- 1National Reference Laboratory of Veterinary Drug Residues (HZAU), Ministry of Agriculture Key Laboratory for the Detection of Veterinary Drug Residues in Foods, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
- 2Ministry of Agriculture Laboratory for Risk Assessment of Quality and Safety of Livestock and Poultry Products, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides (QdNOs) are a class of bioreductive compounds, however, their antibacterial mechanisms are still unclarified. The aim of this study was to assess the ability of two representative QdNO drugs, cyadox (CYA) and olaquindox (OLA), to produce reactive oxide species (ROS) in Gram-positive anaerobe Clostridium perfringens CVCC1125 and Gram-negative anaerobe Brachyspira hyodysenteriae B204. In addition, the effects of QdNOs on the integrity of bacterial cell walls and membranes as well as the morphological alterations and DNA oxidative damage in C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae were analyzed. It was demonstrated that under anaerobic conditions, QdNOs were metabolized into the reduced products which did not show any antibacterial activity. A significant dose-related increase of intracellular ROS level and intracellular hydroxyl radicals were evident in bacteria exposed to QdNOs. The result of biochemical assay showed that the cell walls and membranes of the bacteria treated with QdNOs were damaged. After exposure to 1/2MIC to 4MIC of CYA and OLA, C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae became elongated and filamentous. Morphological observation with scanning and transmission electron microscopes revealed rupture, loss of cytoplasmic material and cell lysis in QdNO-treated bacteria, indicating serious damage of cells. There was an increase of 8-OHdG in the two strains treated by QdNOs, but it was lower in C. perfringens CVCC1125 than in B. hyodysenteriae B204. Agarose gel electrophoresis showed the degradation of chromosomal DNA in both of the two anaerobes treated by QdNOs. The results suggest that QdNOs may kill C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae via the generation of ROS and hydroxyl radicals from the bacterial metabolism of QdNOs, which cause oxidative damage in bacteria under anaerobic conditions.
Introduction
Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives (QdNOs), including carbadox, OLA, mequindox, quinocetone, and CYA, are a class of synthetic heterocycles that are known as potent antibacterial agents against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, especially anaerobes. Carbadox, OLA, mequindox are commonly used as feed additives to prevent bacterial infectious disease and improve animal growth in livestock and poultry (Cheng et al., 2016).
Clostridium perfringens is a Gram-positive spore-forming obligate anaerobe that causes food poisoning, gas gangrene, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea (Farzan et al., 2013; Uzal et al., 2014). Swine dysentery (SD) is a common disease caused by the anaerobic intestinal Brachyspira hyodysenteriae among pigs worldwide (Moxley and Duhamel, 1999), which contributes to major production losses. Recently, an increase of antimicrobial resistance to antibiotics used for routine treatment of SD has been observed in most European countries (Alvarez-Ordonez et al., 2013), and this may be caused by excessive use of antibiotics (Domadia et al., 2008). C. perfringens with decreased susceptibility to metronidazole (Alvarez-Perez et al., 2016) was found to be sensitive to CYA and OLA in the study of our laboratory. Besides, carbadox used to be added to feed or drinking water for the treatment of SD (Sabbatini, 2009).
However, carbadox, OLA, and mequindox were shown to have genetic and carcinogenic toxicity to eukaryotic cell (Liu et al., 2016). CYA is a novel QdNO derivative, and is a safe member of the QdNO family according to the microbiological safety evaluation of CYA (Hao et al., 2013).
Previous studies have revealed that QdNOs are DNA synthesis inhibitors, which can cause cytotoxic DNA strand breaks in Escherichia coli (Suter et al., 1978; Ganley et al., 2001; Cheng et al., 2015). There is no evidence that QdNOs can covalently bind to DNA (Ganley et al., 2001). Though recent study has provided support for the involvement of free radicals induced by QdNOs in E. coli (Cheng et al., 2015), it remains unclear how QdNOs modify the structure of DNA. Moreover, the existing knowledge about the antibacterial action of QdNOs has only been studied in E. coli, and little is known about their antibacterial modes in Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes.
In this study, the mechanisms of the antibacterial action of QdNOs against Gram-positive anaerobe C. perfringens and Gram-negative anaerobe B. hyodysenteriae were investigated. The measurement of free radicals in Gram-positive bacteria and anaerobes treated by QdNOs was complementary to the study of antibacterial mechanism of QdNOs in E. coli. The effects of QdNOs on the integrity of cell walls and cell membrane as well as DNA damage were analyzed. This study provides new insights into the effectiveness and the underlying mechanism of QdNOs against anaerobes to contribute to the development of new QdNOs.
Materials and Methods
Drugs and Chemicals
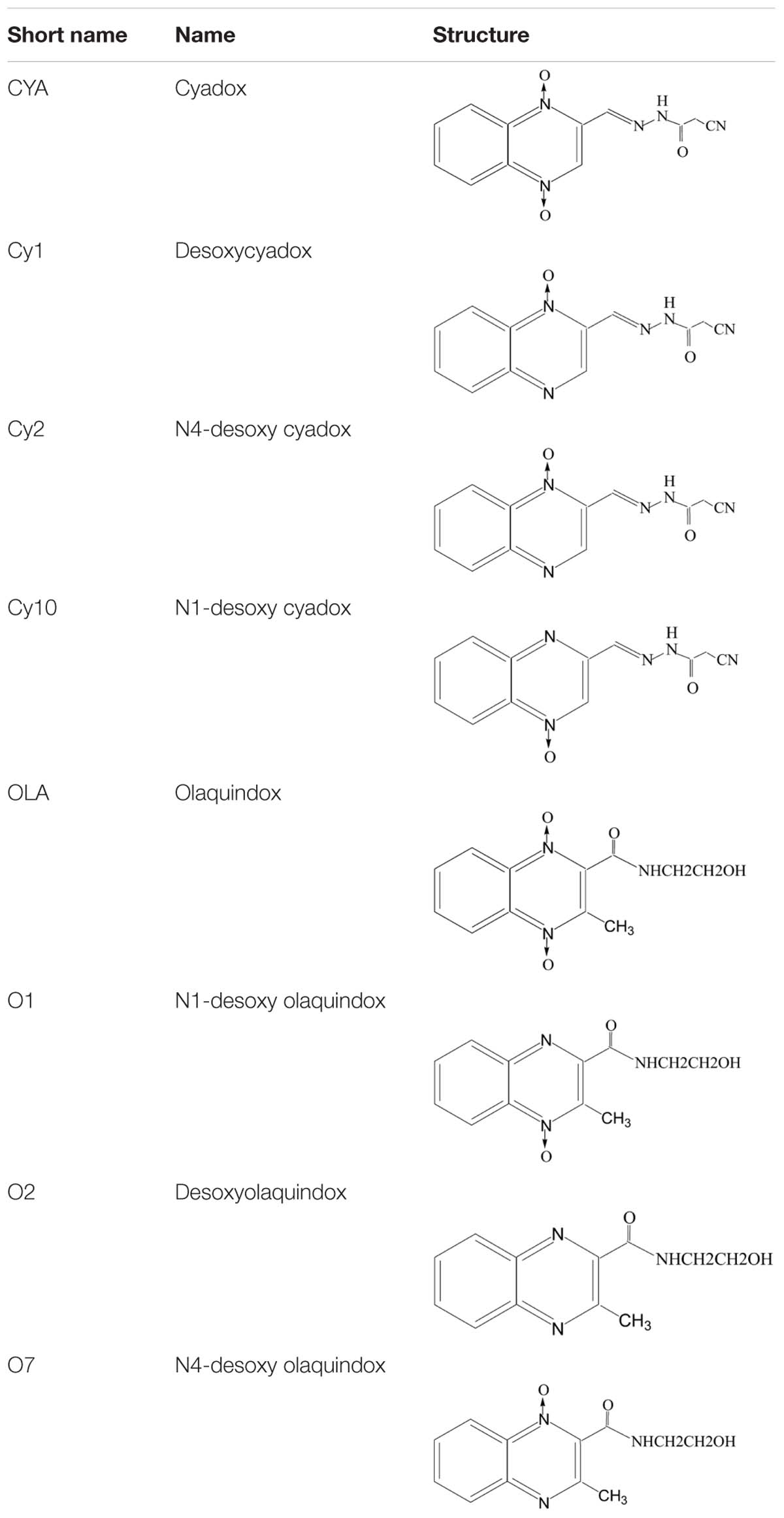
Cyadox, bisdesoxycyadox (Cy1), Cy2 and Cy10, OLA, olaquindox-4-monoxide (O1), olaquindox-1-monoxide (O7), and bisdesoxyolaquindox (O2) (Table 1) were synthesized by the Institute of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals (HZAU) (Wuhan, China). ALP detection kit and ROS assay kit were obtained from Beyotime (Shenzhen, China). 3′-(p-hydroxyphenyl) fluorescein (HPF) was acquired bought from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit was obtained from QIAGEN (Nasdaq, Germany). OxiSelect Oxidative DNA Damage ELISA Kit was obtained from Cell Biolabs (Santiago, USA). All other chemicals and reagents commercially available were of the highest analytical grade.
Bacteria Strains and Culture Conditions
Pig-origin C. perfringens CVCC1125 (type A) was obtained from the China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control (IVDC) and B. hyodysenteriae B204 (ATCC31212) was acquired from the ATCC.
Clostridium perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were incubated, respectively, on trypticase soy agar (TSA) plates supplemented with 5% sheep blood and BHI broth supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum broth anaerobically (80% N2, 10% H2, 10% CO2) at 37°C for 24 or 72 h as previously described before (Lugsomya et al., 2012).
