
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 09 January 2025
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1507274
 Eslam Elashkar1
Eslam Elashkar1 Rihaf Alfaraj2
Rihaf Alfaraj2 Ola M. El-Borady3
Ola M. El-Borady3 Mahmoud M. Amer1
Mahmoud M. Amer1 Abdelazeem M. Algammal4
Abdelazeem M. Algammal4 Azza S. El-Demerdash5*†
Azza S. El-Demerdash5*†Background: Klebsiella pneumoniae is a significant nosocomial pathogen that has developed resistance to multiple antibiotics, often forming biofilms that enhance its virulence. This study investigated the efficacy of a novel nanoformulation, AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, in combating K. pneumoniae biofilms.
Methods: Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed to assess the antibiotic resistance profile of K. pneumoniae isolates. The antibiofilm activity of AgNPs@chitosan-NaF was evaluated using crystal violet staining and scanning electron microscopy. The underlying mechanisms of action were investigated through gene expression analysis.
Results: The majority of K. pneumoniae isolates exhibited high levels of multidrug resistance. AgNPs@chitosan-NaF demonstrated superior biofilm inhibition compared to AgNPs@chitosan, significantly reducing biofilm biomass and disrupting biofilm architecture at MICs ranging from 0.125 to 1 μg/mL. Mechanistic studies revealed that the nanoformulation downregulated the expression of key biofilm-associated genes, including treC, fimA, mrkA, and ecpA. While AgNPs@chitosan-NaF exhibited a concentration-dependent cytotoxic effect on both normal and cancer cell lines, minimal cytotoxicity was observed at concentrations below 31.25 μg/mL.
Conclusion: This study highlights the synergistic effect of silver nanoparticles, chitosan, and sodium fluoride in combating K. pneumoniae biofilms. The nanoformulation, AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, emerges as a promising therapeutic strategy to address the challenge of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections.
Klebsiella pneumoniae, a significant pathogen, poses a serious threat to global health due to its ability to form robust biofilms and develop multidrug resistance (Al Bshabshe et al., 2020). Biofilms, communities of bacteria embedded in a protective matrix, shield K. pneumoniae from antibiotics and other stressors, making infections difficult to treat. The emergence of multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae strains has further complicated treatment options, contributing to high mortality rates, especially in vulnerable populations (El-Demerdash et al., 2018, 2023a; Guerra et al., 2022). Additionally, the biofilm-forming nature of K. pneumoniae can lead to persistent infections, requiring prolonged treatment and increasing the risk of complications (Abbas et al., 2024).
The development of innovative antimicrobial methods is essential to combat biofilm-forming bacteria, which often exhibit resistance to conventional antibiotics (Sharaf et al., 2022; El-Demerdash et al., 2023d; Ibrahim, 2023).
Nanoparticles, with their large surface area and tunable surface chemistry, offer a promising alternative to traditional antibiotics for combating multidrug-resistant (MDR) pathogens (Rudramurthy et al., 2016). Silver nanoparticles, in particular, have demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity and the ability to disrupt biofilm formation, a critical challenge in treating bacterial infections (Mba and Nweze, 2021; Saad et al., 2024). This has fueled increased research into nanoparticles as a potential solution to overcome antibiotic resistance (Franci et al., 2015; Abd El-Emam et al., 2024; Hashem et al., 2024).
Chitosan, a natural biopolymer, exhibits antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility, making it a promising candidate for biomedical applications. Chitosan nanoparticles, combining the advantages of chitosan with the unique properties of nanomaterials, have demonstrated potent antimicrobial activity against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi. Additionally, these nanoparticles have shown promise in combating biofilm formation, a critical challenge in treating infections caused by multidrug-resistant pathogens (El-Naggar et al., 2022; Ali et al., 2023; Desai et al., 2023).
This study aims to investigate the antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles encapsulated in chitosan (AgNPs@chitosan) and further enhanced with sodium fluoride (AgNPs@chitosan-NaF) against Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms. We characterized the physicochemical properties of the nanocomposites, evaluate their antibiofilm activity using quantitative assays, and explored their mechanisms of action by examining biofilm architecture and gene expression. Additionally, we assessed the cytotoxicity of the nanocomposites against normal and cancer cell lines to evaluate their biocompatibility.
Silver nitrate (AgNO₃), sodium borohydride (NaBH₄), chitosan (medium molecular weight, 50–190 kDa, deacetylation degree 90.2%), and sodium fluoride (NaF) were purchased from Merck, Germany, and Fluka, Germany. Glacial acetic acid was obtained from ADWIC, Egypt. Double-distilled water was used to prepare all solutions. All chemicals were of analytical grade and used without further purification.
• Chitosan solution preparation: 0.075 g of chitosan was dissolved in 200 mL of 2% acetic acid solution and stirred overnight at 600 rpm at room temperature.
• AgNPs@chitosan synthesis: 60 mL of the cooled chitosan solution was mixed with 4.0 mL of 0.012 M AgNO₃ solution for 15 min. Then, 0.3 mL of 0.8 M NaBH₄ was added dropwise to the mixture under constant stirring for 15 min, resulting in the formation of AgNPs@chitosan.
• AgNPs@chitosan-NaF synthesis: 0.1 g of NaF was added to the AgNPs@chitosan solution after the complete addition of NaBH₄.
• Morphology and size: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to examine the morphology and size distribution of the synthesized nanoparticles.
• Zeta potential: Zeta potential measurements were conducted to assess the surface charge of the nanoparticles.
• Optical properties: UV–Vis spectroscopy was employed to analyze the optical properties of the nanoparticles.
• Functional groups: Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was used to identify the functional groups present in the nanoparticles.
• Crystalline structure: X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to determine the crystalline structure and phase purity of the nanoparticles.
A cell viability assay was performed using the MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) method. To enhance cell adhesion, cells were seeded at a density of 1×105 cells/mL in 96-well plates and then incubated for 24 h at 37°C with 5% CO2. After removing the culture medium, AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF nanoparticles were serially diluted in fresh medium and added to the cells. Control wells only received the culture medium. The plates were then incubated at 37°C for another 24 h.
Next, 20 μL of MTT solution (5 mg/mL in PBS) was added to each well followed by a 4-h incubation at 37°C. After dissolving the formazan crystals in 100 μL of DMSO, the absorbance was measured at 560 nm using a microplate reader Cell viability was calculated relative to the control group (Hao et al., 2013).
Cells were observed under an inverted microscope after 48 h of exposure to different concentrations of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF or the control. The morphology of normal WI-38 and A549 ATCC-185 cancer cell lines was examined for any changes, and images were captured.
A total of 57 clinical specimens (19 blood, 19 urine, and 19 sputum samples) were collected from patients at Benha Fever Hospital in Beha City, Egypt. Additionally, 32 mastitic milk samples from various farms and 31 minced meat samples from supermarkets in Sharkia governorate were obtained. All samples were collected under strict hygienic conditions.
Klebsiella species were isolated from clinical and environmental samples using selective MacConkey agar. Pink, mucoid colonies were further purified and subjected to Gram staining and biochemical tests, including TSI, oxidase, indole, urease, and motility tests, for presumptive identification (Garcia, 2010).
Klebsiella pneumoniae was confirmed through PCR amplification of the 16S rRNA gene. Genomic DNA was extracted from bacterial isolates using the QIAamp DNA Mini Kit. PCR amplification was performed using specific primers targeting the 16S rRNA gene (Table 1). A positive control strain (Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 13883) and a negative control (no template) were included in each PCR run.
Biofilm formation was quantified using the crystal violet staining method (Stepanović et al., 2000). Bacterial suspensions were cultured in 96-well microtiter plates for 24 h. After removing the planktonic cells, adherent biofilms were stained with crystal violet and the bound dye was solubilized with ethanol-acetone. The absorbance of the solubilized dye at 595 nm was measured to determine biofilm biomass. Isolates were classified as strong, moderate, weak, or non-biofilm producers based on their absorbance values relative to a positive control strain.
In accordance with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommendations, antimicrobial susceptibility testing was conducted using the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method (Bauer et al., 1966). Muller-Hinton agar (MHA) served as the growth medium. Antimicrobial disks were placed on MHA plates after standardized bacterial suspensions were inoculated. The following antibiotic disks were used: ampicillin (AM, 10 μg), amoxicillin (AX, 25 μg), amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AMC, 30 μg), amikacin (AK, 30 μg), azithromycin (AZM, 15 μg), aztreonam (ATM, 10 μg), clindamycin (DA, 2 μg), cefodroxil (CFR, 30 μg), chloramphenicol (C, 30 μg), ceftriaxone (CRO, 30 μg), cefoxitin (FOX, 30 μg), ciprofloxacin (CIP, 5 μg), cefaclor (CEC, 30 μg), ceftazidime (CAZ, 30 μg), doxycycline (DO, 30 μg), erythromycin (E, 15 μg), gatifloxacin (GAT, 5 μg), gentamicin (CN, 10 μg), levofloxacin (LEV, 5 μg), nalidixic acid (NA, 30 μg), nitrofurantoin (F, 300 μg), norfloxacin (NOR, 10 μg), ofloxacin (OFX, 5 μg), penicillin (P, 10 μg), sulbactam/ampicillin (SAM, 20 μg), tetracycline (TE, 30 μg), trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT, 25 μg), and tobramycin (TOB, 10 μg) obtained from Bioclone (Turkey) and Oxoid (England). Plates were incubated at 37°C for 18–24 h, and inhibition zone diameters were measured to determine antimicrobial susceptibility (CLSI, 2020). Multidrug-resistant isolates were defined as those exhibiting resistance to three or more distinct classes of antibiotics (MDR) and categorized with the recommendation of Tambekar et al. (2006).
