- 1Henan Provincial Engineering Laboratory of Insects Bio-reactor, Henan Provincial Engineering and Technology Center of Health Products for Livestock and Poultry, Nanyang Normal University, Nanyang, Henan, China
- 2Guangxi Key Laboratory of Animal Breeding, Disease Control and Prevention, College of Animal Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 3College of Veterinary Medicine, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 4College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
- 5Department of Zoology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Polygonatum kingianum is a well-known medicinal herb with proven bioactivities; however, little is known about the effects of its polysaccharide on intestinal injuries in animals induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Methods: A total of 30 Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice were divided into control (CH), induced (MH), and treated (H) groups. Mice in group H were supplemented with 100 mg/kg Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharides, while groups C and M were treated with the same amount of normal saline by gavage for 18 days. On the 18th day animals in groups M and H were induced by LPS (10 mg/kg).
Results: The results showed the weight of mice in group MH significantly dropped (P < 0.0001), while mice in the PK group had a higher weight (P < 0.01). Pathological analysis found that the majority of the villi in mice induced by LPS were broken and short, while PK-treated animals had longer and considerably integrated villi. The villi length in groups CH (P < 0.0001) and H (P < 0.0001) was longer than that in group M, and the value of villi length/crypt depth in group MH was smaller than that in groups CH (P < 0.0001) and H (P < 0.0001), while the crypt depth in group MH was higher than in groups CH (P < 0.0001) and H (P < 0.0001). Serum inspection showed that MAD (P < 0.05), IL-1β (P < 0.05), IL-6 (P < 0.05), and TNF-α (P < 0.01) were significantly higher in group MH, while SOD (P < 0.001), T-AOC (P < 0.01), and GSH-Px (P < 0.01) were notably higher in groups CH and H. Microbiome sequencing of mice obtained 844,477 raw and 725,469 filtered reads. There were 2,407 ASVs detected in animals, and there were 312 and 328 shared ASVs between CH and MH, and CH and H, respectively. There were 5 phyla and 20genera of remarkable bacteria found among mice groups including genera of Escherichia, Pseudomonas_E, Mailhella, Paramuribaculum, NM07-P-09, Odoribacter, Nanosyncoccus, SFM01, Onthenecus, Clostridium_Q, UBA6985, Ructibacterium, UBA946, Lachnoclostridium_B, Evtepia, CAG-269, Limivicinus, Formimonas, Dehalobacterium, Dwaynesavagella, and UBA6985. We revealed that Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide could alleviate intestinal injuries by promoting oxidation resistance, decreasing inflammatory responses, and accommodating the intestinal microbiota of mice.
Discussion: Our results suggest the possibility of developing novel therapies for intestinal diseases.
1 Introduction
The intestine is a complex organ that plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient assimilation, immune function, and overall host health (Hickey et al., 2023). Intestinal injury is a common symptom of many conditions, including radiation therapy-related diseases (Lin et al., 2023), heat stress (Li et al., 2020), inflammatory bowel disease (Li H. et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023a,b), and infectious diseases (Donaldson et al., 2022). However, treating intestinal damage remains challenging, and novel therapies are urgently needed (Ling et al., 2024; Cho et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2022).
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been used effectively to treat different diseases in history (Huang et al., 2021), such as ulcerative colitis (Liu et al., 2022), liver disease (Zhu et al., 2023), and inflammatory bowel disease (Yang L. et al., 2021). Polygonatum kingianum is a well-known medicinal herb in TCM, grown in Yunnan, China. It is known for its bioactivities, including immuno-enhancement, anti-aging, anti-fatigue properties, and the regulation of glucolipid metabolism (Dong et al., 2021; Li X. et al., 2023). There are several effective constituents in this herb-like plant: polysaccharides, saponins, phenolics, and flavonoids (Yang et al., 2020). Previous studies found that Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide (PKP) could promote glucolipid metabolism (Gu et al., 2020), regulate microbiota and short-chain fatty acids (Yang M. et al., 2021), and enhance immunity (Su et al., 2023).
The gut microbiota is composed of billions of microorganisms including prokaryotes and eukaryotes (Lozupone et al., 2012), which play important roles in the host's immunity, nutrient absorption, metabolism, and overall health (Adak and Khan, 2019). Gut dysbiosis was associated with inflammatory, metabolic, and neurodegenerative diseases (Levy et al., 2017), Crohn's disease (Caparrós et al., 2021), and inflammatory bowel diseases (Haneishi et al., 2023). Lipopolysaccharide is a crucial adjective membrane structural component of Gram-negative microbes (Sweeney and Lowary, 2019), which can stimulate immune response and promote the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors (Mohr et al., 2022). Previous studies reported that LPS caused intestinal damage and intestinal flora disorder (Izadparast et al., 2022; Yan et al., 2022). However, little information is available regarding the influence of Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide on intestinal injuries in animals induced by LPS. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the mediating effect of PKP on mice challenged by LPS by regulating antioxidant ability and microbiota.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animal experiment
Thirty ICR mice (4 weeks, 22.81 ± 0.98 g) with the same amount of male and female animals were procured from the experimental animal center at Yangzhou University. All those rodents were given 3 days for acclimatization and then divided into control (CH), induced (MH), and treated (H) groups. Mice in the H group were supplemented with 100 mg/kg Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide (Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China), while the C and M groups were treated with an even volume of normal saline by gavage for 18 days. On the 18th, animals in the M and H groups were induced by LPS (10 mg/kg) (Meng et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024), and then those animals were euthanized to obtain blood and intestine samples the next day.
2.2 Pathological staining
Approximately 1–2 cm tissue samples of the jejunum and ileum from mice in the CH, MH, and H groups were kept in formaldehyde solution (4%) for more than 2 days and then used for H&E staining in Wuhan Pinuofei Biological Technology (China). Pathological examination was performed using Olympus CX23 (Olympus Co., Japan), and the villus height and crypt depth of enteric samples were measured as per the guidelines of published studies (He et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2022).
2.3 Serum oxidation resistance and inflammation levels detection
All the mice blood samples were centrifuged at 4,000 g x 8 min to isolate serums for oxidation resistance and inflammation level detection using assay kits of malonaldehyde; superoxide dismutase; total anti-oxidation capacity; glutathione peroxidase; interleukins-−1β, IL-6, and IL-10; and tumor necrosis factor alpha bought from Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute (Nanjing, China) and Solarbio Life Science (China).
2.4 Flora sequencing
The microbial DNA of rectal contents from three mice in each group was extracted by applying a stool genomic DNA extraction kit (Solarbio, China). The product quality was then confirmed using a NanoDrop OneC (Thermo Scientific, USA) and agarose gel electrophoresis (1.2%), as previously described in studies by Mattei et al. (2019) and Zhang X. et al. (2022). The V3-4 gene of 16S rRNA of the microbes in mice in different groups was magnified by piloting objective primers 338F/806R (F: 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′, R:5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) (Yu et al., 2020). Finally, sequencing libraries for mice from the C, M, and H groups were constructed using an NGS Tn5 DNA library prep kit (Ruikang Technology Co., LTD, Beijing, China) for further sequencing through the Illumina platform at Bioyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) (Kong et al., 2024).
2.5 Sequencing data analysis
The raw sequencing data from mice in groups C, M, and H were quality-filtered using DADA2 (Callahan et al., 2016), and characteristic tabulation of amplicon sequence variant (ASV) was generated using QIIME2 (Nagarajan et al., 2023). The co-existing ASVs were examined and presented using a Venn map (Dou et al., 2023). ANOVA and LEfSe were used to screen markedly different bacterial taxa between rodent animal groups (Wells et al., 2022; Lv et al., 2023). The diversity analysis of alpha (observed species, Chao1, Shannon, Simpson, Faith's PD, and Pielou's evenness) and beta diversity (principal coordinate analysis and non-metric multidimensional scaling) analyses were performed to estimate the bacterial diversity, evenness, and richness of samples and group structure variation in mice samples using QIIME2 (Long et al., 2023; Zhong et al., 2023; Deng et al., 2021; Zhang Y. et al., 2022). Finally, the microflora function was predicted using PICRUSt2 (Li et al., 2023a,b), and functional differences among the CH, MH, and H groups were examined by annotating with the KEGG and MetaCyc databases.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Variances among the CH, MH, and H groups were assessed using ANOVA and Student's t-test relying on IBM SPSS (26.0). The mice data were presented as means ± standard deviation (SD), with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 PK relieved intestinal damage in mice caused by LPS
The body weight of animals in the PK group was marginally higher than that in the CH and MH groups (Figure 1A), and after LPS inducing, the weight of mice in the MH group significantly dropped (P < 0.0001), while mice in the PK group had a higher weight (P < 0.01) (Figure 1B). Pathological analysis found that the majority of the villi in mice induced by LPS were broken and short, while PK-treated animals had longer and considerably integrated villi. The villi length in the CH (P < 0.0001) and H (P < 0.0001) groups was longer than that in the M group, and the value of villi length/crypt depth in the MH group was smaller than that in the CH (P < 0.0001) and H (P < 0.0001) groups, while the crypt depth in the MH was higher than that in the CH (P < 0.0001) and H groups (P < 0.0001) (Figures 1C, D).
