
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 06 December 2024
Sec. Microbe and Virus Interactions with Plants
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1505368
 Yujie Zhou1,2,3
Yujie Zhou1,2,3 Zhizhou He1,2,3
Zhizhou He1,2,3 Qiuyun Lin1,2,3
Qiuyun Lin1,2,3 Yuehui Lin1,2,3
Yuehui Lin1,2,3 Kaiyi Long1,2,3
Kaiyi Long1,2,3 Zhenyu Xie1,2,3*
Zhenyu Xie1,2,3* Wei Hu1,2,3*
Wei Hu1,2,3*Salt is a primary factor limiting the utilization of saline lands in coastal beach areas, with rhizosphere microorganisms playing a crucial role in enhancing crop stress resistance and exhibiting high sensitivity to environmental changes. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is the preferred crop for reclaiming salinized soils. This study determined the microbial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice under different salt stress treatments by high-throughput sequencing. We found that salt stress changed the bacterial community diversity, structure and function in rhizosphere soil of rice. Salt stress significantly reduced the richness and diversity of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. The bacterial community was characterized by higher abundance of the phyla Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria; the relative abundances of Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota and Myxococcota were decreased, while Bacteroidota and Cyanobacteria were increased under salt stress. The functions of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice mainly include chemoheterotrophy, aerobic_chemoheterotrophy, phototrophy etc., chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy were significantly higher NS3 (adding 3‰ NaCl solution to the base soil) treatment than NS6 (adding 6‰ NaCl solution to the base soil) treatment. These findings provide a theoretical foundation for the development of specialized salt-tolerant microbial agents for rice cultivation and offer a viable strategy for improving the soil environment of saline coastal lands through the application of beneficial microorganisms.
Soil salinization represents a critical and escalating threat to global agricultural productivity. Presently, approximately 6% of the world’s arable land is affected by salinity, with nearly one-third of irrigated farmland experiencing salinization (Zhai et al., 2023). Projections suggest that by 2050, up to 50% of arable land may be at significant risk of salinity (Pitman and Läuchli, 2002; Jamil et al., 2011; Islam et al., 2021).
Soil salinization poses a significant and escalating threat to global agricultural productivity by adversely affecting numerous morphological and physiological processes in plants, including nutrient uptake, seed germination, and overall growth. Salt stress is recognized as one of the most formidable abiotic stresses impacting crop development (Ponce et al., 2021). The accumulation of salts in the soil not only restricts plant growth but also leads to substantial reductions in crop yields (Qin et al., 2016). Rice is one of the most widely cultivated food crops globally and a staple for over half of the world’s population (Nam MyungHee et al., 2015), is often selected for the reclamation of salinized lands. However, rice is inherently sensitive to soil salinity, particularly to sodium chloride (NaCl), making salinity a critical environmental factor that adversely affects its growth, and lead to substantial reductions in rice productivity (Guo et al., 2023).
The rhizosphere, being the most active microhabitat in the soil, serves as the primary zone for nutrient acquisition by plants. Rhizosphere microorganisms play a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling, which are essential for plant growth, development, and stress resistance. Consequently, there is growing interest in understanding how rhizospheric conditions influence plant stress tolerance. However, these microbial communities are highly sensitive to environmental fluctuations (Degens et al., 2000; Mendes et al., 2011). Research has demonstrated that salt stress induces significant alterations in the structure and composition of soil microbial communities, leading to imbalances in the proportions of functional, beneficial and harmful bacteria within the rhizosphere (Zhang and Yu, 2001). Specifically, salt stress affects both the type and community composition of rhizosphere microorganisms (Kielak et al., 2008).
Soil salinity exerts profound effects on the activity, diversity, and structural dynamics of microbial communities (Chandrasekaran et al., 2014). Changes in salinity levels can result in the loss or activation of certain bacterial species, further disrupting microbial balance (Rath et al., 2019). For instance, studies have shown that Betaproteobacteria become more prevalent in highly saline layers, while the relative abundances of Alphaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria remain stable despite variations in salinity (Jiang et al., 2007). These findings underscore the necessity for detailed investigations into the effects of salinity on bacterial community dynamics to better understand and mitigate the impacts of soil salinization on agricultural systems. Research suggests that soil salinity has exerts detrimental effects on soil microbial communities (Li et al., 2021). Consequently, to enhance rice adaptation to salt stress, it is imperative to investigate the responses of rhizosphere microorganisms under saline conditions. In recent years, researchers have sought to elucidate the potential contributions of rhizosphere microorganisms to plant salt tolerance, extensively examining both the direct and indirect mechanisms through which these microorganisms enhance plant resilience (Yang et al., 2009; Van Dam and Bouwmeester, 2016). Various microorganisms identified in rice under salt stress conditions have been shown to significantly bolster the plant’s ability to withstand salinity, demonstrating notable growth-promoting effects and substantial application potential (Gu et al., 2024). Examples of such beneficial microorganisms include Bacillus spp. (Misra et al., 2017), Microbacterium ginsengiterrae (Qi et al., 2023), Pseudomonas punonensis, and Chryseobacterium taeanense (Ma et al., 2024). These findings underscore the critical role of rhizosphere microorganisms in mitigating the adverse impacts of soil salinity on crop performance and highlight their potential in sustainable agricultural practices aimed at enhancing crop resilience and productivity.
In this study, the bacterial community 16S rRNA genes were sequenced using the MiSeq high-throughput sequencing platform. The diversity, structure and function of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil of rice were analyzed under varying levels of salt stress. The primary objective was to elucidate the alterations in the rhizosphere bacterial community in response to salt stress and to investigate the relationship between bacterial diversity, structure and function with salinity levels in rice rhizosphere soils. The findings aim to provide a theoretical foundation for the development of specialized salt-tolerant microbial agents for rice cultivation and offer a viable strategy for improving the soil environment of saline lands through the application of beneficial microorganisms.
The study was conducted in the rainproof greenhouses at the Rice Test Base of the Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute (109.85°E, 19.83°N), Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, located in Danzhou City, Hainan Province, China. The experimental site belongs to the tropical monsoon climate. Six rice varieties (Reyan 2, Yanxian156, Reke 203, ST002, ST003, and ST0014) were selected for pot experiments from August to November 2023. The experimental soil was sourced from the paddy fields that has been used for rice cultivation in previous years. Each pot is filled with 0.06 cubic meters of dry soil. Three treatments were set up as control treatment (CK, adding fresh water to the base soil, the freshwater used in the experiment had a salinity below 0.2 g/L), 3‰ NaCl stress (NS3, adding 3‰ NaCl solution to the base soil) and 6‰ NaCl stress (NS6, adding 6‰ NaCl solution to the base soil). Each treatment was replicated three times for each variety.