To evaluate the antibacterial effectiveness of the synthetic nano particles. We utilized the agar well diffusion method (Venkataraju et al., 2014). A consistent suspension of Klebsiella pneumoniae was evenly spread on nutrient agar plates. Wells were created in the agar using aseptic techniques, and a predetermined volume of the nanoparticle suspension was added to each well. Control wells containing only the solvent were also included. The plates were incubated aerobically at 37°C for 24 h. The antibacterial potency of the nanoparticles was determined by measuring the diameter of the inhibition zones surrounding the wells.
Using the broth microdilution method, we determined the MIC values for both the synthesized nanoparticles and antibiotics according to the criteria outlined by (CLSI, 2020). We created a series of two-fold dilutions of the test compounds in a 96-well microtiter plate, with the highest concentration being 1,024 μg/mL. An overnight culture of Klebsiella pneumoniae was adjusted to a final concentration of approximately 5 × 105 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL. A volume of 100 μL of the bacterial suspension was added to each well containing the test compounds. The plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of the test compound that inhibited visible bacterial growth.
Analysis to visualize the morphological changes in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms induced by antibiotic treatment and nanoparticle exposure, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was employed. Biofilm samples were collected and processed for TEM analysis according to standard protocols. Briefly, biofilms were fixed with glutaraldehyde, dehydrated, embedded in resin, and sectioned for imaging. TEM analysis was performed using a JEOL-JSM-5500LV microscope operated at an acceleration voltage of 80 kV.
Total RNA was extracted from bacterial cultures using the QIAamp RNeasy Mini Kit and quantified using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer. RNA purity was assessed by calculating the A260/A280 and A260/A230 ratios, where values of 1.8–2.0 and 2.0–2.2, respectively, indicate high-quality RNA. qPCR analysis was performed using SYBR Green chemistry on a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System utilizing primers listed in Table 1. A 20 μL reaction mixture containing 10 μL of 2x HERA SYBR® Green RT-qPCR Master Mix (Willowfort, United Kingdom), 1 μL of RT Enzyme Mix (20X), 1 μL of each primer (20 pmol), 3 μL of nuclease-free water, and 5 μL of RNA template was prepared. The program included an initial denaturation step at 94°C for 15 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation (94°C for15s), annealing (55°C for 30s), and extension (72°C for 30s). A final extension step at 72°C for 10 min concluded the reaction. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCt method, with the 16S rRNA gene serving as a reference gene (Yuan et al., 2006).
Data were edited in MS Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, United States). The Levene and Shapiro–Wilk tests were conducted in order to check for normality and homogeneity of variance (Razali and Wah, 2011). One way- Anova of statistical analysis system (SAS, 2012) was used for assessing gene transcription of treC, fimA, mrkA, and espA. Multiple comparisons among means were carried out by the Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (Steel and Torrie, 1980). Results of antimicrobial resistant were examined by fisher exact test. Results were expressed as means ± SE. A logistic regression model (PROC LOGISTIC;) was run with the level of significance set at α = 0.05 to examine the effects of potential risk factors, including clinical samples, sex, age, sample sources, and sample type on the prevalence of Klebsiella. Statistical significance was accepted at probability less than 0.05.
UV–Vis absorption spectra of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF exhibited characteristic surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peaks centered at approximately 413 nm and 415 nm, respectively (Figure 1). The appearance of these SPR peaks confirmed the formation of AgNPs within the chitosan matrix. TEM images of the two synthesized AgNPs samples clearly show the formation of uniform, well-defined particles, confirming their characteristic SPR peaks.
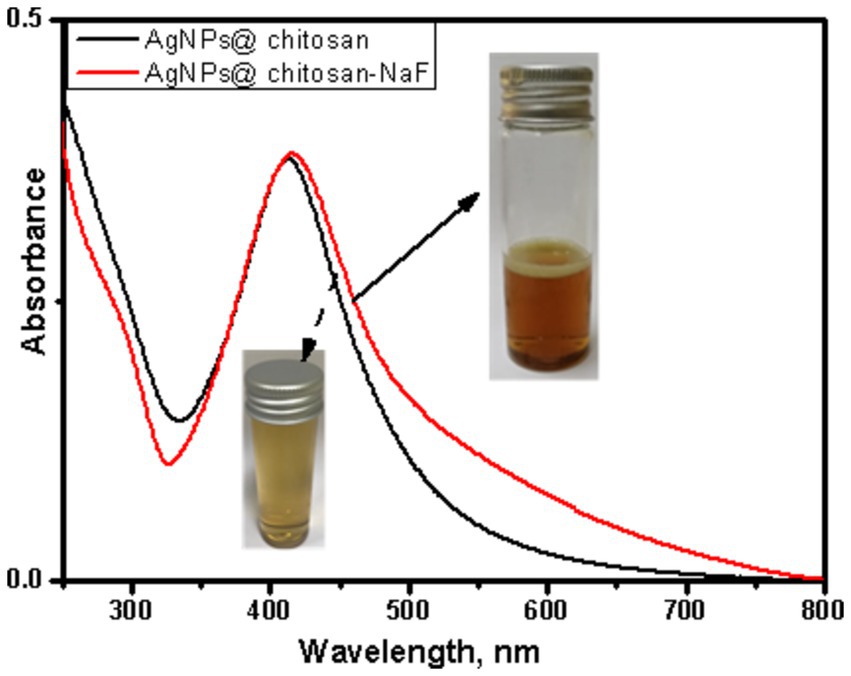
Figure 1. UV–Vis absorption spectra of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, and the inset is their photo images.
The morphological characteristics of the two synthesized nanocomposites were investigated using HR-TEM. Figure 2A demonstrates a representative TEM image of AgNPs@chitosan that appeared as agglomerated small particles. These agglomerates look like flowers in the range of 100 nm. Additionally, the TEM images of AgNPs@chitosan-NaF signify the formation of small spherical AgNPs dispersed over a chitosan matrix (Figure 2B).
The elemental composition of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF was determined using EDX analysis. The EDX spectrum of AgNPs@chitosan revealed the presence of carbon (25%), oxygen (49.5%), nitrogen (16.42%), and silver (8.75%) (Figure 3A). For AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, the EDX spectrum showed peaks corresponding to carbon (29.96%), oxygen (49.35%), nitrogen (1.09%), silver (2.1%), and fluorine (0.79%) (Figure 3B).
Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was employed to investigate the chemical interactions between chitosan and AgNPs in the synthesized nanocomposites. The FTIR spectra of chitosan, AgNPs@chitosan, and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF are shown in Figures 4A–C. Compared to pure chitosan, the spectra of the nanocomposites exhibited shifts in the characteristic peaks corresponding to the O-H, N-H, and C-O-C stretching vibrations. A new peak at approximately 661 cm−1 emerged in the spectra of the nanocomposites (Table 2).
The crystalline structure of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF was investigated using XRD analysis. The XRD patterns exhibited characteristic diffraction peaks at approximately 38°, 44°, 64°, and 77° 2θ, corresponding to the (111), (200), (220), and (311) planes of face-centered cubic (fcc) silver, respectively (Figures 5A,B). Broad diffraction peaks in the range of 10–25° 2θ were attributed to the amorphous nature of chitosan.
The cytotoxicity of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF was calculated based on the growth inhibition compared to the control group. AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF were tested against WI-38 were isolated from human fetal normal lung fibroblast cells, (Figures 6A,B), and A549 ATCC-185 were isolated from lung carcinoma epithelial cells (Figures 6C,D), at concentrations of 7.81 to 1,000 μg mL−1 to determine their ability to inhibit normal and cancer cell growth. The test was conducted for 24 h at 37°C. For each concentration, there were three duplicates in addition to the untreated control sample. The rate of growth inhibition for AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF relative to the control group, which grew at 100%, was used to calculate the severity of the toxicological impact.
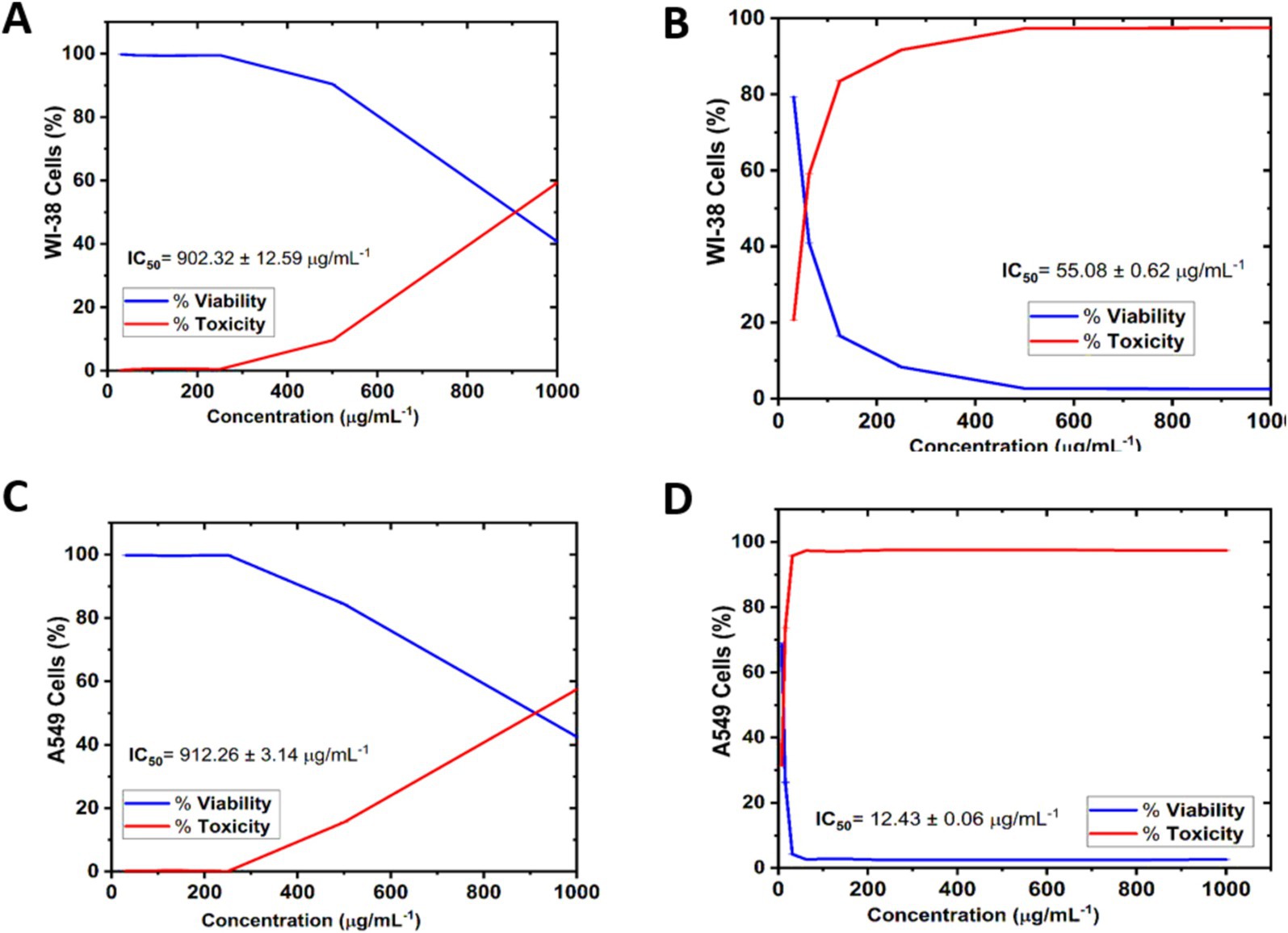
Figure 6. Cell viability and Cytotoxicity of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF on normal lung fibroblast WI-38 cells (A,B), and lung carcinoma epithelial A549 ATCC-185 cells (C,D) for 24 h. The results were taken from replicated (n = 3) (Mean ± SD).
