
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol., 08 June 2022
Sec. Antimicrobials, Resistance and Chemotherapy
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.925291
This article is part of the Research TopicDiscovery of Novel Plant-Derived Compounds with Antibacterial Actions Against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria, Volume IIView all 5 articles
 Yanlong Wen1,2,3
Yanlong Wen1,2,3 Wenyun Li1,2,3
Wenyun Li1,2,3 Rongzhen Su1
Rongzhen Su1 Min Yang1,2,3
Min Yang1,2,3 Nan Zhang1
Nan Zhang1 Ximing Li1,2,3
Ximing Li1,2,3 Lingfei Li1,3,4*
Lingfei Li1,3,4* Jun Sheng2,3*
Jun Sheng2,3* Yang Tian1,2,3,4*
Yang Tian1,2,3,4*Moringin [4-(α-L-rhamnosyloxy) benzyl isothiocyanate] is an isothiocyanate from Moringa oleifera seeds. It is the bioactivated form of the glucosinolate precursor glucomoringin with various health benefits. However, few studies have examined the antibacterial activity of moringin. This study aimed to investigate the antimicrobial activity and mechanism of moringin against Listeria monocytogenes. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and growth curves were used to evaluate the bacteriostatic effect of moringin against L. monocytogenes. Transcriptome analysis by RNA sequencing was performed to elucidate the underlying mechanism of moringin against L. monocytogenes. The transcriptome results were validated. The results showed that moringin inhibited the growth of L. monocytogenes with a MIC of 400 μM. RNA sequencing results showed that the differences in the expression of genes related to the cell wall and membrane biosynthesis, phosphotransferase system (PTS), oxidative stress, energy metabolism, and DNA binding were significantly affected. As with the transcriptome results, the results of the mechanism verification found that moringin damaged the integrity of the cell wall and cell membrane, stimulated oxidative stress, interfered with energy metabolism and DNA replication, and finally led to the death of L. monocytogenes. The present study provides evidence that moringin exhibits strong antimicrobial activity against L. monocytogenes and insight into its potential mechanism.
Listeria monocytogenes, a partly anaerobic gram-positive bacillus, is widely found in water, soil, and plants (Gasanov et al., 2005; Wu et al., 2021). L. monocytogenes can contaminate foods, such as milk (Hunt et al., 2017), meat products (Liu et al., 2019), and vegetables (Beuchat, 1996). It can grow during processing and transportation and survive low temperatures and harsh conditions (Low and Donachie, 1997; Zhao et al., 2020b). L. monocytogenes is a zoonotic bacterium that can cause meningitis, sepsis, gastroenteritis, and other diseases in humans and animals (Portnoy et al., 1992; Low and Donachie, 1997). From 2013 to 2017, a total of 211 cases of L. monocytogenes infection were reported by the China Foodborne Disease Surveillance Network, and the number is increasing year by year (Li et al., 2019b). Human listeriosis, which is caused by the pathogen L. monocytogenes, accounts for approximately 1,600 cases and 250 deaths per year in the United States (Scallan et al., 2011). Between 2017 and 2018, there were 978 listeriosis cases recorded in South Africa, resulting in 183 deaths (Vhiriri et al., 2020). In addition, listeriosis caused by L. monocytogenes is ranked by the World Health Organization (WHO) as one of the deadliest food-borne diseases, and it has a 20–30% mortality rate (Mpondo et al., 2021), making it severe public health concern posing a great threat to human health.
Generally, antibiotics or chemical preservatives are used to inhibit L. monocytogenes. However, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics and chemical preservatives may cause adverse side effects on humans that are more harmful than the microbes themselves (Tian et al., 2012; Ordoñez et al., 2022). The emergence of safety risks from antibiotic-resistant bacteria and the risks of using chemical preservatives have both received increasing attention. Currently, thermal sterilization is the primary technical means of ensuring food safety. However, excessive heating can destroy heat-sensitive nutrients in foods (Mangundayao and Yasurin, 2017). Therefore, research on natural and safe antibacterial substances has become a priority.
Isothiocyanates (ITCs) are a class of sulfur-containing organic compound widely found in cruciferous plants that have biological activities, such as antibacterial (Romeo et al., 2018a,b), antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects (Burčul et al., 2018). Some isothiocyanates, such as allyl isothiocyanate, benzyl isothiocyanate, phenethyl isothiocyanate, and sulforaphane, have been shown to possess substantial chemo-preventative activity against various human malignancies (Singh and Singh, 2012). Moringin is a structurally unique isothiocyanate with an additional sugar residue in the side chain. Moringa seeds are a better source of moringin and contain glucomoringin approximately 8–10% (Mathiron et al., 2018). Studies have shown that moringin has anti-inflammatory (Cheenpracha et al., 2010), hypotensive (Faizi et al., 1994), and anticancer (Giacoppo et al., 2017) activities. However, little has been reported on the antibacterial activity of moringin and its inhibitory mechanism.
In the present study, the antibacterial activity of moringin against L. monocytogenes was evaluated by inhibition zones, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), and growth curves, and the differential gene expression was analyzed by transcriptomic technology. Furthermore, the effects of moringin on the cell morphology, cell membrane integrity, oxidative stress, energy metabolism, and DNA of L. monocytogenes were investigated to elucidate the potential mechanism by which moringin inhibits L. monocytogenes.
The L. monocytogenes NDKM-NR-2019-034 used in the present study was isolated from bovine milk by our research group and identified using morphological and molecular biological methods. The strain was inoculated into the nutrient broth (NB) and cultured at 37°C for 18 h to the logarithmic growth phase. Moringin was obtained from Moringa seeds with reference to a previous method (Xie et al., 2021).
The antimicrobial effect of moringin against L. monocytogenes was examined via the broth microdilution method (Moreira et al., 2005). The suspension of L. monocytogenes (106 CFU/ml) was incubated with 50–400 μΜ of moringin in nutrient broth. The minimum concentration of added moringin that inhibits visible bacterial growth is defined as the MIC.
Growth curves were constructed according to the previously described method (Shi et al., 2016). The concentration of the bacterial solution was precisely adjusted to 106 CFU/ml, and 10 μl of inoculum solution was added to each well of the 96-well plate. An equal volume (240 μl) of NB containing different concentrations of moringin was added to each well to obtain the final concentrations of 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC, and the inoculum solution without moringin was used as the control. All plates were incubated at 37°C. Cell growth was monitored every 3 h by measuring the optical density at 600 nm with a BioTek microplate reader (Molecular Device, United States).
L. monocytogenes were treated with a 1/2 MIC concentration of moringin. Transcriptome sequencing analysis was performed on four treated samples and four control samples. The OD260/OD280 ratio of the RNA was determined using a Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher, United States). Prior to library formation, rRNA was removed using the Ribo-Zero rRNA Removal Kit (Epicentre, San Diego, CA, United States), and mRNAs were split into ~200 bp pieces using metal ions. The mRNA fragments were reverse transcribed into first-strand cDNA, followed by second-strand cDNA synthesis. Then, the UNG enzyme was used to digest the second-strand cDNA to generate libraries. Quality control was performed on the sequencing data, and low-quality reads were eliminated. Raw reads were filtered to generate clean reads and then submitted to bioinformatics analysis. The resulting high-quality reads were mapped onto the L. monocytogenes reference genome (accession No. GCA_004771175.1). The transcriptome sequencing data were analyzed using the free online platform of Majorbio Cloud Platform.1
To assess the accuracy of the transcriptome sequencing analysis, qRT-PCR validation was performed using the same RNA samples as were used for RNA-Seq. Some differentially expressed genes were chosen from the transcriptome analysis, and the relative expression levels of these genes were determined using the 2−ΔΔCT method after normalization, with 16S rRNA serving as the internal reference gene. The primer sequences used in this study are shown in Table 1.
The morphological changes of L. monocytogenes after treatment with moringin were observed by SEM. Bacterial cells were cultured with media containing 1/2 MIC and 1 MIC concentrations of moringin, respectively, without moringin as a control. Treated and non-treated bacteria were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. After incubation, cells were collected by centrifugation at 6,000 g for 10 min, washed three times with PBS buffer, and then incubated with 2.5% glutaraldehyde in PBS at 4°C overnight. Following three washes with PBS, samples were treated with ascending concentrations of ethanol (30, 50, 70, 80, 90, and 100%). The samples were vacuum freeze-dried, fixed on an SEM mount, sputter-coated with gold under a vacuum, and observed by FlexSEM 1000 SEM (Hitachi High-Technologies, Tokyo, Japan).
