- 1College of Animal Science, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Yunfu Branch, Guangdong Laboratory for Lingnan Modern Agriculture, Yunfu, China
Introduction: Avian orthoreovirus (ARV) is a significant pathogen causing viral arthritis, leading to substantial economic losses in the poultry industry worldwide.
Methods: A novel ARV strain, designated FJ202311, was isolated from a broiler farm in Fujian Province, China. Whole-genome sequencing was conducted using next-generation sequencing with MGI technology, and phylogenetic analysis of the sigma C amino acid sequence was performed. Comparative sequence analysis identified unique genetic features of FJ202311. Pathogenicity studies were carried out by inoculating broilers with the isolated strain and monitoring clinical signs, weight gain, and histopathological changes.
Results: The complete genome of FJ202311 was determined to be 23,495 base pairs in length, encoding 12 major proteins. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that FJ202311 forms a distinct genotypic cluster, exhibiting only 47.1% to 59.3% sequence identity to 16 reference ARV strains. Notably, 50 unique amino acid substitutions were identified in the sigma C protein. Pathogenicity tests demonstrated that FJ202311 caused severe arthritis and tenosynovitis in broilers. Infected birds exhibited significant weight loss compared to controls, with reductions of 11.78% and 8.93% at 14 and 21 days post-infection, respectively.
Discussion: This study highlights the unique molecular and pathogenic characteristics of the novel ARV strain FJ202311, contributing to our understanding of ARV diversity and epidemiology in China. These findings underscore the importance of continuous monitoring and provide insights for developing improved prevention and control strategies against ARV.
Introduction
Avian orthoreovirus (ARV) is a significant avian pathogen associated with various diseases in chickens, leading to substantial economic losses in the global poultry industry. ARV-induced viral arthritis and tenosynovitis primarily affect the joints and tendons, causing swelling, lameness, and reduced mobility, which negatively impact feed efficiency and weight gain (Sellers, 2017). Hepatitis, characterized by liver inflammation and dysfunction, can result in systemic effects such as jaundice and impaired growth (Mandelli et al., 1978). Respiratory diseases manifest as coughing, sneezing, and labored breathing, often exacerbated by secondary bacterial or viral infections (Fahey and Crawley, 1954). Runting-stunting syndrome is marked by uneven growth and underdeveloped chicks, leading to economic losses due to poor flock uniformity (Goodwin et al., 1993). Malabsorption syndrome causes nutrient malabsorption, diarrhea, poor growth, and reduced performance (Page et al., 1982). Neurological signs, including tremors, ataxia, and paralysis, significantly impair bird welfare (Van de Zande and Kuhn, 2007). Immunosuppression compromises the immune system, increasing susceptibility to secondary infections and reducing vaccine efficacy (Neelima et al., 2003). ARV infects various avian species, including chickens (Chen et al., 2019), turkeys (Sharafeldin et al., 2014), ducks (Wang et al., 2020), geese (Palya et al., 2003), pigeons (Vindevogel et al., 1982), ostriches (Sakai et al., 2009), and wild birds (Huhtamo et al., 2007). The virus is transmitted both horizontally and vertically, with intestinal shedding lasting longer than respiratory shedding, making contaminated feces a primary source of contact transmission. Vertical transmission occurs through eggs, allowing infected breeder hens to pass the virus to a small proportion of chicks (Sellers, 2022; Rafique et al., 2024). The first ARV strain was isolated in 1954 from chickens with respiratory disease (Fahey and Crawley, 1954), and its role as a causative agent of viral arthritis was identified in Walker et al. (1972). ARV infections have since spread globally, causing economic losses in regions including the USA (Lu et al., 2015), Israel (Dawe et al., 2022), Brazil (De Carli et al., 2020), Canada (Palomino-Tapia et al., 2018), Korea (Noh et al., 2018), and China (Teng et al., 2014).
ARV is a member of the genus Orthoorthoreovirus of the family Reoviridae, and has double-stranded RNA genome with 10 segments (Rafique et al., 2024). Based on their electrophoretic mobility, ARV genome can be classified into three size classes: three large segments (L1, L2, L3), three middle segments (M1, M2, M3) and four small segments (S1, S2, S3, S4) (Rafique et al., 2024), encoding 8 structural proteins (λA, λB, λC, μA, μB, σA, σB, and σC) and 4 non-structural proteins (μNS, σNS, p10, and p17) (Varela and Benavente, 1994). The λA protein, encoded by the L1 gene, plays a crucial role in viral replication and assembly. The λB protein, encoded by the L2 gene, facilitates RNA polymerase activity, which is essential for viral RNA synthesis. The λC protein, encoded by the L3 gene, forms turret-like structures at the fivefold axis of the core, enabling interactions with the outer capsid during viral assembly. The μA protein, encoded by the M1 gene, contributes to the stability and integrity of the capsid. The μB protein, encoded by the M2 gene, undergoes myristoylation, which is necessary for its functionality, aiding viral replication and the formation of viral factories. The μNS protein, encoded by the M3 gene, accumulates in viral factories, potentially assisting in RNA packaging and replication. The σA protein, encoded by the S2 gene, interferes with host antiviral responses by inhibiting dsRNA-dependent protein kinases and IFN production. The σB protein, encoded by the S3 gene, is essential for pathogenesis and the elicitation of group-specific neutralizing antibodies. The σNS protein, encoded by the S4 gene, accelerates RNA folding and promotes specific RNA–RNA interactions required for genome replication. The p10 protein, encoded by the S1 gene, enhances membrane permeability, induces syncytium formation, and triggers apoptosis, contributing to virulence. The p17 protein, also encoded by the S1 gene, accumulates in the nucleus to modulate immune responses, block signaling pathways, and regulate interferon production. Among these proteins, the sigma C (σC) protein, encoded by the S1 segment, is highly variable, involving viral attachment and entry and the production of type-specific neutralizing antibodies (Liu et al., 2003; Rafique et al., 2024). Accrording to the amino acid sequence of the σC protein, ARV isolates are usually classified into six genotypes: I, II, III, IV, V, and VI (Tang et al., 2016; De la Torre et al., 2021).
In China, ARV infection was first reported in 1985 (Chen et al., 2019). Although several commercial vaccines against ARV are available, the cases of viral arthritis induced by ARV variants increased in Chinese poultry farms in recent years, indicating that these commercial vaccines might confer partial protection against different novel ARV strains (Chen et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2022). While several ARV strains have been identified and studied, there is limited information on the genetic diversity and pathogenicity of emerging ARV variants circulating in China. Additionally, the role of the highly variable S1 gene in ARV virulence and immune evasion remains poorly understood. In this study, we isolated a novel ARV strain from a chicken flock in Fujian province of China. The whole-genome sequencing and analysis revealed that this strain is genetically distinct from known ARV strains, particularly exhibiting extremely significant variability in the S1 gene compared to other genotypic clusters. Furthermore, pathogenicity analysis indicated that this novel strain causes severe arthritis and tenosynovitis in broiler chickens. These findings enhanced our understanding of the epidemiological evolution of ARV and provided essential insights for the control of ARV.
Materials and methods
Sample collection and processing
In November 2023, the clinical samples (including tendon and cecal tonsils) were collected from 25-day-old white-feathered Cobb broilers exhibiting arthritis, tenosynovitis, and poor production performance in Fujian Province. These samples were homogenized in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at pH 7.4 to create a 20% (w/v) tissue suspension. The suspensions underwent 3 cycles of freezing and thawing, followed by clarification through centrifugation at 6,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C. The supernatants were subsequently harvested for virus isolation and viral nucleic acid extraction. Viral nucleic acid extraction was performed using the MagaBio Plus Viral DNA/RNA Purification Kit (Bioer, Hangzhou, China) and the nucleic acid purification system (Bioer, Hangzhou, China), following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Detection of ARV and other pathogens
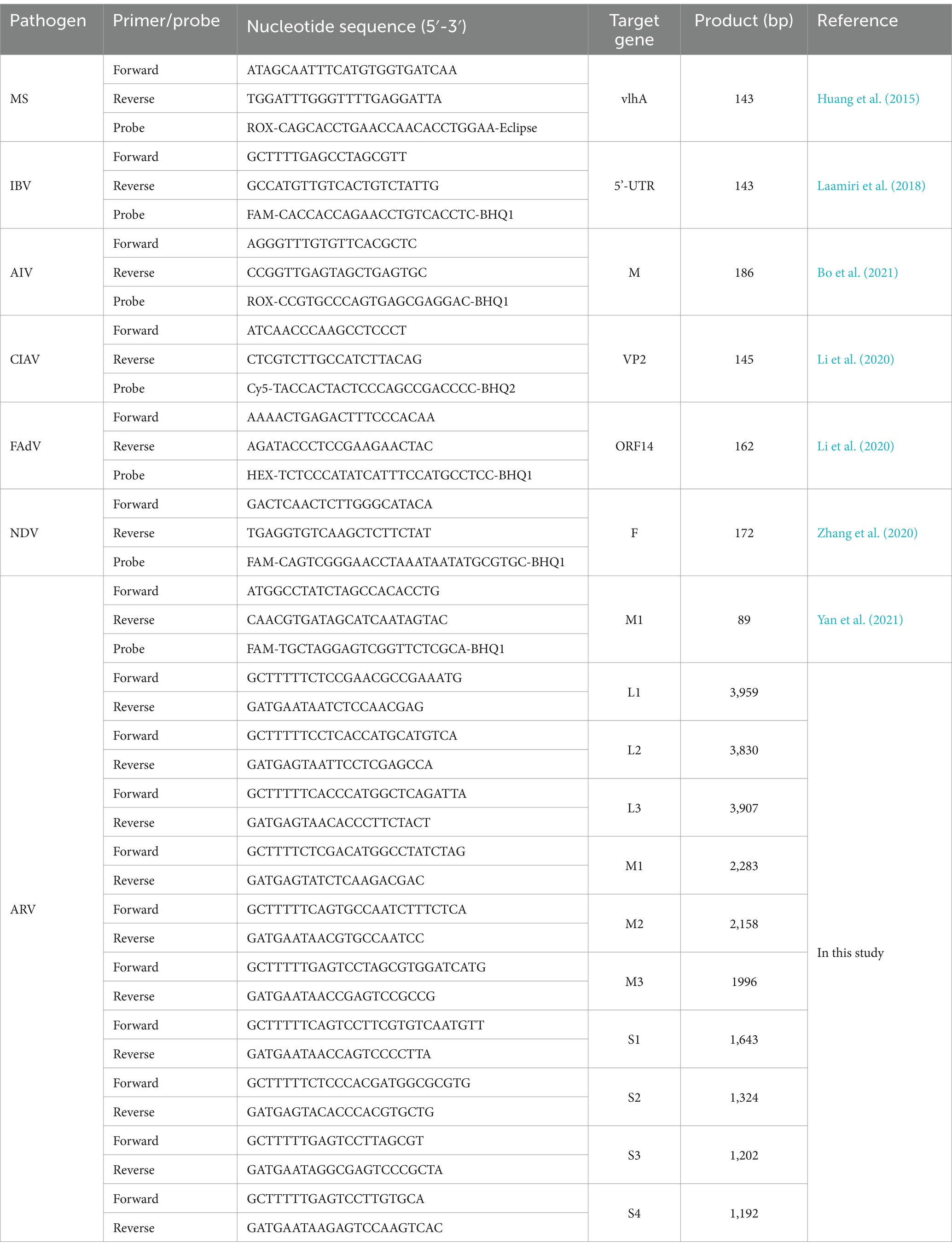
The M1 gene of ARV was amplified using universal primers and probe (Table 1) by the real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay as previously described (Yan et al., 2021). To determining co-infection, the existences of other pathogens, including Mycoplasma synoviae (MS) (Huang et al., 2015), fowl adenovirus (FAdV) (Li et al., 2020), chicken infectious anemia virus (CIAV) (Li et al., 2020), avian influenza virus (AIV) (Bo et al., 2021), infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) (Laamiri et al., 2018), and Newcastle disease virus (NDV) (Zhang et al., 2020), were detected from ARV-positive samples by real-time PCR with primers and probes (Table 1) as described previously with minor modifications.
