
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Microbiol., 31 March 2025
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 16 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2025.1443430
 Sadia Abbas1†
Sadia Abbas1† Rabia Kanwar1†
Rabia Kanwar1† Kaleem Ullah2
Kaleem Ullah2 Rimsha Kanwal1
Rimsha Kanwal1 Mamoon Tajamal1
Mamoon Tajamal1 Muhammad Aamir Aslam1*
Muhammad Aamir Aslam1* Abid Ahmad3
Abid Ahmad3 Abdul Qadeer4*
Abdul Qadeer4* Hsun-Yu Huang5*
Hsun-Yu Huang5* Chien-Chin Chen6,7,8,9,10*
Chien-Chin Chen6,7,8,9,10*Klebsiella pneumoniae is a notorious, Gram-negative pathogen and is a leading cause of healthcare settings and community-acquired infections. This is the commensal of human microbiota and can invade and cause infections in different body parts. The global emergence of antibiotic resistance in K. pneumoniae has become a major challenge in the whole medical community. Alternative paths to treat the infections caused by these MDR pathogens are needed as these bacteria become resistant to last-resort antibiotics like colistin. The lytic bacteriophages (phages) are the bacteria's natural predators and can rapidly eliminate the bacterial cells. Phages are abundant in nature and have recently been found to be effective tools in modern biotechnology. They can be used to control the bacterial infectious diseases. They can be manipulated easily and potentially used in therapeutics, biotechnology, and research. Several studies, both in vitro and in vivo, have demonstrated the possible applications of the lytic phages in treating K. pneumoniae superbug strains. Phage endolysins have drawn the scientific world's attention because of their involvement in phage adsorption and bacterial capsules digestion. These phage-encoded enzymes digest the polysaccharide components of bacterial cell walls by recognizing and binding them. Phage lysins, being strong biological agents, are capable of effectively and swiftly eliminating bacteria. This review summarizes the information on phages of K. pneumoniae and phage-based therapies to target their bacterial hosts.
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a facultative, anaerobic, opportunistic pathogen of the Klebsiella genus of the Enterobacteriaceae family that was first isolated from the lungs of pneumonia patients by Carl Friedlander in 1882. They are rod-shaped, non-motile, and encapsulated bacteria (Mohammadi et al., 2023a). K. pneumoniae is ubiquitous in water, soil, sewage, plants, and animals and frequently colonizes mucosal surfaces, invades, and causes infections in different body sites. The ability of this pathogen to evade the immune system, its increasing antibiotic resistance, and the spread of hypervirulent strains has become a challenge in healthcare settings (Choby et al., 2020; Ballén et al., 2021). Immunocompromised patients, neonates, and the elderly are more vulnerable to infections. Bacterial infections are more common in healthcare settings and spread via direct contact with an infected person (Santajit and Indrawattana, 2016). It is mainly responsible for urinary and respiratory tract infections and wound and soft tissue infections and is extensively present in medically used devices such as ventilators, catheters, contaminated surfaces, and other instrumentations (Yan et al., 2016; Maebed et al., 2021). It is the second most common pathogen after E. coli that causes nosocomial and community-acquired infections (Moya and Maicas, 2020). This pathogen belongs to the ESKAPE group, which includes the Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter species that are mainly responsible for the majority of nosocomial infections and can escape from the biocidal activity of the antibiotics (Hoenes et al., 2021; Sethuvel et al., 2023). K. pneumoniae follows the model of “the best defense for a pathogen is a good defense” instead of “the good defense for a pathogen is a good offense.” That ability makes the bacteria escape and sustain their life in the host. The hyper-virulent strains of K. pneumoniae are more virulent compared to classical K. pneumoniae strains and cause community-acquired infections even in healthy individuals, and are more difficult to control and treat due to high occurrence at the multiplication sites and subsequent spread (Holt et al., 2015). Hypermucoviscous K. pneumoniae can metastatically spread from one organ to another organ, which is rare for enteric Gram-negative bacilli in the presence of host immunological defense. Capsule polysaccharide (CPS) protects the bacteria and has a role in the resistance to antimicrobial peptides, phagocytosis suppression of early inflammatory response, and inhibition of DC maturation (Paczosa and Mecsas, 2016). The hypervirulent K. pneumoniae is responsible for pyogenic liver abscesses, meningitis, endophthalmitis, and septic arthritis (Choby et al., 2020).
In recent years, antimicrobial resistance has become a major challenge and causes a variety of nosocomial infections that can be problematic (Amraei et al., 2022). The majority of the antibiotic-resistant mechanisms have been acquired through horizontal gene transfer, imparting a high level of resistance to β-lactam and quinolone classes of antibiotics (Mohammadi et al., 2023a). Due to the growing worldwide problem of antibiotic resistance, the World Health Organization recognizes K. pneumoniae as a species of major importance and encourages the development of new antibiotics and other treatment options (Tacconelli, 2017). One of the most promising alternatives to antibiotics is the use of bacteriophages and phage-based products (Czaplewski et al., 2016). Bacteriophage therapy is described as administering whole lytic phage or purified phage particles to a patient to lyse the bacterial pathogen causing the infection (Kutter et al., 2010). it is a promising strategy to combat the infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Antibiotic resistance and antibiotic-sensitive bacteria are both effectively treated using phage therapy. Their function is bactericidal rather than bacteriostatic, killing their target pathogens and suppressing bacterial development toward resistance (Chan et al., 2018).
Bacteriophages are the bacterial predators and obligate intracellular parasites that lyse the bacteria and have the advantage of being highly specific to their bacterial hosts, which reduces the risk of disrupting the natural microbiome and causing collateral damage to healthy cells (Pirnay et al., 2015). Bacteriophages, due to their high diversity, are found in a variety of environments, such as the human gut, soil, sewage water, and aquatic systems (Zhu et al., 2022). They are 10 times the number of bacteria present in the environment and have multiple applications due to their lifestyle and unique properties. Bacteriophage degrading enzymes, as antibacterial agents, are becoming more and more desirable, particularly against antibiotic-resistant pathogens, and phage-associated lysins and endolysins have become the prominent new antimicrobials. As recombinant proteins, the usage of purified endolysins to lyse the bacteria was documented in 1959. Endolysins are highly evolved enzymes that efficiently lyse the bacterial host cell wall by hydrolyzing the four primary bonds in peptidoglycan components, causing the cell wall to break (Abdelrahman et al., 2021). They work in association with holin proteins and provide the lysins access to the peptidoglycan layer by perforating the inner cell membrane. Because the peptidoglycan layer gives the cell its structural integrity and rigidity, its degradation causes the cell wall to become unstable and eventually rupture because of variations in the osmotic pressures inside the cell and in the environment. Endolysins administered exogenously can have a direct impact on specific Gram-positive bacteria because they lack the outer membrane. In the case of Gram-negative bacteria, endolysin-induced lysis has just evolved and requires spanin complexes for the outer membrane disruption, which catalyzes the outer and inner membrane fusion. Several studies have been conducted on the efficacy of phage lysins in treating systemic and mucosal infections to determine the validity of their bactericidal potential (Belay et al., 2018).
A large spectrum of bacterial components provide the virulence attributes of encapsulated K. pneumoniae that lead to infections and antibiotic resistance (Figure 1). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), capsule polysaccharide (CPS), fimbriae, and siderophores (Ali et al., 2022), including enterobactin and aerobactin, are the critical virulence factors of K. pneumoniae. A few virulence factors, like capsule, fimbriae, and biofilm formation, are the origin of classical pathogenesis and are present in nearly all isolates. LPS is composed of three important components: Lipid A, core, and O antigen. The host immune system initiates the cascade of reactions by identifying the LPS, but the pathogen can modify the LPS in parts that are not recognized by the host immune cells, allowing it to successfully uphold the infection (Llobet et al., 2015). The CPS is essential in the escape of K. pneumoniae from the host. The CPS is the top protective layer engaged in the initial interaction between the host and the bacteria. The CPS locus contains several genes that are critical for the synthesis of CPS. The biosynthesis of CPS is mediated by the RmpA gene, a characteristic of hvKP, and is a plasmid-located virulence factor. The binding and adherence of the infectious agent to the host mucosal surface enable it to survive and establish the infection inside the host, and the bacterial component, which helps it to adhere to the host cell surface, is the fimbriae or pilli, and it is an important virulence factor for the bacteria (Navon-Venezia et al., 2017). During infection, like other human pathogens, K. pneumoniae requires iron molecules from its host cell as it is very critical for propagation and growth. For this purpose, siderophores play an important role and have a high affinity for iron binding. K. pneumoniae is a significant contributor to antibiotic resistance in addition to being widely prevalent, as it shows the non-susceptible rates against the four major classes of antibiotics, which include the carbapenems, quinolones, aminoglycosides, and third generation cephalosporins. It emphasizes the significant contribution of this pathogen to the worldwide burden of antibiotic resistance. A major class of antibacterial agents used in human medicine is the β-lactam antibiotics that have been clinically used since the 1940s, and it includes penicillin, carbapenems, cephalosporins, monobactam, and β-lactamase inhibitors, these are most widely used antibiotics with a β-lactam ring in their molecular structure. The β-lactamase production is the first defense strategy adopted by K. pneumoniae to resist the antibiotics, which is followed by alteration in permeability. The β-lactamase genes, SHV-1 and TEM-2, were identified as a result of penicillin resistance in 1960 in K. pneumoniae (Wang et al., 2020). Due to the presence of SHV-1 β-lactamase encoded on the chromosome, K. pneumoniae is resistant to carbenicillin and ampicillin. Shortly after, an ESBL gene SHV-2 and another plasmid-mediated ESBL gene TEM-3 from this infectious agent were reported. Carbapenemase production, activation of efflux pumps and ESBLs, and AmpC cephalosporinases overexpression with less expression of OMPs are the main carbapenem-resistant mechanisms. The decreased susceptibility to carbapenemase is also associated with disruption of OmpK35, and OmpK36. In K. pneumoniae, the IMP-1 metallo-enzyme was the first detected carbapenemase that was reported in Japan in 1991. Undoubtedly, blaKPC became the highly impacting carbapenemase, with blaKPC-2 and blaKPC-3 being the most frequent genes (Lee et al., 2016), and incredibly common in strains linked to hospital outbreaks in many different countries. The DNA replication is inhibited by the Quinolone antibiotics that target the bacterial topoisomerases. The most frequent use of the quinolones caused its resistance (Naeem et al., 2016). The chromosomal mutations in DNA gyrase, quinolone binding targets, and topoisomerase IV having parC-parE subunits are the major resistance mechanisms, but the more common mutations in gyrA and parC were recognized earlier in K. pneumoniae than mutations in gyrB and pare (Guillard et al., 2016). Aminoglycosides, protein synthesis inhibitors, were replaced by fluoroquinolones, carbapenems, and third-generation cephalosporins due to high antibiotic resistance (Krause et al., 2016) gained through mechanisms involving drug modification enzymes with acetylation, adenylation, or phosphorylation activities (Peirano et al., 2014). The other resistance mechanisms in K. pneumoniae against aminoglycosides include loss of KpnO, a putative porin, and cell permeability modifications because of changes in AcrAB-TolC and KpnEF efflux pump systems (Padilla et al., 2010). Table 1 represents the data of antibiotic resistance genes in K. pneumoniae.
