- 1Department of Developmental Psychiatry, Institute of Mental Health, Singapore, Singapore
- 2Central Region, Institute of Mental Health, Singapore, Singapore
- 3Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
- 4Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
- 5Research Division, Institute of Mental Health, Singapore, Singapore
Objective: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder. Increasing evidence suggests that it is potentially related to gut microbiota, but no prior bibliometric analysis has been performed to explore the most influential works in the relationships between ASD and gut microbiota. In this study, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the most-cited articles in this field, aiming to provide insights to the existing body of research and guide future directions.
Methods: A search strategy was constructed and conducted in the Web of Science database to identify the 100 most-cited papers in ASD and gut microbiota. The Biblioshiny package in R was used to analyze and visualize the relevant information, including citation counts, country distributions, authors, journals, and thematic analysis. Correlation and comparison analyses were performed using SPSS software.
Results: The top 100 influential manuscripts were published between 2000 and 2021, with a total citation of 40,662. The average number of citations annually increased over the years and was significantly correlated to the year of publication (r = 0.481, p < 0.01, Spearman’s rho test). The United States was involved in the highest number of publications (n = 42). The number of publications in the journal was not significantly related to the journal’s latest impact factor (r = 0.016, p > 0.05, Spearman’s rho test). Co-occurrence network and thematic analysis identified several important areas, such as microbial metabolites of short-chain fatty acids and overlaps with irritable bowel syndrome.
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis provides the key information of the most influential studies in the area of ASD and gut microbiota, and suggests the hot topics and future directions. The findings of this study can serve as a valuable reference for researchers and policymakers, guiding the development and implementation of the scientific research strategies in this area.
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by deficits in social communication and interaction, alongside the manifestation of repetitive and restrictive behavior patterns (APA, 2022). The global prevalence of ASD has been estimated to be around 1%, and the prevalence estimates have increased over time in various countries (Zeidan et al., 2022). Persons with ASD may have emotional and behavioral problems, such as self-harm, aggression, temper tantrums, and property destruction (Jang et al., 2011). They often have other psychiatric conditions, such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis (Dan et al., 2020). The economic costs of ASD are huge, and they include costs for healthcare services, special education, production loss for persons with ASD, lost productivity for caregivers, and respite care (Rogge and Janssen, 2019). In the United States, it has been reported that the average yearly expenditure for emergency room services is $15,929 for ASD, compared to $2,598 for non-ASD; and yearly expenditure for outpatient visits is $4,375 for ASD compared to $824 for non-ASD (Vohra et al., 2017). In the United Kingdom, it has been estimated that adolescents with ASD who need additional special education or residential schooling can cost £10,507 in 6 months (Barrett et al., 2015).
The composition of the gut microbiota has been reported to be associated with ASD. The gut microbiota has a very diverse composition and is composed of bacteria, as well as fungi, viruses and protists (Enaud et al., 2018). It has a bidirectional connection with the central nervous system. Millions of nerve cells in the gut form the enteric nervous system which is recognized as a second brain (Gershon, 1999). The microbiota-gut-brain axis has been studied and the bidirectional communication of this pathway occurs through various mechanisms, including enteric nervous system, autonomic nervous system, immune system, hormones, and neurotransmitters (Cryan and Dinan, 2012). Possible involvement of a microbial element in the pathogenesis of ASD was first reported in 1998, when Bolte (1998) introduced the hypothesis that Clostridium tetani neurotoxin was transported from the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system via the vagus nerve, causing symptoms of ASD. The link between gut microbiota and ASD has been studied in animal models. One study published in 2019 that transplanted gut microbiota from human ASD patients into germ-free mice revealed development of hallmark autistic behaviors in the recipient animals (Sharon et al., 2019). The association between gut microbiota and ASD has also been reported in human studies. For example a pyrosequencing study observed that Bacteroidetes were present at high levels in the persons with ASD, while Firmicutes were more abundant in the healthy control group (Finegold et al., 2010).
Given the rising trend of interest related to ASD and gut microbiota, it is worthwhile to identify the most influential scientific achievements amidst the abundance of literature in this research area. Bibliometric analysis is a widely used, rigorous approach for exploring extensive scientific datasets and extracting useful information, such as author names, total citations, and country distributions (Donthu et al., 2021). It can visualize the detailed results and help researchers to develop a thorough understanding of the research trajectory in the field and identify research hotspots and gaps. For example, a recent bibliometric analysis presents a comprehensive global overview of artificial intelligence in life science research and suggests that coordinated international research efforts are necessary to advance this research area (Schmallenbach et al., 2024). As bibliometric analysis offers both quantitative and qualitative insights into the influence and evolution of academic communication, it assists policymakers to track emerging trends and make informed choices about research funding and collaboration strategies (Hassan and Duarte, 2024).
To the best of our knowledge, no prior bibliometric analysis has been performed to explore the most influential works in the field of ASD and gut microbiota. This study seeks to fill this gap by conducting an in-depth analysis of the most-cited articles concerning the intersection of ASD and gut microbiota, with the goal of providing valuable insights to the existing body of research and guiding researchers and policymakers in evaluating and making informed decisions related to this field.
Materials and methods
Article selection
The Clarivate Analytics Web of Science database was used to identify relevant articles in this current bibliometric review. The Web of Science database has the capability to retrieve numerous articles with comprehensive details, including titles, author names, total download times, and total citations. It is an extensive repository which includes major journals across more than 170 subjects (Quan et al., 2024). In addition, it enhances coverage by including citations from scientific publications dating back to 1900 and encompasses all significant high-impact scientific journals (Martin-Martin et al., 2018; Tomova et al., 2015). Various studies, including those on gut microbiota and other diseases, have relied solely on the Web of Science database as their primary source for conducting bibliometric analyses (Chang et al., 2023; Ring et al., 2020; Wan et al., 2022; Ying et al., 2022).
To find pertinent articles, several recent systematic reviews related to ASD or gut microbiota were referenced to create search terms (Lewandowska-Pietruszka et al., 2023; Perna et al., 2023; Wang A. et al., 2023). Besides, an information specialist was consulted to help in further refinement of the search strategies and ensure the comprehensive retrieval of all relevant articles. The following search terminologies were used in this bibliometric review: TS = (“autism” OR “autistic” OR “Asperger*” OR “pervasive developmental disorder*”) AND TS = (“microbiome*” OR “microbiota*” OR “flora*” OR “microbe*” OR “microflora*” OR “microbial”). The terminology TS denotes a search focused on the topic of interest.
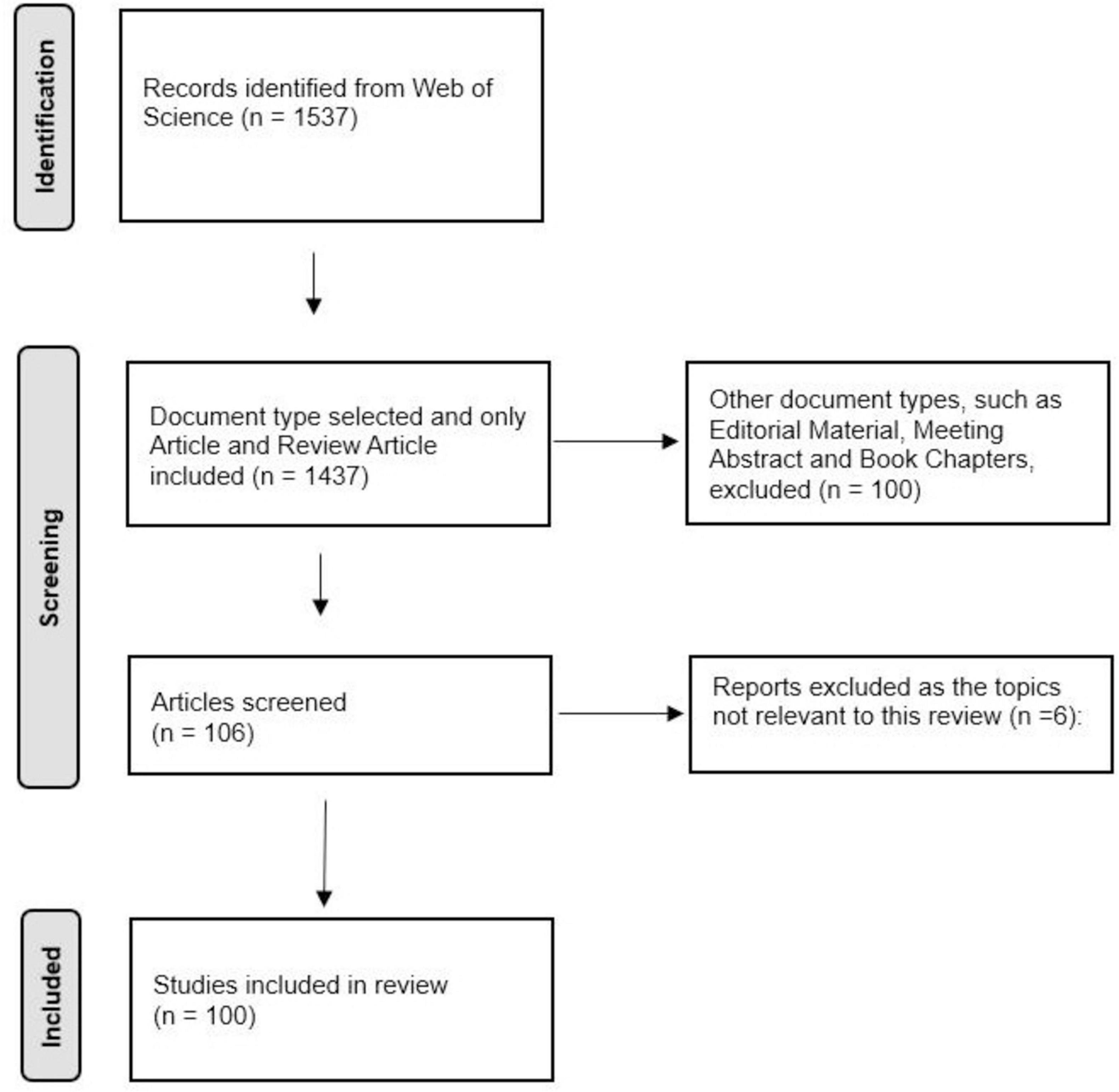
Using this approach, the Web of Science database was systematically searched in January 2024. No restrictions were implemented in terms of the language of articles and the publication dates. The publications were ranked according to the number of citations, and they were then reviewed to identify the 100 most-cited papers. Studies were included if (1) one of their focuses was related to the topic of ASD and gut microbiota, (2) the type of the document was either Article or Review Article according to the Web of Science database. Other types of documents, such as Editorial Material, Meeting Abstract, and Book Chapters, were excluded. Two authors (JY and MZ) independently performed the selection of the top 100 papers with the most citations, based on the title and abstract and reading the full texts if needed. If any disagreement arose, a third author was consulted to achieve an agreement.
Data analysis
The bibliometric data analysis was performed using Biblioshiny package in R (Version 4.3.2) (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017). The Biblioshiny package was previously utilized for this type of analysis in various areas, such as the application of deep learning in cancer (Wang R. et al., 2024), the use of monoclonal antibodies for atherosclerosis (Ma et al., 2023), and the global impact of metaproteomics research (Ascandari et al., 2023). All data were downloaded from the Web of Science database and imported into Biblioshiny, which could convert and analyze the information, including the authors, years of publication, number of citations, and distribution of countries/regions. The study type was categorized into three main groups: (1) animal studies, which incorporated animal models in their study design; (2) human studies, which involved persons with ASD; and (3) reviews, encompassing literature reviews or systematic reviews. The impact factor of each journal was extracted from the Clarivate Analytics Journal Citation Reports.
All statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS software (Version 25). The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to test the normality of the distribution of variables. Spearman’s rho test was applied to assess the correlations between two variables. Mann–Whitney U test was performed to assess for any statistically significant differences between two groups, and the Kruskal–Wallis test was conducted to compare the differences between three or more groups. All p values were two-tailed, and a p-value of ≤0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Overview
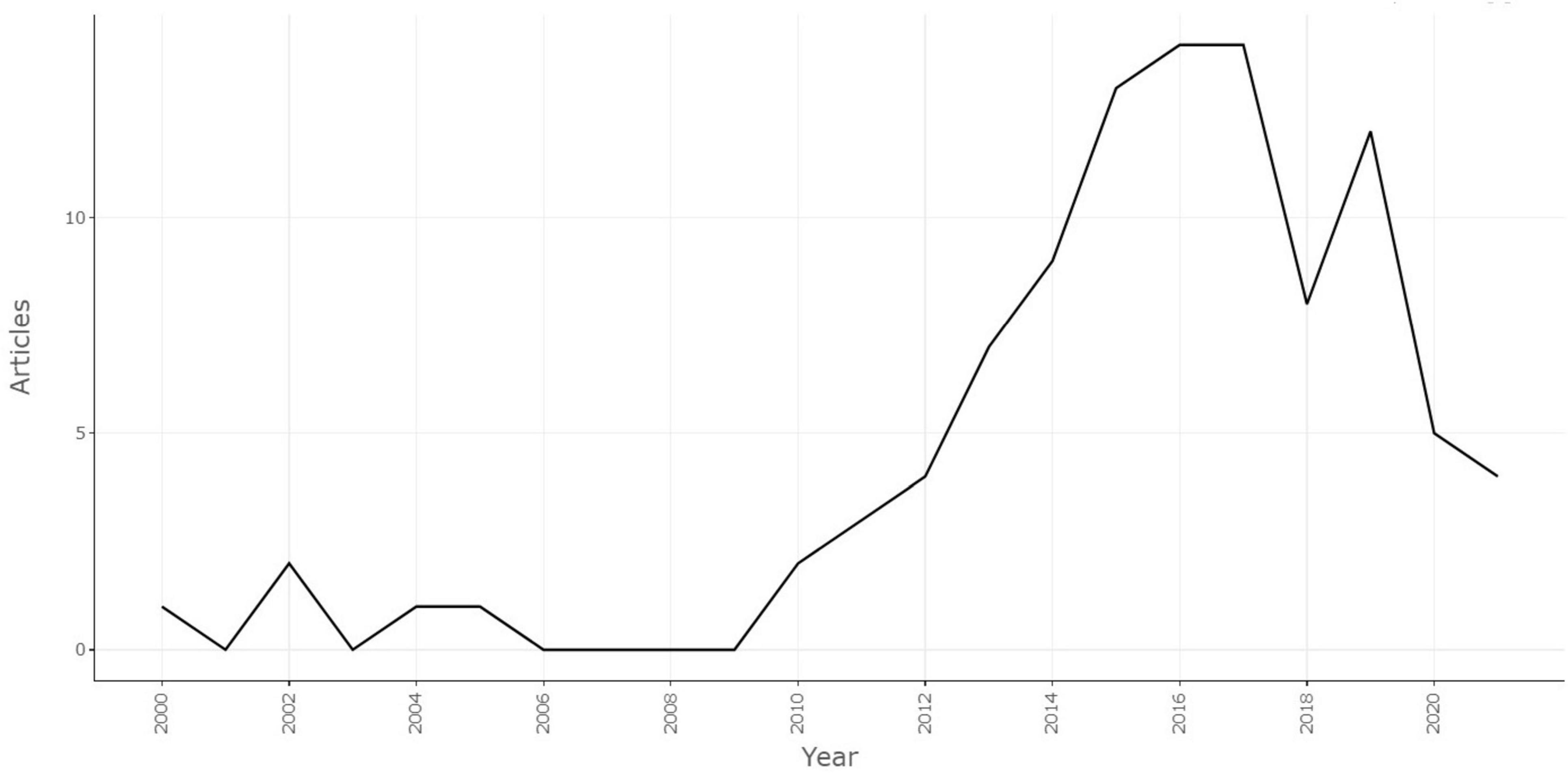
A total of 1,537 articles were retrieved from the Web of Science database on 10 January 2024, and the 100 most-cited papers were identified after screening. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) was used to describe the detailed screening process (Figure 1). General information of the selected articles is detailed in Table 1. The trends of the annual publications of the 100 most-cited articles are described in Figure 2.
Citations
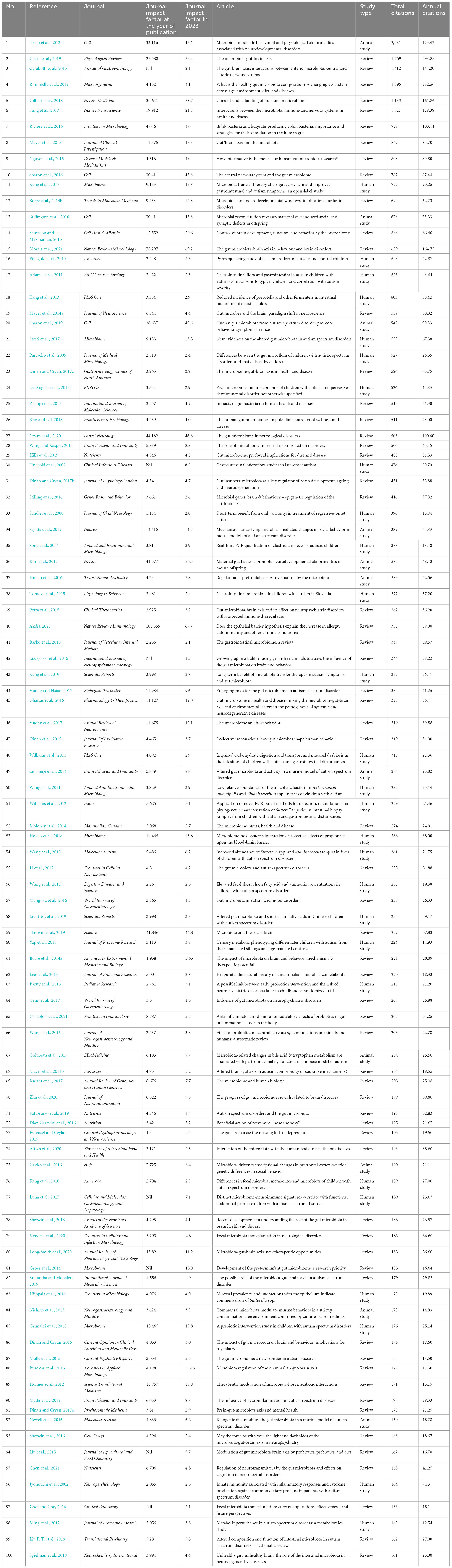
The total citation frequency for all the 100 selected articles was 40,662, with a median citation of 280.5. The number of citations for each article ranged from 161 to 2,081. The top article with the most total citations was “Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders” by Hsiao et al. (2013) (total citations of 2,081). The most-cited human study was “Microbiota transfer therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: an open-label study” by Kang et al. (2017) (total citations of 722), while the most cited randomized clinical trial was “A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: a randomized trial” by Pärtty et al. (2015) (total citations of 212).
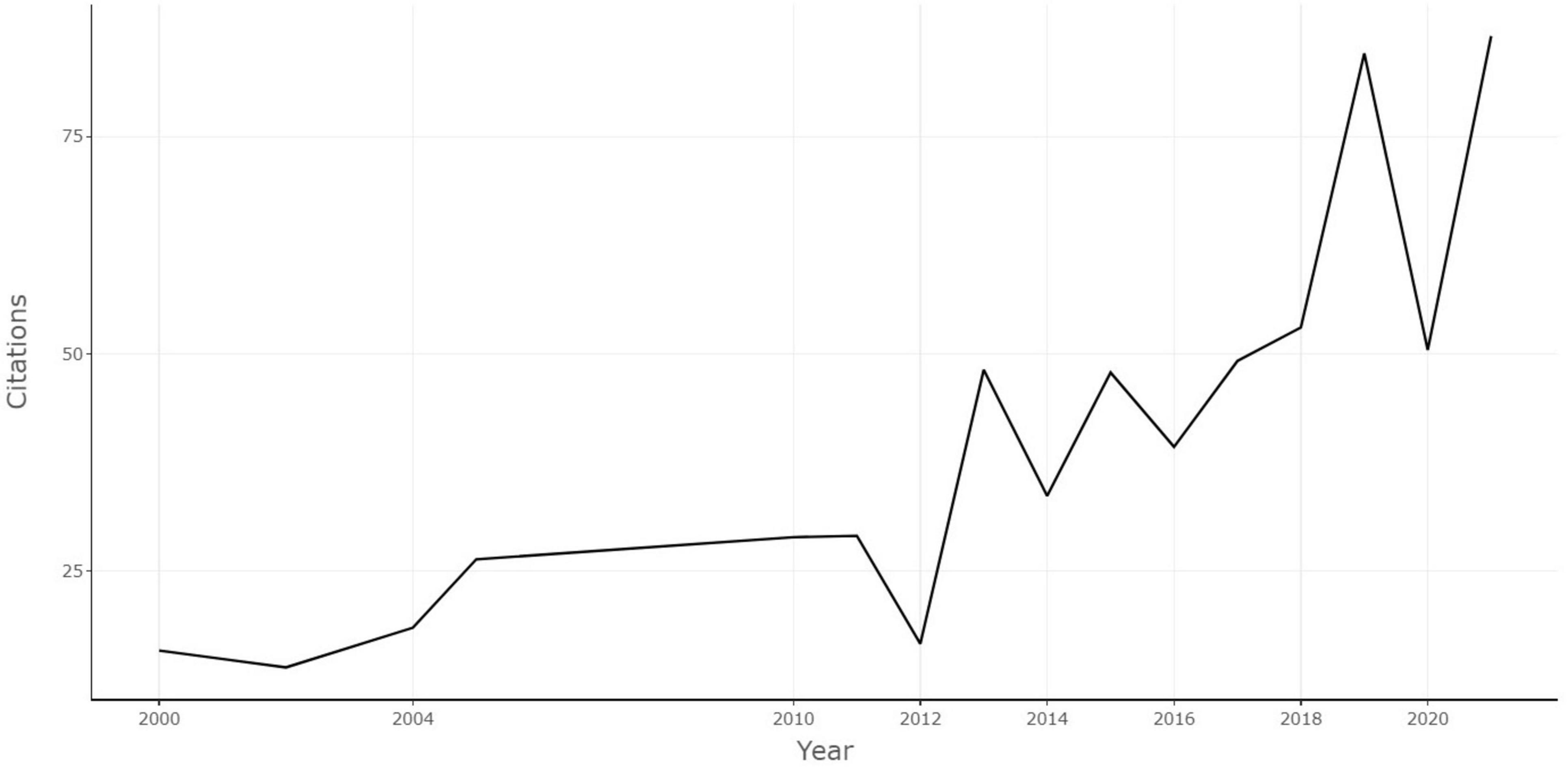
To exclude the effect of year on citation numbers, the annual citation rate was analyzed. Figure 3 demonstrates the trends of citations per year of the 100 selected articles. The annual citation rate was trending upward overall from 2000 to 2021. The annual citation was 15.8 in 2000, and it reached the peak in 2021 with annual citations of 86.6. The annual citation rate of each paper ranged from 7.13 to 294.83. The top article with the most annual citations was “The microbiota-gut-brain axis” by Cryan et al. (2019) (annual citations of 294.83).
