
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Microbiol. , 11 October 2019
Sec. Extreme Microbiology
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02354
 Dong Xue1,2
Dong Xue1,2 Yun Chen1,3
Yun Chen1,3 Jiang Li1
Jiang Li1 Jiahui Han1
Jiahui Han1 Yingying Liu1
Yingying Liu1 Shijie Jiang4
Shijie Jiang4 Zhengfu Zhou1
Zhengfu Zhou1 Wei Zhang1
Wei Zhang1 Ming Chen1
Ming Chen1 Min Lin1
Min Lin1 Marc Ongena2*
Marc Ongena2* Jin Wang1*
Jin Wang1*Small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are a class of regulatory molecules, which remain understudied in bacteria. In the extremophilic bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans, although hundreds of ncRNAs have been identified, few have been characterized in detail. In this study, we report the identification and characterization of a novel heat-inducible ncRNA named DnrH. Heat tolerance analysis showed that deleting DnrH significantly inhibited viability in response to high temperature conditions. Comparative phenotypic and qRT-PCR analyses of a DnrH mutant (ΔDnrH) and wild-type (WT) D. radiodurans suggested that DnrH is potentially involved in regulating the expression of the heat shock-related gene Hsp20. Microscale thermophoresis and genetic complementation showed that a 28-nucleotide (nt) sequence in the stem-loop structure of DnrH (143–170 nt) pairs with its counterpart in the coding region of Hsp20 mRNA (91–117 nt) via a 22 nt region. In vivo, mutation of the 22-nt region in the D. radiodurans genome led to a reduction in heat tolerance similar to that observed in the DnrH-mutant. Our results show that DnrH positively influences heat tolerance by increasing the transcription of Hsp20 mRNA, demonstrating, for the first time, a ncRNA that directly controls the expression of a heat stress-resistance gene. This work provides new insight into the heat stress response mechanism of D. radiodurans as well as other extremophiles that express similar Hsp20 proteins.
Small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play critical roles in gene expression at the posttranscriptional level and are recognized as key transcriptional regulators in bacteria (Liu and Camilli, 2010; Arnvig et al. 2011; Acebo et al., 2012). Generally, ncRNAs remain untranslated with typical lengths ranging from approximately 50 to 500 nucleotides (nt) (Wassarman, 2002). Over the past decades, many ncRNAs have been identified both in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria (Wassarman et al., 1999; Del Val et al., 2007; Mandin et al., 2007; Landt et al., 2008; Arnvig et al., 2011; Acebo et al., 2012) and these have been divided into four groups as follows: cis-encoded, trans-encoded, protein-binding, and CRISPR ncRNAs. Trans-encoded ncRNAs are the best characterized and most extensively studied (Wagner and Romby, 2015) and exert their regulatory functions through imperfect base-pairing to modulate target mRNA stability and/or translation (Richards and Vanderpool, 2011; Storz et al., 2011). Nonetheless, a wide range of physiological functions may be regulated by ncRNAs, many of which are related to environmental changes, such as iron limitation, acidity, osmotic shock, envelops stress, temperature, and nutrient stress (Lybecker and Samuels, 2007; Jin et al., 2009; Patel et al., 2009; Boysen et al., 2010; Fantappiè et al., 2011; Fröhlich et al., 2012; Barreto et al., 2016).
Deinococcus radiodurans is a model species best known for its extraordinary resistance to diverse environmental stress factors, such as ionizing radiation, ultraviolet irradiation, desiccation, oxidation, and temperature (Blasius et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2008; Daly, 2009; Patel et al., 2009; Bauermeister et al., 2011; Timmins and Moe, 2016). Because of its genetic operability and extreme resistance, D. radiodurans thus represents a leading model to study various extreme stress environments. Temperature fluxes have been reported to be a vital factor for bacterial life, affecting metabolism, and protein unfolding and aggregation in microbes and leading to a higher risk of cell death (Lesley et al., 2002; Ventura et al., 2006). Studying the regulatory mechanisms involved in temperature stress responses of D. radiodurans may provide new insights into the stress response of other unrelated species. Multiple genes associated with heat tolerance have been identified in D. radiodurans and the first study of heat stress in D. radiodurans was published in 1988. Results from this study suggested that proteins synthesized de novo during incubation at different temperature intervals (exposure to 52°C for 30 min, with immediate subsequent transfer to 30°C or 42°C for various intervals) are involved either in the thermotolerance phenomenon itself or the recovery from injury (Harada and Oda, 1988). In the year following the aforementioned study, various heat-inducible proteins were discovered (generally, by proteomics analyses), including Hsp20, GroEL, DnaK, SodA, Csp, and Protease I (Airo et al., 2004; Schmid et al., 2005c). Sig1 was determined to be essential for induction of the heat shock proteins groESL and dnaKJ (Schmid and Lidstrom, 2002; Schmid et al., 2005a), whereas hspR binds HAIR sites in close proximity to promoter regions, thereby directly inhibiting the expression of regulated genes encoding chaperone proteins and proteases (Schmid et al., 2005b). Recently, an analysis of two small heat shock proteins (sHSPs; IbpA, and IbpB) showed that in D. radiodurans, these proteins are very different in term of their quaternary structures and chaperone properties and were considered to represent a second type of bacterial two-component sHsp systems (Bepperling et al., 2012). More recently, DdrI (encoded by DR_0997) was reported enhance heat tolerance in D. radiodurans (Meyer et al., 2018).
Using a genome-wide RNA sequencing approach, Tsai et al. (2015) identified 41 ncRNA candidates; however, functional characterizations of these molecules are still lacking. Considering that ncRNAs often act as regulators in response to various stresses, it is plausible that they could play important roles in the extremophilic properties of D. radiodurans. In this study, we describe the function and targets of a novel ncRNA that is potentially involved in heat tolerance in D. radiodurans. This ncRNA was designated DnrH (D. radiodurans ncRNA response to heat stress) and its expression was found to be upregulated during heat stress. Further characterization and target identification showed that DnrH functions by directly binding Hsp20 mRNA, which provides evidence of a novel posttranscriptional regulatory mechanism underlying the heat stress response of D. radiodurans.
All strains and plasmids used in this study are described in Table 1. D. radiodurans was obtained from China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC 1.633, Beijing, China). D. radiodurans and derivatives were routinely cultured in TGY broth (1% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, and 0.1% glucose) or on TGY plates supplemented with agar (1.5%) at 30°C. Escherichia coli strains were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or on LB plates supplemented with agar (1.5%) at 37°C. When required, ampicillin, kanamycin, spectinomycin, and chloromycetin were added to final concentrations of 50, 20, 340, and 3.4 μg/mL, respectively.
Cells cultured to OD600 = 2 were harvested by centrifugation at 7000 × g for 3 min, washed twice in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 0.02% KH2PO4, 0.29% Na2HPO4 ⋅ 12H2O, 0.8% NaCl, 0.02% KCl, pH 7.5), and resuspended in TGY broth to a final OD600 = 2 (107 cells/mL). Then, cells were treated at 48°C. These cells were harvested by centrifugation at 12,000 × g for 3 min and stored at −80°C. The untreated cells (30°C) were also harvested and stored in the same manner. Total cells from D. radiodurans were prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States) with Lysing Matrix Tubes (MP Bio, CA, United States) and total cellular RNA was extracted with the PureLink RNA Mini Kit (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States) following the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA purity was assessed using absorbance readings (260 nm/280 nm) with a NanoDrop® spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States).
