- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Guangxi University, Nanning, China
- 2College of Animal Science and Technology, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China
The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) is widely present in mammalian bodies, showing high affinity for various exogenous substances such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and coumarin. Under physiological conditions, AhR mainly participates in regulating the body’s immune response, cell proliferation, and apoptosis among a series of processes. Recent studies have revealed a close connection between AhR and lipid metabolism. The gut microbiota plays a significant role in regulating host lipid metabolism. Growing evidence suggests an inseparable link between gut microbiota and AhR signaling. This review summarizes the relationship between AhR and lipid metabolism disorders, as well as the interaction between gut microbiota and AhR, exploring how this interaction modulates host lipid metabolism.
Introduction
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-dependent transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the regulatory network of the interaction between gut microbiota and the host (Hornedo-Ortega et al., 2018). Evidence suggested that AhR plays an important role in regulating metabolites involved in many biochemical pathways affecting biosynthesis and metabolism of fatty acids, bile acids, gut microbiome products, antioxidants, choline derivatives, and uremic toxins, with a central role in metabolism and signaling between multiple organs and across multiple scales (Granados et al., 2022). It was initially identified as a receptor that binds to environmental pollutant dioxins, primarily involved in detoxification and metabolic processes of dioxins and their analogs. Recent research has shown that the functions of AhR were much broader than previously understood. Further studies have shown that activating AhR influenced the differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis of fat cells, regulating fat production (Kwack and Lee, 2000). Importantly, AhR sensed the ligands from diet, gut microbiota and host metabolites to regulate the host’s physiological functions by triggering a series of signal transduction processes. For example, Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage can be converted into AhR ligand precursors, indole-3-carbinol (I3C) and indole-3-acetonitrile (I3ACN), through enzymatic breakdown (Ito et al., 2007). Under the action of gastric acid, these precursors further transform into high-affinity AhR ligands such as 3,3′-diindolylmethane (DIM) and indole [3,2-b] carbazole (ICZ) (Bjeldanes et al., 1991). I3C and its condensation products have potential effects in treating inflammatory bowel diseases by modulating the differentiation and function of T cells (Treg cells) through AhR activation, while reducing the number of helper T cells (Th cells) to alleviate intestinal inflammation (Rouse et al., 2013). Additionally, the plant-derived compound resveratrol can inhibit AhR activity by blocking the binding of AhR with its ligands, potentially reversing the imbalance of Th17/Treg cells in patients with autoimmune diseases and showing therapeutic potential for AhR-mediated diseases (Guo et al., 2019). In vitro experiments have shown that the flavonoid compound genistein can activate AhR through negative regulation of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), promoting the expression of downstream target genes CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 (Gong F. et al., 2016; Gong P. et al., 2016). Plant extracts of the flavonoid compound cardamonin (CDN) can act as an exogenous ligand for AhR and play a crucial regulatory role in alleviating intestinal inflammation (Wang et al., 2018). Certain metabolites produced by gut microbiota such as tryptamine, indole, and their derivatives can also function as AhR ligands, inducing the production of IL-22 by intestinal immune cells and participating in gut homeostasis (Zindl et al., 2022). However, the AhR signaling mechanism by which gut microbiota regulate host lipid metabolism is unclear. Lipid metabolism disruption leads to a range of health issues such as obesity, hyperlipidemia (Li J. et al., 2016; Li M. et al., 2016), and cardiovascular diseases (Lee et al., 2005). Therefore, a thorough investigation into the mechanism by which gut microbiota modulates host lipid metabolism via AhR is beneficial for providing new insights and strategies for the prevention and treatment of related diseases.
AhR structure
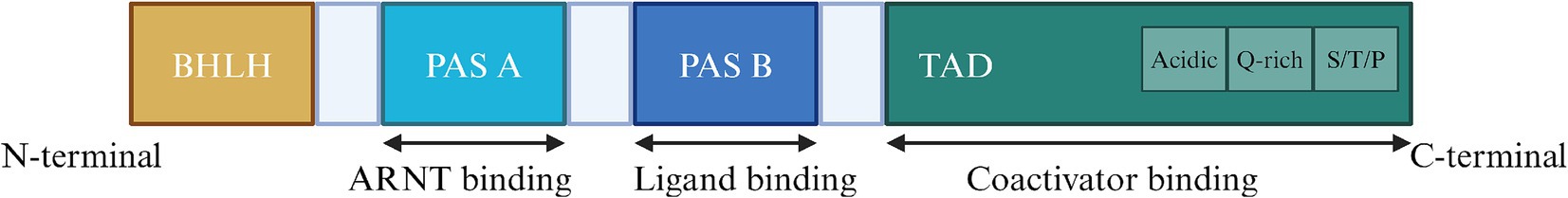
The structure of AHR determines its biological function. (Figure 1).AhR is a transcription factor whose activation relies on ligands, which is member of the basic Helix–Loop–Helix (bHLH)-Per-ARNT-Sim (PAS) family (Fukunaga et al., 1995) and its protein encoded by the AhR gene consists of 848 amino acids (Itoh et al., 1998). The structure of AhR is divided into three segments: the N-terminal, DNA-binding domain, and C-terminal (Hankinson, 1995). The AhR protein consists of three domains: bHLH, PAS, and TAD (Trans activation domain). The bHLH domain located at the N-terminus facilitates AhR binding to the promoter region of target genes and protein dimerization (Murre et al., 1989). The PAS domain is divided into PAS-A and PAS-B2, with PAS-A binding to the AhR nuclear translocator (arnt) and PAS-B binding to AhR ligands (Fukunaga et al., 1995), mediates protein dimerization. What’s more, the TAD at the C terminus is involved in protecting relevant coactivator factors. It comprises three subdomains, with the first two subdomains are enriched in acidic residues and glutamine, while the third subdomain is enriched in serine, threonine, and proline (S/T/P) (Lin et al., 2022).
The BHLH domain is located at the N terminus, initiates AhR binding and mediating protein dimerization, the PAS domain is the binding site for ARNT and AhR ligands, and the TAD at the C terminus, involved in transcription activation, containing three subdomains, the first rich in acidic residues, the second rich in glutamine, and the third rich in serine, threonine, and proline.
AhR expression
AhR exists in the form of a cytoplasmic protein complex composed of HSP90, p32, and XAP-2 within the cytoplasm of cells (Zhu et al., 2021), translocates to the nucleus upon activation by agonists and binds to aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) or hypoxia-inducible factor 1β (HIF-1β), which interacts with xenobiotic response elements (XREs) to control the expression of key genes (Bahman et al., 2024). AhR is present in various tissues and cells of vertebrates, such as the intestines, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and is expressed in various types of cells in the body, including immune cells, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and stromal cells (Stockinger et al., 2014). Among these, immune cells are one of the main sites of AhR gene expression, especially macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes (Trikha and Lee, 2020), which play an important role in immune responses and inflammatory reactions. Li et al. discovered that the AhR signal plays a significant regulatory role in the expression of CD117 on the surface of ILC3 (type 3 innate lymphoid cells), and in patients with Crohn’s disease (CD), attenuation of the AhR signal can lead to the transformation of ILC3 into ILC1, thereby increasing inflammation in the terminal ileum (Li J. et al., 2016; Li M. et al., 2016). Climaco-Arvizu et al. reported that AhR could regulate the differentiation of IBD intestinal macrophages. Loss of the AhR gene enhances inflammatory M1 polarization of macrophages, weakens anti-inflammatory M2 polarization, and affects the production and secretion of inflammatory factors, thereby regulating inflammation development (Climaco-Arvizu et al., 2016). In addition to immune cells, epithelial cells and endothelial cells are also important sites of AhR gene expression (Major et al., 2023; Juan et al., 2006). Then researchers found that endothelial cells have higher levels of AhR expression compared to immune cells and epithelial cells through immunofluorescence detection techniques (Major et al., 2023). Further studies showed that AhR was expressed in many types of lung cells, and the cells with high expression mainly included lung endothelial cells and alveolar cells, affecting lung barrier function (Pang et al., 2017).