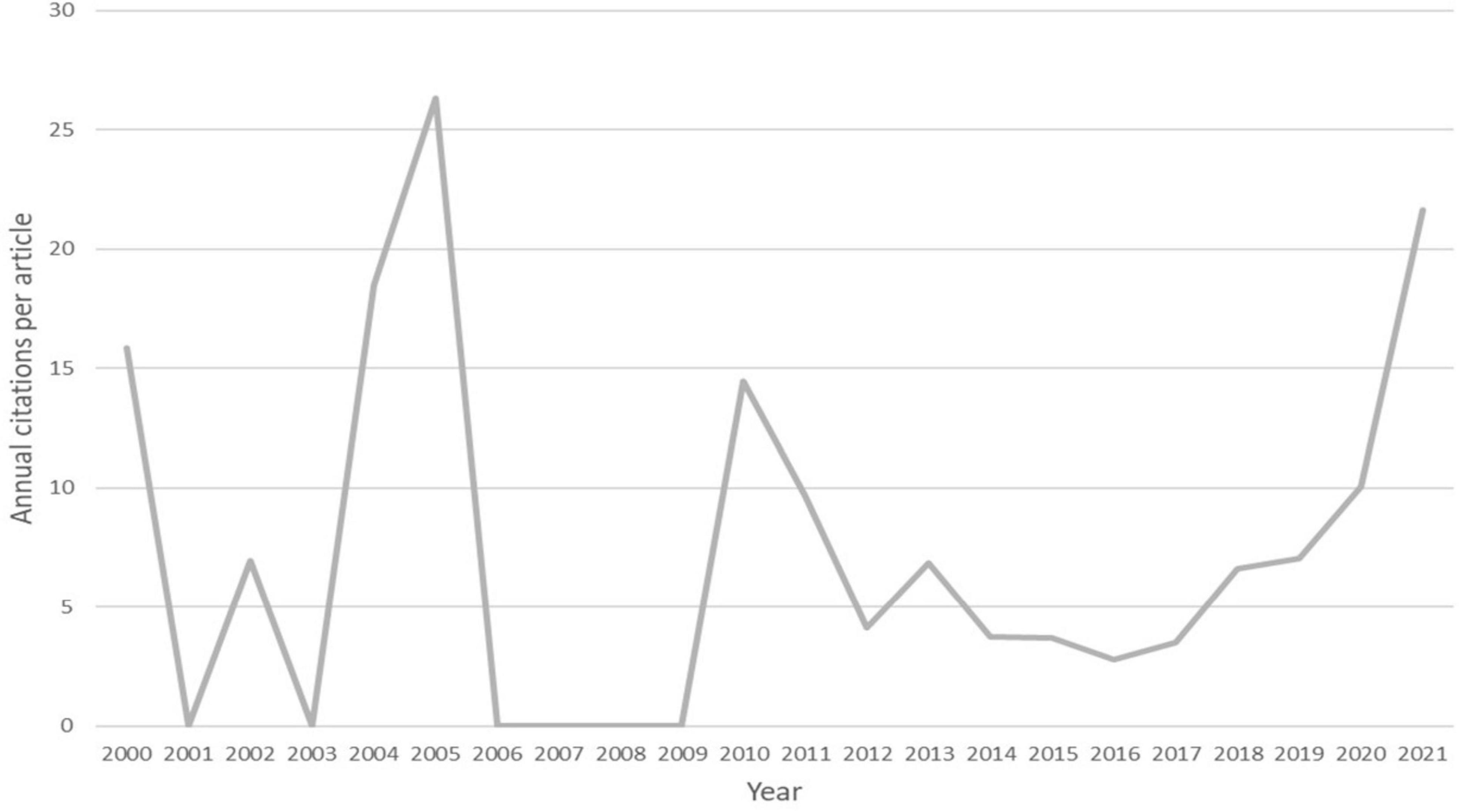
To better understand the relationship between annual citations and annual publications, the average number of citations per article per year was calculated. Figure 4 presents this average citation count for each year. The trend was fluctuating prior to 2013, as there were fewer than five articles published each year. However, as the annual number of publications increased in recent years, the trend showed an overall upward trajectory.
The total citation rate of an article was not significantly correlated to the year of publication (r = 0.097, p > 0.05, Spearman’s rho test). However, the annual citation rate of an article was significantly related to the year of publication (r = 0.481, p < 0.01, Spearman’s rho test).
Among the 100 selected articles, there were 11 animal studies, 27 human studies, and 62 reviews. The total citation rate and annual citation rate were not significantly different between the three study types (p > 0.05, Kruskal–Wallis test). When combining animal and human studies into a single category of experimental studies, the citation rates for clinical studies were still not significantly different from those of review articles (p > 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test).
Countries
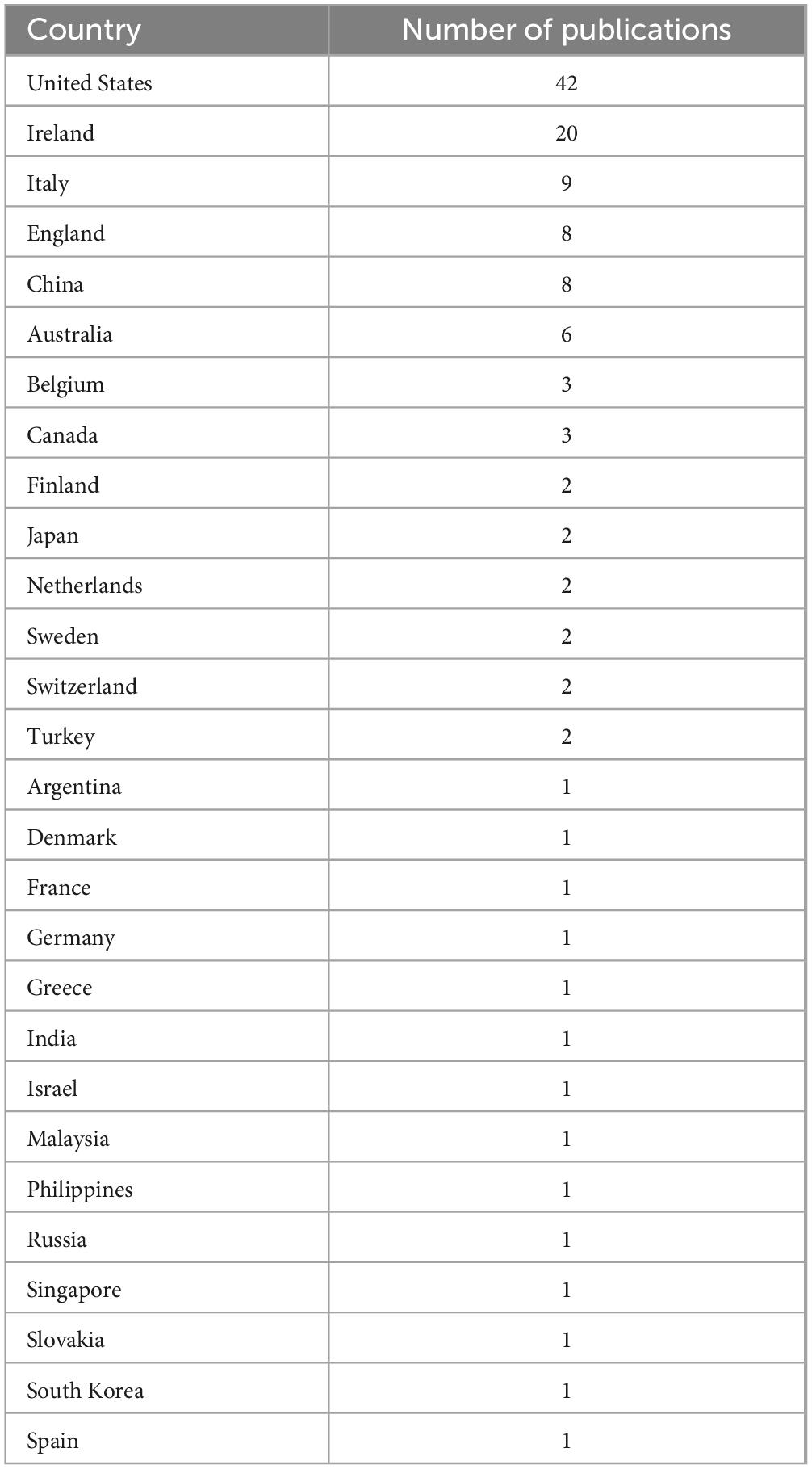
There were 28 countries involved in the 100 most-cited articles. The United States was involved in the highest number of publications (n = 42), followed by Ireland (n = 20), Italy (n = 9), England (n = 8), and China (n = 8). The details of the number of publications of each country are listed in Table 2.
There were 20 countries which had collaborations with others. Figure 5 displays the collaboration network between these countries. The color of the node in Figure 5 represents different collaboration cluster, the width of the curved line indicates the link strength, and the distance between the nodes denotes approximate relatedness among the nodes. The United States had the most collaborations with other countries, and worked closely with the United Kingdom, Ireland, and China.

Figure 5. Collaboration network between countries. The color of the node represents different collaboration cluster, the width of the curved line indicates the link strength, and the distance between the nodes denotes approximate relatedness among the nodes.
Authors
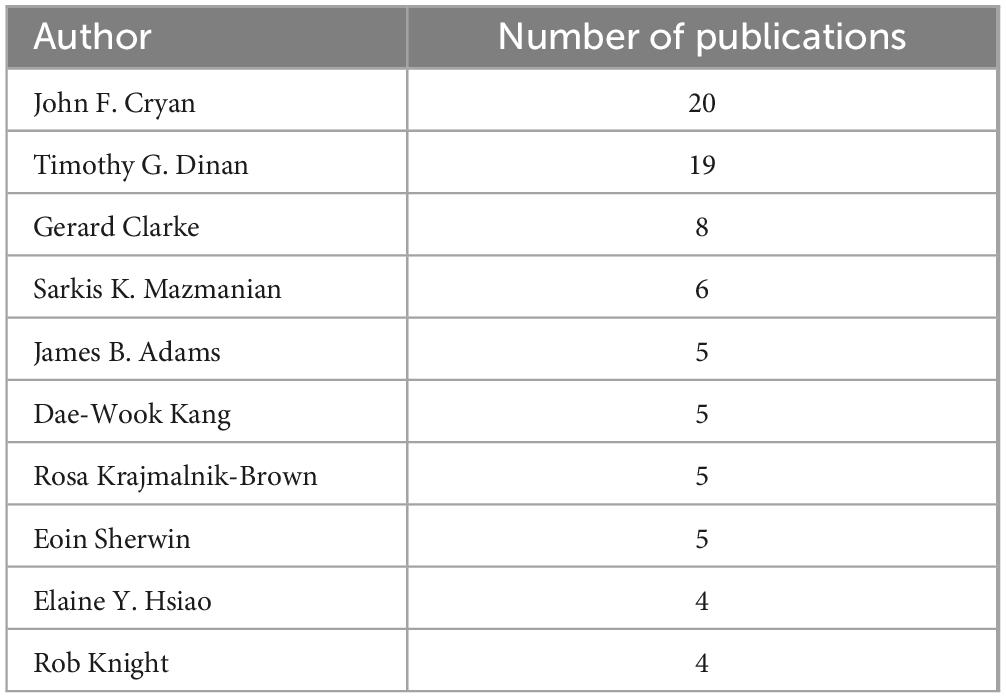
Among the 491 authors involved in the 100 most-cited articles, 8 authors published 5 or more articles. John F. Cryan was the most productive author, with 20 articles, followed by Timonthy G. Dinan with 19 articles. Table 3 lists the top 10 authors with most published articles.
Most authors collaborated with others to publish their papers. However, Cezmi A. Akdis published a notable single-authored article titled “Does the epithelial barrier hypothesis explain the increase in allergy, autoimmunity and other chronic conditions?” in Nature Reviews Immunology. He is a professor in University of Zürich Medical Faculty and the Director of the Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research in Davos, Switzerland (Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research, 2024).
Among all the authors, Timothy G. Dinan and John F. Cryan collaborated most frequently. Timothy G. Dinan is a Professor of Psychiatry at University College Cork (University College Cork, 2024), while John F. Cryan is a Professor and Chair, Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience, University College Cork (APC Microbiome Ireland, 2024). Notably, many frequent collaborators are from the same institutions. For example, Emeran A. Mayer, the Director of the Gail and Gerald Oppenheimer Family Center for Neurobiology of Stress and a Professor of Psychology Medicine (UCLA Brain Research Institute, 2024), and Kirsten Tillisch, a Professor of Medicine and gastroenterologist with a clinical interest in chronic pain and functional gastrointestinal disorders (UCLA Health, 2024), are both based at the University of California, Los Angeles, United States. Likewise, Elaine Holmes and Jeremy K. Nicholson are affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine at Imperial College London, United Kingdom. Elaine Holmes is a Professor of Chemical Biology with research interests in discovering and developing metabolic biomarkers for disease in personalized healthcare and population studies (Imperial College London, 2024a). Jeremy K. Nicholson, an Emeritus Professor of Biological Chemistry, focuses on personalized healthcare through metabolic phenotyping and systems medicine (Imperial College London, 2024b). All these researchers contributed to their collaborative works with their unique expertise and a shared focus on interactions between the brain, gut, and microbiome. The research area of autism and gut microbiota brought together experts from diverse disciplines, including psychiatry, neuroscience, gastroenterology, biological chemistry, and chemical biology.
Figure 6 illustrates the collaboration network between the authors who had at least three collaborations. The color of the node represents different collaboration cluster, the width of the curved line indicates the link strength, and the distance between the nodes denotes approximate relatedness among the nodes.
