
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 28 February 2025
Sec. Microbe and Virus Interactions with Plants
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1514551
Fire blight and black shoot blight diseases, caused by Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia pyrifoliae, respectively, continue to spread several areas in Korea, despite intensive efforts by the government to control diseases. The distribution pattern of fire blight and black shoot blight is different from each other in Korea. Consequently, it is required to investigate the pathogenicity of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae in apple trees. The disease severity of fire blight and black shoot blight was compared in this study by an artificial inoculation of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae suspensions into the abaxial veins of apple leaves and measuring their pathogenicity at varying temperatures. Furthermore, disease severity was assessed by inoculating E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae in apple flowers and assessing their pathogenicity at various temperatures. The E. amylovora-inoculated flowers displayed greater disease index than E. pyrifoliae-inoculated flowers at temperatures ranging from 18°C to 25°C. Upon examining the population sizes of E amylovora and E. pyrifoliae in flowers using a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the Ct value of E. amylovora was found to be lower in the style including stigma and hypanthium than the Ct value of E. pyrifoliae, except at 18°C. Hypanthium contained E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 at >107 and 105 CFU/mL, respectively at 15°C. Furthermore, in this study, we investigated the population size of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae in apple flowers in relation to temperature in order to clarify the differences in their pathogenicity.
Fire blight is one of the most destructive bacterial diseases of several fruit crops, including apples, pears and other rosaceous plants; it is caused by the pathogen Erwinia amylovora (Medhioub et al., 2022). Due to the severity of its pathogenicity, it has become the global concern, resulting in reduced agricultural output. Fire blight was identified in apples, Asian pears, and Chinese quince in Korea in 2015 (Park et al., 2016; Myung et al., 2016). In 2020, fire blight occurred in 744 orchards in Korea. Fire blight symptoms appear in all plant organs, such as blossoms, shoots, twigs, fruits, and the rootstock near the graft union on the lower trunk (Eastgate, 2000). The infected tissue is observed to turn brown to black, resulting in gradual death (Jung et al., 2023). It has been reported that infected flowers also become a pathway for the expansion of the disease (Kharadi et al., 2021). Most recently, blight symptoms were observed in Chinese hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) caused by E. amylovora in Korea (Lim et al., 2023), and an apricot (Prunus armeniaca) orchard during an outbreak of fire blight that had affected a nearby apple orchard (Lee et al., 2021). The pathogen can infect all host tissues at various times during the season, making it challenging to control fire blight (Santander and Biosca, 2017).
Erwinia pyrifoliae, another species within the genus Erwinia, is a necrotrophic pathogen that causes black shoot blight in Asian pears (Pyrus pyrifolia) in Korea. Initially, the pathogen was consistently isolated from orchards in Chuncheon in 1995. It was then inoculated on agar plates and then identified through morphological and molecular means (Kim et al., 1999; Rhim et al., 1999). Black shoot blight was first observed in pear trees in Korea; however, it has also been shown to affect apple trees (Han et al., 2016). E. pyrifoliae has only been detected in Korea, with the exception of strawberries in the Netherlands (Wenneker and Bergsma-Vlami, 2015). The symptoms of black shoot blight in pear trees appear blackish blight in twigs and black stripes on leaves (Kim et al., 1999; Lee et al., 2020). Over the last decade, black shoot blight caused by E. pyrifoliae has mostly occurred in apple trees (Lee et al., 2023).
The morphological, cultural, and biochemical characteristics of E. pyrifoliae were similar to those of E. amylovora (Kim et al., 1999; Shrestha et al., 2003); however, there are temperature-driven differences in the growth rates of the two species. Specifically, E. pyrifoliae is more cold-tolerant than E. amylovora (Shrestha et al., 2005). Additionally, some studies have presented molecular evidence regarding the differences between E. pyrifoliae and E. amylovora (Jock and Geider, 2004; McGhee et al., 2002).
Erwinia amylovora can infect various parts of trees, including flowers, shoots, and rootstocks. Its infection of the flowers, known as blossom blight, is the most important within the context of disease outbreak and management (Bubán et al., 2003). This is because the flowers provide a nutrient-rich and moist environment suitable for the epiphytic growth of E. amylovora (Norelli and Brandl, 2004). In flower infection, E. amylovora occurs the rapid multiplication in the stigma and then moves down toward the hypanthium. Once the flowers have been infected, the pathogens quickly spread to the branches and other parts of the tree (Cui et al., 2021). In a previous study, it has been reported that the population size of E. pyrifoliae on the surface of pear blossoms was significantly smaller than the population size of E. amylovora, which suggests that E. pyrifoliae does not grow as optimally as does E. amylovora on pear blossoms at 23°C, as determined using real-time PCR (Lehman et al., 2008).
Since the detection of fire blight in Korea in 2015, E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae have been detected simultaneously different outbreaks. Fire blight and black shoot blight have spread to several areas of Korea, despite intensive efforts by the Korean government to restrict their spread (Choi et al., 2022). The pattern of distribution and occurrence of fire blight and black shoot blight was different in Korea. Therefore, studying the pathogenicity of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae in apple trees is crucial. In this study, differences in the dynamics of the two diseases are found to be due to differences in the pathogenicity of the two pathogens in apple trees. In particular, the movement and proliferation of the two pathogens in apple flowers were affected by temperature, and the population sizes in apple flowers was lower than of E. pyrifoliae in not only style including stigma but also hypanthium.
