- 1Division of Microbial Ecology, Department of Microbiology and Ecosystem Science, Centre for Microbiology and Environmental Systems Science CeMESS, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 2Doctoral School in Microbiology and Environmental Science, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
- 3Joint Microbiome Facility of the Medical University of Vienna and the University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
Keystone species are thought to play a critical role in determining the structure and function of microbial communities. As they are important candidates for microbiome-targeted interventions, the identification and characterization of keystones is a pressing research goal. Both empirical as well as computational approaches to identify keystones have been proposed, and in particular correlation network analysis is frequently utilized to interrogate sequencing-based microbiome data. Here, we apply an established method for identifying putative keystone taxa in correlation networks. We develop a robust workflow for network construction and systematically evaluate the effects of taxonomic resolution on network properties and the identification of keystone taxa. We are able to identify correlation network keystone species and genera, but could not detect taxa with high keystone potential at lower taxonomic resolution. Based on the correlation patterns observed, we hypothesize that the identified putative keystone taxa have a stabilizing effect that is exerted on correlated taxa. Correlation network analysis further revealed subcommunities present in the dataset that are remarkably similar to previously described patterns. The interrogation of available metatranscriptomes also revealed distinct transcriptional states present in all putative keystone taxa. These results suggest that keystone taxa may have stabilizing properties in a subset of community members rather than global effects. The work presented here contributes to the understanding of correlation network keystone taxa and sheds light on their potential ecological significance.
1 Introduction
Microbiomes are characterized by diverse interspecific and microbe-environment interactions. The net outcome of microbial activities and interactions produces the observed community structure and function, and interactions are thought to be crucial for maintaining community stability and conferring resistance and resilience in the face of disturbance. Borrowing a concept from macro-ecology (Paine, 1969), the idea of keystone species has intrigued many microbiologists as a potential ecological mechanism that facilitates community stability and resilience. Microbial keystones, whether defined at a species level or a higher taxonomic grouping, are characterized as highly interconnected taxa that exert a strong influence on the entire community, shaping the microbiome irrespective of their abundance (Hausmann et al., 2019). Loss of a keystone taxon from the community would be expected to disrupt the microbiome and cause major shifts in community composition and function. Their crucial role in maintaining community structure is what makes keystone taxa a particularly interesting target for human gut microbiome research.
The gut microbiome is essential for human physiological function and health by performing many important services including metabolizing complex food molecules (Hamaker and Tuncil, 2014), training the immune system (Zheng et al., 2020), and providing colonization resistance against pathogens (Brugiroux et al., 2017). The composition of the gut microbial community is highly individualized (Lloyd-Price et al., 2017) and in particular effected by diet and geographical location (Wilson et al., 2020). A so-called westernized diet, high in fat but low in fiber, has been linked to diseases such as type 2 diabetes (Sharma and Tripathi, 2019) and colorectal cancer (Arita and Inagaki-Ohara, 2019). Identifying keystone taxa in the healthy gut microbiome and understanding their role in the community could provide us with novel microbiome-targeted intervention strategies for altered community compositions related to diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disease, and obesity (Carding et al., 2015). Some species have been proposed as keystones in the human gut microbiome based on empirical evidence, such as Akkermansia muciniphila (Belzer et al., 2017) and Christensenella minuta (Mazier et al., 2021).
A. muciniphila was shown to facilitate the growth of butyrate producers by degrading host-derived mucosal sugars in a mucus-dependent cross-feeding community (Belzer et al., 2017). C. minuta showed protective properties against diet-induced obesity in mouse models and modulated the intestinal microbiota in an in vitro model inoculated with fecal samples from obese individuals (Mazier et al., 2021). However, the experimental identification of keystone taxa in the human gut microbiome is challenging as intervention studies are difficult to conduct and animal and in vitro models can have limited translatability for the human gut microbiome. Consequently, researchers have moved towards bioinformatics and data analysis to identify putative keystone taxa, utilizing methods such as presence-absence analysis (Amit and Bashan, 2023), linear regression (Fisher and Mehta, 2014) and machine learning algorithms (Wang et al., 2024).
A popular approach to identify keystone taxa in microbiomes is to use sequencing-based microbial abundance profiles to construct and analyze correlation or co-occurrence networks (Faust and Raes, 2012). The assumption is that positive or negative interspecific interactions, be they direct or indirect, lead to positive or negative correlations between the abundances of the respective taxa. It has been shown by Berry and Widder (2014) that in simulated communities certain network features, namely node degree, closeness centrality, betweenness centrality and transitivity, are indicative of a taxon’s keystone potential and can be used to identify keystone taxa with 85% accuracy.
Several studies have identified putative keystone taxa based on correlation network analysis (Fisher and Mehta, 2014; Goodrich et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2019) and proposed them as targets for subsequent experimental studies. However, we still lack an understanding of what ecological features these keystones share or which functional niches they occupy that lead to their observed characteristics in correlation networks (Banerjee et al., 2018). We can speculate that a keystone taxon provides a conserved, specific function in the gut microbiome that is not provided by other taxa and is therefore crucial in maintaining community structure and function (Ze et al., 2012; Cartmell et al., 2018). Alternatively, keystone taxa might be functionally versatile and able to fill available ecological niches, thereby providing the needed functional redundancy and resilience to microbial communities (Weiss et al., 2023). One can also imagine a mixture of both functions, either provided by a single taxon or a keystone guild. Keystone taxa may be part of the common core microbiome, the component found across a large proportion of communities, but are closer in concept to an ecological core microbiome, the component disproportionally important for shaping the community (Risely, 2020).
With this study, we aim to further our understanding of putative keystone taxa in the human gut microbiome. We establish a workflow to construct robust and statistically significant correlation networks with FastSpar (Watts et al., 2019) and identify correlation network keystones based on their network features, as proposed by Berry and Widder (2014). We then utilize this workflow to interrogate the prokaryotic gut microbiota using publicly available metagenomes and metatranscriptomes from large human gut microbiome studies based in the USA. We find that detection of network keystones is highly sensitive to taxonomic resolution and are able to identify putative keystone taxa only at species and genus level. Correlation network analysis further suggests a community stabilizing effect of putative keystone taxa and reveals co-occurring subcommunities present across gut microbiomes.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Processing of raw data
We analyzed metagenome and metatranscriptome reads from two publicly available datasets, a cohort of patients with inflammatory bowel disease as well as healthy control patients (Schirmer et al., 2018) and a cohort of adult men (Mehta et al., 2018). The sequencing data is available on the Sequence Read Archive under BioProject PRJNA389280 and BioProject PRJNA354235, respectively. The raw reads were preprocessed with trimmomatic (Bolger et al., 2014) (with settings leading: 3, trailing: 3, sliding window: 4:15, minlen: 50). We removed samples with fewer than one million reads from further analyses and, in the Schirmer dataset, used only samples from participants not diagnosed with IBD. We then randomly selected one sample per participant to ensure statistical independence of the samples. The trimmed reads were processed using HUMAnN 3.0.0 (Beghini et al., 2021). In further analyses we only considered reads mapped to reference genomes and discarded unmapped reads (leading to a total of 123,109,687 metagenome reads and 115,784,680 metatranscriptome reads). Briefly, HUMAnN 3.0.0 first estimates community composition with MetaphlAn 3.0.7 (Beghini et al., 2021) and then maps reads to a community pangenome with bowtie2 (Langmead and Salzberg, 2012). This results in both taxonomic as well as functional profiles of the metagenome and metatranscriptome reads. We used the setting rel_ab_w_read_stats in MetaphlAn 3.0.7 to estimate both relative abundances and total reads mapped to a reference genome. In the functional profiles we further grouped reads mapped to gene families into Enzyme Commission numbers (ECs) using the HUMAnN 3.0.0 function humann_regroup_table with - -groups uniref90_level4ec.
2.2 Principal coordinate analysis of community profiles
In order to visualize community similarity and overlap between the two analyzed datasets, we computed the robust Aitchison distance between samples with the function vegandist in the R package vegan (Oksanen et al., 2022), using the total estimated reads output from MetaphlAn 3.0.7 on species resolution. We then performed a principal coordinate analysis on these distances using the function cmdscale in the R package stats (Dalgaard, 2010).
2.3 Computation of correlation networks
We computed binary Jaccard similarities of community composition at species resolution between samples to estimate whether the communities were similar enough to compute correlation networks. Berry and Widder (2014) suggest an overall site similarity (Jaccard similarity) of at least 20% and we observed a mean Jaccard similarity of 36%. We computed correlations between taxa using FastSpar (Watts et al., 2019) with the settings - -iterations 100 (corresponds to rounds of SparCC correlation estimations), - -exclude_iterations 20 (number of times highly correlated taxa pairs are discovered and excluded), - -threshold 0.1 (minimum threshold to exclude correlated taxa pairs) and - -number 1000 (number of bootstraps). FastSpar is a C++ implementation of the correlation network analysis algorithm SparCC (Friedman and Alm, 2012). In short, these algorithms use log-transformed components to estimate linear Pearson correlations to account for the compositional nature of metagenomic data. In order to estimate the significance of observed correlations, FastSpar uses a permutation-based approach to generate a null distribution that observed correlations are then compared against. We used the total estimated reads output from MetaphlAn 3.0.7 (Beghini et al., 2021) as abundance estimates for each taxon. We computed correlations between taxa at the taxonomic resolution of order, family, genus and species. To ensure robust results, we subsampled our combined datasets. Specifically, we used FastSpar to compute correlation networks on a random subsample of 50 samples and repeated this process 1,000 times. We then built a consensus network using only correlations with a p-value ≤0.05 in at least 200 iterations. The correlation strength in the consensus network was estimated as the mean correlation strength of significant correlations across all iterations. This workflow is visualized in Figure 1. We calculated network features, namely modularity, cohesion, relative node degree, closeness centrality, betweenness centrality and transitivity, using the R package igraph (Csárdi et al., 2023). Following the suggestion of Berry and Widder (2014) we estimated each taxon’s potential to act as a keystone using the network features relative node degree, betweenness centrality and transitivity. We excluded closeness centrality from our calculations in order to reduce collinearity of features. As shown by Berry and Widder (2014), correlation network keystone taxa show a high relative node degree and transitivity as well as low betweenness centrality. We therefore computed the keystone potential (=KP) of each taxon as (relative node degree * transitivity)/betweenness centrality. We consider taxa a keystone if they show a particularly high KP as compared to all other prevalent taxa (taxa present in at least 20% of samples). Namely, we chose a cut-off of median + 5× median absolute deviation of KP (cut-off KP = 22) after visually examining the entire distribution. We furthermore grouped the prevalent taxa into clusters using the function cluster_fast_greedy with default settings in the R package igraph (Csárdi et al., 2023) on positive correlation networks, in which only correlations with a correlation strength >0 are considered. We visualized correlation networks using Cytoscape version 3.8.0 (Shannon et al., 2003).
