- 1State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Silviculture, College of Forestry and Biotechnology, Zhejiang A&F University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Chemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
- 3Center for Large-Scale Cell-Based Screening, Faculty of Science, University of Gothenburg, Gothenburg, Sweden
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is an important inorganic salt. It is not only widely used in industrial production and daily life, but is also the main stress in alkaline saline soil. NaHCO3 has a strong ability to inhibit the growth of fungi in both natural environment and daily application. However, the mechanism by which fungi respond to NaHCO3 stress is not fully understood. To further clarify the toxic mechanisms of NaHCO3 stress and identify the specific cellular genes and pathways involved in NaHCO3 resistance, we performed genome-wide screening with NaHCO3 using a Saccharomyces cerevisiae deletion mutant library. A total of 33 deletion mutants with NaHCO3 sensitivity were identified. Compared with wild-type strains, these mutants had significant growth defects in the medium containing NaHCO3. Bioinformatics analysis found that the corresponding genes of these mutants are mainly enriched in the cell cycle, mitophagy, cell wall integrity, and signaling pathways. Further study using transcriptomic analysis showed that 309 upregulated and 233 downregulated genes were only responded to NaHCO3 stress, when compared with yeast transcriptomic data under alkaline and saline stress. Upregulated genes were mainly concentrated in amino acid metabolism, steroid biosynthesis, and cell wall, while downregulated genes were enriched in various cellular metabolisms. In summary, we have identified the cellular pathways and key genes that respond to NaHCO3 stress in the whole genome, providing resource and direction for understanding NaHCO3 toxicity and cellular resistance mechanisms.
Introduction
NAHCO3 also known as baking soda, is often used as the main component of carbon dioxide sources in baking powder, beverages, dry powder fire extinguishers, and many other applications. It is also widely used in industrial production and the medical field. For example, NaHCO3 is often used as a filler for industrial production of fiber and rubber. Its medical use has gradually expanded from simple metabolic acidosis treatment to the remission and treatment of respiratory, digestive, circulatory, immune system, and cancer diseases (Choi and Kim, 2012; Di Iorio et al., 2019). However, unreasonable use can lead to cytotoxicity and environmental pollution.
In addition, NaHCO3 and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) are the most common alkaline salts, which are the main stress components in saline–alkali soils (Xiao-shan et al., 2017). Worldwide, 434 million hectares soils are affected by saline–alkali stress due to the accumulation of NaHCO3 and Na2CO3 (Shi and Sheng, 2005; Jin et al., 2017; Xiang et al., 2019). The effects of NaHCO3 on the growth of plants, especially crops, have been extensively studied due to its important economic interests (Sun et al., 2016; Xiang et al., 2019; Fan et al., 2021). However, research on fungal diversity in saline–alkali land has been lacking for a long time, although it is known that fungal growth in saline–alkali land is generally inhibited (Wei and Zhang, 2018).
Moreover, there are many examples of using NaHCO3 to inhibit fungi, or using together with yeast in daily production and life. For example, the combine use of live yeast and NaHCO3 for dietary feed additives in domestic animals (Galip, 2006; Marden et al., 2008). NaHCO3 inhibits the production of pathogenic toxins and enhances biocontrol efficacy of antagonistic yeasts on postharvest fungal diseases (Samapundo et al., 2007; Geng et al., 2011; Letscher-Bru et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2020). NaHCO3 is also widely used to formulate toothpaste, mouthwashes, and cosmetic products. There are some reports that NaHCO3 possesses antimicrobial activity against oral microorganisms (Bidra et al., 2011; Fu et al., 2014). Therefore, it is urgent to clarify the reasons for the influence of NaHCO3 on the growth of fungi and the resistance mechanism of fungi to NaHCO3.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a representative of fungi. It not only has high scientific research value, but also has a very broad application in production and life, and has extremely high economic value. The life regulation mechanisms in S. cerevisiae are homologous with and highly similar to other fungi and those multicellular organisms. Saccharomyces cerevisiae, however, has the advantages of a short growth cycle, clear genetic background, easy gene manipulation, and wide application, making it an important model organism for basic and applied research (Gershon and Gershon, 2000). Saccharomyces cerevisiae has established multiple sets of genome-wide genetic modification libraries, which are widely used in cell biology, genetics, pharmacy, and drug mechanism research (Bammert and Fostel, 2000). A large body of work has been carried out using yeast whole-genome screening. For example, Baetz et al. (2004) using whole-genome screening and found that dihydromotuporamine C can directly affect the biosynthesis of sphingolipid in yeast; McLaughlin et al. (2009) uncovered a critical role for mitochondrial translation and membrane maintenance in trichothecene toxicity through high-throughput screening of a yeast deletion mutant library; and our lab used whole-genome screening to characterize how oxidative phosphorylation plays a critical role in cellular tolerance to lithium hexafluorophosphate (Jin et al., 2021).
At present, a large number of studies have been carried out in yeast on the response of osmotic, oxidative, and alkaline pH stress (Thorpe et al., 2004; Melamed et al., 2008; Serra-Cardona et al., 2015; Liang et al., 2018). However, the response and resistance mechanisms of yeast under NaHCO3 stress are unclear; the damage caused by NaHCO3 is more serious and complex, and the mechanism of its stress signal perception, transduction, and resistance warrants clarification. Identifying the genes that respond to NaHCO3 stress can aid in the understanding of the genetic basis of resistance to saline–alkali stress and can provide valuable information for guiding scientific use in daily life and improving the organism’s resistance. The aim of the present study is to reveal the key genes and cellular pathways of cellular resistance to NaHCO3, at the genomic level, in S. cerevisiae.
Materials and Methods
Yeast Strain and Culture Conditions
All strains and mutants in this study are based on the S. cerevisiae strain BY4741 (MATa; his3Δ-1; leu2Δ-0; met15Δ-0; and ura3Δ-0). The collection analyzed here, called the SGA-V2 collection, contains about 4,200 mutants (with mutations in non-essential genes), and was a gift provided by Prof. Charles Boone (University of Toronto, Canada; Tong et al., 2001, 2004). Mutant his3Δ::KanR in this collection was designed as the control strain and added as a border around four edges of each plate (Tong and Boone, 2007). The strains were grown at 30°C, in YPD medium (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, and 2% glucose) with 200 mg·L−1 G418 (YPD + G418). NaHCO3-containing plates were made with YPD agar medium that was supplemented with 40 mM NaHCO3 and 200 mg·L−1 G418. For the yeast growth curve, the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) absorbance value of yeast BY4741 under different NaHCO3 concentration treatments was measured using Ultrospec 2100 pro (Biochrom, United Kingdom) spectrophotometer. The measurement was performed every 2 h and the growth curve was drawn.
Genome-Wide NaHCO3 Screen
The collection of yeast gene deletion mutants was arrayed in 384 formats. Firstly, the strains, in 384-well frozen stock plates, were spotted onto YPD agar plates with G418 added (YPD + G418 plates) using the 384-pining replicator operated by Singer Rotor (Singer Instruments, United Kingdom), and the plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days. Then, the 384-clone array in each plate was replicated in quadruplicate to a new plate containing either no NaHCO3 or 40 mM NaHCO3 to generate a 1,536-density array, with four replications per plate for each strain. These array plates were incubated for 2 days at 30°C before imaging with PhenoBooth (Singer Instruments, United Kindom). SGAtools1 (Wagih et al., 2013) was used to evaluate the growth of individual strains with or without NaHCO3 treatment. The score for each strain was calculated based on standardized colony size for control and NaHCO3 treatment. Mutants that were sensitive to NaHCO3 (with a cutoff of less than −0.3) were selected, according to previous experimental studies (Babazadeh et al., 2019). This value was chosen because a score value lower than −0.3 usually indicates a relatively strong inhibitory effect, and most of the colonies screened with a score value lower than −0.3 can be confirmed by other methods. This experiment was performed in three independent replicates.
Spot Tests Analysis
Adjust the strains cultured overnight to an OD600 = 0.1 and cultured in YPD + G418 liquid medium at 30°C until reaching OD600 = 0.5. Then, cultures were serially diluted in a 10-fold gradient and spotted on plates with different treatments. After 48 h incubation at 30°C, yeast growth was imaged and analyzed.