The transcriptional start site of DnrH was determined using the 5′ RACE kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, an initial strand of cDNA was generated using a sequence-specific primer (i.e., GSP1) to the DnrH gene. The first strand cDNA was purified, and the 3′ end of the cDNA was tailed with dATP by the recombinant terminal transferase. The amplification of dA-tailed cDNA was performed using the sequence-specific primer GSP2 and the anchor primer provided by the 5′ RACE system. The sequence-specific primer GSP3 was using for the second amplification round. Primers GSP1, GSP2, and GSP3, specific for the DnrH gene and tested here are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The 5′ RACE products were cloned into the pJET1.2/blunt vector (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States) and sequenced to map the 5′ end of the transcript.
The DnrH-mutant strain was generated by replacing the target gene with a kanamycin resistance cassette via fusion PCR recombination, as previously described (Sheng et al., 2005). Briefly, fusion PCR products for the DnrH deletions were constructed in two steps. In the first step, PCR was used to generate fragments complementary to the kanamycin-resistance gene from the plasmid pKatAPH3 (920 bp) and the upstream (515 bp) and downstream (529 bp) regions of the DnrH sequence using the appropriate primer pairs (Supplementary Table S1). In the second step, the upstream, kanamycin-resistance gene, and downstream fragments were annealed at their overlapping regions and PCR amplified the product as a single fragment using the outer primers (1964 bp). The resulting PCR fragment was directly transformed into D. radiodurans and colonies resistant to kanamycin (20 μg/mL) were selected. The mutant was subsequently verified by PCR and DNA sequencing. The successfully constructed mutant was named ΔDnrH.
The pRADZ3 vector is generally used for complementation experiments with D. radiodurans. This plasmid was digested with HindIII/BamHI, and the DnrH gene was ligated into linear pRADZ3 to generate the complementation plasmid Z3-DnrH. The complementary strain was constructed by transforming Z3-DnrH into ΔDnrH and was selected with 20 μg/mL kanamycin and 3.4 μg/mL chloramphenicol. This strain was confirmed by PCR and Sanger sequencing. This successfully constructed DnrH-complemented strain was named cDnrH. Similarly, the Hsp20 mutant, complementary strain, and specific point mutants (introduced by site-directed mutagenesis) were constructed using the same method with specific primers (Supplementary Table S1).
Total RNA was extracted using the PureLink RNA Mini Kit (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, cDNA synthesis was performed using the PrimeScriptTM RT reagent kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa) as described in the manufacturer’s protocol. Subsequently, qRT-PCR was performed using ChamQ SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., China) with an AB7500 Fast Real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, United States). The primers are listed in Supplementary Table S1. The 16S (DR_r06) rRNA gene was used as the endogenous reference control to normalize for differences in total RNA quantity, and the relative gene expression was quantified by the 2–ΔΔCT method. Three biological replicates for each condition were conducted.
D. radiodurans wild-type (WT), mutant (ΔDnrH), and complementary (cDnrH) strains were grown in shacked (220 rpm) TGY cultures in triplicate at 30°C. The OD600 of each sample was measured every 4 h.
WT, ΔDnrH, cDnrH, and all the other mutant derivatives were cultured in TGY broth with appropriate antibiotics to OD600 = 2 at 30°C and were then shifting to 48°C for 4 h. Subsequently, 100 μL of the cell suspension was aliquoted into 900 μL of PBS, after which 10-fold serial dilutions were made for all strains, and 8 μL of each dilution was spotted onto TGY agar plates. These plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days before colony growth was observed and calculated. The survival rate was expressed as the percentage of the number of colonies in the treated samples compared to those in untreated controls. All assays were performed in triplicate.
The northern blot method was used as previously described (Zhan et al., 2016). Briefly, total RNA was isolated from WT and derivatives grown under heat stress and normal conditions. Next, 30-nt single-strand DNA probes were synthesized (Supplementary Table S1), and the 5′ end of the synthesized product was labeled with digoxigenin (Sangon Biotech, Shanghai, China). RNA samples (10 μg) were separated on 8% denaturing gels using 3.2 mL UreaGel 29:1 Concentrate (National Diagnostics, Atlanta, United States), 5.8 mL UreaGel Diluent (National Diagnostics, Atlanta, United States), 1 mL UreaGel Buffer (National Diagnostics, Atlanta, United States), 4 μL TEMED (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, United States), and 40 μL 10% ammonium persulfate (Sigma-Aldrich, MO, United States). The gel was transferred to a nylon membrane using a semi-dry transfer cell and then incubated at 60°C for 1–2 h with freshly prepared cross-linking EDC reagent. The membrane was then hybridized with the suitable digoxigenin labeled probe overnight at 37°C and washed with a low stringent buffer and high stringent buffer. Next, the membrane was incubated in blocking buffer for 3 h at room temperature. Then, the membrane was placed in the blocking buffer with a DIG antibody solution prepared by mixing a DIG antibody solution with blocking buffer at a ratio of 1:15,000 for 30 min. The membrane was washed in DIG washing buffer four times for 15 min each. The membrane was incubated in detection buffer for 5 min and incubated in CSPD solution in the dark for 15 min. Band intensity was analyzed using an Amersham imager 600 RGB (GE, Healthcare, United States).
MST experiments were performed according to a previous report (Jerabek-Willemsen et al., 2011). A set of 30-nt ncRNA oligonucleotides, containing wild-type (wt) or mutated (mut) base-pairing regions of DnrH or complementary regions of Hsp20 mRNA were synthesized by GenePharma (GenePharma, Shanghai, China), as listed in Supplementary Table S2. The wt and mut DnrH probe molecules were labeled with 6-carboxyfluorescein. 4 μL of sample containing 200 nM labeled probe and increasing concentrations of a non-labeled competitor (from 18.3 nM to 600 μM) were loaded on standard treated glass capillaries (Monolith NT.115 Series Capillaries, Cat#MO-K002) and measurements were carried out using a Monolith NT.115 instrument (NanoTemper Technologies, Germany) at room temperature in diethylpyrocarbonate water with 40% excitation power and medium MST-Power. The dissociation constants (Kd) were calculated as previously described (Lippok et al., 2012). Data analyses were performed using Nanotemper Analysis software (NanoTemper Technologies, Germany).
DnrH was identified based on our Illumina RNA sequencing (NCBI database Sequence Read Archive, Accession number: SUB5875813) and a previous report (Tsai et al., 2015). DnrH was significantly upregulated (6.54-fold) under heat stress and was selected to elucidate its physiological role in response to this pressure (Figure 1A). We therefore speculated that DnrH may positively regulated the tolerance of D. radiodurans.
