
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol., 05 November 2024
Sec. Microbiotechnology
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1478305
This article is part of the Research TopicMicrobial Biotechnologies for Efficient Wastewater Treatment and Resource RecoveryView all 13 articles
Manganese (Mn) oxidation processes have garnered significant attention recently due to their potential for degrading organic pollutants. These processes are primarily catalyzed by Mn(II) oxidases. Salinicola tamaricis F01, an endophytic bacterium derived from wetland plants, has demonstrated Mn(II)-oxidizing capacity. In this study, a catalase-peroxidase, StKatG2, was cloned and overexpressed in Escherichia coli from the strain F01. The purified recombinant StKatG2 exhibited Mn(II)-oxidizing activity with Km and Kcat values of 2.529 mmol/L and 2.82 min−1, respectively. Optimal catalytic conditions for StKatG2 were observed at pH 7.5 and 55°C, with 45.1% activity retention after an 8-h exposure to 80°C. The biogenic manganese oxides produced by StKatG2 exhibited mixed-valence states with Mn(II), including Mn(III), Mn(IV), and Mn(VII). Furthermore, StKatG2 demonstrated superior decolorization efficiency for malachite green (MG), achieving decolorization rates of 73.38% for 20 mg/L MG and 60.08% for 50 mg/L MG, while degrading MG into 4-(dimethylamino)benzophenone. Therefore, the catalase-peroxidase StKatG2 exhibits multifunctionality in Mn(II)-oxidizing activity and has the potential to serve as an environmentally friendly enzyme for MG removal.
Malachite green (4-[(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-phenyl-methyl]-N, N-dimethyl aniline; MG) is a synthetic triarylmethane dye used in the food industry, medical disinfection, and for coloring various materials like leather and fabrics (Rashtbari and Dehghan, 2021; Sahu and Poler, 2024). However, MG in wastewater poses serious health risks, including teratogenic, carcinogenic, and mutagenic effects (Ng et al., 2013; Sartape et al., 2013; Shivaraju et al., 2017; Rout and Jena, 2021). MG is highly stable and resistant to degradation due to its three benzene rings (Xu et al., 2006). Only a few enzymes, such as triphenylmethane reductase (TMR) (Wang et al., 2012; Shang et al., 2019), manganese peroxidase (Yang et al., 2016), laccase (Casas et al., 2009), and tyrosinase (Shedbalkar et al., 2008), can degrade or modify MG. However, incomplete enzymatic conversion can increase the toxicity of MG by-products (Zhou et al., 2019). Moreover, the limited natural production and instability of some enzymes under high temperatures and ionic conditions restrict their applicability (Martins et al., 2015). Therefore, it is crucial to develop new and viable enzymatic approaches for the degradation of these dyes.
Biogenic manganese (Mn) oxidation, driven by Mn(II)-oxidizing microorganisms, is an effective method for degrading organic pollutants (Tran et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023). These microorganisms use enzymatic oxidases to produce biogenic manganese oxides (BioMnOx), which have high redox potential and strong adsorptive capacity. BioMnOx can oxidize various organic pollutants, such as phenols, chlorinated phenols, chlorinated anilines, atrazine, and various inorganic pollutants. For example, a Mn(II)-oxidizing microbial community in rivulet sediment, comprising core microbes such as Sphingobacterium and Bacillus, effectively decolorizes dyes (Wan et al., 2020). Moreover, the combination of the Mn(II)-oxidizing bacterium Pantoea eucrina SS01 and its BioMnOx efficiently and sustainably degrade MG (Sun et al., 2021). Previous research shows that Mn(II)-oxidizing bacteria use Mn(II) oxidases, which include Multi-Copper Oxidases (MCOs), Mn peroxidases (MnPs), and Mn catalases, for Mn(II) oxidation (Zhou and Fu, 2020). These Mn oxidases show minimal sequence similarities and are predominantly large enzymes with challenges in heterologous gene expression (Zhou and Fu, 2020). Their role in dye degradation is not well-explored. Among these, only MnP has been identified as a viable system for Mn(II)-dependent reactions, enabling the in vitro degradation of MG and recalcitrant polymeric dyes (Moreira et al., 2001; Champagne and Ramsay, 2005; Saravanakumar et al., 2013).
Recently, a catalase-peroxidase designated as StKatG (referred to as StKatG1 in this study) from Salinicola tamaricis F01, an endophytic Mn(II)-oxidizing bacterium isolated from the halophyte Tamarix chinensis Lour, has been identified as a distinct clade of bacterial Mn(II) oxidases (Zhao et al., 2023). This enzyme is capable of converting Mn(II) into biogenic Mn oxides, including MnO2, Mn3O4, and Mn oxalate (Zhao et al., 2023), which may hold potential applications in the adsorption and oxidation of organic pollutants. Beyond its Mn(II) oxidizing capabilities, catalase-peroxidase is a versatile enzyme with Mn(II) oxidizing, catalase, peroxidase, and peroxynitritase activities. It can catalyze multiple reactions, such as hydroxylation, epoxidation, halogenation of C-H bonds, and transformations of aromatic groups and biophenols (Takio et al., 2021; Shen and Wang, 2024). Although limited information exists regarding the application of catalase-peroxidase in the degradation of organic pollutants, a thermostable catalase-peroxidase from Thermobacillus xylanilyticus has shown efficacy in oxidizing small aromatic compounds derived from lignins (Fall et al., 2023). Further research into the potential enhancement of catalase-peroxidase activity by Mn(II) could be valuable, as it may expand the enzyme’s applicability in organic pollutant degradation.
The study aimed to investigate the decolorization capability of the catalase-peroxidases toward MG. Salinicola tamaricis F01 contains two catalase-peroxidases, both of which demonstrated the ability to decolorize MG, with StKatG2 exhibiting superior efficacy. Previous research has identified StKatG1 as a Mn(II) oxidase. This study further characterized the Mn(II)-oxidizing activity and MG decolorization capability of StKatG2. Additionally, the efficient heterologous expression of StKatG2 enhanced its potential utility in environmental remediation.
The catalase-peroxidase sequences were obtained from PeroxiBase1 (Passardi et al., 2007), where they have been verified and annotated. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using Clustal Omega2, while structural alignment was conducted with the ESPript program suite3. The phylogenetic tree was generated using MEGA7, employing the maximum likelihood method as described by Kumar et al. (2016) and the Jones-Taylor-Thornton (JTT) model, with 1,000 bootstrap replicates (Jones et al., 1992). The structure of StKatG1 and StKatG2 was predicted using the machine learning algorithm AlphaFold3 (v3.0)4. PyMOL software5 was utilized for the structural alignment of the homology model with the AlphaFold3 structure, as well as for calculating and visualizing root mean square deviations.
The Salinicola tamaricis F01 strain was cultured on LB5 medium (peptone 10 g/L, yeast powder 5 g/L, NaCl 50 g/L, agar 15 g/L) at 30°C for 48 h. Genomic DNA of strain F01 was isolated using the Qiagen genomic DNA isolation kit. The stkatG2 gene was amplified from the genomic DNA using the primers 5’-GGAATTCCATATGATGAGT GAAGAGATCAAGATCGGTGG-3′ (with the NdeI restriction site underlined) and 5’-CGCGGATCCGAGACGTCGAAGCGGTC GTG-3′ (with the BamHI restriction site underlined) for cloning into the pET-22b (+) expression vector, which includes a C-terminal hexahistidine tag. The recombinant plasmid was constructed as described and subsequently transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 competent cells (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Transformants were selected on LB24 medium (peptone 10 g/L, yeast powder 24 g/L, NaCl 50 g/L, agar 15 g/L) with 50 μg/mL ampicillin.
The correct transformants were cultured to an OD600 nm of 0.6 in LB24 medium containing 50 μg/mL ampicillin. To induce the expression of recombinant StKatG2, 0.05 mmol/L isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added. The culture was incubated at 20°C for 10 h. Cells were lysed by suspending them in a 50 mmol/L solution of Tris–HCl (pH 7.4) and sonicated on ice to facilitate further disruption (20 kHz power for 12 min with 5 s burst sonication cycles at 5 s intervals). At 4°C, the crude enzyme solution was purified using a nickel column (Yeasen, Shanghai, China), with 4 mL of HisSep Ni-NTP Agarose Resin loaded into the purification column. Lysis Buffer (50 mmol/L NaH2PO4, 300 mmol/L NaCl, 10 mmol/L imidazole, pH 8.0) was employed for equilibration, followed by the introduction of 20 mL of crude enzyme solution into the nickel column resin. After washing away impurities with Wash Buffer (50 mmol/L NaH2PO4, 300 mmol/L NaCl, 20 mmol/L imidazole, pH 8.0), StKatG2 was eluted using Elution Buffer (50 mmol/L NaH2PO4, 300 mmol/L NaCl, 250 mmol/L imidazole, pH 8.0) and 7.5 mL was collected, and subsequently dialyzed for 12 h in a 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl solution (pH 7.4). The purified protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the StKatG2 protein concentration was determined using a BCA kit (Yeasen, Shanghai, China).
To evaluate the molecular weight of the proteins, purified protein samples were subjected to chromatographic separation and molecular weight determination using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) technology (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States, Ultimate 3,000 Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography System, Q Exactiv™ Hybrid Quadrupole-Orbitrap™ Mass Spectrometer High Resolution Mass Spectrometer).