The effect of moringin on the cell membrane integrity of L. monocytogenes was detected by propidium iodide (PI) staining according to a previously reported method (Tang et al., 2010). Bacterial suspensions treated with different concentrations of moringin were incubated at 37°C for 24 h and then fixed with PI (final concentration of 10 μg/ml) for 20 min at 4°C in the dark. After that, bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation at 6,000 g for 10 min, washed with 0.85% NaCl solution, and resuspended in the same saline to reach a concentration of 1 × 106 CFU/ml before analysis. PI staining of the cells was observed with an inverted fluorescence microscope (Leica DMI 3000B, Germany).
Malondialdehyde (MDA) was determined by the microscale MDA assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) according to a previously described protocol (Kim et al., 2020). L. monocytogenes cells were collected by centrifugation at 6,000 rpm for 10 min (106 CFU/ml) and then washed twice with PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4). Cells treated with different concentrations of moringin (0, 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC) were resuspended in PBS and sonicated on ice. The remaining debris was removed by centrifugation at 15,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min. The supernatant was taken for MDA measurement according to the MDA assay kit’s instructions. The protein content was measured using a total protein quantitative assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China), using bovine serum albumin as the standard.
Intracellular ROS levels were measured using the Reactive Oxygen Species Assay Kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China) according to the instructions. Briefly, cells treated with different concentrations of moringin (0, 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC) were incubated with 20 μM dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) in Hanks’ balanced salt buffer for 30 min at 37°C. The ROS levels were measured using a fluorescence microplate reader (BioTek, HIM, United States) with an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 525 nm.
Molecular docking was performed using AutoDock Vina software (Trott and Olson, 2010). The crystal structure of DNA was obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank2 (PDB entry: 453D). The 3D structure of moringin was retrieved from PubChem.3 The input files were prepared by the AutodockTools 1.5.6 package (Sanner, 1999; Morris et al., 2009). Briefly, all water molecules and ligands inside the DNA model were removed, polar hydrogen atoms were added, and the Gasteiger charge was calculated. The binding sites were determined from the model’s intrinsic ligand (center_x = 15.117, center_y = 15.117, center_z = 8.718, size_x = 58, size_y = 56, size_z = 52). The grid box determination was conducted with a spacing of 0.375 Å. The final confirmation was selected according to the output binding affinity and calculated by Autodock Vina using its intrinsic AMBER forcefield scoring function. Interactions were analyzed by Ligplot+ software (Laskowski and Swindells, 2011) and visualized by PyMOL software.4
ATP was determined according to a modified method referenced elsewhere (Zou et al., 2015). Intracellular ATP was detected using an ATP assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). Cell suspensions (106 CFU/ml) were treated with four concentrations of moringin (0, 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC). Briefly, 100 μl of the enzyme working solution was added to each well of the 96-well plate, mixed thoroughly, and kept at room temperature for 5 min. Then, an L. monocytogenes solution containing 20 μl of ATP lysate was transferred to each well of a 96-well plate (containing the enzyme working solution) and mixed quickly with a pipette. After an interval of at least 2 s, the ATP levels were measured using a BioTek microplate reader (Molecular Device, United States).
The concentration of the L. monocytogenes solution was adjusted to 106 CFU/ml, washed three times with PBS, and then centrifuged at 3,000 g for 10 min, followed by resuspension in PBS. Different concentrations of moringin were added to make the final concentrations of 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC, with the moringin-free inoculum solution used as a control. The ATPase activity was measured as described previously with slight modifications according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China; Zhan et al., 2011).
The statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism 5.0 software. Comparisons between two groups were made using an independent t-test (two-tailed method), with a significance level of p < 0.05.
The inhibitory results of different concentrations of moringin on L. monocytogenes are presented in Table 2. After 24 h of incubation, no colony growth was observed in the moringin-containing plates when the mass concentration of moringin was 400 μM, indicating that the MIC of moringin on L. monocytogenes was 400 μM.
Different concentrations of moringin were used to treat L. monocytogenes to further investigate the inhibitory effect of moringin against L. monocytogenes (Figure 1). The results showed that 1 MIC and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin could completely inhibit the growth of L. monocytogenes, and 1/2 MIC also showed a certain inhibitory effect.
A total of 2,699 genes were detected in L. monocytogenes in the control and the moringin-treated groups. Among them, 38 and 117 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were unique to the control and the moringin-treated groups, respectively (Figure 2A). A total of 794 genes were upregulated, and 606 genes were downregulated (Figure 2B).
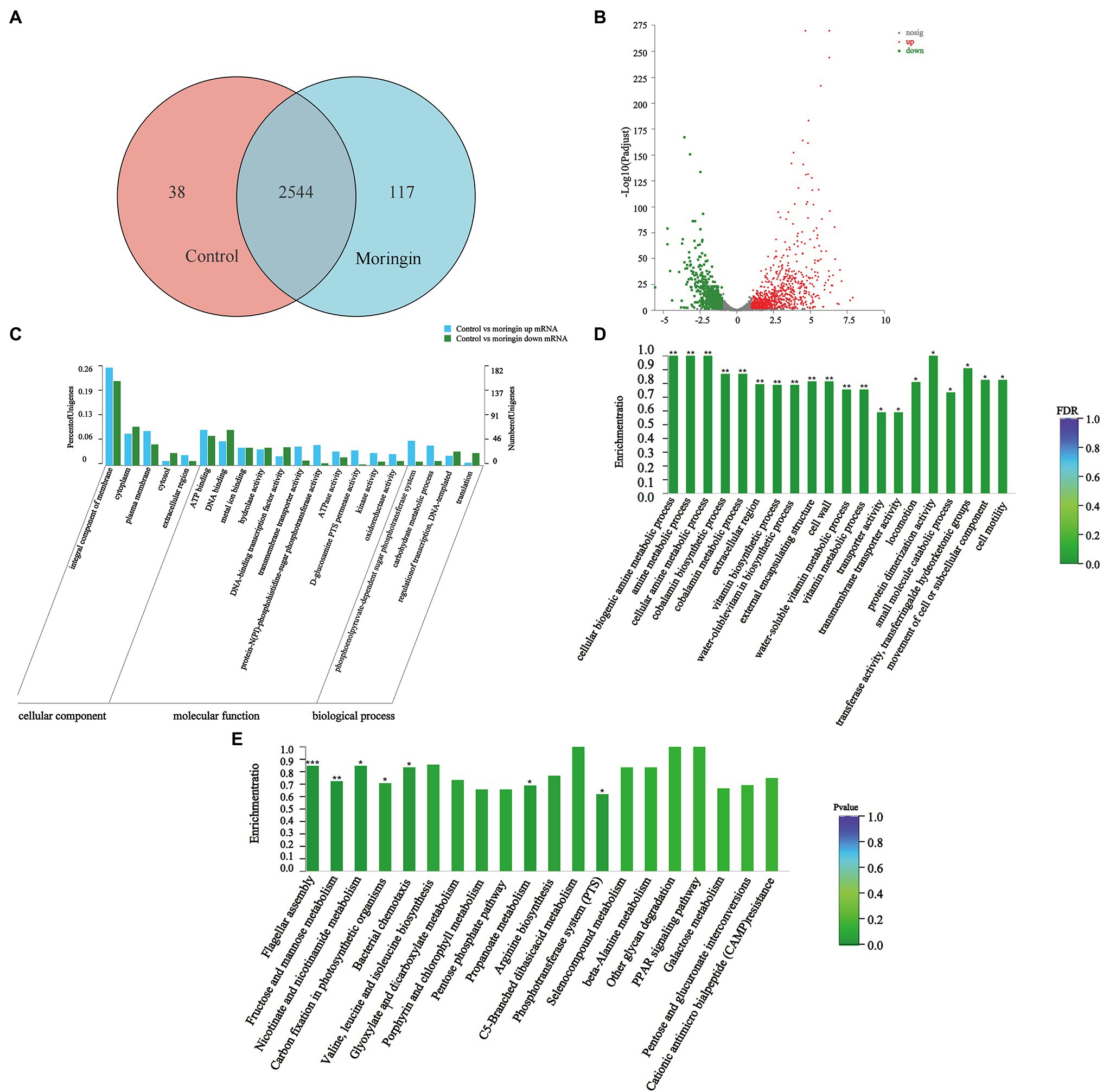
Figure 2. Transcriptome analyses of Listeria monocytogenes after treatment with moringin. (A) Venn diagram. (B) Percentages of up- and downregulated genes for each group indicated on a volcano plot. (C) GO classification of DEGs. (D) GO enrichment of DEGs. (E) Statistical enrichment of differentially expressed genes in KEGG pathways. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.
