- 1Department of Family Medicine, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 2College of Metrology and Measurement Engineering, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou, China
- 3Department of General Practice, The First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
- 4Department of Cardiology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
- 5Department of Nephrology, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Introduction: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in pathogenic microbiology has accelerated research and innovation. This study aims to explore the evolution and trends of AI applications in this domain, providing insights into how AI is transforming research and practice in pathogenic microbiology.
Methods: We employed bibliometric analysis and topic modeling to examine 27,420 publications from the Web of Science Core Collection, covering the period from 2010 to 2024. These methods enabled us to identify key trends, research areas, and the geographical distribution of research efforts.
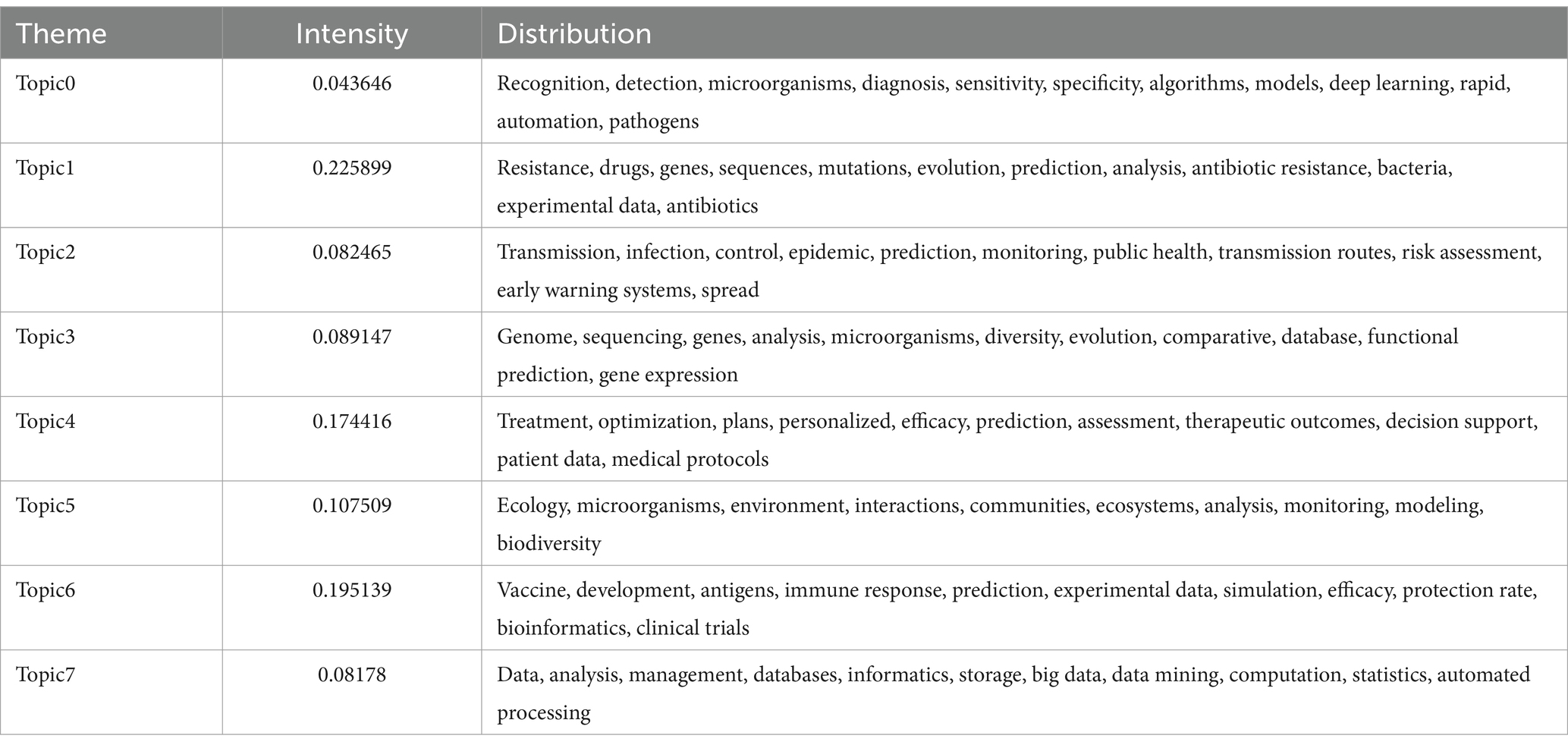
Results: Since 2016, there has been an exponential increase in AI-related publications, with significant contributions from China and the USA. Our analysis identified eight major AI application areas: pathogen detection, antibiotic resistance prediction, transmission modeling, genomic analysis, therapeutic optimization, ecological profiling, vaccine development, and data management systems. Notably, we found significant lexical overlaps between these areas, especially between drug resistance and vaccine development, suggesting an interconnected research landscape.
Discussion: AI is increasingly moving from laboratory research to clinical applications, enhancing hospital operations and public health strategies. It plays a vital role in optimizing pathogen detection, improving diagnostic speed, treatment efficacy, and disease control, particularly through advancements in rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing and COVID-19 vaccine development. This study highlights the current status, progress, and challenges of AI in pathogenic microbiology, guiding future research directions, resource allocation, and policy-making.
1 Introduction
Pathogenic microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, cause infections and diseases in hosts. Since the 1960s, the widespread use of antibiotics has driven the evolution of these microorganisms through natural selection, gene recombination, and horizontal gene transfer (HGT), leading to antibiotic resistance (AMR).
AMR results in millions of deaths annually worldwide, posing a severe threat to public health (Saha and Sarkar, 2021; Uddin et al., 2021). Traditional culture-based methods fail to address the increasing genetic diversity and resistance of pathogens. In the era of big data, research on pathogenic microorganisms heavily relies on high-throughput sequencing, metagenomics, proteomics, and targeted techniques (Lewis et al., 2021; Wani et al., 2022). Effectively organizing, analyzing, and interpreting the vast amounts of biomedical data generated has emerged as a new challenge.
AI, a field that simulates and extends human intelligence through computational devices, provides powerful tools to address these challenges. Machine learning (ML) improves computer performance through pattern recognition and analysis, enabling precise microbial classification, biomarker identification, small molecule compound library screening, and novel anti-infective drug discovery.
Deep learning (DL), comprising multilayer neural networks, boosts data generation capabilities for pathogenic microorganisms through neural networks, generative models, and variational autoencoders (Huo and Wang, 2024; Wong et al., 2023). Computer vision (CV) rapidly detects pathogens in microscope or fluorescence sensor images (Zhao et al., 2024; Matias et al., 2021). Natural language processing (NLP) automatically identifies information from scientific literature on pathogen research (Jimeno-Yepes and Verspoor, 2023) and analyzes bacteriophage genomes to predict their life cycles (Tynecki et al., 2020).
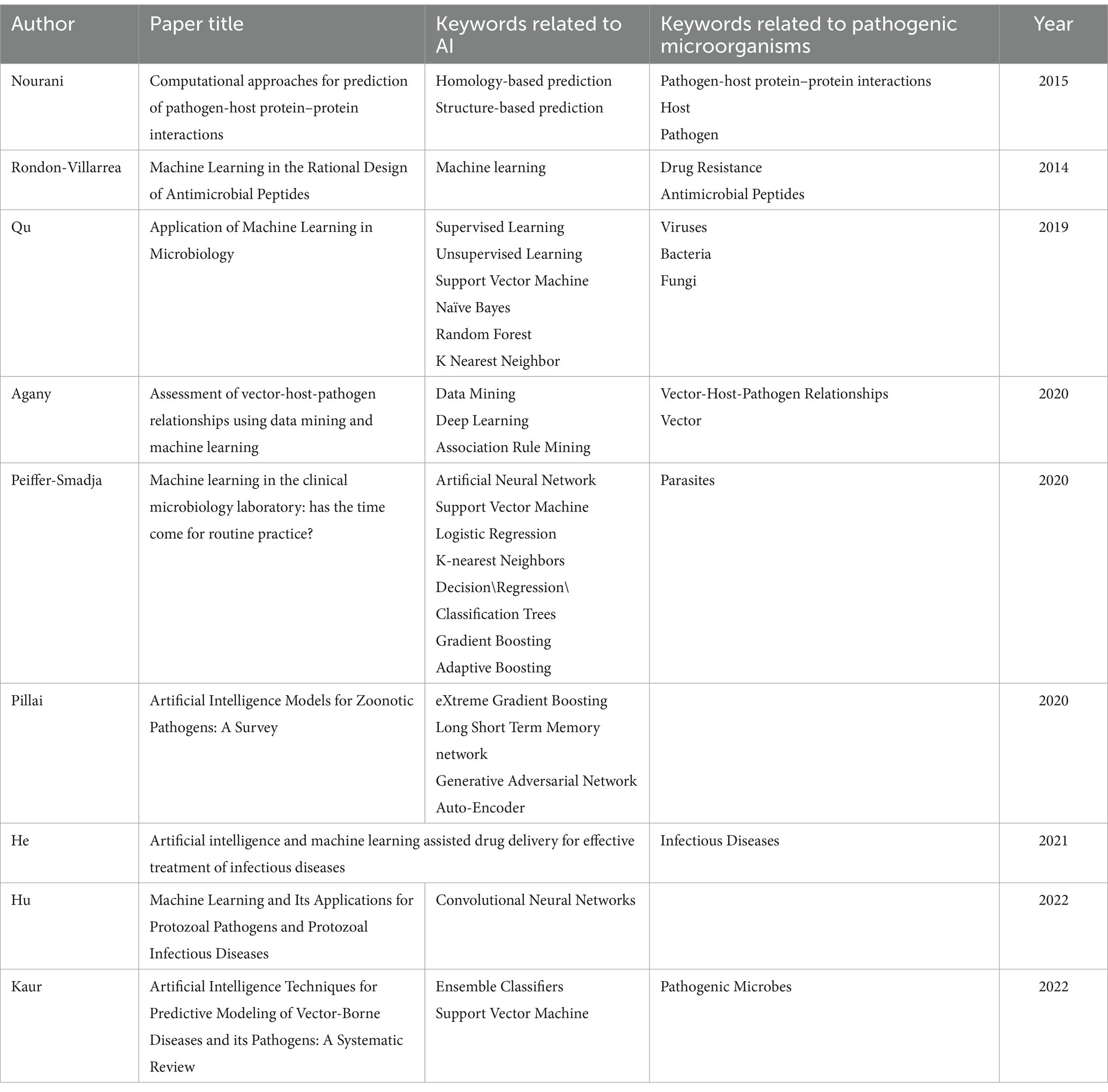
The application of AI in pathogenic microbiology has been widely explored, with many scholars evaluating its use in related research. Literature reviews date back to 2014. Specifically, Nourani et al. studied ML, homology prediction, and structural prediction in predicting pathogen-host protein interactions (PHI) between 2009 and 2014, crucial for understanding infection mechanisms (Nourani et al., 2015). Rondon-Villarreal et al. reviewed ML in antimicrobial peptide design, a potential new class of antimicrobial drugs to combat AMR (Rondon-Villarreal et al., 2014). Qu et al. comprehensively reviewed ML in microbiology, covering microbial classification from high-throughput sequencing data, environmental and host phenotype prediction, and microbial-disease association analysis (Qu et al., 2019). Agany et al. explored data mining and ML in understanding vector-host-pathogen relationships from 2012 to 2020, highlighting advances in DL and association rule analysis (Agany et al., 2020). Peiffer-Smadja et al. studied ML in clinical microbiology, identifying 97 ML systems aimed at assisting clinical microbiologists with bacterial, parasitic, viral, and fungal infection analysis and antimicrobial sensitivity assessment up to 2020 (Peiffer-Smadja et al., 2020). Pillai et al. summarized various AI models (e.g., logistic regression, random forests, support vector machines, neural networks, ensemble methods) in predicting zoonotic disease outbreaks and identifying risk factors (Pillai et al., 2022). He et al. introduced AI’s role in infectious disease drug delivery, including drug development, resistance prediction, dose optimization, and drug combination selection (He et al., 2021). Hu et al. discussed ML’s broad applications in protozoan pathogen and infectious disease research, covering detection, diagnosis, monitoring, host–parasite interactions, drug discovery, and vaccine development (Hu et al., 2022). Kaur et al. reviewed AI techniques in predicting and monitoring vector-borne diseases and their pathogens, noting significant progress in disease prediction, vector identification, and outbreak monitoring through ML and DL (Kaur et al., 2022).
