- School of Public Health and Emergency Management, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects more than 90% of the human population worldwide and establishes lifelong infection in hosts by switching between latent and lytic infection. EBV latency can be reactivated under appropriate conditions, leading to expression of the viral lytic genes and production of infectious progeny viruses. EBV reactivation involves crosstalk between various factors and signaling pathways, and the subsequent complicated virus-host interplays determine whether EBV continues to propagate. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying these processes remain unclear. In this review, we summarize the critical factors regulating EBV reactivation and the associated mechanisms. This encompasses the transcription and post-transcriptional regulation of immediate-early (IE) genes, the functions of viral factors on viral DNA replication and progeny virus production, the mechanisms through which viral proteins disrupt and inhibit the host’s innate immune response, and the host factors that modulate EBV reactivation. Finally, we explore the potential applications of novel technologies in studying EBV reactivation, providing novel insights into the investigation of mechanisms governing EBV reactivation and the development of anti-EBV therapeutic strategies.
1 Introduction
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) belongs to the gamma herpesvirus family and is recognized as the first human tumor virus (Epstein, 2012; Damania et al., 2022). It is associated with a variety of human diseases, including infectious mononucleosis (IM), Burkitt lymphoma (BL), Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), gastric carcinoma (GC), and multiple sclerosis (MS) (Kutok and Wang, 2006; Damania et al., 2022). EBV primarily initiates infection in the oral epithelial cells, where it then undergoes lytic replication to release progeny virus particles that subsequently infect B lymphocytes. Within these B cells, EBV establishes a latent infection that can be maintained for a lifetime or reactivated to produce new virus particles (Mesri et al., 2014; Scott, 2017). The latent infection and lytic replication of EBV are the keys to its typical life cycle and contribute significantly to its pathogenesis. During latency, EBV establishes one of the four distinct latency patterns (Latency 0, Latency I, Latency II, and Latency III) in B cells, which is represented by the expression of distinct gene sets (Münz, 2019). Meanwhile, the viral genome persists in the host nucleus as a circular extrachromosomal episome. This allows for the establishment of latent infection, as the virus can remain dormant within host cells. The viral episome can anchor to host chromatin via viral antigen EBNA1, and the virus capitalizes on the conditions of host DNA replication to transmit its genome through cell division. The virus remains latent for life within the host and yet a fraction of the virus population still reactivates to enter the lytic cycle.
In contrast, lytic replication is marked by the collective expression of viral genes, the production of infectious progeny viruses, and cell death. EBV lytic replication is initially dependent on the viral immediate-early (IE) proteins Zta and Rta, which are encoded by EBV genes BZLF1 and BRLF1, respectively. These two proteins activate other viral lytic genes and eventually induce lytic replication, among which they are involved not only in DNA replication, protein synthesis, and progeny virus production but also operate with various cellular factors-related signaling pathways (Feederle et al., 2000). Additionally, the genes regulated by Zta and Rta mediate viral immune evasion. Thus, the intervention of EBV reactivation and the subsequent activation of lytic gene functions not only have the potential to limit the transmission of EBV but also offer promising treatment options for EBV-induced malignancies. Furthermore, advancements in various new technologies can provide valuable insights into the critical mechanisms underlying EBV reactivation from multiple perspectives.
To summarize, EBV latency is required for the establishment of a long-term infection, and infectious virus particles are produced during lytic replication. The switch of latency and lytic replication ensures the continuous transmission of EBV infection among the human population. In this review, we summarize the current progress of the identified factors controlling EBV reactivation and provide an overview of how these key factors co-operate to regulate this process. Finally, we highlight the potential applications of novel technologies to further research on EBV reactivation.
2 EBV reactivation starts with the expression of viral immediate-early proteins
2.1 Zta and Rta initiate EBV reactivation
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation is regulated by various cellular signaling pathways and can be activated under various stimuli, such as hypoxia (Jiang et al., 2006), 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) (Baumann et al., 1998), B-cell receptor (BCR) activation (Murata and Tsurumi, 2014), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) inducers (Yiu et al., 2020). Although how these stimuli initially induce EBV reactivation remains incompletely understood, the cascades following reactivation are triggered uniformly by viral immediate-early proteins Zta and Rta. They are the first two viral proteins actively expressed upon EBV reactivation, while both of them are silenced in EBV latently infected cells (Israel and Kenney, 2003; Kenney and Mertz, 2014). The expression of Zta and Rta marks the onset of the EBV lytic cycle, initiating a multi-stage biological process in which EBV-encoded lytic proteins and various host factors play complex and pivotal roles. Zta and Rta can also activate their promoters (Israel and Kenney, 2003), further boosting the expression of subsequent EBV early and late genes through positive feedback. They serve as transcriptional activators for lytic gene expression by binding to host transcription factors and specific response elements (Urier et al., 1989; Gruffat et al., 1990; Heilmann et al., 2012). Additionally, they are involved in viral genome replication after the onset of reactivation (Rennekamp et al., 2010; El-Guindy et al., 2013). Therefore, the expression of Zta and Rta is essential for the initiation of EBV reactivation, triggering a series of intricate cascading events, including EBV lytic gene expression, viral genome replication, virus particle assembly, and the release of progeny virions.
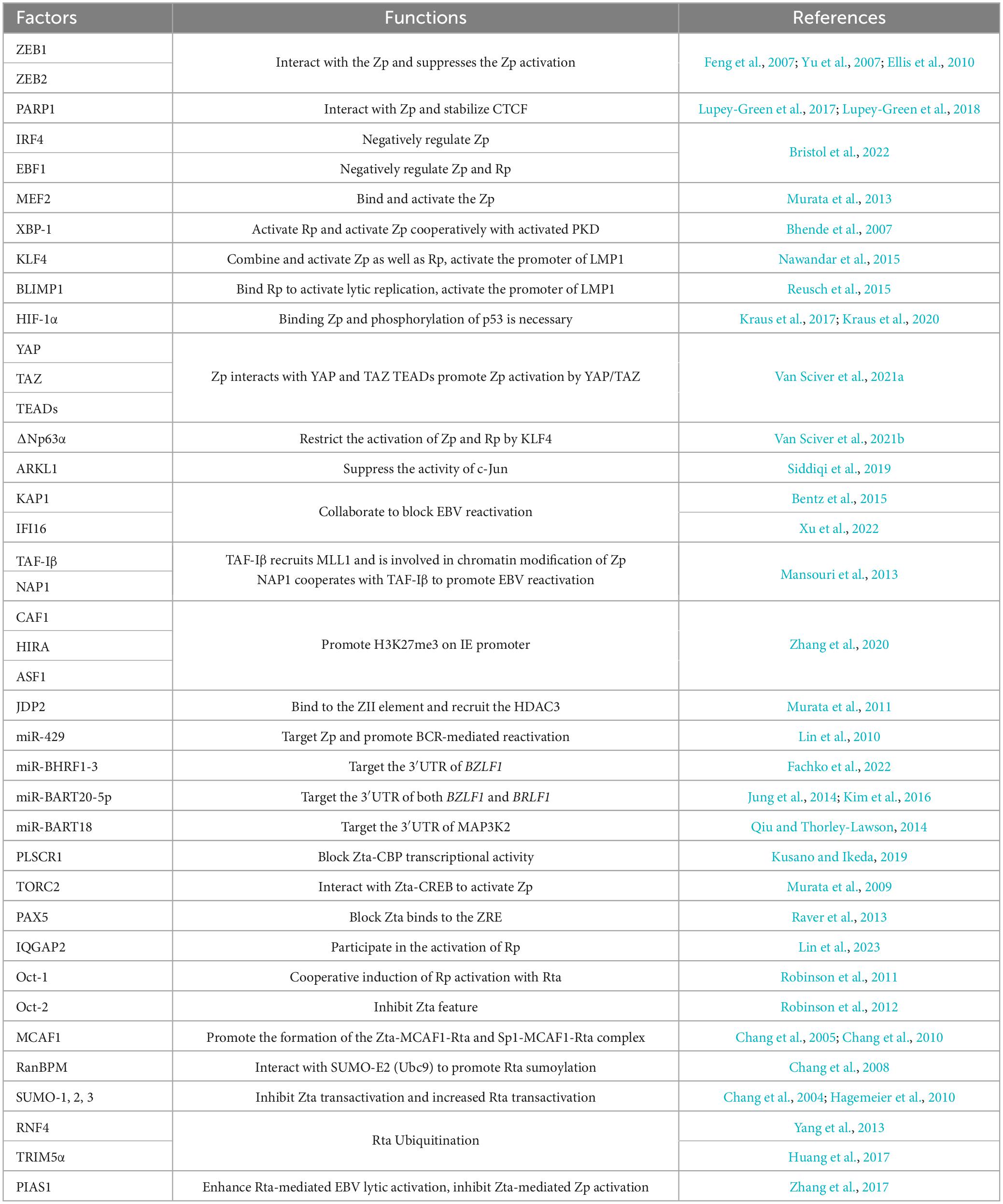
2.2 Transcriptional activity of Zp and Rp is tightly regulated
Given the crucial roles of Zta and Rta in EBV reactivation, transcription factors orchestrate the regulation of BZLF1 or BRLF1 transcription by specifically targeting their promoters (Figure 1A and Table 1). Various transcriptional activators and repressors are demonstrated to bind to BZLF1 and BRLF1, whose expression then determines the state of EBV infection (Spitz and Furlong, 2012; Lambert et al., 2018; Pope and Medzhitov, 2018). ZEBs silence the promoter of BZLF1 (Zp) in a cell-dependent manner, thus promoting the maintenance of viral latency. In particular, ZEB1 directly binds to the Zp, and its overexpression reduces the activity of Zp, suggesting its role in suppressing EBV lytic replication (Feng et al., 2007; Yu et al., 2007). Similar to ZEB1, ZEB2/SIP1 can bind to the same sites on Zp and inhibit BZLF1 expression to maintain EBV latency (Ellis et al., 2010). PARP1 has also been shown to bind Zp and suppress EBV reactivation, further contributing to cell proliferation and LMP1-mediated oncogenesis (Martin et al., 2016; Lupey-Green et al., 2017; Hulse et al., 2018). Additionally, IRF4 negatively regulates the activity of Zp, while EBF1 negatively regulates the activity of both Zp and Rp (Bristol et al., 2022). In contrast, the MEF2 transcription factor family binds and activates Zp (Murata et al., 2013). XBP-1 can activate Rp independently, whereas the activation of Zp by XBP-1 requires cooperation with PKD (Bhende et al., 2007). KLF4 and BLIMP1 are two differentiation-dependent transcription factors that synergistically induce EBV lytic replication. Among them, KLF4 can bind to and activate both Zp and Rp (Nawandar et al., 2015). BLIMP1 may bind to Rp and indirectly induce transcription of Zp and Rp (Reusch et al., 2015). KLF4 and BLIMP1 also synergistically activate LMP1, which promotes lytic replication in EBV-infected epithelial cells by enhancing the expression of Zta and Rta (Nawandar et al., 2017). HIF-1α directly binds to Zp, not Rp, to induce EBV reactivation, which requires phosphorylated p53 as a co-activator for the induction of the BZLF1 gene (Kraus et al., 2017; Kraus et al., 2020). The Hippo signaling effectors YAP and TAZ interact with Zp in epithelial cells to activate BZLF1 expression, and TEADs enhance the activation of YAP/TAZ on Zp (Van Sciver et al., 2021a). In epithelial cells, ΔNp63α maintains EBV latency, while in Burkitt lymphoma, TAp63α restrains the activation of EBV. ΔNp63α can block the activation of Zp which is mediated by KLF4 and Rta protein (Van Sciver et al., 2021b). The transcriptional activator C-Jun binds to and activates Zp (Flemington and Speck, 1990; Liang et al., 2002), whereas ARKL1 interacts with C-Jun, inhibiting the activity of C-Jun and negatively regulating EBV reactivation. The interaction between ARKL1 and C-Jun is mediated by the CK2 kinase-regulating subunit CK2β (Siddiqi et al., 2019). KAP1 is also an important factor in the maintenance of viral latency, whose sumoylation binds to the lytic promoters and suppresses their transcriptional activity (Bentz et al., 2015). Additionally, IFI16 and KAP1 function together to silence BZLF1 expression (Xu et al., 2022). In summary, these cellular factors can directly bind to Zp and Rp or recruit other factors for binding, thereby modulating their transcription activity and initiating subsequent processes in EBV reactivation.