Figure 2C shows the gene ontology (GO) categorization of the up- and downregulated genes in the treated cells. For the cellular component categories, the majority of GO terms were related to the integral component of the membrane. For molecular function categories, most GO terms were associated with ATP binding and DNA binding. For biological process categories, most GO terms were related to the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar phosphotransferase system.
The enrichment of GO groups was evaluated to better visualize the findings (Figure 2D). Many genes involved in cellular components were altered, such as cell wall (GO:0005618), external encapsulating structure (GO:0030312), and extracellular region (GO:0005576). This suggested that exposure to moringin caused changes in cell structure and cellular components. In addition, the expression levels of biological process genes were significantly different in L. monocytogenes after moringin treatment, especially in the cellular biogenic amine metabolic process (GO:0006576), amine metabolic process (GO:0009308), and cellular amine metabolic process (GO:0044106), indicating that moringin affected the metabolism of L. monocytogenes.
Finding alterations in biological functions is crucial in determining how antimicrobial activity works. The biological roles of genes were studied at the molecular, cellular, and organism levels using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis (Figure 2E). In this study, seven pathways were found to be significantly enriched (p < 0.05) in L. monocytogenes after moringin treatment, including one from environmental information processing pathways, two from cellular processing pathways, and four from metabolism pathways. Nearly 57% of the pathways with significant alterations were associated with metabolism, suggesting that the mechanism by which L. monocytogenes was inhibited by moringin may involve metabolic changes in cells.
Additionally, a KEGG pathway analysis showed that moringin treatment affected peptidoglycan biosynthesis related to the L. monocytogenes cell wall structure and significantly downregulated the MurA and MurC genes (Supplementary Figure S1); significantly upregulated the PotA and PotD genes related to cell membrane integrity in the ABC transport system and significantly downregulated the opuA, opuB, and opuC genes (Supplementary Figure S2); significantly upregulated the FliH and FliI, FlgL and FlgK, CheA and Che genes related to cell movement (Supplementary Figures S3, S4); significantly upregulated phosphotransferase system MltA, GatA, GatB, and GatC genes (Supplementary Figure S5); and all genes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle related to energy metabolism were significantly downregulated (Supplementary Figure S6).
Seven DEGs (given in Table 1) were chosen for qRT-PCR assays to confirm the reliability of the RNA-Seq data. The results showed that the variation in trends of these seven genes based on qRT-PCR was consistent with those obtained by transcriptome sequencing (Figure 3A). The expression levels of the seven genes obtained by the transcriptomic analysis were positively correlated with those obtained by qRT-PCR (r = 0.90, p = 0.0048; Figure 3B).
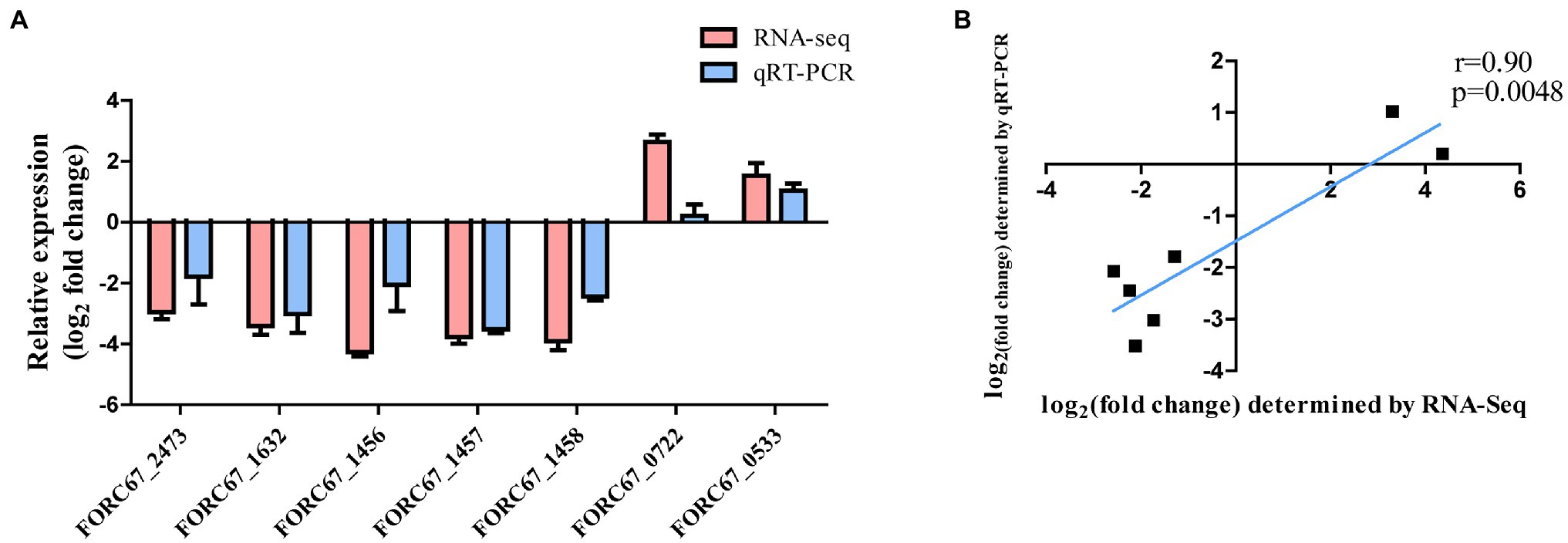
Figure 3. Comparison of RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR results. (A) Gene expression levels of RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR analysis. (B) Gene expression correlation analysis.
The cell membrane or cell wall is the integral component of all bacterial cells and is critical for bacterial protection. Once the outer membrane or cell wall of the bacteria is destroyed by physical or chemical action, the components of the cytoplasm leak out, resulting in bacteriostatic and bactericidal actions. Since the results of transcriptome sequencing showed that many genes involved in cellular components were altered after moringin treatment, the surface structure and morphology of L. monocytogenes were investigated by SEM. As shown in Figure 4, normal L. monocytogenes showed a rod-shaped, intact, round, and smooth surface. In contrast, after moringin treatment, the cell surface of L. monocytogenes was disrupted, the cells appeared wrinkled, the contents of cells leaked out, and many cells adhered together.
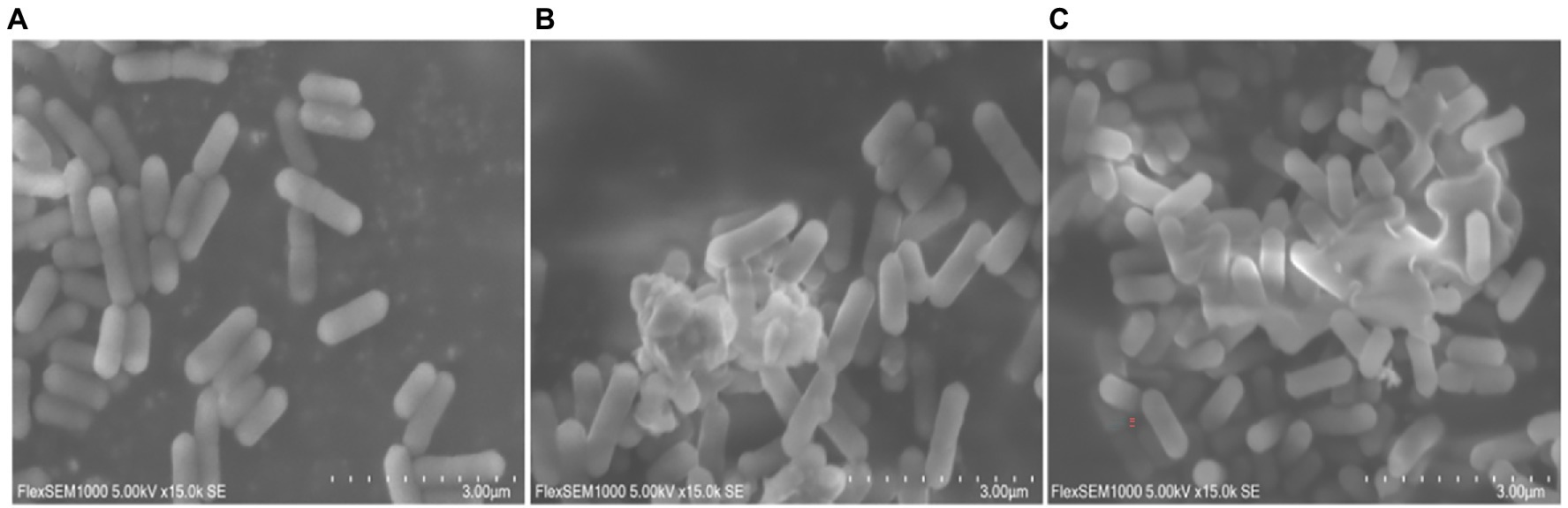
Figure 4. Effect of moringin on the surface structure and morphology of Listeria monocytogenes by SEM. (A) Untreated Listeria monocytogenes. (B) Listeria monocytogenes treated with moringin at 1/2 MIC. (C) Listeria monocytogenes treated with moringin at 1 MIC.