Despite several studies exploring the application of AI in specific areas of pathogenic microbiology, a systematic analysis of the overall development trends and knowledge structure of the field is lacking. Previous literature reviews have primarily focused on AI’s performance in specific application scenarios. These studies provide important references for understanding AI’s value in specific applications but fail to offer a comprehensive grasp of the overall development landscape of AI in pathogenic microbiology research.
In this context, bibliometrics and topic modeling offer powerful methods to explore and understand scientific research in this domain. Bibliometrics, a statistical method widely used to analyze publication trends and relationships in the medical field, includes evaluative and relational bibliometrics. The latter reveals hidden relationships and research status by analyzing metadata from authors, papers, and journals (Ninkov et al., 2022). Topic modeling, a natural language processing technique, identifies latent semantic patterns in document collections, helping researchers discover cross-disciplinary themes and research trends. Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) is the most widely utilized technique for this purpose (Vayansky and Kumar, 2020). This study aims to conduct a large-scale quantitative analysis of AI applications in the field of pathogenic microbiology through bibliometrics and topic modeling methods. Compared to existing studies, this paper has the following innovations and contributions: (1) By utilizing 27,420 publications spanning 2010 to 2024, the study conducts a comprehensive quantitative analysis of the field for the first time, covering a wide scope; (2) The integration of bibliometrics and topic modeling techniques not only reveals research hotspots and trends but also deeply explores the potential knowledge structure; and (3) A systematic review of AI’s advancements in eight major application areas within pathogenic microbiology provides a scientific basis for future research directions and resource allocation.
2 Methods
2.1 Data collection
To ensure the scientific rigor and authority of the literature review, we retrieved data from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC), the oldest and most widely used research publication and citation database globally (Birkle et al., 2020). The citation index includes various versions of WoSCC, such as the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED), Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), Current Chemical Reactions (CCR-EXPANDED), and Index Chemicus (IC).
The search terms were derived from key phrases mentioned in previous review articles on AI applications in pathogenic microbiology (Table 1). The final search string was: TS = (“Pathogen-host protein–protein interactions” OR Host OR Pathogen OR “Drug Resistance” OR “Antimicrobial Peptides” OR Viruses OR Bacteria OR Fungi OR “Vector-Host-Pathogen Relationships” OR Vector OR Parasites OR “Infectious Diseases” OR “Pathogenic Microbes”).
AND TS = (“Deep Learning” OR “Association Rule Mining” OR “Artificial Neural Network” OR “Support Vector Machine” OR “K-nearest Neighbors” OR “Decision Trees” OR “Regression Trees” OR “Classification Trees” OR “Gradient Boosting” OR “Adaptive Boosting” OR “eXtreme Gradient Boosting” OR “Long Short Term Memory network” OR “Generative Adversarial Network” OR “Auto-Encoder” OR “Convolutional Neural Networks” OR “Ensemble Classifiers” OR “Support Vector Machine”). This search yielded 151,593 results.
2.1.1 Screening criteria
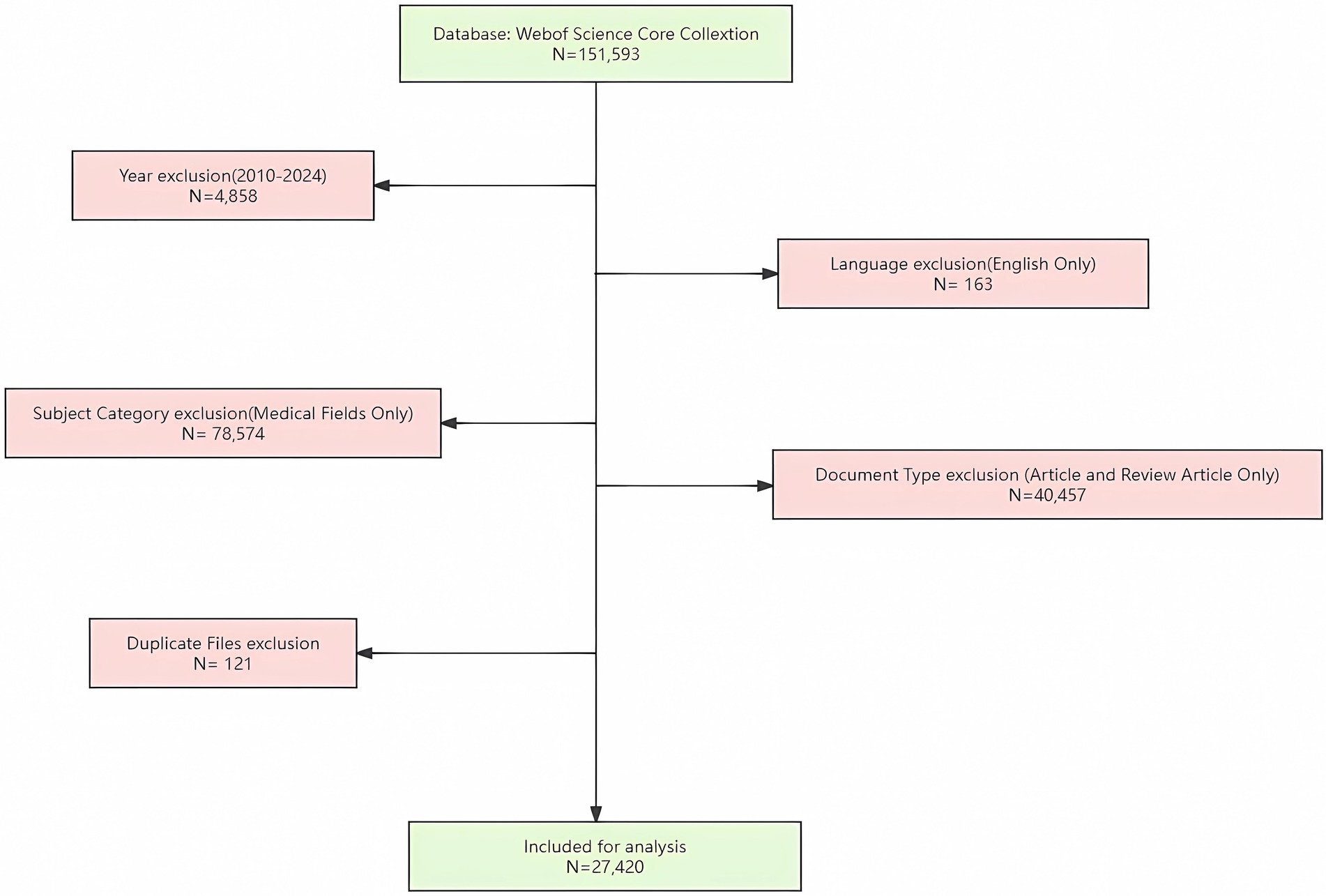
Inclusion and exclusion criteria were established to filter the results. The inclusion criteria focused on research articles related to AI and pathogenic microorganisms. Exclusion criteria were set for outdated articles, non-English literature, irrelevant disciplines, conference abstracts, and duplicate documents. The screening was performed independently by two authors to ensure accuracy and consistency. The specific steps were:
1. Year Limitation: Restricting the publication years to 2010–2024 eliminated 4,858 articles. This timeframe was selected because the rapid advancements in AI and pathogenic microbiology, particularly the widespread application of metagenomics and high-throughput sequencing, began around 2010 (Sheetal Ambardar et al., 2016; Park et al., 2016).
2. Language Restriction: Non-English articles (163) were removed to ensure the inclusion of high-impact research and important results published in major journals.
3. Disciplinary Focus: Articles from non-medical fields (78,574), such as engineering or computer science, were excluded. These fields often focus more on technical developments and algorithm optimization, which could introduce noise into the bibliometric analysis.
4. Document Type: Only “Article” and “Review Article” categories were included, eliminating 40,457 documents from other types like proceeding papers, book chapters, letters, and news items.
5. Duplicate Removal: Using Endnote software, 121 duplicate documents were automatically removed to ensure data uniqueness and completeness.
The final dataset comprised 27,420 articles for analysis (Figure 1).
2.2 Bibliometric analysis
The data was exported in plain text format, including full records and cited references. The clean dataset was imported into three software programs for visualization analysis: R-Bibliometrix 4.3.1, CiteSpace 6.1.R6 (64-bit) Advanced, and VOSviewer 1.6.19.
2.2.1 Bibliometrix
This R-based bibliometric analysis package, launched in 2017, offers robust data processing and multi-dimensional chart generation capabilities (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017; Arruda et al., 2022). We used Bibliometrix 4.3.1 to analyze annual publications, author H-indices, productivity over time, high-impact journals, and highly cited papers.
