- 1Pathogen-Host-Environment Interactions Research Laboratory, Institute of Biology, College of Science, University of the Philippines Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines
- 2Microbiology Division, Institute of Biological Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños, College, Laguna, Philippines
The emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Salmonella is recognized as a significant public health problem worldwide. This study investigated the occurrence of MDR Salmonella serovars in chicken meat from wet markets in Metro Manila, Philippines from February to July 2022. Using whole genome sequencing (WGS) and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance (AMR) testing, the serovar, drug resistance, and virulence profiles of Salmonella isolates were characterized. Out of 253 chicken cut samples, 95 S. enterica isolates representing 15 distinct serovars were recovered. The most common was S. enterica serovar Infantis (51.58%), followed by S. Brancaster (9.47%), S. Anatum (7.37%), S. London (7.37%), S. Uganda (6.32%), and S. Derby (4.21%). Phenotypic AMR testing revealed that 73.68% of the isolates were resistant to at least one drug class, and 45.26% were MDR. A wide array of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) associated with resistance to 12 different drug classes was identified, including three β-lactamase gene variants: blaCTX-M-65, blaTEM-1, and blaTEM-176. Some of these ARGs were located on MDR plasmids, such as those on IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3, IncFIA(HI1)_1_HI1, and IncX1_1. A total of 131 virulence genes were detected, some of which conferred pESI-like characteristics to S. Infantis. These findings highlight a potential public health risk posed by pathogenic MDR Salmonella in chicken meat and underscore the urgent need for further research and coordinated AMR surveillance in the Philippines, aiming to stimulate national efforts to combat AMR.
1 Introduction
One of the most prominent public health crises worldwide is antimicrobial resistance (AMR), which is the loss of effectiveness of antimicrobials against infections as a result of their abuse and misuse. In 2019, AMR was estimated to have caused 4.95 million deaths worldwide (Murray et al., 2022) which is not far from the 2050 estimate of 10 million deaths annually (O’Neill, 2014). AMR is a multifaceted and gradually spiraling issue that emerged and disseminated through selective pressure from inappropriate human medicine, improper agricultural practices, and environmental pollution. The One Health approach is a multisectoral effort to address AMR and promote human, animal, and environmental health, which are mutually dependent (McEwen and Collignon, 2018). Bacteria exposed to selective pressure from antimicrobials can become resistant and also possess antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) that can be mobilized through horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of mobile genetic elements to other potential pathogens, which present significant threats in clinical treatments. This led to the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR), which is the resistance to three or more groups of antimicrobials (Magiorakos et al., 2012), as well as resistance to last resort antibiotics such as colistin (Algammal et al., 2023). In fact, MDR pathogens have been widely reported in food animals and clinical samples, potentially attributed to the improper usage of this antibiotic in livestock and human medicine (Danaei et al., 2023).
Salmonella enterica is one of the most common foodborne pathogens worldwide, comprising over 2,600 serovars. Based on the type of disease, S. enterica can be classified as typhoidal or non-typhoidal. Non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) can cause gastroenteritis and invasive systemic disease (Dieye et al., 2022). NTS is also considered zoonotic, and, therefore, can be carried by many animal species, which can lead to contamination of the environment and food supplies (He et al., 2020; Nhung et al., 2024). Compounding the problem is the ability of NTS to acquire multiple ARGs that confer MDR, limiting treatment options. The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights this issue by categorizing extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella and other Enterobacteriaceae as critical priorities for research and development of new antimicrobials, while fluoroquinolone-resistant NTS is listed in high priority (World Health Organization, 2024). Therefore, controlling the spread of MDR NTS is crucial for public health, as it impacts food safety throughout the entire farm-to-fork continuum (Nhung et al., 2024).
With the advent of whole genome sequencing (WGS), uncovering important ARGs and virulence factors in foodborne pathogens like Salmonella has become a more cost-effective and comprehensive alternative to conventional typing methods for public health surveillance (Yan et al., 2024). This study investigated the AMR and virulence profiles of 95 S. enterica isolates from chicken meat sold in wet markets in Metro Manila, employing phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing, WGS, and bioinformatic analysis. While many developed countries have already established their AMR surveillance systems to combat the spread of highly pathogenic MDR pathogens [Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS), n.d.], similar coordinated efforts are lacking in the Philippines. Thus, this study aimed to explore the distribution of ARGs and virulence genes, as well as the serotypes and phylogenetic relationships of MDR Salmonella isolates. The findings will provide insights into the current status of AMR in foodborne pathogens in the Philippines, and help inform future public health strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sample collection, isolation, and confirmation of Salmonella enterica
Chicken samples, supplied by local farms to slaughterhouses, were collected from public wet markets in Eastern (San Juan City and Quezon City), Northern (Malabon City), and Southern (Muntinlupa City) Metro Manila, Philippines between February and July 2022. Raw cut-up samples, including breast, wings, drumstick, and thigh, were collected in sterile plastic bags and transported to the laboratory for processing. The isolation of Salmonella was performed according to the methods outlined by Ng and Rivera (2015). Twenty-five grams of chicken samples were added into 225 mL buffered peptone water (BD Difco, NJ, United States) in a sterile Rollbag® (Interscience, France) and homogenized in BagMixer® 400 (Interscience, France) for 1 min, and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Following the pre-enrichment, 0.1 mL of the sample was added to 10 mL Rappaport-Vassiliadis (RV) broth (Difco, BD, Sparks, MD) and incubated at 42°C for 24 h. From the incubated RV broth, colony isolation was done on xylose lysine deoxycholate (XLD) agar (BD Diagnostics System, NJ, United States) incubated at 37°C for 18 to 24 h. Presumptive S. enterica colonies, i.e., colonies with black centers and clear or transparent halo were then streaked on nutrient agar (BD Diagnostics System, NJ, United States) for PCR confirmation.
Extraction of DNA was done using DNA purification kit (Monarch®, New England BioLabs, MA, United States). Confirmation of S. enterica isolates was done by amplifying the invA gene as outlined by Ng and Rivera (2015).
2.2 Antimicrobial resistance testing
The VITEK® 2 Compact 60 ID/AST System and AST-GN70 card panel (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France) were used to test the resistance of the S. enterica isolates against 15 antimicrobial agents: Penicillins—ampicillin (AMP); β-lactam combination agent—ampicillin/sulbactam (AMS), and piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP); Cephems—cefazolin (CZN), ceftriaxone (CTR), and cefepime (CEF); Monobactams—aztreonam (AZT); Carbapenems—ertapenem (ETP), and meropenem (MEM); Aminoglycosides—amikacin (AMK), gentamicin (GEN), and tobramycin (TOB); Quinolones—ciprofloxacin (CIP); Glycylcycline—tigecycline (TGC); Nitrofurans—nitrofurantoin (NFN); and Folate pathway antagonists—trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT). For quality control, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 was used as the reference strain. For the interpretation of the minimum inhibitory concentration, breakpoints from CLSI M100 34th edition (CLSI, 2024) were used in the analysis.
2.3 Whole-genome sequencing, assembly, and bioinformatics analysis
The 95 isolates from chicken cut samples were sent for Illumina library construction and sequencing at the DNA Sequencing Core Facility of the Philippine Genome Center. Libraries were prepared using Nextera XT DNA library preparation kit (ILMN FC-131-1096) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The resulting libraries were checked for size and concentration using TapeStation 2200 and Qubit dsDNA assay. The libraries were sequenced using NovaSeq 6000. The resulting paired-end reads (2 × 150 bp) were checked for quality using FastQC v0.12.1 (Andrews, 2010), and were trimmed using fastp 0.23.2 (Chen, 2023). Unicycler v0.5.0 (Wick et al., 2017) was used as a SPAdes-optimizer in the assembly of the Illumina reads. The quality of the assembled genomes was evaluated using QUAST 5.2.0 (Mikheenko et al., 2018). The assembled genomes (length: 4.6 to 5.7 Mbp; N50: 57.9 Kbp to 754.8 Kbp) were annotated using Prokka 1.14.6 (Seemann, 2014). Serovar prediction was performed using Salmonella in silico typing resource (SISTR) tool v1.1.1 (Yoshida et al., 2016). The presence of ARGs, virulence genes, and plasmids were detected using ABRicate V1.0.1 (Seemann, 2020) which combined data with 95% nucleotide identity and 60% coverage from CARD-RGI (Alcock et al., 2023), VFDB (Liu et al., 2022), and PlasmidFinder 2.1 (Carattoli et al., 2014; Camacho et al., 2009). In addition, point mutations were screened using AMRFinderPlus (Feldgarden et al., 2021), employing the same nucleotide identity and coverage cutoff. Gene annotations were recovered from the respective databases, unless specified.
2.4 Multilocus sequence typing and phylogenetic analysis
The FASTQ raw reads of the 95 Salmonella isolates were uploaded to Enterobase (https://enterobase.warwick.ac.uk/). Multilocus sequence typing (MLST) analysis was done using the seven housekeeping gene loci, aroC, dnaN, hemD, hisD, purE, sucA, and thrA, to identify sequence types (STs) and eBurst Groups (eBGs) of the isolates.