Propidium iodide (PI) dye can only penetrate the damaged cells and bind to nucleic acids, resulting in increased fluorescence intensity. The effect of moringin on the cell membrane integrity of L. monocytogenes was investigated by a fluorescence probe (Figure 5). The results showed that the fluorescence was enhanced with increasing chorismate concentration. This result indicated that 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin induced cell membrane damage, reduced cell membrane integrity, and increased cell membrane permeability. In addition, with increasing moringin concentration, the cell membrane damage of L. monocytogenes was enhanced.
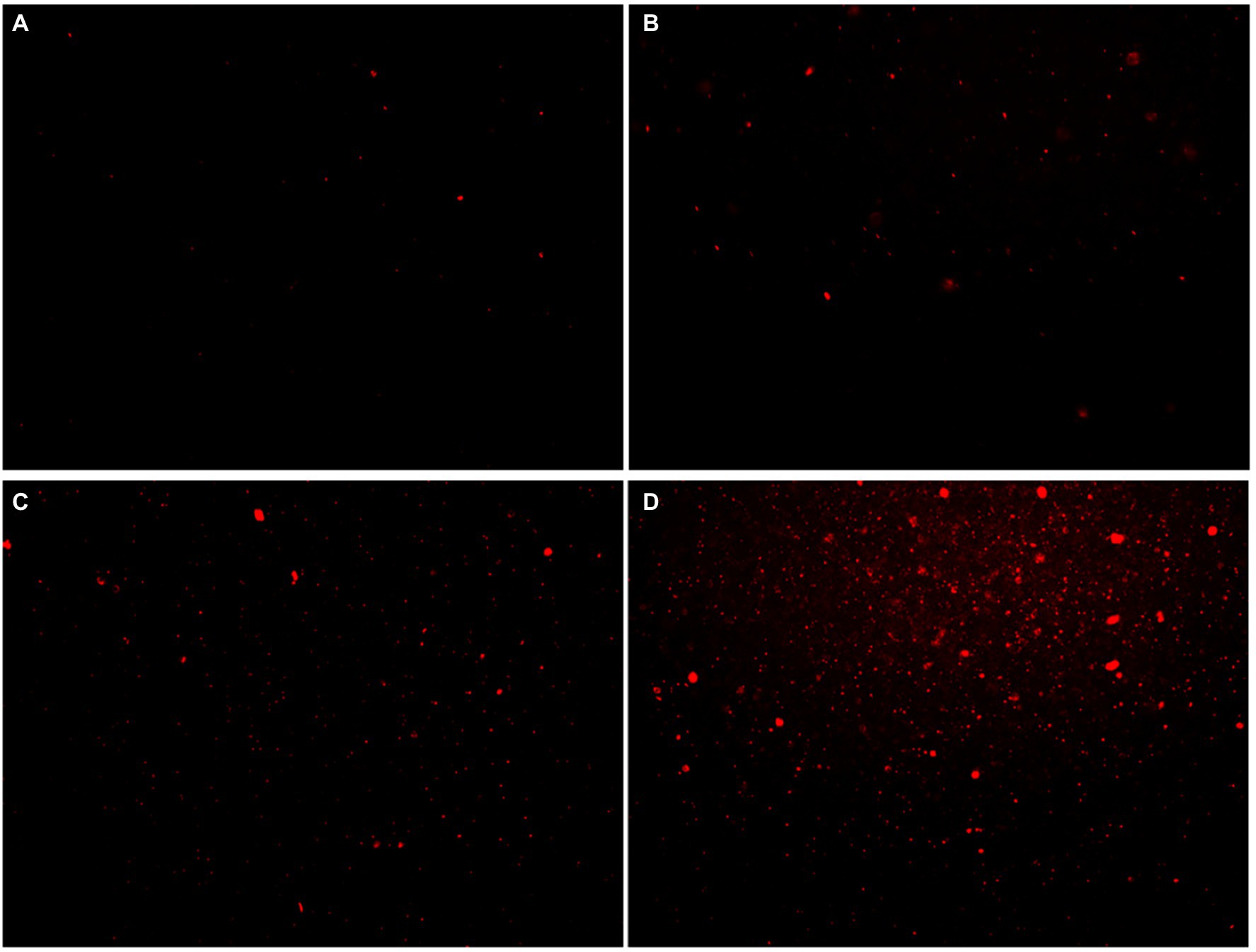
Figure 5. Effects of moringin on cell membrane integrity of Listeria monocytogenes by inverted fluorescence microscope. (A) Untreated Listeria monocytogenes. (B) Listeria monocytogenes treated with moringin at 1/2 MIC. (C) Listeria monocytogenes treated with moringin at 1 MIC. (D) Listeria monocytogenes treated with moringin at 2 MIC.
The transcriptome sequencing results suggested that moringin may induce oxidative stress in cells. The intracellular MDA contents and ROS activity were evaluated in this study. The MDA content results are shown in Figure 6A. After treatment with 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, or 2 MIC concentrations of moringin, the MDA levels were significantly increased due to oxidative stress injury (p < 0.001). Furthermore, in comparison with those of the control group, the ROS levels in cells were significantly higher after treatment with 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin (Figure 6B).
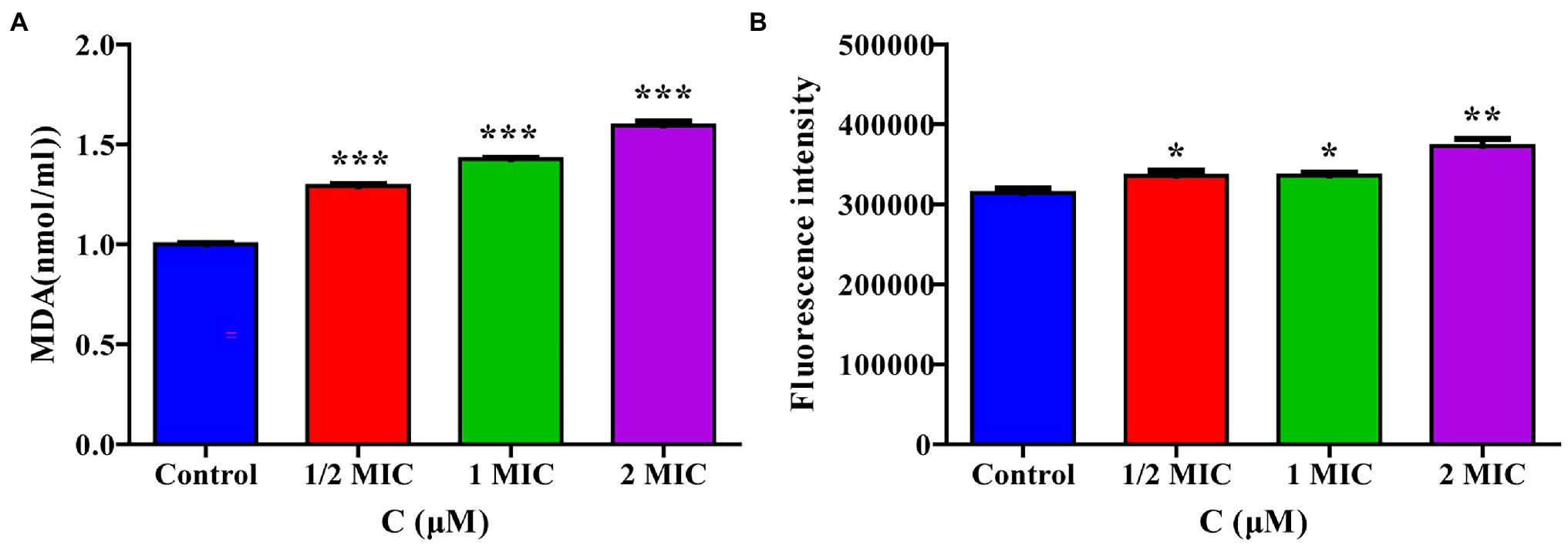
Figure 6. Effect of moringin on oxidative stress apoptosis in Listeria monocytogenes. (A) MDA level activity exposure to different concentrations of moringin. (B) ROS activity exposure to different concentrations of moringin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.