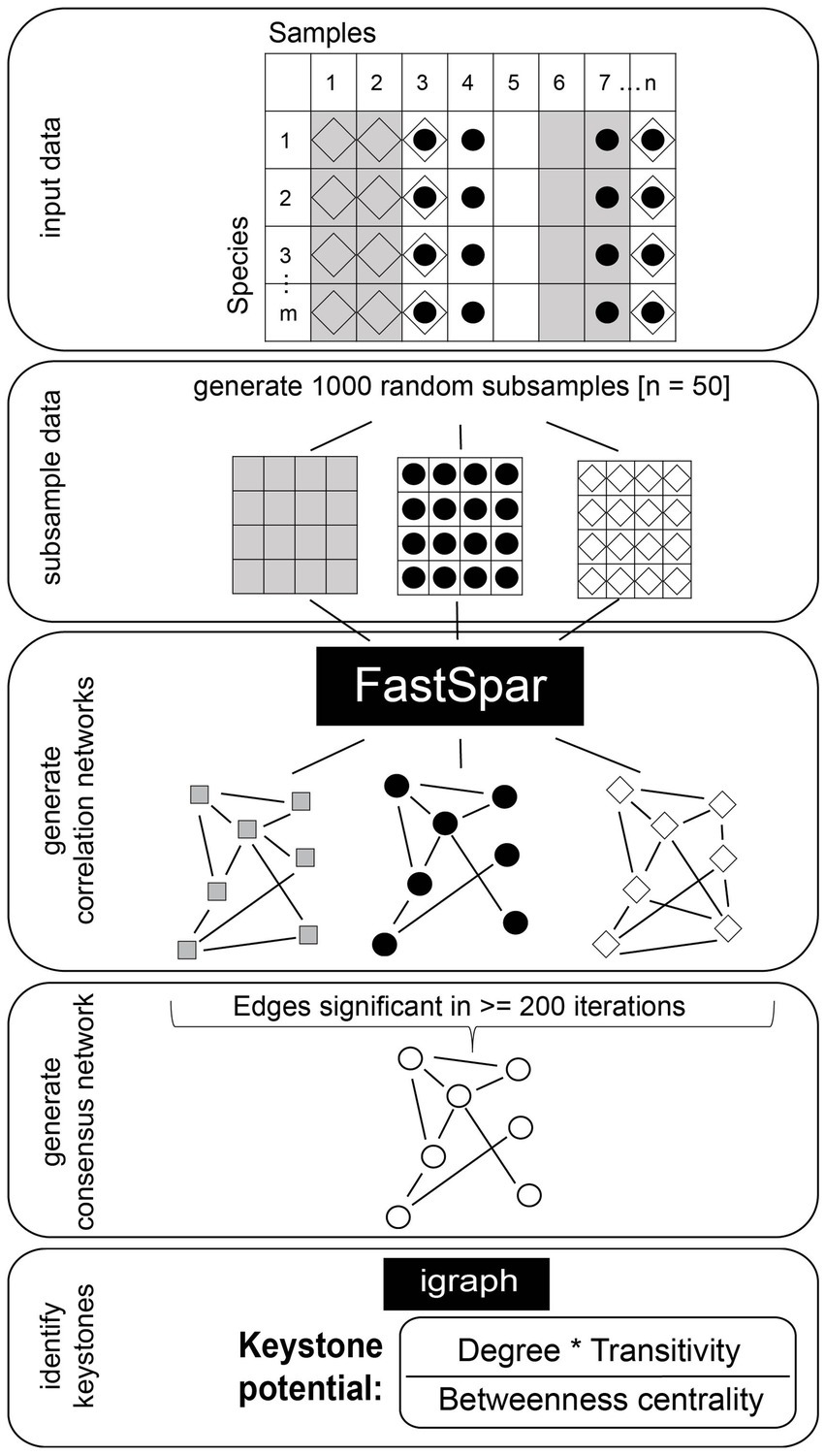
Figure 1. Workflow for the construction of robust and significant correlation networks. The dataset is subsampled 1,000 times and correlation networks are constructed from subsamples using FastSpar. Correlations identified as significant in ≥200 iterations are used to construct a consensus network. The mean correlation strength of all significant correlations is used as the correlation strength for the consensus network. Igraph is used to calculate relative node degree, transitivity and betweenness centrality.
2.4 Functional potential of keystone taxa
We investigated the functional potential of keystone taxa using the pathabundances output from HUMAnN 3.0.0 (Beghini et al., 2021). In short, pathway abundances are computed on community level as well as for individual taxa based on the abundances of the individual component reactions constituting an entire pathway. The pathway definitions used are based on MetaCyc (Caspi et al., 2016).
2.5 Transcriptional stability and transcriptional states of keystone taxa
In order to estimate functional stability of taxa we computed pairwise Sorenson similarities on the presence and absence of gene families using the function betadiver in the R package vegan (Oksanen et al., 2022). We performed k-means clustering to further analyze the functional profiles of the keystone taxa and identify different transcriptional states. For this analysis we opted to use the functional resolution of ECs provided by HUMAnN 3.0.0 (Beghini et al., 2021) (function humann_regroup_table with - - groups uniref90_level4ec) and normalized copies per million to the total transcription attributed to each taxon per sample. We use the function fviz_nbclust in the R package factoextra (Kassambara and Mundt, 2020) to choose the optimal number of clusters (with a k.max—maximum number of clusters—of 10) by computing the average silhouette width for each number of clusters and choosing the highest score. For this number of clusters, we then performed k-means clustering using the function kmeans in the R packages stats (Dalgaard, 2010). However, if we observed clusters containing only 1 or 2 samples, we excluded these samples from the analysis and repeated the process. In order to gain some insights into which ECs are particularly important for distinguishing the observed transcriptional states, we performed random forest analyses. A random forest analysis is a classifying algorithm based on decision trees that calculates importance metrics for the features used to cluster a dataset. In order to estimate the significance of these importance metrics we used the function rfPermute in the R package rfPermute (Archer, 2023). This function computes a null distribution of importance metrics by permuting the response variable and calculates p-values for the observed importances. We used the mean decrease in accuracy as the importance metric for our analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Establishing a workflow to build significant and robust correlation networks
In this study, we established a workflow that results in correlation networks based on both highly significant as well as robust correlations (Figure 1). A major concern when constructing correlation networks is the inherent compositionality of community abundance profiles derived from sequencing data, which can lead to spurious correlations. We utilized FastSpar (Watts et al., 2019), a C++ implementation of the well-established tool SparCC (Friedman and Alm, 2012), which identifies significant correlations and excludes spurious correlations based on a bootstrapping algorithm. We constructed correlation networks with FastSpar on subsamples from two publicly available datasets (Mehta et al., 2018; Schirmer et al., 2018) that we combined for our analysis. Subsequently we constructed a consensus network based only on correlations that were identified as significant in at least 20% of the individually constructed networks. This workflow ensures that correlations kept in the consensus network are representative of both the entire dataset as well as subsamples. We used this procedure to identify taxa that robustly exhibit correlation network keystone features in the gut microbiomes studied.
3.2 Community structure and species properties
In order to evaluate keystone taxa in the healthy human gut microbiome, we leveraged two large studies of healthy human adults, which included 580 paired metagenome and metatranscriptome samples from 131 individuals (Mehta et al., 2018; Schirmer et al., 2018). We first computed community composition profiles using HUMAnN 3.0.0 (Beghini et al., 2021). We then estimated whether the community compositions of the two datasets were similar enough to be combined by performing an ordination analysis and computing the similarity between communities on a species level. This revealed that while samples from the two datasets are somewhat separated, they still exhibit a strong overlap (Supplementary Figure S1A). To ensure statistical independence between samples we randomly selected one sample per participant, resulting in an even larger overlap between the two datasets (Supplementary Figure S1B). To further confirm the validity of combining datasets, we investigated the site similarity of the included samples by computing the overall Jaccard similarity between the communities (presence and absence of species), as suggested by Berry and Widder (2014). Overall, the studied communities exhibit a similarity of 36%, exceeding the suggested lower limit of 20%. These results confirmed the suitability of combining the datasets for computing correlation networks and estimating keystone potential. To gain a better understanding of the data used for this study, we analyzed relative abundance, prevalence and transcriptional contribution of prevalent species (Supplementary Figure S1C). We observed a large variance in relative abundance across samples, both within and between species. As expected, several species of Bacteroides, such as Bacteroides vulgatus [85% sample prevalence, 9% mean relative abundance (sd 10%)], Bacteroides uniformis [93% sample prevalence, 8% mean relative abundance (sd 7%)] and Bacteroides stercoris [51% sample prevalence, 4% mean relative abundance (sd 9%)], as well as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii [99% sample prevalence, 7% mean relative abundance (sd 5%)] and Prevotella copri [20% sample prevalence, 5% mean relative abundance (sd 14%)] are highly abundant in the dataset. More abundant species also tend to contribute more strongly to metatranscriptomes. This could reflect actual contribution to transcription, but may also be a result of better annotation quality in reference genomes from highly abundant species. While many highly abundant species are also highly prevalent across the dataset, there are multiple exceptions. Most notable and well known is the low prevalence of P. copri, a species that has previously been observed to be abundant in certain gut microbiomes while mostly absent in many others, particularly in cohorts from Europe and North America (Tett et al., 2019). In order to avoid spurious correlations and ensure high sensitivity (Berry and Widder, 2014) we focused our analysis on taxa exhibiting a prevalence of at least 20% across all studied samples and constructed correlation networks as described above.
