- 1National Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, Hubei Hongshan Laboratory, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, the Cooperative Innovation Centre for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China
- 3College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
Streptococcus species are important pathogens implicated in bovine mastitis, causing considerable economic losses within the global dairy industry. With the development of multidrug-resistant bacteria, it is crucial to develop novel antibiotic alternatives. Here, we constructed a novel chimeric endolysin, Cly2v, which comprises the Ply2741 CHAP domain (1-155aa) and the PlyV12 CBD domain (146-314aa). Biochemical characterization analysis indicated that Cly2v exhibits a melting temperature of 50.7°C and retains stable bactericidal activity at pH = 3–10. In vitro experiments demonstrated that Cly2v exhibited more efficient bactericidal activity against Streptococcus compared to the parental endolysin Ply2741. Cly2v (25 μg/mL) can effectively inhibit and reduce biofilms formed by Streptococcus, resulting in a 68 and 44% reduction in OD590nm for S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1 biofilms. Notably, in a mouse mastitis model, treatment with Cly2v (50 μg/gland) led to a reduction in bacterial load by 2.16 log10CFU/ml and decreased inflammatory cytokine levels in mammary tissue. To our knowledge, this represents the first application of a chimeric endolysin in the treatment of early-stage mouse mastitis induced by streptococci. Additionally, in a systemic infection model, treatment with Cly2v (400 μg/mouse) provided protection rates of up to 100 and 78% against S. agalactiae ATCC13813 infections when challenged for 1 h and 3 h, respectively. Furthermore, a significant reduction in bacterial loads was observed in the blood and organs compared to the PBS group. In summary, Cly2v possesses significant potential as an alternative antibiotic for the treatment of streptococci-induced bovine mastitis and systemic infections.
1 Introduction
Bovine mastitis severely threatens the production and quality of the dairy products, resulting in significant substantial economic losses (Kayano et al., 2018; Pang et al., 2018; Guo et al., 2024). As a widespread infectious disease, large-scale dairy farms in seven provinces of China suffered economic losses of up to $76,000 per month due to bovine mastitis between 2015 and 2017 (He et al., 2020). Additionally, mastitis pathogens can be transmitted to humans through unpasteurized milk, posing a threat to public health (Oliver and Murinda, 2012). With the advancement of mastitis diagnostic techniques and the growing awareness of the disease’s impact among livestock veterinarians, bovine mastitis has become a major research highlight in the global veterinary field.
Bovine mastitis represents a multifaceted disease influenced by a range of contributing factors (Viguier et al., 2009). Previous research indicated that approximately 130 pathogens are relevant to bovine mastitis (Kabelitz et al., 2021). Streptococci including Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus uberis, and Streptococcus dysgalactiae, are among the leading pathogens responsible for bovine mastitis worldwide (Ajose et al., 2022; Dyson et al., 2022). Bacteria may spread from infected cows to healthy herds via contaminated milking towels and contact with personnel (Sharun et al., 2021). Additionally, streptococci such as S. agalactiae can cause severe infections in humans, posing significant zoonotic risks (Raabe and Shane, 2019). The traditional method for treating and preventing bacterial bovine mastitis relies on antibiotics (Zamojska et al., 2021). However, the increasing prevalence of the antibiotic-resistant bacteria severely limit the effectiveness of these treatments (El-Sayed and Kamel, 2021). Consequently, it is crucial to explore and develop novel alternative agents to treat bovine mastitis caused by streptococci.
Endolysins, which are hydrolytic enzymes derived from bacteriophages, have emerged as a promising novel alternative antimicrobial agent against multi-drug resistant bacteria (Yang et al., 2014b). Unlike phages, endolysins exhibit advantages such as a broad host spectrum, low resistance development, and high safety (Lu et al., 2021). Furthermore, endolysins have exhibited independent bactericidal activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Fischetti et al. found that PlySs2 exhibits broad bactericidal activity against Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus species, making it the lysin with the broadest known bactericidal spectrum (Gilmer et al., 2013). Doehn et al. found that Cpl-1 not only prevents acute otitis media in mouse models but also treats systemic infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae (McCullers et al., 2007; Doehn et al., 2013). Additionally, endolysins generally have a modular structure, which allows for the replacement and modification, providing more options for clinical treatment (Murray et al., 2021). A few studies have demonstrated that chimeric endolysins possess broader potential for application compared to their parental endolysins. Yang et al. developed a chimeric lysin ClyH, which exhibited remarkable bactericidal activity against Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains compared to lysostaphin and its parental endolysin (Yang et al., 2014b). Duan et al. demonstrated that, compared to LysGH15, the chimeric endolysin ClyQ not only has a broader lytic spectrum but also diminished the onset of bacterial resistance when used in combination with mupirocin (Duan et al., 2023). However, to our knowledge, there are few reports on chimeric endolysins aimed at treating bovine mastitis induced by streptococci.
Here, we constructed a novel chimeric lysin, Cly2v, which consists of the Ply2741 CHAP domain and the PlyV12 cell-wall binding domain (CBD). Compared to its parental endolysin Ply2741, Cly2v exhibited more efficient bactericidal activity against Streptococcus species causing bovine mastitis and significantly inhibited and removed bacterial biofilms. In addition, in a mouse mastitis model, Cly2v significantly reduced bacterial load and inflammatory cytokine levels in mammary tissue. Meanwhile, Cly2v could treat systemic infections caused by S. agalactiae ATCC13813. Our study not only provides a novel antibiotic alternative to combat streptococci-induced bovine mastitis and systemic infections but also enhances the understanding of the engineering of novel chimeric endolysins.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Cells and bacteria
HEK-293 T, PK15, and IPEC-J2 cells were cultured in DMEM medium (Gibco, United States), supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, United States), and incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Streptococcus were cultured in Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) and Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA) media (BD, United States) containing 5% (v/v) FBS (Every Green, China). The strains used in this research are detailed in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2 Construction, expression, and purification of Cly2v
The genomic fragments encoding the endolysins PlyV12 (Genbank ID: AAT01859.1) and Ply2741 (Genbank ID: PQ213358) were synthesized by Tsingke Biotechnology, Co., Ltd. The chimeric endolysin Cly2v was constructed by fusing the Ply2741 CHAP domain (1-155aa) with the PlyV12 CBD domain (146-314aa) via overlap PCR. The Cly2v gene was subsequently cloned into the pCold™ II plasmid (Takara, Japan) following digestion with BamHI and HindIII. The specific primers used in this research are detailed in Supplementary Table S2.
The recombinant plasmid pCold-Cly2v was introduced into E. coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells and grown in LB medium supplemented with 100 μg/mL ampicillin at 37°C until OD600nm reached to 0.6. After inducing with 0.6 mM Isopropyl β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) at 16°C for 18 h, the cells were harvested by ultracentrifugation and resuspended in binding buffer (20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH = 7.5). The samples were broken using a cell pressure crusher and centrifuged at 10000 × g for 20 min at 4°C to harvested the crude recombinant protein. And then, the crude endolysin was purified via affinity chromatography (AFC) and size exclusion chromatography (SEC) according to the protocols. Briefly, His-tagged protein was purified using a His-Trap FF column (Cytiva, United States) with elution buffer (20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 300 mM imidazole pH = 7.5), followed by further purification using a HiLoad Superdex 200pg column (Cytiva, United States) with SEC buffer (20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH = 7.5).
2.3 Bioinformatics and structural analysis of Cly2v
The physicochemical properties and hydrophobicity of Cly2v were analyzed using Expasy.1 The three-dimensional (3D) structure prediction was conducted via the Colabfold webserver (Mirdita et al., 2022), with visualization and analysis performed using PyMOL. The secondary structure was further determined through circular dichroism as described previously (Luo et al., 2020). Briefly, the endolysin was adjusted to a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL in SEC buffer. The experiments were conducted on a J-1500 CD Spectrometer using a 0.1 cm quartz cuvette (JASCO, Japan), measuring wavelengths from 190 nm to 260 nm. The CDNN V2.1 software was used to calculate the secondary structure results.
2.4 Biological characterization of Cly2v
The effect of temperature and pH on bactericidal activity were determined by turbidity reduction assay as described previously (Gilmer et al., 2013). Briefly, Cly2v was incubated at different temperatures. Then, 100 μL of Cly2v were taken every 10 min and mixed with 100 μL of S. agalactiae ATCC13813, which adjusted with PBS to OD600nm = 0.8 (approximately 2.5 × 108 CFU/mL). After incubation at 37°C for 30 min, the absorbance at OD600nm was determined, with PBS serving as the negative control. For the pH stability, Cly2v was mixed with different pH buffers (20 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 3.0 to 6.0), 20 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7 to 8), and 20 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 9.0 to 10.0)) and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. To ensure consistent pH conditions, the bacteria were also resuspended in the respective pH buffers and adjusted to OD600nm = 0.8 (approximately 2.5 × 108 CFU/mL). Subsequently, Cly2v was mixed with the bacteria and incubated at 37°C for 30 min before measuring the absorbance at OD600nm. Different pH buffers served as controls to reduce experimental errors from pH effects on bacterial viability. The relative activity of Cly2v under different temperature and pH conditions was expressed as a percentage of the maximum enzyme activity. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
The thermal stability of Cly2v was assessed using nano differential scanning fluorimetry (nanoDSF) with the Prometheus NT.48 (Nano Temper, Germany). The experiments were conducted over a temperature range of 20°C to 95°C, with a rate of 1°C/min. The first derivative F350/F330 was automatically calculated and the melting temperature (Tm) was determined at the peak of the derivative curve.
