- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Gansu Agricultural University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Lanzhou Witsen Biotechnology Co., LTD, Lanzhou, China
- 3Department of Disease Control, Gansu Fishery Technology Extension Station, Lanzhou, China
Aeromonas sobria is an opportunistic pathogen that can infect humans, animals and aquatic species, which is widely distributed in different aquatic environments and products. In recent years, with the rapid expansion of intensive aquaculture, the disease caused by A. sobria has occurred. This study aims to understand the pathogenic characteristics of A. sobria and provide scientific basis for the prevention and control of the epidemic. The dominant strain As012 was isolated from the diseased rainbow trout during the outbreak. Through physiological and biochemical experiments, sequencing and phylogenetic tree analysis of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes, the strain As012 was identified as A. sobria. The clinical signs of the diseased rainbow trout in the experimental infection were consistent with those in the farm, and the LD50 was 1.0 × 106.6 CFU/mL. The histopathological lesions in the gills, heart, liver, spleen and intestines were mainly extensive hemorrhage. In addition, eight virulence genes were screened from strain As012, including Act, Aer, AexT4, Alt, ahyB, ascV, Nuc and Hly. The strain As012 can grow in the environment with pH 1–11, temperature 8–43°C and NaCl concentration 0–8%. The drug sensitivity results showed that it was resistant to 12 antibiotics including penicillin G, vancomycin, and clindamycin, and highly sensitive to 16 antibiotics including cefazolin, ciprofloxacin, and furadantin. The results showed that A. sobria, the dominant strain isolated from diseased rainbow trout, was the main pathogen causing the epidemic in the farm. The strain As012 has a very wide range of growth and strong pathogenicity, causing widespread hemorrhaging in various tissues of rainbow trout. It is multi-resistant, but highly sensitive to cephalosporins, quinolones, nitrofurans and sulfonamides. Among them, ciprofloxacin will be one of the effective antibiotics for preventing and controlling A. sobria infection in Chinese aquaculture.
1 Introduction
The rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) belongs to the order Salmoniformes, family Salmonidae, and genus Oncorhynchus. It is native to North America and has become one of the most widely farmed cold-water fish species in the world (Walter Devaa et al., 2023). At present, rainbow trout has been farmed in China for 65 years (Guo et al., 2016), and is favored by consumers for its fast growth, delicious meat, and rich nutrition. According to the relevant data from the Food and Aquaculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the world production of rainbow trout increased from 848,100 tons to 7.524 million tons during the period 2010–2018 (FAO, 2020). In recent years, with the gradual deterioration of the global water quality (Macêdo et al., 2021) and the continuous expansion of intensive aquaculture scale (Naderi et al., 2017; da Costa et al., 2019), bacterial diseases of rainbow trout have been continuously occurring. Among them, Aeromonas hydrophila (Cao et al., 2020) and Aeromonas salmonicida (Liu et al., 2022) are common pathogens in rainbow trout, while there are few reports of A. sobria infection in this aquatic fish.
A. sobria belongs to family Aeromonadaceae and genus Aeromonas. It is a Gram-negative, single-flagellated, rod-shaped, facultative anaerobic bacterium that prefers moderate temperatures (Popoff and Lallier, 1984; Yang et al., 2017). It is widely distributed in different aquatic environments and aquatic products, and is an opportunistic pathogen that can co-infect humans, livestock and aquaticanimals (Mesías et al., 2020; Majeed et al., 2023). In human reports, infection with A. sobria can cause meningitis, fasciitis, gastroenteritis, bacteremia, and even death due to sepsis in severe cases (Spadaro et al., 2014; Parras et al., 1993; Gelbart et al., 1985). In aquaculture, A. sobria can infect various aquatic animals, including tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) (Li and Cai, 2011; Yang et al., 2021), African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) (Abdel Rahman et al., 2023), sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) (Soliman, 2022), Koi Carp (Cyprinus carpio) (Byadgi et al., 2018), grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) (Mayrhofer et al., 2020), loach (Misgurnus mizolepis) (Yu et al., 2015) and bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) (Yang et al., 2017), causing major symptoms such as skin ulcers, tail rot, fin corrosion, ascites, and hemorrhagic septicemia. Among them, the incidence rate of A. sobria infection in carp is 100% (Han et al., 2005) and the mortality rate is 66.67% (Abdel Rahman et al., 2022), which has caused huge economic losses to the aquaculture industry. Studies have shown that the clinical signs of specific bacterial isolates are different in different fish (Chen et al., 2019). However, the clinical signs and pathogenicity of A. sobria infected rainbow trout are still unknown.
Bacterial pathogens often invade host cells and cause host diseases or even death through adhesion, invasion, proliferation in vivo and toxin production, which involves the secretion and expression of multiple virulence factors (Qian et al., 2021). Among them, virulence factors in Aeromonas include aerolysin (Aer), cytotoxic enterotoxin (Act, Alt, Ast), aggregation substance (Asa), polar flagella (Fla), lateral flagella (LafA), hemolysin (hly), lipase (Lip), serine protease (Ser), elastase (ahyB, ela), cholesterol acyltransferase (gcaT), nuclease (Nuc), DNase (exu), Type III secretion system (AscV, AexT4, aopP), etc. (Sen and Rodgers, 2004; Nam and Joh, 2007; Nawaz et al., 2010; Burr and Frey, 2007; Alwan et al., 2022; Chacón et al., 2004). However, the secretion and expression of virulence factors are often closely related to the growth characteristics of strains (De Silva et al., 2018). Up to now, there is still a lack of relevant research on virulence factors, growth characteristics, and histopathological characteristics of A. sobria.
As we all know, drug susceptibility testing is an important method to evaluate the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, and is also the scientific basis for effective treatment of bacterial diseases. Studies on the drug sensitivity of bacteria in the genus Aeromonas showed that A. hydrophila derived from the Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) was sensitive to quinolones, aminoglycosides, nitrofurans, chloramphenicol, and tetracyclines (Bakiyev et al., 2022); A. veronii isolated from the Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) is sensitive to aminoglycosides, carbapenems, and nitrofurans (Chen et al., 2019); A. caviae from the source of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) is highly sensitive to enrofloxacin, norfloxacin, streptomycin, and amikacin (Xue et al., 2022). However, current research on the antibiotic susceptibility of A. sobria is limited. Among them, the A. sobria derived from tilapia has multi-resistance to commonly used antibiotics (Li and Cai, 2011). However, the sensitivity of A. sobria isolated from rainbow trout to antibiotics is still unclear.
In mid-June 2023, the dominant strain As012 was isolated from diseased rainbow trout during the epidemic. A large number of experiments were performed, including physiological and biochemical identification, sequencing analysis and phylogenetic tree construction of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes, experimental infection, screening of virulence gene, observation of growth characteristics, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. The purpose is to identify the pathogenic bacteria of this outbreak and provide scientific basis for prevention and control of the epidemic, and lay a foundation for the study of the pathogenic characteristics and mechanism of isolate As012.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 The situation of the farm during the outbreak of the epidemic
A rainbow trout farm in Gansu Province mainly raised rainbow trout and a small amount of Gansu golden trout in cages. In mid-June 2023, during the late stage of the large-scale melting of ice and snow, a large number of rainbow trout in the farm suddenly died. Among them, the death occurred in rainbow trout weighing about 15 g, 30 g and 300 g, and in Gansu golden trout weighing about 300 g, but mainly in rainbow trout weighing 15 g and 30 g. The large fish that died had significant bleeding in the fins and tail, while the small fish that died did not have obvious bleeding characteristics, and some even had no visible lesions on their body surface. Ultimately, the mortality rate of rainbow trout in the farm reached 65%. In order to determine the pathogen of this outbreak, thirty diseased rainbow trout with obvious symptoms were randomly selected and quickly brought back to the laboratory.
2.2 Isolation of pathogens and observation of clinical signs of diseased rainbow trout
2.2.1 Parasitological evaluation
Three rainbow trout were randomly selected and their muscles, hearts, livers, kidneys, spleens and brains were collected and examined carefully for parasites under an optical microscope (CX23, Olympus, Japan).
2.2.2 Viral evaluation
Refer to the diagnosis of infectious hematopoietic necrosis in the national standards of the People's Republic of China (GB/T 15805.2-2017). The liver, kidney and spleen of 5 rainbow trout were taken as one sample, and a total of 3 samples were collected. After homogenization, approximately 50 mg of each sample was taken for viral RNA extraction. The remaining samples were diluted with DMEM medium (Gibco, China) containing 1% penicillin and streptomycin, and incubated at 15°C for 2 h. Then, the supernatant of the diluted solution was inoculated into a monolayer of carp epithelioma cells (EPC) and cultured at 15°C for 2 weeks. At the same time, viral RNA was extracted from the homogenized tissue using a viral RNA extraction kit (TaKaRa, Japan) and reverse transcribed into cDNA. Next, using cDNA as template, PCR amplification was performed based on specific primers for the infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) G gene (F: 5′-AGAGATCCCTACACCAGAGAC-3′ and R: 5′-TTGCACGGAAACAACACCACCA-3′, 693 bp) and the infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) VP2 gene (F: 5′-GTGCTGGCCACAAACGACAAC-3′ and R: 5′-AATTGGTCTGCCGTTCCTA-3′, 599 bp) (Lopez-Jimena et al., 2010).
2.2.3 Isolation of pathogenic bacteria and observation of clinical signs
under sterile conditions, three rainbow trout with typical clinical signs were disinfected with 75% alcohol and then dissected to observe the lesions. Meanwhile, the lesions and coelomic cavities of liver, kidney and spleen were dipped with sterile inoculating loops and streaked on the Luria-Bertani (LB) medium plate. The plates were incubated at 18°C for 32 h. Then, based on the morphological characteristics of the colonies, different colonies were selected and purified for three times. Finally, the bacterial solution was mixed with glycerol at 6:4 (v:v) and stored at −80°C.