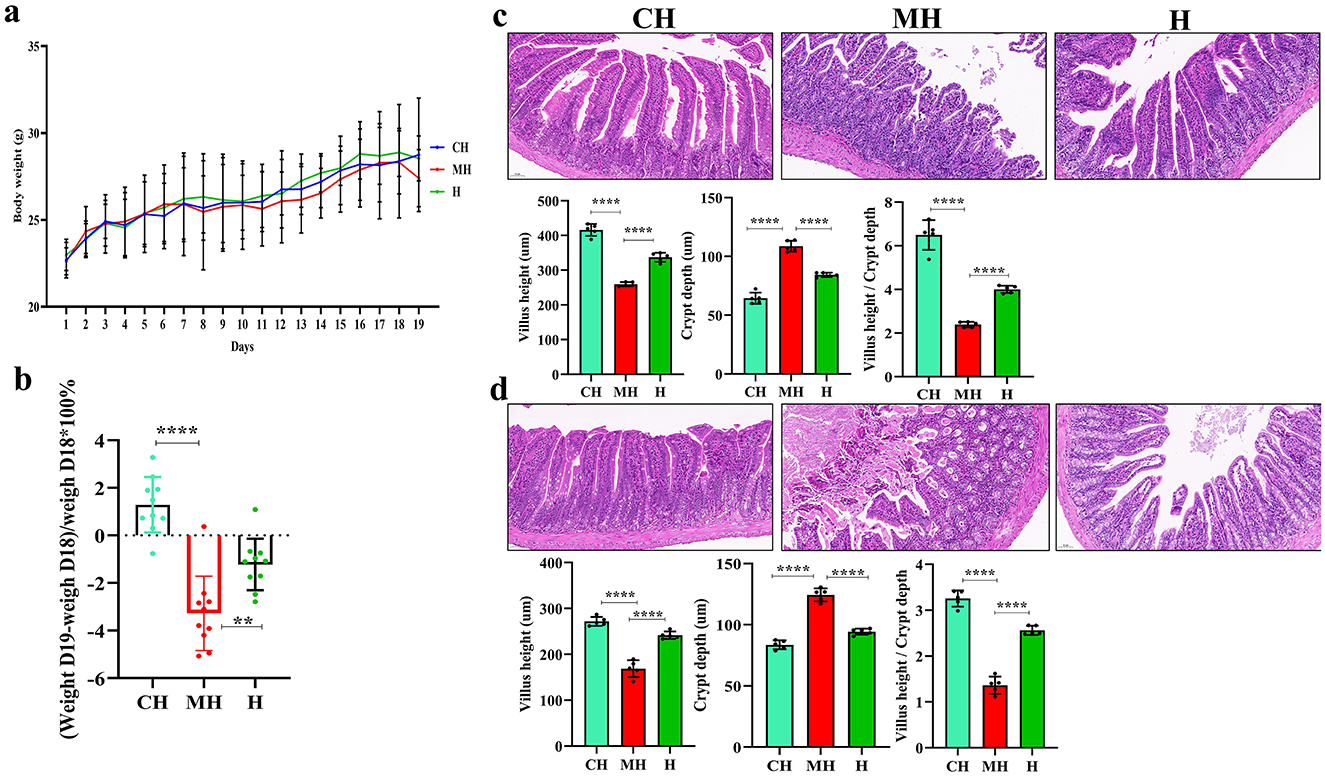
Figure 1. PK remitted intestinal damages in mice induced by LPS. (A) body weights, (B) weight changes after LPS inducing, (C) pathological analysis of the jejunum, (D) pathological analysis of the ileum. Scale bar 50 mm. Significance is presented as **P < 0.01 and ****P < 0.0001; data are presented as the mean ± SEM.
3.2 PK-mediated serum oxidation resistance and inflammation levels
Serum inspection showed that MAD (P < 0.05), IL-1β (P < 0.05), IL-6 (P < 0.05), and TNF-α (P < 0.01) were significantly higher in the MH group, while SOD (P < 0.001), T-AOC (P < 0.01), and GSH-Px (P < 0.01) were notably higher in the CH and H groups (Figure 2).
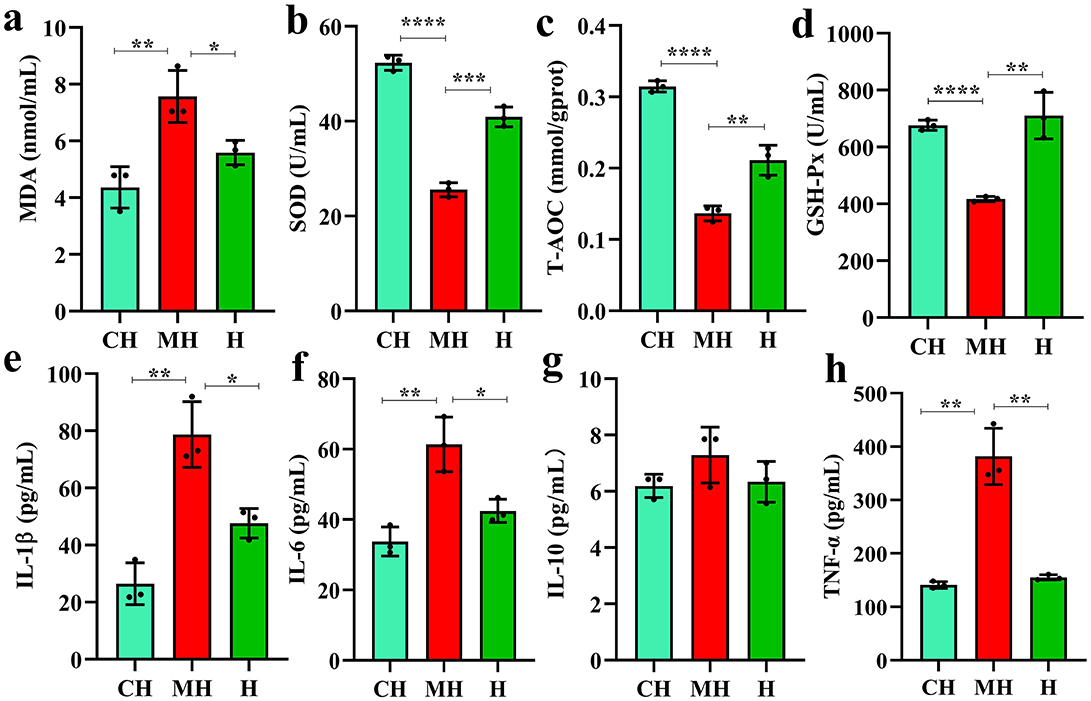
Figure 2. PK-mediated serum oxidation resistance and inflammation levels. (A) MDA, (B) SOD, (C) T-AOC, (D) GSH-Px, (E) IL-1β, (F) IL-6, (G) IL-10, (H) TNF-α. Significance is presented as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001; data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3).