Gut microbiota regulates lipid metabolism by AhR signal
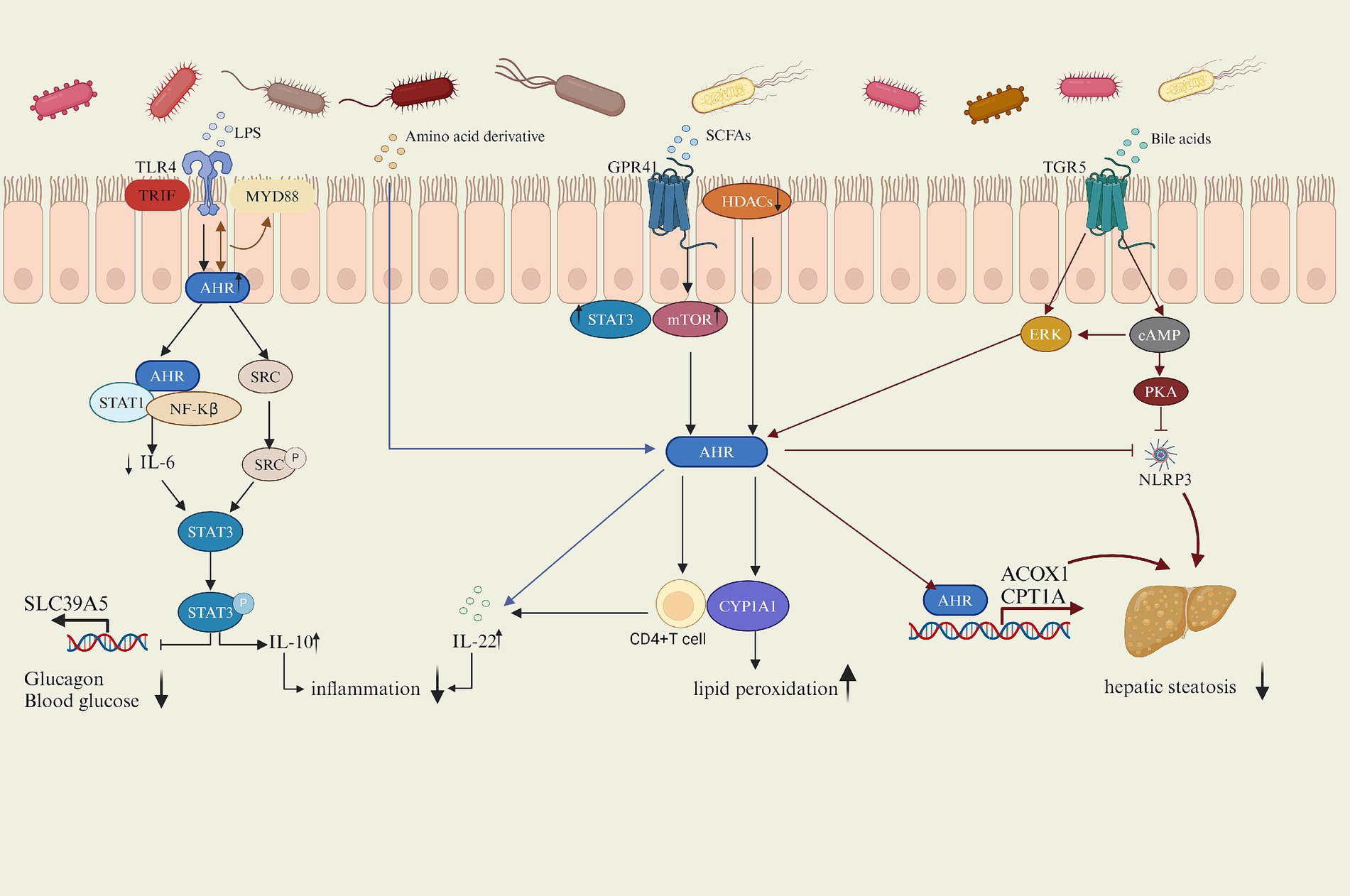
Increasing evidence suggested that AhR played a crucial role in regulating lipid metabolism, with the gut microbiota influencing AhR activity through its metabolites such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), amino acid derivative, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAS) and bile acids (BAS) or direct interactions, thereby modulating the host’s physiological processes (Figure 2). This article will explore the potential mechanisms by which the gut microbiota affects host lipid metabolism via the AhR signaling pathway, focusing on the gut microbiota itself and its metabolites influencing AhR activity.
AhR activation reduces IL-6 secretion by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway induced by LPS, IL-6 activates stat3 and inhibits the transcription and expression of zinc transporter SLC39A5, AhR enhances IL-10 levels by upregulating Src-STAT3 signaling triggered by LPS, alleviating lipid metabolism disorders. SCFAs exacerbates lipid peroxidation by inhibiting HDACS and increasing the expression of CYP1A1. SCFAs increase the AhR expression in CD4 T cells by activating STAT3 and mTOR signaling pathways after binding to the GPR41 and then promoted the production of IL-22; amino acids also promote IL-22 production after being metabolized by microorganisms into AhR ligands, and the increase of IL-22 improves hyperglycemia. BAs bind to TGR5 to increase AHR expression and promote transcription of ACOX 1 and CPT 1 A by triggering CAMP-ERK pathway and inhibit NLRP3 activity by triggering CAMP-PKA pathway, while AHR also inhibit activation of NLRP3, thus inhibiting hepatic steatosis.
LPS and AhR
LPS is a complex sugar-lipid-protein compound and a major component of bacterial endotoxins found widely in the outer walls of Gram-negative bacteria. Inside the host, LPS is recognized by the immune system as a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), triggering an inflammatory response, and classical signaling involves the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)(Facchini et al., 2020), which is a protein associated with the immune system and inflammatory responses, mainly expressed in lymphocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, and cardiomyocytes (Biemmi et al., 2020), playing a crucial role in the host’s immune system. Activation of TLR4 triggers MyD88-and TRIF-dependent signaling pathways (Sun et al., 2019). It recruits myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and activates MyD88-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway, inducing the production of inflammatory factors (Wang B. et al., 2023; Wang Y. et al., 2023). AhR was expressed in peritoneal macrophages stimulated by LPS, being induced by TLR signaling. In the LPS signaling pathway, AhR can negatively regulate it by interacting with Stat1. In macrophages, the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is activated, forming a complex with the transcription factors STAT1 and NF-kB, inhibiting NF-kB-mediated downstream factor IL-6 transcription, resulting in suppressed IL-6 expression, thus alleviating LPS-induced inflammatory response (Kimura et al., 2009). IL-6, as a pro-inflammatory factor, whose down-regulation inhibited hepatocyte adipogenesis and reduced macrophage inflammatory response. Blocking IL-6 signaling reduced the occurrence of NAFLD (Park et al., 2023) and inhibited obesity-related ventricular arrhythmias (Aromolaran et al., 2024). Moreover, IL-6 activated stat3, increased stat3 phosphorylation, and inhibited the transcription and expression of zinc transporter SLC39A5, thereby increasing glucagon secretion and the risk of T2D (Chen et al., 2023). Furthermore, LPS also triggered the AhR-mediated activation of the Src-STAT3 signaling pathway (Zhu et al., 2018). AhR in the cytoplasm upregulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of Src kinase (Src). Src, as a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, participated in various cellular signaling transduction processes, significantly affecting cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation (Brown and Cooper, 1996), catalyzing the phosphorylation of STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription3) and leading to the activation of STAT3. Then STAT3 translocated to the nucleus and regulated the transcriptional expression of relevant genes. Src-STAT3 signaling pathway further promotes the secretion of IL-10 through AhR mediation, collectively inhibiting the inflammatory phenotype of macrophages. IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, suppresses the production and release of various inflammatory mediators, thereby attenuating the metabolic inflammation (Zhu et al., 2018). Adipose tissue-derived stem cells (ADSCs) promoted the expression of IL-10 to ameliorate hyperglycemia and insulin resistance and prevented T2D (Zhang et al., 2017). Overexpression of IL-10 had also been shown to restore intestinal repair after HFD feeding, normalizing barrier repair in HFD-treated mice (Hill et al., 2023). These studies indicated that the expression level of IL-10 is closely related to lipid metabolism. Interestingly, AhR was also shown to have an interaction with TLR4 and together regulate the downstream factor MyD88 (Zhang et al., 2023). These results indicate an inhibitory effect on the LPS-induced inflammatory response by enhancing the activation of AhR, suggesting that AhR agonists such as related ligands or probiotics can be used in clinical application to mitigate the inflammatory effects of LPS. For example, the AhR endogenous ligand indole-3-lactic acid (ILA) significantly attenuated NF-κB activation in macrophages (Calzetta et al., 2022) and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alleviated LPS-induced intestinal inflammation through the AhR/STAT3 pathway (Wang et al., 2024).
SCFAs and AhR
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAS) are metabolites generated by intestinal flora through biotransformation, mainly including acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid (He et al., 2020), in which Bacteroides mainly produce acetic acid and propionic acid, while Firmicutes mainly produce butyric acid (Macfarlane and Macfarlane, 2003). After SCFAS are uptaken by the intestine, it undergoes a series of transformation processes in the liver, mainly producing acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA, which participate in several biological metabolic pathways, such as glycogen synthesis, gluconeogenesis process and cholesterol synthesis, and then affect the host lipid metabolism (den Besten et al., 2013). SCFAs are reported to enhance gene expression mediated by the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and significantly increase the expression of AhR response genes such as Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) by inhibiting the activity of histone deacetylases (HDACs) (Jin et al., 2017). Interestingly, overexpression of CYP1A1 exacerbated lipid peroxidation in the NAFLD model (Huang et al., 2018). Moreover, butyrate also increased the AhR expression in CD4 T cells by activating the STAT3 and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathways after binding to the G-protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41) and then promoted the production of IL-22 (Yang et al., 2020). IL-22 plays an important role in lipid metabolism, as it improves insulin sensitivity, protects the intestinal mucosal barrier, reduces endotoxemia and chronic inflammation, IL-22 receptor-deficient and high-fat-fed mice are prone to metabolic disorders, while administration of exogenous IL-22 to obese mice reversed the induced symptoms like hyperglycemia and insulin resistance (Wang et al., 2014).