2.3 Identification of strain As012
2.3.1 Identification of physiological and biochemical characteristics
The physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain As012 were determined using microbiochemical reaction tube (Hangzhou Binhe Microbial Reagent Co., LTD., China). These included arginine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, lysine decarboxylase, amino acid control, citrate, nitrate reduction, urea, esculin, peptone water, β-galactoside (ONPG), sucrose, maltose, xylose, hydrogen sulfide (H2S), glucose, arginine dihydrolase, lactose, mannose, wood alcohol, trehalose, ethylene glycol, N-acetylglucosamine, meliobiose, fructose, phosphate-glucose peptone water, sorbitol and phenylalanine deaminase. At the same time, the purified strain As012 was cultured on starch-agar plate at 18°C for 32 h, and then the changes of the colony were observed by drops of iodine solution. Among them, the standard strain of A. sobria (ATCC 43979) was used as a control. The results were observed after incubation according to the manufacturer's instructions.
2.3.2 Identification of molecular biology
The genomic DNA of strain As012 obtained by bacterial DNA extraction kit (TIANGEN, China) was used as template for PCR amplification based on specific primers of 16S rRNA gene (27F: 5′-AGAGTTTGATCATGGCTCAG-3′ and 1492R: 5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) (Borrell et al., 1997) and gyrB gene (3F: 5′-TCCGGCGGTCTGCACGGCGT-3′ and 14R: 5′-TTGTCCGGGTTGTACTCGTC-3′) (Yáñez et al., 2003). The PCR reaction system was Premix Taq™ (TaKaRa, Japan) 12.5 μL, template DNA 1 μL, upstream and downstream primers each 1 μL, and ddH2O 9.5 μL. The PCR reaction conditions were predenaturation at 94°C for 5 min, 35 cycles of amplification with denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing at 60°C (16S rRNA gene) or 55°C (gyrB gene) for 30 s, extension at 72°C for 2 min; final extension at 72°C for 5 min and then store at 4°C. After the PCR products were detected to be qualified by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, they were sent to Jinweizhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) for sequencing using the ABI 3730 sequencing platform. The sequencing results were spliced and compared by BLAST, and the phylogenetic trees of isolate As012 were constructed using MEGA 11.0 software.
2.4 Experimental infection
Eighty healthy rainbow trout (weight 30 ± 6 g) were provided by the Cold Water Fish Breeding Center in Jingtai County, Gansu Province (Baiyin, China). They were kept in circulating water at 15 ± 1°C and fed with commercial fish food (Shandong Hanye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) at 9:00 and 17:30 every day. First, two rainbow trout that had been domesticated for two weeks were randomly selected and their livers, kidneys, and spleens were taken for bacterial isolation. Then, under the condition of determining the absence of pathogenic bacteria infection, the rainbow trout were randomly divided into six groups, with 10 fish in each group. Meanwhile, strain As012 cultured at 18°C for 24 h was washed three times with 0.85% physiological saline and resuspended. The concentration of bacterial suspension measured by plate counting method was 1.0 × 109 CFU/mL. Subsequently, 1 mL of the original bacterial suspension was taken, and the concentrations of bacterial suspension obtained by gradient dilution method were 1.0 × 108, 1.0 × 107, 1.0 × 106 and 1.0 × 105 CFU/mL in sequence. Next, rainbow trout in five experimental groups were injected with different concentrations of bacterial solution through the base of their pectoral fins (200 μL/fish), while the control group was injected with the same volume of physiological saline. Finally, the number of rainbow trout deaths was counted at 17:00 every day and observed continuously for 7 days. In addition, bacteria were isolated again from the liver, spleen, kidney and coelomic cavity of experimentally infected rainbow trout and identified according to the method in Part 1.3.2. All experimental procedures were conducted in strict accordance with the guidelines of the Animal Experimental Ethics Committee of Gansu Agricultural University.
2.5 Histopathological observation
The gills, heart, liver, spleen and intestinal tissues of naturally dead rainbow trout were fixed in 10% neutral formalin solution for 15 days. The paraffin sections (4 μm) were prepared according to conventional methods. After HE staining, the sections were scanned using a digital microtome scanner (DX1), and the SlideViewer software was used to select the field of view.
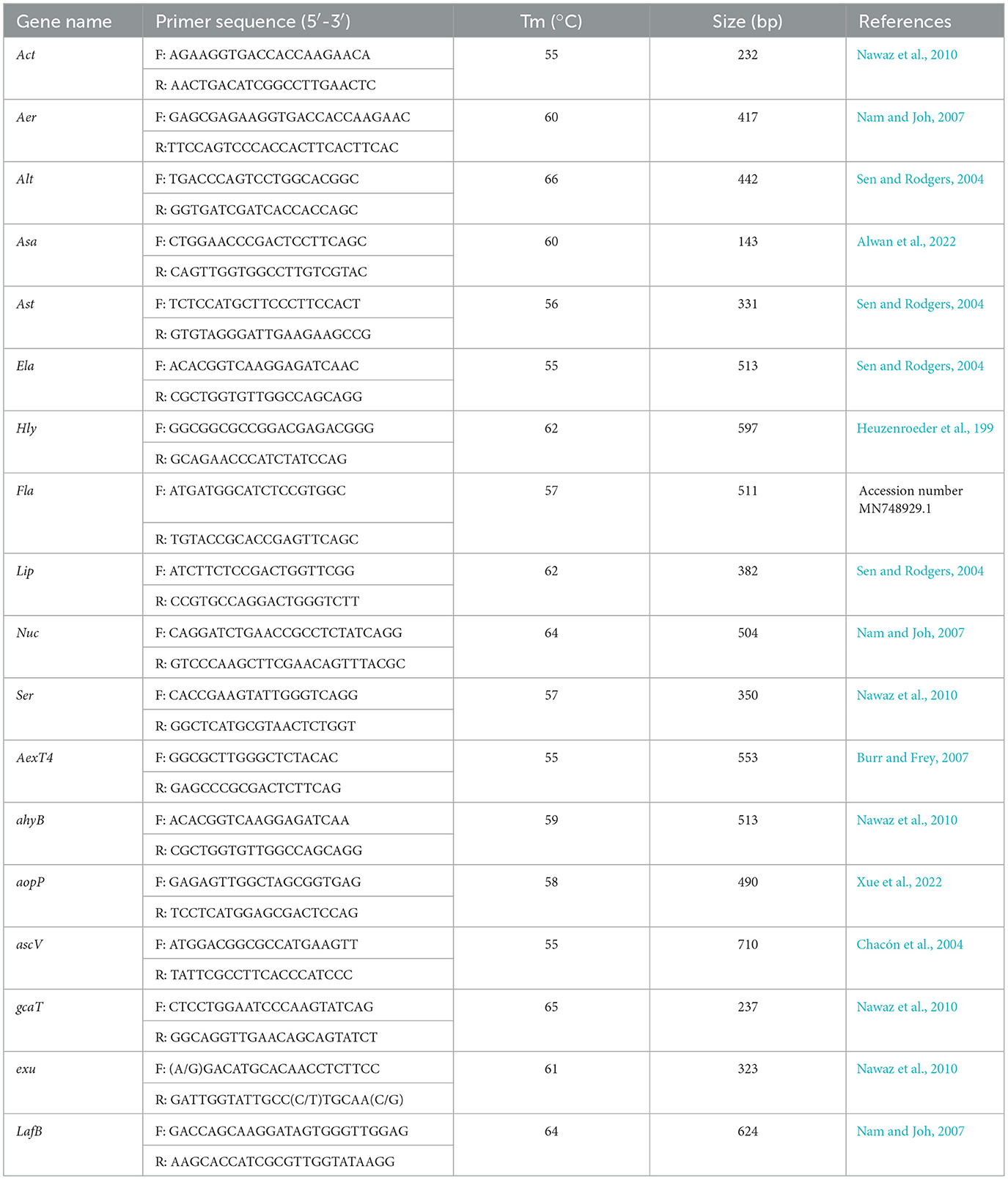
2.6 Screening of virulence genes
The virulence genes of strain As012 were screened based on the virulence genes reported in the genus Aeromonas. Among them, 18 virulence genes were Act, Aer, Alt, Asa, Ast, Ela, Hly, Fla, Lip, Nuc, Ser, AexT4, ahyB, aopP, ascV, gcaT, exu and LafB. The specific information of all primers is shown in Table 1. The reaction system of PCR amplification was carried out according to Part 1.3.2. Each PCR reaction commenced with predenaturation at 94°C for 5 min, then 35 cycles of amplification, and finally extension at 72°C for 5 min. Each cycle included denaturation at 94°C for 1 min, annealing for 30 s and extension at 72°C for 2 min. The annealing temperatures were performed according to Tm values in Table 1. The PCR products were detected by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis.
2.7 Growth characteristics
When strain As012 was cultured in LB medium until the OD600nm value reached 1.5, the bacterial solution was added into the new LB medium at a ratio of 1‰ (v:v) and cultured at 200 rpm. The absorbance value (OD600nm) under different temperature, pH and NaCl concentration was determined. Among them, the effect of temperature on the growth of strain As012 were assessed at 8°C, 13°C, 18°C, 23°C, 28°C, 33°C, 38°C, 43°C, and 48°C in LB medium with pH value of 7 and NaCl concentration of 1%. The impact of pH on the growth was investigated in LB medium at 18°C, 1% NaCl concentration and pH values of 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 and 13. The effects of NaCl concentrations on the growth were evaluated in LB medium with temperature of 18°C, pH of 7 and NaCl concentration of 0–8%.