2.2.2 CiteSpace
Developed by Professor Chaomei Chen in 2004, CiteSpace is a Java-based scientific literature analysis software capable of document co-citation, collaboration network, and burst term analysis (Chen, 2018). We used CiteSpace 6.1.R6 (64-bit) Advanced to generate co-occurrence maps of institutions.
2.2.3 VOSviewer
Launched in 2010, VOSviewer is a software tool for creating and exploring maps based on network data, offering network, overlay, and density visualizations (Arruda et al., 2022). We used VOSviewer for author and country co-occurrence collaboration analysis.
2.3 Topic modeling analysis
Compared to traditional bibliometric keyword clustering methods, topic modeling offers more precise and detailed research classifications, uncovering the underlying structures and dynamic trends within research fields. In our study, we employed Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) for topic modeling using the Python Gensim library. LDA is a generative model that leverages unsupervised machine learning to analyze large volumes of unstructured data, eliminating the need to divide data into training and test sets. It assumes that documents comprise multiple topics, each represented by a probability distribution over words (Chauhan and Shah, 2021; Yang et al., 2024).
Initially, we conducted text preprocessing, including the removal of stopwords and punctuation, as well as stemming, to ensure data consistency and cleanliness. Subsequently, we set the parameters for the topic modeling. Optimization of topics was performed through perplexity and coherence evaluation. Finally, we generated the topic-word distribution and a topic-term relationship network graph.
The specific hyperparameter choices for the LDA model were as follows: alpha = “symmetric” (symmetric prior), and eta = None (default prior). These parameters control the prior beliefs regarding the document-topic and topic-word distributions. The chunksize was set to 2000, meaning that the corpus of 27,420 documents was divided into approximately 14 chunks for processing, thereby avoiding the necessity of loading all documents into memory simultaneously. The passes parameter was set to 1 since the model’s performance was satisfactory with a single pass through the corpus. The model was trained using the LdaModel class provided by Gensim, which implements an online LDA algorithm that enables streaming and incremental training of the corpus, thereby effectively handling large-scale text data. The save and load methods were used for model persistence, ensuring the reproducibility of the experimental results.
3 Results
3.1 Publication trends analysis
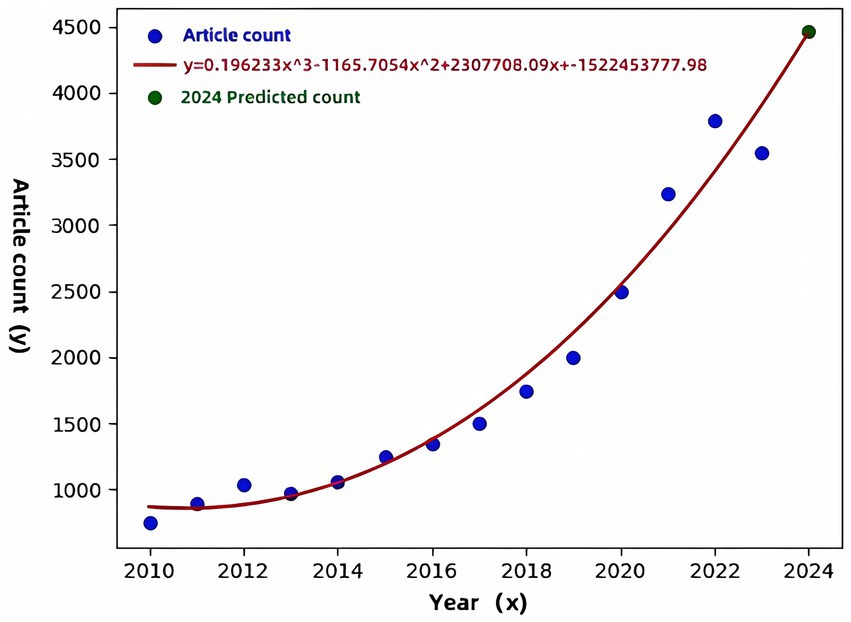
Polynomial regression analysis (Figure 2) from 2010 to 2023 reveals a significant upward trend in the number of publications, with exponential growth evident since 2016. The number of publications is projected to reach approximately 4,500 by 2024. This growth is primarily attributed to the increase in interdisciplinary collaboration, the impact of global health challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic, and the rapid advancements in AI and computational technologies, particularly breakthroughs in deep learning algorithms, convolutional neural networks, and disease prediction models since 2016 (Jelodar et al., 2019).
3.2 Authors
Figure 3A presents the metrics for the top four contributing authors. Wang Wei leads with 69 publications and an H-index of 25, signifying that at least 25 publications have been cited at least 25 times (Zhang et al., 2022). Wang Jing was notably prolific in 2018, publishing 11 papers and achieving a Total Citations per Year (TCpY) score of 98.67 (Figure 3B). VOSviewer analysis (Figures 3C,D) of 70 authors, each with a minimum of 5 publications and 1,000 citations, reveals three primary collaborative groups centered around Li Hao, Zhang Wei, and Wang Lie. Notably, Zhang Wei’s collaborative network is the largest, comprising 13 members. The collaboration between Li Hao and Chen Wei is the most frequent, with 28 co-authored papers (Bihari et al., 2023).
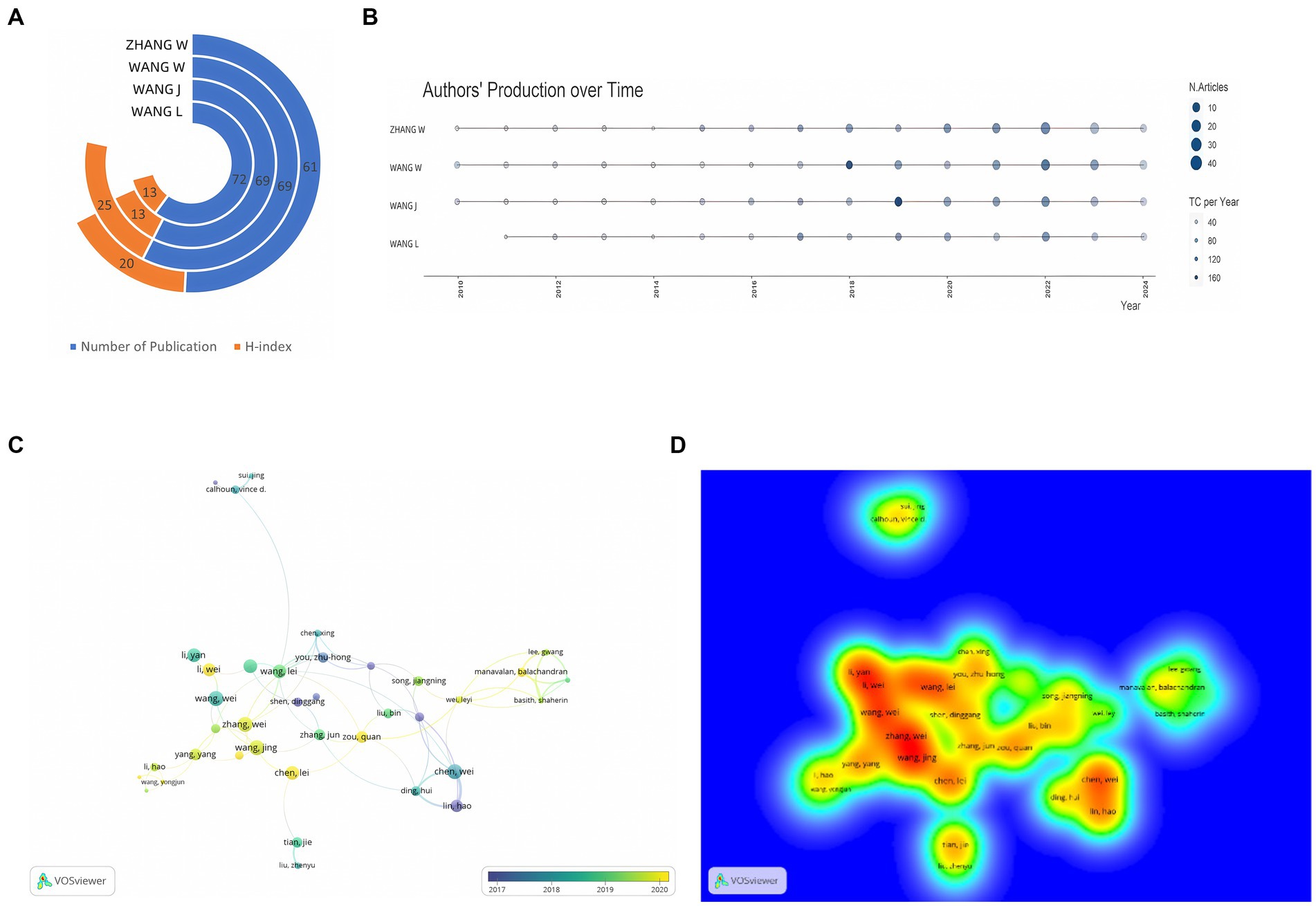
Figure 3. (A) Total number of publications and H-index of top 4 authors; (B) Authors’ production over time; (C) Network visualization of author co-authorship analysis; (D) Density visualization of author co-authorship analysis.