Data Processing and Bioinformatics Analysis
Candidate hits were analyzed for enrichment in the Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases by comparing with corresponding background set of genes, using ClueGO in Cytoscape with a cutoff of p < 0.05. The functional classification analysis was based on the functional description from the Saccharomyces Genome Database.2 The location distribution of selected genes associated with NaHCO3 sensitivity was determined through the Yeast GFP Fusion localization database3 (Huh et al., 2003). Venn diagram analysis was performed by using Venny 2.1.4
Transcriptional RNA Sequence Analysis
Dilute overnight cultured saturated yeast cells into fresh YPD liquid medium to OD600 = 0.1. At this time, NaHCO3 was added to the experimental group to make the final concentration of 40 mM, while the control group was not added. Harvest cells grown at 200 rpm, 30°C to OD600 = 0.85 for transcriptome sequencing, with four sample replicates making up the set for each treatment. Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Thermo Fisher, 15,596,018), and total RNA quantity and purity were analyzed using a Bioanalyzer 2100 and an RNA 6000 Nano LabChip Kit (Agilent, CA, United States, 5,067–1,511). High-quality RNA reads with an RNA integrity number >7.0 were used to construct cDNA library for sequencing. The cDNAs in the library were sequenced on an Illumina NovaseqTM 6000 platform to generate 2 × 150 bp paired-end reads. Cutadapt was used to remove the Illumina adapter contamination and for trimming the reads and clipping the low-quality bases. After this processing, at least 5 Gb of clean reads were obtained. Gene differential expression analysis was performed by DESeq2 software between two different groups. The genes with the parameter of false discovery rate below 0.05 and absolute fold change ≥2 were considered to represent differentially expressed genes (Love et al., 2014).
Results
The Genome-Wide Screen Identified Deletion Mutants With Increased Sensitivity to NaHCO3
NAHCO3 is an important material in the field of industrial production, food, and drug additives. Although NaHCO3 is widely used for fungal inhibition, few studies were carried out on its inhibitory mechanism. In order to improve our ability to use NaHCO3 scientifically, we must improve our understanding of the intracellular actions and pathways of NaHCO3 and the mechanisms of cell response to NaHCO3 stress. Toward this end, we performed genome-wide screening of genes responding to NaHCO3 stress using the SGA-V2 library of S. cerevisiae single-gene deletion mutants (Tong et al., 2001, 2004). Firstly, the concentration of NaHCO3 for genome-wide screening was determined. For this, we randomly selected the culture plate designated SGA-V2-2. Each 384-arrayed mutant group was replicated in quadruplicate to yield a 1,536 array, using a Singer Rotor, and the strains in the 1,536-array were cultivated on culture plates containing different concentrations of NaHCO3. The plates were cultured at 30°C for 48 h and then photographed. The concentration at which the growth size of the wild-type strain in the outermost two rows of the culture plate was reduced by about 1/3 to 1/2, compared with the growth state of the wild-type strain on the 0 mM culture plate, was selected for screening. Using this process, we determined that the concentration of 40 mM NaHCO3 would be an appropriate concentration for genome-wide screening (Figure 1). The growth phenotypes of the mutants that were sensitive to NaHCO3 differed significantly between the control and experimental plates. Taking the SGA-V2-2 culture plate as an example, compared with the control group, the sensitive strain showed significant growth defects in the experimental group treated with 40 mM NaHCO3 (Figure 1).
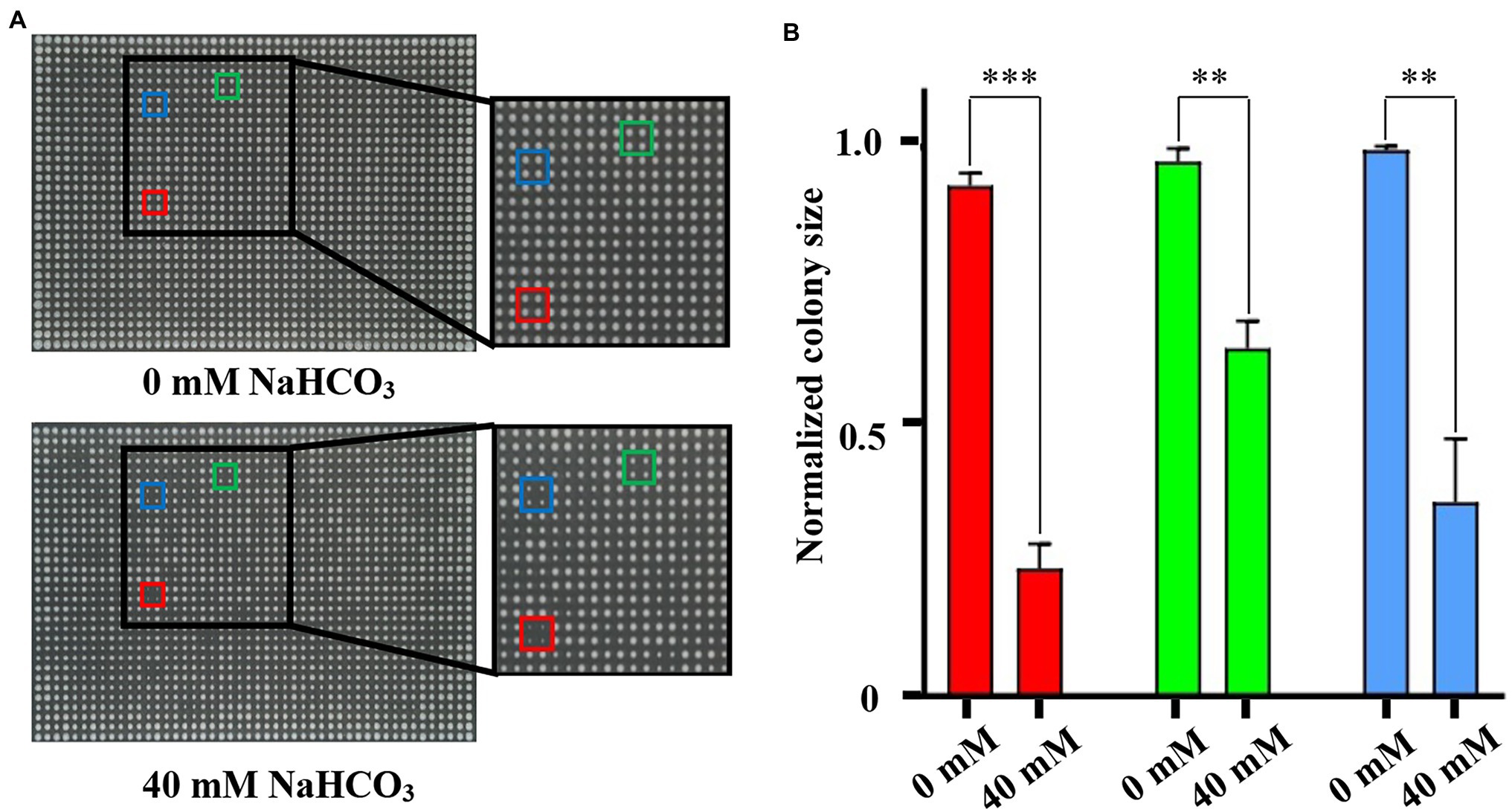
Figure 1. Identification of appropriate NaHCO3 concentration for genome-wide screening using plate SGA-V2-2. (A) The different colored boxes frame the growth of the same mutant on 0 and 40 mM NaHCO3, respectively. (Red: rvs161Δ; Green: ste50Δ; and Blue: pho2Δ). Compared with the control, the same strains in the experimental group of 40 mM NaHCO3 showed obvious growth defects. (B) The colony sizes of the framed strains in (A) were analyzed. Error bars indicate standard error. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test.
We screened the entire collection (about 4,200 gene deletion mutants) on YPD + G418 agar plates containing 0 or 40 mM NaHCO3. These deletion mutants were distributed in 14 culture plates. The culture plates were incubated at 30°C for 48 h, and the images of the control plates and experimental plates were collected by PhenoBooth and uploaded to the SGAtools website for quantification and analysis. On the basis of three independent repeated tests, with screening criteria set to score value from the SGAtools website of three times less than −0.3 and the p value of less than 0.05, we confirmed that 69 deletion mutants showed sensitivity to NaHCO3 (Supplementary Table S1). Compared with the control group, the colony size of these sensitive deletion mutant strains showed a significant reduction, indicating that 40 mM NaHCO3 has a significant inhibitory effect on them.