For cell viability, AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF samples at 31.25 and 1,000 μg mL−1 caused significant changes in normal WI-38 cells in a concentration-dependent manner compared with the control. Where, Figures 6A,B show that the WI-38 cells treated with AgNPs@chitosan-NaF exhibited clear cell destruction and were more impacted than those treated with AgNPs@chitosan. AgNPs@chitosan-NaF showed the morphological characteristics of apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner at 31.25 to 62.5 μg mL−1. While, the cells treated with AgNPs@chitosan showed less uniformity, with membrane integrity loss, rounding, and shrinking, but remained intact at AgNPs@chitosan concentrations of 500 and 1,000 μg mL−1.
Overall, all the tested concentrations showed cytocompatibility at concentrations of up to at least 500 μg mL–1 (>90.42%) of AgNPs@chitosan, and 31.25 μg mL−1 (>79.28%) of AgNPs@chitosan-NaF after 24 h of incubation onto WI-38 cells, additionally, up to at least 500 μg mL−1 (>84.39%) of AgNPs@chitosan, and 7. 81 μg mL−1 (>68.47%) of AgNPs@chitosan-NaF after 24 h of incubation onto A549 ATCC-185 cells (Figures 6C,D).
For cytotoxicity of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF against of normal lung fibroblast WI-38 cells, and of lung carcinoma epithelial A549 cells was dose-dependent at an inhibition concentration of 50% (IC50). The cytotoxicity values (IC50 values) were 902.32 ± 12.59 μg mL−1, and 55.08 ± 0.62 μg mL−1 for the AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, respectively against WI-38 cells. While, IC50 values were 912.26 ± 3.14 μg mL−1, and 12.43 ± 0.06 μg mL−1 for the AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, respectively, against A549 ATCC-185 cells. Further evaluation of the AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF showed the lowest level of cytotoxic activity against WI-38 cells against WI-38 cells at a concentration of less than 1,000 μg mL−1 (>59.25%),and at a concentration of less than 62.5 μg mL−1 (>59.10%), respectively (Figures 6A,B), and cytotoxic activity against A549 ATCC-185 cells at a concentration of less than 1,000 μg mL−1 (>57.45%),and at a concentration of less than 15.62 μg mL−1 (>73.67%), respectively (Figures 6C,D).
The morphological characteristics of untreated cells, as well as normal WI-38 and A549 ATCC-185 cancer cell lines treated with different amounts of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF were compared (Figures 7, 8). Absorbance values obtained after capturing the red dye a long with the appropriate concentrations of AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF used in the viability studies, were analyzed using the 3 T3 Phototox program to assess the concentrations of the produced samples in various cell lines.
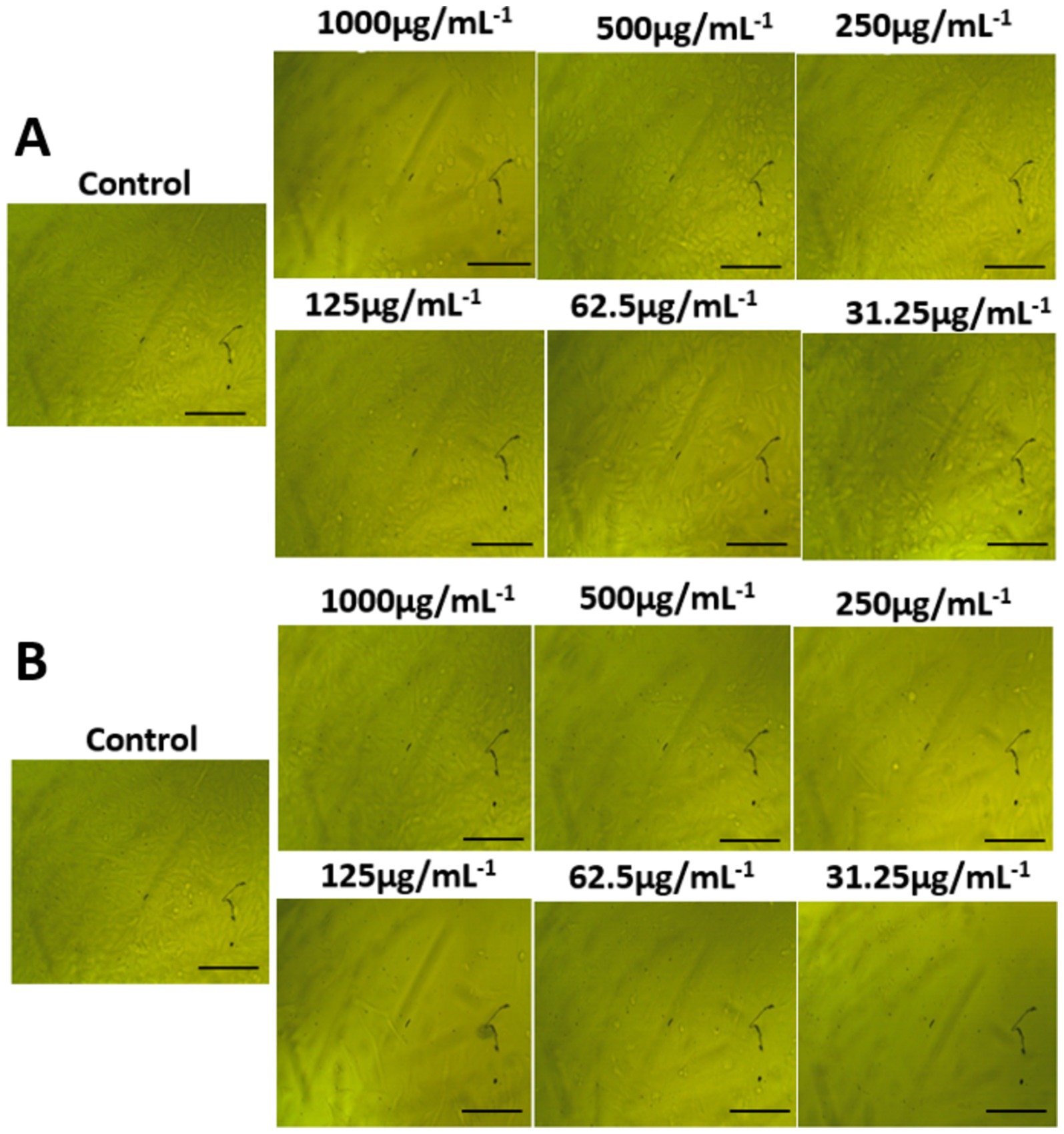
Figure 7. Morphological features on normal lung fibroblast WI-38 cells of (A) AgNPs@chitosan and (B) AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, the images were taken from the cells were treated with an average size of 10 nm for 24 h.
