- 1College of Pharmaceutical Science & Moganshan Research Institute at Deqing County, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China
- 2School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
Airborne fungi and bacteria have been extensively studied by researchers due to their significant effects on human health. We provided an overview of the distribution and sources of airborne pathogenic microbes, and a detailed description of the detrimental effects that these microorganisms cause to human health in both outdoor and indoor environments. By analyzing the large body of literature published in this field, we offered valuable insights into how airborne microbes influence our well-being. The findings highlight the harmful consequences associated with the exposure to airborne fungi and bacteria in a variety of natural and human-mediated environments. Certain demographic groups, including children and the elderly, immunocompromised individuals, and various categories of workers are particularly exposed and vulnerable to the detrimental effect on health of air microbial pollution. A number of studies performed up to date consistently identified Alternaria, Cladosporium, Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Fusarium as the predominant fungal genera in various indoor and outdoor environments. Among bacteria, Bacillus, Streptococcus, Micrococcus, Enterococcus, and Pseudomonas emerged as the dominant genera in air samples collected from numerous environments. All these findings contributed to expanding our knowledge on airborne microbe distribution, emphasizing the crucial need for further research and increased public awareness. Collectively, these efforts may play a vital role in safeguarding human health in the face of risks posed by airborne microbial contaminants.
1 Introduction
Airborne microorganisms, particularly bacteria and fungi, have been identified as a possible source of significant hazards to human health, potentially leading to a spectrum of pathologic conditions ranging from infectious diseases to allergic and toxic reactions (Pastuszka et al., 2000; Hedayati et al., 2005; Simon-Nobbe et al., 2008; Fernstrom and Goldblatt, 2013). When human individuals breathe in either indoor or outdoor air, they are exposed to a substantial number of microbial cells, some of which can act as pathogens or trigger allergic conditions (Barberán et al., 2015a). Therefore, exposure to airborne microorganisms represents a serious risk for human health, resulting in various respiratory disease and infections (Shams-Ghahfarokhi et al., 2014). This risk is further amplified by the extensive dispersion potential of these microorganisms through air currents, enabling their inhalation, ingestion, or contact with individuals who have not had direct exposure to the original source of infection (Fernstrom and Goldblatt, 2013). Fungi are an essential part of airborne microbial communities, given their abundance and wide distribution in a number of environmental sources, such as soil, water and decaying vegetation (Horner et al., 2004; Sen and Asan, 2009; Kalyoncu, 2010; Chakrabarti et al., 2012). The attention on airborne fungal contaminants has dramatically increased together with the evidence of the health hazards directly caused by the fungal spores themselves or by the metabolites released by the fungal particles present in the air that people inhale (Shams-Ghahfarokhi et al., 2014). Apart from the potential for fungal infections ranging from mild to life-threatening, including those acquired in healthcare settings, the health impacts of fungal bioaerosols encompass allergenic, toxigenic and inflammatory effects (Fischer and Dott, 2003; Hedayati et al., 2005; Simon-Nobbe et al., 2008). Fungal spores have the capacity to act as reservoirs for significant quantities of toxic secondary metabolites, specifically mycotoxins, thereby presenting a potential health hazard when inhaled via airborne bioaerosols and dust (Araujo and Cabral, 2010; Shams-Ghahfarokhi et al., 2014). Under special circumstances, the release of pathogenic bioaerosols into the air may also occur as a discharge from the respiratory tract of infected individuals, during routine activities, such as talking, sneezing, coughing, and breathing (Han et al., 2013; Prussin and Marr, 2015; Madhwal et al., 2020), consequently contributing to an increased risk of exposure, particularly in public spaces characterized by intense human presence, such as subway and train stations, places of worship, market areas, and hospitals (Dong and Yao, 2010; Alananbeh et al., 2017; Madhwal et al., 2020). In particular, it is noteworthy that nosocomial infections transmitted through airborne routes can further amplify the likelihood of wound infections within specific healthcare settings (Fleischer et al., 2006). It has been hypothesized that high concentrations of fungal volatile organic compounds in outdoor environments have the ability to impact human health by inducing symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritation of the eyes, throat, and nose (Rolle-Kampczyk et al., 2000; Araujo and Cabral, 2010). Extensive research efforts have been dedicated to the analysis of fungal communities in indoor and outdoor environments (Wu et al., 2000; Shelton et al., 2002; Hedayati et al., 2005; Muafa et al., 2024). Numerous studies have shed light on the identity and concentration of dominant fungal genera in the atmosphere, including Cladosporium, Alternaria, Aspergillus, and Penicillium. Among them, Cladosporium has emerged as the dominant taxon responsible for the presence of allergic fungal spores in various regions (Kalyoncu, 2010; Chakrabarti et al., 2012; Lang-Yona et al., 2012; Fernstrom and Goldblatt, 2013; Sepahvand et al., 2013). As far as airborne bacteria are concerned, these microorganisms exhibit a wide distribution within the lower atmosphere, encompassing a vast range of habitats. Pathogenic bacteria are of particular importance from the medical point of view, since they have significant effects on human health (Burrows et al., 2009; Bowers et al., 2011; Fan C. et al., 2019; Hu et al., 2020). These pathogens have a greater ability to grow and survive in harsh environments compared to non-pathogenic bacteria. For instance, under extreme air pollution, pathogenic bacteria can increase their relative abundance, thus posing significant health hazard to humans (Lee and Lee, 2016; Liu et al., 2018). Bacteria can be found in the atmosphere either as single cells or in association with various particles such as spores, soil, dust, leaves, and other microorganisms (Tong and Lighthart, 2000; Maron et al., 2005; Maki et al., 2008). Once bacteria originated from different sources enter the air environment, they can be transported upward by convective air currents, and due to their small size, they can persist in the atmosphere for a long time (Smets et al., 2016). Notably, bacteria have been observed traveling across continents, especially when associated with dust storms originating from deserts or areas affected by drought (Kellogg and Griffin, 2006; Polymenakou et al., 2008; Lim et al., 2011; Hara and Zhang, 2012; Barberán et al., 2014). This ability of bacteria to be transported over long distances through the atmosphere may results in the potential spreading of certain diseases to different regions (Hara and Zhang, 2012; Fan C. et al., 2019). The airborne transmission of bacteria may involve various well-known pathogenic genera, such as Neisseria, Staphylococcus, and Corynebacterium, which have both pro-inflammatory and pathogenic properties. Neisseria, Corynebacterium, and Bacillus have been reported as prominent causative agents of anthrax, diphtheria, and meningitis (Tettelin et al., 2000; Klee et al., 2010; Fan C. et al., 2019), while the species Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a notable example of a pathogenic bacterium that significantly contributes (10–20%) to infections in hospital settings (Fan C. et al., 2019). Overall, given the tremendous impact of airborne fungi and bacteria on human health, which results in the insurgence of various infectious diseases, allergic reactions, and toxic effects, it is crucial to achieve a comprehensive understanding of microbial community diversity and structure in different air environments. The primary objective of this review is to provide valuable insights into the spatial occurrence and distribution of airborne pathogenic microbes in both outdoor and indoor environments, with a particular focus on their adverse effects on human well-being. Our aim is to provide comprehensive information on the human health hazard created by the presence of microorganisms in the air, which could help in the development of effective strategies for mitigating the adverse effects associated with microbial pollution.
2 Sources of airborne fungi
Airborne fungi can be found in different indoor and outdoor air environments, originating from a variety of natural sources, including vegetation, soil, dust, water, and human activities, such as agriculture, composting, construction, demolition, and other occupations (Gilbert and Duchaine, 2009; Pecoraro et al., 2013; Qi et al., 2020). Understanding the sources and properties of airborne fungi is critical for determining their potential influence on human health and implementing suitable mitigation strategies. Depending on factors including vegetation type, geographic location, and weather conditions, the diversity and concentration of airborne fungi might vary between different places (Awad, 2005). Numerous studies suggest that vegetation constitutes a main source of fungal particles that are released into the surrounding air environments (Awad, 2005; Lymperopoulou et al., 2016; Pecoraro et al., 2012, 2021). It has been shown that various microbes colonize the phylloplane (Mercier and Lindow, 2000), which plays a significant role in the presence of airborne fungi, while high concentrations of fungal spores in the air may be caused by the extensive microbial covering of leaves (Qi et al., 2020). According to a study conducted by Qi et al. (2020), focusing on urban and mountainous regions of Xi’an City, China, the main local source of airborne fungi was the surface of the leaves across all seasons, with a significantly lower contribution from the soil. Humans and animals, under particular pathologic conditions, can also be a source of fungi. For instance, the skin-associated fungal genus Microsporum has been predominantly found in animal and human hair (Qi et al., 2020), having the ability to induce various human adverse health conditions and to increase the chances of developing psoriasis (Machado et al., 2005; Qi et al., 2020). Such fungal species, commonly associated with the human skin, can be disseminated into the air upon skin shedding (Prussin and Marr, 2015; Findley et al., 2013). A number of both organic and inorganic environmental sources, such as dust and water, may also contribute to the presence and abundance of fungi in the air. In a study conducted at five different subway stations in Seoul City, the analyzed 12 stagnant water and five settled dust samples exhibited significantly high fungal concentrations and were considered an important potential source of airborne fungi (Cho et al., 2006). A large body of literature reported that outdoor air can be a source for different indoor airborne fungi (Adams et al., 2013; Barberán et al., 2015a). A study conducted in one of the Singapore library buildings revealed that the concentrations of indoor fungi were roughly 50 times lower than those found in outdoor air (Goh et al., 2000). However, airborne fungi can also be generated from indoor sources such as sinks and shower faucets (Prussin and Marr, 2015), which have been reported to aerosolize Aspergillus spp. and Fusarium spp. in hospital settings (Anaissie et al., 2002). Residential showers have also been found to produce bioaerosols containing Alternaria alternata, Penicillium spp., Cladosporium spp., Acremonium spp., and Paecilomyces variotii (Prussin and Marr, 2015).
3 Health implications of exposure to airborne fungi
Airborne fungi pose significant health concerns for humans worldwide (Wu et al., 2000; Atya et al., 2019; Tiew et al., 2020; Fisher et al., 2022; Nageen et al., 2023; Kasprzyk et al., 2021). A number of airborne fungal species cause various health problems, including allergic reactions, infectious diseases, toxicosis reactions, respiratory ailments and pathologic conditions like aspergillosis, asthma, hypersensitivity, and pneumonitis (Wu et al., 2000; Górny et al., 2002; Patel et al., 2018; Odebode et al., 2020; Sio et al., 2021; Pashley and Wardlaw, 2021; Nageen et al., 2023). The number of people, particularly children, affected by fungal-related disorders is on the rise (Makri and Stilianakis, 2008). As airborne spores of diverse fungal species disperse in the atmosphere, they contribute to air pollution, which can have potential implications for human health (Shelton et al., 2002; Nageen et al., 2021). In fact, humans are exposed to a substantial number of fungal spores on a daily basis, inhaling between 1,000 and 10 billion spores per day (Gao et al., 2022). This continuous and significant exposure to fungal bioaerosol emphasizes the necessity of understanding the link between airborne fungi and human health, particularly as far as respiratory problems, such as asthma, are concerned. Numerous studies have consistently revealed a strong association between exposure to airborne fungi, asthma and sensitization to fungal allergens. For instance, in a study conducted in Tucson, Arizona, a significant correlation between severity of asthma and positive skin tests for Alternaria mold was observed in a group of individuals (Martinez et al., 1997). In Sweden and Switzerland, 3–4% of asthma patients showed positive reactivity to fungal allergens, whereas in the United States, the proportion rose significantly to 80% (Kasprzyk, 2008; D'amato and Spieksma, 1995). In another study, a positive skin test for at least one of the fungal species (Alternaria tenuis, Epicoccum nigrum, Cladosporium cladosporioides, and Helminthosporium maydis) was found in 54% of patients admitted to the intensive care unit for asthma (Black et al., 2000). Sensitization to Alternaria alternata or Cladosporium herbarum was linked to severe asthma in a number of European nations, as well as in New Zealand, Australia, and United States, according to a study involving 1,132 patients (Zureik et al., 2002). In England, UK, adult patients with severe asthma showed a higher prevalence of positive skin tests for different molds, including A. fumigatus, C. herbarum, A. alternata, Penicillium notatum, and the yeast Candida albicans, compare to individuals with moderate or mild asthma (O'Driscoll et al., 2005).