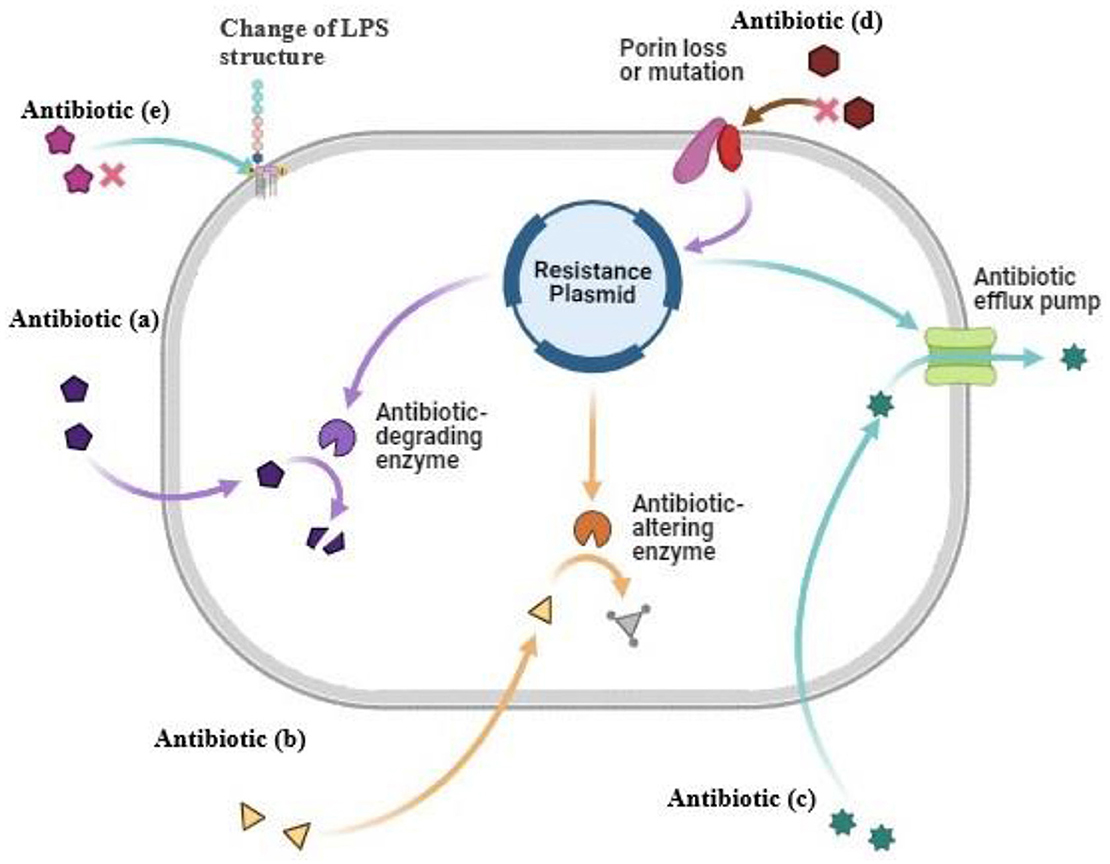
Figure 1. Antibiotic resistance mechanism in K. pneumoniae. (a) Antibiotic degrading enzymes degrade the antibiotic (b) Antibiotic altering enzymes alter modified the antibiotic (c) Antibiotic efflux pump cause pumping out of antibiotic before it reaches the target (d) Modification in cell wall porins (e) Change of LPS structure of cell wall.
The therapeutic use of phages against bacterial infections has gained momentum due to the emergence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria such as multi-drug resistant K. pneumoniae. Felix d'Herelle was the first to propose the therapeutic use of bacteriophages in 1917 to treat the infections of clinically important pathogens in humans and animals. Several factors are involved in the selection of bacteriophages for bacteriophage therapy. Firstly, phages should continue to be effective in eliminating the K. pneumoniae (Fang and Zong, 2022; Habibinava et al., 2022). The host range, strictly lytic nature, stable and able to replicate in the host, synergistic therapeutic effects coupled with antibiotics and other phages in the form of a phage cocktail to inhibit the development of antibiotic resistance (Al-Ishaq et al., 2020). When evaluating the phages, in vitro analysis of phage lysis is done by incubating phage with cultures of K. pneumoniae (Hesse et al., 2021). Several mouse models have been established to investigate the phages of K. pneumoniae, such as sepsis (Vinodkumar et al., 2005), lobar pneumonia (Chhibber et al., 2008), liver abscesses (Hung et al., 2011), and burn wound infections (Malik and Chhibber, 2009). The therapeutic efficacy of tailed bacteriophage BPA43 was assessed in a BALB/c pneumonic mouse model, which was infected with virulent K. pneumoniae. There was a great reduction in the bacterial count in the lungs of mice after 2 h of post-challenge with K. pneumoniae (Anand et al., 2020). The bacteriophage Kpn5 against K. pneumoniae B5055 was effective in treating burn wound infections in murine and mice models when compared with silver nitrate and gentamicin (Kumari et al., 2009). Phage KPO1K2, encapsulated within a liposome, was found to be efficacious in treating lobar pneumonia in BALB/c mice caused by intranasal inoculation of K. pneumoniae B5055. Phage therapy was also postponed by around 3 days. This highlights the need to research multiple transport techniques for phage treatment, not just from a logistical aspect but also in determining the most efficient strategy based on the type of contamination and the depth of incubation in compliance with the treatment (Chadha et al., 2017). The use of a phage cocktail (made up of Kpn1, Kpn2, Kpn3, Kpn4, and Kpn5) caused a decrease in bacterial load. A mouse infected with K. pneumoniae ST258 was rescued by combined phage therapy that showed the least phage resistance frequency and more survival rate (Hesse et al., 2021), another phage cocktail (Katrice−16) made up of eight lytic phages was identified for its potential use against 56 strains of K. pneumoniae ST16. The Katrice-16 was highly active in in-vitro as well as in human fluid (Martins et al., 2022) against K. pneumoniae, which is mostly responsible for burn wound infections. Many phages have been used against that like phage KØ1, phage P?Bw-Kp1, phage P?Bw-Kp2, phage P?Bw-Kp3 (Torabi et al., 2021), a lytic phage vB-KpneM-Isf48 (Komijani et al., 2017), and phage ZCKP8 (Fayez et al., 2021). A phage cocktail of three lytic phages named GH-K1, GH-K2, and GH-K3 was specific to K. pneumoniae strain K7 (Wu et al., 2019). Multiple studies have found that combining antibiotics and phages has a greater antibacterial impact than either drug alone (Viertel et al., 2014). The synergistic effects of phage with antibiotics established the more favorable effects, such as the combination of ceftriaxone with phage vB-1086 showing great activity to inhibit biofilm formation (Xu et al., 2022). Similarly, phage-ciprofloxacin and phage-meropenem synergism are also effective in impeding biofilm formation compared to individual treatments (Shi et al., 2020). Furthermore, choosing effective phages for the bacteria to be targeted can boost phage performance, phage cocktails are used to improve the impact of phages on Klebsiella populations and are considered crucial for the efficacy of phage therapy (Chan et al., 2013). Table 2 shows the data of some recently isolated phages against K. pneumoniae.