For four pathogens (ARV, AIV, IBV, NDV), the extracted viral RNA was tested by real-time PCR by using the Hifair V C58P2 Multiplex One Step RT-qPCR Probe Kit (Yeasen, Shanghai, China) under the following reaction conditions: 50°C for 20 min; 95°C for 5 min; the cycling step was repeated for 40 cycles at 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 30 s. For three other pathogens (MS, FAdV and CIAV), the extracted DNA was tested by real-time PCR by using the Hieff Unicon® Universal TaqMan multiplex qPCR master mix (Yeasen, Shanghai, China) under the following reaction conditions: 95°C for 5 min; the cycling step was repeated for 40 cycles at 95°C for 15 s, 60°C for 30 s.
Virus isolation in LMH cells
For virus isolation, only ARV-positive tissue samples were used to isolate ARV on Leghorn male hepatoma (LMH) cells (ATCC #CRL-2117). Briefly, the LMH cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (BOVOGEN, Melbourne, Australia) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. The ARV-positive supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm filter (Millipore, Tullagreen, Carrigtwohill, Ireland). The sterile filtrates were then overlaid onto LMH cell monolayers in 12-well plates. After 1 h of absorption at 37°C, the supernatant was discarded, the LMH cells were washed three times with PBS, and fresh DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic was added. After a 72-h incubation period, the supernatant and cells were harvested through three freeze–thaw cycles for the next round of virus propagation and real-time PCR detection. Following three blind passages of infected cells, the culture supernatants were harvested and stored at −80°C for further analysis. Additionally, the median tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) was determined as previously described (Yan et al., 2021).
Electron microscopy
Electron microscopic observation was conducted as described previously with some modifications (De Carlo and Harris, 2011). Briefly, ARV-infected LMH cells were harvested and subjected to three freeze–thaw cycles, and centrifugated at 8,000× g for 30 min at 4°C. The mixture was then ultracentrifuged at 100,000 × g for 2 h at 4°C. The pellet was resuspended in PBS buffer and negatively stained with 2% phosphotungstic acid. After blotting and drying, the grids were examined using an electron microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
Immunofluorescence assay (IFA)
The immunofluorescence assay (IFA) was performed with modifications as described previously (Yan et al., 2021). Briefly, ARV-infected or mock-infected LMH cell monolayers were washed twice with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature. The fixed cells were then permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 (Solarbio, Beijing, China) for 30 min, blocked with 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 1 h at room temperature, and washed three times with PBS. Subsequently, the cells were incubated with an anti-ARV p10 antibody (Zhongnong Yiyou Medical Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangdong, China) at a dilution of 1:500 overnight at 4°C. After three washes with PBS, the cells were incubated with FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) at a dilution of 1:1,000 for 1 h at at room temperature. All images were captured and processed using a fluorescence microscope (Leica, Wetzlarm, Germany).
High-throughput sequencing and analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the FJ202311 strain using a Magnetic Bead Method Nucleic Acid Extraction Kit (Baybiopure, Guangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Following RNA extraction, ribosomal RNA (rRNA) was removed using the MGIEasy rRNA Depletion Kit (MGI Tech). RNA libraries were then prepared using the MGISP-Smart 8 sample preparation system (MGI Tech). Finally, the RNA libraries were sequenced on an MGISEQ-2000RS sequencer (MGI Tech) using 100-nt single-read sequencing.
The CLC Genomics Workbench version 24.0.1 (Qiagen) was used for viral genome assembly. Adapters and non-target sequences, including mRNA, rRNA, and chicken sequences, were trimmed off. Sequence assembly and analysis were performed using the de novo assembly tool and the map reads to reference tool within the CLC software, employing default parameters as previously described (Zeden and Grundling, 2023).
Additionally, ten PCR primers were designed (Table 1), and PCR amplification followed by Sanger sequencing was performed to confirm the results of next-generation sequencing. Briefly, all gel-purified PCR products were cloned into the pMD19-T vector (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) and then transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). Three or more positive clones for each PCR product were selected and sent to Sangon Biotech Company (Guangzhou, China) for sequencing. The nucleotide sequences were submitted to GenBank.
Sequence comparison, phylogenetic analysis and recombination analysis
The homology identity of nucleotide and amino acid sequences was determined using 16 ARV reference sequences with the EditSeq and MegAlign programs of the DNAstar Lasergene 7.1 software (DNAStar, Madison, WI, USA). Sequence alignments were performed using the Clustal W method, and phylogenetic analysis of the nucleotide and amino acid sequences was constructed using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates in the MEGA software (version 7.0). Comparative analysis of whole genome alignment of the FJ202311 strain and the 16 ARV reference strains (Table 2) was conducted on the mVISTA online platform.1
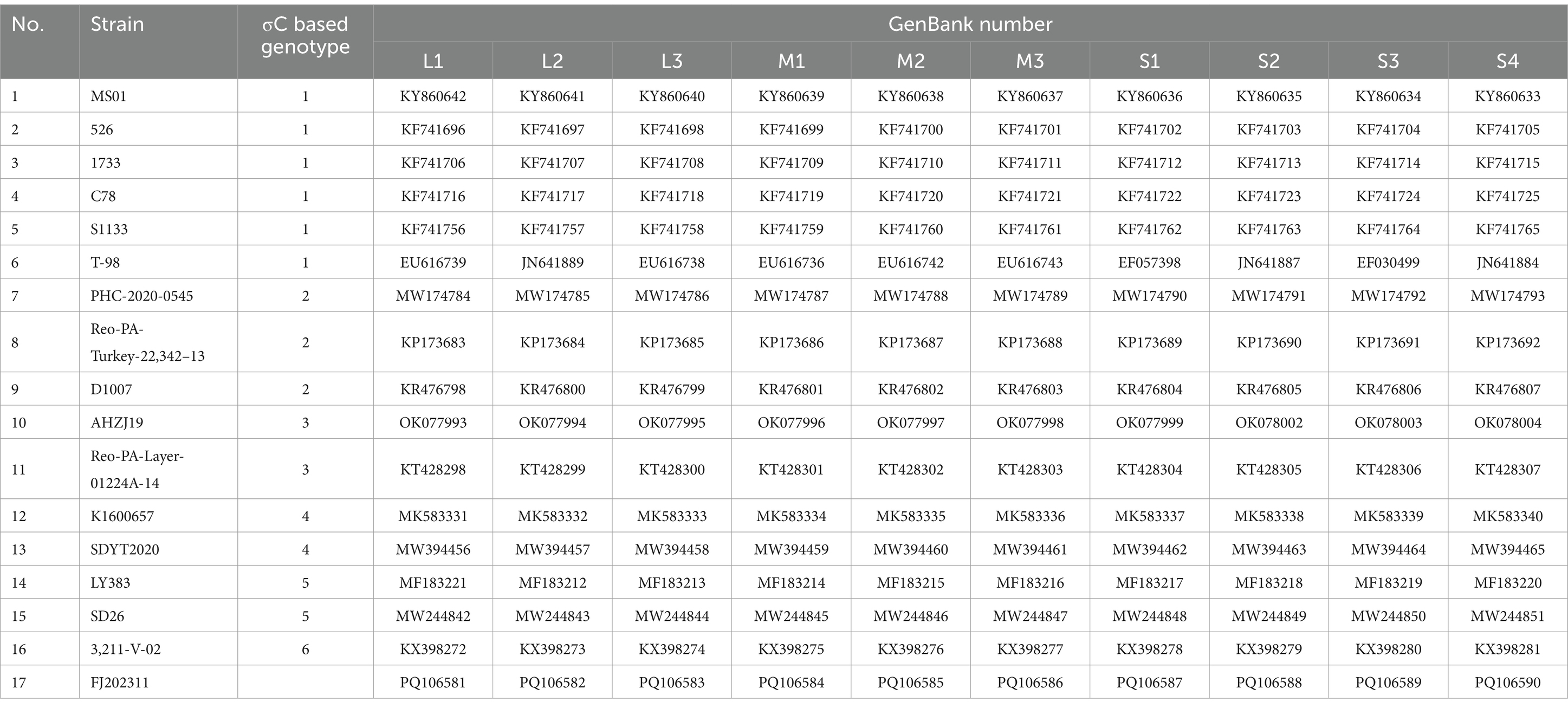
Table 2. The 16 ARV reference strains and the FJ202311 strain retrieved from the GenBank database used in the analysis.
Pathogenicity analyses of the ARV
To assess the pathogenicity of the ARV isolate FJ202311, challenge studies were performed in chickens. A total of 40 healthy Cobb broilers (7-day-old), confirmed to be free of common avian pathogens, were obtained from Guannan Wen’s Food Co., Ltd., Jiangsu, China. The broilers were randomly assigned to two groups (n = 20 per group): an infection group and a control group. The infection group was inoculated via footpad injection with 0.1 mL of virus suspension containing 10^6 TCID50 of ARV, while the control group received 0.1 mL of PBS via the same route. Each group was housed separately in isolators under controlled conditions. Clinical signs, body weight, and mortality were recorded throughout the experimental period of 21 days. At 7, 14, and 21 days post-infection (dpi), three chickens from each group were randomly selected and euthanized for necropsy. Tissue samples, including heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, bursa of Fabricius, pancreas, small intestine, proventriculus, gizzard, thymus, cecal tonsil, and tendon, along with blood sample and cloacal swab, were collected to evaluate viral distribution and shedding. Additionally, tendon samples were fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for subsequent histopathological analysis. Serum samples were collected from chickens to detect ARV-specific antibodies using a commercial ID Screen® Avian Reovirus indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (IDvet, Grabels, France).
Statistical analysis
All experiments were conducted independently in triplicate, producing consistent results. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviations (SD). Statistical significance was evaluated using GraphPad Prism software (version 6.0). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant, while p-values of <0.01 were regarded as highly significant.
Results
Clinical history and virus detection
The primary clinical symptoms observed in the affected 25-day-old white-feathered Cobb chickens included arthritis, tenosynovitis, and reduced production performance. Post-mortem examinations revealed significant swelling and hemorrhages in the tarsal joints. Out of 30 tissue samples, 19 (63%) tested positive for avian reovirus (ARV) using real-time RT-PCR. All samples were negative for MS, FAdV, CIAV, AIV, IBV, and NDV as confirmed by real-time PCR or real-time RT-PCR.