3.3 Institutions
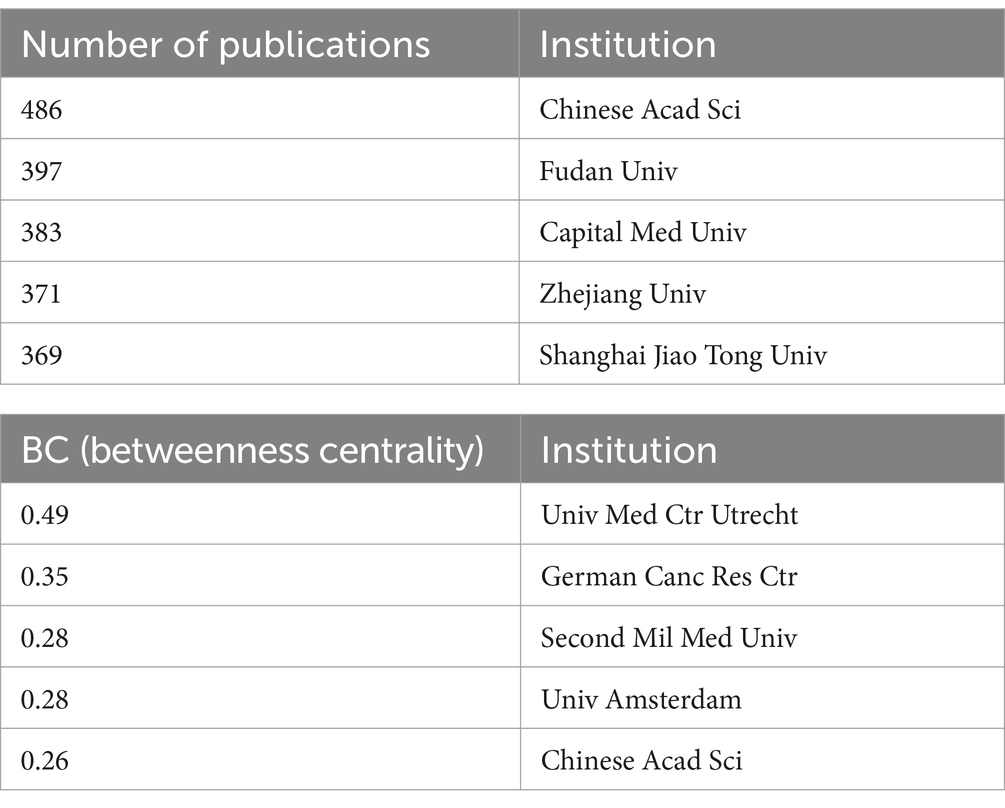
Figure 4 illustrates that there are 917 collaborative interactions among 776 institutions. Although the overall network density is low (0.003), certain institutions display frequent and intensive collaborations. This phenomenon can be attributed to the high specialization in pathogenic microbiology and AI technologies, which leads collaborations to be concentrated among a select few capable institutions. As shown in Table 2, the Chinese Academy of Sciences leads with 486 publications, while the Universitair Medisch Centrum Utrecht demonstrates significant research impact with a betweenness centrality of 0.49.
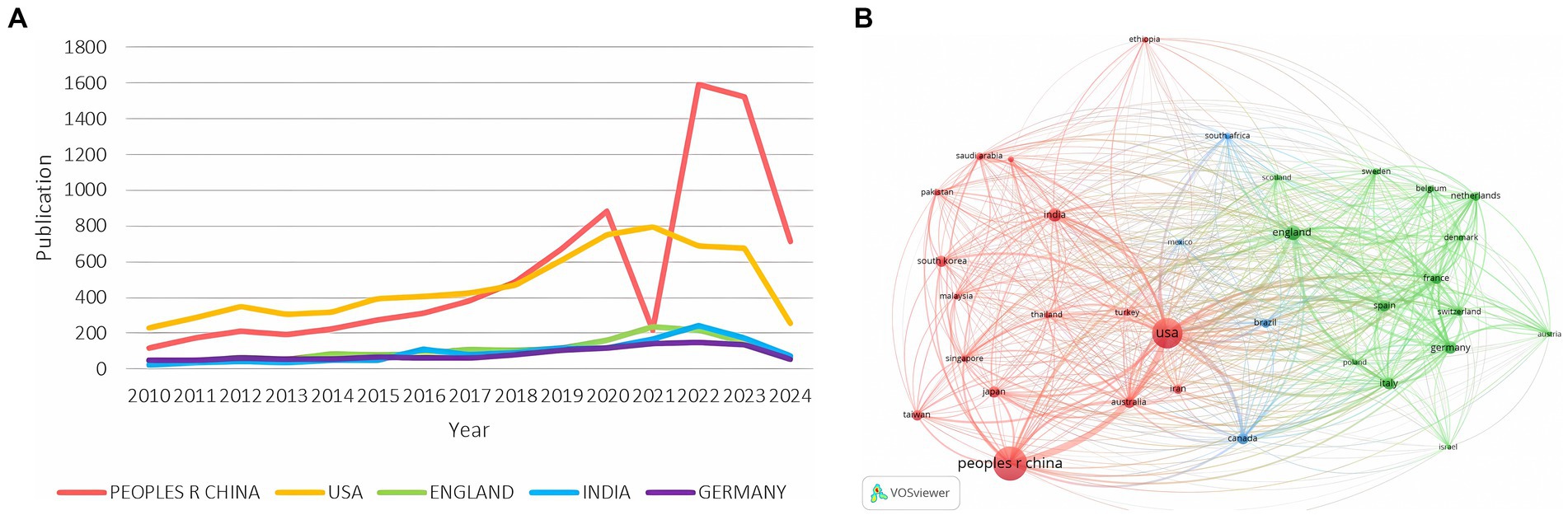
3.4 Countries
Figure 5A indicates that China and the United States have been leading in pathogenic microbiology research. Notably, China’s publication volume significantly decreased in 2021, likely due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, since 2022, China’s publication rate has grown exponentially, surpassing other countries. VOSviewer analysis (filtering for countries with at least *100 publications) revealed an international collaboration network comprising 32 countries. The thickness of the connecting lines indicates collaboration strength, with China and the U.S. exhibiting the tightest cooperation (link strength = 974). This suggests 974 instances of collaboration between researchers from these two countries, reflecting their central role and significant advantages in knowledge and resource sharing, which are crucial for advancing pathogenic microbiology research and addressing global health challenges (Figure 5B).
3.5 Journals
In analyzing the evolution and trends of AI in pathogenic microbiology research, we identified the top ten journals in this field, including their H-index, impact factor, and JCR indicators (Table 3). These metrics reflect the research activity and the journals’ influence within the academic community. “Computers in Biology and Medicine” has the highest number of publications in this field, while “Clinical Infectious Diseases,” the only Q1 journal among the top ten by publication volume, is the most cited, demonstrating its authority. Notably, four of the top ten journals are Q2, indicating that research outcomes are increasingly being published in higher-quality journals.
3.6 Topic modeling
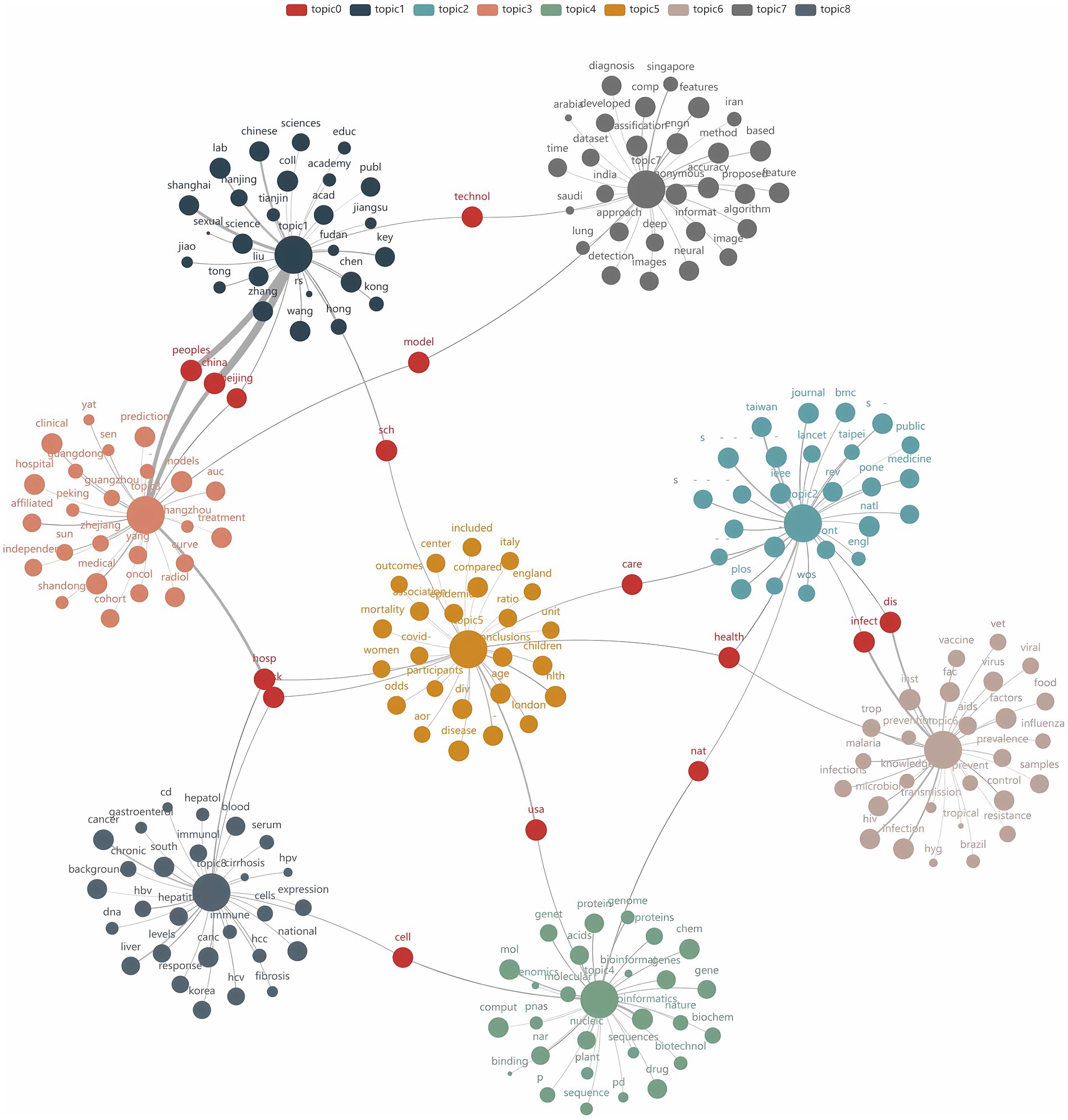
To determine the optimal number of topics, we undertook the following steps: First, we trained LDA models with varying numbers of topics (2 to 15) and calculated their perplexity scores on the test set. Lower perplexity indicates a better model fit (Figure 6A). Second, we computed the topic coherence score for each model, which measures the semantic consistency of words within a topic; higher values indicate more coherent topic structures (Figure 6B). Finally, we plotted perplexity and coherence scores on a scatter plot (Figure 6C). The top-right region of the plot shows data points for 8, 9, 10, and 12 topics, which performed well in balancing perplexity and coherence. Further manual analysis revealed that although 9, 10, and 12 topics offered higher model performance, they led to overly fine and dispersed classifications, which are impractical for real-world applications. An 8-topic model provided an efficient and practical classification structure, laying a solid foundation for further interpretation. Consequently, we selected the 8-topic model. The resulting themes include AI in pathogen detection, drug resistance, transmission and control, genomics, treatment optimization, ecology, vaccine development, and data analysis and management (Table 4). A word cloud was then utilized to visually represent the intrinsic connections between different research themes, with each cluster marked in different colors. The clusters were interconnected through shared keywords (red nodes), and the size of each node reflected keyword frequency, while the thickness of connecting lines indicated the distribution strength of words within specific topics (Figure 7).