A survey was conducted to investigate the occurrence of fire blight from 2015 to 2022 and black shoot blight disease from 1995 to 2022 in apple orchards in Korea. The following are the 28 localities from 6 provinces in which the survey for the occurrence of fire blight disease was conducted from 2016 to 2021: Eleven places in Gyeonggi (Yeoncheon, Paju, Yangju, Namyangju, Gwangju, Yongin, Icheon, Pyeongtaek, Anseong, Yeoju, and Hwaseong), four places in Gangwon (Pyeongchang, Wonju, Yeongwol, and Hongcheon), six places in Chungbuk (Jecheon, Chungju, Eumseong, Danyang, Jincheon, and Goesan), four places in Chungnam (Cheonan, Dangjin, Yesan, and Asan), two places in Gyeongbuk (Yeongju and Andong), and one place in Jeonbuk (Iksan). The survey for the occurrence of black shoot blight was conducted from 1995 to 2022 in 5 provinces, 26 cities which are as follows: nine places in Gyeonggi (Gapyeong, Pocheon, Yangpyeong, Namyangju, Yangju, Goyang, Anseong, Gwangju, and Yeoncheon), eleven places in Gangwon (Wonju, Hongcheon, Yanggu, Hoengseong, Yeongwol, Cheorwon, Chuncheon, Hwacheon, Pyeongchang, Goseong, and Inje), three places in Chungbuk (Jecheon, Chungju, and Eumseong), one place in Chungnam (Cheonan), and two places in Gyeongbuk (Yeongju and Mungyeong). For the disease occurrence analysis, the suspected samples were collected from orchards of various places and tested for the disease outbreak.
The bacterial pathogens, such as E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 used in this study were isolated from infected pear and apple trees in Korea in 2015 (Park et al., 2018); these samples were plated on King’s B and Luria Bertani (LB) media, respectively, and cultured at 27°C for 48 h. Bacterial cell suspensions were prepared by diluting in sterile distilled water (SDW) until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached 1.0. Motility was assessed following the method described by Edmunds et al. (2013), with some modifications. Briefly, 10 μL of overnight grown E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 cultures were stab-inoculated onto 0.3% LB agar plates, and incubated at various temperatures, including 14°C, 18°C, and 27°C for 48 h. The diameter traveled from the inoculation site was measured using analog calipers (Hitec, Germany). The assay was repeated at least once in triplicates.
The pathogenicity test was carried out on apple fruits following the method described by Lee et al. (2021). Before inoculation, bacterial suspensions of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 cultured at 27°C for 48 h in LB medium were suspended with SDW and adjusted to a concentration of 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL. For the pathogenicity test on fruits, healthy immature apple (Malus domestica cv. Fuji) fruits were surface-disinfected with 70% ethanol for 30 s, and rinsed with SDW. The fruits were then dried and wounded by piercing them 2 to 3 mm deep with a sterile pin. The incision site was then inoculated with 10 μL bacterial suspensions (1.5 × 108 CFU/mL). The inoculated fruits were placed in a plastic box containing moist paper to maintain the humidity, and incubated for 10 days at various temperatures, such as 12°C, 18°C, 21°C, and 27°C. The symptoms, such as necrosis and bacterial ooze out observed at inoculated sites by two bacteria, E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 were compared with non-inoculated fruits. The pathogenicity tests were repeated at least once in triplicates.
For the pathogenicity test on leaves, the upper third and fourth leaves on apple shoot were collected from the greenhouse at the National Institute of Agricultural Sciences (NAS). The petioles of the abaxial side of apple leaves were punctured with a sterile needle and inoculated with 2 μL of each bacterial suspension. The inoculated leaves were placed in a square plate containing moist tissue paper and incubated the plates at 14°C, 16°C, and 18°C for 15 days, and then leaves were monitored for the development of disease symptoms. Disease symptoms were scored using a disease index scale ranging from 0 to 5 ratings (where 0 = no symptoms, 1 = lesions with <10% disease incidence, 2 = lesions with 11 to 20%, 3 = lesions with 21 to 40%, 4 = lesions with 41 to 70%, 5 = symptoms with >71 to 100%). The disease ratings on apples leaves were explained in Supplementary Figure S1A. The experiment was repeated at least once in triplicates.
One year old crab potted apple (Malus sieboldii) plants were purchased from the local market and grown under greenhouse conditions at NAS until flowerings. Flowers of similar size were detached from the potted plants and each flower was placed in a single Eppendorf vial (2 mL) containing SDW. After 24 h, all the flowers were inoculated with bacterial suspensions (106 CFU/mL) of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327; approximately 0.2 μL of inoculum was applied per flower by touching a droplet to each stigma (i.e., normally 3–4 per flower). Fifteen flowers from each treatment were maintained in a plastic box and assessed after 5 days. Disease symptoms were scored using a disease index scale ranging from 0 to 5 ratings (where 0: no necrosis; 1: necrosis on the stigma; 2: necrosis visible on the stigma and hypanthium; 3: necrosis extending into the ovary, no farther than the widest point; 4: necrosis extending to the base of the ovary; 5: necrosis extending into the peduncle). The disease ratings on apple flowerbuds were explained in Supplementary Figure S1B.
After assessing the disease severity, stigmas of all flowers were collected along with portions of the supporting styles. The hypanthium was partially isolated by removing the petals, calyx, and pedicel. The stigma and hypanthium of the sampled style were placed in a sterile 1.5 mL micro centrifuge tubes containing 100 and 1,000 μL sterile buffer (10 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.0), respectively. The samples were macerated and incubated at 23°C for 30 min. The experiment was performed twice with five replicates (flowers). The template for real-time PCR was directly derived from the processed sample lysis. Duplex real-time PCR using a HelixDtec™ EAEP detection kit (Cat no. EAEP-T100, Nanohelix, Daejeon, Korea) was used to compare E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae populations in style, stigma and hypanthium. Real-time PCR was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions using the Bio-Rad CFX maestro software (BioRad, Hercules, CA, United States). This experiment was performed at least three times.
Statistical analyses were performed using the R software (ver. 4.2.3.). Data were analyzed using either Student’s t-test (normality test passed) or the Mann–Whitney Rank sum test (normality test failed). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Since the 2015 outbreak of the fire blight in Korea, it has been spread to 28 cities in 6 provinces (Figure 1A). The distribution pattern of the fire blight indicates that it has been primarily disseminated in central regions. On the other hand, black shoot blight, an endemic pathogen, has been spread in 26 cities in five provinces over 20 years (Figure 1B). Black shoot blight was distributed throughout the northern region, with the exception of Yeongju and Mungyeong (Figure 1B).
