- 1State Key Laboratory Base of Cell Differentiation and Regulation, College of Life Science, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China
- 2School of Public Health, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing, China
A corrigendum on
Plastic biodegradation by in vitro environmental microorganisms and in vivo gut microorganisms of insects
by Yang, X.-G., Wen, P.-P., Yang, Y.-F., Jia, P.-P., Li, W.-G., and Pei, D.-S. (2023). Front. Microbiol. 13:1001750. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1001750
In the published article, there was an error in a section title. Instead of Biodegradation of plastics by insects, it should be Biodegradation of plastics by insects and other invertebrate.
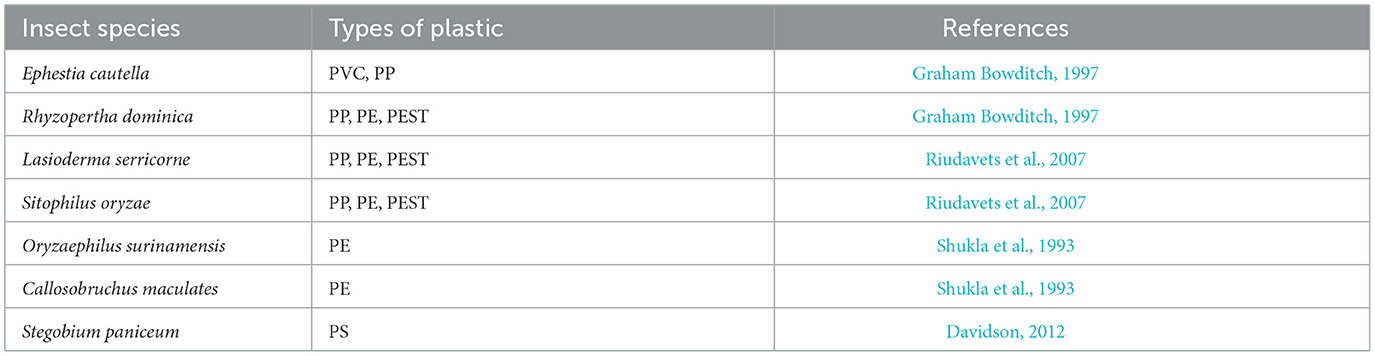
In the published article, there was an error in Tables 2, 3 as published. The heading Insect species in the first cell of the first column and row of Tables 2, 3 were incorrect, due to the fact that not all species listed in these tables are insects. For instance, Achatina fulica is not an insect but rather a mollusk belonging to the class Gastropoda. Sphaeroma terebrans is not an insect but rather an Arthropoda belonging to the class Crustacea.
The corrected Tables 2, 3 and their captions appear below.
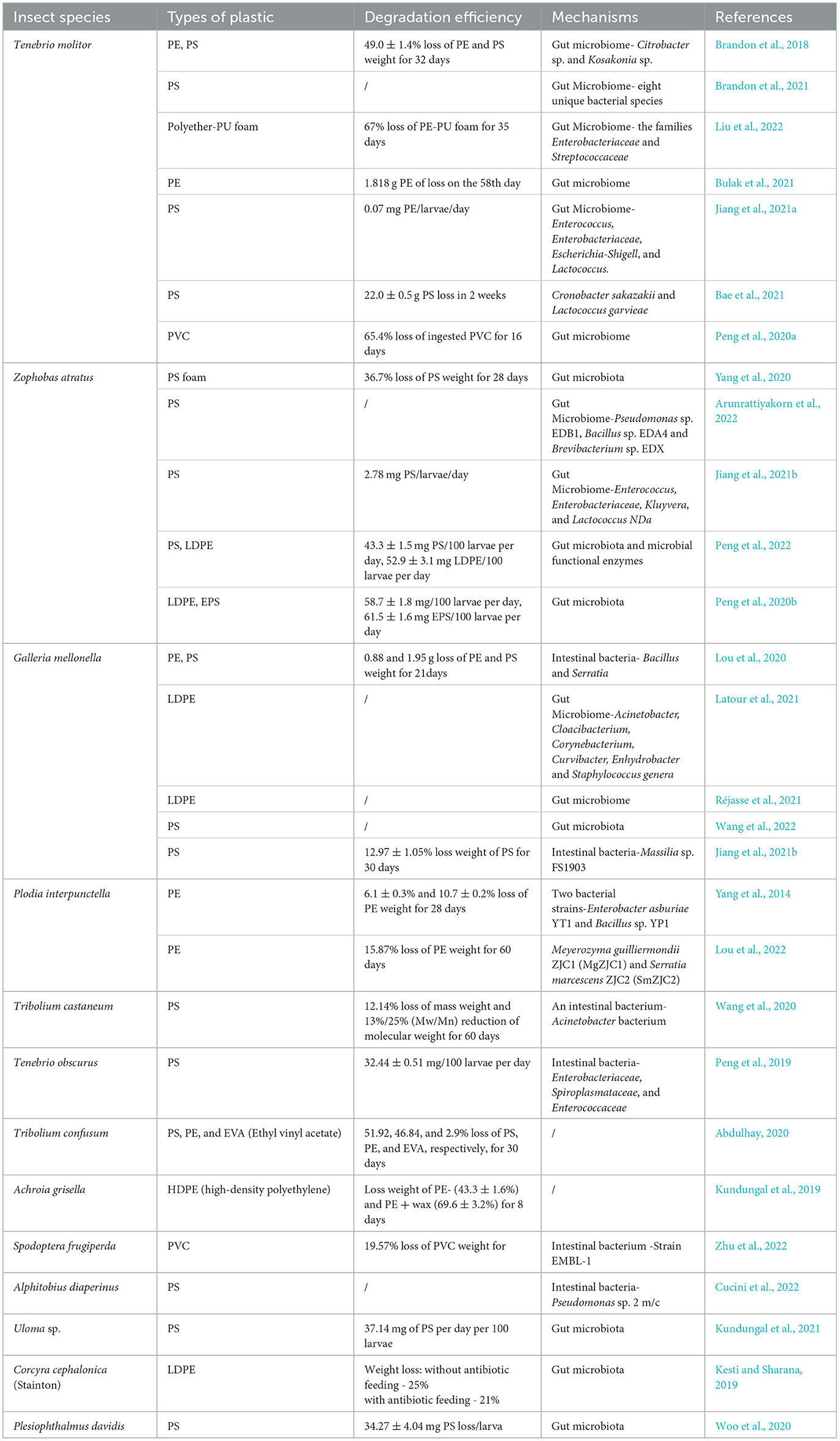
Table 2. The confirmed plastic-degrading insects and their ability to degrade diverse plastic materials.
In the published article, there was an error. A correction has been made to the Biodegradation of plastics by insects, paragraph two. The statement is incomplete, as the species enumerated in Tables 2, 3 are not entirely composed of insects. This sentence previously stated:
“Due to different insect species, plastic materials, and evaluation methods, it is difficult to simply describe the differences in the degradation rates of various insects, but specific degradation efficiency data are summarized in Table 2. In addition, except for the insects that confirmed their capabilities of plastic biodegradation, other insects were also reported to eat plastics (Table 3), but their degradation abilities need further studies”.
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Due to different invertebrate species, plastic materials, and evaluation methods, it is difficult to simply describe the differences in the degradation rates of various insects, but specific degradation efficiency data are summarized in Table 2. In addition, except for the invertebrates that confirmed their capabilities of plastic biodegradation, other invertebrates were also reported to eat plastics (Table 3), but their degradation abilities need further studies”.