Manganese chloride (MnCl2) was employed as the substrate to evaluate the Mn(II) oxidation activity of the recombinant StKatG2 enzyme in HEPES buffer at pH 8.0. The buffer composition included 59 mmol/L NaCl, 10 mmol/L CaCl2, 0.4 mmol/L NADḤNa2 (Sigma), 1 mmol/L H2O2, 1 μmol/L heme (Sigma) in 50 mmol/L, and 10 μmol/L pyrroloquinoline quinone (Sigma) (Kono and Fridovich, 1983). The reaction mixture was incubated for 10 h at 30°C. A 300 μL aliquot of each sample was reacted for 2 h at 30°C with 60 μL of LBB (Sigma, 0.04%, w/v) (Jones et al., 2019) and 900 μL of acetic acid (45 mmol/L). The activity was assessed by monitoring the absorbance at 620 nm and the equilibrated potassium permanganate concentration.
To determine the kinetic constant of recombinant StKatG2, various concentrations of MnCl2 (ranging from 0–80 mmol/L) were incubated with 0.4 mg/mL of StKatG2 for 10 h at 30°C in 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl (pH 7.4) (Jang et al., 2005). The values for Km and Vmax were derived using non-linear regression fitting.
The effect of temperature on the enzymatic activity of StKatG2 was investigated by incubating the reaction mixture at temperatures ranging from 25 to 80°C under standard assay conditions at pH 7.0. The residual enzyme activity was evaluated at 50°C, with the maximum enzyme activity defined as 100%. Additionally, the optimal pH was determined by varying pH values from 4.0 to 8.0 while maintaining a constant temperature of 50°C.
To assess thermostability, StKatG2 samples were incubated at different temperatures (50, 60, 70, and 80°C) for various time intervals. Subsequently, residual activity was measured at 50°C and compared with protein samples stored on ice, which was considered to represent 100% activity.
EDTA and several metal ions, including Ca2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, Mg2+, Zn2+, and Ni2+, were incubated with StKatG2 at final concentrations ranging from 0.1 mmol/L to 10 mmol/L at 50°C for a duration of 10 h. The effects of these ions on the activity of recombinant StKatG2 were then evaluated.
The MnCl2 (50 mmol/L) and various auxiliary components were reacted with recombinant StKatG2 (0.5 mg/mL) at 55°C for 10 h. The fresh Mn oxides (BioMnOx) pellets were collected by centrifugation (10,000 × g, 10 min), and washed three times with deionized water before drying for 12 h at 55°C. Surface topography observations were performed using a scanning electron microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States, Apreo 2C) at 5.00 kV, equipped with an Oxford X-Max 80T EDX system (Oxford Instruments Ultim Max 65, Oxford, United Kingdom) for energy dispersive analysis of BioMnOx.
The phases were determined by scanning the dry form of the dioxide using an X-ray diffractometer (Beijing Purkinje General Instrument Co, China, X-D6) in the 2θ range of 5–85°. The valence state and composition of Mn were identified using the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS; ESCALAB XI+, Thermo Fischer, United States).
The MG decolorization experiments were conducted in 2 mL tubes using a reciprocating shaker set at 30°C and 120 rpm. The reaction mixture comprised a 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl buffer containing 20 mg/L, 50 mg/L, and 80 mg/L of MG, along with 500 μg/mL of purified recombinant StKatG1 or StKatG2. Control groups were established that excluded the StKatG1 or StKatG2 enzymes. The absorbance of MG at 620 nm was measured using a UV spectrophotometer. The formula for calculating the decolorization rate is as follows:
All experiments were performed in triplicate.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS) was employed to detect malachite green (MG) and its degradation products (Daneshvar et al., 2007). The malachite green or its metabolites were dried, dissolved in 1 mL of methanol, and subsequently injected into an Agilent 1,290 Infinity II HPLC system (Agilent, Santa Clara, United States) at a volume of 3 μL. This system was equipped with a reversed-phase C-18 analytical column and coupled to a quadrupole mass spectrometer. Methanol served as the mobile phase, with a flow rate of 0.6 mL min−1. The initial methanol proportion was set at 5%, which was gradually increased to 95% over 10 min, maintained at 95% for an additional 2 min, and then reduced back to 5% over 2 min. The entire analytical process lasted for a total of 20 min (Han et al., 2020). The analysis utilized electrospray ionization (ESI) in positive ion mode, and the data were processed using Qualitative Analysis B.05.00 software (Agilent, United States).
The protonation state of all compounds was set at pH 7.4, and the compounds were converted to three-dimensional structures using Open Babel (O'Boyle et al., 2011). AutoDock Tools (ADT3) were utilized to prepare and parametrize the receptor protein and ligands. Docking grid files were generated using the AutoGrid feature of Sitemap, and docking simulations were performed with AutoDock Vina (1.2.0) (Trott and Olson, 2010; Eberhardt et al., 2021). The optimal pose was selected for interaction analysis. Finally, the protein-ligand interaction figure was generated using PyMOL.
Two catalase-peroxidases, StKatG1 (~80 kDa) and StKatG2 (~85 kDa), were identified from S. tamaricis F01. While StKatG1 has been confirmed to exhibit Mn(II) oxidation activities in previous research (Zhao et al., 2017; Zhao et al., 2023), the function of StKatG2 remains uncharacterized. StKatG2 shares 53.6% amino acid sequence identity with StKatG1 (Figure 1A and Supplementary Figure S1). Phylogenetic analysis revealed that StKatG1 clusters with catalase-peroxidases from Burkholderia pseudomallei, Salmonella enterica, and Escherichia coli, among others, whereas StKatG2 is distantly related (Figure 1B). Alphafold3 (v3.0) analysis indicated that StKatG2 possesses a typical catalase-peroxidase structure, comprising 23 α-helices, 22 short 3 10 helices, and 13 β-strands, with the critical histidine-arginine pair (His-112 and Arg-108) located in α-helix 4, essential for H2O2 breakdown (Poulos and Kraut, 1980). Additionally, StKatG2 also contains the triad His295-Asp406-Trp347 as the proximal heme iron ligand, along with Asp-130, Arg-444, and Tyr-248, which act as a molecular switch regulating catalase activity (Regelsberger et al., 2000; Jakopitsch et al., 2003; Yu et al., 2003; Singh et al., 2004; Carpena et al., 2005). A comparison of the structures of StKatG1 and StKatG2 revealed significant similarities, with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 0.98 Å. Both StKatG1 and StKatG2 exhibit three types of secondary structures: α-helices, short 3_10 helices, and β-strands. StKatG1 contains 24 α-helices, whereas StKatG2 has 23. In contrast, StKatG1 features 17 3_10 helices, while StKatG2 possesses 22. Regarding β-strands, StKatG1 has 10, compared to 13 in StKatG2 (Figure 1C). In conclusion, despite being derived from the same organism, StKatG1 and StKatG2 demonstrate notable distinctions in both sequence and structure.