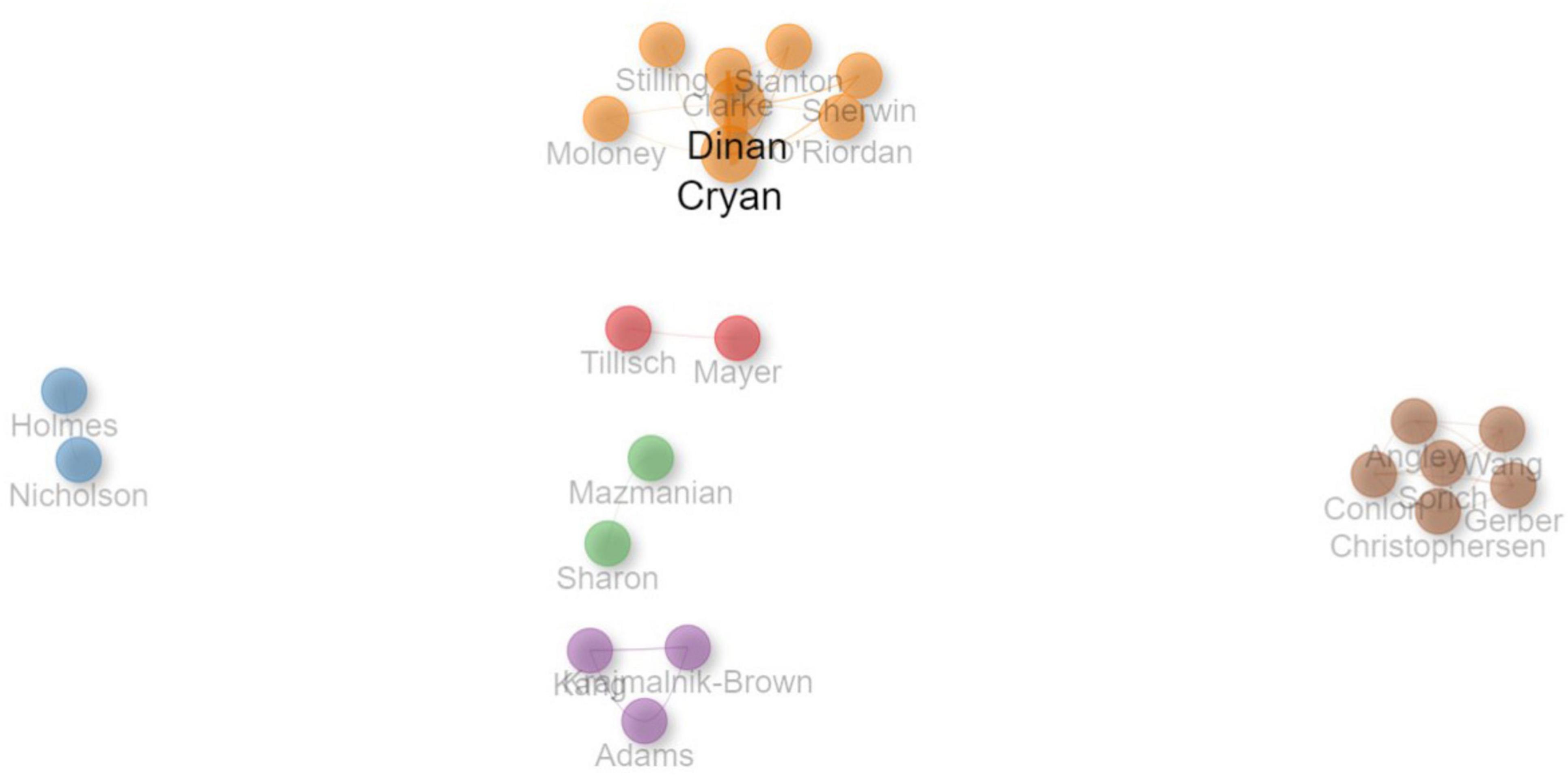
Figure 6. Collaboration network between authors. The color of the node represents different collaboration cluster, the width of the curved line indicates the link strength, and the distance between the nodes denotes approximate relatedness among the nodes.
Journals
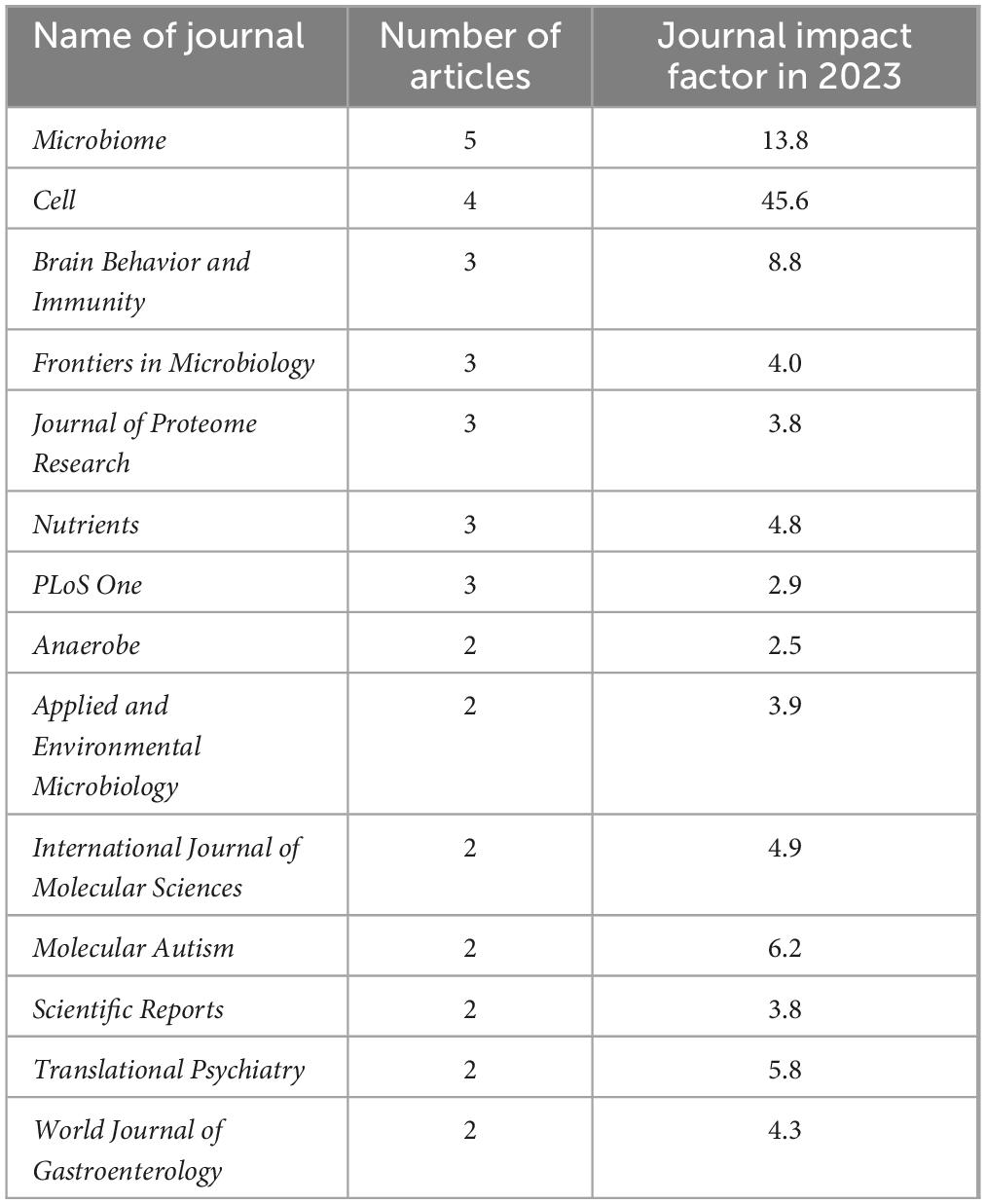
The 100 selected articles were published in 76 journals. The latest impact factors of the journals ranged from 2.0 to 69.2. Nature Reviews Microbiology was the journal with the highest impact factor, and published the article “The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders.” Journal of Child Neurology, with the lowest impact factor (impact factor of 1.134 at the time of publication and impact factor of 2 in 2023), published the paper “Short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism.” Among the 76 journals, 14 published at least 2 of the selected articles. Microbiome was the most productive journal, with five articles, followed by Cell with four articles. Brain Behavior and Immunity, Frontiers in Microbiology, Journal of Proteome Research, Nutrients, and PLoS One all published three articles. The number of publications of the 100 most-cited articles in that journal was not significantly related to the journal’s latest impact factor (r = 0.016, p > 0.05, Spearman’s rho test). The list of journals with at least two publications is presented in Table 4.
KeyWords Plus
KeyWords Plus refer to indexed keywords derived from the titles of referenced articles that occur at least twice in the bibliography, and they offer valuable insights into research trends (Tomaszewski, 2023). Figure 7 provides an overview of the most-used KeyWords Plus. The most popular KeyWords Plus were “intestinal microbiota” (n = 35), “irritable bowel syndrome” (n = 25), and “chain fatty acids” (n = 24). To better understand the development of KeyWords Plus, the frequency of the original authors’ keywords was analyzed. Figure 8 presents an overview of the frequency of authors’ keywords, where larger font sizes indicate higher frequencies. In comparison to the authors’ keywords, certain KeyWords Plus, such as “irritable bowel syndrome” and “chain fatty acids,” appeared more frequently, highlighting emerging trends in this field. It was also observed that some KeyWords Plus, such as “obesity” and “probiotics” were used less frequently than the authors’ keywords.

Figure 8. The most-used authors’ keywords. The font size is proportional to the frequency of the word.
Figure 9 illustrates the co-occurrence network of KeyWords Plus. The size of the node is proportional to the frequency of the word, the color of the node represents different cluster, and the width of the curved line indicates the link strength. The most popular word “intestinal microbiota” was linked to many other words, such as “autism,” “brain,” “children,” and “irritable bowel syndrome.”
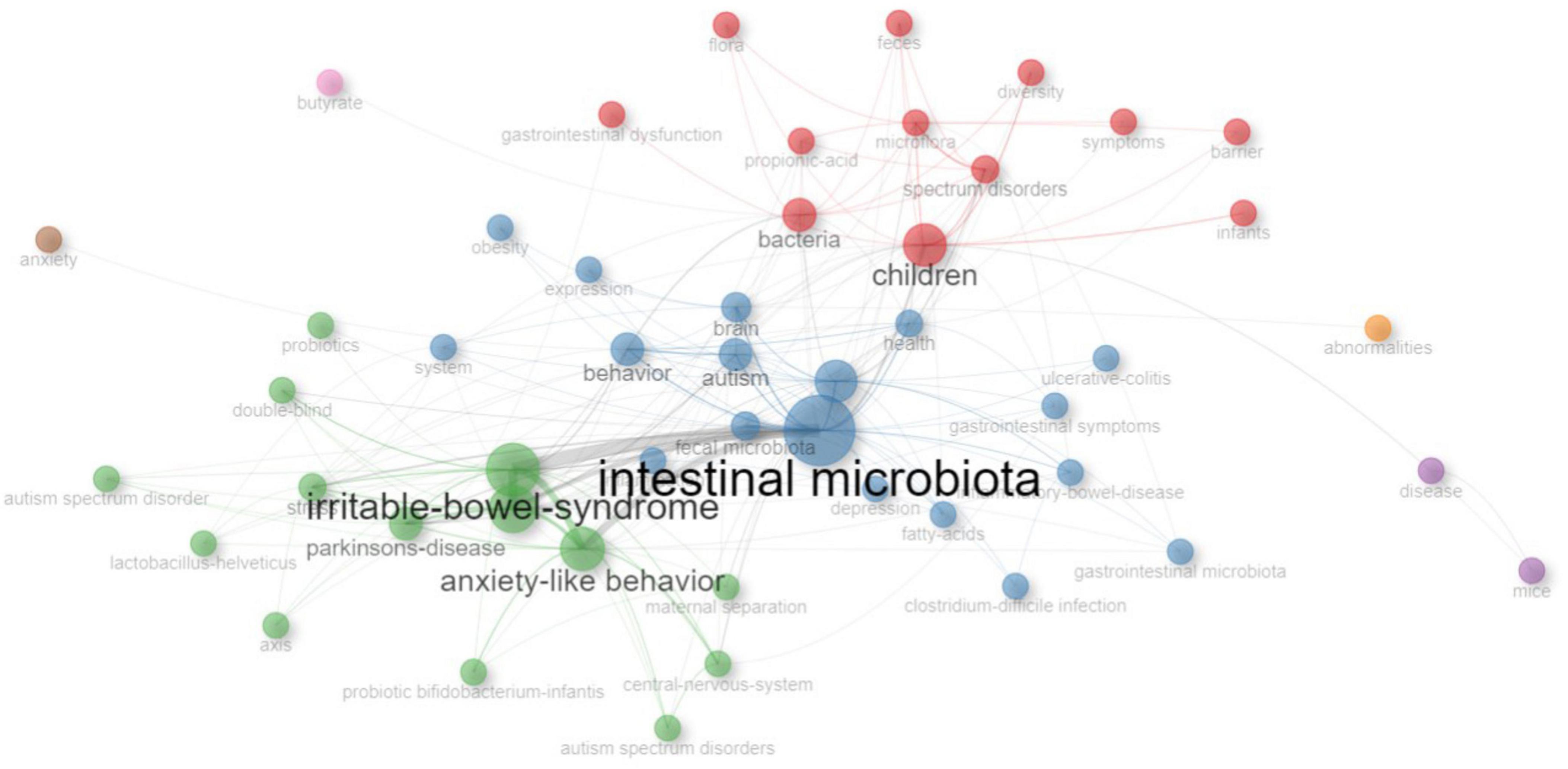
Figure 9. The co-occurrence network of KeyWords Plus. The size of the node is proportional to the frequency of the word, the color of the node represents different cluster, and the width of the curved line indicates the link strength.