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdulhay, H. (2020). Biodegradation of plastic wastes by confused flour beetle Tribolium confusum Jacquelin du Val larvae. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 8, 201–206. doi: 10.35495/ajab.2019.11.515
Arunrattiyakorn, P., Ponprateep, S., Kaennonsang, N., Charapok, Y., Punphuet, Y., Krajangsang, S., et al. (2022). Biodegradation of polystyrene by three bacterial strains isolated from the gut of Superworms (Zophobas atratus larvae). J. Appl. Microbiol. 132, 2823–2831. doi: 10.1111/jam.15474
Bae, J., Cho, H. W., Jung, H., Park, J., Yun, S., Ha, S., et al. (2021). Changes in Intestinal Microbiota Due to the Expanded Polystyrene Diet of Mealworms (Tenebrio molitor). Indian J. Microbiol. 61, 130–136. doi: 10.1007/s12088-021-00922-w
Brandon, A. M., Gao, S. H., Tian, R., Ning, D., Yang, S. S., Zhou, J., et al. (2018). Biodegradation of Polyethylene and Plastic Mixtures in Mealworms (Larvae of Tenebrio molitor) and Effects on the Gut Microbiome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 6526–6533. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b02301
Brandon, A. M., Garcia, A. M., Khlystov, N. A., Wu, W. M., and Criddle, C. S. (2021). Enhanced bioavailability and microbial biodegradation of polystyrene in an enrichment derived from the gut microbiome of tenebrio molitor (Mealworm Larvae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 2027–2036. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04952
Bulak, P., Proc, K., Pytlak, A., Puszka, A., Gawdzik, B., and Bieganowski, A. (2021). Biodegradation of different types of plastics by tenebrio molitor insect. Polymers 13, 3508. doi: 10.3390/polym13203508
Cucini, C., Funari, R., Mercati, D., Nardi, F., Carapelli, A., and Marri, L. (2022). Polystyrene shaping effect on the enriched bacterial community from the plastic-eating Alphitobius diaperinus (Insecta: Coleoptera). Symbiosis 86, 305–313. doi: 10.1007/s13199-022-00847-y
Davidson, T. M. (2012). Boring crustaceans damage polystyrene floats under docks polluting marine waters with microplastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 64, 1821–1828. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.06.005
Graham Bowditch, T. (1997). Penetration of Polyvinyl Chloride and Polypropylene Packaging Films by Ephestia cautella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Larvae, and Tribolium confusum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) Adults. J. Econ. Entomol. 90, 1028–1031
Jiang, S., Su, T., Zhao, J., and Wang, Z. (2021a). Biodegradation of polystyrene by tenebrio molitor, galleria mellonella, and zophobas atratus larvae and comparison of their degradation effects. Polymers 13, 3539. doi: 10.3390/polym13203539
Jiang, S., Su, T., Zhao, J., and Wang, Z. (2021b). Isolation, identification, and characterization of polystyrene-degrading bacteria from the gut of galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Larvae. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 736062. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.736062
Kesti, S., and Sharana, S. (2019). First report on biodegradation of low density polyethylene by rice moth larvae, Corcyra cephalonica (Stainton). Holistic Appr. Environ. 9, 79–83. doi: 10.33765/thate.9.4.2
Kundungal, H., Gangarapu, M., Sarangapani, S., Patchaiyappan, A., and Devipriya, S. P. (2019). Efficient biodegradation of polyethylene (HDPE) waste by the plastic-eating lesser waxworm (Achroia grisella). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 18509–18519. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-05038-9
Kundungal, H., Synshiang, K., and Devipriya, S. P. (2021). Biodegradation of polystyrene wastes by a newly reported honey bee pest Uloma sp. larvae: An insight to the ability of polystyrene-fed larvae to complete its life cycle. Environ. Chall. 4, 100083. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2021.100083
Latour, S., Noël, G., Serteyn, L., Sare, A. R., Massart, S., Delvigne, F., et al. (2021). Multi-omics approach reveals new insights into the gut microbiome of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae) exposed to polyethylene diet. bioRxiv.2021.2006.2004.446152. doi: 10.1101/2021.06.04.446152
Liu, J., Liu, J., Xu, B., Xu, A., Cao, S., Wei, R., et al. (2022). Biodegradation of polyether-polyurethane foam in yellow mealworms (Tenebrio molitor) and effects on the gut microbiome. Chemosphere 304, 135263. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135263
Lou, H., Fu, R., Long, T., Fan, B., Guo, C., Li, L., et al. (2022). Biodegradation of polyethylene by Meyerozyma guilliermondii and Serratia marcescens isolated from the gut of waxworms (larvae of Plodia interpunctella). Sci. Total Environ. 853, 158604. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158604