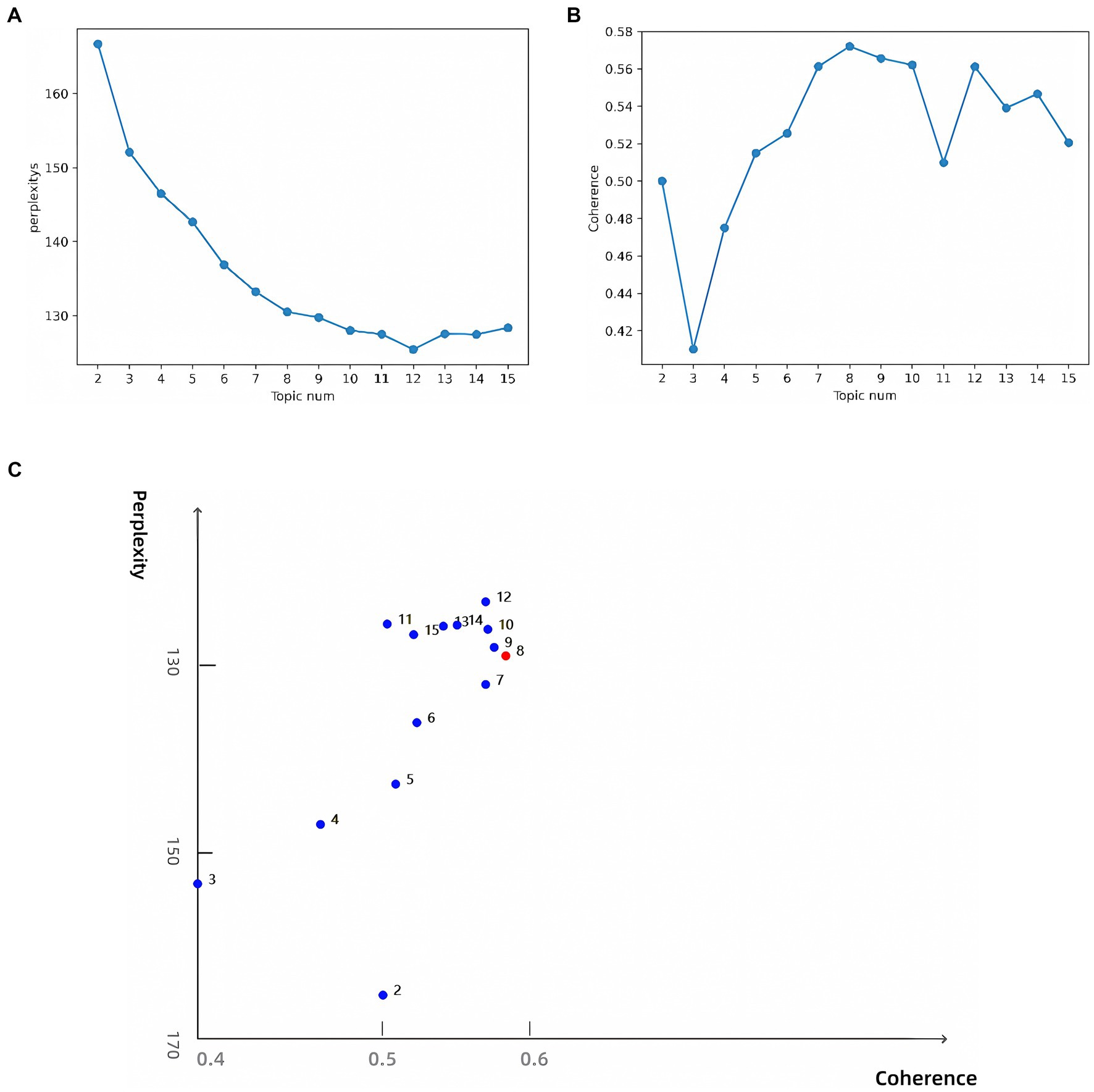
Figure 6. (A) Perplexity for topics 2–15; (B) Coherence for topics 2–15; (C) Topic model optimal parameter selection diagram.
4 Discussion
4.1 Eight major topics
This section summarizes the eight topics identified through topic modeling and discusses the research advancements within each domain.
4.1.1 Application of artificial intelligence in pathogen detection
Traditional diagnostic methods, such as microbial culture and isolation, are often time-consuming and prone to false-negative results (Daim et al., 2006). The application of multi-modal data fusion techniques in pathogen detection has gained significant attention in recent years. These techniques integrate image data with genetic data to provide more comprehensive and accurate diagnostic outcomes. For instance, Khan et al. (2019) developed models using automated image capture technology and convolutional neural networks (CNN), successfully classifying and identifying Gram-stained blood cultures. Their model achieved a classification accuracy of 94.9% for both Gram-positive cocci and Gram-negative bacteria. By integrating microbial genome sequencing data with the capabilities of CNNs, researchers can further subtype pathogens based on pattern recognition. This multi-modal fusion approach significantly enhances sensitivity and specificity in diagnostics by simultaneously analyzing the visual and genetic characteristics of pathogens, thus making pathogen diagnosis more efficient and precise.
Additionally, machine learning models can rapidly analyze complex data patterns, thereby improving diagnostic speed and accuracy (Smith et al., 2018). For instance, models used for DNA sequencing can quickly process the genomes of bacteria and viruses (Ali et al., 2023).
4.1.2 Application of artificial intelligence in antimicrobial resistance research
Artificial intelligence has been effectively utilized in the analysis and prediction of microbial drug resistance, marking a significant advancement in antimicrobial resistance research. The increasing prevalence of resistant bacteria underscores the critical importance of analyzing genomic and sequence data. Traditional antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) methodologies require a minimum of 4 days, which is excessively time-consuming for urgent clinical scenarios where swift decision-making is crucial, especially in the face of rapidly spreading infections (Mardis, 2008). This predicament underscores the urgent need for innovative diagnostic techniques that can adapt to the rapid evolution of antibiotic resistance.
The integration of techniques like MALDI-TOF MS with sophisticated data analysis algorithms has been shown to expedite the identification of resistant strains (Garcia et al., 2024). A retrospective clinical case study involving 63 patients revealed that adopting such methodologies would have altered the clinical management of nine patients, benefiting eight of them (89%). Consequently, machine learning based on MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry emerges as an essential new tool for therapy optimization and antibiotic stewardship (Theodosiou and Read, 2023). Deep learning algorithms, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, can perform rapid and accurate antibiotic susceptibility testing by classifying bacteria into active or non-active strains (Weis et al., 2022).
AI technologies, encompassing machine learning and natural language processing, enable the processing of vast quantities of genomic data, which leads to the identification of resistance-associated genetic mutations and evolutionary patterns (Yu et al., 2018). This capability not only enhances our understanding of how bacteria develop drug resistance but also provides invaluable insights for novel drug development (Zhou and Troyanskaya, 2015). Furthermore, machine learning models have the potential to predict mutational trends and resistance to specific drugs, thereby aiding clinicians in selecting the most effective treatment regimens (Gupta et al., 2021).
4.1.3 Application of artificial intelligence in pathogen transmission and control
Artificial intelligence demonstrates significant potential in monitoring and controlling pathogen transmission. By employing machine learning to recognize transmission patterns, it provides vital decision support for public health authorities, enabling the implementation of more effective outbreak control strategies (Májek et al., 2021). AI can analyze historical epidemic data to predict future disease transmission (Ren et al., 2023). Additionally, AI technologies are utilized for real-time monitoring of infection trends, allowing rapid responses to outbreaks. AI-driven warning systems enhance the predictive capacity for future outbreaks, improving resource allocation and management strategies (Vahedi et al., 2021). These technologies provide scientific evidence for disease control and prevention, bolstering the resilience of public health systems.
4.1.4 Application of artificial intelligence in pathogen genomics
Deep learning, as a crucial AI technology, offers new perspectives and tools for analyzing diversity and evolution in pathogen genomics research. Xu et al. employed deep learning algorithms to efficiently identify various antimicrobial peptides from metagenomic data, significantly advancing the development of next-generation antimicrobials (Wang et al., 2024). AI’s ability to analyze large volumes of genomic sequence data allows it to identify and compare genetic characteristics of diverse microorganisms, revealing their evolutionary relationships and functional traits (Xu et al., 2020). This robust potential for genome annotation and functional prediction provides vital support for microbial ecology and functional research (Angly et al., 2006). Furthermore, constructed databases allow for in-depth exploration of complex interactions between microorganisms and environmental contexts (Sun et al., 2023). This provides valuable insights for research in microbial genomics, ecological analysis, and disease prevention.
4.1.5 Application of artificial intelligence in optimization of treatment strategies
Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in optimizing treatment strategies for pathogens. By analyzing clinical data, AI can predict the efficacy of various treatment regimens and adjust strategies in real-time according to individual patient condition changes. Li Jinquan utilized AI to identify differences in high-dimensional features of antimicrobial candidate proteins, discovering the best-in-class lytic enzyme LLysSA9, effective in treating bovine mastitis and combating Staphylococcus aureus infections (Hirose et al., 2024). This personalized medicine approach not only enhances treatment outcomes but also reduces unnecessary treatments and potential side effects. AI-powered decision support systems integrate medical literature, patient data, and clinical trial results to provide scientific foundations for optimizing treatment plans (Wong et al., 2023).
Moreover, AI excels in drug repurposing and new drug development, using models to simulate the effects of different drugs on pathogens, thereby advancing personalized treatment (Zhang et al., 2024). Liu G et al. highlighted challenges in discovering new antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii through traditional screening methods, while James J. Collins and colleagues utilized machine learning to screen approximately 7,500 molecules, swiftly identifying those inhibiting A. baumannii growth in vitro (Melo et al., 2021). Khaledi et al. predicted antimicrobial susceptibility based on genomic and transcriptomic markers, enhancing diagnostic performance by identifying resistance characteristics early in disease progression (Liu et al., 2023).
4.1.6 Application of artificial intelligence in ecology studies of pathogens
The application of artificial intelligence in ecological studies of pathogens opens up new avenues for understanding the ecological roles of microorganisms in various environments (Khaledi et al., 2020). Neural network technology, in particular, demonstrates remarkable performance in this domain. For instance, the vedoNet neural network algorithm, developed by Ananthakrishnan et al., integrates microbiome and clinical data and achieves superior classification capability for clinical remission in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Detailed research indicates that early trajectories of microbiome changes can serve as markers for treatment response (Lopatkin and Collins, 2020). Additionally, machine learning and data mining techniques are extensively applied to model and predict microbial community behavior under various environmental conditions, thus helping to reduce disease incidence associated with environmental changes (Ananthakrishnan et al., 2017). This interdisciplinary research not only enhances the understanding of microbial ecology but also provides a scientific foundation for formulating effective environmental management strategies.