Thematic analysis
The thematic map analysis based on KeyWords Plus is illustrated in Figure 10. A thematic map allows four typologies of themes to be categorized based on their placement in specific quadrants. Themes in the upper-right quadrant are identified as motor themes, characterized by both high density and centrality, signifying their development and relevance in the research field. In the upper-left quadrant, themes are classified as niche themes, marked by high density but low centrality, indicating their isolated development. Themes in the lower-left quadrant have low centrality and density, suggesting they are weakly developed and marginal. In the lower-right quadrant are basic themes, featuring high centrality (relevance) and low density (less development). As illustrated in Figure 8, several pertinent themes are discernible in this research field, such as chain-fatty acids, bacteria, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
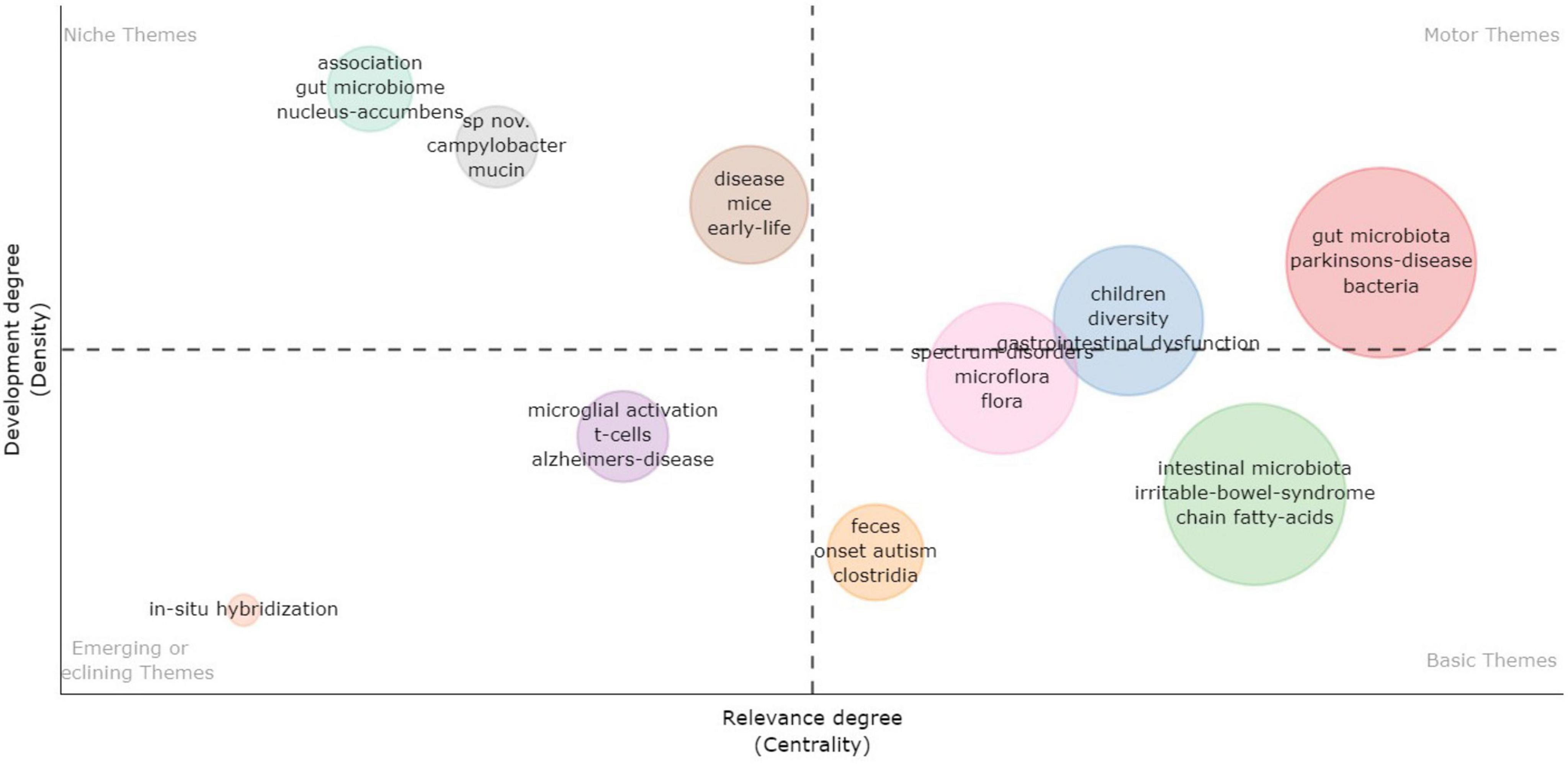
Figure 10. Thematic map analysis based on KeyWords Plus. Upper-right quadrant: motor themes – high density (developed) and high centrality (relevant); upper-left quadrant: niche themes – high density (developed) and low centrality (less relevant); lower-left quadrant: emerging or declining themes – low density (less developed) and low centrality (less relevant); lower-right quadrant: basic themes – low density (less developed) and high centrality (relevant).
Discussion
General information
This study combined bibliometric analysis with network visualization to identify the first 100 highly impactful manuscripts in the field of ASD and gut microbiota, based on global citation frequency. It highlights the contributions that have driven substantial progress in this field, identifies the current research trends, and provides guidance for future research directions. Various aspects in this research domain were explored, including the top articles with most citations, correlations between citation rates and publication time, distribution of involved countries, contributions of key authors, impactful journals with most publications, and relevant themes in this field.
Among the 100 most-cited articles in the current review, the average number of citations annually increased over the years and was significantly correlated to the year of publication. However, there was no significant association between total number of citations and time of publication. These trends are consistent with bibliometric analyses in other areas, such as burns (Ring et al., 2020) and insomnia (Wan et al., 2022). This is likely due to the tendency of total citations to favor older publications, as more recent papers have a shorter duration to accumulation citations. The average number of citations annually, as different from the total citations, can eliminate the effect of time on citation numbers and provide a more accurate view of the immediate impact of the articles. Besides, as the association between autism and gut microbiota is a rapidly evolving field (Wang Q. et al., 2023), newer studies in this research area often receive high initial attention and are cited more frequently within the initial years, as they may represent cutting-edge findings or novel methodologies, leading to an increase in annual citation averages over time. The area in autism and gut microbiota may be different from foundational research which tends to accumulate citations consistently over long periods and has obscured direct association with the time of publication. Overall, the quantity of citations of an article is a useful proxy to indicate the significant of the study (Landreneau et al., 2020). It can be implied that the influence of research in autism and gut microbiota has been steadily increasing over the years.
In terms of the distribution of countries, the United States contributed to the largest volume of the publications, followed by other countries, such as Ireland, England, and China. These findings are similar to bibliometric reviews in other conditions, such as schizophrenia (Yang et al., 2022) and intellectual disability (Ying et al., 2022). The United States holds a competitive edge in this research domain and is likely to have a significant impact on the direction of research in this field and maintain the most robust global collaborations. The information of the distribution of countries can be valuable for researchers seeking to choosing the most suitable place for additional training or collaborative opportunities.
Each journal contributed one to five of the 100 most-cited articles. The number of the articles that the journal contributed was not related to the impact factor of the journal. These findings are consistent with other review papers on impactful studies, such as the landmark studies in burns (Ring et al., 2020). The impact factor was first introduced by Garfield (2006) and was commonly used as a measure to indicate the significance of a journal within its respective field. The impact factor pertains exclusively to journals and does not extend to individual articles. Thus, it is possible for a highly impactful study to be published in a journal with low impact factor. In the current review, one of the highly cited papers “short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism” was published in 2000 in Journal of Child Neurology, a journal with an impact factor of 1.134 at the time of publication. At that time this article was submitted to a low impact journal was likely due to several reasons. This article focused on short-term effects in a small sample with preliminary nature of findings (Sandler et al., 2000) and this could make high-impact journal hesitant to publish it. Besides, at that time the concept of a link between autism and gut microbiota was not widely accepted, especially in high-impact journals. In addition, the authors at that time might not be aware of the significance of their work or chose the journal based on the audience specialization and journal readership. Nonetheless, this article is one of the early works to suggest a potential link between gut microbiota and autism and is one of the foundational references for researchers exploring this area. It has subsequently cited by numerous papers published in high-impact journals, such as Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (Hung and Margolis, 2024), Clinical Microbiology Reviews (Yadegar et al., 2024), and Microbiome (LaPelusa et al., 2021).
Our findings share certain similarities with other bibliometric analyses on gut microbiota in various conditions. For example, a bibliometric analysis on gut microbiota and Parkinson’s disease identified similar main research topics, including “short-chain fatty acids,” “probiotics,” and ‘inflammation” (Li et al., 2024). Another similar analysis on gut microbiota and obesity found similar top journals in this area, such as Nutrients, Scientific Reports, and Frontiers in Microbiology (Wang M. et al., 2024). Various bibliometric analyses related to gut microbiota revealed an overall upward trend in the number of publications and the United States being one of the leading countries in those research fields (Li et al., 2024; Ouyang et al., 2024; Wang M. et al., 2024). Together with other studies on similar fields of investigation, this current study can offer a clear insight into the current research landscape and emerging trends, serving as a valuable reference for researchers entering this field of gut microbiota.
Influential studies
The most-cited article among all the selected papers was “Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders” by Hsiao et al. (2013) published in Cell. This is a landmark study, as it demonstrated gastrointestinal barrier defects and microbiota changes in the maternal immune activation mouse model with autistic symptoms. This study found that treatment with the human commensal Bacteroides fragilis corrected gut permeability defects, altered the composition of the microbiota, regulated the serum levels of the metabolite of 4-ethylphenylsulfate, and alleviated abnormal communicative, anxiety-like, stereotyped, and sensorimotor behaviors. It proposed a groundbreaking idea that ASD could be potentially a disorder related to the gut, and that therapies involving the microbiome might offer a safe and effective approach to treating the disorder.
The human study with most citations was “Microbiota transfer therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: an open-label study” authored by Kang et al. (2017) and published in Microbiome. In this open-label clinical trial, the efficacy of Microbiota Transfer Therapy was evaluated in terms of its impact on gut microbiota, gastrointestinal and autistic symptoms in children diagnosed with ASD. This study found that the abundance of Bifidobacterium, Prevotella, and Desulfovibrio increased after the intervention and the improvement persisted till the end of 8 weeks follow-up. These findings are promising and represent a pivotal advancement in understanding the relationship between gut microbiota and ASD.
The randomized clinical trial among the 100 most-cited articles was performed by Pärtty et al. (2015) who wrote the article “A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: a randomized trial” published in Pediatric Research. In this clinical trial, 75 infants were randomized to receive Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG or placebo during their first 6 months of life and were followed up for 13 years. At 13 years old, Asperger syndrome or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder was diagnosed in 17.1% of children in the placebo group, while none in the probiotic group. This influential study demonstrated, for the first time, that certain probiotics could potentially mitigate the risk of developing specific neurodevelopmental disorders.