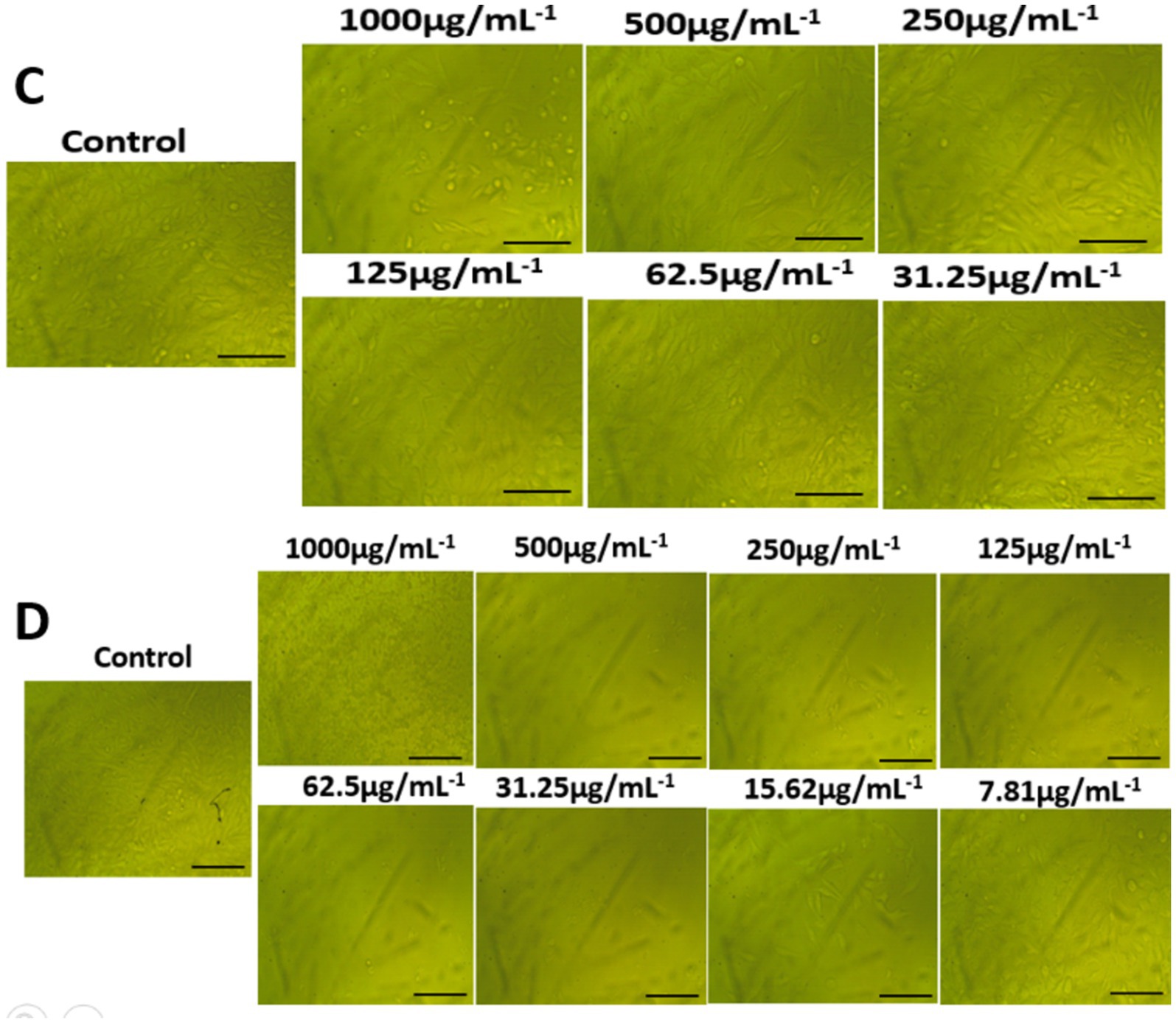

Figure 8. Morphological features on lung carcinoma epithelial A549 cells of (A) AgNPs@chitosan and (B) AgNPs@chitosan-NaF, the images were taken from the cells were treated with an average size of 10 nm for 24 h.
The prevalence of K. pneumoniae was determined to be 12.5% (15/120) based on genotypic identification using 16S rRNA gene-specific primer. Amplicon size analysis confirmed the identity of K. pneumoniae isolates, with a characteristic 130 bp band observed.
Logistic regression analysis identified several factors associated with the prevalence of Klebsiella. Clinical source was a significant predictor, with blood and sputum samples showing a lower risk compared to urine samples. Females were more likely to be colonized with Klebsiella than males. Age group analysis revealed a decreased risk of Klebsiella colonization in individuals aged 31–40 years and ≤ 41 years compared to the 20–30 age group. Additionally, human-derived samples exhibited a higher risk of Klebsiella colonization compared to animal and food samples, with minced meat samples showing the highest risk (Table 3).
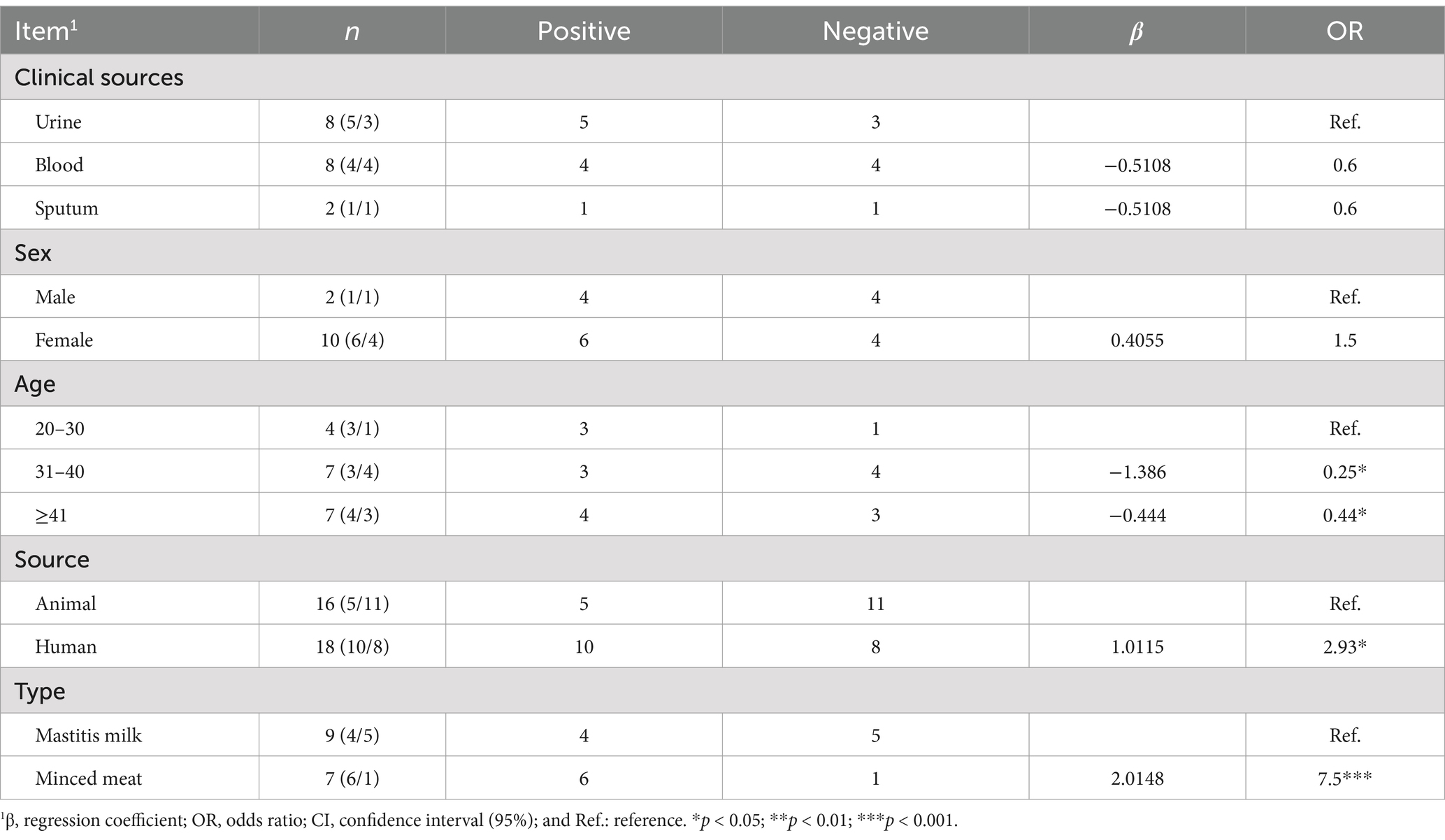
Table 3. Logistic regression analysis of different risk factors associated with the prevalence of Klebsiella.
Biofilm quantification analyses showed that 100% of the isolates were biofilm producers. The obtained isolates of this study had the following results for the categories of biofilm production: 25% weakly adherent, 37.5% moderately adherent, and 37.5% strongly adherent.
The antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of Klebsiella isolates from human and animal sources exhibited significant differences (p < 0.001). Isolates from animal sources demonstrated higher overall resistance rates compared to human isolates. Notably, all animal isolates were susceptible to chloramphenicol, while a high resistance rate was observed for doxycycline in mastitis milk samples. In contrast, human isolates exhibited a wider range of antibiotic resistance, with the highest resistance rates observed for chloramphenicol, gentamicin, and ceftriaxone.
Analysis of antimicrobial resistance patterns based on clinical source, gender, and age revealed significant variations. Urine and blood samples exhibited higher resistance rates compared to sputum samples. Females demonstrated higher resistance rates than males, particularly for chloramphenicol. Older age groups showed higher resistance rates compared to younger age groups (Figures 8–10; Table 3).