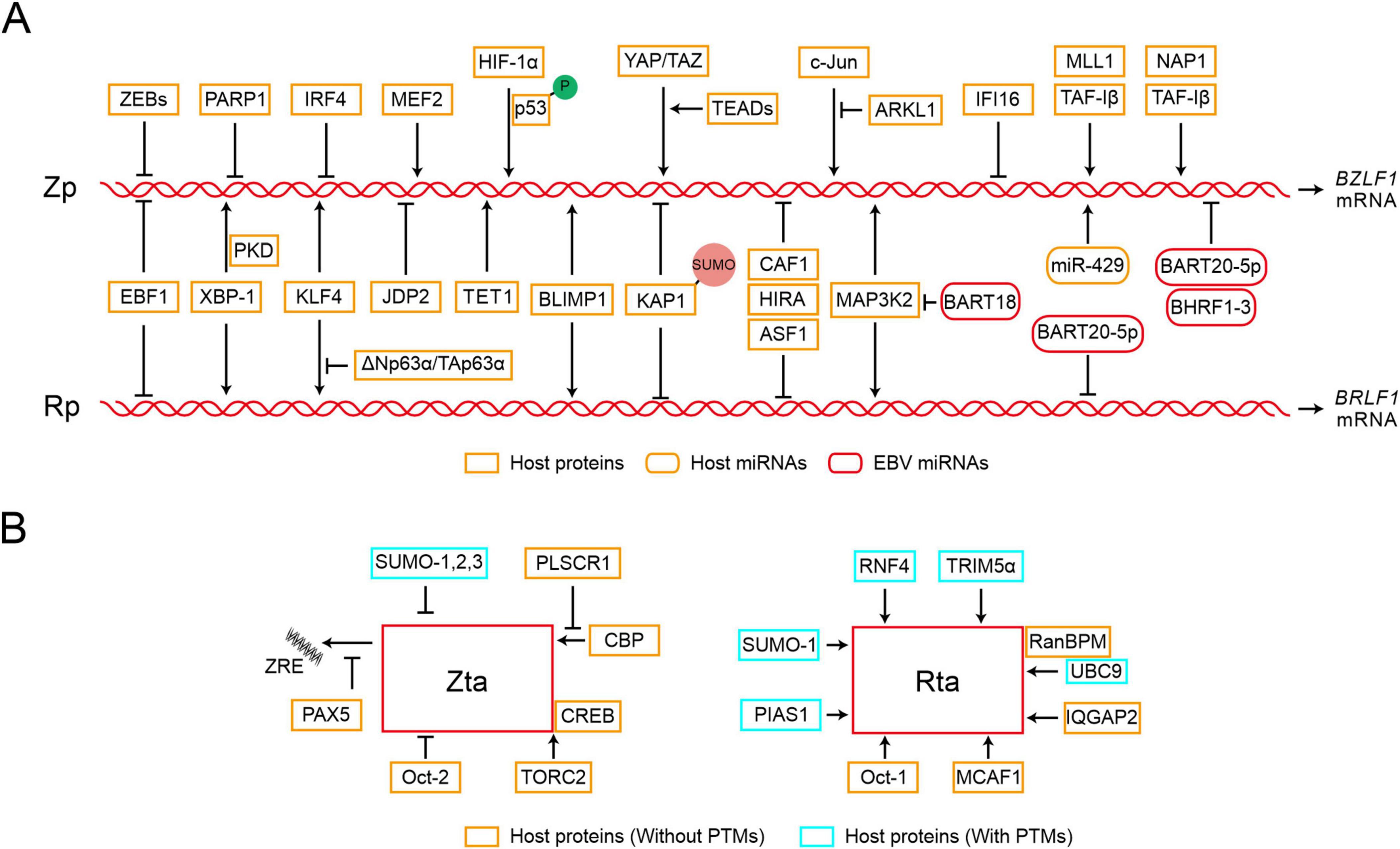
Figure 1. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation starts with the expression of viral immediate-early proteins. (A) Transcription initiation of BZLF1 and BRLF1 is tightly regulated by various factors. The diagram only depicts the regulatory relationships between transcription factors and Zp or Rp and is not related to their regulatory positions. Zp, the promoter of BZLF1; Rp, the promoter of BRLF1. P, phosphorylation; SUMO, sumoylation. (B) The functions of Zta and Rta can be targeted through interactions with specific factors, whether or not post-translational modifications (PTMs) are involved. ZRE, Zta response element.
The transcription of Zp and Rp is also regulated by epigenetic modifications. Zp and Rp are heavily methylated and silenced in latent infection, whereas histone acetylation of Zp and Rp enhances gene accessibility and promotes the binding of transcription factors during lytic replication (Speck et al., 1997; Miller et al., 2007; Woellmer and Hammerschmidt, 2013; Daskalogianni et al., 2015; Guo and Gewurz, 2022). In epithelial cells, TAF-Iβ recruits host methyltransferase MLL1 to promote H3K4 dimethylation and H4K8 acetylation, leading to the chromatin modifications of Zp region and the following EBV reactivation (Mansouri et al., 2013). CAF1, HIRA, and ASF1 are host factors that cooperatively load histone H3 and H4 onto the EBV genome, inhibiting the activity of IE promoter mediated by H3K27me3 and thus hindering lytic reactivation. Depletion of CAF1 protein induces EBV reactivation in Burkitt lymphoma cells (Zhang et al., 2020). JDP2 has been shown to bind to the Z II element of Zp and recruit HDAC3, reducing histone acetylation on the promoter and inhibiting EBV reactivation (Murata et al., 2011). The host factor C-Jun facilitates the binding of TET1 to Zp, enhancing the demethylation of Zp and activating BZLF1 expression (Zhang et al., 2016). When these inhibitory histone modifications are relieved, the transcription factors can bind to the promoters of lytic genes and activate EBV lytic replication (Jung et al., 2007; Murata et al., 2012; Guo and Gewurz, 2022). DNA methylation is not always detrimental to EBV lytic replication, for instance, Zta can specifically bind to the methyl-Zta responsive element (meZRE) and activate lytic gene promoters in a methylation-dependent manner, thereby disrupting epigenetic silencing (Bergbauer et al., 2010; Kalla et al., 2012; Almohammed et al., 2018). Furthermore, Zp and Rp can be targeted by various miRNAs. Following BCR stimulation in plasma cells, the increasing miR-429 disrupts EBV latency by targeting Zp (Lin et al., 2010). EBV miR-BHRF1-3 targets the 3′UTR region of BZLF1 gene and attenuates Zta expression (Fachko et al., 2022). Similarly, EBV miR-BART20-5p binds to the 3′ UTR region of these two IE genes, resulting in transcription inhibition (Jung et al., 2014). EBV miR-BART18 targets the 3′ UTR of MAP3K2 mRNA, affecting the expression of both BZLF1 and BRLF1 (Qiu and Thorley-Lawson, 2014).
Therefore, the activity of IE promoter, Zp and Rp, is modulated by transcriptional regulatory factors and epigenetic modifications, which collectively control EBV reactivation through regulating the expression of IE genes.
2.3 Host factors target Zta and Rta to regulate EBV reactivation
In addition to the transcription activity, the host proteins interact with Zta or Rta and modulate their capabilities in EBV reactivation (Figure 1B and Table 1). PLSCR1 can directly interact with Zta, antagonize the interaction between Zta and CBP, and further block the transcriptional activity of the Zta-CBP complex (Kusano and Ikeda, 2019). In Zta-mediated transcriptional activation, TORC2 acts as a co-activator and interacts with the Zta-CREB complex to activate Zp transcription, which involves the calcineurin-TORC pathway (Murata et al., 2009). PAX5 interacts directly with Zta and inhibits Zta-mediated lytic gene expression (Raver et al., 2013). PAX5 can also bind to viral TRs (tandem terminal repeats) and regulate the expression of viral genes (Arvey et al., 2012; Lee et al., 2015; Lee et al., 2016). IQGAP2 co-localizes with Rta in the nucleus and participates in the activation of Rp (Lin et al., 2023). Oct-1 and Oct-2 induce EBV reactivation through interactions with Rta and Zta, respectively. In particular, Oct-1 synergistically induces viral reactivation through direct interaction with Rta, which is independent of Oct-1 binding with DNA (Robinson et al., 2011). In contrast, Oct-2 negatively regulates virus reactivation by inhibiting the functions of Zta protein (Robinson et al., 2012). MCAF1 serves as an interaction partner for both Zta and Rta, facilitating their synergistic activation. The interaction between MCAF1 and Rta promotes the formation of Sp1-MCAF1-Rta complex at the Sp1 binding site, which ultimately results in the activation of Rp (Chang et al., 2005). In addition, the Zta-MCAF1-Rta complex also binds to the Zta response element (ZRE) and synergistically promotes the expression of EBV lytic genes (Chang et al., 2010). RanBPM simultaneously interacts with SUMO-E2 enzyme Ubc9 and Rta, which promotes SUMO-1-mediated Rta sumoylation and the transactivation activity of Rta (Chang et al., 2008).
Post-translational modifications (PTMs), such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, and other covalent modifications are capable of regulating the associated activity of Zta or Rta (Walsh et al., 2005). The phosphorylation of Zta and Rta has been shown to affect the binding of Zta to DNA, and the transactivation capabilities of both Zta and Rta (Francis et al., 1999; Bhende et al., 2005; Asai et al., 2006). Furthermore, four lysine residues on Zta are targets of ubiquitination, and the ubiquitination of Zta is essential for progeny production in the viral lytic replication (Zhao et al., 2020). All SUMO isoforms 1, 2, and 3 can induce Zta sumoylation at the lysine residue 12 (Murata et al., 2010). Although sumoylation does not alter Zta localization, it inhibits the transactivation ability of Zta and the Zta-mediated lytic cycle (Hagemeier et al., 2010). In contrast, Rta transactivation activity is enhanced during SUMO-1-mediated sumoylation (Chang et al., 2004). Two E3 ubiquitin ligases, RNF4 and TRIM5α, interact with Rta and promote its ubiquitination, restricting viral lytic replication (Yang et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2017). RNF4 can target SUMO-2-conjugated Rta and knockouts of both RNF4 and TRIM5α increase Rta expression. PIAS1 enhances Rta-mediated activation of EBV lytic genes via sumoylation, but PIAS1 inhibits Zta and C/EBP β-mediated Zp activation, and this inhibition does not rely on its SUMO ligase activity (Zhang et al., 2017). Therefore, the host proteins interact with viral IE proteins and modulate their activities, potentially depending on the post-translational modifications, which play crucial roles in EBV reactivation.