Antibacterial Susceptibility Test
The MICs of QdNOs and their metabolites against C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 were determined by the agar dilution method according to the M11-A7 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (CLSI, 2007).
Intracellular ROS and Hydroxyl Radical Measurement
The bacterial culture (about 107 CFU/mL, McFarland standard 0.5 for C. perfringens and McFarland standard 1 for B. hyodysenteriae) was treated with QdNOs at different concentrations under anaerobic conditions and incubated for indicated times at 37°C. The reactions were stopped at 4°C. DCFH-DA was used to detect intracellular ROS in C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae, respectively, by fluorescence microplate reader according to the a prior study (Cheng et al., 2015). The samples were analyzed for ROS generation using fluorescence excitation and emission wavelengths at 488 and 525 nm by fluorescence microplate reader, respectively.
3-(p-aminophenyl) fluorescein (APF) (Invitrogen, Canada) was used for the detection of hydroxyl radicals in bacteria treated by QdNOs. A generation of hydroxyl radical was monitored by adding 10 μM of APF to each tube containing bacterial inoculum and drug dilutions (5 mL). The samples were analyzed for hydroxyl radical generation using fluorescence excitation and emission wavelengths at 490 and 530 nm by fluorescence microplate reader, respectively.
2.5 mM (85 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control for C. perfringens CVCC1125 and 300 μM (10.2 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control for B. hyodysenteriae B204 (Stanton et al., 2008b).
Cell Wall Integrity Measurement
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme present in the periplasmic space of the bacteria (Arokiyaraj et al., 2015). ALP was measured in QdNO-treated bacterial culture (about 106 CFU/mL) using an ALP assay kit (Beyotime, Shenzhen, China). This assay involved a colorimetric determination of para-nitrophenol (p-nitrophenol) released from para-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP) with absorption which can be detected at 405 nm by microplate reader. After incubation, cell free supernatants were collected. All the treatments were compared with control wells (cells without treatment) and the final results were expressed in units/liter (Arokiyaraj et al., 2015).
Cell Membrane Integrity Measurement
Bacterial cell membrane integrity was examined by determining the release of intracellular materials as previously described (Eom et al., 2014). Bacterial cells (about 106 CFU/mL) of C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae were harvested by centrifugation at 3500 rpm for 10 min and washed twice by 0.9% NaCl solution. The bacteria suspensions were exposed to QdNOs at the indicated concentrations and tested at 30 min intervals during 120 min. Subsequently the release of intracellular materials absorbing at 260 nm was determined using a UV spectrometer, which were interpreted to be mostly DNA and RNA (Chen and Cooper, 2002).
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Bacteria (about 106 CFU/mL) were exposed to different concentrations of CYA or OLA at indicated time under anaerobic conditions. Enrofloxacin, a DNA-damaging fluoroquinolone which can induce SOS response leading to the filamentation of bacteria (Piddock et al., 1990), was used as a positive control drug. Samples were washed with PBS and fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde overnight at 4°C. After washing with PBS three times, the cells were dehydrated in a gradually increased concentration series (30, 50, 70, 85, and 95%) of ethanol solution for 15 min. The cells were then washed in 100% ethanol for 20 min twice before being freeze-dried and coated with gold and subjected to SEM analysis (JSM-6390LV, Japan) (Kumar Tyagi et al., 2013; Cheng et al., 2015).
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Bacteria (about 106 CFU/mL) were exposed to QdNOs (enrofloxacin was used as a positive control drug), then were harvested by centrifugation, washed thrice with 0.1M PBS (pH 7.4), and fixed in 0.2% glutaraldehyde in 0.1 M cacodylate buffer for 4 h at 4°C, and then fixed in the perfluorocarbon containing 1% osmium tetroxide for 1 h. After three rinses in pure perfluorocarbon, the samples were dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained, and imaged with a TEM (H-7650, Japan) as previously described (Kumar Tyagi et al., 2013).
Detection of QdNO-Induced Chromosomal DNA Damage
Bacterial cultures (about 106 CFU/mL) in early exponential growth phase in BHI broth were treated with different concentrations of drugs. Enrofloxacin (2 μg/ml) was used as the positive DNA-damaging agent for C. perfringens, and 200 μM, (6.8 μg/mL) H2O2 was use as positive agent for B. hyodysenteriae by agarose gel electrophoresis (Matson et al., 2005).
OxiSelect Oxidative DNA Damage ELISA Kit (Cell Biolabs, Santiago, CA, USA) were used to detect DNA oxidative damage (Matson et al., 2005). 2.5 mM (85 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as the positive for C. perfringens, and 200 μM (6.8 μg/mL) H2O2 was use as positive agent for B. hyodysenteriae.
The DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Nasdaq, Germany) was used to extract chromosomal DNA of C. perfringens, using the Gram-positive bacterial protocol, while the Gram-negative bacterial protocol of DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit was used to extract B. hyodysenteriae chromosomal DNA as previously described (La et al., 2014). DNA was resuspended in sterile water and stored at -20°C.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) with all data represented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) from at least three independent experiments. Data analyses were done using the t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and p-value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
The Antibacterial Activities of QdNOs and Their Metabolites against C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae
Cyadox was metabolized into Cy1 and Cy2 in C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 under anaerobic conditions (Supplementary Figure S1). OLA was metabolized into O1 and O2 in these two species under anaerobic conditions (Supplementary Figure S2), indicating that QdNO was mainly reduced at the two N-oxide groups on the quinoxaline ring. The MICs for QdNOs against C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 are presented in Table 2. The MIC values of both CYA and OLA on C. perfringens CVCC1125 were 1 μg/ml. CYA and OLA had a MIC value of 0.031 and 0.0625 μg/ml for B. hyodysenteriae B204, respectively. Although both species were susceptible to QdNOs, the N-deoxy metabolites of QdNOs showed no antibacterial activity (MIC > 128 μg/ml) (Table 2), indicating that the two N-oxide groups were necessary for the antibacterial activity of QdNOs against these two anaerobes.
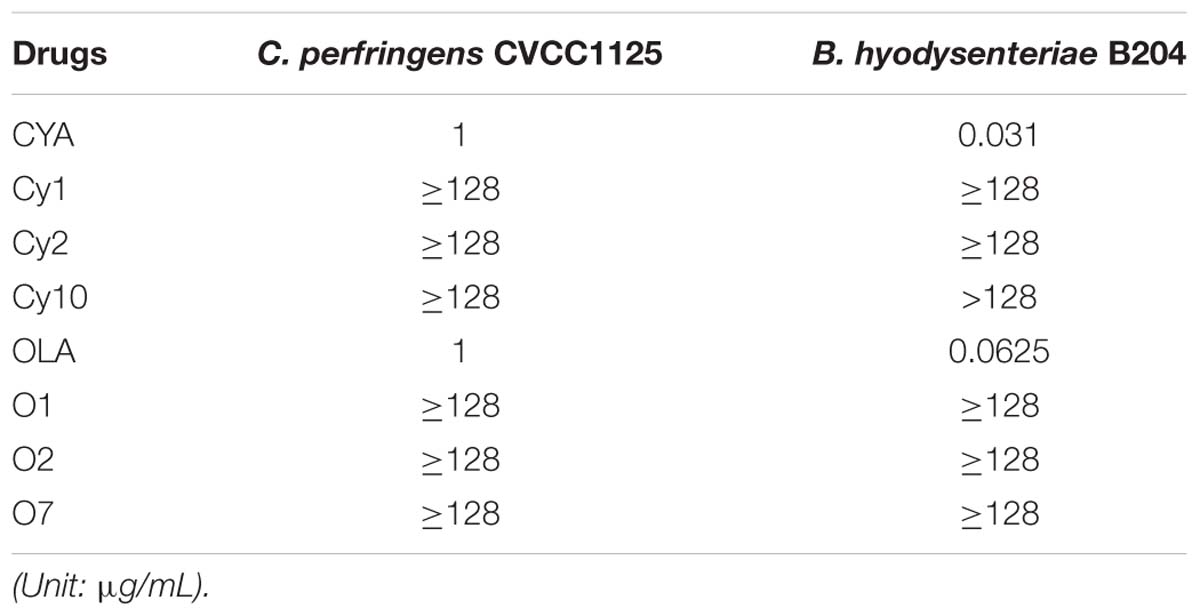
TABLE 2. Minimum inhibitory concentration of CYA, OLA and their metabolites against C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae under anaerobic conditions.
Clostridium perfringens CVCC1125 growths measured by OD at 600 nm (the culture OD) treated with low concentrations CYA and OLA (0.5 and 1 μg/ml) were less affected compared to the groups treated with high concentration CYA and OLA (2 and 4 μg/ml) (Supplementary Figures S3A,B). C. perfringens CVCC1125 growth treated by 2 μg/ml CYA and OLA was greatly inhibited (little increase in the culture) from 0 to 4 h. C. perfringens CVCC1125 growth treated by 4 μg/ml CYA and OLA was greatly inhibited for nearly 6 h, but the culture OD increased slowly after that. B. hyodysenteriae B204 growth treated with 0.031 μg/ml CYA (Supplementary Figure S3C) and 0.0625 μg/ml OLA (Supplementary Figure S3D) was inhibited (a slower increase in the culture OD from 0 to 12 h compared to the untreated B. hyodysenteriae cells). B. hyodysenteriae B204 growth treated with high concentration QdNOs (0.125 μg/ml CYA and 0.25 μg/ml OLA) was greatly affected (the culture OD declined from 2 to 12 h), suggesting that the cells were killed. While, B. hyodysenteriae B204 growth treated by 0.016 μg/ml CYA and 0.031 μg/ml OLA was less influenced compared to B. hyodysenteriae cells treated with high concentration QdNOs. So QdNOs are concentration-dependent antibacterials for C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204.
