- 1Department of Pathological Anatomy and Forensic Medicine, West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov Medical University, Aktobe, Kazakhstan
- 2Department of Oncology, Medical Center of West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov Medical University, Aktobe, Kazakhstan
Introduction: Gastric cancer in young people is a global health burden, although it is less common than in other age groups. The use of biomarkers is developing in the diagnosis, treatment selection and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. In this bibliometric analysis we aim to evaluate the progress of this knowledge, trend topic development and scientific teams and countries involvements in the topic of biomarkers role in gastric cancer in young patients.
Methods: The data were obtained from Scopus (536 publications) for the period 1993–2024, all relevant metadata were analyzed using RStudio and Biblioshiny package to perform global trends and hotspots analysis.
Results: Publication trends show a constant increase in interest in gastric cancer biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (7.71% per year). The leading countries were China, USA, and Japan, between which there is strong and sustained collaborations. International co-authorship is relatively low (19.4%). The most prolific research centers were Sungkyunkwan University, Sun Yat-sen University, and Fudan University. The most productive researchers were Zhang X., Wang Y., and Li Y. Keywords analysis showed an increase in mentions of topics related to diagnostics (biomarkers, immunohistochemistry), personalized medicine and prognosis.
Conclusion: Bibliometric analysis of more than three decades research articles on gastric cancer biomarkers in young patients showed a steady increase, with strong contributions from leading countries and institutions, highlighting the growing focus on diagnostics, personalized medicine, and prognosis.
1 Introduction
Gastric cancer is one of the major global health burdens, ranking fifth in incidence and fourth in mortality worldwide (1, 2). Gastric cancer in young people (aged ≤45 years) accounts for less than 10% of all new cases (3). Gastric cancer has different age characteristics depending on the region. In most countries, it is considered a disease of old age, and its prevalence increases with age. Although the overall incidence of gastric cancer has decreased in recent decades and is projected to continue to decrease, many epidemiological studies in the East, West (4, 5) and USA (6) showed an increasing trend in morbidity. Due to the lack of obvious symptoms and rapid tumor progression, diagnosis and treatment are often delayed in young cancer patients (7). GC in young patients has more aggressive biological behavior than in middle-aged and elderly patients (8). A significant proportion of young patients often have a more advanced stage of the disease compared to older patients (3), and the prognosis remains unfavorable (9).
It is known that the clinical and pathological features of young patients with gastric cancer differ from those of older patients. Patients with gastric cancer aged 40 years and younger exhibit a number of distinctive characteristics compared to patients in the older age group (over 40 years). In particular, they are more often women, have more aggressive forms of the disease, are more likely to have undifferentiated and diffuse tumor types, and have a positive family history of cancer. In addition, this group has an increased rate of recurrence in the remaining part of the stomach (10). Younger patients diagnosed with gastric cancer are more likely to have tumors with signet ring cell or diffuse histology, metastatic disease, and germline mutations in the CDH1 gene compared with older patients (11). Wang et al. talk about the exclusive location of SDH-deficient GIST tumors in the stomach, the manifestation of a predisposition to children and young people with a predominance of the female sex (12). However, despite this, 5-year survival in young patients is higher than in older patients (13). With the advent of the era of personalized cancer treatment, the lack of biological information such as morphology, size, and enhancement of lesions, which are traditionally assessed by visual examination and do not take into account tumor heterogeneity, is becoming apparent. This deficit is gradually being filled by biomarkers that provide more accurate molecular and genetic profiling of tumors, improving diagnosis and the selection of personalized therapies (14, 15).
A large number of prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer have been identified thanks to the development of bioinformatics methods (16, 17). As already mentioned, gastric cancer in its early stages has no specific clinical signs, and most patients consult a doctor at a middle or late stage, which leads to an unfavorable prognosis. Therefore, it is extremely important to study the mechanisms of gastric cancer and find biomarkers for its early detection (18) and forecast. There is also an urgent need to develop new biomarkers that will allow physicians to more accurately predict the course of the disease and make informed decisions regarding therapy. The use of several biomarkers together facilitates a more comprehensive assessment of the patient’s condition and can significantly improve the accuracy of predicting disease outcomes (2).
Bibliometric analysis helps to achieve a qualitative and quantitative analysis of publications devoted to the study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients, using a multidisciplinary approach to sort out research areas and understand the trends and directions of research (19).