Comparing genomic sequences of Caudovirales, the lytic K. pneumoniae phages reveal some similarities and differences. For instance, there is a possibility that recently identified phages of K. pneumoniae polysaccharide depolymerase are involved in breaking down the outer layer that surrounds the bacterium (Kesik-Szeloch et al., 2013; Fokine and Rossmann, 2014; Jamal et al., 2015). The degradation by phage depolymerizes that enable K. pneumoniae to eradicate its biofilm (Taha et al., 2018) as well as make it prone to killing with antibiotics, phages, and immune clearance (Kesik-Szeloch et al., 2013). Furthermore, in the laboratory, depolymerase activity becomes apparent by lytic haloes produced around clear zones of lysis on pyoverdine plates after inoculating K. pneumoniae along with phage particles. This is now the basis for many novel phage laboratory methods, which include defining the specificity of a given phage against its host range (Hughes et al., 1998).
However, for initial identification, Ackermannviridae, Myoviridae, Podoviridae, and Siphoviridae differences can be helpful. Restriction analysis that involves the cleavage of phage DNA by bacterial restriction enzymes can also assist with the determination of phage genome size in addition to having some of the useful characteristics of the known phages before in-depth characterization, and it is possible to reveal the presence of forms of the phage tails with the help of transmission electron microscope. The phylogenetic analysis revealed that various phages of Klebsiella belong to the recognized genera within the Siphoviridae, Myoviridae, Podoviridae, and Ackermannviridae families, whereas others are rooted in novel lineages without an official viral classification (Kesik-Szeloch et al., 2013).
Specifically, they must be able to attach to a specific target bacterial host cell before initiating the lytic phase of its life cycle. It achieves this by first identifying and attaching itself to a receptor on the host cell's outer membrane. It is there where the phage receptor will interact with host receptor, which allows accessibility to infected bacteria and guides them for viral DNA transfer into their stealer cell. Adsorption can occur on any outer structure in different phages to host but in case of gram-negative bacteria such as K. pneumoniae adsorption may be either by pili, capsule, LPS or bunch of other structures outside the bacterial cell wall (Bertozzi Silva et al., 2016). Flu phage1/9 binds at any of these three sites on the host's exterior to infect its E. coli hosts; so, it sets boundaries for what we can call as a “host” (D'Andrea et al., 2017). Further illustrated the fine specificity of their modern lytic phage ϕBO1E which exclusively lysed KPC-producing (i.e., clade II) but no other strains with only clade I species showing that there was inherent sensitivity and concurred and did not kill strains within clade I because it recognizes some capsular polysaccharides that are unique among strains from only one major subgroup. However, their experiment showed that KPO1K2 targeting the K. pneumoniae B5055 is effective against multiple isolates of E. coli in addition to several influenzas of both species also indicating a wider scavenger range than clade selective ϕBO1E (Verma et al., 2009a).
As for their therapeutic application, it has been accepted that lytic phages with wide host specificity on the species level are more advantageous in combating bacterial infection than phages with limited host specificity on the strain level. Such targeted phages are ineffective for hypothetical or prophylactic treatment and would make use of infective agent detection before administration of phages. Moreover, even if phages to be used were to be classified as being broad host range phages, these phages would, in the general sense, be more specific than antibiotics (Loc-Carrillo and Abedon, 2011). Therefore, broadening the phage treatment's range of activity has led to the concept of phage cocktails, that can increase the number of phage particles in a single treatment (Gu et al., 2012), and even modification of the factitious host range by merging the tail structures of different bacteriophages (Yosef et al., 2017).
The potential therapeutic benefits of phages that infect K. pneumoniae have garnered significant interest. Several factors should be considered when selecting phages for therapeutic purposes. First thing, phages must be capable of effectively eradicating K. pneumoniae. In vitro appraisals of burst size and phage lysis are conducted on K. pneumoniae cultures during the phage characterization, phages that can cause the rapid lysis and release such several particles will generate clear, sizeable plaques. Furthermore, phages having a large host range are often considered more favorable compared to ones with a small host range to target multiple strains at once (Harper, 2018). Second thing, lytic phages have the capability to clear the bacteria rapidly and effectively due to their life cycle unlike lysogenic phages, which remain dormant by incorporating the genetic information in the host's genome for an undetermined amount of time. Furthermore, the lysogenic phage can potentially transfer genes into the bacteria that enable them to produce toxins and exhibit antibiotic resistance, exacerbate the infection, and make treatment more challenging (Harper, 2018).
Prior to human trials, any therapeutic candidate must first undergo safety and efficacy testing in an appropriate animal or insect model based on in vitro research. The efficacy of phage treatment toward diseases such as wounds and infections of soft tissues (Kumar et al., 2010), bacteremia (Vinodkumar et al., 2005), and pneumonia (Cao et al., 2022) was researched using mouse models in the instance of K. pneumoniae phage, which closely imitates the range of diseases caused by the bacteria in humans. Simultaneously, the effectiveness of the lytic phages and phage-encoded molecules in eradicating infections caused by K. pneumoniae has been tested using Galleria mellonella larvae (Manohar et al., 2018). Several murine-based experiments have been conducted by Kumari and colleagues in an effort to determine the K. pneumoniae phage Kpn5 potential for therapeutic use. Among the five phages, isolated from sewage material (Kumari et al., 2010), Kpn5 was found to be most efficient in BALB/c mice models, unlike the other four phages when used against K. pneumoniae B5055 (Kumari et al., 2009) to treat burn wound infections. Kpn5 was administered intraperitoneally and resulted in an average survival rate of 9.66% compared to 0% for the negative controls. In addition, Kpn5 was found to be superior when compared to topical treatment with both antimicrobial agents (gentamicin and silver nitrate) (Kumari et al., 2011) and natural products (Aloevera gel and honey) (Kumari et al., 2010) offering reduced mortality rate and higher protection levels. However, irrespective of the promising results, the authors acknowledge the probability that K. pneumoniae acquiring resistance against Kpn5, as pointed out in the in vitro trials (Cao et al., 2015). However, they did not provide information regarding the host range of phage by using only one K. pneumoniae strain all over their investigations.
Another important aspect to take into account is the phage delivery method in the phage treatment. For instance, intravenous injection is used in the majority of cases in human treatment, unlike intraperitoneal injection, which is not often employed. Cao et al. (2015) conducted the experiments to treat murine-lobar pneumonia and found that intranasal administration of phage 1513 could develop an 80% survival rate in Swiss Webster mice, 2 h after nasal delivery of MDR K. pneumoniae 1513, compared to 0% in negative controls, in addition, noticeably decreased lung injury. The intraperitoneal inoculation of phage SS into BALB/c following intranasal administration of K. pneumoniae B5055, as determined (Chhibber et al., 2008) caused complete elimination of the bacteria in five days rather than 10 days in mice without treatment. Even though a 6 h delay post-inoculation made the treatment ineffective, according to the author's demonstration, Singla et al. (2015) exhibited that a liposome enclosed KPO1K2 phage was efficient for the treatment of lobar pneumonia induced by intranasal administration of K. pneumoniae B5055, regardless the therapy was postponed for up to 3 days, in BALB/c mice. Although the comparison cannot be made directly among studies because of the differentiations in the phage selection in the published studies, it emphasizes the significance of examining various phage therapy delivery strategies. This is not just important from an economical perspective moreover for determine the most effective mechanism based on the kind of infection and duration of incubation before therapy. Furthermore, the investigations just examined the in vivo impact of phage treatment on a single K. pneumoniae strain and did not provide information about the host range of phages. Consequently, more research should focus on determining if the corresponding phages' host ranges are sufficient for their potential therapeutic interests.
Even though several investigations have demonstrated that K. pneumoniae phages can effectively eradicate infection in Galleria and murine models, it is now necessary to consider the impact of phage infection on the microbial community (i.e., metabolome, gut microbiota) when evacuating phages (either alone or in phage cocktail) patient decontamination measure. A common bacterial population in the human gut showed a rise in phage resistance (28 to 68%) upon infection with lytic phages, as shown by Hsu et al. (2019). This observation revealed the phage infection impact on the system, as it led to quantitative changes in both susceptible and resistant isolates. Instead of eliminating the target species, phage infection altered the ecosystem to create a more hospitable gut environment. The effectiveness of phages that target Enterococcus feacalis was lessened in altering the microbiota, in contrast to the phages of E. coli and Clostridium sporogenes, which significantly decreased the population of Bacteroides vulgates, Proteus mirabilis, and Parabacteroides distasonis by 106g-1 stool and the populations of Akkermansia muciniphila and B. fragilis by 108g-1 stool. Phage-induced perturbation of the microbiota had an impact on the metabolome as well. In the presence of phages, the abundance of 17% of the compounds under investigation changed considerably. Hsu et al. detected that during the initial phage infection, two-fold decrease in tryptamine, the metabolite that is microbiome-associated and helps in gastrointestinal transport acceleration in mice. The finding suggests that systemic health can be affected by targeting microbiome modification by phage infection.