Virus isolation and identification
The ARV strain FJ202311 was isolated on LMH cells through successive generations of culture, and its biological characteristics were evaluated. No cytopathic effect (CPE) were observed in the untreated control LMH cells (Figure 1A). As shown in Figure 1B, the infected LMH cells showed clear cytopathic effect (CPE) after three serial cell passages, and typical syncytial lesions characterized by numerous cells fusing into discs of varying sizes were observed at 48 h post-infection (hpi). To confirm ARV replication in LMH cells, viral RNA was extracted from the infected cells and tested by ARV-specific real-time RT-PCR. The FJ202311 strain was only positive for ARV whereas negative for other common viruses, such as AIV, IBV, NDV, MS, FAdV, and CIAV. No green fluorescence signal was detected in the untreated control LMH cells (Figure 1C). The presence of the ARV strain in LMH cells was further confirmed by immunofluorescence assay (IFA), which detected green fluorescence signals in the LMH cells infected with FJ202311 (Figure 1D). Additionally, spherical virus particles, approximately 80 nm in diameter with an icosahedral shape, were observed using electron microscopy, consistent with the morphological characteristics of ARV (Figure 1E).
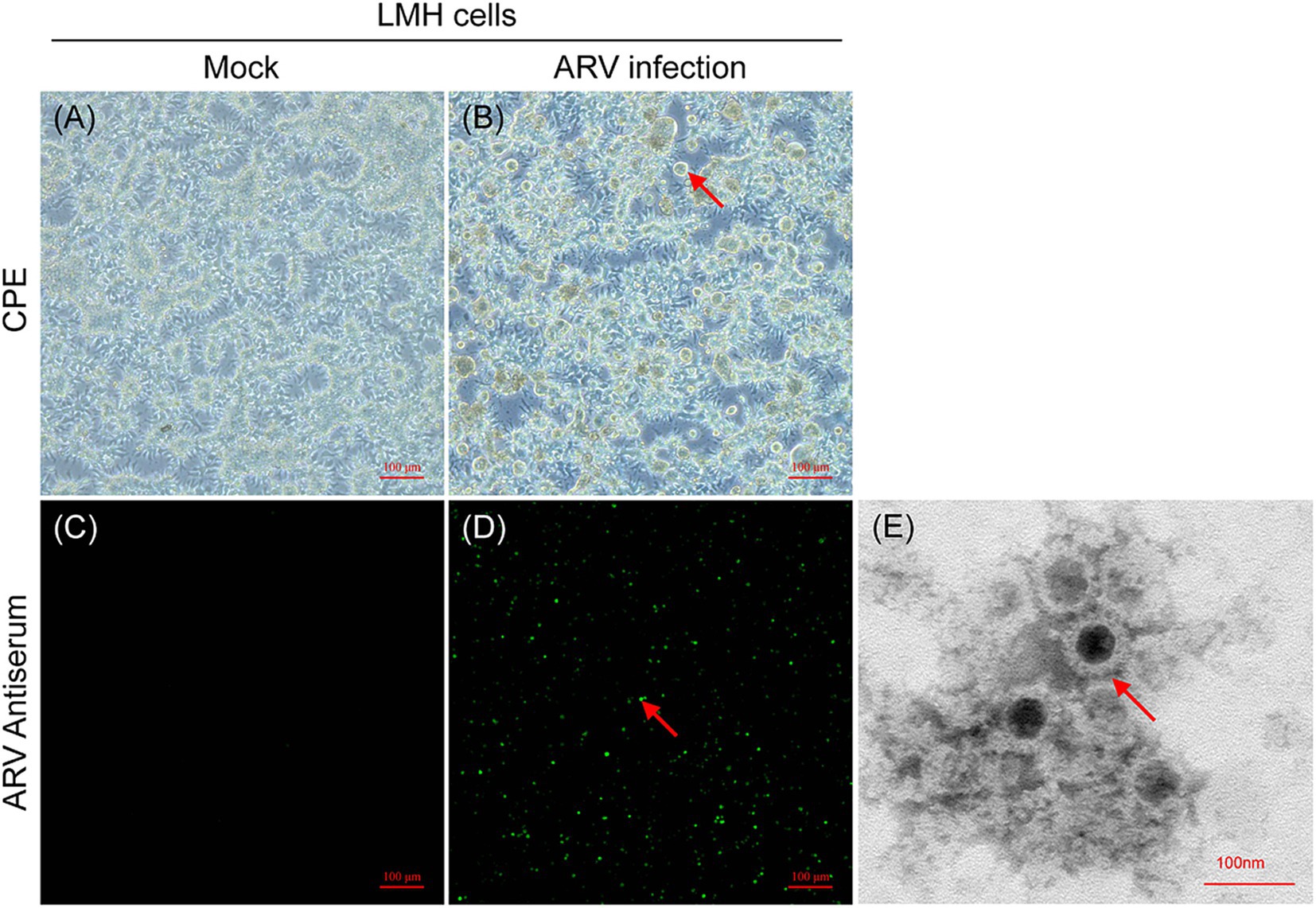
Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of the ARV FJ202311 strain. (A) Mock-infected LMH cells at 48 h post-infection (hpi). (B) ARV-infected LMH cells showing extensive cell fusion into disc-like structures (indicated by arrows) at 48 hpi. (C,D) Immunofluorescence assay (IFA) at 48 hpi using anti-ARV p10 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. Specific green fluorescence is observed in infected LMH cells (indicated by arrows). (E) Electron micrographs of ARV-inoculated LMH cells. Spherical ARV particles are visible (indicated by arrow).
Genomic characterization
The CLC Genomics Workbench software was utilized for viral genome assembly. A total of 34,466,524 paired-end sequencing reads, each 100 bases in length, were generated by the MGISEQ sequencer, resulting in 1.45 Gb of clean data (excluding adaptors, mRNA, rRNA, and chicken sequences). The CLC Map Reads to Reference tool was employed to analyze the original sequences, showing that 19,144,330 reads supported the full genome of the FJ202311 strain, with an average coverage depth of 81,491 reads (Figure 2). Additionally, the full genome of the FJ202311 strain was verified through PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing conducted by Sangon (Shanghai, China).
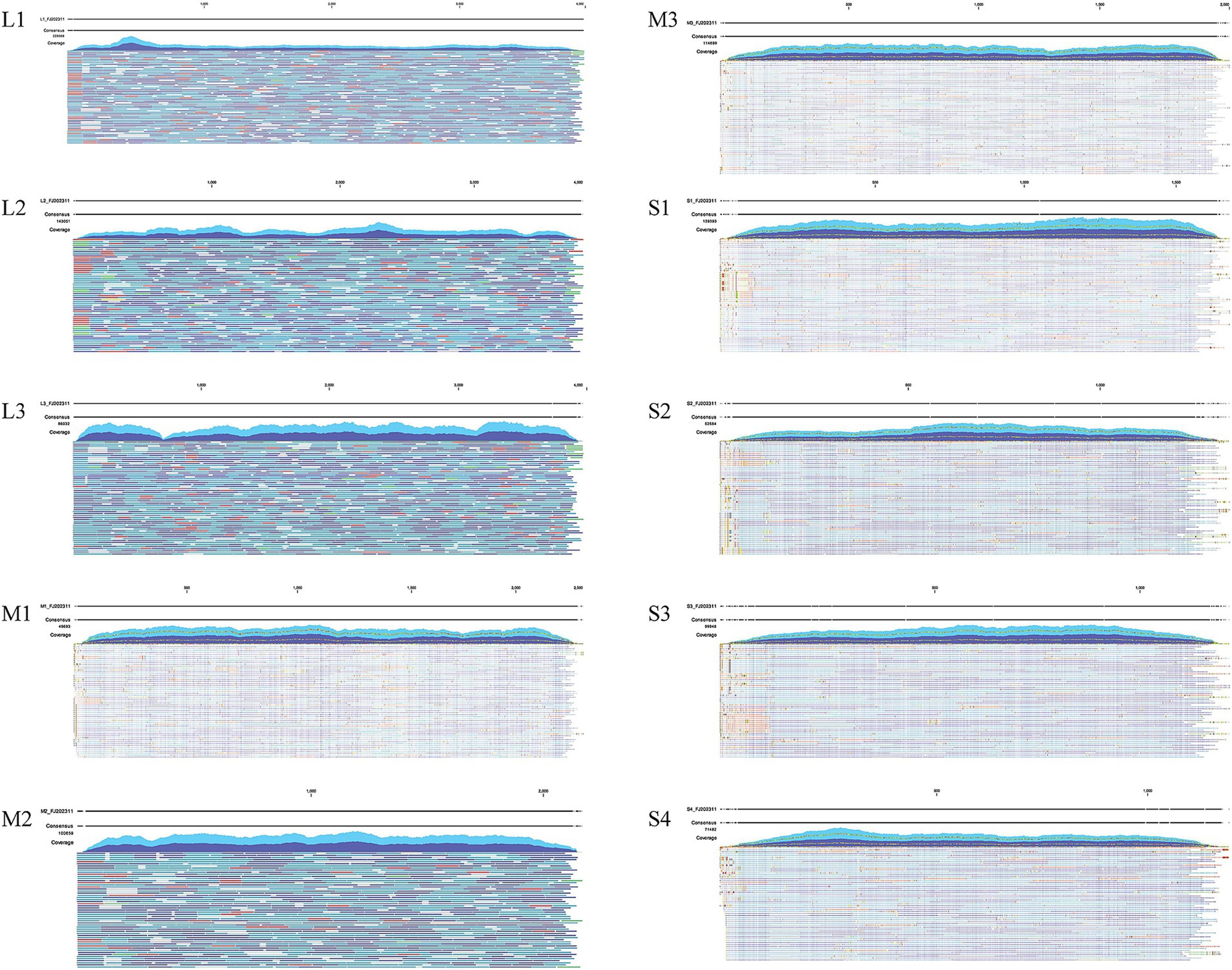
Figure 2. Genome coverage analysis of ARV strain FJ202311. A total of 19,144,330 reads were mapped to the complete genome of FJ202311, yielding an average coverage depth of 81,491 reads.