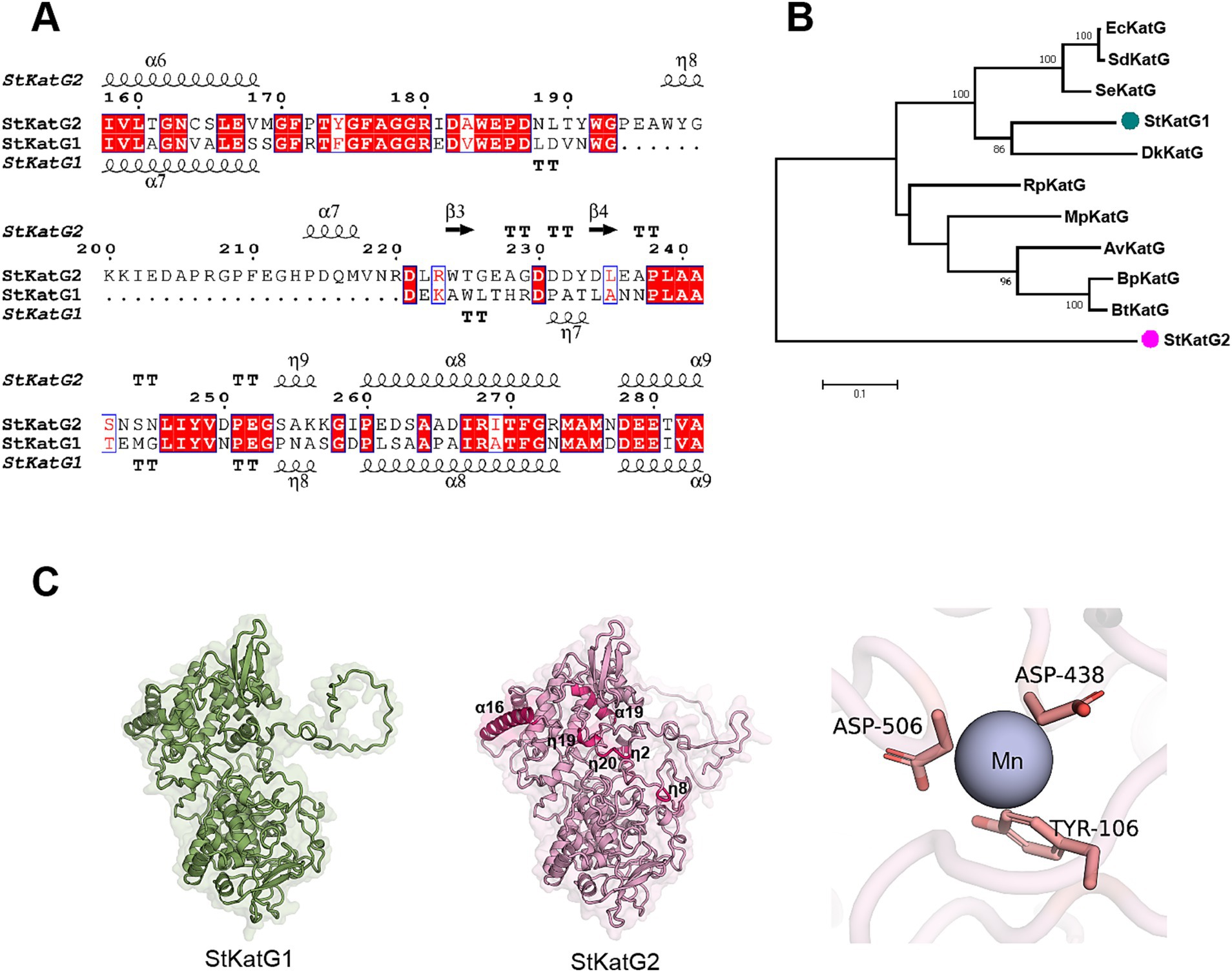
Figure 1. Comparison of amino acid sequences of StKatG homologs. (A) Sequence alignment of StKatG1 and StKatG2. The sequences were aligned using the Clustal Omega and treated with ESPript 3 (https://espript.ibcp.fr/). The secondary structure elements presented on top were obtained from the predicted StKatG2 structure using Alphafold3 (α, α-helices; η, 3 10 helices; β, β-strands. TT, turns). Identical and similar residues are displayed in red and blue boxes, respectively. (B) Phylogenetic tree of KatG proteins from Salinicola tamaricis and other species. StKatG1 and StKatG2, Salinicola tamaricis KatGs; DkKatG, Drosophila kikkawai KatG; BpKatG, Burkholderia pseudomallei KatG; SeKatG, Salmonella enterica KatG; EcKatG, Escherichia coli KatG; SdKatG, Shigella dysenteriae KatG; RpKatG, Ralstonia pickettii KatG; BtKatG, Burkholderia thailandensis KatG; MpKatG, Methylibium petroleiphilum KatG; AvCP01, Azotobacter vinelandii KatG. The evolutionary analyses were conducted based on amino acid homology using the MEGA7. Bootstrap values are shown at branch points. (C) Predicted structures of StKatG1 and StKatG2 using AlphaFold3, with the manganese binding site in StKatG2 represented as a purple sphere.
To investigate the function of the StKatG2 protein, the full-length gene (2,297 bp) was cloned and inserted into the pET-22b (+) expression vector with a His6-tag at the C-terminal (Supplementary Figures S2, S3). The resulting recombinant plasmid was confirmed through double digestion with NdeI and BamHI restriction enzymes, yielding a correct 2.3 kb DNA fragment. Subsequently, the recombinant plasmid was transformed into E. coli BL21, and transformants on LB medium supplemented with ampicillin (50 μg/mL) were selected via colony PCR. The purified recombinant StKatG2 protein was obtained using an immobilized Ni2+-affinity column. A total of 20 mL of crude proteins (1792.71 μg/mL) was subjected to an immobilized Ni2+-affinity column, resulting in 7.5 mL of eluted proteins with a concentration of 229 μg/mL. Analysis by SDS-PAGE (10%) revealed a band at approximately about 85 kDa (Supplementary Figures S4, S5), consistent with the expected mass of StKatG2. The HPLC-MS result demonstrated that the actual molecular weight of StKatG2 was 86.97 kDa (Supplementary Figure S6B and Supplementary Tables S1, S2).
The manganese-oxidizing activity of recombinant StKatG2 was assessed using the LBB method (Jones et al., 2019). Upon reaction of StKatG2 with MnCl2 in 50 mmol/L Tris–HCl (pH 7.4) buffer, insoluble brown particles were observed. Subsequent mixing of the reaction solution with the LBB solution resulted in a blue color change (Figure 2A). These reactions confirmed the formation of Mn oxides, demonstrating the ability of recombinant StKatG2 to oxidize Mn(II).

Figure 2. Characterization of StKatG2. (A) The LBB assay for the formation of Mn oxides by incubating purified recombinant StKatG2 (0.3 mg protein/mL) with MnCl2 (50 mmol/L). Tube 1–3: sample after 24 h of incubation in the presence of StKatG2; tube 4: Negative control after 24 h in the absence of StKatG2. (B) The reaction kinetics of StKatG2 (0.3 mg protein/mL) were analyzed using various concentrations of MnCl2. The data presented are the averages of three independent experiments, accompanied by standard error bars. The curve was fitted using the Michaelis–Menten equation.
The oxidation ability of StKatG2 toward Mn(II) was further analyzed by calculating kinetic values at different concentrations of MnCl2. A Michaelis–Menten plot was generated through non-linear regression curve fitting (Figure 2B). Table 1 provides a comparison of the kinetic characteristics of various manganese-catalases. It is evident that the Km value of StKatG2 is 2.529 mmol/L, higher than that of StKatG1 (Zhao et al., 2023). Moreover, the Km value of StKatG2 was found to be lower than those of most reported multicopper oxidases, suggesting that StKatG2 has a higher affinity for the substrate and greater manganese oxidation capacity. The Vmax value for StKatG2 was determined to be 10.07 μmol/L·min−1, slightly lower than StKatG1 (Zhao et al., 2023), which exhibited a Vmax of 10.3 μmol/L·min−1. This implies that StKatG1 has a slightly higher maximum velocity in the catalytic reaction compared to StKatG2. The Kcat of StKatG2 is 2.82 min−1, slightly higher than that of StKatG1 with a Kcat value of 2.78 min−1, indicating a slightly superior catalytic performance in terms of substrate turnover for StKatG2. These differences in kinetic values between StKatG1 and StKatG2 may be attributed to variances in enzyme structure, active site residues, or the microenvironment surrounding the active site, which could impact the efficiency of the catalytic reaction.
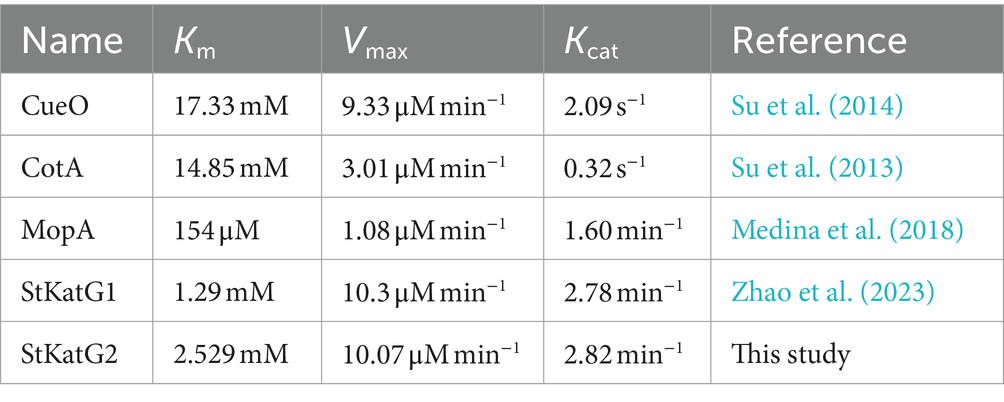
Table 1. Comparison of the kinetic parameters for StKatG2 and other characterized manganese oxidases.
In order to further characterize the biogenic manganese oxides (BioMnOx) catalyzed by StKatG2, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) combined with energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) was conducted. Unlike layered sheet-like structure of BioMnOx catalyzed by StKatG1 (Zhao et al., 2023), the BioMnOx nanoparticles produced by StKatG2 appeared somewhat spherical or irregular, arranged closely with void spaces between them (Figures 3A,B). EDS analysis revealed the elemental composition on the surface of the BioMnOx particles, with mass fractions of 21.97% C, 13.64% O, and 64.39% Mn, and atomic fractions of 47.46% C, 22.12% O, and 30.41% Mn (Figure 3C).