Rice seeds were separately sown in seedling trays according varieties, and transplanted into pots once they reached the four-leaf one-heart stage. Following standard fertilization management for rice, urea and compound fertilizer (N:P:K = 16:16:16) were applied during the experiment. Sixteen plants were maintained per pot (76 cm × 56 cm). A ruler with a consistent scale was inserted into each pot to monitor the water level, maintaining a water layer of approximately 2–3 cm. Salinity was monitored daily using a salinometer, and NaCl solution or fresh water was added as necessary to ensure that the salt concentration in each pot remained relatively stable throughout the experiment. In this experiment, a variation of ±0.5‰ in salt concentration was considered within the normal range.
Salt stress treatment was discontinued 2 weeks before rice maturity and harvest, allowing the soil moisture to naturally dry out. When rice was harvested at maturity, rice plants were carefully excavated to preserve intact root systems. Bulk soil was gently shaken off, and rhizosphere soil adhering to the root surfaces (approximately 2 mm) was collected using sterile brushes. Three plants constituted one replicate. A total of 54 rhizosphere soil samples were collected. Soil samples were transported to the laboratory on dry ice and subsequently stored at −80°C for DNA extraction.
Total genomic DNA was extracted from 54 rhizosphere soil samples using the MJ-soil DNA Extraction Kit (Yuhua Company, China) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and concentration of the extracted DNA were assessed by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis and quantified using a NanoDrop™ 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, United States). The bacterial 16S rRNA genes were amplified using the primer pairs 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) with barcodes. Each sample has three replicates in the PCR amplification process. PCR reactions were conducted with TransStart FastPfu DNA Polymerase (TransGen AP221–02) in a 20 μL reaction volume, comprising 4 μL of 5× FastPfu Buffer, 2 μL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 0.8 μL. PCR reactions were conducted with TransStart FastPfu DNA Polymerase (TransGen AP221-02) in a 20 μL reaction volume, comprising 4 μL of 5× FastPfu Buffer, 2 μL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 0.8 μL each of forward and reverse primers (5 μM), 10 ng of template DNA, 0.2 μL of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA), and ddH₂O to reach the final volume. The amplification protocol included an initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, followed by 27 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 55°C for 30 s, and extension at 72°C for 45 s, culminating in a final extension at 72°C for 10 min and a hold at 10°C until manually terminated. The PCR products of the same sample were purified by extraction from a 2% agarose gel using a DNA gel recovery and purification kit (PCR Clean Up Kit, Yuhua Company, China). Finally, the purified PCR products were quantified using a Qubit™ 4.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA).
Sequencing libraries were subsequently generated using a TruSeq™ DNA Sample Prep Kit. Finally, the cloned libraries were pooled in equimolar amounts and paired-end sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq PE300 platform (Illumina, San Diego, USA).
The resulting high-quality sequences were subsequently clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) at a 97% similarity threshold using Uparse (version 7.0.1090), and chloroplast sequences were excluded from all samples. For each OTU, the most abundant sequence was selected as the representative sequence. Taxonomic classification of these representative sequences was performed using the RDP Classifier (version 2.2) against the Silva 16S rRNA gene database (Release 138).
Alpha diversity indices (Chao, Ace, Shannon, and Simpson) were calculated with Mothur v1.30.1 (Schloss et al., 2009). The Venn diagrams depicting the common and unique Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) among the groups were generated using R software (version 3.3.1). Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) was used to analyze the similarity or difference in sample community composition. To further identify biomarkers distinguishing between groups, Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) coupled with LEfSe analysis was conducted (Segata et al., 2011). Predicting the functions of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice by Functional Annotation of Prokaryotic Taxa (Louca et al., 2016). The Kruskal-Wallis H test was utilized to evaluate statistically significant differences of alpha diversity indices, taxa at the phylum and function in different salt stress treatments. All analysis were performed using the online Majorbio Cloud Platform.
After quality filtering, a total of 3,713,250 sequences were obtained for the bacterial community analysis. The 18,563 OTUs were identified from sequences with >97% similarity. Specifically, the CK, NS3, and NS6 treatments yielded 13,782, 12,326, and 12,009 OTUs, respectively. Among these, 7,930 OTUs were common to all three groups, accounting for 42.72% of the total OTUs. The unique OTUs were 3,291, 1,682, and 1,966 in the CK, NS3, and NS6 treatments, representing 17.73, 9.06, and 10.59% of the total OTUs, respectively (Figure 1). These results indicate both similarities and differences in the microbial community among the three treatment groups.
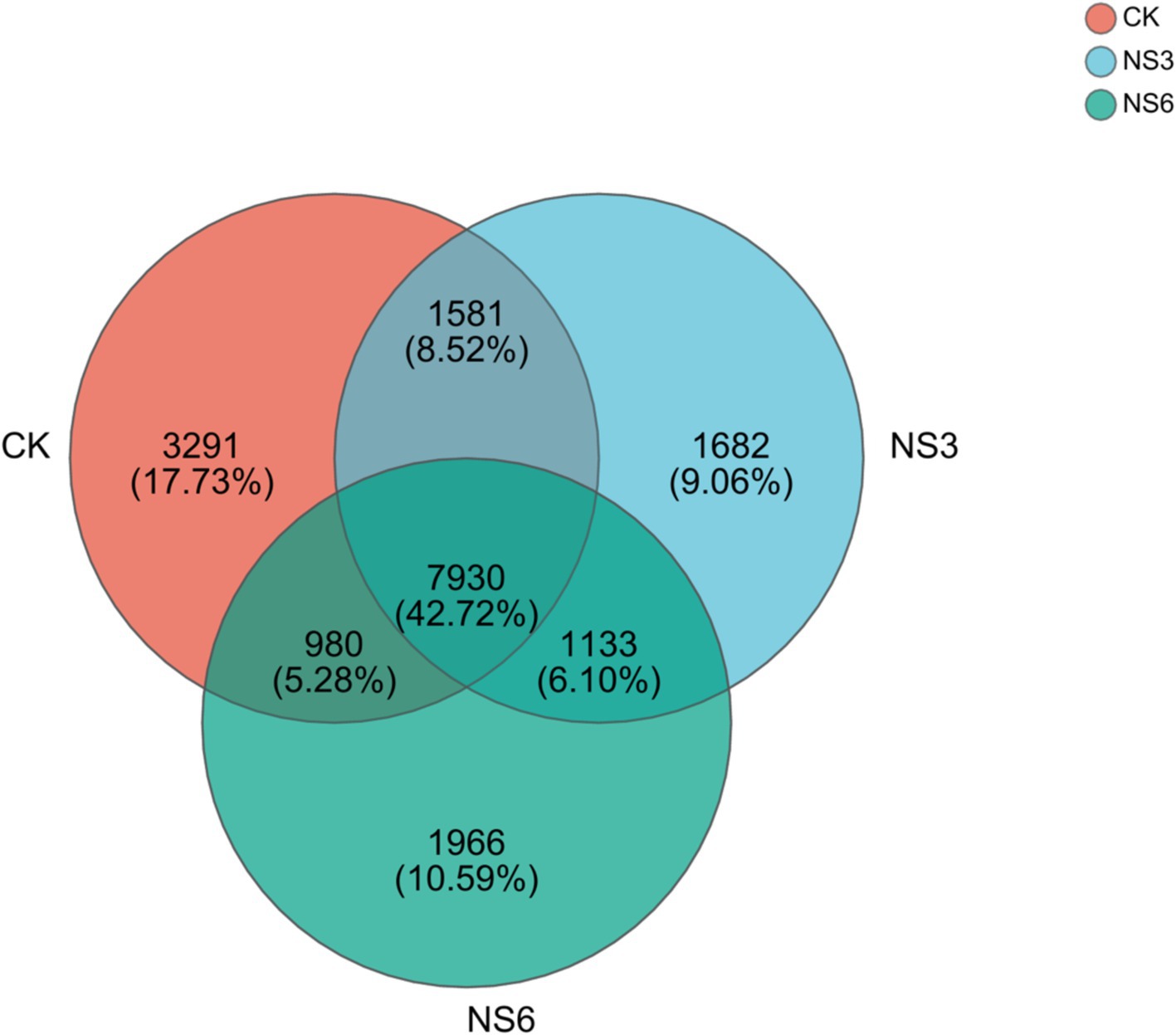
Figure 1. Venn diagram of bacterial OTUs in the rhizosphere soil of rice. CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
The bacterial sequences were classified into 62 phyla, 194 classes, 475 orders, 802 families, and 1,578 genera. To further elucidate the bacterial community structure, we analyzed the abundance distributions at the phylum and genus levels for each soil group. In terms of relative abundance, Chloroflexi (29.12%), Proteobacteria (13.13%), and Actinobacteria (10.88%) were the dominant phyla. These were followed by Firmicutes, Acidobacteria, Desulfobacterota, Bacteroidota, Cyanobacteria, Myxococcota, Patescibacteria and Gemmatmonadota of each phylum with relative abundances exceeding 2.00% (Figure 2).