The practical challenges related to phage therapy in developed countries like the EU and the UK represent a significant obstacle that requires attention. Currently, the safety, manufacturing, and applications of virus-based infection control techniques remain largely unregulated. The most recent attempt to address these regulatory challenges was a phase II clinical trial supported by the European Commission. This clinical trial known as PhagoBurn, was first anticipated as a multicenter, randomized, single-blind, and controlled clinical trial of phage therapy conducted between 2013 and 2017. While adhering to Good clinical trial (GCP) and good manufacturing practices (GMP) standards. Phagoburn aimed to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of phage-treated burn wound infections, and it contributed to the establishment of a protocol for phage therapy (Jault et al., 2019). Only temporary accommodations were achieved. Although recommendations for further clinical trials were made, no substantial efforts have been made to advance the regulatory framework. Furthermore, if regulations are revised to accommodate phage therapy, questions arise regarding the position of phage product manufacturers on intellectual property rights. Specifically, is it feasible to patent and commercialize naturally occurring biological organisms, or is patentability limited to phage-antibiotic combinations and phage cocktails exhibiting unique antibacterial properties? To cater to the specific needs of individual patients, it may be necessary for phage cocktails to be trademarked and sold as distinct products, or perhaps such cocktails could be designed for subsequent modification to address particular patient requirements (Bhattarai et al., 2018). The lack of a clearly defined, commercially viable pathway for technology development may deter pharmaceutical companies from investing in the research and development of such therapeutics.
Several in-vitro studies have shown that bacterial resistance is increasing day by day against phage therapy. There is a need to find an alternative therapeutic strategy to overcome bacterial resistance (Cao et al., 2015; Kumari et al., 2010; Tabassum et al., 2018). The combinational treatment, either the combination of antibacterial drugs with phages or a cocktail of phages, is a new approach to reducing bacterial resistance. Many researchers are using this new approach for the treatment of phage-resistant strains of K. pneumoniae (Chadha et al., 2016; Verma et al., 2009b; Gu et al., 2012). Chadha et al. observed the efficacy of a single phage in contrast to a phage cocktail in BALB/c mice for the treatment of K. pneumoniae B5055. The results of this showed that a phage cocktail (combination of Kpn1, Kpn2, Kpn3, Kpn4, and Kpn5) reduces the bacterial load in a shorter period as compared to individual phages. Another study confirmed these results by studying the efficacy of a single phage in contrast to a phage cocktail for the reduction of bacterial load. A phage cocktail (a combination of three lytic phages GH-K1, GH-K2, and GH-K3) that have different but overlapping host specificities for the treatment of K. pneumoniae strain K7. The results suggest that the co-culture of the phage cocktail and K7 decreased the production of phage-resistant variants of K7 and reduced the bacterial load as compared to a single phage. Furthermore, the phage cocktail induction in bacteremia mice infected by K7 increases the survival rate of mice and lowers the blood bacterial count as compared to individual phage induction in mice (Gu et al., 2012). Verma et al. explored the new strategy in combination therapy. They used a combination of ciprofloxacin and lytic phages for the treatment of K. pneumoniae biofilms. The authors found that this combination reduced the development of ciprofloxacin-resistant and phage-resistant strains of K. pneumoniae and has a greater effect against biofilms than individual treatments. These studies proved that combination therapy is more effective for the treatment of infectious diseases and for preventing the emergence of bacterial resistance (Verma et al., 2009b).
The use of phages for clinical trials involving humans faced regulatory friction in the West as compared to Eastern Europe and the former Soviet Union, which used phages in healthcare units for many years (Kutter et al., 2010). For example, the Herzfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy in Poland and the Eliava Institute of Bacteriophages, Microbiology, and Virology in Georgia produce and supply phage products for human use (Furfaro et al., 2018). The regulatory friction has slowed the use of phages for human trials. The unique nature of phages as self-replicating and evolving biological entities demands new rules and regulations for their production, safety, and use as compared to traditional therapeutic agents. The lack of these regulations overcomes their advancements as well as pharmaceutical companies also have a lack of interest due to the concept of personalized medicine related to phage therapy. The concept of personalized medicine makes the approval process more difficult and lengthier for human trials (Debarbieux et al., 2016). Despite these challenges, the Belgian government has stated the implementation of a magisterial phage regulatory framework. Pharmacists prepared non-authorized phage products based on physician prescriptions for individual patients. The phages can occasionally be used in Europe under Article 37, the Declaration of Helsinki (Pirnay et al., 2018). The use of phages for human trials has been carried out despite these hurdles. Dutch clinician successfully treated the renal transplant patient with a recurrent urinary tract infection (Gonzalez-Menendez et al., 2018) infected by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) K. pneumoniae with the combination of phages and meropenem. The treatment of meropenem alone failed to treat the infection. The patient got phage therapy from Eliava Institute, and the patient sustained infection-free after the therapy. This result proved that combination therapy was effective (Kuipers et al., 2019). Italian clinicians also successfully used the phage cocktail for the treatment of invasive infections MDR, KPC-3-harboring K. pneumoniae (ST307). Phages are used for the decolonization of bacteria from the gut. Gut decolonization is a critical step to prevent future infection and the growth of resistant bacteria. The results showed that this treatment has no adverse effects (Corbellino et al., 2020). A prospective study related to the use of phage cocktails and phage for the treatment of skin ulcers was performed in India. These ulcers were showing resistance against antibiotics due to bacterial biofilms. However, phages successfully treated the skin ulcer and eradicated the biofilm formation (Patel et al., 2021). These studies demonstrate the potential use of phage therapy for the treatment of resistant bacteria and to overcome the effect of antibiotic resistance. These studies showed that clinical success shows the effectiveness of phage therapy as an alternative approach to antibiotic treatments.
Utilization of phage-derived Peptides instead of whole phage provides another alternative therapy option for multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae. This kind of therapy has the potential to be beneficial as it is more convenient and expeditious to get clinical authorization for the recombinant protein. These phage-derived proteins tend to be utilized in their intact form against MDR bacterial pathogens like K. pneumoniae or as an integral part of a combination strategy to replace or boost existing antibiotics. Phage-derived peptides are formed during the lytic cycle of phage and help in bacteriophage in several functions, such as phage adsorption to the bacterial cell wall, infectivity, replication, and release of phage progeny. There are various antimicrobial peptides against MDR K. pneumoniae that have potent antimicrobial activity (Majkowska-Skrobek et al., 2018). These phage-derived proteins are polysaccharide depolymerase, peptidoglycan hydrolases, and virion-associated lysins. Bacteriophages use endolysins, which are lytic enzymes, at the terminal stage of their multiplication cycle to hydrolyze the peptidoglycan in the bacterial cell wall, resulting in the rapid lysis and the release of their progeny (Matsuzaki et al., 2005).
Phage-derived peptides mostly include peptidoglycan hydrolase enzymes and polysaccharides depolymerases. These proteins act as enzymes and are commonly present in tail spikes and play an important role in effectively infecting bacteria after adsorption. Polysaccharide depolymerase catalyzes the bacterial cell wall's carbohydrates. On the other hand, peptidoglycan hydrolases attack the peptidoglycan layer and its breakdown, breaching the bacterial cell to get entry into the cell cytoplasm, where it deposits its genetic material (Drulis-Kawa et al., 2015). Three types of proteins, namely Spanin, holins, and endolysins, have been synthesized upon bacterial infection that play a critical role in making phage particles and bacterial cell wall lysis to release virions. Holins are hydrophobic and involved in the permeability of the inner cell membrane and make way for the other protein endolysin to attack the cell wall and destroy the peptidoglycan layer. Spanins are commonly involved in the disruption of Gram-negative bacterial cell membranes. Following this lysis, bacterial cell death occurs due to osmolysis.
The capsule is the most significant cause of immune evasion in K. pneumoniae. Therefore, it has been the primary target for recombinant phage protein studies. Tail fibers of phage KP32 have an additional Tail tubular protein A (TTPA) that exhibits the activity of polysaccharide depolymerase (Pyra et al., 2017). An analogous method of cloning, expression, and spot test was performed (Pan et al., 2017). In this study, nine polysaccharide depolymerases have been identified. These were produced by phage ΦK64-1 isolated against K. pneumoniae. Each of these enzymes displayed specific activity in different capsular types with a wide range of hosts. This finding is intriguing since it not only validates the role of enzymes in determining the host specificity of phages. It also supports the concept of recombinant enzymes, which can target various strains of K. pneumoniae. In addition, many in vivo studies have been conducted to examine the impact of polysaccharide depolymerase upon infection of K. pneumoniae. A polysaccharide depolymerase derived from KP36, named depoKP36, was identified, cloned, and expressed in E. coli (Majkowska-Skrobek et al., 2016). This enzyme developed haloes in spot test on the bacterial lawns culture on an agar plate. Furthermore, the efficacy of this enzyme was evaluated in treating infection in G. mellonella. All larvae died with no treatment, while up to 40% lived upon treatment with enzymes after infection. Even when the enzyme was introduced to the bacteria before infection, the mortality rate was only 23%. These findings demonstrate that the decapsulating effect of depoKP36 on K. pneumoniae resulted in a lower ability of K. pneumoniae to deal with the immunological response.
Considerable research has been carried out on endolysins for their potency against Gram-positive bacterial cell walls. This is because Gram-negative bacterial cells, like K. pneumoniae possess an outer membrane, which prevents endolysin activity when spanins are not present. However, some recently conducted studies have also shown positive results on the potency of these enzymes against Gram-negative bacteria. Recombinant endolysin of KP27 (K. pneumoniae phage derived) effectively infects the other gram-negative bacteria as well. The findings indicate that in order to effectively tackle K. pneumoniae, therapies based on endolysin have to be complemented by an outer membrane permeabilizing compound (Majkowska-Skrobek et al., 2016).