3.3 Correlation networks reveal a loss of structure and keystone potential at lower taxonomic resolution
Previous work has shown that closely related taxa can form networks to utilize complex substrates in the human gut (Rakoff-Nahoum et al., 2014), but stable interactions between distantly related taxa have been also observed (Rao et al., 2021). It is, however, poorly understood how taxonomic resolution affects correlation analysis and specifically the identification of putative keystones. We therefore computed correlation networks at different taxonomic resolutions (order, family, genus and species) and investigated their structure. Overall, networks showed reduced modularity with increased taxonomic resolution (genus and species), while cohesion decreased from species- to order-level networks (Figure 2A). Modularity measures the extent to which a given network is divided into modules, with a higher modularity indicating greater divisions within the network. In contrast, the cohesion of a network estimates the minimum number of nodes that need to be removed to result in a weakly connected network, and a higher cohesion therefore indicates a more tightly connected network. Constructing correlation networks at low taxonomic resolution produced weakly connected networks while networks constructed at genus- and species-level are more cohesive and less modular. This observation is further confirmed by the observed distributions of network features, namely relative node degree (ND), transitivity (T) and betweenness centrality (BC). The relative degree of a node (=a taxon) is the number of edges a node has (correlations to another node) relative to the size of the network (total number of nodes). Transitivity indicates whether all nodes correlated with a given node are in turn correlated. The betweenness centrality of a node estimates how many shortest paths between two nodes (smallest number of edges connecting two nodes within a network) go through this given node. Correlation network keystones are characterized by high node degree, high transitivity and low betweenness centrality (Berry and Widder, 2014). The probability density functions of these network features, particularly transitivity and betweenness centrality, are flatter at lower taxonomic resolution (Figure 2B). In the node degree distribution, we observe a slight flattening as well as a general shift towards a higher degree at lower taxonomic resolution. Flatter probability density functions, and therefore a more equal distribution of network features across all taxa, suggest that any one taxon is less likely to exhibit a high keystone potential. We confirm this by computing the keystone potential (=KP), using the formula KP = (ND*T)/BC, and comparing it across taxonomic resolutions (Figure 2C). As expected, we observe very low KP at family and order level, indicating that such broad taxonomic groups are unlikely to exhibit structuring effects on the overall community (Supplementary Table S1). In contrast, we see both genera and species with a high potential to act as correlation network keystones. Interestingly, the pattern of KP is not consistent from genus to species, with some taxa exhibiting a higher potential at genus level and seemingly losing it at species level and vice versa. We also observe that degree and betweenness centrality tend to be positively correlated in both genera and species and consequently taxa with a high keystone potential show a surprisingly low degree, but high transitivity (Figure 2D; Supplementary Figure S2). In summary, these results suggest that correlation network keystones are solely found within genera or species, and we thus focused our downstream analyses on these two taxonomic levels.
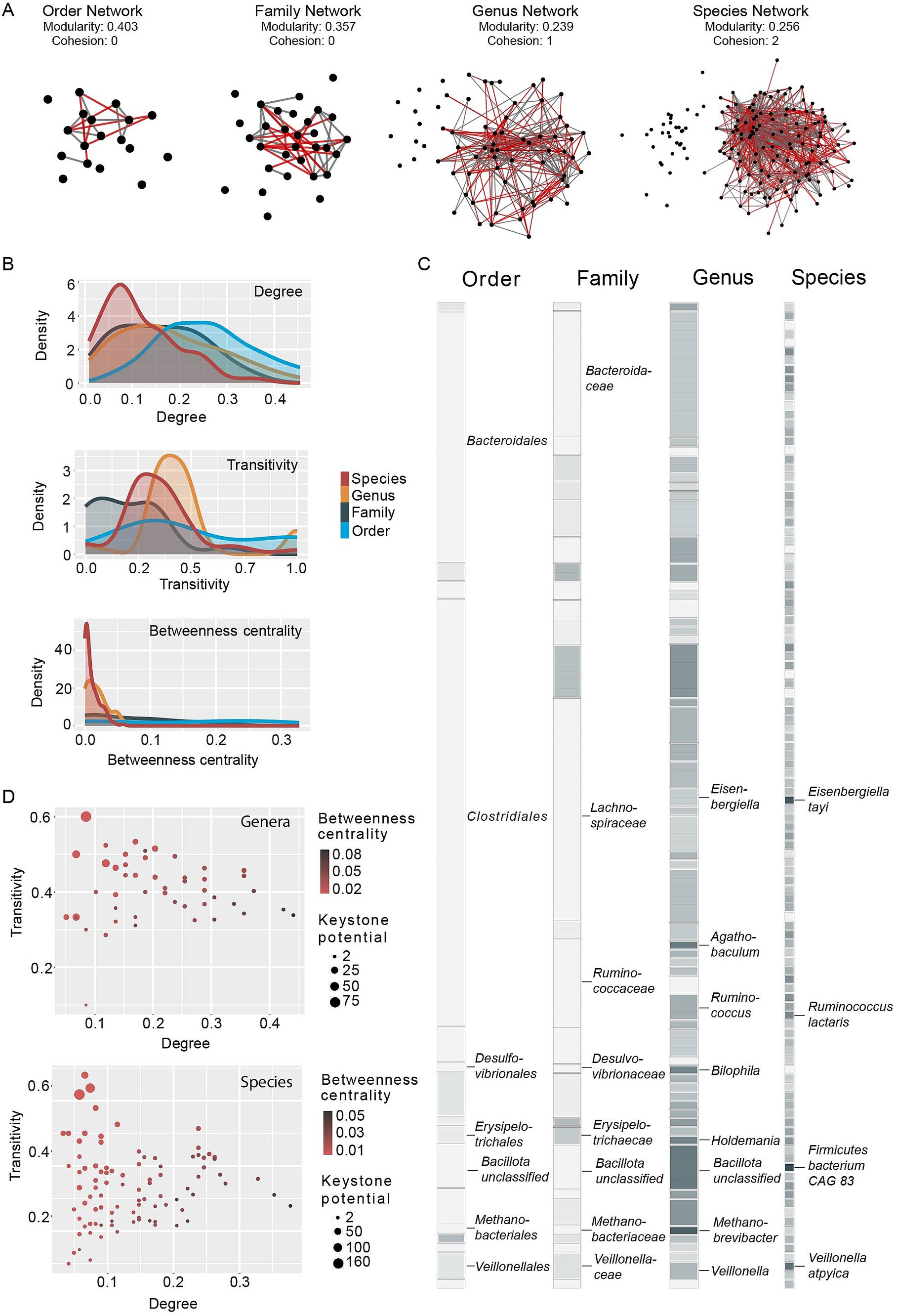
Figure 2. Distribution of correlation network features and keystone potential. (A) Correlation networks constructed on order, family, genus and species level. Network nodes (black circles) indicate taxa, network edges connecting the circles indicate positive (gray) and negative (red) correlations between taxa. Nodes without edges did not show significant correlations in ≥200 subsamples (see materials and methods section). The network layout was computed in Cytoscape (Shannon et al., 2003) using the layout option “Prefuse Force Directed Layout.” In this layout nodes (taxa) with a higher number of significant correlations between them are placed closer together. (B) Density functions of relative node degree (relative to total network size), transitivity and betweenness centrality of taxa within a correlation network, colored by taxonomic resolution. (C) Keystone potential of taxa present in ≥20% of analyzed samples. The keystone potential of each taxon is indicated as a colored square, with white indicating very low keystone potential and dark gray indicating high keystone potential. (D) Relationship between mean degree and transitivity of network nodes. Circle size represents keystone potential and red (grey) circle color indicates low (high) betweenness centrality.
3.4 Few taxa have a relatively high keystone potential
We next analyzed the distribution of keystone potential in genera and species to better understand the network properties of correlation network keystones. Both on genus as well as on species level the distribution of keystone potential is strongly skewed to the right and only few taxa show a particularly high KP when compared to all other taxa (Figures 3A,B, respectively). This aligns well with our understanding of keystones and is to be expected based on the probability density functions of the network features used to compute KP (Figure 2B). Specifically, 8.8% of prevalent genera and 3.6% of prevalent species show a KP above 22 (see materials and methods section) and are therefore considered putative keystones in our analysis. On genus level Methanobrevibacter (KP = 92), Agathobaculum (KP = 39), Bilophila (KP = 30) and Holdemania (KP = 30) (Table 1) have a notably high potential to act as correlation network keystones. We also observe a group of unclassified Bacillota (KP = 41) with high KP, but as this group of species is likely not phylogenetically coherent, we did not include it in further analyses. On species level, Firmicutes bacterium CAG 83 (unclassified Bacillota, KP = 169), Eisenbergiella tayi (KP = 126), Veillonella atypica (KP = 52) and Ruminococcus lactaris (KP = 27) are putative keystones (Table 1). With the exception of the genera Methanobrevibacter and Bilophila, which belong to the phylum Euryarchaeota and Thermodesulfobacteriota, respectively, all of these taxa are Bacillota. When we compare the KP of each species with its respective KP on genus level, there is no clear pattern (Figure 3C). This suggests that certain genera may act as a keystone towards other genera but lose this potential on species level, and vice versa. We observe this for Agathobaculum, Bilophila, Holdemania and Methanobrevibacter. These four genera show a high KP, but the respective species exhibit low KP (Figure 2C). This is a particularly surprising observation considering that only one species belonging to each of these genera is present in the datasets, namely Agathobaculum butyriciproducens, Bilophila wadsworthia, Holdemania filiformis and Methanobrevibacter smithii. These keystone genera are effectively keystone species that seem to have stronger network keystone properties when considering intergenic correlations. The correlations might be diluted on a species level and intergenic correlations may be distributed amongst multiple species with differing abundance patterns. Conversely, particular species have a high KP that is diluted when observed on genus level, as can be seen for V. atypica and E. tayi. The species within one genus may rarely co-occur, resulting in opposing correlation patterns and leading to a low KP on genus level. Ultimately, only few taxa in species and genus correlation networks exhibit a high potential to act as keystones, while the vast majority of taxa do not show the characteristics of putative keystones.