2.5 Lytic spectrum and bactericidal activity assay
To explore the lytic spectrum of Cly2v against Streptococcus species that caused mastitis, the turbidity reduction assay was conducted as described previously (Gilmer et al., 2013; Li et al., 2023). Mid-logarithmic phase bacteria were adjusted with PBS to OD600nm = 0.6–0.8. Then, 100 μL of the bacteria was mixed with 100 μL of endolysin (50 μg/mL) in a 96-well plate. The absorbance was measured at OD600nm after a 30-min incubation at 37°C. The turbidity reduction ratio was calculated as described below. Ply2741 was used as the parental endolysin control.
To evaluate the bactericidal efficiency of Cly2v, logarithmic phase bacteria were mixed with Cly2v (100 μg/mL), while PBS served as a negative control. Following a 1 h incubation at 37°C, the mixture was plated on TSA to determine bacterial counts. Moreover, the bactericidal efficiency of Cly2v was evaluated via bactericidal kinetics curve assay. In brief, Cly2v (50 μg/mL) was incubated with bacteria, and bacterial counts were determined by serial dilutions on TSA plates at 5 min intervals for 45 min.
2.6 Evaluation of biofilm formation ability in Streptococcus
The biofilm-formation ability of Streptococcus was determined via the crystal violet staining method as described previously (Wang et al., 2023). Briefly, overnight cultured bacteria (~5 × 108 CFU/mL) were diluted in TSB medium at a ratio of 1:100. Subsequently, 100 μL of the bacteria and 100 μL of PBS were inoculated into a 96-well plate to form biofilms, while TSB medium served as the control. After incubation at 30°C for 24 h, the wells were washed three times with PBS and dried at room temperature. Each well was stained with 200 μL of crystal violet and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Finally, after washing the wells with PBS, 33% acetic acid was added to each well to dissolve the stain, and absorbance was measured at 590 nm. The experiments were conducted for three times.
2.7 Antibiofilm activity of Cly2v
To investigate the inhibitory ability of Cly2v against biofilms, overnight cultures of S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1 (~5 × 108 CFU/mL) were diluted at a 1:100 ratio. Subsequently, the bacteria were mixed with different doses of Cly2v (5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, and 25 μg/mL) and ampicillin (5 μg/mL) in a 96-well plate to form biofilms after incubation at 30°C for 24 h, with PBS serving as the control. Some wells were washed three times with PBS, resuspended in PBS, and then plated on TSA plates for colony counting. In other wells, biofilm formation ability was determined using the crystal violet staining method.
To investigate the effect of Cly2v on mature biofilms, S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1 (~5 × 108 CFU/mL) were diluted at a 1:100 ratio and inoculated into a 96-well plate without treatment to form biofilms. After incubation at 30°C for 24 h, different doses of Cly2v (10 μg/mL, 25 μg/mL, and 50 μg/mL) and ampicillin (5 μg/mL) were added to the wells, and the mixture was incubated at 37°C for 3 h. After incubation, the biofilms were determined by crystal-violet staining method and bacterial counts as described above. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.8 Scanning electron microscope
The morphological changes of bacterial mature biofilms treated with Cly2v were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) as described previously (Duan et al., 2023). Briefly, mid-logarithmic phase bacteria (~2 × 108 CFU/mL) were inoculated at a 1:100 ratio in a 24-well plate with coverslips and cultured at 30°C for 24 h to form biofilms. Subsequently, Cly2v (100 μg/mL) was added and the mixture were incubated at 37°C for 3 h to remove the biofilms. The samples were then washed with PBS and fixed with 2% glutaraldehyde for 2 h, followed by six washes with ddH2O. Finally, after spraying with gold, the coverslips were observed using scanning electron microscope (NTC JSM-6390LV, Japan).
2.9 Bactericidal activity of Cly2v in milk
The bactericidal activity of Cly2v in milk was evaluated as described previously (Wang et al., 2023). In brief, S. agalactiae ATCC13813 (1 × 105 CFU/mL) was grown in the whole milk at 37°C. After incubation for either 1 h and 2 h, 50 μg/mL of Cly2v was added to the milk and incubated at 37°C for 1 h. Subsequently, samples were serially diluted in ten-fold and plated on the TSA plates for colony counting. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
2.10 Toxicity of Cly2v on mammals’ cells and mouse tissues
To evaluate the toxicity of Cly2v on mammalian cells, a CCK-8 assay was carried out as described previously (Zhao et al., 2018). Cells, specifically PK15, IPEC-J2, and HEK-293 T were seeded at a density of 1 × 105 cells per well. Subsequently, cells were exposed with varying concentrations of Cly2v (200 μg/mL and 400 μg/mL) and incubation for 2 h, with PBS serving as the control. Cells viability was evaluated via the CCK-8 kit (MCE, United States) following the protocols, and the absorbance was measured at 450 nm. All the experiments were conducted for three times.
The toxicity of Cly2v to mouse tissues was further evaluated in a mouse model. Female specific-pathogen-free (SPF) BALB/c mice were divided into 3 groups (n = 5) and each group received an intraperitoneal injection of 400 μg or 800 μg of Cly2v, with PBS serving as the control. The survival rate and physiological condition of the mice were monitored for 5 days, and mouse organs were collected for pathological analysis at 5 d.
2.11 Mouse mastitis model
A mouse mastitis model was constructed as described previously to explore the efficacy of Cly2v against the bovine mastitis in vivo (Gutiérrez et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023). Briefly, female SPF BALB/c mice were synchronized for pregnancy by circadian cycle adjustment. At 14 to 21 days postpartum, the pups were allowed to nurse for 1 h to fully deplete the milk. Subsequently, the offspring were removed to establish the mastitis model while ensuring that the lactating females remained in the lactation period. Mice were anesthetized with 1.25% avertin, and a small incision of approximately 0.5 mm was made on the L4 and R4 mammary glands to expose the mammary duct. Then, S. agalactiae ATCC13813 (104 CFU/gland) was administered through the mammary duct, except for the control group. After 1 h post-infection, the L4 and R4 mammary glands were injected with PBS, Ply2741 (50 μg/gland), Cly2v (50 μg/gland), or Ceftiofur (25 μg/gland) to establish the PBS-treated group (n = 5), Ply2741-treated group (n = 5), Cly2v-treated group (n = 5), and antibiotic-treated group (n = 5). At 48 h post-treatment, the mice were humanely euthanized, and the L4 and R4 mammary glands were harvested and mixed. The mammary tissue samples were completely homogenized and serially diluted in a ten-fold series for viable cell counting. Inflammatory cytokine levels (TNF-α and IL-6) in the mammary tissues were determined via qRT-PCR assay. Additionally, mammary tissues were collected for histopathological analysis after 48 h of treatment.
2.12 RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and qRT-PCR
The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokine (TNF-α and IL-6) were determined by qRT-PCR assay (Wang et al., 2023). Briefly, TRIpure reagent (Aidlab, China) was used to extracted total RNA from mammary tissues. Subsequently, the extracted RNA was then reverse transcribed into cDNA, and qRT-PCR assay was performed on Applied Biosystems ViiA™7 system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) with Hieff ® qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix (Yeasen, China). The formula 2-ΔΔCt was used to analyzed the data and the GAPDH gene was served as the internal gene. The primers used in this assay are detailed in Supplementary Table S2.
2.13 Mouse systemic infection model
Five-week-old female SPF mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (n = 6 for each group) and each group injected intraperitoneally with S. agalactiae ATCC13813 at doses of 4 × 109 CFU, 2 × 109 CFU, 1 × 109 CFU, 5 × 108 CFU, and 2.5 × 108 CFU, respectively. Equal volumes of PBS were served as a control. The survival rate of mice was monitored and recorded for 48 h to determine the lethal dose. The minimum challenge dose that resulted in the death of all mice within 48 h was used for the survival rate experiment, while the maximum challenge dose that all mice survived was used for the bacterial load assay.
To explore the therapeutic effect of Cly2v on systemic infection caused by S. agalactiae, mice were randomly divided into 4 groups (n = 6 per group), Group I, II, III, and IV. Group I, II, and III was injected intraperitoneally with 1 × 109 CFU of S. agalactiae ATCC13813, with Group IV received an equal volume of PBS serving as the control. After 1 h post-infection, group II, III, and IV were treated with 200 μg or 400 μg doses of Cly2v, respectively, while the Group I received PBS as the control. The survival rate of mice was monitored for 5 d. Additionally, a survival experiment was established for treatment with Cly2v at 3 h post-infection. Mice were randomly divided into 3 groups (n = 9 per group) and were intraperitoneally injected with 1 × 109 CFU of S. agalactiae ATCC13813. After 3 h of infection, the mice in each group were treated with 200 μg or 400 μg of Cly2v, with an equal volume of PBS serving as the control. The survival rate of the mice was recorded for 5 days.