2.8 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
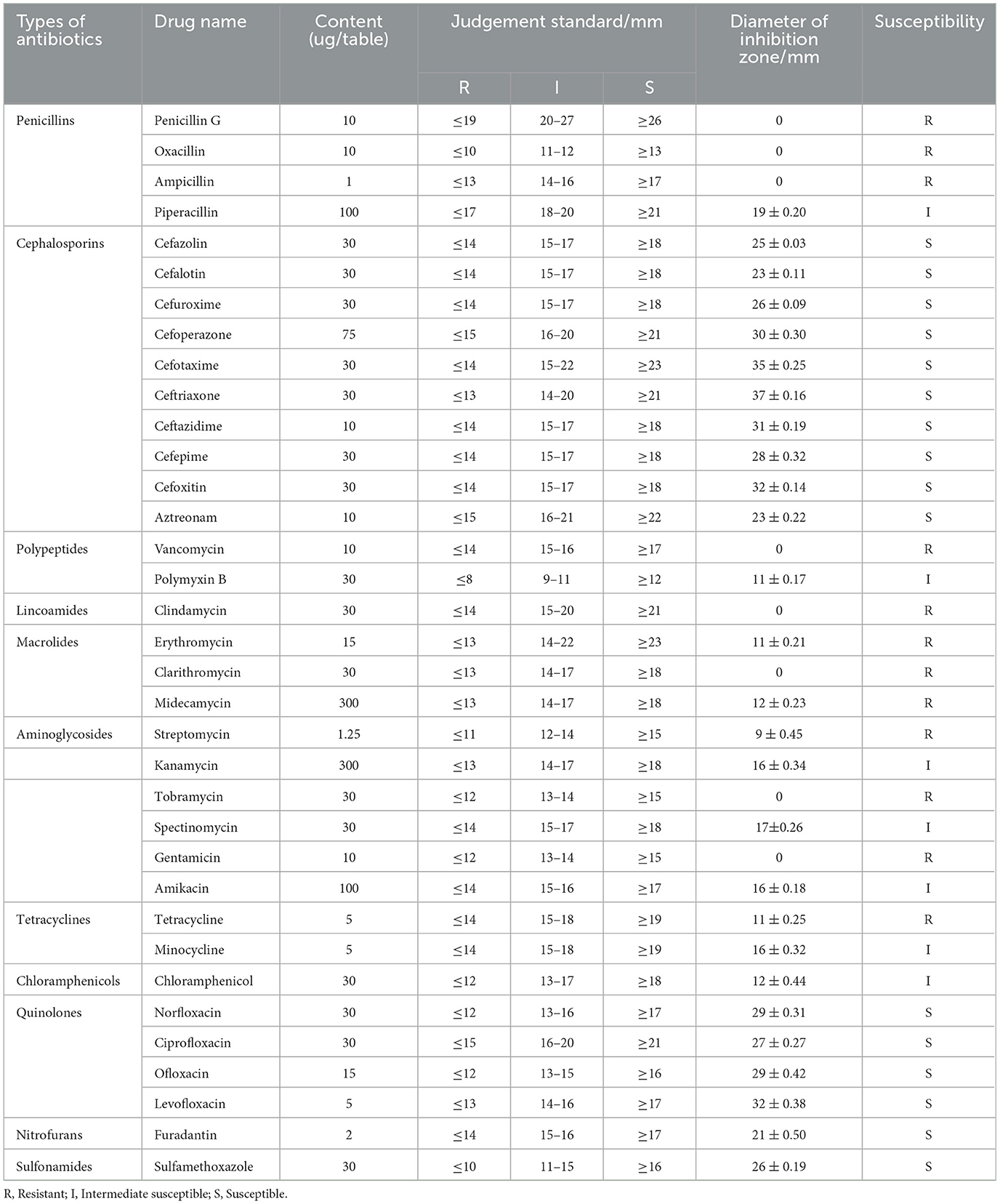
The sensitivity of strain As012 to antibiotics was tested using the disk diffusion method (Hangzhou Binhe Microbial Reagents Co., LTD., China), which contained 35 antibiotics. According to the instructions provided by the manufacturer, 100 uL bacterial solution with a concentration of 1 × 105 CFU/mL was evenly spread on the LB medium plate, and then the drug-sensitive papers were affixed to the plate using sterile tweezers. Among them, each antibiotic pasted 3 drug-sensitive papers. Next, after incubating the plates at 18°C for 24 h, the diameters of the inhibition zones for each antibiotic were measured. Finally, the average diameter of the inhibition zones of the three drug-sensitive papers was used as the antibacterial result of the antibiotic. The sensitivity of strain As012 to antibiotics was determined based on the range of the inhibition zone set by the manufacturer.
3 Results
3.1 Isolation of pathogens and observation of clinical signs of diseased rainbow trout
3.1.1 Isolation of pathogenic bacteria
No parasites were found in the tissue during parasitological evaluation. During the virological evaluation, no cytopathic effect was observed in EPCs, and no target bands were detected in PCR amplification. Therefore, the rainbow trout in this farm have been ruled out of the possibility of parasitic and viral infection. During the bacteriological examination, the dominant strain isolated was temporarily named As012.
3.1.2 Observation of clinical signs of diseased rainbow trout
The diseased rainbow trout in the farm showed obvious clinical signs, including white gill filaments with large amounts of mucus (Figure 1A), hyperemia on the body surface (Figure 1B), swelling, bleeding, and decay of the fins (Figures 1B, 1C). The liver showed punctate hemorrhage and grayish necrotic lesions (Figure 1D). The intestines were congested, hemorrhagic, and devoid of chyme (Figure 1E).
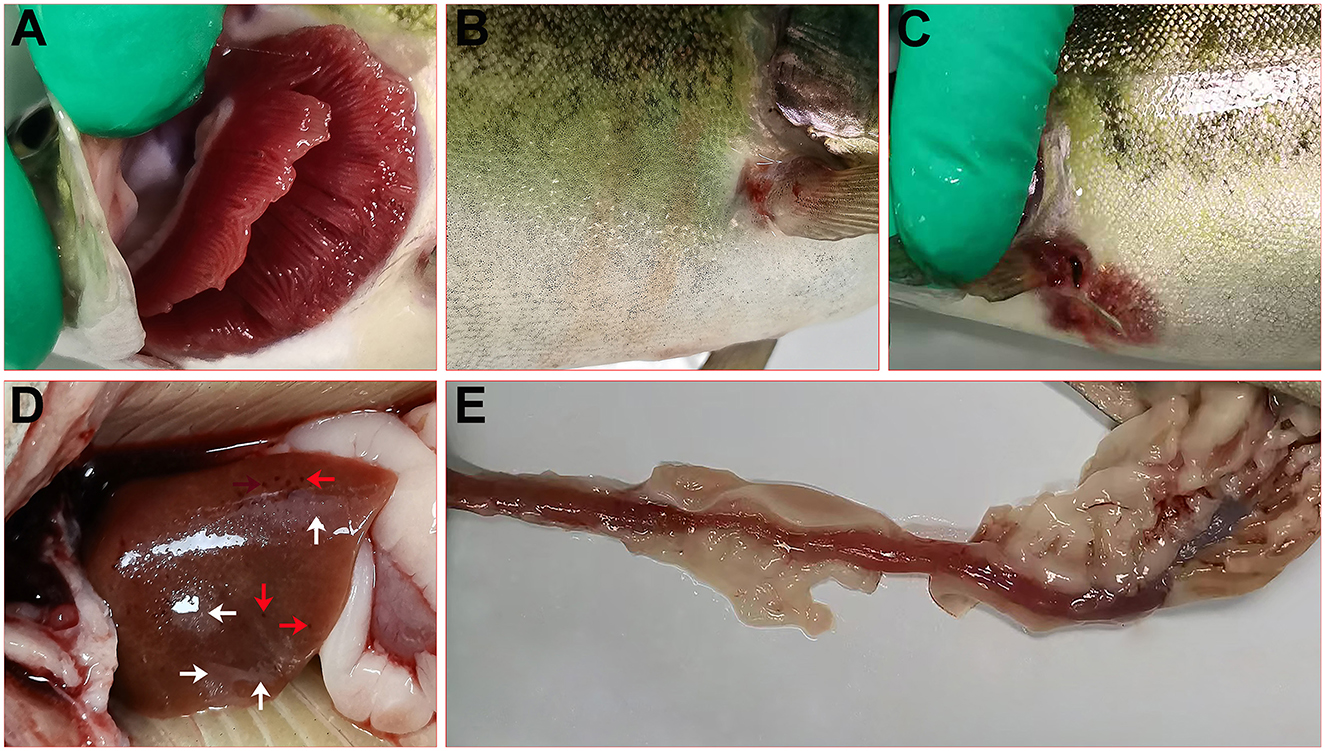
Figure 1. Clinical signs of diseased rainbow trout. (A) White gill filaments with large amounts of mucus. (B) Hyperemia on the body surface and swelling of the fins. (C) Bleeding and decay of the fins. (D) Bleeding (red arrow) and necrosis (white arrow) in the liver. (E) Intestinal congestion and hemorrhage.
3.2 Identification of strain As012
3.2.1 Physiological and biochemical identification
The results of physiological and biochemical tests were shown in Table 2. The strain As012 showed positive reaction in ornithine decarboxylase, lysine decarboxylase, amino acid control, urea, sucrose, maltose, xylose, glucose, lactose, mannose, wood alcohol, trehalose, ethylene glycol, N-acetylglucosamine, meliobiose, fructose, sorbitol, phenylalanine deaminase and starch. The reaction was negative in arginine decarboxylase, citrate, nitrate reduction, esculin, peptone water, β-galactoside (ONPG), H2S, arginine dihydrolase and phosphate-glucose peptone water. Except for phosphate-glucose peptone water and sorbitol, the remaining items were consistent with the characteristics of standard strain A. sobria. In addition, the results of strain As012 and standard strain A. sobria in xylose and starch were completely opposite to those of A. veronii (Chen et al., 2019). Therefore, the strain As012 was preliminarily identified as A. sobria.