QdNO-Induced ROS and Hydroxyl Radical Production
Under anaerobic conditions, ROS were detected in C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 exposed to QdNOs (Figures 1A,B). The levels of ROS in QdNOs or H2O2-treated cells were significantly higher than that of ROS in control cells from the time period of 30 to180 min.
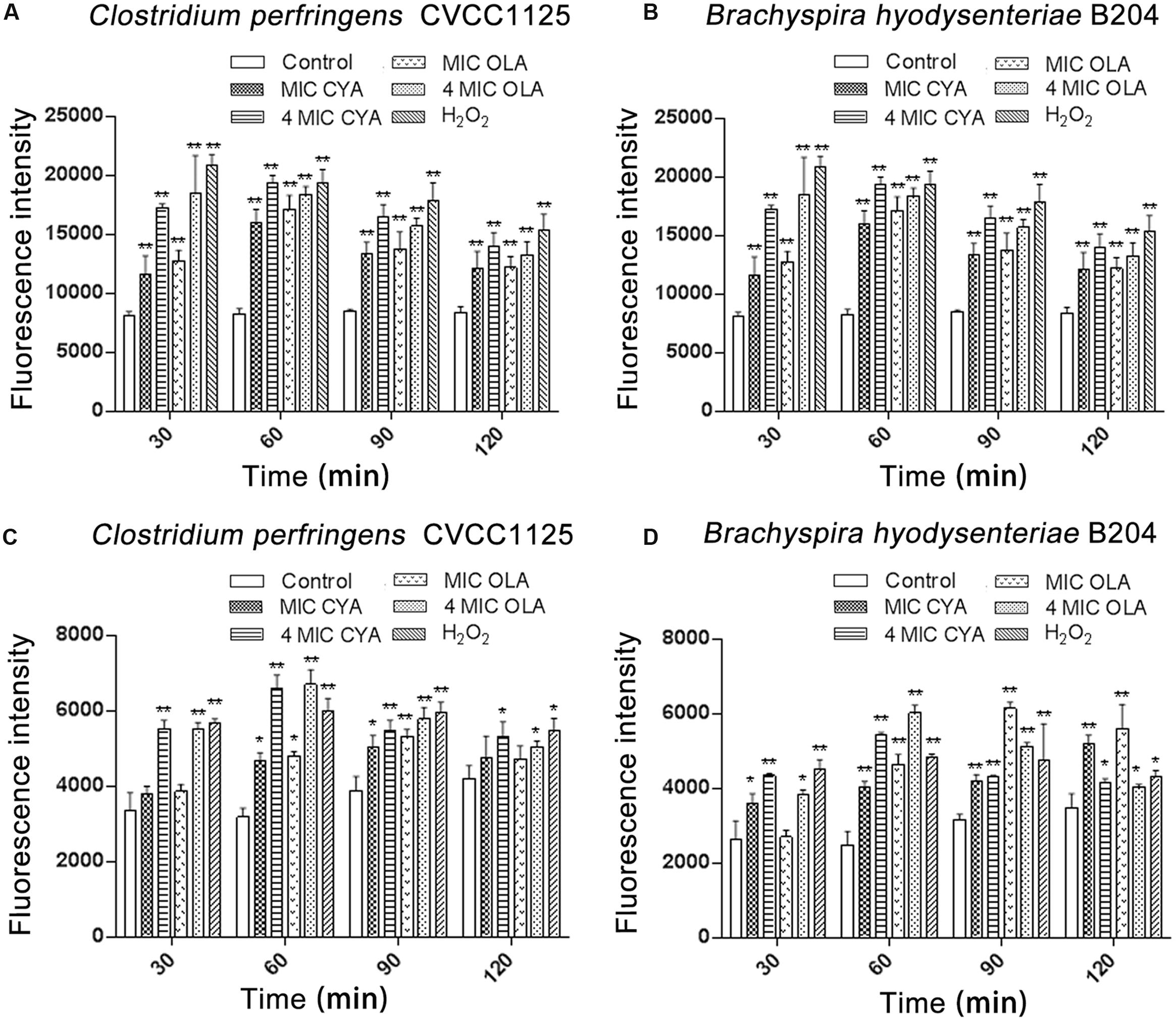
FIGURE 1. Intracellular levels of ROS (A,B) and hydroxyl radicals (C,D) in Clostridium perfringens and Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. (A,C) Under anaerobic conditions, C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA, and 2.5 mM (85 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control. (B,D) Under anaerobic conditions, B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA, and 300 μM (10. 2 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control. The levels of ROS (A,B) and hydroxyl radicals (C,D) were determined as described in the section “Materials and Methods.” Data were shown as mean ± SD (error bar), n = 3. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
Besides, under anaerobic conditions, QdNOs induced a release of hydroxyl radicals (Figures 1C,D), and the HPF fluorescence intensity in C. perfringens CVCC1125 was observed under fluorescence microscope (Supplementary Figure S4). The levels of hydroxyl radicals in QdNOs or H2O2-treated cells were significantly higher than the level of ROS in control cells.
The production of ROS and hydroxyl radicals increased in C. perfringens CVCC1125 or B. hyodysenteriae B204 incubated with an increasing concentration of QdNOs, with statistical significances between different doses, indicating that the ROS and hydroxyl radical formation were dose-dependent.
Effect of QdNOs on the Integrity of Bacterial Cell Wall
In our study, the ALP levels in the C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae cells were increased upon treatment with QdNOs compared to the non-treated groups (Figure 2). In the present results, the increase of the amount of ALP upon CYA and OLA addition was greater in C. perfringens than in B. hyodysenteriae, probably because that C. perfringens is a spore-forming obligate anaerobe, which produces higher amounts of ALP during phosphate starvation and sporulation (Tsai and Su, 1999; Sebastian and Ammerman, 2009).
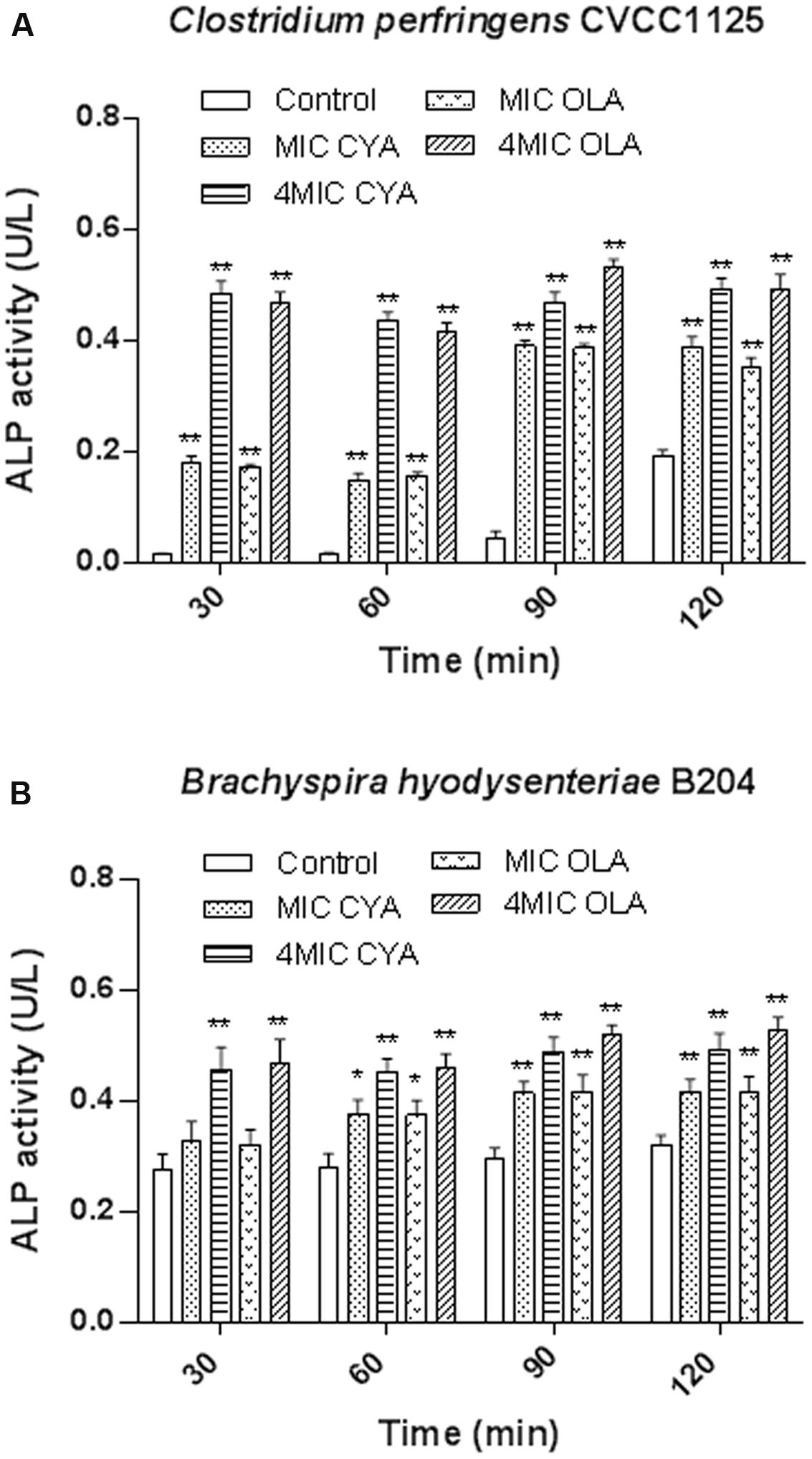
FIGURE 2. The effects of QdNOs on the cell wall integrity of C. perfringens CVCC1125 (A) and B. hyodysenteriae B204 (B). (A) Under anaerobic conditions, C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA. (B) Under anaerobic conditions, B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA. The ALP level was determined by fluorescence microplate reader as described in the material and methods. Data were shown as mean ± SD (error bar), n = 3. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
Effect of QdNOs on the Integrity of Bacterial Membrane
The release of cell materials absorbing at 260 nm, mainly DNA or RNA materials leaked from the cells. These results show that leakage of A260 absorbing material from the bacterial cells increased with increasing QdNOs concentration and exposure time (Figure 3). When C. perfringens cells and B. hyodysenteriae cells were treated with 4MIC CYA and 4MIC OLA, absorbance of the suspensions at 260 nm increased significantly up to120 min. But the leakage of A260 absorbing material from C. perfringens cells and B. hyodysenteriae cells treated with MIC CYA and MIC OLA increased slowly. So the release rate of the intracellular components showed a dose-dependent increasing tendency, suggesting that the membrane integrity was significantly affected by high concentration of QdNOs.