3.3 PK partly renovated the composition of intestine microflora in mice
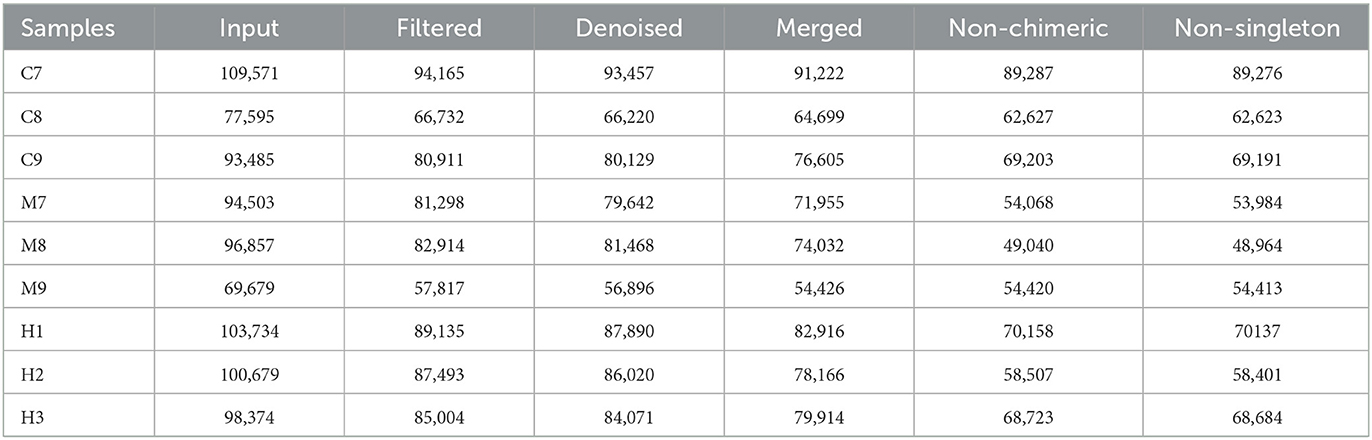
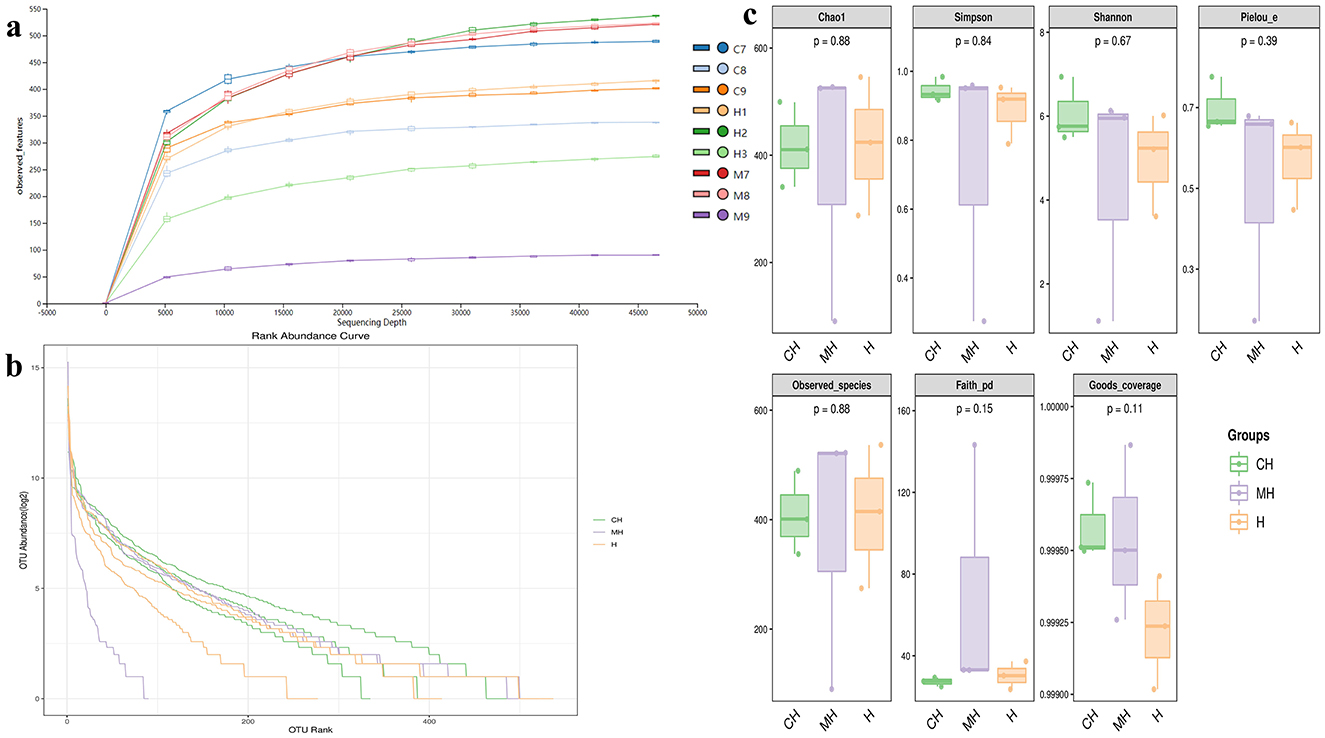
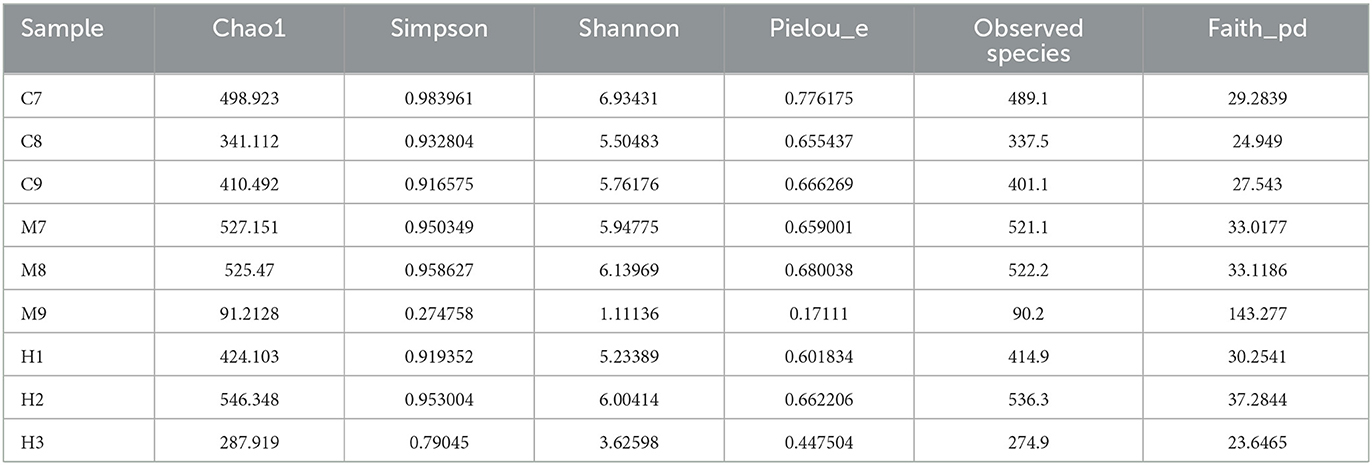
Over 1CH), 69,600 (MH), and 98,300 (H) raw reads and 66,700 (CH), 57,800 (MH), and 85,000 (H) filtered sequences were identified in mice (Table 1). Alpha diversity calculation found that the rarefaction curves of all mice were horizontal lines after a short rise (Figure 3A), and the rank abundance curves in groups CH, MH, and H were all flat horizontal lines (Figure 3B), which revealed that those mice samples were sufficient with higher evenness. The index result presented no noticeable difference among the CH, MH, and H groups (Figure 3C; Table 2).
At the phylum level, Bacteroidota (45.74%), Firmicutes_D (34.09%), and Firmicutes_A (7.87%) were the dominating phyla in the CH group, Campylobacterota (34.14%), Bacteroidota (27.70%), and Firmicutes_D (17.67%) were the primary phyla in group MH, while Proteobacteria (36.67%), Firmicutes_D (22.09%), and Bacteroidota (22.00%) were mainly found in group H (Figure 4A). At the class level, Bacteroidia (45.74%), Bacilli (34.09%), and Clostridia (7.87%) were the primary classes in group CH, Campylobacteria (34.14%), Bacteroidia (27.70%), and Bacilli (17.67%) were the primary classes in the MH group, while Gammaproteobacteria (36.67%), Bacilli (22.09%), and Bacteroidia (22.00%) were the primary classes in the H group (Figure 4B). At the order level, Bacteroidales (45.16%), Erysipelotrichales (23.90%), and Lactobacillales (7.49%) were the dominating orders in CH, Campylobacterales (34.14%), Bacteroidales (27.58%), and Lactobacillales (15.30%) were the main orders in MH, while Enterobacterales_A (36.28%), Bacteroidales (21.94%), and Lactobacillales (17.88%) were mainly detected in H (Figure 4C). At the family level, Muribaculaceae (38.84%), Erysipelotrichaceae (23.46%), and Lactobacillaceae (5.75%) were the primary families in CH, Helicobacteraceae (34.14%), Muribaculaceae (22.03%), and Lactobacillaceae (9.07%) were the primary families in MH, while Enterobacteriaceae_A (36.27%), Lactobacillaceae (17.46%), and Muribaculaceae (15.98%) were the main families in H (Figure 4D). At the genus level, Faecalibaculum (17.67%), unclassified_Muribaculaceae (9.93%), and Paramuribaculum (7.86%) were mainly examined in CH, Helicobacter_D (34.02%), unclassified_Muribaculaceae (6.89%), and Lactobacillus (6.60%) were the stable genera in MH, while Escherichia (35.67%), Lactobacillus (12.10%), and Akkermansia (5.31%) were the primary genera in group H (Figure 4E).