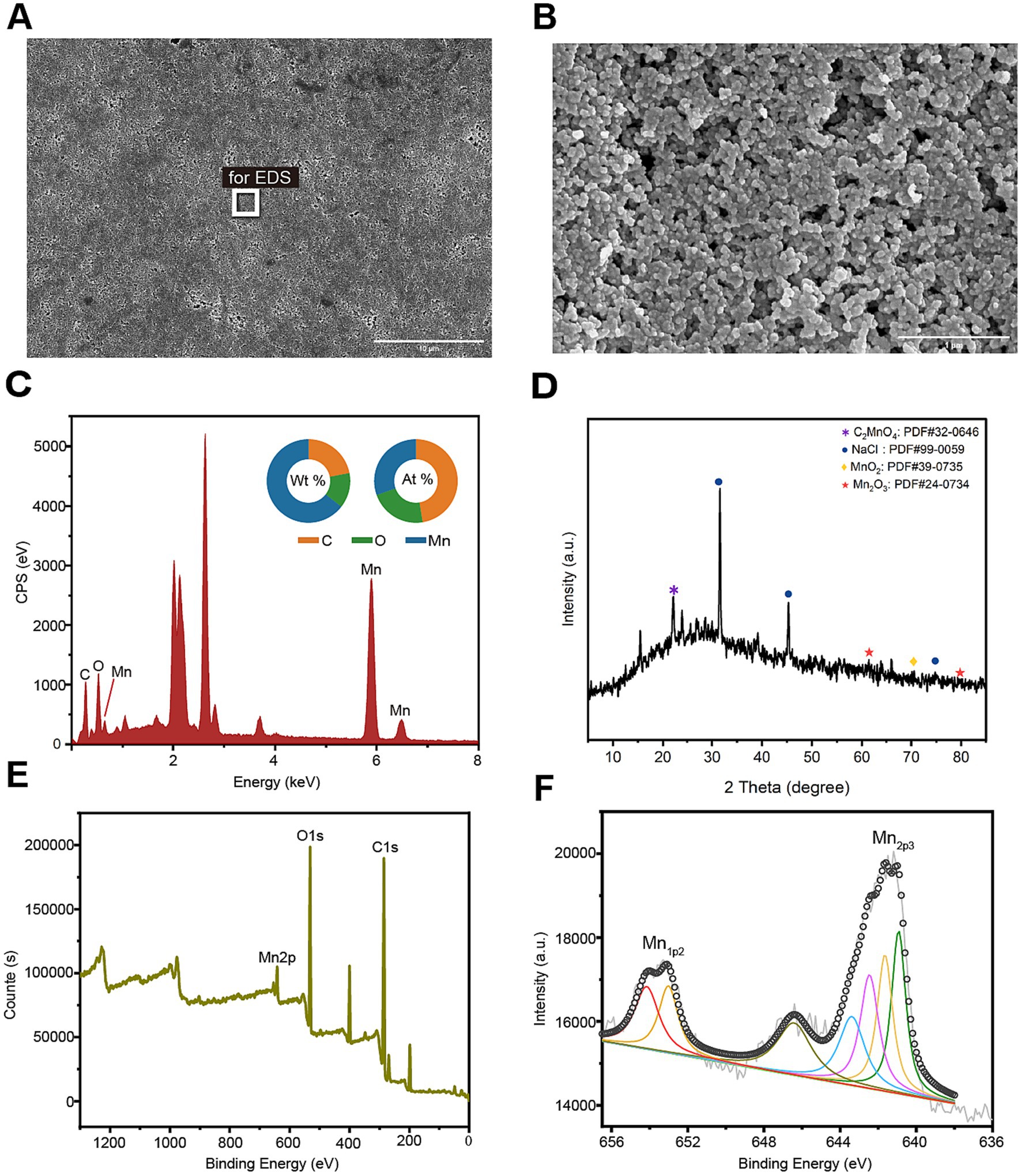
Figure 3. Morphology and composition of BioMnOx catalyzed by StKatG2. The BioMnOx were obtained through incubation of MnCl2 (50 mmol/L) and StKatG2 (0.5 mg/mL) at 50°C for 10 h. (A) The SEM photograph of the Mn oxide aggregates produced by StKatG2. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The SEM photograph of the Mn oxide aggregates at a different magnification with (A). Scale bar, 1 μm. (C) The EDS spectrum showing the Mn composition of the aggregates. The rectangle shown in figure A indicates the selected position of the aggregates. The unlabeled peaks are Au formed by the spray gold treatment. (D) The XRD pattern of the BioMnOx produced by StKatG2. (E) XPS wide scan patterns. (F) The deconvoluted profile of the specific Mn 2p1/2 and Mn 2p2/3 spectrum for the BioMnOx.
To analyze the phase of the product, X-ray diffraction (XRD) was utilized for qualitative analysis of the phase composition of bio-manganese oxide (Figure 3D). The results revealed that the primary phase composition of bio-manganese oxide consisted of MnO2 (JCPDS 39–0735), Mn2O3 (JCPDS 24–0734), and C2MnO4 (JCPDS 32–0646). These findings suggest that the Mn compounds catalyzed by StKatG2 exhibit multiple oxidation states. Furthermore, notable peaks of NaCl (JCPDS 99–0059) were observed, likely attributed to the incorporation of sodium chloride during the preparation of BioMnOx.
Valence states compositions in the BioMnOx were identified through photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The XPS analysis showed two peaks in Mn2p1/2 and five in Mn2p3/2 (Figure 3E), consistently indicating that the BioMnOx produced by StKatG2 is a mixed-valence manganese compound. Specifically, XPS measurements revealed the presence of four valence states: Mn(II), Mn(III), Mn(IV), and Mn(VII) in the BioMnOx (Figure 3F). The multiple oxidation states in the BioMnOx product catalyzed by StKatG2 are similar to those catalyzed by StKatG1, which also exhibits mixed valences (Zhao et al., 2023).
The impact of pH conditions on the Mn(II)-oxidizing activity of StKatG2 was investigated. The optimal pH for StKatG2 to exhibit Mn(II)-oxidizing activity was found to be 7.5 (Figure 4A). The relative enzyme activity of StKatG2 is only 8.3% at pH 4.0, and the highest enzyme activity was observed around 7.5, which indicated that neutral or slightly alkaline environments were beneficial to the Mn(II)-oxidizing activity of StKatG2. This trend is consistent with other studies on manganese oxidases, such as CopA with an optimal pH of 8.0. CueO, another manganese oxidase, shows peak activity between pH 7.6 and 8.2, with minimal oxidation activity below pH 7.0 (Su et al., 2014). These findings suggest that most manganese oxidases involved in biomanganese oxidation exhibit maximal enzyme activity in neutral to alkaline pH ranges, while chemical oxidation of manganese becomes predominant at pH levels above 8.0, as demonstrated by the control sample without StKatG2 (Supplementary Figure S7).
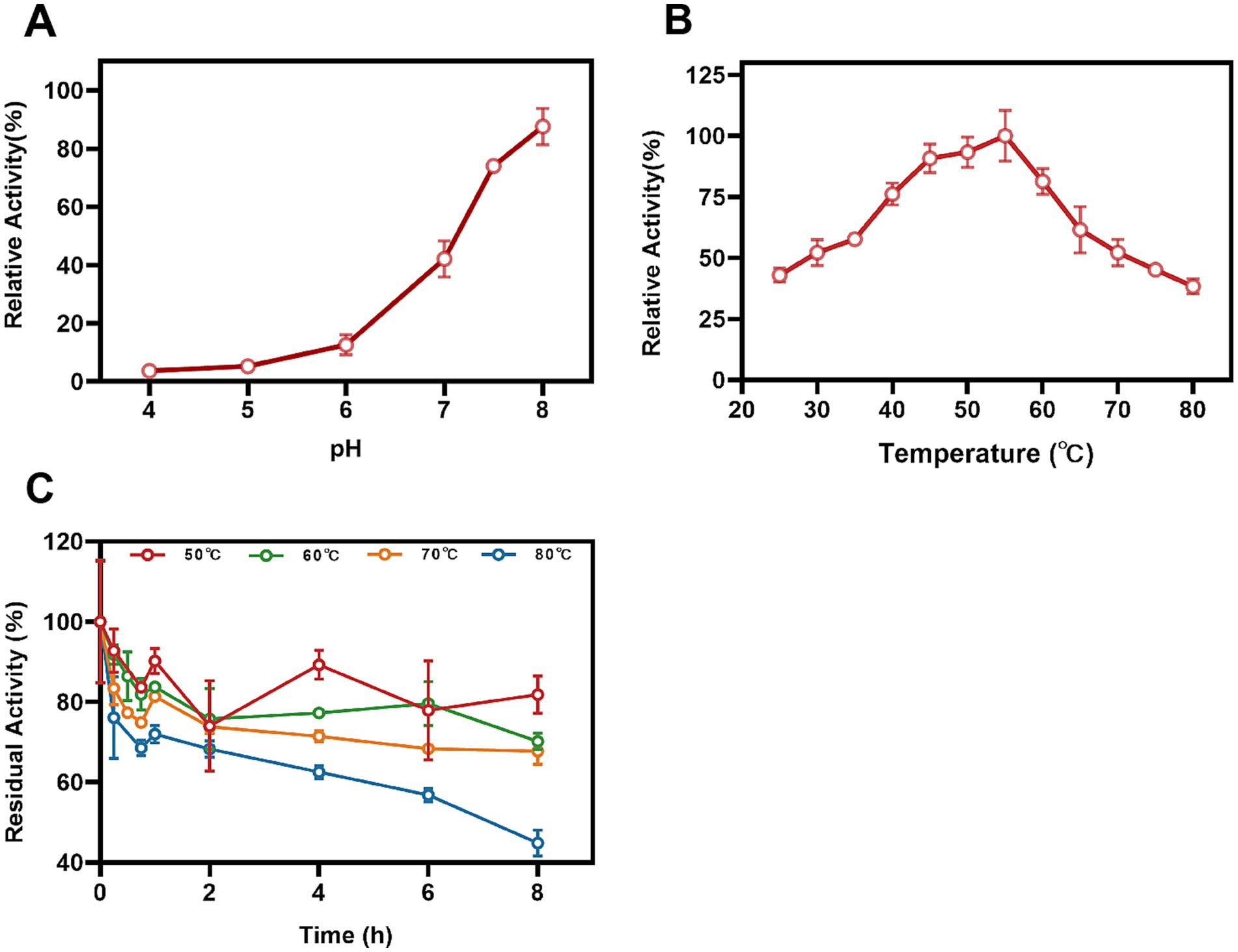
Figure 4. Effects of temperature and pH on Mn(II)-oxidizing activities of StKatG2. (A) Mn(II)-oxidizing activities of StKatG2 at different pH values. (B) Mn(II)-oxidizing activities of StKatG2 at different temperatures. (C) Thermostability of StKatG2 at various temperatures. StKatG2 was incubated at 50°C (red circles), 60°C (green circles), 70°C (orange triangles), and 80°C (blue triangles) for different time intervals, with residual activities measured at 50°C. The error bars indicate standard deviation.