The core-regions of the isolates were analyzed using ParSNP software v2.0.6, with the following Salmonella genomes (BioSample No.) included in the analysis: S. Typhimurium LT2 (SAMN03470047), S. Typhimurium (SAMN10833329), S. Saintpaul (SAMN40973940), S. Breda (SAMN13906412), S. Kentucky (SAMN43547925), S. London (SAMN38156060), S. Anatum (SAMN41786477), S. Isangi (SAMN08951104), S. Amager (SAMN44253386), S. Uganda (SAMN43080519), S. Livingstone (SAMN02698174), S. Lexington (SAMN02843465), S. Derby (SAMN14341256), S. Albany (SAMN43079470), S. Brancaster (SAMN10425346), and S. Infantis (SAMN44253386). Identical and unique sequences across all genomes were identified to make multiple sequence alignment. From 112,878 core genome single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) alignment, a maximum likelihood tree was inferred using RAxML-NG v1.2.2 GTRGAMMA substitution model with 100 bootstrap replicates (Kozlov et al., 2024). The tree was visualized, mid-rooted, and annotated using iTOL v 6.9.1 (Letunic and Bork, 2024).
2.5 Data visualization
The heatmaps of ARGs, plasmid replicons, and virulence genes were created using TBTools (Chen et al., 2020). In the analysis, the proportion of serovars possessing ARGs, virulence genes, and plasmids was indicated by values between 0 and 1, and default Euclidean distance and complete clustering method were employed.
3 Results
3.1 Serovars, MLST, and eBGs
Of the 253 chicken cuts collected from four cities in Metro Manila between February and July 2022, 95 isolates of S. enterica were recovered: 74 (77.89%) from San Juan City, 17 (17.89%) from Muntinlupa City, 4 (4.21%) from Quezon City, and 1 (1.05%) from Malabon City. In silico serotyping using SISTR (Figure 1) revealed that these isolates belonged to 15 distinct serovars. The most frequent serovar was S. Infantis, accounting for 51.58% (n = 49) of the isolates, followed by S. Brancaster (9.47%, n = 9), S. Anatum (7.37%, n = 7), S. London (7.37%, n = 7), S. Uganda (6.32%, n = 6), and S. Derby (4.21%, n = 4). Other serovars included monophasic S. Typhimurium I 1,4,[5],12:i:-, S. Breda, S. Albany, and S. Kentucky, each representing 2.11% (n = 2). Single isolates of serovars Livingstone, Lexington, Saintpaul, Amager, and Isangi were also identified.
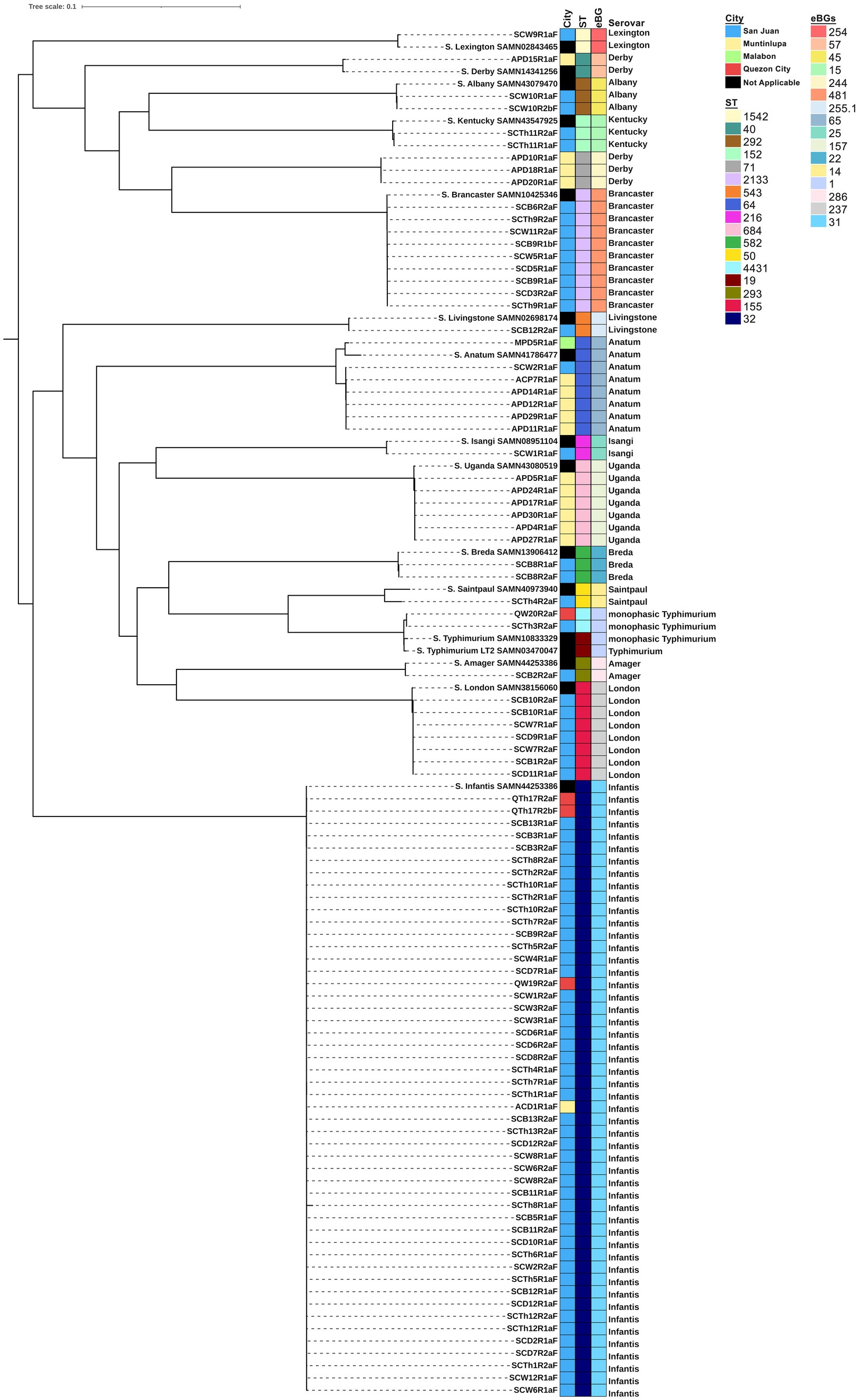
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of S. enterica isolates (n = 95). A core genome analysis was performed using ParSNP software v2.0.6 and a maximum likelihood tree was inferred using RAxML v.1.2.2. The tree was visualized, mid-rooted, and annotated using iTOL v 6.9.1. Sampling location, sequence type (ST), eBurst Groups (eBGs) and serotypes are visualized with the phylogenetic tree. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium LT2, BioSample No. SAMN03470047, was used as the reference genome.
San Juan City yielded 13 distinct serovars, Muntinlupa City had four, Quezon City had two, and Malabon City had one. Monophasic S. Typhimurium I 1,4,[5],12:i:-, Anatum, and Infantis were isolated from more than one city, whereas the remaining serovars were isolated from a single location. Based on the MLST, these serovars belonged to 16 distinct sequence types (STs) and eBurst Groups (eBGs), with each serovar assigned a unique ST and eBG, except for S. Derby, which was associated with two STs (ST 40 and ST 71) and eBGs (57 and 244). From the maximum likelihood tree, these Derby isolates formed different clades separated by 27,401 SNP differences. Interestingly, these Derby isolates were all isolated from Muntinlupa, with the lone ST 40 possessing more ARGs than the three ST 71. All isolates clustered together with their respective reference genome, except for monophasic S. Typhimurium I 1,4,[5],12:i:-, which formed a closely related sub-clade with SAMN10833329 due to 723 SNP differences.
3.2 Antimicrobial resistance phenotype
Based on VITEK® 2 AST results, the most common resistance phenotypes observed among the S. enterica isolates were against ampicillin (AMP; 63.2%), nitrofurantoin (NFN; 51.6%), tobramycin (TOB; 47.4%), gentamycin (GEN; 44.2%), cefazolin (CZN; 43.2%), ceftriaxone (CTR; 43.2%), aztreonam (AZT; 21.0%), and ciprofloxacin (CIP; 13.7%) (Figure 2A). Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT) resistance was observed in 11.6% of the isolates, while only five isolates (5.3%) were resistant to ampicillin/sulbactam (AMS). All isolates were susceptible to piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP), cefepime (CEF), ertapenem (ETP), meropenem (MEM), amikacin (AMK), and tigecycline (TGC).