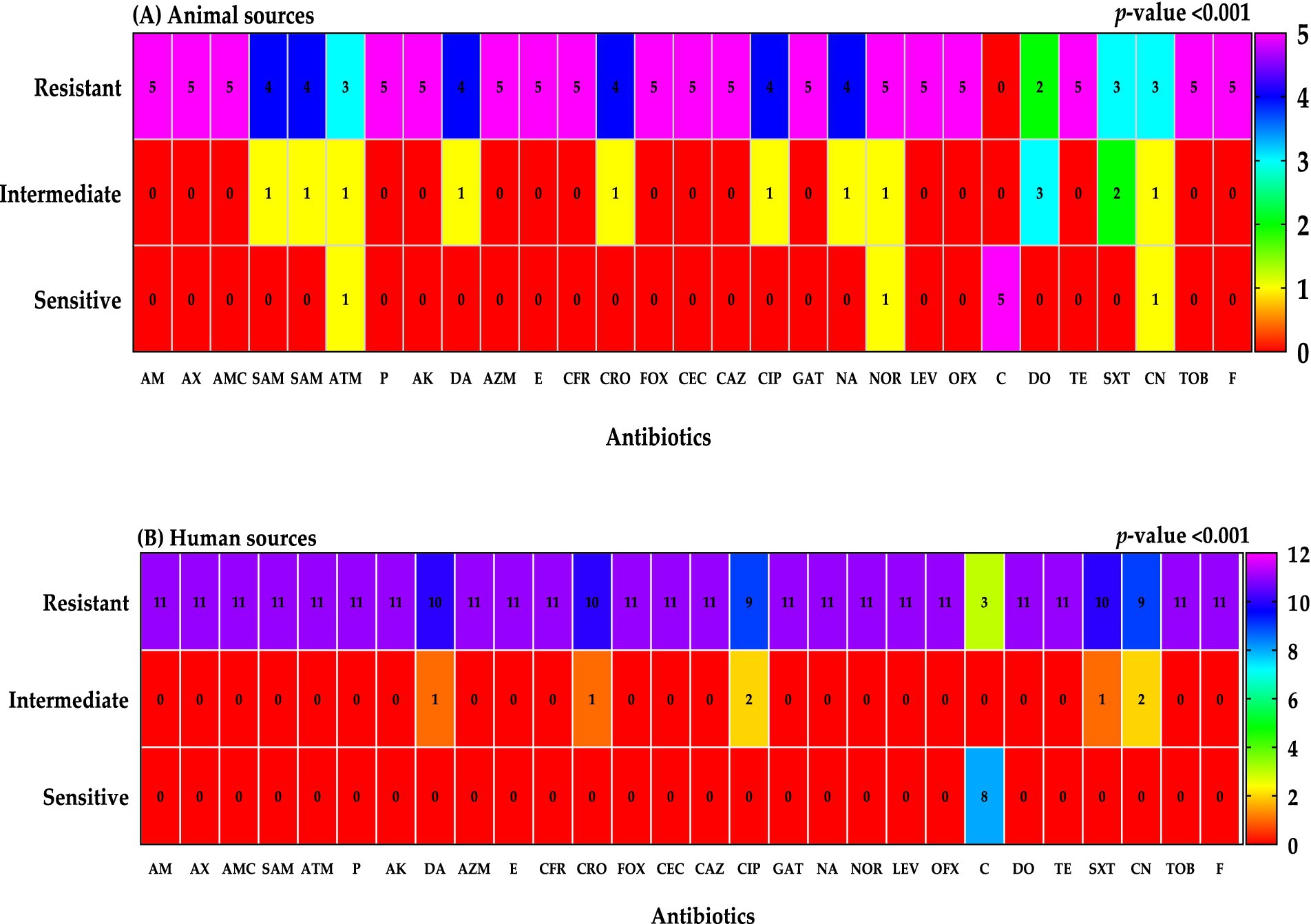
Figure 9. Resistant classifications to antibiotics were categorized by sample sources; animal sources (A) and human sources (B).
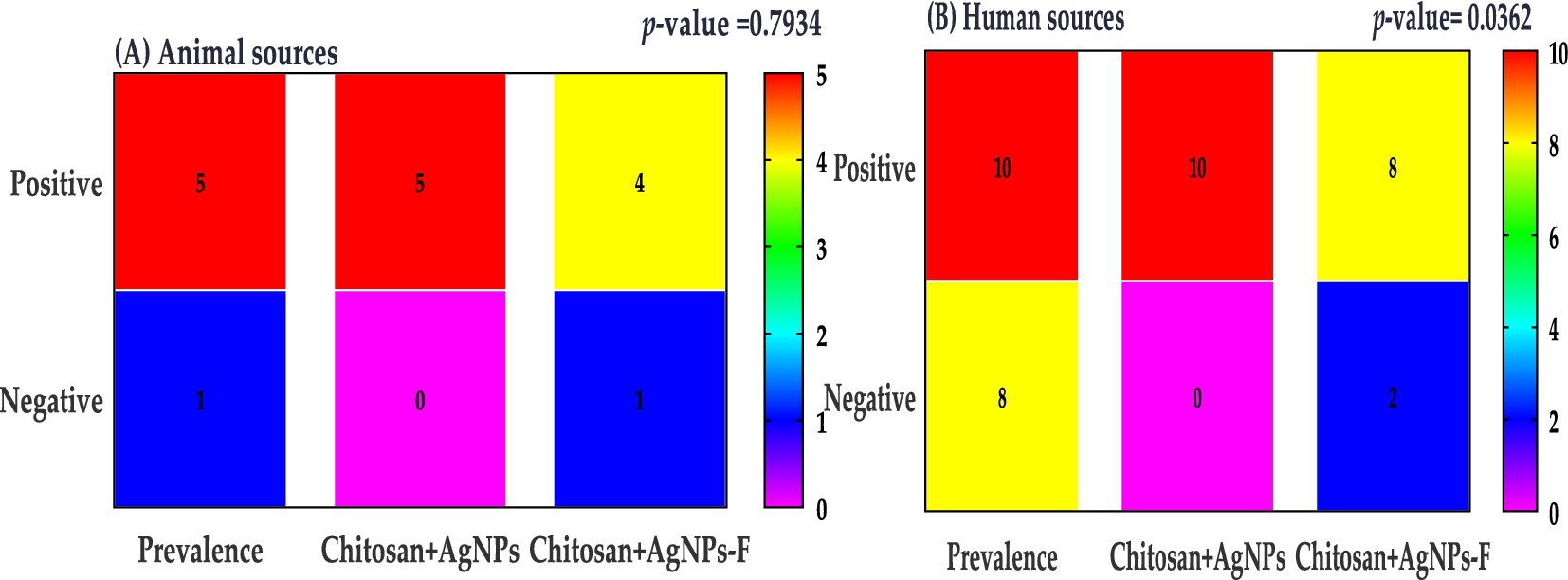
Figure 10. Klebsiella prevalence were categorized by sample sources; animal sources (A) and human sources (B).
The AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF nanocomposites demonstrated potent antibacterial activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. This was evidenced by the formation of inhibition zones ranging from 20 to 35 mm in the agar diffusion assay and MICs ranging from 0.125 to 1 μg/mL.
The provided electro-micrograph images depicted the ultrastructural morphology of K. pneumoniae biofilm, both untreated and treated with chitosan-silver nanoparticle composites. The dark regions in the images represent the bacterial cells and extracellular matrix of the biofilm, while the lighter areas may indicate voids or spaces within the biofilm structure (Figure 11). The image of the untreated Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm likely shows a dense, interconnected network of bacterial cells embedded in a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). This matrix provides protection for the bacteria and contributes to the biofilm’s resistance to antibiotics and other stresses. The images of the biofilm treated with Chitosan@AgNPs-F show the profound disruptions in the biofilm structure, such as decreased bacterial density, increased porosity, or detachment of bacterial cells. These changes could be indicative of the antibiofilm activity of the treatment.
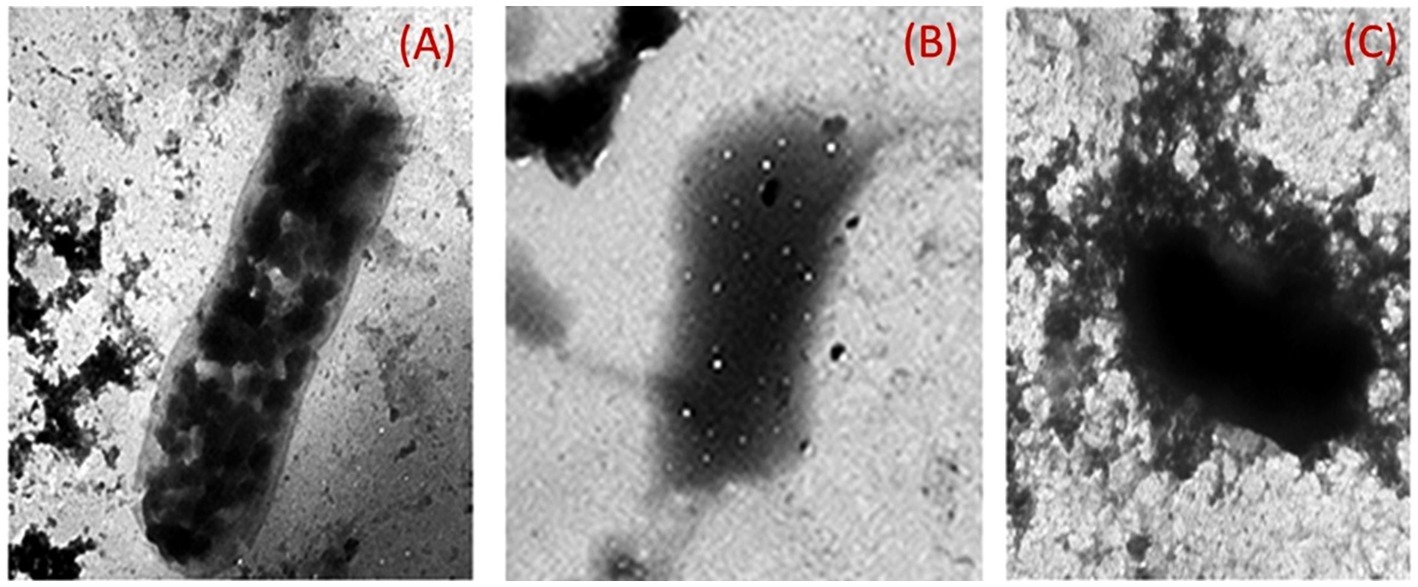
Figure 11. Transmission electron micrographs of K. pneumoniae cells; (A) Untreated K. pneumoniae cells; (B) K. pneumoniae cells treated with AgNPs@chitosan and (C) K. pneumoniae cells treated with AgNPs@chitosan-NaF.
The present results clearly indicated that the transcription of treC, fimA, mrkA, and espA was significantly down regulated in both two treated group compared to the control group, minimized in the group received chitosan+AgNPs-F (p < 0.05; Figure 12).