Artilysin or Synthetic lysins were created by combining a phage endolysin and an outer-membrane-destabilizing peptide to address the demand for extra outer membrane permeabilizing agents for the management of Gram-negative bacteria infections (Briers et al., 2014b). Although artilysins targeted precisely for K. pneumoniae are yet to be identified, they have been effectively produced for the treatment of P. aeruginosa infections (Briers et al., 2014a) and Acinetobacter baumannii infections (Defraine et al., 2016). This method enables the invention of synthetic endolysins for human use against both multidrug-resistant gram-negative species and K. pneumoniae.
In comparison to other antibacterial agents that include antibiotics, phages can exhibit a wider range of modes of action and, in many situations, are safer. Because of their prevalence and our frequent exposure to them in the environment (Sulakvelidze et al., 2001), phages are generally regarded as safe, and they have been employed widely in some parts of the world with no reports of negative effects (Pirnay et al., 2011). Despite this hopeful outlook, the safety of phage therapy must be confirmed by sophisticated scientific investigations. One of the primary hurdles for phage therapy is the novel safety implications of using self-replicating biological organisms in humans. For instance, toxin encoding and antibiotic-resistant genes carried by the phages can be transferred to the other bacteria through the transduction process (Colavecchio et al., 2017; Abedon, 2018). The proper screening of the potentially dangerous genes is done throughout the process when investigating the phages for therapeutic purposes. Phages containing hazardous products can be purified during the formulation process. Bacteriophages, especially phage cocktails, have little effect on the commensal microbiota because of their high specificity toward the bacteria, and they only infect a small number of specific bacterial species. The possibility of phages encoding harmful genes can be prevented by avoiding the usage of temperate phages. Another obstacle for phage therapy is figuring out how to capitalize on these beneficial characteristics in light of current regulatory standards, as well as how phages can fit into the current economic frameworks that support the distribution and usage of antibacterial drugs (Townsend et al., 2021). To present, just a few clinical trials have been conducted, in all these studies, no major adverse effects were seen.
An inherent challenge in phage treatment is the safety concerns related to the application of self-replicating biological organisms in human beings. As an example, it is clear that phages can transport AMR genes (Colavecchio et al., 2017) and toxins encoding genes (Strauch et al., 2001) from one bacterium to another through a process known as transduction. Achieving accurate characterization is crucial when evaluating phages for uses in therapy, and the detection of potentially deleterious genes can frequently be tracked throughout this procedure. Nevertheless, the lack of detrimental genes do not ensure the safety and reliability of phage.
The inherent characteristic of a lytic bacteriophage is to proliferate itself by infecting bacterial cells. Although the main objective of phage treatment is to achieve this, little investigation has been carried out on the possible negative impact of this behavior. A key aspect to consider is that phages targeting a wide variety of hosts, or those seen in a phage cocktail, frequently qualify as more suitable for phage treatment. The latest study demonstrates that the introduction of a monophage therapy in mouse microbiota could indeed disrupt the composition of the microbiome (Hsu et al., 2019). How much of an effect would the treatment usage of phages likely have on the indigenous microbiota of human beings? Does using mono phages therapy, with a limited host range, provide a safer approach for mitigating disturbance of the microbiome? If such is the case, phage therapy will depend on the very precise identification of the targeted bacteria and the availability of the appropriate phage for treatment. On the other hand, this specific adverse reaction may be considered tolerable, comparable to the situation with present antibiotic therapies. Furthermore, there is a lack of clinical studies that have evaluated the safety of phage treatment in human beings. In addition, the existing studies have been characterized by restricted numbers of participants and have often depended on data supplied by patients (Furfaro et al., 2018).
Emerging advancements in recombinant enzyme technology have shown promising alternative therapeutic options against resistant strains of K. pneumoniae. The capsular degradation is the most critical by polysaccharide depolymerase, making these enzymes a potent therapeutic agent against K. pneumoniae and its associated biofilms. Synthetic endolysins can function as autonomous antimicrobial agents against infections. Continued investigation is necessary in this field to fully understand the capabilities of phage-derived recombinant proteins in harnessing bacterial infections. One more perspective to be covered in the future is to investigate the methods by which these proteins reduce bacterial growth and eradicate infection. This will significantly enhance the potential of this endolysin. One significant benefit of engineered proteins for human use is the presence of clearly defined and established norms and regulations in Europe and the UK that cover their manufacturing, safety, and implementation rules. On the other hand, whole phage therapy lacks such standard protocols.
The growing rate of infections from hospitals and communities produced by multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae is swiftly emerging as a public health threat globally. Along with MDR strains of K. pneumoniae, the emergence of hypervirulent strains is also a worldwide issue. K. pneumoniae has become an important concern over its non-resistant analogs of today are more than a century old. In reaction, research endeavors have started to investigate a previously neglected method of treating bacterial infections, namely bacteriophage treatment. It is becoming very evident that bacteriophages and their proteins have potential therapeutic effects against these MDR strains and can be used as an alternative approach over conventional antibiotics toward which pathogens become resistant. Nevertheless, the arena of phage treatment is still in its early stages and is limited to challenges. But there is still hope for some innovative approach can be recognized to overcome these obstacles.
SA: Writing – original draft. RKanwar: Writing – original draft. KU: Writing – original draft. RKanwal: Writing – original draft. MT: Writing – original draft. MA: Writing – review & editing. AA: Writing – original draft. AQ: Writing – review & editing. H-YH: Writing – review & editing. C-CC: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
β-lactamase, Beta lactamase; blaGES, Guiana Extended Spectrum (GES) β-lactamases; blaVEB, Vietnamese Extended-Spectrum Beta-lactamase; blaTEM-3, beta-lactamase temoniera; blaSHV-1, Beta lactamase sulfhydryl variable-1 CPS, Capsule Polysaccharide; CTX-M, Cefotaximase-Munich DC, Dendritic Cell; dsRNA, Double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; ESKAPE, Enterococcus faecium; Staphylococcus aureus; gyrA, DNA gyrase subunit A; gyrB, DNA gyrase subunit B; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Acinetobacter baumannii; Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter; ESBL, Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases; EPS, Extracellular polymeric substances; K. pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae; KdeA, Klebsiella drug efflux; LPS, Lipopolysaccharide; lpxM, lipid X monophosphate; MDR, Multidrug-resistant; MRC1, Mannose Receptor C-Type 1; mgrB, microcin resistance gene B NDM, New Delhi metallo beta lactamase; OmpK36, outer membrane protein of Klebsiella; pmrC, phosphoethanolamine transferase C; ramA, resistance antibiotic multiple pbgP, Porphobilinogen deaminase gene pmrE, Polymyxin-Resistance Genes; parC, Topoisomerase IV subunit C; parE, Topoisomerase IV subunit E; pmrA, polymyxin resistance and lipid A; pmrD, Polymyxin B resistance protein D; Qnr, Quinolone resistance; RamA, resistance antibiotic multiple A; ssDNA, Single stranded deoxyribonucleic acid; ssRNA, Single stranded ribonucleic acid; sul1, sulfonamide resistance gene 1; sul2, sulfonamide resistance gene 2; sul3, sulfonamide resistance gene 3; tetA, Tetracycline resistance protein; class E; VIM, Verona Integron-encoded Metallo-β-lactamase.