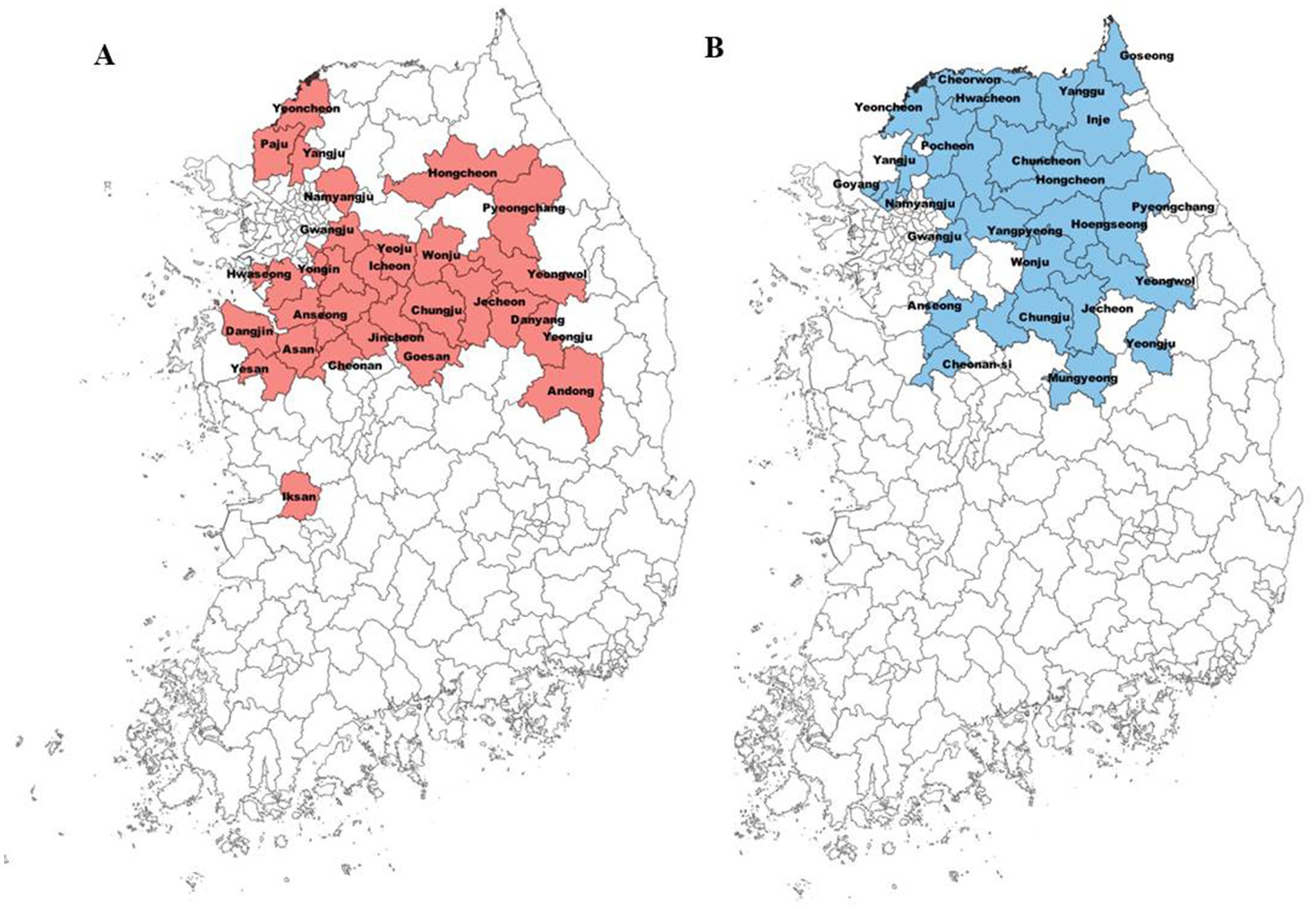
Figure 1. Distribution of fire blight and black shoot blight among cities in Korea. The colored ones have high occurrence of these diseases. Red and blue colors indicate the cities where fire blight (A) and black shoot blight (B) were reported, respectively.
When two pathogens were cultured at different temperatures, such as 14°C, 18°C, and 27°C, E. amylovora TS3128 has been displayed to exhibit a greater motility than the pathogen E. pyrifoliae at all temperatures (Figure 2). However, the highest motility in E. amylovora has been observed as 89.67 mm in diameter at 27°C, while the motility of other pathogen E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 was only 36 mm in diameter 48 h after incubation. The motility of E. amylovora TS3128 was increased with increasing temperature; while the motility of E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 reduced with increasing temperature (Figure 2). Whereas no growth was observed in the control plates.

Figure 2. Effect of different temperatures on motility of two pathogens (E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327). The plates contained semi-solid LB medium with 0.3% agar were inoculated with bacterial suspensions of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327. Diameters of the motility of E. amylovora TS3128 (black bar) and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 (gray bar) in semi-solid medium were recorded 48 h after incubation at 14°C, 18°C, and 27°C. The experiment was repeated once with triplicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) based on Student’s t-test.
The pathogenicity of two pathogens E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 was tested on two plant materials, such as immature apple fruits and leaves at different temperatures ranging from 12°C to 27°C. E. amylovora TS3128 exhibited more severe symptoms at temperatures ranging from 18°C to 21°C in immature apple fruits compared to E. pyrifoliae YKB12327, where the symptoms started to appear at 21°C (Figure 3A). The pathogenicity of E. amylovora TS3128 differs from that of E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 at 18°C. The pathogenicity assay demonstrated that both bacteria caused severe symptoms, with the symptoms being most severe at 27°C. To compare the pathogenicity between E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 on apple leaves at low temperatures, the disease index scale ranging from 0 to 5 was developed based on disease severity score (0–100%) (Figure 3B). Disease index on apple leaves by the pathogen E. amylovora TS3128 has been found to show higher than the disease index by E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 at temperatures 16 and 18°C (Figure 3B). The symptoms corresponding to disease severity of E. amylovora TS3128 were indicated by an index of more than 4.2 at 18°C. In contrast, the disease index for E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 has been shown to be 2.2. On the other hand, no symptoms were developed on non-inoculated (control) apple fruits.