4.1.7 Application of artificial intelligence in vaccine development
Traditional vaccine development has largely relied on laborious experimental methods that, while effective, are often time-consuming and have limited success rates (Ai et al., 2020). Recently, data mining and big data analytics have paved new pathways for vaccine development, with artificial intelligence (AI) revolutionizing the field as a tool for antigen selection and immunogen design (Brisse et al., 2020). By utilizing advanced algorithms, AI extracts crucial data from extensive genomic datasets, protein structure information, and immune system interactions, quickly identifying potential vaccine candidate antigens (Aswathy and Sumathi, 2024). For example, AI-driven neural network prediction models trained on a large dataset of over 24,000 peptides can accurately recognize key epitopes detected by the immune system. Prioritizing these epitopes and recommending experimental validation allows AI to significantly shorten the discovery time while minimizing resource investment (Olawade et al., 2024).
By integrating AI algorithms with experimental validation and clinical trials, the vaccine development process is substantially accelerated. This data-driven approach enhances vaccine development efficiency and demonstrates significant potential during global health crises (Ward et al., 2021). During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI played a crucial role in quickly identifying novel antigens through detailed data mining, providing essential support for the rapid development of vaccines (Brisse et al., 2020). In mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines, AI not only optimized vaccine sequences but also effectively screened delivery vectors, improving overall research and development efficiency (Federico et al., 2023).
4.1.8 Application of artificial intelligence in data analysis and management of pathogens
With the explosion of data volume, the application of AI in image data processing technology for pathogen detection becomes increasingly critical (Zhang et al., 2023). Traditional detection methods, such as nucleic acid and immunological assays, are often time-consuming and complex (Haymond and McCudden, 2021). Through the incorporation of machine learning, particularly deep convolutional neural network (CNN)-based image processing algorithms, AI can rapidly process and analyze microscopic image data, automatically identifying pathogens, thus significantly reducing diagnostic time. For instance, Rahman et al. utilized the DenseNet CNN model to classify 89 fungal genera from microscopic images, achieving a prediction accuracy of 65.35% (Whiley and Taylor, 2016), marking a notable enhancement in detection efficiency. Tao Chenglong integrated the HMI system with Buffer Net, developing a CNN-based AI-assisted system for rapid and automatic bacterial identification (Rahman et al., 2023). Additionally, Devan et al. employed a transfer learning method based on CNN, requiring minimal preprocessing to detect HCMV nucleocapsids in TEM images (Tao et al., 2022). In tuberculosis detection, Kuok et al. attained an 86% detection rate using a region-refined Faster R-CNN algorithm to automatically detect acid-fast bacilli on slides, significantly outperforming the traditional support vector machine (SVM) method, which had a detection rate of 70.93% (Shaga Devan et al., 2021). Chung et al. combined MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry) with CNN technology for the rapid identification of hemolytic streptococci, quickly pinpointing infection sources, effectively preventing epidemic spread, and providing robust technical support for public health management (Kuok et al., 2019).
4.2 Interconnections among topics
As illustrated in Figure 7, there is significant lexical overlap among the various research topics, reflecting a strong interconnection and a trend towards interdisciplinary integration in the field. In the topic modeling analysis, drug resistance (Topic 1) and vaccine development (Topic 6) exhibited the highest weights (0.226 and 0.195, respectively). The growing global challenge of bacterial drug resistance and the threat from emerging infectious diseases in recent years have heightened the need for large-scale immunization efforts. AI contributes to the rapid development of vaccines by accelerating antigen identification and predicting immune responses.
Genomics research (Topic 3) and drug resistance research (Topic 1) are closely linked through shared genetic analysis methods. Genomics plays a critical role in drug resistance research; AI can swiftly analyze genomic sequencing data to identify and classify antibiotic resistance genes (Qu et al., 2019), and this genomic data can be integrated into machine learning models to predict antibiotic sensitivity and resistance phenotypes (Chung et al., 2019).
The word cloud also reveals a synergy between transmission control (Topic 2) and ecological research (Topic 5), particularly in environmental monitoring. For example, combining AI algorithms to develop predictive models can forecast high- and low-risk areas for pathogen outbreaks under future climate conditions. This approach is especially effective when linking climatology research (analyzing factors such as temperature and precipitation) with ecological studies (focusing on pathogen vectors or hosts), thereby significantly enhancing the predictive accuracy and interpretability of these models, enabling precise control and prevention (Melo et al., 2021; Farooq et al., 2022).
Data analysis and management (Topic 7) appears to be a crucial link across all research topics. Data analysis and management is not merely an independent theme but rather a key element throughout the pathogen research process. AI algorithms heavily depend on the quality of pathogen data and metadata to enhance research accuracy and reliability. From pathogen detection to predicting antibiotic resistance and optimizing treatments, substantial amounts of genomic sequencing data, electronic health records, and other clinical data are collected, processed, and analyzed, forming the training datasets for machine learning models.
4.3 Practical applications
The application of artificial intelligence in pathogen research is gradually transitioning from laboratory research to clinical practice, with official approval in certain regions. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Clever Culture Systems’ APAS Compact system for the automated assessment of plates in clinical microbiology laboratories, demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity in detecting urine cultures (Peiffer-Smadja et al., 2020).
Many hospitals have already implemented AI for pathogen detection. Taiwan’s Tri-Service General Hospital, along with four secondary hospitals, has successfully deployed a solution powered by an AI clinical decision support system (AI-CDSS) to expedite the detection of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (KP). This system integrates MALDI-TOF MS technology with machine learning algorithms, accelerating the prediction of bacterial resistance—particularly to carbapenems and colistin—by 1 day compared to traditional antibiotic susceptibility tests (AST). It provides healthcare professionals with resistance probability scores through a web interface, enabling rapid and informed treatment decisions (Ali et al., 2024). Massachusetts General Hospital employs AI to assess the risk of Clostridium difficile infections. In a multicenter study involving at least nine hospitals, Dascena’s machine learning algorithms have been used for early sepsis detection and stratification, antimicrobial prescription recommendations, and resistant microorganism colonization predictions, demonstrating the potential to reduce hospital mortality rates, shorten hospital stays, and decrease 30-day readmission rates (Jian et al., 2024; Shimabukuro et al., 2017; Burdick et al., 2020).
AI and machine learning (ML) technologies are also extensively applied in addressing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs). AI systems are capable of predicting surgical site infections (SSIs), hospital-acquired pneumonia (HCAP), and hospital-acquired urinary tract infections (HA-UTI) (McCoy and Das, 2017). For instance, a machine learning model monitoring SSI in colon surgeries has reduced manual workload by 83.9% (Radaelli et al., 2024). A new AI-based training and monitoring system (AITMS) has improved personal protective equipment (PPE) wearing and doffing skills, successfully reducing pathogen infection rates from 1.31 to 0.58% in a Japanese hospital (Cho et al., 2024). The University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics utilized machine learning to decrease surgical site infection rates by 74%, while Philips’ “Connected Care” system reduced detection time for nosocomial infections by 87% (Huang et al., 2023).
Artificial intelligence has also played a practical role in global public health. Systems like HealthMap utilize natural language processing to analyze online news and professional resources, providing global alert information for outbreaks such as the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (Agrebi and Larbi, 2020; Ali et al., 2023). The U.S. CDC employs machine learning models to predict influenza trends (Hossain and Househ, 2016). During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI technologies were implemented in genomic classification, lineage mapping, and optimization of testing strategies. The ZOE COVID Study collected symptom data via a smartphone app, offering invaluable insights for public health (Reich et al., 2019). Singapore airport implemented thermal imaging for temperature monitoring of potential infections, combining physiological parameters with advanced analytical methods to classify high-risk influenza patients (Menni et al., 2020).
4.4 Opportunities and challenges
The real-world application of artificial intelligence (AI) in pathogen research is still in its infancy; however, it reveals immense potential for development while facing numerous challenges and obstacles. The following are four key directions for enhancing AI application in this field:
Advanced Machine Learning Algorithms: With the increase in computational power and data accumulation, more sophisticated and accurate deep learning models can be applied to pathogen research to improve the accuracy of disease prediction and enhance the capability to handle multidimensional data.
Richer Sample Data: By collecting additional sample data from diverse clinical settings worldwide, AI systems can improve their generalization ability, thereby increasing their robustness across varied medical environments.
User-Friendly Interface Design: Developing intuitive and easy-to-use interfaces, along with providing adequate training for healthcare professionals, can significantly promote the widespread application of AI technologies in clinical practice.
Application of Extreme Value Theory: Integrating extreme value theory with robust statistical methods in epidemiology and public health can aid in the early detection of anomalies in transmission dynamics. This is particularly beneficial for the early warning of rare infectious events, such as emerging infectious diseases, providing strong support for public health interventions.
However, several challenges must be overcome to advance AI applications:
High Costs: The development, deployment, and maintenance of AI models are capital-intensive. Solutions include utilizing open-source AI tools and models and creating government subsidy policies to lower the barrier to technology access.
Training and Talent Shortage: Healthcare professionals require appropriate training to effectively use AI tools. This issue can be addressed by implementing targeted AI training programs and cultivating more medical professionals with expertise in AI.
Data Quality and Accessibility: High-quality data is crucial for training AI models. Challenges can be tackled by establishing standardized data-sharing mechanisms, improving data collection and annotation methods, and enhancing data security and privacy protections.
Ethical and Legal Issues: The use of AI in medical decision-making involves ethical and legal responsibilities. This necessitates the development of ethical guidelines and legal regulations for AI applications, clearly defining accountability and establishing effective oversight mechanisms to ensure lawful and compliant use of AI systems.
Model Explainability: The “black box” nature of AI models affects their applicability and acceptance in clinical practice. Therefore, developing more interpretable AI models can help clinicians understand their decision processes, thereby increasing trust and encouraging their use (Sun et al., 2015; Hassija et al., 2024).
5 Conclusion
In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in pathogenic microbiology research using bibliometrics and topic modeling. We examined 27,420 relevant publications from 2010 to 2024, uncovering an exponential growth trend in publications since 2016, primarily focused on eight key areas: pathogen detection, antibiotic resistance prediction, transmission and control, genomic analysis, therapeutic optimization, ecological studies, vaccine development, and data management systems.