3.2.2 Sequencing analysis of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes
The length of 16S rRNA (GenBank accession number: PQ517010) and gyrB (GenBank accession number: PQ527032) gene sequences were 1417 bp and 1013 bp, respectively. PCR amplification results were shown in Figures 2A, 2B. The compared results showed that the similarity between the 16S rRNA gene sequence with A. sobria NR_037012.2 was 99.86%, and the similarity between the gyrB gene sequence with A. sobria AB473159.1 was 98.41%. At the same time, phylogenetic trees were constructed using gene sequences of 16S rRNA (Figure 2C) and gyrB (Figure 2D), and the results showed that strain As012 clustered with A. sobria in the same branch. In summary, the strain As012 was identified as A. sobria.
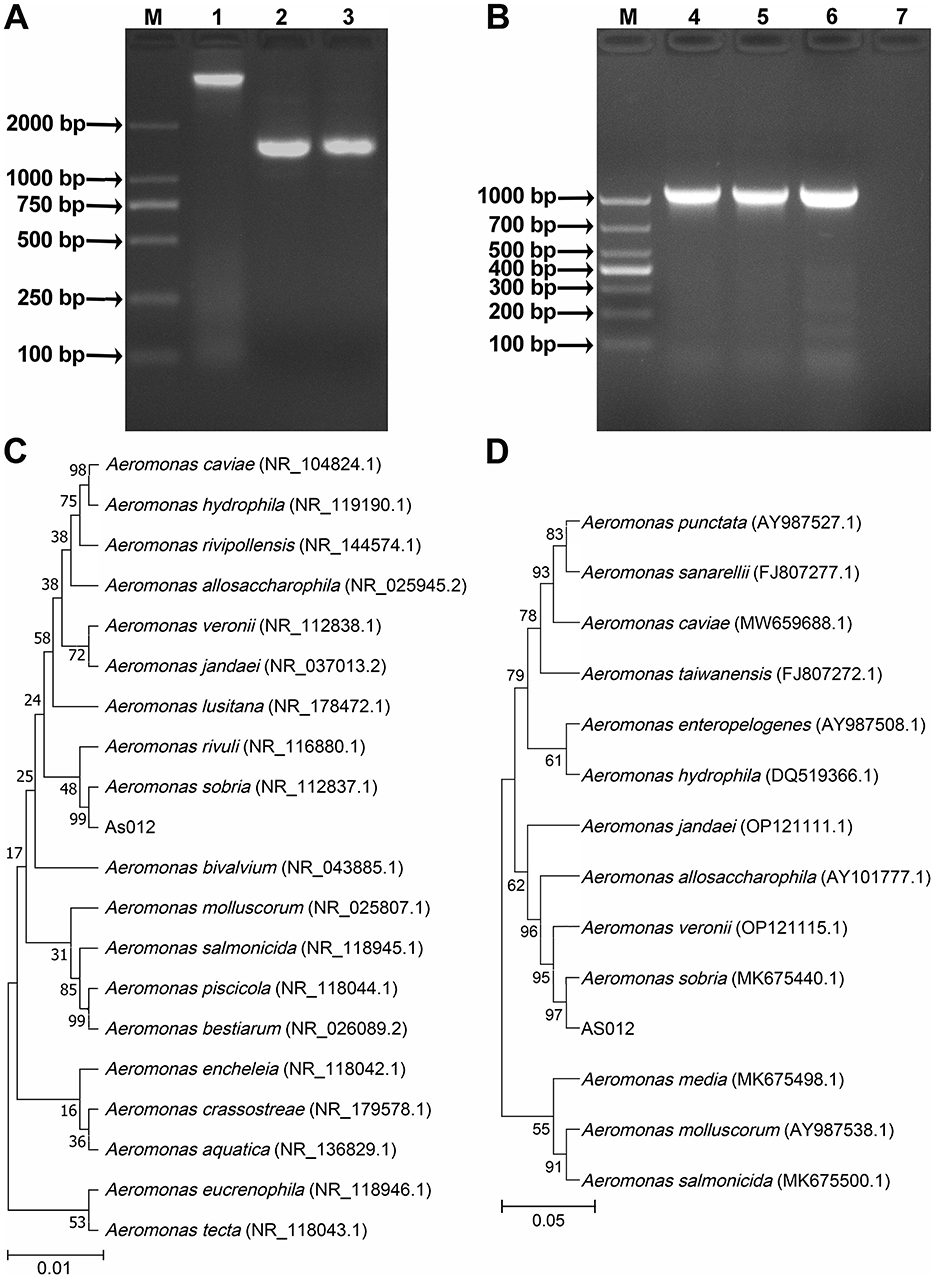
Figure 2. PCR amplification and phylogenetic tree construction of 16S rRNA and gyrB genes. (A) PCR amplification results of 16S rRNA gene. (B) PCR amplification results of gyrB gene. (C) Phylogenetic tree of 16S rRNA gene sequence. (D) Phylogenetic tree of gyrB gene sequence. M: Marker; 1: Genomic DNA of strain As012; 2-3: 16S rRNA gene; 4-6: gyrB gene; 7: Negative control.
3.3 Experimental infection
The first death occurred in rainbow trout at 12 h after injection of A. sobria solution. The clinical signs of experimentally infected rainbow trout were consistent with those of similar-sized fish in the farm. In addition, the dominant strain A. sobria was isolated again from the liver, spleen, kidney and coelomic cavity of the experimentally infected rainbow trout, indicating that A. sobria was the main pathogen causing the outbreak in the farm.
When rainbow trout were infected with different concentrations of A. sobria solution on day 7, the cumulative mortality of 1.0 × 109 and 1.0 × 108 CFU/mL groups was 100%. The cumulative mortality rates of the 1.0 × 107, 1.0 × 106 and 1.0 × 105 CFU/mL groups were 60%, 20% and 10%, respectively. However, there were no deaths in the control group (Figure 3). The LD50 of strain As012 was calculated by the Karber method to be 1.0 × 106.6 CFU/mL (Markus et al., 1995).
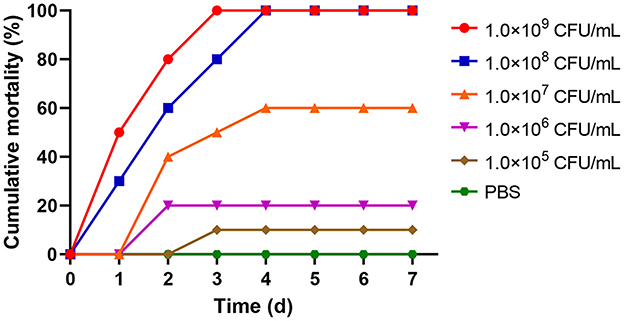
Figure 3. The cumulative mortality of rainbow trout infected with different concentrations of strain As012.
3.4 Histopathological observation of rainbow trout
Compared with the control group (Figures 4A, 4A1, 4B, 4B1, 4C, 4C1, 4D, 4D1, 4E, 4E1), the naturally infected rainbow trout showed obvious pathological changes. Among them, the branchial lamella became shorter, hypertrophied and hemorrhagic (Figures 4F, 4F1). There was extensive diffuse hemorrhage in the heart, liver and spleen (Figures 4G–4I), with large amounts of hemosiderin deposition and inflammatory cell infiltration (Figures 4G1, 4H1, 4I1). The intestinal villi were bleeding, damaged, and shed, with inflammatory cell infiltration between epithelial cells and vacuolation of cells in the mucosal layer (Figures 4J, 4J1). In summary, A. sobria infection mainly causes extensive hemorrhaging in the tissues of rainbow trout.