4 Common pathogenic airborne fungi
4.1 Alternaria
Alternaria, one of the most common fungi in the atmosphere, holds particular importance in the field of aerobiology due to its association with various human health conditions. Among the numerous Alternaria species present in the air, A. alternata was described as one of the most abundant fungi in indoor environments in the United States (Woudenberg et al., 2015; Nascimento et al., 2019). Alongside Aspergillus and Cladosporium, Alternaria has garnered attention as a dominant fungal genus in both indoor and outdoor environments of various countries (Sharma et al., 2011; Fang et al., 2013; Nascimento et al., 2019). Alternaria fungi are closely related to the development of immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated respiratory diseases (Khosravi et al., 2009; Fuiano et al., 2012). Downs et al. (2001) observed a significant correlation between the concentration of Alternaria airborne fungi and the increase in airway responsiveness and respiratory symptoms. The literature consistently supports the association of Alternaria species with various health issues, including asthma, allergic rhinosinusitis, oculomycosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis, and skin infections (Pulimood et al., 2007; Pastor and Guarro, 2008; Nascimento et al., 2019; Mohammad and Khalil, 2022). Pulimood et al. (2007) notably observed that individuals sensitive to Alternaria allergens have exacerbated asthma symptoms after exposure to this group of fungi. The presence of Alternaria spores in the air has been linked to an increase in hospitalization rates among children and adolescents with asthma, emphasizing the potential impact of this fungal genus on public health (Tham et al., 2017; Nascimento et al., 2019).
4.2 Cladosporium
Cladosporium fungi have been linked to a variety of health problems, including pulmonary diseases, cutaneous infections, and phaeohyphomycosis (Castro et al., 2013; Nascimento et al., 2019). In particular, the genus Cladosporium has been recognized as a main air contaminant in hospital settings (Maldonado-Vega et al., 2014; Chaivisit et al., 2018; Nascimento et al., 2019). In a study conducted in Barcelona, Spain, Cladosporium was the prevalent fungal genus in nasal microbiota samples from both allergic and healthy individuals, with C. herbarum and C. cladosporioides being the dominant species. In the latter study, antigen-specific IgE and histamine release tests on patients with bronchial asthma and/or rhinosinusitis revealed that 26% of the tested individuals were sensitized to Cladosporium (Sellart-Altisent et al., 2007). The link between human health problems and Cladosporium fungi, including the development of allergies and asthma, has been largely documented. A study conducted in Poland reported on peaks of intensity for Cladosporium-related allergic symptoms occurring in summer and autumn (Bednarz et al., 2016). Cladosporium cladosporioides is known to cause subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (Gugnani et al., 2006; Sang et al., 2012). Castro et al. (2013) reported on a notable case of a 27-year-old female immunocompetent chemical engineer employed at a cork company in Portugal who suffered from a pulmonary infection caused by C. cladosporioides.
4.3 Penicillium
Penicillium fungi are mainly pathogenic to individuals with immunocompromised systems, resulting from an initial HIV infection or various medical treatments (Barcus et al., 2005; Nascimento et al., 2019). The first human infection caused by this fungal genus was recorded in 1973, when Penicillium marneffei was isolated from the spleen of a patient with Hodgkin’s disease (Nascimento et al., 2019), which highlighted the potential risk of exposure to this pathogenic fungus, particularly for persons with health problems. In addition to its pathogenic properties as agent of respiratory infections, wheezing, and allergic reactions, such as allergic alveolitis and allergic asthma, Penicillium has garnered considerable scientific attention due to its classification as one of the most common allergenic fungal taxa in indoor and outdoor environments (Goodman et al., 2011; Abdel Hameed et al., 2009; Pashley and Wardlaw, 2021; Hughes et al., 2022). Multiple studies have demonstrated that Penicillium fungi cause allergic reactions, particularly asthma (Bundy et al., 2009; Knutsen et al., 2012). Penicillium has been explicitly linked to an increase in peak expiratory flow variability among young asthmatic patients (Bundy et al., 2009). Exposure to a significant amount of Penicillium spores was found to lead to the development of both immediate and delayed asthma symptoms in sensitive people (Knutsen et al., 2012; Al-Shaarani et al., 2023). This implies that exposure to Penicillium can cause respiratory symptoms and exacerbations, which may have an effect on the exposed individuals’ lung function and general respiratory health (Gent et al., 2012; Baxi et al., 2016). It also emphasizes the need for efficient ways to reduce indoor exposure to Penicillium, especially in environments where people with respiratory disorders spend a lot of time. Therefore, the presence and abundance of Penicillium in indoor and outdoor air environments have received substantial interest from researchers. For instance, an investigation conducted in urban outdoor environments in Tianjin, China, revealed that Penicillium was the third most abundant fungal genus recorded (Nageen et al., 2023), while a study conducted in a research and teaching building of Tianjin University (Tianjin, China) reported that Penicillium was the fourth most diverse fungal genus in the various analyzed indoor and outdoor building environments. The latter findings underscored the extensive distribution of Penicillium in the studied environments, and the potential risk of exposure for people to this pathogenic fungal genus.
4.4 Fusarium
Fusarium species commonly thrive and grow in agricultural settings and have the ability to produce toxic secondary metabolites called mycotoxins that contaminate crops (e.g., barley, rice, and corn) during growth, harvesting, transportation and storage stages (Goswami and Kistler, 2004; Antonissen et al., 2014; Shams-Ghahfarokhi et al., 2014). Exposure to these mycotoxins can have negative effects on human health, including the potential disruption of the immune system and the damage of the intestinal epithelium (Maresca, 2013; Liew and Mohd-Redzwan, 2018; Nafis et al., 2024). Notably, Fusarium has been implicated in a wide array of infections, particularly among immunocompromised individuals (Nascimento et al., 2019). The available literature indicates that exposure to this fungal genus has the potential to induce allergies that may contribute to the development of asthma in susceptible individuals (Khosravi et al., 2012). Hoff et al. (2003) effectively isolated and described an allergen produced by Fusarium culmorum, which was reactive in 44% of sera from people who were at risk for allergies (Hoff et al., 2003). Furthermore, species of Fusarium are increasingly recognized as novel human pathogens, commonly isolated from ocular tissues and less frequently from skin blood and nails, with a higher incidence seen in immunocompromised hematological patients (Tupaki-Sreepurna and Kindo, 2018).
4.5 Aspergillus
Aspergillus fungi, commonly found in various environments, include approximately 20 distinct species capable of inducing diseases in human hosts (Dagenais and Keller, 2009; Nageen et al., 2023). The spores of this fungal species have been found to predominate in the air during the fall and winter seasons in the United Kingdom, raising concerns on the possibility of human exposure (Millington and Corden, 2005). Among Aspergillus species, A. fumigatus is one of the most common human pathogenic fungi, responsible for over 90% of all cases of invasive aspergillosis (IA), as well as for life-threatening lung infections and allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (Dagenais and Keller, 2009; Nafis et al., 2023). IA have a death rate of 60–90% because of difficulties in diagnosis, lack of effective anti-fungal therapies, and the rise of drug-resistant strains. The severity of these infections largely depends on the immune system and general health conditions of susceptible individual (Singh and Paterson, 2005; Vödisch et al., 2009). The small size of A. fumigatus conidia allows them to move deep into the respiratory system, colonizing the alveoli as the primary step of systemic Aspergillus infections (McCormick et al., 2010). Besides, A. fumigatus, together with A. flavus and A. niger, have the capacity to infect tissues not only within the respiratory system, but also eyes, skin, central nervous system, and nails (Patterson et al., 2016; Tsai et al., 2019; Lai et al., 2020; Jing et al., 2022). Aspergillus flavus is an opportunistic fungal pathogen that can colonize the respiratory tract and cause invasive aspergillosis, fatal infections, especially in immunocompromised patients (Curbelo et al., 2015; Lu et al., 2022; Nafis et al., 2024). Previous studies have also reported that inhalation or ingestion of A. flavus, known for its production of aflatoxin B, can result in the development of lung cancer in humans (Georggiett et al., 2000; Marchese et al., 2018). Aspergillus niger is recognized as a pathogenic fungus and a potent allergen, associated with lung infections. It can also cause invasive aspergillosis, systemic mycosis, cutaneous infections, allergic bronchopulmonary diseases, and, in some cases, pneumonia (Bulpa et al., 2007; Person et al., 2010; Marr et al., 2002).
5 Sources of airborne bacteria
Airborne bacteria originate from various sources, including dust, soil, plants, water bodies, animals, and humans (Bowers et al., 2011; Fan X. Y. et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2018; Mu et al., 2020). Various studies conducted worldwide have highlighted the importance of soil and leaf surfaces as the main contributors to bacterial presence in the lower atmosphere (Brodie et al., 2007; Bowers et al., 2011; Gao et al., 2017; Ruiz-Gil et al., 2020). For instance, a study conducted in mountainous and urban areas of Xi’an City, China, suggested that the primary sources of airborne bacteria in summer and autumn are soil and leaf surfaces (Mu et al., 2020). Another study indicated that airborne bacterial communities are similar to those found in soil (Brodie et al., 2007), possibly due to the influence of land-use type, as different habitats act as sources of bacteria that can be released into the air, potentially affecting the overall diversity and concentration of airborne microbes (Després et al., 2007; Redford et al., 2010). Deserts and dry areas have been previously reported as major sources of aerosolized bacteria attached to dust particles that are abundantly generated in these environments, forming aerosols capable of traveling long distances with the assistance of wind (Maki et al., 2008). Marine environments also contribute to aerosolizing bacteria through water surface, aided by sea sprays generated by high winds and breaking waves (Graham et al., 2018; Ruiz-Gil et al., 2020). Airborne bacteria can also originate from anthropic activities and human-mediated environments, including wastes from hospitals, houses, and pet feces in urban environments, as well as agricultural practices, livestock farming, and waste treatment, such as wastewater management and composting (Ruiz-Gil et al., 2020) in rural areas. In particular, composting involves thermophilic actinomycetes, which play a fundamental role in the degradation process, but can also trigger allergic responses in humans, including asthma and hypersensitivity pneumonitis (Sharma et al., 2014). Dog feces, especially in urban environments, can represent an unexpected important source of bacteria in the atmosphere, especially during the winter season, according to a study conducted in the Midwestern United States (Bowers et al., 2011). Plants and animals (e.g., dogs and cats) have also been observed to release microorganisms into the air, making a notable contribution to the indoor bacterial flora (Barberán et al., 2015b; Xie et al., 2021). Wastewater treatment plants are another important source of bacterial bioaerosols. Many studies consistently demonstrated that the microorganisms present in these wastewater facilities contribute notably to the overall composition of airborne bacterial communities in surrounding areas (Degois et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2021). Metalworking fluids used in engineering environments may show the presence of Gram-negative bacteria. These bacteria produce endotoxins, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) molecules located in the outer envelope of the bacterial cell walls, also known as pyrogens due to their ability to induce fever. Exposure to endotoxins can lead to flu-like symptoms, including inhalation fever, thus making it essential to address the impact of such molecules on human health, particularly in occupational settings where metalworking fluids are prevalent (Passman and Küenzi, 2020). Human bodies and daily activities may contribute to the release of substantial amounts of bacterial aerosols, which can result in potential health risks and contribute to outdoor and indoor air pollution (Xie et al., 2021). Specifically, different types of bacteria inhabit various internal and external parts of the human body, such as skin and digestive tract, which harbor approximately 1012–1014 microbial species (Costello et al., 2009; Xie et al., 2021). Consequently, humans have become the most dominant source of bacterial bioaerosols, particularly in indoor environments, directly influencing the composition and structure of airborne microbial flora (Hospodsky et al., 2015). Legionella pneumophila is commonly present in aquatic environments, including both natural reservoirs, such as rivers and lakes, as well as human-made settings, like air-conditioning systems, cooling towers, humidifiers, and public showers (Graells et al., 2018; Sánchez-Parra et al., 2019). This highly adaptable bacterium, which exhibits resilience across a wide range of temperatures, is known to cause Legionnaires’ disease, a severe form of pneumonia, and Pontiac fever, a type of legionellosis that does not involve pneumonia but has been linked to many cases of Legionnaires’ disease in the US and Europe (Blatny et al., 2011; Van Heijnsbergen et al., 2015). Legionella bacteria are primarily transmitted through the inhalation of aerosols containing the microbes, which leads to the development of severe respiratory infections, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems (Allegra et al., 2016).
