A Corrigendum on
Effect of Divalent Cations (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, and Sr) on Microbially Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation and Mineralogical Properties
by Kim, Y., Kwon, S., and Roh, Y. (2021). Front. Microbiol. 12:646748. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.646748
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 1 as published. It was found that the graph in Figure 1H was duplicated in Figure 1C. The corrected Figure 1 appears below with the duplicated graph deleted and the missing graph of Figure 1C inserted.
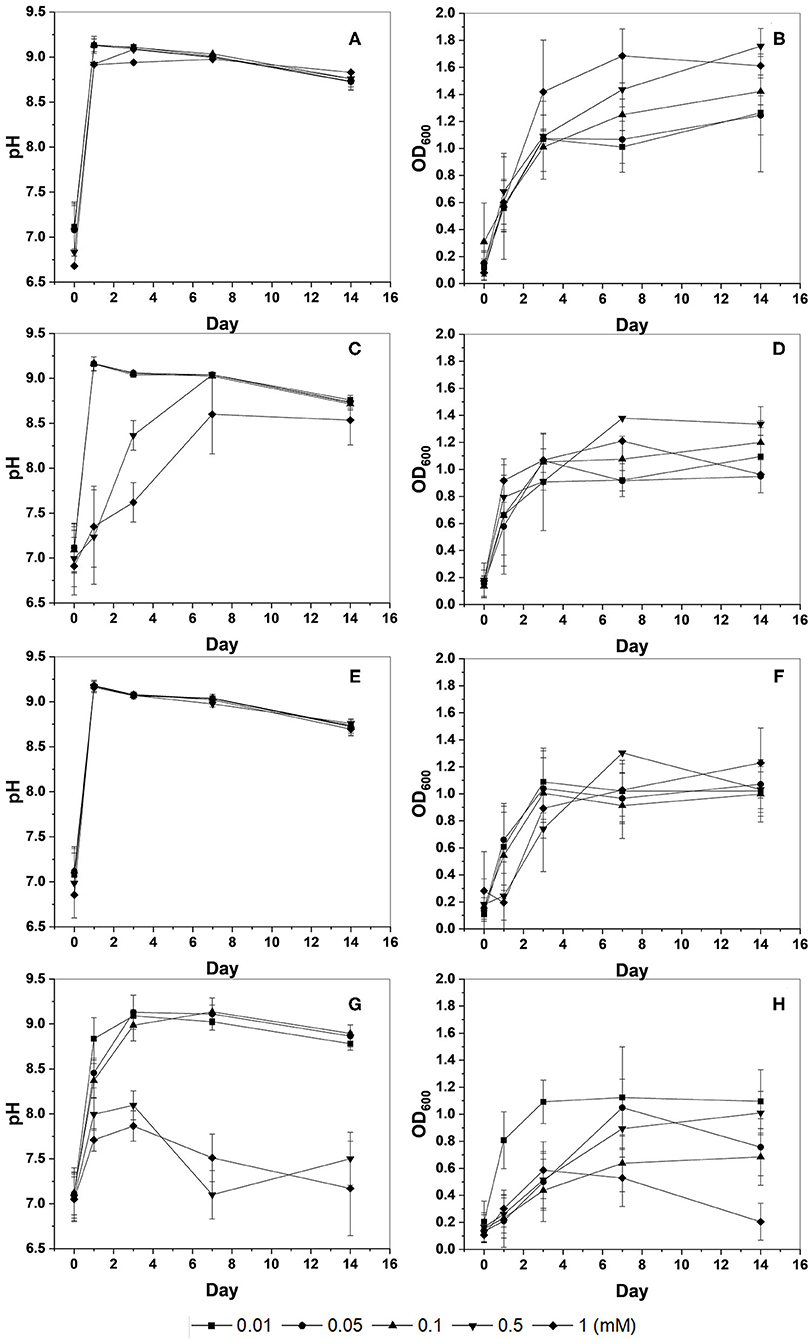
Figure 1. Changes in pH and optical density (OD600) of KCTC 3558 culture at various metal concentrations (mM): Cu (A,B); Zn (C,D); Pb (E,F); and Cd (G,H).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: urea hydrolysis, Sporosarcina pasteurii, bioremediation, heavy metals, bio-co-precipitation
Citation: Kim Y, Kwon S and Roh Y (2021) Corrigendum: Effect of Divalent Cations (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, and Sr) on Microbially Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation and Mineralogical Properties. Front. Microbiol. 12:721478. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.721478
Received: 07 June 2021; Accepted: 14 June 2021;
Published: 12 July 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Kim, Kwon and Roh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yul Roh, cm9oeUBqbnUuYWMua3I=
 Yumi Kim
Yumi Kim Sunki Kwon
Sunki Kwon Yul Roh
Yul Roh