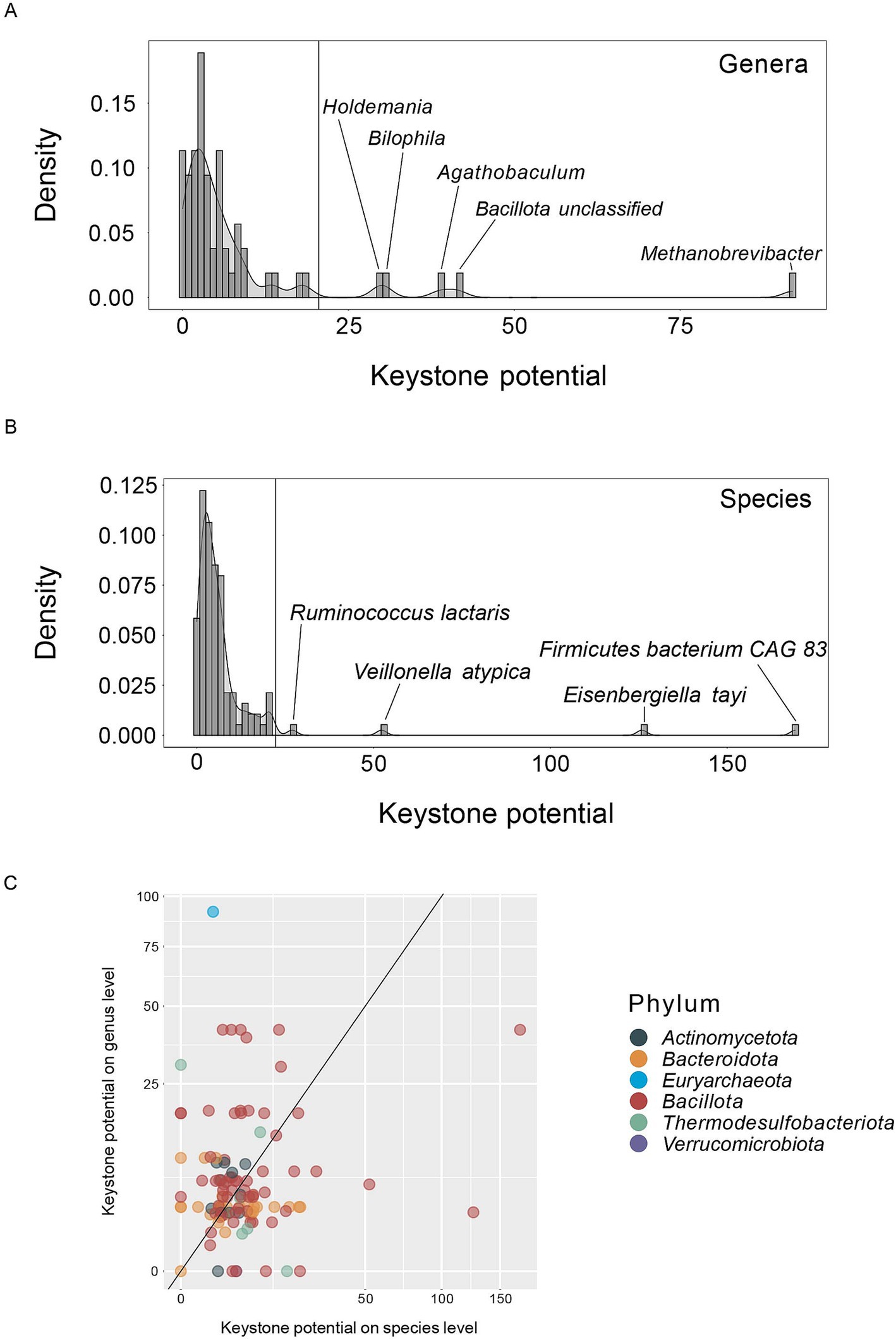
Figure 3. Density functions of keystone potential on (A) genus and (B) species level. Inserts show the taxa with the highest keystone potential. Horizontal lines indicate the keystone potential cut-off for taxa considered a keystone. The cut-off is set at median + 5× median absolute deviation. (C) Keystone potential on species level versus keystone potential on genus level, shown on a logarithmic scale. The diagonal line indicates a 1:1 linear relationship. Colors indicate the phylum of each taxon.
3.5 Correlation patterns indicate that keystone taxa may facilitate community stability
It has been suggested that in a highly diverse and functionally redundant system, such as the human gut microbiome, stability is facilitated by a high number of negative interactions, preventing the formation of positive feedback loops (Coyte et al., 2015). However, we observe that more than 50% of correlations in the analyzed networks are positive (Figure 4A). This is even more pronounced in species that belong to the same genus, where almost 75% of observed within-genus correlations are positive (Figure 4B). Putative keystone genera show a contrasting pattern, with around 60% negative correlations (Figure 4C) and genera that are strongly correlated with a keystone exhibit weaker within-genus correlations (Figure 4D). These results suggest that single-species keystone genera might provide community stability by counteracting positive feedback loops within other genera and dampening correlations. We also observe that larger genera exhibit weaker positive correlations within a respective genus (Supplementary Figure S3A) which may be a result of functional redundancy in these more closely related taxa. On both genus as well as species level we observe that taxa correlated with a keystone taxon (first neighbors of keystones) are in general correlated to more taxa than those not correlated to a keystone. First neighbors of keystones also tend to have weaker correlations (Supplementary Figures S3B,C, respectively). These observations further point towards a potential stabilizing effect of putative keystone taxa.
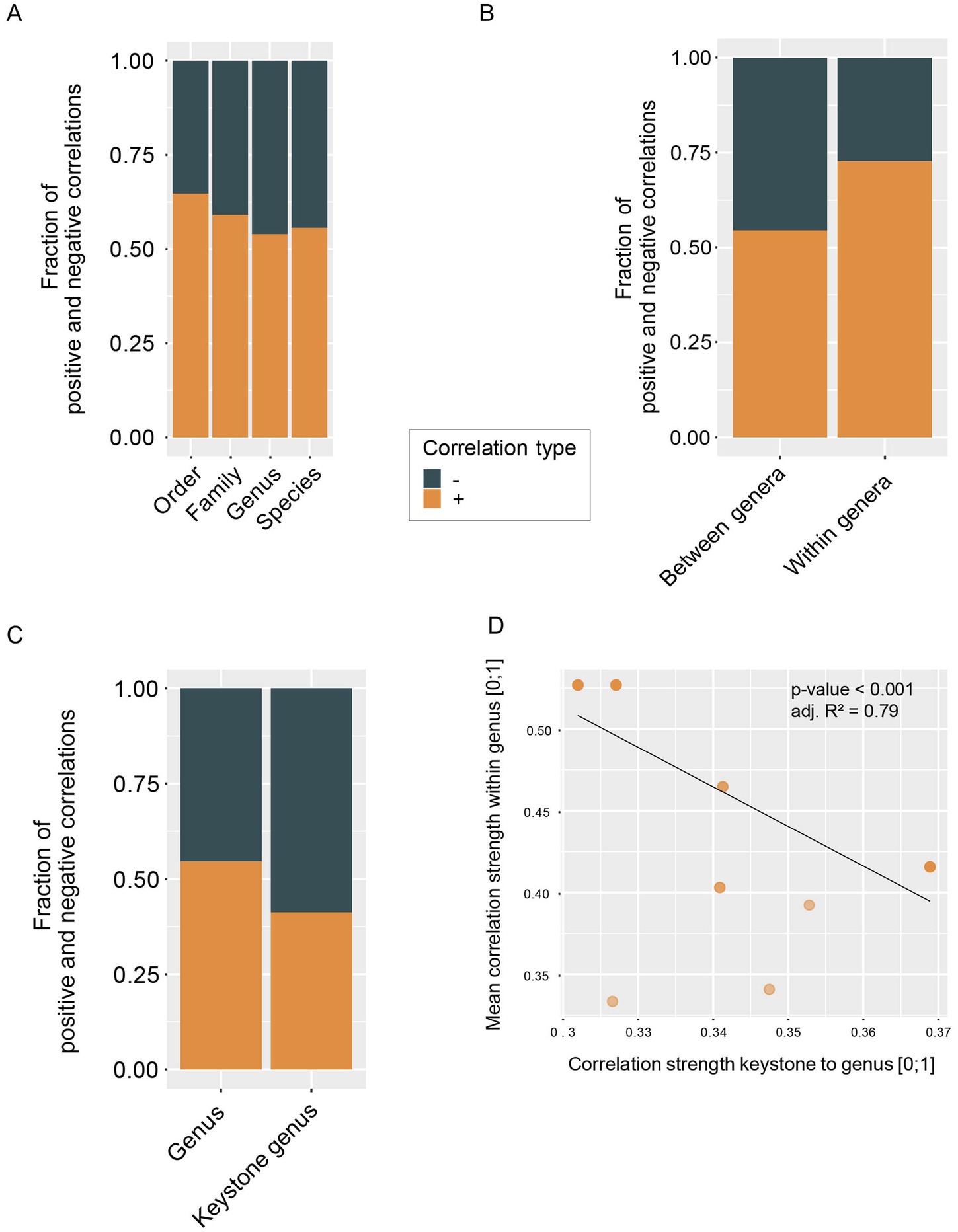
Figure 4. Fractions of negative and positive correlations (A) between taxa at different taxonomic resolution, (B) between genera and within genera and (C) of keystone genera and non-keystone genera. (D) Absolute correlation strength from keystone genera to other genera versus the mean absolute correlation strength within the respective genera (linear model: p-value <0.001, adj. R2 = 0.79).
3.6 Correlation patterns reveal co-occurring clusters of taxa
To gain a better understanding of the community assembly characteristics of putative keystone taxa, we investigated the co-occurrence patterns of all prevalent species and genera. We constructed positive correlation networks, considering only correlations with a correlation strength >0, and performed a clustering analysis on these networks. This analysis revealed four distinct clusters of species that are highly positively correlated with each other and that show fewer positive correlations to species of other clusters (Figure 5A). Each keystone species is a member of a different species cluster, indicating that keystone species are not highly correlated with each other. In contrast, keystone genera do not fall into separate clusters in the genus network, despite the presence of again four clusters (Figure 5B). Specifically, Bilophila and Holdemania are part of one cluster while Agathobaculum and Methanobrevibacter are located in another. The remaining two clusters are a cluster including Bacteroides, a highly diverse and abundant genus, and a cluster including Prevotella, a genus with, as previously mentioned, distinct abundance patterns. It should further be noted that high abundance is not a necessity for a correlation network keystone (Supplementary Figure S1C). In fact, amongst all prevalent taxa (at least 20% prevalence), keystones exhibit medium to low mean relative abundance. Examining the distribution of all network clusters across samples, we observe a gradient of community compositions both on species and genus level (Supplementary Figure S4). At both taxonomic resolutions there are two dominant clusters that generally comprise the majority of the community. However, all four respective clusters co-occur in most samples and the composition ranges from heavily dominated by one cluster to almost equal contribution of each cluster. This observation is in accordance with recently described enterosignatures of gut microbial communities (Frioux et al., 2023) and may point towards a modular gut microbiome composed of distinct groups of co-occurring taxa.