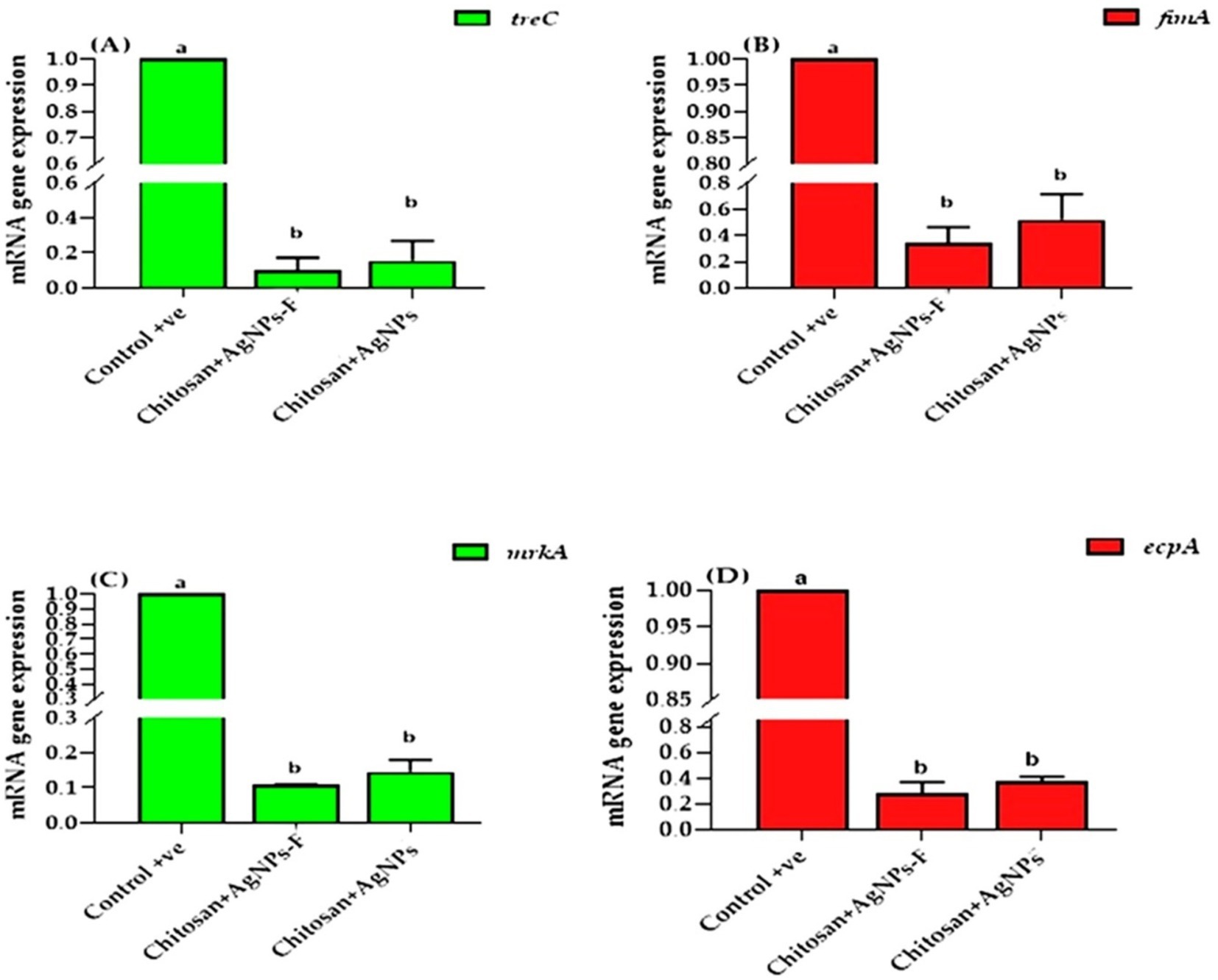
Figure 12. The effects of two tested silver nanoparticle-based biomaterial treatments on the expression of key biofilm genes in K. pneumoniae: treC (A), fimA (B), mrkA (C), and espA (D). The data is presented as means ± SEM.
The UV–Vis absorption spectra findings are consistent with previous studies reporting the SPR band of AgNPs in the range of 400–420 nm. As reported by Mehr et al. (2015) well-defined silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) exhibit a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at wavelengths less than 420 nm. The presence of a clear SPR peak in the UV–Vis spectra indicates the successful synthesis of AgNPs within the chitosan matrix.
The change observed in the AgNPs shape in both samples is tentatively attributed to the presence of NaF, which acts as an additional capping agent besides NaBH4. Consequently, the particle’s shape changed from a flowered-like shape into well-dispersed small spherical particles. This finding is consistent with previous reports by Larm et al. (2019) who confirmed the instability of NaBH4-capped AgNPs using TEM imaging.
The presence of fluorine in the AgNPs@chitosan-NaF nanocomposite is particularly significant as it suggests that NaF has been successfully incorporated into the chitosan matrix. This could potentially enhance the properties of the nanocomposite, such as its antimicrobial activity or biocompatibility.
The shifts in the characteristic peaks and the emergence of a new peak at 661 cm−1 in the FTIR spectra of the nanocomposites indicate the formation of chemical interactions between chitosan functional groups and AgNPs. This suggests that the AgNPs are successfully incorporated within the chitosan matrix, which could enhance the stability and properties of the nanocomposite. The presence of Ag-O bonds, as indicated by the new peak at 661 cm−1, further supports the formation of AgNPs within the chitosan matrix (Pawar et al., 2016).
The XRD results confirmed the formation of crystalline silver nanoparticles within the chitosan matrix, consistent with previous findings by Kaur et al. (2013). The presence of both silver and chitosan peaks in the XRD patterns indicated the successful formation of the AgNPs@chitosan and AgNPs@chitosan-NaF nanocomposites. The crystalline structure of the silver nanoparticles and their interaction with the chitosan matrix may influence the overall physiochemical properties of the nanocomposites (Govindan et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2016; Chicea et al., 2024). Further characterization studies are needed to elucidate the precise relationship between the nanocomposite structure and their biological activities.
Of interest, the AgNPs@chitosan-NaF nanocomposites exhibited selective cytotoxicity toward cancer cells, with lower toxicity observed against normal lung fibroblast WI-38 cells compared to lung carcinoma epithelial A549 cells. These findings suggest that AgNPs@chitosan-NaF may have potential as targeted anticancer agents. However, further in vivo studies are needed to validate their efficacy and safety. In vitro cytotoxicity studies have limitations in fully recapitulating the complex biological environment in vivo, including the extracellular matrix and the immune system response. Therefore, preclinical studies are essential to assess the pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and potential toxicity of AgNPs@chitosan-NaF in animal models. By addressing these limitations, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the therapeutic potential of these nanocomposites for cancer treatment beside Klebsiella treatment.
It was observed that the high dosage of AgNPs@chitosan did not exhibit any cytotoxic effect over a 24 h. This lack of cytotoxicity may be attributed to the gradual release of silver ions from the gel matrix. This discovery suggests that chitosan may be used as a capping ingredient in nanoparticles due to its biocompatibility (AshaRani et al., 2009). Our results are comparable to the findings reported in previous studies (Freire et al., 2016; Wongpreecha et al., 2018). The observed cytotoxicity of AgNPs@chitosan coated with NaF at varying doses may be attributed to the induction of reactive oxygen species by the presence of AgNPs, which is well recognized as a significant contributor to DNA damage. The genotoxicity resulting from the action of reactive oxygen species has been previously shown in the case of metal oxide nanoparticles and AgNPs that are capped with starch (AshaRani et al., 2009; Yang et al., 2009). The potential for further harm arises from the interaction between silver ions and DNA, resulting in alterations to the structure of DNA. Therefore, the findings of this study suggest that AgNPs@chitosan do not exhibit cytotoxic or genotoxic properties on normal cells. However, it is seen that these nanoparticles induce toxic effects when administered at concentrations beyond a certain threshold. The microscopic examination of WI-38 and A549 ATCC-185 cells treated with a bactericidal dosage of AgNPs@chitosan did not reveal any discernible alterations in comparison to the control cells. However, exposure to a high dose (up to 500 μg mL−1) resulted in anomalous cellular shape and a limited number of cellular extensions. This phenomenon may be attributed to disruptions in cytoskeletal functionality induced by the administration of nanoparticles.
The prevalence of Klebsiella colonization has been reported to vary widely across different populations, ranging from 5 to 87.7% (Shu et al., 2009; Shon et al., 2013; Zheng et al., 2018). In the present study, the prevalence of Klebsiella species among all obtained samples was determined to be 12.5% (15/120), with all isolates identified as K. pneumoniae through genotypic assay.
The Klebsiella prevalence finding is lower than that of Al Bshabshe et al. (2020) who reported 39%, but higher than a previous study at 9.9% (Ripabelli et al., 2018). The higher incidence of K. pneumoniae in our study highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and implantation of infection control strategies to address the spread of this pathogen. The increased prevalence of K. pneumoniae in our study compared to earlier studies could be attributed to various factors, such as differences in study populations, healthcare facilities, or geographic locations. Additionally, the higher percentage of Klebsiella infections found in recent research may be due to the use of more sensitive diagnostic techniques. Compared to other common pathogens in these infected cases, K. pneumoniae is a significant concern due to its ability to form biofilms and produce extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), which confer resistance to many antibiotics (Vuotto et al., 2014; Costa, 2019; Ebrahem et al., 2024). Therefore, the relatively high prevalence of Klebsiella pneumoniae in our study underscores the need for effective infection prevention and control strategies.
These risk factors analysis that certain patient populations and sample types are at an increased risk for Klebsiella colonization. This highlights the need for targeted infection control measures, such as catheter care, hand hygiene, antibiotic stewardship, environmental disinfection, and surveillance, to reduce the burden of Klebsiella infections.
These findings of biofilm quantification suggest that different strains or clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae may have distinct biofilm-forming capacities (Zheng et al., 2018). Biofilm formation is often associated with increased antibiotic resistance and can complicate the treatment of infections. Furthermore, the ability of K. pneumoniae to form biofilms can contribute to the persistence of infections and the spread of the bacteria in healthcare settings (Guerra et al., 2022). Effective infection prevention and control measures, including proper hand hygiene, disinfection of surfaces, and antibiotic stewardship, are essential to address the challenge of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms.