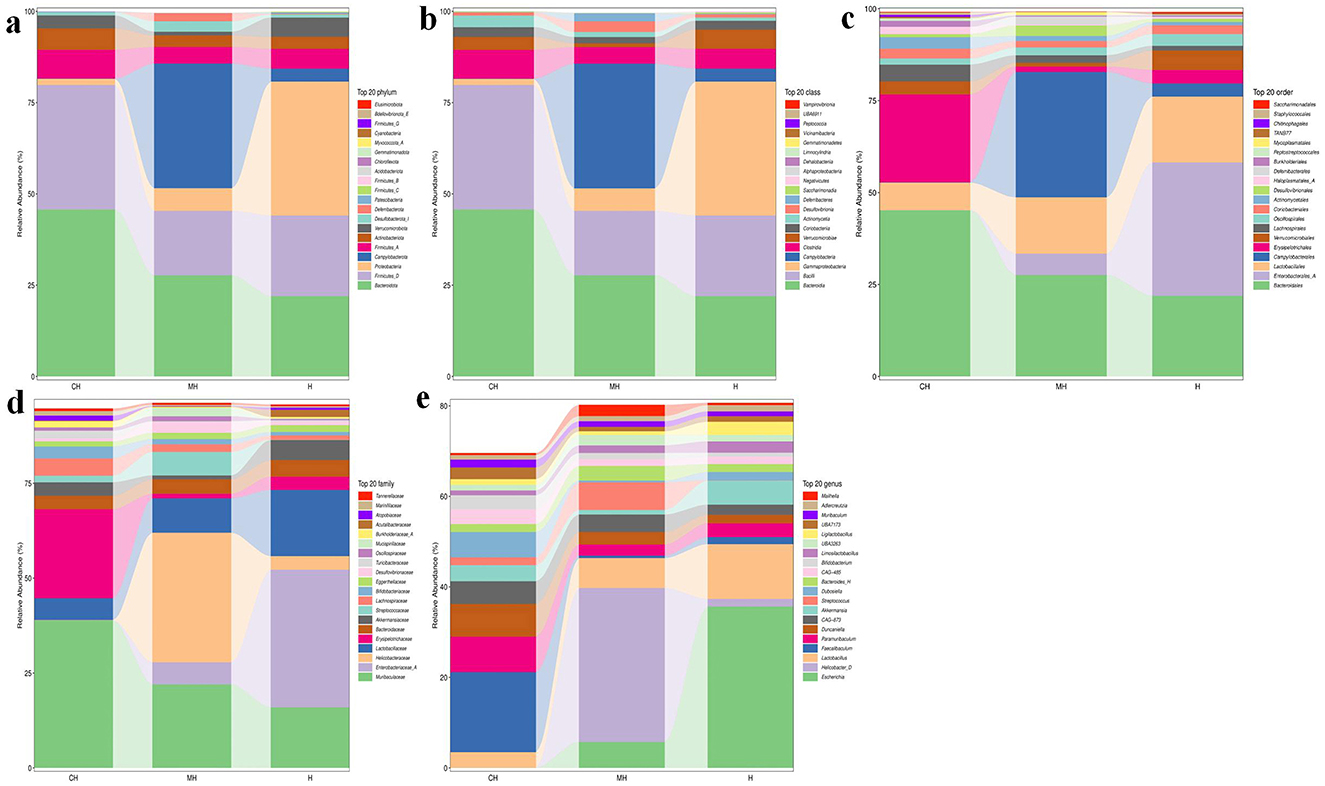
Figure 4. PK-mediated the intestinal microbiota in LPS-induced mice in different taxa. (A) phylum, (B) class, (C) order, (D) family, (E) genus.
3.4 PK affected the bacteria abundance in the intestinal flora of mice induced by LPS
The Venn graph revealed that there were 2,407 ASVs detected in animals, and 239 ASVs were found in all groups. There were 312 and 328 shared ASVs between CH and MH, and CH and H, respectively (Figure 5A). Beta diversity analysis showed that the distance between CH and H was shorter than between CH and MH; however, it was not significant (P > 0.05) (Figures 5B–E). Heatmap analysis showed that Enterenecus, UBA3263, Bacteroides_H, Mailhella, Malacoplasma_A, Kineothrix, Helicobacter_D, Mucispirillum, Lawsonibacter, CAG-83, Streptococcus, and Rikenella were higher in MH, Dubosiella, Cryptobacteroides, NM07-P-09, Anaerotruncus, Odoribacter, Parasutterella, OLB9, UBA7173, Turicimonas, CAG-485, Faecalibaculum, Romboutsia_B, Turicibacter, Paramuribaculum, Prevotella, Duncaniella, Parabacteroides_B, UBA3282, Bifidobacterium, and Muribaculum were higher in CH, while Limosilactobacillus, Lactobacilus, Adlercreutzia, Ligilactobacillus, Escherichia, Phocaeucola_A, Helicobacter_C, Eubacterium R, and Klebsielia is changed (Figure 6A). LEfSe showed that Limivicinus (P < 0.05), Staphylococcaceae (P < 0.05), Peptostreptococcaceae (P < 0.05), Staphylococcales (P < 0.05), Staphylococcus (P < 0.05), Mammaliicoccus (P < 0.05), and Romboutsia_B (P < 0.05) were significantly higher in CH, while Helicobacter_D (P < 0.05) was significantly higher in MH (Figure 6B).
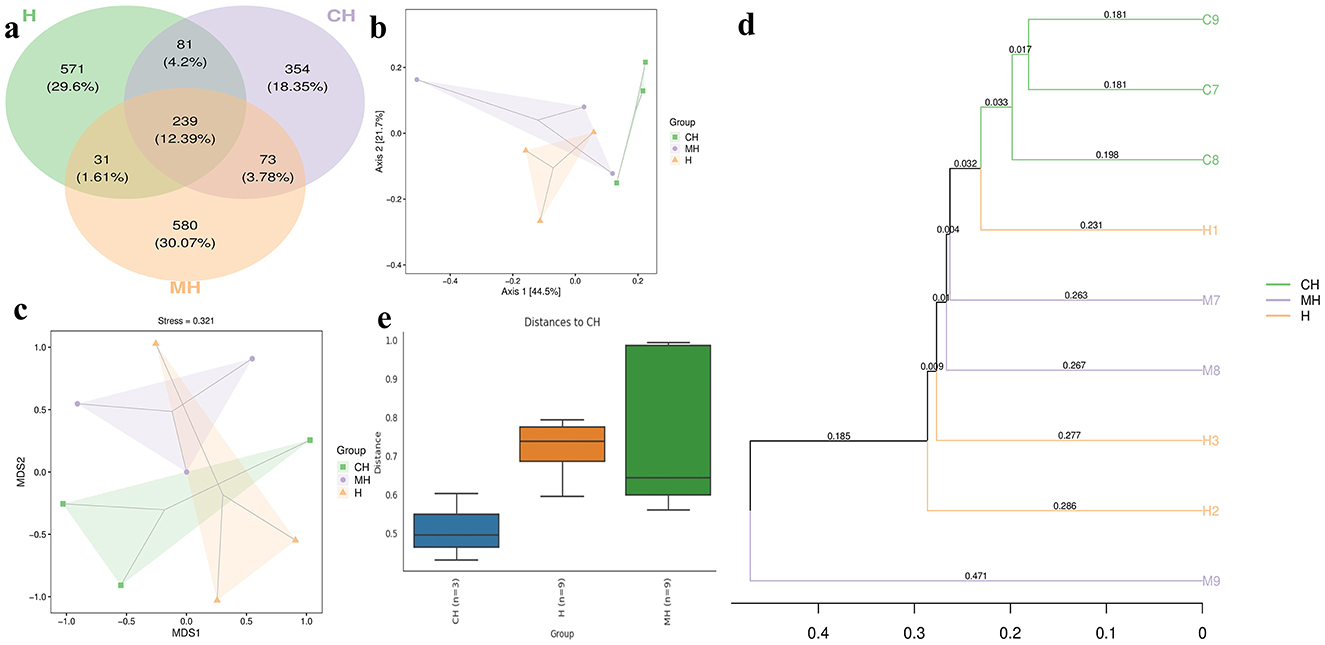
Figure 5. ASV Venn map and beta diversity of the gut flora in mice in different groups. (A) Venn chart, (B) PCo-A, (C) NMDS, (D) UPGMA, (E) group distance.