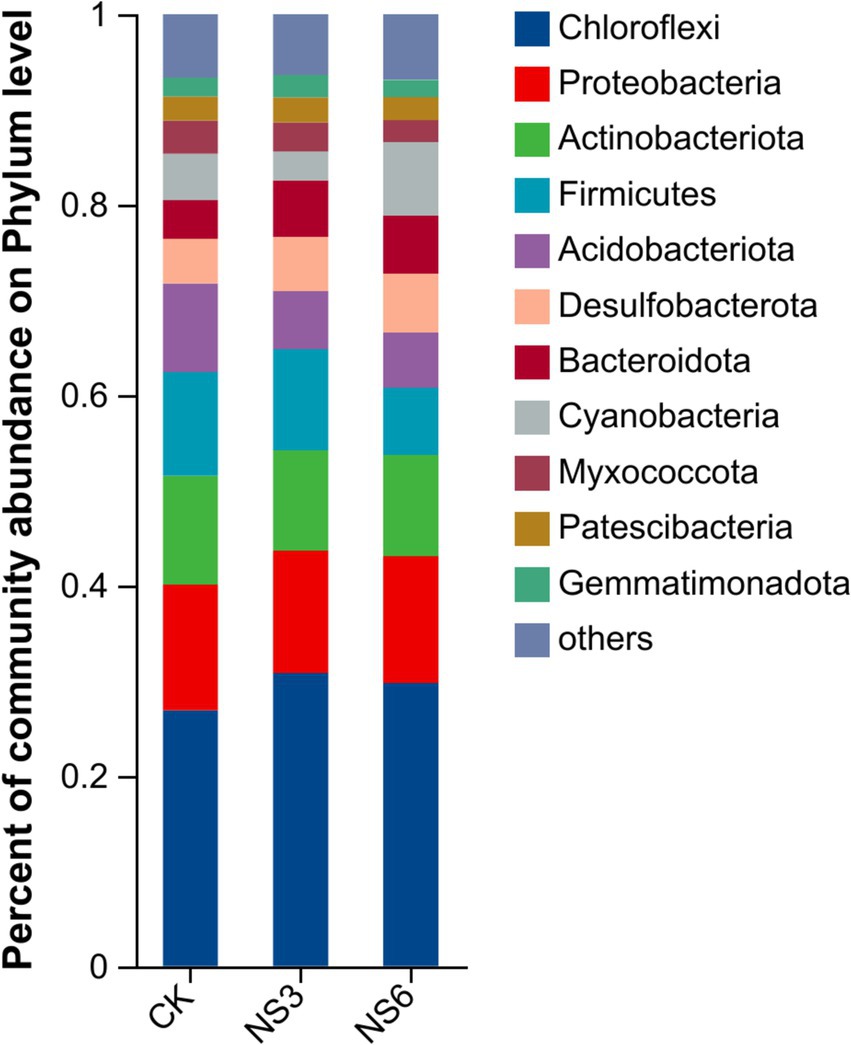
Figure 2. Relative abundance at the phylum level of the bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of rice.
The genera with relative abundances >1% were depicted in a column chart. The predominant genera identified in the rice rhizosphere soils included norank_f Anaerolineaceae (5.92%), norank_f norank_o SBR1031 (4.06%), Anaerolinea (2.81%), norank_f norank_o SJA (2.52%), norank_f norank_o Ardenticatenales (2.18%), and Nocardioides (2.12%), each accounting for more than 2.00% of the relative abundance (Figure 3).
Alpha diversity analyses were conducted to evaluate the richness and diversity of the microbial communities. The results indicated that the richness indices—Chao, Ace, and Shannon—were significantly higher in the control treatments compared to the 3 and 6‰ NaCl treatments. In contrast, the Simpson index was significantly lower in the control treatments than in the 6‰ NaCl treatments (Figure 4). Based on these alpha diversity indices, it can be inferred that salt stress reduces both the richness and diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil of rice.
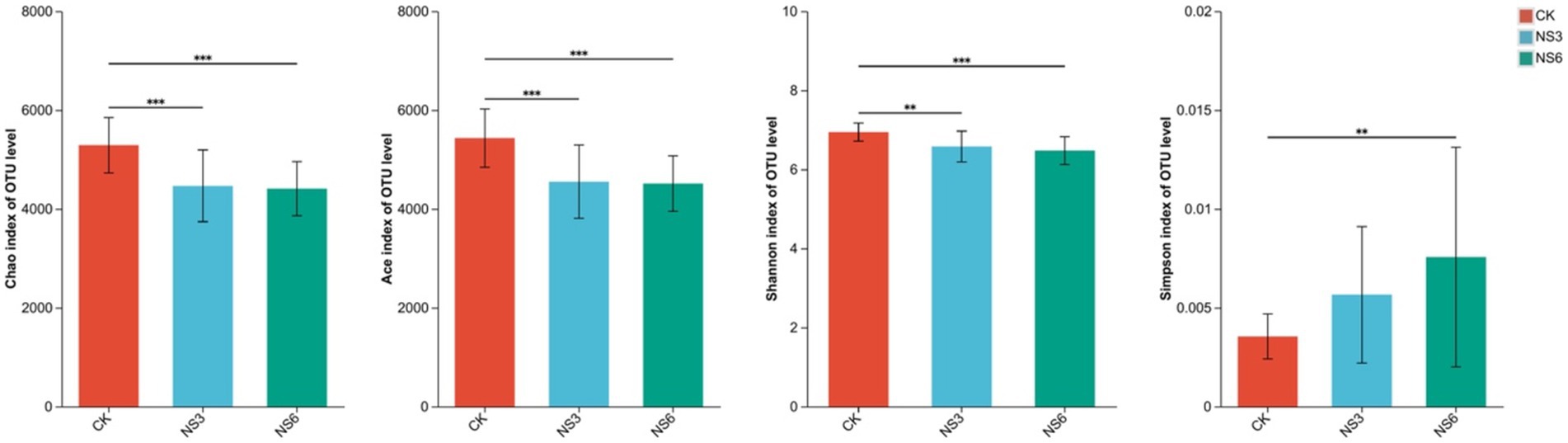
Figure 4. Alpha diversity indices of the bacterial community in rhizosphere soil of rice. CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
PCoA analysis shows that bacterial community structures were distinctly grouped and bacterial significant changed (p = 0.001) by control (CK) treatment and NaCl stress treatments. The samples of control (CK) treatment were clustered in PC1; while the samples of NS3 and NS6 treatments with NaCl stress were relatively close in distance, and similarity in community composition (Figure 5).