Spot Test to Verify Screening Results
In order to verify the accuracy of the genome-wide screening results, the drop test experiment was performed to verify the growth phenotypes of the 69 selected deletion mutants. As shown in Figure 2, 33 of the 69 deletion mutants display enhanced growth defect when exposed to 40 mM NaHCO3 compared to the control strain, although they were inhibited to varying degrees, implying the importance of the 33 genes deleted in sensitive mutants in NaHCO3 resistance. The information of the 33 mutants together with their quantitative fitness scores is summarized in Table 1. Among these, 16 mutants barely grew on the plates with 40 mM NaHCO3, including pho86Δ, pho80Δ, pho81Δ, and pho2Δ, which were deficient in genes related to phosphate metabolism and the cell cycle, as well as kex2Δ, ymr031w-aΔ, cnb1Δ, gas1Δ, slt2Δ, sla1Δ, ppm1Δ, swi4Δ, fyv4Δ, rps28bΔ, mrx6Δ, and aim26Δ, which were deficient in genes playing important roles in the process of cell metabolism and maintenance of the normal growth state. Therefore, since many genes were identified to be involved in NaHCO3 resistance, the inhibitory effect of NaHCO3 is not achieved through a single pathway, but may involve a variety of cellular responses. Previous studies have revealed a set of multidrug-resistant genes which are required for a large multitude of stresses. Our deletion mutant array contains 14 genes characterized previously as contributors to general multidrug resistance, including GAS1, MNN10, SLT2, RVS161, SLA1, PHO80, KRE1, CNB1, PMT2, LEM3, KEX2, FAB1, ECM33, and YME1 (Parsons et al., 2004, 2006; Hillenmeyer et al., 2008). In addition, some genes with unknown function, such as DUF1, AIM26, YBL094C, and YMR031W-A, were also revealed through the screening to be involved. At present, the functions of these genes in resistance to NaHCO3 have not been fully elaborated. Knowledge of these functions would be helpful in exploring the new mechanism implied by these results.
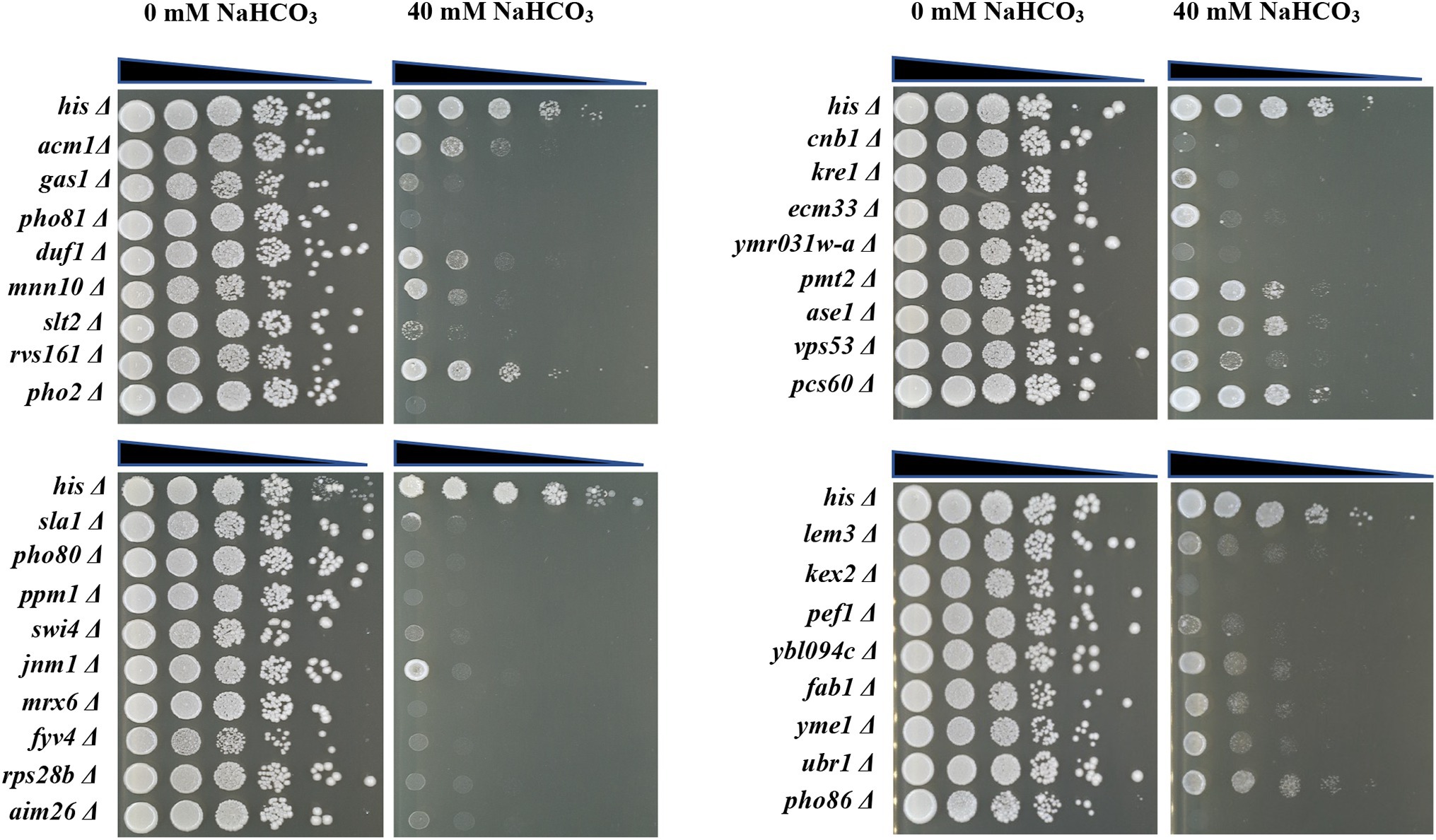
Figure 2. Spot test of the 33 selected deletion mutants. The control strain and deletion mutants were grown to mid-log phase in YPD + G418 liquid medium and then diluted to an OD600 = 0.5. Each strain was serially diluted in a 10-fold gradient and 5 μl were spotted onto YPD + G418 agar plates either containing 0 mM NaHCO3 or 40 mM NaHCO3 and incubated at 30°C. Plates were photographed after 48 h.
Classification of Genes Related to NaHCO3 Resistance
To further analyze the functions and pathways of the genes involved in NaHCO3 responses, functional classification of the 33 genes was performed according to the functional description from the Saccharomyces Genome Database.5 Most of the genes were placed into specific functional categories, including cell cycle, cell wall, calcium signaling pathway, intracellular transport, and mitophagy (Figure 3A). Cellular localization analysis showed that DUF1, CNB1, SLA1, PCS60, RVS161, and RPS28B were localized in the cytoplasm; FAB1 was localized in vacuoles; FYV4 and YME1 were localized in mitochondria; KRE1, PMT2, LEM3, and PHO86 were localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER); PHO2 was localized in the nucleus; and SWI4, PEF1, SLT2, PHO80, and PHO81 were localized in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus (Figure 3B). Although PHO2 is also involved in phosphate metabolism as PHO80 and PHO81, it might only play a role in the nucleus. GAS1 participates in the biosynthesis and morphogenesis of the cell wall and is distributed in the nucleus, mitochondria, and ER (Figure 3B). Together, it suggested that NaHCO3 has widespread effects on the yeast physiology, and the integrity of these cellular processes plays a key role in the response of cells to NaHCO3 stress.