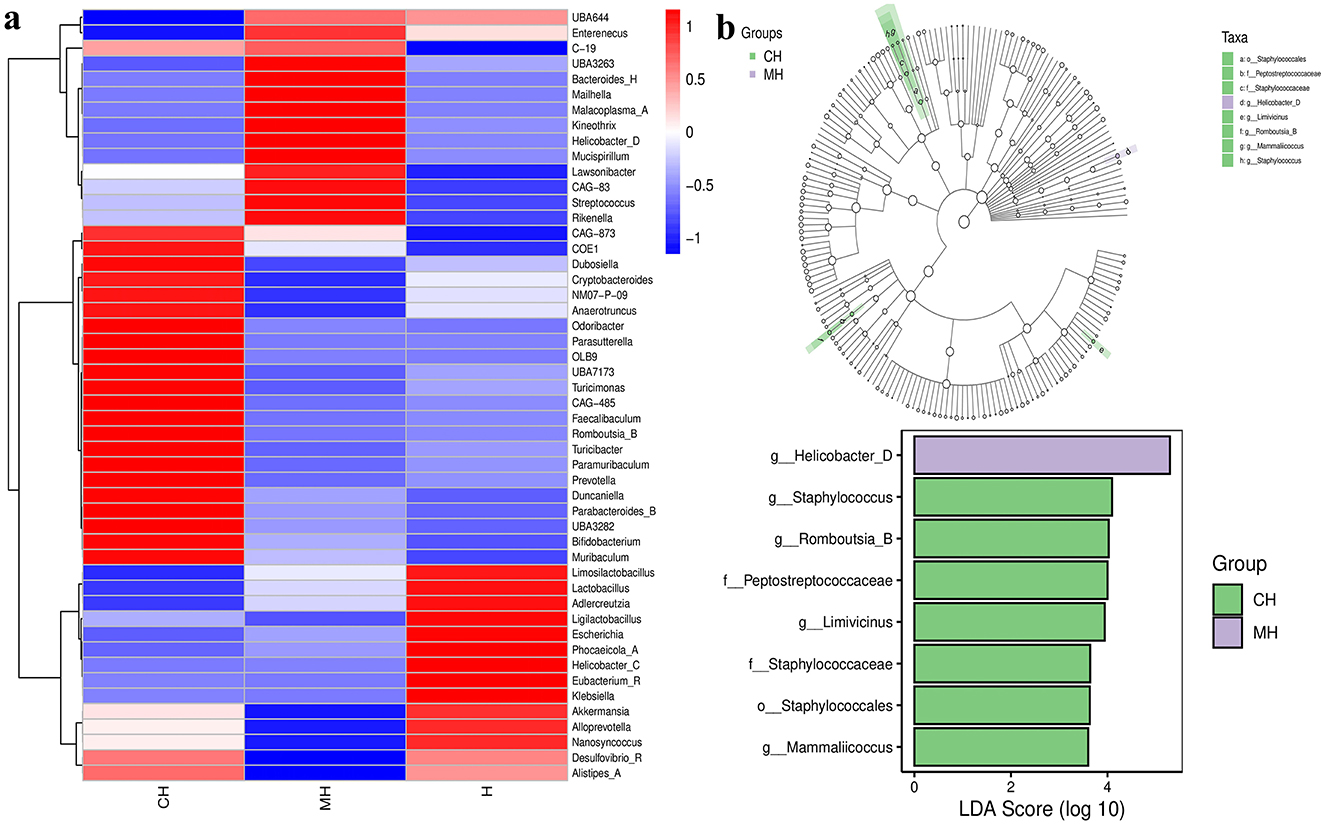
Figure 6. Heatmap and LEfSe analysis of mice microbiota in different groups. (A) Heatmap, (B) LEfSe.
ANOVA analysis showed that compared to group CH, the phylum of Proteobacteria was significantly higher in H (P < 0.05), Desulfobacterota_I (P < 0.05) was markedly higher in group MH, while Patescibacteria was significantly higher in group CH than in MH. The enrichment of Gemmatimonadota (P < 0.01) and Firmicutes_B (P < 0.05) in animals in groups MH and H was obviously lower than that in CH (Figure 7A). Compared to the genus in group CH, Escherichia (P < 0.05) and Pseudomonas_E (P < 0.05) were dramatically higher in H, Mailhella (P < 0.05) was higher in MH, while Paramuribaculum (P < 0.05), NM07-P-09 (P < 0.05), Odoribacter (P < 0.05), Nanosyncoccus (P < 0.05), SFMI01 (P < 0.05), Onthenecus (P < 0.05), Clostridium_Q (P < 0.05), UBA6985 (P < 0.01), and Ructibacterium (P < 0.05) were significantly lower in MH, and UBA946 (P < 0.05) and Lachnoclostridium_B (P < 0.001) were significantly lower in group H. The abundances of Evtepia (P < 0.05), CAG-269 (P < 0.05), Limivicinus (P < 0.05), Formimonas (P < 0.05), and Dehalobacterium (P < 0.05) in group CH were significantly higher than those in groups BH and H. Dwaynesavagella (P < 0.05) and UBA6985 (P < 0.05) in group H were significantly higher than those in group MH (Figure 7B).
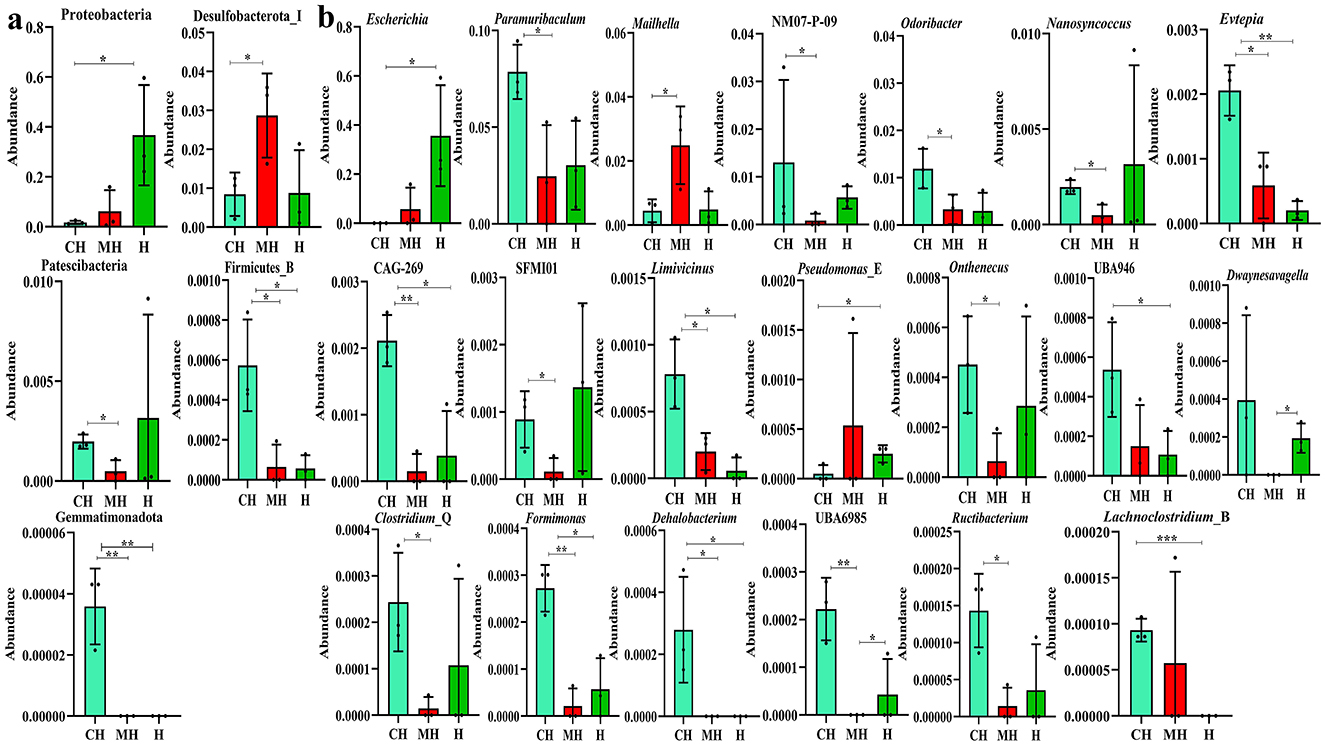
Figure 7. Revealing microbiota differences in mice in different groups using ANOVA analysis. (A) phyla, (B) genus. Significance is presented as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3).