The above transcriptome sequencing results suggested that DNA binding-related genes were changed after the treatment of L. monocytogenes with moringin. Therefore, molecular mock docking of moringin and DNA was performed. DNA and moringin were relatively easily bound together, which showed that moringin fit into the grooves in the DNA (Figure 7A). Interaction analysis showed that moringin formed hydrogen bonds with DNA bases (Figure 7B). O6 of moringin formed a 2.78 Å hydrogen bond with G4 (A), a 3.28 Å hydrogen bond with C21 (B), and two hydrogen bonds with G22 (B), with lengths of 3.20 Å and 2.94 Å, respectively. Additionally, some hydrophobic interactions were observed between moringin and A5 (A), A6 (A), T7 (A), T20 (B), and C23 (B). The 3D visualization of the complex is shown in Figure 7C. Both the interaction analysis and the free energy calculation indicated that the binding between DNA and moringin was stable. As with the transcriptome analysis, moringin may insert into the DNA base pairs of L. monocytogenes and impede DNA replication.
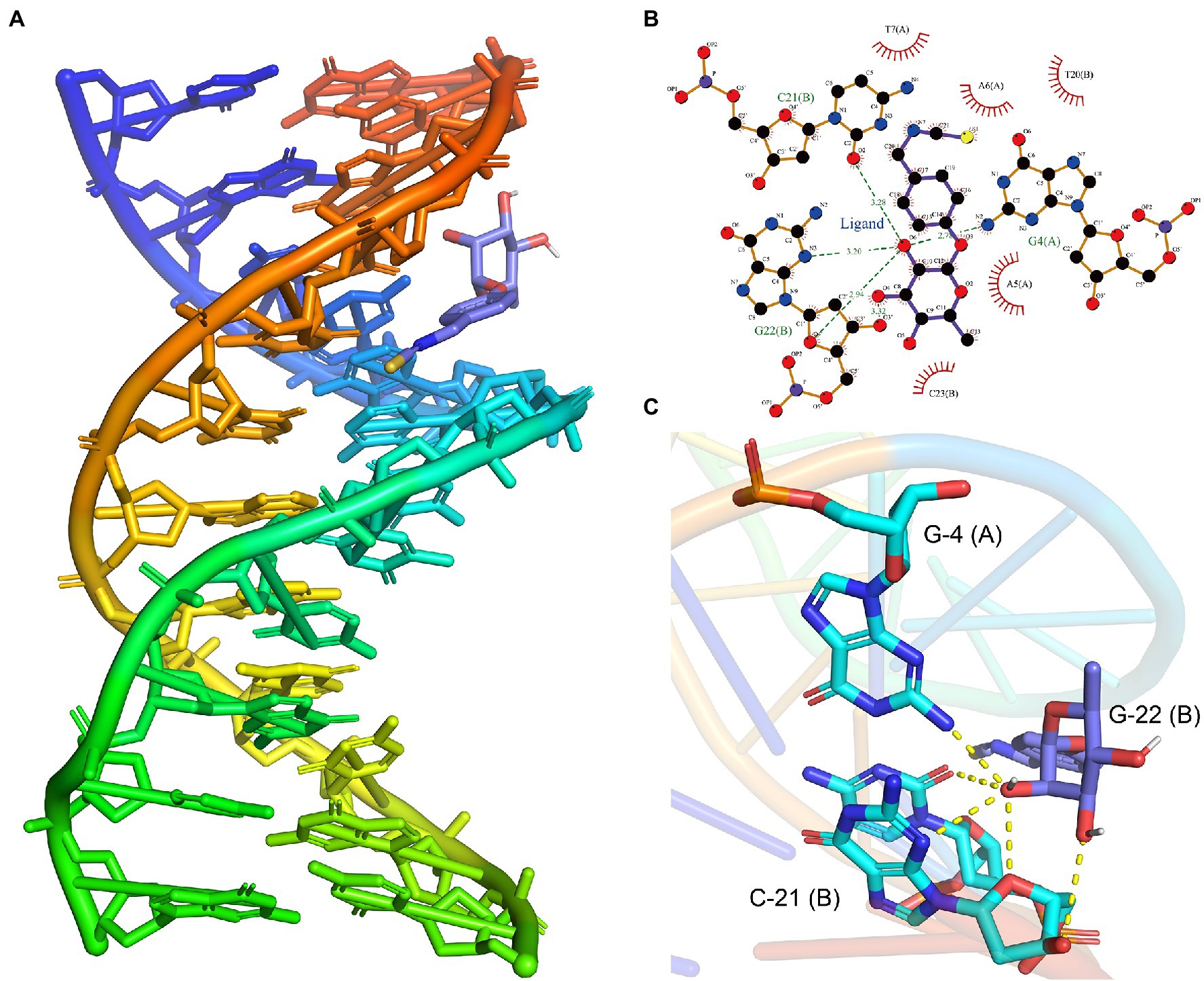
Figure 7. Effects of moringin on DNA of Listeria monocytogenes by molecular docking. (A) Binding poses between moringin and DNA. (B) The 2D plot of the interactions between moringin and DNA. (C) The 3D plot of the interactions, with different base names marked. The letters in parentheses represented different strands of DNA.
To verify the effect of moringin treatment on energy metabolism in L. monocytogenes, the intracellular ATP content and ATPase activity were measured. As shown in Figure 8A, the intracellular ATP concentrations in L. monocytogenes decreased significantly after treatment with 1 MIC and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin, compared with those of the control group.
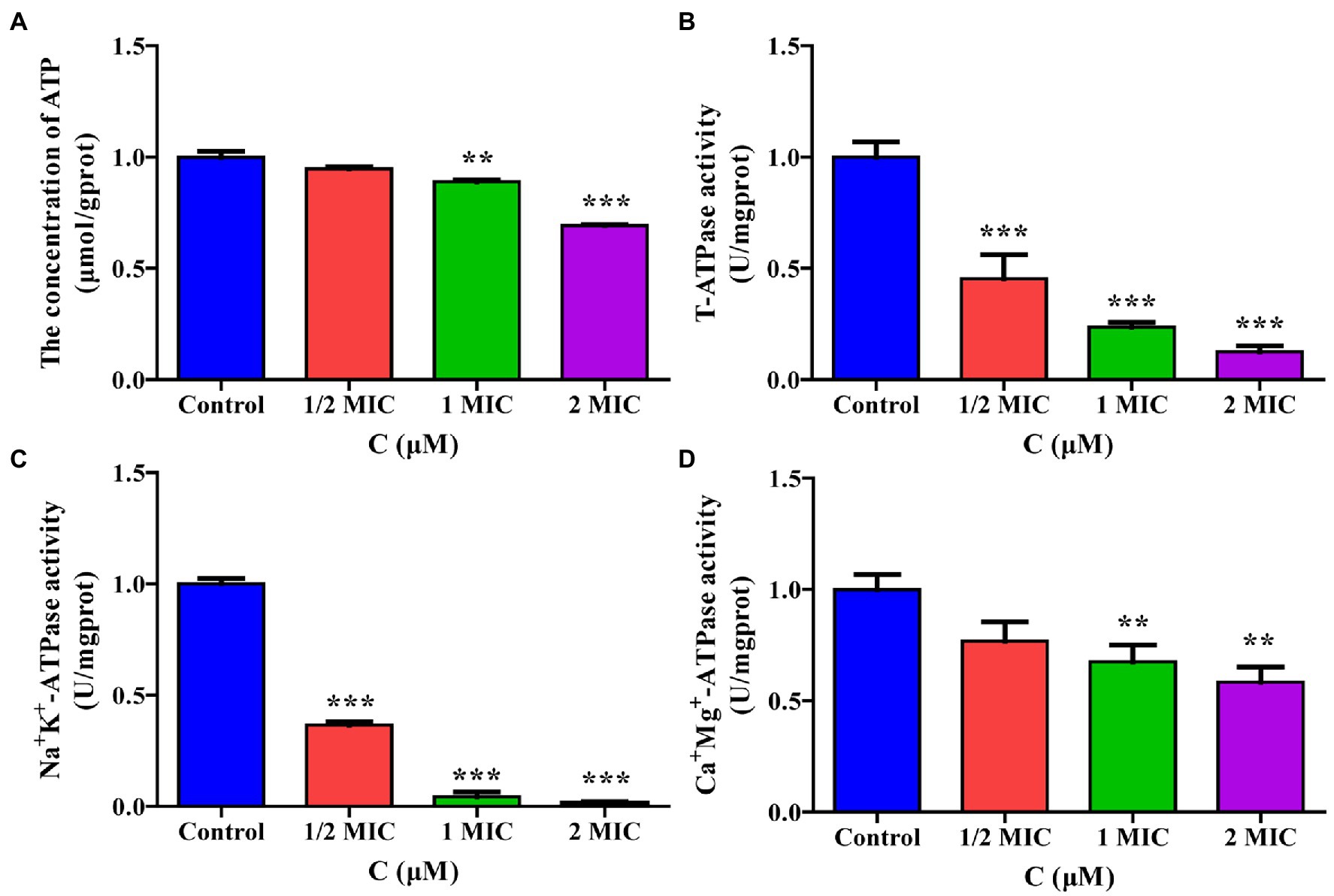
Figure 8. Effect of moringin on energy metabolism in Listeria monocytogenes. (A) ATP levels exposure to different concentrations of moringin. (B) T-ATPase activity exposure to different concentrations of moringin. (C) Na+K+-ATPase activity exposure to different concentrations of moringin. (D) Ca2+Mg2+-ATPase activity exposure to different concentrations of moringin. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.