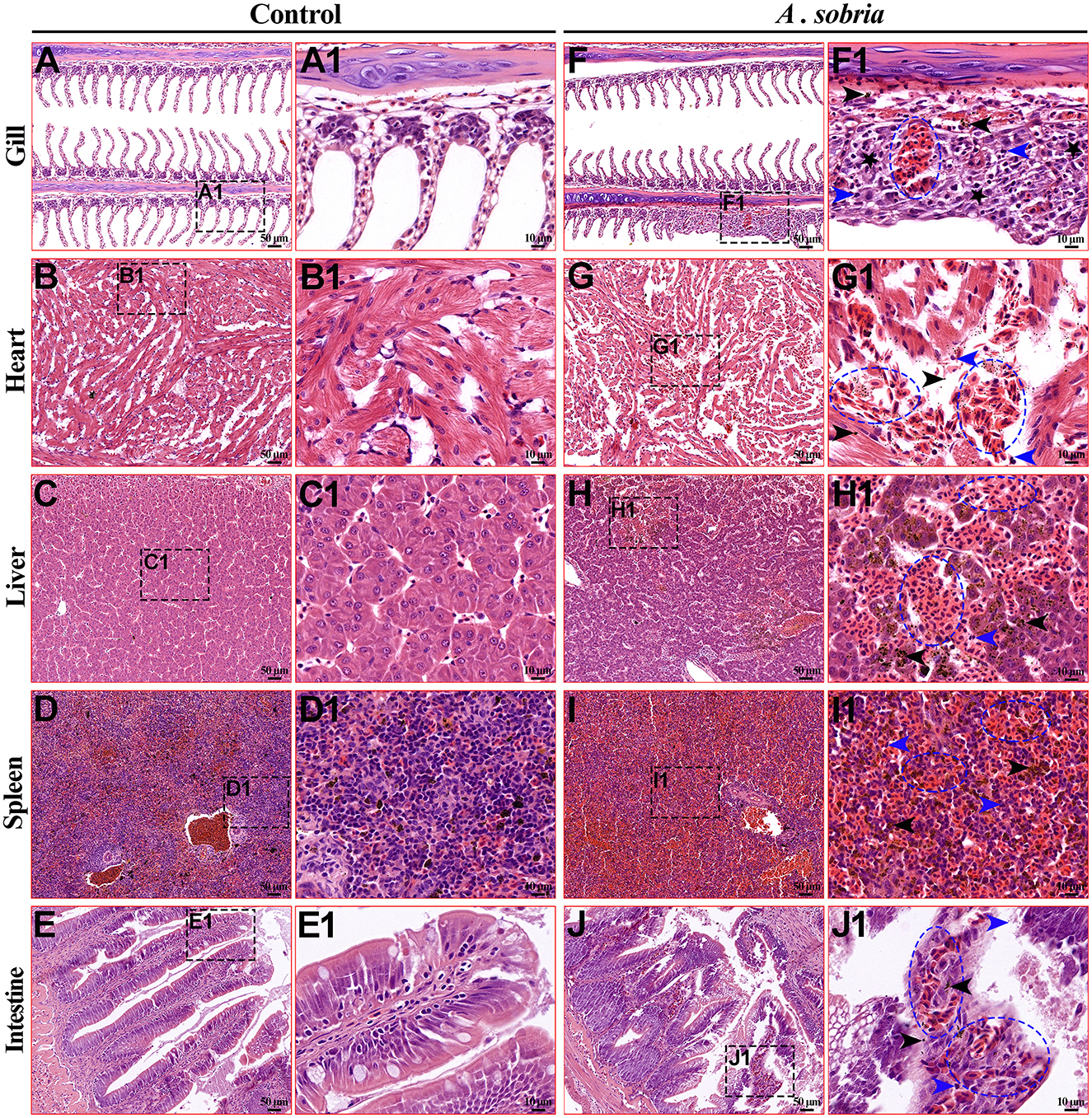
Figure 4. Histological lesions of the diseased rainbow trout. (A–E) were the gills, heart, liver, spleen and intestine of the control group, with a microscope magnification of 200x. (F–J) were the gills, heart, liver, spleen and intestine of the infected group, with a microscope magnification of 200x. (A1–J1) were the local magnified images of (A–J) respectively, with a microscopic magnification of 1,000x. Among them, the pathological changes of the tissue mainly include bleeding (blue ellipse), inflammatory cell infiltration (blue arrow), deposition of hemosiderin (black arrow), and hyperplasia (black pentagram).
3.5 Screening results of virulence genes
In this study, 18 virulence genes related to the genus Aeromonas were screened by PCR amplification. Eight virulence genes (Act, Aer, AexT4, Alt, ahyB, ascV, Nuc, and Hly) were amplified in strain As012, and the fragment sizes were basically consistent with the target gene fragment sizes (Figure 5).
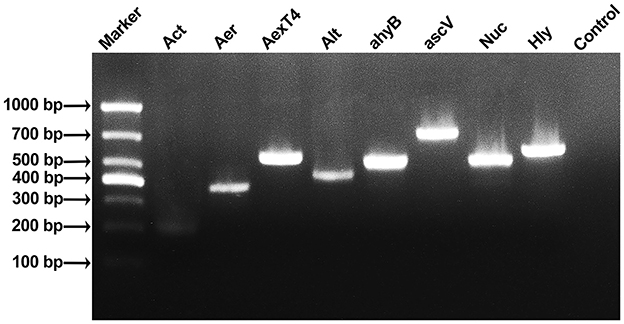
Figure 5. Results of PCR amplification of virulence genes of strain As012. The eight virulence genes were Act, Aer, AexT4, Alt, ahyB, ascV, Nuc, and Hly.
3.6 Growth characteristics of strain As012
Under the conditions of T = 18°C, pH = 7 and NaCl = 1%, the growth curve of strain As012 showed that the slow growth phase was 0–2 h, the logarithmic growth phase was 2–16 h, and the bacterial growth entered the stable phase after 16 h (Figure 6A).
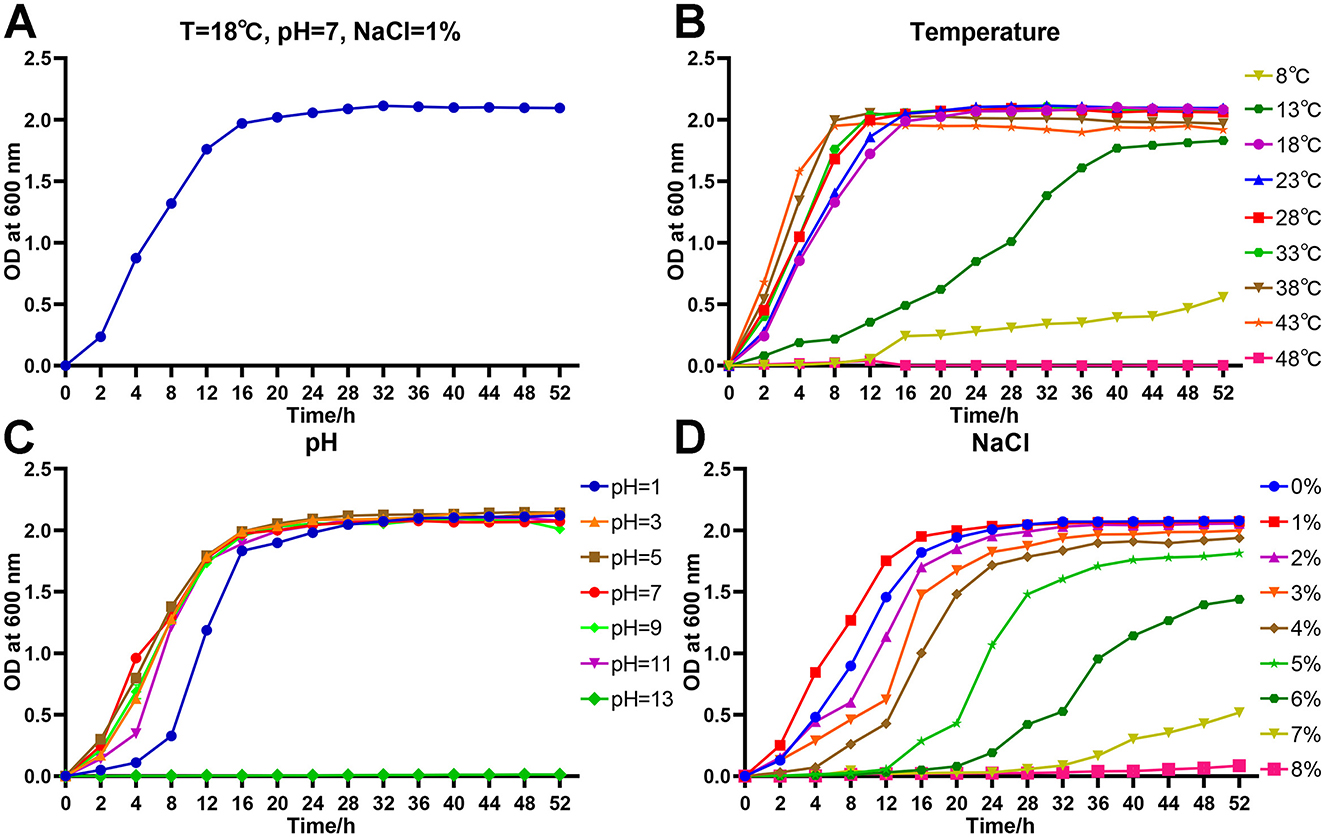
Figure 6. Growth characteristics of strain As012. (A) Growth curve under the conditions of T=18°C, pH=7, and NaCl=1%. (B) Growth curves at different temperatures. (C) Growth curves at different pH values. (D) Growth curves at different NaCl concentrations.
The strain As012 grew well at temperatures of 18–43°C and all entered stable growth phase after 16 h (Figure 6B). However, the strain began to enter stable growth phase with OD600nm < 2.0 when growing at 13°C for 40 h. It grew slowly at 8°C and OD600nm was about 0.5 at 52 h. The strain As012 grew well at pH values of 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11, and all entered the stable phase after 24 h (Figure 6C). However, the growth of strain As012 was completely inhibited at pH=13.
The strain As012 was able to grow under conditions of NaCl concentrations ranging from 0% to 8% (Figure 6D). Among them, the strain As012 grew best at NaCl concentration of 1% and entered the stable phase after 16 h. Subsequently, as the NaCl concentration increased, the slow growth phase of strain As012 gradually prolonged. At the same time, under the condition of NaCl concentration of 2–6%, the time point for strain As012 to enter the stable growth phase was continuously delayed, and the OD600nm value of the stable phase gradually decreased.
3.7 Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
The results of the antimicrobial susceptibility testing showed (Table 3) that the strain As012 was highly sensitive to four classes of antibiotics, including cephalosporins (cefazolin, cefalotin, cefuroxime, cefoperazone, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime, cefoxitin, aztreonam), quinolones (norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin), nitrofurans (furadantin), and sulfonamides (sulfamethoxazole). It was intermediately sensitive to piperacillin, polymyxin B, kanamycin, spectinomycin, amikacin, minocycline, chloramphenicol. And it was resistant to penicillins (penicillin G, oxacillin, ampicillin), polypeptides (vancomycin), lincoamides (clindamycin), macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin, midecamycin), aminoglycosides (streptomycin, tobramycin, gentamicin and tetracycline). Among them, the strain As012 was the most sensitive to cephalosporins, followed by quinolones, sulfonamides and nitrofurans.