Abdelrahman, F., Easwaran, M., Daramola, O. I., Ragab, S., Lynch, S., Oduselu, T. J., et al. (2021). Phage-encoded endolysins. Antibiotics 10:124. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10020124
Abedon, S. T. (2018). “Bacteriophage clinical use as antibacterial “drugs”: utility and precedent,” in Bugs as Drugs: Therapeutic Microbes for the Prevention and Treatment of Disease, eds R. A. Britton and P. B. Vadivaloo (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley_Blackwell), 417–451. doi: 10.1128/9781555819705.ch19
Alfei, S., and Schito, A. M. (2022). β-lactam antibiotics and β-lactamase enzymes inhibitors, part 2: our limited resources. Pharmaceuticals 15:476. doi: 10.3390/ph15040476
Ali, S., Alam, M., Hasan, G. M., and Hassan, M. I. (2022). Potential therapeutic targets of Klebsiella pneumoniae: a multi-omics review perspective. Brief. Funct. Genomics 21, 63–77. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elab038
Al-Ishaq, R. K., Skariah, S., and Büsselberg, D. (2020). Bacteriophage treatment: critical evaluation of its application on World Health Organization priority pathogens. Viruses 13:51. doi: 10.3390/v13010051
Amraei, S., Eslami, G., Taherpour, A., and Hashemi, A. (2022). Relationship between MOX genes and antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains in nosocomial infections. Micro Nano Bio. Aspects 1, 12–17. doi: 10.22034/mnba.2022.155320
Anand, T., Virmani, N., Kumar, S., Mohanty, A.K., Pavulraj, S., Bera, B. C., et al. (2020). Phage therapy for treatment of virulent Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in a mouse model. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Res. 21, 34–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2019.09.018
Aslan, A. T., and Akova, M. (2022). The role of colistin in the era of new β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations. Antibiotics 11:277. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020277
Ballén, V., Gabasa, Y., Ratia, C., Ortega, R., Tejero, M., and Soto, S. (2021). Antibiotic resistance and virulence profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from different clinical sources. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:738223. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.738223
Belay, M., Sisay, T., and Wolde, T. (2018). Bacteriophages and phage products: applications in medicine and biotechnological industries, and general concerns. Sci. Res. Essays 13, 55–70. doi: 10.5897/SRE2017.6546
Bertozzi Silva, J., Storms, Z., and Sauvageau, D. (2016). Host receptors for bacteriophage adsorption. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 363:fnw002. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnw002
Bhattarai, Y., Williams, B. B., Battaglioli, E. J., Whitaker, W. R., Till, L., Grover, M., et al. (2018). Gut microbiota-produced tryptamine activates an epithelial G-protein-coupled receptor to increase colonic secretion. Cell Host Microbe 23, 775–785. e775. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.05.004
Bird, J. T., Burke, K. A., Urick, C. D., Braverman, J. L., Mzhavia, N., Ellison, D. W., et al. (2024). Genome sequence of the Klebsiella quasipneumoniae bacteriophage EKq1 with activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Resour. Announce. 13, e00954–e00923. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00954-23
Boyd, S. E., Livermore, D. M., Hooper, D. C., and Hope, W. W. (2020). Metallo-β-lactamases: structure, function, epidemiology, treatment options, and the development pipeline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64, e00397–e00420. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00397-20
Briers, Y., Walmagh, M., Grymonprez, B., Biebl, M., Pirnay, J. P., Defraine, V., et al. (2014a). Art-175 is a highly efficient antibacterial against multidrug-resistant strains and persisters of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 3774–3784. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02668-14
Briers, Y., Walmagh, M., Van Puyenbroeck, V., Cornelissen, A., Cenens, W., Aertsen, A., et al. (2014b). Engineered endolysin-based “Artilysins” to combat multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens. mBio 5, e01379–e01314. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01379-14
Bush, N. G., Diez-Santos, I., Abbott, L. R., and Maxwell, A. (2020). Quinolones: mechanism, lethality and their contributions to antibiotic resistance. Molecules 25:5662. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235662
Cao, F., Wang, X., Wang, L., Li, Z., Che, J., Wang, L., et al. (2015). Evaluation of the efficacy of a bacteriophage in the treatment of pneumonia induced by multidrug resistance Klebsiella pneumoniae in mice. BioMed Res. Int. 2015:752930. doi: 10.1155/2015/752930
Cao, Z., Sugimura, N., Burgermeister, E., Ebert, M.P., Zuo, T., and Lan, P. (2022). The gut virome: a new microbiome component in health and disease. EBioMed. 81:104113. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104113
Chadha, P., Katare, O. P., and Chhibber, S. (2016). In vivo efficacy of single phage versus phage cocktail in resolving burn wound infection in BALB/c mice. Microb. Pathogen. 99, 68–77. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.08.001
Chadha, P., Katare, O. P., and Chhibber, S. (2017). Liposome loaded phage cocktail: enhanced therapeutic potential in resolving Klebsiella pneumoniae mediated burn wound infections. Burns 43, 1532–1543. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2017.03.029
Chan, B. K., Abedon, S. T., and Loc-Carrillo, C. (2013). Phage cocktails and the future of phage therapy. Future Microbiol. 8, 769–783. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.47
Chan, B. K., Turner, P. E., Kim, S., Mojibian, H. R., Elefteriades, J. A., and Narayan, D. (2018). Phage treatment of an aortic graft infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Evol. Med. Pub. Health 2018, 60–66. doi: 10.1093/emph/eoy005
Chhibber, S., Kaur, S., and Kumari, S. (2008). Therapeutic potential of bacteriophage in treating Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-mediated lobar pneumonia in mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 57, 1508–1513. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.2008/002873-0
Choby, J., Howard-Anderson, J., and Weiss, D. S. (2020). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae- clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 287, 283–300. doi: 10.1111/joim.13007
Colavecchio, A., Cadieux, B., Lo, A., and Goodridge, L. D. (2017). Bacteriophages contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance genes among foodborne pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae family-a review. Front. Microbiol. 8:271343. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01108
Corbellino, M., Kieffer, N., Kutateladze, M., Balarjishvili, N., Leshkasheli, L., Askilashvili, L., et al. (2020). Eradication of a multidrug-resistant, carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate following oral and intra-rectal therapy with a custom made, lytic bacteriophage preparation. Clin. Infect Dis. 70, 1998–2001. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz782
Czaplewski, L., Bax, R., Clokie, M., Dawson, M., Fairhead, H., Fischetti, V. A., et al. (2016). Alternatives to antibiotics-a pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 16, 239–251. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00466-1
Dalmolin, T. V., de Lima-Morales, D., and Barth, A. L. (2018). Plasmid-mediated colistin resistance: what do we know? J. Infectiol. Epidemiol. 1, 16–22. doi: 10.29245/2689-9981/2018/2.1109
D'Andrea, M. M., Marmo, P., Henrici De Angelis, L., Palmieri, M., Ciacci, N., Di Lallo, G., et al. (2017). ϕBO1E, a newly discovered lytic bacteriophage targeting carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of the pandemic clonal group 258 clade II lineage. Sci. Rep. 7:2614. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02788-9
De Angelis, G., Del Giacomo, P., Posteraro, B., Sanguinetti, M., and Tumbarello, M. (2020). Molecular mechanisms, epidemiology, and clinical importance of β-lactam resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:5090. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145090
Debarbieux, L., Pirnay, J.-P., Verbeken, G., De Vos, D., Merabishvili, M., Huys, I., et al. (2016). A bacteriophage journey at the European medicines agency. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 363:fnv225. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv225
Defraine, V., Schuermans, J., Grymonprez, B., Govers, S. K., Aertsen, A., Fauvart, M., et al. (2016). Efficacy of artilysin art-175 against resistant and persistent Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 60, 3480–3488. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00285-16
Drulis-Kawa, Z., Majkowska-Skrobek, G., and Maciejewska, B. (2015). Bacteriophages and phage-derived proteins—application approaches. Curr Med Chem 22, 1757–1773. doi: 10.2174/0929867322666150209152851
Duarte, J., Máximo, C., Costa, P., Oliveira, V., Gomes, N. C., Romalde, J. L., et al. (2024). Potential of an isolated bacteriophage to inactivate Klebsiella pneumoniae: preliminary studies to control urinary tract infections. Antibiotics 13:195. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13020195
Eskenazi, A., Lood, C., Wubbolts, J., Hites, M., Balarjishvili, N., Leshkasheli, L., et al. (2022). Combination of pre-adapted bacteriophage therapy and antibiotics for treatment of fracture-related infection due to pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Commun. 13:302. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27656-z
Fang, Q., and Zong, Z. (2022). Lytic phages against ST11 K47 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and the corresponding phage resistance mechanisms. Msphere 7, e00080–e00022. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00080-22
Fayez, M. S., Hakim, T. A., Agwa, M. M., Abdelmoteleb, M., Aly, R. G., Montaser, N. N., et al. (2021). Topically applied bacteriophage to control multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infected wound in a rat model. Antibiotics 10:1048. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10091048
Fokine, A., and Rossmann, M. G. (2014). Molecular architecture of tailed double-stranded DNA phages. Bacteriophage 4:e28281. doi: 10.4161/bact.28281
Furfaro, L. L., Payne, M. S., and Chang, B. J. (2018). Bacteriophage therapy: clinical trials and regulatory hurdles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:376. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00376