The results from topic modeling indicate that the application of AI in pathogen research has become diverse and specialized. For instance, in pathogen detection, AI has significantly improved diagnostic speed and accuracy through the integration of multimodal data fusion technologies. In the realm of antibiotic resistance prediction, machine learning and deep learning models have expedited the identification and analysis of resistance genes. In vaccine development, AI has facilitated rapid progress in antigen recognition and immunogen design, thus playing a critical supportive role in the development of COVID-19 vaccines.
Despite AI’s substantial potential in pathogenic microbiology research, its practical implementation remains in the early stages and faces numerous challenges. Key factors limiting effective AI application include the acquisition and sharing of high-quality data, AI system interpretability, ethical and legal responsibilities, and the high cost of development. To foster further advancements in this field, we recommend strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration to enrich AI model training data, enhancing the user-friendliness of AI tools to promote their adoption and application in clinical practice, and supporting policies to reduce the economic barriers to AI utilization. Addressing these issues collaboratively will enable a fuller realization of AI technologies in tackling challenges in the field of pathogenic microbiology, ultimately contributing to the resilience of health management and public health systems and providing unprecedented opportunities to address global public health challenges.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
TT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. FZ: Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. ML: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZQ: Writing – review & editing. WW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing. YW: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. YL: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. J-HW: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Agany, D. D. M., Pietri, J. E., and Gnimpieba, E. Z. (2020). Assessment of vector-host-pathogen relationships using data mining and machine learning. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 18, 1704–1721. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.06.031
Agrebi, S., and Larbi, A. (2020). “Use of artificial intelligence in infectious diseases” in Artificial intelligence in precision health. ed. D. Barh (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 415–438.
Ai, D., Wang, Y., Li, X., and Pan, H. (2020). Colorectal cancer prediction based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis and variational autoencoder. Biomol. Ther. 10:1207. doi: 10.3390/biom10091207
Ali, T., Ahmed, S., and Aslam, M. (2023). Artificial intelligence for antimicrobial resistance prediction: challenges and opportunities towards practical implementation. Antibiotics 12:523. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030523
Ali, F., Rehman, A., and Hameed, A. (2024). “Climate change impact on plant pathogen emergence: artificial intelligence (AI) approach” in Plant quarantine challenges under climate change anxiety. eds. K. A. Abd-Elsalam and S. M. Abdel-Momen (Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland), 281–303.
Ananthakrishnan, A. N., Luo, C., Yajnik, V., Khalili, H., Garber, J. J., Stevens, B. W., et al. (2017). Gut microbiome function predicts response to anti-integrin biologic therapy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Cell Host Microbe 21, 603–610.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2017.04.010
Angly, F. E., Felts, B., Breitbart, M., Salamon, P., Edwards, R. A., Carlson, C., et al. (2006). The marine viromes of four oceanic regions. PLoS Biol. 4:e368. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040368
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informet. 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Arruda, H., Silva, E. R., and Lessa, M. (2022). VOSviewer and Bibliometrix. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 110, 392–395. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2022.1434
Aswathy, R., and Sumathi, S. (2024). The evolving landscape of cervical cancer: breakthroughs in screening and therapy through integrating biotechnology and artificial intelligence. Mol. Biotechnol. 1–17. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01124-7
Bihari, A., Tripathi, S., and Deepak, A. (2023). A review on h-index and its alternative indices. J. Inf. Sci. 49, 624–665. doi: 10.1177/01655515211014478
Birkle, C., Pendlebury, D. A., Schnell, J., and Adams, J. (2020). Web of science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quant. Sci. Stud. 1, 363–376. doi: 10.1162/qss_a_00018
Brisse, M., Vrba, S. M., Kirk, N., Liang, Y., and Ly, H. (2020). Emerging concepts and technologies in vaccine development. Front. Immunol. 11:583077. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583077
Burdick, H., Pino, E., Gabel-Comeau, D., McCoy, A., Gu, C., Roberts, J., et al. (2020). Effect of a sepsis prediction algorithm on patient mortality, length of stay and readmission: a prospective multicentre clinical outcomes evaluation of real-world patient data from US hospitals. BMJ Health Care Inform. 27:e100109. doi: 10.1136/bmjhci-2019-100109
Chauhan, U., and Shah, A. (2021). Topic modeling using latent Dirichlet allocation: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 54, 1–35. doi: 10.1145/3462478
Chen, C. (2018). Visualizing and exploring scientific literature with Citespace: an introduction. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Human Information Interaction & Retrieval [New York, NY, United States: Association for Computing Machinery (ACM Press)], (pp. 369–370).
Cho, S. Y., Kim, Z., Chung, D. R., Cho, B. H., Chung, M. J., Kim, J. H., et al. (2024). Development of machine learning models for the surveillance of colon surgical site infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 146, 224–231. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2023.03.025
Chung, C. R., Wang, H. Y., Lien, F., Tseng, Y. J., Chen, C. H., Lee, T. Y., et al. (2019). Incorporating statistical test and machine intelligence into strain typing of Staphylococcus haemolyticus based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Front. Microbiol. 10:2120. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02120
Daim, T. U., Rueda, G., Martin, H., and Gerdsri, P. (2006). Forecasting emerging technologies: use of bibliometrics and patent analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 73, 981–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2006.04.004
Farooq, Z., Rocklöv, J., Wallin, J., Abiri, N., Sewe, M. O., Sjödin, H., et al. (2022). Artificial intelligence to predict West Nile virus outbreaks with eco-climatic drivers. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 17:100370. doi: 10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100370
Federico, L., Malone, B., Tennøe, S., Chaban, V., Osen, J. R., Gainullin, M., et al. (2023). Experimental validation of immunogenic SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes identified by artificial intelligence. Front. Immunol. 14:1265044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1265044
Garcia, E., Diep, J. K., Sharma, R., and Rao, G. G. (2024). Model-based learn and confirm: designing effective treatment regimens against multidrug resistant gram-negative pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 63:107100. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2024.107100
Gupta, R., Srivastava, D., Sahu, M., Tiwari, S., Ambasta, R. K., and Kumar, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence to deep learning: machine intelligence approach for drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 25, 1315–1360. doi: 10.1007/s11030-021-10217-3
Hassija, V., Chamola, V., Mahapatra, A., Singal, A., Goel, D., Huang, K., et al. (2024). Interpreting black-box models: a review on explainable artificial intelligence. Cogn. Comput. 16, 45–74. doi: 10.1007/s12559-023-10179-8
Haymond, S., and McCudden, C. (2021). Rise of the machines: artificial intelligence and the clinical laboratory. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 6, 1640–1654. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfab075
He, S., Leanse, L. G., and Feng, Y. (2021). Artificial intelligence and machine learning assisted drug delivery for effective treatment of infectious diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 178:113922. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.113922
Hirose, Y., Zielinski, D. C., Poudel, S., Rychel, K., Baker, J. L., Toya, Y., et al. (2024). A genome-scale metabolic model of a globally disseminated hyperinvasive M1 strain of Streptococcus pyogenes. mSystems 9, e00736–e00724. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00736-24
Hossain, N., and Househ, M. (2016). “Using HealthMap to analyse Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) data” in Unifying the applications and foundations of biomedical and health informatics. eds. J. Mantas, A. Hasman, P. Gallos, A. Kolokathi, and M. S. Househ. (Amsterdam, Netherlands: IOS Press), 150–157.
Hu, R. S., El Hesham, A., and Zou, Q. (2022). Machine learning and its applications for protozoal pathogens and protozoal infectious diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:882995. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.882995
Huang, T., Ma, Y., Li, S., Ran, J., Xu, Y., Asakawa, T., et al. (2023). Effectiveness of an artificial intelligence-based training and monitoring system in prevention of nosocomial infections: a pilot study of hospital-based data. Drug Discov. Ther. 17, 351–356. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2023.01068
Huo, D., and Wang, X. (2024). A new era in healthcare: the integration of artificial intelligence and microbial. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 23:100319. doi: 10.1016/j.medntd.2024.100319
Jelodar, H., Wang, Y., and Yuan, C. (2019). Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and topic modeling: models, applications, a survey. Multimed. Tools Appl. 78, 15169–15211. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6894-4
Jian, M. J., Lin, T. H., and Chung, H. Y. (2024). Artificial intelligence-clinical decision support system in infectious disease control: combatting multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with machine learning. Infect. Drug Resist. 17, 2899–2912. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S470821
Jimeno-Yepes, A. J., and Verspoor, K. (2023). Classifying literature mentions of biological pathogens as experimentally studied using natural language processing. J. Biomed. Semantics 14:1. doi: 10.1186/s13326-023-00282-y
Kaur, I., Sandhu, A. K., and Kumar, Y. (2022). Artificial intelligence techniques for predictive modeling of vector-borne diseases and its pathogens: a systematic review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 29, 3741–3771. doi: 10.1007/s11831-022-09724-9
Khaledi, A., Weimann, A., Schniederjans, M., Asgari, E., Kuo, T. H., Oliver, A., et al. (2020). Predicting antimicrobial resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa with machine learning-enabled molecular diagnostics. EMBO Mol. Med. 12:e10264. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201910264
Khan, Z. A., Siddiqui, M. F., and Park, S. (2019). Current and emerging methods of antibiotic susceptibility testing. Diagnostics 9:49. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9020049
Kuok, C. P., Horng, M. H., Liao, Y. M., Chow, N. H., and Sun, Y. N. (2019). An effective and accurate identification system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis using convolutional neural networks. Microsc. Res. Tech. 82, 709–719. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23217
Lewis, W. H., Tahon, G., Geesink, P., Sousa, D. Z., and Ettema, T. J. G. (2021). Innovations to culturing the uncultured microbial majority. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 225–240. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00458-8