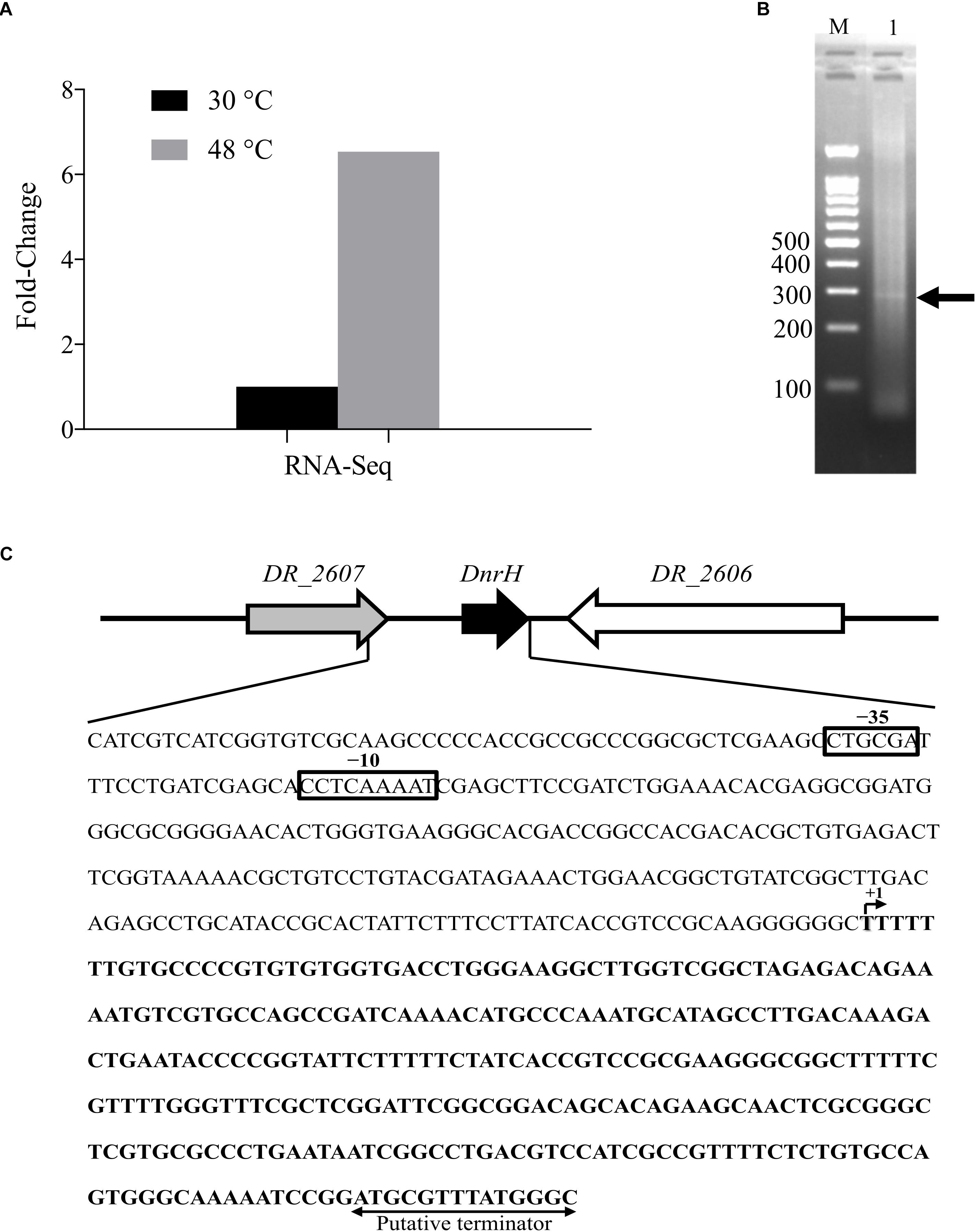
Figure 1. Locus features and the expression of DnrH. (A) The expression of DnrH at 30 and 48°C based on RNA-Seq. (B) PCR results of 5′ RACE. The bands are indicated by arrows. Lane M: 100-bp DNA Ladder (Transgen Biotech), cropped from Supplementary Figure S1 lane M; Lane 1: 5′ RACE of DnrH, cropped from Supplementary Figure S1 lane 3. (C) Physical map and nucleotide sequence of the DnrH region of Deinococcus radiodurans. Promoter elements (−35 and −10 box) are depicted in solid boxes. +1, transcription start site mapped by 5′ RACE; arrowheads, putative transcriptional terminator.
The transcriptional start site of DnrH was then determined by 5′RACE analysis. The results showed that DnrH starts at position 2615872 in chromosome 1, extending 294 nt (Figures 1B,C). It was located in a 490 bp intergenic region between DR_2606 (encoding a putative primosomal protein N’) and DR_2607 (encoding a MoaE–MoaD fusion protein) (Figure 1C). The promoter regions (–35 and –10 boxes) were predicted by BPROM (Solovyev and Salamov, 2011) 222 and 191 nt upstream of the transcription start site. Since it is conserved in other Deinococci (Figure 2A), it is speculated that the region must serve the same purpose throughout the genus. Secondary structure alignment revealed that DnrH contains multiple stem loop structures (Figure 2B).
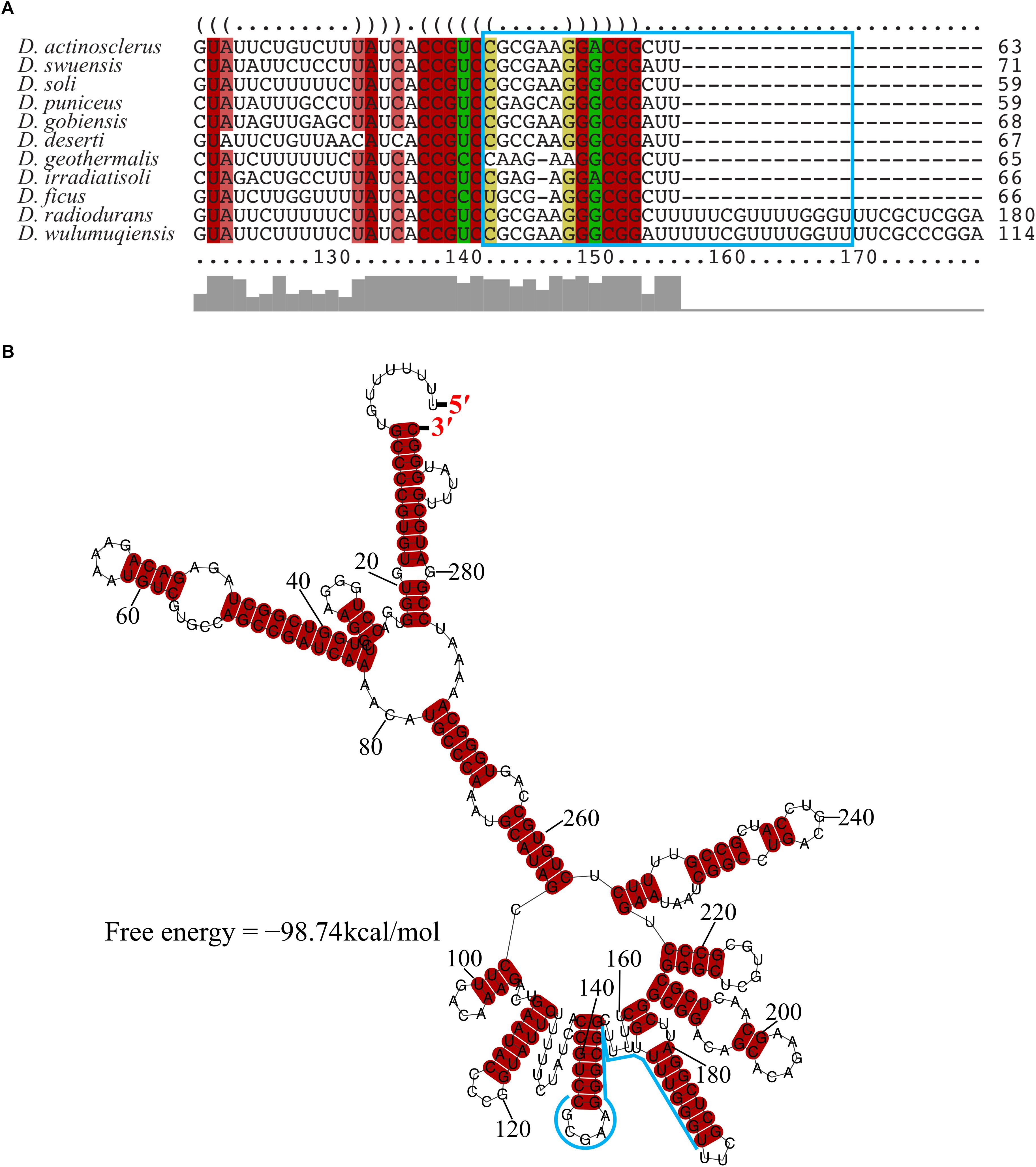
Figure 2. Conservation of DnrH sequence and structure. (A) Multi-sequence alignment of DnrH homolog performed with LocARNA (Will et al., 2012). The colors indicate the structural conservation, for which red indicates 100% of the structural sequence is identical, brown indicates that one nucleotide is changed, and green indicates that two nucleotides are changed. (B) Secondary structure prediction performed with RNAalifold (Bernhart et al., 2008). The potential interaction region of DnrH is indicated in blue.