Gonzalez-Menendez, E., Fernandez, L., Gutierrez, D., Rodriguez, A., Martinez, B., and Garcia, P. (2018). Comparative analysis of different preservation techniques for the storage of Staphylococcus phages aimed for the industrial development of phage-based antimicrobial products. PLoS ONE 13:e0205728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205728
Gu, J., Liu, X., Li, Y., Han, W., Lei, L., Yang, Y., et al. (2012). A method for generation phage cocktail with great therapeutic potential. PLoS ONE 7:e31698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031698
Guillard, T., de Jong, A., Limelette, A., Lebreil, A., Madoux, J., De Champs, C., et al. (2016). Characterization of quinolone resistance mechanisms in Enterobacteriaceae recovered from diseased companion animals in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 194, 23–29. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.11.033
Habibinava, F., Soleimani, M., Sabouri, S., Zargar, M., and Zolfaghari, M. R. (2022). Isolating and sequencing vB_Kpn_3, a lytic bacteriophage against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 17, 235–249. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2020-0272
Harper, D. R. (2018). Criteria for selecting suitable infectious diseases for phage therapy. Viruses 10:177. doi: 10.3390/v10040177
Hesse, S., Malachowa, N., Porter, A.R., Freedman, B., Kobayashi, S.D., Gardner, D. J., et al. (2021). Bacteriophage treatment rescues mice infected with multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST258. MBio 12, e00034–e00121. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00034-21
Hoenes, K., Bauer, R., Meurle, T., Spellerberg, B., and Hessling, M. (2021). Inactivation effect of violet and blue light on ESKAPE pathogens and closely related non-pathogenic bacterial species-a promising tool against antibiotic-sensitive and antibiotic-resistant microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 11:612367. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.612367
Holt, K. E., Wertheim, H., Zadoks, R. N., Baker, S., Whitehouse, C. A., Dance, D., et al. (2015). Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, E3574–E3581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501049112
Hsu, B. B., Gibson, T. E., Yeliseyev, V., Liu, Q., Lyon, L., Bry, L., et al. (2019). Dynamic modulation of the gut microbiota and metabolome by bacteriophages in a mouse model. Cell Host Microbe 25, 803–814. e805. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.05.001
Hughes, K. A., Sutherland, I., Clark, J., and Jones, M. (1998). Bacteriophage and associated polysaccharide depolymerases-novel tools for study of bacterial biofilms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 85, 583–590. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.853541.x
Hung, C.-H., Kuo, C.-F., Wang, C.-H., Wu, C.-M., and Tsao, N. (2011). Experimental phage therapy in treating Klebsiella pneumoniae-mediated liver abscesses and bacteremia in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 1358–1365. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01123-10
Hussain, H. I., Aqib, A. I., Seleem, M. N., Shabbir, M. A., Hao, H., Iqbal, Z., et al. (2021). Genetic basis of molecular mechanisms in β-lactam resistant gram-negative bacteria. Microb. Pathogen. 158:105040. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105040
Jamal, M., Hussain, T., Das, C. R., and Andleeb, S. (2015). Characterization of Siphoviridae phage Z and studying its efficacy against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae planktonic cells and biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 64, 454–462. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000040
Jault, P., Leclerc, T., Jennes, S., Pirnay, J. P., Que, Y.-A., Resch, G., et al. (2019). Efficacy and tolerability of a cocktail of bacteriophages to treat burn wounds infected by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PhagoBurn): a randomised, controlled, double-blind phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 19, 35–45. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30482-1
Jian, Z., Zeng, L., Xu, T., Sun, S., Yan, S., Yang, L., et al. (2021). Antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria: occurrence, spread, and control. J. Basic Microbiol. 61, 1049–1070. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100201
Kalali, N., Kadkhoda, Z., Amid, R., Ghourchian, S., and Douraghi, M. (2022). Identification of oral anaerobic bacteria and the beta-lactamase resistance genes from Iranian patients with periodontitis. Anaerobe 75:102515. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2022.102515
Kesik-Szeloch, A., Drulis-Kawa, Z., Weber-Dabrowska, B., Kassner, J., Majkowska-Skrobek, G., Augustyniak, D., et al. (2013). Characterising the biology of novel lytic bacteriophages infecting multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Virol. J. 10, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-100
Komijani, M., Bouzari, M., and Rahimi, F. (2017). Detection and characterization of a novel lytic bacteriophage (vB-KpneM-Isf48) against Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from infected wounds carrying antibiotic-resistance genes (TEM, SHV, and CTX-M). Iran. Red. Crescent Med. J. 19:e34475. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.34475
Krause, K. M., Serio, A. W., Kane, T. R., and Connolly, L. E. (2016). Aminoglycosides: an overview. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Med. 6:a027029. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027029
Kuipers, S., Ruth, M. M., Mientjes, M., de Sévaux, R. G. L., and van Ingen, J. (2019). A Dutch case report of successful treatment of chronic relapsing urinary tract infection with bacteriophages in a renal transplant patient. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64, e01281–e01319. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01281-19
Kumar, S., Harja, K., and Chhibber, S. (2010). Evidence to support the therapeutic potential of bacteriophage Kpn5 in burn wound infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in BALB/c mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 935–941. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0909.09010
Kumari, S., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2009). Efficacy of bacteriophage treatment in murine burn wound infection induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 19, 622–628. doi: 10.4014/jmb.0808.493
Kumari, S., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2010). Isolation and characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae specific bacteriophages from sewage samples. Folia Microbiol. 55, 221–227. doi: 10.1007/s12223-010-0032-7
Kumari, S., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2011). Bacteriophage versus antimicrobial agents for the treatment of murine burn wound infection caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055. J. Med. Microbiol. 60, 205–210. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.018580-0
Kunhikannan, S., Thomas, C. J., Franks, A. E., Mahadevaiah, S., Kumar, S., and Petrovski, S. (2021). Environmental hotspots for antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiol. Open 10:e1197. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1197
Kutter, E., De Vos, D., Gvasalia, G., Alavidze, Z., Gogokhia, L., Kuhl, S., et al. (2010). Phage therapy in clinical practice: treatment of human infections. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 11, 69–86. doi: 10.2174/138920110790725401
Lee, C.-R., Lee, J. H., Park, K. S., Kim, Y. B., Jeong, B. C., and Lee, S. H. (2016). Global dissemination of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: epidemiology, genetic context, treatment options, and detection methods. Front. Microbiol. 7:184902. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00895
Li, J., Yan, B., He, B., Li, L., Zhou, X., Wu, N., et al. (2023). Development of phage resistance in multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with reduced virulence: a case report of a personalised phage therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 29, 1601. e1601–1601. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.08.022
Li, P., Shen, K., Zhang, Y., Ying, J., Zhu, T., Liu, Y., et al. (2018). Characterization of a novel bla KLUC variant with reduced β-lactam resistance from an IncA/C group plasmid in a clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate. Front. Microbiol. 9:1908. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01908
Llobet, E., Martínez-Moliner, V., Moranta, D., Dahlström, K. M., Regueiro, V., Tomás, A., et al. (2015). Deciphering tissue-induced Klebsiella pneumoniae lipid A structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, E6369–E6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508820112
Loc-Carrillo, C., and Abedon, S.T. (2011). Pros and cons of phage therapy. Bacteriophage 1, 111–114. doi: 10.4161/bact.1.2.14590
Lomovskaya, O., Rubio-Aparicio, D., Tsivkovski, R., Loutit, J., and Dudley, M. (2022). The ultrabroad-spectrum beta-lactamase inhibitor QPX7728 restores the potency of multiple oral beta-lactam antibiotics against beta-lactamase-producing strains of resistant Enterobacterales. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 66, e02168–e02121. doi: 10.1128/aac.02168-21
Lv, F., Cai, J., He, Q., Wang, W., Luo, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Overexpression of efflux pumps mediate pan resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 11. Microb. Drug Resist. 27, 1405–1411. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0395
Maebed, A. Z. M., Gaber, Y., Bakeer, W., and Dishisha, T. (2021). Microbial etiologies of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) in intensive care unit of Beni-Suef University's Hospital. Beni-Suef Uni. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 10, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s43088-021-00130-x
Majkowska-Skrobek, G., Łatka, A., Berisio, R., Maciejewska, B., Squeglia, F., Romano, M., et al. (2016). Capsule-targeting depolymerase, derived from Klebsiella KP36 phage, as a tool for the development of anti-virulent strategy. Viruses 8:324. doi: 10.3390/v8120324
Majkowska-Skrobek, G., Latka, A., Berisio, R., Squeglia, F., Maciejewska, B., Briers, Y., et al. (2018). Phage-borne depolymerases decrease Klebsiella pneumoniae resistance to innate defense mechanisms. Front Microbiol 9:2517. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02517
Malik, R., and Chhibber, S. (2009). Protection with bacteriophage KØ1 against fatal Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced burn wound infection in mice. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 42, 134–140.