BAs and AhR
Bile acids are vital signaling molecules synthesized from cholesterol in the liver, with the classic pathway of their synthesis triggered by cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) catalyzing cholesterol 7α-site hydroxylation (Ahmad and Haeusler, 2019). The host often promotes the utilization of bile acids through enterohepatic circulation, approximately 95% of primary bile acids are reabsorbed at the terminal ileum and return to the liver via the portal vein; a small portion of primary bile acids are catalyzed by BAs salt hydrolase (BSH) enzymes from gut microbiota into free BAs, which undergo conversion into secondary bile acids through pathways like dehydrogenation and dehydroxylation under the influence of intestinal flora (Hsu and Schnabl, 2023). Microorganisms expressing BSH are primarily members of the Firmicutes phylum (Jones et al., 2008), disturb the gut ecology, while in IBD, BSH-producing Firmicutes were reduced (Ramos and Papadakis, 2019), impeding the conversion of PBAs to SBAs and thereby affecting bile acid metabolism. Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) play a protective role in IBD models (Panda et al., 2023), Furthermore, AhR regulated the development, proliferation, and function of intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) (Li et al., 2011), which may be beneficial for gut microbial balance and Maintenance of firmicutes diversity in IBD, thus enhancing secondary bile acid generation. SBAs inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory genes by activating the membrane receptor TGR5 (Duboc et al., 2013), suggesting a potential synergistic effect between bile acids and AhR in suppressing inflammatory responses. TGR5 activation on ciliated and non-ciliated bile ducts triggered downstream signaling pathways such as expression of cAMP, AKT, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) (Guo et al., 2016). Meanwhile TGR5 as a membrane-bound receptor played a significant role in glucose metabolism (Hui et al., 2020), lipid metabolism (Arab et al., 2017), and anti-inflammatory immune regulation (Chiang, 2013). For example, TGR5 suppressed the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by activating intracellular signaling pathways, particularly the cAMP-PKA axis (Tian et al., 1999). NLRP3 inflammasome, a crucial innate immune molecule, promotes the release of pro-inflammatory factors and exacerbates inflammatory responses when activated. Studies on TGR5−/− mouse models show that genetic deficiency leads to overactive NLRP3 inflammasomes, resulting in elevated pro-inflammatory factors and enhanced M1 polarization of macrophages in adipose tissue (Shi et al., 2021), exacerbating inflammation. While the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activity reduced liver inflammation and fibrosis and improved NAFLD (Shen Q. et al., 2023; Shen X. et al., 2023). As a negative regulator of NLRP3 inflammasomes, AhR inhibited the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes, the reason is that AhR bound to its endogenous ligand and inhibited NF-κB transcription, leading to reduced NLRP3 transcription (Huai et al., 2014; Qiao et al., 2022). Furthermore, TGR5 activated the ERK to induce phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) in mitochondria dynamics. Activation of the ERK pathway can induce phosphorylation of Drp1 (Prieto et al., 2016), leading to mitochondrial fission, increasing the rate of fatty acid beta-oxidation while reducing fat accumulation. Additionally, cAMP is also involved in ERK signal transduction (Enserink et al., 2002). In cilia-related liver disorders such as autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney diseases, cAMP levels are elevated and TGR5 is overexpressed in cholangiocytes but not localized on cilia. In ciliary cholangiocytes, TGR 5 agonists reduced cAMP levels and cell proliferation, but ERK signaling was activated, and the cAMP levels also affected the phosphorylation of ERK (Masyuk et al., 2013). The activation of ERK promoted AHR expression, then AHR directly binded to the promoter regions of the key fatty acid oxidation enzymes ACOX 1 and CPT1A to transcribe and activate their expression and then achieved normal fatty acid oxidation function, thus inhibiting hepatic steatosis (Han et al., 2021). Interestingly the upregulation of ERK signaling can inhibit AhR expression (Jiang et al., 2021), suggesting that activation of ERK pathway can inhibit AhR signaling and thus affect lipid metabolism.
Amino acids (AAs) and AhR
Most amino acids are absorbed in the small intestine, while those not absorbed enter the colon to participate in microbial metabolism processes, leading to the production of various metabolites such as ammonia, amines, short-chain fatty acids, branched-chain fatty acids, hydrogen sulfide, organic acids, and phenols (Abdallah et al., 2020; Ma and Ma, 2019). Studies indicate that branched-chain amino acids and aromatic amino acids play crucial roles in lipid metabolism disorders associated with obesity, insulin resistance, diabetes, and fatty liver (Ejtahed et al., 2020). And aromatic amino acids mainly include phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan, which activate the AhR to induce downstream pathway alterations (Yang et al., 2019). The ability of gut microbes to metabolize tryptophan is reduced, which lowering the activation of AhR to promote metabolic disease (Natividad et al., 2018), suggesting that AhR may regulate lipid metabolism through the gut microbiota. Tryptophan is a crucial source of endogenous AhR ligand precursors (Liu et al., 2021) and its metabolites such as kynurenine and the photoproduct 6-formylindolo [3,2-b] carbazole (FICZ), can bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in the intestine, thereby regulating the function and differentiation of intestinal immune cells (Gutiérrez-Vázquez and Quintana, 2018). Kynurenine promoted the differentiation of CD4+ naïve T cells into anti-inflammatory Treg cells (Mezrich et al., 2010), while FICZ, as a high-affinity ligand for AhR, activated the AhR signaling pathway at extremely low concentrations (Rannug and Fritsche, 2006), upregulating the expression of the cytochrome P450 family 1.
(CYP1) family of genes. Further CYP1A1 rapidly degraded FICZ, forming a negative feedback regulatory mechanism to ensure a low level of FICZ in the gastrointestinal tract (Wei et al., 2000). However, FICZ also induced the differentiation of Th17 cells and the expression of the inflammatory factor IL-17, which inhibited the differentiation of Treg cells (Quintana et al., 2008). Studies have shown that gut microbiota metabolized tryptophan into indole and its derivatives, thereby participating in the regulation of AhR signaling. For instance, tryptophan was metabolized by Lactobacillus reuteri to indole-3-aldehyde (Zelante et al., 2013). In mouse models, this substance can activate AhR and induce the production of IL-22, which plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal mucosal immune homeostasis. Additionally, tryptophan metabolites from other commensal microbiota, such as indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-aldehyde, tryptamine, and 3-methylindole (Shen et al., 2022; Dang et al., 2023), also exhibit AhR agonist activity, suggesting a potentially significant role in intestinal immune regulation. The microbial community in the gut generates AhR agonists during tryptophan metabolism, supporting the growth and development of ILC3 in the intestine. AhR is an essential transcription factor for ILC3 (Li J. et al., 2016; Li M. et al., 2016), ILC3 is a critical member of the intestinal mucosal immune system, and the dysfunction of ILC3s may lead to inflammatory diseases in intestinal mucosal tissues (Cording et al., 2018). What’s more, ILC3 protected the body from damage by the symbiotic microbiome through producing key anti-inflammatory factors, such as IL-22 and IL-17A (Shen Q. et al., 2023; Shen X. et al., 2023), to prevent inflammation in adipose tissue.