To further investigate the effect of DnrH on heat tolerance in D. radiodurans, the DnrH-knockout strain ΔDnrH and a plasmid-based complementation strain cDnrH were constructed. The results of northern blot and qRT-PCR assay showed the significant upregulation of DnrH in heat stress response (Figure 3A). The effect of this mutation on the growth potential of the bacterium was examined (Figure 3B). The growth of the mutant did not show any significant difference compared to that of the WT, and the complementation strain showed a slight decrease in growth during the stationary period compared to that in ΔDnrH and the WT. This decrease maybe caused by the insert plasmid (Figure 3B). In order to further determine the role of DnrH in D. radiodurans under heat stress, the ΔDnrH, cDnrH and WT strains were exposed to high temperature 48°C for 4 h. The relative survival ratios of different strains under heat stress were determined by the recovered colony forming units on TGY plates and showed a higher sensitivity of ΔDnrH than the WT under heat stress while cDnrH exhibited no significant difference (Figure 3C). These results strongly suggest that DnrH act as an important positive regulator in the response to heat stress.
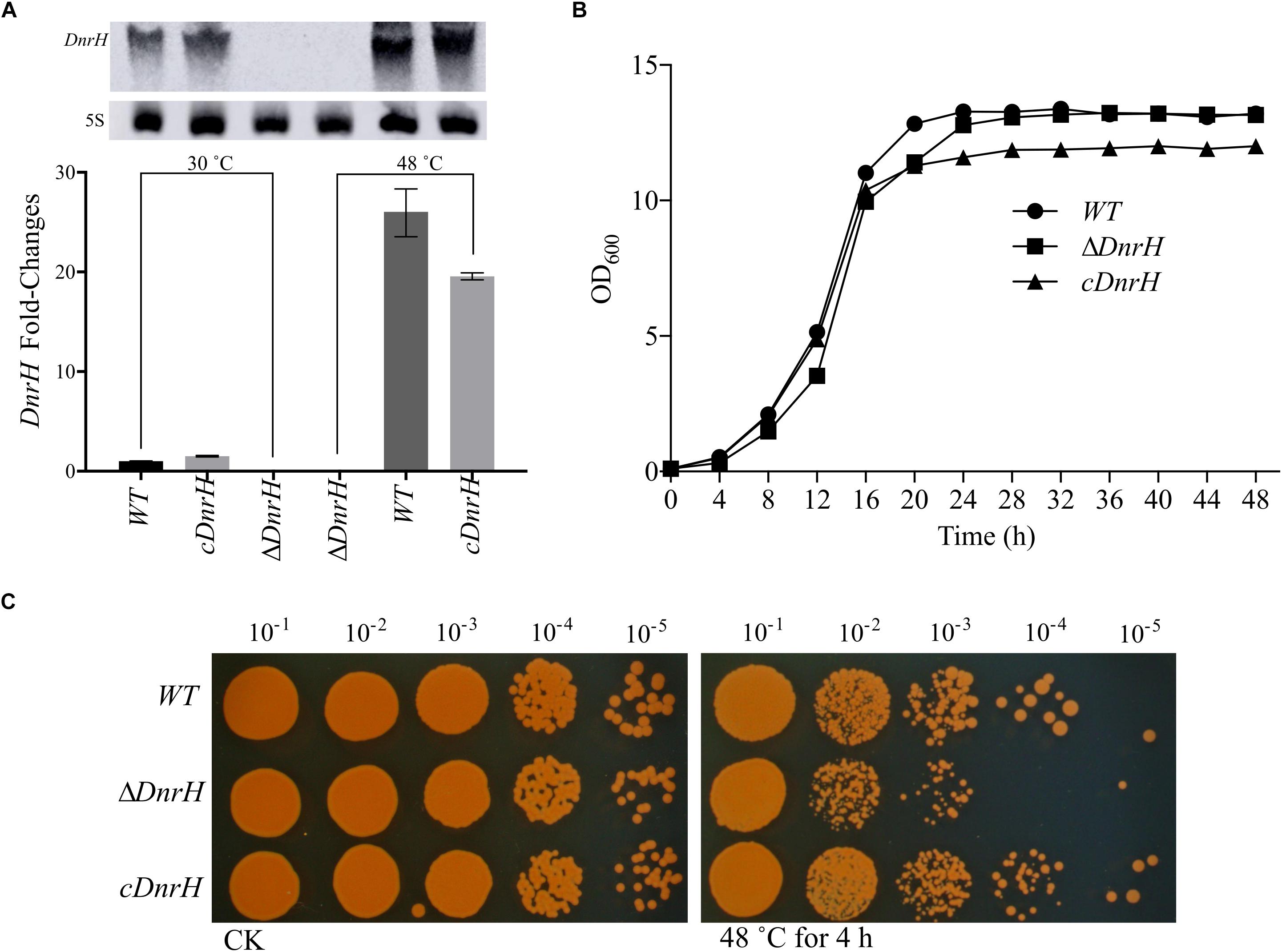
Figure 3. Transcriptional and functional analysis of DnrH ncRNA in Deinococcus radiodurans. (A) DnrH transcription under heat stress conditions in the WT, ΔDnrH (mutant), and cDnrH (complemented) strains. Total RNA was extracted, and the expression of DnrH was measured by qRT-PCR. (Inset) RNA northern blot assay using RNA extracted from the same strains under the same conditions and hybridized with the DnrH-specific probe. Measurements were normalized to the WT values, and fold differences are plotted. (B) Growth curves of WT, ΔDnrH, and cDnrH in TGY broth. The error bars represent the calculated standard deviation of the measurements of three biological replicates. (C) Serial 10-fold dilutions of OD-standardized cultures were spotted on TGY plates after exposure to 48°C.
To identify the potential targets of DnrH, we used qRT-PCR analyses to evaluate the transcriptional levels of heat-related genes in D. radiodurans (see Supplementary Figure S2). The highly expressed heat-induced genes were selected for further measurements of their relative expression levels in the presence and absence of DnrH under heat stress. As shown in Figure 4A, the transcriptional level of Hsp20 in ΔDnrH was significantly decreased compared to that in the WT, whereas its expression in cDnrH was consistent with that in the WT strain. This phenomenon was also observed by northern blotting (Figure 4B).