For bacterial load assay, mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (n = 9 per group), and each mouse was injected intraperitoneally of 2.5 × 108 CFU of S. agalactiae ATCC13813. The treatment group received 200 μg of Cly2v, while the control group was injected with PBS at 1 h post-infection. Mice were humanely euthanized after 6, 18, and 30 h of treatment, and blood, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, and kidneys organs were harvested. After homogenization and ten-fold dilution, the samples were plated on TSA plates for colony counting to determine the bacterial load in the organs.
2.14 Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and the normality of the data was analyzed using the Anderson-Darling test (N > 6) and Quantile-Quantile plots (N < 6). Statistical significance was analyzed using one- and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with GraphPad Prism (version 8). p values < 0.05 was considered statistically significant (*).
3 Results
3.1 Construction and structure analysis of Cly2v
To enhance the bactericidal activity of endolysins, we constructed a novel chimeric endolysin, Cly2v. Cly2v consisted of the CHAP domain from the S. suis endolysin Ply2741 and the CBD domain from the E. faecalis phage endolysin PlyV12. These two domains were connected by a flexible linker (GGSSGS) (Figure 1A). As shown in Supplementary Figure S1A, physicochemical analysis indicated that the theoretical isoelectric point and instability index of Cly2v were 9.52 and 27.69, respectively. Hydropathy analysis revealed that the GRAVY index of Cly2v was −0.413, with a higher number of hydrophilic residues compared to hydrophobic residues, indicating that Cly2v had the potential for soluble expression in vitro. After purification by AFC and SEC, Cly2v exhibited high purity in SDS-PAGE gel with the expected molecular weight (Figure 1B).
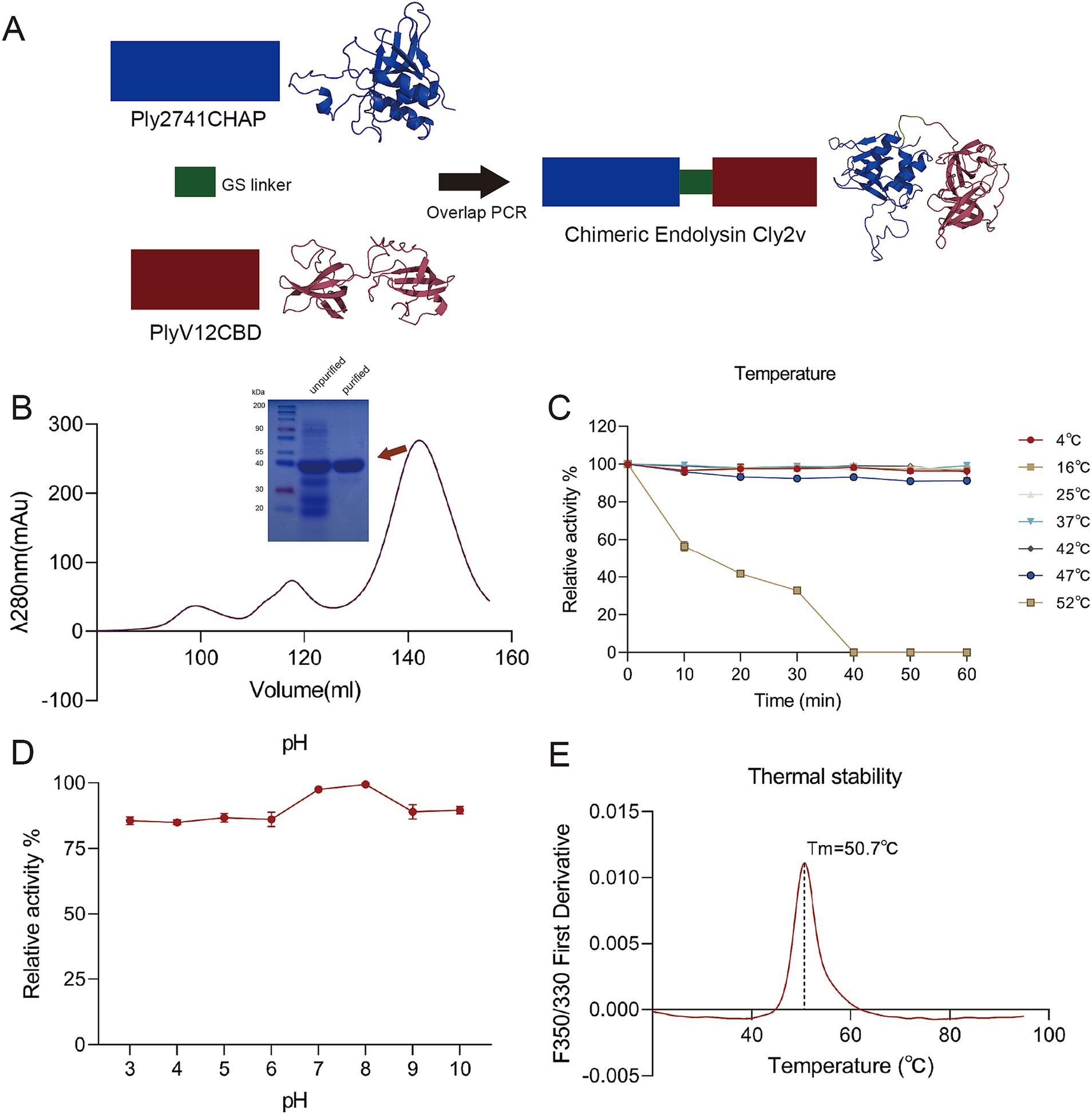
Figure 1. Construction and structure analysis of the chimeric endolysin Cly2v. (A) Schematic diagram and 3D structure of Cly2v. Cly2v was composed of the CHAP domain from Ply2741 and the CBD domain from PlyV12. The 3D structure was predicted using ColabFold. (B) Cly2v was purified by size exclusion chromatography and identified by SDS-PAGE gel, with the Cly2v protein having a molecular weight of 36 kDa. (C,D) Bactericidal activity of Cly2v under different temperatures (C) and pH conditions (D). Results are the means of three independent experiments. (E) The thermal stability analysis of Cly2v, with the spectra determined from 20°C to 95°C. Results represent the means of three independent experiments.
Additionally, circular dichroism and colabfold were used to analyze the secondary structure of Cly2v. The results showed that the proportions of α-helices, β-strands, and coils in Cly2v were 6.7, 41.9, and 33.4%, respectively (Supplementary Figure S1B). Specifically, the Cly2v consisted of 5 α-helices and 15 β-strands (Supplementary Figure S1C).
3.2 Biochemical characterization of Cly2v
The influence of temperature and pH on the bactericidal activity of the chimeric endolysin Cly2v were further evaluated. The results showed that Cly2v maintained over 90% activity between 4°C and 47°C. However, the bactericidal activity decreased significantly when the temperature increased to 52°C, and Cly2v was completely inactivated after incubation for 40 min at 52°C (Figure 1C). As shown in Figure 1D, Cly2v was able to maintain the bactericidal activity between pH = 3.0–10.0, with an optimal pH of 7.0–8.0. Additionally, thermal stability analysis revealed that the melting temperature (Tm) of Cly2v was 50.7°C, indicating that Cly2v could undergo denaturation and unfolding at temperatures above 50.7°C (Figure 1E). This result was consistent with the observation that Cly2v was inactivated at 52°C.
3.3 Cly2v exhibits broad-spectrum and high-efficiency bactericidal activity against streptococcal species causing mastitis in vitro
As shown in Figure 2A, Cly2v exhibited broad-spectrum bactericidal activity against various strains, including S. agalactiae, S. dysgalactiae, and S. uberis. Specifically, Cly2v demonstrated lytic efficiency greater than 40% in 12 out of 22 tested strains. More importantly, Cly2v exhibited higher bactericidal activity against streptococcal species causing mastitis compared with the parental endolysin Ply2741, indicating that Cly2v, a chimeric endolysin constructed based on the Ply2741, had better potential for the treatment of streptococci-induced mastitis in dairy cows.