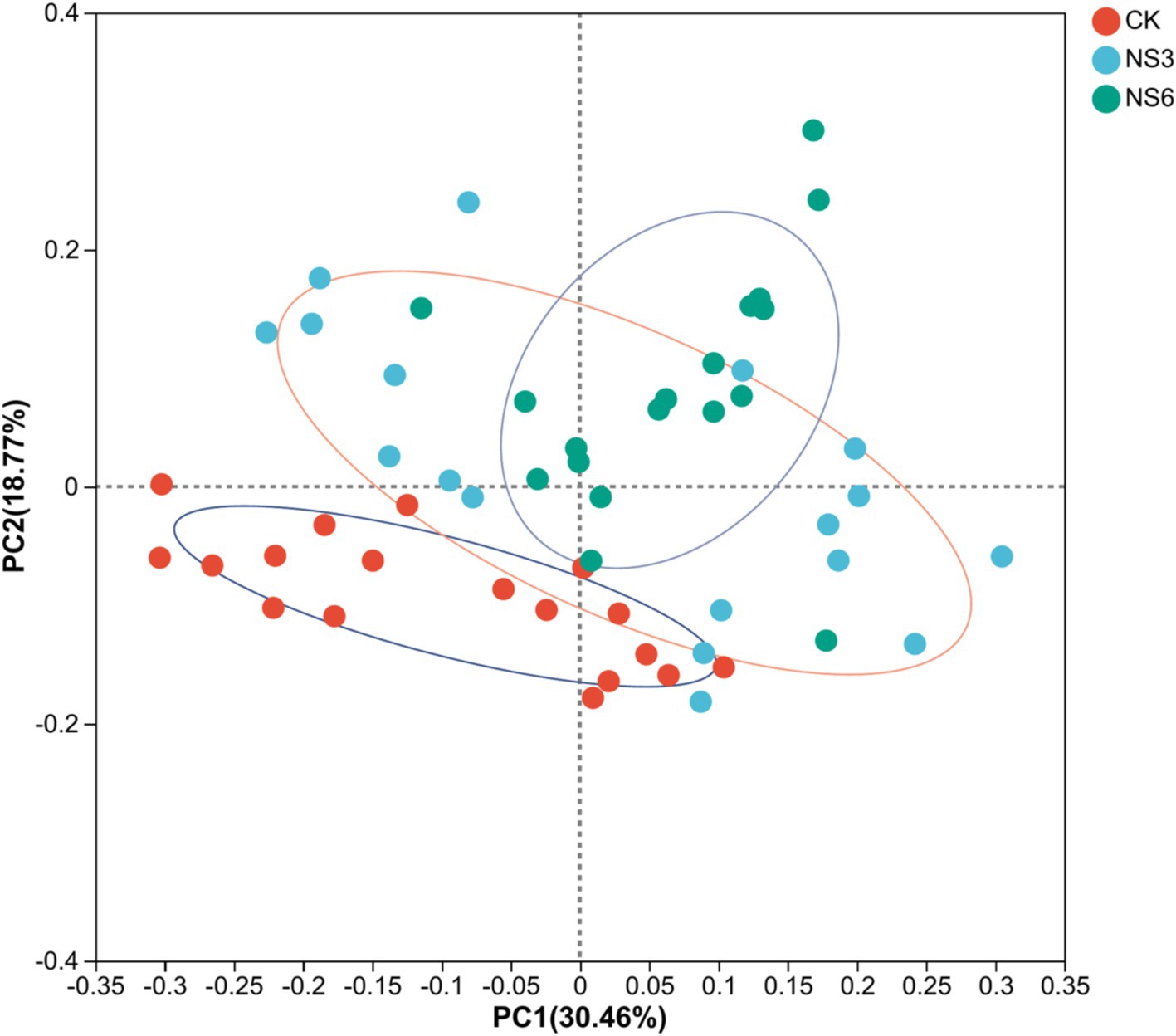
Figure 5. PCoA analysis of bacterial distributions in rhizosphere soil of rice at different treatments. CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
To elucidate the differences in bacterial community structures among the various treatments, significance inter group differences of phylum in bacterial communities with relative abundance >2% was examined. The results indicated that the phyla Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota, Bacteroidota, Cyanobacteria and Myxococcota exhibited significant differences among treatments (p < 0.01). Specifically, the relative abundances of Firmicutes and Acidobacteriota in the control (CK) treatment were significantly higher than those in the NS3 andNS6 treatment. Similarly, the relative abundances of Myxococcota in the control (CK) treatment and NS3 were significantly higher than those in the NS6 treatment. In contrast, the relative abundances of Bacteroidota were significantly higher in NS6 compared to CK and NS3, and Cyanobacteria was significantly higher in NS6 compared to NS3 (Figure 6). Overall, salt stress reduced the relative abundances of Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota and Myxococcota, while increasing the relative abundances of Bacteroidota and Cyanobacteria.