3 EBV reactivation is subject to multiple layers of regulation after initiation
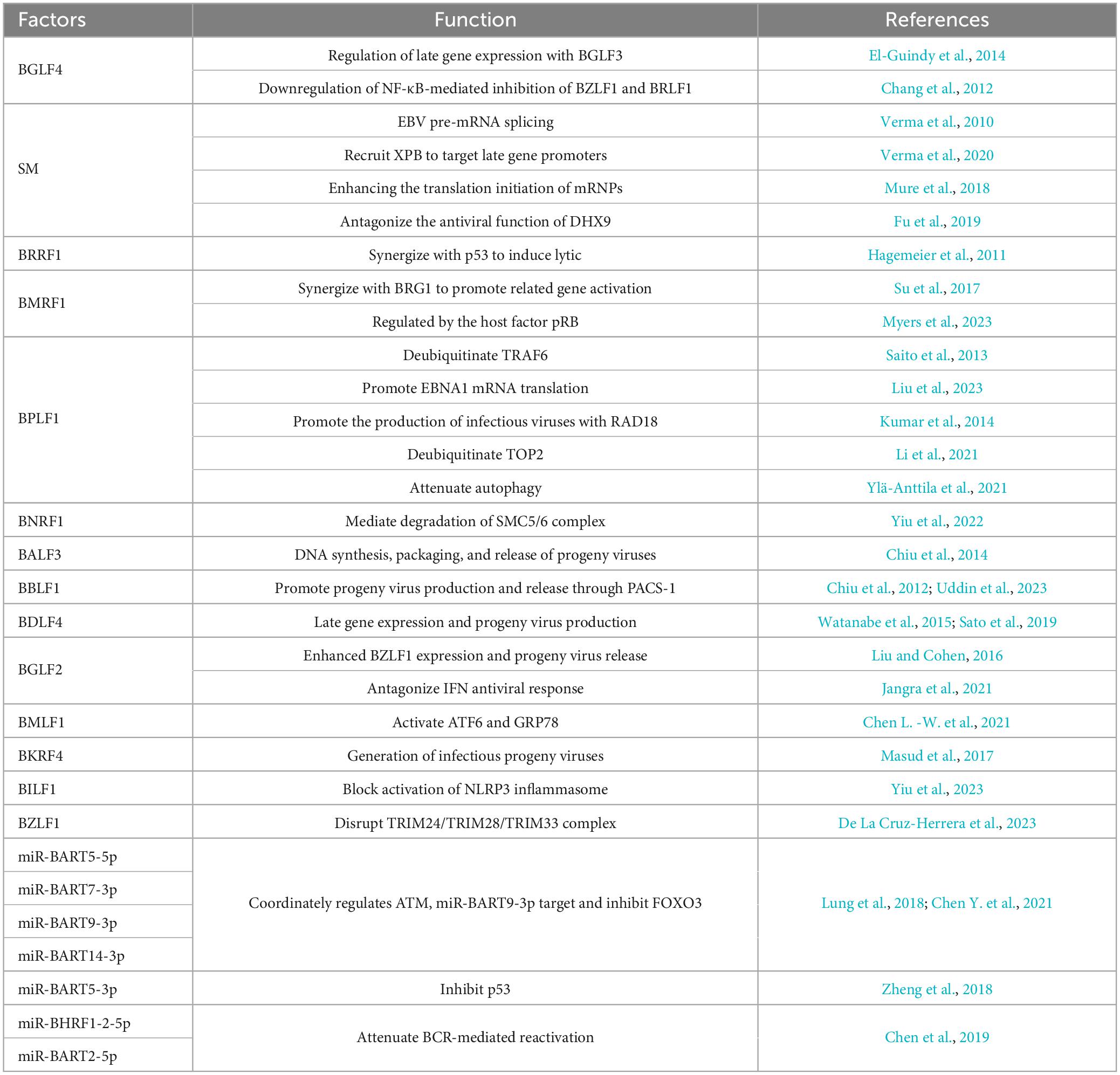
3.1 EBV-encoded proteins function in lytic replication
The expression of EBV lytic genes determines the progression of a lytic cycle (Figure 2A and Table 2). During viral DNA replication, EBV-encoded proteins not only regulate the replication of viral genome but also hijack or antagonize host factors to control host DNA replication. BGLF4, an EBV-encoded protein kinase, not only activates the expression of BGLF3, but together they control post-replication processes and regulate the expression of late genes (El-Guindy et al., 2014). BGLF4 also phosphorylates UXT at the threonine-3 site, weakening the interaction between UTX and p65, which represses NF-κB-mediated BZLF1 and BRLF1 expression and promotes the viral lytic cycle (Chang et al., 2012). EBV-encoded nuclear protein SM is essential for lytic gene expression. SM binds to and stabilizes mRNA, modulating the splicing of cellular and viral pre-mRNAs, which depends on the interaction between SM and the SR splicing factor, specifically SRp20 (Verma et al., 2010). Additionally, as a transcription activator, SM binds to and recruits cellular XPB (xeroderma pigmentosum group B-complementing protein, a subunit of TFII H), subsequently targeting the promoters of late genes (Verma et al., 2020). SM also binds to CBC, eIF4F, and PABP, thereby enhancing the translation initiation of mRNPs, which are involved in protein synthesis (Mure et al., 2018). BRRF1 interacts with TRAF2 and induces lytic gene expression in a TRAF2-dependent manner. BRRF1 also co-activates lytic replication with p53. In the absence of p53, BRRF1-mediated activation of lytic genes is significantly reduced (Hagemeier et al., 2011).
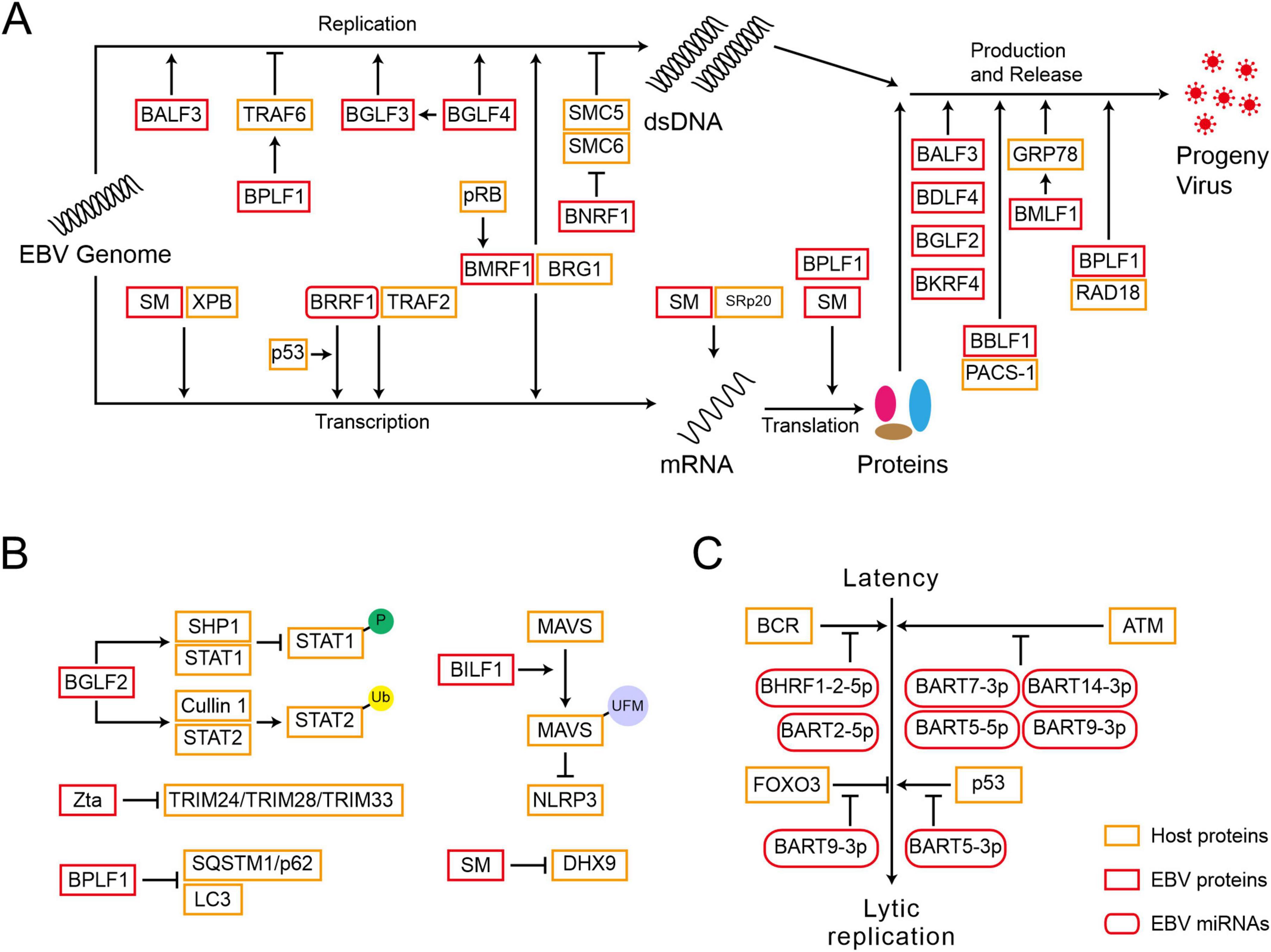
Figure 2. Epstein-Barr virus reactivation is subject to multiple layers of regulation after initiation. (A) EBV-encoded proteins function in the lytic gene expression, viral DNA replication, and progeny virus production. (B) EBV-encoded proteins disrupt the host’s innate immune response to promote reactivation. P, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitination; UFM, UFMylation. (C) EBV-encoded miRNAs are crucial for reactivation.
The cofactor of viral DNA polymerase, BMRF1, is a key protein for lytic DNA replication. BMRF1 promotes the activation of BcLF1 and BLLF1 through interacting with the transcription regulator BRG1 (Su et al., 2017). The cellular pRb facilitates lytic reactivation, whose deletion inhibits lytic replication and BMRF1 expression in differentiated epithelial cells (Myers et al., 2023). The host factor TRAF6, once activated by polyubiquitin chain conjugation, binds to LMP1 and mediates NF-κB signaling, which inhibits the viral lytic cycle. However, EBV-encoded BPLF1 interacts with and deubiquitinates TRAF6, thereby inhibiting the LMP1-mediated NF-κB pathway and promoting viral DNA replication (Saito et al., 2013). Meanwhile, BPLF1 promotes the translation of EBNA1 mRNA (Liu et al., 2023). The host SMC5/6 complex recognizes and occupies R-loops, which are essential for DNA double-strand separation and the loading of core replication proteins during the lytic cycle, inhibiting the synthesis of EBV genome (Yiu et al., 2022). EBV-encoded BNRF1 membrane protein degrades the SMC5/6 complex through calpain proteolysis and the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin-7 dependent proteasome degradation pathway, allowing EBV to escape host restriction on viral genome replication and the production of infectious progeny virions (Yiu et al., 2022). Therefore, EBV-encoded proteins are key regulators in controlling the processes of viral lytic replication.