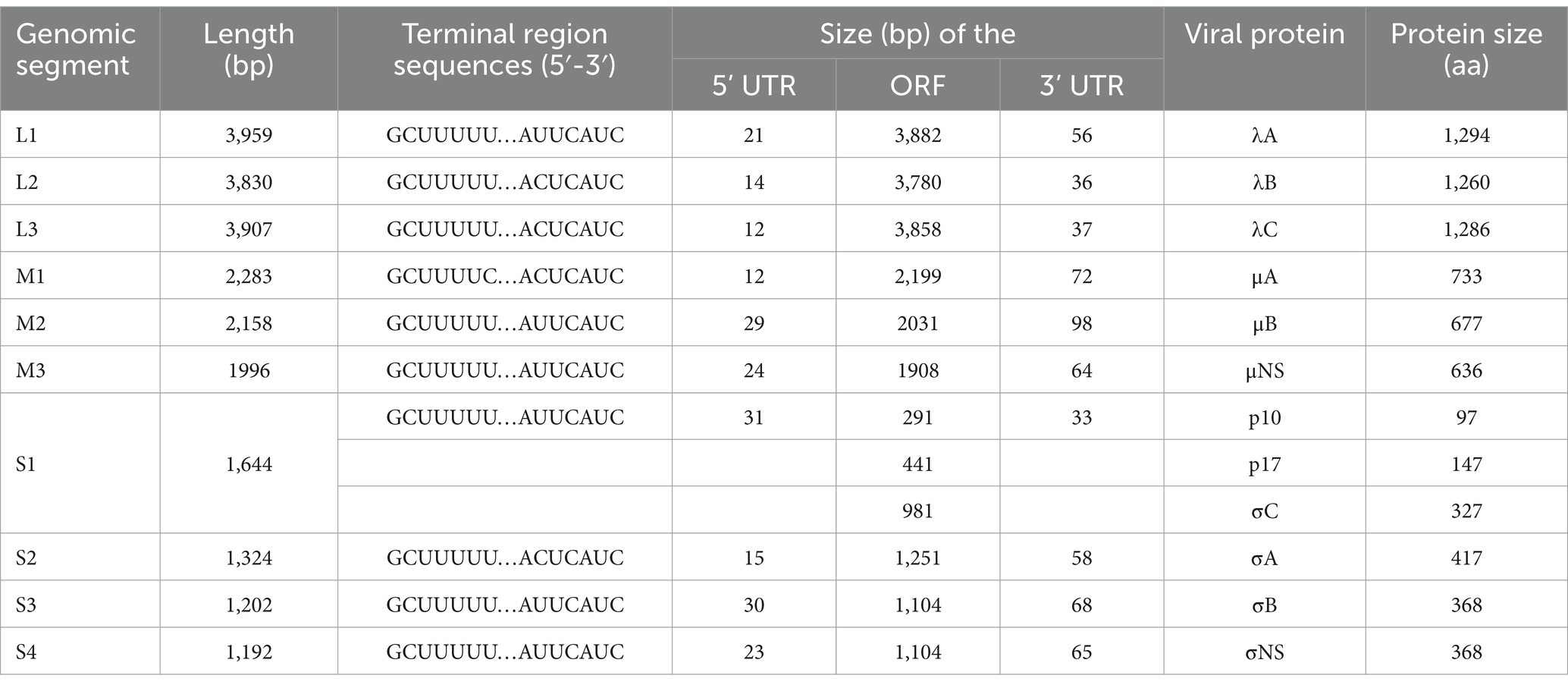
The whole genome sequence of the FJ202311 strain was obtained and deposited in GenBank under accession numbers PQ106581 to PQ106590. As shown in Table 3, the genome of the FJ202311 strain is 23,495 nucleotides (nt) in length, comprising 10 dsRNA segments, which range from 3,959 bp (L1) to 1,192 bp (S4). In the 5’ UTR, the M1 fragment of the FJ202311 strain contains a GCUUUUC motif, while the remaining nine fragments feature a GCUUUUU motif. In the 3’ UTR, four fragments (L2, L3, M1, S2) share an ACUCAUC motif, whereas the remaining six fragments exhibit an AUUCAUC motif.
Sequence comparison
The nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the FJ202311 isolate were most similar to the PHC-2020-0545 strain in the λC-, μNS-, and σNS-encoding genes (nt: 89.9–92.9%; aa: 94.8–98.6%), the AHZJ19 strain in the λB-encoding gene (nt: 91.9%; aa: 98.7%) and σA-encoding gene (nt: 97.8%; aa: 99.3%), the SDYT2020 strain in the λA-encoding gene (nt: 97.3%; aa: 99.5%), and the K1600657 strain in the σB-encoding gene (nt: 91.5%; aa: 96.7%). Additionally, the FJ202311 isolate was similar to the AHZJ19 strain (nt: 97.7%; aa: 98.5%) and the PHC-2020-0545 strain (nt: 96.5%; aa: 98.6%) in the μA-encoding gene, the 526 strain (nt: 86.3%; aa: 95.7%) and the SD26 strain (nt: 86%; aa: 96.5%) in the μB-encoding gene, the LY383 and SD26 strains (nt: 79.7%) and the K1600657 and 3,211-V-02 strains (aa: 85%) in the p10-encoding gene, and the LY383 and SD26 strains (nt: 71.7%; aa: 72.1%) in the p17-encoding gene.
Furthermore, we compared and analyzed the σC amino acid sequences of FJ202311 with the other 16 ARV reference strains. It is notable that the FJ202311 isolate in S1 segment σC-encoding gene has lower identity with the 16 reference strains (nt: 52.5–61.6%; aa:47.1–59.3%). The amino acid alignment of the σC genes showed that 50 amino acids were identified only in the FJ202311 isolate at positions 7 (L), 23 (M), 36 (Q), 37 (I), 38 (L), 51 (L), 52 (E), 65 (V), 78 (K), 81 (R), 82 (I), 83 (D), 88 (N), 94 (R), 95 (N), 108 (H), 115 (D), 117 (V), 118 (A), 119 (G), 120 (D), 121 (I), 122 (L), 125 (N), 126 (N), 144 (E), 146 (S), 147 (A), 156 (H), 158 (G), 159 (Y), 161 (N), 169 (I), 194 (A), 199 (K), 200 (I), 213 (Y), 215 (T), 247 (I), 252 (K), 254 (V), 256 (K), 282 (L), 287 (Q), 294 (F), 307(V), 308 (N), 311 (F), 317 (Y), 319 (N) (Figure 3). The σC proteins were predicted to have molecular weights of 35.2 kDa (the FJ202311 isolate), 34.8 kDa (S1133), 35.1 kDa (PHC-2020-0545), 35.1 kDa (AHZJ19), 35.0 kDa (SDYT2020), 34.8 kDa (LY383) and 35.3 kDa (3211-V-02), and pI of 5.13 (the FJ202311 isolate), 4.76 (S1133), 4.92 (PHC-2020-0545), 4.77 (AHZJ19), 4.69 (SDYT2020), 4.89 (LY383) and 4.82 (3211-V-02). These results indicate slight differences in the size and isoelectric point of σC proteins between the FJ202311 isolate and the 16 reference strains.
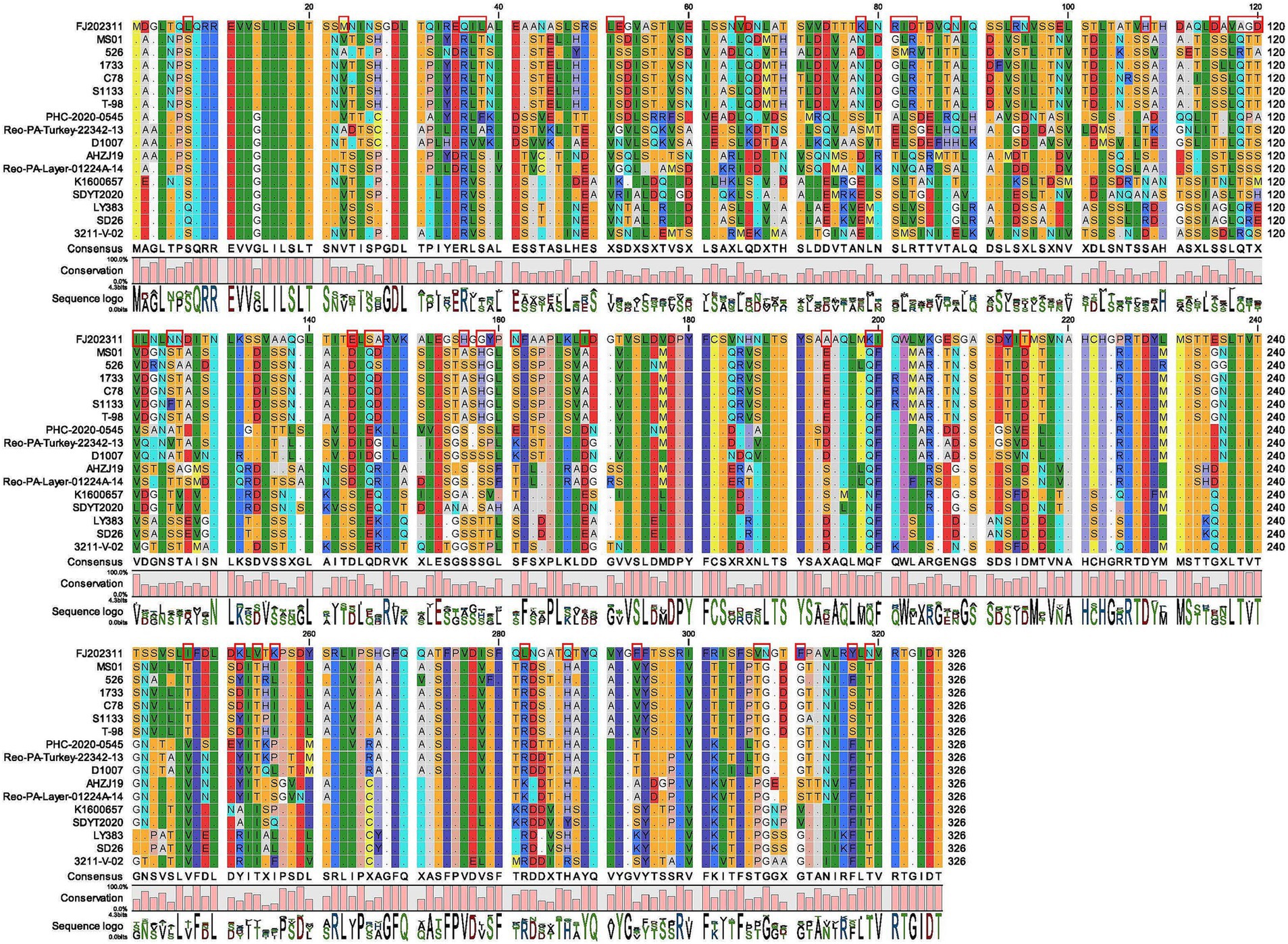

Figure 3. Sequence comparison of the σC amino acid between the FJ202311 strain and 16 other ARV reference strains. The red box highlights amino acids unique to the FJ202311 isolate.
Phylogenetic analysis and visualization analysis
For further analysis of the genetic evolution of the FJ202311 strain, amino acid sequences of the 12 proteins from each strain were subjected to phylogenetic analyses using MEGA 7 software. As shown in Figure 4, the σC phylogenetic tree revealed that the 16 reference strains clustered into six genotypes, whereas the FJ202311 strain formed a distinct cluster, exhibiting extremely high variability compared to strains in other clusters.