The impactful paper published in the journal with the lowest impact factor among all the included articles was “Short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism” by Sandler et al. (2000) published in Journal of Child Neurology. This open-label clinical trial demonstrated the short-term improvement in autistic symptoms after oral vancomycin treatment among 11 children with regressive-onset ASD. This early study, published in July 2000, indicated the potential existence of a gut-brain connection in a subgroup of children with both ASD and diarrhea.
Future outlook
The co-occurrence network of KeyWords Plus and thematic analysis in this study identified several important hotspots and future directions in this research area, such as microbial metabolites of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), role of bacteria, and overlaps of IBS.
Short-chain fatty acids are monocarboxylic acids containing fewer than six carbon atoms (Schonfeld and Wojtczak, 2016). The majority of SCFAs in the human intestine are acetic acid, butyric acid and propionic acid (Iniguez-Gutierrez et al., 2020). These organic acids result from the fermentation of dietary fiber and resistant starch in the intestine (Portincasa et al., 2022). Several well-designed animal studies have been performed to explore the relationship between SCFAs and ASD. For example, one study in Canada found that rats treated with propionic acid displayed more stereotypic behavior, nose pokes and locomotive activity (Meeking et al., 2020). Studies in human participants have also reported changes in SCFAs in the stool of ASD subjects. One recent study revealed that children with ASD and constipation had excessive propionic acid in feces (He et al., 2023). This study provided new clues to understand the etiology and biomarkers for ASD. However, the results in human studies are inconsistent (Lagod and Naser, 2023). The variability in human study outcomes highlights the need for further research on SCFA levels in individuals with ASD.
The composition of bacteria in the human gastrointestinal tract is complex. There are still inconsistences regarding the association between different bacteria and ASD in different studies. Some studies have reported higher abundance of Lactobacillus in ASD (Pulikkan et al., 2018; Strati et al., 2017), while it is also reported that Lactobacillus has decreased levels (Iovene et al., 2017). The diversity of gut microbiota has been reported to be either increased (Coretti et al., 2017) or decreased (Dan et al., 2020) in persons with ASD. Besides, the ratio between Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes in persons with ASD has been reported higher in some studies (Strati et al., 2017), and lower in other studies (Zhang et al., 2018). It has been pointed out that the inconsistent conclusions between different studies are likely due to various reasons, including underpowered research design and variation in use of multiple testing corrections (Li et al., 2022). In addition, gut microbiota composition may also be affected by other factors, such as age, body mass index, and dietary habits (Rinninella et al., 2019). Future investigations with more comprehensive and standardized methods may shed light on the intricate connections linking gut bacteria and ASD.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic gastrointestinal disease with the core clinical symptoms of recurrent abdominal discomfort or pain, and altered bowel habits (Huang et al., 2023). IBS is commonly observed as a comorbid condition in individuals with ASD (Penzol et al., 2019). In conditions such as IBS and ASD, where dysbiosis is potentially present, the utilization of prebiotics and probiotics may serve as a low-risk therapeutic approach to improve symptoms (Abdellatif et al., 2020). One recent pilot randomized clinical trial published in Cell Host & Microbe tested the effect of bacterial species Limosilactobacillus reuteri in children with ASD and found that the bacteria significantly improved the social functioning (Mazzone et al., 2024). Results in recent studies are compelling to encourage additional future research on utilizing probiotics or specific microbes as treatment options for persons with ASD.
Limitations
Although this study provides valuable and comprehensive insights to help researchers and policymakers to understand the research trends and guide feature decision-making, it has several limitations. First, the literature search was conducted only in the Web of Science database. While the Web of Science is the leading database in scientometrics and many studies rely solely on it for bibliometric analysis, our findings could be more comprehensive if additional databases were included. Second, although bibliometric analysis provides a broad overview of research trends and networks, it may lack in-depth analysis as it does not evaluate the quality of the numerous studies. Third, this research field is advancing rapidly. It is possible that some recently published high-quality studies may be overlooked, due to the low accumulated citation numbers.
Conclusion
The present study, to our knowledge, is the first bibliometric analysis to comprehensively explore the 100 most-cited articles in the field of ASD and gut microbiota. By identifying and analyzing these pivotal studies, we provide a detailed overview of the most influential research in this domain. The results highlight key trends, emerging topics, and potential future directions for investigation. This analysis not only illuminates the current landscape of research but also offers valuable insights for researchers, clinicians, and policymakers. It serves as a critical reference for guiding the development and focus of future scientific inquiries and clinical practices related to ASD and gut microbiota.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. K-CW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yasmin Lynda Munro, the information specialist from the Nanyang Technological University for her assistance in refining the search strategy.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdellatif, B., McVeigh, C., Bendriss, G., and Chaari, A. (2020). The promising role of probiotics in managing the altered gut in autism spectrum disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:4159.
Adams, J. B., Johansen, L. J., Powell, L. D., Quig, D., and Rubin, R. A. (2011). Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal status in children with autism-comparisons to typical children and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-22
Akdis, C. A. (2021). Does the epithelial barrier hypothesis explain the increase in allergy, autoimmunity and other chronic conditions? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 21, 739–751.
Altves, S., Yildiz, H. K., and Vural, H. C. (2020). Interaction of the microbiota with the human body in health and diseases. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 39, 23–32.
APA (2022). Diagnostic and Statistical Mannual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, Text Revision. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
APC Microbiome Ireland (2024). Available online at: https://www.ucc.ie/en/apc/people/principalinvestigators/johncryan/ (accessed December 15, 2024).
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 11, 959–975.
Ascandari, A., Aminu, S., Safdi, N. E. H., El Allali, A., and Daoud, R. (2023). A bibliometric analysis of the global impact of metaproteomics research. Front. Microbiol. 14:1217727. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1217727
Barko, P. C., McMichael, M. A., Swanson, K. S., and Williams, D. A. (2018). The gastrointestinal microbiome: a review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 32, 9–25.
Barrett, B., Mosweu, I., Jones, C. R., Charman, T., Baird, G., Simonoff, E., et al. (2015). Comparing service use and costs among adolescents with autism spectrum disorders, special needs and typical development. Autism 19, 562–569. doi: 10.1177/1362361314536626
Borre, Y. E., Moloney, R. D., Clarke, G., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2014a). The impact of microbiota on brain and behavior: mechanisms & therapeutic potential. Microb. Endocrinol. 817, 373–403.
Borre, Y. E., O’Keeffe, G. W., Clarke, G., Stanton, C., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2014b). Microbiota and neurodevelopmental windows: implications for brain disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 20, 509–518.
Buffington, S. A., Di Prisco, G. V., Auchtung, T. A., Ajami, N. J., Petrosino, J. F., and Costa-Mattioli, M. (2016). Microbial reconstitution reverses maternal diet-induced social and synaptic deficits in offspring. Cell 165, 1762–1775. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.001
Burokas, A., Moloney, R. D., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2015). Microbiota regulation of the mammalian gut-brain axis. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 91, 1–62.
Carabotti, M., Scirocco, A., Maselli, M. A., and Severi, C. (2015). The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 28, 203–209.
Cenit, M. C., Sanz, Y., and Codoñer-Franch, P. (2017). Influence of gut microbiota on neuropsychiatric disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 23, 5486–5498.
Chang, Y., Ou, Q., Zhou, X., Liu, J., and Zhang, S. (2023). Global research trends and focus on the link between colorectal cancer and gut flora: a bibliometric analysis from 2001 to 2021. Front. Microbiol. 14:1182006. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1182006
Chen, Y. J., Xu, J. Y., and Chen, Y. (2021). Regulation of neurotransmitters by the gut microbiota and effects on cognition in neurological disorders. Nutrients 13:2099.
Choi, H. H., and Cho, Y. S. (2016). Fecal microbiota transplantation: current applications, effectiveness, and future perspectives. Clin. Endosc. 49, 257–265.
Coretti, L., Cristiano, C., Florio, E., Scala, G., Lama, A., Keller, S., et al. (2017). Sex-related alterations of gut microbiota composition in the BTBR mouse model of autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 7:45356. doi: 10.1038/srep45356
Cristofori, F., Dargenio, V. N., Dargenio, C., Miniello, V. L., Barone, M., and Francavilla, R. (2021). Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front. Immunol. 12:578386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
Cryan, J. F., and Dinan, T. G. (2012). Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13, 701–712. doi: 10.1038/nrn3346
Cryan, J. F., O’Riordan, K. J., Cowan, C. S. M., Sandhu, K. V., Bastiaanssen, T. F. S., Boehme, M., et al. (2019). The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1877–2013.
Cryan, J. F., O’Riordan, K. J., Sandhu, K., Peterson, V., and Dinan, T. G. (2020). The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 19, 179–194.
Dan, Z., Mao, X., Liu, Q., Guo, M., Zhuang, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2020). Altered gut microbial profile is associated with abnormal metabolism activity of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Gut Microbes 11, 1246–1267.
De Angelis, M., Piccolo, M., Vannini, L., Siragusa, S., De Giacomo, A., Serrazzanetti, D. I., et al. (2013). Fecal microbiota and metabolome of children with autism and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. PLoS One 8:e76993. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076993
de Theije, C. G. M., Wopereis, H., Ramadan, M., van Eijndthoven, T., Lambert, J., Knol, J., et al. (2014). Altered gut microbiota and activity in a murine model of autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 37, 197–206. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.005
Diaz-Gerevini, G. T., Repossi, G., Dain, A., Tarres, M. C., Das, U. N., and Eynard, A. R. (2016). Beneficial action of resveratrol: how and why? Nutrition 32, 174–178.
Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2015). The impact of gut microbiota on brain and behaviour: implications for psychiatry. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 18, 552–558.
Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2017a). Brain-gut-microbiota axis and mental health. Psychosom. Med. 79, 920–926.
Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2017b). Gut instincts: microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, ageing and neurodegeneration. J. Physiol. (Lond) 595, 489–503. doi: 10.1113/JP273106
Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2017c). The microbiome-gut-brain axis in health and disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 46, 77–89.
Dinan, T. G., Stilling, R. M., Stanton, C., and Cryan, J. F. (2015). Collective unconscious: how gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr. Res. 63, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.02.021
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus Res. 133, 285–296.
Enaud, R., Vandenborght, L. E., Coron, N., Bazin, T., Prevel, R., Schaeverbeke, T., et al. (2018). The mycobiome: a neglected component in the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Microorganisms 6:22. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6010022
Evrensel, A., and Ceylan, M. E. (2015). The Gut-brain axis: the missing link in depression. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 13, 239–244.
Fattorusso, A., Di Genova, L., Dell’Isola, G. B., Mencaroni, E., and Esposito, S. (2019). Autism spectrum disorders and the gut microbiota. Nutrients 11:521.
Finegold, S. M., Dowd, S. E., Gontcharova, V., Liu, C., Henley, K. E., Wolcott, R. D., et al. (2010). Pyrosequencing study of fecal microflora of autistic and control children. Anaerobe 16, 444–453. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.06.008
Finegold, S. M., Molitoris, D., Song, Y. L., Liu, C. X., Vaisanen, M. L., Bolte, E., et al. (2002). Gastrointestinal microflora studies in late-onset autism. Clin. Infect Dis. 35, S6–S16. doi: 10.1086/341914
Fung, T. C., Olson, C. A., and Hsiao, E. Y. (2017). Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 145–155.
Gacias, M., Gaspari, S., Santos, P. M. G., Tamburini, S., Andrade, M., Zhang, F., et al. (2016). Microbiota-driven transcriptional changes in prefrontal cortex override genetic differences in social behavior. eLife 5:e13442. doi: 10.7554/eLife.13442
Gershon, M. D. (1999). The enteric nervous system: a second brain. Hosp. Pract. 34, 31–2, 5–8, 41–2 passim.
Ghaisas, S., Maher, J., and Kanthasamy, A. (2016). Gut microbiome in health and disease: linking the microbiome-gut-brain axis and environmental factors in the pathogenesis of systemic and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 158, 52–62. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.012
Gilbert, J. A., Blaser, M. J., Caporaso, J. G., Jansson, J. K., Lynch, S. V., and Knight, R. (2018). Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 24, 392–400.