AhR and lipid metabolism disorder
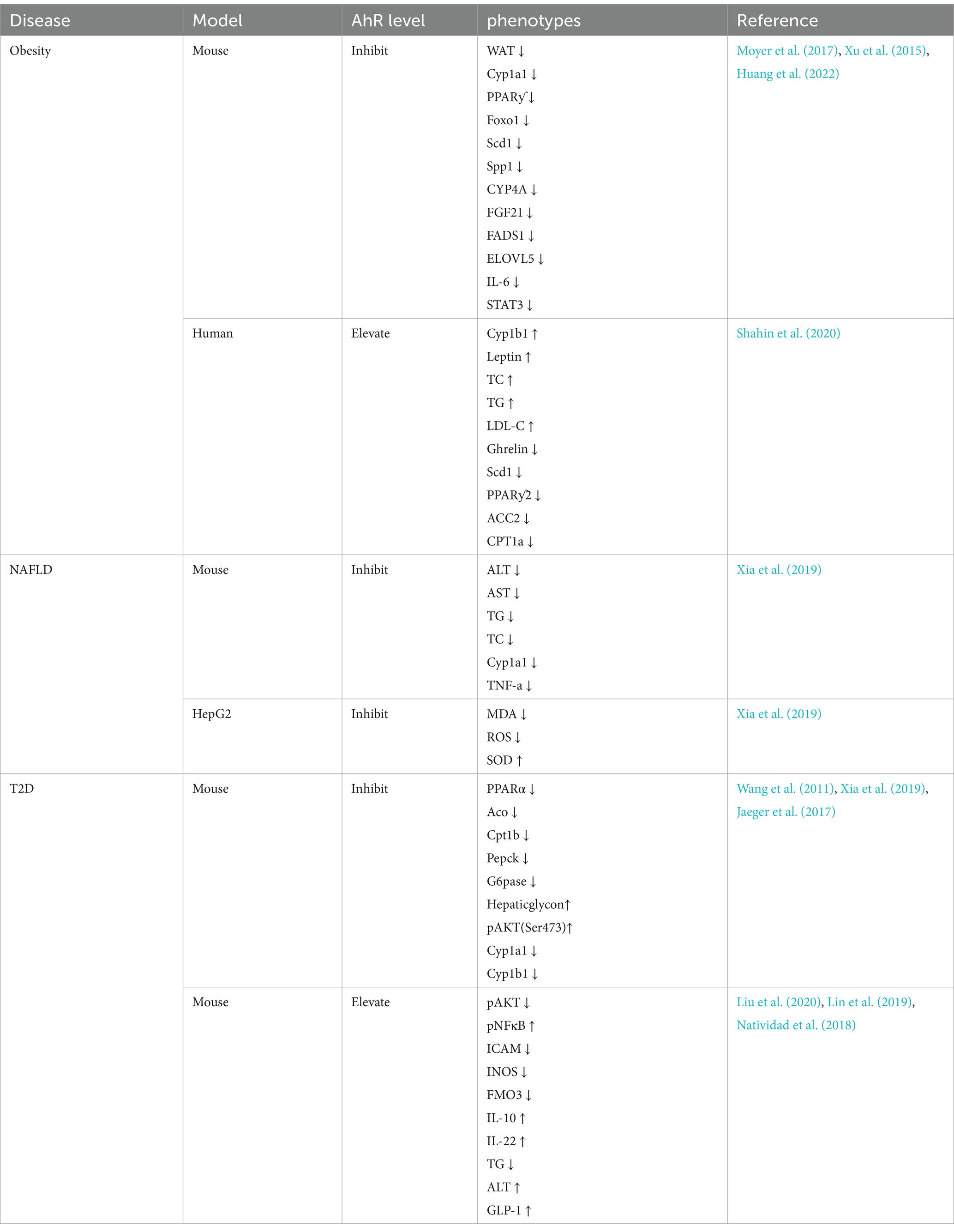
AhR plays a crucial role in numerous biological processes, including immune responses, cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as maintaining homeostasis (Wang et al., 2022). However, an increasing number of studies indicates that AhR plays an important role in lipid metabolism, causing lipid metabolic diseases such as obesity (Kerley-Hamilton et al., 2012), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (Moyer et al., 2017), and type 2 diabetes (T2D) (Wang et al., 2011). The expression of lipid metabolism-related phenotypes in these disease models can be promoted or inhibited by adjusting AhR levels. (Table 1) Therefore, it is necessary to study the effect of AhR on lipid metabolism in detail in order to use it as a potential therapeutic target for lipid metabolism diseases.
AhR and obesity
With the improvement of living standards, obesity is becoming more common and prevalent worldwide. Obesity refers to the excessive accumulation of fat in the body, mainly caused by the excessive accumulation of triglycerides in the body (Twig et al., 2020). Typically characterized by exceeding the normal weight range and an increase in body fat percentage, obesity is associated with various chronic diseases and health issues, severely affecting the quality of life (Piché et al., 2020). Therefore, finding effective methods to address obesity is crucial. Obesity affected the diversity of the gut microbiota, with a decrease in the abundance of Bacteroidetes and increased proportion of Firmicutes in obese individuals, suggesting a possible role in regulating obesity by remodeling gut microbial community structure (Ley et al., 2005). Studies have shown that the activation of AhR induced obesity (Kerley-Hamilton et al., 2012), It may be because the aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor (AhRR) was significantly down-regulated in obese populations, while AhR and CYP1B1 are significantly upregulated, indicating that AhRR may regulate obesity by inhibiting AhR expression through the AhR-CYP1B1 axis (Shahin et al., 2020). AhR deficiency significantly reduced weight gain and adiposity, increasing the protein and mRNA expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which activates thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT) and gWAT, thus increasing metabolic rate and energy expenditure, preventing obesity induced by a high-fat diet (Girer et al., 2019), making it a potential target for obesity treatment. Studies have shown that Kynurenine caused obesity by activating AHR (Moyer et al., 2016), while obesity and hepatic steatosis were prevented by inhibiting AhR, the AhR antagonist naphthoflavone (aNF) prevented and reversed obesity in high-fat diet mice by inhibiting AhR and related genes in its network, such as CYP1B1 and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) (Moyer et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2015). CYP1B1 is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily that is involved in metabolizing endogenous compounds including steroid hormones and lipids, which regulate metabolism, accumulation, and distribution in adipose tissue. The expression of CYP1B1 influenced the development of obesity, in CYP1B1-null mice, the expression level of SCD1 was reduced, which inhibited obesity and thus affected lipid metabolism (Li et al., 2014). Further research found that SCD1 is a delta-9 fatty acid desaturase that catalyzes the synthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids. Similarly, SCD1-deficient mice reduced lipid synthesis and enhanced insulin sensitivity, promoting the suppression of obesity (Flowers and Ntambi, 2008). In obese patients, tryptophan was preferentially catabolized through the kynurenine pathway (KP), leading to an excessive increase in the concentration of kynurenine (Kyn) in the blood, which activated AhR and then transcribed STAT3 expression to enhance the secretion of IL-6 (Huang et al., 2022), which maintained the proliferation rates of obese adipose tissue (Ackermann et al., 2024). In contrast, knockdown of AhR from adipocytes abolished the effects of Kyn and prevented obesity.
AhR and NAFLD
NAFLD refers to the pathological condition where the liver accumulates fat without excessive alcohol consumption. NAFLD is the most common chronic liver disease (Zhou et al., 2020) and a significant component of metabolic syndrome (Haas et al., 2016), which included obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterolemia (Chen et al., 2012). The spectrum of NAFLD ranges from simple steatosis (fatty liver) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis (Schuster et al., 2018). Activation of the AhR has been shown to affect lipid metabolism in the liver, including synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. Abnormal fat accumulation in the liver is a primary feature, and AhR activation can induce lipid deposition, potentially directly impacting the pathogenesis of NAFLD (Podechard et al., 2009). It has been observed that the activation of AhR signaling pathway indirectly induced the accumulation of lipid droplets in rat hepatocytes (Neuschäfer-Rube et al., 2015). The AhR-CYP1A1 signaling pathway was activated to cause intracellular lipid droplet accumulation in Hepatitis C virus (HCV) (Ohashi et al., 2018). As an exogenous ligand for the AhR, the Sulforaphane (SFN) can regulated the intestinal microflora of high-fat diet mice to prevent NAFLD by activating the AhR/SREBP-1C pathway, reduced the protein levels of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1C), acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), and fatty acid synthase (FAS), And then regulates hepatic lipid metabolism, And to prevent NAFLD (Xu et al., 2021). Further studies showed that AhR promoted the absorption of fatty acids by activating its transcriptional target CD36.(Lee et al., 2010). Overexpression of the AhR in the liver significantly upregulates the expression of the fatty acid translocase (FAT) CD36 in mouse liver cells, promoting the uptake of fatty acids by liver cells (Yao et al., 2016), which exacerbated lipid deposition in the liver, leading to liver damage and promoting the development of NAFLD. AhR ligand 3-methylcholanthrene (3MC) also significantly increased the expression level of fatty acid translocase in liver by activating AhR, inducing hepatic steatosis (Kawano et al., 2010). Estrogen deficiency is one of the main causes of obesity and NAFLD (Zhu et al., 2020). However, the administration of endogenous agonists of AhR such as cinnabarinic acid (CA) down-regulated CD36 and reduced the uptake of free fatty acids in hepatocytes, thus achieving the inhibition of hepatic steatosis and liver injury (Patil et al., 2022). Importantly, CYP1A1 is an estrogen-metabolizing enzyme, and increased activity of CYP1A1 leads to estrogen deficiency (Niwa et al., 2015), for example, Benzo[a]pyrene (Bap) promoted the transcription and overexpression of CYP1A1 by activating the AhR pathway, inhibiting estrogen’s protective effect on the liver, significantly increasing the risk of NAFLD (Mumtaz et al., 2022). In addition, alpha-naphthoflavone, as an AhR inhibitor, alleviated NAFLD by inhibiting the AhR-CYP1A1 pathway (Xia et al., 2019). The AhR-CYP1A1 axis regulates lipid peroxidation by influencing the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Huang et al., 2018). When the expression of AhR increases, the CYP1A1 also increases to enhance ROS (Cui et al., 2024) while excess ROS will lead to the production of lipid peroxides such as malondialdehyde (MDA), which may exacerbate oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage (Wang B. et al., 2023; Wang Y. et al., 2023) and promote the production of NAFLD (Zhao et al., 2023).