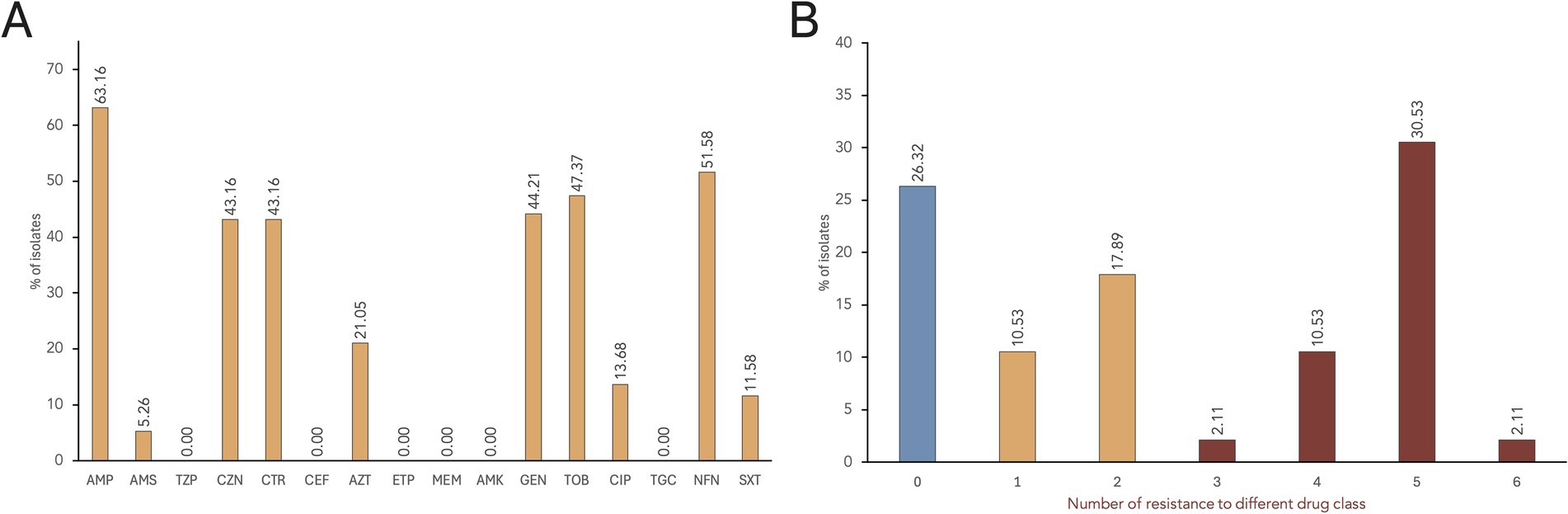
Figure 2. AMR rates of S. enterica isolates. (A) The proportion of isolates showing resistance phenotype against each antimicrobial tested. Antimicrobials tested: Penicillins—ampicillin (AMP); β-lactam combination agent—ampicillin/sulbactam (AMS), and piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP); Cephems—cefazolin (CZN), ceftriaxone (CTR), and cefepime (CEF); Monobactams—aztreonam (AZT); Carbapenems—ertapenem (ETP), and meropenem (MEM); Aminoglycosides—amikacin (AMK), gentamicin (GEN), and tobramycin (TOB); Quinolones—ciprofloxacin (CIP); Glycylcycline—tigecycline (TGC); Nitrofurans—nitrofurantoin (NFN); and Folate pathway antagonists—trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT). (B) Distribution of multidrug resistant S. enterica isolates.
Seventy isolates (73.7%) exhibited resistance to at least one antimicrobial drug class, while 25 isolates were susceptible to all tested antimicrobials (Figure 2B). A total of 17 distinct AMR profiles were identified among the 95 S. enterica isolates (Supplementary Table S1). MDR, or resistance to three or more drug class (Magiorakos et al., 2012), was observed in 45.3% of the isolates (n = 43), with the majority being S. Infantis (n = 37). Most of the isolates (30.5%) showed resistance to five drug classes, with AMP-CZN-CTR-AZT-GEN-TOB-NFN as the common MDR phenotype. Furthermore, resistance to six antimicrobial classes was observed in two S. Infantis isolates: SCD2R1a (AMP-CZN-CEF-GEN-TOB-CIP-NFN-SXT) and SCTh13R2a (AMP-CZN-CEF-AZT-GEN-TOB-NFN-SXT).
3.3 Antimicrobial resistance genes
A total of 50 ARGs conferring resistance to 12 distinct drug classes using CARD and AMRFinderPlus were identified (Figure 3). These drug classes include aminoglycosides, β-lactams, folate pathway inhibitors, fluoroquinolones, phenicols, tetracyclines, aminocoumarin, phosphonics, lincosamides, and peptide antibiotics. The identified ARGs are either acquired or produced through point mutations and are encoded in the chromosome or plasmids. Notably, 11 of these genes encode subunits of multidrug efflux pumps that confer resistance to multiple antibiotics. The number of ARGs per genome ranges from 22 to 36 genes, with S. London and S. Infantis isolates harboring the highest number of ARGs.
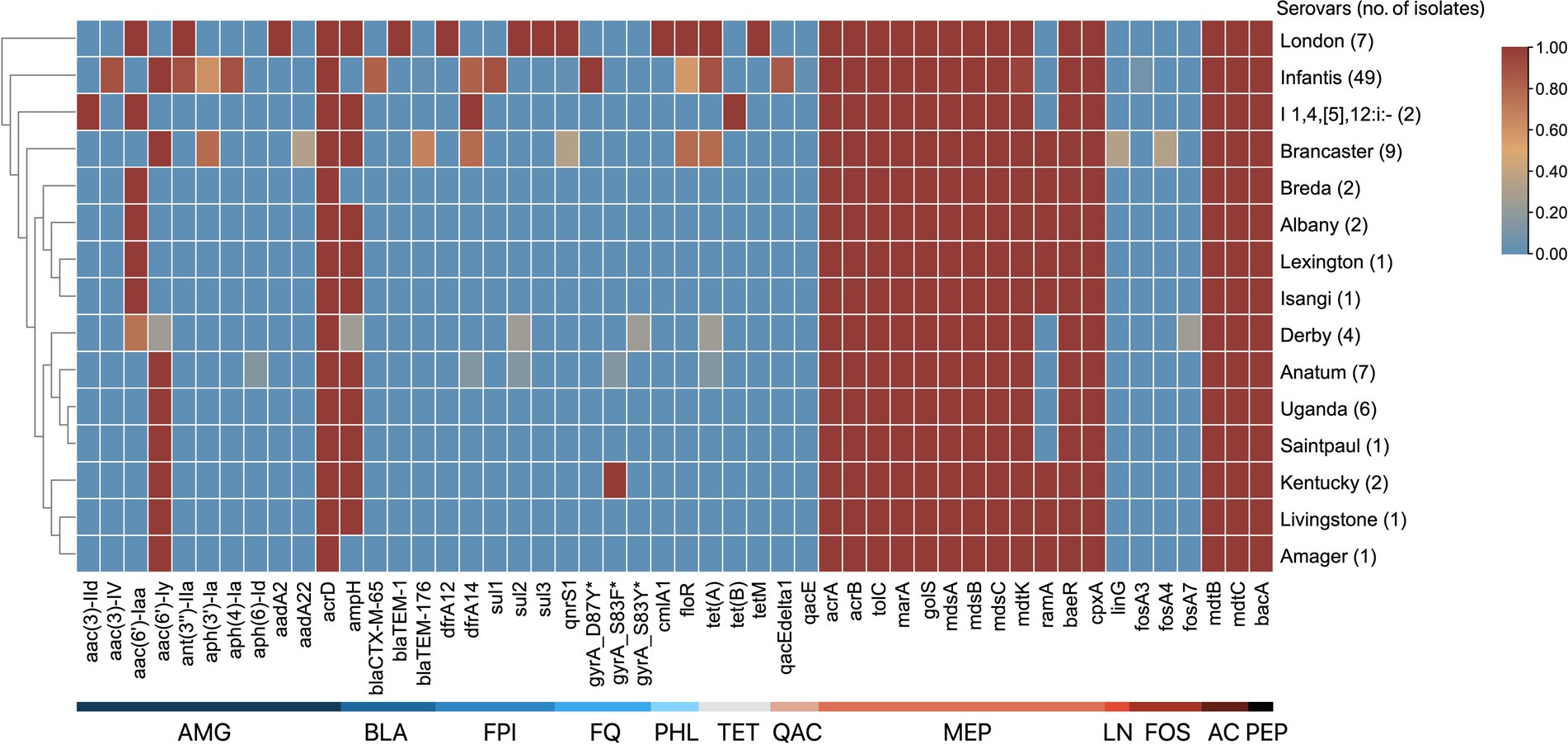
Figure 3. ARG patterns of S. enterica serovars. The serovars are clustered by their similarities in ARGs. The antimicrobial class of ARGs are indicated by the labels at the bottom: aminoglycosides (AMG), β-lactams (BLA), folate pathway inhibitors (FPI), fluoroquinolones (FQ), phenicols (PHL), tetracyclines (TET), quaternary ammonium compounds (QAC), multidrug (MEP), lincosamides (LN), fosfomycins (FOS), aminocoumarins (AC), and peptide antibiotics (PEP). The proportion of serovars possessing ARGs ranges from 0 to 1, where absence is 0 and is blue, and presence in all isolates is 1 and is red.