Overall, bibliometric analysis provides valuable information about the publication landscape devoted to this topic. The aim of this bibliometric analysis is to review the global scientific literature on biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients over the past 31 years. The study aims to systematize existing knowledge, identify current global publication trends, leading authors and most cited references, as well as to analyze the current state and summarize research hot spots. This study effectively represents a comprehensive global roadmap for navigating future research in this area.
2 Methods
2.1 Eligibility criteria and data source
The analysis included only original research articles published in English. The data were obtained from the Scopus database, and all relevant metadata were extracted in BibTeX format. The data presented in the accompanying BibTeX file (Table 1) were subsequently analyzed using RStudio 2024.12.0.
2.2 Search strategy
2.2.1 Source of data used in the analysis
In this research study, an extensive search was conducted in Scopus, which was chosen as the main and only database. We used combinations of Boolean and wildcard search operators to identify relevant keywords for our study (Table 1). The search was conducted in November 2024, and the comprehensive search strategy is outlined in Figure 1. Articles that were considered irrelevant based on their failure to meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria were systematically excluded.
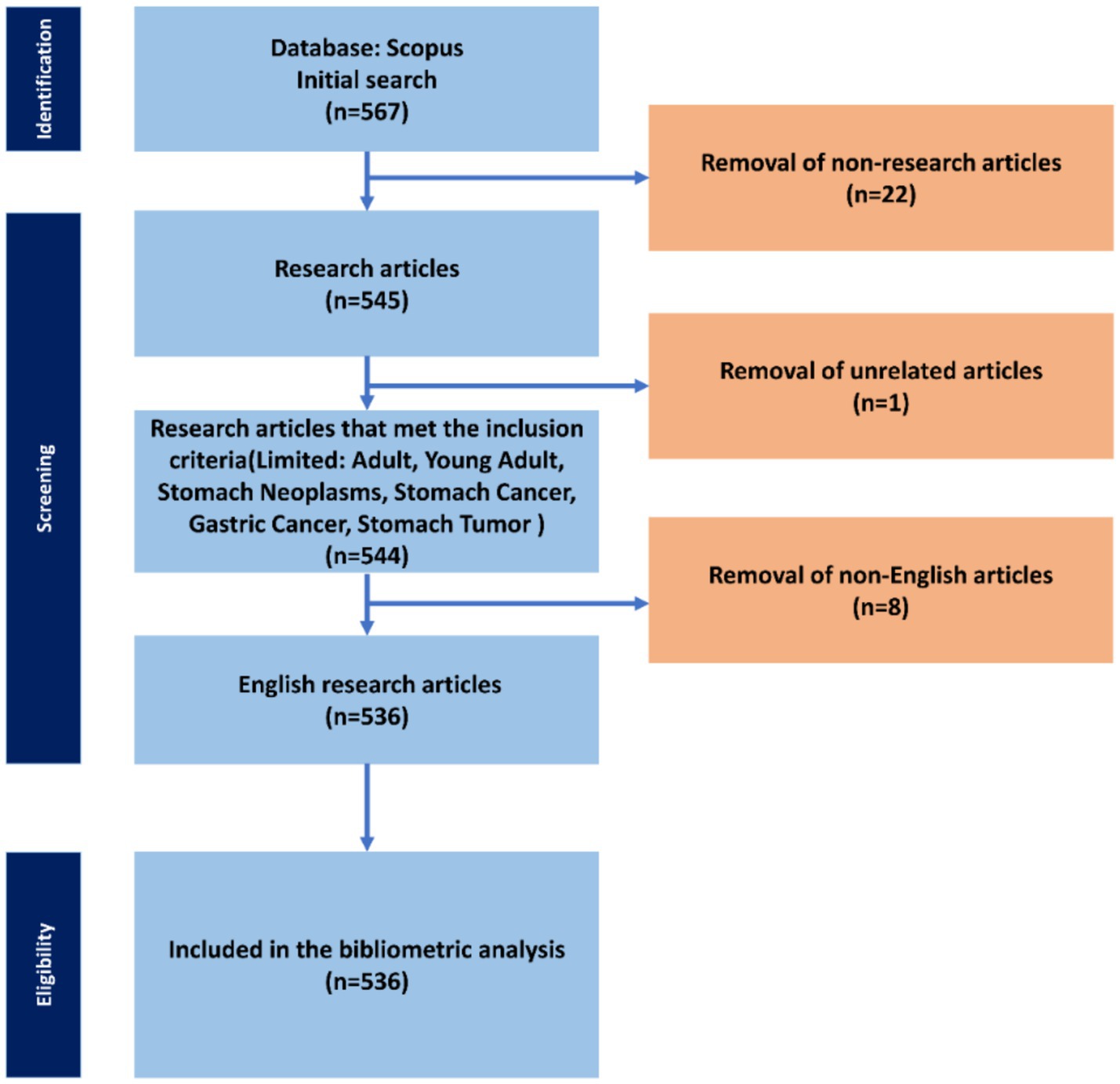
Figure 1. Flow chart of selection of research articles of biomarkers used in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
2.2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We applied the following inclusion criteria: research articles, articles containing the keywords: Adult, Young Adult, Stomach Neoplasms, Stomach Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Stomach Tumor, articles in English. Exclusion criteria: articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria, articles not in English. After this process, a total of 536 research articles were imported for bibliometric analysis.