6 Health implications of exposure to airborne bacteria
As the prevalent microorganisms in the atmosphere, bacteria play an important role in shaping ecological balance and affecting human health (Hu et a., 2020). Airborne bacteria pose health risks to both residents and workers in different environments, potentially causing allergies, respiratory infections, and other systemic diseases (Yang et al., 2019; Passi et al., 2021). Inhaling pathogenic airborne bacteria can lead to various diseases and allergic reactions, such as pneumonia, asthma, rhinitis, and pharyngitis, especially in children and elder individuals (Passi et al., 2021). Different bacterial species have the ability to target specific organs within the human body, inducing various infections (Doron and Gorbach, 2008). For instance, Staphylococcus aureus, which is commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes, can trigger soft tissue and skin infections (Dayan et al., 2016). Besides, this bacterial species has the potential to disseminate throughout the bloodstream, causing infections in different body sites including lungs, heart valves, and abdomen (Doron and Gorbach, 2008; Dayan et al., 2016). Neisseria meningitidis primarily targets lungs and meninges, causing pneumonia and meningitis, respectively (Doron and Gorbach, 2008). Bacterial presence in the air is influenced by the ability of these microorganisms to colonize and grow in various liquids and surfaces (Gonzalez-Martin, 2019). Under suitable nutritional and physical conditions, bacteria can be released into the air, which enables them to be aerosolized and easily inhaled by the exposed individuals (Gonzalez-Martin, 2019). Acinetobacter species play a crucial role as causative agents of nosocomial infections in healthcare settings (Hwang and Park, 2014). For instance, A. lwoffii is a common Gram-negative bacterium capable of causing bacteremia, particularly in immunocompromised patients (Guo et al., 2021). Bacteroides fragilis is an opportunistic human pathogen that can cause intra-abdominal, skin, soft tissue, and postoperative wound infections (Guo et al., 2021). Streptococcus pneumoniae is a common pathogenic agent that can induce pneumonia and meningitis, particularly in children (Mehr and Wood, 2012). Different species of Streptococcus have been known to induce various infections and pathological conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, bacteremia, shock, neonatal sepsis, and meningitis (Mehr and Wood, 2012; Guo et al., 2021). Prevotella, a common Gram-negative bacterial genus found in the human oral cavity, can lead to some periodontal diseases (Ibrahim et al., 2017; Du et al., 2018). Erysipelothrix is a group of Gram-positive bacteria that has been reported as a cause of erysipelas in humans and swine (Du et al., 2018). Enterobacter is a pathogenic Gram-negative bacterial taxon that is predominantly isolated from patients in intensive treatment units and has the ability to cause bacteremia and other infections (Okatani et al., 2000; Du et al., 2018). Rickettsia species have been reported as causative agents of different human diseases, including Brill-Zinsser disease, spotted fever, and epidemic typhus (Du et al., 2018).
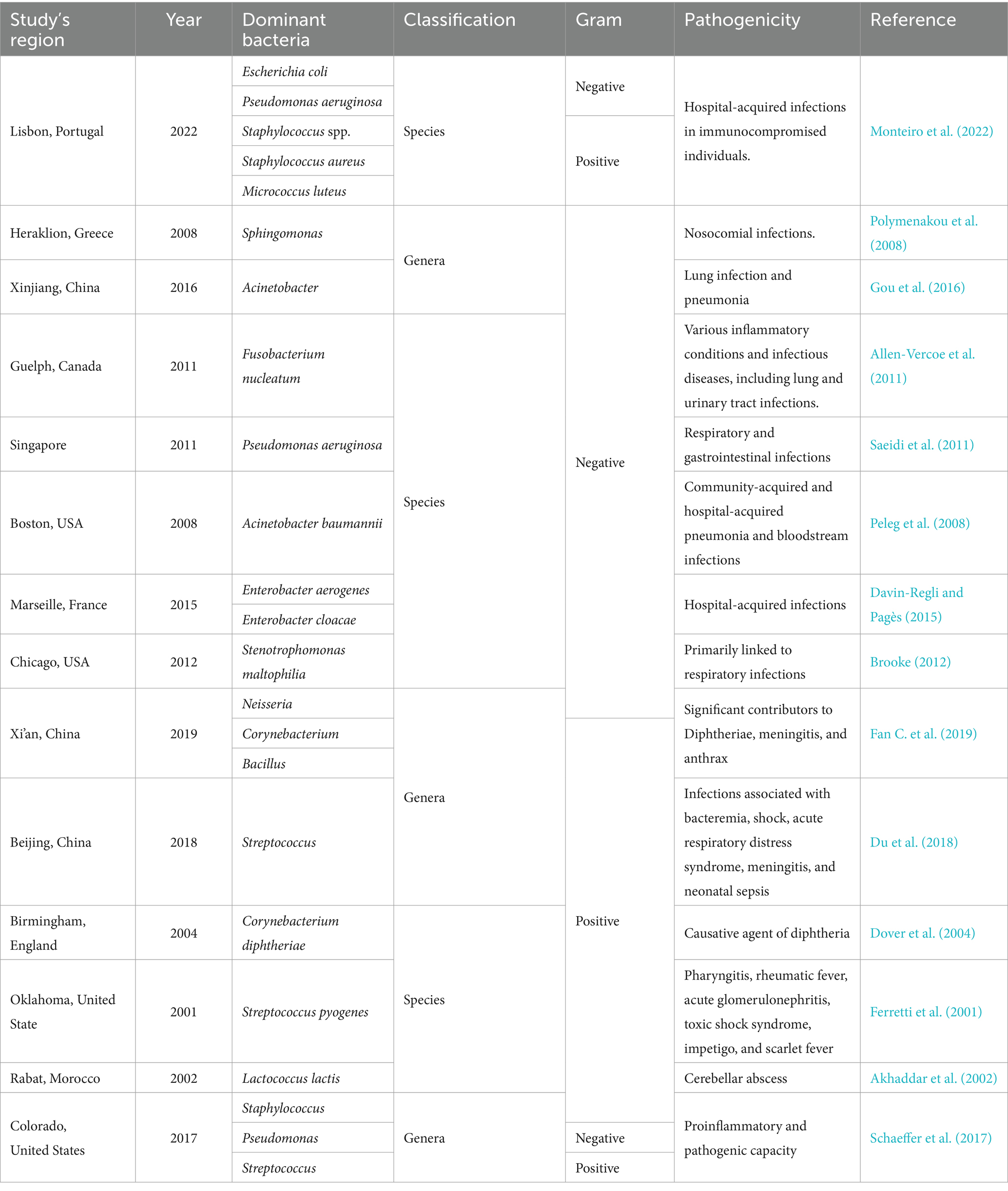
7 Common pathogenic airborne bacteria
Bacterial communities exhibit spatial and temporal variations depending on many factors such as seasonal changes, weather and environmental conditions, and human activities, which contribute to regional disparities (Bertolini et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2022). These variations may result in different diseases caused by the varying microbes in different regions and periods of the year (Table 1). A comparison of bacterial community structures at phylum and genus levels across different regions revealed distinct variations (Zhang et al., 2022). At phylum level, Proteobacteria emerged as the predominant group in studies conducted in Toyama, Japan (Tanaka et al., 2019), while Actinobacteria and Firmicutes were found to be the dominant groups in Beijing and Jinan, respectively (Wang et al., 2015; Xu et al., 2017). At genus level, in different studies conducted in China, it was reported that Sphingomonas was the most abundant genus in Urumqi city (Gou et al., 2016), while in Qingdao, Jinan, and Xi’an the most dominant genera were Acinetobacter, Lactococcus, and Pseudomonas, respectively (Wang et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2017). In Hong Kong, a variety of human pathogenic bacterial genera were detected in the air, including Legionella, Shigella, Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Salmonella (Woo et al., 2013). Sphingomonas was the dominant airborne bacterial genus in a study conducted in Heraklion, Greece (Polymenakou et al., 2008). A research carried out in Po Valley (Italy), one of the most urbanized and polluted regions in Europe, showed that Staphylococcus and Sphingomonas were the dominant airborne pathogenic bacteria (Innocente et al., 2017). In a study conducted in Beijing, the bacterial composition of PM2.5, analyzed at different seasons and air pollution levels, revealed the presence of five pathogenic taxa including Streptococcus, Prevotella, Rickettsia, Enterobacteria, and Erysipelothrix (Du et al., 2018). Various studies carried out in Europe have consistently indicated that Gram-positive cocci bacteria, particularly species of Staphylococcus and Micrococcus, are commonly found in indoor air environments, whereas some Gram-negative bacteria, including the Pseudomonadaceae family and Aeromonas species, are often present but in lower abundance. Similarly, in a study conducted in the United States, Gram-positive cocci bacteria were also reported as prevalent in the indoor and outdoor environments analyzed in a large building consisting of 100 offices (Tsai and Macher, 2005).
8 Variation in susceptibility to airborne microbes
Susceptibility to airborne microbes, including fungi and bacteria, shows a significant variation among different human groups and populations. This susceptibility is affected by different factors, including occupational hazards, environmental conditions, and individual health status (Makri and Stilianakis, 2008). In general, infants, elderly, and immunocompromised patients, as well as individuals engaged in particular occupations (e.g., agriculture, healthcare, and construction) are at higher health risk by exposure to airborne microbes than other people (Madhwal et al., 2020). A study conducted in Hanoi, Vietnam, revealed that infants and young children were at a higher risk of developing respiratory disorders attributed to the high concentrations of airborne microbial particles in the city’s air (Luong et al., 2017). Elderly individuals could also be particularly susceptible to air pollutants exposure, primarily due to their compromised immune systems and the prevalence of underlying chronic diseases (Madureira et al., 2015). Farmers represent a category of workers highly susceptible to airborne microbes originating from dust, soil, and/or leaf surfaces, and commonly suffer from various health problems, notably allergic skin diseases, as a result of direct contact with microbes during their farming activities (Kasprzyk, 2008). They may also suffer from some respiratory diseases due to exposure to some pathogenic fungal spores (Kasprzyk, 2008). Similarly, healthcare workers are at significant risk of exposure to airborne microbes due to the nature of their daily work, which puts them in close contact with diverse patients, thus potentially resulting in the transmission of some infectious diseases through air routes (Zemouri et al., 2017; Wilson et al., 2020). Additionally, healthcare workers frequently employ instruments or intervention methods that may generate bio-aerosols, further increasing their exposure to airborne microbial hazards (Zemouri et al., 2017). Other various occupational groups, including transportation employees (e.g., traffic police and subway station workers), roadside workers (municipal and construction workers, etc.), markets and restaurants workers, as well as daily commuters, have been consistently reported in the literature as highly susceptible groups particularly exposed to bioaerosol at different sites (Kim et al., 2011; Madhwal et al., 2020; Al-Shaarani et al., 2023).