AhR and T2D
T2D is the most common type of diabetes globally, accounting for over 90% of all diabetes cases. Unlike type 1 diabetes, T2D is characterized by insulin resistance and/or dysfunction of pancreatic β-cells, leading to sustained high blood sugar levels and the former is due to autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells (ElSayed et al., 2023). Abnormal expression of AhR will result in imbalanced glucose and lipid metabolism, indicating a crucial role of AhR in regulating these processes in the body (Biljes et al., 2015). Thus, AhR may be a key factor in the development of diabetes. The development of T2D is associated with a state of chronic low-grade inflammation (Gong F. et al., 2016; Gong P. et al., 2016). In high sugar-induced insulin resistance and diabetes complications, AhR is crucial for maintaining ILC3, promoting the development and maturation of ILC3, and stimulating the secretion of IL-22 by ILC3 to inhibit inflammation levels, thereby preserving intestinal homeostasis (Artis and Spits, 2015; Kobayashi et al., 2014). IL-22 released by ILC3 cells protected pancreatic islet beta cells from inflammation and glucotoxicity, potentially reversing the damage caused by hyperglycemia to pancreatic islet beta cells, thus improving insulin sensitivity (Abadpour et al., 2018). Furthermore, AhR ligands enhanced intestinal defense mechanisms, reduced bacterial translocation and systemic inflammation, effectively reversing glucose intolerance and insulin resistance induced by diabetes (Liu et al., 2020). The indirubin, an AhR agonist, induced the secretion of IL-10 and IL-22 by activating AhR to prevent high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice model (Lin et al., 2019). Other AhR agonists, such as indoles, have been shown to effectively stimulate the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), thus improving insulin resistance and alleviate symptoms of T2D (Natividad et al., 2018). Further studies have found that tryptophan, as a ligand of AHR, was metabolized by gut microbiota into 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) promoting the ubiquitin–proteasome degradation of Suv39h1 by activating AhR, thereby stimulating TSC2 expression and inhibiting the activation of mTORC1 signaling, which would promote insulin signaling, improve glucose intolerance and reduce the risk of T2D (Du et al., 2024). However, it has also been shown that lack of AhR improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance (Wang et al., 2011) by increasing energy expenditure and ameliorating high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice (Jaeger et al., 2017). Although these results are inconsistent, the important role of AhR cannot be ignored. Thus, further investigation and confirmation are needed on how AhR specifically affects glucose metabolism and T2D.
Limitations and future direction
Increasing evidences demonstrate that AhR signaling is associated with lipid metabolism, and although some significant progress has been gained about AhR regulating lipid metabolism, translating these findings into clinical treatment and preventive strategies still faces many challenges. The gut microbiome is highly diverse, containing thousands of different microbial species. There are complex interrelationships among these microorganisms, including symbiosis, competition and antagonism. Even though certain microorganisms have been found to be associated with AHR activation and lipid metabolism changes, the role of these microorganisms may be altered by the influence of other microorganisms in the context of the entire microbial community. AHR is a pleiotropic transcription factor, in addition to regulating the genes involved in lipid metabolism. It is also involved in many other biological processes, such as immune response, cell proliferation, and differentiation. AHR can regulate the expression of numerous genes that may have different functions in different cell types and physiological conditions. Therefore, it is difficult to distinguish between the direct and indirect effects of AHR on lipid metabolism and how these effects are synergized in complex physiological and pathological processes.
At present, relevant studies mainly focus on animal models and cell experiments, such as mice, rats and liver cell lines (Zhao et al., 2022). While these studies provide us with valuable experimental evidence, there are certain physiological and metabolic differences between animal models and humans, so these results may not fully reflect the real situation in the human body. In addition, different research teams use different experimental conditions and methods, resulting in a certain diversity of research results, which makes it difficult to interpret and apply these results. Some studies have shown that AhR is protective against diet-induced metabolic syndrome (Wada et al., 2016), while others are negative (Korecka et al., 2016). The AhR signaling pathway involves multiple molecular and cellular processes, so the experimental design needs to be highly precise and complex to accurately simulate what is really happening in vivo. However, these complex interactions may not be fully captured by the current experimental methods, the specific molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways still require further intensive investigation.
Author contributions
WZ: Writing – original draft. ML: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing. CH: Writing – review & editing. JY: Writing – review & editing. JM: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abadpour, S., Halvorsen, B., Sahraoui, A., Korsgren, O., Aukrust, P., and Scholz, H. (2018). Interleukin-22 reverses human islet dysfunction and apoptosis triggered by hyperglycemia and LIGHT. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 60, 171–183. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0182
Abdallah, A., Elemba, E., Zhong, Q., and Sun, Z. (2020). Gastrointestinal interaction between dietary amino acids and gut microbiota: with special emphasis on host nutrition. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 21, 785–798. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200212095503
Ackermann, J., Arndt, L., Fröba, J., Lindhorst, A., Glaß, M., Kirstein, M., et al. (2024). IL-6 signaling drives self-renewal and alternative activation of adipose tissue macrophages. Front Immunol. 15:1201439. Published 2024 Feb 28. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1201439
Ahmad, T. R., and Haeusler, R. A. (2019). Bile acids in glucose metabolism and insulin signalling - mechanisms and research needs. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 15, 701–712. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0266-7
Arab, J. P., Karpen, S. J., Dawson, P. A., Arrese, M., and Trauner, M. (2017). Bile acids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. Hepatology 65, 350–362. doi: 10.1002/hep.28709
Aromolaran, K. A., Corbin, A., and Aromolaran, A. S. (2024). Obesity arrhythmias: role of IL-6 trans-signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:8407. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158407
Artis, D., and Spits, H. (2015). The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 517, 293–301. doi: 10.1038/nature14189
Bahman, F., Choudhry, K., Al-Rashed, F., Al-Mulla, F., Sindhu, S., and Ahmad, R. (2024). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor: current perspectives on key signaling partners and immunoregulatory role in inflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 15:1421346. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1421346
Biemmi, V., Milano, G., Ciullo, A., Cervio, E., Burrello, J., Dei Cas, M., et al. (2020). Inflammatory extracellular vesicles prompt heart dysfunction via TRL4-dependent NF-κB activation. Theranostics 10, 2773–2790. doi: 10.7150/thno.39072
Biljes, D., Hammerschmidt-Kamper, C., Kadow, S., Diel, P., Weigt, C., Burkart, V., et al. (2015). Impaired glucose and lipid metabolism in ageing aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficient mice. Excli J. 14, 1153–1163. doi: 10.17179/excli2015-638
Bjeldanes, L. F., Kim, J. Y., Grose, K. R., Bartholomew, J. C., and Bradfield, C. A. (1991). Aromatic hydrocarbon responsiveness-receptor agonists generated from indole-3-carbinol in vitro and in vivo: comparisons with 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9543–9547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9543
Brown, M. T., and Cooper, J. A. (1996). Regulation, substrates and functions of src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287, 121–149. doi: 10.1016/0304-419X(96)00003-0
Calzetta, L., Pistocchini, E., Cito, G., Ritondo, B. L., Verri, S., and Rogliani, P. (2022). Inflammatory and contractile profile in LPS-challenged equine isolated bronchi: evidence for IL-6 as a potential target against AhR in equine asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 73-74:102125. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2022.102125
Chen, W., Cui, W., Wu, J., Zheng, W., Sun, X., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Blocking IL-6 signaling improves glucose tolerance via SLC39A5-mediated suppression of glucagon secretion. Metabolism 146:155641. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155641
Chen, L. Y., Qiao, Q. H., Zhang, S. C., Chen, Y. H., Chao, G. Q., and Fang, L. Z. (2012). Metabolic syndrome and gallstone disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 18, 4215–4220. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4215
Chiang, J. Y. (2013). Bile acid metabolism and signaling. Compr. Physiol. 3, 1191–1212. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120023
Climaco-Arvizu, S., Domínguez-Acosta, O., Cabañas-Cortés, M. A., Rodríguez-Sosa, M., Gonzalez, F. J., Vega, L., et al. (2016). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor influences nitric oxide and arginine production and alters M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Life Sci. 155, 76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.001
Cording, S., Medvedovic, J., Lécuyer, E., Aychek, T., Déjardin, F., and Eberl, G. (2018). Mouse models for the study of fate and function of innate lymphoid cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 48, 1271–1280. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747388
Cui, J., Chen, W., Zhang, D., Lu, M., Huang, Z., and Yi, B. (2024). Metformin attenuates PM2.5-induced oxidative stress by inhibiting the AhR/CYP1A1 pathway in proximal renal tubular epithelial cells. Toxicol Mech. Methods 34, 1022–1034. doi: 10.1080/15376516.2024.2378296