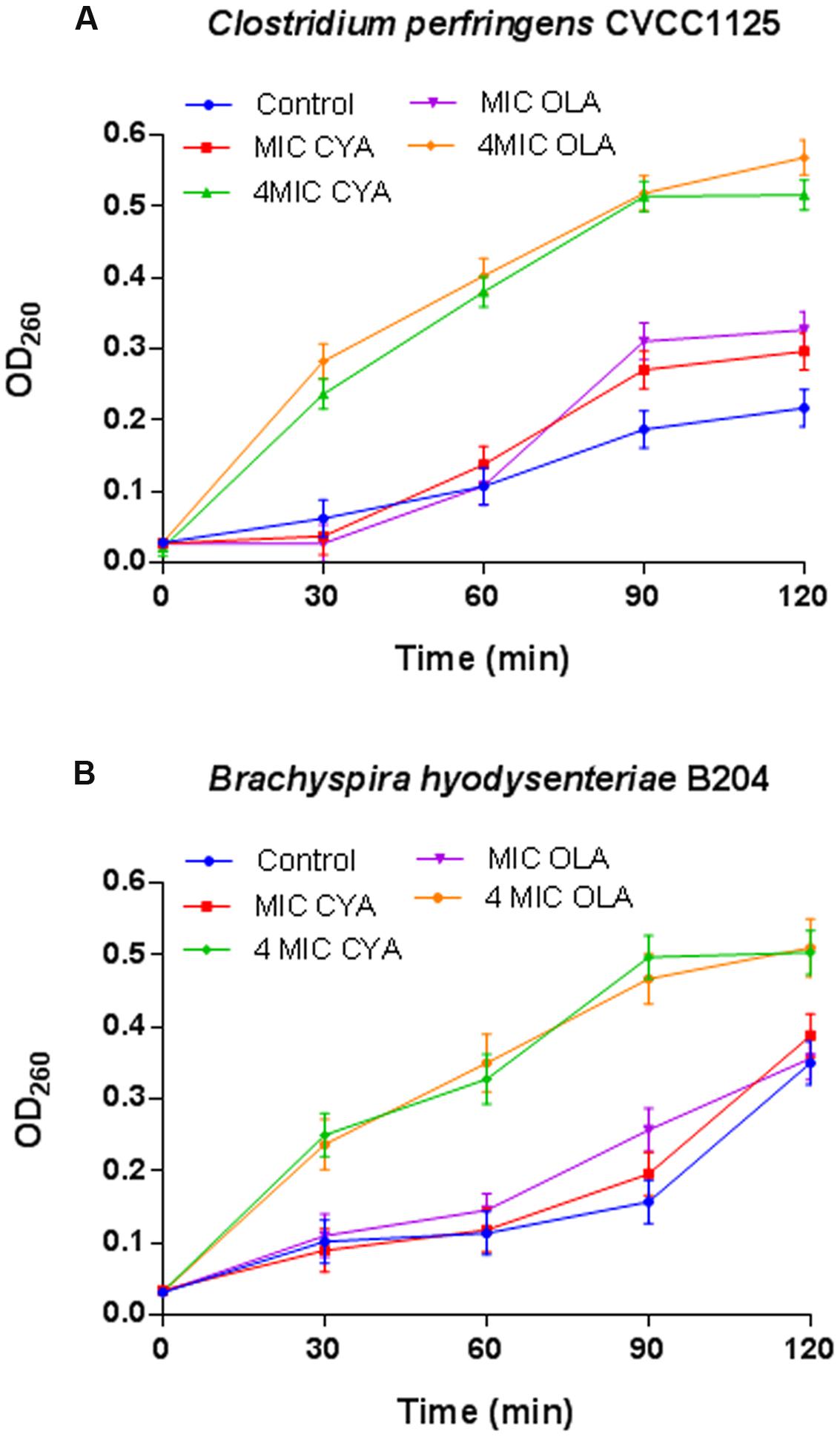
FIGURE 3. Effects of QdNOs on cell membrane integrity of C. perfringens CVCC1125 (A) and B. hyodysenteriae B204 (B). (A) Under anaerobic conditions, C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA. (B) Under anaerobic conditions, B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were treated with indicated concentration of CYA or OLA. The release of cell materials absorbing at 260 nm was determined by a UV spectrometer as described in the material and methods. Data were shown as mean ± SD (error bar), n = 3.
Morphological Alterations of C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae Exposed to QdNOs
After exposure to 1/2MIC to 4MIC of CYA and OLA, C. perfringens CVCC1125 and B. hyodysenteriae B204 became elongated as observed by light microscope (Supplementary Figure S5) and SEM (Figure 4), indicating that the cell division was halted. C. perfringens CVCC1125 treated with CYA and OLA appeared longer, with rougher surface (Figures 4C,F), and became deformed and cracked (Figures 4D,E) in comparison to the control. The control appeared as intact rod shape and with a completely smooth surface (Figure 4A). The untreated B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells exhibited a typical smooth helical form with pointed ends which separated with each other (Figure 4G), while cells treated with CYA or OLA appeared to be aggregated, retracted (Figures 4H,K,L), partially deformed (Figures 4I,J), and with rough surface (Figures 4H–L).
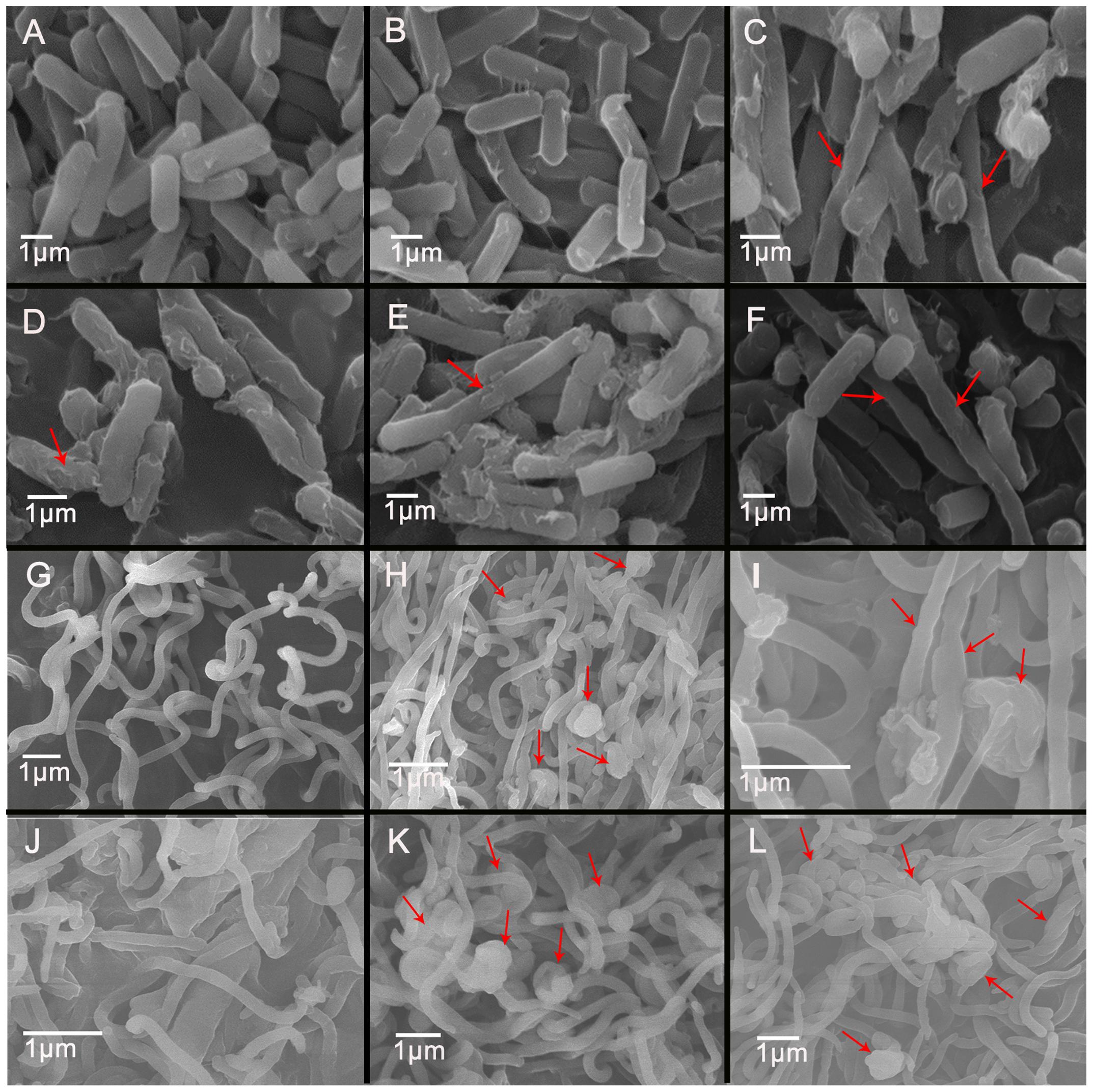
FIGURE 4. Scanning electron microscopy of C. perfringens (A–F) and B. hyodysenteriae (G–L) cells exposed to QdNOs. C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were untreated (A) or treated with 0.08% DMSO (B), 1 μg/mL CYA (C), 4 μg/mL CYA (D), 1 μg/mL OLA (E), and 1 μg/mL enrofloxacin as positive control (F) under anaerobic conditions for 6 h. B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were untreated (G) or treated with 0.031 μg/mL CYA (H), 0.031 μg/mL CYA (I), 0.125 μg/mL CYA (J), and 0.0625 μg/mL OLA (K) and 8 μg/mL enrofloxacin as positive control (L) under anaerobic conditions for 6 h.