4 Discussion
The reported pathogenic bacteria in genus Aeromonas that can cause bacterial diseases in aquatic animals include A. hydrophila (Guo et al., 2024), A. veronii (Zhu et al., 2023), A. salmonicida (Liu et al., 2023), A. caviae (Xue et al., 2022), A. jandaei (Chen et al., 2024), A. sobria (Byadgi et al., 2018), etc. The diseases caused by them in aquaculture often occur in aquatic animals with deteriorating water quality (Alwan et al., 2022), impaired organism, or low immune function (Song et al., 2023). In this study, the region was in the late stage of large-scale melting of ice and snow when the epidemic occurred. The deterioration of water quality and the rise in water temperature have led to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which meets the environmental conditions for the occurrence of Aeromonas diseases. In addition, studies have shown that lower water temperatures will slow down the metabolic rate of fish, leading to reduced immunity (Flinders and Magoulick, 2017; Song et al., 2019; Le Morvan et al., 1998). After enduring a cold and long winter, the rainbow trout in this farm are currently in a phase of weakened immune function. At this time, in intensive farming, improper management can easily lead to the outbreak of bacterial diseases. Therefore, after excluding the possibility of parasitic and viral infections, the dominant strain As012 isolated from the diseased fish may be the main pathogen responsible for the outbreak of the epidemic in this farm.
The results of physiological and biochemical identification of strain As012 showed that it was negative for nitrate reduction and phosphate glucose peptone water, and positive for sorbitol. The remaining characteristics were completely consistent with the standard strain of A. sobria, but also very close to those of A. veronii (Chen et al., 2019). The difference is that the starch agar plate test in this study showed that strain As012 can utilize starch, which is completely consistent with previous studies (Langó et al., 2002), indicating that A. sobria can produce enzymes that decompose and utilize starch. However, A. veronii is unable to utilize starch (Chen et al., 2019). Whether this difference can be directly used as the only characteristic distinguishing A. sobria from A. veronii has not been confirmed. In this case, it is necessary to use molecular biological methods to classify and identify bacteria. Among them, 16S rRNA gene sequencing is one of the most commonly used methods for bacterial species identification and phylogenetic analysis (Ntushelo, 2013). However, the high conservation of 16S rRNA gene sequence leads to low discrimination among closely related species, especially when studying bacteria of the genus Aeromonas (Chen et al., 2019; Küpfer et al., 2006). It is documented that the gyrB gene is more prone to mutation without changing the amino acid sequence, and this mutation precisely makes it easier to distinguish closely related strains (Watanabe et al., 2001; Zhu et al., 2023). More and more studies have combined 16S rRNA with gyrB gene sequences for species identification and phylogenetic analysis of Salmonella (Tajbakhsh et al., 2011), Flavobacterium (Peeters and Willems, 2011), Nocardia (Takeda et al., 2010), and Aeromonas (Küpfer et al., 2006), and all have achieved satisfactory results. In this study, the sequencing results were Blast compared, and the results showed that the 16S rRNA and gyrB gene sequences of strain As012 had the highest homology with the known A. sobria. Meanwhile, phylogenetic analysis of the two sequences showed that they clustered into the same clade as A. sobria. Therefore, the dominant strain As012 isolated from the current outbreak was successfully identified as A. sobria.
Virulence factors are not only the criteria to judge the virulence and toxicity of pathogens (Jiang et al., 2023; Cepas and Soto, 2020), but also the key to reveal the mechanism of bacterial infection (Howden et al., 2023). In this study, 8 virulence genes were detected in strain As012 among the 18 virulence genes related to the genus Aeromonas, including Act, Aer, AexT4, Alt, ahyB, ascV, Nuc and Hly. Previous studies have detected Act, Aer, Alt, and Nuc genes from different sources of A. sobria (Alwan et al., 2022; Nam and Joh, 2007), suggesting that the five virulence genes present in A. sobria may not be affected by the source of the strain. Among them, Aer, a gene encoding aerolysin, was first discovered in A. hydrophila and plays a key role in pathogen migration and invasion of pathogens (Abrami et al., 2003). The enterotoxin genes encoded by Act and Alt are closely related to gastroenteritis and diarrhea (Albert et al., 2000). The elastase encoded by ahyB gene supports pathogen infection and colonization by destroying tissues and degrading immune proteins (Song et al., 2018). The hemolysin encoded by the Hly gene can destroy cell membranes, leading to the lysis of red blood cells, and assist bacteria to escape the host's inflammatory response (Gao et al., 2013). The AscV gene is a highly conserved endosomal component of the Type III secretion system (T3SS) (Burr et al., 2002). Studies have shown that the mutation or deletion of AscV gene will lead to the closure of secretory channels of T3SS, preventing the secretion and translocation of cytotoxins such as AexT and AexU, thereby significantly reducing the virulence of A. hydrophila and A. salmonicida (Fadl et al., 2006; Burr et al., 2005). Therefore, the presence of the AscV gene in this study indicates that the strain As012 has strong pathogenicity. At present, AexT4 and Nuc genes have been detected in the isolates of A. hydrophila, A. veronii and A. caviae (Aravena-Román et al., 2014; Nam and Joh, 2007), but their functions are still unclear. At the same time, the synergistic effect of multiple virulence factors is the key factor leading to the high pathogenicity of pathogens to the body (Beaz-Hidalgo and Figueras, 2013; Zhao et al., 2020). Studies have shown that when Aeromonas carries the Aer and Hly genes, it can cause massive bleeding and hemolysis in host tissues (Xu et al., 2022) and is considered as a potential foodborne pathogen (Reyes-Rodríguez et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2023). In addition, studies have shown that strains containing both Aer and Act genes are virulent strains (Gashgari and Selim, 2015). The pathological results of this study showed that the infected rainbow trout had extensive hemorrhage in various tissues and a large amount of hemosiderin deposition in the heart, liver and spleen, which may be the result of the combined action of multiple virulence factors such as Hly, Aer and Act in A. sobria.
As is well known, the adaptability of bacteria to pH, temperature, salt concentration directly determines their survival and reproductive ability in different environments. This study showed that strain As012 could grow in environments with pH of 1–11, temperature of 8–43°C, and salt concentration of 0–8%, which was similar to the growth characteristics of A. allosaccharophila (Shao et al., 2023), A. veronii (Chen et al., 2019) and A. hydrophila (Bakiyev et al., 2022). The difference is that the strain As012 is more tolerant to acids, bases and high concentrations of salts, indicating that the growth environment of this strain is more extensive. In actual aquaculture, temperature is the key factor determining the speed of bacterial reproduction (Janda and Abbott, 2010). For example, bacterial diseases rarely occur in the cold winters, but they frequently break out in spring, summer and autumn when the environment temperature is 15–40°C. The optimal growth temperature of rainbow trout is 13–18°C (Magoulick and Wilzbach, 1998), which is suitable for the growth and reproduction of A. sobria. In addition, the tolerance of A. sobria to salt indicates that it not only affects the development of freshwater aquaculture, but may also exist in seawater and related products. Therefore, the special growth characteristics will bring great challenges for the prevention and control of A. sobria.
At present, antibiotics remain the most economical and effective strategy for the prevention and treatment of bacterial diseases. In this study, A. sobria was most sensitive to cephalosporins (cefazolin, cefalotin, cefuroxime, cefoperazone, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime, cefepime, cefazolin, and aztreonam), followed by quinolones (norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and levofloxacin), sulfonamides (sulfamethoxazole), and nitrofurans (furadantin). At present, according to the provisions of the “Aquaculture Drug Use White Paper No. 1 and No. 2 in 2022” issued by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China, and combined with the drug sensitivity results of this experiment, ciprofloxacin and its related preparations can be used to effectively prevent and treat A. sobria in practical aquaculture. In addition, A. sobria was resistant to penicillins (penicillin G, oxacillin, ampicillin), polypeptides (vancomycin), lincoamides (clindamycin), macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin, madecycin) and aminoglycosides (streptomycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, tetracycline), indicating that this strain was a multidrug-resistant bacterium. Meanwhile, Comparing the antibiotic sensitivity results of this study with those of A. sobria strain PY36 from tilapia, which revealed that A. sobria from different animal sources have different antibiotic resistance spectra. For example, The strain As012 from rainbow trout is resistant to erythromycin, streptomycin, and tetracycline, while the strain PY36 from tilapia is highly sensitive to them (Li and Cai, 2011). This phenomenon has also been reported in A. veronii (Hu et al., 2023) and A. jandaei (Chen et al., 2024), which may be the result of continuous selection of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria during long-term evolution due to different growth environments. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor daily antibiotic resistance in the prevention and control of bacterial diseases in aquaculture, and to use antibiotics reasonably and effectively during outbreaks of diseases.
In summary, A. sobria, the dominant strain isolated from the diseased rainbow trout in this study, is the main pathogen causing the outbreak in this farm. The characteristic studies showed that the strain not only has a very wide range of growth, but also has strong pathogenicity, causing extensive hemorrhaging in various tissues of rainbow trout. The strain was highly sensitive to 16 antibiotics such as cefazolin, ciprofloxacin, and furadantin; Moderately sensitive to 7 antibiotics including piperacillin, polymyxin B, kanamycin, etc.; Resistant to 12 antibiotics including penicillin G, vancomycin, and clindamycin. Among them, ciprofloxacin will be one of the preferred antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of A. sobria in Chinese aquaculture. This study will provide reference for the prevention and treatment of A. sobria diseases and lay a foundation for the study of its pathogenic mechanism.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the NCBI repository, accession numbers PQ517010 and PQ527032.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee of Gansu Agricultural University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
L-PL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-DF: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. P-TK: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. X-YG: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. G-WZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JP: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. J-XL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. W-DZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32460869) and the National Youth Natural Science Foundation of China (3190190384).