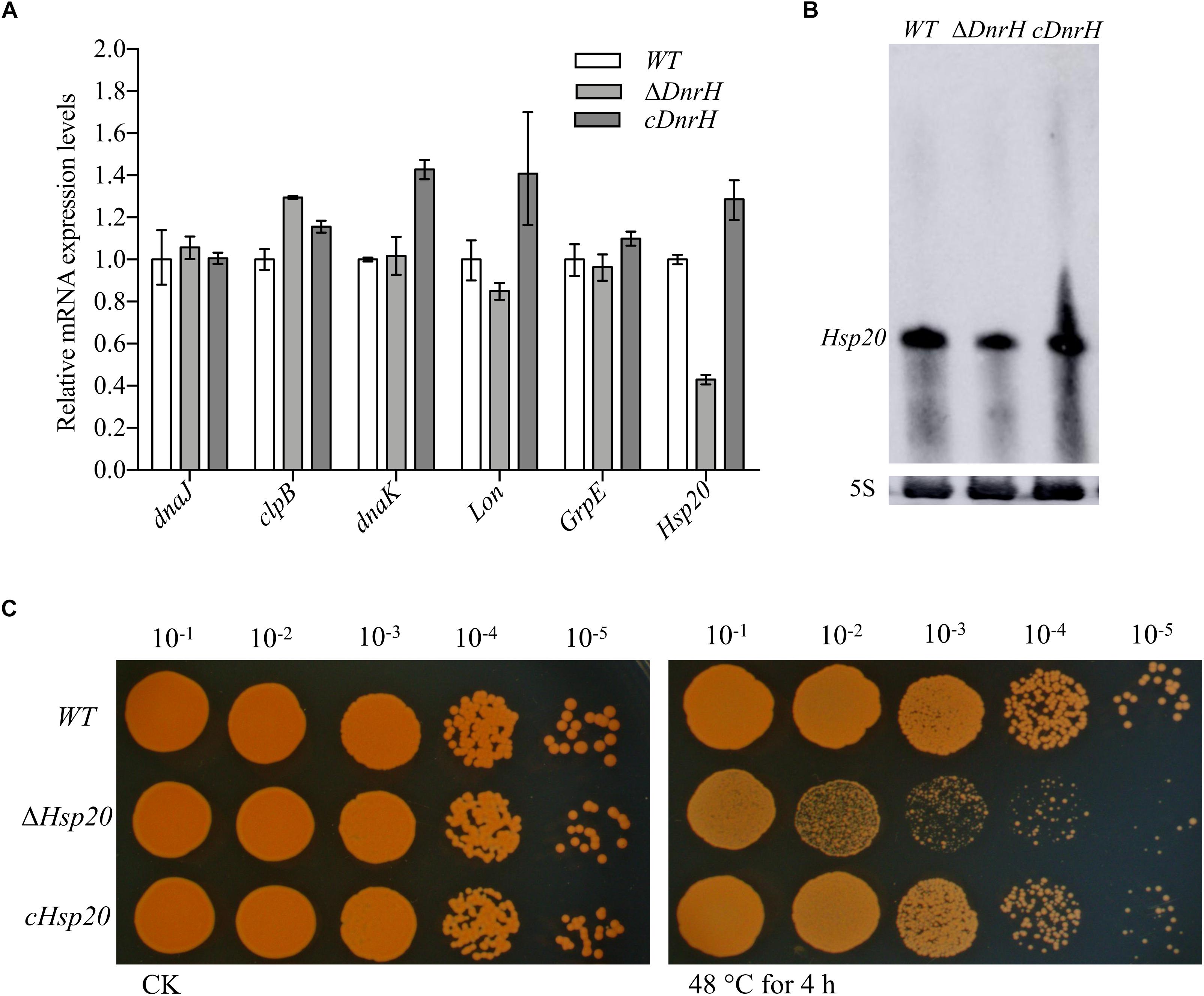
Figure 4. Effect of the presence or absence of DnrH on heat-related genes expression and phenotypic analysis of Hsp20 during heat stress. (A) Expression of the most upregulated heat-related genes comparing ΔDnrH (mutant) and WT strains. Relative levels of transcripts are presented as the mean values ± SD, calculated from three sets of independent experiments, and normalized to levels in the WT strain. (B) RNA northern blot assay using RNA extracted from the same strains under the same conditions and hybridized with the Hsp20-specific probe. (C) Serial 10-fold dilutions of OD-standardized cultures were spotted on TGY plates after exposure to 48°C.
Hsp20 is described as a molecular chaperone that can prevent the aggregation of denatured proteins during abiotic stresses (Muthusamy et al., 2017). We constructed and tested the Hsp20-knockout mutant (Δhsp20) and complementary strain (chsp20) and data showed that Δhsp20 was more sensitive to heat stress at 48°C than the WT strain, whereas chsp20 was essentially identical to the WT with respect to this property (Figure 4C). These results indicate that the loss of hsp20 gene markedly affects heat stress tolerance in D. radiodurans.
Combining qRT-PCR, bioinformatics analysis, and heat phenotype assay experiments, we preliminarily concluded that Hsp20 is the target of DnrH during the regulation of heat stress tolerance. According to the structure predicted by RNAalifold (see Supplementary Figure S3), Hsp20 can form a stable secondary structure with -202.77 kcal/mol free energy. In addition, the computational RNA predictive interaction online tool IntaRNA (Mann et al., 2017) revealed that DnrH (91–117 bp) can bind Hsp20 (143–170 bp) with an interaction energy of -14.2573 kcal/mol. The binding sites of the Hsp20 mRNA are located on a typical stem-loop structure in DnrH (Figure 5A). To further validate this, a set of 30-nt ncRNA oligonucleotides containing the wt or mut sequences were synthesized and the interaction between fluorescently labeled DnrH-wt or DnrH-mut probes and the non-labeled competitor molecule on Hsp20 mRNA was assayed using MST, which allows for the sensitive measurement of molecular interactions in solution. Results indicated that DnrH-wt binds Hsp20 mRNA at low micromolar concentrations in the titrant, exhibiting a dissociation constant (Kd) of 28.34 ± 4.7 μM, which suggests a relatively strong interaction. In contrast, the mutant derivative (DnrH-mut) harboring substitutions in all complementary bases displayed a complete defect in binding to Hsp20 mRNA (Figure 5B).
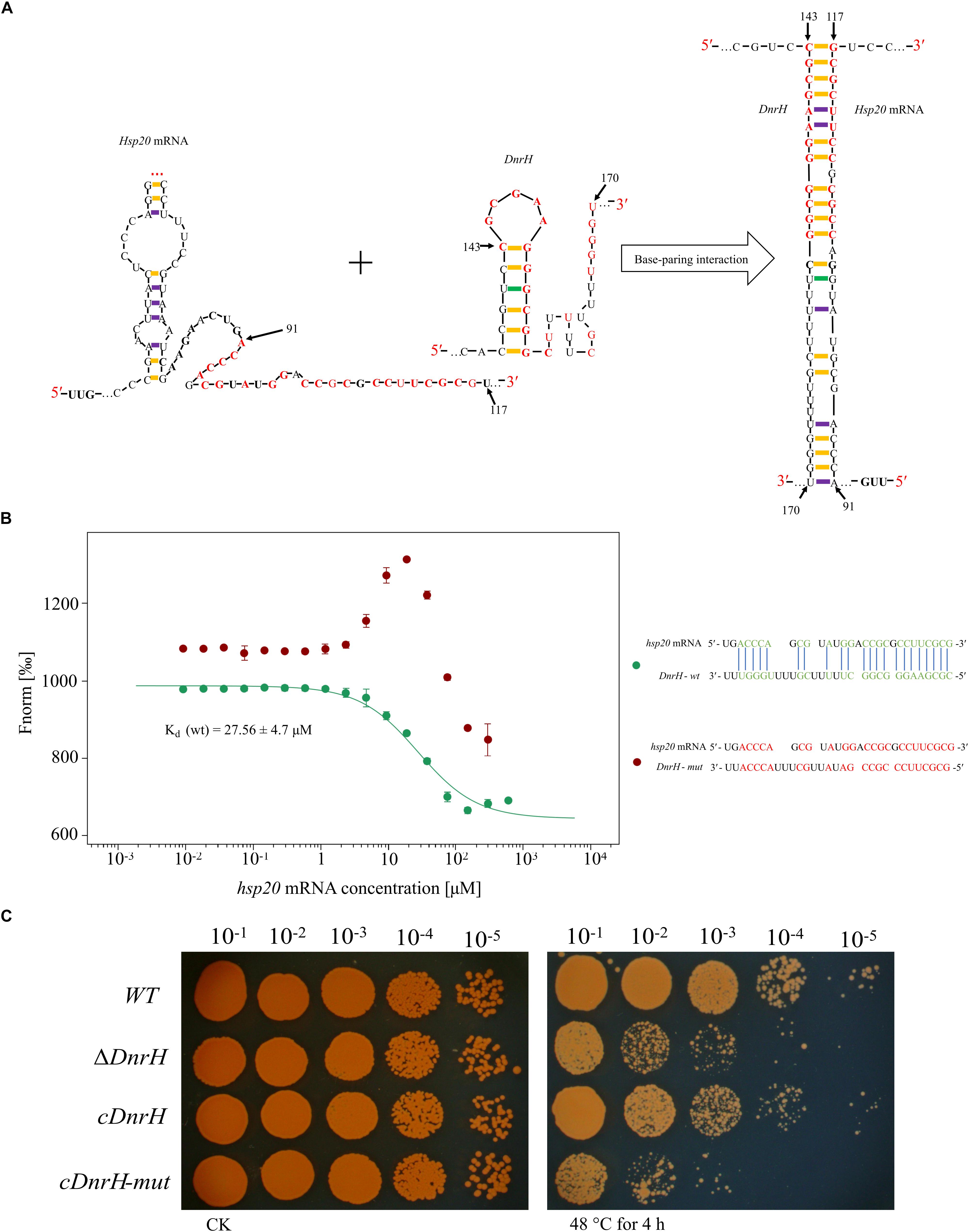
Figure 5. Interaction between DnrH and Hsp20 mRNA in vitro and in vivo. (A) Schematic of the interaction between DnrH and Hsp20 mRNA based on IntaRNA. Exemplary interaction between Hsp20 and DnrH. The region of the interaction is depicted in red bold letters. (B) Interactions between FAM-labeled 5′ upstream region of DnrH-wt [green, Kd (wt)], DnrH-mut (red) and Hsp20 mRNA. All interactions were measured using Monolith NT.115 and Kd-values were calculated based on at least three independent replicates using the Nanotemper MO. Affinity Analysis Software. (C) Serial 10-fold dilutions of OD-standardized cultures were spotted on TGY plates after exposure to 48°C.