The effect of moringin on the activities of total ATPase (T-ATPase), Na+K+-ATPase, and Ca+Mg+-ATPase of L. monocytogenes are shown in Figures 8B–D. The activities of T-ATPase and Na+K+-ATPase in L. monocytogenes were significantly decreased after treatment with 1/2 MIC, 1 MIC, and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin compared to those of the control group (p < 0.001; Figures 8B,C). Additionally, the Ca+Mg+-ATPase activity of L. monocytogenes was significantly decreased after treatment with 1 MIC and 2 MIC concentrations of moringin y (p < 0.01; Figure 8D).
Moringin results from the myrosinase hydrolysis of glucomoringin, the most abundant glucosinolate in Moringa oleifera seeds (Rajan et al., 2016). In this study, the antibacterial activity of moringin against the food-borne pathogen L. monocytogenes was investigated, and its mechanism was elucidated at the molecular level for the first time. We found that moringin inhibits the growth of L. monocytogenes by disrupting cell wall and cell membrane structure, stimulating oxidative stress, interfering with energy metabolism and DNA replication, and ultimately leading to its death. Understanding moringin’s antimicrobial action route will aid in its use in the food sector and boost the added value of M. oleifera seeds, which is critical for regional economic development.
In the present study, the MIC of moringin against L. monocytogenes was 400 μM (0.124 mg/ml; Table 2). Compared to that of phenyllactic acid (1.25 mg/ml; Ning et al., 2017) and the lectin from pomegranate sarcotesta (0.0125 mg/ml; Silva et al., 2021), moringin showed a moderate inhibitory effect against L. monocytogenes. Moringin is one of the isothiocyanates. Due to the structure of the carbon chains of isothiocyanates, they tend to have different MICs. For example, the MICs of phenylethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) against Shiga toxin-producing and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli were both 400 μmol/L (Yang et al., 2020). Other research has reported that the MIC of sulforaphene against Helicobacter pylori was 600 mg/ml (Lim et al., 2016). The strong antibacterial activity of moringin may be attributed to the fact that it is a isothiocyanate, like benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) and phenylethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC).
The transcriptome enables us to examine the whole response simultaneously and globally at the transcriptional level. Transcriptome technology has become a vital tool in the biological sciences (Masri et al., 2021). RNA-seq has sped research to better understand the complexities of gene expression, regulation, and networks (Daniel et al., 2015). We employed transcriptomic approaches to obtain a better understanding of the possible connections between moringin and L. monocytogenes. As demonstrated by comparing RNA-seq data from the experimental and control groups, moringin affects the integrity of cell walls and cell membranes, induces oxidative stress, and impairs energy metabolism and DNA replication. These results were subsequently verified through a validation of the antibacterial mechanism.
Peptidoglycan is the major component of bacterial cell walls and plays a crucial role in maintaining cell wall integrity and bacterial morphology (Typas et al., 2011). Peptidoglycan is considered a specific target for many drugs (Typas et al., 2011). In the present study, the transcriptomic results showed the MurA and MurC genes, which are associated with peptidoglycan biosynthesis, were significantly downregulated in the moringin-treated group (Supplementary Figure S1). As with the transcriptome results, SEM revealed that moringin treatment inhibited L. monocytogenes by disrupting the structure of the cell wall (Figure 4). ABC transporter proteins are a group of biological transport proteins with a wide range of functions in the plasma membrane of microorganisms. They are mainly responsible for the ATP-driven transport of various substrates across the membrane (Kafantaris et al., 2021). In this study, the ABC transporter was also regulated (Supplementary Figure S2). Spermidine and putrescine are important polyamines. Alterations in the transport capacity of polyamines may affect cell proliferation and differentiation (Kashiwagi et al., 1995, 1996). The PotA is a membrane-associated protein, and PotD is a periplasmic substrate-binding protein. The PotA and PotD genes are involved in the spermidine/putrescine transport system. Their expression levels were both upregulated in this study. In addition, genes for osmoprotectant, such as opuA, opuB, and opuC, were downregulated, suggesting that cells are affected by osmotic stress (Ko et al., 1994; Ko and Smith, 1999). The influxes of PI indicated that moringin damaged the membrane, decreasing its integrity and increasing its permeability (Figure 5). Cell wall and cell membrane have been extensively studied as antimicrobial targets. Once the structure of the cell wall and cell membrane is damaged, it leads to leakage of nucleic acids and proteins from the cell, causing irreversible damage and eventually cell death. The present study suggests that Moringin damaged the integrity cell wall of L. monocytogenes, and increased the permeability of the cell membrane. In agreement with our study, the study by Zhao et al. (2020a) also found significant changes in the permeability of the cell membrane of L. monocytogenes with increased nucleic acid and protein leakage when nisin and grape seed extract were combined.
Cell motility plays an essential role in host–microbe interactions. The colonization and virulence properties of bacteria include several biological processes, including signal transduction, chemotaxis, and flagellar motility (Vasconcelos et al., 2018). Flagellar motility and chemotaxis are two critical features of bacterial attachment that enable them to survive in various environments (Schurch et al., 2015). The flagellum comprises the basal part, the flagellar hook, and the flagellar filament. The basal body, which is embedded in the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane, acts as a molecular motor; the flagellar hook, which connects the motor spindle to the flagellar filament, acts as a torque transmitter; and the filament, which is driven by the motor, rotates and generates propulsive force to drive the bacteria (Tu et al., 2020). In this study, treatment with moringin resulted in significant upregulation of the FliH and FliI genes (Supplementary Figure S3), indicating that moringin may have inhibited the function of the flagellar energy export system of L. monocytogenes to some extent through the upregulation of these two genes. In turn, the FlgL and FlgK genes of flagellar hooks were also upregulated (Supplementary Figure S3), leading to an increase in bacterial motility. Interestingly, the genes CheA and CheY genes, which are associated with chemotaxis, were also significantly upregulated in L. monocytogenes after moringin treatment (Supplementary Figure S4). It is possible that L. monocytogenes transmits stimulus signals from the external environment to flagellin to respond to chemotaxis accordingly.
The phosphotransferase system (PTS) involves the uptake and phosphorylation of carbohydrates from the extracellular environment (Kotrba et al., 2001). In this study, the genes MltA, GatA, GatB, and GatC, which are related to the phosphotransferase system, were significantly upregulated after treatment with moringin, indicating an increase in carbohydrate uptake, which may be a self-protective strategy of L. monocytogenes to maintain carbohydrate metabolism for cellular energy supply under moringin stress (Supplementary Figure S5).
The oxidative stress response of pathogens to external stimuli is generally used to understand their acclimatization mechanisms (Maurya et al., 2020). In the present study, intracellular ROS and MDA production were increased (Figure 6), verifying that ROS and MDA-mediated oxidative stress played a significant role in the antimicrobial effect of moringin against L. monocytogenes. Previous studies have found that the generation of ROS could lead to DNA damage (Salehi et al., 2018). DNA is one of the most important genetic materials, and its disruption could hamper gene expression, thereby leading to the blocking of normal enzyme and receptor synthesis and further causing the death of bacteria (Li et al., 2019a). In this study, GO analysis showed that moringin could affect the DNA binding (Figure 2C). Thus, we further investigated the interaction of moringin with DNA by molecular docking (Figure 7). The results suggested that moringin could probably bind to DNA and lead to changes in DNA conformation and structure. Therefore, the results of this study indicated that DNA might be another antibacterial target of moringin, which enriched the knowledge of the antibacterial mechanism of moringin.