3.2 EBV-encoded proteins play critical roles in virus assembly and progeny production
After the EBV genome completes replication, the virus synthesizes capsid proteins and assembles progeny virus particles within the host cell, ultimately releasing infectious virus particles to infect other cells (Figure 2A and Table 2). EBV-encoded BALF3 is involved not only in viral DNA synthesis but also in the packaging and release of mature virus particles (Chiu et al., 2014). BBLF1 is a myristoylated and palmitoylated protein, whose myristoylation enhances its stability and facilitates its membrane anchoring in the trans-Golgi network (TGN). Through interaction with PACS-1, a cytoplasmic protein, BBLF1 mediates retrograde transport from endosomes to the TGN and supports the production of progeny viruses (Chiu et al., 2012). The NED region of BBLF1 is key to the release of mature virus particles (Uddin et al., 2023). BDLF4, a viral protein expressed early in viral lysis, is a component of the lytic gene regulatory complex. BDLF4 knockout severely restricts the expression of late genes and reduces the production of progeny virus (Watanabe et al., 2015). By hijacking the host CDK2 complex, BDLF4 is phosphorylated at multiple amino acid residues, preventing its degradation through ubiquitin-mediated pathways. Among these residues, the phosphorylation of Thr-91 is critical for maintaining BDLF4 stability (Sato et al., 2019). BGLF2 enhances Zta expression in both B cells and gastric cancer cells, promoting the release of progeny viruses through the p38 signaling pathway. In contrast, its absence impairs reactivation triggered by inducers (Liu and Cohen, 2016). BMLF1 activates the UPR (unfolded protein response) sensor ATF6 by initiating the proteolytic cleavage, which transcriptionally activates the GRP78 promoter, a central regulator in the UPR, via ER stress response elements. Although the deletion of GRP78 does not affect the expression of EBV cleavage genes, it reduces the production of viral particles (Chen L. -W. et al., 2021). BKRF4, a late lytic protein, has a limited impact on viral gene replication and protein expression, yet it is crucial for the production of infectious progeny viruses (Masud et al., 2017). BPLF1 modulates the DNA damage response induced by EBV lytic replication, collaborating with RAD18 to enhance the production of infectious viruses (Kumar et al., 2014). BPLF1 also deubiquitinates TOP2, inhibiting the DNA damage response induced by TOP2 and promoting viral production (Li et al., 2021). These EBV-encoded proteins are responsible for regulating virus assembly and progeny production by modulating various cellular factors.
3.3 EBV-encoded proteins disrupt the host’s innate immune response to promote reactivation
To successfully replicate and propagate within the infected cells, EBV has evolved various strategies to evade the host’s innate immune surveillance (Figure 2B and Table 2). EBV-encoded BGLF2 is an essential factor to counteract the interferon (IFN)-mediated antiviral response. BGLF2 can recruit the SHP1 phosphatase to STAT1 and inhibit the phosphorylation of STAT1. Additionally, BGLF2 recruits STAT2 to the E3 ubiquitin ligase Cullin 1, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation (Jangra et al., 2021). EBV G-protein-coupled receptor BILF1 recruits the E3 ligase UFL1 (UFM1 specific ligase 1) to facilitate the interaction between MAVS and UFM1 (ubiquitin fold modifier 1), leading to the MAVS UFMylation. This process results in MAVS degradation via the mitochondrial-lysosomal pathway, thus blocking the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes (Yiu et al., 2023). EBV-encoded SM protein inhibits the transcriptional activation of DHX9, counteracting its antiviral function and reducing the effects of host immunity during reactivation (Fu et al., 2019). Cellular RNA Helicase DHX9 enhances the antiviral innate immunity in the host, limiting the production of EBV viral particles. TRIM24 and TRIM33 are cellular antiviral factors that inhibit BZLF1 expression, however, Zta interacts with these two proteins in EBV reactivation, leading to the destruction of the TRIM24-TRIM28-TRIM33 complex and the degradation of TRIM24 and TRIM33 (De La Cruz-Herrera et al., 2023). Autophagy impairs virus replication and transmission, but BPLF1 targets and inhibits the recruitment of selective autophagy receptor SQSTM1/p62 to LC3, reducing the adverse effects of autophagy on the lytic cycle (Ylä-Anttila et al., 2021).
In conclusion, the replication of the EBV genome, the production of progeny viruses, and the host’s immune response induced by various factors constitute an interconnected regulatory network. The balance among these components ultimately determines the progression following reactivation.
3.4 EBV-encoded miRNAs are crucial for reactivation
In addition to the EBV-encoded proteins described above, the process of EBV reactivation is also regulated by distinct miRNAs (Figure 2C and Table 2). EBV miR-BART20-5p blocks BAD-induced Caspase-3-dependent cellular apoptosis, thus contributing to the maintenance of EBV latency (Kim et al., 2016). Four EBV miR-BARTs (BART5-5p, BART7-3p, BART9-3p, and BART14-3p) cooperatively regulate and suppress ATM, resulting in the disruption of EBV reactivation (Lung et al., 2018). Another EBV miR-BART5-3p maintains latency by suppressing p53 expression (Zheng et al., 2018). EBV miR-BART9-3p, along with its homologous miR-141-3p, targets and inhibits the expression of the host transcription factor FOXO3 during BCR cross-linking, thereby reducing its inhibitory effect on BCR-induced viral lytic activation (Chen Y. et al., 2021). In contrast, EBV miR-BHRF1-2-5p, miR-BART2-5p, and the host miR-17-5p have been shown to weaken the BCR-mediated reactivation of EBV in vivo (Chen et al., 2019).
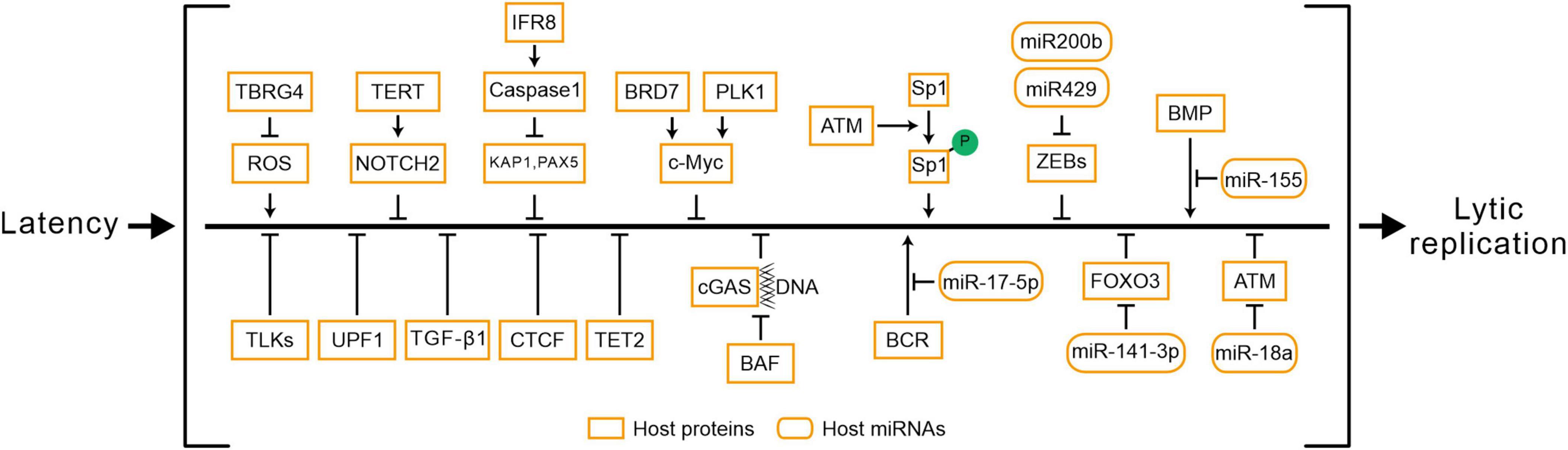
4 Host factors determine the progress of EBV reactivation
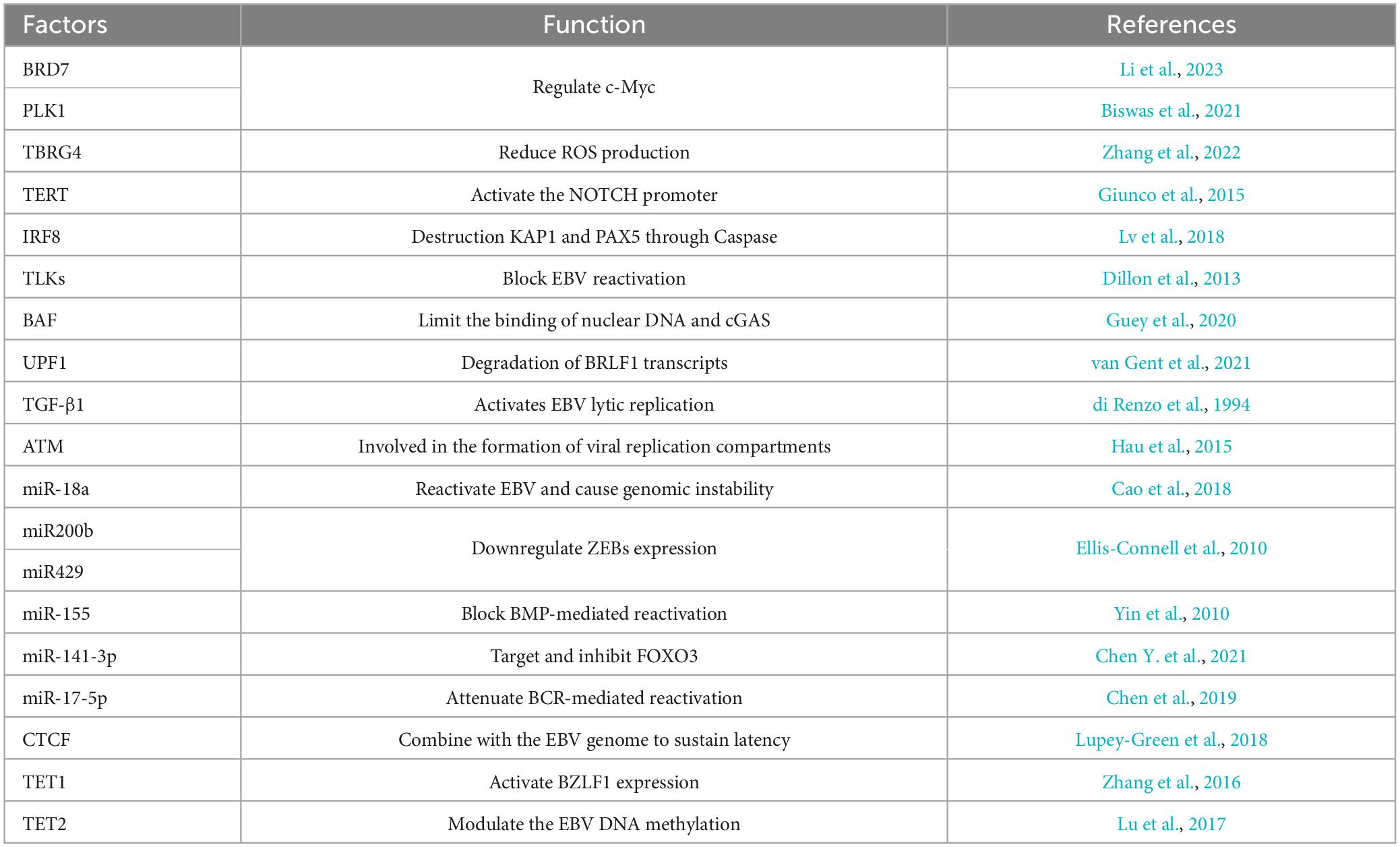
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation involves the crosstalk of multiple signaling pathways, and the processes are also regulated by various host factors (Figure 3 and Table 3). The abundance of Myc protein serves as a checkpoint switch for EBV lytic replication (Guo et al., 2020), and cytokines regulate EBV reactivation by modulating Myc expression (Biswas et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023). BRD7 binds with EBNA1 and co-localizes in the promoter of c-Myc to regulate c-Myc transcriptional activation, furthermore, BRD7 deficiency activates the Myc-mediated lytic cycle (Li et al., 2023). PLK1 may restrict EBV reactivation through the regulation of c-Myc activity, and inhibition of PLK1 promotes EBV reactivation (Biswas et al., 2021). ROS has been shown to function as a stimulator for lytic EBV reactivation (Yiu et al., 2020), while TBRG4 reduces ROS generation in host cells and inhibits EBV lytic replication (Zhang et al., 2022). TERT maintains EBV latency through the NOTCH2/BATF pathway. Firstly, the expression of TERT is correlated with BATF and NOTCH2. Secondly, TERT activates the NOTCH promoter in a dose-dependent manner (Giunco et al., 2015). During lytic induction, IRF8 enhances Caspase expression and activation (Lv et al., 2018), which subsequently destabilizes EBV reactivation suppressors such as KAP1 (Bentz et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2022), PAX5 (Arvey et al., 2012; Raver et al., 2013; Lee et al., 2015; Lee et al., 2016). Another family of host factors, TLKs, plays a role in the reactivation of EBV during its latent phase, and the knockout of TLKs leads to EBV reactivation (Dillon et al., 2013). BAF restricts the binding of nuclear DNA to cGAS and suppresses its activity to promote EBV reactivation (Guey et al., 2020; Broussard et al., 2023). UPF1 mediates the nonsense-mediated decay of BRLF1 transcripts, controlling the reactivation of EBV (van Gent et al., 2021). In Burkitt lymphoma cell lines, TGF-β1 is shown to activate EBV lytic replication (di Renzo et al., 1994). In NPC cells, EBV lytic infection induces ATM activation. Subsequently, the phosphorylation of Sp1 at the serine-101 residue mediated by ATM activation contributes to the formation of viral replication compartment (Hau et al., 2015).