To determine the optimal temperature for Mn(II) oxidizing activity, StKatG2 was evaluated across a temperature range of 25–80°C. The study revealed that the recombinant StKatG2 exhibited its peak enzymatic activity at 55°C (Figure 4B). Notably, the enzyme retained 40% activity at lower temperatures (25°C) and maintained over 80% activity within the 45–55°C range. However, enzyme activity significantly decreased beyond 55°C, with a sharp drop to 38.3% at 80°C. These findings indicate that StKatG2 is a mesophilic enzyme. Moreover, the optimal temperature for manganese oxidase activity in recombinant StKatG2 was higher than that observed for StKatG1 (50°C) (Zhao et al., 2023).
Thermostability of StKatG2 was evaluated by subjecting the protein to different temperatures (50, 60, 70, and 80°C) for a specific duration, followed by measuring residual activity at 55°C (Figure 4C). After an 8-h exposure to 50°C, the enzyme retained 82.3% of its activity, surpassing StKatG1, which only maintained 73.6% activity under similar conditions (Zhao et al., 2023). Notably, StKatG2 demonstrated superior thermal stability, retaining 45.1% activity after 8-h exposure to 80°C. In contrast, StKatG1 lost 92% of its activity when exposed to 80°C for 8 h (Zhao et al., 2023). These results collectively indicate that StKatG2 exhibits robust thermal stability in high-temperature environments and shows promise for broader applications in such environments.
The impact of metal ions and the chelating agent EDTA on the enzymatic activity of StKatG2 was assessed (Figure 5). EDTA significantly suppressed the Mn(II)-oxidizing activity of StKatG2, suggesting a reliance on divalent metal ions. At a concentration of 0.1 mmol/L, Fe3+ inhibited the enzyme activity (Figure 5A), likely because of its structural and chemical similarity to Mn, leading to potential competition for binding sites on the enzyme and consequent disruption of its structure. Moreover, the addition of 0.1 mmol/L Cu2+, Mg2+, and Zn2+ enhanced the enzyme activity, possibly by forming a metalloenzyme complex that boosts enzymatic function. However, a higher concentration (10 mmol/L) of Cu2+ and Zn2+ almost completely inhibited the enzymatic activity, while Fe3+ at the same concentration affected the final detection outcome due to its inherent color, which holds no analytical value (Figure 5C).
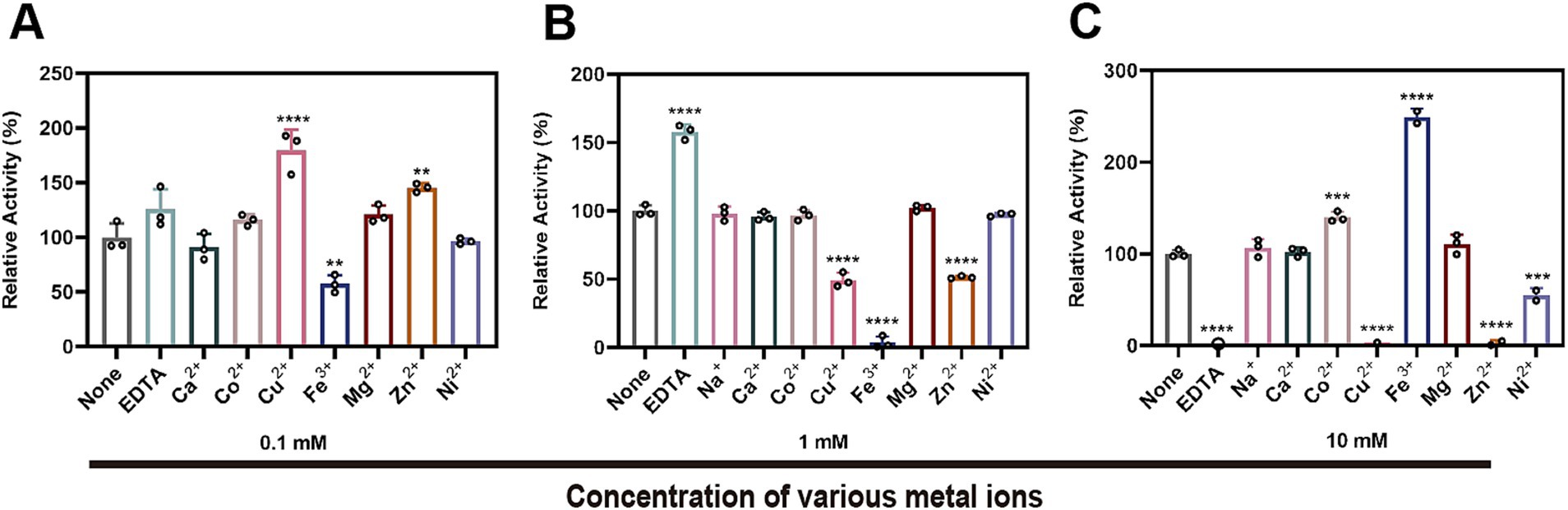
Figure 5. Effects of different metal ions and EDTA on the Mn(II)-oxidizing activity of StKatG2. Effects of different concentrations of metal ions and EDTA at 0.1 mM (A), 1 mM (B), and 10 mM (C) on enzymatic activity the Mn(II)-the oxidizing activity of StKatG2. **, ***, and **** represent significant differences from the control group (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).
To evaluate the performance of recombinant StKatG2, toxic malachite green was utilized as the research material. Upon mixing with the enzyme solution, the decolorization ability was monitored. StKatG2 exhibited the fastest decolorization efficiency within the initial 15 min for both 20 mg/L and 50 mg/L of malachite green, peaking around 30 min, with a decolorization rate of up to 30% after 4 h of action (Figure 6). Although the BioMnOx structures of StKatG1 and StKatG2 are similar and the kinetic values of Mn(II) are also comparable (Supplementary Table S3), StKatG2 exhibits excellent decolorization efficiency for malachite green. After 4 h of treatments, the maximum decolorization rates of StKatG2 reached 73.38% for 20 mg/L MG and 60.08% for 50 mg/L MG (Figure 6A), while StKatG1 for 20 mg/L mg and 50 mg/L mg were 63.91 and 51.78%, respectively (Figure 6B). When the concentration of MG reaches 80 mg/L, the decolorization rates of StKatG1 and StKatG2 were 34.63 and 18.37%, respectively (Supplementary Figure S8). These findings highlight StKatG2 as a promising biological approach for the efficient degradation of malachite green within a short period.