The energy balance in organisms can be severely affected by environmental stress, which requires additional energy to maintain or restore dynamic equilibrium (Wang et al., 2018). In most organisms, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) is a vital pathway for energy production (Korotetskiy et al., 2020). In this study, moringin downregulated the expression of all genes associated with the TCA cycle (Supplementary Figure S6) and upregulated most genes related to fructose, mannose, and propionate metabolism (Supplementary Figures S7, S8). ATP plays a key role in cellular energy metabolism. Our results demonstrated that the ATPase activity and the ATP content of cyanobacteria decreased significantly after treatment with moringin (Figure 8). Therefore, moringin may interfere with energy metabolism by affecting the carbohydrate metabolism of L. monocytogenes, further affecting the use of its catabolic products for cellular repair and thus inhibiting bacterial growth.
This research studied the antimicrobial effect and its potential mechanism of moringin against L. monocytogenes. Listeria monocytogenes is a highly dangerous bacterial pathogen that can cause a severe and often fatal disease, once persons are infected by it. Listeria innocua is an innocuous subspecies of Listeria with high morphological, serological, and biochemical characteristics similar to L. monocytogenes (Chen et al., 2019). Therefore, for safety reasons, L. innocua can be used as a suitable alternative for food safety research.
In summary, this study evaluated the inhibitory activity and mechanism of moringin against the food-borne pathogen L. monocytogenes. It was found that moringin inhibited the growth of L. monocytogenes in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The transcriptome results suggested that moringin significantly affected genes related to the cell wall and membrane, oxidative stress, energy metabolism, cell motility, and DNA binding. We further verified that, as with the transcriptomic results, moringin inhibited L. monocytogenes by disrupting the cell wall and membrane structure and composition, inducing oxidative stress, interfering with energy metabolism, affecting cell motility, and preventing DNA replication.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
YW: conceptualization, investigation, writing—original draft, and project administration. WL: investigation, methodology, and validation. RS, MY, XL, and NZ: validation. LL: conceptualization, supervision, writing—review and editing, and project administration. JS and YT: conceptualization, supervision, and project administration. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by the “Major Project of Science and Technology Department of Yunnan Province” (2018ZI001 and 202002AA100005), “YEFICRC project of Yunnan provincial key programs” (2019ZG009), and “Yunnan Province Young and Middle-aged Academic and Technical Leaders Reserve Talents Project” (2018HB040).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
This is a short text to acknowledge the contributions of specific colleagues, institutions, or agencies that aided the efforts of the authors.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.925291/full#supplementary-material
Beuchat, L. R. (1996). Listeria monocytogenes: incidence on vegetables. Food Control 7, 223–228. doi: 10.1016/S0956-7135(96)00039-4
Burčul, F., Generalić Mekinić, I., Radan, M., Rollin, P., and Blažević, I. (2018). Isothiocyanates: cholinesterase inhibiting, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 33, 577–582. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1442832
Cheenpracha, S., Park, E. J., Yoshida, W. Y., Barit, C., Wall, M., Pezzuto, J. M., et al. (2010). Potential anti-inflammatory phenolic glycosides from the medicinal plant Moringa oleifera fruits. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 6598–6602. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2010.03.057
Chen, L., Zhang, H., Liu, Q., Pang, X., Zhao, X., and Yang, H. (2019). Sanitising efficacy of lactic acid combined with low-concentration sodium hypochlorite on Listeria innocua in organic broccoli sprouts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 295, 41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.02.014
Daniel, S., Paniz-Mondolfi, A., and Monzon, F. (2015). Transcriptome Sequencing (RNA-Seq). New York: Springer.
Faizi, S., Siddiqui, B. S., Saleem, R., Siddiqui, S., Aftab, K., and Gilani, A. H. (1994). Isolation and structure elucidation of new nitrile and mustard oil glycosides from Moringa oleifera and their effect on blood pressure. J. Nat. Prod. 57, 1256–1261. doi: 10.1021/np50111a011
Gasanov, U., Hughes, D., and Hansbro, P. M. (2005). Methods for the isolation and identification of Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes: a review. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29, 851–875. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.002
Giacoppo, S., Iori, R., Rollin, P., Bramanti, P., and Mazzon, E. (2017). Moringa isothiocyanate complexed with α-cyclodextrin: a new perspective in neuroblastoma treatment. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17:362. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1876-z
Hunt, K., Butler, F., and Jordan, K. (2017). Uncoupling ‘growth’ and ‘increasing cell numbers’ of Listeria monocytogenes in naturally contaminated milk from a sub-clinically infected cow. Food Control 71, 228–233. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.07.002
Kafantaris, I., Tsadila, C., Nikolaidis, M., Tsavea, E., Dimitriou, T. G., Iliopoulos, I., et al. (2021). Transcriptomic analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa response to pine honey via RNA sequencing indicates multiple mechanisms of antibacterial activity. Foods 10:936. doi: 10.3390/foods10050936
Kashiwagi, K., Endo, H., Kobayashi, H., Takio, K., and Igarashi, K. (1995). Spermidine-preferential uptake system in Escherichia coli. ATP hydrolysis by PotA protein and its association with membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 25377–25382. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25377
Kashiwagi, K., Pistocchi, R., Shibuya, S., Sugiyama, S., Morikawa, K., and Igarashi, K. (1996). Spermidine-preferential uptake system in Escherichia coli. Identification of amino acids involved in polyamine binding in PotD protein. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12205–12208. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.21.12205
Kim, S., Woo, E. R., and Lee, D. G. (2020). Apigenin promotes antibacterial activity via regulation of nitric oxide and superoxide anion production. J. Basic Microbiol. 60, 862–872. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202000432
Ko, R., and Smith, L. T. (1999). Identification of an ATP-driven, osmoregulated glycine betaine transport system in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 4040–4048. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.9.4040-4048.1999
Ko, R., Smith, L. T., and Smith, G. M. (1994). Glycine betaine confers enhanced osmotolerance and cryotolerance on Listeria monocytogenes. J. Bacteriol. 176, 426–431. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.2.426-431.1994
Korotetskiy, I., Shilov, S., Reva, O., Kuznetsova, Т., Jumagaziyeva, A., Akhmatullina, N., et al. (2020). Gene expression profiling of multi-drug resistant E. coli after exposure by nanomolecular iodine-containing complex. News Natl. Acad. Sci. Repub. Kazakhstan 4, 10–18. doi: 10.32014/2020.2519-1629.27
Kotrba, P., Inui, M., and Yukawa, H. (2001). Bacterial phosphotransferase system (PTS) in carbohydrate uptake and control of carbon metabolism. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 92, 502–517. doi: 10.1263/jbb.92.502
Laskowski, R. A., and Swindells, M. B. (2011). LigPlot+: multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 51, 2778–2786. doi: 10.1021/ci200227u
Li, W., Bai, L., Ma, X., Zhang, X., Li, X., Yang, X., et al. (2019b). Sentinel lListeriosis surveillance in selected hospitals, China, 2013-2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 25, 2274–2277. doi: 10.3201/eid2512.180892
Li, K., Guan, G., Zhu, J., Wu, H., and Sun, Q. (2019a). Antibacterial activity and mechanism of a laccase-catalyzed chitosan–gallic acid derivative against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 96, 234–243. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.09.021
Lim, S., Han, S.-W., and Kim, J. (2016). Sulforaphene identified from radish (Raphanus sativus L.) seeds possesses antimicrobial properties against multidrug-resistant bacteria and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Funct. Foods 24, 131–141. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.04.005
Liu, C.-X., Xiao, Y.-P., Hu, D.-W., Liu, J.-X., Chen, W., and Ren, D.-X. (2019). The safety evaluation of chilled pork from online platform in China. Food Control 96, 244–250. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.09.025
Low, J. C., and Donachie, W. (1997). A review of Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis. Vet. J. 153, 9–29. doi: 10.1016/S1090-0233(97)80005-6
Mangundayao, K., and Yasurin, P. (2017). Bioactivity of Moringa oleifera and its applications: a review. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 11, 43–50. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.11.1.07
Masri, A., Khan, N. A., Zoqratt, M., Ayub, Q., Anwar, A., Rao, K., et al. (2021). Transcriptome analysis of Escherichia coli K1 after therapy with hesperidin conjugated with silver nanoparticles. BMC Microbiol. 21:51. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02097-2