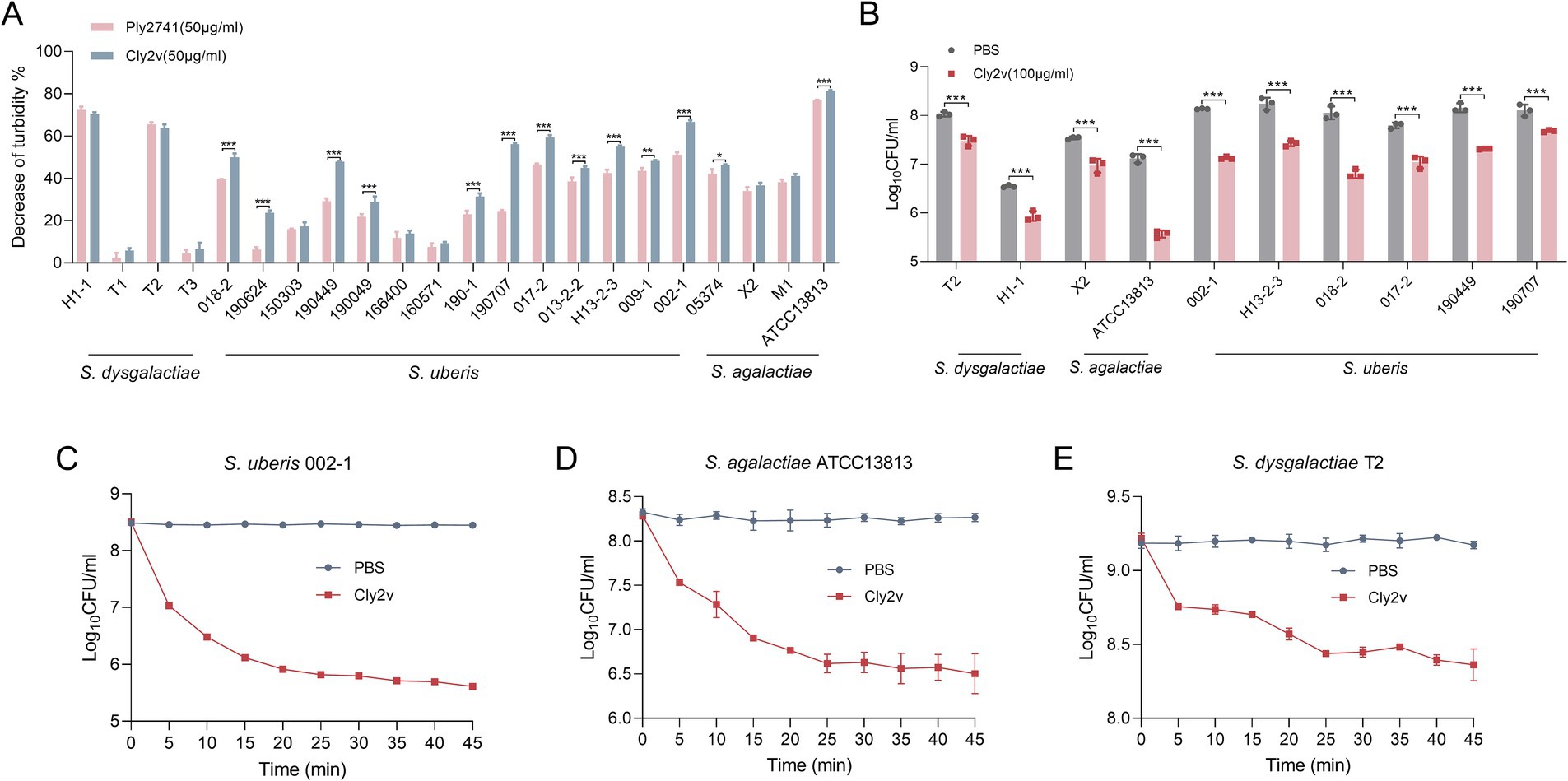
Figure 2. Host spectrum and bactericidal activity of Cly2v. (A) Host spectrum of Cly2v and parental endolysin Ply2741. Different Streptococcus (S. agalactiae, S. dysgalactiae, and S. uberis) were used as test strains. (B) Bactericidal activity of Cly2v against various Streptococcus. The number of viable bacteria was evaluated after treatment with 100 μg/mL of Cly2v for 1 h. (C–E) Bactericidal kinetics curve of Cly2v against Streptococcus. The number of bacteria was measured over 45 min following the mixing of 50 μg/mL of Cly2v with the S. uberis 002-1 (C), S. agalactiae ATCC13813 (D), and S. dysgalactiae T2 (E). Experimental data are shown as the mean of three independent experiments, with statistical analysis performed using two-way ANOVA (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
Additionally, the bactericidal activity of Cly2v was determined by measuring changes in bacterial colony counts after treatment. The results showed that Cly2v significantly reduced the bacterial count in all 10 selected streptococcal strains, particularly in S. agalactiae ATCC13813 strain, where 100 μg/mL of Cly2v led to a reduction from 7.12 log10CFU/ml to 5.57 log10CFU/ml, resulting in a reduction of 97.22% in bacterial count (Figure 2B). Subsequently, we evaluated the bactericidal kinetics curve of Cly2v. The results showed that 50 μg/mL of Cly2v was able to reduce the bacterial count of S. uberis 002–1 from 8.47 log10CFU/ml to 5.82 log10CFU/ml (a reduction percentage of 99.77%) (Figure 2C), S. agalactiae ATCC13813 from 8.24 log10CFU/ml to 6.63 log10CFU/ml (a reduction percentage of 97.56%) (Figure 2D), and S. dysgalactiae T2 from 9.18 log10CFU/ml to 8.44 log10CFU/ml (a reduction percentage of 81.70%) (Figure 2E) within 25 min.
3.4 Cly2v significantly inhibits and reduces biofilms of Streptococcus
Among the 18 tested strains, S. agalactiae X2, S. uberis 002–1, S.dysgalactiae T1, and S. uberis 018–2 showed the ability to form strong biofilms (Supplementary Figure S2). Due to the poor lytic activity of Cly2v against 018–2 and T1, we selected the strains S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1 for subsequent experiments. The results showed that Cly2v significantly inhibited biofilm formation in both S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1. At a concentration of 25 μg/mL, Cly2v decreased the OD590nm absorbance of biofilms by 68% (p < 0.001) and 44% (p < 0.001) for X2 and 002–1 (Figure 3A), respectively, while the bacterial counts decreased from 6.77 log10CFU/ml to 4.07log10CFU/ml and from 6.06 log10CFU/ml to 4.65 log10CFU/ml, corresponding to reductions of 99.80 and 96.09% (Figure 3B). Compared to Cly2v, ampicillin exhibited a stronger inhibitory effect on biofilm formation, with OD590nm absorbance decreasing by 84 and 68%, respectively. For established biofilms, Cly2v can significantly remove the biofilms in a dose-dependent manner. As shown in Figure 3C, Cly2v (50 μg/mL) significantly reduced the OD590nm absorbance of biofilms by 58% for X2 (p < 0.001) and 42% for 002–1 (p < 0.001). Additionally, Cly2v decreased the viable cell counts from 6.56 log10CFU/ml to 5.98 log10CFU/ml for X2 and from 5.73 log10CFU/ml to 3.48 log10CFU/ml for 002–1, corresponding to reductions of 73.74 and 99.45% (Figure 3D). Notably, ampicillin demonstrated no effect on mature biofilms.
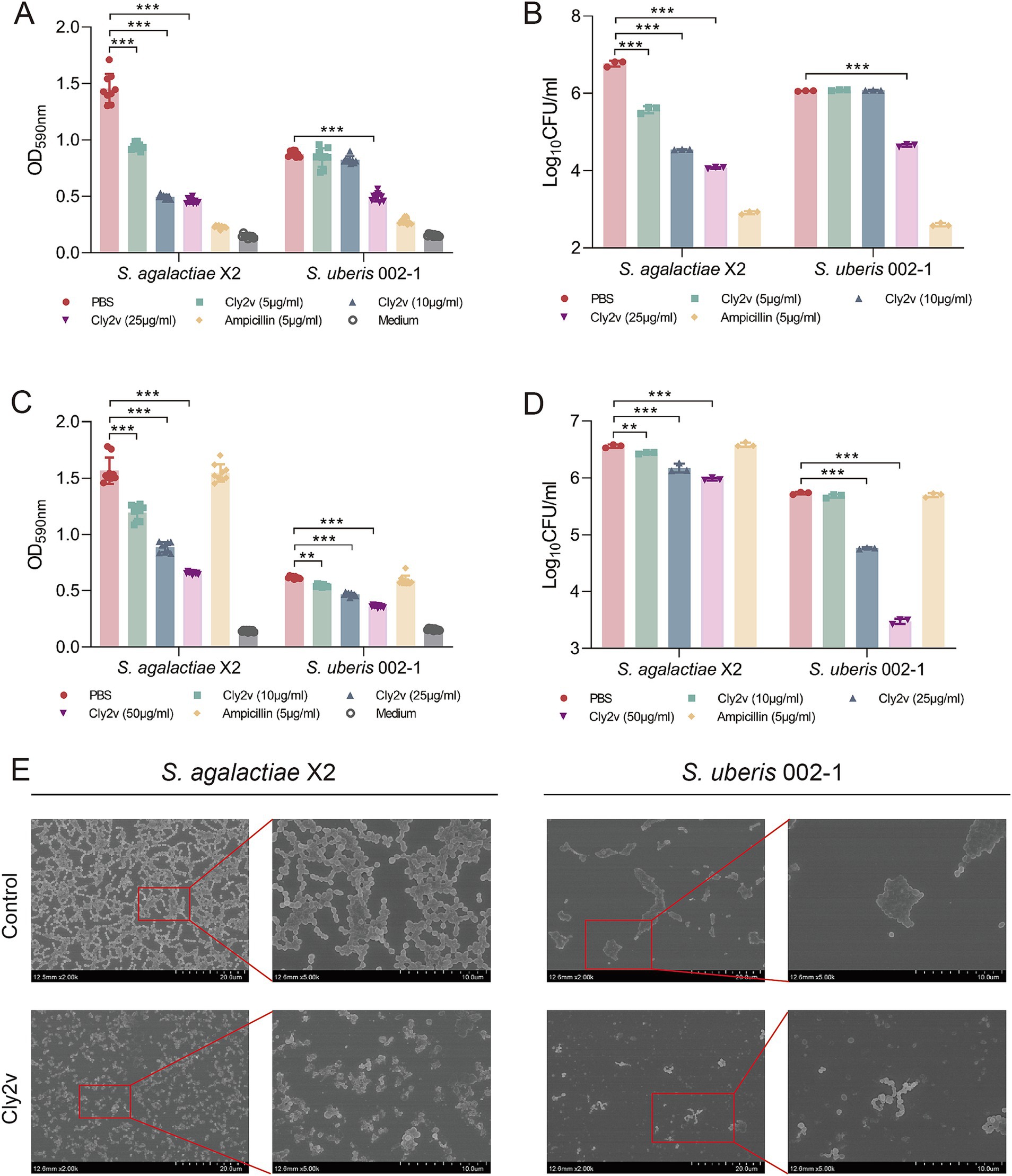
Figure 3. Effects of Cly2v on bacterial biofilms. (A,B) The inhibitory effect of Cly2v on biofilm formation was measured by absorbance at OD590nm (A) and viable cell counts (B) after mixing different dose of Cly2v with bacteria. (C,D) Effect of Cly2v on mature bacterial biofilms. The absorbance at OD590nm (C) and the number of viable cells (D) were measured after treatment with different dose of Cly2v. The experimental results are presented as the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed using two-way ANOVA (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001). (E) SEM results of Cly2v (100 μg/mL) removing mature biofilms of S. agalactiae X2 and S. uberis 002–1. Magnification: × 2000 (left) and × 5,000 (right).