Conflict of interest
L-PL and J-XL were employed by Lanzhou Witsen Biotechnology Co., LTD.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel Rahman, A. N., Masoud, S. R., Fouda, M. M. S., Abdel-Warith, A. W. A., Younis, E. M., Khalil, S. R., et al. (2023). Antimicrobial efficacy of magnetite nanoparticles against Aeromonas sobria challenge in African catfish: biochemical, protein profile, and immuno-antioxidant indices. Aquacult. Rep. 32, 101692–101692. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101692
Abdel Rahman, A. N., Van Doan, H., Elsheshtawy, H. M., Dawood, A., Salem, S. M. R., Sheraiba, N. I., et al. (2022). Dietary Salvia officinalis leaves enhances antioxidant-immune-capacity, resistance to Aeromonas sobria challenge, and growth of Cyprinus carpio. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 127, 340–348. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.06.030
Abrami, L., Fivaz, M., Glauser, P. E., Sugimoto, N., Zurzolo, C., and van der Goot, F. G. (2003). Sensitivity of polarized epithelial cells to the pore-forming toxin aerolysin. Infect. Immun. 71, 739–746. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.739-746.2003
Albert, M. J., Ansaruzzaman, M., Talukder, K. A., Chopra, A. K., Kuhn, I., Rahman, M., et al. (2000). Prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Aeromonas spp. isolated from children with diarrhea, healthy controls, and the environment. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 3785–3790. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.10.3785-3790.2000
Alwan, Z. H. O., Lilo, R. A., and Mohsen, L. Y. (2022). Antibiotic resistance profile and virulence factor genes of Aeromonas sobria isolated from AL-Hillah River in Babel (Iraq). J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 14, 868–875. doi: 10.31018/jans.v14i3.3538
Aravena-Román, M., Inglis, T. J., Riley, T. V., and Chang, B. J. (2014). Distribution of 13 virulence genes among clinical and environmental Aeromonas spp. in Western Australia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 33, 1889–1895. doi: 10.1007/s10096-014-2157-0
Bakiyev, S., Smekenov, I., Zharkova, I., Kobegenova, S., Sergaliyev, N., Absatirov, G., et al. (2022). Isolation, identification, and characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila from critically endangered Acipenser baerii. Aquacult. Rep. 26, 101293–101293. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101293
Beaz-Hidalgo, R., and Figueras, M. J. (2013). Aeromonas spp. whole genomes and virulence factors implicated in fish disease. J. Fish Dis. 36, 371–388. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12025
Borrell, N., Acinas, S. G., Figueras, M. J., and Martínez-Murcia, A. J. (1997). Identification of Aeromonas clinical isolates by restriction fragment length polymorphism of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 1671–1674. doi: 10.1128/jcm.35.7.1671-1674.1997
Burr, S. E., and Frey, J. (2007). Analysis of type III effector genes in typical and atypical Aeromonas salmonicida. J. Fish Dis. 30, 711–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00859.x
Burr, S. E., Pugovkin, D., Wahli, T., Segner, H., and Frey, J. (2005). Attenuated virulence of an Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida type III secretion mutant in a rainbow trout model. Microbiology 151, 2111–2118. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27926-0
Burr, S. E., Stuber, K., Wahli, T., and Frey, J. (2002). Evidence for a type III secretion system in Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida. J. Bacteriol. 184, 5966–5970. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.21.5966-5970.2002
Byadgi, O., Chen, Y. C., Maekawa, S., Wang, P. C., and Chen, S. C. (2018). Immune-related functional differential gene expression in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio) after challenge with Aeromonas sobria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19:2107. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072107
Cao, Y., Li, S., Han, S., Wang, D., Zhao, J., Xu, L., et al. (2020). Characterization and application of a novel Aeromonas bacteriophage as treatment for pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 523, 735193–735193. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735193
Cepas, V., and Soto, S. M. (2020). Relationship between virulence and resistance among gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 9:719. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9100719
Chacón, M. R., Soler, L., Groisman, E. A., Guarro, J., and Figueras, M. J. (2004). Type III secretion system genes in clinical Aeromonas isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42, 1285–1287. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.3.1285-1287.2004
Chen, F., Sun, J., Han, Z., Yang, X., Xian, J. A., Lv, A., et al. (2019). Isolation, identification and characteristics of aeromonas veronii from diseased crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio). Front. Microbiol. 10:2742. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02742
Chen, M., Xue, M., Chen, J., Xiao, Z., Hu, X., Zhang, C., et al. (2024). Isolation, identification and characterization of Aeromonas jandaei from diseased Chinese soft-shell turtles. J. Fish Dis. 47, e13919. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13919
da Costa, O. T. F., Dias, L. C., Malmann, C. S. Y., de Lima Ferreira, C. A., do Carmo, I. B., Wischneski, A. G., et al. (2019). The effects of stocking density on the hematology, plasma protein profile and immunoglobulin production of juvenile tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum) farmed in Brazil. Aquaculture 499, 260–268. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.09.040
De Silva, P. M., Chong, P., Fernando, D. M., Westmacott, G., and Kumar, A. (2018). Effect of incubation temperature on antibiotic resistance and virulence factors of Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 17978. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 62, e01514–e01517. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01514-17
Fadl, A. A., Galindo, C. L., Sha, J., Erova, T. E., Houston, C. W., Olano, J. P., et al. (2006). Deletion of the genes encoding the type III secretion system and cytotoxic enterotoxin alters host responses to Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Microb. Pathog. 40, 198–210. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2006.01.003
FAO (2020). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. Rome, Italy: Sustainability in Action.
Flinders, J. M., and Magoulick, D. D. (2017). Spatial and temporal consumption dynamics of trout in catch-and-release areas in Arkansas tailwaters. T. Am. Fish. Soc. 146, 432–449. doi: 10.1080/00028487.2017.1281169
Gao, S., Zhao, N., Amer, S., Qian, M., Lv, M., Zhao, Y., et al. (2013). Protective efficacy of PLGA microspheres loaded with divalent DNA vaccine encoding the ompA gene of Aeromonas veronii and the hly gene of Aeromonas hydrophila in mice. Vaccine 31, 5754–5759. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.053
Gashgari, R. M., and Selim, S. A. (2015). Detection and characterization of antimicrobial resistance and putative virulence genes in Aeromonas veronii Biovar Sobria isolated from gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 12, 806–811. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2015.1976
Gelbart, S. M., Prabhudesai, M., and Magee, S. M. (1985). A case report: Aeromonas sobria gastroenteritis in an adult. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 83, 389–391. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.389
Guo, H., Gu, W., Yang, R., and Wang, B. (2016). Multivariate diallel cross-analyses for body weight of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, in China. J. World Aquacult. Soc. 48, 240–247. doi: 10.1111/jwas.12350
Guo, S., Wan, Q., Xu, M., Chen, M., and Chen, Z. (2024). Transcriptome analysis of host anti-Aeromonas hydrophila infection revealed the pathogenicity of A. hydrophila to American eels (Anguilla rostrata). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 148:109504. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109504
Han, Y., Liu, M., and Jiang, Y. P. (2005). Study on the pathogens of bleeding disease in Cyprinus carpio haematopterus Temminck et Schlegel and drug sensitivity test. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 36, 593–597.
Heuzenroeder, M. W., Wong, C. Y., and Flower, R. L. (1999). Distribution of two hemolytic toxin genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas spp.: correlation with virulence in a suckling mouse model. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 174, 131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13559.x
Howden, B. P., Giulieri, S. G., Wong Fok Lung, T., Baines, S. L., Sharkey, L. K., Lee, J. Y. H., et al. (2023). Staphylococcus aureus host interactions and adaptation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 380–395. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00852-y
Hu, X., Xiao, Z., Li, B., Xue, M., Jiang, N., Fan, Y., et al. (2023). Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of Aeromonas veronii from Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Trionyx sinensis). Microorganisms 11:1304. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051304
Janda, J. M., and Abbott, S. L. (2010). The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 23, 35–73. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00039-09
Jiang, Y., Hu, X., Fan, S., Liu, W., Chen, J., Wang, L., et al. (2023). RVFScan predicts virulence factor genes and hypervirulence of the clinical metagenome. Brief. Bioinform. 24:bbad403. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad403
Küpfer, M., Kuhnert, P., Korczak, B. M., Peduzzi, R., and Demarta, A. (2006). Genetic relationships of Aeromonas strains inferred from 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56, 2743–2751. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63650-0
Langó, Z., Borsodi, A. K., and Micsinai, A. (2002). Comparative studies on Aeromonas strains isolated from Lakes Balaton (Hungary) and Fertó/Neusiedlersee (Hungary). Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 49, 37–45. doi: 10.1556/amicr.49.2002.1.4
Le Morvan, C., Troutaud, D., and Deschaux, P. (1998). Differential effects of temperature on specific and nonspecific immune defences in fish. J. Exp. Biol. 201, 165–168. doi: 10.1242/jeb.201.2.165
Lee, H. J., Tokle, I. F., Lunestad, B. T., Lerfall, J., Hoel, S., and Jakobsen, A. N. (2023). The effect of food processing factors on the growth kinetics of Aeromonas strains isolated from ready-to-eat seafood. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 384:109985. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109985
Li, Y., and Cai, S. H. (2011). Identification and pathogenicity of Aeromonas sobria on tail-rot disease in Juvenile Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Curr. Microbiol. 62, 623–627. doi: 10.1007/s00284-010-9753-8
Liu, M., Yang, X., Zeng, C., Zhao, H., Li, J., Hou, Z., et al. (2022). Transcriptional signatures of immune, neural, and endocrine functions in the brain and kidney of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to Aeromonas salmonicida infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1340. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031340
Liu, Y., Li, X., Xia, Y., Cheng, J., Zhou, C., and Liu, P. (2023). Gut microbial and metabolic characterization of Atlantic salmon (Salmon salar) challenged with Aeromonas salmonicida. Aquaculture 570, 739420–739420. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739420
Lopez-Jimena, B., Garcia-Rosado, E., Infante, C., Cano, I., Manchado, M., Castro, D., et al. (2010). Detection of infectious pancreatic necrosis virus (IPNV) from asymptomatic redbanded seabream, Pagrus auriga Valenciennes, and common seabream, Pagrus pagrus (L.), using a non-destructive procedure. J. Fish Dis. 33, 311–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01123.x
Macêdo, R. L., Franco, A. C. S., Russo, P., Collart, T., Mammola, S., Jeppesen, E., et al. (2021). Climate and landscape changes enhance the global spread of a bloom-forming dinoflagellate related to fish kills and water quality deterioration. Ecol. Indic. 133, 108408–108408. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108408
Magoulick, D. D., and Wilzbach, M. A. (1998). Effect of temperature and macrohabitat on interspecific aggression, foraging success, and growth of brook trout and rainbow trout pairs in laboratory streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 127, 708–717.