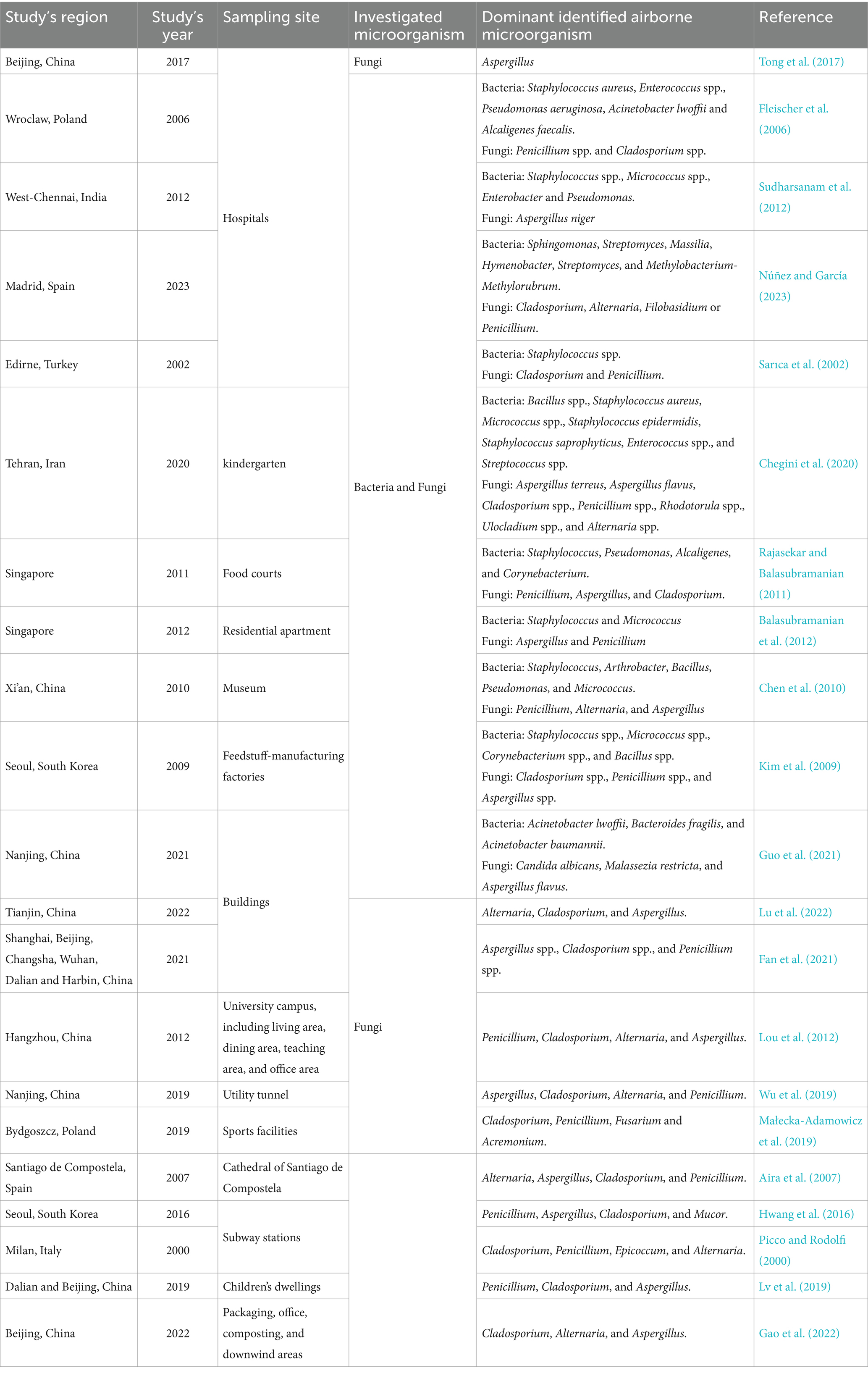
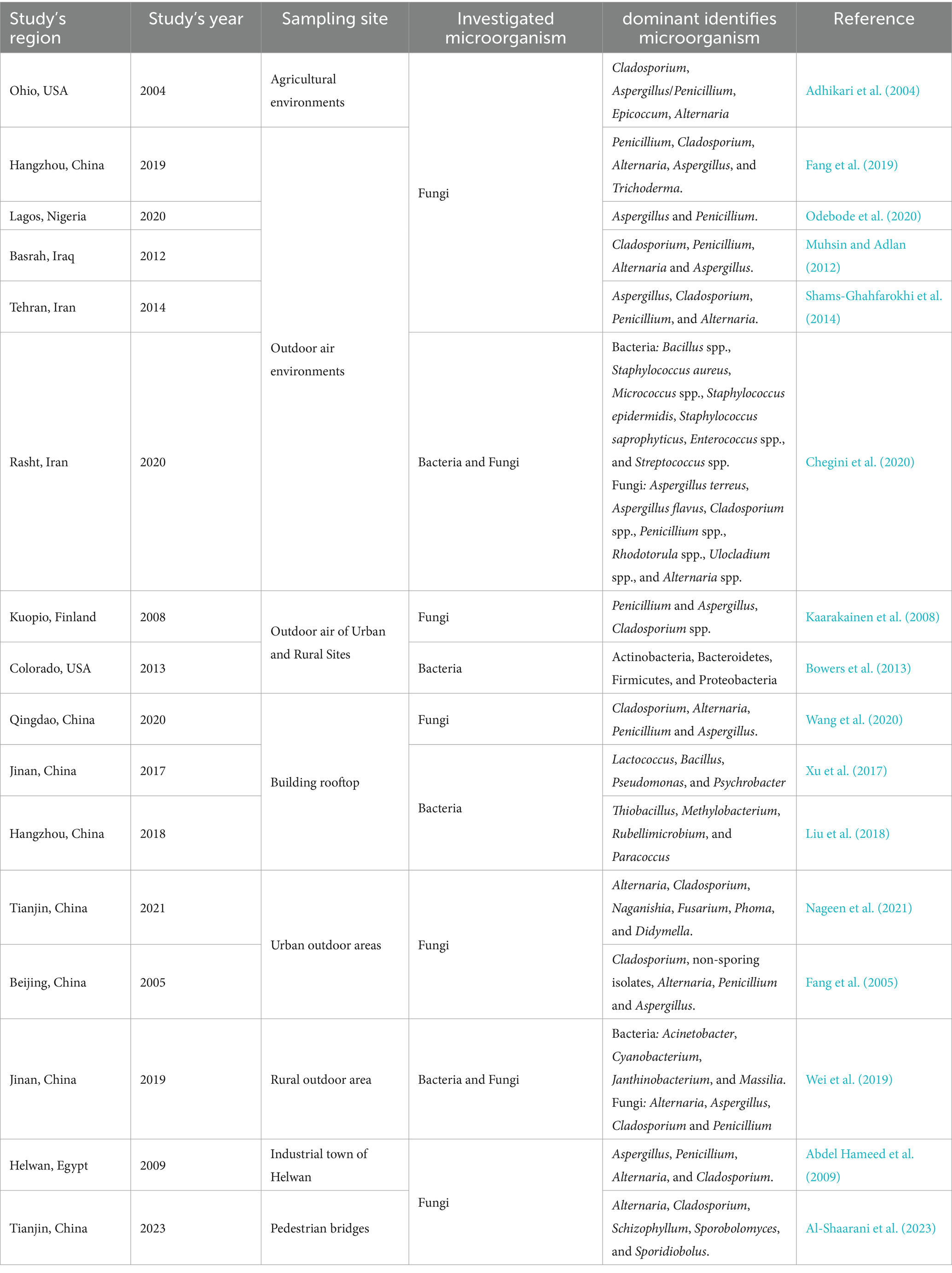
9 Common indoor versus outdoor airborne fungi and bacteria
Both outdoor urban and rural areas and indoor air environments, such as homes, offices, hospitals, schools, subway stations, etc., may represent reservoirs for a wide range of microorganisms, particularly fungi and bacteria (Figure 1; Tables 2, 3). These microbes have the potential to impact the overall ambient air quality and pose significant health hazards to human individuals within the above-mentioned places (Simon-Nobbe et al., 2008; Fernstrom and Goldblatt, 2013; Yuan et al., 2022). Numerous global research efforts have been directed toward investigating airborne microbes in various indoor and outdoor settings. These studies have revealed that the diversity of microbes detected may vary depending on various influencing factors, such as the investigated places or regions, sampling methods, seasonal changes, and specific environmental conditions (Adhikari et al., 2004; Fleischer et al., 2006; Wei et al., 2019; Chegini et al., 2020; Núñez and García, 2023). For instance, in a study conducted at a hospital in Madrid, Spain, it was reported that Sphingomonas, Massilia, Hymenobacter, Streptomyces, and Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum were the prevalent isolated bacterial genera, while in terms of fungi, the dominant genera were Alternaria, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Filobasidium (Núñez and García, 2023). In contrast, at a university hospital in Turkey, the prevalent airborne bacterial species isolated were Staphylococcus spp., while the frequently isolated fungal genera were Cladosporium and Penicillium. However, in general, the literature consistently reports Alternaria, Cladosporium, Penicillium, Aspergillus, and Fusarium as the most common identified fungal genera in the indoor and outdoor air environments (Tables 2, 3). Similarly, Bacillus, Streptococcus, Micrococcus, Enterococcus, and Pseudomonas have been consistently documented as the dominant bacterial genera (Tables 2, 3). For example, studies conducted in various regions, such as Ohio, United States (Adhikari et al., 2004), Hangzhou, China (Fang et al., 2019; Lou et al., 2012), Qingdao, China (Wang et al., 2020), Basrah, Iraq (Muhsin and Adlan, 2012), Helwan, Egypt (Abdel Hameed et al., 2009), Santiago de Compostela, Spain (Aira et al., 2007), and Nanjing, China (Wu et al., 2019), consistently reported Alternaria, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and Aspergillus as the predominant fungal genera in different outdoor and indoor air environments.
10 Conclusion and future directions
This review sheds light on the strong association between airborne fungi and bacteria and their impact on human health. Findings from a large number of studies clearly suggest that exposure to airborne microbes in various outdoor and indoor environments can have harmful effects on the human body, including infections, allergies, and toxic reactions, as well as many respiratory ailments. Therefore, it is important to prioritize heightened attention toward individuals who are exposed to airborne microbes, particularly toward vulnerable members of human populations such as children, elderly, patients with weakened immune systems, and various industry workers, such as those in the healthcare, construction, and agriculture sectors, who have consistently been reported as the most susceptible groups in different studies worldwide. It is also important to address the effect of different factors, such as regional differences, climate change, and other environmental parameters, on airborne microbial spread and growth. These factors could influence the risks associated with microbial presence in the air, emphasizing the need for future directions on air pollution monitoring and prevention. It would be necessary to develop new methods that allow real-time monitoring and easy detection of airborne microorganism outbreaks to facilitate the implementation of effective control measures. Additionally, it is crucial to highlight the need for future research focusing on the development of new technologies and strategies that could help in mitigating microbial hazards. This includes improving ventilation systems, exploring the use of antimicrobial coatings, especially in the healthcare sector, and promoting proper hygiene practices.
Author contributions
AA-S: Writing – original draft. LP: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel Hameed, A. A., Khoder, M. I., Yuosra, S., Osman, A. M., and Ghanem, S. (2009). Diurnal distribution of airborne bacteria and fungi in the atmosphere of Helwan area, Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 407, 6217–6222. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.08.028
Adams, R. I., Miletto, M., Taylor, J. W., and Bruns, T. D. (2013). Dispersal in microbes: fungi in indoor air are dominated by outdoor air and show dispersal limitation at short distances. ISME J. 7, 1262–1273. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2013.28
Adhikari, A., Reponen, T., Lee, S. A., and Grinshpun, S. A. (2004). Assessment of human exposure to airborne fungi in agricultural confinements: personal inhalable sampling versus stationary sampling. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 11, 269–277.