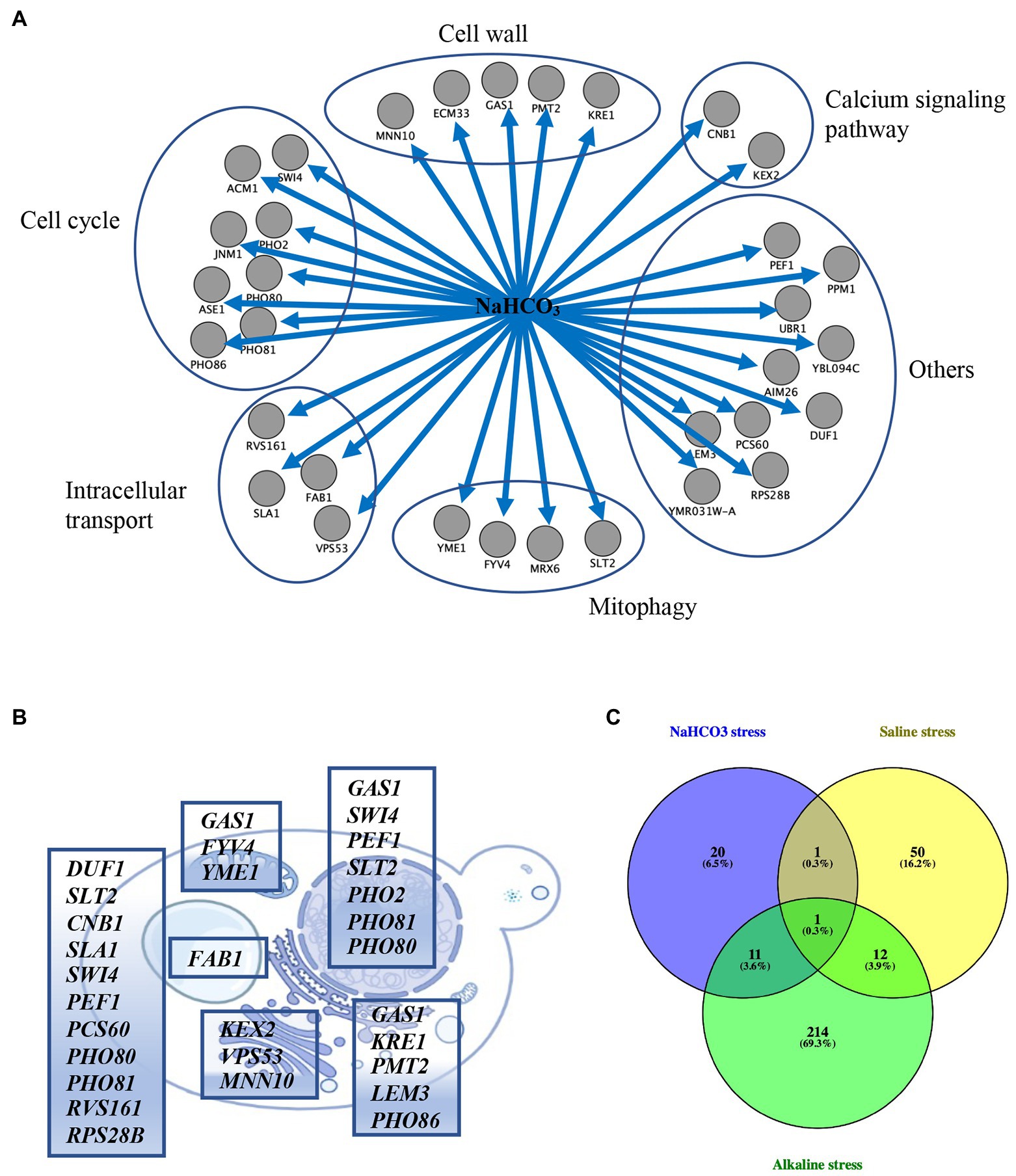
Figure 3. Enrichment and localization analysis of the 33 selected genes. (A) Functional classification of the 33 genes. (B) Cellular localization of the 33 selected genes. These genes are distributed in the cytoplasm, nucleus, Golgi, vacuole, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondrion. (C) Venn diagram analysis of the 33 selected genes vs. the 238 and 64 genes whose deletion results in growth defects under alkaline and saline stress, respectively.
Previous studies have determined the genes in yeast whose deletion result in alkaline pH sensitivity and salt sensitivity through conventional genetic screens (Giaever et al., 2002; Serrano et al., 2004). In order to analysis whether the 33 genes we identified are specifically response to NaHCO3 or are involved in general stress response, we compared the 33 mutants with the 238 mutants showing defective growth under alkaline stress yielded from previous studies (Giaever et al., 2002; Serrano et al., 2004; Loha et al., 2018). Twelve genes were identified as overlapping (Figure 3C; Supplementary Table S2), including GAS1, PHO80, PHO81, PHO2, PHO86, SLT2, CNB1, KRE1, SWI4, AIM26, KEX2, and FAB1. Likewise, analysis of the set of genes induced by both salt stress and NaHCO3 exposure yielded two genes (Giaever et al., 2002; Figure 3C; Supplementary Table S2), including CNB1 and PEF1. These overlapped genes indicated that cells might share overlapping mechanisms of resistance to different kinds of stresses.
NaHCO3 Stress on Yeast Are Beyond the Combination of High pH and Salt
In order to reveal whether toxic effects of NaHCO3 is a combination of mechanisms coming from high pH and salt, we measured the pH of the medium under different stresses. The final pH of YPD medium is 6.35 under normal conditions. This is consistent with the fact that yeast prefers an acidic external pH to maintain proton gradient over the plasma membrane. However, the medium containing 40 mM NaHCO3 used in our study has a pH of 7.15, which, although close to neutral pH, is more alkaline than that under normal conditions. Then, the 33 mutants were tested for growth on plates containing 40 mM NaCl or at pH 7.15, respectively. These mutants were found to be not significantly sensitive to medium with the same concentration of Na+ (40 mM NaCl; Figure 4), indicating that effects of Na+ in NaHCO3 stress are limited to a small proportion. When exposed to media at pH 7.15, gas1Δ, kex2Δ, pho80Δ, and pho86Δ exhibit defective growth, while other mutants did not show significant differences (Figure 4). This is consistent with previous reports that these four genes are essential for the response to high pH (Giaever et al., 2002; Serrano et al., 2004; Loha et al., 2018). Other reported alkaline-sensitive mutants were not validated in our drop test experiments, probably because the pH we used was close to neutral rather than alkaline. Therefore, although NaHCO3 stress could induce the growth defect of certain alkaline-sensitive mutants, the toxic effect of NaHCO3 was more profound than that of NaOH at the same pH.
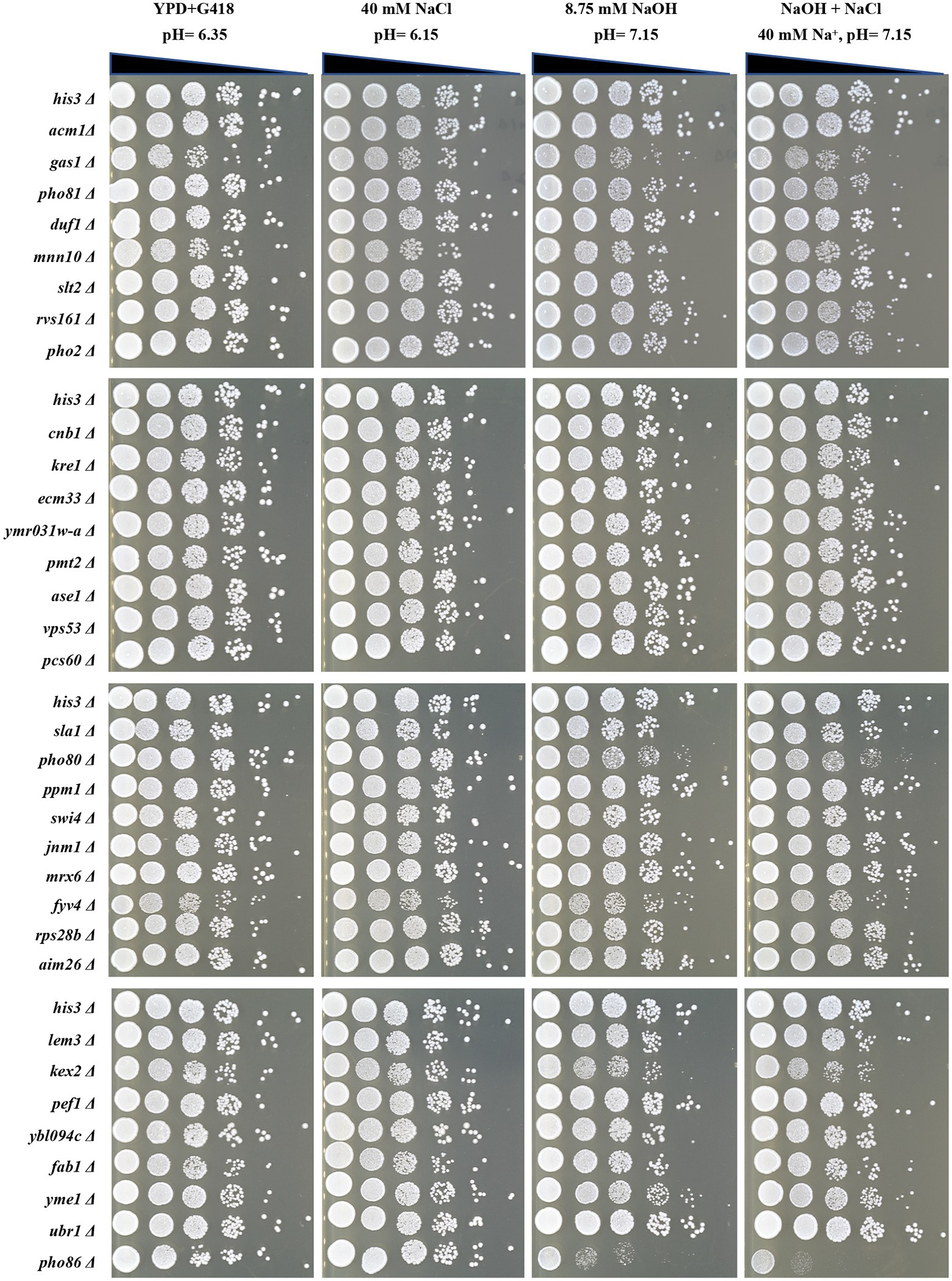
Figure 4. Spot test of the 33 selected deletion mutants under stresses with the same pH and Na+ concentration as 40 mM NaHCO3. The control strain and deletion mutants were grown to mid-log phase in YPD + G418 liquid medium and then diluted to an OD600 = 0.5. Each strain was serially diluted in a 10-fold gradient and 5 μl were spotted onto differently treated agar plates. The pH = 7.15 plates were adjusted with NaOH. Plates were incubated at 30°C and photographed after 48 h.