Transmission electron microscopy demonstrated that the untreated C. perfringens cells showed a regular outlined cell wall, a cell membrane closely to the cell wall, regularly distributed cytoplasm (Figure 5A), and unusual cell division (Figures 5B,F) were observed. While some spores in QdNO-treated C. perfringens cells was also observed in almost all the treated groups, Figure 5E is shown for OLA-treated C. perfringens. Moreover, some C. perfringens cells showed wide range of abnormalities and extensive ultrastructure damages (Figures 5C,D). In B. hyodysenteriae, the untreated cells revealed regularly distributed cytoplasm and normal periplasmic space (Figure 5G), while QdNO-treated cells revealed a large loss of cytoplasmic material (Figures 5H–L) and irregular morphological structure (Figures 5I,K).
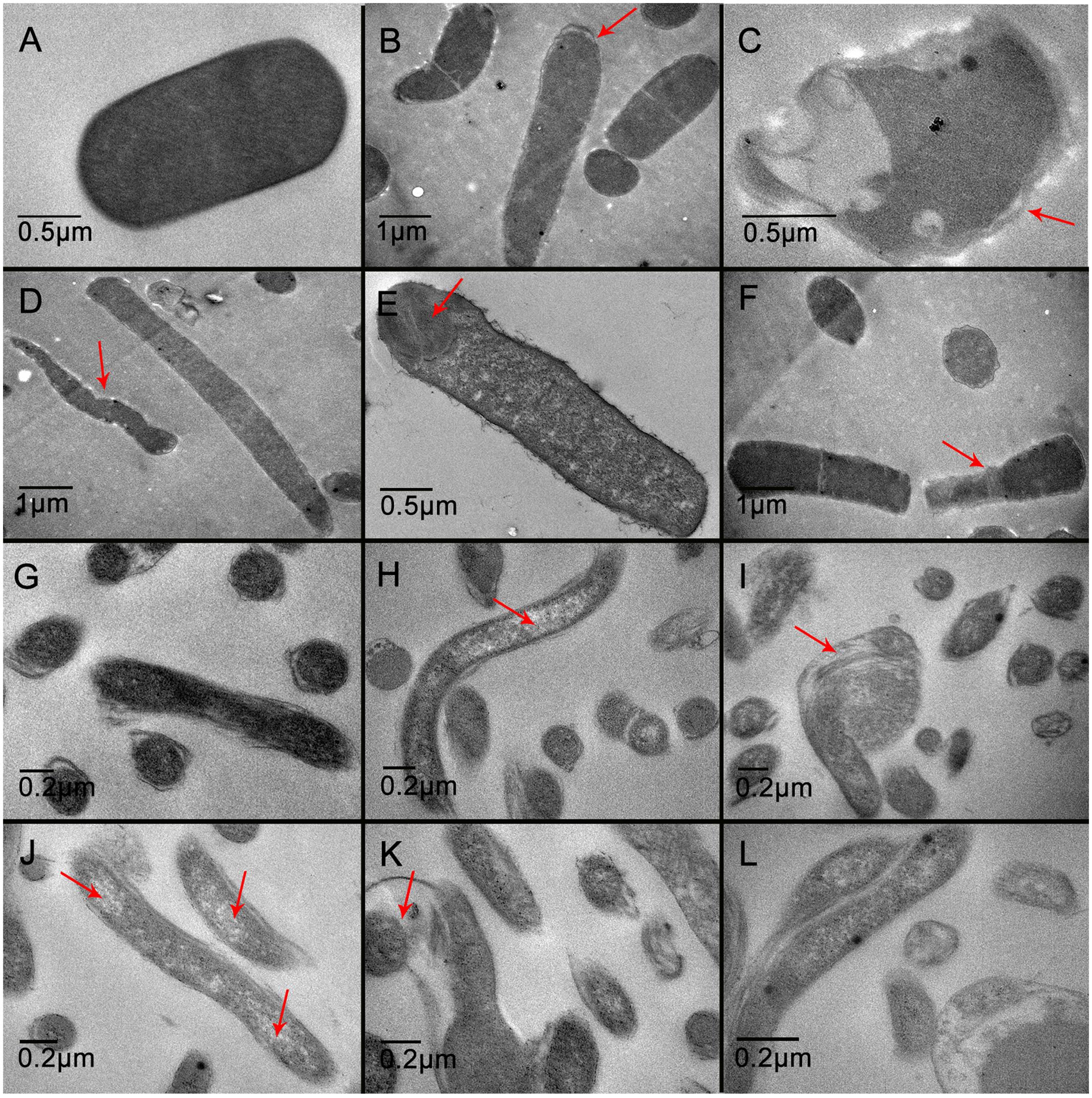
FIGURE 5. Transmission electron microscopy of C. perfringens (A–F) and B. hyodysenteriae (G–L) cells exposed to QdNOs. C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were untreated (A) or treated with 1 μg/mL CYA (B), 4 μg/mL CYA (C), 1 μg/mL OLA (D), 4 μg/mL OLA (E), and 1 μg/mL enrofloxacin (F) as positive control under anaerobic conditions for 6 h. B. hyodysenteriae cells were untreated (G) or treated with 0.031 μg/mL CYA (H), 0.125 μg/mL CYA (I), 0.0625 μg/mL OLA (J), 0.25 μg/mL OLA (K), and 8 μg/mL enrofloxacin as positive control (L) under anaerobic conditions for 6 h.
QdNO-Induced DNA Damage in C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae
When C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells and B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were incubated with QdNOs for 6 h, the 8-OHdG level significantly increased compared with the non-treated group (Figure 6). B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells produced higher level of 8-OHdG than that of C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells after treatment with QdNOs, probably because B. hyodysenteriae B204 was more sensitive to QdNOs, resulting in a low ability of resistance to oxidative damage.
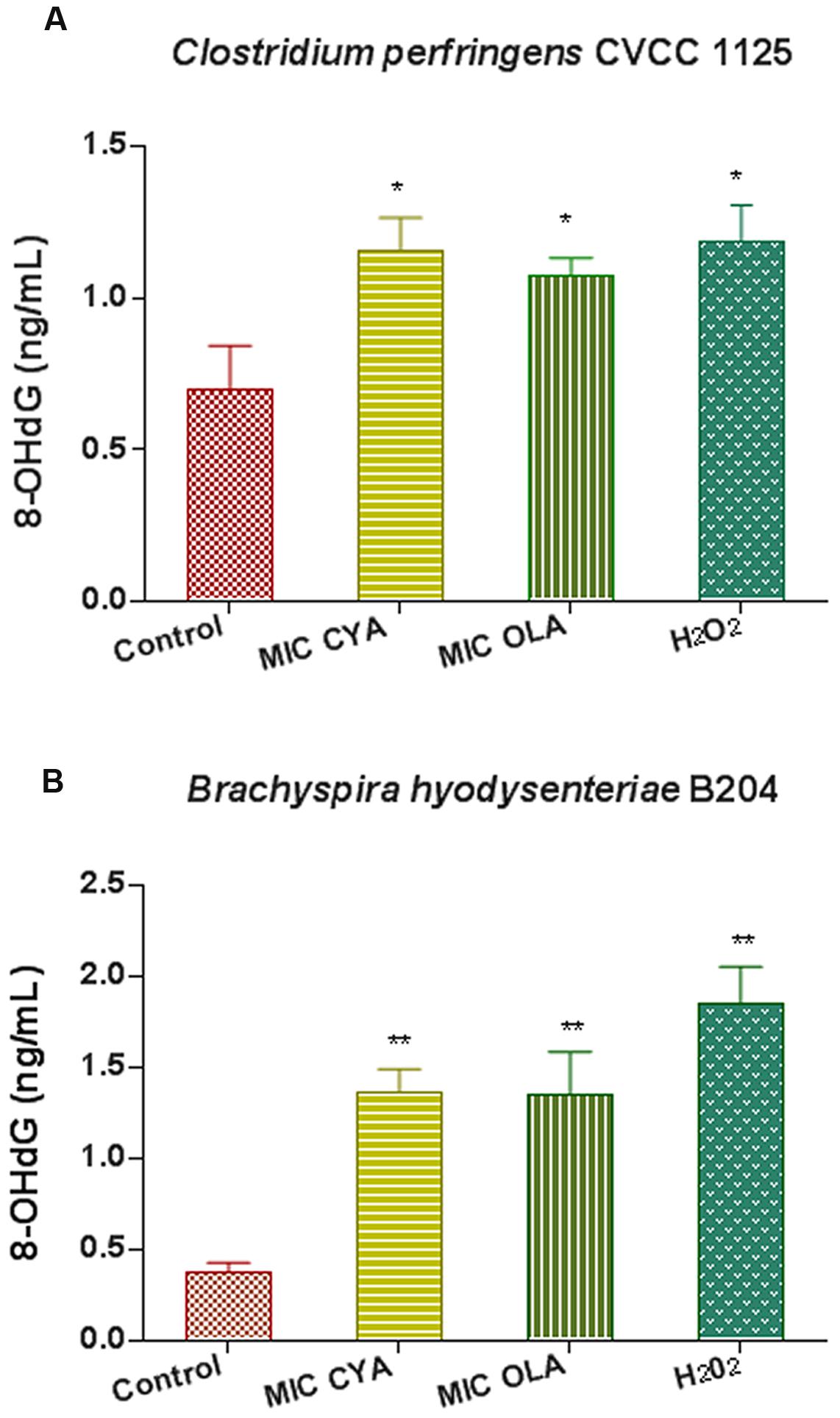
FIGURE 6. Oxidative damage of DNA in C. perfringens (A) and B. hyodysenteriae (B) exposed to QdNOs. (A) Under anaerobic conditions, C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells were treated with MIC of CYA and OLA, and 2.5 mM (85 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control drug. (B) Under anaerobic conditions, B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells were treated with MIC of CYA and OLA, and 200 μM (6.8 μg/mL) H2O2 was used as positive control. The 8-OHdG level was detected by OxiSelect Oxidative DNA Damage ELISA Kit. Data were shown as mean ± SD (error bar), n = 3. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
The QdNO-induced DNA fragmentations are shown in Figure 7. The chromosome DNA showed laddering of DNA and the degradation degree increased with an increase of drug concentration in C. perfringens cells treated with QdNOs (Figure 7A). There was also a degradation of chromosome DNA in B. hyodysenteriae cells treated by QdNOs and H2O2 (Figure 7B). Besides, there was a band in the chromosome DNA of B. hyodysenteriae with a molecular size of about 7.5 kb, which is in accordance with the size of the purified bacteriophage designated VSH-1 (VSH for virus of Serpulina hyodysenteriae) (Humphrey et al., 1995; Stanton et al., 2008a,b).