Dang, G., Wen, X., Zhong, R., Wu, W., Tang, S., Li, C., et al. (2023). Pectin modulates intestinal immunity in a pig model via regulating the gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolite-AhR-IL22 pathway. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 14:38. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00838-z
den Besten, G., Lange, K., Havinga, R., van Dijk, T. H., Gerding, A., van Eunen, K., et al. (2013). Gut-derived short-chain fatty acids are vividly assimilated into host carbohydrates and lipids. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 305, G900–G910. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00265.2013
Du, W., Jiang, S., Yin, S., Wang, R., Zhang, C., Yin, B. C., et al. (2024). The microbiota-dependent tryptophan metabolite alleviates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance through the hepatic AhR/TSC2/mTORC1 axis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 121:e2400385121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2400385121
Duboc, H., Rajca, S., Rainteau, D., Benarous, D., Maubert, M. A., Quervain, E., et al. (2013). Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 62, 531–539. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302578
Ejtahed, H. S., Angoorani, P., Soroush, A. R., Hasani-Ranjbar, S., Siadat, S. D., and Larijani, B. (2020). Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in obesity: a systematic review. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 39, 65–76. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2019-026
ElSayed, N. A., Aleppo, G., and Aroda, V. R. (2023). 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 46, S19–S40. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S002
Enserink, J. M., Christensen, A. E., de Rooij, J., van Triest, M., Schwede, F., Genieser, H. G., et al. (2002). A novel Epac-specific cAMP analogue demonstrates independent regulation of Rap1 and ERK. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 901–906. doi: 10.1038/ncb874
Facchini, F. A., di, D., Barresi, S., Luraghi, A., Minotti, A., Granucci, F., et al. (2020). Effect of chemical modulation of toll-like receptor 4 in an animal model of ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 76, 409–418. doi: 10.1007/s00228-019-02799-7
Flowers, M. T., and Ntambi, J. M. (2008). Role of stearoyl-coenzyme a desaturase in regulating lipid metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 19, 248–256. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e3282f9b54d
Fukunaga, B. N., Probst, M. R., Reisz-Porszasz, S., and Hankinson, O. (1995). Identification of functional domains of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 29270–29278. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29270
Girer, N. G., Carter, D., Bhattarai, N., Mustafa, M., Denner, L., Porter, C., et al. (2019). Inducible loss of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor activates Perigonadal white fat respiration and Brown fat thermogenesis via fibroblast growth factor 21. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:950. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040950
Gong, P., Madak-Erdogan, Z., Flaws, J. A., Shapiro, D. J., Katzenellenbogen, J. A., and Katzenellenbogen, B. S. (2016). Estrogen receptor-α and aryl hydrocarbon receptor involvement in the actions of botanical estrogens in target cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 437, 190–200. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.08.025
Gong, F., Wu, J., Zhou, P., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2016). Interleukin-22 might act as a double-edged sword in type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 8254797–8254712. doi: 10.1155/2016/8254797
Granados, J. C., Falah, K., Koo, I., Morgan, E. W., Perdew, G. H., Patterson, A. D., et al. (2022). AhR is a master regulator of diverse pathways in endogenous metabolism. Sci. Rep. 12:16625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20572-2
Guo, C., Chen, W. D., and Wang, Y. D. (2016). TGR5, not only a metabolic regulator. Front. Physiol. 7:646. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00646
Guo, N. H., Fu, X., Zi, F. M., Song, Y., Wang, S., and Cheng, J. (2019). The potential therapeutic benefit of resveratrol on Th17/Treg imbalance in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Int. Immunopharmacol. 73, 181–192. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.061
Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C., and Quintana, F. J. (2018). Regulation of the immune response by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Immunity 48, 19–33. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.12.012
Haas, J. T., Francque, S., and Staels, B. (2016). Pathophysiology and mechanisms of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 78, 181–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105331
Han, Q., Chen, H., Wang, L., An, Y., Hu, X., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Systemic deficiency of GHR in pigs leads to hepatic steatosis via negative regulation of AHR signaling. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 17, 4108–4121. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.64894
Hankinson, O. (1995). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 35, 307–340. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.35.040195.001515
He, J., Zhang, P., Shen, L., Niu, L., Tan, Y., Chen, L., et al. (2020). Short-chain fatty acids and their association with Signalling pathways in inflammation, glucose and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:6356. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176356
Hill, A. A., Kim, M., Zegarra-Ruiz, D. F., Chang, L. C., Norwood, K., Assié, A., et al. (2023). Acute high-fat diet impairs macrophage-supported intestinal damage resolution. JCI Insight 8:e164489. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.164489
Hornedo-Ortega, R., Da Costa, G., Cerezo, A. B., Troncoso, A. M., Richard, T., and Garcia-Parrilla, M. C. (2018). In vitro effects of serotonin, melatonin, and other related indole compounds on amyloid-β kinetics and neuroprotection. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62:383. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201700383
Hsu, C. L., and Schnabl, B. (2023). The gut-liver axis and gut microbiota in health and liver disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 719–733. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00904-3
Huai, W., Zhao, R., Song, H., Zhao, J., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., et al. (2014). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity by inhibiting NLRP3 transcription. Nat. Commun. 5:4738. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5738
Huang, B., Bao, J., Cao, Y. R., Gao, H. F., and Jin, Y. (2018). Cytochrome P450 1A1 (CYP1A1) catalyzes lipid peroxidation of oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells. Biochemistry 83, 595–602. doi: 10.1134/S0006297918050127
Huang, T., Song, J., Gao, J., Cheng, J., Xie, H., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). Adipocyte-derived kynurenine promotes obesity and insulin resistance by activating the AhR/STAT3/IL-6 signaling. Nat. Commun. 13:3489. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31126-5
Hui, S., Huang, L., Wang, X., Zhu, X., Zhou, M., Chen, M., et al. (2020). Capsaicin improves glucose homeostasis by enhancing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through the regulation of bile acid metabolism via the remodeling of the gut microbiota in male mice. FASEB J. 34, 8558–8573. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902618RR
Ito, S., Chen, C., Satoh, J., Yim, S., and Gonzalez, F. J. (2007). Dietary phytochemicals regulate whole-body CYP1A1 expression through an arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-dependent system in gut. J. Clin. Invest. 117, 1940–1950. doi: 10.1172/JCI31647
Itoh, A., Miyabayashi, T., Ohno, M., and Sakano, S. (1998). Cloning and expressions of three mammalian homologues of Drosophila slit suggest possible roles for slit in the formation and maintenance of the nervous system. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 62, 175–186. doi: 10.1016/S0169-328X(98)00224-1
Jaeger, C., Xu, C., Sun, M., Krager, S., and Tischkau, S. A. (2017). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are protected from high fat diet-induced changes in metabolic rhythms. Chronobiol. Int. 34, 318–336. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2016.1256298
Jiang, Y., Xiao, H., Sun, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., and Luo, B. (2021). LMP2A suppresses the role of AhR pathway through ERK signal pathway in EBV-associated gastric cancer. Virus Res. 297:198399. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198399
Jin, U. H., Cheng, Y., Park, H., Davidson, L. A., Callaway, E. S., Chapkin, R. S., et al. (2017). Short chain fatty acids enhance aryl hydrocarbon (ah) responsiveness in mouse Colonocytes and Caco-2 human Colon Cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 7:10163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10824-x
Jones, B. V., Begley, M., Hill, C., Gahan, C. G., and Marchesi, J. R. (2008). Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 13580–13585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804437105
Juan, S. H., Lee, J. L., Ho, P. Y., Lee, Y. H., and Lee, W. S. (2006). Antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of 3-methylcholanthrene, an aryl-hydrocarbon receptor agonist, in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 530, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.11.023
Kawano, Y., Nishiumi, S., Tanaka, S., Nobutani, K., Miki, A., Yano, Y., et al. (2010). Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor induces hepatic steatosis via the upregulation of fatty acid transport. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 504, 221–227. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.09.001
Kerley-Hamilton, J. S., Trask, H. W., and Ridley, C. J. (2012). Obesity is mediated by differential aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in mice fed a Western diet. Environ. Health Perspect. 120, 1252–1259. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1205003
Kimura, A., Naka, T., Nakahama, T., Chinen, I., Masuda, K., Nohara, K., et al. (2009). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in combination with Stat1 regulates LPS-induced inflammatory responses. J. Exp. Med. 206, 2027–2035. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090560
Kobayashi, T., Okada, M., Ito, S., Kobayashi, D., Ishida, K., Kojima, A., et al. (2014). Assessment of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition therapy on periodontal condition in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 85, 57–67. doi: 10.1902/jop.2013.120696