To observe the morphological changes in bacterial biofilms after Cly2v treatment, we employed scanning electron microscopy (SEM) experiment. The results demonstrated that, compared to the control group, the established biofilms treated with Cly2v exhibited a loose adherence, with no contiguous biofilm formation and a significant reduction in viable cell counts (Figure 3E). These results indicated that Cly2v not only significantly inhibited the formation of bacterial biofilms but also effectively removed mature biofilms.
3.5 Cly2v effectively reduces streptococci in whole milk
Streptococci-induced bovine mastitis can adversely impact milk quality. Therefore, we investigated the bactericidal activity of Cly2v against S. agalactiae ATCC13813 in whole milk. As shown in Supplementary Figure S3, after incubating milk with S. agalactiae ATCC13813 for 1 h, the addition of Cly2v led to a significant decrease in bacterial counts, with the counts decreasing from 6.51 log10CFU/ml to 6.09 log10CFU/ml, corresponding to a reduction of approximately 62.0% (p < 0.05).Additionally, Cly2v was added to infected milk at 100 μg/mL after 2 h infection, and the bacterial count decreased from 7.15 log10CFU/ml to 6.49 log10CFU/ml (approximately 74.2% reduction, p < 0.01). These results indicated that Cly2v could significantly reduce streptococci in whole milk.
3.6 Cly2v exhibits significant therapeutic potential against early-stage streptococci-induced mastitis in mice
To investigate the therapeutic effect of Cly2v in bovine mastitis, we established a mouse mastitis model and treated it with Cly2v. Ply2741 and ceftiofur were served as the parental endolysin control and positive control, respectively (Figure 4A). As shown in Figure 4B, Cly2v significantly reduced the bacterial burden in mouse mammary tissues, decreasing the bacterial counts from 5.99 log10CFU/g to 3.83 log10CFU/g, representing a reduction of 99.3% (p < 0.001). Additionally, compared to the parental endolysin Ply2741, the reduction in bacterial burden in mouse mammary tissues after Cly2v treatment was more substantial (p < 0.01). Notably, the ceftiofur-group also reduced bacterial counts to 3.68 log10CFU/g, comparable to the effect observed with Cly2v treatment (p > 0.05). Moreover, Cly2v, Ply2741, and ceftiofur treatments significantly decreased the mRNA levels of inflammatory factors in mouse mammary tissues. After treatment with Cly2v, TNF-α and IL-6 levels decreased by 15.77-fold (Figure 4C) and 2.51-fold (Figure 4D), respectively, with no significant difference compared to the antibiotic group. Histopathological analysis revealed that after infection with S. agalactiae, there was significant thickening of the alveolar wall in the mammary tissue of mice, accompanied by severe edema, congestion, and a large number of inflammatory cells and erythrocyte infiltration, compared to the control group. After treatment with Cly2v, Ply2741, and ceftiofur, the mammary tissues exhibited minimal pathological alterations, with the Cly2v-group showing the least pathological damage (Figure 4E). These results indicated that Cly2v significantly reduced bacterial load in early-stage mouse mastitis models, demonstrating its potential as a treatment for streptococci-induced mastitis.

Figure 4. Therapeutic effects of Cly2v on early-stage S. agalactiae ATCC13813-induced mouse mastitis. (A) Schematic representation of the early-stage mouse mastitis treatment model. (B) Bacterial load of S. agalactiae ATCC13813 in mouse mammary tissue after treatment with Cly2v (50 μg/gland), Ply2741 (50 μg/gland), and ceftiofur (25 μg/gland). (C,D) The mRNA levels of TNF-α (C) and IL-6 (D) in mouse mammary tissue measured by qRT-PCR and analyzed by the formula 2-ΔΔCt after treatment. (E) Histopathological changes in mouse mammary tissue after treatment with PBS, Cly2v, Ply2741, ceftiofur, and control. The experimental results are presented as the mean of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was analyzed using one-way ANOVA (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
3.7 Cly2v exhibits no significant toxicity in mammalian cells and mice organs
To evaluate the toxicity of Cly2v on mammalian cells, a CCK8 assay was employed. As shown in Supplementary Figure S4A, the results showed that the survival rates of HEK-293 T, PK15, and IPEC-J2 cells exceeded 100% at concentrations at 200 μg/mL and 400 μg/mL, indicating that Cly2v exhibited no significant toxicity to mammalian cells. Additionally, the toxicity evaluation results indicated that mice receiving intraperitoneal injections of 400 μg, and 800 μg of Cly2v exhibited a 100% survival rate and maintained normal physiological conditions (Supplementary Figure S4B). Pathological analysis indicated that, similar to the PBS group, mice administered 800 μg of Cly2v exhibited no significant pathological damage in their organs (Supplementary Figure S4C).
3.8 Cly2v exhibits therapeutic efficacy in mice with systemic streptococci infections
To investigate the therapeutic effects of Cly2v on systemic infection caused by Streptococcus, we first determined the optimal challenge dose of S. agalactiae ATCC13813. The mice challenged with a dose of 1 × 109 CFU/mouse died within 48 h, while those infected with a dose of 2.5 × 108 CFU survived for 48 h (Supplementary Table S3). Consequently, the optimal infection dose of S. agalactiae ATCC13813 for the survival rate experiment was 1 × 109 CFU, while the challenge dose for the bacterial load assay was 2.5 × 108 CFU.
To further evaluated the therapeutic efficacy of Cly2v against S. agalactiae infection in vivo, we established a systemic infection model in mice and treated with different doses of Cly2v. The results demonstrated that Cly2v exhibited significant protection for mice infected with S. agalactiae ATCC13813. Mice administered an intraperitoneal injection of 200 μg of Cly2v had a survival rate of 83% within 5 days, and those given a dose of 400 μg had a survival rate of 100%, whereas all mice in the control group died within 24 h (Figure 5A). Additionally, the bacterial load in the blood and various organs of mice was determined at different time points following treatment to further evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of the chimeric endolysin Cly2v. The results demonstrated a significant reduction in bacterial load in the blood and organs at 6 h, 18 h, and 30 h post-treatment (Figure 5B). Specifically, at 30 h post-treatment, the bacterial loads in the blood, heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys were 1.49 log10CFU/mL, 2.22 log10CFU/g, 2.37 log10CFU/g, 3.33 log10CFU/g, 3.68 log10CFU/g, and 2.82 log10CFU/g, representing decreases of 90.1, 99.7, 99.7, 99.7, 96.6, and 99.3%, respectively. Notably, treatment with 400 μg of Cly2v at 3 h post-infection provided a protection rate of 78% (Figure 5C). Although this was less effective compared to treatment at 1 h post-infection, Cly2v still demonstrated efficacy against late-stage sepsis induced by streptococcal infection.