Manohar, P., Nachimuthu, R., and Lopes, B. S. (2018). The therapeutic potential of bacteriophages targeting gram-negative bacteria using Galleria mellonella infection model. BMC Microbiol. 18 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1234-4
Martins, W. M., Li, M., Sands, K., Lenzi, M. H., Portal, E., Mathias, J., et al. (2022). Effective phage cocktail to combat the rising incidence of extensively drug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 16. Emerg. Micro. Infect. 11, 1015–1023. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2051752
Matsuzaki, S., Rashel, M., Uchiyama, J., Sakurai, S., Ujihara, T., Kuroda, M., et al. (2005). Bacteriophage therapy: a revitalized therapy against bacterial infectious diseases. J. Infect. Chemother. 11, 211–219. doi: 10.1007/s10156-005-0408-9
Mohammadi, M., Saffari, M., and Siadat, S. D. (2023a). Phage therapy of antibiotic-resistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae, opportunities and challenges from the past to the future. Folia Microbiol. 68, 357–368. doi: 10.1007/s12223-023-01046-y
Mohammadi, M., Saffari, M., Siadat, S. D., Hejazi, S. H., Shayestehpour, M., Motallebi, M., et al. (2023b). Isolation, characterization, therapeutic potency, and genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage vB_KshKPC-M against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains (CRKP) isolated from ventilator-associated pneumoniae (VAP) infection of COVID-19 patients. Ann. Clini. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 22:18. doi: 10.1186/s12941-023-00567-1
Moya, C., and Maicas, S. (2020). Antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains: mechanisms and outbreaks. Proceedings. 66:11. doi: 10.3390/proceedings2020066011
Mulani, M. S., Kumkar, S. N., and Pardesi, K. R. (2022). Characterization of novel Klebsiella phage PG14 and its antibiofilm efficacy. Microbiol. Spect. 10, e01994–e01922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01994-22
Naeem, A., Badshah, S. L., Muska, M., Ahmad, N., and Khan, K. (2016). The current case of quinolones: synthetic approaches and antibacterial activity. Molecules 21:268. doi: 10.3390/molecules21040268
Nam, Y. S., Cho, S. Y., Yang, H. Y., Park, K. S., Jang, J.-H., Kim, Y.-T., et al. (2013). Investigation of mutation distribution in DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV genes in ciprofloxacin-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae isolated from blood cultures in a tertiary care university hospital in South Korea, 2005–2010. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 41, 126–129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.10.004
Navon-Venezia, S., Kondratyeva, K., and Carattoli, A. (2017). Klebsiella pneumoniae: a major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41, 252–275. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux013
Osei Sekyere, J., Govinden, U., Bester, L., and Essack, S. (2016). Colistin and tigecycline resistance in carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacteria: emerging resistance mechanisms and detection methods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 121, 601–617. doi: 10.1111/jam.13169
Paczosa, M. K., and Mecsas, J. (2016). Klebsiella pneumoniae: going on the offense with a strong defense. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 80, 629–661. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00078-15
Padilla, E., Llobet, E., Doménech-Sánchez, A., Martínez-Martínez, L., Bengoechea, J. A., and Albertí, S. (2010). Klebsiella pneumoniae AcrAB efflux pump contributes to antimicrobial resistance and virulence. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 177–183. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00715-09
Pan, Y. J., Lin, T. L., Chen, C. C., Tsai, Y. T., Cheng, Y. H., Chen, Y. Y., et al. (2017). Klebsiella phage ΦK64-1 encodes multiple depolymerases for multiple host capsular types. J. Virol. 91, e02457–16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02457-16
Patel, D. R., Bhartiya, S. K., Kumar, R., Shukla, V. K., and Nath, G. (2021). Use of customized bacteriophages in the treatment of chronic nonhealing wounds: a prospective study. Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 20, 37–46. doi: 10.1177/1534734619881076
Peirano, G., Ahmed-Bentley, J., Fuller, J., Rubin, J. E., and Pitout, J. D. (2014). Travel-related carbapenemase-producing gram-negative bacteria in Alberta, Canada: the first 3 years. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52, 1575–1581. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00162-14
Pirnay, J.-P., Blasdel, B. G., Bretaudeau, L., Buckling, A., Chanishvili, N., Clark, J.R., et al. (2015). Quality and safety requirements for sustainable phage therapy products. Pharma. Res. 32, 2173–2179. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1617-7
Pirnay, J.-P., De Vos, D., Verbeken, G., Merabishvili, M., Chanishvili, N., Vaneechoutte, M., et al. (2011). The phage therapy paradigm: prêt-à-porter or sur-mesure? Pharm. Res. 28, 934–937. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0313-5
Pirnay, J. P., Verbeken, G., Ceyssens, P. J., Huys, I., De Vos, D., Ameloot, C., et al. (2018). The magistral phage. Viruses 10:64. doi: 10.3390/v10020064
Pyra, A., Brzozowska, E., Pawlik, K., Gamian, A., Dauter, M., and Dauter, Z. (2017). Tail tubular protein A: a dual-function tail protein of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage KP32. Sci. Rep. 7:2223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02451-3
Santajit, S., and Indrawattana, N. (2016). Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in ESKAPE pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016:2475067. doi: 10.1155/2016/2475067
Sawa, T., Kooguchi, K., and Moriyama, K. (2020). Molecular diversity of extended-spectrum β-lactamases and carbapenemases, and antimicrobial resistance. J. Intensive Care 8:13. doi: 10.1186/s40560-020-0429-6
Sethuvel, D. P. M., Bakthavatchalam, Y. D., Karthik, M., Irulappan, M., Shrivastava, R., Periasamy, H., et al. (2023). β-lactam resistance in ESKAPE pathogens mediated through modifications in penicillin-binding proteins: an overview. Inf. Dis. Ther. 12, 829–841. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00771-8
Shahzad, S., Willcox, M. D., and Rayamajhee, B. (2023). A review of resistance to polymyxins and evolving mobile colistin resistance gene (MCR) among pathogens of clinical significance. Antibiotics 12:1597. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111597
Shi, Y., Chen, Y., Yang, Z., Zhang, Y., You, B., Liu, X., et al. (2020). Characterization and genome sequencing of a novel T7-like lytic phage, kpssk3, infecting carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Virol. 165, 97–104. doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04447-y
Singla, S., Harjai, K., Katare, O. P., and Chhibber, S. (2015). Bacteriophage-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier: improved pharmacokinetics mediates effective resolution of Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced lobar pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 212, 325–334. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv029
Strauch, E., Lurz, R., and Beutin, L. (2001). Characterization of a Shiga toxin-encoding temperate bacteriophage of Shigella sonnei. Infect. Immun. 69, 7588–7595. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.12.7588-7595.2001
Sulakvelidze, A., Alavidze, Z., and Morris Jr, J. G. (2001). Bacteriophage therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 649–659. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.3.649-659.2001
Tabassum, R., Shafique, M., Khawaja, K. A., Alvi, I. A., Rehman, Y., Sheik, C. S., et al. (2018). Complete genome analysis of a Siphoviridae phage TSK1 showing biofilm removal potential against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 8:17904. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36229-y
Tacconelli, E. (2017). Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development. WHO.
Taha, O. A., Connerton, P. L., Connerton, I. F., and El-Shibiny, A. (2018). Bacteriophage ZCKP1: a potential treatment for Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from diabetic foot patients. Front. Microbiol. 9:2127. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02127
Tang, K., and Zhao, H. (2023). Quinolone antibiotics: resistance and therapy. Infect. Drug Resist. 16, 811–820. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S401663
Torabi, L. R., Naghavi, N. S., Doudi, M., and Monajemi, R. (2021). Efficacious antibacterial potency of novel bacteriophages against ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from burn wound infections. Iran. J. Microbiol. 13:678. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v13i5.7435
Townsend, E. M., Kelly, L., Gannon, L., Muscatt, G., Dunstan, R., Michniewski, S., et al. (2021). Isolation and characterization of Klebsiella phages for phage therapy. Ther. Appl. Res. 2, 26–42. doi: 10.1089/phage.2020.0046
Verma, V., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2009a). Characterization of a T7-like lytic bacteriophage of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055: a potential therapeutic agent. Curr. Microbiol. 59, 274–281. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9430-y
Verma, V., Harjai, K., and Chhibber, S. (2009b). Restricting ciprofloxacin-induced resistant variant formation in biofilm of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055 by complementary bacteriophage treatment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 64, 1212–1218. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp360
Viertel, T. M., Ritter, K., and Horz, H.-P. (2014). Viruses versus bacteria-novel approaches to phage therapy as a tool against multidrug-resistant pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69, 2326–2336. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku173
Vinodkumar, C., Neelagund, Y., and Kalsurmath, S. (2005). Bacteriophage in the treatment of experimental septicemic mice from a clinical isolate of multidrug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Commun. Dis. 37, 18–29.
Wang, G., Zhao, G., Chao, X., Xie, L., and Wang, H. (2020). The characteristic of virulence, biofilm and antibiotic resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health 17:6278. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176278
Wei, H., Liu, X., Pang, X., and Ma, N. (2024). Phage: tackling drug-resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4713374 (accessed February 5, 2024).
Wu, Y., Wang, R., Xu, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X., Qiu, J., et al. (2019). A novel polysaccharide depolymerase encoded by the phage SH-KP152226 confers specific activity against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae via biofilm degradation. Front. Microbiol. 10:2768. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02768
Xu, T., Wu, X., Cao, H., Pei, T., Zhou, Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2022). The characteristics of multilocus sequence typing, virulence genes and drug resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from cattle in Northern Jiangsu, China. Animals 12:2627. doi: 10.3390/ani12192627
Yan, Q., Zhou, M., Zou, M., and Liu, W.-E. (2016). Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae induced ventilator-associated pneumonia in mechanically ventilated patients in China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 35, 387–396. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2551-2
Yosef, I., Goren, M. G., Globus, R., Molshanski-Mor, S., and Qimron, U. (2017). Extending the host range of bacteriophage particles for DNA transduction. Mol. Cell 66, 721–728. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.025
Zaki, B. M., Fahmy, N. A., Aziz, R. K., Samir, R., and El-Shibiny, A. (2023). Characterization and comprehensive genome analysis of novel bacteriophage, vB_Kpn_ZCKp20p, with lytic and anti-biofilm potential against clinical multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13:1077995. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1077995
Zhu, Y., Huang, W. E., and Yang, Q. (2022). Clinical perspective of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Infect. Drug Resist. 15, 735–746. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S345574
Zhuang, M., Achmon, Y., Cao, Y., Liang, X., Chen, L., Wang, H., et al. (2021). Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 285:117402. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117402
Keywords: K. pneumoniae, antibiotic resistance, bacteriophages, phage therapy, endolysins
Citation: Abbas S, Kanwar R, Ullah K, Kanwal R, Tajamal M, Aslam MA, Ahmad A, Qadeer A, Huang H-Y and Chen C-C (2025) Bacteriophage therapy: a possible alternative therapy against antibiotic-resistant strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 16:1443430. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1443430
Received: 04 June 2024; Accepted: 07 March 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Sevcan Aydin, Istanbul University, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Puey Ounjai, Mahidol University, ThailandCopyright © 2025 Abbas, Kanwar, Ullah, Kanwal, Tajamal, Aslam, Ahmad, Qadeer, Huang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muhammad Aamir Aslam, YWFtaXIuYXNsYW1AdWFmLmVkdS5waw==; Abdul Qadeer, cWFkZWVya3RrODQ4QHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Hsun-Yu Huang, Y3ljaDA3MTE0QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==; Chien-Chin Chen, aGxtYXJrY0BnbWFpbC5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.