- 1Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Ege University, Izmir, Türkiye
- 2Department of Civil, Geological, and Environmental Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada
- 3Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Atılım University, Ankara, Türkiye
- 4Department of Process Engineering and Technology of Polymer and Carbon Materials, Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Wrocław, Poland
Editorial on the Research Topic
Reviews in membrane modules and processes
The design of membrane modules plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of membrane processes used in various applications such as water treatment, resource recovery, and energy production (Kabay et al., 2022). A well-optimized module design enhances mass and heat transfer, minimizes fouling, and improves operational stability, making membrane technologies more viable for industrial and municipal use (Ismail et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2013).
The design of membrane modules for membrane processes hinges on several critical parameters to ensure efficiency, durability, and adaptability across various applications. These parameters are shown in Figure 1.
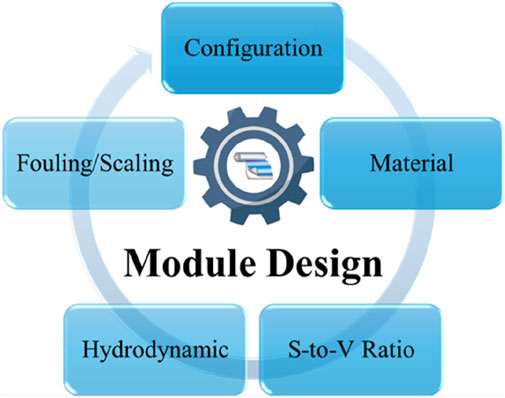
Figure 1. Main parameters in module design for membrane processes (S-to-V ratio stands for surface to volume ratio).
Membrane material must be chemically compatible and mechanically durable for long-term performance and cleaning (Warsinger et al., 2018). Module configurations, such as spiral wound or hollow fiber, aim to maximize packing density while ensuring ease of maintenance. A high surface area-to-volume ratio is crucial for enhanced flux but must be balanced against pressure drop considerations (Karabelas et al., 2015). Effective hydrodynamic design ensures uniform flow distribution, reduces dead zones, and minimizes fouling through turbulence promoters or optimized spacers (Ibrahim et al., 2025). Additionally, fouling and scaling control features, such as anti-fouling coatings or spacer designs, enhance performance and facilitate cleaning, making these parameters integral to robust and efficient module design (Jørgensen et al., 2023; Abid et al., 2017).
For example, in nanofiltration (NF), module design influences salt rejection rates, flux performance, and energy efficiency, which are critical for applications like softening and desalination (Chong and Fane, 2021). Similarly, in membrane distillation (MD), the module design, including membrane arrangement and thermal integration, significantly impacts the recovery of clean water and valuable resources from challenging feed streams such as brines and industrial effluents (Ali et al., 2024). In membrane bioreactors (MBRs), as another example, module design directly affects aeration efficiency, fouling control, and energy consumption, which are crucial for treating municipal and industrial wastewater while maintaining high-quality effluent standards (Wang et al., 2009; Kharraz et al., 2022). Advances in module designs, such as spacer configurations, hollow fiber membranes, and spiral wound setups, are pivotal for pushing the boundaries of performance and ensuring sustainable and cost-effective solutions in these membrane-based processes (Wan et al., 2021; Lee et al., 2016). The Web of Science Engin shows 15411 hints for the phrase ‘membrane module’ and counts 946 reviews. This Research Topic covers four review papers on “Membrane modules and processes”.
One of the review papers was written by Kim et al. on “Recent Advances of Membrane-Based Hybrid Membrane Bioreactors for Wastewater Reclamation”. The state-of-art of the MBR integrated with desalination technologies to improve effluent quality and membrane performance as well as optimize it for wastewater reuse applications was described in the paper. A detailed literature information about membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems which are actively used as membrane-based wastewater process was mentioned. Then conventional MBR combined with NF/RO membrane system was explained in details. In this part of review, the factors (such as membranes employed, recovery and brine circulation ratio, MBR operation conditions, feed pretreatment of NF/RO) affecting the performance of the integrated MBR + NF/RO system, Later, Hybrid MBR systems such as NF-MBR, FO (forward osmosis)-MBR, MD-MBR were summarized.
The second review by Tarun et al., is on “Tuning of polymeric membranes to mitigate fouling and removal of dissolved compounds for wastewater treatment”. This review particularly focused on progress and challenges in membrane processes for fouling strategies and salt rejection in case of ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, nanofiltration, forward osmosis, ion exchange membrane process, membrane distillation, pervaporation. Additionally, progress and challenges in the fabrication of various modules (flat sheet, spiral wound, tubular, hollow fiber) for fouling issues were described together with methods to mitigate fouling.
In the third review, “Microfiltration membranes: fabrication, physical morphology, and fouling characterization techniques” were presented by Altinkaya. Past and current developments in characterization methods of physical morphology and fouling for microfiltration membranes along with their manufacturing methods were explained in the review article. Also, some future directions on this topic were outlined.