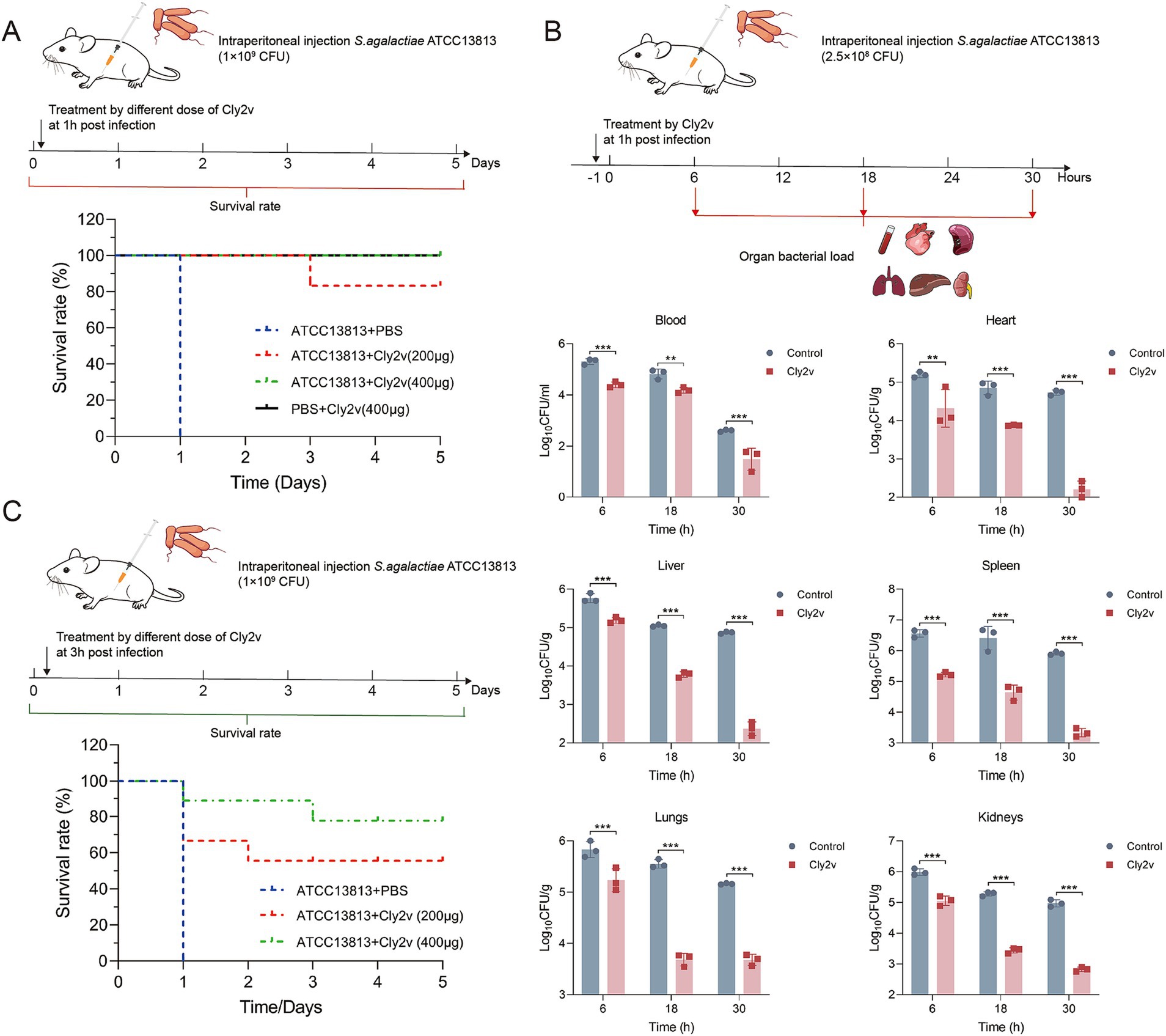
Figure 5. Therapeutic effects of Cly2v on systemic infection caused by S. agalactiae ATCC13813. (A) The survival rate of mice treated with 200 μg or 400 μg of Cly2v after 1 h of infection with 1 × 109 CFU of S. agalactiae ATCC13813 (n = 6). (B) Bacterial load in blood, heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys of mice at 6 h, 18 h, and 30 h post-treatment with Cly2v. (C) Survival rate of mice challenged with 1 × 109 CFU of S. agalactiae ATCC13813 after treatment with Cly2v (200 μg and 400 μg) at 3 h post-infection (n = 9). The experimental results are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was analyzed using two-way ANOVA (* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001).
4 Discussion
Bovine mastitis is regarded as a significant challenge in the dairy farming industry, threatening the advancement of livestock production and causing substantial economic losses (Rollin et al., 2015; Nyman et al., 2018). Streptococcus, including S. uberis, S. agalactiae, and S. dysgalactiae, are major pathogens responsible for bovine mastitis (Kabelitz et al., 2021). Although antibiotics are commonly used to combat bovine mastitis, the prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria and the risk of antibiotic residues in the food chain and dairy products highlight the urgent need to develop novel antibiotic alternatives.(Gomes and Henriques, 2016; Tomazi and dos Santos, 2020). Endolysins have been widely reported for their independent bactericidal activity in vitro and gathered significant attention from researchers (Fischetti, 2010; Linden et al., 2021).
Endolysins usually possess a classic modular structure which provide new directions for modification and design (Yang et al., 2014a). In this study, we constructed a novel chimeric endolysin, Cly2v, which was composed of the CHAP catalytic domain of Ply2741 and the CBD domain of PlyV12. In vitro experiments demonstrated that Cly2v exhibited stronger bactericidal activity against S. uberis, S. agalactiae, and S. dysgalactiae compared to the parental endolysin Ply2741 (Figure 2A). This adaptive modification could expand the application scenarios of endolysins, allowing for the development of more effective chimeric endolysins targeting different pathogens. Yang et al. demonstrated that the S. suis was more susceptible to chimeric endolysin ClyV rather than its parental endolysin GBS180 (Huang et al., 2020). Additionally, the chimeric endolysin ClyQ showed a broader lytic spectrum and delayed the development of mupirocin resistance in S. aureus compared to its parental endolysin LysGH15 (Duan et al., 2023). The CHAP domain usually plays a catalytic role on the bacterial peptidoglycan, while the CBD domain is able to binds to peptidoglycan sites on the bacterial cell wall (Gonzalez-Delgado et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2020). The CBD domain is critical for the bactericidal spectrum and activity. Gu et al. demonstrated that LysGH15CBD can only bind to S. aureus, thus exhibiting lytic activity exclusively against this species (Gu et al., 2011) species. Conversely, the chimeric endolysin Ply187N-V12C, constructed by Dong et al., displays a broader lytic spectrum and enhanced activity because its V12CBD can bind to Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Enterococcus species (Dong et al., 2015). Compared to the parental endolysin Ply2741, Cly2v possesses the same CHAP domain. The enhanced activity of Cly2v may be attributed to the stronger binding affinity of CBD to Streptococcus causing bovine mastitis, thereby maximizing the catalytic function of the CHAP domain (Dong et al., 2015). These results imply that modifying and designing endolysins can significantly enrich the endolysin database and enhance their bactericidal activity and application prospects.
Bacteria typically form biofilms by extracellular polymer, which confer resistance to antibiotics and the host immune system (Berger et al., 2010). Biofilms can increase tolerance to antibiotics by up to 1,000-fold and serve as reservoirs for multidrug-resistant bacteria (Hall and Mah, 2017). Bacterial biofilms, along with somatic cells, can clog mammary ducts, making it difficult for antibiotics to penetrate the mammary tissue effectively (Gutiérrez et al., 2020). Remarkably, the chimeric endolysin Cly2v not only inhibited the formation of bacterial biofilms but also significantly removed mature biofilms. After treatment with Cly2v, bacterial biofilms became noticeably thinner, and the biomass significantly decreased (Figure 3E). Bacteria can resist antibiotic eradication by adapting to a biofilm lifestyle or by ceasing growth due to nutrient limitation (Ciofu et al., 2022). However, endolysins are independent of bacterial metabolic mechanisms by directly targeting bacterial peptidoglycans and penetrating deeper into the bacteria. Additionally, certain components in milk may affect the efficacy of endolysins against mastitis. Therefore, we investigated the bactericidal activity of Cly2v in milk. Compared to PBS buffer, the bactericidal activity of Cly2v was significantly reduced in milk. Previous studies have found that fat globules in milk could bind to host bacteria, leading to aggregation and bacterial clumping, which might affect the stability and bactericidal activity of endolysins in milk (O’Flaherty et al., 2005; Schmelcher et al., 2012).