Korecka, A., Dona, A., Lahiri, S., Tett, A. J., al-Asmakh, M., Braniste, V., et al. (2016). Bidirectional communication between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and the microbiome tunes host metabolism. NPJ Biofilms Microb. 2:16014. doi: 10.1038/npjbiofilms.2016.14
Kwack, S. J., and Lee, B. M. (2000). Correlation between DNA or protein adducts and benzo[a]pyrene diol epoxide I-triglyceride adduct detected in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 21, 629–632. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.4.629
Lee, D. H., Folsom, A. R., and Jacobs, D. R. (2005). Iron, zinc, and alcohol consumption and mortality from cardiovascular diseases: the Iowa Women's health study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81, 787–791. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/81.4.787
Lee, J. H., Wada, T., Febbraio, M., He, J., Matsubara, T., Lee, M. J., et al. (2010). A novel role for the dioxin receptor in fatty acid metabolism and hepatic steatosis. Gastroenterology 139, 653–663. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.033
Ley, R. E., Bäckhed, F., Turnbaugh, P., Lozupone, C. A., Knight, R. D., and Gordon, J. I. (2005). Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 11070–11075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504978102
Li, J., Doty, A., and Glover, S. C. (2016). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling involves in the human intestinal ILC3/ILC1 conversion in the inflamed terminal ileum of Crohn's disease patients. Inflamm Cell Signal. 3:e1404. doi: 10.14800/ics.1404
Li, Y., Innocentin, S., Withers, D. R., Roberts, N. A., Gallagher, A. R., Grigorieva, E. F., et al. (2011). Exogenous stimuli maintain intraepithelial lymphocytes via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Cell 147, 629–640. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.025
Li, F., Jiang, C., Larsen, M. C., Bushkofsky, J., Krausz, K. W., Wang, T., et al. (2014). Lipidomics reveals a link between CYP1B1 and SCD1 in promoting obesity. J. Proteome Res. 13, 2679–2687. doi: 10.1021/pr500145n
Li, M., Shu, X., Xu, H., Zhang, C., Yang, L., Zhang, L., et al. (2016). Integrative analysis of metabolome and gut microbiota in diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats treated with berberine compounds. J. Transl. Med. 14:237. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0987-5
Lin, L., Dai, Y., and Xia, Y. (2022). An overview of aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in the last two decades (2002-2022): a medicinal chemistry perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 244:114845. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114845
Lin, Y. H., Luck, H., Khan, S., Schneeberger, P. H. H., Tsai, S., Clemente-Casares, X., et al. (2019). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist indigo protects against obesity-related insulin resistance through modulation of intestinal and metabolic tissue immunity. Int. J. Obes. 43, 2407–2421. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0340-1
Liu, W. C., Chen, P. H., and Chen, L. W. (2020). Supplementation of endogenous AhR ligands reverses insulin resistance and associated inflammation in an insulin-dependent diabetic mouse model. J. Nutr. Biochem. 83:108384. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108384
Liu, J. R., Miao, H., Deng, D. Q., Vaziri, N. D., Li, P., and Zhao, Y. Y. (2021). Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolism mediates renal fibrosis by aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling activation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 909–922. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03645-1
Ma, N., and Ma, X. (2019). Dietary amino acids and the gut-microbiome-immune Axis: physiological metabolism and therapeutic prospects. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 18, 221–242. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12401
Macfarlane, S., and Macfarlane, G. T. (2003). Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 62, 67–72. doi: 10.1079/PNS2002207
Major, J., Crotta, S., Finsterbusch, K., Chakravarty, P., Shah, K., Frederico, B., et al. (2023). Endothelial AhR activity prevents lung barrier disruption in viral infection. Nature 621, 813–820. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06287-y
Masyuk, A. I., Huang, B. Q., Radtke, B. N., Gajdos, G. B., Splinter, P. L., Masyuk, T. V., et al. (2013). Ciliary subcellular localization of TGR5 determines the cholangiocyte functional response to bile acid signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 304, G1013–G1024. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00383.2012
Mezrich, J. D., Fechner, J. H., Zhang, X., Johnson, B. P., Burlingham, W. J., and Bradfield, C. A. (2010). An interaction between kynurenine and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor can generate regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 185, 3190–3198. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903670
Moyer, B. J., Rojas, I. Y., Kerley-Hamilton, J. S., Hazlett, H. F., Nemani, K. V., Trask, H. W., et al. (2016). Inhibition of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor prevents Western diet-induced obesity. Model for AHR activation by kynurenine via oxidized-LDL, TLR2/4, TGFβ, and IDO1. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 300, 13–24. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.03.011
Moyer, B. J., Rojas, I. Y., Kerley-Hamilton, J. S., Nemani, K. V., Trask, H. W., Ringelberg, C. S., et al. (2017). Obesity and fatty liver are prevented by inhibition of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in both female and male mice. Nutr. Res. 44, 38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.06.002
Mumtaz, H., Hameed, M., Sangah, A. B., Zubair, A., and Hasan, M. (2022). Association between smoking and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Southeast Asia. Front. Public Health 10:1008878. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1008878
Murre, C., McCaw, P. S., and Baltimore, D. (1989). A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell 56, 777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-X
Natividad, J. M., Agus, A., Planchais, J., Lamas, B., Jarry, A. C., Martin, R., et al. (2018). Impaired aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand production by the gut microbiota is a key factor in metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 28, 737–749.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.07.001
Neuschäfer-Rube, F., Schraplau, A., Schewe, B., Lieske, S., Krützfeldt, J. M., Ringel, S., et al. (2015). Arylhydrocarbon receptor-dependent mIndy (Slc13a5) induction as possible contributor to benzo[a]pyrene-induced lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. Toxicology 337, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2015.08.007
Niwa, T., Murayama, N., Imagawa, Y., and Yamazaki, H. (2015). Regioselective hydroxylation of steroid hormones by human cytochromes P450. Drug Metab. Rev. 47, 89–110. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2015.1011658
Ohashi, H., Nishioka, K., Nakajima, S., Kim, S., Suzuki, R., Aizaki, H., et al. (2018). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-cytochrome P450 1A1 pathway controls lipid accumulation and enhances the permissiveness for hepatitis C virus assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 19559–19571. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005033
Panda, S. K., Peng, V., Sudan, R., Ulezko Antonova, A., di Luccia, B., Ohara, T. E., et al. (2023). Repression of the aryl-hydrocarbon receptor prevents oxidative stress and ferroptosis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Immunity 56, 797–812.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.023
Pang, L. P., Li, Y., Zou, Q. Y., Zhou, C., Lei, W., Zheng, J., et al. (2017). ITE inhibits growth of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Exp. Lung Res. 43, 283–292. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2017.1367868
Park, J., Zhao, Y., Zhang, F., Zhang, S., Kwong, A. C., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). IL-6/STAT3 axis dictates the PNPLA3-mediated susceptibility to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 78, 45–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.022
Patil, N. Y., Rus, I., Downing, E., Mandala, A., Friedman, J. E., and Joshi, A. D. (2022). Cinnabarinic acid provides Hepatoprotection against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 383, 32–43. doi: 10.1124/jpet.122.001301
Piché, M. E., Tchernof, A., and Després, J. P. (2020). Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 126, 1477–1500. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316101
Podechard, N., Le Ferrec, E., Rebillard, A., Fardel, O., and Lecureur, V. (2009). NPC1 repression contributes to lipid accumulation in human macrophages exposed to environmental aryl hydrocarbons. Cardiovasc. Res. 82, 361–370. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp007
Prieto, J., León, M., Ponsoda, X., Sendra, R., Bort, R., Ferrer-Lorente, R., et al. (2016). Early ERK1/2 activation promotes DRP1-dependent mitochondrial fission necessary for cell reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 7:11124. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11124
Qiao, P., Zhang, C., Yu, J., Shao, S., Zhang, J., Fang, H., et al. (2022). Quinolinic acid, a tryptophan metabolite of the skin microbiota, negatively regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome through AhR in psoriasis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 142, 2184–2193.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.01.010
Quintana, F. J., Basso, A. S., Iglesias, A. H., Korn, T., Farez, M. F., Bettelli, E., et al. (2008). Control of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature 453, 65–71. doi: 10.1038/nature06880
Ramos, G. P., and Papadakis, K. A. (2019). Mechanisms of disease: inflammatory bowel diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 94, 155–165. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.09.013
Rannug, A., and Fritsche, E. (2006). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor and light. Biol. Chem. 387, 1149–1157. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.143
Rouse, M., Singh, N. P., Nagarkatti, P. S., and Nagarkatti, M. (2013). Indoles mitigate the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by induction of reciprocal differentiation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 169, 1305–1321. doi: 10.1111/bph.12205