We also conducted an experimental group that exposed to NaOH and NaCl at the same time, allowing the concentration of Na+ to 40 mM, and the pH to 7.15, the same Na+ concentration and pH as 40 mM NaHCO3. However, a synergistic enhancing effect between NaCl and NaOH stress was not observed in this study. Among 33 mutants, only gas1Δ, kex2Δ, pho80Δ, and pho86Δ exhibited significantly decreased sensitivity, while others did not (Figure 4). This implies that NaHCO3 has a more specific mechanism of toxicity than the combination of salt stress and alkali stress, although cells may share overlapping control mechanisms for resistance to both alkaline stress and NaHCO3 stress.
Global Transcriptional Changes in Response to NaHCO3 Stress
In order to further explore the mechanism of cells responding to NaHCO3, we conducted transcriptomic analysis of the changes in genes under NaHCO3 stress. We first measured the growth curve of yeast at different NaHCO3 concentrations. It can be seen that as the concentration of NaHCO3 increased, the growth of the yeast was significantly inhibited (Figure 5A). Among the different concentrations tested, 40 mM NaHCO3 was considered the most suitable condition. At this concentration, cell growth was significantly inhibited, but with the extension of culture time, the cells could still reach a certain growth density. After 10 h of growth under the condition of 40 mM NaHCO3, the cells began to enter the early phase of the logarithmic growth phase. At this time, the effect of NaHCO3 on the cells should have been reflected at the transcription level. Thus, the gene expression changes were analysis under the condition of 40 mM NaHCO3.
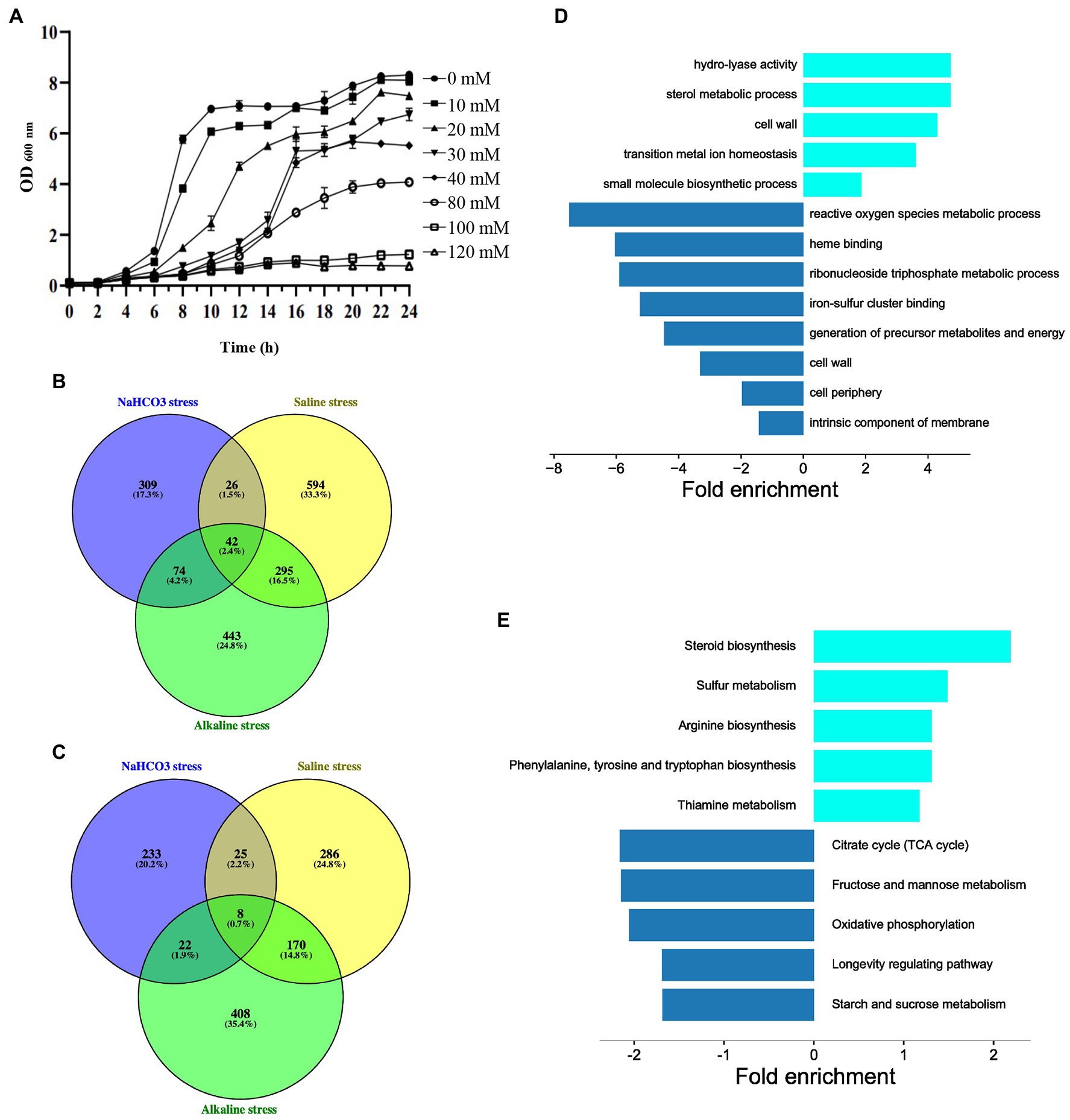
Figure 5. Transcriptional analysis of gene expression under NaHCO3 treatment. (A) Growth curve of BY4741 under different concentrations of NaHCO3. (B) Venn diagram analysis of 451 upregulated genes under NaHCO3 stress vs. the 854 and 957 genes which also are upregulated under alkaline and saline stress, respectively. (C) Venn diagram analysis of 288 downregulated genes under NaHCO3 stress vs. the 608 and 489 genes, which are also downregulated under alkaline and saline stress, respectively. (D) GO enrichment analysis of 309 upregulated and 233 downregulated genes that only respond to NaHCO3 stress. (E) KEGG enrichment analysis of 309 upregulated and 233 downregulated genes that only respond to NaHCO3 stress.
Whole transcriptome sequencing revealed that, compared with the control group, after 40 mM NaHCO3 treatment, the expression levels of 451 genes were significantly upregulated, and the expression levels of 288 genes were significantly downregulated (Supplementary Table S3). Then, correlation estimate for the 33 NaHCO3-resistant genes tested in both genome-wide screen and transcriptomic analysis was performed to verify whether the expression of the genes required for growth is also significantly increased. However, these 33 genes were unexpectedly either downregulated or unchanged. We speculate that these genes may function through post-translational modifications, or their downregulation may be part of a general downregulation effect on metabolism, associated with slow cell growth.