2.3 Bibliometric analysis
Data management and bibliometric analysis were performed using the Biblioshiny package (RStudio 2024.12.0 + 467 “Kousa Dogwood”). The analysis covered a 31-year period, focusing exclusively on research articles. Top institutions were identified based on the volume of publications related to biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
In addition, we constructed collaborative networks involving 1,226 research institutions for research articles. These networks were developed using clustering and data normalization algorithms applied to 536 research articles, guided by the association parameter. Authors with significant contributions were identified based on the frequency of their published articles. The analysis also included identifying the 10 most frequently cited articles and the top journals in the field. This study further explored the interactions between 10 key journals, research areas and countries that contributed to the study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients over the past 31 years. To visualize the global scientific collaborations, the connections were presented on a world map. The tree map visualization highlighted the 10 most frequently used keywords in publications on the topic. Finally, the thematic structure of the research was also examined.
3 Results
3.1 Key characteristics of the review of retrieved research articles
We initially retrieved 567 articles from the Scopus database. After applying the eligibility criteria and excluding 31 ineligible studies, we considered a total of 536 research articles for our bibliometric analysis (Figure 1). Scientific articles from 211 sources were analyzed. The annual growth rate of 7.71% is moderately high, which reflects the sustainable interest of the scientific community in new discoveries and funding of research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. The rate of international co-authorship is relatively low (19.4%), indicating a relatively low trend of international collaboration in this area, which requires increase. A high degree of collectivity is noticeable (9.64 co-authors per document), which is most likely due to the fact that research in this area is often carried out by large interdisciplinary groups. The study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients has a sustainable interest and has already achieved a stable level of publication activity, as evidenced by the average document age of 7.85 years. The indicator of 53.56 citations per article per year is quite high, which indicates the preservation of high scientific significance of research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. Research articles written by US researchers dominate in terms of average citation rates with 4,279 and 12,345 citations per article per year, respectively. The US has traditionally been a leader in many scientific fields, and the high citation rate of these publications is an indicator of their influence and importance at the global level in this research area. A total of 3,691 authors from 57 countries participated in the 536 research studies included in the analysis. This shows that the study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients has attracted the attention of scientists from different parts of the world, which may indicate the global importance of the considered field. However, a higher percentage of international co-authorship could highlight an even greater degree of interaction between countries, which is not observed. A large set of 1,188 author keywords and their analysis can provide important insights into the structure of studies, the main topics and directions in the scientific field, as well as possible points for further study and improvement.
3.2 Trends in publications and citations
There is marked variability in the number of publications on this topic over the 31-year period from 1993 to 2024, which may indicate different stages of scientific interest, economic factors, or changes in the priorities of research groups. In particular, at the beginning (1993 and 1994) minimal figures were recorded – one article per year, which may indicate the initial stage of studying this topic. The period from 1995 to 2007 is characterized by a sharp decline in the number of publications, which may be due to limited attention to biomarkers in the context of gastric cancer, insufficient development of the field, or priority given to other scientific areas. The smallest number of scientific publications occurred in 1993, 1994, 2008, 2023, during these years from 1 to 7 scientific articles were published per year. Since 2014, there has been a significant increase in the number of publications, as evidenced by two peaks in 2014 (59 publications) and 2020 (57 publications), indicating a resurgence of interest in this topic (Table 2). This may be due to improvements in diagnostic technologies, increased awareness of the importance of biomarkers, and the development of new therapeutic methods.