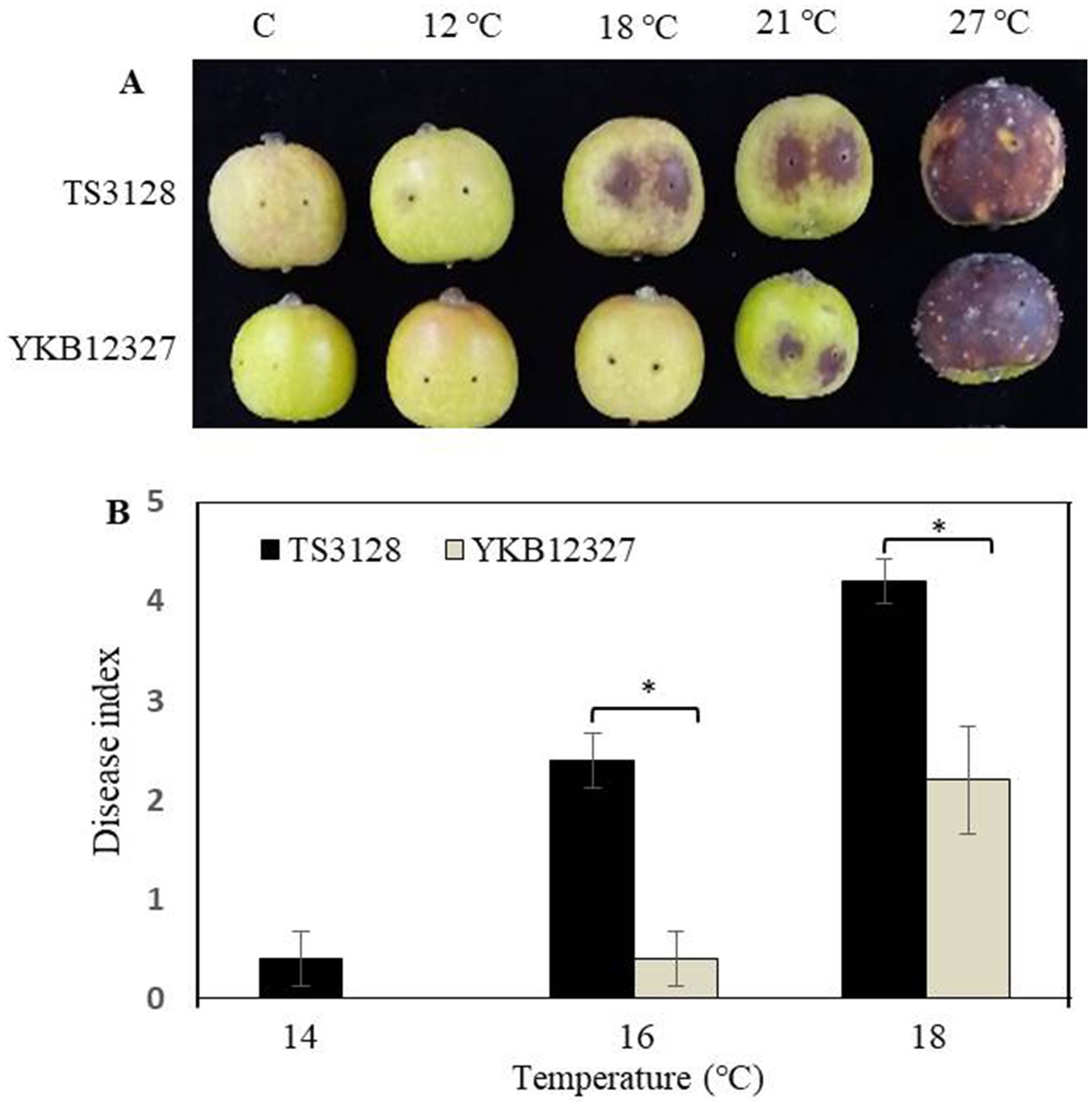
Figure 3. Effect of temperature on pathogenicity of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 on apple fruits and leaves by an artificial inoculation. (A) The development of disease symptoms on wounded apple fruits 10 d after inoculation (dai) was characterized by necrosis and browning followed by rotting, while no disease symptoms were developed on non-inoculated fruits (control). (B) Disease index in apple leaves infected with E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae at different temperatures (14°C, 16°C, and 18°C). The disease symptoms were developed on inoculated leaves, and no symptoms were developed on non-inoculated leaves. The experiment was repeated at least once in triplicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) based on Student’s t-test.
When the stigma of the flower was infected with E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 pathogen suspensions, the infection progressed through the style. Disease symptoms were developed more on stigmas inoculated with E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 than in E. amylovora TS3128-inoculated stigmas, which implies that E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 also causes equal damage to the crop as that of E. amylovora TS3128. However, when the pathogenicity of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 on apple flowers were compared at different temperatures, the virulence of the E. amylovora TS3128 was found to be greater than the virulence of the pathogen E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 on stigmas of the apple flowers at all temperatures (10 to 25°C). The flowers inoculated with E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 showed increased disease symptoms at 18°C and higher temperatures (Figure 4A). The flowers inoculated with E. amylovora TS3128 showed a higher disease index than those infected with E. pyrifoliae YKB12327, while no symptoms were observed in the non-inoculated (control group) apple flowers.