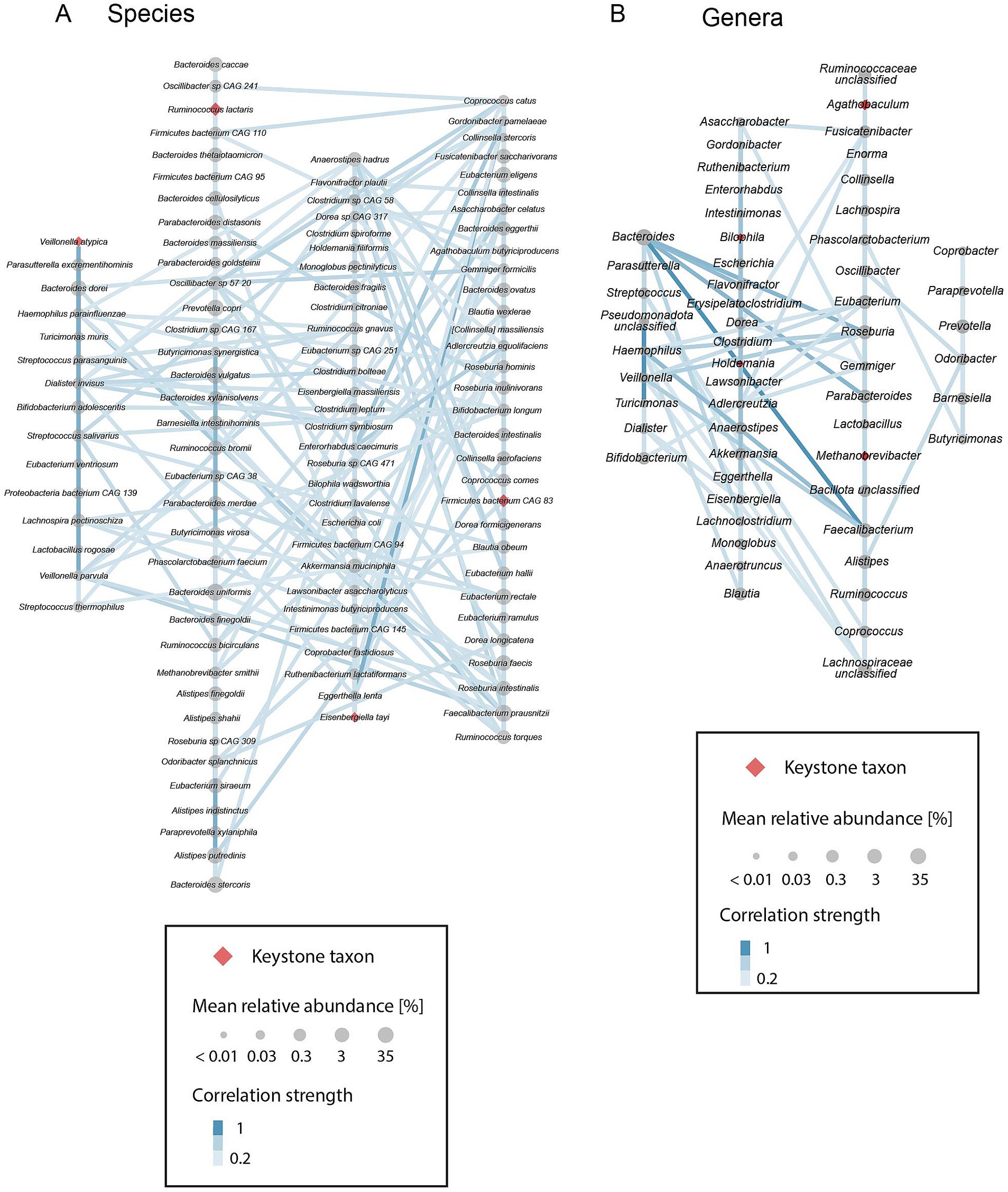
Figure 5. Positive correlation networks of prevalent (present in ≥20% of analyzed samples) (A) species and (B) genera. Gray circles indicate taxa, red diamonds indicate identified correlation network keystone taxa. Circle and diamond size represent the mean relative abundance of taxa. Edges between circles indicate positive correlations. Light blue indicates a weak correlation, darker blue indicates a stronger correlation. Taxa are organized into 4 clusters of strongly positively correlated species and genera, respectively, as identified with a fast greedy clustering algorithm.
3.7 Keystone taxa are transcriptionally versatile and show distinct transcriptional states
In an effort to elucidate the functional role of putative keystone taxa, we investigated their genomic potential and transcriptional versatility. No genomic features were identified to be distinctive of keystone taxa (Supplementary Figure S5), so we focused on analyzing their transcriptional versatility and potential transcriptional states. We estimated the transcriptional versatility of prevalent taxa by computing pairwise Sorensen similarities on the presence and absence of gene families in the metatranscriptomes. The average transcriptional similarity of keystone taxa ranges from fairly high (Holdemania: 0.7, R. lactaris: 0.64) to the lower end of the observed range (Bilophila: 0.22, E. tayi: 0.18) (Supplementary Figure S6). However, as is the case for most of the prevalent taxa, transcriptional similarity within each keystone taxon varies strongly across all analyzed samples. This suggests that keystone taxa do not occupy a conserved ecological niche—as inferred by transcriptional profiles—but are rather functionally versatile and potentially occupy different ecological niches within different gut microbial communities. Based on these observations we performed clustering analyses on the transcriptional profiles of the keystone taxa to identify potentially differing transcriptional states. We were able to identify two to three discrete transcriptional states for most keystone taxa (Figures 6, 7), with the exceptions of Holdemania and V. atypica. In these two cases very few reads mapped to known gene families and fewer still could be grouped into known Enzyme Commission numbers (ECs), indicating low annotation rates in their reference genomes. Consequently, a clustering analysis based on transcriptional profiles could not be performed for these two taxa.
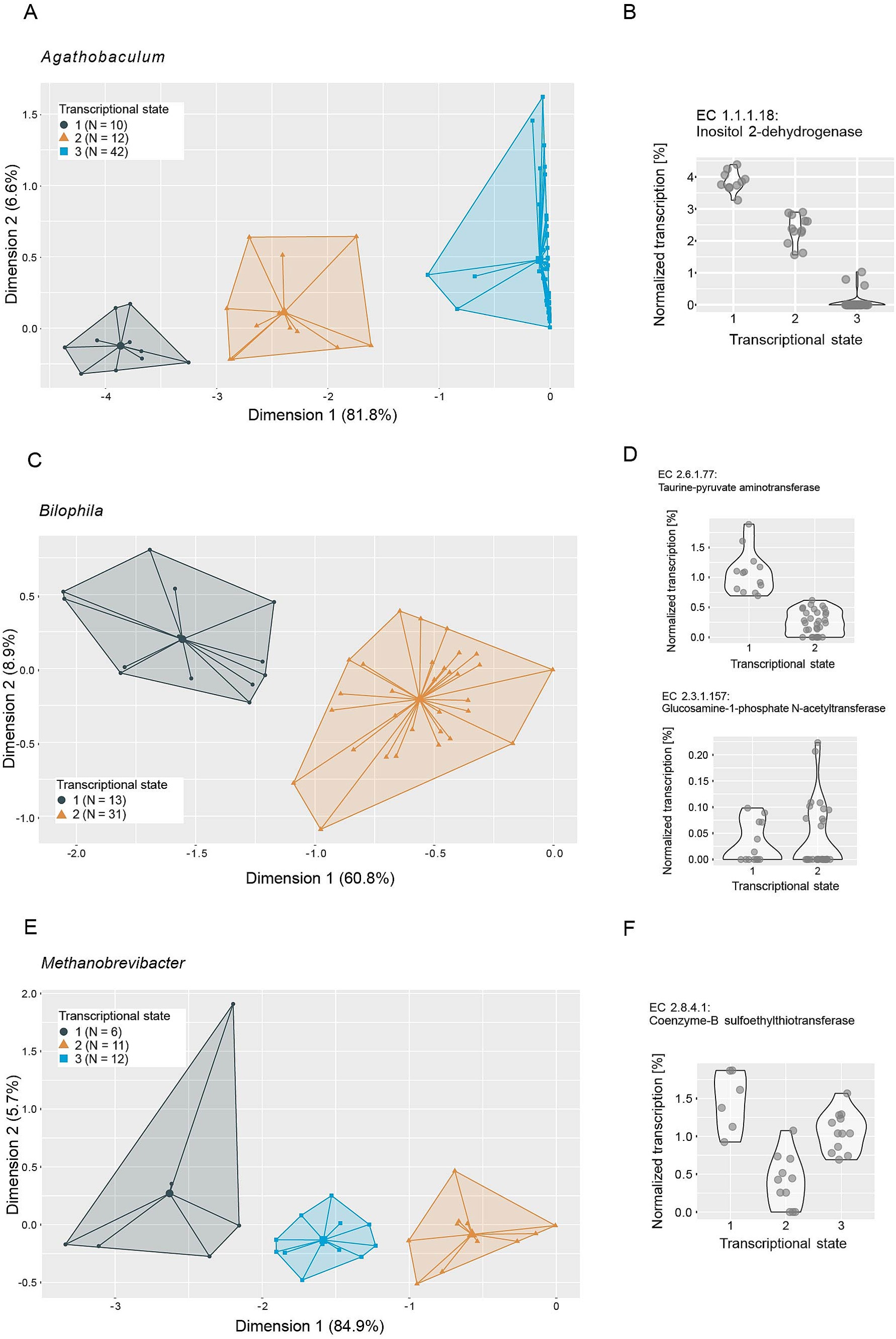
Figure 6. Ordination plots depicting principal component analyses of metatranscriptomes of (A) Agathobaculum, (C) Bilophila and (E) Methanobrevibacter. Metatranscriptome reads were mapped to reference genomes, grouped to Enzyme Commission numbers (ECs) and normalized to the total number of reads mapped to each taxon per sample. Colors and icons indicate transcriptional states identified through k-means clustering (average silhouette width: Agathobaculum: 0.87, Bilophila: 0.92, Methanobrevibacter: 0.86). Normalized transcription of example ECs identified as important in distinguishing the transcriptional states through a random forest model are depicted in panels (B,D,F), respectively.