In order to validate this putative Hsp20 binding sites onto DnrH, mutated DnrH was cloned into the pRAZ3 plasmid to obtain a recombinant vector (pRAZ3-DnrH-mut). pRAZ3-DnrH-mut was transformed into the DnrH-mutant ΔDnrH to construct a complementary strain (cDnrH-mut). Heat stress experiments showed that the complementary strain cDnrH-mut could not rescue the heat-resistance phenotype (Figure 5C). This result was in agreement with the fact that DnrH-mut lost its ability to bind Hsp20 mRNA. Therefore, we concluded that it is highly likely that DnrH enhances heat tolerance in D. radiodurans based on a regulatory affect mediated by its 22-nt base-pair complementarity with Hsp20 mRNA molecules.
The heat response of D. radiodurans is considered a classical stress-induced regulatory system that is characterized by extensive transcriptional reprograming. Most current research has led to the discovery and characterization of new heat-related proteins, such as sigma factor, groESL, HspR and DdrI (Airo et al., 2004; Schmid et al., 2005a, b; Meyer et al., 2018). Although much effort has been made to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the tolerance of D. radiodurans to heat stress, gene expression reprograming is complex and not yet fully understood. Many ncRNAs have been reported to be associated with bacterial responses to various enviromental stresses (Delihas and Forst, 2001; Majdalani et al., 2001; Masse and Gottesman, 2002; Citartan et al., 2016). While there has been a rapid increase in the identification of bacterial ncRNAs over the last few years, the identification of mRNA targets and the study of ncRNAs’ functions have progressed more slowly. So far, to our knowledge, no ncRNAs with a regulatory role in heat tolerance in extreme bacteria have been reported. Our work shows that DnrH could be the first ncRNA with direct roles in regulating heat tolerance in the model extremophilic bacterium D. radiodurans. As revealed by qRT-PCR and northern blot analysis, DnrH is expressed at a higher level under heat stress, and accordingly, the survival of ΔDnrH was reduced in response to heat stress conditions as compared to that with the WT strain.
To fully understand the function of DnrH in response to heat stress, the regulatory mechanisms of such factors must be identified. ncRNAs usually regulate other genes at the post-transcriptional level by directly or indirectly base-pairing with the target gene mRNA (Storz et al., 2011; Wagner and Romby, 2015). We identified as target the heat shock protein Hsp20 reported to assist in the refolding and hydrolysis of abnormal proteins (Bepperling et al., 2012). Moreover, previous studies have reported that the expression of Hsp20 is increased following exposure to various stresses, including temperature changes (Schmid et al., 2005b; Singh et al., 2014). Here we show that the expression of Hsp20 is significantly down-regulated in the absence of DnrH and provide strong indications for Hsp20 mRNA being a direct target of DnrH. Further, results of MST and genetic complementation suggested that Hsp20 mRNA is a direct target of DnrH. The location of this interaction indicated that DnrH asserts its positive regulatory effect on Hsp20 expression by assisting in ribosome binding.
sHsps can be considered guardians of proteins, especially upon exposure to sudden protein toxic stresses that lead to the accumulation and aggregation of denatured forms. Hsp20 belongs to the large spherical homo-oligomeric sHsps, which are constitutively active and form stable substrate complexes (Haslbeck et al., 2005). Our data confirmed that Hsp20 contribute to heat tolerance (Figure 4C), which is consistent with previously reported results (Airo et al., 2004). Further, in vivo transcriptional analysis indicated that Hsp20 transcripts accumulate to high levels during heat stress, again confirming the role of Hsp20 in high temperature adaptation. A working model, which integrates DnrH and Hsp20 mRNA in response to heat stress is presented in Figure 6. The precise molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of DnrH activities are not yet known and require further investigation. Considering that Hsp20 functions as a chaperon protein, regulation by DnrH might be a two-step process in which DnrH regulates Hsp20 and then affects the transcription of downstream genes. This hypothesis also requires further research.