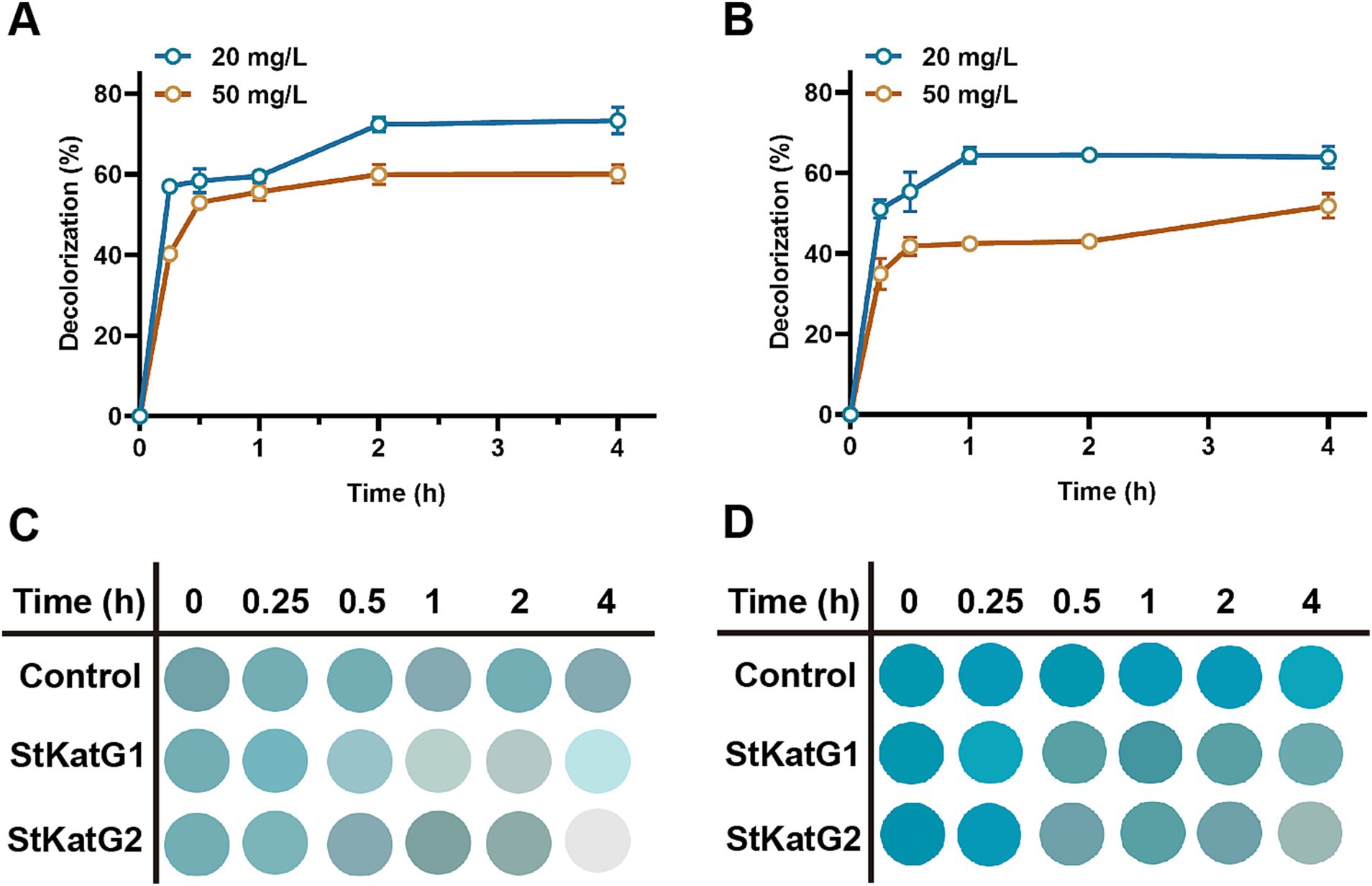
Figure 6. Decolorization of MG mediated by StKatGs. (A) The decolorization rate of MG by StKatG2. (B) The decolorization rate of MG by StKatG1. (C) Decolorization of MG at an initial concentration of 20 mg/L by StKatG2 and StKatG1. (D) Decolorization of MG at an initial concentration of 50 mg/L by StKatG2 and StKatG1.
To further investigate the decolorization mechanism of MG by treatment with StKatG2, the MG metabolites were analyzed using HPLC-MS. Following treatment with StKatG2, the MG peak, which exhibited a retention time of 6.845 min, was found to be reduced (Figure 7A). In contrast, several peaks with retention times ranging from 5 to 8 min increased (Figure 7B) when compared to the control setup. Three distinct peaks were identified as MG metabolites in the StKatG2 treatment setup (Figures 7C–E): malachite green (7.153 min, m/z = 329), leucomalachite green (6.845 min, m/z = 315), and 4-(dimethylamino) benzophenone (7.791 min, m/z = 226). The latter is recognized as a degradation metabolite of MG (Yang et al., 2015; Abu-Hussien et al., 2022). The process of MG degradation catalyzed by StKatG2 is illustrated in Figure 7F.
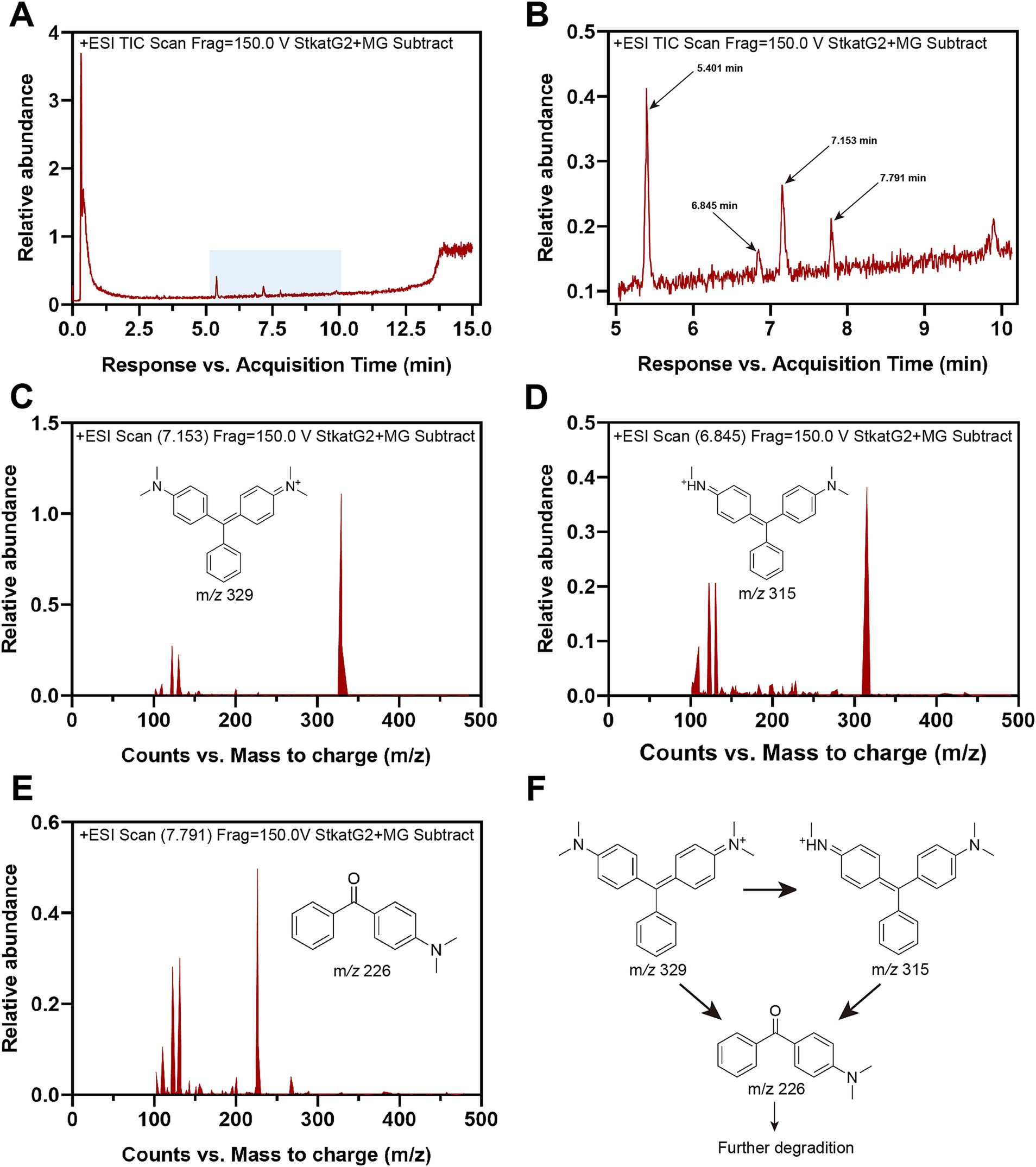
Figure 7. HPLC-MS analysis of MG metabolites catalyzed by StKatG2. (A) HPLC-MS spectrum of the MG degradation products by StKatG2. (B) Higher magnification view of the HPLC-MS spectrum of (A). (C) Malachite green (m/z = 329, retention time 7.153 min). (D) Leucomalachite Green (m/z = 315, retention time 6.845 min). (E) 4-(dimethylamino) benzophenone (m/z = 226, retention time 7.791 min). (F) Proposed removal pathways of MG by StKatG2, based on the results obtained from HPLC-MS.
Furthermore, We conducted an analysis of the interactions between the proteins and MG (Supplementary Figure S9). Utilizing these interaction forces, the binding energy of the StKatG1-MG and StKatG2-MG complexes were determined to be −7.5 kcal/mol and −8.0 kcal/mol, respectively (Supplementary Figure S9). Molecular docking results indicate that MG interacts with both StKatG1 and StKatG2, with a position away from the heme binding sites, Mn2+ binding sites, and the H2O2 catalytic pocket. Moreover, the docking positions of StKatG1 and StKatG2 with MG are inconsistent, which may contribute to the differing decolorization efficiencies observed for MG. When heme and Mn2+ combine with StKatG2 for manganese oxidation, this interaction may influence the molecular conformation of the proteins and release redox forces, ultimately leading to MG decolorization.