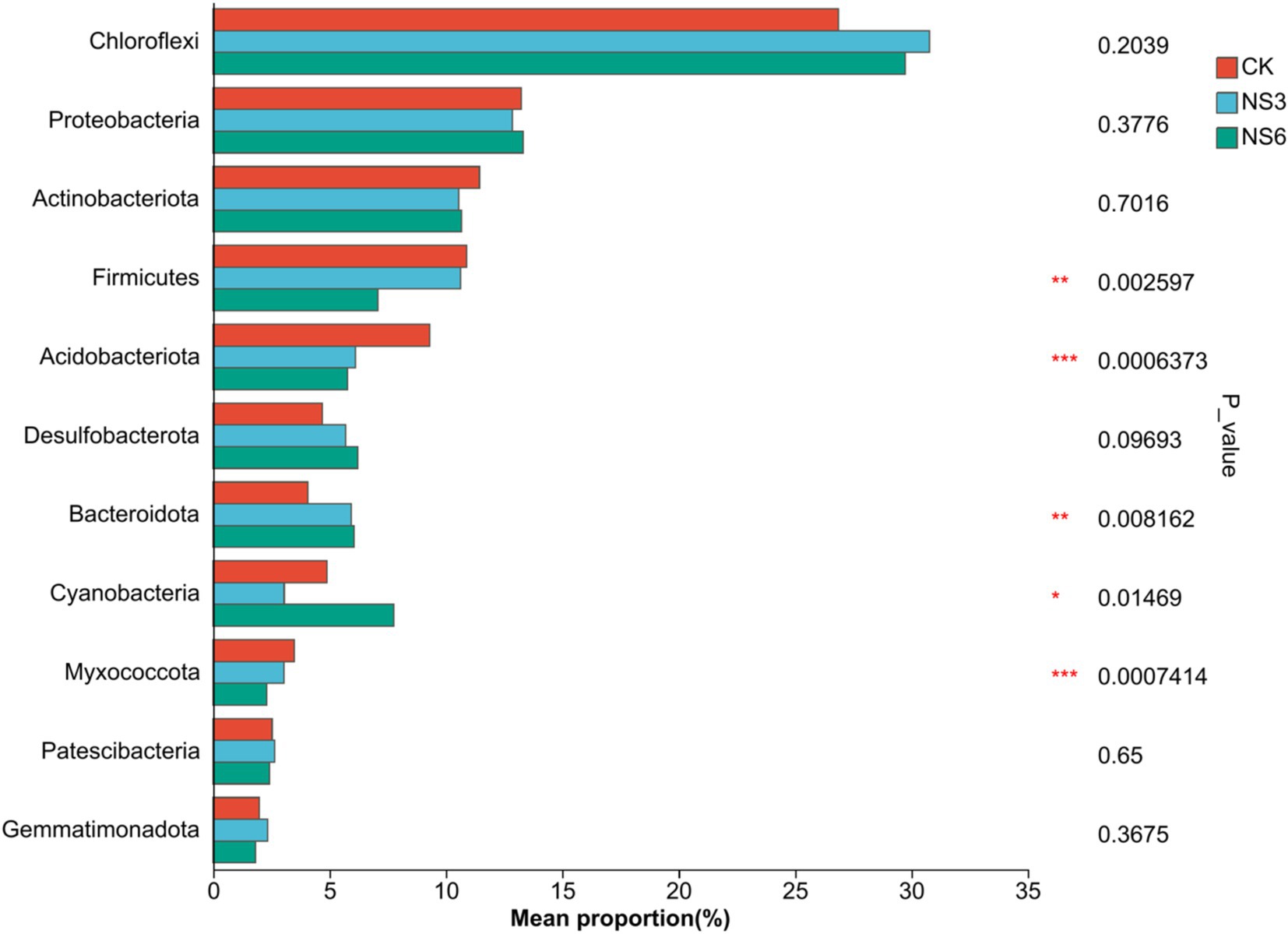
Figure 6. The differences of dominant bacteria groups at the level of phylum. CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
LEfSe analysis reveald that eight bacterial branch enriched in the rhizosphere soil of rice under CK treatment, Cylindrospermum_PMC238_04, Ellin6067, RBG-13-54-9 (from order to genus), Subgroup_18 (from class to genus), Methylocystis, Sporomusaceae (from class to family), Subgroup_17 (from order to genus) and Myxococcaceae. Six bacterial branch enriched in rhizosphere soil of rice under NS6 treatment, MBIC10003 (from order to family), Tropicimonas (from order to genus), PHOS-HE36 (from family to genus), Prolixibacteraceae (from family to genus), Chloroplast (from order to genus) and Azospirillaceae. But no significant enrichment was detected in rhizosphere soil of rice under NS3 treatment (Figure 7).
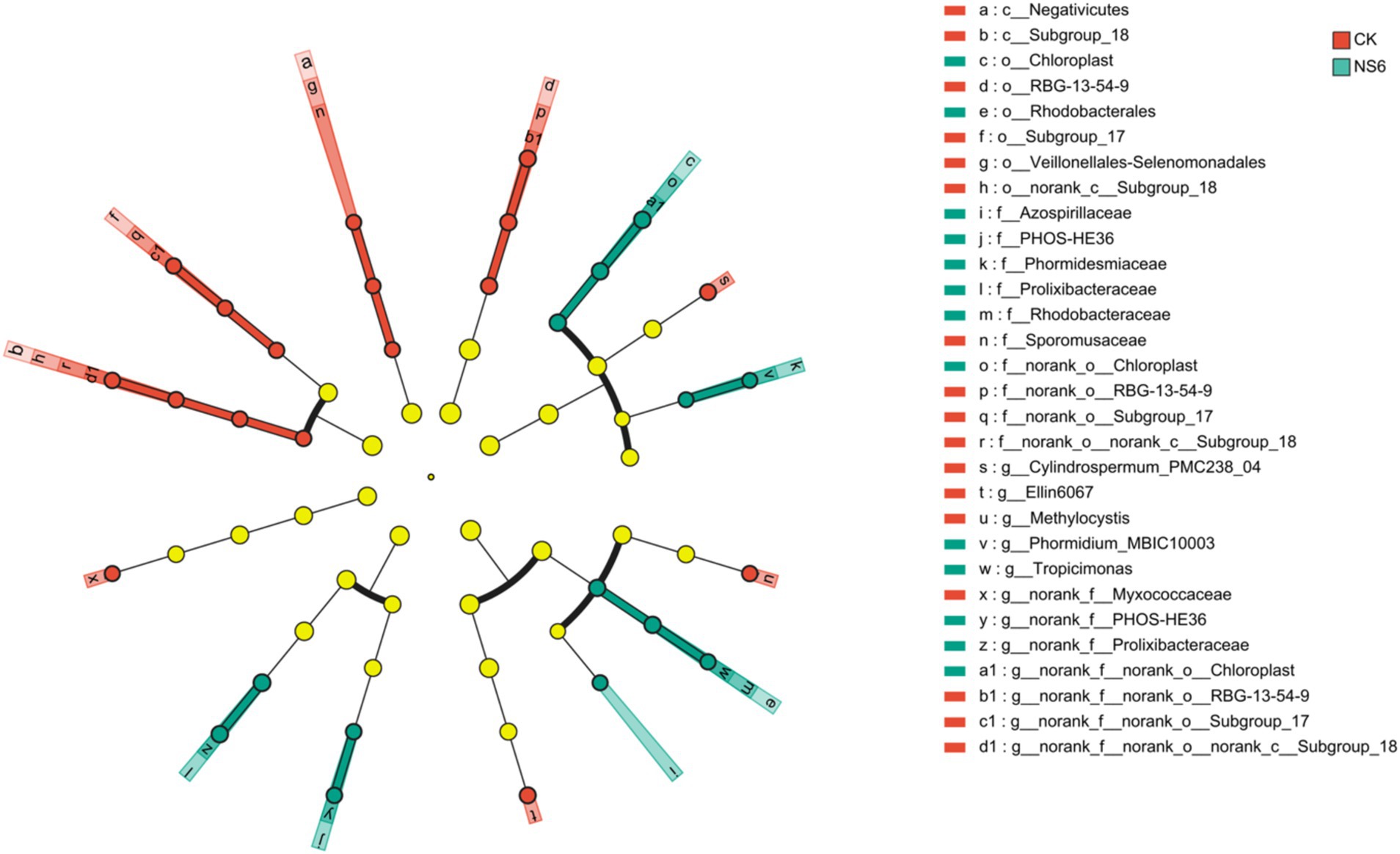
Figure 7. Discriminant analysis of taxa enrichment in each salt stress treatment (LDA scores is 3). CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
Bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice are involved in diverse functional pathways, the top 10 functions with total abundance included chemoheterotrophy, aerobic_chemoheterotrophy, phototrophy, photoautotrophy, cyanobacteria, oxygenic_photoautotrophy, aromatic_compound_degradation, animal_parasites_or_symbionts, nitrogen_fixation and human_pathogens_all. Further functional differences were tested among different salt stress treatments. The results showed that there was significantly difference (p < 0.01) in the functions of chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy in rhizosphere soil bacterial communities of rice under different salt stress treatments (Figure 8). Among them, chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy were significantly in NS3 treatment higher than NS6 treatment.