Majeed, S., De Silva, L. A. D. S., Kumarage, P. M., and Heo, G. J. (2023). Occurrence of potential virulence determinants in Aeromonas spp. isolated from different aquatic environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 134:lxad031. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxad031
Markus, R. A., Frank, J., Groshen, S., and Azen, S. P. (1995). An alternative approach to the optimal design of an LD50 bioassay. Stat. Med. 14, 841–852. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780140812
Mayrhofer, R., Menanteau-Ledouble, S., Pucher, J., Focken, U., and El-Matbouli, M. (2020). Aeromonas spp. suggested as the causative agents of red spot disease in northern Vietnamese grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 139, 113–119. doi: 10.3354/dao03479
Mesías, F., Gerpe, D., Hurtado, C., Llanco, L., Serrano-Martínez, E., and Romalde, J. L. (2020). Draft genome sequence of Aeromonas sobria strain CHT-30, isolated from a diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Peru. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 9, e00110–e00120. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00110-20
Naderi, M., Keyvanshokooh, S., Salati, A. P., and Ghaedi, A. (2017). Effects of chronic high stocking density on liver proteome of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 43, 1373–1385. doi: 10.1007/s10695-017-0378-8
Nam, I. Y., and Joh, K. (2007). Rapid detection of virulence factors of Aeromonas isolated from a trout farm by hexaplex-PCR. J. Microbiol. 45, 297–304.
Nawaz, M., Khan, S. A., Khan, A. A., Sung, K., Tran, Q., Kerdahi, K., et al. (2010). Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol. 27, 327–331. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2009.11.007
Ntushelo, K. (2013). Identifying bacteria and studying bacterial diversity using the 16S ribosomal RNA gene-based sequencing techniques: a review. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 7, 5533–5540. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2013.5966
Parras, F., Díaz, M. D., Reina, J., Moreno, S., Guerrero, C., and Bouza, E. (1993). Meningitis due to Aeromonas species: case report and review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 17, 1058–1060. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.6.1058
Peeters, K., and Willems, A. (2011). The gyrB gene is a useful phylogenetic marker for exploring the diversity of Flavobacterium strains isolated from terrestrial and aquatic habitats in Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 321, 130–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02326.x
Popoff, M. R., and Lallier, R. (1984). Biochemical and serological characteristics of Aeromonas. Method. Microbiol. 1, 127–145. doi: 10.1016/S0580-9517(08)70389-1
Qian, Y., Xia, L., Wei, L., Li, D., and Jiang, W. (2021). Artesunate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation by reducing alpha-toxin synthesis. Arch. Microbiol. 203, 707–717. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-02077-6
Reyes-Rodríguez, N. E., Salgado-Miranda, C., Flores-Valle, I. T., González-Gómez, M., Soriano-Vargas, E., Peláez-Acero, A., et al. (2019). Molecular identification and virulence potential of the genus aeromonas isolated from wild rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in Mexico. J. Food Prot. 82, 1706–1713. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-545
Sen, K., and Rodgers, M. (2004). Distribution of six virulence factors in Aeromonas species isolated from US drinking water utilities: a PCR identification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 97, 1077–1086. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02398.x
Shao, G. Y., Wang, S., Jiang, X. S., Tian, Q., Lu, Y., Cheng, B., et al. (2023). Isolation, identification and characterization of Aeromonas allosaccharophila from infected farmed leech (Whitmania pigra) in Jiangsu, China. Aquaculture 576, 739867–739867. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739867
Soliman, M. K. (2022). Treatment of MAS caused by Aeromonas sobria in European seabass. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 26, 535–556. doi: 10.21608/ejabf.2022.264476
Song, H., Xu, D., Tian, L., Chen, R., Wang, L., Tan, P., et al. (2019). Overwinter mortality in yellow drum (Nibea albiflora): insights from growth and immune responses to cold and starvation stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 92, 341–347. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.06.030
Song, M. F., Zhang, D. X., Zhang, H. P., Chen, L., Kang, Y. H., Zhang, L., et al. (2018). Research advances of virulence factors in Aeromonas veronii. Chin. Vet. Sci. 48, 1038−1042. doi: 10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.2018.0152
Song, Y., Wang, L. F., Zhou, K., Liu, S., Guo, L., Ye, L. Y., et al. (2023). Epidemiological characteristics, virulence potential, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and phylogenetic analysis of Aeromonas caviae isolated from extra-intestinal infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 13:1084352. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1084352
Spadaro, S., Berselli, A., Marangoni, E., Romanello, A., Colamussi, M. V., Ragazzi, R., et al. (2014). Aeromonas sobria necrotizing fasciitis and sepsis in an immunocompromised patient: a case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 8:315. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-8-315
Tajbakhsh, M., Nayer, B. N., Motavaze, K., Kharaziha, P., Chiani, M., Zali, M. R., et al. (2011). Phylogenetic relationship of Salmonella enterica strains in Tehran, Iran, using 16S rRNA and gyrB gene sequences. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 5, 465–472. doi: 10.3855/jidc.1504
Takeda, K., Kang, Y., Yazawa, K., Gonoi, T., and Mikami, Y. (2010). Phylogenetic studies of Nocardia species based on gyrB gene analyses. J. Med. Microbiol. 59, 165–171. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.011346-0
Walter Devaa, J. C., Nithaniyal, S., Panneerselvam, V., and Uthandakalaipandian, R. (2023). Origin and history of introduction of rainbow trout, oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792) stocks in Southern India as inferred from Y-linked marker. Asian Fisheries Sci. 36:0. doi: 10.33997/j.afs.2023.36.2.003
Watanabe, K., Nelson, J., Harayama, S., and Kasai, H. (2001). ICB database: the gyrB database for identification and classification of bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 344–345. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.344
Xu, H., Xu, R., Wang, X., Liang, Q., Zhang, L., Liu, J., et al. (2022). Co-infections of Aeromonas veronii and Nocardia seriolae in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Microb. Pathog. 173:105815. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105815
Xue, M., Xiao, Z., Li, Y., Jiang, N., Liu, W., Meng, Y., et al. (2022). Isolation, identification and characteristics of Aeromonas caviae from diseased largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fishes 7, 119–119. doi: 10.3390/fishes7030119
Yáñez, M. A., Catalán, V., Apráiz, D., Figueras, M. J., and Martínez-Murcia, A. J. (2003). Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 875–883. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02443-0
Yang, M. J., Jiang, M., Peng, X. X., and Li, H. (2021). Myo-inositol restores tilapia's ability against infection by Aeromonas sobria in higher water temperature. Front. Immunol. 12:682724. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.682724
Yang, Q. H., Zhou, C., Lin, Q., Lu, Z., He, L. B., and Guo, S. L. (2017). Draft genome sequence of Aeromonas sobria strain 08005, isolated from sick Rana catesbeiana. Genome Announc. 5, e01352–e01316. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.01352-16
Yu, J., Koo, B. H., Kim, D. H., Kim, D. W., and Park, S. W. (2015). Aeromonas sobria infection in farmed mud loach (Misgurnus mizolepis) in Korea, a bacteriological survey. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 16, 194−201.
Zhao, X. L., Wu, G., Chen, H., Li, L., and Kong, X. H. (2020). Analysis of virulence and immunogenic factors in Aeromonas hydrophila: towards the development of live vaccines. J. Fish Dis. 43, 747–755. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13174
Zhu, C., Yang, C., Li, F., Lv, G., Ren, C., Chu, P., et al. (2023). Isolation, identification of an Aeromonas veronii strain, and the immune response of hybrid sturgeon (Acipenser baerii ♀ × Acipenser schrenckii ♂) to the bacteria. Aquaculture 577, 739966–739966. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2023.739966
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene, gyrB gene, histopathology, virulence genes, growth characteristics, antibiotic sensitivity
Citation: Liu L-P, Fang Y-D, Kang P-T, Gao X-Y, Zhang G-W, Pan J, Lu J, Liu J-X and Zhang W-D (2025) Isolation, identification and characteristics of Aeromonas sobria from diseased rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Front. Microbiol. 15:1499126. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1499126
Received: 20 September 2024; Accepted: 03 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited by:
Jesus L. Romalde, University of Santiago de Compostela, SpainReviewed by:
Guilherme Campos Tavares, Federal University of Minas Gerais, BrazilVikash Kumar, Central Inland Fisheries Research Institute (ICAR), India
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Fang, Kang, Gao, Zhang, Pan, Lu, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wang-Dong Zhang, YXdhbmcwMDFAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Li-Ping Liu
Li-Ping Liu Ying-Dong Fang
Ying-Dong Fang Peng-Tian Kang3
Peng-Tian Kang3 Jia Lu
Jia Lu Wang-Dong Zhang
Wang-Dong Zhang