Although Cly2v had shown high efficiency bactericidal activity against streptococci-induced mastitis in vitro and in whole milk, previous studies suggested that the in vitro bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents such as endolysins does not always correlate with bactericidal activity within mammary tissues (Apparao et al., 2009; Demon et al., 2012). This phenomenon may be due to interactions between bacteria and host immune cells in the mammary tissue, which can lead to a decrease in drug efficacy in mammary gland (Demon et al., 2013). Therefore, it is crucial to establish suitable animal models to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of drugs. Mouse mastitis models have been widely used for evaluating agents for mastitis (Sanchez et al., 1994). Previous studies on the clinical application of endolysins in bovine mastitis have primarily focused on S. aureus (Zdunczyk and Janowski, 2020). Only natural endolysins Ply0643 and Lys0859 have shown significant therapeutic effects against streptococci-induced bovine mastitis in murine mastitis models (Liu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). In a mouse model, Cly2v could significantly reduce the bacterial load and inflammatory cytokines levels in mouse mammary tissues, demonstrating significant therapeutic efficacy against early-stage streptococci-induced mouse mastitis (Figures 4B–E). Schmelcher et al. found that treatment with λSA2 (25 μg/gland) and B30 (250 μg/gland) reduced the number of S. agalactiae in the mouse mammary gland by 2.0 and 4.5 log at 45 min post-infection, respectively (Schmelcher et al., 2015). Similarly, the endolysin Ply0643 (100 μg/gland) effectively treated S. agalactiae-induced bovine mastitis, reducing bacterial counts in mammary tissue from 6.4 × 104 CFU/g to 4 × 102 CFU/g at 1 h post-infection (Liu et al., 2022). Although the number of bacteria decreased by Cly2v in the mammary gland less than B30, it can exert bactericidal activity at a lower dose, suggesting that Cly2v could be more cost-effective in future clinical applications.
Notably, treatment at 1 h post-infection may lead to insufficient colonization of bacteria in the mammary tissue. However, Schmelcher et al. found that the time interval between infection and treatment may not be critical, potentially due to the relatively low number of resident phagocytes in mouse mammary tissue, which leads to a faster infection rate compared to cows (Schmelcher et al., 2012). Guo et al. also demonstrated significant therapeutic efficacy with phage therapy at 6 h post-infection (Guo et al., 2024). Therefore, the effect of Cly2v in the treatment of late-stage bovine mastitis warrants further investigation. To our knowledge, Cly2v is the first chimeric endolysin evaluated in a mouse model of streptococci-induced mastitis, highlighting the potential of engineered endolysins for treating bovine mastitis and significantly enriching the endolysin database. Additionally, endolysins demonstrated significant efficacy in treating multidrug-resistant bacteria (Zhang et al., 2023), suggesting that Cly2v may also have advantages for treating MDR infections in bovine mastitis. Future research will focus on exploring the combination of endolysin Cly2v with antibiotics to assess their synergistic effects against bacterial infections.
Streptococcus agalactiae is not only a major pathogen of bovine mastitis but also causes serious diseases such as meningitis, neonatal pneumonia, and sepsis (Johri et al., 2006). Bacterial mastitis can further lead to severe systemic infections. Therefore, we established a systemic infection model with S. agalactiae to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of Cly2v. Remarkably, Cly2v significantly improved the survival rate of mice infected with S. agalactiae, with a dose of 200 μg/mouse resulting in an 83% survival rate (Figure 5B). Furthermore, treatment with Cly2v led to a significant reduction in bacterial load in the blood and various organs. Interestingly, when treatment with 400ug of Cly2v at 3 h post-infection, the survival rate of the mice was only 78%. While Xi et al. observed that systemic infection occurred within 1 h after Streptococcus infection (Xi et al., 2023), delaying treatment until 3 h post-infection may result in irreversible damage to the mice tissues and organs, leading to a decreased survival rate. However, these results still demonstrated the significant efficacy of Cly2v in treating bacterial systemic infections. Importantly, Cly2v exhibited no toxicity to both the mammal cells and animal. These findings underscore the substantial potential of Cly2v as a novel antibiotic alternative.
In summary, we constructed a novel chimeric endolysin, Cly2v, which demonstrates more efficient bactericidal activity against Streptococcus causing bovine mastitis in vitro compared to the parental endolysin Ply2741. Additionally, in mouse models, Cly2v showed significant therapeutic effects against both early-stage mouse bovine mastitis and systemic infections induced by S. agalactiae. These results underscore the substantial potential of Cly2v in treating bacterial mastitis and provide new support and insights for further modification of endolysins.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.27108784.v1.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Huazhong Agricultural University (HZAUMO-2024-0212 and HZAUMO-2024-0276). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Data curation, Conceptualization. XL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation. JJ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Data curation. XL: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. XD: Writing – review & editing. DH: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. PQ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Agricultural Science and Technology Research project of Hubei Province (HBNYHXGG2023-3), the National Program on Key Research Project of China (2022YFD1800800), “Yingzi Tech and Huazhong Agricultural University Intelligent Research Institute of Food Health” (No. IRIFH202209; IRIFH202301), and the National Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology (AML2023B11).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the National Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology Core Facility and we would be grateful to Jing Yuan, Limin He, Fangkui Wang and Shaoran Zhang for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1482189/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
Ajose, D. J., Oluwarinde, B. O., Abolarinwa, T. O., Fri, J., Montso, K. P., Fayemi, O. E., et al. (2022). Combating bovine mastitis in the dairy sector in an era of antimicrobial resistance: ethno-veterinary medicinal option as a viable alternative approach. Front. Vet. Sci. 9:322. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.800322
Apparao, M. D., Ruegg, P. L., Lago, A., Godden, S., Bey, R., and Leslie, K. (2009). Relationship between in vitro susceptibility test results and treatment outcomes for gram-positive mastitis pathogens following treatment with cephapirin sodium. J. Dairy Sci. 92, 2589–2597. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1693
Berger, C. N., Sodha, S. V., Shaw, R. K., Griffin, P. M., Pink, D., Hand, P., et al. (2010). Fresh fruit and vegetables as vehicles for the transmission of human pathogens. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 2385–2397. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02297.x
Ciofu, O., Moser, C., Jensen, P. O., and Hoiby, N. (2022). Tolerance and resistance of microbial biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 621–635. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00682-4
Demon, D., Breyne, K., Schiffer, G., and Meyer, E. (2013). Antimicrobial efficacy of intramammary treatment with a novel biphenomycin compound against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, and Escherichia coli-induced mouse mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 96, 7082–7087. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-7011
Demon, D., Ludwig, C., Breyne, K., Guédé, D., Dörner, J. C., Froyman, R., et al. (2012). The intramammary efficacy of first generation cephalosporins against Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in mice. Vet. Microbiol. 160, 141–150. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.05.017
Doehn, J. M., Fischer, K., Reppe, K., Gutbier, B., Tschernig, T., Hocke, A. C., et al. (2013). Delivery of the endolysin Cpl-1 by inhalation rescues mice with fatal pneumococcal pneumonia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 68, 2111–2117. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt131
Dong, Q. H., Wang, J., Yang, H., Wei, C. H., Yu, J. P., Zhang, Y., et al. (2015). Construction of a chimeric lysin Ply187N-V12C with extended lytic activity against staphylococci and streptococci. Microb. Biotechnol. 8, 210–220. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12166
Duan, X. C., Li, X. X., Li, X. M., Wang, S., Zhang, F. Q., and Qian, P. (2023). Exploiting broad-Spectrum chimeric Lysin to cooperate with mupirocin against Staphylococcus aureus-induced skin infections and delay the development of mupirocin resistance. Microbiology. Spectrum 11:22. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05050-22
Dyson, R., Charman, N., Hodge, A., Rowe, S. M., and Taylor, L. F. (2022). A survey of mastitis pathogens including antimicrobial susceptibility in southeastern Australian dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 105, 1504–1518. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20955
El-Sayed, A., and Kamel, M. (2021). Bovine mastitis prevention and control in the post-antibiotic era. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 53:236. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02680-9
Fischetti, V. A. (2010). Bacteriophage endolysins: a novel anti-infective to control gram-positive pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 300, 357–362. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.04.002
Gilmer, D. B., Schmitz, J. E., Euler, C. W., and Fischetti, V. A. (2013). Novel bacteriophage lysin with broad lytic activity protects against mixed infection by Streptococcus pyogenes and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57, 2743–2750. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02526-12
Gomes, F., and Henriques, M. (2016). Control of bovine mastitis: old and recent therapeutic approaches. Curr. Microbiol. 72, 377–382. doi: 10.1007/s00284-015-0958-8
Gonzalez-Delgado, L. S., Walters-Morgan, H., Salamaga, B., Robertson, A. J., Hounslow, A. M., Jagielska, E., et al. (2020). Two-site recognition of peptidoglycan by lysostaphin SH3b. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16, 24–30. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0393-4