3.5 PK affected the intestinal flora function of mice induced by LPS
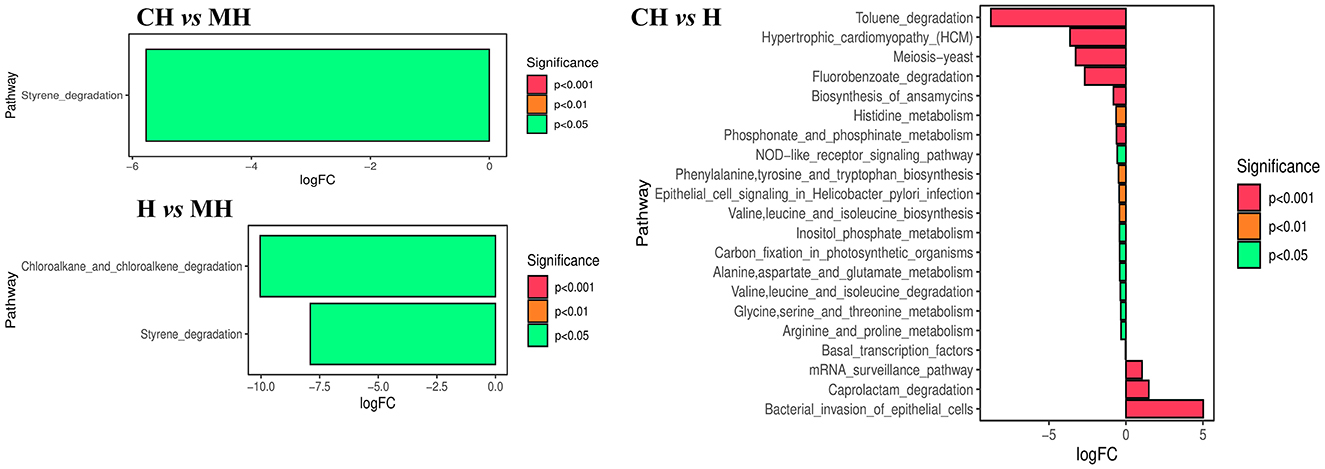
The KEGG analysis found that styrene degradation in group CH (P < 0.05) and H (P < 0.05) was significantly lower than that in group MH. The degradation of chloroalkane and chloroalkene in H was observed to be lower than that in MH (P < 0.05). Pathways of bacterial invasion of epithelial cells (P < 0.0001), mRNA surveillance pathway (P < 0.0001), and caprolactam degradation (P < 0.0001) were significantly higher in CH, while toluene degradation (P < 0.0001), meiosis yeast (P < 0.0001), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (P < 0.0001), for benzoate degradation (P < 0.0001), biosynthesis of annamycin's (P < 0.001), phosphonate and phosphonate metabolism (P < 0.001), histidine metabolism (P < 0.01), valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis (P < 0.01), epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection (P < 0.01), phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosynthesis (P < 0.01), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway (P < 0.05), inositol phosphate metabolism (P < 0.05), arginine and proline metabolism(P < 0.05), valine, leucine, and isoleucine degradation (P < 0.05), basal transcription factors (P < 0.05), alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism (P < 0.05), carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms (P < 0.05) and glycine, serine and threonine metabolism(P < 0.05) in H is decreased (Figure 8).
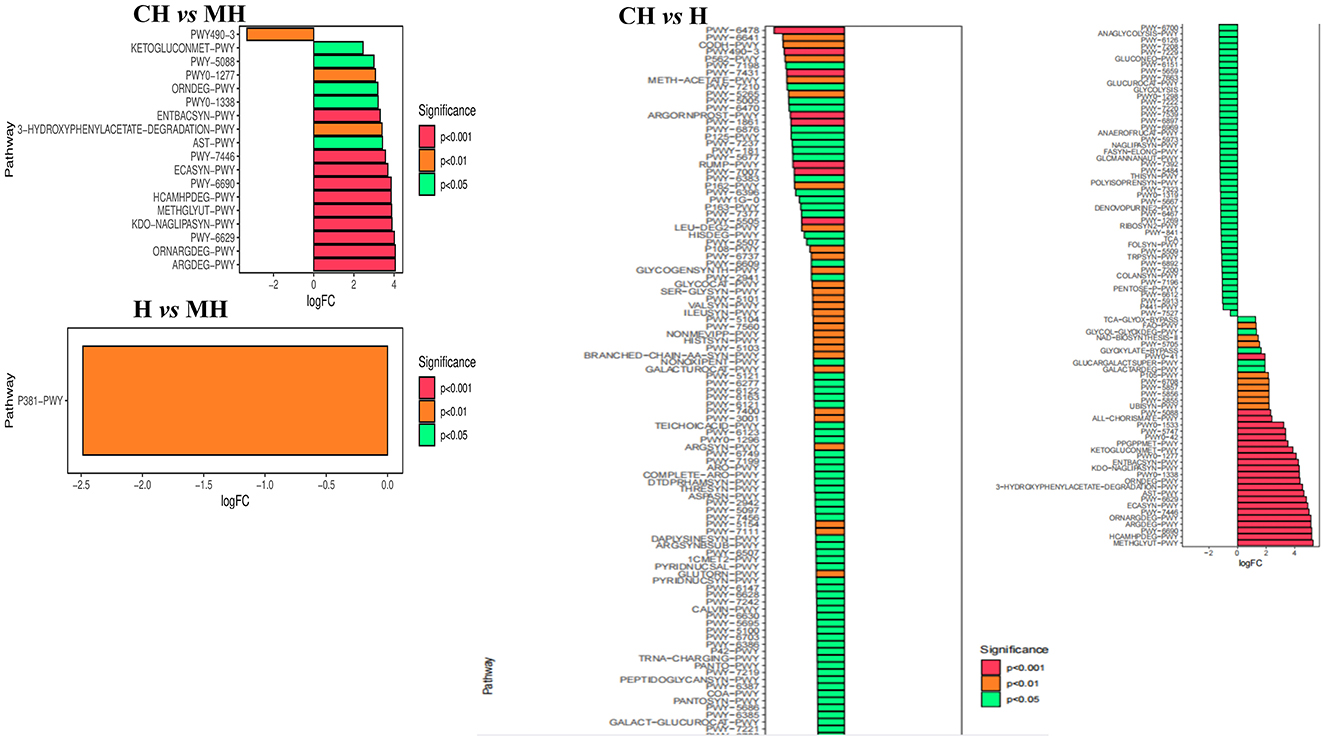
The MetaCyc pathway analysis showed that PWY-6629 (P < 0.0001), Argdeg-PWY (P < 0.0001), Ornargdeg-PWY (P < 0.0001), Methglyyt-PWY (P < 0.0001), Kdo-Naglipasyn-PWY (P < 0.0001), Ecasyn-PWY (P < 0.0001), Entbacsyn-PWY (P < 0.0001), Hcamhpdeg-PWY (P < 0.001), PWY-6690 (P < 0.001), PWY-7446 (P < 0.001), 3-Hydroxyphenylacetate-Degradation-PWY (P < 0.01), PWY0-1277 (P < 0.01), PWY0-1338 (P < 0.05), PWY-5088 (P < 0.05), Ast-PWY (P < 0.05), Ketogluconmet-PWY (P < 0.05), and Orndeg-PWY (P < 0.05) were markedly higher in group CH, while PWY490-3 (P < 0.01) was higher in group MH. P381-PWY in MH was significantly higher in group MH than in group H (P < 0.01). There were 186 dramatically different pathways between groups CH and H, such as Methglyut-PWY (P < 0.0001), Hcamhpdeg-PWY (P < 0.0001), and PWY-6690 (P < 0.0001) were significantly higher in group CH, while PWY-7007 (P < 0.0001), PWY490-3 (P < 0.0001), PWY-6478 (P < 0.0001), and others were significantly higher in group H (Figure 9).
4 Discussion
Plant polysaccharides are natural macromolecules that have gained increasing attention in pharmacological research (Yin et al., 2019). These polysaccharides exhibit a range of biofunctions, including immune adjustment, antioxidant properties, anti-inflammation effects, anti-tumor activity, and anti-microbe functions (Yin et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2018). Among them, PKP is an important herbal polysaccharide that has received relatively little attention. In this study, we examined the therapeutic effects of PKP on intestinal injuries in mice challenged with LPS, focusing on its antioxidant properties and microbiota composition.
The weigh analysis showed that LPS caused obvious weight loss in mice (Figure 1), which was in agreement with a previous study (Zhang et al., 2019), and PKP could increase the body weight of mice significantly. Pathological results further showed that LPS seriously damaged the villi integrity in mice with shorter villi length and higher crypt depth, while animals supplemented with PKP had better villi with longer villi length and lower crypt depth (Figure 1). Those results demonstrated that PKP could alleviate weight loss in LPS-induced animals by maintaining the integrity of the villi.
Then, we analyzed the serum antioxidant properties and inflammation levels of mice and found that LPS increased the levels of MAD, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, while it reduced the levels of SOD, T-AOC, and GSH-Px in mice (Figure 2), which were in line with the results reported in LPS-induced animals (Bian et al., 2022; Cao et al., 2018). GSH-Px, SOD, and T-AOC are important antioxidant enzymes inhibiting oxidation damage caused by reactive oxygen species accumulation due to the imbalance of oxidation–reduction homeostasis induced by LPS (Shu et al., 2022). MAD is a well-known biomarker of oxidative stress (Tsikas, 2017). The lower contents of this enzyme and higher levels of antioxidant enzymes in PKP-treated animals showed that PKY could mediate intestinal damage by enhancing antioxidant capacity in mice. IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α are commonly recognized pro-inflammatory factors in many pathological reactions (Zheng et al., 2023). The lower levels of those inflammatory factors in PKY-treated mice showed that this polysaccharide could decrease inflammatory response in animals.
