Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review
- 1Environmental Engineering Laboratory, Department of Civil Engineering, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, South Korea
- 2Disasters Prevention Research Institute, Yeungnam University, Gyeongsan, Korea
- 3Department of Microbiology, Bose Institute, Kolkata, India
A corrigendum on
Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review
by Ghosal, D., Ghosh, S., Dutta, T. K., and Ahn, Y. (2016). Front. Microbiol. 7:1369. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01369
Due to an inadvertent error, Louvado et al. (2015) was noted cited in the footnotes of Table 1. The corrected Table 1 along with the footnote appears below. The authors apologize for this error. This does not affect the scientific conclusions of the article in any way.
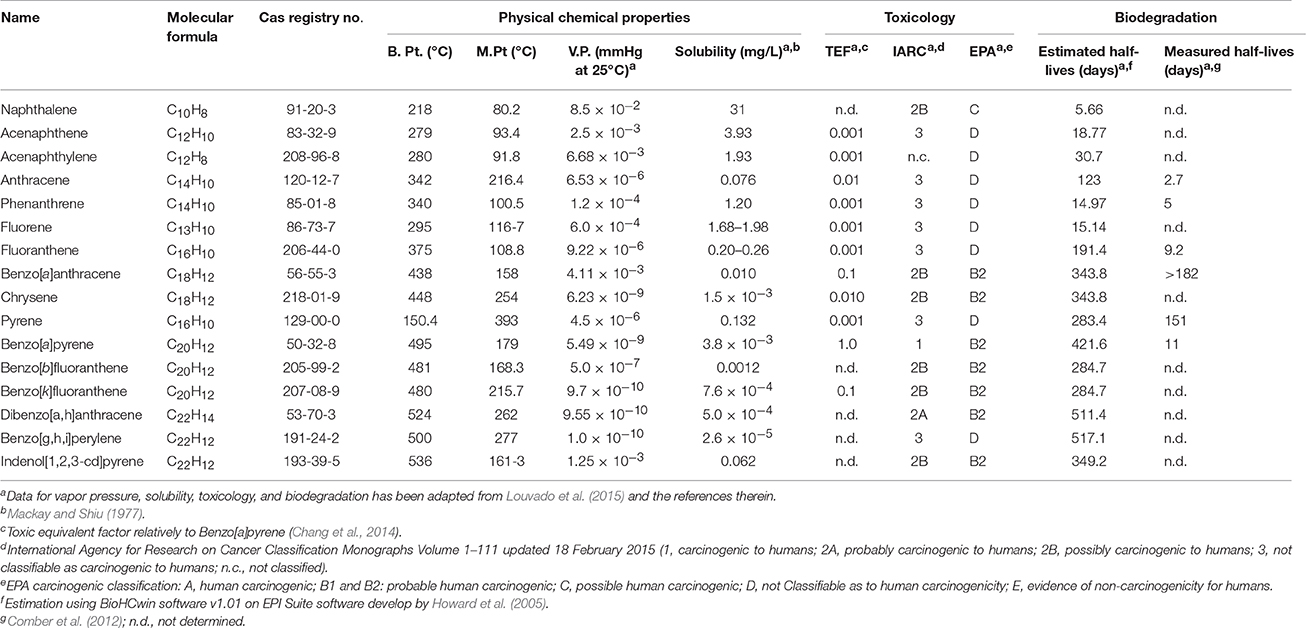
Table 1. Physical-chemical properties and some relevant information of 16 PAHs enlisted as priority pollutants by US EPA.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Yeungnam University Research Grant (2015).
References
Chang, W. T., Fang, M. D., Lee, C. L., and Brimblecombe, P. (2014). Measuring bioavailable PAHs in estuarine water using semipermeable membrane devices with performance reference compounds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 89, 376–383. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.09.031
Comber, M. I. H., den Haan, K. H., Djemel, N., Eadsforth, C. V., King, D., Paumen, M. L., et al. (2012). Primary Biodegradation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Seawater. Concawe Report, No.10/12. Brussels: Concawe.
Howard, P., Meylan, W., Aronson, D., Stiteler, W., Tunkel, J., Comber, M., et al. (2005). A new biodegradation prediction model specific to petroleum hydrocarbons. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 24, 1847–1860. doi: 10.1897/04-453R.1
Louvado, A., Gomes, N. C., Simões, M. M., Almeida, A., Cleary, D. F., and Cunha, A. (2015). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in deep sea sediments: microbe-pollutant interactions in a remote environment. Sci. Total Environ. 526, 312–328. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.048
Keywords: biodegradation, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs), bacteria, fungi, algae
Citation: Ghosal D, Ghosh S, Dutta TK and Ahn Y (2016) Corrigendum: Current State of Knowledge in Microbial Degradation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Review. Front. Microbiol. 7:1837. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01837
Received: 20 October 2016; Accepted: 01 November 2016;
Published: 15 November 2016.
Edited and reviewed by: Pankaj Kumar Arora, M. J. P. Rohilkhand University, India
Copyright © 2016 Ghosal, Ghosh, Dutta and Ahn. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tapan K. Dutta, tapan@jcbose.ac.in
Youngho Ahn, yhahn@ynu.ac.kr
 Debajyoti Ghosal1
Debajyoti Ghosal1 Youngho Ahn
Youngho Ahn