Gu, J., Lu, R., Liu, X., Han, W., Lei, L., Gao, Y., et al. (2011). LysGH15B, the SH3b domain of staphylococcal phage endolysin LysGH15, retains high affinity to staphylococci. Curr. Microbiol. 63, 538–542. doi: 10.1007/s00284-011-0018-y
Guo, M., Zhang, Y., Wu, L., Xiong, Y., Xia, L., Cheng, Y., et al. (2024). Development and mouse model evaluation of a new phage cocktail intended as an alternative to antibiotics for treatment of Staphylococcus aureus-induced bovine mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 107, 5974–5987. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-24540
Gutiérrez, D., Garrido, V., Fernández, L., Portilla, S., Rodríguez, A., Grilló, M. J., et al. (2020). Phage lytic protein LysRODI prevents staphylococcal mastitis in mice. Front. Microbiol. 11:7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00007
Hall, C. W., and Mah, T. F. (2017). Molecular mechanisms of biofilm-based antibiotic resistance and tolerance in pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41, 276–301. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fux010
He, W. J., Ma, S. Z., Lei, L., He, J. J., Li, X., Tao, J., et al. (2020). Prevalence, etiology, and economic impact of clinical mastitis on large dairy farms in China. Vet. Microbiol. 242:108570. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108570
Huang, L., Luo, D., Gondil, V. S., Gong, Y., Jia, M., Yan, D., et al. (2020). Construction and characterization of a chimeric lysin ClyV with improved bactericidal activity against Streptococcus agalactiae in vitro and in vivo. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 1609–1619. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10325-z
Johri, A. K., Paoletti, L. C., Glaser, P., Dua, M., Sharma, P. K., Grandi, G., et al. (2006). Group B: global incidence and vaccine development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 932–942. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1552
Kabelitz, T., Aubry, E., van Vorst, K., Amon, T., and Fulde, M. (2021). The role of Streptococcus spp. in bovine mastitis. Microorganisms 9:1497. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071497
Kayano, M., Itoh, M., Kusaba, N., Hayashiguchi, O., Kida, K., Tanaka, Y., et al. (2018). Associations of the first occurrence of pathogen-specific clinical mastitis with milk yield and milk composition in dairy cows. J. Dairy Res. 85, 309–316. doi: 10.1017/S0022029918000456
Li, X. X., Zhang, F. Q., Wang, S., Duan, X. C., Hu, D. Y., Gao, D. Y., et al. (2023). Streptococcus suis prophage lysin as a new strategy for combating streptococci-induced mastitis and Streptococcus suis infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 78, 747–756. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad006
Linden, S. B., Alreja, A. B., and Nelson, D. C. (2021). Application of bacteriophage-derived endolysins to combat streptococcal disease: current state and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 68, 213–220. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2021.01.012
Liu, G. J., Zhang, S. Y., Gao, T. T., Mao, Z., Shen, Y. L., Pan, Z. H., et al. (2022). Identification of a novel broad-spectrum endolysin, Ply0643, with high antibacterial activity in mouse models of streptococcal bacteriaemia and mastitis. Res. Vet. Sci. 143, 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.12.014
Lu, Y. F., Wang, Y. R., Wang, J., Zhao, Y., Zhong, Q., Li, G., et al. (2021). Phage Endolysin LysP108 showed promising antibacterial potential against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 11:430. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.668430
Luo, D. H., Huang, L., Gondil, V. S., Zhou, W. L., Yang, W., Jia, M. H., et al. (2020). A choline-recognizing monomeric Lysin, ClyJ-3m, shows elevated activity against. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 64:311. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00311-20
McCullers, J. A., Karlström, Å., Iverson, A. R., Loeffler, J. M., and Fischetti, V. A. (2007). Novel strategy to prevent otitis media caused by colonizing Streptococcus pneumoniae. PLoS Pathog. 3:e28. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030028
Mirdita, M., Schütze, K., Moriwaki, Y., Heo, L., Ovchinnikov, S., and Steinegger, M. (2022). ColabFold: making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 19, 679–682. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01488-1
Murray, E., Draper, L. A., Ross, R. P., and Hill, C. (2021). The advantages and challenges of using Endolysins in a clinical setting. Viruses-Basel 13:680. doi: 10.3390/v13040680
Nyman, A. K., Fasth, C., and Waller, K. P. (2018). Intramammary infections with different non-staphylococci in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 101, 1403–1418. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13467
O’Flaherty, S., Coffey, A., Meaney, W. J., Fitzgerald, G. F., and Ross, R. P. (2005). Inhibition of bacteriophage K proliferation on Staphylococcus aureus in raw bovine milk. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 41, 274–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01762.x
Oliver, S. P., and Murinda, S. E. (2012). Antimicrobial resistance of mastitis pathogens. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 28:165. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2012.03.005
Pang, M. D., Xie, X., Bao, H. D., Sun, L. C., He, T., Zhao, H., et al. (2018). Insights into the bovine Milk microbiota in dairy farms with different incidence rates of subclinical mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 9:2379. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02379
Raabe, V. N., and Shane, A. L. (2019). Group B streptococcus (Streptococcus agalactiae). Microbiol. Spectr. 7:18. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0007-2018
Rollin, E., Dhuyvetter, K. C., and Overton, M. W. (2015). The cost of clinical mastitis in the first 30 days of lactation: an economic modeling tool. Prev. Vet. Med. 122, 257–264. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2015.11.006
Sanchez, M. S., Ford, C. W., and Yancey, R. J. (1994). Efficacy of tumor-necrosis-factor-alpha and antibiotics in therapy of experimental murine staphylococcal mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 77, 1259–1266. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(94)77065-X
Schmelcher, M., Powell, A. M., Becker, S. C., Camp, M. J., and Donovan, D. M. (2012). Chimeric phage lysins act synergistically with lysostaphin to kill mastitis-causing Staphylococcus aureus in murine mammary glands. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 2297–2305. doi: 10.1128/Aem.07050-11
Schmelcher, M., Powell, A. M., Camp, M. J., Pohl, C. S., and Donovan, D. M. (2015). Synergistic streptococcal phage λSA2 and B30 endolysins kill streptococci in cow milk and in a mouse model of mastitis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99, 8475–8486. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6579-0
Sharun, K., Dhama, K., Tiwari, R., Gugjoo, M. B., Yatoo, M. I., Patel, S. K., et al. (2021). Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: a comprehensive review. Vet. Q. 41, 107–136. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2021.1882713
Tomazi, T., and dos Santos, M. V. (2020). Antimicrobial use for treatment of clinical mastitis in dairy herds from Brazil and its association with herd-level descriptors. Prev. Vet. Med. 176:104937. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2020.104937
Viguier, C., Arora, S., Gilmartin, N., Welbeck, K., and O'Kennedy, R. (2009). Mastitis detection: current trends and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 27, 486–493. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.05.004
Wang, S., Mirmiran, S. D., Li, X., Li, X., Zhang, F., Duan, X., et al. (2023). Temperate phage influence virulence and biofilm-forming of salmonella typhimurium and enhance the ability to contaminate food product. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 398:110223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110223
Xi, H., Fu, Y., Chen, C., Feng, X., Han, W., Gu, J., et al. (2023). Aerococcus viridans phage Lysin AVPL had lytic activity against Streptococcus suis in a mouse bacteremia model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:670. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316670
Yang, H., Yu, J. P., and Wei, H. P. (2014a). Engineered bacteriophage lysins as novel anti-infectives. Front. Microbiol. 5:542. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00542
Yang, H., Zhang, Y., Yu, J., Huang, Y., Zhang, X. E., and Wei, H. (2014b). Novel chimeric lysin with high-level antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 58, 536–542. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01793-13
Zamojska, D., Nowak, A., Nowak, I., and Macierzynska-Piotrowska, E. (2021). Probiotics and Postbiotics as substitutes of antibiotics in farm animals: a review. Animals 11:431. doi: 10.3390/ani11123431
Zdunczyk, S., and Janowski, T. (2020). Bacteriophages and associated endolysins in therapy and prevention of mastitis and metritis in cows: current knowledge. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 218:106504. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2020.106504
Zhang, H., Zhang, X., Liang, S., Wang, J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, W., et al. (2023). Bactericidal synergism between phage endolysin Ply2660 and cathelicidin LL-37 against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 9:385:16. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00385-5
Zhao, H. L., Wu, B. Q., Luo, Y., Zhang, W. Y., Hao, Y. L., Liang, J. J., et al. (2018). Exogenous hydrogen sulfide ameliorates high glucose-induced myocardial injury & inflammation the CIRP-MAPK signaling pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells. Life Sci. 208, 315–324. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.05.051
Keywords: chimeric endolysin, bovine mastitis, therapeutic evaluation, systemic infection, Streptococcus, bactericidal activity
Citation: Wang S, Li X, Ji J, Li X, Zhu H, Duan X, Hu D and Qian P (2024) A novel chimeric endolysin Cly2v shows potential in treating streptococci-induced bovine mastitis and systemic infections. Front. Microbiol. 15:1482189. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1482189
Edited by:
Oscar Juarez, Illinois Institute of Technology, United StatesReviewed by:
Dexi Li, Henan Agricultural University, ChinaMartín Andrés González-Montalvo, Illinois Institute of Technology, United States
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Li, Ji, Li, Zhu, Duan, Hu and Qian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ping Qian, cWlhbnBAbWFpbC5oemF1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shuang Wang
Shuang Wang Xinxin Li1,2,3†
Xinxin Li1,2,3† Xiangmin Li
Xiangmin Li Ping Qian
Ping Qian