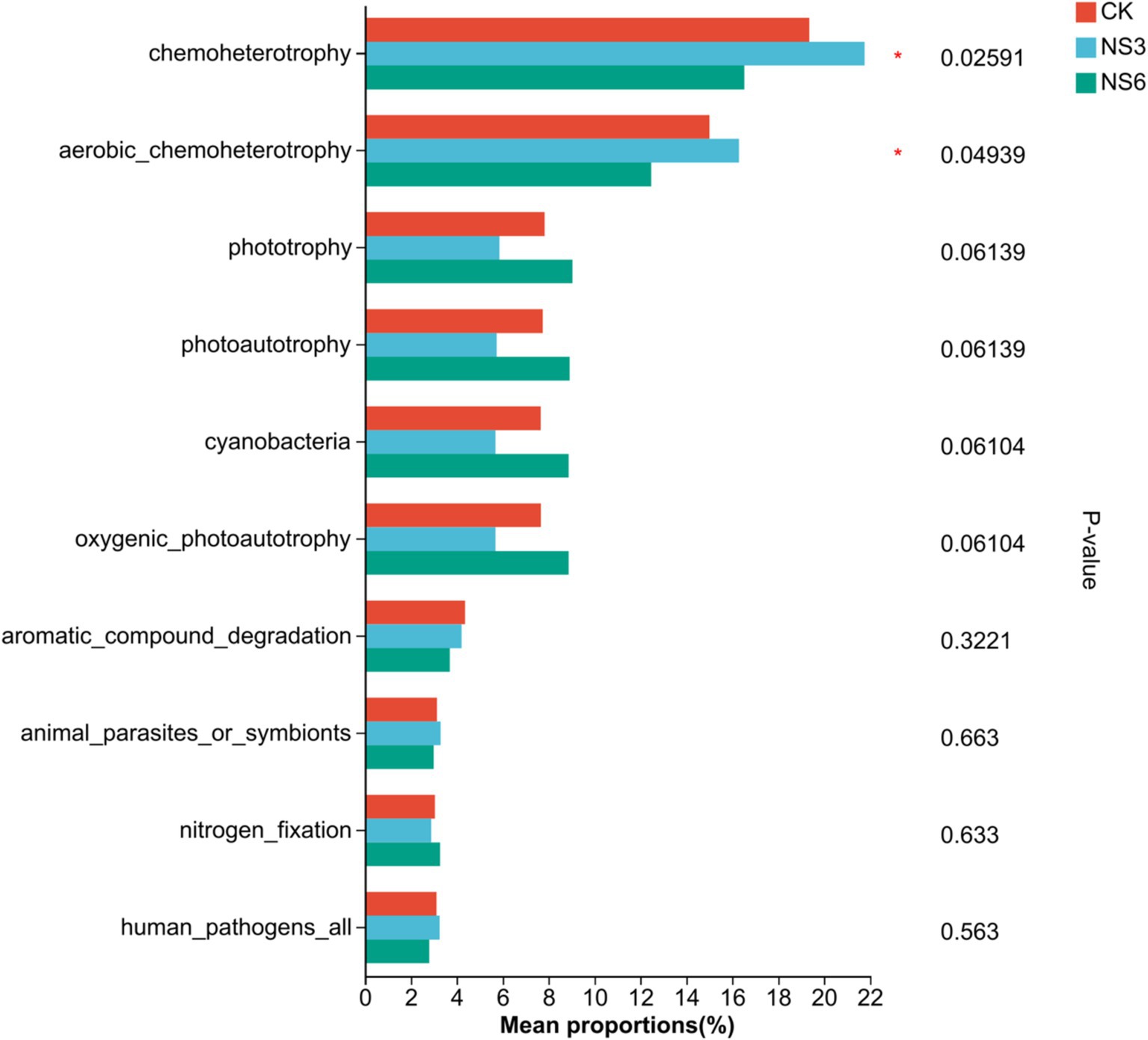
Figure 8. Prediction of bacterial function in rhizosphere soil of rice. CK, control treatment; NS3, 3‰ NaCl stress treatment; NS6, 6‰ NaCl stress treatment.
Salt stress modulates the microbial diversity and community composition of rhizosphere soil by altering its ecological factors (Rosier et al., 2016; Macabuhay et al., 2022). Previous studies have demonstrated that salt stress diminishes the richness of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil (Wu et al., 2010). Additionally, both the richness and diversity of bacterial communities typically decline with increasing salinity levels (Zhao et al., 2020). Under saline-alkali conditions, the growth of rhizosphere microorganisms is inhibited, leading to a significant reduction in community richness (Baumann et al., 2013). In the present study, the richness and diversity indices of bacterial communities subjected to salt stress treatments were markedly lower than those observed in the control (CK) group. Consequently, it can be inferred that salt stress substantially reduces the richness and diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil of rice, thereby corroborating the findings of previous research.