Liu, G., Catacutan, D. B., Rathod, K., Swanson, K., Jin, W., Mohammed, J. C., et al. (2023). Deep learning-guided discovery of an antibiotic targeting Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat. Chem. Biol. 19, 1342–1350. doi: 10.1038/s41589-023-01349-8
Lopatkin, A. J., and Collins, J. J. (2020). Predictive biology: modelling, understanding and harnessing microbial complexity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 18, 507–520. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-0372-5
Májek, P., Lüftinger, L., Beisken, S., Rattei, T., and Materna, A. (2021). Genome-wide mutation scoring for machine-learning-based antimicrobial resistance prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:13049. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313049
Mardis, E. R. (2008). Next-generation DNA sequencing methods. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 9, 387–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164359
Matias, A. V., Amorim, J. G. A., Macarini, L. A. B., Cerentini, A., Onofre, A. S. C., Onofre, F. B. D. M., et al. (2021). What is the state of the art of computer vision-assisted cytology? A systematic literature review. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 91:101934. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.101934
McCoy, A., and Das, R. (2017). Reducing patient mortality, length of stay and readmissions through machine learning-based sepsis prediction in the emergency department, intensive care unit and hospital floor units. BMJ Open Qual. 6:e000158. doi: 10.1136/bmjoq-2017-000158
Melo, M. C. R., Maasch, J. R. M. A., and de la Fuente-Nunez, C. (2021). Accelerating antibiotic discovery through artificial intelligence. Commun. Biol. 4:1050. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02586-0
Menni, C., Valdes, A. M., Freidin, M. B., Sudre, C. H., Nguyen, L. H., Drew, D. A., et al. (2020). Real-time tracking of self-reported symptoms to predict potential COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 1037–1040. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0916-2
Ninkov, A., Frank, J. R., and Maggio, L. A. (2022). Bibliometrics: methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect. Med. Educ. 11, 173–176. doi: 10.1007/s40037-021-00695-4
Nourani, E., Khunjush, F., and Durmuş, S. (2015). Computational approaches for prediction of pathogen-host protein-protein interactions. Front. Microbiol. 6:94. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00094
Olawade, D. B., Teke, J., Fapohunda, O., Weerasinghe, K., Usman, S. O., Ige, A. O., et al. (2024). Leveraging artificial intelligence in vaccine development: a narrative review. J. Microbiol. Methods 224:106998. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2024.106998
Park, S. J., Saito-Adachi, M., Komiyama, Y., and Nakai, K. (2016). Advances, practice, and clinical perspectives in high-throughput sequencing. Oral Dis. 22, 353–364. doi: 10.1111/odi.12403
Peiffer-Smadja, N., Dellière, S., Rodriguez, C., Birgand, G., Lescure, F. X., Fourati, S., et al. (2020). Machine learning in the clinical microbiology laboratory: has the time come for routine practice? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 26, 1300–1309. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.02.006
Pillai, N., Ramkumar, M., and Nanduri, B. (2022). Artificial intelligence models for zoonotic pathogens: a survey. Microorganisms 10:1911. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101911
Qu, K., Guo, F., Liu, X., Lin, Y., and Zou, Q. (2019). Application of machine learning in microbiology. Front. Microbiol. 10:827. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00827
Radaelli, D., Di Maria, S., and Jakovski, Z. (2024). Advancing patient safety: the future of artificial intelligence in mitigating healthcare-associated infections: a systematic review. Healthcare 12:1996. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12191996
Rahman, M. A., Clinch, M., Reynolds, J., Dangott, B., Meza Villegas, D. M., Nassar, A., et al. (2023). Classification of fungal genera from microscopic images using artificial intelligence. J. Pathol. Inform. 14:100314. doi: 10.1016/j.jpi.2023.100314
Reich, N. G., McGowan, C. J., Yamana, T. K., Tushar, A., Ray, E. L., Osthus, D., et al. (2019). Accuracy of real-time multi-model ensemble forecasts for seasonal influenza in the US. PLoS Comput. Biol. 15:e1007486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007486
Ren, J., Liu, M., Liu, Y., and Liu, J. (2023). TransCode: uncovering COVID-19 transmission patterns via deep learning. Infect. Dis. Poverty 12:14. doi: 10.1186/s40249-023-01052-9
Rondon-Villarreal, P., Sierra, D., and Torres, R. (2014). Machine learning in the rational design of antimicrobial peptides. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 10, 183–190. doi: 10.2174/1573409910666140624124807
Saha, M., and Sarkar, A. (2021). Review on multiple facets of drug resistance: a rising challenge in the 21st century. J. Xenobiot. 11, 197–214. doi: 10.3390/jox11040013
Shaga Devan, K., Walther, P., von Einem, J., Ropinski, T., Kestler, H., and Read, C. (2021). Improved automatic detection of herpesvirus secondary envelopment stages in electron microscopy by augmenting training data with synthetic labelled images generated by a generative adversarial network. Cell. Microbiol. 23:e13280. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13280
Sheetal Ambardar, S. A., Rikita Gupta, R. G., Deepika Trakroo, D. T., Lal, R., and Vakhlu, J. (2016). High throughput sequencing: an overview of sequencing chemistry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 56, 394–404. doi: 10.1007/s12088-016-0606-4
Shimabukuro, D. W., Barton, C. W., Feldman, M. D., Mataraso, S. J., and das, R. (2017). Effect of a machine learning-based severe sepsis prediction algorithm on patient survival and hospital length of stay: a randomised clinical trial. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 4:e000234. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000234
Smith, K. P., Kang, A. D., and Kirby, J. E. (2018). Automated interpretation of blood culture gram stains by use of a deep convolutional neural network. J. Clin. Microbiol. 56, e01521–e01517. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01521-17
Sun, G., Matsui, T., and Hakozaki, Y. (2015). An infectious disease/fever screening radar system which stratifies higher-risk patients within ten seconds using a neural network and the fuzzy grouping method. J. Infect. 70, 230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2014.12.007
Sun, T., Niu, X., He, Q., Chen, F., and Qi, R. Q. (2023). Artificial intelligence in microbiomes analysis: a review of applications in dermatology. Front. Microbiol. 14:1112010. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1112010
Tao, C., Du, J., Tang, Y., Wang, J., Dong, K., Yang, M., et al. (2022). A deep-learning-based system for rapid genus identification of pathogens under hyperspectral microscopic images. Cells 11:2237. doi: 10.3390/cells11142237
Theodosiou, A. A., and Read, R. C. (2023). Artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning: potential resources for the infection clinician. J. Infect. 87, 287–294. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2023.07.006
Tynecki, P., Guziński, A., Kazimierczak, J., Jadczuk, M., Dastych, J., and Onisko, A. (2020). PhageAI-bacteriophage life cycle recognition with machine learning and natural language processing. bioRxiv :2020.07.11.198606. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.11.198606
Uddin, T. M., Chakraborty, A. J., Khusro, A., Zidan, B. M. R. M., Mitra, S., Emran, T. B., et al. (2021). Antibiotic resistance in microbes: history, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 14, 1750–1766. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.020
Vahedi, B., Karimzadeh, M., and Zoraghein, H. (2021). Spatiotemporal prediction of COVID-19 cases using inter-and intra-county proxies of human interactions. Nat. Commun. 12:6440. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26742-6
Vayansky, I., and Kumar, S. A. P. (2020). A review of topic modeling methods. Inf. Syst. 94:101582. doi: 10.1016/j.is.2020.101582
Wang, D., Lang, J. C., and Chen, Y. H. (2024). Assessment of using Google trends for real-time monitoring of infectious disease outbreaks: a measles case study. Sci. Rep. 14:9470. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60120-8
Wani, A. K., Roy, P., Kumar, V., and Mir, T. G. (2022). Metagenomics and artificial intelligence in the context of human health. Infect. Genet. Evol. 100:105267. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105267
Ward, D., Higgins, M., Phelan, J. E., Hibberd, M. L., Campino, S., and Clark, T. G. (2021). An integrated in silico immuno-genetic analytical platform provides insights into COVID-19 serological and vaccine targets. Genome Med. 13, 4–12. doi: 10.1186/s13073-020-00822-6
Weis, C., Cuénod, A., Rieck, B., Dubuis, O., Graf, S., Lang, C., et al. (2022). Direct antimicrobial resistance prediction from clinical MALDI-TOF mass spectra using machine learning. Nat. Med. 28, 164–174. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01619-9
Whiley, H., and Taylor, M. (2016). Legionella detection by culture and qPCR: comparing apples and oranges. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 42, 65–74. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.885930
Wong, F., de la Fuente-Nunez, C., and Collins, J. J. (2023). Leveraging artificial intelligence in the fight against infectious diseases. Science 381, 164–170. doi: 10.1126/science.adh1114
Xu, X., Gao, Z., and Yang, F. (2020). Antidiabetic effects of Gegen Qinlian decoction via the gut microbiota are attributable to its key ingredient berberine. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 18, 721–736. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2019.09.007
Yang, Y., Ngai, E. W. T., and Wang, L. (2024). Resistance to artificial intelligence in healthcare: literature review, conceptual framework, and research agenda. Inf. Manag. 61:103961. doi: 10.1016/j.im.2024.103961
Yu, H., Jing, W., and Iriya, R. (2018). Phenotypic antimicrobial susceptibility testing with deep learning video microscopy. Anal. Chem. 90, 6314–6322. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01128
Zhang, T., Chen, J., and Lu, Y. (2022). Identification of technology frontiers of artificial intelligence-assisted pathology based on patent citation network. PLoS One 17:e0273355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273355
Zhang, Y., Li, R., Zou, G., Guo, Y., Wu, R., Zhou, Y., et al. (2024). Discovery of antimicrobial lysins from the “dark matter” of uncharacterized phages using artificial intelligence. Adv. Sci. 11:e2404049. doi: 10.1002/advs.202404049
Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Lin, A., Xu, C., Li, Z., Liu, K., et al. (2023). Algorithm for optimized mRNA design improves stability and immunogenicity. Nature 621, 396–403. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06127-z
Zhao, J., Han, M., Ma, A., Jiang, F., Chen, R., Dong, Y., et al. (2024). A machine vision-assisted Argonaute-mediated fluorescence biosensor for the detection of viable Salmonella in food without convoluted DNA extraction and amplification procedures. J. Hazard. Mater. 466:133648. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.133648
Keywords: pathogenic microorganisms, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), bibliometrics, topic modeling, antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
Citation: Tian T, Zhang X, Zhang F, Huang X, Li M, Quan Z, Wang W, Lei J, Wang Y, Liu Y and Wang J-H (2024) Harnessing AI for advancing pathogenic microbiology: a bibliometric and topic modeling approach. Front. Microbiol. 15:1510139. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1510139
Edited by:
Chen Li, Northeastern University, ChinaReviewed by:
Yuzhuo Gu, Beihang University, ChinaHanyu Tian, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen, China
Copyright © 2024 Tian, Zhang, Zhang, Huang, Li, Quan, Wang, Lei, Wang, Liu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuting Wang, ODk3MjU5NTY3QHFxLmNvbQ==; Ying Liu, c2psaXV5aW5nQHNqLWhvc3BpdGFsLm9yZw==; Jia-He Wang, d2FuZ2poMUBzai1ob3NwaXRhbC5vcmc=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Tian Tian
Tian Tian Xuan Zhang1†
Xuan Zhang1† Fei Zhang
Fei Zhang Minglin Li
Minglin Li Jia-He Wang
Jia-He Wang