Lou, Y., Ekaterina, P., Yang, S. S., Lu, B., Liu, B., Ren, N., et al. (2020). Biodegradation of polyethylene and polystyrene by greater wax moth larvae (Galleria mellonella L.) and the effect of co-diet supplementation on the core gut microbiome. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 2821–2831. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b07044
Peng, B.-Y., Chen, Z., Chen, J., Yu, H., Zhou, X., Criddle, C. S., et al. (2020a). Biodegradation of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) in Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) larvae. Environ. Int. 145, 106106. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106106
Peng, B.-Y., Li, Y., Fan, R., Chen, Z., Chen, J., Brandon, A. M., et al. (2020b). Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene and polystyrene in superworms, larvae of Zophobas atratus (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae): Broad and limited extent depolymerization. Environ. Pollut. 266, 115206. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115206
Peng, B.-Y., Sun, Y., Wu, Z., Chen, J., Shen, Z., Zhou, X., et al. (2022). Biodegradation of polystyrene and low-density polyethylene by Zophobas atratus larvae: Fragmentation into microplastics, gut microbiota shift, and microbial functional enzymes. J. Cleaner Prod. 367, 132987. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132987
Peng, B. Y., Su, Y., Chen, Z., Chen, J., Zhou, X., Benbow, M. E., et al. (2019). Biodegradation of Polystyrene by Dark (Tenebrio obscurus) and Yellow (Tenebrio molitor) Mealworms (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 53, 5256–5265. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.8b06963
Réjasse, A., Waeytens, J., Deniset-Besseau, A., Crapart, N., Nielsen-Leroux, C., and Sandt, C. (2021). Plastic biodegradation: do Galleria mellonella larvae - bio-assimilate polyethylene? A spectral histology approach using isotopic labelling and infrared microspectroscopy. bioRxiv.2021.2010.2008.463624. doi: 10.1101/2021.10.08.463624
Riudavets, J., Salas, I., and Pons, M. J. (2007). Damage characteristics produced by insect pests in packaging film. J. Stored Prod. Res. 43, 564–570. doi: 10.1016/j.jspr.2007.03.006
Shukla, R. M., Chand, G., Chandra, M., and Saini, M. L. (1993). Comparative resistance of different packaging materials to stored grain insects. Plant Prot. Bull. 45, 21–23.
Wang, S., Shi, W., Huang, Z., Zhou, N., Xie, Y., Tang, Y., et al. (2022). Complete digestion/biodegradation of polystyrene microplastics by greater wax moth (Galleria mellonella) larvae: Direct in vivo evidence, gut microbiota independence, and potential metabolic pathways. J. Hazardous Mater. 423, 127213. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127213
Wang, Z., Xin, X., Shi, X., and Zhang, Y. (2020). A polystyrene-degrading Acinetobacter bacterium isolated from the larvae of Tribolium castaneum. Sci. Total Environ. 726, 138564. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138564
Woo, S., Song, I., and Cha, H. J. (2020). Fast and Facile Biodegradation of Polystyrene by the Gut Microbial Flora of Plesiophthalmus davidis Larvae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 86, e01361–e01320. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01361-20
Yang, J., Yang, Y., Wu, W. M., Zhao, J., and Jiang, L. (2014). Evidence of polyethylene biodegradation by bacterial strains from the guts of plastic-eating waxworms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 13776–13784. doi: 10.1021/es504038a
Yang, Y., Wang, J., and Xia, M. (2020). Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating superworms Zophobas atratus. Sci. Total Environ. 708, 135233. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135233
Keywords: enzyme, gut microbes, insects, invertebrate, plastic biodegradation
Citation: Yang X-G, Wen P-P, Yang Y-F, Jia P-P, Li W-G and Pei D-S (2024) Corrigendum: Plastic biodegradation by in vitro environmental microorganisms and in vivo gut microorganisms of insects. Front. Microbiol. 15:1444678. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1444678
Received: 25 June 2024; Accepted: 25 June 2024;
Published: 08 July 2024.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2024 Yang, Wen, Yang, Jia, Li and Pei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: De-Sheng Pei, cGVpZHNAY3FtdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xian-Guang Yang
Xian-Guang Yang Ping-Ping Wen
Ping-Ping Wen Yi-Fan Yang1,2
Yi-Fan Yang1,2 De-Sheng Pei
De-Sheng Pei