Golubeva, A. V., Joyce, S. A., Moloney, G., Burokas, A., Sherwin, E., Arboleya, S., et al. (2017). Microbiota-related changes in bile acid & tryptophan metabolism are associated with gastrointestinal dysfunction in a mouse model of autism. Ebiomedicine. 24, 166–178.
Grimaldi, R., Gibson, G. R., Vulevic, J., Giallourou, N., Castro-Mejía, J. L., Hansen, L. H., et al. (2018). A prebiotic intervention study in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Microbiome 6:133. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0523-3
Groer, M. W., Luciano, A. A., Dishaw, L. J., Ashmeade, T. L., Miller, E., and Gilbert, J. A. (2014). Development of the preterm infant gut microbiome: a research priority. Microbiome 2:38.
Hassan, W., and Duarte, A. E. (2024). Bibliometric analysis: a few suggestions. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 49:102640.
He, J., Gong, X., Hu, B., Lin, L., Lin, X., Gong, W., et al. (2023). Altered gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in Chinese children with constipated autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 13:19103.
Hiippala, K., Kainulainen, V., Kalliomäki, M., Arkkila, P., and Satokari, R. (2016). Mucosal prevalence and interactions with the epithelium indicate commensalism of Sutterella spp. Front. Microbiol. 7:1706. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01706
Hills, R. D., Pontefract, B. A., Mishcon, H. R., Black, C. A., Sutton, S. C., and Theberge, C. R. (2019). Gut microbiome: profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients 11:1613.
Hoban, A. E., Stilling, R. M., Ryan, F. J., Shanahan, F., Dinan, T. G., Claesson, M. J., et al. (2016). Regulation of prefrontal cortex myelination by the microbiota. Transl. Psychiatry 6:e774.
Holmes, E., Kinross, J., Gibson, G. R., Burcelin, R., Jia, W., Pettersson, S., et al. (2012). Therapeutic modulation of microbiota-host metabolic interactions. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:137rv6.
Hoyles, L., Snelling, T., Umlai, U. K., Nicholson, J. K., Carding, S. R., Glen, R. C., et al. (2018). Microbiome-host systems interactions: protective effects of propionate upon the blood-brain barrier. Microbiome 6:55. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0439-y
Hsiao, E. Y., McBride, S. W., Hsien, S., Sharon, G., Hyde, E. R., McCue, T., et al. (2013). Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 155, 1451–1463.
Huang, K. Y., Wang, F. Y., Lv, M., Ma, X. X., Tang, X. D., and Lv, L. (2023). Irritable bowel syndrome: epidemiology, overlap disorders, pathophysiology and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 29, 4120–4135.
Hung, L. Y., and Margolis, K. G. (2024). Autism spectrum disorders and the gastrointestinal tract: insights into mechanisms and clinical relevance. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 21, 142–163. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00857-1
Imperial College London (2024a). Imperial College London, Biological Chemistry. Available online at: https://profiles.imperial.ac.uk/j.nicholson (accessed December 15, 2024).
Imperial College London (2024b). Imperial College London, Chemical Biology. Available online at: https://profiles.imperial.ac.uk/elaine.holmes (accessed December 15, 2024).
Iniguez-Gutierrez, L., Godinez-Mendez, L. A., Fafutis-Morris, M., Padilla-Arellano, J. R., Corona-Rivera, A., Bueno-Topete, M. R., et al. (2020). Physiological concentrations of short-chain fatty acids induce the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps in vitro. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 34:2058738420958949. doi: 10.1177/2058738420958949
Iovene, M. R., Bombace, F., Maresca, R., Sapone, A., Iardino, P., Picardi, A., et al. (2017). Intestinal dysbiosis and yeast isolation in stool of subjects with autism spectrum disorders. Mycopathologia 182, 349–363.
Jang, J. N., Dixon, D. R., Tarbox, J., and Granpeesheh, D. (2011). Symptom severity and challenging behavior in children with ASD. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 5, 1028–1032.
Jyonouchi, H., Sun, S. N., and Itokazu, N. (2002). Innate immunity associated with inflammatory responses and cytokine production against common dietary proteins in patients with autism spectrum disorder. Neuropsychobiology 46, 76–84. doi: 10.1159/000065416
Kang, D. W., Adams, J. B., Coleman, D. M., Pollard, E. L., Maldonado, J., McDonough-Means, S., et al. (2019). Long-term benefit of Microbiota Transfer Therapy on autism symptoms and gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 9:5821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42183-0
Kang, D. W., Adams, J. B., Gregory, A. C., Borody, T., Chittick, L., Fasano, A., et al. (2017). Microbiota Transfer Therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: an open-label study. Microbiome 5:10.
Kang, D. W., Ilhan, Z. E., Isern, N. G., Hoyt, D. W., Howsmon, D. P., Shaffer, M., et al. (2018). Differences in fecal microbial metabolites and microbiota of children with autism spectrum disorders. Anaerobe 49, 121–131.
Kang, D. W., Park, J. G., Ilhan, Z. E., Wallstrom, G., LaBaer, J., Adams, J. B., et al. (2013). Reduced incidence of prevotella and other fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic children. PLoS One 8:e68322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068322
Kho, Z. Y., and Lal, S. K. (2018). The human gut microbiome - a potential controller of wellness and disease. Front. Microbiol. 9:1835. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01835
Kim, S., Kim, H., Yim, Y. S., Ha, S., Atarashi, K., Tan, T. G., et al. (2017). Maternal gut bacteria promote neurodevelopmental abnormalities in mouse offspring. Nature 549:528–532.
Knight, R., Callewaert, C., Marotz, C., Hyde, E. R., Debelius, J. W., McDonald, D., et al. (2017). The microbiome and human biology. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 18, 65–86.
Lagod, P. P., and Naser, S. A. (2023). The role of short-chain fatty acids and altered microbiota composition in autism spectrum disorder: a comprehensive literature review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:17432. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417432
Landreneau, J. P., Weaver, M., Delaney, C. P., Aminian, A., Dimick, J. B., Lillemoe, K. D., et al. (2020). The 100 most cited papers in the history of the American surgical association. Ann. Surg. 271, 663–670.
LaPelusa, M., Donoviel, D., Branzini, S. E., Carlson, P. E. Jr., Culler, S., Cheema, A. K., et al. (2021). Microbiome for Mars: surveying microbiome connections to healthcare with implications for long-duration human spaceflight, virtual workshop, July 13, 2020. Microbiome 9:2. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00951-5
Lees, H. J., Swann, J. R., Wilson, I. D., Nicholson, J. K., and Holmes, E. (2013). Hippurate: the natural history of a mammalian-microbial cometabolite. J. Proteome Res. 12, 1527–1546. doi: 10.1021/pr300900b
Lewandowska-Pietruszka, Z., Figlerowicz, M., and Mazur-Melewska, K. (2023). Microbiota in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:16660.
Li, G., Song, B., Wang, C., Tang, D., Li, K., He, X., et al. (2022). Diet, microbe, and autism: cause or consequence? Cell Host Microbe 30, 5–7.
Li, Q. R., Han, Y., Dy, A. B. C., and Hagerman, R. J. (2017). The gut microbiota and autism spectrum disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 11:120. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00120
Li, X., Hao, X., Chen, C., Zhai, C., Pan, T., Zhou, X., et al. (2024). Trends and hotspots on the relationship between gut microbiota and Parkinson’s Disease: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 14:1421270. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1421270
Liu, F. T., Li, J., Wu, F., Zheng, H. M., Peng, Q. L., and Zhou, H. W. (2019). Altered composition and function of intestinal microbiota in autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review. Transl. Psychiatry 9:43.
Liu, S. M., Li, E. Y., Sun, Z. Y., Fu, D. J., Duan, G. Q., Jiang, M. M., et al. (2019). Altered gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids in Chinese children with autism spectrum disorder. Sci. Rep. 9:287.
Liu, X. F., Cao, S. Q., and Zhang, X. W. (2015). Modulation of gut microbiota brain axis by probiotics, prebiotics, and diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63, 7885–7895.
Long-Smith, C., O’Riordan, K. J., Clarke, G., Stanton, C., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2020). Microbiota-gut-brain axis: new therapeutic opportunities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 60, 477–502.
Luczynski, P., Neufeld, K. A. M., Oriach, C. S., Clarke, G., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2016). Growing up in a bubble: using germ-free animals to assess the influence of the gut microbiota on brain and behavior. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 19:pyw020. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw020
Luna, R. A., Oezguen, N., Balderas, M., Venkatachalam, A., Runge, J. K., Versalovic, J., et al. (2017). Distinct microbiome-neuroimmune signatures correlate with functional abdominal pain in children with autism spectrum disorder. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 3, 218–230. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2016.11.008
Ma, J., Zhao, K., Zhu, Y., Xu, W., Huang, J., Wei, X., et al. (2023). Bibliometric analysis of monoclonal antibodies for atherosclerosis. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 19:2266926.
Mangiola, F., Ianiro, G., Franceschi, F., Fagiuoli, S., Gasbarrini, G., and Gasbarrini, A. (2016). Gut microbiota in autism and mood disorders. World J. Gastroenterol. 22, 361–368.
Martin-Martin, A., Orduna-Malea, E., and Delgado, L.-C. E. (2018). Coverage of highly-cited documents in Google scholar, web of science, and Scopus: a multidisciplinary comparison. Scientometrics 116, 2175–2188. doi: 10.1007/s11192-020-03690-4
Matta, S. M., Hill-Yardin, E. L., and Crack, P. J. (2019). The influence of neuroinflammation in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 79, 75–90.
Mayer, E. A., Knight, R., Mazmanian, S. K., Cryan, J. F., and Tillisch, K. (2014a). Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience. J. Neurosci. 34, 15490–15496.
Mayer, E. A., Padua, D., and Tillisch, K. (2014b). Altered brain-gut axis in autism: comorbidity or causative mechanisms? Bioessays 36, 933–939.
Mayer, E. A., Tillisch, K., and Gupta, A. (2015). Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J. Clin. Invest. 125, 926–938.
Mazzone, L., Dooling, S. W., Volpe, E., Uljarevic, M., Waters, J. L., Sabatini, A., et al. (2024). Precision microbial intervention improves social behavior but not autism severity: a pilot double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Cell Host Microbe 32, 106–16.e6.
Meeking, M. M., MacFabe, D. F., Mepham, J. R., Foley, K. A., Tichenoff, L. J., Boon, F. H., et al. (2020). Propionic acid induced behavioural effects of relevance to autism spectrum disorder evaluated in the hole board test with rats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 97:109794. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109794
Ming, X., Stein, T. T. P., Barnes, V., Rhodes, N., and Guo, L. N. (2012). Metabolic perturbance in autism spectrum disorders: a metabolomics study. J. Proteome Res. 11, 5856–5862.
Moloney, R. D., Desbonnet, L., Clarke, G., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2014). The microbiome: stress, health and disease. Mamm. Genome 25, 49–74.
Morais, L. H., Schreiber, H. L., and Mazmanian, S. K. (2021). The gut microbiota-brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 241–255.
Mulle, J. G., Sharp, W. G., and Cubells, J. F. (2013). The gut microbiome: a new frontier in autism research. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 15:337.
Newell, C., Bomhof, M. R., Reimer, R. A., Hittel, D. S., Rho, J. M., and Shearer, J. (2016). Ketogenic diet modifies the gut microbiota in a murine model of autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 7:37. doi: 10.1186/s13229-016-0099-3
Nguyen, T. L. A., Vieira-Silva, S., Liston, A., and Raes, J. (2015). How informative is the mouse for human gut microbiota research? Dis. Model. Mech. 8, 1–16. doi: 10.1242/dmm.017400
Nishino, R., Mikami, K., Takahashi, H., Tomonaga, S., Furuse, M., Hiramoto, T., et al. (2013). Commensal microbiota modulate murine behaviors in a strictly contamination-free environment confirmed by culture-based methods. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 25, 521–528. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12110
Ouyang, Q., Yu, H., Xu, L., Yu, M., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Relationship between gut microbiota and multiple sclerosis: a scientometric visual analysis from 2010 to 2023. Front. Immunol. 15:1451742. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451742
Parracho, H., Bingham, M. O., Gibson, G. R., and McCartney, A. L. (2005). Differences between the gut microflora of children with autistic spectrum disorders and that of healthy children. J. Med. Microbiol. 54, 987–991.