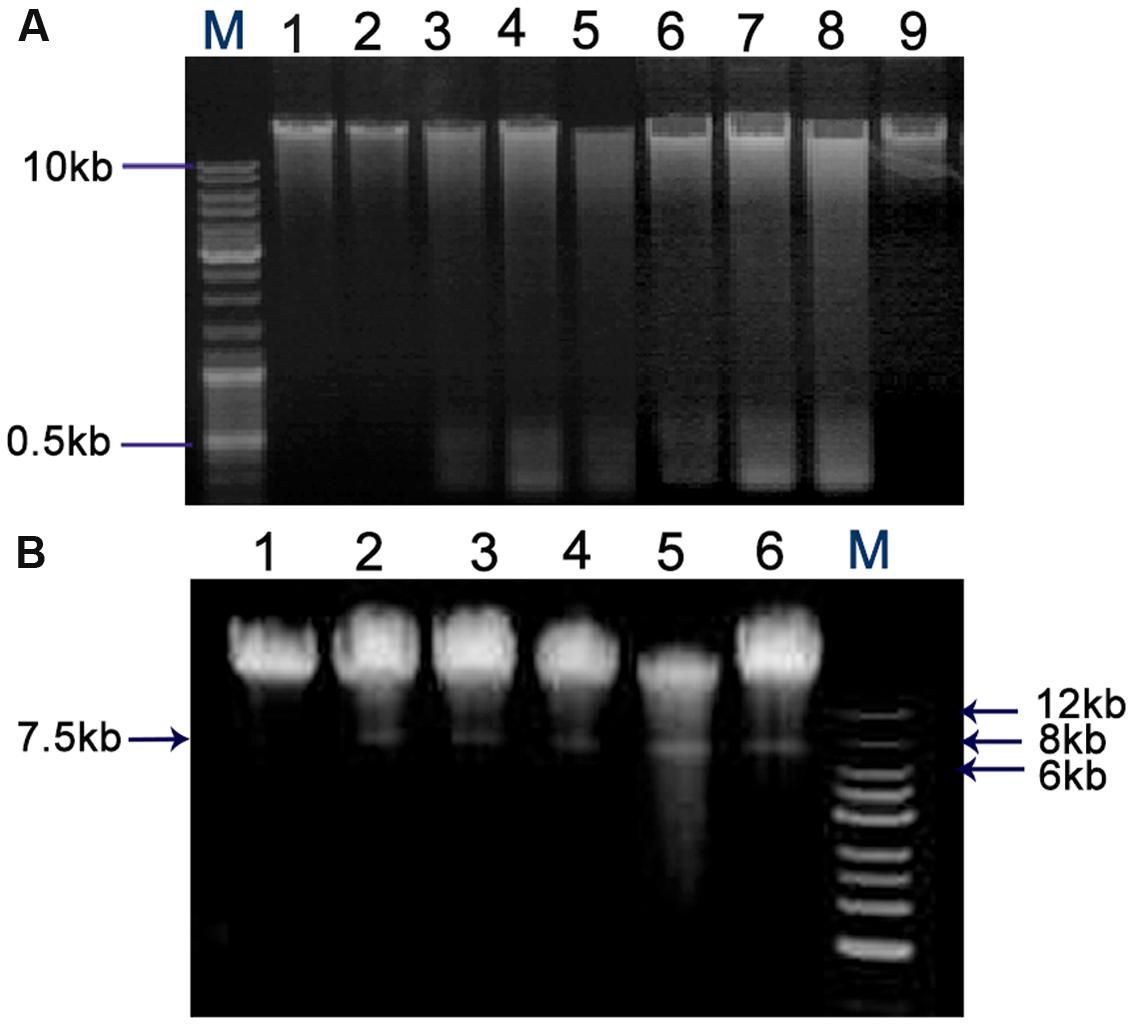
FIGURE 7. Chromosome DNA damages in C. perfringens (A) and B. hyodysenteriae cells (B) treated by QdNOs. (A) C. perfringens CVCC1125 cells incubated with different concentrations of CYA (lane 1, control; lane 2, 0.08% DMSO; lane 3, 1 μg/mL CYA; lane 4, 2 μg/mL CYA; lane 5, 4 μg/mL CYA); and OLA (lane 6, 1 μg/mL OLA; lane 7, 2 μg/mL OLA; lane 9, control) at 37°C for 6 h under anaerobic condition. 2 μg/mL enrofloxacin (lane 8) was used as the positive control drug. (B) B. hyodysenteriae B204 cells incubated with different concentrations of OLA CYA and (lane 1, control; lane 2, 0.0625 μg/mL OLA; lane 3, 0.031 μg/mL CYA; lane 4, 0.0625 μg/mL CYA; lane 5, 0.125 μg/mL CYA) at 37°C, for 6 h under anaerobic condition. 200 μM H2O2 (lane 6) was used as the positive control. Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to detect DNA damage. M, DNA maker.
Discussion
Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides belong to the heterocyclic family of benzodiazepine with its N–O groups situated at 1- and 4-positions which are considered to contribute to antibacterial activities and other versatile abilities (Hennessey and Edwards, 1972; Cheng et al., 2016). In this study, we have presented evidence that CYA and OLA were reduced in C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae cells and their reduced products did not show any antibacterial activity under anaerobic conditions (Table 2), indicating that the reduction potential of QdNOs, which may generate free radical intermediates, contributes to their antibacterial action, consistent with the earlier report studied in E. coli (Cheng et al., 2015). Like tirapazamine (TPZ) (Shinde et al., 2010), enzymatic reduction of QdNOs under hypoxic conditions results in a one-electron reduction product that has been characterized as a free radical intermediate but its exact structure is not clear. The free radical intermediate is unstable, and in the presence of oxygen, the active intermediate is oxidized back to non-toxic prototypical drug (Silva and O’Brien, 1993). This is thought to be the basis for the selective toxicity of QdNOs under anaerobic conditions. Xanthine oxidase is one of the QdNO metabolic enzymes in bacteria (Ganley et al., 2001; Cheng et al., 2015), and CYA is reduced to 4-cyadox monoxide and 1-cyadox monoxide and desoxycyadox. Moreover, the antibacterial activity of QdNOs is inhibited when the xanthine oxidase inhibitor, oxypurinol, is incubated with bacteria (Cheng et al., 2015). It is also found that cyadox can be enzymatically reduced to 4-cyadox monoxide and 1-cyadox monoxide by aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase in the cytosol and by cytochrome b5 reductase in the microsomes of pig cells (Zheng et al., 2011). On the other hand, cyadox is only reduced to 4-cyadox monoxide in the non-enzymatic reduction mediated by heme groups of catalase and cytochrome P450 (Zheng et al., 2011). Our results suggest that CYA was reduced to 4-cyadox monoxide and desoxycyadox and OLA were reduced to 1-olaquindox monoxide and desoxyolaquindox in C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae. This may due to the enzymatic and non-enzymatic N-oxide reductive system in the two anaerobes that can reduce CYA and OLA in two different pathways.