Of the 50 ARGs identified, 12 (24.0%) confer resistance to aminoglycosides. The acrD, gene encoding an efflux pump, and kdpE, a transcriptional regulator, were present in all isolates. In addition, gene variants that encode aminoglycoside modifying enzymes — aac, aadA, and ant—were identified in several serovars. Four distinct β-lactam resistance genes were identified: ampH, which was present in all serovars except S. Infantis, S. Breda, S. Amager, and three S. Derby isolates; blaCTX-M-65 found in 40 of 49 S. Infantis isolates; blaTEM-1, detected in serovar London; and blaTEM-176, identified in 6 of 9 S. Brancaster isolates. Two antifolate resistance genes were observed: dfrA12, found in serovar London, and dfrA14, which was present in monophasic S. Typhimurium isolates, and selected S. Brancaster, S. Infantis, and S. Anatum isolates. Three variants of the sul gene, which confers resistance to sulfonamides, were identified in certain serotypes: sul1 was detected in 44 of 49 of S. Infantis isolates; sul2 was found in all S. London, one S. Anatum, and one S. Derby isolates; and sul3 was identified in all S. London isolates. For quinolone and fluoroquinolone resistance, qnrS1 was found in all S. London, and some S. Brancaster, and S. Infantis isolates. In addition, point mutations in the DNA gyrase subunit A were also noted: gyrA_D87Y detected in all S. Infantis isolates; gyrA_S83F in S. Kentucky and one S. Anatum isolate; and gyrA_S83Y in one S. Derby isolate. Regarding chloramphenicol resistance, only two efflux pump genes were detected among the isolates: cmlA1 found only in serovar London, and floR detected in S. London isolates, and selected S. Brancaster and S. Infantis isolates. For tetracyclines, three resistance genes were identified: tet(A) in S. London isolates, and selected S. Anatum, S. Derby, S. Brancaster, and S. Infantis isolates; tet(B) in monophasic S. Typhimurium; and tetM in S. London.
Several multidrug efflux pump component genes were detected across all isolates: acrAB-tolC genes, which code for a tripartite resistance-nodulation-division (RND) efflux pump, and their positive regulators sdiA and marA, that can transport tetracyclines, phenicols, rifamycins, penams, glycylcyclines, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones, and other disinfecting and antiseptic agents out of the cell; mdsABC, which code for another tripartite RND-type efflux pump, and its positive regulator golS, used in exporting β-lactams, chloramphenicol, and thiamphenicols; and baeR and cpxA, which are associated in pumping out aminocoumarin and aminoglycoside antibiotics. Other notable ARGs include gene variants that encode resistance to fosfomycins (fosA3, fosA4, and fosA7); genes qacE/E∆1 in S. Infantis that confer resistance against quaternary ammonium compounds, such as benzalkonium chloride.
3.4 Plasmid profiles
In silico typing using PlasmidFinder identified 19 distinct plasmid replicons in 86.32% of the isolates (n = 82) (Figure 4). Each isolate contained between one and eight plasmid replicons, with the highest number found in two S. Brancaster isolates. The most common plasmid replicon was IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3, present in 48 of 49 S. Infantis isolates. This was followed by the ColRNAI replicon, which was present in S. Derby, monophasic S. Typhimurium, S. Amager, and selected S. Brancaster, S. Infantis, and S. Anatum isolates.
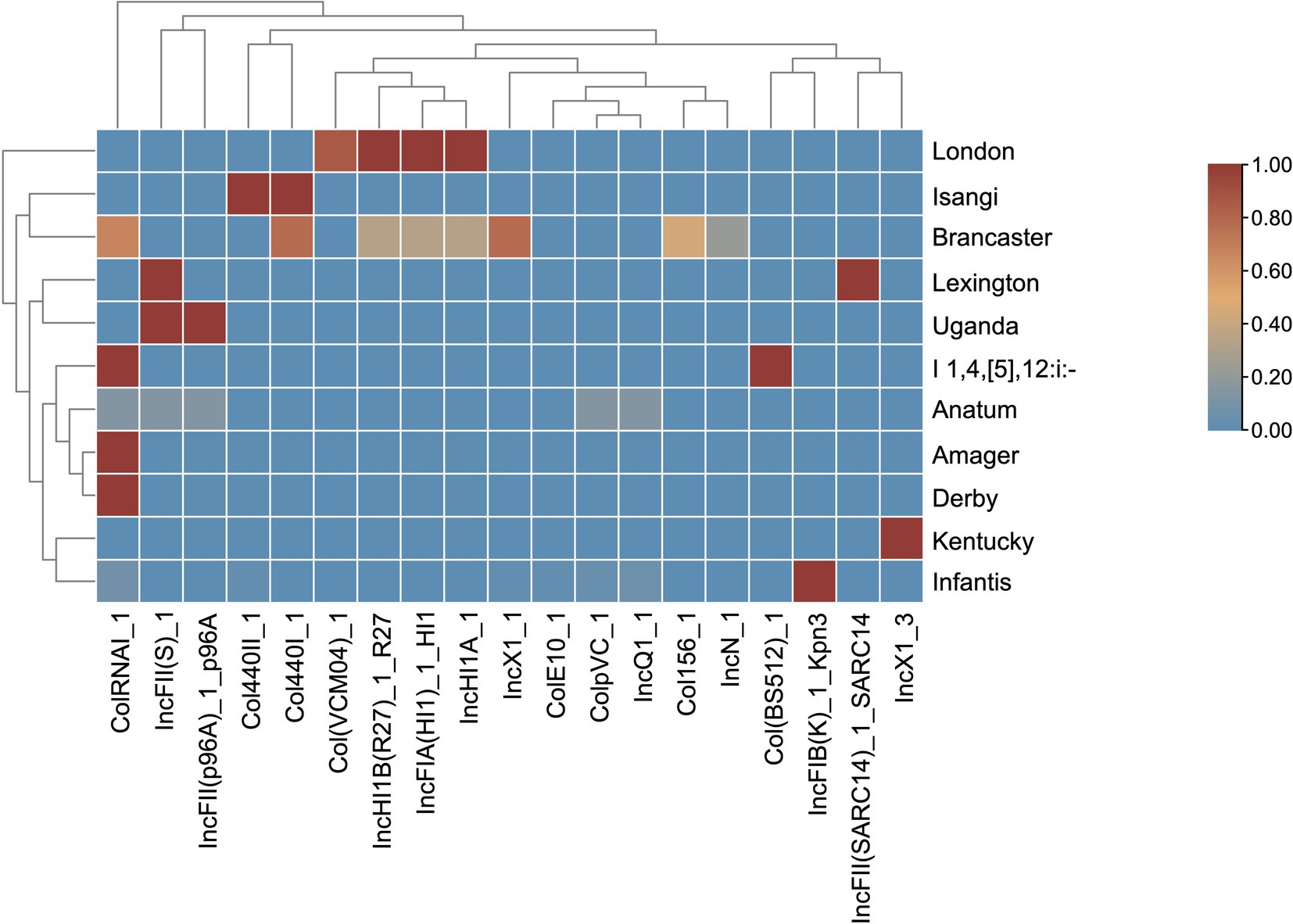
Figure 4. Heat map of the plasmid profiles of S. enterica serovars. The plasmids are clustered by their prevalence similarities. The proportion of serovars possessing plasmids ranges from 0 to 1, where absence is 0 and is blue, and presence in all isolates is 1 and is red.
No plasmids were detected in S. Livingstone, S. Saintpaul, S. Breda, and S. Albany isolates. Some plasmid replicons were unique to a single serovar: Col(BS512) in monophasic S. Typhimurium, ColE10 in one S. Infantis isolate, IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3 in the majority of S. Infantis isolates, IncFII(SARC14) in S. Lexington, IncN in two S. Brancaster isolates, and IncX1_3 in S. Kentucky isolates. In contrast, other plasmid types were detected in two to five different serovars. Interestingly, IncFIA(HI1), IncHI1A, and IncHI1B(R27) were harbored by the same set of S. London and S. Brancaster isolates.
3.5 Virulence genes
A total of 131 virulence genes associated with various virulence mechanisms were identified across the S. enterica isolates. Each isolate contained 96–119 of these genes. Notably, 63.36% of the genes (n = 83) were present in all isolates, while 48 genes were identified as variable virulence factors (Figure 5).