The last review paper written by Gül et al. focused on “Reverse electrodialysis process-a pioneering technology for energy generation by salinity gradient”. The review summarizes the recent developments of ion exchange membranes employed for RED studies, membrane fouling and stack design of reverse electrodialysis.
The above review papers demonstrate the interdisciplinary fields of membrane science and technology, covering materials, chemistry, chemical engineering and environmental engineering. In addition, these review papers clearly indicate the flexibility of membrane processes in various applications including wastewater treatment and energy production. We consider that much remains to be explored as the field of membrane modules and processes continues to expand.
Author contributions
NK: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MA: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. EG: Writing–review and editing. MB: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the contributors for their great efforts to publish their review papers in the frame of this Research Topic. We acknowledge the support of the Editor-in-Chief, Prof. Michael Guiver as well as the editorial staff of Frontiers for their supports.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abid, H. S., Johnson, D. J., Hashaikeh, R., and Hilal, N. (2017). A review of efforts to reduce membrane fouling by control of feed spacer characteristics. Desalination 420, 384–402. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2017.07.019
Ali, A., Shirazi, M. M., Nthunya, L., Castro-Muñoz, R., Ismail, N., Tavajohi, N., et al. (2024). Progress in module design for membrane distillation. Desalination 581, 117584. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2024.117584
Chong, T. H., and Fane, A. G. (2021). “Nanofiltration module design and operation,” in Nanofiltration (Wiley), 95–135. doi:10.1002/9783527824984.ch3
Ibrahim, Y., Aytaç, E., Khanzada, N. K., Khayet, M., and Hilal, N. (2025). The role of feed spacers in membrane technology: 45 years of research. Sep. Purif. Technol. 357, 130109. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2024.130109
Ismail, A. F., Khulbe, K. C., and Matsuura, T. (2015). “Membrane modules and process design,” in Gas separation membranes (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 221–240. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-01095-3_5
Jørgensen, M. K., Paulsen, F. K., Bentien, A., Kjul, A. R., Poulsen, M., Mikkelsen, L. M., et al. (2023). Membrane fouling monitoring by 3ω sensing. Sci. Rep. 13, 15237. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-42337-1
Kabay, N., Shirazi, M. M. A., Güler, E., and Bryjak, M. (2022). Grand challenges in membrane modules and processes. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 1. doi:10.3389/frmst.2022.913597
Karabelas, A. J., Kostoglou, M., and Koutsou, C. P. (2015). Modeling of spiral wound membrane desalination modules and plants – review and research priorities. Desalination 356, 165–186. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2014.10.002
Kharraz, J. A., Khanzada, N. K., Farid, M. U., Kim, J., Jeong, S., and An, A. K. (2022). Membrane distillation bioreactor (MDBR) for wastewater treatment, water reuse, and resource recovery: a review. J. Water Process Eng. 47, 102687. doi:10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102687
Lee, J.-Y., Tan, W. S., An, J., Chua, C. K., Tang, C. Y., Fane, A. G., et al. (2016). The potential to enhance membrane module design with 3D printing technology. J. Memb. Sci. 499, 480–490. doi:10.1016/j.memsci.2015.11.008
Wan, C. F., Yang, T., Lipscomb, G. G., Stookey, D. J., and Chung, T.-S. (2021). “Design and fabrication of hollow fiber membrane modules,” in Hollow fiber membranes (Elsevier), 225–252. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-821876-1.00007-X
Wang, Y., Brannock, M., and Leslie, G. (2009). Membrane bioreactors: overview of the effects of module geometry on mixing energy. Asia-Pacific J. Chem. Eng. 4, 322–333. doi:10.1002/apj.248
Warsinger, D. M., Chakraborty, S., Tow, E. W., Plumlee, M. H., Bellona, C., Loutatidou, S., et al. (2018). A review of polymeric membranes and processes for potable water reuse. Prog. Polym. Sci. 81, 209–237. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2018.01.004
Keywords: membrane, membrane processes, membrane modules, membrane bioreactor, membrane fouling, microfiltration, reverse electrodialysis, water treatment
Citation: Kabay N, A. Shirazi MM, Güler E and Bryjak M (2025) Editorial: Reviews in membrane modules and processes. Front. Membr. Sci. Technol. 3:1542869. doi: 10.3389/frmst.2024.1542869
Received: 10 December 2024; Accepted: 23 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Gianluca Di Profio, National Research Council (CNR), ItalyCopyright © 2025 Kabay, A. Shirazi, Güler and Bryjak. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nalan Kabay, bmFsYW4ua2FiYXlAZ21haWwuY29t
 Nalan Kabay
Nalan Kabay Mohammad M. A. Shirazi
Mohammad M. A. Shirazi Enver Güler
Enver Güler Marek Bryjak
Marek Bryjak