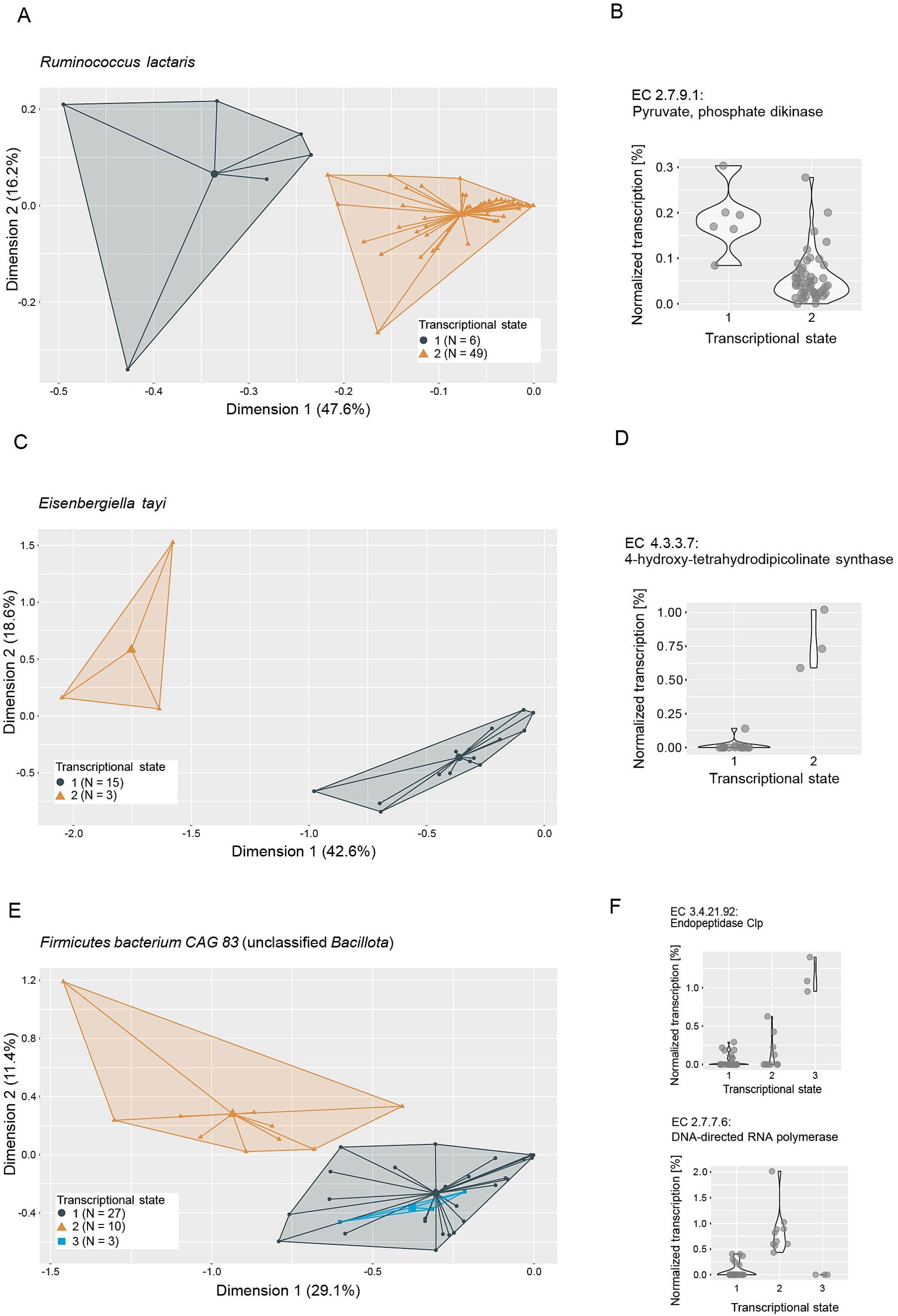
Figure 7. Ordination plots depicting principal component analyses of metatranscriptomes of (A) Ruminococcus lactaris, (C) Eisenbergiella tayi and (E) Firmicutes bacterium CAG 83 (unclassified Bacillota). Metatranscriptome reads were mapped to reference genomes, grouped to Enzyme Commission numbers (ECs) and normalized to the total number of reads mapped to each taxon per sample. Colors and icons indicate transcriptional states identified through k-means clustering (average silhouette width: R. lactaris: 0.92, E. tayi: 0.78, Firmicutes bacterium CAG 83: 0.81). Normalized transcription of example ECs identified as important in distinguishing the transcriptional states through a random forest model are depicted in panels (B,D,F), respectively.
We next performed random forest machine-learning analyses to identify individual ECs that distinguish the transcriptional states (Figures 6, 7; Supplementary Table S1). For Bilophila, this revealed two ECs with contrasting transcription profiles (Figures 6C,D). Taurine-pyruvate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.77), is involved in taurine and hypotaurine metabolism and shows higher relative transcription in the samples in transcriptional state 1. Taurine metabolism is well described in Bilophila and may be linked to disease phenotypes (Natividad et al., 2018; Peck et al., 2019). Glucosamine-1-phosphate N-acetyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.157), which shows higher relative transcription in transcriptional state 2, is involved in the metabolism of various amino sugars and nucleotide sugars, such as glucose or extracellular N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine. For Methanobrevibacter, we could identify three transcriptional states that are likely related to methane metabolism (Figure 6E). Coenzyme-B sulfoethylthiotransferase (EC 2.8.4.1), the enzyme that catalyzes the final step of methanogenesis, was the most important in distinguishing these states (Figure 6F). Our analysis revealed three additional ECs involved in methane metabolism (EC 2.3.1.101, Formylmethanofuran-tetrahydromethanopterin formyltransferase, EC 1.17.1.9, Formate dehydrogenase and EC 4.1.2.43, 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase) as important in distinguishing transcriptional states (Supplementary Table S3). Two transcriptional states were identified in E. tayi (Figure 7C). Notably, all three ECs identified as important in distinguishing these transcriptional states are involved in the biosynthesis of lysine (Figure 7D). The proportion of E. tayi transcription dedicated to these enzymes seems to be higher in transcriptional state 2, pointing towards an upregulation of lysine biosynthesis.
It is important to note that a large proportion of metatranscriptome reads could not be grouped into any known ECs. We still chose the higher resolution of ECs over gene families to gain more insight into the function of the transcripts at the expense of losing a larger proportion of reads. We would also like to point out that the presence of transcriptional states is not unique to keystone taxa and that we could observe similar patterns in many other taxa. Despite these limitations, the data point towards the presence of functionally versatile keystone taxa in the gut microbial community.
4 Discussion
The aim of the present study is to elucidate the potential ecological role of correlation network keystone taxa of the human gut microbiome and gain a better understanding of how these analyses tie into other avenues of human gut microbiome research. In order to identify correlation network keystones, we developed a workflow based on a bootstrapping approach and a subsampling regime that enables the construction of robust and statistically significant correlation networks. We only observe high keystone potential of any taxa in genus- and species-level networks (Figure 2C), in contrast to previous suggestions of higher-order keystones (Trosvik and de Muinck, 2015). Due to the combination of different network features in our approach and the observed positive relationship between mean degree and betweenness centrality, the identified putative keystone taxa show a surprisingly low mean degree (Figure 2D). This result contrasts a more traditional understanding of keystone taxa as network hubs (nodes with a high number of edges) (Paine, 1969; Faust and Raes, 2012; Liu et al., 2019; Varsadiya et al., 2021). While we were able to identify taxa with a high keystone potential in the genus-level correlation network, they are interestingly all single-species genera, meaning that no other species belonging to these genera were detected in the analyzed samples. However, the respective species of these single-species genera are not identified as keystone species in the species-level network. This indicates that they exert their influence on other genera rather than other species. We hypothesize that the correlations to other species may be weak because they are spread amongst many species of individual genera, but on genus-level these correlations aggregate to stronger correlations which lead to the detection of single-species keystone genera. Conversely, we may miss correlations due to intraspecific genetic variability that is only detectable at strain level. These dilutions of the correlation signal may occur to a different extent across taxa due to different genetic boundaries across taxonomic clades. A lower taxonomic resolution inevitably increases the functional potential of a taxon and broadens its ecological niche, which thereby likely weakens direct and indirect interactions between taxa. This would also explain the more evenly distributed correlations between orders and families when compared to genera and species and the lower keystone potentials. Keystone taxa are of great interest for systematic microbiome engineering, for example for the restoration of a perturbed gut microbiome through the introduction or targeted manipulation of keystones. In applied fields a microbial species or genus may well present a more practical target, as opposed to broader taxonomic groups.
Overall, the correlation networks have a high percentage of positive correlations (Figure 4A). This is somewhat surprising, as work by Coyte et al. (2015) has suggested that a diverse microbial community can only be stable when the majority of interactions are negative. Interestingly, the single-species keystone genera identified through our analysis have a considerably higher percentage of negative correlations to other genera (Figure 4C; Table 1). These high numbers of negative correlations with keystone taxa may provide stability to the microbial community, especially considering the particularly high percentage of positive correlations between species of the same genus (Figure 4B). The negative correlations with keystone genera potentially counteract these positive correlations that could otherwise result in positive feedback loops and lead to instability. Coyte et al. (2015) identify the dampening of these positive feedback loops as one mechanism for stabilization of a community. They furthermore suggest weaker ecological interactions as an additional stabilization mechanism. We indeed observe that the stronger the correlation of a keystone to a genus, the weaker the correlations between the species of the respective genus (Figure 4D), suggesting that the keystone genera may be both dampening positive feedback loops and weakening intergenic correlations. We additionally find that species’ positive correlations tend to be weaker in larger genera (Supplementary Figure S3A). This result supports another observation by Coyte et al. (2015) that functional redundancy in closely related taxa provides stability by replacing few strong interactions with many weaker interactions. In general, taxa correlated to a keystone taxon tend to have more, but weaker correlations (Supplementary Figures S3B,C), again indicating a stabilizing effect from keystone taxa.
In both the species- as well as genus-level network we identified four clusters of co-occurring taxa (Figure 5). The analyzed gut microbiomes all consisted of more than one cluster, both on species as well as genus level, resulting in a compositional gradient ranging from strongly dominated by a particular cluster to a fairly even distribution of all four clusters (Supplementary Figure S3). Frioux et al. (2023) recently described similar patterns in the genus composition of gut microbial communities. They identified five so-called enterosignatures (commonly co-occurring genera) that, in combination, can accurately describe most healthy gut microbiomes. These five enterosignatures show strong similarities to the genus clusters we were able to identify in our correlation network. Specifically, ES-Firm (enterosignature with a high contribution of various Bacillota) and ES-Prev (dominated by Prevotella) correspond to cluster 3 and cluster 4 in Figure 4, respectively. An enterosignature mainly found in the gut microbiome of infants, ES-Bifi, does not have a corresponding genus cluster in the cohort we analyzed, which consists solely of adults. However, the main genera of ES-Bifi, namely Bifidobacterium, Streptococcus, Veillonella, Enterococcus and Haemophilus, are members of genus cluster 1, together with Bacteroides, one of the main genera in ES-Bact. The remaining cluster 2 includes Escherichia, the main contributor to ES-Esch, and Blautia, a strong contributor to ES-Firm, but most genera in this cluster were not reported as strongly contributing to an enterosignature. These differences may be due to differences in the applied methods (correlation analysis vs. non-negative matrix factorization) as well as size and diversity of the analyzed cohorts. While not a perfect match to the described enterosignatures, the genus clusters we identified are still remarkably similar in composition. In contrast to the study by Frioux et al. (2023) we focused on the analysis of samples from healthy adults and can therefore not draw any conclusions on the relationship between the identified keystones and disease states. The presence of the keystones does not imply a healthy microbiome nor does their absence imply a perturbed microbiome.