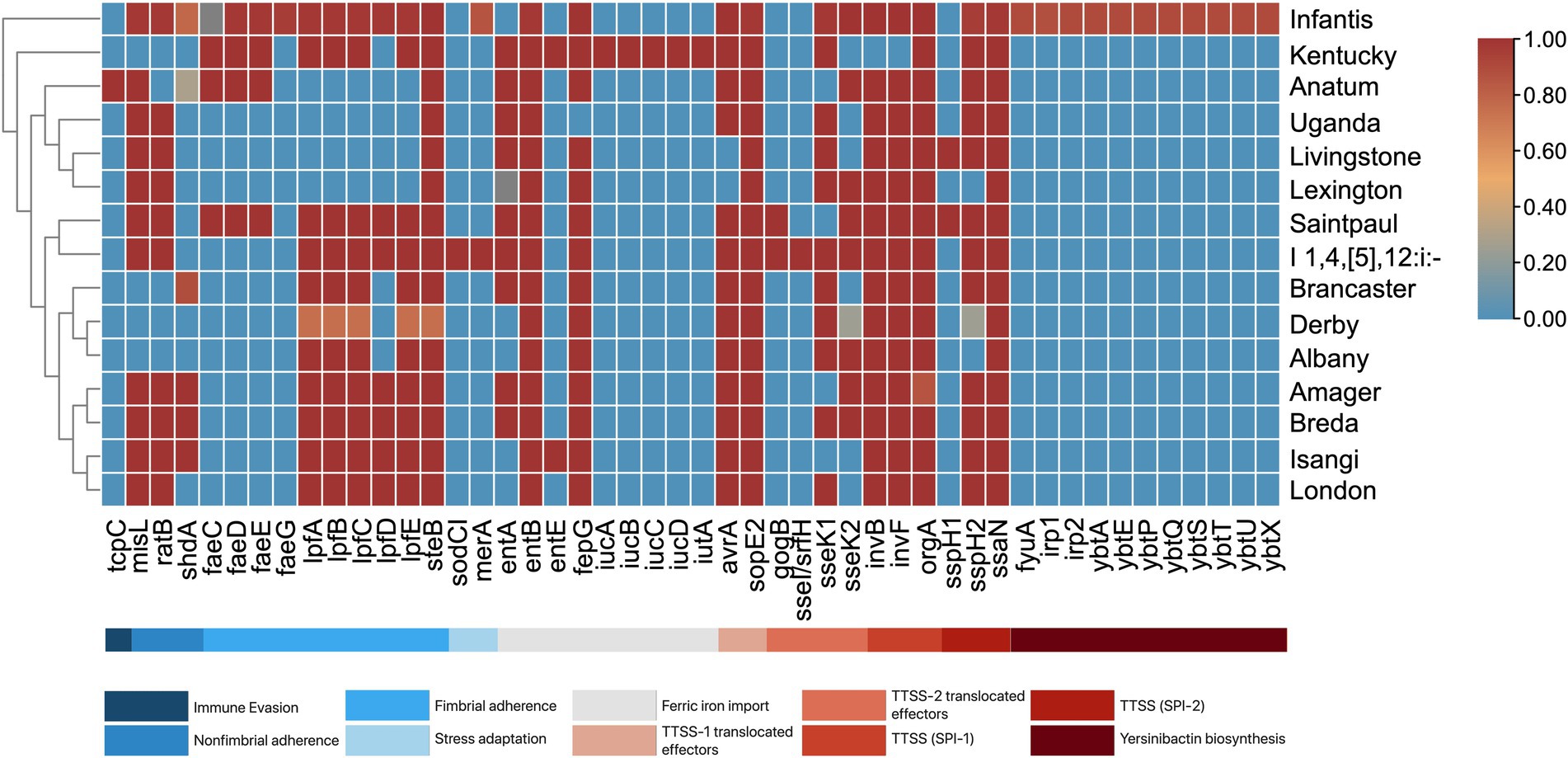
Figure 5. Virulence genes present among S. enterica serovars. The serovars are clustered by their similarities in virulence genes. The proportion of serovars possessing virulence genes ranges from 0 to 1, where absence is 0 and is blue, and presence in all isolates is 1 and is red.
All isolates were found to harbor genes encoding Type 1 (fimCDFHI) and Type 3 (orgABC, prgHIJK, invA, sseABCDEFGm, pipB, sifAB, sipABCD, sopBDD2) secretion systems. Among the serovars, S. Infantis exhibited the highest number of virulence factors (117 to 119 genes). This abundance is attributed to several genes exclusive to S. Infantis, including the ybtAEPQSTUX operon, fyuA, irp-1, irp-2, and faeG. Additionally, S. Infantis, along with monophasic S. Typhimurium, also contained the mer operon. Other notable serovar-specific genes include tcpC in S. Anatum, sodCI, and sseI/srfH in monophasic S. Typhimurium, and iucABCD and iutA in S. Kentucky.
4 Discussion
The results of the serovar prediction reveal a wide variety of serovars circulating in chicken meat sold in wet markets in Metro Manila. It showed the dominance of S. Infantis among the studied Salmonella isolates, which is consistent with previous studies in chicken meat in the U.S., Europe, and Asia (McMillan et al., 2022; Mora et al., 2024; Kim et al., 2024; Mattock et al., 2024). One possible reason for the increased detection of S. Infantis is the presence of plasmid of emerging S. Infantis or pESI, which has been detected in poultry, chicken meat, and clinical isolates across South America, Europe, Africa, and Asia (McMillan et al., 2022; Mattock et al., 2024). Other significant serovars detected in our study include Brancaster, Anatum, London, and Uganda, all of which have been previously detected in either poultry or poultry products (Xu et al., 2021; Khoo et al., 2023; Mora et al., 2024; Sodagari et al., 2023). Notably, we also detected the rare serovar Isangi, marking its first reported detection in the Philippines. Previous reports of serovar Isangi in Brazil and South Africa are linked to poultry production (dos Santos et al., 2023; Vilela et al., 2023). Interestingly, serovar Enteritidis was absent in our study, despite it being one of the dominant NTS serovars in clinical isolates in the country (Lagrada et al., 2022).
MLST analysis revealed that the isolates belong to 16 distinct STs and eBGs. Particularly, most isolates belonged to ST 32 (S. Infantis, eBG 31), consistent with the study of Mattock et al. (2024), where 99% (n = 5,205) of S. Infantis were classified as ST 32, and only few belong to ST 2283 and ST 2146. Other serovars belong to unique STs and eBGs, except for S. Derby, which was linked to STs 40 and 71. Sévellec et al. (2018) previously reported that serovar Derby is polyphyletic and can be divided into four distinct lineages, with ST 40 and 71 being associated with poultry. Although the monophasic S. Typhimurium isolates in our study shared a single eBG with the reference S. Typhimurium, they formed distinct but closely related sub-clade from the reference due to differences in sequence types (STs 4,431 and 19, respectively). Documentation on ST 4431 in literature is scarce and those that are deposited in EnteroBase are associated with human and clinical isolates. This study is among the few to report this ST in animal meat, and its previous isolations in humans might present a possible health risk.
All the serovars were isolated from a single city except for monophasic S. Typhimurium, S. Anatum, and S. Infantis. Serovars that were isolated from a single location and formed a single clade could be possibly sourced from the same farm or slaughterhouse. In contrast, serovars isolated from multiple locations and still formed a single clade could be attributed to farms supplying live birds to various slaughterhouses, which then distributed chicken meat from these slaughterhouses to different wet markets across cities (Mora et al., 2024).
A significant proportion of our isolates exhibited resistance to at least one antimicrobial drug class, with 45.26% categorized as MDR. Phenotypic resistance was notably high against β-lactams (penicillins, cephems, and monobactams), aminoglycosides, and nitrofurans. In serovars Uganda, Anatum, and monophasic Typhimurium, β-lactam resistance can be partly attributed to ampH gene and the multidrug efflux pump mdsABC. For serovars Infantis, London, and Brancaster, resistance is associated with β-lactamase gene variants: blaCTX-M-65, blaTEM-1, and blaTEM-176, respectively. Previous studies have reported the presence of these bla genes in these serovars from chicken meat (Chin et al., 2017; Brown et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2023). Particularly concerning is the blaCTX-M-65 variant in S. Infantis, which has facilitated its emergence and spread in poultry and its products (Alzahrani et al., 2023). Genetically related strains of S. Infantis carrying blaCTX-M-65 have also been found in retail meat and human isolates in the U.S. (Brown et al., 2018). The presence of ESBLs in these isolates is alarming, as it removes ceftriaxone and ampicillin as treatment option against salmonellosis (Brown et al., 2018).
Resistance to aminoglycosides, such as tobramycin (TOB, 47.37%), and gentamicin (GEN, 44.21%), was also common among the isolates. This may be due to the presence of acrD efflux pump or drug inactivation through aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes (AMEs). Several AME genes were detected, including variants encoding acetyltansferases (aac(3)-IId, aac(3)-IV, aac(6′)-Iy, aac(6′)-Iaa), nucleotidyltransferases (ant(3″)-IIa, aadA2, and aadA22) and phosphotransferases (aph(4)-Ia, and aph(6)-Id). Isolates did not show detectable resistance genes against nitrofurans (nfsA and nfsB), suggesting that resistance might be due to unknown resistance mechanisms or new ARG variants that are yet to be discovered (Alzahrani et al., 2023; Petrin et al., 2023). The use of nitrofurantoin in humans for urinary tract infections and in animals as growth promoters (Mohakud et al., 2023) may have contributed to selective pressure for new ARGs.