Aira, M. J., Jato, V., Stchigel, A. M., Rodríguez-Rajo, F. J., and Piontelli, E. (2007). Aeromycological study in the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela (Spain). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 60, 231–237. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2007.02.007
Akhaddar, A., El Mostarchid, B., Gazzaz, M., and Boucetta, M. (2002). Cerebellar abscess due to Lactococcus lactis a new pathogen. Acta Neurochir. 144, 305–306. doi: 10.1007/s007010200041
Alananbeh, K. M., Boquellah, N., Kaff, N. A., and Al Ahmadi, M. (2017). Evaluation of aerial microbial pollutants in Al-haram Al-Nabawi during pilgrimage of 2013. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 24, 217–225. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.08.003
Allegra, S., Leclerc, L., Massard, P. A., Girardot, F., Riffard, S., and Pourchez, J. (2016). Characterization of aerosols containing Legionella generated upon nebulization. Sci. Rep. 6:33998. doi: 10.1038/srep33998
Allen-Vercoe, E., Strauss, J., and Chadee, K. (2011). Fusobacterium nucleatum: an emerging gut pathogen? Gut Microbes 2, 294–298. doi: 10.4161/gmic.2.5.18603
Al-Shaarani, A. A. Q. A., Quach, Z. M., Wang, X., Muafa, M. H. M., Nafis, M. M. H., and Pecoraro, L. (2023). Analysis of airborne fungal communities on pedestrian bridges in urban environments. Microorganisms 11:2097. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11082097
Anaissie, E. J., Stratton, S. L., Dignani, M. C., Lee, C. K., Mahfouz, T. H., Rex, J. H., et al. (2002). Cleaning patient shower facilities: a novel approach to reducing patient exposure to aerosolized Aspergillus species and other opportunistic molds. Clin. Infect. Dis. 35, e86–e88. doi: 10.1086/342305
Antonissen, G., Martel, A., Pasmans, F., Ducatelle, R., Verbrugghe, E., Vandenbroucke, V., et al. (2014). The impact of Fusarium mycotoxins on human and animal host susceptibility to infectious diseases. Toxins 6, 430–452. doi: 10.3390/toxins6020430
Araujo, R., and Cabral, J. P. (2010). Fungal air quality in medical protected environments. Air Qual. 357:382. doi: 10.5772/9766
Atya, A. K., Alyasiri, M. H., Altamimy, R., and Ethaib, S. (2019). Assessment of airborne Fungi in indoor environment for biological lab rooms. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 13, 2281–2286. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.13.4.42
Awad, A. H. A. (2005). Vegetation: a source of air fungal bio-contaminant. Aerobiologia 21, 53–61. doi: 10.1007/s10453-004-5878-1
Balasubramanian, R., Nainar, P., and Rajasekar, A. (2012). Airborne bacteria, fungi, and endotoxin levels in residential microenvironments: a case study. Aerobiologia 28, 375–390. doi: 10.1007/s10453-011-9242-y
Barberán, A., Dunn, R. R., Reich, B. J., Pacifici, K., Laber, E. B., Menninger, H. L., et al. (2015a). The ecology of microscopic life in household dust. Proc. Biol. Sci. 282, 212–220. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.1139
Barberán, A., Henley, J., Fierer, N., and Casamayor, E. O. (2014). Structure, inter-annual recurrence, and global-scale connectivity of airborne microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 487, 187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.030
Barberán, A., Ladau, J., Leff, J. W., Pollard, K. S., Menninger, H. L., Dunn, R. R., et al. (2015b). Continental-scale distributions of dust-associated bacteria and fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 5756–5761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420815112
Barcus, A. L., Burdette, S. D., and Herchline, T. E. (2005). Intestinal invasion and disseminated disease associated with Penicillium chrysogenum. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 4:21. doi: 10.1186/1476-0711-4-21
Baxi, S. N., Portnoy, J. M., Larenas-Linnemann, D., and Phipatanakul, W. (2016). Exposure and health effects of Fungi on humans. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 4, 396–404. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.01.008
Bednarz, A., Lipiec, A., Rapiejko, P., Myszkowska, D., Ziemianin, M., Rapiejko, A., et al. (2016). Cladosporium spores in the air of selected polish cities in 2015. Alergoprofil 12, 36–40.
Bertolini, V., Gandolfi, I., Ambrosini, R., Bestetti, G., Innocente, E., Rampazzo, G., et al. (2013). Temporal variability and effect of environmental variables on airborne bacterial communities in an urban area of northern Italy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 6561–6570. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4450-0
Black, P. N., Udy, A. A., and Brodie, S. M. (2000). Sensitivity to fungal allergens is a risk factor for life-threatening asthma. Allergy 55, 501–504. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2000.00293.x
Blatny, J. M., Ho, J., Skogan, G., Fykse, E. M., Aarskaug, T., and Waagen, V. (2011). Airborne Legionella bacteria from pulp waste treatment plant: aerosol particles characterized as aggregates and their potential hazard. Aerobiologia 27, 147–162. doi: 10.1007/s10453-010-9184-9
Bowers, R. M., McLetchie, S., Knight, R., and Fierer, N. (2011). Spatial variability in airborne bacterial communities across land-use types and their relationship to the bacterial communities of potential source environments. ISME J. 5, 601–612. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.167
Bowers, R. M., Clements, N., Emerson, J. B., Wiedinmyer, C., Hannigan, M. P., and Fierer, N. (2013). Seasonal variability in bacterial and fungal diversity of the near-surface atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 12097–12106.
Brodie, E. L., DeSantis, T. Z., Moberg Parker, J. P., Zubietta, I. X., Piceno, Y. M., and Andersen, G. L. (2007). Urban aerosols harbor diverse and dynamic bacterial populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 299–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608255104
Brooke, J. S. (2012). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: an emerging global opportunistic pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 25, 2–41. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00019-11
Bulpa, P., Dive, A., and Sibille, Y. (2007). Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 30, 782–800. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00062206
Bundy, K. W., Gent, J. F., Beckett, W., Bracken, M. B., Belanger, K., Triche, E., et al. (2009). Household airborne Penicillium associated with peak expiratory flow variability in asthmatic children. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 103, 26–30. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60139-1
Burrows, S. M., Elbert, W., Lawrence, M. G., and Pöschl, U. (2009). Bacteria in the global atmosphere–part 1: review and synthesis of literature data for different ecosystems. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 9, 9263–9280. doi: 10.5194/acp-9-9263-2009
Castro, A. S., Oliveira, A., and Lopes, V. (2013). Pulmonary phaeohyphomycosis: a challenge to the clinician. Eur. Respir. Rev. 22, 187–188. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00007512
Chaivisit, P., Fontana, A., Galindo, S., Strub, C., Choosong, T., Kantachote, D., et al. (2018). Airborne Bacteria and Fungi distribution characteristics in natural ventilation system of a University Hospital in Thailand. Environ. Asia 11, 53–66. doi: 10.14456/ea.2018.22
Chakrabarti, H. S., Das, S., and Gupta-Bhattacharya, S. (2012). Outdoor airborne fungal spora load in a suburb of Kolkata, India: its variation, meteorological determinants and health impact. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 22, 37–50. doi: 10.1080/09603123.2011.588323
Chegini, F. M., Baghani, A. N., Hassanvand, M. S., Sorooshian, A., Golbaz, S., Bakhtiari, R., et al. (2020). Indoor and outdoor airborne bacterial and fungal air quality in kindergartens: seasonal distribution, genera, levels, and factors influencing their concentration. Build. Environ. 175:106690. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106690
Chen, Y. P., Cui, Y., and Dong, J. G. (2010). Variation of airborne bacteria and fungi at emperor Qin's Terra-cotta museum, Xi'an, China, during the “Oct. 1” gold week period of 2006. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 17, 478–485.
Cho, J. H., Min, K. H., and Paik, N. W. (2006). Temporal variation of airborne fungi concentrations and related factors in subway stations in Seoul, Korea. Nt. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 209, 249–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2005.10.001
Costello, E. K., Lauber, C. L., Hamady, M., Fierer, N., Gordon, J. I., and Knight, R. (2009). Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 326, 1694–1697. doi: 10.1126/science.1177486
Curbelo, J., Galván, J. M., and Aspa, J. (2015). Updates on Aspergillus, Pneumocystis and other opportunistic pulmonary mycoses. Arch. Bronconeumol. 51, 647–653. doi: 10.1016/j.arbr.2015.09.012
Dagenais, R. T. R., and Keller, N. P. (2009). Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 22, 447–465. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00055-08
D'amato, G., and Spieksma, F. T. M. (1995). Aerobiologic and clinical aspects of mould allergy in Europe. Allergy 50, 870–877. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1995.tb02492.x
Davin-Regli, A., and Pagès, J. M. (2015). Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae; versatile bacterial pathogens confronting antibiotic treatment. Front. Microbiol. 6:392. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00392
Dayan, G. H., Mohamed, N., Scully, I. L., Cooper, D., Begier, E., Eiden, J., et al. (2016). Staphylococcus aureus: the current state of disease, pathophysiology and strategies for prevention. Expert Rev. Vaccines 15, 1373–1392. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2016.1179583
Degois, J., Clerc, F., Simon, X., Bontemps, C., Leblond, P., and Duquenne, P. (2017). First metagenomic survey of the microbial diversity in bioaerosols emitted in waste sorting plants. Ann. Work Expo. Health 61, 1076–1086. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxx075
Després, V. R., Nowoisky, J. F., Klose, M., Conrad, R., Andreae, M. O., and Pöschl, U. (2007). Characterization of primary biogenic aerosol particles in urban, rural, and high-alpine air by DNA sequence and restriction fragment analysis of ribosomal RNA genes. Biogeosciences 4, 1127–1141. doi: 10.5194/bg-4-1127-2007
Dong, S., and Yao, M. (2010). Exposure assessment in Beijing, China: biological agents, ultrafine particles, and lead. Environ. Monit. Assess. 170, 331–343. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-1236-7
Doron, S., and Gorbach, S. L. (2008). Bacterial infections: overview. Int. Encycl. Public Health, 273–282. doi: 10.1016/B978-012373960-5.00596-7
Dover, L. G., Cerdeño-Tárraga, A. M., Pallen, M. J., Parkhill, J., and Besra, G. S. (2004). Comparative cell wall core biosynthesis in the mycolated pathogens, mycobacterium tuberculosis and Corynebacterium diphtheriae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 28, 225–250. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2003.10.001
Downs, S. H., Mitakakis, T. Z., Marks, G. B., Car, N. G., Belousova, E. G., Leüppi, J. D., et al. (2001). Clinical importance of Alternaria exposure in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 164, 455–459. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.3.2008042
Du, P., Du, R., Ren, W., Lu, Z., and Fu, P. (2018). Seasonal variation characteristic of inhalable microbial communities in PM2. 5 in Beijing city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 610, 308–315. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.097
Fan, X. Y., Gao, J. F., Pan, K. L., Li, D. C., Dai, H. H., and Li, X. (2019). More obvious air pollution impacts on variations in bacteria than fungi and their co-occurrences with ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in PM2. 5. Environ. Pollut. 251, 668–680. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.004
Fan, C., Li, Y., Liu, P., Mu, F., Xie, Z., Lu, R., et al. (2019). Characteristics of airborne opportunistic pathogenic bacteria during autumn and winter in Xi'an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 672, 834–845. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.412
Fan, G., Xie, J., Yoshino, H., Yanagi, U., Zhang, H., Li, Z., et al. (2021). Investigation of fungal contamination in urban houses with children in six major Chinese cities: genus and concentration characteristics. Build. Environ. 205:108229. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108229
Fang, Z., Ouyang, Z., Hu, L., Wang, X., Zheng, H., and Lin, X. (2005). Culturable airborne fungi in outdoor environments in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 350, 47–58. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.032
Fang, Z. G., Ouyang, Z. Y., Liu, P., Sun, L., and Wang, X. Y. (2013). Airborne fungal community composition in indoor environments in Beijing. Huanjing Kexue 34, 2031–2037.