Furthermore, the host factors regulate EBV reactivation via epigenetic modifications (Pei et al., 2020). After hypoxia-induced DNA damage response in B cells, ATM activation suppresses EBV lytic gene expression and reduces viral load. The host miR-18a suppresses the ATM-mediated DNA damage response in an EBV-dependent manner, leading to EBV reactivation and host genomic instability (Cao et al., 2018). Host miR-200b and miR-429 induce viral lytic replication and the production of infectious progeny viruses by downregulating ZEBs expression (Ellis-Connell et al., 2010). Another host miR-155 restricts BMP-mediated EBV reactivation (Yin et al., 2010). Extensive methylation of the viral genome in latency leads to the silencing of lytic genes (Woellmer and Hammerschmidt, 2013; Germi et al., 2016). The host factor TET2, in cooperation with EBNA2, modulates the DNA methylation status of EBV, and the knockout of TET2 promotes the expression of lytic genes (Lu et al., 2017). Additionally, CTCF maintains EBV latency by binding to the viral genome, while PARP1 promotes CTCF expression and stabilizes CTCF binding, which facilitates the maintenance of EBV latency (Lupey-Green et al., 2018). In summary, the reactivation of EBV is a complex process involving the interplay of multiple mechanisms, regulated by a diverse range of host factors and miRNAs (Supplementary Table 1).
5 Novel insights to explore the mechanisms of EBV reactivation
The emergence of numerous innovative technologies and methodologies enables a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying EBV latency and reactivation. First of all, Alphafold3 is a powerful tool capable of predicting the structures of complexes involving proteins and nucleic acids, despite the limitation of predicting only static structures (Hsu et al., 2014). Utilizing Alphafold3 to model the known host factors and their binding sites, we could unveil identical or similar structural domains in these factors when bound to Zp and Rp. This approach can guide the development of specific small-molecule drugs through virtual screening. Additionally, Alphafold3 can be harnessed to predict the structures of lesser-known EBV gene products, providing valuable insights into their functions and interactions with the host.
Secondly, the rapid development in Natural Language Processing (NLP) also brings novel insights for biomedical research. Multiple pre-trained models, like BioGPT (Luo et al., 2022), have enabled us to access the biomedical literature with higher accuracy and availability. Based on the abstract texts of 21 million articles, researchers mapped the entire biomedical literature landscape onto a two-dimensional (2D) plot, enabling available cross-referencing of biomedical metadata (González-Márquez et al., 2024). Concerning EBV infection, we have developed a functional encyclopedia of EBV-related cellular pathways and signaling networks from 36,105 EBV-relevant scientific publications (Yu et al., 2024). NLP methods have also been shown to elucidate molecular regulatory pathways. reguloGPT is developed to successfully infer the m6A-specific knowledge graph and demonstrate its utility in elucidating m6A’s regulatory mechanisms across various cancer phenotypes (Wu et al., 2024). Applications of the NLP techniques bear high potential in the assistance of unveiling new targets for EBV reactivation.
Thirdly, the emerging gene editing technologies will greatly expand our capacity to elucidate virus-host interactions and develop targeted antiviral strategies. For instance, CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) and CRISPR activation (CRISPRa) are endogenous gene regulation systems derived from the CRISPR/Cas9 platform (Tian et al., 2019; Tian et al., 2021). Both techniques mediate gene expression without inducing double-strand breaks (DSBs), thereby preserving the genomic sequence. In the context of gene function studies, CRISPRa-mediated transcriptional activation overcomes the limitations of cDNA overexpression. CRISPRi and CRISPRa can also be employed to modulate non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Thus, genome-wide CRISPRi/a screens in EBV studies may facilitate the discovery of additional ncRNAs associated with viral latency and lytic cycle regulation. Furthermore, another gene editing technology, base editors, can mediate conversions among the four DNA bases without inducing DSBs (Anzalone et al., 2020). Given that EBV encodes several critical oncogenic and enzymatic proteins that regulate its life cycle, the base editor screens may assist in identifying key functional domains and sites within these proteins, thereby advancing both basic research and drug development efforts. Furthermore, the EBV genome exists as circular episomes within the host cells, and isolating these episomes has posed a significant limitation in functional studies. Recent studies have successfully isolated human extrachromosomal DNAs using CRISPR-CATCH (Hung et al., 2022). By further refining and optimizing this technique, we may be able to isolate EBV episomes for subsequent studies on the biological functions.
Finally, the combined use of multiple omics approaches enables a comprehensive understanding of the impact of EBV infection on host cells and the key mechanisms underlying virus infection. For instance, a combined analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics has identified IDO1 as a critical host factor for establishing EBV latency in B cells; inhibiting IDO1 disrupts EBV-induced B cell transformation (Müller-Durovic et al., 2024). Integrating metabolomics with proteomics may reveal additional vital metabolic pathways altered by EBV infection. Consequently, the approved metabolic regulators could be used to modulate human metabolic pathways, alleviating symptoms associated with EBV-associated diseases. The concurrent application of various omics technologies with CRISPR techniques also aids in elucidating the key mechanisms of EBV infection. For example, the integration of metabolomics with CRISPR system has demonstrated that methionine metabolism is a significant pathway for maintaining EBV latency (Guo et al., 2022). By leveraging a combination of techniques, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complex interactions between EBV and its host, thereby guiding the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
The emerging technologies mentioned above, including structural prediction tools, literature data mining tools, and genome editing tools give us access to an unprecedented amount of data to screen for critical factors underlying EBV reactivation. For instance, CRISPRi using the lytic model will produce thousands of essential target genes for EBV reactivation. Multimodal analysis combining RNA-seq will reveal the functional key regulators. Furthermore, mass spectrometry combined with protein-protein docking screen enables the identification of co-regulators and the discovery of molecular mechanisms. Despite these rapid technological innovations, the complexity of biological systems, particularly the intricate and diverse machinery involved in virus-host interactions, still requires careful experimentation and thorough evaluation to dissect and unveil the nuanced mechanisms.
6 Conclusion
Epstein-Barr virus is widespread across the globe and is associated with a variety of human diseases. EBV is almost impossible to be cleared from the host due to its effective latency and periodic reactivation that is initiated by appropriate signals. Development of an effective druggable target to mitigate EBV reactivation bears an important therapeutic opportunity for curing EBV-related diseases. Inhibiting the lytic genes is also an effective means to treat EBV infections. However, discovering the ultimate cure for EBV-induced diseases remains a significant challenge. In this review, we summarize the key factors governing EBV reactivation, including factors involved in regulating IE gene expression, the functions of IE gene products, viral replication, the release of progeny virions, and the innate immune response triggered by viral infection. In conclusion, given the abundance of cellular regulatory elements, the critical factors may be still hiding beneath cloaks and silently puppeteering the pathogenic events through unknown mechanisms. Integrating established virological research methods with novel technologies could facilitate the identification of key regulators in the EBV reactivation, and ultimately eradicate the negative effects of EBV on human well-being.
Author contributions
YW: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science, Technology, and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (grant no. JCYJ20230807093208017 to YP) and the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (grant no. 2024A1515013126 to YP).