Mathiron, D., Iori, R., Pilard, S., Soundara Rajan, T., Landy, D., Mazzon, E., et al. (2018). A combined approach of NMR and mass spectrometry techniques applied to the α-cyclodextrin/moringin complex for a novel bioactive formulation. Molecules 23:1714. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071714
Maurya, R., Singh, Y., Sinha, M., Singh, K., Mishra, P., Singh, S. K., et al. (2020). Transcript profiling reveals potential regulators for oxidative stress response of a necrotrophic chickpea pathogen Ascochyta rabiei. Biotech 10:117. doi: 10.1007/s13205-020-2107-8
Moreira, M. R., Ponce, A. G., del Valle, C. E., and Roura, S. I. (2005). Inhibitory parameters of essential oils to reduce a foodborne pathogen. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 38, 565–570. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2004.07.012
Morris, G. M., Huey, R., Lindstrom, W., Sanner, M. F., Belew, R. K., Goodsell, D. S., et al. (2009). AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 30, 2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21256
Mpondo, L., Ebomah, K. E., and Okoh, A. I. (2021). Multidrug-resistant Listeria species shows abundance in environmental waters of a key district municipality in South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:481. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18020481
Ning, Y., Yan, A., Yang, K., Wang, Z., Li, X., and Jia, Y. (2017). Antibacterial activity of phenyllactic acid against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli by dual mechanisms. Food Chem. 228, 533–540. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.112
Ordoñez, R., Atarés, L., and Chiralt, A. (2022). Antibacterial properties of cinnamic and ferulic acids incorporated to starch and PLA monolayer and multilayer films. Food Control 136:108878. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.108878
Portnoy, D. A., Chakraborty, T., Goebel, W., and Cossart, P. (1992). Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 60, 1263–1267. doi: 10.1007/BF01962083
Rajan, T. S., Giacoppo, S., Iori, R., De Nicola, G. R., Grassi, G., Pollastro, F., et al. (2016). Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of a combination of cannabidiol and moringin in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Fitoterapia 112, 104–115. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.05.008
Romeo, L., Iori, R., Rollin, P., Bramanti, P., and Mazzon, E. (2018a). Isothiocyanates: an overview of their antimicrobial activity against human infections. Molecules 23:624. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030624
Romeo, L., Lanza Cariccio, V., Iori, R., Rollin, P., Bramanti, P., and Mazzon, E. (2018b). The α-cyclodextrin/moringin complex: a new promising antimicrobial agent against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 23:2097. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1876-z
Salehi, F., Behboudi, H., Kavoosi, G., and Ardestani, S. K. (2018). Oxidative DNA damage induced by ROS-modulating agents with the ability to target DNA: A comparison of the biological characteristics of citrus pectin and apple pectin. Sci. Rep. 8:13902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32308-2
Sanner, M. F. (1999). Python: a programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 17, 57–61. doi: 10.1016/S1093-3263(99)00019-4
Scallan, E., Hoekstra, R. M., Angulo, F. J., Tauxe, R. V., Widdowson, M.-A., Roy, S. L., et al. (2011). Foodborne illness acquired in the United States-major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17, 7–15. doi: 10.3201/eid1701.p11101
Schurch, N. J., Gierliński, P. S. M., Cole, C., Sherstnev, A., Singh, V., Wrobel, N., et al. (2015). Evaluation of tools for differential gene expression analysis by RNA-seq on a 48 biological replicate experiment. Quant. Biol. 2, 1–31. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1505.02017
Shi, C., Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Zheng, Z., Yang, M., Ben, H., et al. (2016). Antimicrobial effect of lipoic acid against Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Control 59, 352–358. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.05.041
Silva, P. M., Silva, J. N. O., Silva, B. R., Ferreira, G. R. S., Gaião, W. D. C., Recio, M. V., et al. (2021). Antibacterial effects of the lectin from pomegranate sarcotesta (PgTeL) against Listeria monocytogenes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 131, 671–681. doi: 10.1111/jam.14978
Singh, S. V., and Singh, K. (2012). Cancer chemoprevention with dietary isothiocyanates mature for clinical translational research. Carcinogenesis 33, 1833–1842. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs216
Tang, H., Zhang, P., Kieft, T. L., Ryan, S. J., Baker, S. M., Wiesmann, W. P., et al. (2010). Antibacterial action of a novel functionalized chitosan-arginine against gram-negative bacteria. Acta Biomater. 6, 2562–2571. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.01.002
Tian, B., Fadhil, N. H., Powell, J. E., Kwong, W. K., Moran, N. A., and Kolter, R. (2012). Long-term exposure to antibiotics has caused accumulation of resistance determinants in the gut microbiota of honeybees. MBio 3:e00377-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00377-12
Trott, O., and Olson, A. J. (2010). AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 31, 455–461. doi: 10.1002/jcc.21334
Tu, C., Nie, H., Meng, L., Wang, W., Li, H., Yuan, S., et al. (2020). Novel mutations in SPEF2 causing different defects between flagella and cilia bridge: the phenotypic link between MMAF and PCD. Hum. Genet. 139, 257–271. doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02110-0
Typas, A., Banzhaf, M., Gross, C. A., and Vollmer, W. (2011). From the regulation of peptidoglycan synthesis to bacterial growth and morphology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 10, 123–136. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2677
Vasconcelos, N. G., Croda, J., and Simionatto, S. (2018). Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: a review. Microb. Pathog. 120, 198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.036
Vhiriri, E. P., Irwin, Y., Laubscher, R., and Tandlich, R. (2020). Legislation and policy analysis on management of listeriosis epidemic disaster in South Africa. Am. J. Disaster Med. 15, 113–128. doi: 10.5055/ajdm.2020.0361
Wang, N., Qian, Z., Luo, M., Fan, S., Zhang, X., and Zhang, L. (2018). Identification of salt stress responding genes using transcriptome analysis in green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19:3359. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113359
Wu, J., Zhao, L., Lai, S., and Yang, H. (2021). NMR-based metabolomic investigation of antimicrobial mechanism of electrolysed water combined with moderate heat treatment against Listeria monocytogenes on salmon. Food Control 125:107974. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107974
Xie, J., Qian, Y., Yang, Y., Peng, L., Mao, J., Yang, M., et al. (2021). Moringa oleifera isothiocyanate from seeds inhibits the growth and migration of renal cancer cells by regulating the PTP1B-dependent Src/Ras/Raf/Erk signaling pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:790618. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.790618
Yang, C.-X., Wu, H.-T., Li, X.-X., Wu, H.-Y., Niu, T.-X., Wang, X.-N., et al. (2020). Comparison of the inhibitory potential of benzyl isothiocyanate and phenethyl isothiocyanate on Shiga toxin-producing and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 118:108806. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108806
Zhan, L., Peng, W., Sun, W., and Xu, E. (2011). Hypoxic preconditioning induces neuroprotection against transient global ischemia in adult rats via preserving the activity of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase. Neurochem. Int. 59, 65–72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.04.016
Zhao, X., Chen, L., Wu, J., He, Y., and Yang, H. (2020a). Elucidating antimicrobial mechanism of nisin and grape seed extract against Listeria monocytogenes in broth and on shrimp through NMR-based metabolomics approach. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 319:108494. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108494
Zhao, X., Chen, L., Zhao, L., He, Y., and Yang, H. (2020b). Antimicrobial kinetics of nisin and grape seed extract against inoculated Listeria monocytogenes on cooked shrimps: survival and residual effects. Food Control 115:107278. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107278
Keywords: isothiocyanate, moringin, Moringa oleifera seeds, antibacterial activity, Listeria monocytogenes
Citation: Wen Y, Li W, Su R, Yang M, Zhang N, Li X, Li L, Sheng J and Tian Y (2022) Multi-Target Antibacterial Mechanism of Moringin From Moringa oleifera Seeds Against Listeria monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 13:925291. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.925291
Received: 21 April 2022; Accepted: 16 May 2022;
Published: 08 June 2022.
Edited by:
Hongshun Yang, National University of Singapore, SingaporeReviewed by:
Patrick Rollin, Université d’Orléans, FranceCopyright © 2022 Wen, Li, Su, Yang, Zhang, Li, Li, Sheng and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingfei Li, bGluZ2ZlaWxpQDE2My5jb20=; Jun Sheng, c2hlbmdqdW5feW5hdUAxNjMuY29t; Yang Tian, dGlhbnlhbmcxMjA4QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.