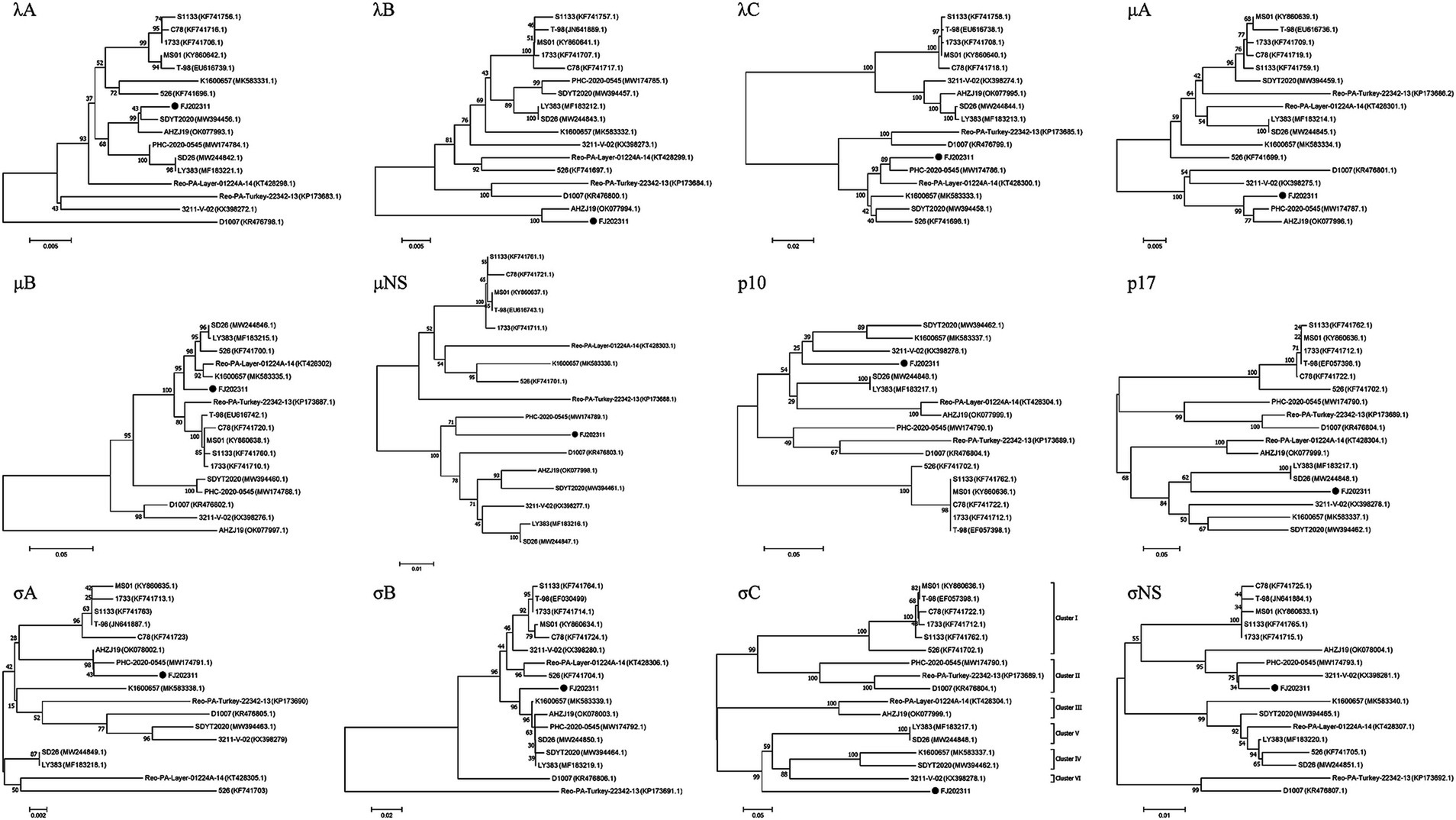
Figure 4. Phylogenetic trees constructed using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA 7.0 based on the 12 proteins (λA, λB, λC, μA, μB, μNS, p10, p17, σA, σB, σC, σNS). The FJ202311 strain is indicated by a black circle.
In the λA phylogenetic tree, the FJ202311 isolate and the SDYT2020 strain clustered on the same branch, consistent with sequence comparison results. Similarly, in the λB phylogenetic tree, the FJ202311 isolate and the AHZJ19 strain appeared on the same branch, corroborating the sequence comparison findings. The phylogenetic trees for the λC and μNS proteins showed that the FJ202311 isolate clustered with the PHC-2020-0545 strain, in agreement with the sequence comparisons. For the μA and σA proteins, the phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the FJ202311 isolate, the PHC-2020-0545 strain, and the AHZJ19 strain clustered on the same branch. In the p17 phylogenetic tree, the FJ202311 isolate was grouped on the same branch with the LY383 and SD26 strains. The σNS phylogenetic tree placed the FJ202311 isolate, the PHC-2020-0545 strain, and the 3,211-V-02 strain on the same branch. In addition, the μB phylogenetic tree grouped the FJ202311 isolate on the same branch as five other strains (LY383, SD26, 526, Reo-PA-Layer-01224A-14, and K1600657). The σB phylogenetic tree placed the FJ202311 isolate with six other strains (LY383, SD26, SDYT2020, PHC-2020-0545, AHZJ19, and K1600657). Similarly, the p10 phylogenetic tree grouped the FJ202311 isolate on the same branch as three strains (SDYT2020, 3,211-V-02, and K1600657).
For a whole genome comparison of the FJ202311 strain with the other 16 reference strains, full genomic sequences were analyzed using the mVISTA online platform. As depicted in Figure 5, the highest nucleotide sequence similarities were observed in the L2, M1, and S2 segments of the AHZJ19 strain; in the L3, M3, and S4 segments of the PHC-2020-0545 strain; in the L1 segment of the SDYT2020 strain; in the M2 segment of the SD26 strain; and in the S3 segment of the K1600657 strain. Most importantly, the FJ202311 isolate exhibited significantly low sequence identity with the other 16 reference strains in the S1 segment, which encodes the virus attachment protein σC. This suggests that a vaccine formulated with the classical strain may be ineffective against this novel strain.
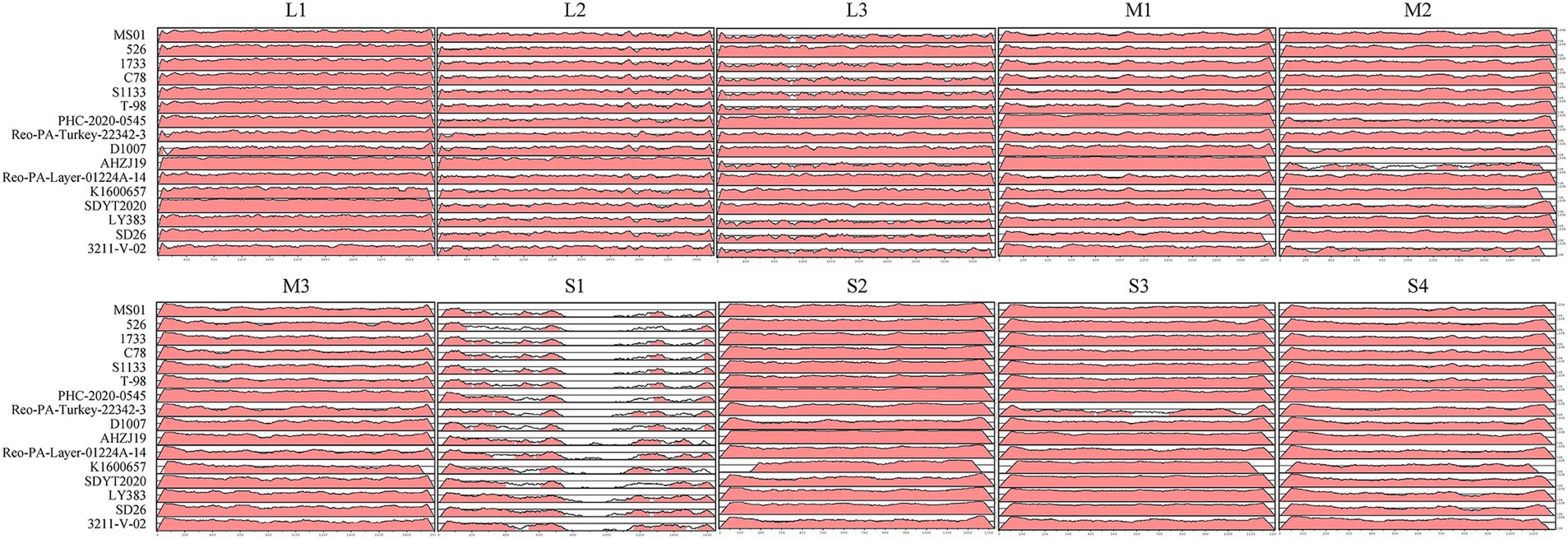
Figure 5. Visualization of the complete genome of the FJ202311 strain and 16 ARV reference strains using the mVISTA online platform. Regions in red denote nucleotide sequence similarities ≥90%, while white regions represent similarities <90%.
Pathogenicity analysis
The pathogenicity of the cell-cultured ARV strain FJ202311 (fourth passage), was evaluated in 7-day-old broiler chickens. Throughout the experiment, no clinical signs, gross lesions, or histological abnormalities were observed in the control group (Figures 6A–C). In contrast, chickens in the infected group displayed signs of depression and stunted growth, though no mortality occurred. Swelling of the footpads was first observed at 2 days post-infection (dpi), progressively extended to the tarsal joints by 7 dpi. By 14 and 21 dpi, the tarsal joints were markedly swollen and exhibited a bluish-purple discoloration (Figure 6D). Gross examination of the infected chickens revealed intra-tarsal joint hemorrhages (Figure 6E), while no significant macroscopic lesions were detected in other organs at 14 and 21 dpi. Histopathological analysis showed significant tissue damage localized to the tendons, including disrupted collagen fibers, extensive connective tissue proliferation, focal lymphocytic infiltration, and perivascular cuffing (Figure 6F). These observations indicate a localized inflammatory response in the tendons and surrounding tissues. By 14 and 21 dpi, the mean body weight of infected chickens was significantly lower than that of the control group, with reductions of 11.78 and 8.93%, respectively (p < 0.01) (Figure 7A). Additionally, ARV-infected chickens exhibited a strong humoral immune response, with antibody levels significantly increased by 47.73-fold and 154.15-fold at 14 and 21 dpi, respectively, compared to the control group (p < 0.01) (Figure 7B).