In this study, Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria were identified as the primary bacterial phyla in the rhizosphere soil under salt stress, followed by Firmicutes, Acidobacteria, Desulfobacterota, Bacteroidota, and Cyanobacteria. This composition is consistent with findings from most previous studies (Ma and Gong, 2013; Canfora et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2022). The prevalence of these bacterial taxa may be attributed to their participation in various nutrient cycling and biogeochemical processes, thereby playing significant roles in ecosystem services. The relative abundance of Chloroflexi was the highest in this study, potentially due to the long-term flooding of paddy soils, which generates methane emissions that are oxidized by aerobic methane-oxidizing bacteria. Chloroflexi are a group of methane-oxidizing bacteria that play a crucial role in methane conversion and carbon cycling in paddy soils. Studies have confirmed that Chloroflexi possess highly diverse metabolic capabilities. In terms of energy metabolism, Chloroflexi can perform both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Additionally, they can oxidize methane through metabolic pathways, utilize CO₂ as a carbon source for energy production, and degrade refractory carbon compounds under conditions of low nutrient availability (Zhang et al., 2019; Xian et al., 2020). Proteobacteria represent the largest and most diverse bacterial phylum. Many groups within Proteobacteria are capable of nitrogen fixation and adapting to various complex environments. Their extensive phylogenetic and ecological significance makes Proteobacteria the most common microbial group in saline soils (Ladha and Reddy, 2003; Ma and Gong, 2013). The predominance of Proteobacteria in the rhizosphere of most plant species may be attributed to their rapid growth rates (Yang et al., 2017). Actinobacteriota are known to participate in carbon fixation within specific ecological niches (Bryant et al., 2012) and are dominant phyla in secondary saline-alkali soils (Niu et al., 2017). Actinobacteriota are recognized as one of the most prevalent phyla in these environments. These functional microorganisms enriched in the rhizosphere are instrumental in mediating soil nutrient transformation and enhancing the environmental adaptability of microbial communities (Vacheron et al., 2013). Their presence in this study indicates that microbial distributions in similar salt-stressed environments exhibit certain similarities, reinforcing the notion that comparable ecological pressures select for analogous microbial assemblages.
Salinity level control the composition and functional potential of microbial community (Wang et al., 2018). Significant differences demonstrated that salt stress reduced the relative abundances of Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota and Myxococcota, while increasing the relative abundances of Bacteroidota and Cyanobacteria. This indicated that salt stress alters the distribution of bacterial abundances. This is similar to the research results of other scholars. Shi et al. (2021) believe that the relative abundances of Acidobacteriota and Myxococota were significantly decreased in salt-treated soil, while the abundance of Bacteroidota was higher in salt-treated soil. The relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Cyanobacteria higher of NS6 in our study may be related to its salt tolerance. Research suggests that Bacteroidetes exhibit strong resistance to high-salt environments and are the dominant species in saline-alkali soils (Li et al., 2021). Cyanobacteria has strong salt tolerance, endowed with the potential to curb the negative impacts of salt stress, and to be more efficient in mitigating the deleterious effects caused by the salinity conditions (Padhi et al., 1997; Bello et al., 2021). Chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy were significantly in NS3 treatment higher than NS6 treatment in our study. They are two functions are considered extensive ecosystem functions and are performed by most microorganisms (Rivett and Bell, 2018). This indicates that high salinity level exerted inhibitory effect on chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil of rice. But mechanisms influencing bacterial community function in rhizosphere soil of rice under salinization should be further studied.
In conclusion, this study showed that salt stress changed the diversity, structure and function of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. Salt stress reduces the richness and diversity of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. The bacterial community was characterized by the dominant bacterial belong to the phyla Chloroflexi, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria. The relative abundances of Firmicutes, Acidobacteriota and Myxococcota were decreased, while Bacteroidota and Cyanobacteria were increased under salt stress. The functions mainly include chemoheterotrophy, aerobic_chemoheterotrophy, phototrophy etc., chemoheterotrophy and aerobic_chemoheterotrophy were significantly higher NS3 treatment than NS6 treatment of bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. These results provide a new way for improving the salt tolerance of rice cultivation on saline soil.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
YZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZH: Validation, Writing – review & editing. QL: Resources, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. KL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZX: Resources, Writing – original draft. WH: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (No. 1630032021015), and Natural Scientific Foundation of Hainan (Nos. 320RC727, 323RC533, and 323RC532).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Baumann, K., Dignac, M.-F., Rumpel, C., Bardoux, G., Sarr, A., Steffens, M., et al. (2013). Soil microbial diversity affects soil organic matter decomposition in a silty grassland soil. Biogeochemistry 114, 201–212. doi: 10.1007/s10533-012-9800-6
Bello, A. S., Ben-Hamadou, R., Hamdi, H., Saadaoui, I., and Ahmed, T. (2021). Application of cyanobacteria (Roholtiella sp.) liquid extract for the alleviation of salt stress in bell pepper (capsicum annuum L.) plants grown in a soilless system. Plan. Theory 11:104. doi: 10.3390/plants11010104
Bryant, D. A., Liu, Z., Li, T., Zhao, F., Costas, A. M. G., Klatt, C. G., et al. (2012). Comparative and functional genomics of anoxygenic green bacteria from the taxa Chlorobi, Chloroflexi, and Acidobacteria. Funct. Genomics Evol. Photosynthetic Syst. 22, 47–102. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-1533-2_3
Canfora, L., Bacci, G., Pinzari, F., Lo Papa, G., Dazzi, C., and Benedetti, A. (2014). Salinity and bacterial diversity: to what extent does the concentration of salt affect the bacterial community in a saline soil? PLoS One 9:e106662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106662
Chandrasekaran, M., Boughattas, S., Hu, S., Oh, S.-H., and Sa, T. (2014). A meta-analysis of arbuscular mycorrhizal effects on plants grown under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 24, 611–625. doi: 10.1007/s00572-014-0582-7
Degens, B. P., Schipper, L. A., Sparling, G. P., and Vojvodic-Vukovic, M. (2000). Decreases in organic C reserves in soils can reduce the catabolic diversity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 32, 189–196. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(99)00141-8
Gu, H., Hu, S., Zhao, Q., Liu, C., and Meng, L. (2024). The study on enhancing salt tolerance of Rice by rhizosphere microorganisms. Crops 4, 8–13. doi: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2024.04.002
Guo, W., Fu, Y., Sun, Z., and Zheng, Z. (2023). The correlation analysis between the morphological indices and salt tolerance in different rice germplasm under the salt stress. J. Pant Genetic Res. 3, 245–251.
Islam, M. T., Ckurshumova, W., Fefer, M., Liu, J., Uddin, W., and Rosa, C. (2021). A plant based modified biostimulant (copper chlorophyllin), mediates defense response in Arabidopsis thaliana under salinity stress. Plan. Theory 10:625. doi: 10.3390/plants10040625
Jamil, A., Riaz, S., Ashraf, M., and Foolad, M. (2011). Gene expression profiling of plants under salt stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 30, 435–458. doi: 10.1080/07352689.2011.605739
Jiang, H., Dong, H., Yu, B., Liu, X., Li, Y., Ji, S., et al. (2007). Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka, a hypersaline lake on Tibetan plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 9, 2603–2621. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01377.x
Kielak, A., Pijl, A. S., Van Veen, J. A., and Kowalchuk, G. A. (2008). Differences in vegetation composition and plant species identity lead to only minor changes in soil-borne microbial communities in a former arable field. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 63, 372–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00428.x
Ladha, J., and Reddy, P. (2003). Nitrogen fixation in rice systems: state of knowledge and future prospects. Plant Soil 252, 151–167. doi: 10.1023/A:1024175307238
Li, M., Ma, F., and Zhang, J. (2021). Effects of rice planting years on physicochemical properties and bacterial community structure in saline\| alkali soil. CABI Datab. 39, 194–202.