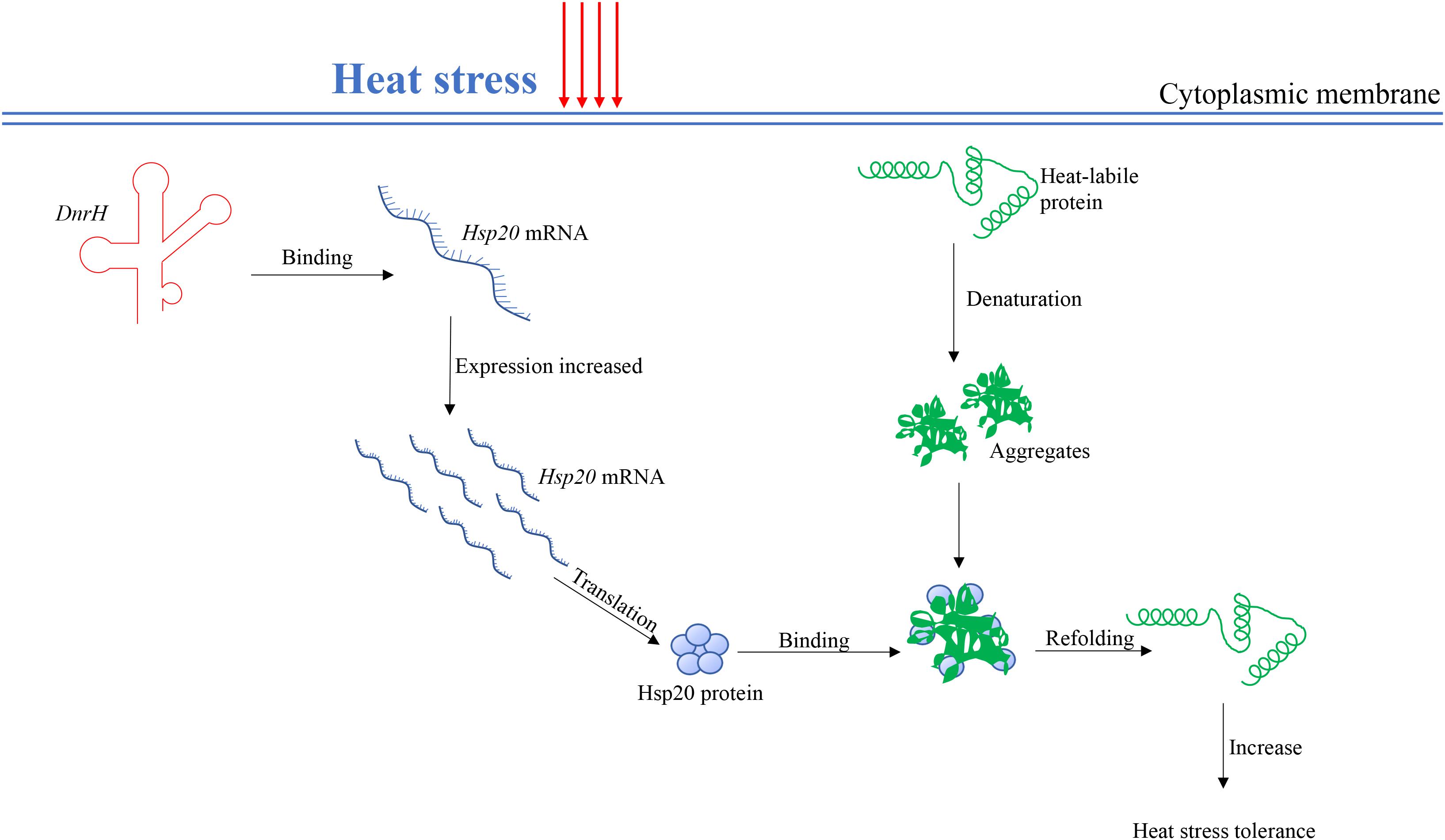
Figure 6. A proposed working model for the DnrH-mediated regulatory network in heat stress response in Deinococcus radiodurans. DnrH act as a riboregulator efficiently binds Hsp20 mRNA to increase heat stress tolerance. This regulation integrates adaptation to heat stress with other cellular metabolic processes helps to protect cells against heat stress damage. For more details, see the results or discussion.
All datasets generated for this study are included in the manuscript/Supplementary Files.
DX, JW, and ML conceived and designed the study. DX performed the experiment, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. MO and JW analyzed the data and critically revised the manuscript. All authors discussed the results, participated in revising the manuscript, and commented on and approved the manuscript for publication.
This work was funded by Key Research and Development Projects (Nos. 2018YFA0901000 and 2018YFA0901003), the Ministry of Agriculture Transgenic Program (No. 2016ZX08009003-002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31800061, 31570080, and 31500063), and the China Scholarship Council. We appreciate the support of the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of CAAS.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02354/full#supplementary-material
Acebo, P., Martin-Galiano, A. J., Navarro, S., Zaballos, Á, and Amblar, M. (2012). Identification of 88 regulatory small RNAs in the TIGR4 strain of the human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. RNA 18, 530–546. doi: 10.1261/rna.027359.111
Airo, A., Chan, S. L., Martinez, Z., Platt, M. O., and Trent, J. D. (2004). Heat shock and cold shock in Deinococcus radiodurans. Cell Biochem. Biophys 40, 277–288. doi: 10.1385/CBB:40:3:277
Arnvig, K. B., Comas, I., Thomson, N. R., Houghton, J., Boshoff, H. I., Croucher, N. J., et al. (2011). Sequence-based analysis uncovers an abundance of non-coding RNA in the total transcriptome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLoS Pathog. 7:e1002342. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002342
Barreto, B., Rogers, E., Xia, J., Frisch, R. L., Richters, M., Fitzgerald, D. M., et al. (2016). The small RNA GcvB promotes mutagenic break repair by opposing the membrane stress response. J. Bacteriol. 198, 3296–3308. doi: 10.1128/jb.00555-16
Bauermeister, A., Moeller, R., Reitz, G., Sommer, S., and Rettberg, P. (2011). Effect of relative humidity on Deinococcus radiodurans’ resistance to prolonged desiccation, heat, ionizing, germicidal, and environmentally relevant UV radiation. Microb. Ecol. 61, 715–722. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9785-4
Bepperling, A., Alte, F., Kriehuber, T., Braun, N., Weinkauf, S., Groll, M., et al. (2012). Alternative bacterial two-component small heat shock protein systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 20407–20412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1209565109
Bernhart, S. H., Hofacker, I. L., Will, S., Gruber, A. R., and Stadler, P. F. (2008). RNAalifold: improved consensus structure prediction for RNA alignments. BMC Bioinformatics 9:474. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-474
Blasius, M., Sommer, S., and Hübscher, U. (2008). Deinococcus radiodurans: what belongs to the survival kit? Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 43, 221–238. doi: 10.1080/10409230802122274
Boysen, A., Møller-Jensen, J., Kallipolitis, B., Valentin-Hansen, P., and Overgaard, M. (2010). Translational regulation of gene expression by an anaerobically induced small non-coding RNA in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 10690–10702. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.089755
Citartan, M., Raabe, C. A., Hoe, C. H., Rozhdestvensky, T. S., and Tang, T. H. (2016). “Bacterial sRNAs: regulation in Stress,” in Stress and Environmental Regulation of Gene Expression and Adaptation in Bacteria, ed. F. J. de Bruijn, (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons).