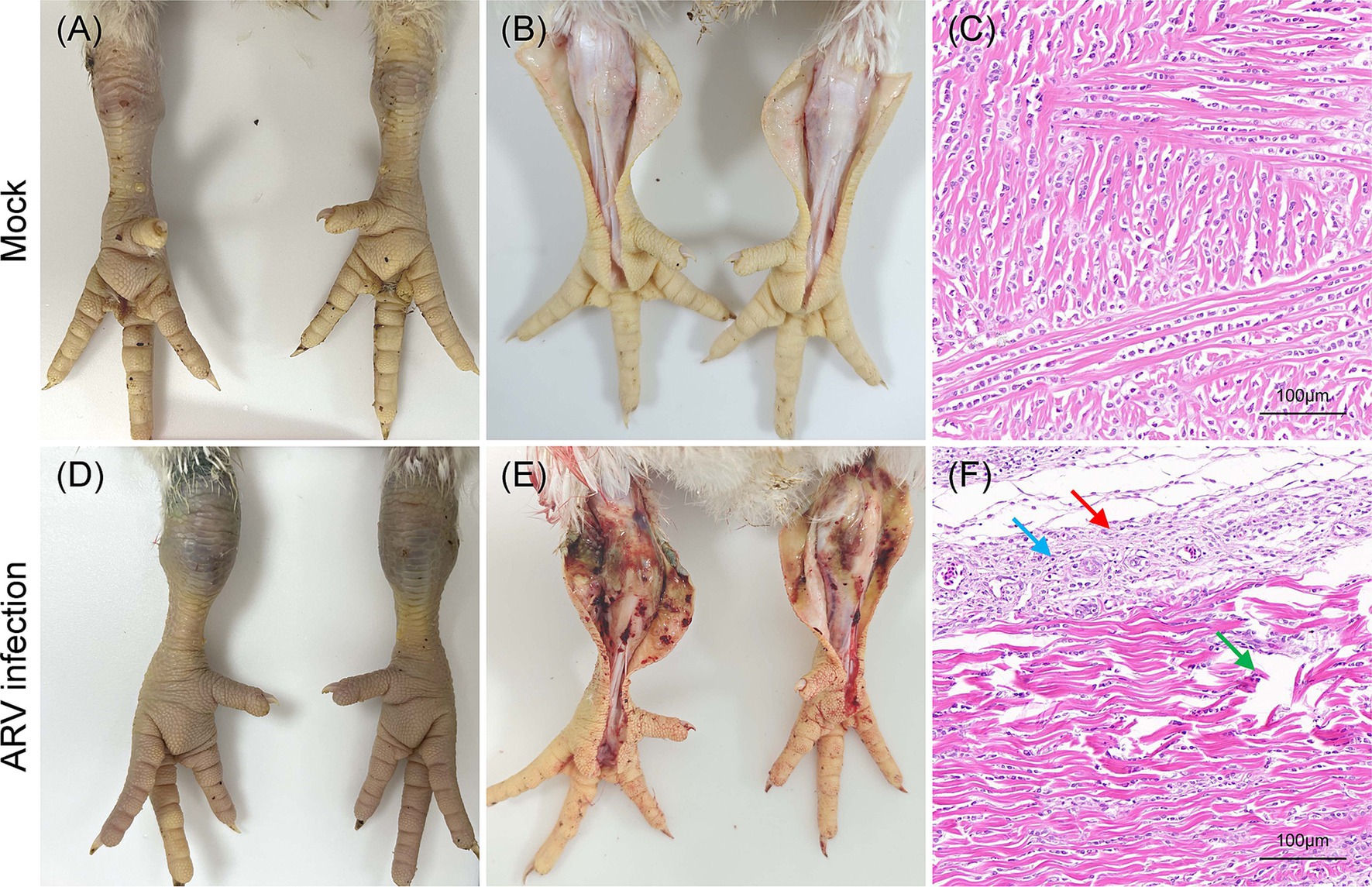
Figure 6. Clinical signs, gross lesions and histological analysis in broilers inoculated with ARV strain FJ202311 at 14 dpi. (A) Normal joint appearance in the control group. (B) Normal articular cavity appearance in the control group. (C) Normal tendon appearance in the control group. (D) Swollen joints and bluish-purple discoloration of the tarsal joint in the infected group. (E) Severe hemorrhage in the tarsal joint of infected broilers. (F) Histopathological analysis showing local collagen fiber disruption (green arrow), significant connective tissue proliferation (black arrow), and focal lymphocyte infiltration (blue arrow) in the tendon.
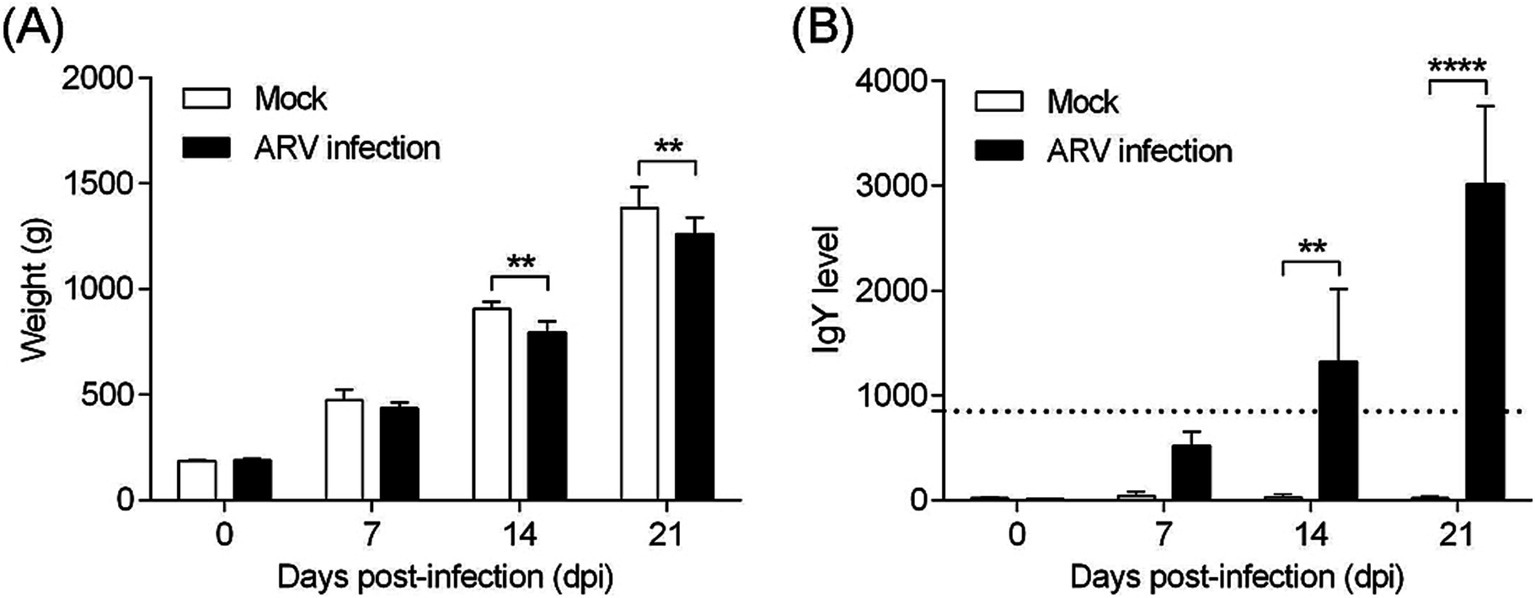
Figure 7. Body weight and ARV-specific antibody levels in broilers. (A) Body weight changes in broilers from each group throughout the experiment. (B) ARV-specific antibody levels in broilers from each group during the challenge study. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks, **** p < 0.0001 and ** p < 0.01.
Viral distribution and shedding
The distribution and shedding patterns of ARV strain FJ202311 were determined using real-time RT-PCR to quantify viral RNA levels in various tissues, blood, and cloacal swabs. As shown in Figure 8, viral loads peaked at 7 dpi, with the highest levels observed in the tendon (10^5.93 copies/g), followed by the cecal tonsils (10^5.32 copies/g). By 14 dpi, viral loads had significantly decreased in most tissues but remained elevated in the tendons (10^5.02 copies/g) and cecal tonsils (10^4.05 copies/g). At 21 dpi, viral RNA persisted at lower levels, with tendons showing the highest residual viral load (10^4.74 copies/g).
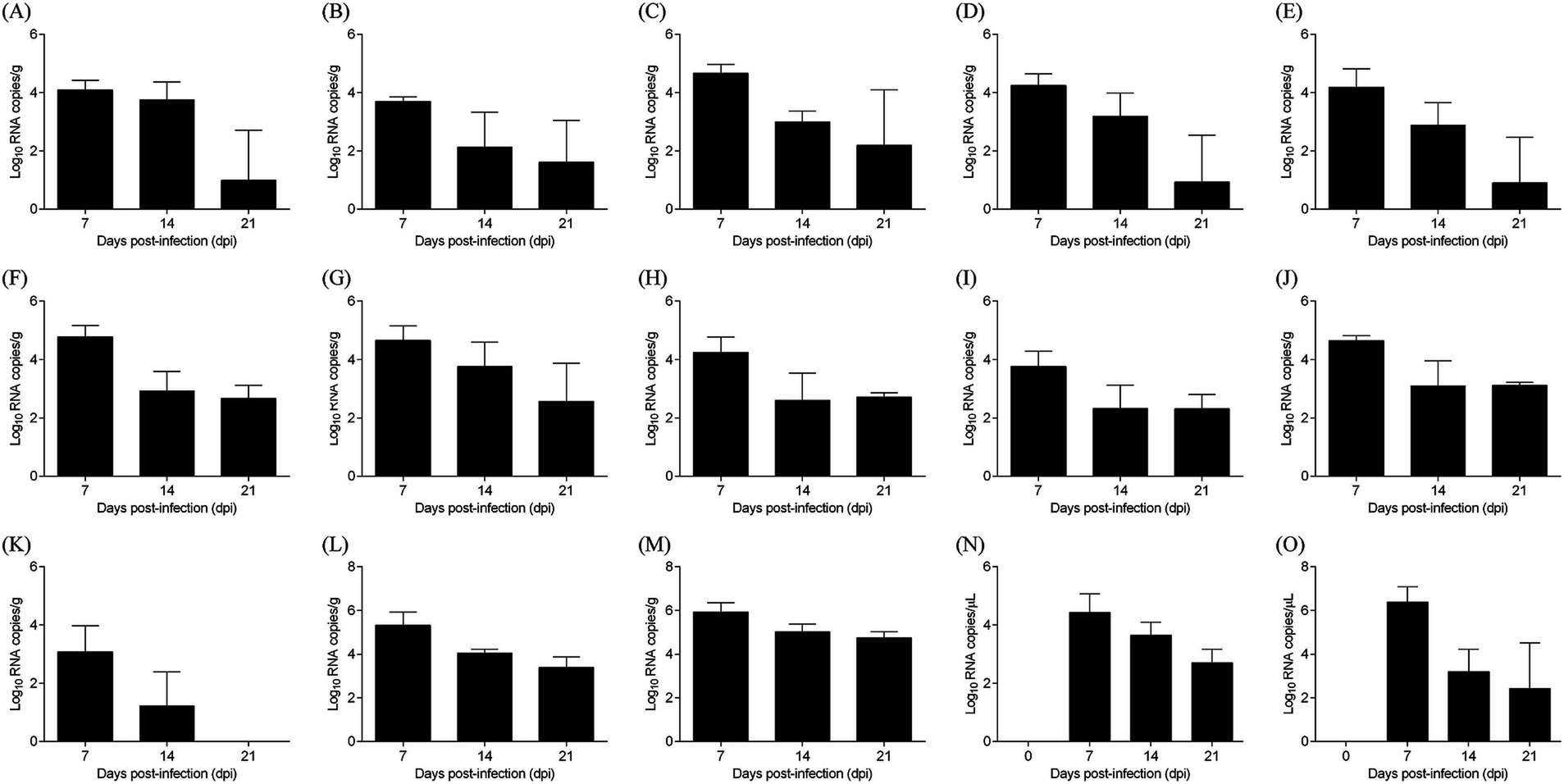
Figure 8. Virus distribution in various samples from ARV-infected chickens. (A) Heart, (B) Liver, (C) Spleen, (D) Lung, (E) Kidney, (F) Bursa of Fabricius, (G) Pancreas, (H) Small intestine, (I) Proventriculus, (J) Gizzard, (K) Thymus, (L) Cecal tonsil, (M) Tendon, (N) Blood, (O) Cloacal swab.
Cloacal swabs revealed continuous viral shedding from 7 to 21 dpi, with a peak at 7 dpi (10^6.38 copies/μL), highlighting the potential for environmental transmission. No viral RNA was detected in control chickens. These results demonstrate the broad tissue tropism of FJ202311, with a strong preference for tendon tissues, and provide valuable insights into the strain’s pathogenicity and transmission dynamics.