Fang, Z., Zhang, J., Guo, W., and Lou, X. (2019). Assemblages of culturable airborne fungi in a typical urban, tourism-driven center of Southeast China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 19, 820–831. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2018.02.0042
Fernstrom, A., and Goldblatt, M. (2013). Aerobiology and its role in the transmission of infectious diseases. J. Pathog. 2013:493960. doi: 10.1155/2013/493960
Ferretti, J. J., McShan, W. M., Ajdic, D., Savic, D. J., Savic, G., Lyon, K., et al. (2001). Complete genome sequence of an M1 strain of Streptococcus pyogenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4658–4663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.071559398
Findley, K., Oh, J., Yang, J., Conlan, S., Deming, C., Meyer, J. A., et al. (2013). Topographic diversity of fungal and bacterial communities in human skin. Nature 498, 367–370. doi: 10.1038/nature12171
Fischer, G., and Dott, W. (2003). Relevance of airborne fungi and their secondary metabolites for environmental, occupational and indoor hygiene. Arch. Microbiol. 179, 75–82. doi: 10.1007/s00203-002-0495-2
Fisher, M. C., Alastruey-Izquierdo, A., Berman, J., Bicanic, T., Bignell, E. M., Bowyer, P., et al. (2022). Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 557–571. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00720-1
Fleischer, M., Bober-Gheek, B., Bortkiewicz, O., and Rusiecka-Ziólkowskaa, J. (2006). Microbiological control of airborne contamination in hospitals. Indoor Built Environ. 15, 53–56. doi: 10.1177/1420326X06062230
Fuiano, N., Fusilli, S., and Incorvaia, C. (2012). A role for measurement of nasal IgE antibodies in diagnosis of Alternaria-induced rhinitis in children. Allergol. Immunopathol. 40, 71–74. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2011.03.010
Gao, J. F., Fan, X. Y., Li, H. Y., and Pan, K. L. (2017). Airborne bacterial communities of PM2. 5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei megalopolis, China as revealed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: a case study. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 17, 788–798. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2016.02.0087
Gao, M., Yu, A., Chen, M., Qiu, T., Guo, Y., Sun, X., et al. (2022). Airborne fungi and human exposure in different areas of composting facilities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 243:113991. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113991
Gent, J. F., Kezik, J. M., Hill, M. E., Tsai, E., Li, D. W., and Leaderer, B. P. (2012). Household mold and dust allergens: exposure, sensitization and childhood asthma morbidity. Environ. Res. 118, 86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2012.07.005
Georggiett, O. C., Muino, J. C., Montrull, H., Brizuela, N., Avalos, S., and Gomez, R. M. (2000). Relationship between lung cancer and aflatoxin B1. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Med. 57, 95–107.
Gilbert, Y., and Duchaine, C. (2009). Bioaerosols in industrial environments: a review. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 36, 1873–1886. doi: 10.1139/L09-117
Goh, I., Obbard, J. P., Viswanathan, S., and Huang, Y. (2000). Airborne bacteria and fungal spores in the indoor environment. A case study in Singapore. Acta Biotechnol. 20, 67–73. doi: 10.1002/abio.370200111
Gonzalez-Martin, C. (2019). Airborne infectious microorganisms. Encycl. Microbiol., 52–60. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-809633-8.13002-X
Goodman, V., Müller, A., Gröger-Arndt, H., Schlosser, D., Jehmlich, N., Treudler, R., et al. (2011). Identification of spore specific allergens from Penicillium chrysogenum. J. Integr. Omics 1, 272–279. doi: 10.5584/jiomics.v1i2.75
Górny, R. L., Reponen, T., Willeke, K., Schmechel, D., Robine, E., Boissier, M., et al. (2002). Fungal fragments as indoor air biocontaminants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 3522–3531. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.7.3522-3531.2002
Goswami, R. S., and Kistler, H. C. (2004). Heading for disaster: Fusarium graminearum on cereal crops. Mol. Plant Pathol. 5, 515–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2004.00252.x
Gou, H., Lu, J., Li, S., Tong, Y., Xie, C., and Zheng, X. (2016). Assessment of microbial communities in PM1 and PM10 of Urumqi during winter. Environ. Pollut. 214, 202–210. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.073
Graells, T., Hernández-García, M., Pérez-Jové, J., Guy, L., and Padilla, E. (2018). Legionella pneumophila recurrently isolated in a Spanish hospital: two years of antimicrobial resistance surveillance. Environ. Res. 166, 638–646. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.045
Graham, K. E., Prussin, A. J., Marr, L. C., Sassoubre, L. M., and Boehm, A. B. (2018). Microbial community structure of sea spray aerosols at three California beaches. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 94:fiy005. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy005
Gugnani, H. C., Ramesh, V., Sood, N., Guarro, J., Moin-Ul-Haq,, Paliwal-Joshi, A., et al. (2006). Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium oxysporum and its treatment with potassium iodide. Med. Mycol. 44, 285–288. doi: 10.1080/13693780500294824
Guo, K., Qian, H., Ye, J., Sun, F., Zhuge, Y., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Assessment of airborne bacteria and fungi in different-type buildings in Nanjing, a hot summer and cold winter moist Chinese city. Build. Environ. 205:108258. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.108258
Han, Z. Y., Weng, W. G., and Huang, Q. Y. (2013). Characterizations of particle size distribution of the droplets exhaled by sneeze. J. R. Soc. Interface 10:20130560. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0560
Hara, K., and Zhang, D. (2012). Bacterial abundance and viability in long-range transported dust. Atmos. Environ. 47, 20–25. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.11.050
Hedayati, M. T., Mayahi, S., Aghili, R., and Goharimoghadam, K. (2005). Airborne fungi in indoor and outdoor of asthmatic patients’ home, living in the city of sari. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 4, 189–191.
Hoff, M., Ballmer-Weber, B. K., Niggemann, B., Cistero-Bahima, A., San Miguel-Moncın, M., Conti, A., et al. (2003). Molecular cloning and immunological characterisation of potential allergens from the mould Fusarium culmorum. Mol. Immunol. 39, 965–975. doi: 10.1016/S0161-5890(03)00026-9
Horner, W. E., Worthan, A. G., and Morey, P. R. (2004). Air-and dustborne mycoflora in houses free of water damage and fungal growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 6394–6400. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6394-6400.2004
Hospodsky, D., Yamamoto, N., Nazaroff, W. W., Miller, D., Gorthala, S., and Peccia, J. (2015). Characterizing airborne fungal and bacterial concentrations and emission rates in six occupied children's classrooms. Indoor Air 25, 641–652. doi: 10.1111/ina.12172
Hu, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., Zhou, M., Lou, L., et al. (2020). Temporal discrepancy of airborne total bacteria and pathogenic bacteria between day and night. Environ. Res. 186:109540. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109540
Hughes, K. M., Price, D., Torriero, A. A. J., Symonds, M. R. E., and Suphioglu, C. (2022). Impact of fungal spores on asthma prevalence and hospitalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:4313. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084313
Hwang, S. H., and Park, J. B. (2014). Comparison of culturable airborne bacteria and related environmental factors at underground subway stations between 2006 and 2013. Atmos. Environ. 84, 289–293. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.11.064
Hwang, S. H., Park, W. M., Ahn, J. K., Lee, K. J., Min, K. B., and Park, J. B. (2016). Relationship between culturable airborne bacteria concentrations and ventilation systems in underground subway stations in Seoul, South Korea. Air Quality Atmosphere Health 9, 173–178. doi: 10.1007/s11869-015-0316-9
Ibrahim, M., Subramanian, A., and Anishetty, S. (2017). Comparative pan genome analysis of oral Prevotella species implicated in periodontitis. Funct. Integr. Genomics 17, 513–536. doi: 10.1007/s10142-017-0550-3
Innocente, E., Squizzato, S., Visin, F., Facca, C., Rampazzo, G., Bertolini, V., et al. (2017). Influence of seasonality, air mass origin and particulate matter chemical composition on airborne bacterial community structure in the Po Valley, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 593-594, 677–687. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.199
Jing, R., Yang, W. H., Xiao, M., Li, Y., Zou, G. L., Wang, C. Y., et al. (2022). Species identification and antifungal susceptibility testing of Aspergillus strains isolated from patients with otomycosis in northern China. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 55, 282–290. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.03.011
Kaarakainen, P., Meklin, T., Rintala, H., Hyvärinen, A., Kärkkäinen, P., Vepsäläinen, A., et al. (2008). Seasonal variation in airborne microbial concentrations and diversity at landfill, urban and rural sites. CLEAN Soil Air Water 36, 556–563. doi: 10.1002/clen.200700179
Kalyoncu, F. (2010). Relationship between airborne fungal allergens and meteorological factors in Manisa City, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 165, 553–558. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-0966-x
Kasprzyk, I. (2008). Aeromycology--main research fields of interest during the last 25 years. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 15, 1–7.
Kasprzyk, I., Grinn-Gofroń, A., Ćwik, A., Kluska, K., Cariñanos, P., and Wójcik, T. (2021). Allergenic fungal spores in the air of urban parks. Aerobiologia 37, 39–51. doi: 10.1007/s10453-020-09671-7
Kellogg, C. A., and Griffin, D. W. (2006). Aerobiology and the global transport of desert dust. Trends Ecol. Evol. 21, 638–644. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2006.07.004
Khosravi, A. R., Fatahinia, M., Shokri, H., and Yadegari, M. H. (2012). Allergens from Fusarium solani identified by immunoblotting in asthma patients in Iran. Arh. Hig. Rada Toksikol. 63, 1–6. doi: 10.2478/10004-1254-63-2012-2155
Khosravi, A. R., Saghazadeh, M., and Shokri, H. (2009). Detection of specific anti-Alternaria alternata IgE in asthmatic patients. J. Mycol. Méd. 19, 173–177. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2009.04.003
Kim, K. Y., Kim, Y. S., Kim, D., and Kim, H. T. (2011). Exposure level and distribution characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in Seoul metropolitan subway stations. Ind. Health 49, 242–248. doi: 10.2486/indhealth.MS1199
Kim, K. Y., Kim, H. T., Kim, D., Nakajima, J., and Higuchi, T. (2009). Distribution characteristics of airborne bacteria and fungi in the feedstuff-manufacturing factories. J. Hazard. Mater. 169, 1054–1060. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.04.059
Klee, S. R., Brzuszkiewicz, E. B., Nattermann, H., Brüggemann, H., Dupke, S., Wollherr, A., et al. (2010). The genome of a Bacillus isolate causing anthrax in chimpanzees combines chromosomal properties of B. cereus with B. anthracis virulence plasmids. PLoS One 5:e10986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010986
Knutsen, A. P., Bush, R. K., Demain, J. G., Denning, D. W., Dixit, A., Fairs, A., et al. (2012). Fungi and allergic lower respiratory tract diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 129, 280–291. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.12.970
Lai, C. C., Wang, C. Y., and Hsueh, P. R. (2020). Co-infections among patients with COVID-19: the need for combination therapy with non-anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 53, 505–512. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.013
Lang-Yona, N., Dannemiller, K., Yamamoto, N., Burshtein, N., Peccia, J., Yarden, O., et al. (2012). Annual distribution of allergenic fungal spores in atmospheric particulate matter in the eastern Mediterranean; a comparative study between ergosterol and quantitative PCR analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 12, 2681–2690. doi: 10.5194/acp-12-2681-2012
Lee, K. Y., and Lee, B. J. (2016). Structure, biology, and therapeutic application of toxin–antitoxin systems in pathogenic bacteria. Toxins 8:305. doi: 10.3390/toxins8100305
Liew, W. P. P., and Mohd-Redzwan, S. (2018). Mycotoxin: its impact on gut health and microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 8:60. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00060
Lim, N., Munday, C. I., Allison, G. E., O'Loingsigh, T., De Deckker, P., and Tapper, N. J. (2011). Microbiological and meteorological analysis of two Australian dust storms in April 2009. Sci. Total Environ. 412, 223–231. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.030
Liu, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, H., Yao, X., Zhou, M., Wang, J., et al. (2018). Effect of air pollution on the total bacteria and pathogenic bacteria in different sizes of particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 233, 483–493. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.070
Lou, X., Fang, Z., and Gong, C. (2012). Assessment of culturable airborne fungi in a university campus in Hangzhou, Southeast China. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 6, 1197–1205. doi: 10.5897/AJMR11.1189
Lu, Y., Wang, X., Almeida, L. C. D. S., and Pecoraro, L. (2022). Environmental factors affecting diversity, structure, and temporal variation of airborne fungal communities in a research and teaching building of Tianjin University, China. J. Fungi 8:431. doi: 10.3390/jof8050431
Luong, L. M. T., Phung, D., Sly, P. D., Morawska, L., and Thai, P. K. (2017). The association between particulate air pollution and respiratory admissions among young children in Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 578, 249–255. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.08.012
Lv, Y., Wang, Z., Zhao, T., Fu, B., Chen, B., Xie, J., et al. (2019). Indoor environment in children’s dwellings in Dalian and Beijing, China. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 25, 373–386. doi: 10.1080/23744731.2018.1533337
Lymperopoulou, D. S., Adams, R. I., and Lindow, S. E. (2016). Contribution of vegetation to the microbial composition of nearby outdoor air. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 3822–3833. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00610-16
Machado, A. P., Hirata, S. H., Ogawa, M. M., Tomimori-Yamashita, J., and Fischman, O. (2005). Dermatophytosis on the eyelid caused by Microsporum gypseum. Mycoses 48, 73–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2004.01053.x
Madhwal, S., Prabhu, V., Sundriyal, S., and Shridhar, V. (2020). Ambient bioaerosol distribution and associated health risks at a high traffic density junction at Dehradun city, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 192:196. doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-8158-9
Madureira, J., Paciência, I., Rufo, J. C., Pereira, C., Teixeira, J. P., and de Oliveira Fernandes, E. (2015). Assessment and determinants of airborne bacterial and fungal concentrations in different indoor environments: homes, child day-care centres, primary schools and elderly care centres. Atmos. Environ. 109, 139–146. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.03.026
Maki, T., Susuki, S., Kobayashi, F., Kakikawa, M., Yamada, M., Higashi, T., et al. (2008). Phylogenetic diversity and vertical distribution of a halobacterial community in the atmosphere of an Asian dust (KOSA) source region, Dunhuang City. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 1, 81–89. doi: 10.1007/s11869-008-0016-9
Makri, A., and Stilianakis, N. I. (2008). Vulnerability to air pollution health effects. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 211, 326–336. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2007.06.005
Maldonado-Vega, M., Peña-Cabriales, J. J., De Los Santos Villalobos, S., Castellanos-Arevalo, A. P., Camarena-Pozos, D., Arevalo-Rivas, B., et al. (2014). Bioaerosols and air quality assessment in two hospitals located in Leon, Guanajuato, Mexico. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 30, 351–363.