The issue of textile industry dyeing wastewater is a significant concern in terms of wastewater pollution. Traditional dye restoration methods are often costly and can lead to the production of harmful byproducts. Enzymatic degradation technology offers a promising solution to these challenges, paving the way for a more sustainable environment. MG is a banned triphenylmethane dye that is still being used illegally in certain regions (Bañ Uelos et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2019). Enzymes involved in the decolorization of triphenylmethane dyes can be categorized into two groups based on their specificity. The first group includes manganese peroxidases (Yang et al., 2016) and laccases (Casas et al., 2009), which act non-specifically through radical chain reactions to decolorize dyes (Azmi et al., 1998). The second group consists of enzymes specifically targeted at decolorizing triphenylmethane dyes, with triphenylmethane reductases being the sole members. However, these enzymes can only convert MG to LMG, which remains toxic to humans and other organisms (Persson et al., 2003; Zhou et al., 2019). In this study, we investigated the decolorization capabilities of MG using the catalase-peroxidases StKatG1 and StKatG2. With heme and methionine-tyrosine-tryptophan cofactors, catalase-peroxidase displays versatile functionality, exhibiting both peroxidase and catalase activities (Zámocký et al., 2009). Previous research has shown its effectiveness in treating wastewater containing Reactive Black 5, Allura Red, Fuchsine, and Acid Red 37 (Taslimi et al., 2013). Our findings further highlight the potential of catalase-peroxidase in decolorizing MG in textile bleaching effluent.
The catalase-peroxidase degradation pathway, while not completely understood, may play an indirect role in the degradation of dyes. Textile dyes can induce oxidative stress and generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS are then converted into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by superoxide dismutase (SOD), which is subsequently neutralized by catalase-peroxidase, leading to efficient dye removal under high-stress conditions (Takio et al., 2021). This study indicates that catalase-peroxidase StKatG2 also exhibits Mn(II)-oxidizing activities, which may synergistically enhance the removal of MG. This process is similar to that of another Mn(II) oxidase, MnP (Xiu, 2013). The heme in the enzyme reacts with H2O2 to generate highly reactive intermediates, causing the Mn(II) oxidase to transition into an oxidized state and facilitate the oxidation of Mn(II) to Mn(III). Subsequently, through a mechanism involving two successive electron transfer reactions, substrates like MG dyes can reduce the enzyme back to its original form. Mn(III) can be further oxidized to Mn(IV) via disproportionation (Soldatova et al., 2017; Tao et al., 2017), acting as an active oxidant and strong adsorbent, thereby enhancing the adsorption and oxidation of textile dyes (Zhou et al., 2018; Sun et al., 2021). Additionally, the BioMnOx produced by StKatG2 contains multiple valences, including Mn(II), Mn(III), Mn(IV), and Mn(VII). Mixed-valence Mn oxide generally exhibits higher electrical conductivity compared to single-valence states like Mn(III) or Mn(IV), making it more effective in adsorbing and oxidizing dyes (Zener, 1951). The synergistic effects of StKatG2’s multifunctionality may facilitate rapid start-up and stable operation in the removal of MG contaminants.
Comparatively, the catalase-peroxidase StKatG2 demonstrates a greater capacity to decolorize MG than StKatG1, despite their similar BioMnOx structures and comparable kinetic values for Mn(II). Although StKatG1 and StKatG2 share 53.6% amino acid identity, phylogenetic analysis indicates that they are distantly related. Notably, several differences exist between the two proteins, primarily located within the α-helix regions. Specifically, StKatG1 lacks the α7 helix found in StKatG2, while StKatG2 possesses a greater number of turns compared to StKatG1. This variation in the number of secondary structures may lead to deformation of the active pocket, resulting in differing binding efficiencies and varying decolorization effects.
Taken together, this study demonstrated that the catalase-peroxidase StKatG2 not only exhibited Mn(II)-oxidizing activity but also had the ability to decolorize MG. The successful cloning and overexpression of the StKatG2 gene in E. coli suggest a potential large-scale application for MG remediation in aquaculture. Furthermore, StKatG2 showed high stability at high temperatures and a wide range of pH and temperature tolerances, expanding its potential use in harsh environments. The findings of this research offer an environmentally-friendly solution that could be applied in aquaculture to effectively remove MG and reduce its accumulation in aquatic organisms, thereby ensuring the production of safe aquaculture products.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
MyD: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WW: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XQ: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. MxD: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. GZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution in 2021, the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant no. ZR2024MC202), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 31640002).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1478305/full#supplementary-material
1. ^http://peroxibase.toulouse.inra.fr
2. ^https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw
3. ^http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/ESPript
Abu-Hussien, S. H., Hemdan, B. A., Alzahrani, O. M., Alswat, A. S., Alatawi, F. A., Alenezi, M. A., et al. (2022). Microbial degradation, spectral analysis and toxicological assessment of malachite green dye by Streptomyces exfoliatus. Molecules 27:6456. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196456
Azmi, W., Sani, R. K., and Banerjee, U. C. (1998). Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dyes. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 22, 185–191. doi: 10.1016/s0141-0229(97)00159-2
Bañ Uelos, J., García, O., El-Ghenymy, A., Rodriguez, F., Godínez, L., and Brillas, E. (2016). Advanced oxidation treatment of malachite green dye using a low cost carbon-felt air-diffusion cathode. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 2066–2075. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.03.012
Carpena, X., Wiseman, B., Deemagarn, T., Singh, R., Switala, J., Ivancich, A., et al. (2005). A molecular switch and electronic circuit modulate catalase activity in catalase-peroxidases. EMBO Rep. 6, 1156–1162. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400550
Casas, N., Parella, T., Vicent, T., Caminal, G., and Sarrà, M. (2009). Metabolites from the biodegradation of triphenylmethane dyes by Trametes versicolor or laccase. Chemosphere 75, 1344–1349. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.02.029
Champagne, P. P., and Ramsay, J. A. (2005). Contribution of manganese peroxidase and laccase to dye decoloration by Trametes versicolor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69, 276–285. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-1964-8
Daneshvar, N., Ayazloo, M., Khataee, A. R., and Pourhassan, M. (2007). Biological decolorization of dye solution containing malachite green by microalgae Cosmarium sp. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 1176–1182. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2006.05.025
Eberhardt, J., Santos-Martins, D., Tillack, A. F., and Forli, S. (2021). AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: new docking methods, expanded force field, and Python bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 61, 3891–3898. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00203
Fall, I., Czerwiec, Q., Abdellaoui, S., Doumèche, B., Ochs, M., Rémond, C., et al. (2023). A thermostable bacterial catalase-peroxidase oxidizes phenolic compounds derived from lignins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 107, 201–217. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12263-9
Han, S., Han, W., Chen, J., Sun, Y., Dai, M., and Zhao, G. (2020). Bioremediation of malachite green by cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 engineered with a triphenylmethane reductase gene. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 104, 3193–3204. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10438-w
Jakopitsch, C., Auer, M., Regelsberger, G., Jantschko, W., Furtmüller, P. G., Rüker, F., et al. (2003). Distal site aspartate is essential in the catalase activity of catalase-peroxidases. Biochemistry 42, 5292–5300. doi: 10.1021/bi026944d
Jang, M. S., Lee, Y. M., Kim, C. H., Lee, J. H., Kang, D. W., Kim, S. J., et al. (2005). Triphenylmethane reductase from Citrobacter sp. strain KCTC 18061P: purification, characterization, gene cloning, and overexpression of a functional protein in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 7955–7960. doi: 10.1128/aem.71.12.7955-7960.2005
Jones, M. R., Luther, G. W. 3rd, Mucci, A., and Tebo, B. M. (2019). Concentrations of reactive Mn(III)-L and MnO(2) in estuarine and marine waters determined using spectrophotometry and the leuco base, leucoberbelin blue. Talanta 200, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.026
Jones, D. T., Taylor, W. R., and Thornton, J. M. (1992). The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 8, 275–282. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.3.275
Kono, Y., and Fridovich, I. (1983). Isolation and characterization of the pseudocatalase of Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 6015–6019. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)32365-2
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054
Li, K., Xu, A., Wu, D., Zhao, S., Meng, T., and Zhang, Y. (2021). Degradation of ofloxacin by a manganese-oxidizing bacterium Pseudomonas sp. F2 and its biogenic manganese oxides. Bioresour. Technol. 328:124826. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124826
Liu, Y., Li, J., Zeng, J., Yu, X., Sun, X., Zhou, Z., et al. (2023). Complete oxidative degradation of diclofenac via coupling free radicals and oxygenases of a micro/nanostructured biogenic Mn oxide composite from engineered Pseudomonas sp. MB04R-2. J. Hazard. Mater. 456:1657. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131657
Martins, L. O., Durão, P., Brissos, V., and Lindley, P. F. (2015). Laccases of prokaryotic origin: enzymes at the interface of protein science and protein technology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 911–922. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1822-x
Medina, M., Rizo, A., Dinh, D., Chau, B., Omidvar, M., Juarez, A., et al. (2018). MopA, the Mn oxidizing protein from Erythrobacter sp. SD-21, requires Heme and NAD(+) for Mn(II) oxidation. Front. Microbiol. 9:2671. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02671
Moreira, M. T., Palma, C., Mielgo, I., Feijoo, G., and Lema, J. M. (2001). In vitro degradation of a polymeric dye (poly R-478) by manganese peroxidase. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 75, 362–368. doi: 10.1002/bit.10052