Discussion
Reoviruses infect a wide range of hosts, including birds, mammals, and humans, demonstrating remarkable evolutionary adaptability and zoonotic potential (Sellers, 2022; Diller et al., 2023; Song et al., 2008). Their substantial economic impact on the poultry industry, coupled with potential health risks to humans, underscores the necessity for continuous monitoring and characterization of emerging strains (David and Lemay, 2023; Rafique et al., 2024). Since ARV-associated arthritis and tenosynovitis were first described in domestic poultry during the 1950s, numerous strains with varying pathogenicity and host impacts have been reported worldwide, posing significant challenges to epidemic control (Chen et al., 2019; Nour et al., 2023; Rafique et al., 2024). ARVs are primarily transmitted horizontally within flocks via the fecal-oral route, with some strains also capable of vertical transmission (Rafique et al., 2024). In China, ARV infections were first reported in 1985 (Wang et al., 1985), with a marked increase in cases since 2008 (Chen et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2023). The dynamic nature and rapid adaptation of ARV strains necessitate ongoing surveillance, development of strain-specific vaccines, and effective management strategies to safeguard poultry health and industry sustainability. In this study, we successfully isolated a novel ARV strain, FJ202311, from a 25-day-old white-feathered Cobb chicken flock in Fujian Province that exhibited clinical signs of arthritis, tenosynovitis, and poor growth. The FJ202311 strain induced severe arthritis and tenosynovitis in broiler chickens, demonstrating its pathogenic potential and significant impact on poultry health. This novel strain represents a valuable resource for virological and serological studies and future vaccine development.
The stable Leghorn male hepatoma (LMH) cell line, commonly used for ARV isolation, was employed to successfully culture the FJ202311 strain. The strain exhibited extensive cytopathic effects (CPE) characteristic of ARV infections, including the formation of large, fused “bloom-like” structures (Lu et al., 2015; Tang et al., 2015). The high viral titer of 10^8.33 TCID50/mL reflects the strain’s robust replication capacity and adaptability to in vitro conditions. Immunofluorescence and electron microscopy confirmed the isolate as an ARV, displaying the typical icosahedral morphology. These findings are consistent with established ARV isolation methodologies and provide a reliable foundation for further genomic and pathogenicity studies (Yan et al., 2021; Nour et al., 2023).
The complete genome of the FJ202311 strain was obtained by next-generation sequencing and verified by PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing. The whole genome of the FJ202311 isolate was 23,495 nucleotides in length, consist of 10 dsRNA segments ranging from 3,959 bp (L1) to 1,192 bp (S4). Previous studies have shown that the 5’ UTRs and 3’ UTRs of the ARV genome segment are highly conserved, with motifs such as 5’-GCUUUUU-3′ in the 5’ UTRs, and 5′ -UCAUC-3′ in the 3’ UTRs (Su et al., 2006). The FJ202311 strain exhibited these conserved motifs, with minor variations in the M1 segment (GCUUUUC motif). Additionally, the highest nucleotide sequence similarities were observed in the L2, M1, and S2 segments with the AHZJ19 strain; in the L3, M3, and S4 segments with the PHC-2020-0545 strain; in the L1 segment with the SDYT2020 strain; in the M2 segment with the SD26 strain; and in the S3 segment with the K1600657 strain. However, the S1 segment, encoding the σC protein, displayed only 52.5–61.6% nucleotide identity with the 16 reference strains, underscoring its genetic uniqueness.
The σC protein, the most variable ARV protein, mediates viral attachment to host cells, a critical step in infection initiation. It also induces type-specific neutralizing antibodies, playing a pivotal role in host immune response and vaccine development. Its high variability, driven by immune pressure, contributes to viral adaptation and strain diversification, serving as a key marker for ARV classification. Previous studies have categorized ARV strains into six genotypic clusters based on σC sequences (Lu et al., 2015; Ayalew et al., 2017; Palomino-Tapia et al., 2018). For example, Palomino-Tapia et al. (2018) classified ARV strains into Clusters 1–6 in Western Canada during 2012–2017. Similarly, Lu et al. (2015) categorized ARV strains into Clusters 1–6 in Pennsylvania, USA, from 2011–2014. Liu et al. (2023) also divided ARV strains into Clusters 1–6 in China between 2019–2020. In our study, phylogenetic analysis of the σC gene placed FJ202311 in a distinct cluster, separate from the six known genotypic clusters of ARV strains (Lu et al., 2015). The strain exhibited significant amino acid variability (47.1–59.3% identity) compared to reference strains, with 50 unique residues identified in the FJ202311 σC protein. This variability is likely linked to the strain’s ability to adapt to different host environments and may play a role in its pathogenicity. The size and isoelectric point of the σC protein also exhibited slight differences, further emphasizing the strain’s genetic divergence. These findings suggest that FJ202311 represents a novel genotypic lineage, highlighting the ongoing genetic evolution of ARV.
The clinical manifestations of ARV infections are highly variable, with distinct genotypes associated with specific disease symptoms (Rafique et al., 2024). Among these, tenosynovitis and arthritis are the predominant clinical manifestations observed across most ARV genotypes (Rafique et al., 2024). For example, Genotype I is most frequently linked to tenosynovitis and arthritis, where affected birds exhibit swelling and inflammation of the tendons and joints, leading to lameness and impaired mobility. Additionally, this genotype is associated with malabsorption syndrome, characterized by diarrhea, nutrient malabsorption, and poor growth. Respiratory symptoms such as coughing and nasal discharge may also occur, complicating the disease profile (Kant et al., 2003; Hellal et al., 2013; De Carli et al., 2020). Genotype II predominantly causes tenosynovitis and arthritis, similar to Genotype I, but is also closely associated with runting-stunting syndrome. This condition results in uneven growth, underdeveloped chicks, and significant flock performance losses (Kant et al., 2003; De Carli et al., 2020; Kovacs et al., 2022). Genotypes III and V primarily present with tenosynovitis and arthritis, with less frequent reports of other clinical signs. These genotypes cause severe lameness and reduced activity, which adversely impact feed intake and weight gain in affected birds (Kant et al., 2003; Liu et al., 2003; De Carli et al., 2020). Genotype IV exhibits a broader clinical spectrum, combining tenosynovitis, arthritis, runting-stunting syndrome, and malabsorption syndrome. This broader range of symptoms increases the difficulty of diagnosis and control, as affected birds may show signs of multiple overlapping conditions, leading to significant economic losses (Kant et al., 2003; Liu et al., 2003). Genotype VI is characterized exclusively by tenosynovitis and arthritis, which are marked by joint swelling, heat, and pain, causing pronounced lameness. Although restricted to musculoskeletal symptoms, the severity of these signs can result in significant morbidity and mortality in affected flocks (Lu et al., 2015; Egana-Labrin et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2019). In this study, the novel FJ202311 strain caused severe tenosynovitis and arthritis in broilers, consistent with previous findings on highly pathogenic ARV strains. Clinically, infected broilers exhibited characteristic swelling of the footpads and tarsal joints, progressing to bluish-purple discoloration and significant gross pathology. Histopathological analysis revealed marked collagen fiber disruption, connective tissue proliferation, and focal lymphocytic infiltration in tendon tissues. These findings highlight the localized inflammatory response and structural damage caused by the FJ202311 strain. These lesions resulted in significant growth retardation, with infected broilers exhibiting an 11.78 and 8.93% decrease in mean body weight compared to control broilers at 14 and 21 dpi, respectively.
Interestingly, quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed significantly higher levels of viral RNA in tendon tissues compared to other organs, confirming that tendons are the primary target organ for ARV infection. This observation aligns with previous studies (Jiang et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2021) and underscores the critical role of tissue tropism in ARV pathogenesis. The pronounced viral load in tendons correlates with the observed clinical and histopathological changes, further emphasizing the diagnostic importance of tendon lesions in ARV-infected birds. Additionally, mutations in the σC protein may enhance the strain’s binding affinity to tendon-specific receptors, contributing to its tissue tropism and pathogenicity. This study provides valuable insights into the FJ202311 strain’s characteristics and pathogenicity. However, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, only broiler chickens were investigated, despite ARV infections being reported across various avian species. This focus on broilers may limit the generalizability of the findings to other poultry or avian species, such as layers and turkeys. Future studies should consider a broader range of species to better understand the host range and pathogenic diversity of ARV strains. Additionally, the molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis remain unclear. Investigating these mechanisms could elucidate host-pathogen interactions and inform the development of more effective vaccines.
In summary, this study successfully isolated and characterized the novel ARV strain FJ202311, which demonstrated considerable genetic variability and induced severe clinical symptoms, including arthritis, tenosynovitis, and impaired growth in infected chickens. These findings not only enhance our understanding of the epidemiological evolution of ARV but also emphasize the critical need for continuous monitoring and genetic analysis of circulating strains. The insights gained from this study regarding the pathogenicity and genetic diversity of ARV are essential for developing more effective control strategies and vaccines. By advancing our knowledge of ARV’s clinical manifestations and transmission dynamics, this research provides a robust foundation for improving disease prevention, surveillance, and management practices. Ultimately, these efforts will contribute to enhanced poultry health and the long-term sustainability of the poultry industry.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by the Animal Care Committee of South China Agricultural University (approval ID: SYXK-2019-0136). All study procedures and animal care activities were conducted per the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
SC: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JY: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft. LL: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. YG: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. SY: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZS: Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. SZ: Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. XL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WL: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YD: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Methodology. LY: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. FC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Program of Yunfu city [2024090301, 2024020101, and 2023020102], the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation [2023020102], and the Science and Technology Plan Program of Guangdong Province [2023B1212070018].