Daly, M. J. (2009). A new perspective on radiation resistance based on Deinococcus radiodurans. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 237–245. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2073
Del Val, C., Rivas, E., Torres-Quesada, O., Toro, N., and Jiménez-Zurdo, J. I. (2007). Identification of differentially expressed small non-coding RNAs in the legume endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti by comparative genomics. Mol. Microbiol. 66, 1080–1091. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05978.x
Delihas, N., and Forst, S. (2001). MicF: an antisense RNA gene involved in response of Escherichia coli to global stress factors. J. Mol. Biol. 313, 1–12. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5029
Fantappiè, L., Oriente, F., Muzzi, A., Serruto, D., Scarlato, V., and Delany, I. (2011). A novel Hfq-dependent sRNA that is under FNR control and is synthesized in oxygen limitation in Neisseria meningitidis. Mol. Microbiol. 80, 507–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07592.x
Fröhlich, K. S., Papenfort, K., Berger, A. A., and Vogel, J. (2012). A conserved RpoS-dependent small RNA controls the synthesis of major porin OmpD. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 3623–3640. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1156
Harada, K., and Oda, S. (1988). Induction of thermotolerance by split-dose hyperthermia at 52°C in Deinococcus radiodurans. Agric. Biol. Chem. 52, 2393–2396. doi: 10.1080/00021369.1988.10869056
Haslbeck, M., Miess, A., Stromer, T., Walter, S., and Buchner, J. (2005). Disassembling protein aggregates in the yeast cytosol: the cooperation of HSP26 with SSA1 and HSP104. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 23861–23868. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502697200
Jerabek-Willemsen, M., Wienken, C. J., Braun, D., Baaske, P., and Duhr, S. (2011). Molecular interaction studies using microscale thermophoresis. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 9, 342–353. doi: 10.1089/adt.2011.0380
Jin, Y., Watt, R. M., Danchin, A., and Huang, J. D. (2009). Small noncoding RNA GcvB is a novel regulator of acid resistance in Escherichia coli. BMC Genomics 10:165. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-165
Landt, S. G., Abeliuk, E., McGrath, P. T., Lesley, J. A., McAdams, H. H., and Shapiro, L. (2008). Small non-coding RNAs in Caulobacter crescentus. Mol. Microbiol. 68, 600–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06172.x
Lesley, S. A., Graziano, J., Cho, C. Y., Knuth, M. W., and Klock, H. E. (2002). Gene expression response to misfolded protein as a screen for soluble recombinant protein. Protein Eng. 15, 153–160. doi: 10.1093/protein/15.2.153
Lippok, S., Seidel, S. A. I., Duhr, S., Uhland, K., Holthoff, H. P., Jenne, D., et al. (2012). Direct detection of antibody concentration and affinity in human serum using microscale thermophoresis. Anal. Chem. 84, 3523–3530. doi: 10.1021/ac202923j
Liu, J. M., and Camilli, A. (2010). A broadening world of bacterial small RNAs. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 13, 18–23. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.11.004
Lybecker, M. C., and Samuels, D. S. (2007). Temperature-induced regulation of RpoS by a small RNA in Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 64, 1075–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05716.x
Majdalani, N., Chen, S., Murrow, J., St. John, K., and Gottesman, S. (2001). Regulation of RpoS by a novel small RNA: the characterization of RprA. Mol. Microbiol. 39, 1382–1394. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02329.x
Mandin, P., Geissmann, T., Cossart, P., Repoila, F., and Vergassola, M. (2007). Identification of new noncoding RNAs in Listeria monocytogenes and prediction of mRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 962–974. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1096
Mann, M., Wright, P. R., and Backofen, R. (2017). IntaRNA 2.0: enhanced and customizable prediction of RNA-RNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W435–W439. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx279
Masse, E., and Gottesman, S. (2002). A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99, 4620–4625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.032066599
Meyer, L., Coste, G., Sommer, S., Oberto, J., Confalonieri, F., Servant, P., et al. (2018). DdrI, a cAMP receptor protein family member, acts as a major regulator for adaptation of Deinococcus radiodurans to various stresses. J. Bacteriol. 200:e00129-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00129-18
Muthusamy, S. K., Dalal, M., Chinnusamy, V., and Bansal, K. C. (2017). Genome-wide identification and analysis of biotic and abiotic stress regulation of small heat shock protein (HSP20) family genes in bread wheat. J. Plant Physiol. 211, 100–113. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.01.004
Patel, B. A., Moreau, M., Widom, J., Chen, H., Yin, L., Hua, Y., et al. (2009). Endogenous nitric oxide regulates the recovery of the radiation-resistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans from exposure to UV light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 18183–18188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907262106
Richards, G. R., and Vanderpool, C. K. (2011). Molecular call and response: the physiology of bacterial small RNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1809, 525–531. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.07.013
Schmid, A. K., Howell, H. A., Battista, J. R., Peterson, S. N., and Lidstrom, M. E. (2005a). Global transcriptional and proteomic analysis of the Sig1 heat shock regulon of Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Bacteriol. 187, 3339–3351. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.10.3339-3351.2005
Schmid, A. K., Howell, H. A., Battista, J. R., Peterson, S. N., and Lidstrom, M. E. (2005b). HspR is a global negative regulator of heat shock gene expression in Deinococcus radiodurans. Mol. Microbiol. 55, 1579–1590. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04494.x
Schmid, A. K., Lipton, M. S., Mottaz, H., Monroe, M. E., Smith, R. D., and Lidstrom, M. E. (2005c). Global whole-cell FTICR mass spectrometric proteomics analysis of the heat shock response in the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Proteome Res. 4, 709–718. doi: 10.1021/pr049815n
Schmid, A. K., and Lidstrom, M. E. (2002). Involvement of two putative alternative sigma factors in stress response of the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6182–6189. doi: 10.1128/jb.184.22.6182-6189.2002
Sheng, D., Gao, G., Tian, B., Xu, Z., Zheng, Z., and Hua, Y. (2005). RecX is involved in antioxidant mechanisms of the radioresistant bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 244, 251–257. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.051
Singh, H., Appukuttan, D., and Lim, S. (2014). Hsp20, a small heat shock protein of Deinococcus radiodurans, confers tolerance to hydrogen peroxide in Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 1118–1122. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1403.03006
Solovyev, V., and Salamov, A. (2011). “Automatic annotation of microbial genomes and metagenomic sequences,” in In Metagenomics and its Applications in Agriculture, Biomedicine and Environmental Studies, ed. R. W. Li, (Hauppauge, NY: Nova Science Publishers), 61–78.
Storz, G., Vogel, J., and Wassarman, K. M. (2011). Regulation by small RNAs in bacteria: expanding frontiers. Mol. Cell. 43, 880–891. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.022
Timmins, J., and Moe, E. (2016). A decade of biochemical and structural studies of the DNA repair machinery of Deinococcus radiodurans: major Findings, functional and mechanistic insight and challenges. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 14, 168–176. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.04.001
Tsai, C.-H., Liao, R., Chou, B., and Contreras, L. M. (2015). Transcriptional analysis of Deinococcus radiodurans reveals novel small RNAs that are differentially expressed under ionizing radiation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81, 1754–1764. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03709-14
Ventura, M., Canchaya, C., Zhang, Z., Bernini, V., Fitzgerald, G. F., and Van Sinderen, D. (2006). How high G+C gram-positive bacteria and in particular bifidobacteria cope with heat stress: protein players and regulators. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30, 734–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2006.00031.x
Wagner, E. G. H., and Romby, P. (2015). Small RNAs in bacteria and archaea: who they are, what they do, and how they do it. Adv. Genet. 90, 133–208. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2015.05.001
Wang, L., Xu, G., Chen, H., Zhao, Y., Xu, N., Tian, B., et al. (2008). DrRRA: a novel response regulator essential for the extreme radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans. Mol. Microbiol. 67, 1211–1222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06113.x
Wassarman, K. M. (2002). Small RNAs in bacteria: diverse regulators of gene expression in response to environmental changes. Cell 109, 141–144. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00717-1
Wassarman, K. M., Zhang, A., and Storz, G. (1999). Small RNAs in Escherichia coli. Trends Microbiol. 7, 37–45. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(98)01379-1
Will, S., Joshi, T., Hofacker, I. L., Stadler, P. F., and Backofen, R. (2012). LocARNA-P: accurate boundary prediction and improved detection of structural RNAs. RNA 18, 900–914. doi: 10.1261/rna.029041.111
Keywords: small non-coding RNA, Deinococcus radiodurans, heat stress, DnrH, Hsp20 mRNA
Citation: Xue D, Chen Y, Li J, Han J, Liu Y, Jiang S, Zhou Z, Zhang W, Chen M, Lin M, Ongena M and Wang J (2019) Targeting Hsp20 Using the Novel Small Non-coding RNA DnrH Regulates Heat Tolerance in Deinococcus radiodurans. Front. Microbiol. 10:2354. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02354
Received: 03 June 2019; Accepted: 27 September 2019;
Published: 11 October 2019.
Edited by:
Nils-Kaare Birkeland, University of Bergen, NorwayReviewed by:
Ruben Michael Ceballos, University of Arkansas, United StatesCopyright © 2019 Xue, Chen, Li, Han, Liu, Jiang, Zhou, Zhang, Chen, Lin, Ongena and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Marc Ongena, TWFyYy5PbmdlbmFAdWxnLmFjLmJl; Jin Wang, d2FuZ2ppbkBjYWFzLmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.