Resistance to ciprofloxacin (CIP, 13.68%) and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT, 11.58%) were less common among our isolates. In our S. Infantis isolates, ciprofloxacin resistance appears to be partly attributed to a point mutation in gyrA (D87Y), a key target for quinolones (Qian et al., 2020). Additionally, the plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance gene qnrS1 was identified, and co-carried with blaTEM-1 and blaTEM-176 in S. London and S. Brancaster, respectively. Although qnr expression has been shown to reduce the bactericidal efficacy of ciprofloxacin (Chen et al., 2024), both serovars remained susceptible. This suggests that the resistance conferred by qnrS1 in these serovars is insufficient to meet the resistance threshold for ciprofloxacin, implying that the acquisition of other qnr gene variants or mutations in the topoisomerase genes may be needed to achieve resistance (Salah et al., 2019). As for trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, the presence of both dfrA and sul gene variants in S. London (dfrA12 and sul2) and S. Infantis (dfrA14 and sul1) might explain their resistance. These resistance genes are linked to either class 1 integrons (dfrA12, dfrA14, and sul1) or small nonconjugative plasmids (sul2) (Antunes et al., 2005).
Notably, all isolates were susceptible to tigecycline (TGC), despite the presence of multidrug efflux pump acrAB. This may be explained by a higher epidemiological cut-off value for tigecycline compared to the resistance level conferred by the ARGs (Petrin et al., 2023), resulting in isolates being classified as susceptible. Additionally, our isolates were susceptible to both ertapenem and meropenem, and ARGs related to carbapenem resistance were not detected.
The majority of the MDR isolates (37 of 43) belonged to serovar Infantis. The proportion of MDR among Infantis isolates in our study (75.51%) is comparable to the 75% observed in South America (76%), but higher than rates reported in Asia (55%), Europe (42%), and North America (27%) (Mattock et al., 2024). This may be attributed to the ARGs possessed by the isolates, wherein each genome contained 22 to 33 ARGs, with 81.63% of the isolates harboring blaCTX-M-65. In addition, it has been found that S. Infantis isolates from poultry and poultry products have considerably more ARGs compared to human and environmental isolates, and 73% of poultry isolates across continents were MDR (Mattock et al., 2024). This only highlights the role of S. Infantis in poultry and poultry products as a major reservoir of ARGs, and emphasizes the potential risks associated with the spread of these resistance genes in humans and the environment.
The spread of ARGs can be linked to HGT facilitated by mobile genetic elements, such as plasmids. Particularly concerning are conjugative plasmids (IncC, IncF, IncHI, IncN, and IncX) that are self-transmissible, allowing them to increase the spread of ARGs (McMillan et al., 2020a; Wang and Dagan, 2024). Among the plasmids identified in our isolates, IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3 was the most common, being identified in S. Infantis isolates. IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3 is recognized as one of the contributors to the dominance of the serovar in poultry in Europe and the U.S. (Alzahrani et al., 2023), and is known to carry blaCTX-M-65 and ARG variants of dfrA, floR, aph, and aac (Hull et al., 2022; Russo et al., 2024). Other MDR plasmids identified in the study include IncFIA(HI1)_1_HI1 and IncX1_1. These plasmids are recognized for carrying a class 1 integron, as reported by several studies (Juraschek et al., 2021; Syed Abu Thahir et al., 2023; Puangseree et al., 2024). The IncFIA(HI1)_1_HI1 in our S. London isolates carries a diverse array of resistance genes, including cmlA1, florR, tetA, blaTEM-1, sul2, aadA2, ant3, qnrS1, and dfrA12. As for IncX1 detected in S. Brancaster, it carries aph(3′)-Ia, blaTEM-176, dfrA14, floR, qnrS1, and tetA, which is consistent with the findings of previous studies (Juraschek et al., 2021; Syed Abu Thahir et al., 2023).
Virulence genes play a crucial role in enabling Salmonella to cause disease by allowing it to survive and establish infection in the host (Retamal et al., 2022). Key virulence genes that encode Type 1 and Type 3 secretion systems, crucial for the initial stages of Salmonella invasion (Bao et al., 2020), were found in all isolates. Other virulence genes were exclusively found in specific serovars, enhancing their adaptive capacity to survive and cause infection (Retamal et al., 2022). In our study, we identified sodCI and sseI/srfH exclusively in serovar monophasic Typhimurium. The sodCI encodes a periplasmic superoxide dismutase, which protects S. Typhimurium from phagocytic superoxide (Tidhar et al., 2015). Meanwhile, the sseI/srfH gene contributes to the serovar’s ability to maintain long-term system infection in the spleen and liver (McLaughlin et al., 2009). We also found iucABCD and iutA genes exclusively in S. Kentucky. These genes encode for aerobactin, a siderophore that enhances the serovar’s survivability during systemic dissemination by aiding in iron acquisition (Fricke et al., 2009; Wellawa et al., 2020).
Among the S. enterica isolates, S. Infantis isolates showed the highest number of virulence determinants attributed to its serovar-specific genes. In particular, the presence of genes encoding the Ybt system (fyuA, irp1, irp2, and ybtAEPQSTUX) was detected in selected isolates. These genes encode for yersiniabactin, a siderophore that increases the ability of Salmonella to survive in low-iron environments (Russo et al., 2024). Since Salmonella growth is restricted in low-iron conditions found in eggs and live poultry, the presence of the Ybt system gives S. Infantis a significant advantage, enabling it to thrive where other strains struggle (McMillan et al., 2020b). Additionally, 47 of 49 S. Infantis isolates carried the faeG gene, which encodes fimbriae that enhance host colonization capability (Lee et al., 2021). Both S. Infantis and monophasic S. Typhimurium also harbored the mer operon, conferring resistance to mercury. Co-selection of antimicrobial and heavy metal resistance is common among Gram-negative bacteria (Mustafa et al., 2021), and the horizontal transfer of these determinants within the S. Infantis population constitutes a public health risk. Overall, the presence of ybt operon, faeG, mer operon, along with IncFIB(K)_1_Kpn3 and blaCTX-M-65 confers the S. Infantis isolates the pESI-like characteristic (García-Soto et al., 2020; Russo et al., 2024). This makes it the first documented pESI-like characteristics in Salmonella in the Philippines. These multiple resistance determinants have positioned S. Infantis as an emerging dominant serovar, particularly in broiler and chicken meat (Mughini-Gras et al., 2021).
The emergence of pathogenic MDR S. enterica strains poses significant food safety risks, underscoring the need for robust epidemiological monitoring and effective mitigation strategies across the food chain (Tang et al., 2022). The historical use of antimicrobials in livestock and poultry for disease treatment, prevention, and growth promotion has exerted selective pressure that drives the emergence of AMR. In the Philippines, poultry farms have reported the use of a range of antimicrobials, including aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, penicillins, phenicols, phosphonics, polypeptides, tetracyclines, and folate pathway inhibitors (Barroga et al., 2020). At the farm level, animals are often asymptomatic carriers of Salmonella, which, along with their acquired ARGs, can easily spread to humans and the environment (Tang et al., 2022). Studies have shown that ARGs can contaminate air, water, and soil impacted by livestock waste (He et al., 2020). It is also possible that spread of MDR Salmonella happens through the meat distribution chain, such as in slaughterhouses and wet markets, where surfaces can harbor resistant bacteria, potentially stabilizing ARGs within food processing environments (Petrin et al., 2023).
Our study is part of a bigger project that aimed to recover S. enterica from pork and chicken samples from cities in Metro Manila. This serves as a baseline set of genomic data for S. enterica from chicken meat in Metro Manila, which can be used as a basis for lobbying national efforts for further research and coordinated AMR surveillance in the Philippines.