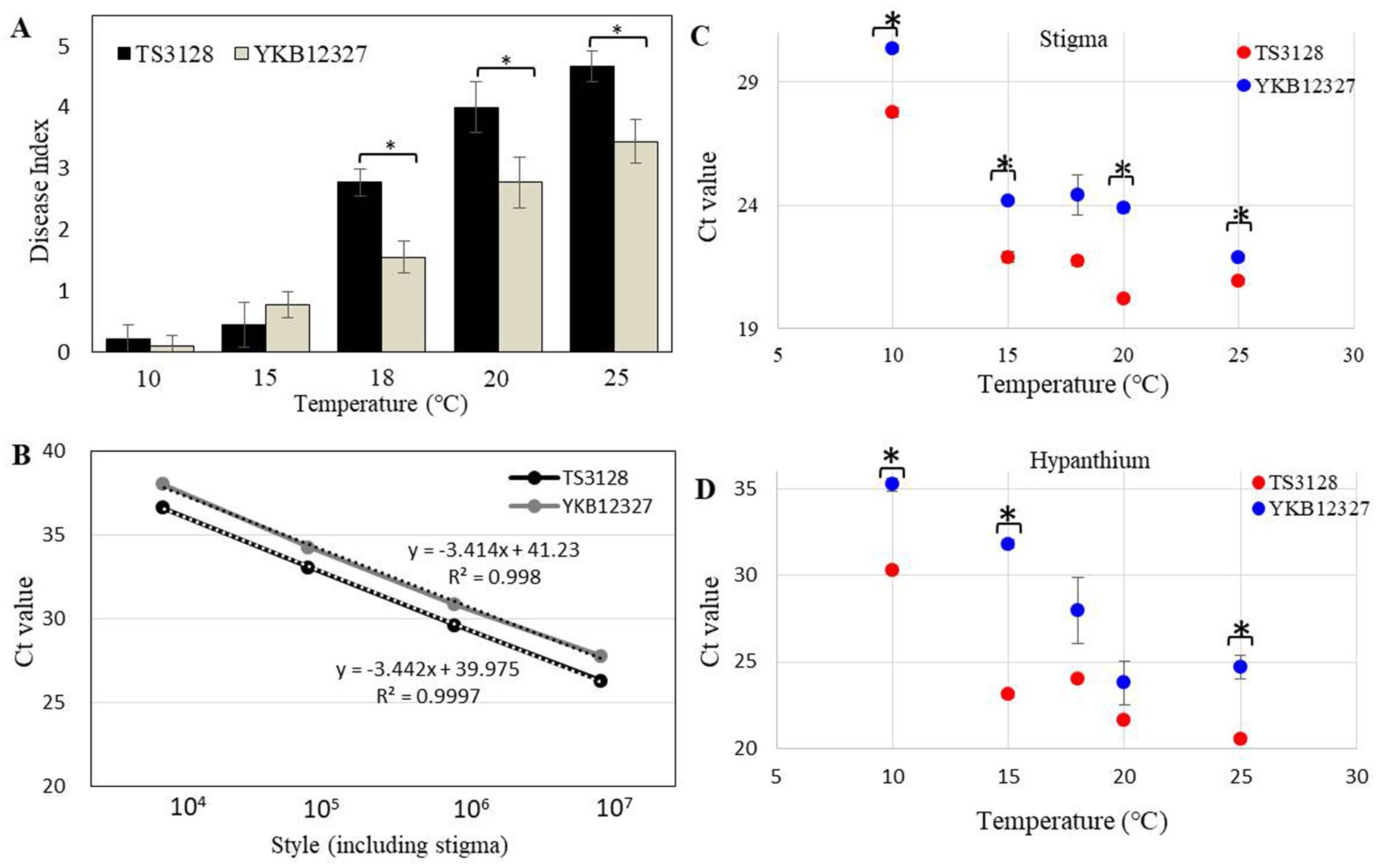
Figure 4. Disease index in apple flowers inoculated with E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 and their population size using a duplex real-time PCR. (A) Disease index in apple flowers inoculated with E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 at different temperatures ranging from 10°C to 25°C. The experiment was repeated at least once in triplicates. (B) Standard curve for real-time PCR of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 (serially diluted (107 to 104) in water). The R2 value of each curve was >0.99. Population size of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 on the styles of apple flowers, including the stigma (C) and hypanthium (D), assessed using a real-time PCR. Red and blue shading indicates fire blight and black shoot blight, respectively. Asterisks indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) based on Student’s t-test.
The duplex standard curves for E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 are shown in Figure 4B. The mean threshold cycle (Ct) value (n = 3) was plotted against the density of bacterial cells (104–107 CFU/mL) to construct standard curves (Table 1). The Ct values of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 cells (107 CFU/mL) were 26.27 and 27.74, respectively. The Ct value in the real-time PCR increases as the population density of bacterial cells decreases.

Table 1. Mean threshold cycles (Ct) of 10-fold dilution series of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 cell suspensions using a real-time PCR.
The Ct value of E. amylovora TS3128 was found to be lower than that of E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 in the style, which included stigma and hypanthium, except at 18°C, when the population sizes of E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 in apple flowers were compared using the real-time PCR (Figure 4C). The style including stigma was cultured at 20°C after inoculation, and the maximal difference in population size between E. amylovora TS3128 and E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 was observed. However, the two pathogens did not exhibit statistically significant difference in their population sizes in the hypanthium (Figure 4D). Nevertheless, E. pyrifolia YKB12327 exhibited a substantial lower population size in hypanthium at 15°C and lower temperatures than E. amylovora TS3128. Moreover, the population size of E. amylovora TS3128 in the hypanthium was >107 CFU/mL, while that of E. pyrifoliae YKB12327 was approximately 105 CFU/mL at 15°C. Consequently, the two pathogens exhibited a population size divergence of approximately 102 CFU/mL at 15°C.
In this study, we discuss the variations in pathogenicity between E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae, which cause fire blight and black shoot blight, respectively. These two diseases have resulted in severe economic losses in Korea by destroying a substantial quantity of fruits that could have been exported (Park et al., 2017). The number of orchards infected with fire blight is greater than that of orchards infected with black shoot blight, despite the fact that fire blight first appeared in Korea 20 years prior to black shoot blight (Ham et al., 2020; Lee and Lee, 2022). Furthermore, fire blight disease spreads more rapidly in the central region rather than in the northern region; nevertheless, black shoot blight is more prevalent in the northern region, which has a relatively low average temperature. Although the phenotypical characteristics of E. pyrifoliae are similar to those of E. amylovora, a detailed study has demonstrated that these two pathogens differ from each other; with E. pyrifoliae having greater cold tolerance than E. amylovora (Shrestha et al., 2005).