Furthermore, we performed microbiome sequencing of mice and obtained 844,477 raw and 725,469 filtered reads (Table 1). There were 2,407 ASVs detected in animals, and there were 312 and 328 shared ASVs between CH and MH, and CH and H, respectively (Figure 5A). A noticeable difference in alpha diversity was not detected in mice, which was in agreement with the results in LPS-stimulated animals (Li et al., 2023a,b), but not in line with the results in LPS-challenged laying hens (Feng et al., 2023) and piglets (Li et al., 2024). In different taxa, LPS changed the structure of microbiota and the potential function of mice, and PKP could partly restore the microbiota composition and function of mice (Figures 4, 8, 9). At the phylum level, the ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidota was 0.92, 0.64, and 1.00 in CH, MH, and H, respectively. As the Firmicutes/Bacteroidota value is accepted as an indicator of dysbiosis (Xu et al., 2023), the current results confirmed that PKP could regulate the microbiota of mice. Finally, we explored the obviously changed bacteria among different mice groups and found 5 phyla and 20 genera of remarkable bacteria (Figure 7). Among them, a higher enrichment of Mailhella was examined in Mycoplasma hyorhinis-infected pigs (Zhang et al., 2023); the lower enrichment of these genera in group H inferred that PKP could regulate intestinal damage by inhibiting the growth of Mailhella. A lower abundance of Clostridium was detected in preclinical Alzheimer's disease (Jung et al., 2022). The higher enrichment of these genera in group H showed that PKP could maintain intestine health by promoting the colonization of Clostridium. Paramuribaculum is a butyrate-producing and commensal genus (Fang et al., 2023). The higher enrichment of these bacteria in group H revealed that PKP could keep the intestine healthy by promoting the growth of butyrate-producing bacteria.
5 Conclusion
We demonstrated that Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide could alleviate intestinal injuries by promoting oxidation resistance, decreasing inflammatory responses, and accommodating the intestinal microbiota of mice. Our results suggest the possibility of developing novel therapies for intestinal diseases.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1149202.
Ethics statement
All the experiment operations were under the instructions and approval of Laboratory Animals Research Center of Jiangsu, China and the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Agricultural University (NJAU.No20240226021). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
RQ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CP: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QW: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. XX: Methodology, Writing – original draft. JL: Methodology, Writing – original draft. SC: Investigation, Writing – original draft. KL: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DF: Software, Writing – review & editing. YW: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Henan Provincial Scientific and Technological Research Project (grant no: 242102110024) and “14th Five-Year Plan” National Key Research and Development Project: Screening and Mechanism of Antibacterial synergistic Active Compounds (2023YFD1800100). The authors extend their appreciation to Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2025R965), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the assistance from colleagues in the Institute of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine of Nanjing Agricultural University and Yunnan Agricultural University. The authors extend their appreciation to Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2025R965), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adak, A., and Khan, M. R. (2019). An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 76, 473–493. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2943-4
Bian, X. X., Zhao, X., Ma, C. H., and Shen, C. P. (2022). Arbutin alleviates LPS induced sepsis pneumonia in mice. Evid.-based Complement Altern. Med. 2022:5863952. doi: 10.1155/2022/5863952
Callahan, B. J., Mcmurdie, P. J., Rosen, M. J., Han, A. W., Johnson, A. J. A., and Holmes, S. P. (2016). DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 13, 581–583. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3869
Cao, S., Zhang, Q., Wang, C., Wu, H., Jiao, L., Hong, Q., et al. (2018). LPS challenge increased intestinal permeability, disrupted mitochondrial function and triggered mitophagy of piglets. Innate Immun. 24, 221–230. doi: 10.1177/1753425918769372
Caparrós, E., Wiest, R., Scharl, M., Rogler, G., Gutiérrez Casbas, A., Yilmaz, B., et al. (2021). Dysbiotic microbiota interactions in Crohn's disease. Gut Microbes 13, 1949096–1949096. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1949096
Chen, X., Kong, Q., Zhao, X., Zhao, C., Hao, P., Irshad, I., et al. (2022). Sodium acetate/sodium butyrate alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced diarrhea in mice via regulating the gut microbiota, inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant levels, and NLRP3/Caspase-1 signaling. Front. Microbiol. 13:1036042. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1036042
Cho, M., Bu, Y., Park, J. W., Rahman, H., and Ko, S. J. (2021). Efficacy of complementary medicine for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced small intestinal injuries: a narrative review. Medicine 100:e28005. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028005
Deng, Y., Tang, D., Hou, P., Shen, W., Li, H., Wang, T., et al. (2021). Dysbiosis of gut microbiota in patients with esophageal cancer. Microb. Pathog. 150:104709. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104709
Donaldson, A. L., Harris, J. P., Vivancos, R., O'Brien, S. J., and Riddle, M. S. (2022). Symptom profiling for infectious intestinal disease (IID): Do symptom profiles alter with age? PLoS ONE 17:e0269676. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269676
Dong, J., Gu, W., Yang, X., Zeng, L., Wang, X., Mu, J., et al. (2021). Crosstalk between Polygonatum kingianum, the miRNA, and gut microbiota in the regulation of lipid metabolism. Front. Pharmacol. 12:740528. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.740528
Dou, Y., Wen, M., Shen, H., Zhang, S., Jiang, G., Qiao, Y., et al. (2023). Intestinal microbiota differences in Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp between greenhouse and aquaponic rearing. Life 13:525. doi: 10.3390/life13020525
Fang, C., Cheng, J., Jia, W., and Xu, Y. (2023). Akkermansia muciniphila ameliorates alcoholic liver disease in experimental mice by regulating serum metabolism and improving gut dysbiosis. Metabolites 13:1057. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101057
Feng, J., Li, Z., Ma, H., Yue, Y., Hao, K., Li, J., et al. (2023). Quercetin alleviates intestinal inflammation and improves intestinal functions via modulating gut microbiota composition in LPS-challenged laying hens. Poultry Sci. 102:102433. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102433
Gu, W., Wang, Y., Zeng, L., Dong, J., Bi, Q., Yang, X., et al. (2020). Polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum improve glucose and lipid metabolism in rats fed a high fat diet. Biomed. Pharmacother. 125:109910. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109910
Haneishi, Y., Furuya, Y., Hasegawa, M., Picarelli, A., Rossi, M., and Miyamoto, J. (2023). Inflammatory bowel diseases and gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:3817. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043817
He, Y., Xu, M., Lu, S., Zou, W., Wang, Y., Fakhar-E-Alam Kulyar, M., et al. (2023). Seaweed polysaccharides treatment alleviates injury of inflammatory responses and gut barrier in LPS-induced mice. Microb. Pathog. 180:106159. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2023.106159
Hickey, J. W., Becker, W. R., Nevins, S. A., Horning, A., Perez, A. E., Zhu, C., et al. (2023). Organization of the human intestine at single-cell resolution. Nature 619, 572–584. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05915-x
Huang, K., Zhang, P., Zhang, Z., Youn, J. Y., Wang, C., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: efficacies and mechanisms. Pharmacol. Ther. 225:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107843
Izadparast, F., Riahi-Zajani, B., Yarmohammadi, F., Hayes, A. W., and Karimi, G. (2022). Protective effect of berberine against LPS-induced injury in the intestine: a review. Cell Cycle 21, 2365–2378. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2100682
Jung, J. H., Kim, G., Byun, M. S., Lee, J. H., Yi, D., Park, H., et al. (2022). Gut microbiome alterations in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. PLoS ONE 17:e278276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278276
Kong, Q., Chen, X., Liu, Y., Ali, F., Idrees, A., Ataya, F. S., et al. (2024). Sodium acetate and sodium butyrate attenuate diarrhea in yak calves by regulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Heliyon 10:e26564. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26564
Levy, M., Kolodziejczyk, A. A., Thaiss, C. A., and Elinav, E. (2017). Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 219–232. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.7
Li, C., Wang, Y., Zhao, X., Li, J., Wang, H., Ren, Y., et al. (2024). Comparative analysis of intestinal inflammation and microbiota dysbiosis of LPS-challenged piglets between different breeds. Animals 14:665. doi: 10.3390/ani14050665
Li, H., Wang, K., Hao, M., Liu, Y., Liang, X., Yuan, D., et al. (2023). The role of intestinal microecology in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer: a review. Medicine 102:e36590. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036590
Li, L., Tan, H., Zou, Z., Gong, J., Zhou, J., Peng, N., et al. (2020). Preventing necroptosis by scavenging ROS production alleviates heat stress-induced intestinal injury. Int. J. Hyperthermia. 37, 517–530. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2020.1763483
Li, X., Mei, M., Pu, X., Chen, X., Li, X., Meng, F., et al. (2023). Protective effect and mechanism of Polygonatum kingianum against hypoxia-induced injury. Heliyon 9:e14353. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14353