Acknowledgments
We apologize to the colleagues whose contributions to this field could not be cited due to space limitations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1505191/full#supplementary-material
References
Almohammed, R., Osborn, K., Ramasubramanyan, S., Perez-Fernandez, I. B., Godfrey, A., Mancini, E. J., et al. (2018). Mechanism of activation of the BNLF2a immune evasion gene of Epstein-Barr virus by Zta. J. Gen. Virol. 99, 805–817. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001056
Anzalone, A. V., Koblan, L. W., and Liu, D. R. (2020). Genome editing with CRISPR–Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 824–844. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0561-9
Arvey, A., Tempera, I., Tsai, K., Chen, H.-S., Tikhmyanova, N., Klichinsky, M., et al. (2012). An atlas of the Epstein-Barr virus transcriptome and epigenome reveals host-virus regulatory interactions. Cell Host Microbe 12, 233–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.008
Asai, R., Kato, A., Kato, K., Kanamori-Koyama, M., Sugimoto, K., Sairenji, T., et al. (2006). Epstein-Barr virus protein kinase BGLF4 is a virion tegument protein that dissociates from virions in a phosphorylation-dependent process and phosphorylates the viral immediate-early protein BZLF1. J. Virol. 80, 5125–5134. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02674-05
Baumann, M., Mischak, H., Dammeier, S., Kolch, W., Gires, O., Pich, D., et al. (1998). Activation of the Epstein-Barr virus transcription factor BZLF1 by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced phosphorylation. J. Virol. 72, 8105–8114. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.10.8105-8114.1998
Bentz, G. L., Moss, C. R., Whitehurst, C. B., Moody, C. A., and Pagano, J. S. (2015). LMP1-induced sumoylation influences the maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus latency through KAP1. J. Virol. 89, 7465–7477. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00711-15
Bergbauer, M., Kalla, M., Schmeinck, A., Göbel, C., Rothbauer, U., Eck, S., et al. (2010). CpG-methylation regulates a class of Epstein-Barr virus promoters. PLoS Pathog. 6:e1001114. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001114
Bhende, P. M., Dickerson, S. J., Sun, X., Feng, W.-H., and Kenney, S. C. (2007). X-box-binding protein 1 activates lytic Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in combination with protein kinase D. J. Virol. 81, 7363–7370. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00154-07
Bhende, P. M., Seaman, W. T., Delecluse, H.-J., and Kenney, S. C. (2005). BZLF1 activation of the methylated form of the BRLF1 immediate-early promoter is regulated by BZLF1 residue 186. J. Virol. 79, 7338–7348. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7338-7348.2005
Biswas, A., Zhou, D., Fiches, G. N., Wu, Z., Liu, X., Ma, Q., et al. (2021). Inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) facilitates reactivation of gamma-herpesviruses and their elimination. PLoS Pathog. 17:e1009764. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009764
Bristol, J. A., Brand, J., Ohashi, M., Eichelberg, M. R., Casco, A., Nelson, S. E., et al. (2022). Reduced IRF4 expression promotes lytic phenotype in Type 2 EBV-infected B cells. PLoS Pathog. 18:e1010453. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010453
Broussard, G., Ni, G., Zhang, Z., Li, Q., Cano, P., Dittmer, D. P., et al. (2023). Barrier-to-autointegration factor 1 promotes gammaherpesvirus reactivation from latency. Nat. Commun. 14:434. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35898-2
Cao, P., Zhang, M., Wang, L., Sai, B., Tang, J., Luo, Z., et al. (2018). miR-18a reactivates the Epstein-Barr virus through defective DNA damage response and promotes genomic instability in EBV-associated lymphomas. BMC Cancer 18:1293. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5205-9
Chang, L.-K., Chuang, J.-Y., Nakao, M., and Liu, S.-T. (2010). MCAF1 and synergistic activation of the transcription of Epstein–Barr virus lytic genes by Rta and Zta. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 4687–4700. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq243
Chang, L.-K., Chung, J.-Y., Hong, Y.-R., Ichimura, T., Nakao, M., and Liu, S.-T. (2005). Activation of Sp1-mediated transcription by Rta of Epstein–Barr virus via an interaction with MCAF1. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 6528–6539. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki956
Chang, L.-K., Lee, Y.-H., Cheng, T.-S., Hong, Y.-R., Lu, P.-J., Wang, J. J., et al. (2004). Post-translational modification of Rta of Epstein-Barr virus by SUMO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 38803–38812. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405470200
Chang, L.-K., Liu, S.-T., Kuo, C.-W., Wang, W.-H., Chuang, J.-Y., Bianchi, E., et al. (2008). Enhancement of transactivation activity of Rta of Epstein-Barr virus by RanBPM. J. Mol. Biol. 379, 231–242. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.011
Chang, L.-S., Wang, J.-T., Doong, S.-L., Lee, C.-P., Chang, C.-W., Tsai, C.-H., et al. (2012). Epstein-Barr virus BGLF4 kinase downregulates NF-κB transactivation through phosphorylation of coactivator UXT. J. Virol. 86, 12176–12186. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01918-12
Chen, L.-W., Wang, S.-S., Hung, C.-H., Hung, Y.-H., Lin, C.-L., and Chang, P.-J. (2021). The Epstein-Barr virus lytic protein BMLF1 induces upregulation of GRP78 expression through ATF6 activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:4024. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084024
Chen, Y., Fachko, D. N., Ivanov, N. S., and Skalsky, R. L. (2021). B Cell receptor-responsive miR-141 enhances Epstein-Barr virus Lytic cycle via FOXO3 inhibition. Msphere 6, e0093–21. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00093-21
Chen, Y., Fachko, D., Ivanov, N. S., Skinner, C. M., and Skalsky, R. L. (2019). Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 15:e1007535. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007535
Chiu, S.-H., Wu, M.-C., Wu, C.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Lin, S.-F., Hsu, J. T.-A., et al. (2014). Epstein-Barr virus BALF3 has nuclease activity and mediates mature virion production during the lytic cycle. J. Virol. 88, 4962–4975. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00063-14
Chiu, Y.-F., Sugden, B., Chang, P.-J., Chen, L.-W., Lin, Y.-J., Lan, Y.-C., et al. (2012). Characterization and intracellular trafficking of Epstein-Barr virus BBLF1, a protein involved in virion maturation. J. Virol. 86, 9647–9655. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01126-12
Damania, B., Kenney, S. C., and Raab-Traub, N. (2022). Epstein-Barr virus: Biology and clinical disease. Cell 185, 3652–3670. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.08.026
Daskalogianni, C., Pyndiah, S., Apcher, S., Mazars, A., Manoury, B., Ammari, N., et al. (2015). Epstein–Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 and ZEBRA: Targets for therapeutic strategies against EBV-carrying cancers. J. Pathol. 235, 334–341. doi: 10.1002/path.4431
De La Cruz-Herrera, C. F., Tatham, M. H., Siddiqi, U. Z., Shire, K., Marcon, E., Greenblatt, J. F., et al. (2023). Changes in SUMO-modified proteins in Epstein-Barr virus infection identifies reciprocal regulation of TRIM24/28/33 complexes and the lytic switch BZLF1. PLoS Pathog. 19:e1011477. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011477
di Renzo, L., Alttok, A., Klein, G., and Klein, E. (1994). Endogenous TGF−β contributes to the induction of the EBV lytic cycle in two burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 57, 914–919. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570623
Dillon, P. J., Gregory, S. M., Tamburro, K., Sanders, M. K., Johnson, G. L., Raab-Traub, N., et al. (2013). Tousled-like kinases modulate reactivation of gammaherpesviruses from latency. Cell Host Microbe 13, 204–214. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.12.005
El-Guindy, A., Ghiassi-Nejad, M., Golden, S., Delecluse, H.-J., and Miller, G. (2013). Essential role of Rta in lytic DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. J. Virol. 87, 208–223. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01995-12
El-Guindy, A., Lopez-Giraldez, F., Delecluse, H.-J., McKenzie, J., and Miller, G. (2014). A locus encompassing the Epstein-Barr virus bglf4 kinase regulates expression of genes encoding viral structural proteins. PLoS Pathog. 10:e1004307. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004307
Ellis, A., Wang, Z., Yu, X., and Mertz, J. (2010). Either ZEB1 or ZEB2/SIP1 can play a central role in regulating the Epstein-Barr virus latent-lytic switch in a cell-type-specific manner. J. Virol. 84, 6139–6152. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02706-09
Ellis-Connell, A. L., Iempridee, T., Xu, I., and Mertz, J. E. (2010). Cellular microRNAs 200b and 429 regulate the Epstein-Barr virus switch between latency and lytic replication. J. Virol. 84, 10329–10343. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00923-10
Epstein, A. (2012). Burkitt lymphoma and the discovery of Epstein-Barr virus. Br. J. Haematol. 156, 777–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.09008.x
Fachko, D. N., Chen, Y., and Skalsky, R. L. (2022). Epstein-Barr virus miR-BHRF1-3 targets the BZLF1 3’UTR and regulates the lytic cycle. J. Virol. 96, e01495–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01495-21
Feederle, R., Kost, M., Baumann, M., Janz, A., Drouet, E., Hammerschmidt, W., et al. (2000). The Epstein-Barr virus lytic program is controlled by the co-operative functions of two transactivators. Embo J. 19, 3080–3089. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.12.3080
Feng, W.-H., Kraus, R. J., Dickerson, S. J., Lim, H. J., Jones, R. J., Yu, X., et al. (2007). ZEB1 and c-Jun levels contribute to the establishment of highly lytic Epstein-Barr virus infection in gastric AGS cells. J. Virol. 81, 10113–10122. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00692-07
Flemington, E., and Speck, S. H. (1990). Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J. Virol. 64, 1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990
Francis, A., Ragoczy, T., Gradoville, L., Heston, L., El-Guindy, A., Endo, Y., et al. (1999). Amino acid substitutions reveal distinct functions of serine 186 of the ZEBRA protein in activation of early lytic cycle genes and synergy with the Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator. J. Virol. 73, 4543–4551. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.4543-4551.1999
Fu, W., Verma, D., Burton, A., and Swaminathan, S. (2019). Cellular RNA helicase DHX9 interacts with the essential Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein SM and restricts EBV lytic replication. J. Virol. 93, e01244–18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01244-18
Germi, R., Guigue, N., Lupo, J., Semenova, T., Grossi, L., Vermeulen, O., et al. (2016). Methylation of Epstein–Barr virus Rta promoter in EBV primary infection, reactivation and lymphoproliferation. J. Med. Virol. 88, 1814–1820. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24524
Giunco, S., Celeghin, A., Gianesin, K., Dolcetti, R., Indraccolo, S., and De Rossi, A. (2015). Cross talk between EBV and telomerase: The role of TERT and NOTCH2 in the switch of latent/lytic cycle of the virus. Cell Death Dis. 6:e1774. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.145
González-Márquez, R., Schmidt, L., Schmidt, B. M., Berens, P., and Kobak, D. J. (2024). The landscape of biomedical research. Patterns 5:100968. doi: 10.1016/j.patter.2024.100968
Gruffat, H., Manet, E., Rigolet, A., and Sergeant, A. (1990). The enhancer factor R of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 6835–6843. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6835
Guey, B., Wischnewski, M., Decout, A., Makasheva, K., Kaynak, M., Sakar, M. S., et al. (2020). BAF restricts cGAS on nuclear DNA to prevent innate immune activation. Science 369, 823–828. doi: 10.1126/science.aaw6421
Guo, R., and Gewurz, B. E. (2022). Epigenetic control of the Epstein-Barr lifecycle. Curr. Opin. Virol. 52, 78–88. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.013
Guo, R., Jiang, C., Zhang, Y., Govande, A., Trudeau, S. J., Chen, F., et al. (2020). MYC controls the Epstein-Barr virus lytic switch. Mol. Cell 78, 653–669.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.025
Guo, R., Liang, J. H., Zhang, Y., Lutchenkov, M., Li, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Methionine metabolism controls the B cell EBV epigenome and viral latency. Cell Metab. 34, 1280–1297.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.008
Hagemeier, S. R., Barlow, E. A., Kleman, A. A., and Kenney, S. C. (2011). The Epstein-Barr virus BRRF1 protein, Na, induces lytic infection in a TRAF2-and p53-dependent manner. J. Virol. 85, 4318–4329. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01856-10