In 2020, 744 orchards in Korea were affected by fire blight, 73% of 744 orchards were apple orchards, while the remaining 27% were pear orchards (Lee et al., 2022). Over the last decade, black shoot blight caused by E. pyrifoliae has mostly affected apple trees (Choi et al., 2022). Apple trees infected with fire blight and black shoot blight may support the rapid growth of the pathogen. Therefore, it is necessary to study the ecological aspects such as the pathogenicity of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae on apple trees. E. amylovora TS3128 has been found to grow faster than E. pyrifoliae. Our findings imply that swimming motility on a semi-solid medium contributes to the virulence of E. amylovora TS3128 at 27°C. Our finding are corroborated by a recent study (Tao et al., 2023), which stated that motility was identified as a pathogenic characteristics of Erwinia sorbitol sp. Nov. Similarly, a previous study by Hossain et al. (2005) demonstrated that the motility of Erwinia carotovora played a role in its virulence on tobacco leaves. Conversely, Kharadi et al. (2019) have reported that pathogens with low amylovoran production were not phytopathogenic. The motility of bacteria might be attributed to the formation of flagella, which played a vital role in the survival of the bacteria upon production of amylovoran for the attachment to host cell surfaces (Santander et al., 2014).
Temperature is known as one of the environmental parameters required to achieve the high cell density needed for flower infection (MAAARO, 2011). According to Santander and Biosca (2017), the ideal temperature for the growth of E. amylovora is 28°C. However, it was recently shown that the pathogenicity of E. amylovora persists even at lower temperatures (14°C and 4°C). Previously, Shrestha et al. (2005) reported that E. pyrifoliae grew faster at lower temperatures ranging from 12 to 21°C than E. amylovora. The difference in growth rate at these temperatures indicated that E. pyrifoliae is more cold-tolerant than E. amylovora. In general, rising temperatures encourage the growth and spread of plant diseases, particularly fungi (Pour et al., 2020) and bacteria (Devi et al., 2022), while also affecting host defensive mechanisms. In our study, the growth of E. amylovora was higher than that of E. pyrifoliae; and it exhibited higher level of pathogenicity in immature apple fruits.
In order to compare the pathogenicity of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae on flowers, it is necessary to investigate the population size of the two pathogens. In recent years, the real-time PCR method has been employed as a simple and sensitive method for the detection of E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae (Ham et al., 2022). In particular, the real-time PCR diagnostic and droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) kits for detecting E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae, have been commercialized in Korea (He et al., 2023). The population size of E. pyrifoliae was significantly smaller than that of E. amylovora in apple flowers at temperatures between 10 and 25°C. This is in consistent with a recent study by Choi et al. (2022), in which E. amylovora was shown to have larger colony numbers than E. pyrifoliae when co-cultured in liquid media and co-inoculated into immature apple fruits. A previous study showed that E. pyrifoliae did not grow as well as E. amylovora did when pear flowers were infected with E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae and incubated at 23°C (Lehman et al., 2008). The real-time PCR revealed that the E. amylovora population grew to a larger size in the stigma than the E. pyrifoliae population and this growth has continued into the hypanthium. A previous study suggested that E. amylovora migrates through the stigma and inside the style to other plant tissues (van der Zwet and Keil, 1979). This is corroborated by a recent report, in which it has been displayed about the Type III secretion systems (T3SS), a bacterial secretion system that secretes their effector proteins into the host cell cytoplasm to facilitate the virulence mechanism (Pester et al., 2012). This model of infection is based on E. amylovora migrating down the flower stigma, swimming through nectar, and subsequently suppressing host defenses to invade the base of the flower through natural openings which is due to the stigma of the flower (Schachterle et al., 2022). Previous research has demonstrated that the moisture from rain or dew is required for E. amylovora cells to migrate from the stigma tip to the style of the flower, where the pathogen infects flowers through natural openings in the hypanthium, resulting in blossom blight (Thomson, 1986; Bayot and Ries, 1986). When shoot becomes infected, E. amylovora cells may migrate systemically through infected leaf and stem tissue toward the main trunk of the tree (Schachterle et al., 2022). As part of this migration, stem tissue can release oozing droplets in varying numbers and locations. Additional research has demonstrated that E. amylovora cells form biofilms in xylem vessels, obstructing water movement and causing wilting symptoms of fire blight (Peng et al., 2020). In contrast, Spinelli et al. (2007) found that E. amylovora migrated primarily into xylem vessels after reaching the nectar cup, despite the fact that the cortical parenchyma was also colonized in severely infected tissues.