We observe distinct transcriptional states in all putative keystone taxa that can be attributed to differential transcription of particular ECs. In a small synthetic gut microbial community, Shetty et al. (2022) observed shifting functional roles of species in an otherwise compositionally and functionally fairly stable community. These observations suggest functional versatility that enables these taxa to adjust their metabolism to available resources and shifting ecological niches. Particularly striking is the high number of ECs from Methanobrevibacter involved in methane metabolism that we could identify as important in distinguishing the transcriptional states of Methanobrevibacter. In Bilophila, we identified an EC involved in taurine and hypotaurine metabolism as important in distinguishing transcriptional states and an EC potentially involved in host glycan degradation that shows an opposing transcription pattern, suggesting a metabolic shift. These findings are consistent with the idea that the gut microbiome needs to be able to accommodate a diverse and variable set of available resources as well as dynamic interplay with the host. Together with the stabilizing effects previously discussed, functional versatility may be another mechanism enabling keystone taxa to exert their influence on the microbial community.
In an intriguing study on gnotobiotic mice, Weiss et al. (2023) observe that functional roles of individual taxa are strongly dependent on the environment and question the existence of universally valid keystone species in the gut microbiome. While we also observe that the transcriptional activity of keystones is variable, our results suggest that the complex intestinal microbial community is modular and keystone taxa exert a stabilizing effect on subsets of the microbiome. These subsets are relatively independent and co-occur in individual gut microbiomes at various frequencies. However, experimental validation is needed to strengthen this hypothesis and in particular to further our understanding of the metabolic interplay underlying the observed dynamics (Tudela et al., 2021).
5 Limitations of the study
The present study has several limitations. We focused exclusively on the analysis of publicly available data and no experimental validation was carried out. Metagenome and metatranscriptome reads were mapped to reference genomes and analyzed on different taxonomic resolutions up to species. Consequently, strain-level variation has not been taken into account and the reliance on reference genomes further reduces the genetic variation represented in this study. We also recognize that correlation networks can reflect other ecological processes beyond interactions such as habitat filtering. Additionally, our analyses focused only on prevalent taxa and therefore would miss any less common keystone taxa. Our observations are furthermore limited to the distal colon, while community composition as well as functionality may differ in more proximal parts of the intestines. Lastly, the data we used for this study consisted of two cohorts with limited demographic diversity and different putative keystones may be present in other populations. Our study focused on healthy adults from the USA and does not represent and cannot readily be translated to other world populations.
6 Conclusion
In this study we developed a pipeline (available on github) for the robust construction and analysis of correlation networks and the identification of putative keystone taxa, namely Agathobaculum butyriciproducens, Bilophila wadsworthia, Eisenbergiella tayi, Firmicutes bacterium CAG 83 (unclassified Bacillota, Holdemania filiformis, Methanobrevibacter smithii, Ruminococcus lactaris and Veillonella atypica). Through a comprehensive analysis of the constructed correlation networks we are able to show that correlation networks and their properties are highly sensitive to taxonomic resolution. Furthermore, we identified signatures of potentially community stabilizing interaction patterns reflected in the correlation networks as well as co-occurring sub-communities in the human gut microbiome that show a high similarity to previously described enterosignatures. The ecological significance of correlation network keystones is still an open question. Nevertheless, we see indications that keystone taxa may have a local stabilizing effect on sub-communities of the gut microbiome. This suggests that it is unlikely that there are individual taxa that globally affect the entire community. We rather hypothesize that keystone taxa act as stabilizing agents in relatively independently co-occurring subsets of the microbiome.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA354235/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA389280/. Code and a wrapper function for the established workflow to construct correlation networks and compute keystone potential of individual taxa can be found at: https://github.com/fbauchinger/correlation.network.keystones_workflow.
Ethics statement
Ethical approval was not required for the study involving humans in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
FB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DB: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by ERC starting grant 714623 “FunKeyGut” and the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) (10.55776/COE7). Work in the laboratory of DB is supported by the FWF project MAINTAIN DOC 69 doc.fund (10.55776/DOC69).
Acknowledgments
A previous version of this work was deposited on a preprint server (Bauchinger et al., 2023).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1454634/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahn, S., Jin, T.-E., Chang, D.-H., Rhee, M.-S., Kim, H. J., Lee, S. J., et al. (2016). Agathobaculum butyriciproducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a strict anaerobic, butyrate-producing gut bacterium isolated from human faeces and reclassification of Eubacterium desmolans as Agathobaculum desmolans comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 66, 3656–3661. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001195
Amir, I., Bouvet, P., Legeay, C., Gophna, U., and Weinberger, A. (2014). Eisenbergiella tayi gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human blood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 907–914. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.057331-0
Amit, G., and Bashan, A. (2023). Top-down identification of keystone taxa in the microbiome. Nat. Commun. 14:3951. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39459-5
Archer, E. (2023). rfPermute: estimate permutation p-values for random forest importance metrics. Available at: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rfPermute/index.html. (Accessed September 22, 2023)
Arita, S., and Inagaki-Ohara, K. (2019). High-fat-diet-induced modulations of leptin signaling and gastric microbiota drive precancerous lesions in the stomach. Nutrition 67–68:110556. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2019.110556
Banerjee, S., Schlaeppi, K., and van der Heijden, M. G. A. (2018). Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 567–576. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0024-1
Baron, E. J., Summanen, P., Downes, J., Roberts, M. C., Wexler, H., and Finegold, S. M. (1989). Bilophila wadsworthia, gen. nov. and sp. nov., a unique gram-negative anaerobic rod recovered from appendicitis specimens and human faeces. Microbiology 135, 3405–3411. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3405
Bauchinger, F., Seki, D., and Berry, D. (2023). Characteristics of putative keystones in the healthy adult human gut microbiome as determined by correlation network analysis. bioRxiv. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.20.567895. [Epub ahead of preprint]
Beghini, F., McIver, L. J., Blanco-Míguez, A., Dubois, L., Asnicar, F., Maharjan, S., et al. (2021). Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. eLife 10:e65088. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65088
Belzer, C., Chia, L. W., Aalvink, S., Chamlagain, B., Piironen, V., Knol, J., et al. (2017). Microbial metabolic networks at the mucus layer lead to diet-independent butyrate and vitamin B12 production by intestinal symbionts. mBio 8:e00770. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00770-17
Bernard, K., Burdz, T., Wiebe, D., Balcewich, B. M., Zimmerman, T., Lagacé-Wiens, P., et al. (2017). Characterization of isolates of Eisenbergiella tayi, a strictly anaerobic gram-stain variable bacillus recovered from human clinical materials in Canada. Anaerobe 44, 128–132. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2017.03.005
Berry, D., and Widder, S. (2014). Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 5:219. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00219
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M., and Usadel, B. (2014). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114–2120. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Brugiroux, S., Beutler, M., Pfann, C., Garzetti, D., Ruscheweyh, H.-J., Ring, D., et al. (2017). Genome-guided design of a defined mouse microbiota that confers colonization resistance against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Nat. Microbiol. 2, 16215–16212. doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.215
Carding, S., Verbeke, K., Vipond, D. T., Corfe, B. M., and Owen, L. J. (2015). Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota in disease. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 26:26191. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v26.26191
Cartmell, A., Muñoz-Muñoz, J., Briggs, J. A., Ndeh, D. A., Lowe, E. C., Baslé, A., et al. (2018). A surface endogalactanase in Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron confers keystone status for arabinogalactan degradation. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 1314–1326. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0258-8
Caspi, R., Billington, R., Ferrer, L., Foerster, H., Fulcher, C. A., Keseler, I. M., et al. (2016). The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, D471–D480. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1164
Coyte, K. Z., Schluter, J., and Foster, K. R. (2015). The ecology of the microbiome: networks, competition, and stability. Science 350, 663–666. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2602
Csárdi, G., Nepusz, T., Müller, K., Horvát, S., Traag, V., Zanini, F., et al. (2023). igraph for R: R interface of the igraph library for graph theory and network analysis. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.8240644
Dalgaard, P. (2010). R Development Core Team (2010): R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Available at: https://research.cbs.dk/en/publications/r-development-core-team-2010-r-a-language-and-environment-for-sta. (Accessed September 22, 2023).