Pärtty, A., Kalliomäki, M., Wacklin, P., Salminen, S., and Isolauri, E. (2015). A possible link between early probiotic intervention and the risk of neuropsychiatric disorders later in childhood: a randomized trial. Pediatr. Res. 77, 823–828. doi: 10.1038/pr.2015.51
Penzol, M. J., Salazar de Pablo, G., Llorente, C., Moreno, C., Hernandez, P., Dorado, M. L., et al. (2019). Functional gastrointestinal disease in autism spectrum disorder: a retrospective descriptive study in a clinical sample. Front. Psychiatry 10:179. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00179
Perna, J., Bellato, A., Ganapathy, P. S., Solmi, M., Zampieri, A., Faraone, S. V., et al. (2023). Association between Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and vision problems. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry. 28, 5011–5023.
Petra, A. I., Panagiotidou, S., Hatziagelaki, E., Stewart, J. M., Conti, P., and Theoharides, T. C. (2015). Gut-microbiota-brain axis and its effect on neuropsychiatric disorders with suspected immune dysregulation. Clin. Ther. 37, 984–995. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.04.002
Portincasa, P., Bonfrate, L., Vacca, M., De Angelis, M., Farella, I., Lanza, E., et al. (2022). Gut microbiota and short chain fatty acids: implications in glucose homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1105.
Pulikkan, J., Maji, A., Dhakan, D. B., Saxena, R., Mohan, B., Anto, M. M., et al. (2018). Gut microbial dysbiosis in indian children with autism spectrum disorders. Microb. Ecol. 76, 1102–1114. doi: 10.1007/s00248-018-1176-2
Quan, L., Dai, J., Luo, Y., Wang, L., Liu, Y., Meng, J., et al. (2024). The 100 top-cited studies in systemic lupus erythematosus: a bibliometric analysis. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 20:2387461. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2387461
Ring, J., Castanov, V., McLaren, C., Hajjar, A. E. J., and Jeschke, M. G. (2020). Scientific impact and clinical influence: identifying landmark studies in burns. J. Burn Care Res. 41, 1240–1252. doi: 10.1093/jbcr/iraa083
Rinninella, E., Raoul, P., Cintoni, M., Franceschi, F., Miggiano, G. A. D., Gasbarrini, A., et al. (2019). What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms 7:14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7010014
Riviere, A., Selak, M., Lantin, D., Leroy, F., and De Vuyst, L. (2016). Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut. Front. microbiol. 7:979. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00979
Rogge, N., and Janssen, J. (2019). The economic costs of autism spectrum disorder: a literature review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 49, 2873–2900.
Sampson, T. R., and Mazmanian, S. K. (2015). Control of brain development Function, and Behavior by the Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 17, 565–576.
Sandler, R. H., Finegold, S. M., Bolte, E. R., Buchanan, C. P., Maxwell, A. P., Väisänen, M. L., et al. (2000). Short-term benefit from oral vancomycin treatment of regressive-onset autism. J. Child Neurol. 15, 429–435. doi: 10.1177/088307380001500701
Schmallenbach, L., Barnighausen, T. W., and Lerchenmueller, M. J. (2024). The global geography of artificial intelligence in life science research. Nat. Commun. 15:7527.
Schonfeld, P., and Wojtczak, L. (2016). Short- and medium-chain fatty acids in energy metabolism: the cellular perspective. J. Lipid Res. 57, 943–954. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R067629
Sgritta, M., Dooling, S. W., Buffington, S. A., Momin, E. N., Francis, M. B., Britton, R. A., et al. (2019). Mechanisms underlying microbial-mediated changes in social behavior in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder. Neuron 101:246–259.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.018
Sharon, G., Cruz, N. J., Kang, D. W., Gandal, M. J., Wang, B., Kim, Y. M., et al. (2019). Human gut microbiota from autism spectrum disorder promote behavioral symptoms in mice. Cell 177, 1600–18.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.004
Sharon, G., Sampson, T. R., Geschwind, D. H., and Mazmanian, S. K. (2016). The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell. 167, 915–932.
Sherwin, E., Bordenstein, S. R., Quinn, J. L., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2019). Microbiota and the social brain. Science 366:587.
Sherwin, E., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2018). Recent developments in understanding the role of the gut microbiota in brain health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1420, 5–25. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13416
Sherwin, E., Sandhu, K. V., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2016). May the force be with you: the light and dark sides of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in neuropsychiatry. CNS Drugs 30, 1019–1041. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0370-3
Song, Y. L., Liu, C. X., and Finegold, S. A. (2004). Real-time PCR quantitation of clostridia in Feces of autistic children. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 6459–6465.
Spielman, L. J., Gibson, D. L., and Klegeris, A. (2018). Unhealthy gut, unhealthy brain: the role of the intestinal microbiota in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem. Int. 120, 149–163.
Srikantha, P., and Mohajeri, M. H. (2019). The possible role of the microbiota-gut-brain-axis in autism spectrum disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:2115.
Stilling, R. M., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2014). Microbial genes, brain & behaviour - epigenetic regulation of the gut-brain axis. Genes Brain Behav. 13, 69–86.
Strati, F., Cavalieri, D., Albanese, D., De Felice, C., Donati, C., Hayek, J., et al. (2017). New evidences on the altered gut microbiota in autism spectrum disorders. Microbiome 5:24.
Swiss Institute of Allergy and Asthma Research (2024). Immunology. Available online at: https://www.siaf.uzh.ch/immunology.html& (accessed December 15, 2024).
Tomaszewski, R. (2023). Visibility, impact, and applications of bibliometric software tools through citation analysis. Scientometrics 128, 4007–4028. doi: 10.1007/s11192-023-04725-2
Tomova, A., Husarova, V., Lakatosova, S., Bakos, J., Vlkova, B., Babinska, K., et al. (2015). Gastrointestinal microbiota in children with autism in Slovakia. Physiol. Behav. 138, 179–187.
UCLA Brain Research Institute (2024). Available online at: https://bri.ucla.edu/people/emeran-mayer/ (accessed December 15, 2024).
UCLA Health (2024). Available online at: https://www.uclahealth.org/providers/kirsten-tillisch (accessed December 15, 2024).
University College Cork (2024). Available online at: https://research.ucc.ie/profiles/2001/t.dinan@ucc.ie#section1 (accessed December 15, 2024).
Vendrik, K. E. W., Ooijevaar, R. E., de Jong, P. R. C., Laman, J. D., van Oosten, B. W., van Hilten, J. J., et al. (2020). Fecal microbiota transplantation in neurological disorders. Front. Cell Infect. 10:98. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00098
Vohra, R., Madhavan, S., and Sambamoorthi, U. (2017). Comorbidity prevalence, healthcare utilization, and expenditures of Medicaid enrolled adults with autism spectrum disorders. Autism 21, 995–1009. doi: 10.1177/1362361316665222
Vuong, H. E., and Hsiao, E. Y. (2017). Emerging roles for the gut microbiome in autism spectrum disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 81, 411–423.
Vuong, H. E., Yano, J. M., Fung, T. C., and Hsiao, E. Y. (2017). The microbiome and host behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 40, 21–49.
Wan, Q., Liu, K., Wang, X., Luo, S., Yuan, X., Wang, C., et al. (2022). The top 100 most cited papers in insomnia: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Psychiatry 13:1040807. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1040807
Wang, A., Zhao, J., Qin, Y., Zhang, Y., Xing, Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Alterations of the gut microbiota in the lupus nephritis: a systematic review. Ren Fail. 45:2285877. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2285877
Wang, H. Y., Lee, I. S., Braun, C., and Enck, P. (2016). Effect of probiotics on central nervous system functions in animals and humans: a systematic review. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 22, 589–605.
Wang, L., Christophersen, C. T., Sorich, M. J., Gerber, J. P., Angley, M. T., and Conlon, M. A. (2011). Low Relative abundances of the mucolytic bacterium Akkermansia muciniphila and Bifidobacterium spp. in feces of children with autism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 6718–6721. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05212-11
Wang, L., Christophersen, C. T., Sorich, M. J., Gerber, J. P., Angley, M. T., and Conlon, M. A. (2013). Increased abundance of Sutterella spp. and Ruminococcus torques in feces of children with autism spectrum disorder. Mol. Autism 4:42. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-42
Wang, L., Christophersen, C. T., Sorich, M. J., Gerber, J. P., Angley, M. T., and Conlon, M. A. (2012). Elevated fecal short chain fatty acid and ammonia concentrations in children with autism spectrum disorder. Dig. Dis. Sci. 57, 2096–2102. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2167-7
Wang, M., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Jian, E., Ye, P., Jiang, H., et al. (2024). Research trends between childhood obesity and gut microbiota: a bibliometric analysis (2002-2023). Front. Microbiol. 15:1461306. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1461306
Wang, Q., Yang, Q., and Liu, X. (2023). The microbiota-gut-brain axis and neurodevelopmental disorders. Protein Cell 14, 762–775.
Wang, R., Huang, S., Wang, P., Shi, X., Li, S., Ye, Y., et al. (2024). Bibliometric analysis of the application of deep learning in cancer from 2015 to 2023. Cancer Imaging 24:85. doi: 10.1186/s40644-024-00737-0
Wang, Y., and Kasper, L. H. (2014). The role of microbiome in central nervous system disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 38, 1–12.
Williams, B. L., Hornig, M., Buie, T., Bauman, M. L., Paik, M. C., Wick, I., et al. (2011). Impaired carbohydrate digestion and transport and mucosal dysbiosis in the intestines of children with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. PLoS One 6:e24585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024585
Williams, B. L., Hornig, M., Parekh, T., and Lipkin, W. I. (2012). Application of novel PCR-based methods for detection, quantitation, and phylogenetic characterization of Sutterella species in intestinal biopsy samples from children with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. Mbio 3::e00261–11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00261-11
Yadegar, A., Bar-Yoseph, H., Monaghan, T. M., Pakpour, S., Severino, A., Kuijper, E. J., et al. (2024). Fecal microbiota transplantation: current challenges and future landscapes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 37:e0006022. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00060-22
Yang, C., Lin, X., Wang, X., Liu, H., Huang, J., and Wang, S. (2022). The schizophrenia and gut microbiota: a bibliometric and visual analysis. Front. Psychiatry 13:1022472. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1022472
Yap, I. K. S., Angley, M., Veselkov, K. A., Holmes, E., Lindon, J. C., and Nicholson, J. K. (2010). Urinary metabolic phenotyping differentiates children with autism from their unaffected siblings and age-matched controls. J. Proteome Res. 9, 2996–3004. doi: 10.1021/pr901188e
Ying, J., Tan, G. M. Y., and Zhang, M. W. (2022). Intellectual disability and COVID-19: a bibliometric review. Front. Psychiatry. 13:1052929. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1052929
Zeidan, J., Fombonne, E., Scorah, J., Ibrahim, A., Durkin, M. S., Saxena, S., et al. (2022). Global prevalence of autism: a systematic review update. Autism Res. 15, 778–790.
Zhang, M., Ma, W., Zhang, J., He, Y., and Wang, J. (2018). Analysis of gut microbiota profiles and microbe-disease associations in children with autism spectrum disorders in China. Sci. Rep. 8:13981. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32219-2
Zhang, Y. J., Li, S., Gan, R. Y., Zhou, T., Xu, D. P., and Li, H. B. (2015). Impacts of gut bacteria on human health and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 7493–7519.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, autism, gut microbiota, research trends, citations
Citation: Ying J, Zhang MW, Wei K-C, Wong SH and Subramaniam M (2025) Influential articles in autism and gut microbiota: bibliometric profile and research trends. Front. Microbiol. 15:1401597. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1401597
Received: 16 April 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 09 January 2025.
Edited by:
Yu Wang, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Bikash Sahay, University of Florida, United StatesJelena Djokic, University of Belgrade, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Ying, Zhang, Wei, Wong and Subramaniam. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sunny H. Wong, c3Vubnkud29uZ0BudHUuZWR1LnNn; Mythily Subramaniam, bXl0aGlseUBpbWguY29tLnNn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share senior authorship
 Jiangbo Ying
Jiangbo Ying Melvyn Weibin Zhang
Melvyn Weibin Zhang Ker-Chiah Wei1
Ker-Chiah Wei1 Sunny H. Wong
Sunny H. Wong Mythily Subramaniam
Mythily Subramaniam