Louca, S., Parfrey, L. W., and Doebeli, M. (2016). Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 353, 1272–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf4507
Ma, B., and Gong, J. (2013). A meta-analysis of the publicly available bacterial and archaeal sequence diversity in saline soils. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 2325–2334. doi: 10.1007/s11274-013-1399-9
Ma, A., Ren, Y., Wang, J., Yan, H., Shi, C., Shen, Q., et al. (2024). Isolation and application of rhizosphere Core strains to improve salt tolerance of Rice. Acta Pedol. Sin. 61, 1410–1420. doi: 10.11766/trxb202302190069
Macabuhay, A., Arsova, B., Walker, R., Johnson, A., Watt, M., and Roessner, U. (2022). Modulators or facilitators? Roles of lipids in plant root–microbe interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 27, 180–190. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.08.004
Mendes, R., Kruijt, M., De Bruijn, I., Dekkers, E., Van Der Voort, M., Schneider, J. H., et al. (2011). Deciphering the rhizosphere microbiome for disease-suppressive bacteria. Science 332, 1097–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.1203980
Misra, S., Dixit, V. K., Khan, M. H., Mishra, S. K., Dviwedi, G., Yadav, S., et al. (2017). Exploitation of agro-climatic environment for selection of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) deaminase producing salt tolerant indigenous plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 205, 25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.08.007
Nam MyungHee, N. M., Bang EunJung, B. E., Kwon TaekYun, K. T., Kim YuRan, K. Y., Kim EunHee, K. E., Cho KyungWon, C. K., et al. (2015). Metabolite profiling of diverse rice germplasm and identification of conserved metabolic markers of rice roots in response to long-term mild salinity stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 21959–21974. doi: 10.3390/ijms160921959
Niu, S., Long, Y., Li, H., Da, W., Hu, S., Li, W., et al. (2017). Microbial diversity in saline alkali soil from Hexi corridor analyzed by Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing system. Microbiol. China 44, 2067–2078. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.160824
Padhi, H., Rath, B., and Adhikary, S. (1997). Tolerance of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria to NaCl. Biol. Plant. 39, 261–268. doi: 10.1023/A:1001024821525
Pitman, M. G., and Läuchli, A. (2002). Global impact of salinity and agricultural ecosystems. Salinity: Environ. Plants Mol. 3:20. doi: 10.1007/0-306-48155-3_1
Ponce, K. S., Guo, L., Leng, Y., Meng, L., and Ye, G. (2021). Advances in sensing, response and regulation mechanism of salt tolerance in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:2254. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052254
Qi, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, G., Ji, H., Shen, T., and Wu, K. (2023). Identification of saline-alkali tolerant growth-promoting bacterium S4 and its effect on improving saline-alkali tolerance of rice. Shangdong Agric. Sci. 55, 147–154. doi: 10.14083/j.issn.1001-4942.2023.04.019
Qin, Y., Druzhinina, I. S., Pan, X., and Yuan, Z. (2016). Microbially mediated plant salt tolerance and microbiome-based solutions for saline agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 34, 1245–1259. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.08.005
Rath, K. M., Maheshwari, A., and Rousk, J. (2019). Linking microbial community structure to trait distributions and functions using salinity as an environmental filter. MBio 10, 1–14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01607-19
Rivett, D. W., and Bell, T. (2018). Abundance determines the functional role of bacterial phylotypes in complex communities. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 767–772. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0180-0
Rosier, A., Bishnoi, U., Lakshmanan, V., Sherrier, D. J., and Bais, H. P. (2016). A perspective on inter-kingdom signaling in plant–beneficial microbe interactions. Plant Mol. Biol. 90, 537–548. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0433-3
Schloss, P. D., Westcott, S. L., Ryabin, T., Hall, J. R., Hartmann, M., Hollister, E. B., et al. (2009). Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 7537–7541. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09
Segata, N., Izard, J., Waldron, L., Gevers, D., Miropolsky, L., Garrett, W. S., et al. (2011). Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Shi, X., Zhao, X., Ren, J., Dong, J., Zhang, H., Dong, Q., et al. (2021). Influence of peanut, sorghum, and soil salinity on microbial community composition in interspecific interaction zone. Front. Microbiol. 12:678250. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.678250
Vacheron, J., Desbrosses, G., Bouffaud, M.-L., Touraine, B., Moënne-Loccoz, Y., Muller, D., et al. (2013). Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and root system functioning. Front. Plant Sci. 4:356. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00356
Van Dam, N. M., and Bouwmeester, H. J. (2016). Metabolomics in the rhizosphere: tapping into belowground chemical communication. Trends Plant Sci. 21, 256–265. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.008
Wang, H., Gilbert, J. A., Zhu, Y., and Yang, X. (2018). Salinity is a key factor driving the nitrogen cycling in the mangrove sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 631-632, 1342–1349. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.102
Wu, F., Bao, J., and Liu, S. (2010). Effects of salt stress on rhizospheric soil bacterial community structure and cucumber yield. Acta Hortic. Sinica 37:741. doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2010.05.024
Xian, W., Zhang, X., and Li, W. (2020). Research status and prospect on bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Acta Microbiol Sin. 60, 1801–1820. doi: 10.13343/j.cnki.wsxb.20200463
Xu, Z., Liu, C., Shi, J., Shao, X., and Song, Y. (2022). Analysis of bacterial community structure and function in rice rhizosphere soil at different growth stages in rice-crab co cropping paddy field. China Rice 28, 61–66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2022.04.013
Yang, J., Kloepper, J. W., and Ryu, C.-M. (2009). Rhizosphere bacteria help plants tolerate abiotic stress. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 1–4. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.004
Yang, Y., Wang, N., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., and Ye, B. (2017). Comparative analysis of bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere of maize by high-throughput pyrosequencing. PLoS One 12:e0178425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178425
Zhai, C., Zhang, J., Cui, S., Chen, P., and Han, J. (2023). Effects of slow/controlled release fertilizer application on growth, yield and quality of rice under salt stress. Crops. 1, 143–151. doi: 10.16035/j.issn.1001-7283.2023.01.021
Zhang, J., Ke, W., Liu, J., Wang, L., Chen, H., Peng, T., et al. (2019). Influence of water controlling depth on soil microflora and bacterial community diversity in paddy soil. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 17, 277–284. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2009.00277
Zhang, Q., and Yu, X. (2001). Allelopathy in replant problem in forest soil. Allelopath. J. 8, 51–64.
Keywords: Oryza sativa L., salt stress, rhizosphere soil, bacterial community, 16S rRNA
Citation: Zhou Y, He Z, Lin Q, Lin Y, Long K, Xie Z and Hu W (2024) Salt stress affects the bacterial communities in rhizosphere soil of rice. Front. Microbiol. 15:1505368. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1505368
Received: 02 October 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Xiancan Zhu, Anhui Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ayomide Emmanuel Fadiji, Western Sydney University, AustraliaCopyright © 2024 Zhou, He, Lin, Lin, Long, Xie and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenyu Xie, cHpzLXh6aHlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Wei Hu, aHV3ZWkuY2F0YXNAZ21haWwuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.