5 Conclusion
This study revealed a wide variety of S. enterica serovars in chicken meat sold in wet markets in Metro Manila, with S. Infantis identified as the predominant serovar. The majority of isolates exhibited resistance to at least one antimicrobial class, and some possess the MDR phenotype. The presence of plasmids that may carry multiple ARGs, along with several virulence determinants, facilitated the persistence of Salmonella in chicken meat, posing a major food safety concern. It is therefore imperative to limit the risk of MDR Salmonella spreading to humans, other animals, and the environment. With the increasing accessibility of WGS, deeper insights into the genetic basis of MDR emergence are now available. This will aid in the development of targeted control strategies to curb the spread of AMR among bacterial populations.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by National Meat Inspection Service, Philippines. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RP: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WR: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the Department of Agriculture-Biotechnology Program Office, DABIOTECH-R1808: Using genomics to trace Salmonella transmission and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in the poultry and swine food chains in Metropolitan Manila, Philippines and DABIOTECH-R2302: Salmonella enterica characterization of virulence, antimicrobial resistance and detection in eggs, meat, and meat products. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection, analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Alyzza Marie B. Calayag, Khristine B. Balaga, Vanessa Yvonne B. Meclat, and Aryana Lee G. Bertuso for the technical assistance. The first author also acknowledges the support of the Philippine Council for Agriculture, Aquatic and Natural Resources Research and Development (PCAARRD) of the Department of Science and Technology (DOST), through the Graduate Research and Education Assistantship for Technology (GREAT) Program.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1496685/full#supplementary-material
References
Alcock, B. P., Huynh, W., Chalil, R., Smith, K. W., Raphenya, A. R., Wlodarski, M. A., et al. (2023). CARD 2023: expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, D690–D699. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac920
Algammal, A., Hetta, H., Mabrok, M., and Behzadi, P. (2023). Editorial: emerging multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens “‘superbugs’”: A rising public health threat. Front. Microbiol. 14:1135614. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1135614
Alzahrani, K. O., AL-Reshoodi, F. M., Alshdokhi, E. A., Alhamed, A. S., Al Hadlaq, M. A., Mujallad, M. I., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial resistance and genomic characterization of Salmonella enterica isolates from chicken meat. Front. Microbiol. 14:1104164. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1104164
Andrews, S. (2010). FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc
Antunes, P., Machado, J., Sousa, J. C., and Peixe, L. (2005). Dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella enterica strains and relation with integrons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49, 836–839. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.2.836-839.2005
Bao, H., Wang, S., Zhao, J. H., and Liu, S. L. (2020). Salmonella secretion systems: differential roles in pathogen-host interactions. Microbiol. Res. 241:126591. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126591
Barroga, T. R. M., Morales, R. G., Benigno, C. C., Castro, S. J. M., Caniban, M. M., Cabullo, M. F. B., et al. (2020). Antimicrobials used in backyard and commercial poultry and swine farms in the Philippines: A qualitative pilot study. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:329. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00329
Brown, A. C., Chen, J. C., Francois Watkins, L. K., Campbell, D., Folster, J. P., Tate, H., et al. (2018). CTX-M-65 extended-spectrum β-lactamase–producing Salmonella enterica serotype Infantis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 24, 2284–2291. doi: 10.3201/EID2412.180500
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., et al. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Carattoli, A., Zankari, E., Garciá-Fernández, A., Larsen, M. V., Lund, O., Villa, L., et al. (2014). In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 3895–3903. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02412-14
Chen, S. (2023). Ultrafast one-pass FASTQ data preprocessing, quality control, and deduplication using fastp. iMeta 2. doi: 10.1002/imt2.107
Chen, C., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H., He, Y., et al. (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13, 1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen, Y., Liu, L., Guo, Y., Chu, J., Wang, B., Sui, Y., et al. (2024). Distribution and genetic characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance gene qnr among Salmonella strains from chicken in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 12:e0300023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03000-23
Chin, P. S., Yu, C. Y., Ang, G. Y., Yin, W. F., and Chan, K. G. (2017). Draft genome sequence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Brancaster strain PS01 isolated from chicken meat, Malaysia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 9, 41–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.12.017
CLSI (2024). EM100 Connect - CLSI M100 ED34. Available at: https://em100.edaptivedocs.net/GetDoc.aspx?doc=CLSI%20M100%20ED34:2024&sbssok=CLSI%20M100%20ED34:2024%20TABLE%202B-1A&format=HTML#CLSI%20M100%20ED34:2024%20TABLE%202B-1A (Accessed September 8, 2024).
Danaei, B., Sarmastzadeh, T., Khalili, F., Yazarlou, F., Centis, R., D’Ambrosio, L., et al. (2023). The battle against colistin-resistant E. Coli and the need for a one health approach. New Microbes New Infect 54:101161. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2023.101161
Dieye, Y., Hull, D. M., Wane, A. A., Harden, L., Fall, C., Sambe-Ba, B., et al. (2022). Genomics of human and chicken Salmonella isolates in Senegal: broilers as a source of antimicrobial resistance and potentially invasive nontyphoidal salmonellosis infections. PLoS One 17:e0266025. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266025
dos Santos, A. M., Panzenhagen, P., Ferrari, R. G., Carolina de Jesus, A. S., Beatriz Portes, A., Clavelland Ochioni, A., et al. (2023). Characterization of Salmonella Isangi: A global perspective of a rare serovar. Antibiotics 12:1309. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081309
Feldgarden, M., Brover, V., Gonzalez-Escalona, N., Frye, J. G., Haendiges, J., Haft, D. H., et al. (2021). AMRFinderPlus and the reference gene catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci. Rep. 11:12728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91456-0
Fricke, W. F., McDermott, P. F., Mammel, M. K., Zhao, S., Johnson, T. J., Rasko, D. A., et al. (2009). Antimicrobial resistance-conferring plasmids with similarity to virulence plasmids from avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strains in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky isolates from poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 5963–5971. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00786-09
García-Soto, S., Abdel-Glil, M. Y., Tomaso, H., Linde, J., and Methner, U. (2020). Emergence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Infantis of multilocus sequence type 2283 in German broiler farms. Front. Microbiol. 11:1741. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01741
Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) (n.d.). Available at: https://www.who.int/initiatives/glass (Accessed September 9, 2024).
He, Y., Yuan, Q., Mathieu, J., Stadler, L., Senehi, N., Sun, R., et al. (2020). Antibiotic resistance genes from livestock waste: occurrence, dissemination, and treatment. NPJ Clean Water 3:4. doi: 10.1038/s41545-020-0051-0
Hull, D. M., Harrell, E., Harden, L., and Thakur, S. (2022). Multidrug resistance and virulence genes carried by mobile genomic elements in Salmonella enterica isolated from live food animals, processed, and retail meat in North Carolina, 2018–2019. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 378:109821. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109821
Juraschek, K., Käsbohrer, A., Malorny, B., Schwarz, S., Meemken, D., and Hammerl, J. A. (2021). Dissection of highly prevalent qnrS1-carrying IncX plasmid types in commensal escherichia coli from German food and livestock. Antibiotics 10:1236. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10101236
Khoo, E., Roslee, R., Zakaria, Z., and Ahmad, N. I. (2023). Virulence gene profiles and antimicrobial susceptibility of Salmonella Brancaster from chicken. J. Vet. Sci. 24:e82. doi: 10.4142/jvs.23053
Kim, M. B., Jung, H. R., and Lee, Y. J. (2024). Emergence of Salmonella Infantis carrying the pESI megaplasmid in commercial farms of five major integrated broiler operations in Korea. Poult. Sci. 103:103516. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103516
Kozlov, O., BenoitMorelBarbera, P., and ComputationsRedelings, B. (2024). amkozlov/raxml-ng: RAxML-NG v1.2.2. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.11095121
Lagrada, M. L., Argimón, S., Borlasa, J. B., Abad, J. P., Gayeta, J. M., Masim, M. L., et al. (2022). Genomic surveillance of Salmonella spp. in the Philippines during 2013-2014. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 116, 1202–1213. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trac080
Lee, W. W. Y., Mattock, J., Greig, D. R., Langridge, G. C., Baker, D., Bloomfield, S., et al. (2021). Characterization of a pESI-like plasmid and analysis of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica Infantis isolates in England and Wales. Microb. Genom. 7:000658. doi: 10.1099/MGEN.0.000658
Letunic, I., and Bork, P. (2024). Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, W78–W82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae268
Liu, B., Zheng, D., Zhou, S., Chen, L., and Yang, J. (2022). VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D912–D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107
Magiorakos, A. P., Srinivasan, A., Carey, R. B., Carmeli, Y., Falagas, M. E., Giske, C. G., et al. (2012). Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 18, 268–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x
Mattock, J., Chattaway, M. A., Hartman, H., Dallman, T. J., Smith, A. M., Keddy, K., et al. (2024). A one health perspective on Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis, an emerging human multidrug-resistant pathogen. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 30, 701–710. doi: 10.3201/eid3004.231031
McEwen, S. A., and Collignon, P. J. (2018). Antimicrobial resistance: A one health perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 6, 521–547. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.arba-0009-2017