The emergence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella strains highlights the urgent need for effective antimicrobial strategies. In our study, a concerning 87% (n = 13) of isolates were classified as extreme drug-resistant (XDR, resistant to all classes of antimicrobial agents except 2 or fewer), and 13% were pan-resistant (resistant to all antimicrobial agents). Infections caused by these MDR strains are often difficult to treat, leading to prolonged illness, increased mortality, and higher healthcare costs. The limited availability of effective antibiotics can also contribute to the spread of MDR strains, making it challenging to control outbreaks (El Damaty et al., 2023; El-Demerdash et al., 2023c; El-Demerdash et al., 2023b; Megahed et al., 2023). Previous studies have reported similar or even higher rates of MDR K. pneumoniae in various regions worldwide (Moradigaravand et al., 2017; Huynh et al., 2020; Miftode et al., 2021; El-Demerdash et al., 2024). These findings underscore the global nature of this public health crisis. To address the challenge of MDR K. pneumoniae, it is essential to implement comprehensive infection prevention and control measures, promote the appropriate use of antibiotics, and support the development of new antimicrobial agents.
The agar well diffusion and microdilution results align with previous studies on the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles (Bruna et al., 2021; More et al., 2023) and suggest that the incorporation of sodium fluoride may enhance their efficacy. The antibacterial activity of AgNPs is likely due to the release of silver ions, the generation of reactive oxygen species, and physical disruption of bacterial cell components (Ahmad et al., 2017; Tripathi and Goshisht, 2022). The addition of chitosan and sodium fluoride may enhance the antibacterial activity of AgNPs and the generation of ROS through synergistic effects, improved stability, and enhanced penetration into bacterial cells.
The expression of biofilm-associated genes, including treC, fimA, mrkA, and ecpA, was investigated to elucidate the mechanisms underlying biofilm formation by Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. The treC gene, involved in capsular polysaccharide production, and the fimA gene, encoding the major subunit of type 1 fimbriae, are key factors in biofilm initiation and development (Li and Ni, 2023). The mrkA gene has been implicated in the rapid formation of biofilms in Klebsiella pneumoniae (Murphy and Clegg, 2012). While the ecpA gene is associated with virulence and biofilm formation in other bacterial species (Alcántar-Curiel et al., 2013), its role in Klebsiella biofilm development requires further investigation.
The downregulation of these genes suggests that the nanocomposites may interfere with the molecular mechanisms underlying biofilm formation such as quorum sensing, extracellular matrix production, bacterial adhesion, and bacterial metabolism (Afrasiabi and Partoazar, 2024). These findings align with previous studies highlighting the importance of targeting biofilm-associated genes for developing effective antibiofilm strategies (Nadar et al., 2022).
This study investigated the prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and biofilm formation of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, highlighting a significant public health concern due to the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strains. To address this pressing issue, we developed chitosan-based silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) functionalized with sodium fluoride (AgNPs@chitosan-NaF).
The synthesized nanocomposites demonstrated promising antibacterial and antibiofilm activity against K. pneumoniae in vitro. However, further in vivo studies are necessary to validate their efficacy and safety in complex biological environments. Additionally, while the nanocomposites exhibited minimal cytotoxicity at lower concentrations, their potential toxicity at higher doses requires careful consideration and optimization of dosing strategies for clinical applications.
To gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of action, a more comprehensive molecular analysis, beyond biofilm-associated genes, is warranted. Nevertheless, these preliminary findings suggest that AgNPs@chitosan-NaF hold promise as a novel therapeutic approach for combating K. pneumoniae infections. Future research should focus on addressing these limitations and exploring the full potential of these nanocomposites.
DNA sequence generated in this study was submitted to GenBank and assigned the accession number of PQ516970.
The studies involving humans were approved by Human study protocol was approved by the Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University (ZU-IRB/409/2024). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. The animal study was approved by Faculty of Science, Zagazig University (approval number: ZU-IACUC/1/F/261/2023). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
EE: Methodology, Writing – original draft. RA: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. OE-B: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MA: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AA: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. AE-D: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research project was supported by Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2024R1018), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The handling editor FH declared a shared parent affiliation with the author(s) RA at the time of review.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbas, R., Chakkour, M., Zein El Dine, H., Obaseki, E. F., Obeid, S. T., Jezzini, A., et al. (2024). General overview of Klebsiella pneumonia: epidemiology and the role of Siderophores in its pathogenicity. Biology (Basel) 13:78. doi: 10.3390/biology13020078
Abd El-Emam, M. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., Abdo, S. A., Abd-Elfatah, E. B., El-Sayed, M. M., Qelliny, M. R., et al. (2024). The ameliorative role of Aloe vera-loaded chitosan nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus induced acute lung injury: targeting TLR/NF-$κ$B signaling pathways. Open Vet J 14, 416–427. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.38
Afrasiabi, S., and Partoazar, A. (2024). Targeting bacterial biofilm-related genes with nanoparticle-based strategies. Front. Microbiol. 15:1387114. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1387114
Ahmad, A., Wei, Y., Syed, F., Tahir, K., Rehman, A. U., Khan, A., et al. (2017). The effects of bacteria-nanoparticles interface on the antibacterial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Microb. Pathog. 102, 133–142. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.11.030
Al Bshabshe, A., Al-Hakami, A., Alshehri, B., Al-Shahrani, K. A., Alshehri, A. A., Al Shahrani, M. B., et al. (2020). Rising Klebsiella pneumoniae infections and its expanding drug resistance in the intensive care unit of a tertiary healthcare hospital, Saudi Arabia. Cureus 12:10060. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10060
Alcántar-Curiel, M. D., Blackburn, D., Saldaña, Z., Gayosso-Vázquez, C., Iovine, N., la Cruz, M. A., et al. (2013). Multi-functional analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae fimbrial types in adherence and biofilm formation. Virulence 4, 129–138. doi: 10.4161/viru.22974
Ali, N. M., Mohamed, G. A. E., and El-Demerdash, A. S. (2023). Impact of oral administration of Chitosan--nanoparticles on oxidative stress index and gut microbiota of heat stressed broilers. J Adv Vet Res 13, 997–1003.
AshaRani, P. V., Low, G., Hande, M., and Valiyaveettil, S. (2009). Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3, 279–290. doi: 10.1021/nn800596w
Bauer, A. W., Kirby, W. M., Sherris, J. C., and Turck, M. (1966). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45, 493–496. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/45.4_ts.493
Bruna, T., Maldonado-Bravo, F., Jara, P., and Caro, N. (2021). Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:7202. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137202
Chicea, D., Nicolae-Maranciuc, A., and Chicea, L.-M. (2024). Silver nanoparticles-chitosan nanocomposites: a comparative study regarding different chemical syntheses procedures and their antibacterial effect. Materials 17:1113. doi: 10.3390/ma17051113
CLSI (2020). CLSI M100-ED29: 2021 performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. 30th Edn. Philadelphia, PA: CLSI, 50–51.
Costa, D. T. D. (2019). Virulence determinants and antibiotic resistance of extended-Spectrum Beta-lactamase (ESBL) producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from hospital environment. Dhaka: Brac University.
Desai, N., Rana, D., Salave, S., Gupta, R., Patel, P., Karunakaran, B., et al. (2023). Chitosan: a potential biopolymer in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 15:1313. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041313
Ebrahem, A. F., El-Demerdash, A. S., Orady, R. M., and Nabil, N. M. (2024). Modulatory effect of competitive exclusion on the transmission of ESBL E. coli in chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 16, 1087–1098. doi: 10.1007/s12602-023-10095-1
El Damaty, H. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., Abd El-Aziz, N. K., Yousef, S. G., Hefny, A. A., Abo Remela, E. M., et al. (2023). Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibilities of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis isolated from Caseous lymphadenitis of smallholder sheep and goats. Animals 13:2337. doi: 10.3390/ani13142337
El-Demerdash, A. S., Aggour, M. G., El-Azzouny, M. M., and Abou-Khadra, S. H. (2018). Molecular analysis of integron gene cassette arrays associated multi-drug resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates from poultry. Cell. Mol. Biol. 64, 149–156. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2018.64.5.25
El-Demerdash, A. S., Al Atfeehy, N. M., Hamed, R. I., Bakry, N. R., Matter, A. A., and Eid, S. (2023a). Mobile Colistin resistance determinants among Enterobacteriaceae isolated from different poultry species. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 13, 1004–1010.
El-Demerdash, A. S., Alfaraj, R., Fared, F., Saleh, A., Dawwam, G. E., et al. (2024). Essential oils as capsule disruptors: enhancing antibiotic efficacy against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 15:1467460. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1467460
El-Demerdash, A. S., Mohamady, S. N., Megahed, H. M., and Ali, N. M. (2023b). Evaluation of gene expression related to immunity, apoptosis, and gut integrity that underlies Artemisia’s therapeutic effects in necrotic enteritis-challenged broilers. 3 Biotech 13:181. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03560-9
El-Demerdash, A. S., Mowafy, R. E., Fahmy, H. A., Matter, A. A., and Samir, M. (2023c). Pathognomonic features of Pasteurella multocida isolates among various avian species in Sharkia governorate, Egypt. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 39:335. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03774-2
El-Demerdash, A. S., Orady, R. M., Matter, A. A., and Ebrahem, A. F. (2023d). An alternative approach using Nano-garlic emulsion and its synergy with antibiotics for controlling biofilm-producing multidrug-resistant Salmonella in chicken. Indian J. Microbiol. 63, 632–644. doi: 10.1007/s12088-023-01124-2
El-Naggar, N. E.-A., Shiha, A. M., Mahrous, H., and Mohammed, A. B. A. (2022). Green synthesis of chitosan nanoparticles, optimization, characterization and antibacterial efficacy against multi drug resistant biofilm-forming Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 12:19869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24303-5
Franci, G., Falanga, A., Galdiero, S., Palomba, L., Rai, M., Morelli, G., et al. (2015). Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 20, 8856–8874. doi: 10.3390/molecules20058856
Freire, P. L. L., Albuquerque, A. J. R., Farias, I. A. P., da Silva, T. G., Aguiar, J. S., Galembeck, A., et al. (2016). Antimicrobial and cytotoxicity evaluation of colloidal chitosan--silver nanoparticles--fluoride nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 93, 896–903. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.052
Garcia, L. S. (2010). Clinical microbiology procedures handbook. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology Press.