In order to identify the genes specifically response to NaHCO3 stress, we compared our results with different sets of data regarding the transcriptional response to saline stress and alkaline stress (Posas et al., 2000; Rep et al., 2000; Lamb et al., 2001; Yale and Bohnert, 2001; Serrano et al., 2002, 2006; Viladevall et al., 2004; Melamed et al., 2008; Halbeisen and Gerber, 2009; Casado et al., 2011; Casamayor et al., 2012). Around 142 genes upregulated under our condition can be also induced by either saline stress or alkaline stress (Figure 5B; Supplementary Table S4), while 55 genes downregulated under NaHCO3 overlapped with those under either saline stress or alkaline stress (Figure 5C; Supplementary Table S4). These genes may be involved in the general stress response, especially the overlapping genes that are changed under all three stress conditions. Although we cannot rule out the possibility that the remaining 309 upregulated and 233 downregulated genes would display expression changes under other types of stress, such as heat shock, to some extent, it provides a set of key genes for further study of how cells are respond to NaHCO3.
In order to further identify the functional classification of the 309 upregulated and 233 downregulated genes, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis on these genes were performed. Upregulated genes were mainly concentrated in amino acid metabolism, steroid biosynthesis, and cell wall, while downregulated genes were enriched in various cellular metabolisms (Figures 5D,E). It has been demonstrated that under stress, cells tend to optimize cellular resources for stress adaptation, allowing the massive expression of genes involved in stress adaptation, while shutting down the expression of genes involved in proliferation and cell cycle progression (Giaever et al., 2002). Thus, it is reasonable that genes in various cellular metabolisms are downregulated. Although in our study, significantly upregulated genes have poor correlation with their importance in growth fitness, it helps to some extent in our understanding of how cells respond to NaHCO3.
Discussion
NaHCO3 Has a Specific Mechanism of Action Beyond High pH and Salinity
In order to verify whether NaHCO3 has the characteristics of saline stress and alkaline stress, we compared the conditions of yeast external medium under different stresses. About 40 mM NaHCO3 results in an increase in external pH. Although the pH has increased, it is still lower than the pH that researchers usually use to identify alkaline-sensitive mutants (Giaever et al., 2002; Serrano et al., 2004). In addition, most of the 33 mutants lost their sensitivity on NaOH plates with the same pH. Therefore, NaHCO3 must have its own toxicity mechanisms in yeast that different from the alkalinization. Moreover, all 33 NaHCO3-sensitive mutants exhibited similar growth to the control strain when exposed to 40 mM NaCl (same molar quantity of Na+ as 40 mM NaHCO3), indicating that the influence of Na+ in NaHCO3 stress is much weaker. It is reasonable that yeast cells have limited responses to 40 mM Na+ since yeast is highly tolerant to Na+ (Rep et al., 2000; Yale and Bohnert, 2001). More importantly, when yeast cells were exposed to both NaOH and NaCl (40 mM Na+, pH 7.15), the effect of stress on NaHCO3-sensitive mutants was unexpectedly less. These results suggest that NaHCO3 has a distinct cytotoxicity mechanism in yeast.
Common and Specific Genes Regulate Yeast NaHCO3 Sensitivity
Through genome-wide screen and spot test experiment, 33 genes were identified in this study to be important for NaHCO3 resistance. They are mainly enriched in cell wall, calcium signaling, mitophagy, intracellular transport, and cell cycle pathways. Previous studies have identified 238 alkaline-resistant genes and 64 saline-resistant genes in yeast. But only 12 genes and two genes were overlapped with those in the NaHCO3 screen (Figure 3C). This again implies that NaHCO3 may has a specific mode of action and that the cellular responses to NaHCO3 differ from both saline stress and alkaline stress, despite several shared genes were identified.
The 12 genes yielded in both alkaline stress and NaHCO3 exposure include GAS1, PHO80, PHO81, PHO2, PHO86, SLT2, CNB1, KRE1, SWI4, AIM26, KEX2, and FAB1. Among them, KRE1 and PMT2 are involved in 1,6-β-D-glucan and mannose type O-glycan biosynthesis, respectively, and GAS1 encodes β-1,3-glucanosyltransferase (Breinig et al., 2004; de Medina-Redondo et al., 2010; Castells-Ballester et al., 2019). They are required for cell wall synthesis and organization. Therefore, we speculate that NaHCO3 might cause damage to the yeast cell wall and result in the activation of cell surface stressors, which then activate a set of effectors that regulate downstream signaling pathways. This can be confirmed by the enhanced sensitivity to NaHCO3 induced by SLT2 deletion (Figure 2). Slt2 is a component of the MAPK cascade involved in maintaining of cell integrity. There is evidence that the Slt2-regulated MAPK pathway plays important roles in the adaptive response to alkaline stress, the activation of which is largely dependent on the Wsc1 cell surface sensor (Serrano et al., 2006). Therefore, yeast cells may respond to NaHCO3 by activating the same Slt2 MAPK pathway as alkaline stress through cell wall remodeling.
Calcium-activated phosphatase calcineurin is another signaling pathway that integrated into the alkaline stress response mechanism (Serra-Cardona et al., 2015). Cnb1 is the regulatory subunit of the yeast calcium-activated Ser/Thr protein phosphatase calcineurin (Cyert, 2003), and yeast cells under both alkaline stress and saline stress require this gene to maintain fitness. Deletion of CNB1 also results in poor growth under NaHCO3 stress (Figure 2). This means that the calcium-activated phosphatase calcineurin is also essential for dealing with NaHCO3. In addition to the two signaling pathways discussed above, the Rim101/PacC pathway is responsible for a set of alkali-induced responses (Serra-Cardona et al., 2015). However, in our screen, RIM101 deletion did not show significant growth changes in 40 mM NaHCO3. This pathway may not affect the yeast survival capability under NaHCO3 stress.
Evidence indicates that alkalinization also perturbs nutrient uptake of cells, such as phosphate, and it can result in the activation of phosphate acquisition-related genes. Thus, exposure to alkali stress may mimic the situation of phosphate starvation (Ariño, 2010). Genes associated with phosphate starvation responses were also identified in our screen, including PHO2, PHO80, PHO81, and PHO86. Therefore, we speculate that NaHCO3 may have a negative effect on nutrient homeostasis in yeast, as does alkaline stress.
Mitochondria are essential organelles that produce most of the cellular energy, the effective performance of mitochondrial function is essential for optimal cell growth under aerobic conditions. At the same time, however, mitochondria also produce reactive oxygen species that are harmful to cell physiology. Therefore, it is necessary to efficiently clean up damaged and superfluous mitochondria. Appropriate mitophagy is critical for mitochondria and cellular homeostasis. Yeast mitochondrial i-AAA protease Yme1 functions in mitochondrial quality control system by degrading unfolded or misfolded mitochondrial proteins (Weber et al., 1996), and its activity is required for mitophagy (Wang et al., 2013). In our study, YME1 deletion significantly inhibited cell growth under NaHCO3 stress (Figure 2), which was not observed in previous studies of responses to saline and alkaline stress; thus, the induction of mitophagy may be a specific response to NaHCO3 and the normal operation of mitophagy under the influence of NaHCO3 may play an important role in maintaining cell homeostasis. Previous studies have reported that mitophagy in yeast requires the Slt2 MAPK pathway, thus, SLT2 deletion would also affect mitophagy under NaHCO3 stress and lead to sensitive phenotype.
Cross-Stress Adaptation Strategies Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis
In our transcriptomic analysis, amino acid metabolism- and most cell wall-related genes were upregulated. Evidence has found that in Puccinellia tenuiflora, amino acid metabolism pathways are also significantly upregulated under the stress of a salt–alkali environment rich in NaHCO3 (Ye et al., 2019). In addition, cells can also regulate cell wall-related gene expression in the face of stress, changing the cell wall structure to actively respond to environmental changes. Extracellular proteins and receptor-like kinases on the cell membrane can recognize the changed cell wall structure and transmit environmental stress signals to the cell to activate the corresponding signal pathways (Zhao et al., 2018). Salt damage, drought stress, and other osmotic stresses can increase the expression of expandin- and xyloglucan-modifying enzyme genes to reshape the cell wall, also leading to the loss of cell wall Ca2+ and other cell wall changes (Tenhaken, 2014). Indeed, in previous study of yeast genomic expression programs in response to environmental changes, amino acid metabolism- and cell wall metabolism-related genes are environmental stress response genes, and thus, up- or downregulation of these genes is a common response to most of the stressful conditions (Gasch et al., 2000; Causton et al., 2001). Yeast utilizes cross-stress adaptation strategies to cope with diverse stressors. Although the genes that were significantly upregulated in the transcriptomic analysis were poorly correlated with their importance in growth fitness, the results of transcriptome extend our understanding of yeast NaHCO3 responses by providing a set of key genes for further investigation.