Hagemeier, S. R., Dickerson, S. J., Meng, Q., Yu, X., Mertz, J. E., and Kenney, S. C. (2010). Sumoylation of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein inhibits its transcriptional activity and is regulated by the virus-encoded protein kinase. J. Virol. 84, 4383–4394. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02369-09
Hau, P. M., Deng, W., Jia, L., Yang, J., Tsurumi, T., Chiang, A. K., et al. (2015). Role of ATM in the formation of the replication compartment during lytic replication of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J. Virol. 89, 652–668. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01437-14
Heilmann, A. M., Calderwood, M. A., Portal, D., Lu, Y., and Johannsen, E. (2012). Genome-wide analysis of Epstein-Barr virus Rta DNA binding. J. Virol. 86, 5151–5164. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06760-11
Hsu, P. D., Lander, E. S., and Zhang, F. (2014). Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 157, 1262–1278. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.010
Huang, H.-H., Chen, C.-S., Wang, W.-H., Hsu, S.-W., Tsai, H.-H., Liu, S.-T., et al. (2017). TRIM5α promotes ubiquitination of RTA from Epstein–Barr virus to attenuate lytic progression. Front. Microbiol. 7:2129. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02129
Hulse, M., Caruso, L. B., Madzo, J., Tan, Y., Johnson, S., and Tempera, I. (2018). Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 is necessary for coactivating hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent gene expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. PLoS Pathog. 14:e1007394. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007394
Hung, K. L., Luebeck, J., Dehkordi, S. R., Colón, C. I., Li, R., Wong, I. T.-L., et al. (2022). Targeted profiling of human extrachromosomal DNA by CRISPR-CATCH. Nat. Genet. 54, 1746–1754. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01190-0
Israel, B. F., and Kenney, S. C. (2003). Virally targeted therapies for EBV-associated malignancies. Oncogene 22, 5122–5130. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206548
Jangra, S., Bharti, A., Lui, W.-Y., Chaudhary, V., Botelho, M. G., Yuen, K.-S., et al. (2021). Suppression of JAK-STAT signaling by Epstein-Barr virus tegument protein BGLF2 through recruitment of SHP1 phosphatase and promotion of STAT2 degradation. J. Virol. 95, e01027–21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01027-21
Jiang, J.-H., Wang, N., Li, A., Liao, W.-T., Pan, Z.-G., Mai, S.-J., et al. (2006). Hypoxia can contribute to the induction of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic cycle. J. Clin. Virol. 37, 98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2006.06.013
Jung, E. J., Lee, Y. M., Lee, B. L., Chang, M. S., and Kim, W. H. (2007). Lytic induction and apoptosis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer cell line with epigenetic modifiers and ganciclovir. Cancer Lett. 247, 77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2006.03.022
Jung, Y.-J., Choi, H., Kim, H., and Lee, S. K. (2014). MicroRNA miR-BART20-5p stabilizes Epstein-Barr virus latency by directly targeting BZLF1 and BRLF1. J. Virol. 88, 9027–9037. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00721-14
Kalla, M., Göbel, C., and Hammerschmidt, W. (2012). The lytic phase of Epstein-Barr virus requires a viral genome with 5-methylcytosine residues in CpG sites. J. Virol. 86, 447–458. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06314-11
Kenney, S. C., and Mertz, J. E. (eds) (2014). Regulation of the latent-lytic switch in Epstein–Barr virus. Semin. Cancer Biol. 26, 60–68. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.01.002
Kim, H., Choi, H., and Lee, S. K. (2016). Epstein-Barr virus microRNA miR-BART20-5p suppresses lytic induction by inhibiting BAD-mediated caspase-3-dependent apoptosis. J. Virol. 90, 1359–1368. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02794-15
Kraus, R. J., Cordes, B.-I. A., Sathiamoorthi, S., Patel, P., Yuan, X., Iempridee, T., et al. (2020). Reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus by HIF-1α requires p53. J. Virol. 94, e00722–20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00722-20
Kraus, R. J., Yu, X., Cordes, B.-I. A., Sathiamoorthi, S., Iempridee, T., Nawandar, D. M., et al. (2017). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α plays roles in Epstein-Barr virus’s natural life cycle and tumorigenesis by inducing lytic infection through direct binding to the immediate-early BZLF1 gene promoter. PLoS Pathog. 13:e1006404. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006404
Kumar, R., Whitehurst, C. B., and Pagano, J. S. (2014). The Rad6/18 ubiquitin complex interacts with the Epstein-Barr virus deubiquitinating enzyme, BPLF1, and contributes to virus infectivity. J. Virol. 88, 6411–6422. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00536-14
Kusano, S., and Ikeda, M. (2019). Interaction of phospholipid scramblase 1 with the Epstein-Barr virus protein BZLF1 represses BZLF1-mediated lytic gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 15104–15116. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008193
Kutok, J., and Wang, F. (2006). Spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus–associated diseases. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 1, 375–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathol.1.110304.100209
Lambert, S. A., Jolma, A., Campitelli, L. F., Das, P. K., Yin, Y., Albu, M., et al. (2018). The human transcription factors. Cell 172, 650–665. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.029
Lee, N., Moss, W. N., Yario, T. A., and Steitz, J. A. (2015). EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA. Cell 160, 607–618. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.015
Lee, N., Yario, T. A., Gao, J. S., and Steitz, J. A. (2016). EBV noncoding RNA EBER2 interacts with host RNA-binding proteins to regulate viral gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, 3221–3226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601773113
Li, J., Nagy, N., Liu, J., Gupta, S., Frisan, T., Hennig, T., et al. (2021). The Epstein-Barr virus deubiquitinating enzyme BPLF1 regulates the activity of topoisomerase II during productive infection. PLoS Pathog. 17:e1009954. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009954
Li, S., Yang, L., Li, Y., Yue, W., Xin, S., Li, J., et al. (2023). Epstein-Barr virus synergizes with BRD7 to Conquer c-Myc-mediated viral latency maintenance via chromatin remodeling. Microbiol. Spectr. 11, e01237–22. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01237-22
Liang, C.-L., Chen, J.-L., Hsu, Y.-P. P., Ou, J. T., and Chang, Y.-S. (2002). Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 gene is activated by transforming growth factor-β through cooperativity of Smads and c-Jun/c-Fos proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23345–23357. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107420200
Lin, K.-M., Weng, L.-F., Chen, S.-Y. J., Lin, S.-J., and Tsai, C.-H. (2023). Upregulation of IQGAP2 by EBV transactivator Rta and its influence on EBV life cycle. J. Virol. 97, e00540–23. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00540-23
Lin, Z., Wang, X., Fewell, C., Cameron, J., Yin, Q., and Flemington, E. K. (2010). Differential expression of the miR-200 family microRNAs in epithelial and B cells and regulation of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation by the miR-200 family member miR-429. J. Virol. 84, 7892–7897. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00379-10
Liu, J., Nagy, N., Ayala-Torres, C., Aguilar-Alonso, F., Morais-Esteves, F., Xu, S., et al. (2023). Remodeling of the ribosomal quality control and integrated stress response by viral ubiquitin deconjugases. Nat. Commun. 14:8315. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43946-0
Liu, X., and Cohen, J. I. (2016). Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) tegument protein BGLF2 promotes EBV reactivation through activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Virol. 90, 1129–1138. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01410-15
Lu, F., Wiedmer, A., Martin, K. A., Wickramasinghe, P. J., Kossenkov, A. V., and Lieberman, P. M. (2017). Coordinate regulation of TET2 and EBNA2 controls the DNA methylation state of latent Epstein-Barr virus. J. Virol 91:e00804–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00804-17
Lung, R. W., Hau, P. M., Yu, K. H., Yip, K. Y., Tong, J. H., Chak, W. P., et al. (2018). EBV-encoded miRNAs target ATM-mediated response in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 244, 394–407. doi: 10.1002/path.5018
Luo, R., Sun, L., Xia, Y., Qin, T., Zhang, S., Poon, H., et al. (2022). BioGPT: Generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining. Brief. Bioinform. 23:bbac409. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac409
Lupey-Green, L. N., Caruso, L. B., Madzo, J., Martin, K. A., Tan, Y., Hulse, M., et al. (2018). PARP1 stabilizes CTCF binding and chromatin structure to maintain Epstein-Barr virus latency type. J. Virol. 92, e00755–18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00755-18
Lupey-Green, L. N., Moquin, S. A., Martin, K. A., McDevitt, S. M., Hulse, M., Caruso, L. B., et al. (2017). PARP1 restricts Epstein Barr Virus lytic reactivation by binding the BZLF1 promoter. Virology 507, 220–230. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.04.006
Lv, D.-W., Zhang, K., and Li, R. (2018). Interferon regulatory factor 8 regulates caspase-1 expression to facilitate Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in response to B cell receptor stimulation and chemical induction. PLoS Pathog. 14:e1006868. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006868
Mansouri, S., Wang, S., and Frappier, L. (2013). A role for the nucleosome assembly proteins TAF-Iβ and NAP1 in the activation of BZLF1 expression and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. PLoS One 8:e63802. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063802
Martin, K. A., Lupey, L. N., and Tempera, I. (2016). Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1 mediates epigenetic changes in host gene expression through PARP1. J. Virol. 90, 8520–8530. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01180-16
Masud, H. A., Watanabe, T., Yoshida, M., Sato, Y., Goshima, F., Kimura, H., et al. (2017). Epstein-Barr virus BKRF4 gene product is required for efficient progeny production. J. Virol. 91, e00975–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00975-17
Mesri, E. A., Feitelson, M. A., and Munger, K. (2014). Human viral oncogenesis: A cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe 15, 266–282. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.011
Miller, G., El-Guindy, A., Countryman, J., Ye, J., and Gradoville, L. (2007). Lytic cycle switches of oncogenic human gammaherpesviruses1. Adv. Cancer Res. 97, 81–109. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97004-3
Müller-Durovic, B., Jäger, J., Engelmann, C., Schuhmachers, P., Altermatt, S., Schlup, Y., et al. (2024). A metabolic dependency of EBV can be targeted to hinder B cell transformation. Science 385:eadk4898. doi: 10.1126/science.adk4898
Münz, C. (2019). Latency and lytic replication in Epstein–Barr virus-associated oncogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17, 691–700. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0249-7
Murata, T., and Tsurumi, T. (2014). Switching of EBV cycles between latent and lytic states. Rev. Med. Virol. 24, 142–153. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1780
Murata, T., Hotta, N., Toyama, S., Nakayama, S., Chiba, S., Isomura, H., et al. (2010). Transcriptional repression by sumoylation of Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 protein correlates with association of histone deacetylase. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 23925–23935. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.095356
Murata, T., Kondo, Y., Sugimoto, A., Kawashima, D., Saito, S., Isomura, H., et al. (2012). Epigenetic histone modification of Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter during latency and reactivation in Raji cells. J. Virol. 86, 4752–4761. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06768-11
Murata, T., Narita, Y., Sugimoto, A., Kawashima, D., Kanda, T., and Tsurumi, T. (2013). Contribution of myocyte enhancer factor 2 family transcription factors to BZLF1 expression in Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency. J. Virol. 87, 10148–10162. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01002-13
Murata, T., Noda, C., Saito, S., Kawashima, D., Sugimoto, A., Isomura, H., et al. (2011). Involvement of Jun dimerization protein 2 (JDP2) in the maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus latency. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 22007–22016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.199836
Murata, T., Sato, Y., Nakayama, S., Kudoh, A., Iwahori, S., Isomura, H., et al. (2009). TORC2, a coactivator of cAMP-response element-binding protein, promotes Epstein-Barr virus reactivation from latency through interaction with viral BZLF1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 8033–8041. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808466200