Dridi, B., Henry, M., el Khéchine, A., Raoult, D., and Drancourt, M. (2009). High prevalence of Methanobrevibacter smithii and Methanosphaera stadtmanae detected in the human gut using an improved DNA detection protocol. PLoS One 4:e7063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007063
Egland, P. G., Palmer, R. J., and Kolenbrander, P. E. (2004). Interspecies communication in Streptococcus gordonii–Veillonella atypica biofilms: Signaling in flow conditions requires juxtaposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 16917–16922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407457101
Faust, K., and Raes, J. (2012). Microbial interactions: from networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 538–550. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2832
Feng, Z., Long, W., Hao, B., Ding, D., Ma, X., Zhao, L., et al. (2017). A human stool-derived Bilophila wadsworthia strain caused systemic inflammation in specific-pathogen-free mice. Gut Pathog. 9:59. doi: 10.1186/s13099-017-0208-7
Fisher, C. K., and Mehta, P. (2014). Identifying keystone species in the human gut microbiome from metagenomic timeseries using sparse linear regression. PLoS One 9:e102451. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102451
Frankel, A. E., Coughlin, L. A., Kim, J., Froehlich, T. W., Xie, Y., Frenkel, E. P., et al. (2017). Metagenomic shotgun sequencing and unbiased metabolomic profiling identify specific human gut microbiota and metabolites associated with immune checkpoint therapy efficacy in melanoma patients. Neoplasia 19, 848–855. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.08.004
Friedman, J., and Alm, E. J. (2012). Inferring correlation networks from genomic survey data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 8:e1002687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002687
Frioux, C., Ansorge, R., Özkurt, E., Ghassemi Nedjad, C., Fritscher, J., Quince, C., et al. (2023). Enterosignatures define common bacterial guilds in the human gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 31, 1111–1125.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.05.024
Go, J., Chang, D.-H., Ryu, Y.-K., Park, H.-Y., Lee, I.-B., Noh, J.-R., et al. (2021). Human gut microbiota Agathobaculum butyriciproducens improves cognitive impairment in LPS-induced and APP/PS1 mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Res. 86, 96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2020.12.010
Goodrich, J. K., Waters, J. L., Poole, A. C., Sutter, J. L., Koren, O., Blekhman, R., et al. (2014). Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 159, 789–799. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.053
Gophna, U., Konikoff, T., and Nielsen, H. B. (2017). Oscillospiraand related bacteria—from metagenomic species to metabolic features. Environ. Microbiol. 19, 835–841. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13658
Hamaker, B. R., and Tuncil, Y. E. (2014). A perspective on the complexity of dietary fiber structures and their potential effect on the gut microbiota. J. Mol. Biol. 426, 3838–3850. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.07.028
Hausmann, B., Pelikan, C., Rattei, T., Loy, A., and Pester, M. (2019). Long-term transcriptional activity at zero growth of a cosmopolitan rare biosphere member. mBio 10:e02189. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02189-18
Horz, H.-P., and Conrads, G. (2010). The discussion goes on: what is the role of Euryarchaeota in humans? Archaea 2010:967271. doi: 10.1155/2010/967271
Kassambara, A., and Mundt, F. (2020). factoextra: extract and visualize the results of multivariate data analyses. Available at: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/factoextra/index.html. (Accessed September 22, 2023)
Kharofa, J., Apewokin, S., Alenghat, T., and Ollberding, N. J. (2023). Metagenomic analysis of the fecal microbiome in colorectal cancer patients compared to healthy controls as a function of age. Cancer Med. 12, 2945–2957. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5197
Langmead, B., and Salzberg, S. L. (2012). Fast gapped-read alignment with bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 9, 357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923
Lee, D. W., Ryu, Y.-K., Chang, D.-H., Park, H.-Y., Go, J., Maeng, S.-Y., et al. (2022). Agathobaculum butyriciproducens shows neuroprotective effects in a 6-OHDA-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 1168–1177. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2205.05032
Liu, F., Li, Z., Wang, X., Xue, C., Tang, Q., and Li, R. W. (2019). Microbial co-occurrence patterns and keystone species in the gut microbial community of mice in response to stress and chondroitin sulfate disaccharide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:2130. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092130
Liu, A., Ma, T., Xu, N., Jin, H., Zhao, F., Kwok, L.-Y., et al. (2021). Adjunctive probiotics alleviates asthmatic symptoms via modulating the gut microbiome and serum metabolome. Microbiol. Spectr. 9:e0085921. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00859-21
Lloyd-Price, J., Mahurkar, A., Rahnavard, G., Crabtree, J., Orvis, J., Hall, A. B., et al. (2017). Strains, functions and dynamics in the expanded human microbiome project. Nature 550, 61–66. doi: 10.1038/nature23889
Magnúsdóttir, S., Ravcheev, D., de Crécy-Lagard, V., and Thiele, I. (2015). Systematic genome assessment of B-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes. Front. Genet. 6:148. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00148
Mays, T. D., Holdeman, L. V., Moore, W. E. C., Rogosa, M., and Johnson, J. L. (1982). Taxonomy of the genus Veillonella Prévot. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 32, 28–36. doi: 10.1099/00207713-32-1-28
Mazier, W., Le Corf, K., Martinez, C., Tudela, H., Kissi, D., Kropp, C., et al. (2021). A new strain of Christensenella minuta as a potential biotherapy for obesity and associated metabolic diseases. Cells 10:823. doi: 10.3390/cells10040823
Mehta, R. S., Abu-Ali, G. S., Drew, D. A., Lloyd-Price, J., Subramanian, A., Lochhead, P., et al. (2018). Stability of the human faecal microbiome in a cohort of adult men. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 347–355. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0096-0
Miller, T. L., Wolin, M. J., de Macario, E. C., and Macario, A. J. (1982). Isolation of Methanobrevibacter smithii from human feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 43, 227–232. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.227-232.1982
Moore, W. E. C., Johnson, J. L., and Holdeman, L. V. (1976). Emendation of Bacteroidaceae and Butyrivibrio and descriptions of Desulfomonas gen. nov. and ten new species in the genera Desulfomonas, Butyrivibrio, Eubacterium, Clostridium, and Ruminococcus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 26, 238–252. doi: 10.1099/00207713-26-2-238
Moreno-Arrones, O., Serrano-Villar, S., Perez-Brocal, V., Saceda-Corralo, D., Morales-Raya, C., Rodrigues-Barata, R., et al. (2020). Analysis of the gut microbiota in alopecia areata: identification of bacterial biomarkers. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 34, 400–405. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15885
Natividad, J. M., Lamas, B., Pham, H. P., Michel, M.-L., Rainteau, D., Bridonneau, C., et al. (2018). Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Commun. 9:2802. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05249-7
Oksanen, J., Simpson, G. L., Blanchet, F. G., Kindt, R., Legendre, P., Minchin, P. R., et al. (2022). vegan: community ecology package. Available at: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html. (Accessed September 22, 2023).
Paine, R. T. (1969). A note on trophic complexity and community stability. Am. Nat. 103, 91–93. doi: 10.1086/282586
Pearce, C. I., Pattrick, R. A. D., Law, N., Charnock, J. M., Coker, V. S., Fellowes, J. W., et al. (2009). Investigating different mechanisms for biogenic selenite transformations: Geobacter sulfurreducens, Shewanella oneidensis and Veillonella atypica. Environ. Technol. 30, 1313–1326. doi: 10.1080/09593330902984751
Peck, S. C., Denger, K., Burrichter, A., Irwin, S. M., Balskus, E. P., and Schleheck, D. (2019). A glycyl radical enzyme enables hydrogen sulfide production by the human intestinal bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 3171–3176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815661116
Rakoff-Nahoum, S., Coyne, M. J., and Comstock, L. E. (2014). An ecological network of polysaccharide utilization among human intestinal symbionts. Curr. Biol. 24, 40–49. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.10.077
Rao, C., Coyte, K. Z., Bainter, W., Geha, R. S., Martin, C. R., and Rakoff-Nahoum, S. (2021). Multi-kingdom ecological drivers of microbiota assembly in preterm infants. Nature 591, 633–638. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03241-8
Risely, A. (2020). Applying the core microbiome to understand host–microbe systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 89, 1549–1558. doi: 10.1111/1365-2656.13229
Scheiman, J., Luber, J. M., Chavkin, T. A., MacDonald, T., Tung, A., Pham, L.-D., et al. (2019). Meta-omics analysis of elite athletes identifies a performance-enhancing microbe that functions via lactate metabolism. Nat. Med. 25, 1104–1109. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0485-4
Schirmer, M., Franzosa, E. A., Lloyd-Price, J., McIver, L. J., Schwager, R., Poon, T. W., et al. (2018). Dynamics of metatranscription in the inflammatory bowel disease gut microbiome. Nat. Microbiol. 3, 337–346. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0089-z
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303
Sharma, S., and Tripathi, P. (2019). Gut microbiome and type 2 diabetes: where we are and where to go? J. Nutr. Biochem. 63, 101–108. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.10.003
Shetty, S. A., Kostopoulos, I., Geerlings, S. Y., Smidt, H., de Vos, W. M., and Belzer, C. (2022). Dynamic metabolic interactions and trophic roles of human gut microbes identified using a minimal microbiome exhibiting ecological properties. ISME J. 16, 2144–2159. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01255-2
Surono, I. S., Jalal, F., Bahri, S., Romulo, A., Kusumo, P. D., Manalu, E., et al. (2021). Differences in immune status and fecal SCFA between Indonesian stunted children and children with normal nutritional status. PLoS One 16:e0254300. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254300
Tett, A., Huang, K. D., Asnicar, F., Fehlner-Peach, H., Pasolli, E., Karcher, N., et al. (2019). The Prevotella copri complex comprises four distinct clades underrepresented in westernized populations. Cell Host Microbe 26, 666–679.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.08.018
Trosvik, P., and de Muinck, E. J. (2015). Ecology of bacteria in the human gastrointestinal tract—identification of keystone and foundation taxa. Microbiome 3:44. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0107-4
Tudela, H., Claus, S. P., and Saleh, M. (2021). Next generation microbiome research: identification of keystone species in the metabolic regulation of host-gut microbiota interplay. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:719072. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.719072
Varsadiya, M., Urich, T., Hugelius, G., and Bárta, J. (2021). Fungi in permafrost-affected soils of the Canadian Arctic: horizon- and site-specific keystone taxa revealed by co-occurrence network. Microorganisms 9:1943. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091943
Wang, X.-W., Sun, Z., Jia, H., Michel-Mata, S., Angulo, M. T., Dai, L., et al. (2024). Identifying keystone species in microbial communities using deep learning. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 8, 22–31. doi: 10.1038/s41559-023-02250-2
Watts, S. C., Ritchie, S. C., Inouye, M., and Holt, K. E. (2019). FastSpar: rapid and scalable correlation estimation for compositional data. Bioinformatics 35, 1064–1066. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty734
Weiss, A. S., Niedermeier, L. S., von Strempel, A., Burrichter, A. G., Ring, D., Meng, C., et al. (2023). Nutritional and host environments determine community ecology and keystone species in a synthetic gut bacterial community. Nat. Commun. 14:4780. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40372-0
Willems, A., Moore, W. E. C., Weiss, N., and Collins, M. D. (1997). Phenotypic and phylogenetic characterization of some Eubacterium-like isolates containing a novel type B Wall Murein from human feces: description of Holdemania filiformis gen. nov., sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 47, 1201–1204. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-4-1201
Wilson, A. S., Koller, K. R., Ramaboli, M. C., Nesengani, L. T., Ocvirk, S., Chen, C., et al. (2020). Diet and the human gut microbiome: an international review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 65, 723–740. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06112-w
Xi, W., Gao, X., Zhao, H., Luo, X., Li, J., Tan, X., et al. (2021). Depicting the composition of gut microbiota in children with tic disorders: an exploratory study. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 62, 1246–1254. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13409
Ze, X., Duncan, S. H., Louis, P., and Flint, H. J. (2012). Ruminococcus bromii is a keystone species for the degradation of resistant starch in the human colon. ISME J. 6, 1535–1543. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.4
Zheng, D., Liwinski, T., and Elinav, E. (2020). Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 30, 492–506. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0332-7
Keywords: Methanobrevibacter smithii, Bilophila wadsworthia, Holdemania filiformis, Agathobaculum butyriciproducens, Ruminococcus lactaris, Veillonella atypica, Oscillospira, Eisenbergiella tayi
Citation: Bauchinger F, Seki D and Berry D (2024) Characteristics of putative keystones in the healthy adult human gut microbiota as determined by correlation network analysis. Front. Microbiol. 15:1454634. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1454634
Edited by:
M. Pilar Francino, Fundación para el Fomento de la Investigación Sanitaria y Biomédica de la Comunitat Valenciana (FISABIO), SpainReviewed by:
Daniel A. Medina, Universidad San Sebastián, ChileAlfonso Benítez-Páez, Spanish National Research Council (CSIC), Spain
Bruce A. Rosa, Washington University in St. Louis, United States
Copyright © 2024 Bauchinger, Seki and Berry. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: David Berry, ZGF2aWQuYmVycnlAdW5pdmllLmFjLmF0
 Franziska Bauchinger
Franziska Bauchinger David Seki1
David Seki1 David Berry
David Berry