Małecka-Adamowicz, M., Kubera, Ł., Jankowiak, E., and Dembowska, E. (2019). Microbial diversity of bioaerosol inside sports facilities and antibiotic resistance of isolated Staphylococcus spp. Aerobiologia 35, 731–742. doi: 10.1007/s10453-019-09613-y
Marchese, S., Polo, A., Ariano, A., Velotto, S., Costantini, S., and Severino, L. (2018). Aflatoxin B1 and M1: biological properties and their involvement in cancer development. Toxins 10:214. doi: 10.3390/toxins10060214
Maresca, M. (2013). From the gut to the brain: journey and pathophysiological effects of the food-associated trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. Toxins 5, 784–820. doi: 10.3390/toxins5040784
Maron, P. A., Lejon, D. P. H., Carvalho, E., Bizet, K., Lemanceau, P., Ranjard, L., et al. (2005). Assessing genetic structure and diversity of airborne bacterial communities by DNA fingerprinting and 16S rDNA clone library. Atmos. Environ. 39, 3687–3695. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.002
Marr, K. A., Carter, R. A., Crippa, F., Wald, A., and Corey, L. (2002). Epidemiology and outcome of mould infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34, 909–917. doi: 10.1086/339202
Martinez, F. D., Buist, A., Barnes, P., and Barnes, N. (1997). Progression of asthma from childhood to adolescence. Eur. Respir. Rev. 7, 8–10.
McCormick, A., Loeffler, J., and Ebel, F. (2010). Aspergillus fumigatus: contours of an opportunistic human pathogen. Cell. Microbiol. 12, 1535–1543. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01517.x
Mehr, S., and Wood, N. (2012). Streptococcus pneumoniae–a review of carriage, infection, serotype replacement and vaccination. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 13, 258–264. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2011.12.001
Mercier, J., and Lindow, S. E. (2000). Role of leaf surface sugars in colonization of plants by bacterial epiphytes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 369–374. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.1.369-374.2000
Millington, W. M., and Corden, J. M. (2005). Long term trends in outdoor aspergillus/Penicillium spore concentrations in Derby, UK from 1970 to 2003 and a comparative study in 1994 and 1996 with the indoor air of two local houses. Aerobiologia 21, 105–113. doi: 10.1007/s10453-005-4180-1
Mohammad, A., and Khalil, M. (2022). Molecular identification of some allergenic fungi found in household dust in Mosul city. Revis Bionatura 7, 1–8. doi: 10.21931/RB/2022.07.02.23
Monteiro, A., Cardoso, J., Guerra, N., Ribeiro, E., Viegas, C., Cabo Verde, S., et al. (2022). Exposure and health effects of bacteria in healthcare units: an overview. Appl. Sci. 12:1958. doi: 10.3390/app12041958
Mu, F., Li, Y., Lu, R., Qi, Y., Xie, W., and Bai, W. (2020). Source identification of airborne bacteria in the mountainous area and the urban areas. Atmos. Res. 231:104676. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104676
Muafa, M. H. M., Quach, Z. M., Al-Shaarani, A. A. Q. A., Nafis, M. M. H., and Pecoraro, L. (2024). The influence of car traffic on airborne fungal diversity in Tianjin, China. Mycology 15, 506–520. doi: 10.1080/21501203.2023.2300343
Muhsin, T. M., and Adlan, M. M. (2012). Seasonal distribution pattern of outdoor airborne fungi in Basrah city, southern Iraq. J Basrah Res 38, 90–98.
Nafis, M. M. H., Al-Shaarani, A. A. Q. A., Muafa, M. H. M., Wang, Y. W., Deng, C. Y., Gafforov, Y., et al. (2024). Divergent effects of entomopathogenic fungi and medicinal mushroom species on Drosophila melanogaster lifespan. All Life 17:2356838. doi: 10.1080/26895293.2024.2356838
Nafis, M. M. H., Quach, Z. M., Al-Shaarani, A. A. Q. A., Muafa, M. H. M., and Pecoraro, L. (2023). Pathogenicity of aspergillus airborne fungal species collected from indoor and outdoor public areas in Tianjin, China. Pathogens 12:1154. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091154
Nageen, Y., Asemoloye, M. D., Põlme, S., Wang, X., Xu, S., Ramteke, P. W., et al. (2021). Analysis of culturable airborne fungi in outdoor environments in Tianjin, China. BMC Microbiol. 21:134. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02205-2
Nageen, Y., Wang, X., and Pecoraro, L. (2023). Seasonal variation of airborne fungal diversity and community structure in urban outdoor environments in Tianjin, China. Front. Microbiol. 13:1043224. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1043224
Nascimento, J. P. M., López, A. M. Q., Araújo, M. A., Araujo, L. A., and Silva Filho, E. A. (2019). Airborne fungi in indoor hospital environments. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 8, 2749–2772. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2019.801.291
Núñez, A., and García, A. M. (2023). The aerobiome in a hospital environment: characterization, seasonal tendencies and the effect of window opening ventilation. Build. Environ. 230:110024. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110024
Odebode, A., Adekunle, A., Stajich, J., and Adeonipekun, P. (2020). Airborne fungi spores distribution in various locations in Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 192:87. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-8038-3
O'Driscoll, B. R., Hopkinson, L. C., and Denning, D. W. (2005). Mold sensitization is common amongst patients with severe asthma requiring multiple hospital admissions. BMC Pulm. Med. 5:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2466-5-4
Okatani, A. T., Hayashidani, H., Takahashi, T., Taniguchi, T., Ogawa, M., and Kaneko, K. I. (2000). Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of Erysipelothrix spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38, 4332–4336. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.12.4332-4336.2000
Pashley, C. H., and Wardlaw, A. J. (2021). Allergic fungal airways disease (AFAD): An under-recognised asthma endotype. Mycopathologia 186, 609–622. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00562-0
Passi, A., Nagendra, S. M. S., and Maiya, M. P. (2021). Characteristics of indoor air quality in underground metro stations: a critical review. Build. Environ. 198:107907. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2021.107907
Passman, F. J., and Küenzi, P. (2020). Microbiology in water-miscible metalworking fluids. Tribol. Trans. 63, 1147–1171. doi: 10.1080/10402004.2020.1764684
Pastor, F. J., and Guarro, J. (2008). Alternaria infections: laboratory diagnosis and relevant clinical features. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 14, 734–746. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02024.x
Pastuszka, J. S., Paw, U. K. T., Lis, D. O., Wlazło, A., and Ulfig, K. (2000). Bacterial and fungal aerosol in indoor environment in upper Silesia, Poland. Atmos. Environ. 34, 3833–3842. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00527-0
Patel, T. Y., Buttner, M., Rivas, D., Cross, C., Bazylinski, D. A., and Seggev, J. (2018). Variation in airborne fungal spore concentrations among five monitoring locations in a desert urban environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 190:634. doi: 10.1007/s10661-018-7008-5
Patterson, T. F., Thompson, G. R., Denning, D. W., Fishman, J. A., Hadley, S., Herbrecht, R., et al. (2016). Practice guidelines for the diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 63, e1–e60. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw326
Pecoraro, L., Girlanda, M., Kull, T., Perini, C., and Perotto, S. (2012). Molecular identification of root fungal associates in Orchis pauciflora Tenore. Plant Biosyst. 146, 985–991. doi: 10.1080/11263504.2011.634447
Pecoraro, L., Girlanda, M., Kull, T., Perini, C., and Perotto, S. (2013). Fungi from the roots of the terrestrial photosynthetic orchid Himantoglossum adriaticum. Plant Ecology and Evolution 146, 145–152. doi: 10.5091/plecevo.2013.782
Pecoraro, L., Rasmussen, H. N., Gomes, S. I. F., Wang, X., Merckx, V. S. F. T., Cai, L., et al. (2021). Fungal diversity driven by bark features affects phorophyte preference in epiphytic orchids from southern China. Sci. Rep. 11:11287. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90877-1
Peleg, A. Y., Seifert, H., and Paterson, D. L. (2008). Acinetobacter baumannii: emergence of a successful pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 21, 538–582. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00058-07
Person, A. K., Chudgar, S. M., Norton, B. L., Tong, B. C., and Stout, J. E. (2010). Aspergillus niger: an unusual cause of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 59, 834–838. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.018309-0
Picco, A. M., and Rodolfi, M. (2000). Airborne fungi as biocontaminants at two Milan underground stations. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 45, 43–47. doi: 10.1016/S0964-8305(00)00047-0
Polymenakou, P. N., Mandalakis, M., Stephanou, E. G., and Tselepides, A. (2008). Particle size distribution of airborne microorganisms and pathogens during an intense African dust event in the eastern Mediterranean. Environ. Health Perspect. 116, 292–296. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10684
Prussin, A. J., and Marr, L. C. (2015). Sources of airborne microorganisms in the built environment. Microbiome 3:78. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0144-z
Pulimood, T. B., Corden, J. M., Bryden, C., Sharples, L., and Nasser, S. M. (2007). Epidemic asthma and the role of the fungal mold Alternaria alternata. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 120, 610–617. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.04.045
Qi, Y., Li, Y., Xie, W., Lu, R., Mu, F., Bai, W., et al. (2020). Temporal-spatial variations of fungal composition in PM2. 5 and source tracking of airborne fungi in mountainous and urban regions. Sci. Total Environ. 708:135027. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135027
Rajasekar, A., and Balasubramanian, R. (2011). Assessment of airborne bacteria and fungi in food courts. Build. Environ. 46, 2081–2087. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.04.021
Redford, A. J., Bowers, R. M., Knight, R., Linhart, Y., and Fierer, N. (2010). The ecology of the phyllosphere: geographic and phylogenetic variability in the distribution of bacteria on tree leaves. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 2885–2893. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02258.x
Rolle-Kampczyk, U., Müller, A., Diez, U., Rehwagen, M., Schwenke, A., Metzner, G., et al. (2000). Mycotoxins in house dust—an underestimated problem? Mycotoxin Res. 16, 100–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02942993
Ruiz-Gil, T., Acuña, J. J., Fujiyoshi, S., Tanaka, D., Noda, J., Maruyama, F., et al. (2020). Airborne bacterial communities of outdoor environments and their associated influencing factors. Environ. Int. 145:106156. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106156
Saeidi, N., Wong, C. K., Lo, T. M., Nguyen, H. X., Ling, H., Leong, S. S. J., et al. (2011). Engineering microbes to sense and eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a human pathogen. Mol. Syst. Biol. 7:521. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.55
Sánchez-Parra, B., Núñez, A., and Moreno, D. A. (2019). Preventing legionellosis outbreaks by a quick detection of airborne Legionella pneumophila. Environ. Res. 171, 546–549. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.032
Sang, H., Zheng, X. E., Zhou, W. Q., He, W., Lv, G. X., Shen, Y. N., et al. (2012). A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Cladosporium cladosporioides and its treatment. Mycoses 55, 195–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02057.x
Sarıca, S., Asan, A., Otkun, M. T., and Ture, M. (2002). Monitoring indoor airborne fungi and bacteria in the different areas of Trakya University Hospital, Edirne, Turkey. Indoor Built Environ. 11, 285–292. doi: 10.1177/1420326X0201100505
Schaeffer, J. W., Reynolds, S., Magzamen, S., Van Dyke, A., Gottel, N. R., Gilbert, J. A., et al. (2017). Size, composition, and source profiles of inhalable bioaerosols from Colorado dairies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 6430–6440. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b00882
Sellart-Altisent, M., Torres-Rodríguez, J. M., Gómez de Ana, S., and Alvarado-Ramírez, E. (2007). Nasal fungal microbiota in allergic and healthy subjects. Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 24, 125–130. doi: 10.1016/S1130-1406(07)70027-X
Sen, B., and Asan, A. (2009). Fungal flora in indoor and outdoor air of different residential houses in Tekirdag City (Turkey): seasonal distribution and relationship with climatic factors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 151, 209–219. doi: 10.1007/s10661-008-0262-1
Sepahvand, A., Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M., Allameh, A., and Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. (2013). Diversity and distribution patterns of airborne microfungi in indoor and outdoor hospital environments in Khorramabad, Southwest Iran. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 6, 186–192. doi: 10.5812/jjm.5074
Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M., Aghaei-Gharehbolagh, S., Aslani, N., and Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. (2014). Investigation on distribution of airborne fungi in outdoor environment in Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 12:54. doi: 10.1186/2052-336X-12-54
Sharma, M., Dangi, P., and Choudhary, M. (2014). Actinomycetes: source, identification, and their applications. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 3, 801–832.