Govindan, S., Nivethaa, E. A. K., Saravanan, R., Narayanan, V., and Stephen, A. (2012). Synthesis and characterization of chitosan--silver nanocomposite. Appl. Nanosci. 2, 299–303. doi: 10.1007/s13204-012-0109-5
Guerra, M. E. S., Destro, G., Vieira, B., Lima, A. S., Ferraz, L. F. C., Hakansson, A. P., et al. (2022). Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms and their role in disease pathogenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 12:877995. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.877995
Hao, S., Wang, B., Wang, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, B., and Guo, T. (2013). Preparation of Eudragit L 100-55 enteric nanoparticles by a novel emulsion diffusion method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 108, 127–133. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.02.036
Hashem, N. M., Essawi, W. M., El-Demerdash, A. S., and El-Raghi, A. A. (2024). Biomolecule-producing probiotic bacterium Lactococcus lactis in free or Nanoencapsulated form for endometritis treatment and fertility improvement in buffaloes. J. Funct. Biomater. 15:138. doi: 10.3390/jfb15060138
Huynh, B.-T., Passet, V., Rakotondrasoa, A., Diallo, T., Kerleguer, A., Hennart, M., et al. (2020). Klebsiella pneumoniae carriage in low-income countries: antimicrobial resistance, genomic diversity and risk factors. Gut Microbes 11, 1287–1299. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1748257
Ibrahim, M. E. (2023). Risk factors in acquiring multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in a hospital setting in Saudi Arabia. Sci. Rep. 13:11626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38871-7
Kaur, P., Choudhary, A., and Thakur, R. (2013). Synthesis of chitosan-silver nanocomposites and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 4:869.
Larm, N. E., Thon, J. A., Vazmitsel, Y., Atwood, J. L., and Baker, G. A. (2019). Borohydride stabilized gold--silver bimetallic nanocatalysts for highly efficient 4-nitrophenol reduction. Nanoscale Adv. 1, 4665–4668. doi: 10.1039/C9NA00645A
Li, Y., and Ni, M. (2023). Regulation of biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 14:1238482. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1238482
Mba, I. E., and Nweze, E. I. (2021). Nanoparticles as therapeutic options for treating multidrug-resistant bacteria: research progress, challenges, and prospects. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37, 1–30. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03070-x
Megahed, M. M. M., El-Nagar, A. M. A., El-Demerdash, A. S., Ayoub, M. A., and Tolba, H. M. N. (2023). Evaluation and development of diagnostic tools for rapid detection of Riemerella anatipestifer and Pasteurella multocida in ducks. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 10, 211–221. doi: 10.5455/javar.2023.j671
Mehr, F. P., Khanjani, M., and Vatani, P. (2015). Synthesis of nano-ag particles using sodium borohydride. Orient. J. Chem. 31, 1831–1833. doi: 10.13005/ojc/310367
Miftode, I. L., Nastase, E. V., Miftode, R. S., Iancu, L., Luncă, C., Păduraru, D. T., et al. (2021). Insights into multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae urinary tract infections: from susceptibility to mortality. Exp. Ther. Med. 22:1086. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10520
Moradigaravand, D., Martin, V., Peacock, S. J., and Parkhill, J. (2017). Evolution and epidemiology of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in the United Kingdom and Ireland. MBio 8, 10–1128. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01976-16
More, P. R., Pandit, S., De Filippis, A., Franci, G., Mijakovic, I., and Galdiero, M. (2023). Silver nanoparticles: bactericidal and mechanistic approach against drug resistant pathogens. Microorganisms 11:369. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020369
Murphy, C. N., and Clegg, S. (2012). Klebsiella pneumoniae and type 3 fimbriae: nosocomial infection, regulation and biofilm formation. Future Microbiol. 7, 991–1002. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.74
Nadar, S., Khan, T., Patching, S. G., and Omri, A. (2022). Development of antibiofilm therapeutics strategies to overcome antimicrobial drug resistance. Microorganisms 10:303. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020303
Pawar, O., Deshpande, N., Dagade, S., Waghmode, S., and Nigam Joshi, P. (2016). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from purple acid phosphatase apoenzyme isolated from a new source Limonia acidissima. J. Exp. Nanosci. 11, 28–37. doi: 10.1080/17458080.2015.1025300
Razali, N. M., and Wah, Y. B. (2011). Power comparisons of shapiro-wilk, kolmogorov-smirnov, lilliefors and anderson-darling tests. J. Stat. Model. Anal. 2, 21–33.
Ripabelli, G., Tamburro, M., Guerrizio, G., Fanelli, I., Flocco, R., Scutellà, M., et al. (2018). Tracking multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from an Italian hospital: molecular epidemiology and surveillance by PFGE, RAPD and PCR-based resistance genes prevalence. Curr. Microbiol. 75, 977–987. doi: 10.1007/s00284-018-1475-3
Rudramurthy, G. R., Swamy, M. K., Sinniah, U. R., and Ghasemzadeh, A. (2016). Nanoparticles: alternatives against drug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Molecules 21:836. doi: 10.3390/molecules21070836
Saad, M. F., Elsayed, M. M., Khder, M., Abdelaziz, A. S., and El-Demerdash, A. S. (2024). Biocontrol of multidrug resistant pathogens isolated from fish farms using silver nanoparticles combined with hydrogen peroxide insight to its modulatory effect. Sci. Rep. 14:7971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58349-4
SAS (2012). SAS/OR 9.3 User’s guide: Mathematical programming examples, SAS/STAT statistics. North Carolina, CA: SAS Institute.
Sharaf, M., Sewid, A. H., Hamouda, H. I., Elharrif, M. G., El-Demerdash, A. S., Alharthi, A., et al. (2022). Rhamnolipid-coated Iron oxide nanoparticles as a novel multitarget candidate against major Foodborne E. coli serotypes and methicillin-Resistant S. aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e00250–e00222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00250-22
Shon, A. S., Bajwa, R. P. S., and Russo, T. A. (2013). Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: a new and dangerous breed. Virulence 4, 107–118. doi: 10.4161/viru.22718
Shu, H.-Y., Fung, C.-P., Liu, Y.-M., Wu, K.-M., Chen, Y.-T., Li, L.-H., et al. (2009). Genetic diversity of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. Microbiology (N Y) 155, 4170–4183. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.029017-0
Steel, R. G. D., and Torrie, J. H. (1980). Principles and procedures of statistics. New York: McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, 481.
Stepanović, S., Vuković, D., Dakić, I., Savić, B., and Švabić-Vlahović, M. (2000). A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. J. Microbiol. Methods 40, 175–179. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7012(00)00122-6
Tambekar, D. H., Dhanorkar, D. V., Gulhane, S. R., Khandelwal, V. K., and Dudhane, M. N. (2006). Antibacterial susceptibility of some urinary tract pathogens to commonly used antibiotics. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 5:17.
Tripathi, N., and Goshisht, M. K. (2022). Recent advances and mechanistic insights into antibacterial activity, antibiofilm activity, and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Biomater 5, 1391–1463. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00014
Turton, J. F., Perry, C., Elgohari, S., and Hampton, C. V. (2010). PCR characterization and typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae using capsular type-specific, variable number tandem repeat and virulence gene targets. J. Med. Microbiol. 59, 541–547. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.015198-0
Venkataraju, J. L., Sharath, R., Chandraprabha, M. N., Neelufar, E., Hazra, A., and Patra, M. (2014). Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Biochem. Technol. 3, 151–154.
Vuotto, C., Longo, F., Balice, M. P., Donelli, G., and Varaldo, P. E. (2014). Antibiotic resistance related to biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pathogens 3, 743–758. doi: 10.3390/pathogens3030743
Wongpreecha, J., Polpanich, D., Suteewong, T., Kaewsaneha, C., and Tangboriboonrat, P. (2018). One-pot, large-scale green synthesis of silver nanoparticles-chitosan with enhanced antibacterial activity and low cytotoxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 199, 641–648. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.039
Wu, M.-C., Lin, T.-L., Hsieh, P.-F., Yang, H.-C., and Wang, J.-T. (2011). Isolation of genes involved in biofilm formation of a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing pyogenic liver abscess. PLoS One 6:e23500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023500
Yang, H., Liu, C., Yang, D., Zhang, H., and Xi, Z. (2009). Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: the role of particle size, shape and composition. J. Appl. Toxicol. 29, 69–78. doi: 10.1002/jat.1385
Yuan, J. S., Reed, A., Chen, F., and Stewart, C. N. (2006). Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinformatics 7:85. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-85
Zhang, X.-F., Liu, Z.-G., Shen, W., and Gurunathan, S. (2016). Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, properties, applications, and therapeutic approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17:1534. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091534
Keywords: antibiofilm potential, chitosan, cytotoxicity, Klebsiella pneumoniae, silver nanoparticles, sodium fluoride
Citation: Elashkar E, Alfaraj R, El-Borady OM, Amer MM, Algammal AM and El-Demerdash AS (2025) Novel silver nanoparticle-based biomaterials for combating Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 15:1507274. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1507274
Received: 08 October 2024; Accepted: 09 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Fohad Mabood Husain, Department of Food Science and Nutrition, College of Food and Agriculture Sciences, King Saud University, Saudi ArabiaReviewed by:
Anima Nanda, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Elashkar, Alfaraj, El-Borady, Amer, Algammal and El-Demerdash. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Azza S. El-Demerdash, ZHIuYXp6YXNhbGFoQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; ZHJhenphQGFocmkuZ292LmVn
†ORCID: Azza S. El-Demerdash, http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0825-9776
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.