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Guangdong Enterprise Key Laboratory for Animal Health and Environmental Control for supporting this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
Ayalew, L. E., Gupta, A., Fricke, J., Ahmed, K. A., Popowich, S., Lockerbie, B., et al. (2017). Phenotypic, genotypic and antigenic characterization of emerging avian reoviruses isolated from clinical cases of arthritis in broilers in Saskatchewan. Canada. Sci Rep. 7:3565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02743-8
Bo, H., Zhang, Y., Dong, L. B., Dong, J., Li, X. Y., Zhao, X., et al. (2021). Distribution of avian influenza viruses according to environmental surveillance during 2014-2018, China. Infect Dis. Poverty 10:60. doi: 10.1186/s40249-021-00850-3
Chen, H., Yan, M., Tang, Y., and Diao, Y. (2019). Pathogenicity and genomic characterization of a novel avian orthoreovius variant isolated from a vaccinated broiler flock in China. Avian Pathol. 48, 334–342. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2019.1600656
David, D. G., and Lemay, G. (2023). Emerging reoviruses: the next pandemic? Virologie 27, 50–62. doi: 10.1684/vir.2023.1009
Dawe, W. H., Kapczynski, D. R., Linnemann, E. G., Gauthiersloan, V. R., and Sellers, H. S. (2022). Analysis of the immune response and identification of antibody epitopes against the sigma C protein of avian orthoreovirus following immunization with live or inactivated vaccines. Avian Dis. 66, 465–478. doi: 10.1637/aviandiseases-D-22-99992
De Carli, S., Wolf, J. M., Graf, T., Lehmann, F., Fonseca, A., Canal, C. W., et al. (2020). Genotypic characterization and molecular evolution of avian reovirus in poultry flocks from Brazil. Avian Pathol. 49, 611–620. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2020.1804528
De Carlo, S., and Harris, J. R. (2011). Negative staining and cryo-negative staining of macromolecules and viruses for TEM. Micron 42, 117–131. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2010.06.003
De la Torre, D., Astolfi-Ferreira, C. S., Chacon, R. D., Puga, B., and Piantino, F. A. (2021). Emerging new avian reovirus variants from cases of enteric disorders and arthritis/tenosynovitis in Brazilian poultry flocks. Br. Poult. Sci. 62, 361–372. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2020.1864808
Diller, J. R., Thoner, T. J., and Ogden, K. M. (2023). Mammalian orthoreoviruses exhibit rare genotype variability in genome constellations. Infect. Genet. Evol. 110:105421. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2023.105421
Egana-Labrin, S., Hauck, R., Figueroa, A., Stoute, S., Shivaprasad, H. L., Crispo, M., et al. (2019). Genotypic characterization of emerging avian reovirus genetic variants in California. Sci. Rep. 9:9351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45494-4
Fahey, J. E., and Crawley, J. F. (1954). Studies on chronic respiratory disease of chickens II. Isolation of a virus. Can. J. Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 18, 13–21
Goodwin, M. A., Davis, J. F., McNulty, M. S., Brown, J., and Player, E. C. (1993). Enteritis (so-called runting stunting syndrome) in Georgia broiler chicks. Avian Dis. 37, 451–458. doi: 10.2307/1591672
Hellal, K. Y., Bourogaa, H., Gribaa, L., Scott-Algara, D., and Ghram, A. (2013). Molecular characterization of avian reovirus isolates in Tunisia. Virol. J. 10:12. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-12
Huang, L., Xie, Z., Xie, L., Deng, X., Xie, Z., Luo, S., et al. (2015). A duplex real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of avian reovirus and Mycoplasma synoviae. Virol. J. 12:22. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0255-y
Huhtamo, E., Uzcategui, N. Y., Manni, T., Munsterhjelm, R., Brummer-Korvenkontio, M., Vaheri, A., et al. (2007). Novel orthoreovirus from diseased crow, Finland. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 13, 1967–1969. doi: 10.3201/eid1312.070394
Jiang, X., Lin, Y., Yang, J., Wang, H., Li, C., Teng, X., et al. (2021). Genetic characterization and pathogenicity of a divergent broiler-origin orthoreovirus causing arthritis in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 68, 3552–3562. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13961
Jiang, X., Wei, F., He, D., Niu, X., Wu, B., Wu, Q., et al. (2023). Co-circulation of multiple genotypes of ARV in poultry in Anhui, China. Avian Pathol. 52, 389–400. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2023.2226081
Jiang, X., Yao, Z., He, D., Wu, B., Wei, F., Li, G., et al. (2022). Genetic and pathogenic characteristics of two novel/recombinant avian orthoreovirus. Vet. Microbiol. 275:109601. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109601
Kant, A., Balk, F., Born, L., van Roozelaar, D., Heijmans, J., Gielkens, A., et al. (2003). Classification of Dutch and German avian reoviruses by sequencing the sigma C protein. Vet. Res. 34, 203–212. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2002067
Kovacs, E., Varga-Kugler, R., Mato, T., Homonnay, Z., Tatar-Kis, T., Farkas, S., et al. (2022). Identification of the main genetic clusters of avian reoviruses from a global strain collection. Front. Vet. Sci. 9:1094761. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1094761
Laamiri, N., Aouini, R., Marnissi, B., Ghram, A., and Hmila, I. (2018). A multiplex real-time RT-PCR for simultaneous detection of four most common avian respiratory viruses. Virology 515, 29–37. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.021
Li, X., Zhang, K., Pei, Y., Xue, J., Ruan, S., and Zhang, G. (2020). Development and application of an MRT-qPCR assay for detecting coinfection of six vertically transmitted or immunosuppressive avian viruses. Front. Microbiol. 11:1581. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01581
Liu, H. J., Lee, L. H., Hsu, H. W., Kuo, L. C., and Liao, M. H. (2003). Molecular evolution of avian reovirus: evidence for genetic diversity and reassortment of the S-class genome segments and multiple cocirculating lineages. Virology 314, 336–349. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00415-x
Liu, D., Zou, Z., Song, S., Liu, H., Gong, X., Li, B., et al. (2023). Epidemiological analysis of avian reovirus in China and research on the immune protection of different genotype strains from 2019 to 2020. Vaccines 11:485. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020485
Lu, H., Tang, Y., Dunn, P. A., Wallner-Pendleton, E. A., Lin, L., and Knoll, E. A. (2015). Isolation and molecular characterization of newly emerging avian reovirus variants and novel strains in Pennsylvania, USA, 2011-2014. Sci. Rep. 5:14727. doi: 10.1038/srep14727
Mandelli, G., Rampin, T., and Finazzi, M. (1978). Experimental reovirus hepatitis in newborn chicks. Vet. Pathol. 15, 531–543. doi: 10.1177/030098587801500411
Neelima, S., Ram, G. C., Kataria, J. M., and Goswami, T. K. (2003). Avian reovirus induces an inhibitory effect on lymphoproliferation in chickens. Vet. Res. Commun. 27, 73–85. doi: 10.1023/a:1022014825451
Noh, J. Y., Lee, D. H., Lim, T. H., Lee, J. H., Day, J. M., and Song, C. S. (2018). Isolation and genomic characterization of a novel avian orthoreovirus strain in Korea, 2014. Arch. Virol. 163, 1307–1316. doi: 10.1007/s00705-017-3667-8
Nour, I., Alvarez-Narvaez, S., Harrell, T. L., Conrad, S. J., and Mohanty, S. K. (2023). Whole genomic constellation of avian reovirus strains isolated from broilers with arthritis in North Carolina, USA. Viruses 15:191. doi: 10.3390/v15112191
Page, R. K., Fletcher, O. J., Rowland, G. N., Gaudry, D., and Villegas, P. (1982). Malabsorption syndrome in broiler chickens. Avian Dis. 26, 618–624. doi: 10.2307/1589910
Palomino-Tapia, V., Mitevski, D., Inglis, T., van der Meer, F., and Abdul-Careem, M. F. (2018). Molecular characterization of emerging avian reovirus variants isolated from viral arthritis cases in Western Canada 2012-2017 based on partial sigma (sigma)C gene. Virology 522, 138–146. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.06.006
Palya, V., Glavits, R., Dobos-Kovacs, M., Ivanics, E., Nagy, E., Banyai, K., et al. (2003). Reovirus identified as cause of disease in young geese. Avian Pathol. 32, 129–138. doi: 10.1080/030794502100007187
Rafique, S., Rashid, F., Wei, Y., Zeng, T., Xie, L., and Xie, Z. (2024). Avian orthoreoviruses: a systematic review of their distribution, dissemination patterns, and genotypic clustering. Viruses 16:56. doi: 10.3390/v16071056
Sakai, K., Ueno, Y., Ueda, S., Yada, K., Fukushi, S., Saijo, M., et al. (2009). Novel reovirus isolation from an ostrich (Struthio camelus) in Japan. Vet. Microbiol. 134, 227–232. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.08.022
Sellers, H. S. (2017). Current limitations in control of viral arthritis and tenosynovitis caused by avian reoviruses in commercial poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 206, 152–156. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.12.014
Sellers, H. S. (2022). Avian reoviruses from clinical cases of tenosynovitis: an overview of diagnostic approaches and 10-year review of isolations and genetic characterization. Avian Dis. 66, 420–426. doi: 10.1637/aviandiseases-D-22-99990
Sharafeldin, T. A., Mor, S. K., Bekele, A. Z., Verma, H., Goyal, S. M., and Porter, R. E. (2014). The role of avian reoviruses in Turkey tenosynovitis/arthritis. Avian Pathol. 43, 371–378. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2014.940496
Song, L., Zhou, Y., He, J., Zhu, H., Huang, R., Mao, P., et al. (2008). Comparative sequence analyses of a new mammalian reovirus genome and the mammalian reovirus S1 genes from six new serotype 2 human isolates. Virus Genes 37, 392–399. doi: 10.1007/s11262-008-0283-4
Su, Y. P., Su, B. S., Shien, J. H., Liu, H. J., and Lee, L. H. (2006). The sequence and phylogenetic analysis of avian reovirus genome segments M1, M2, and M3 encoding the minor core protein muA, the major outer capsid protein muB, and the nonstructural protein muNS. J. Virol. Methods 133, 146–157. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.10.031
Tang, Y., Lin, L., Sebastian, A., and Lu, H. (2016). Detection and characterization of two co-infection variant strains of avian orthoreovirus (ARV) in young layer chickens using next-generation sequencing (NGS). Sci. Rep. 6:24519. doi: 10.1038/srep24519
Tang, Y., Lu, H., Sebastian, A., Yeh, Y. T., Praul, C. A., Albert, I. U., et al. (2015). Genomic characterization of a Turkey reovirus field strain by next-generation sequencing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 32, 313–321. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.03.029
Teng, L., Xie, Z., Xie, L., Liu, J., Pang, Y., Deng, X., et al. (2014). Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of an avian reovirus genome. Virus Genes 48, 381–386. doi: 10.1007/s11262-013-1029-5
Van de Zande, S., and Kuhn, E. M. (2007). Central nervous system signs in chickens caused by a new avian reovirus strain: a pathogenesis study. Vet. Microbiol. 120, 42–49. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2006.10.024
Varela, R., and Benavente, J. (1994). Protein coding assignment of avian reovirus strain S1133. J. Virol. 68, 6775–6777. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.10.6775-6777.1994
Vindevogel, H., Meulemans, G., Pastoret, P. P., Schwers, A., and Calberg-Bacq, C. M. (1982). Reovirus infection in the pigeon. Ann. Rech. Vet. 13, 149–152.
Walker, E. R., Friedman, M., and Olson, N. (1972). Electron microscopic study of an avian orthoreovirus that causes arthritis. J Ultrastructure Res. 41, 67–79.
Wang, H., Gao, B., Liu, X., Zhang, S., Diao, Y., and Tang, Y. (2020). Pathogenicity of a variant duck orthoreovirus strain in Cherry Valley ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 242:108546. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108546
Wang, X., Tang, X., Liu, Q., Ju, F., and Wang, L. (1985). Application of agar diffusion test to detect chicken viral arthritis. Chin J Prev Vet Med. 3, 26–27.
Yan, T., Guo, L., Jiang, X., Wang, H., Yao, Z., Zhu, S., et al. (2021). Discovery of a novel recombinant avian orthoreovirus in China. Vet. Microbiol. 260:109094. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2021.109094
Zeden, M. S., and Grundling, A. (2023). Bacterial whole-genome-resequencing analysis: basic steps using the CLC genomics workbench software. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2023:pdb.prot107901. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot107901
Zhang, X., Lei, X., Ma, L., Wu, J., and Bao, E. (2019). Genetic and pathogenic characteristics of newly emerging avian reovirus from infected chickens with clinical arthritis in China. Poult. Sci. 98, 5321–5329. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez319
Keywords: avian orthoreovirus, isolation, genomic analysis, phylogenetic analysis, pathogenicity
Citation: Chen S, Yang J, Li L, Guo Y, Yang S, Su Z, Zhao S, Li X, Lin W, Du Y, Yin L, Wang L and Chen F (2025) Characterization and pathogenicity of a novel avian orthoreovirus in China. Front. Microbiol. 15:1529351. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1529351
Edited by:
Anna Luganini, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Mengmeng Zhao, Foshan University, ChinaSolomon Boamah, Gansu Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Yang, Li, Guo, Yang, Su, Zhao, Li, Lin, Du, Yin, Wang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lijuan Yin, d3N5aW5sakAxNjMuY29t; Lianxiang Wang, YW5pbXNjaUAxMjYuY29t; Feng Chen, ZmVuZ2NoQHNjYXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shunyan Chen1†
Shunyan Chen1† Xuesong Li
Xuesong Li Wencheng Lin
Wencheng Lin Feng Chen
Feng Chen