Sharma, R., Deval, R., Priyadarshi, V., Gaur, S. N., Singh, V. P., and Singh, A. B. (2011). Indoor fungal concentration in the homes of allergic/asthmatic children in Delhi, India. Allergy Rhinol. 2, 21–32. doi: 10.2500/ar.2011.2.0005
Shelton, B. G., Kirkland, K. H., Flanders, W. D., and Morris, G. K. (2002). Profiles of airborne fungi in buildings and outdoor environments in the United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 1743–1753. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.1743-1753.2002
Simon-Nobbe, B., Denk, U., Pöll, V., Rid, R., and Breitenbach, M. (2008). The spectrum of fungal allergy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 145, 58–86. doi: 10.1159/000107578
Singh, N., and Paterson, D. L. (2005). Aspergillus infections in transplant recipients. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 18, 44–69. doi: 10.1128/CMR.18.1.44-69.2005
Sio, Y. Y., Pang, S. L., Say, Y. H., Teh, K. F., Wong, Y. R., Shah, S. M. R., et al. (2021). Sensitization to airborne fungal allergens associates with asthma and allergic rhinitis presentation and severity in the Singaporean/Malaysian population. Mycopathologia 186, 583–588. doi: 10.1007/s11046-021-00532-6
Smets, W., Moretti, S., Denys, S., and Lebeer, S. (2016). Airborne bacteria in the atmosphere: presence, purpose, and potential. Atmos. Environ. 139, 214–221. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.05.038
Sudharsanam, S., Swaminathan, S., Ramalingam, A., Thangavel, G., Annamalai, R., Steinberg, R., et al. (2012). Characterization of indoor bioaerosols from a hospital ward in a tropical setting. Afr. Health Sci. 12, 217–225. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v12i2.22
Sun, Y., Xu, S., Zheng, D., Li, J., Tian, H., and Wang, Y. (2018). Effects of haze pollution on microbial community changes and correlation with chemical components in atmospheric particulate matter. Sci. Total Environ. 637, 507–516. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.203
Tanaka, D., Sato, K., Goto, M., Fujiyoshi, S., Maruyama, F., Takato, S., et al. (2019). Airborne microbial communities at high-altitude and suburban sites in Toyama, Japan suggest a new perspective for bioprospecting. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 7:12. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00012
Tettelin, H., Saunders, N. J., Heidelberg, J., Jeffries, A. C., Nelson, K. E., Eisen, J. A., et al. (2000). Complete genome sequence of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strain MC58. Science 287, 1809–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5459.1809
Tham, R., Vicendese, D., Dharmage, S. C., Hyndman, R. J., Newbigin, E., Lewis, E., et al. (2017). Associations between outdoor fungal spores and childhood and adolescent asthma hospitalizations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 139, 1140–1147.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.06.046
Tiew, P. Y., Mac Aogain, M., Ali, N. A. B. M., Thng, K. X., Goh, K., Lau, K. J. X., et al. (2020). The Mycobiome in health and disease: emerging concepts, methodologies and challenges. Mycopathologia 185, 207–231. doi: 10.1007/s11046-019-00413-z
Tong, Y., and Lighthart, B. (2000). The annual bacterial particle concentration and size distribution in the ambient atmosphere in a rural area of the Willamette Valley, Oregon. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 32, 393–403. doi: 10.1080/027868200303533
Tong, X., Xu, H., Zou, L., Cai, M., Xu, X., Zhao, Z., et al. (2017). High diversity of airborne fungi in the hospital environment as revealed by meta-sequencing-based microbiome analysis. Sci. Rep. 7:39606. doi: 10.1038/srep39606
Tsai, M. H., Lin, L. C., Hsu, J. F., Lai, M. Y., Huang, H. R., Chiang, M. C., et al. (2019). Rapid identification of invasive fungal species using sensitive universal primers-based PCR and restriction endonuclease digestions coupled with high-resolution melting analysis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 52, 728–735. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2019.06.001
Tsai, F. C., and Macher, J. M. (2005). Concentrations of airborne culturable bacteria in 100 large US office buildings from the BASE study. Indoor Air 15, 71–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0668.2005.00346.x
Tupaki-Sreepurna, A., and Kindo, A. J. (2018). Fusarium: the versatile pathogen. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 36, 8–17. doi: 10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_16_24
Van Heijnsbergen, E., Schalk, J. A. C., Euser, S. M., Brandsema, P. S., Den Boer, J. W., and De Roda Husman, A. M. (2015). Confirmed and potential sources of Legionella reviewed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 4797–4815. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b00142
Vödisch, M., Albrecht, D., Leßing, F., Schmidt, A. D., Winkler, R., Guthke, R., et al. (2009). Two-dimensional proteome reference maps for the human pathogenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Proteomics 9, 1407–1415. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200800394
Wang, W., Fu, H. L., Wang, T. L., Song, Y., Fu, J., Xiang, M. Q., et al. (2016). Characteristics of microbial aerosols on haze days in autumn in Xi’an, China. Acta Sci. Circumst. 36, 279–288. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.09.070
Wang, B. Y., Lang, J. D., Zhang, L. N., Fang, J. H., Cao, C., Hao, J. M., et al. (2015). Characterizing Beijing's airborne bacterial communities in PM2. 5 and PM1 samples during haze pollution episodes using 16S rRNA gene analysis method. Huanjing Kexue 36, 2727–2734.
Wang, Y., Qi, J., Han, C., Zhang, T., and Zhang, D. (2020). Microbial characteristics of culturable fungi and bacteria in aerosol particles of a coastal region. Aerobiologia 36, 507–525. doi: 10.1007/s10453-020-09648-6
Wei, M., Xu, C., Xu, X., Zhu, C., Li, J., and Lv, G. (2019). Characteristics of atmospheric bacterial and fungal communities in PM2. 5 following biomass burning disturbance in a rural area of North China plain. Sci. Total Environ. 651, 2727–2739. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.399
Wilson, N. M., Norton, A., Young, F. P., and Collins, D. W. (2020). Airborne transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 to healthcare workers: a narrative review. Anaesthesia 75, 1086–1095. doi: 10.1111/anae.15093
Woo, A. C., Brar, M. S., Chan, Y., Lau, M. C. Y., Leung, F. C. C., Scott, J. A., et al. (2013). Temporal variation in airborne microbial populations and microbially-derived allergens in a tropical urban landscape. Atmos. Environ. 74, 291–300. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.03.047
Woudenberg, J. H. C., Van Der Merwe, N. A., Jurjević, Ž., Groenewald, J. Z., and Crous, P. W. (2015). Diversity and movement of indoor Alternaria alternata across the mainland USA. Fungal Genet. Biol. 81, 62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2015.05.003
Wu, P. C., Su, H. J., and Lin, C. Y. (2000). Characteristics of indoor and outdoor airborne fungi at suburban and urban homes in two seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 253, 111–118.
Wu, D., Zhang, Y., Li, A., Kong, Q., Li, Y., Geng, S., et al. (2019). Indoor airborne fungal levels in selected comprehensive compartments of the urban utility tunnel in Nanjing, Southeast China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 51:101723. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101723
Xie, W., Li, Y., Bai, W., Hou, J., Ma, T., Zeng, X., et al. (2021). The source and transport of bioaerosols in the air: a review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 15:44. doi: 10.1007/s11783-020-1336-8
Xu, C., Wei, M., Chen, J., Wang, X., Zhu, C., Li, J., et al. (2017). Bacterial characterization in ambient submicron particles during severe haze episodes at Ji’nan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 580, 188–196. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.11.145
Yang, K., Li, L., Wang, Y., Xue, S., Han, Y., and Liu, J. (2019). Airborne bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant: emission characterization, source analysis and health risk assessment. Water Res. 149, 596–606. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.11.027
Yuan, C. N., Wang, X., and Pecoraro, L. (2022). Environmental factors shaping the diversity and spatial-temporal distribution of indoor and outdoor culturable airborne fungal communities in Tianjin University campus, Tianjin, China. Front. Microbiol. 13:928921. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928921
Zemouri, C., de Soet, H., Crielaard, W., and Laheij, A. (2017). A scoping review on bio-aerosols in healthcare and the dental environment. PLoS One 12:e0178007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178007
Zhang, Y., Guo, C., Ma, K., Tang, A., Goulding, K., and Liu, X. (2022). Characteristics of airborne bacterial communities across different PM2. 5 levels in Beijing during winter and spring. Atmos. Res. 273:106179. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106179
Keywords: human health, airborne microbes, respiratory ailments, allergies, risk exposure, environmental sources, indoor and outdoor environments, pathogenic microorganisms
Citation: Al-Shaarani AAQA and Pecoraro L (2024) A review of pathogenic airborne fungi and bacteria: unveiling occurrence, sources, and profound human health implication. Front. Microbiol. 15:1428415. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1428415
Edited by:
Dimitris Mossialos, University of Thessaly, GreeceReviewed by:
Brian Crook, Health and Safety Laboratory (HSL), United KingdomRegina Sharmila Dass, Pondicherry University, India
Copyright © 2024 Al-Shaarani and Pecoraro. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lorenzo Pecoraro, bG9yZW56by5wZWNvcmFyb0BnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Amran A. Q. A. Al-Shaarani
Amran A. Q. A. Al-Shaarani Lorenzo Pecoraro
Lorenzo Pecoraro