In summary, S. cerevisiae is a model system for the study of fungi and other life. Genome-wide screening is a good strategy to uncover key genes/proteins or functions that allow cells to cope with toxicity. Here, we present high-throughput screening results in a yeast single-gene deletion collection for sensitivity to NaHCO3, and a transcriptomic analysis of the changes in genes under NaHCO3 stress. We screened and confirmed yeast genes that play a key role in responding to NaHCO3 stress, and compared them to genes that play roles in other stressors to find specific genes and pathways. Our present study provides a direction to understand the response mechanism of yeast cells to NaHCO3.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: Sequence Read Archive (SRA), PRJNA808812.
Author Contributions
BL, XJ, and XC designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. XC, TA, and WF performed the experiments. XC, TA, WF, JZ, HZ, and DL analyzed the data. XC and TA mapped all the figures and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32000387 and 31800163) to XC and XJ, and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LQ19C070001) to XC, as well as the Swedish Cancer Fund (Cancerfonden; CAN 2017/643 and 19 0069) and the Swedish Natural Research Council (Vetenskapsrådet; VR 2015-04984 and VR 2019-03604) to BL.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank Charles Boone (Toronto University, Toronto, ON, Canada) for providing us with the SGA-V2 collection.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2022.831973/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Table S1 | Data of the three independent genome-wide screening.
Supplementary Table S2 | List of genes for growth-deficient mutants under alkaline stress or saline stress generated by previous studies.
Supplementary Table S3 | The transcriptome sequencing data under 40 or 0 mM NaHCO3 treatment.
Supplementary Table S4 | List of significantly changed genes in the transcriptome under alkaline stress or saline stress yielded from previous studies.
Footnotes
1. ^http://sgatools.ccbr.utoronto.ca/
2. ^https://www.yeastgenome.org/
3. ^https://yeastgfp.yeastgenome.org/
References
Ariño, J. (2010). Integrative responses to high pH stress in S. cerevisiae. OMICS 14, 517–523. doi: 10.1089/omi.2010.0044
Babazadeh, R., Ahmadpour, D., Jia, S., Hao, X., Widlund, P., Schneider, K., et al. (2019). Syntaxin 5 is required for the formation and clearance of protein inclusions during proteostatic stress. Cell Rep. 28, 2096–2110.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.053
Baetz, K., McHardy, L., Gable, K., Tarling, T., Rebérioux, D., Bryan, J., et al. (2004). Yeast genome-wide drug-induced haploin sufficiency screen to determine drug mode of action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 4525–4530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307122101
Bammert, G. F., and Fostel, J. M. (2000). Genome-wide expression patterns in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparison of drug treatments and genetic alterations affecting biosynthesis of ergosterol. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44, 1255–1265. doi: 10.1128/aac.44.5.1255-1265.2000
Bidra, A. S., Tarrand, J. J., Roberts, D. B., Rolston, K. V., and Chambers, M. S. (2011). Antimicrobial efficacy of oral topical agents on microorganisms associated with radiated head and neck cancer patients: an in vitro study. Quintessence Int. 42, 307–315.
Breinig, F., Schleinkofer, K., and Schmitt, M. J. (2004). Yeast Kre1p is GPI-anchored and involved in both cell wall assembly and architecture. Microbiology 150, 3209–3218. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27175-0
Casado, C., González, A., Platara, M., Ruiz, A., and Ariño, J. (2011). The role of the protein kinase A pathway in the response to alkaline pH stress in yeast. Biochem. J. 438, 523–533. doi: 10.1042/bj20110607
Casamayor, A., Serrano, R., Platara, M., Casado, C., Ruiz, A., and Ariño, J. (2012). The role of the Snf1 kinase in the adaptive response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to alkaline pH stress. Biochem. J. 444, 39–49. doi: 10.1042/bj20112099
Castells-Ballester, J., Rinis, N., Kotan, I., Gal, L., Bausewein, D., Kats, I., et al. (2019). Translational regulation of Pmt1 and Pmt2 by Bfr1 affects unfolded protein O-mannosylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:6220. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246220
Causton, H. C., Ren, B., Koh, S. S., Harbison, C. T., Kanin, E., Jennings, E. G., et al. (2001). Remodeling of yeast genome expression in response to environmental changes. Mol. Biol. Cell 12, 323–337. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.2.323
Choi, S. E., and Kim, H. S. (2012). Sodium bicarbonate solution versus chlorhexidine mouthwash in oral care of acute leukemia patients undergoing induction chemotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. Asian Nurs. Res. 6, 60–66. doi: 10.1016/j.anr.2012.05.004
Cyert, M. S. (2003). Calcineurin signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: how yeast go crazy in response to stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 311, 1143–1150. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(03)01552-3
de Medina-Redondo, M., Arnáiz-Pita, Y., Clavaud, C., Fontaine, T., del Rey, F., Latgé, J. P., et al. (2010). β(1,3)-glucanosyl-transferase activity is essential for cell wall integrity and viability of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. PLoS One 5:e14046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014046
Di Iorio, B. R., Bellasi, A., Raphael, K. L., Santoro, D., Aucella, F., Garofano, L., et al. (2019). Treatment of metabolic acidosis with sodium bicarbonate delays progression of chronic kidney disease: the UBI study. J. Nephrol. 32, 989–1001. doi: 10.1007/s40620-019-00656-5
Fan, Y., Lu, X., Chen, X., Wang, J., Wang, D., Wang, S., et al. (2021). Cotton transcriptome analysis reveals novel biological pathways that eliminate reactive oxygen species (ROS) under sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) alkaline stress. Genomics 113, 1157–1169. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.02.022
Fu, J., Wei, P., Zhao, C., He, C., Yan, Z., and Hua, H. (2014). In vitro antifungal effect and inhibitory activity on biofilm formation of seven commercial mouthwashes. Oral Dis. 20, 815–820. doi: 10.1111/odi.12242
Galip, N. (2006). Effect of supplemental yeast culture and sodium bicarbonate on ruminal fermentation and blood variables in rams. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 90, 446–452. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2006.00625.x
Gasch, A. P., Spellman, P. T., Kao, C. M., Carmel-Harel, O., Eisen, M. B., Storz, G., et al. (2000). Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 4241–4257. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.12.4241
Geng, P., Chen, S., Hu, M., Rizwan-Ul-Haq, M., Lai, K., Qu, F., et al. (2011). Combination of Kluyveromyces marxianus and sodium bicarbonate for controlling green mold of citrus fruit. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 151, 190–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.08.023
Gershon, H., and Gershon, D. (2000). The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, as a model for aging research: a critical review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 120, 1–22. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(00)00182-2
Giaever, G., Chu, A. M., Ni, L., Connelly, C., Riles, L., Véronneau, S., et al. (2002). Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418, 387–391. doi: 10.1038/nature00935
Halbeisen, R. E., and Gerber, A. P. (2009). Stress-dependent coordination of transcriptome and translatome in yeast. PLoS Biol. 7:e1000105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000105
Hillenmeyer, M. E., Fung, E., Wildenhain, J., Pierce, S. E., Hoon, S., Lee, W., et al. (2008). The chemical genomic portrait of yeast: uncovering a phenotype for all genes. Science 320, 362–365. doi: 10.1126/science.1150021
Huh, W. K., Falvo, J. V., Gerke, L. C., Carroll, A. S., Howson, R. W., Weissman, J. S., et al. (2003). Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425, 686–691. doi: 10.1038/nature02026
Jin, S., Xu, C., Li, G., Sun, D., Li, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2017). Functional characterization of a type 2 metallothionein gene, SsMT2, from alkaline-tolerant Suaeda salsa. Sci. Rep. 7:17914. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18263-4
Jin, X., Zhang, J., An, T., Zhao, H., Fu, W., Li, D., et al. (2021). A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a critical role for oxidative phosphorylation in cellular tolerance to lithium hexafluorophosphate. Cell 10:888. doi: 10.3390/cells10040888
Lamb, T. M., Xu, W., Diamond, A., and Mitchell, A. P. (2001). Alkaline response genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their relationship to the RIM101 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 1850–1856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008381200
Letscher-Bru, V., Obszynski, C. M., Samsoen, M., Sabou, M., Waller, J., and Candolfi, E. (2013). Antifungal activity of sodium bicarbonate against fungal agents causing superficial infections. Mycopathologia 175, 153–158. doi: 10.1007/s11046-012-9583-2
Liang, W., Ma, X., Wan, P., and Liu, L. (2018). Plant salt-tolerance mechanism: A review. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 495, 286–291. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.043