In this study, both ROS and hydroxyl radicals were discovered in the two anaerobes treated with QdNOs (Figure 1). Early study has shown that radical scavengers can inhibit the death of E. coli cells and the generation of ROS (Cheng et al., 2015), suggesting that QdNOs kills bacteria by free radicals generated in bacteria during drug metabolism. Some other bactericidal antibiotics with diverse targets are thought to kill bacteria by inducing production of damaging reactive species (Kohanski et al., 2010; Dwyer et al., 2014). The ROS (mainly O2-, H2O2, and ⋅OH) in aerobes have been hypothesized to be originated from the interference of respiration by antibacterial agent action in the presence of oxygen (Dwyer et al., 2014). In E. coli, ⋅OH was not observed but a mass of O2- (Cheng et al., 2015), this may be due to that OH was usually generated via the Fenton reaction which needs the participation of H2O2. H2O2 can be eliminated by catalase, thus the amount of ⋅OH was not obviously in E. coli.
Different from aerobic species, strictly anaerobic micro-organisms have no respiratory (electron-transport) chain (Thauer, 2015), so they cannot generate reactive products from reduction of O2, such as H2O2. Therefore, the Fenton reaction would not occur without H2O2, which affects the formation of hydroxyl free radical via Fenton reaction (Pesakhov et al., 2007). But according to early reports, it is possible that ⋅OH is a metabolic product of QdNOs under anaerobic conditions (Ganley et al., 2001), so in our study, ⋅OH was observed in the two anaerobes. This may be the reason why the two anaerobes are more sensitive to QdNOs than aerobic bacteria. Moreover, our results indicate that CYA and OLA generate ROS and ⋅OH much more efficiently than H2O2 whose concentration is much higher under the conditions tested. This is because that Fenton reaction is not effective enough in the two anaerobes. H2O2 and superoxide do not lead to oxidative damage to nucleotides, but ⋅OH is extremely toxic and will readily damage protein, membrane lipids, DNA and intracellular respiratory system, as well as cell wall.
Protection against free radicals in aerobes and facultative anaerobes is provided by some antioxidative enzymes, which are responsible for the elimination of ROS, the regulation of antioxidative defense and the synthesis of DNA related enzymes, such as DNA mismatch repair enzyme, MutS (Brioukhanov and Netrusov, 2004). Microorganisms with strong antioxidant defense system are thought to have a moderate or high tolerance to the oxidative environment compared to strictly anaerobes which lack an antioxidative enzymatic system or because of antioxidative enzymes displaying low activity (Benov and Fridovich, 1995). Our results suggest that QdNOs have a more effective antibacterial action against B. hyodysenteriae than C. perfringens, possibly because that C. perfringens is an aerotolerant anaerobe, which is more resistant to ROS than B. hyodysenteriae, a strict anaerobe.
The main role of cell wall is to maintain the cell shape to resist the intracellular osmotic pressure of bacteria (Cava et al., 2013), so the damage of bacterial cell wall leads to the change of cell shape (Figure 4). In this study, ALP assay results indicated that the cell wall damage was dose-dependent and compared with Gram-negative bacteria B. hyodysenteriae B204, Gram-positive bacteria C. perfringens CVCC1125 produced higher amounts of ALP (Figure 2). Clostridium organisms are endospore-forming bacteria and are able to differentiate into metabolically inert endospores typically, but not always, upon sensing unfavorable environmental conditions. Exposure to oxygen or other stresses may play a role in triggering the sporulation process (Al-Hinai et al., 2015). In our results, maybe it is oxidative stress caused by ROS that induced the sporulation process in C. perfringens. During sporulation process, bacteria may produce higher amounts of ALP (Chesnut et al., 1991) (Figure 5). Cell membrane also plays an important role in maintaining intracellular osmotic pressure. High level of ROS caused cell membrane damage and the leakage of the intracellular components (Figures 3 and 4).
The elongated and filamentous morphology of E. coli treated by quindoxin was considered to be caused by SOS response (Suter et al., 1978), which is an inducible DNA repair and damage tolerance system regulated mainly by recA and lexA (Craig and Roberts, 1980). lexA was up-regulated obviously in E. coli treated by CYA, and a number of SOS genes were induced in E. coli exposed to QdNOs (Cheng et al., 2015). The elongated and filamentous morphology of many bacteria cells was observed in the case of exposure to the DNA-damaging reagent. Several SOS response proteins are known to regulate cell division and induce filamentation in response to DNA damage and reactive oxidative intermediates, such as YneA in Bacillus subtilis and SulA (SfiA) in E. coli (Brune et al., 2005). Previous work in E. coli treated by CYA has shown that sulA expression is up-regulated in response to DNA damage (Cheng et al., 2015). In our results, both C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae treated by QdNOs were elongated and appeared filamentous morphology was seen (Figure 4; Supplementary Figure S5). This is consistent with previous research, indicating that QdNOs may also induce the SOS response in the two strains.
The presence of 8-OHdG in DNA indicates an oxidative stress which are resulting from ROS (Ihsan et al., 2011). CYA and OLA were less active against Gram-positive bacteria C. perfringens than Gram-negative bacteria B. hyodysenteriae (Table 2), and a higher 8-OHdG level was observed in B. hyodysenteriae than in C. perfringens (Figure 6).
Under anaerobic conditions, QdNOs are enzymatically reduced by bacterial metabolism to products that can interact with bacterial DNA, inducing mutations and DNA strand breaks (Sisson et al., 2000). In our study, QdNOs also induced chromosome DNA strand breaks and degradation (Figure 7). As reported for other bacterial species, an early event for VSH-1 induction by carbadox and H2O2 lead to a recA-centered SOS response (Auchtung et al., 2005). VSH-1 is induced to form viral particles after treatment with mitomycin C in B. hyodysenteriae and are released upon lysis of their host cell (Matson et al., 2005). In response to DNA damage caused by QdNOs, bacteria induce an SOS response to stimulate DNA repair. However, the SOS response may also induce prophage with production of infectious virions.
Conclusion
Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides are a class of hypoxia-selective and redox-activated DNA damaging agents. Oxidative damage to DNA and damage of cell wall and cell membrane of C. perfringens and B. hyodysenteriae via ROS and hydroxyl radical generation occur during the metabolism process in bacteria under anaerobic conditions, resulting in the death of bacteria in the end. The level of intracellular ROS and 8-OHdG suggest that oxidative stress participates in antibacterial activity. Moreover, prophage VSH-1 was induced in B. hyodysenteriae cells. This study suggests that oxygen-free environment contributes to effective generation of free radicals during QdNOs metabolisms and the antimicrobial mechanisms of QdNOs against Gram-positive bacteria and Gram-negative bacteria are nearly the same.
Author Contributions
FX contributed to design, data acquisition and analysis, data interpretation, drafted and critically revised the manuscript. GC contributed to the conception, design, data analysis, data interpretation, critically revised the manuscript and provided funding. YW, HH, XW, DC, DP, and ZL revised the manuscript. MD contributed to conception, and provided funding. ZY contributed to conception. All authors gave final approval to the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Basic Research (973) Program of China (No. 2013CB127201), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2011AA10A214) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31502115).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01948/full#supplementary-material
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
8-OHdG, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine; ALP, Alkaline phosphatase; ATCC, American Type Culture Collection; BHI, brain heart infusion; Cy1, desoxycyadox; Cy2, cyadox-1-monoxide; Cy10, cyadox- 4-monoxide; CYA, Cyadox; DCFH-DA, 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate; HPF, 3′-(p-hydroxyphenyl) fluorescein; HPLC, High Performance Liquid Chromatography; IVDC, China Institute of Veterinary Drug Control; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; O1, olaquindox 4-monoxide; O2, desoxyolaquindox; O7, olaquindox-1-monoxide; OD, optical density; OLA, olaquindox; PBS, phosphate buffer saline; QdNOs, quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SD, Swine dysentery.