Li, Y., Si, H., Ma, Y., Li, S., Gao, L., Liu, K., et al. (2023a). Vitamin D3 affects the gut microbiota in an LPS-stimulated systemic inflammation mouse model. Microbes Infect. 25 , 105180. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105180
Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, D., Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., et al. (2023b). Depletion of gut microbiota influents glucose metabolism and hyperandrogenism traits of mice with PCOS induced by letrozole. Front. Endocrinol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1265152
Lin, Y., Xia, P., Cao, F., Zhang, C., Yang, Y., Jiang, H., et al. (2023). Protective effects of activated vitamin D receptor on radiation-induced intestinal injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 27 , 246–258. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17645
Ling, Z., Wang, Z., Chen, L., Mao, J., Ma, D., Han, X., et al. (2024). Naringenin alleviates radiation-induced intestinal injury by inhibiting TRPV6 in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 68 , e2300745. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202300745
Liu, Y., Li, B., Su, Y., Zhao, R., Song, P., Li, H., et al. (2022). Potential activity of traditional chinese medicine against Ulcerative colitis: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 289, 115084–115084. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115084
Long, E. S., Penalver Bernabe, B., Xia, K., Azcarate-Peril, M. A., Carroll, I. M., Rackers, H. S., et al. (2023). The microbiota-gut-brain axis and perceived stress in the perinatal period. Arch. Women's Ment. Health 26, 227–234. doi: 10.1007/s00737-023-01300-9
Lozupone, C. A., Stombaugh, J. I., Gordon, J. I., Jansson, J. K., and Knight, R. (2012). Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 489, 220–230. doi: 10.1038/nature11550
Lv, J., Wang, J., Yu, Y., Zhao, M., Yang, W., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Alterations of gut microbiota are associated with blood pressure: a cross-sectional clinical trial in Northwestern China. J. Transl. Med. 21:6. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04176-6
Mattei, V., Murugesan, S., Al Hashmi, M., Mathew, R., James, N., Singh, P., et al. (2019). Evaluation of methods for the extraction of microbial dna from vaginal swabs used for microbiome studies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00197
Meng, A., Zhang, X., Pubu, P., Ali, M., Wang, J., Xu, C., et al. (2024). Protective effect of lentinan against LPS-induced injury in mice via influencing antioxidant enzyme activity, inflammatory pathways, and gut microbiota. Pak. Vet. J. 44, 647–656. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2024.225
Mohr, A. E., Crawford, M., Jasbi, P., Fessler, S., and Sweazea, K. L. (2022). Lipopolysaccharide and the gut microbiota: considering structural variation. FEBS Lett. 596 , 849–875. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14328
Nagarajan, A., Scoggin, K., Gupta, J., Threadgill, D. W., and Andrews-Polymenis, H. L. (2023). Using the collaborative cross to identify the role of host genetics in defining the murine gut microbiome. Microbiome 11:1. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01552-8
Peng, S., Xu, C., He, Q., Xu, J., Kiani, F. A., Choudhary, O. P., et al. (2024). Fucoidan alleviates intestine damage in mice induced by LPS via regulation of microbiota. Pak. Vet. J. 44, 517–525. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2024.190
Shu, G., Tang, Z., Du, H., Zheng, Y., Chang, L., Li, H., et al. (2022). Effects of dietary ferulic acid supplementation on hepatic injuries in tianfu broilers challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Toxins 14:227. doi: 10.3390/toxins14030227
Su, L., Li, X., Guo, Z., Xiao, X., Chen, P., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Effects of different steaming times on the composition, structure and immune activity of Polygonatum Polysaccharide. J. Ethnopharmacol. 310, 116351. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116351
Sweeney, R. P., and Lowary, T. L. (2019). New insights into lipopolysaccharide assembly and export Ryan P Sweeney and Todd L Lowary. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 53, 37–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.07.004
Tsikas, D. (2017). Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 524, 13–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2016.10.021
Wang, X., Gao, A., Jiao, Y., Zhao, Y., and Yang, X. (2018). Antitumor effect and molecular mechanism of antioxidant polysaccharides from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in human colorectal carcinoma LoVo cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 108, 625–634. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.006
Wells, P. M., Sprockett, D. D., Bowyer, R. C. E., Kurushima, Y., Relman, D. A., Williams, F. M. K., et al. (2022). Influential factors of saliva microbiota composition. Sci. Rep. 12:1. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23266-x
Xu, H., Fu, J., Luo, Y., Li, P., Song, B., Lv, Z., et al. (2023). Effects of tannic acid on the immunity and intestinal health of broiler chickens with necrotic enteritis infection. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 14:8. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00867-8
Yan, A., Ding, H., Liu, J., Bi, C., Han, Z., Wang, Z., et al. (2022). Black Lycium barbarum polysaccharide attenuates LPS-induced intestine damage via regulation gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 13:1080922. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1080922
Yang, L., Luo, H., Tan, D., Zhang, S., Zhong, Z., Wang, S., et al. (2021). A recent update on the use of Chinese medicine in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Phytomedicine 92:153709. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153709
Yang, M., Meng, F., Gu, W., Fu, L., Zhang, F., Li, F., et al. (2021). Influence of polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum on short-chain fatty acid production and quorum sensing in Lactobacillus faecis. Front. Microbiol. 12:758870. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.758870
Yang, W., Zhao, P., Li, X., Guo, L., and Gao, W. (2022). The potential roles of natural plant polysaccharides in inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 277:118821. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118821
Yang, Y. Q., Li, Y. Q., Yu, L. P., Li, X., Mu, J. K., Shang, J., et al. (2020). Muscle fatigue-alleviating effects of a prescription composed of polygonati rhizoma and notoginseng radix et rhizoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2020:3963045. doi: 10.1155/2020/3963045
Yin, M., Zhang, Y., and Li, H. (2019). Advances in research on immunoregulation of macrophages by plant polysaccharides. Front. Immunol. 10, 145–145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00145
Yu, H. J., Jing, C., Xiao, N., Zang, X. M., Zhang, C. Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2020). Structural difference analysis of adult's intestinal flora basing on the 16S rDNA gene sequencing technology. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 24, 12983–12992. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202012_24203
Zhang, W., Xu, J., Yu, T., and Chen, Q. (2019). Effects of berberine and metformin on intestinal inflammation and gut microbiome composition in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118, 109131–109131. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109131
Zhang, X., Wang, H., Peng, S., Kang, J., Xie, Z., Tang, R., et al. (2022). Effect of microplastics on nasal and intestinal microbiota of the high-exposure population. Front. Public Health 10:1005535. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1005535
Zhang, Y., Cao, M., Li, Y., Lu, P., Dai, G., Zhang, M., et al. (2022). Fecal microbiota transplantation ameliorates bone loss in mice with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis via modulating gut microbiota and metabolic function. J. Orthop. Transl. 37, 46–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.08.003
Zhang, Y., Gan, Y., Bao, H., and Wang, R. (2023). Perturbations of gut microbiome and metabolome of pigs infected with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 103:6219–6232. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12690
Zheng, L., Han, Z., Luo, D., Li, J., Pang, N., Ding, M., et al. (2023). IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α regulation of the chondrocyte phenotype: a possible mechanism of haemophilic cartilage destruction. Hematology 28:2179867. doi: 10.1080/16078454.2023.2179867
Zhong, X., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Cao, H., Zhang, F., and Wang, X. (2023). Gut microbiota signatures in tissues of the colorectal polyp and normal colorectal mucosa, and faeces. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:1054808. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1054808
Keywords: Escherichia, Pseudomonas_E, Mailhella, Paramuribaculum, NM07-P-09, Odoribacter, Nanosyncoccus, SFMI01
Citation: Qiu R, Pan C, Qin Y, Wei Q, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Xie X, Li J, Chen S, Li K, Fouad D, Wu Y and Zhong Q (2025) Polygonatum kingianum polysaccharide alleviated intestinal injuries by mediating antioxidant ability and microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 16:1492710. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1492710
Received: 07 September 2024; Accepted: 03 January 2025;
Published: 30 January 2025.
Edited by:
Ricardo Calhelha, Centro de Investigação de Montanha (CIMO), PortugalReviewed by:
Liwei Guo, Yangtze University, ChinaWeijie Lv, South China Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Qiu, Pan, Qin, Wei, Yu, Zhang, Xie, Li, Chen, Li, Fouad, Wu and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kun Li, bGszMDA1QG5qYXUuZWR1LmNu; Yi Wu, d3V5aTIwMDFjbkAxNjMuY29t; Qiu Zhong, emhvbmdxaXVqb2JAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Reng Qiu
Reng Qiu Chuangye Pan
Chuangye Pan Yuxi Qin2
Yuxi Qin2 Kun Li
Kun Li Yi Wu
Yi Wu Qiu Zhong
Qiu Zhong