Loha, A., Kashyap, A. K., and Sharma, P. (2018). A putative cyclin, SiPHO80 from root endophytic fungus Serendipita indica regulates phosphate homeostasis, salinity and heavy metal toxicity tolerance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 507, 414–419. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.11.053
Love, M. I., Huber, W., and Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Marden, J. P., Julien, C., Monteils, V., Auclair, E., Moncoulon, R., and Bayourthe, C. (2008). How does live yeast differ from sodium bicarbonate to stabilize ruminal pH in high-yielding dairy cows? J. Dairy Sci. 91, 3528–3535. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0889
McLaughlin, J. E., Bin-Umer, M. A., Tortora, A., Mendez, N., McCormick, S., and Tumer, N. E. (2009). A genome-wide screen in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a critical role for the mitochondria in the toxicity of a trichothecene mycotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 21883–21888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909777106
Melamed, D., Pnueli, L., and Arava, Y. (2008). Yeast translational response to high salinity: global analysis reveals regulation at multiple levels. RNA 14, 1337–1351. doi: 10.1261/rna.864908
Parsons, A. B., Brost, R. L., Ding, H., Li, Z., Zhang, C., Sheikh, B., et al. (2004). Integration of chemical-genetic and genetic interaction data links bioactive compounds to cellular target pathways. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 62–69. doi: 10.1038/nbt919
Parsons, A. B., Lopez, A., Givoni, I. E., Williams, D. E., Gray, C. A., Porter, J., et al. (2006). Exploring the mode-of-action of bioactive compounds by chemical-genetic profiling in yeast. Cell 126, 611–625. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.040
Posas, F., Chambers, J. R., Heyman, J. A., Hoeffler, J. P., de Nadal, E., and Ariño, J. (2000). The transcriptional response of yeast to saline stress. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17249–17255. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M910016199
Rep, M., Krantz, M., Thevelein, J. M., and Hohmann, S. (2000). The transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to osmotic shock: Hot1p and Msn2p/Msn4p are required for the induction of subsets of high osmolarity glycerol pathway-dependent genes. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 8290–8300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8290
Samapundo, S., Devlieghere, F., De Meulenaer, B., Lamboni, Y., Osei-Nimoh, D., and Debevere, J. M. (2007). Interaction of water activity and bicarbonate salts in the inhibition of growth and mycotoxin production by Fusarium and Aspergillus species of importance to corn. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 116, 266–274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.01.005
Serra-Cardona, A., Canadell, D., and Ariño, J. (2015). Coordinate responses to alkaline pH stress in budding yeast. Microb. Cell 2, 182–196. doi: 10.15698/mic2015.06.205
Serrano, R., Bernal, D., Simón, E., and Ariño, J. (2004). Copper and iron are the limiting factors for growth of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae in an alkaline environment. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 19698–19704. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313746200
Serrano, R., Martín, H., Casamayor, A., and Ariño, J. (2006). Signaling alkaline pH stress in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae through the Wsc1 cell surface sensor and the Slt2 MAPK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 39785–39795. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604497200
Serrano, R., Ruiz, A., Bernal, D., Chambers, J. R., and Ariño, J. (2002). The transcriptional response to alkaline pH in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for calcium-mediated signalling. Mol. Microbiol. 46, 1319–1333. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03246.x
Shi, D., and Sheng, Y. (2005). Effect of various salt–alkaline mixed stress conditions on sunflower seedlings and analysis of their stress factors. Environ. Exp. Bot. 54, 8–21. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2004.05.003
Sun, X., Sun, M., Jia, B., Qin, Z., Yang, K., Chen, C., et al. (2016). A Glycine soja methionine sulfoxide reductase B5a interacts with the Ca2+/CAM-binding kinase GsCBRLK and activates ROS signaling under carbonate alkaline stress. Plant J. 86, 514–529. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13187
Tenhaken, R. (2014). Cell wall remodeling under abiotic stress. Front. Plant Sci. 5:771. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00771
Thorpe, G. W., Fong, C. S., Alic, N., Higgins, V. J., and Dawes, I. W. (2004). Cells have distinct mechanisms to maintain protection against different reactive oxygen species: oxidative-stress-response genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 6564–6569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0305888101
Tong, A. H. Y., and Boone, C. (2007). “16 high-throughput strain construction and systematic synthetic lethal screening in Saccharomyces cerevisiae,” in Methods in Microbiology. eds. I. Stansfield and M. J. R. Stark (Salt Lake City, USA: Academic Press), 369–707.
Tong, A. H., Evangelista, M., Parsons, A. B., Xu, H., Bader, G. D., Pagé, N., et al. (2001). Systematic genetic analysis with ordered arrays of yeast deletion mutants. Science 294, 2364–2368. doi: 10.1126/science.1065810
Tong, A. H., Lesage, G., Bader, G. D., Ding, H., Xu, H., Xin, X., et al. (2004). Global mapping of the yeast genetic interaction network. Science 303, 808–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1091317
Viladevall, L., Serrano, R., Ruiz, A., Domenech, G., Giraldo, J., Barceló, A., et al. (2004). Characterization of the calcium-mediated response to alkaline stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 43614–43624. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403606200
Wagih, O., Usaj, M., Baryshnikova, A., VanderSluis, B., Kuzmin, E., Costanzo, M., et al. (2013). SGAtools: one-stop analysis and visualization of array-based genetic interaction screens. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, W591–W596. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt400
Wang, K., Jin, M., Liu, X., and Klionsky, D. J. (2013). Proteolytic processing of Atg32 by the mitochondrial i-AAA protease Yme1 regulates mitophagy. Autophagy 9, 1828–1836. doi: 10.4161/auto.26281
Weber, E. R., Hanekamp, T., and Thorsness, P. E. (1996). Biochemical and functional analysis of the YME1 gene product, an ATP and zinc-dependent mitochondrial protease from S. cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 7, 307–317. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.2.307
Wei, Y., and Zhang, S.-H. (2018). Abiostress resistance and cellulose degradation abilities of haloalkaliphilic fungi: applications for saline–alkaline remediation. Extremophiles 22, 155–164. doi: 10.1007/s00792-017-0986-3
Xiang, G., Ma, W., Gao, S., Jin, Z., Yue, Q., and Yao, Y. (2019). Transcriptomic and phosphoproteomic profiling and metabolite analyses reveal the mechanism of NaHCO3-induced organic acid secretion in grapevine roots. BMC Plant Biol. 19:383. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1990-9
Xiao-shan, W., Hai-long, R., Zen-wu, W., Yun-wen, W., and Wei-bo, R. (2017). Effects of neutral salt and alkali on ion distributions in the roots, shoots, and leaves of two alfalfa cultivars with differing degrees of salt tolerance. J. Integr. Agric. 16, 1800–1807. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61522-8
Yale, J., and Bohnert, H. J. (2001). Transcript expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae at high salinity. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 15996–16007. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008209200
Ye, X., Wang, H., Cao, X., Jin, X., Cui, F., Bu, Y., et al. (2019). Transcriptome profiling of Puccinellia tenuiflora during seed germination under a long-term saline-alkali stress. BMC Genomics 20:589. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5860-5
Zhang, X., Li, B., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., and Tian, S. (2020). Antagonistic yeasts: a promising alternative to chemical fungicides for controlling postharvest decay of fruit. J. Fungi 6:158. doi: 10.3390/jof6030158
Keywords: sodium bicarbonate, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, genome-wide screening, NaHCO3, transcriptome
Citation: Cao X, An T, Fu W, Zhang J, Zhao H, Li D, Jin X and Liu B (2022) Genome-Wide Identification of Cellular Pathways and Key Genes That Respond to Sodium Bicarbonate Stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Microbiol. 13:831973. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.831973
Edited by:
Celin Acharya, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC), IndiaReviewed by:
Nuno Pereira Mira, University of Lisbon, PortugalVasanthi Nachiappan, Bharathidasan University, India
Copyright © 2022 Cao, An, Fu, Zhang, Zhao, Li, Jin and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiuling Cao, Y3hpdWxpbmdAY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==; Xuejiao Jin, amlueHVlamlhbzE5OTFAY2F1LmVkdS5jbg==; Beidong Liu, YmVpZG9uZy5saXVAY21iLmd1LnNl
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiuling Cao
Xiuling Cao Tingting An
Tingting An Wenhao Fu1
Wenhao Fu1 Beidong Liu
Beidong Liu