McLaughlin, L. M., Govoni, G. R., Gerke, C., Gopinath, S., Peng, K., Laidlaw, G., et al. (2009). The Salmonella SPI2 effector SseI mediates long-term systemic infection by modulating host cell migration. PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000671. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000671
McMillan, E. A., Jackson, C. R., and Frye, J. G. (2020a). Transferable plasmids of Salmonella enterica associated with antibiotic resistance genes. Front. Microbiol. 11:562181. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.562181
McMillan, E. A., Wasilenko, J. L., Tagg, K. A., Chen, J. C., Simmons, M., Gupta, S. K., et al. (2020b). Carriage and gene content variability of the pESI-like plasmid associated with Salmonella Infantis recently established in United States poultry production. Genes (Basel) 11, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/genes11121516
McMillan, E. A., Weinroth, M. D., and Frye, J. G. (2022). Increased prevalence of Salmonella Infantis isolated from raw chicken and Turkey products in the United States is due to a single clonal lineage carrying the pESI plasmid. Microorganisms 10:1478. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071478
Mikheenko, A., Prjibelski, A., Saveliev, V., Antipov, D., and Gurevich, A. (2018). Versatile genome assembly evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 34, i142–i150. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty266
Mohakud, N. K., Panda, R. K., Singh, D., Patra, S. D., Simnani, F. Z., Sinha, A., et al. (2023). Intrinsic insights to antimicrobial effects of nitrofurantoin to multidrug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium ms202. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165:115180. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115180
Mora, J. F. B., Meclat, V. Y. B., Calayag, A. M. B., Campino, S., Hafalla, J. C. R., Hibberd, M. L., et al. (2024). Genomic analysis of Salmonella enterica from metropolitan Manila abattoirs and markets reveals insights into circulating virulence and antimicrobial resistance genotypes. Front. Microbiol. 14:1304283. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1304283
Mughini-Gras, L., van Hoek, A. H. A. M., Cuperus, T., Dam-Deisz, C., van Overbeek, W., van den Beld, M., et al. (2021). Prevalence, risk factors and genetic traits of Salmonella Infantis in Dutch broiler flocks. Vet. Microbiol. 258:109120. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109120
Murray, C. J., Ikuta, K. S., Sharara, F., Swetschinski, L., Robles Aguilar, G., Gray, A., et al. (2022). Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 399, 629–655. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Mustafa, G. R., Zhao, K., He, X., Chen, S., Liu, S., Mustafa, A., et al. (2021). Heavy metal resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium and its association with disinfectant and antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 12:702725. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.702725
Ng, K. C. S., and Rivera, W. L. (2015). Multiplex PCR-based serogrouping and serotyping of Salmonella enterica from tonsil and jejunum with jejunal lymph nodes of slaughtered swine in metro Manila, Philippines. J. Food Prot. 78, 873–880. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-342
Nhung, N. T., Phu, D. H., Carrique-Mas, J. J., and Padungtod, P. (2024). A review and meta-analysis of non-typhoidal Salmonella in Vietnam: challenges to the control and antimicrobial resistance traits of a neglected zoonotic pathogen. One Health 18:100698. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2024.100698
O’Neill, J. (2014). Antimicrobial resistance: Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. Available at: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-04-2019-new-report-calls-for-urgent-action-to-avert-antimicrobial-resistance-crisis (Accessed September 8, 2024)
Petrin, S., Orsini, M., Massaro, A., Olsen, J. E., Barco, L., Losasso, C., et al. (2023). Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance correlation and plasmid characterization in Salmonella spp. isolates from Italy reveal high heterogeneity among serovars. Front. Public Health 11:1221351. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1221351
Puangseree, J., Prathan, R., Srisanga, S., and Chuanchuen, R. (2024). Molecular basis of the persistence of chloramphenicol resistance among Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. from pigs, pork and humans in Thailand. PLoS One 19:e0304250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304250
Qian, H., Cheng, S., Liu, G., Tan, Z., Dong, C., Bao, J., et al. (2020). Discovery of seven novel mutations of gyrB, parC and parE in Salmonella Typhi and Paratyphi strains from Jiangsu Province of China. Sci. Rep. 10:7359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64346-0
Retamal, P., Gaspar, J., Benavides, M. B., Saenz, L., Galarce, N., Aravena, T., et al. (2022). Virulence and antimicrobial resistance factors in Salmonella enterica serotypes isolated from pigs and chickens in Central Chile. Front. Vet. Sci. 9:971246. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.971246
Russo, I., Fischer, J., Uelze, L., Napoleoni, M., Schiavano, G. F., Andreoni, F., et al. (2024). From farm to fork: spread of a multidrug resistant Salmonella Infantis clone encoding blaCTX-M-1 on pESI-like plasmids in Central Italy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 410:110490. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110490
Salah, F. D., Soubeiga, S. T., Ouattara, A. K., Sadji, A. Y., Metuor-Dabire, A., Obiri-Yeboah, D., et al. (2019). Distribution of quinolone resistance gene (qnr) in ESBL-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. in Lomé, Togo. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 8:104. doi: 10.1186/s13756-019-0552-0
Seemann, T. (2014). Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30, 2068–2069. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Seemann, T. (2020). GitHub - tseemann/abricate::mag_right: Mass screening of contigs for antimicrobial and virulence genes. Available at: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (Accessed September 8, 2024).
Sévellec, Y., Vignaud, M. L., Granier, S. A., Lailler, R., Feurer, C., Le Hello, S., et al. (2018). Polyphyletic nature of Salmonella enterica serotype Derby and lineage-specific host-association revealed by genome-wide analysis. Front. Microbiol. 9:891. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00891
Sodagari, H. R., Shrestha, R. D., Agunos, A., Gow, S. P., and Varga, C. (2023). Comparison of antimicrobial resistance among Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from Canadian Turkey flocks, 2013 to 2021. Poult. Sci. 102:102655. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102655
Syed Abu Thahir, S., Rajendiran, S., Shaharudin, R., and Veloo, Y. (2023). Multidrug-resistant Salmonella species and their mobile genetic elements from poultry farm environments in Malaysia. Antibiotics 12:1330. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081330
Tang, B., Elbediwi, M., Nambiar, R. B., Yang, H., Lin, J., and Yue, M. (2022). Genomic characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica in duck, chicken, and pig farms and retail markets in eastern China. Microbiol. Spectr. 10:e0125722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01257-22
Tidhar, A., Rushing, M. D., Kim, B., and Slauch, J. M. (2015). Periplasmic superoxide dismutase SodCI of Salmonella binds peptidoglycan to remain tethered within the periplasm. Mol. Microbiol. 97, 832–843. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13067
Vilela, F. P., dos Prazeres Rodrigues, D., Allard, M. W., and Falcão, J. P. (2023). The rare Salmonella enterica serovar Isangi: genomic characterization of the antimicrobial resistance, virulence potential and epidemiology of Brazilian strains in comparison to global isolates. J. Med. Microbiol. 72:001736. doi: 10.1099/JMM.0.001736/CITE/REFWORKS
Wang, Y., and Dagan, T. (2024). The evolution of antibiotic resistance islands occurs within the framework of plasmid lineages. Nat. Commun. 15:4555. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48352-8
Wang, Z., Jiang, Y., Xu, H., Jiao, X., Wang, J., and Li, Q. (2023). Poultry production as the main reservoir of ciprofloxacin- and tigecycline-resistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producing Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198.2-2 causing human infections in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 89:e0094423. doi: 10.1128/aem.00944-23
Wellawa, D. H., Allan, B., White, A., and Köster, W. (2020). Iron-uptake systems of chicken-associated Salmonella serovars and their role in colonizing the avian host. Microorganisms 8, 1–25. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081203
Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L., and Holt, K. E. (2017). Unicycler: resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13:e1005595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595
World Health Organization (2024). WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial pathogens of public health importance to guide research, development and strategies to prevent and control antimicrobial resistance. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (Accessed September 8, 2024).
Xu, Z., Wang, M., Wang, C., Zhou, C., Liang, J., Gu, G., et al. (2021). The emergence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella London isolates from human patients, retail meats and chickens in southern China and the evaluation of the potential risk factors of Salmonella London. Food Control 128:108187. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108187
Yan, W., Xu, D., Chen, L., and Wu, X. (2024). Antimicrobial resistance and genome characteristics of Salmonella Enteritidis from Huzhou, China. PLoS One 19:e0304621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304621
Yoshida, C. E., Kruczkiewicz, P., Laing, C. R., Lingohr, E. J., Gannon, V. P. J., Nash, J. H. E., et al. (2016). The Salmonella in silico typing resource (SISTR): an open web-accessible tool for rapidly typing and subtyping draft Salmonella genome assemblies. PLoS One 11:e0147101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147101
Keywords: Salmonella enterica, antimicrobial resistance genes, chicken meat, plasmids, whole genome sequencing, virulence
Citation: Nagpala MJM, Mora JFB, Pavon RDN and Rivera WL (2025) Genomic characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica in chicken meat from wet markets in Metro Manila, Philippines. Front. Microbiol. 16:1496685. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1496685
Edited by:
Sebastian Guenther, University of Greifswald, GermanyReviewed by:
Burkhard Malorny, Federal Institute for Risk Assessment (BfR), GermanyChien-Shun Chiou, Taiwan Centers for Disease Control (CDC), Taiwan
Copyright © 2025 Nagpala, Mora, Pavon and Rivera. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Windell L. Rivera, d2xyaXZlcmFAc2NpZW5jZS51cGQuZWR1LnBo
 Michael Joseph M. Nagpala
Michael Joseph M. Nagpala Jonah Feliza B. Mora
Jonah Feliza B. Mora Rance Derrick N. Pavon
Rance Derrick N. Pavon Windell L. Rivera
Windell L. Rivera