In summary, we have identified two pathogens E. amylovora and E. pyrifoliae that cause fire blight and black shoot blight in apple orchards, in various cities across Korea, respectively. There is a trend in Korea toward more frequent and devastating outbreaks of fire blight than those of black shoot blight despite the erratic nature of fire blight, E. amylovora TS3128 was shown to be more motility than E. pyrifoliae at all temperatures tested, including 14°C, 18°C, and 27°C for swarming motility. The pathogenicity assay showed that both pathogenic bacteria caused severe symptoms, particularly on immature apple fruits at 27°C. We found that E. amylovora grew faster at lower temperatures, although it was more pathogenic than E. pyrifoliae. E. amylovora exhibited a greater movement and proliferation in apple flowers than E. pyrifoliae. Thus, in this study, we precisely evaluated the effect of temperature on the occurrence of these diseases in apple flowers, as well as the variations in black shoot blight. Understanding the characteristics of these two pathogens is necessary for developing science-based disease control policy in the field.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
M-HL: Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KB: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. H-WC: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YL: Data curation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a grant from the Agenda Program (PJ01559401) of the Rural Development Administration (RDA) of the Republic of Korea.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1514551/full#supplementary-material
Bayot, R. G., and Ries, S. M. (1986). Role of motility in apple blossom infection by Erwinia amylovora and studies of fire blight control with attractant and repellent compounds. Phytopathology 76, 441–445. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-76-441
Bubán, T., Orosz-Kovács, Z., and Farkas, Á. (2003). The nectary as the primary site of infection by Erwinia amylovora (Burr.) Winslow et al.: a mini review. Plant Syst. Evol. 238, 183–194. doi: 10.1007/s00606-002-0266-1
Choi, J. H., Kim, J. Y., and Park, D. H. (2022). Evidence of greater competitive fitness of Erwinia amylovora over E. pyrifoliae in Korean isolates. Plant Pathol. J. 38, 355–365. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.04.2022.0056
Cui, Z., Huntley, R. B., Schultes, N. P., Kakar, K. U., Yang, C. H., and Zeng, Q. (2021). Expression of the type III secretion system genes in epiphytic Erwinia amylovora cells on apple stigmas benefits endophytic infection at the hypanthium. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 34, 1119–1127. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-06-21-0152-R
Devi, R., Kaur, T., Kour, D., Yadav, A., Yadav, A. N., Suman, A., et al. (2022). Minerals solubilizing and mobilizing microbiomes: a sustainable approach for managing minerals’ deficiency in agricultural soil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 133, 1245–1272. doi: 10.1111/jam.15627
Eastgate, J. A. (2000). Erwinia amylovora: the molecular basis of fire blight disease. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1, 325–329. doi: 10.1046/j.1364-3703.2000.00044.x
Edmunds, A. C., Castiblanco, L. F., Sundin, G. W., and Waters, C. M. (2013). Cyclic Di-GMP modulates the disease progression of Erwinia amylovora. J. Bacteriol. 195, 2155–2165. doi: 10.1128/JB.02068-12
Ham, H., Kim, K., Yang, S., Kong, H. G., Lee, M. H., Jin, Y. J., et al. (2022). Discrimination and detection of Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia pyrifoliae with a single primer set. Plant Pathol. J. 38, 194–202. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.03.2022.0027
Ham, H., Lee, Y. K., Kong, H. G., Hong, S. J., Lee, K. J., Oh, G. R., et al. (2020). Outbreak of fire blight of apple and Asian pear in 2015–2019 in Korea. Res. Plant Dis. 26, 222–228. doi: 10.5423/RPD.2020.26.4.222
Han, S. H., Yu, J. G., Lee, H. B., Oh, C. S., Yea, M. C., Lee, J. H., et al. (2016). Controlling by effective pruning of twigs showing black shoot blight disease symptoms in apple trees. Res. Plant Dis. 22, 269–275. doi: 10.5423/RPD.2016.22.4.269
He, L., Kim, S. H., and Yu, J. M. (2023). Development of the droplet digital PCR method for the detection and quantification of Erwinia pyrifoliae. Plant Pathol. J. 39, 141–148. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.08.2022.0117
Hossain, M. M., Shibata, S., Aizawa, S. I., and Tsuyumu, S. (2005). Motility is an important determinant for pathogenesis of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 66, 134–143. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2005.06.001
Jock, S., and Geider, K. (2004). Molecular differentiation of Erwinia amylovora strains from North America and of two Asian pear pathogens by analyses of PFGE patterns and hrpN genes. Environ. Microbiol. 6, 480–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2004.00583.x
Jung, Y., Jin, J. H., Jung, M., Hwang, I. S., Vu, N. T., Park, Y. K., et al. (2023). On-site applicable diagnostic fluorescent probe for fire blight bacteria. iScience 26:106557. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106557
Kharadi, R. R., Castiblanco, L. F., Waters, C. M., and Sundin, G. W. (2019). Phosphodiesterase genes regulate amylovoran production, biofilm formation, and virulence in Erwinia amylovora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85:e02233-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02233-18
Kharadi, R. R., Schachterle, J. K., Yuan, X., Castiblanco, L. F., Peng, J., Slack, S. M., et al. (2021). Genetic dissection of the Erwinia amylovora disease cycle. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 59, 191–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-020620-095540
Kim, W. S., Gardan, L., Rhim, S. L., and Geider, K. (1999). Erwinia pyrifoliae sp. nov., a novel pathogen that affects Asian pear trees (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 899–906. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-2-899
Lee, M. H., Ji, S., Ham, H., Kong, H. G., Park, D. S., and Lee, Y. H. (2021). First report of fire blight of apricot (Prunus armeniaca) caused by Erwinia amylovora in Korea. Plant Dis. 105:696. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-20-1973-PDN
Lee, G. M., Ko, S., Oh, E. J., Song, Y. R., Kim, D., and Oh, C. H. (2020). Comparative genome analysis reveals natural variations in the genomes of Erwinia pyrifoliae, a black shoot blight pathogen in apple and pear. Plant Pathol. J. 36, 428–439. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2020.0097
Lee, M. H., and Lee, Y. H. (2022). Population density and internal distribution range of Erwinia amylovora in apple tree branches. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 49, 933–944. doi: 10.7744/kjoas.20220080
Lee, M., Lee, Y. H., Lee, S. C., Choi, H., Yang, M., Moon, J. S., et al. (2023). Occurrence of black shoot blight in apple and pear trees in Korea. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 50, 723–734. doi: 10.7744/kjoas.500411
Lee, H. J., Lee, S. W., Suh, S. J., and Hyun, I. H. (2022). Recent spread and potential pathways for fire blight in South Korea. EPPO Bull. 52, 135–140. doi: 10.1111/epp.12835
Lehman, S. M., Kim, W. S., Castle, A. J., and Svircev, A. M. (2008). Duplex real-time polymerase chain reaction reveals competition between Erwinia amylovora and E. pyrifoliae on pear blossoms. Phytopathology 98, 673–679. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-98-6-0673
Lim, Y., Ham, H., Lee, M., Park, D. S., Roh, E., Park, D. H., et al. (2023). First report of fire blight on Chinese hawthorn (Crataegus pinnatifida) caused by Erwinia amylovora in Korea. Plant Dis. 107:3275. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-23-0703-PDN
MAAARO, (2011). Lutte intégrée contre les ennemis du pommier. Extrait du Publication 310F. Ministère de l’Agriculture, de l’Alimentation et des Affaires Rurales, Ontario.