Mure, F., Panthu, B., Zanella-Cléon, I., Delolme, F., Manet, E., Ohlmann, T., et al. (2018). Epstein-Barr virus protein EB2 stimulates translation initiation of mRNAs through direct interactions with both poly (A)-binding protein and eukaryotic initiation factor 4G. J. Virol. 92, e01917–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01917-17
Myers, J. E., Schaal, D. L., Nkadi, E. H., Ward, B., Bienkowska-Haba, M., Sapp, M., et al. (2023). Retinoblastoma protein is required for Epstein-Barr virus replication in differentiated epithelia. J. Virol. 97, e01032–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01032-22
Nawandar, D. M., Ohashi, M., Djavadian, R., Barlow, E., Makielski, K., Ali, A., et al. (2017). Differentiation-dependent LMP1 expression is required for efficient lytic Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in epithelial cells. J. Virol 91, e02438–16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02438-16
Nawandar, D., Wang, A., Makielski, K., Lee, D., Ma, S., Barlow, E., et al. (2015). Differentiation-dependent KLF4 expression promotes lytic Epstein-Barr virus infection in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 11:e1005195. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005195
Pei, Y., Wong, J. H.-Y., and Robertson, E. S. (2020). Herpesvirus epigenetic reprogramming and oncogenesis. Annu. Rev. Virol. 7, 309–331. doi: 10.1146/annurev-virology-020420-014025
Pope, S. D., and Medzhitov, R. (2018). Emerging principles of gene expression programs and their regulation. Mol. Cell 71, 389–397. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.017
Qiu, J., and Thorley-Lawson, D. A. (2014). EBV microRNA BART 18-5p targets MAP3K2 to facilitate persistence in vivo by inhibiting viral replication in B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 11157–11162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406136111
Raver, R. M., Panfil, A. R., Hagemeier, S. R., and Kenney, S. C. (2013). The B-cell-specific transcription factor and master regulator Pax5 promotes Epstein-Barr virus latency by negatively regulating the viral immediate early protein BZLF1. J. Virol. 87, 8053–8063. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00546-13
Rennekamp, A. J., Wang, P., and Lieberman, P. M. (2010). Evidence for DNA hairpin recognition by Zta at the Epstein-Barr virus origin of lytic replication. J. Virol. 84, 7073–7082. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02666-09
Reusch, J. A., Nawandar, D. M., Wright, K. L., Kenney, S. C., and Mertz, J. E. (2015). Cellular differentiation regulator BLIMP1 induces Epstein-Barr virus lytic reactivation in epithelial and B cells by activating transcription from both the R and Z promoters. J. Virol. 89, 1731–1743. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02781-14
Robinson, A. R., Kwek, S. S., and Kenney, S. C. (2012). The B-cell specific transcription factor, Oct-2, promotes Epstein-Barr virus latency by inhibiting the viral immediate-early protein, BZLF1. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1002516. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002516
Robinson, A. R., Kwek, S. S., Hagemeier, S. R., Wille, C. K., and Kenney, S. C. (2011). Cellular transcription factor Oct-1 interacts with the Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 protein to promote disruption of viral latency. J. Virol. 85, 8940–8953. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00569-11
Saito, S., Murata, T., Kanda, T., Isomura, H., Narita, Y., Sugimoto, A., et al. (2013). Epstein-Barr virus deubiquitinase downregulates TRAF6-mediated NF-κB signaling during productive replication. J. Virol. 87, 4060–4070. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02020-12
Sato, Y., Watanabe, T., Suzuki, C., Abe, Y., Masud, H. A., Inagaki, T., et al. (2019). S-like-phase cyclin-dependent kinases stabilize the Epstein-Barr virus BDLF4 protein to temporally control late gene transcription. J. Virol. 93, e01707–18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01707-18
Scott, R. S. (2017). Epstein–Barr virus: A master epigenetic manipulator. Curr. Opin. Virol. 26, 74–80. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2017.07.017
Siddiqi, U. Z., Vaidya, A. S., Li, X., Marcon, E., Tsao, S. W., Greenblatt, J., et al. (2019). Identification of ARKL1 as a negative regulator of Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. J. Virol. 93, e00989–19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00989-19
Speck, S. H., Chatila, T., and Flemington, E. (1997). Reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus: Regulation and function of the BZLF1 gene. Trends Microbiol. 5, 399–405. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(97)01129-3
Spitz, F., and Furlong, E. E. (2012). Transcription factors: From enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 613–626. doi: 10.1038/nrg3207
Su, M.-T., Wang, Y.-T., Chen, Y.-J., Lin, S.-F., Tsai, C.-H., and Chen, M.-R. (2017). The SWI/SNF chromatin regulator BRG1 modulates the transcriptional regulatory activity of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase processivity factor BMRF1. J. Virol. 91, e02114–16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02114-16
Tian, R., Abarientos, A., Hong, J., Hashemi, S. H., Yan, R., Dräger, N., et al. (2021). Genome-wide CRISPRi/a screens in human neurons link lysosomal failure to ferroptosis. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 1020–1034. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00862-0
Tian, R., Gachechiladze, M. A., Ludwig, C. H., Laurie, M. T., Hong, J. Y., Nathaniel, D., et al. (2019). CRISPR interference-based platform for multimodal genetic screens in human iPSC-derived neurons. Neuron 104, 239–55.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.07.014
Uddin, M. K., Watanabe, T., Arata, M., Sato, Y., Kimura, H., and Murata, T. (2023). Epstein-Barr virus BBLF1 mediates secretory vesicle transport to facilitate mature virion release. J. Virol. 97:e0043723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00437-23
Urier, G., Buisson, M., Chambard, P., and Sergeant, A. (1989). The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 8, 1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x
van Gent, M., Reich, A., Velu, S. E., and Gack, M. U. (2021). Nonsense-mediated decay controls the reactivation of the oncogenic herpesviruses EBV and KSHV. PLoS Biol. 19:e3001097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001097
Van Sciver, N., Ohashi, M., Nawandar, D. M., Pauly, N. P., Lee, D., Makielski, K. R., et al. (2021b). ΔNp63α promotes Epstein-Barr virus latency in undifferentiated epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 17:e1010045. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010045
Van Sciver, N., Ohashi, M., Pauly, N. P., Bristol, J. A., Nelson, S. E., Johannsen, E. C., et al. (2021a). Hippo signaling effectors YAP and TAZ induce Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) lytic reactivation through TEADs in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 17:e1009783. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009783
Verma, D., Bais, S., Gaillard, M., and Swaminathan, S. (2010). Epstein-Barr virus SM protein utilizes cellular splicing factor SRp20 to mediate alternative splicing. J. Virol. 84, 11781–11789. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01359-10
Verma, D., Church, T. M., and Swaminathan, S. (2020). Epstein–Barr virus co-opts TFIIH component XPB to specifically activate essential viral lytic promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 13044–13055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000625117
Walsh, C. T., Garneau-Tsodikova, S., and Gatto, G. J. Jr. (2005). Protein posttranslational modifications: The chemistry of proteome diversifications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44, 7342–7372. doi: 10.1002/anie.200501023
Watanabe, T., Narita, Y., Yoshida, M., Sato, Y., Goshima, F., Kimura, H., et al. (2015). The Epstein-Barr virus BDLF4 gene is required for efficient expression of viral late lytic genes. J. Virol. 89, 10120–10124. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01604-15
Woellmer, A., and Hammerschmidt, W. (2013). Epstein–Barr virus and host cell methylation: Regulation of latency, replication and virus reactivation. Curr. Opin. Virol. 3, 260–265. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.03.005
Wu, X., Zeng, Y., Das, A., Jo, S., Zhang, T., Patel, P., et al. (2024). reguloGPT: Harnessing GPT for knowledge graph construction of molecular regulatory pathways. bioRxiv [Preprint] doi: 10.1101/2024.01.27.577521
Xu, H., Li, X., Rousseau, B. A., Akinyemi, I. A., Frey, T. R., Zhou, K., et al. (2022). IFI16 partners with KAP1 to maintain Epstein-Barr virus latency. J. Virol. 96, e01028–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01028-22
Yang, Y.-C., Yoshikai, Y., Hsu, S.-W., Saitoh, H., and Chang, L.-K. (2013). Role of RNF4 in the ubiquitination of Rta of Epstein-Barr virus. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 12866–12879. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.413393
Yin, Q., Wang, X., Fewell, C., Cameron, J., Zhu, H., Baddoo, M., et al. (2010). MicroRNA miR-155 inhibits bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling and BMP-mediated Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. J. Virol. 84, 6318–6327. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00635-10
Yiu, S. P., Dorothea, M., Hui, K. F., and Chiang, A. K. (2020). Lytic induction therapy against Epstein–Barr virus-associated malignancies: Past, present, and future. Cancers 12:2142. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082142
Yiu, S. P., Guo, R., Zerbe, C., Weekes, M. P., and Gewurz, B. E. (2022). Epstein-Barr virus BNRF1 destabilizes SMC5/6 cohesin complexes to evade its restriction of replication compartments. Cell Rep. 38:110411. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110411
Yiu, S. P., Zerbe, C., Vanderwall, D., Huttlin, E. L., Weekes, M. P., and Gewurz, B. E. (2023). An Epstein-Barr virus protein interaction map reveals NLRP3 inflammasome evasion via MAVS UFMylation. Mol. Cell 83, 2367–2386.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.05.018
Ylä-Anttila, P., Gupta, S., and Masucci, M. G. (2021). The Epstein-Barr virus deubiquitinase BPLF1 targets SQSTM1/p62 to inhibit selective autophagy. Autophagy 17, 3461–3474. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1874660
Yu, J., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Wei, Z., and Pei, Y. (2024). Decoding critical targets and signaling pathways in EBV-mediated diseases using large language models. Viruses 16:1660. doi: 10.3390/v16111660
Yu, X., Wang, Z., and Mertz, J. E. (2007). ZEB1 regulates the latent-lytic switch in infection by Epstein-Barr virus. PLoS Pathog. 3:e194. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030194
Zhang, H., Wong, J. P., Ni, G., Cano, P., Dittmer, D. P., and Damania, B. (2022). Mitochondrial protein, TBRG4, modulates KSHV and EBV reactivation from latency. PLoS Pathog. 18:e1010990. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010990
Zhang, K., Lv, D.-W., and Li, R. (2017). B cell receptor activation and chemical induction trigger caspase-mediated cleavage of PIAS1 to facilitate Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Cell Rep. 21, 3445–3457. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.071
Zhang, W., Han, D., Wan, P., Pan, P., Cao, Y., Liu, Y., et al. (2016). ERK/c-Jun recruits Tet1 to induce Zta expression and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation through DNA demethylation. Sci. Rep. 6:34543. doi: 10.1038/srep34543
Zhang, Y., Jiang, C., Trudeau, S., Narita, Y., Zhao, B., Teng, M., et al. (2020). Histone loaders CAF1 and HIRA restrict Epstein-Barr virus B-cell lytic reactivation. Mbio 11, e01063–20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01063-20
Zhao, M., Nanbo, A., Becnel, D., Qin, Z., Morris, G. F., Li, L., et al. (2020). Ubiquitin modification of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate early transactivator zta. J. Virol. 94, e01298–20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01298-20
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus, virus-host interaction, reactivation, immediate-early proteins, regulation, novel insights
Citation: Wang Y, Yu J and Pei Y (2024) Identifying the key regulators orchestrating Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Front. Microbiol. 15:1505191. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1505191
Received: 02 October 2024; Accepted: 14 November 2024;
Published: 05 December 2024.
Edited by:
Jinlin Li, Uppsala University, SwedenCopyright © 2024 Wang, Yu and Pei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yonggang Pei, cGVpeWdAc3VzdGVjaC5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yaohao Wang
Yaohao Wang Jingwen Yu
Jingwen Yu Yonggang Pei
Yonggang Pei