Ng, I. S., Zheng, X., Chen, B.-Y., Chi, X., Lu, Y., and Chang, C.-S. (2013). Proteomics approach to decipher novel genes and enzymes characterization of a bioelectricity-generating and dye-decolorizing bacterium Proteus hauseri ZMd44. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 18, 8–17. doi: 10.1007/s12257-012-0340-7
O'Boyle, N. M., Banck, M., James, C. A., Morley, C., Vandermeersch, T., and Hutchison, G. R. (2011). Open babel: an open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 3:33. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-33
Passardi, F., Theiler, G., Zamocky, M., Cosio, C., Rouhier, N., Teixera, F., et al. (2007). PeroxiBase: the peroxidase database. Phytochemistry 68, 1605–1611. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.04.005
Persson, B., Kallberg, Y., Oppermann, U., and Jörnvall, H. (2003). Coenzyme-based functional assignments of short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDRs). Chem. Biol. Interact. 143-144, 271–278. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(02)00223-5
Poulos, T. L., and Kraut, J. (1980). The stereochemistry of peroxidase catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 8199–8205. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)70630-9
Rashtbari, S., and Dehghan, G. (2021). Biodegradation of malachite green by a novel laccase-mimicking multicopper BSA-cu complex: performance optimization, intermediates identification and artificial neural network modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 406:124340. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124340
Regelsberger, G., Jakopitsch, C., Rüker, F., Krois, D., Peschek, G. A., and Obinger, C. (2000). Effect of distal cavity mutations on the formation of compound I in catalase-peroxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 22854–22861. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002371200
Rout, D. R., and Jena, H. M. (2021). Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution using reduced graphene oxide as an adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 47, 1173–1182. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.406
Sahu, A., and Poler, J. C. (2024). Removal and degradation of dyes from textile industry wastewater: benchmarking recent advancements, toxicity assessment and cost analysis of treatment processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 12:113754. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2024.113754
Saravanakumar, T., Palvannan, T., Kim, D. H., and Park, S. M. (2013). Manganese peroxidase h4 isozyme mediated degradation and detoxification of triarylmethane dye malachite green: optimization of decolorization by response surface methodology. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 171, 1178–1193. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0220-4
Sartape, A., Mandhare, A., Jadhav, V., Raut, P., Anuse, M., and Kolekar, S. (2013). Removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution with adsorption technique using Limonia acidissima (wood apple) shell as low cost adsorbent. Arab. J. Chem. 10, S3229–S3238. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.12.019
Shang, N., Ding, M., Dai, M., Si, H., Li, S., and Zhao, G. (2019). Biodegradation of malachite green by an endophytic bacterium Klebsiella aerogenes S27 involving a novel oxidoreductase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 103, 2141–2153. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-09583-0
Shedbalkar, U., Dhanve, R., and Jadhav, J. (2008). Biodegradation of triphenylmethane dye cotton blue by Penicillium ochrochloron MTCC 517. J. Hazard. Mater. 157, 472–479. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.01.023
Shen, C., and Wang, Y. (2024). Recent progress on peroxidase modification and application. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04835-w
Shivaraju, H. P., Midhun, G., Anil Kumar, K. M., Pallavi, S., Pallavi, N., and Behzad, S. (2017). Degradation of selected industrial dyes using mg-doped TiO2 polyscales under natural sun light as an alternative driving energy. Appl Water Sci 7, 3937–3948. doi: 10.1007/s13201-017-0546-0
Singh, R., Wiseman, B., Deemagarn, T., Donald, L. J., Duckworth, H. W., Carpena, X., et al. (2004). Catalase-peroxidases (KatG) exhibit NADH oxidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43098–43106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406374200
Soldatova, A. V., Romano, C. A., Tao, L., Stich, T. A., Casey, W. H., Britt, R. D., et al. (2017). Mn(II) oxidation by the multicopper oxidase complex Mnx: a coordinated two-stage Mn(II)/(III) and Mn(III)/(IV) mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 11381–11391. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02772
Su, J., Bao, P., Bai, T., Deng, L., Wu, H., Liu, F., et al. (2013). CotA, a multicopper oxidase from Bacillus pumilus WH4, exhibits manganese-oxidase activity. PLoS One 8:e60573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060573
Su, J., Deng, L., Huang, L., Guo, S., Liu, F., and He, J. (2014). Catalytic oxidation of manganese(II) by multicopper oxidase CueO and characterization of the biogenic Mn oxide. Water Res. 56, 304–313. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.013
Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Zhang, W., Xu, Z., Dai, M., et al. (2021). Combination of the endophytic manganese-oxidizing bacterium Pantoea eucrina SS01 and biogenic Mn oxides: an efficient and sustainable complex in degradation and detoxification of malachite green. Chemosphere 280:130785. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130785
Takio, N., Yadav, M., and Yadav, H. S. (2021). Catalase-mediated remediation of environmental pollutants and potential application – a review. Biocatal. Biotransformation 39, 389–407. doi: 10.1080/10242422.2021.1932838
Tao, L., Stich, T. A., Liou, S. H., Soldatova, A. V., Delgadillo, D. A., Romano, C. A., et al. (2017). Copper binding sites in the manganese-oxidizing Mnx protein complex investigated by Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139, 8868–8877. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02277
Taslimi, P., Nadaroglu, H., and Adıguzel, A. (2013). Removal of some textile dyes from aqueous solution by using a catalase-peroxidase from Aeribacillus pallidus (P26). J Pure Appl Microbiol 7, 2629–2640.
Tran, T. N., Kim, D. G., and Ko, S. O. (2018). Synergistic effects of biogenic manganese oxide and Mn(II)-oxidizing bacterium Pseudomonas putida strain MnB1 on the degradation of 17 α-ethinylestradiol. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 350–359. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.045
Trott, O., and Olson, A. J. (2010). AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334
Wan, W., Xing, Y., Qin, X., Li, X., Liu, S., Luo, X., et al. (2020). A manganese-oxidizing bacterial consortium and its biogenic Mn oxides for dye decolorization and heavy metal adsorption. Chemosphere 253:126627. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126627
Wang, J., Gao, F., Liu, Z., Qiao, M., Niu, X., Zhang, K. Q., et al. (2012). Pathway and molecular mechanisms for malachite green biodegradation in Exiguobacterium sp. MG2. PLoS One 7:e51808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051808
Xiu, Y. (2013). Triphenylmethane dye decoloration using hydrogen peroxide-resistant manganese peroxidase. Microbiology 40, 1356–1364. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2013.08.009
Xu, M., Jun, G., Cen, Y., and Sun, G. (2006). Review of studies on the dye biodegradation. Microbiology 1, 138–143. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2006.01.030
Yang, J., Yang, X., Lin, Y., Ng, T. B., Lin, J., and Ye, X. (2015). Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of malachite green: performance optimization and degradation mechanism. PLoS One 10:e0127714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127714
Yang, X., Zheng, J., Lu, Y., and Jia, R. (2016). Degradation and detoxification of the triphenylmethane dye malachite green catalyzed by crude manganese peroxidase from Irpex lacteus F17. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 23, 9585–9597. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6164-9
Yu, S., Girotto, S., Zhao, X., and Magliozzo, R. S. (2003). Rapid formation of compound II and a tyrosyl radical in the Y229F mutant of Mycobacterium tuberculosis catalase-peroxidase disrupts catalase but not peroxidase function. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 44121–44127. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304757200
Zámocký, M., Furtmüller, P. G., and Obinger, C. (2009). Two distinct groups of fungal catalase/peroxidases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 37, 772–777. doi: 10.1042/bst0370772
Zener, C. (1951). Interaction between the 'd-Shells' in the transition metals II. Ferromagnetic compounds of manganese with perovskite structure. Phys. Rev. 82, 403–405. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.82.403
Zhao, G., Wang, W., Zheng, L., Chen, L., Duan, G., Chang, R., et al. (2023). Catalase-peroxidase StKatG is a bacterial manganese oxidase from endophytic Salinicola tamaricis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 224, 281–291. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.10.123
Zhao, G. Y., Zhao, L. Y., Xia, Z. J., Zhu, J. L., Liu, D., Liu, C. Y., et al. (2017). Salinicola tamaricis sp. nov., a heavy-metal-tolerant, endophytic bacterium isolated from the halophyte Tamarix chinensis Lour. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 67, 1813–1819. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001868
Zhou, H., and Fu, C. (2020). Manganese-oxidizing microbes and biogenic manganese oxides: characterization, Mn(II) oxidation mechanism and environmental relevance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 19, 489–507. doi: 10.1007/s11157-020-09541-1
Zhou, N. Q., Liu, D. F., Min, D., Cheng, L., Huang, X. N., Tian, L. J., et al. (2018). Continuous degradation of ciprofloxacin in a manganese redox cycling system driven by Pseudomonas putida MnB-1. Chemosphere 211, 345–351. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.117
Keywords: catalase-peroxidase, Mn(II) oxidases, malachite green, decolorization ability, enzymic activity
Citation: Ding M, Wang W, Lu Z, Sun Y, Qiao X, Dai M and Zhao G (2024) Catalase-peroxidase StKatG2 from Salinicola tamaricis: a versatile Mn(II) oxidase that decolorizes malachite green. Front. Microbiol. 15:1478305. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1478305
Received: 09 August 2024; Accepted: 21 October 2024;
Published: 05 November 2024.
Edited by:
Muhammad Ali, Trinity College Dublin, IrelandReviewed by:
Shamkant B. Badgujar, Independent Researcher, Jalgaon, IndiaCopyright © 2024 Ding, Wang, Lu, Sun, Qiao, Dai and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guoyan Zhao, emhhb2d1b3lhbkBzZG51LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Guoyan Zhao, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3200-8800
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.