McGhee, G. C., Schnabel, E. L., Maxson-Stein, K., Jones, B., Stromberg, V. K., Lacy, G. H., et al. (2002). Relatedness of chromosomal and plasmid DNAs of Erwinia pyrifoliae and Erwinia amylovora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 6182–6192. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.12.6182-6192.2002
Medhioub, I., Cheffi, M., Tounsi, S., and Triki, M. A. (2022). Study of Bacillus velezensis OEE1 potentialities in the biocontrol against Erwinia amylovora, causal agent of fire blight disease of rosaceous plants. Biol. Control 167:104842. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2022.104842
Myung, I. S., Yun, M. J., Lee, Y. H., Kim, G. D., and Lee, Y. K. (2016). First report of fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora on Chinese quince in South Korea. Plant Dis. 100:2521. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-04-16-0562-PDN
Norelli, J. L., and Brandl, M. T. (2004). Survival and growth of Erwinia amylovora on apple leaves. Acta Hortic. 704, 121–126.
Park, D. H., Lee, Y. G., Kim, J. S., Cha, J. S., and Oh, C. S. (2017). Current status of fire blight caused by Erwinia amylovora and action for its management in Korea. J. Plant Pathol. 99, 59–63.
Park, J., Lee, G. M., Kim, D., Park, D. H., and Oh, C. S. (2018). Characterization of the lytic bacteriophage phiEaP-8 effective against both Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia pyrifoliae causing severe diseases in apple and pear. Plant Pathol. J. 34, 445–450. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.NT.06.2018.0100
Park, D. H., Yu, J. G., Oh, E. J., Han, K. S., Yea, M. C., Lee, S. J., et al. (2016). First report of fire blight disease on Asian pear caused by Erwinia amylovora in Korea. Plant Dis. 100:1946. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-11-15-1364-PDN
Peng, J., Schachterle, J. K., and Sundin, G. W. (2020). Orchestration of virulence factor expression and modulation of biofilm dispersal in Erwinia amylovora through activation of the Hfq-dependent small RNA RprA. Mol. Plant Pathol. 22, 255–270. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13024
Pester, D., Milčevičová, R., Schaffer, J., Wilhelm, E., and Blümel, S. (2012). Erwinia amylovora expresses fast and simultaneously hrp/dsp virulence genes during flower infection on apple trees. PLoS One 7:e32583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032583
Pour, F. N., Ferreira, V., Félix, C., Serôdio, J., Alves, A., Duarte, A. S., et al. (2020). Effect of temperature on the phytotoxicity and cytotoxicity of Botryosphaeriaceae fungi. Fungal Biol. 124, 571–578. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.02.012
Rhim, S. L., Völksch, B., Gardan, L., Paulin, J. P., Langlotz, C., Kim, W. S., et al. (1999). Erwinia pyrifoliae, an Erwinia species different from Erwinia amylovora, causes a necrotic disease of Asian pear trees. Plant Pathol. 48, 514–520. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3059.1999.00376.x
Santander, R. D., and Biosca, E. G. (2017). Erwinia amylovora psychrotrophic adaptations: evidence of pathogenic potential and survival at temperate and low environmental temperatures. PeerJ 5:e3931. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3931
Santander, R. D., Oliver, J. D., and Biosca, E. G. (2014). Cellular, physiological, and molecular adaptive responses of Erwinia amylovora to starvation. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 88, 258–271. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12290
Schachterle, J. K., Gdanetz, K., Pandya, I., and Sundin, G. W. (2022). Identification of novel virulence factors in Erwinia amylovora through temporal transcriptomic analysis of infected apple flowers under field conditions. Mol. Plant Pathol. 23, 855–869. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13199
Shrestha, R., Koo, J. H., Park, D. H., Hwang, I. G., Hur, J. H., and Lim, C. K. (2003). Erwinia pyrifoliae, a causal endemic pathogen of shoot blight of Asian pear tree in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 19, 294–300. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2003.19.6.294
Shrestha, R., Lee, S. H., Hur, J. H., and Lim, C. K. (2005). The effects of temperature, pH, and bactericides on the growth of Erwinia pyrifoliae and Erwinia amylovora. Plant Pathol. J. 21, 127–131. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2005.21.2.127
Spinelli, F., Vanneste, J. L., Ciampolini, F., Cresti, M., Rademacher, W., and Geider, K. (2007). Potential and limits of acylcyclohexanediones for the control of blossom blight in apple and pear caused by Erwinia amylovora. Plant Pathol. 56, 702–710. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3059.2007.01614.x
Tao, Y., Ge, Y., Yang, J., Song, W., Jin, D., Lin, H., et al. (2023). A novel phytopathogen Erwinia sorbitola sp. nov., isolated from the feces of ruddy shelducks. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13:1109634. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1109634
Thomson, S. V. (1986). The role of the stigma in fire blight infections. Phytopathology 76, 476–482. doi: 10.1094/Phyto-76-476
van der Zwet, T., and Keil, H. L. (1979). Fire blight a bacterial disease of rosaceous plants. Washington D.C.: United States Department of Agriculture, Agriculture Handbook 510, 1–200.
Keywords: fire blight, black shoot blight, apple trees, duplex real-time PCR, temperature variation, swarming motility
Citation: Lee M-H, Balaraju K, Choi H-W and Lee YH (2025) Evaluation of pathogenicity variation between two Erwinia species in apples and their population using a duplex real-time PCR method. Front. Microbiol. 16:1514551. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1514551
Received: 21 October 2024; Accepted: 17 February 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Ravinder Kumar, Indian Agricultural Research Institute (ICAR), IndiaReviewed by:
Jeffrey K. Schachterle, Brigham Young University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Lee, Balaraju, Choi and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mi-Hyun Lee, bWloeXVuNzk4QGtvcmVhLmty
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.