, Y., Makimura, K., Kuroda, M., et al. (2019). Clade II Candida auris possess genomic structural variations related to an ancestral strain. PLoS One 14:e0223433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223433
Selmecki, A., Forche, A., and Berman, J. (2010). Genomic plasticity of the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Eukaryot. Cell 9, 991–1008. doi: 10.1128/ec.00060-10
Seyoum, E., Bitew, A., and Mihret, A. (2020). Distribution of Candida albicans and non-albicans Candida species isolated in different clinical samples and their in vitro antifungal suscetibity profile in Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 20:231. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-4883-5
Shinde, R. B., Chauhan, N. M., Raut, J. S., and Karuppayil, S. M. (2012). Sensitization of Candida albicans biofilms to various antifungal drugs by cyclosporine a. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 11:27. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-11-27
Shiyadeh, Z. S., Farahyar, S., Vahedi Larijani, L., Beardsley, J., Nouri, N., Mahmoudi, S., et al. (2024). Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with urinary tract infection in Iran: Candida species distribution and antifungal susceptibility patterns. Antibiotics 13:633. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070633
Singh, S., Barbarino, A., Youssef, E. G., Coleman, D., Gebremariam, T., and Ibrahim, A. S. (2023). Protective efficacy of anti-Hyr1p monoclonal antibody against systemic candidiasis due to multi-drug-resistant Candida auris. J. Fungi. 9:103. doi: 10.3390/jof9010103
Siqueira, A. C., Bernardi, G. A., Arend, L. N. V., Cordeiro, G. T., Rosolen, D., Berti, F. C. B., et al. (2025). Azole resistance and ERG11 mutation in clinical isolates of Candida tropicalis. J. Fungi 11:24. doi: 10.3390/jof11010024
Sobel, J. D. (2022). Ibrexafungerp for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Drugs Today 58, 149–158. doi: 10.1358/dot.2022.58.4.3381586
Stalder, L., Oggenfuss, U., Mohd-Assaad, N., and Croll, D. (2023). The population genetics of adaptation through copy number variation in a fungal plant pathogen. Mol. Ecol. 32, 2443–2460. doi: 10.1111/mec.16435
Szymański, M., Chmielewska, S., Czyżewska, U., Malinowska, M., and Tylicki, A. (2022). Echinocandins – structure, mechanism of action and use in antifungal therapy. J. Enzym. Inhibi. Med. Chem. 37, 876–894. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2050224
Todd, R. T., and Selmecki, A. (2020). Expandable and reversible copy number amplification drives rapid adaptation to antifungal drugs. eLife 9:e58349. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58349
Vandeputte, P., Pineau, L., Larcher, G., Noel, T., Brèthes, D., Chabasse, D., et al. (2011). Molecular mechanisms of resistance to 5-fluorocytosine in laboratory mutants of Candida glabrata. Mycopathologia 171, 11–21. doi: 10.1007/s11046-010-9342-1
Villard, N., Seneviratne, C., Tsoi, J. K., Heinonen, M., and Matinlinna, J. (2015). Candida albicans aspects of novel silane system-coated titanium and zirconia implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 26, 332–341. doi: 10.1111/clr.12338
Wang, R., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Lv, Q., and Yan, L. (2022). Application of the mutant libraries for Candida albicans functional genomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:307. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012307
Wang, Y., Liu, J. Y., Shi, C., Li, W. J., Zhao, Y., Yan, L., et al. (2015). Mutations in transcription factor Mrr2p contribute to fluconazole resistance in clinical isolates of Candida albicans. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 46, 552–559. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2015.08.001
Wang, X., Mohammad, I. S., Fan, L., Zhao, Z., Nurunnabi, M., Sallam, M. A., et al. (2021). Delivery strategies of amphotericin B for invasive fungal infections. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 11, 2585–2604. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.010
Wang, Y., and Xu, J. (2022). Population genomic analyses reveal evidence for limited recombination in the superbug Candida auris in nature. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 20, 3030–3040. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.030