Schuster, S., Cabrera, D., Arrese, M., and Feldstein, A. E. (2018). Triggering and resolution of inflammation in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 349–364. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0009-6
Shahin, N. N., Abd-Elwahab, G. T., Tawfiq, A. A., and Abdelgawad, H. M. (2020). Potential role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in childhood obesity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1865:158714. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158714
Shen, Q., Chen, Y., Shi, J., Pei, C., Chen, S., Huang, S., et al. (2023). Asperuloside alleviates lipid accumulation and inflammation in HFD-induced NAFLD via AMPK signaling pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 942:175504. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175504
Shen, X., Gao, X., Luo, Y., Xu, Q., Fan, Y., Hong, S., et al. (2023). Cxxc finger protein 1 maintains homeostasis and function of intestinal group 3 innate lymphoid cells with aging. Nat. Aging 3, 965–981. doi: 10.1038/s43587-023-00453-7
Shen, J., Yang, L., You, K., Chen, T., Su, Z., Cui, Z., et al. (2022). Indole-3-acetic acid alters intestinal microbiota and alleviates ankylosing spondylitis in mice. Front. Immunol. 13:762580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.762580
Shi, Y., Su, W., Zhang, L., Shi, C., Zhou, J., Wang, P., et al. (2021). TGR5 regulates macrophage inflammation in nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by modulating NLRP3 Inflammasome activation. Front. Immunol. 11:609060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.609060
Stockinger, B., Di Meglio, P., Gialitakis, M., and Duarte, J. H. (2014). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 32, 403–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120245
Sun, L., Liu, W., and Zhang, L. J. (2019). The role of toll-like receptors in skin host defense, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis. J Immunol Res 2019, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2019/1824624
Tian, Y., Ke, S., Denison, M. S., Rabson, A. B., and Gallo, M. A. (1999). Ah receptor and NF-kappaB interactions, a potential mechanism for dioxin toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 510–515. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.1.510
Trikha, P., and Lee, D. A. (2020). The role of AhR in transcriptional regulation of immune cell development and function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 1873:188335. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.188335
Twig, G., Zucker, I., Afek, A., Cukierman-Yaffe, T., Bendor, C. D., Derazne, E., et al. (2020). Adolescent obesity and early-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 43, 1487–1495. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1988
Wada, T., Sunaga, H., Miyata, K., Shirasaki, H., Uchiyama, Y., and Shimba, S. (2016). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor plays protective roles against high fat diet (HFD)-induced hepatic steatosis and the subsequent lipotoxicity via direct transcriptional regulation of Socs3 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 7004–7016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693655
Wang, W. L., Kasamatsu, J., Joshita, S., Gilfillan, S., di Luccia, B., Panda, S. K., et al. (2022). The aryl hydrocarbon receptor instructs the immunomodulatory profile of a subset of Clec4a4+ eosinophils unique to the small intestine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 119:e2204557119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2204557119
Wang, K., Lv, Q., Miao, Y. M., Qiao, S. M., Dai, Y., and Wei, Z. F. (2018). Cardamonin, a natural flavone, alleviates inflammatory bowel disease by the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation via an AhR/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 155, 494–509. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.07.039
Wang, X., Ota, N., Manzanillo, P., Kates, L., Zavala-Solorio, J., Eidenschenk, C., et al. (2014). Interleukin-22 alleviates metabolic disorders and restores mucosal immunity in diabetes. Nature 514, 237–241. doi: 10.1038/nature13564
Wang, Y., Sadike, D., Huang, B., Li, P., Wu, Q., Jiang, N., et al. (2023). Regulatory T cells alleviate myelin loss and cognitive dysfunction by regulating neuroinflammation and microglial pyroptosis via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in LPC-induced demyelination. J. Neuroinflammation 20:41. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02721-0
Wang, B., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, C., Jiang, J., Li, Y., et al. (2023). ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 97, 1439–1451. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03476-6
Wang, Q., Wang, F., Zhou, Y., Li, X., Xu, S., Jin, Q., et al. (2024). Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 relieving intestinal inflammation by modulating intestinal stem cells proliferation and differentiation via AhR/STAT3 pathway in LPS-challenged piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 6096–6109. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05956
Wang, C., Xu, C. X., Krager, S. L., Bottum, K. M., Liao, D. F., and Tischkau, S. A. (2011). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency enhances insulin sensitivity and reduces PPAR-α pathway activity in mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 119, 1739–1744. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1103593
Wei, Y. D., Bergander, L., Rannug, U., and Rannug, A. (2000). Regulation of CYP1A1 transcription via the metabolism of the tryptophan-derived 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 383, 99–107. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2037
Xia, H., Zhu, X., Zhang, X., Jiang, H., Li, B., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Alpha-naphthoflavone attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in oleic acid-treated HepG2 hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 118:109287. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109287
Xu, X., Sun, S., Liang, L., Lou, C., He, Q., Ran, M., et al. (2021). Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and gut microbiota-derived metabolites Indole-3-acetic acid in Sulforaphane alleviates hepatic steatosis in mice. Front. Nutr. 8:756565. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.756565
Xu, C. X., Wang, C., Zhang, Z. M., Jaeger, C. D., Krager, S. L., Bottum, K. M., et al. (2015). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency protects mice from diet-induced adiposity and metabolic disorders through increased energy expenditure. Int. J. Obes. 39, 1300–1309. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.63
Yang, F., Li, J., Deng, H., Wang, Y., Lei, C., Wang, Q., et al. (2019). GSTZ1-1 deficiency activates NRF2/IGF1R Axis in HCC via accumulation of Oncometabolite Succinylacetone. EMBO J. 38:e101964. doi: 10.15252/embj.2019101964
Yang, W., Yu, T., Huang, X., Bilotta, A. J., Xu, L., Lu, Y., et al. (2020). Intestinal microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulation of immune cell IL-22 production and gut immunity. Nat. Commun. 11:4457. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18262-6
Yao, L., Wang, C., Zhang, X., Peng, L., Liu, W., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Hyperhomocysteinemia activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/CD36 pathway to promote hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology 64, 92–105. doi: 10.1002/hep.28518
Zelante, T., Iannitti, R. G., Cunha, C., de Luca, A., Giovannini, G., Pieraccini, G., et al. (2013). Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity 39, 372–385. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.003
Zhang, L., Cheng, D., Zhang, J., Tang, H., Li, F., Peng, Y., et al. (2023). Role of macrophage AhR/TLR4/STAT3 signaling axis in the colitis induced by non-canonical AhR ligand aflatoxin B1. J. Hazard. Mater. 452:131262. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131262
Zhang, J., Deng, Z., Jin, L., Yang, C., Liu, J., Song, H., et al. (2017). Spleen-derived anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 stimulated by adipose tissue-derived stem cells protects against type 2 diabetes. Stem Cells Dev. 26, 1749–1758. doi: 10.1089/scd.2017.0119
Zhao, W., Guo, M., Feng, J., Gu, Z., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Myristica fragrans extract regulates gut microbes and metabolites to attenuate hepatic inflammation and lipid metabolism disorders via the AhR-FAS and NF-κB signaling pathways in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrients 14:1699. doi: 10.3390/nu14091699
Zhao, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, D., Huang, Z., Xiao, X., Zheng, Q., et al. (2023). Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic dysfunction fatty liver disease (MAFLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:17514. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417514
Zhou, J., Zhou, F., Wang, W., Zhang, X. J., Ji, Y. X., Zhang, P., et al. (2020). Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China. Hepatology 71, 1851–1864. doi: 10.1002/hep.31150
Zhu, J., Luo, L., Tian, L., Yin, S., Ma, X., Cheng, S., et al. (2018). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes IL-10 expression in inflammatory macrophages through Src-STAT3 signaling pathway. Front. Immunol. 9:2033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02033
Zhu, Q., Ma, Y., and Liang, J. (2021). AhR mediates the aflatoxin B1 toxicity associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6:432. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00713-1
Zhu, X. Y., Xia, H. G., Wang, Z. H., Li, B., Jiang, H. Y., Li, D. L., et al. (2020). In vitro and in vivo approaches for identifying the role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicol. Lett. 319, 85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.10.010
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor, gut microbiota, lipid metabolism, inflammation, metabolic disease
Citation: Zheng W, Liu M, Lv X, He C, Yin J and Ma J (2025) AhR governs lipid metabolism: the role of gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 16:1442282. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1442282
Edited by:
Abbas Yadegar, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, IranReviewed by:
Sardar Sindhu, Dasman Diabetes Institute, KuwaitArun Karnwal, Graphic Era University, India
Copyright © 2025 Zheng, Liu, Lv, He, Yin and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ma Jie, bWFqaWUyMDIzQGd4dS5lZHUuY24=
 Wanru Zheng
Wanru Zheng Mengkuan Liu
Mengkuan Liu Xinyu Lv1
Xinyu Lv1 Jie Yin
Jie Yin Jie Ma
Jie Ma