References
Al-Hinai, M. A., Jones, S. W., and Papoutsakis, E. T. (2015). The Clostridium sporulation programs: diversity and preservation of endospore differentiation. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 79, 19–37. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00025-14
Alvarez-Ordonez, A., Martinez-Lobo, F. J., Arguello, H., Carvajal, A., and Rubio, P. (2013). Swine dysentery: aetiology, pathogenicity, determinants of transmission and the fight against the disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 10, 1927–1947. doi: 10.3390/ijerph10051927
Alvarez-Perez, S., Blanco, J. L., Pelaez, T., Martinez-Nevado, E., and Garcia, M. E. (2016). Water sources in a zoological park harbor genetically diverse strains of Clostridium perfringens type A with decreased susceptibility to metronidazole. Microb. Ecol. 72, 783–790. doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0772-2
Arokiyaraj, S., Choi, S. H., Lee, Y., Bharanidharan, R., Hairul-Islam, V. I., Vijayakumar, B., et al. (2015). Characterization of ambrette seed oil and its mode of action in bacteria. Molecules 20, 384–395. doi: 10.3390/molecules20010384
Auchtung, J. M., Lee, C. A., Monson, R. E., Lehman, A. P., and Grossman, A. D. (2005). Regulation of a Bacillus subtilis mobile genetic element by intercellular signaling and the global DNA damage response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 12554–12559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505835102
Benov, L., and Fridovich, I. (1995). A superoxide dismutase mimic protects sodA sodB Escherichia coli against aerobic heating and stationary-phase death. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 322, 291–294. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1465
Brioukhanov, A. L., and Netrusov, A. I. (2004). Catalase and superoxide dismutase: distribution, properties, and physiological role in cells of strict anaerobes. Biochemistry (Mosc) 69, 949–962. doi: 10.1023/B:BIRY.0000043537.04115.d9
Brune, I., Brinkrolf, K., Kalinowski, J., Puhler, A., and Tauch, A. (2005). The individual and common repertoire of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators of Corynebacterium glutamicum, Corynebacterium efficiens, Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Corynebacterium jeikeium deduced from the complete genome sequences. BMC Genomics 6:86. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-86
Cava, F., Kuru, E., Brun, Y. V., and de Pedro, M. A. (2013). Modes of cell wall growth differentiation in rod-shaped bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 16, 731–737. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.09.004
Chen, C. Z., and Cooper, S. L. (2002). Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes. Biomaterials 23, 3359–3368. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00036-4
Cheng, G., Li, B., Wang, C., Zhang, H., Liang, G., Weng, Z., et al. (2015). Systematic and molecular basis of the antibacterial action of quinoxaline 1,4-Di-N-Oxides against Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 10:e0136450. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136450
Cheng, G., Sa, W., Cao, C., Guo, L., Hao, H., Liu, Z., et al. (2016). Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-Oxides: biological activities and mechanisms of actions. Front. Pharmacol. 7:64. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00064
Chesnut, R. S., Bookstein, C., and Hulett, F. M. (1991). Separate promoters direct expression of phoAIII, a member of the Bacillus subtilis alkaline phosphatase multigene family, during phosphate starvation and sporulation. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 2181–2190. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02148.x
CLSI (2007). Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Anaerobic Bacteria; Approved Standard-7th Edn. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Craig, N. L., and Roberts, J. W. (1980). E. coli recA protein-directed cleavage of phage lambda repressor requires polynucleotide. Nature 283, 26–30. doi: 10.1038/283026a0
Domadia, P. N., Bhunia, A., Sivaraman, J., Swarup, S., and Dasgupta, D. (2008). Berberine targets assembly of Escherichia coli cell division protein FtsZ. Biochemistry 47, 3225–3234. doi: 10.1021/bi7018546
Dwyer, D. J., Belenky, P. A., Yang, J. H., MacDonald, I. C., Martell, J. D., Takahashi, N., et al. (2014). Antibiotics induce redox-related physiological alterations as part of their lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, E2100–E2109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1401876111
Eom, S. H., Lee, D. S., Jung, Y. J., Park, J. H., Choi, J. I., Yim, M. J., et al. (2014). The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 9795–9804. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6041-8
Farzan, A., Kircanski, J., DeLay, J., Soltes, G., Songer, J. G., Friendship, R., et al. (2013). An investigation into the association between cpb2-encoding Clostridium perfringens type A and diarrhea in neonatal piglets. Can. J. Vet. Res. 77, 45–53.
Ganley, B., Chowdhury, G., Bhansali, J., Daniels, J. S., and Gates, K. S. (2001). Redox-activated, hypoxia-selective DNA cleavage by quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 2395–2401. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0896(01)00163-8
Hao, H., Guo, W., Iqbal, Z., Cheng, G., Wang, X., Dai, M., et al. (2013). Impact of cyadox on human colonic microflora in chemostat models. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 67, 335–343. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2013.08.011
Hennessey, T. D., and Edwards, J. R. (1972). Antibacterial properties of quindoxin: a new growth-promoting agent. Vet. Rec. 90, 187–191. doi: 10.1136/vr.90.7.187
Humphrey, S. B., Stanton, T. B., and Jensen, N. S. (1995). Mitomycin C induction of bacteriophages from Serpulina hyodysenteriae and Serpulina innocens. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 134, 97–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07921.x
Ihsan, A., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, X., Liu, Y., et al. (2011). Long-term mequindox treatment induced endocrine and reproductive toxicity via oxidative stress in male Wistar rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 252, 281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.02.020
Kohanski, M. A., Dwyer, D. J., and Collins, J. J. (2010). How antibiotics kill bacteria: from targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8, 423–435. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2333
Kumar Tyagi, A., Bukvicki, D., Gottardi, D., Veljic, M., Guerzoni, M. E., Malik, A., et al. (2013). Antimicrobial potential and chemical characterization of serbian liverwort (Porella arboris-vitae): SEM and TEM observations. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013:382927. doi: 10.1155/2013/382927
La, T., Phillips, N. D., Thomson, J. R., and Hampson, D. J. (2014). Absence of a set of plasmid-encoded genes is predictive of reduced pathogenic potential in Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. Vet. Res. 45:131. doi: 10.1186/s13567-014-0131-6
Liu, Y., Jiang, W., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Zeng, P., Xue, F., et al. (2016). Cytotoxicity of mequindox and its metabolites in HepG2 cells in vitro and murine hepatocytes in vivo. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 797, 36–45. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.01.002
Lugsomya, K., Tummaruk, P., Hampson, D. J., and Prapasarakul, N. (2012). Development of a modified selective medium to enhance the recovery rate of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and other porcine intestinal spirochaetes from faeces. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 54, 330–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2012.03213.x
Matson, E. G., Thompson, M. G., Humphrey, S. B., Zuerner, R. L., and Stanton, T. B. (2005). Identification of genes of VSH-1, a prophage-like gene transfer agent of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. J. Bacteriol. 187, 5885–5892. doi: 10.1128/jb.187.17.5885-5892.2005
Moxley, R. A., and Duhamel, G. E. (1999). Comparative pathology of bacterial enteric diseases of swine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 473, 83–101. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-4143-1_7
Pesakhov, S., Benisty, R., Sikron, N., Cohen, Z., Gomelsky, P., Khozin-Goldberg, I., et al. (2007). Effect of hydrogen peroxide production and the Fenton reaction on membrane composition of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1768, 590–597. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.12.016
Piddock, L. J., Walters, R. N., and Diver, J. M. (1990). Correlation of quinolone MIC and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis and induction of the SOSresponse in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34, 2331–2336. doi: 10.1128/AAC.34.12.2331
Sabbatini, J. Z. (2009). Progress on the development and single-laboratory validation of a high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of carbadox and pyrantel tartrate in type B and C medicated feeds. J. AOAC Int. 92, 26–33.
Sebastian, M., and Ammerman, J. W. (2009). The alkaline phosphatase PhoX is more widely distributed in marine bacteria than the classical PhoA. ISME J. 3, 563–572. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2009.10
Shinde, S. S., Maroz, A., Hay, M. P., Patterson, A. V., Denny, W. A., and Anderson, R. F. (2010). Characterization of radicals formed following enzymatic reduction of 3-substituted analogues of the hypoxia-selective cytotoxin 3-amino-1,2,4-benzotriazine 1,4-dioxide (tirapazamine). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 2591–2599. doi: 10.1021/ja908689f
Silva, J. M., and O’Brien, P. J. (1993). Molecular mechanisms of SR 4233-induced hepatocyte toxicity under aerobic versus hypoxic conditions. Br. J. Cancer 68, 484–491. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.374
Sisson, G., Jeong, J. Y., Goodwin, A., Bryden, L., Rossler, N., Lim-Morrison, S., et al. (2000). Metronidazole activation is mutagenic and causes DNA fragmentation in Helicobacter pylori and in Escherichia coli containing a cloned H. pylori RdxA(+) (Nitroreductase) gene. J. Bacteriol. 182, 5091–5096. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.18.5091-5096.2000
Stanton, T. B., Humphrey, S. B., Bayles, D. O., and Zuerner, R. L. (2008a). Identification of a divided genome for VSH-1, the prophage-like gene transfer agent of Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. J. Bacteriol. 191, 1719–1721. doi: 10.1128/jb.01359-08
Stanton, T. B., Humphrey, S. B., Sharma, V. K., and Zuerner, R. L. (2008b). Collateral effects of antibiotics: carbadox and metronidazole induce VSH-1 and facilitate gene transfer among Brachyspira hyodysenteriae strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74, 2950–2956. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00189-08
Suter, W., Rosselet, A., and Knusel, F. (1978). Mode of action of quindoxin and substituted quinoxaline-di-N-oxides on Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 13, 770–783. doi: 10.1128/AAC.13.5.770
Thauer, R. K. (2015). My lifelong passion for biochemistry and anaerobic microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 69, 1–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-091014-104344
Tsai, G. J., and Su, W. H. (1999). Antibacterial activity of shrimp chitosan against Escherichia coli. J. Food Prot. 62, 239–243.
Uzal, F. A., Freedman, J. C., Shrestha, A., Theoret, J. R., Garcia, J., Awad, M. M., et al. (2014). Towards an understanding of the role of Clostridium perfringens toxins in human and animal disease. Future Microbiol. 9, 361–377. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.168
Keywords: quinoxaline 1, 4-di-N-oxides, Clostridium perfringens, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, cell wall, cell membrane, DNA damage
Citation: Xu F, Cheng G, Hao H, Wang Y, Wang X, Chen D, Peng D, Liu Z, Yuan Z and Dai M (2016) Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action of Quinoxaline 1,4-di-N-oxides against Clostridium perfringens and Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. Front. Microbiol. 7:1948. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01948
Received: 15 July 2016; Accepted: 21 November 2016;
Published: 05 December 2016.
Edited by:
Yuji Morita, Aichi Gakuin University, JapanReviewed by:
Karl Hassan, Macquarie University, AustraliaJorge Eugenio Vidal, Emory University, USA
Copyright © 2016 Xu, Cheng, Hao, Wang, Wang, Chen, Peng, Liu, Yuan and Dai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Menghong Dai, ZGFpbWVuZ2hvbmdAbWFpbC5oemF1LmVkdS5jbg== Zonghui Yuan, eXVhbjU4MDJAbWFpbC5oemF1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work.
 Fanfan Xu1†
Fanfan Xu1† Guyue Cheng
Guyue Cheng Zonghui Yuan
Zonghui Yuan