Williams, D. W., Jordan, R. P., Wei, X. Q., Alves, C. T., Wise, M. P., Wilson, M. J., et al. (2013). Interactions of Candida albicans with host epithelial surfaces. J. Oral Microbiol. 5:434. doi: 10.3402/jom.v5i0.22434
Xiong, E. H., Zhang, X., Yan, H., Ward, H. N., Lin, Z.-Y., Wong, C. J., et al. (2024). Functional genomic analysis of genes important for Candida albicans fitness in diverse environmental conditions. Cell Rep. 43:114601. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114601
Yang, F., Zhang, L., Wakabayashi, H., Myers, J., Jiang, Y., Cao, Y., et al. (2017). Tolerance to caspofungin in Candida albicans is associated with at least three distinctive mechanisms that govern expression of FKS genes and cell wall remodeling. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61:71. doi: 10.1128/aac.00071-17
Yoo, Y.-J., Kim, A. R., Perinpanayagam, H., Han, S. H., and Kum, K.-Y. (2020). Candida albicans virulence factors and pathogenicity for endodontic infections. Microorganisms 8:1300. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091300
Yue, H., Bing, J., Zheng, Q., Zhang, Y., Hu, T., du, H., et al. (2018). Filamentation in Candida auris, an emerging fungal pathogen of humans: passage through the mammalian body induces a heritable phenotypic switch. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 7, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41426-018-0187-x
Zeng, H., Stadler, M., Abraham, W.-R., Müsken, M., and Schrey, H. (2023). Inhibitory effects of the fungal pigment Rubiginosin C on hyphal and biofilm formation in Candida albicans and Candida auris. J. Fungi 9:726. doi: 10.3390/jof9070726
Zhang, J., Li, L., Lv, Q., Yan, L., Wang, Y., and Jiang, Y. (2019). The fungal CYP51s: their functions, structures, related drug resistance, and inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 10:691. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00691
Zhang, M., Parker, J., An, L., Liu, Y., and Sun, X. (2025). Flexible analysis of spatial transcriptomics data (FAST): a deconvolution approach. BMC Bioinformatics 26:35. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06054-y
Zheng, L., Xu, Y., Wang, C., Dong, Y., and Guo, L. (2024). Parallel evolution of fluconazole resistance and tolerance in Candida glabrata. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 14:1456907. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1456907
Zhou, X., Hilk, A., Solis, N. V., Scott, N., Beach, A., Soisangwan, N., et al. (2024). Single-cell detection of copy number changes reveals dynamic mechanisms of adaptation to antifungals in Candida albicans. Nat. Microbiol. 9, 2923–2938. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01795-7
Zhou, W., Li, X., Lin, Y., Yan, W., Jiang, S., Huang, X., et al. (2021). A comparative transcriptome between anti-drug sensitive and resistant Candida auris in China. Front. Microbiol. 12:708009. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.708009
Zhu, X., Zhao, Y., Jiang, Y., Qin, T., Chen, J., Chu, X., et al. (2017). Dectin-1 signaling inhibits osteoclastogenesis via IL-33-induced inhibition of NFATc1. Oncotarget 8, 53366–53374. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18411
Znaidi, S., Weber, S., Al-Abdin, O. Z., Bomme, P., Saidane, S., Drouin, S., et al. (2008). Genomewide location analysis of Candida albicans Upc2p, a regulator of sterol metabolism and azole drug resistance. Eukaryot. Cell 7, 836–847. doi: 10.1128/ec.00070-08
Keywords: candidiasis, genomics, pathogenicity, drug resistance, virulence factors
Citation: Huang X, Dong Q, Zhou Q, Fang S, Xu Y, Long H, Chen J, Li X, Qin H, Mu D and Cai X (2025) Genomics insights of candidiasis: mechanisms of pathogenicity and drug resistance. Front. Microbiol. 16:1531543. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1531543
Edited by:
Guido Werner, Robert Koch Institute, GermanyReviewed by:
Maria Contaldo, University of Campania L. Vanvitelli, ItalyIfeanyi Elibe, University of Ibadan, Nigeria
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Dong, Zhou, Fang, Xu, Long, Chen, Li, Qin, Mu and Cai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xunchao Cai, Y3hjaDEyMjRAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Dan Mu, bXVkYW5zbWlsZUAxMjYuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
 Xin Huang
Xin Huang Qin Dong1†
Qin Dong1† Xunchao Cai
Xunchao Cai