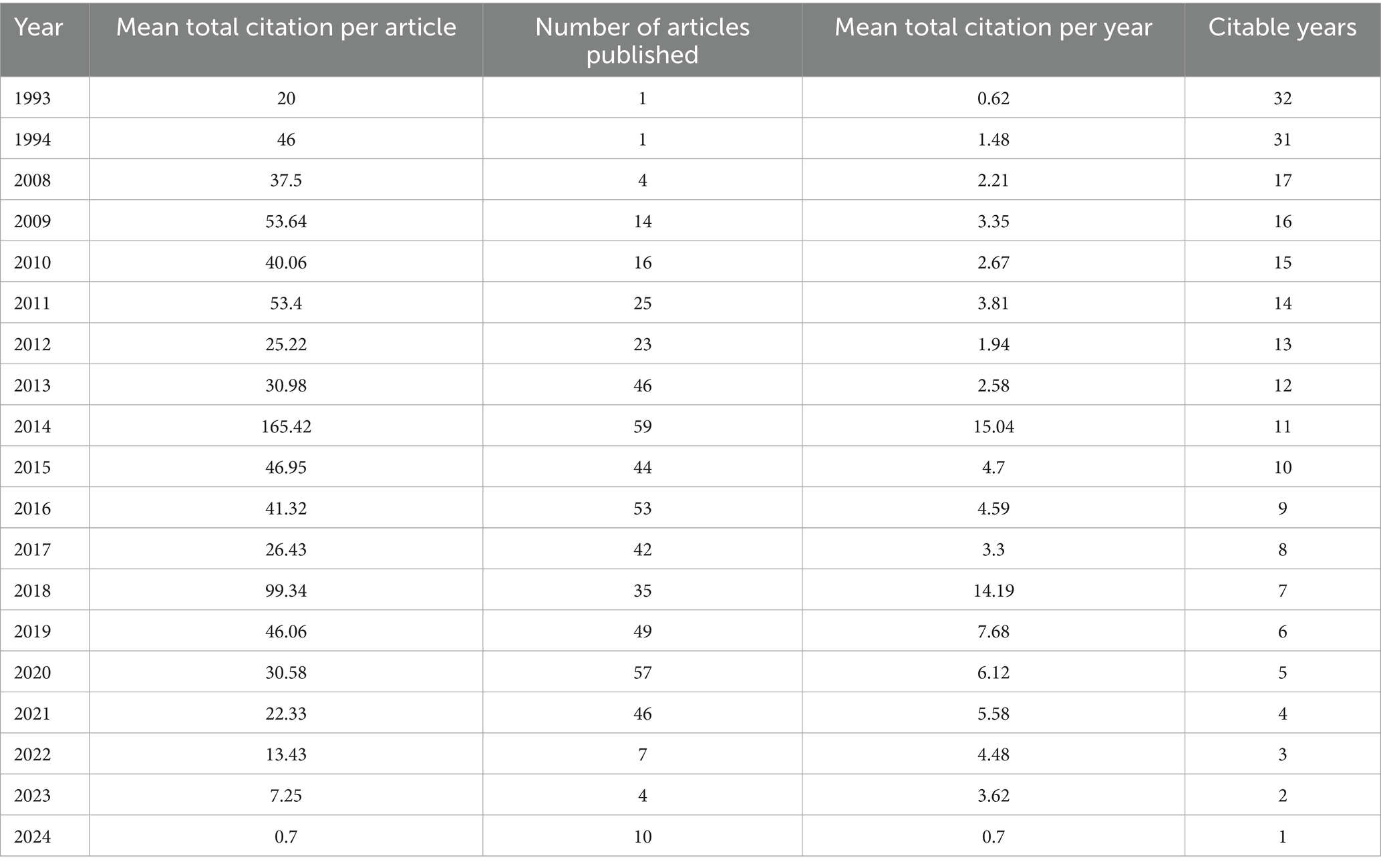
Table 2. Global annual citation rates of research articles of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
The ranking of the 10 most cited publications (Table 3) shows that the greatest contribution to the study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis of gastric cancer in young people was made by works published in 2014. Article by Herbst et al. (2014) on prognostic correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A was the most cited, receiving 4,279 citations. This highlights the key role played by work focused on therapeutic aspects, such as the use of immune agents. An article on circulating tumor DNA, also published in 2014, it ranked second with 3,683 citations, demonstrating the growing interest in molecular diagnostic methods at that time.
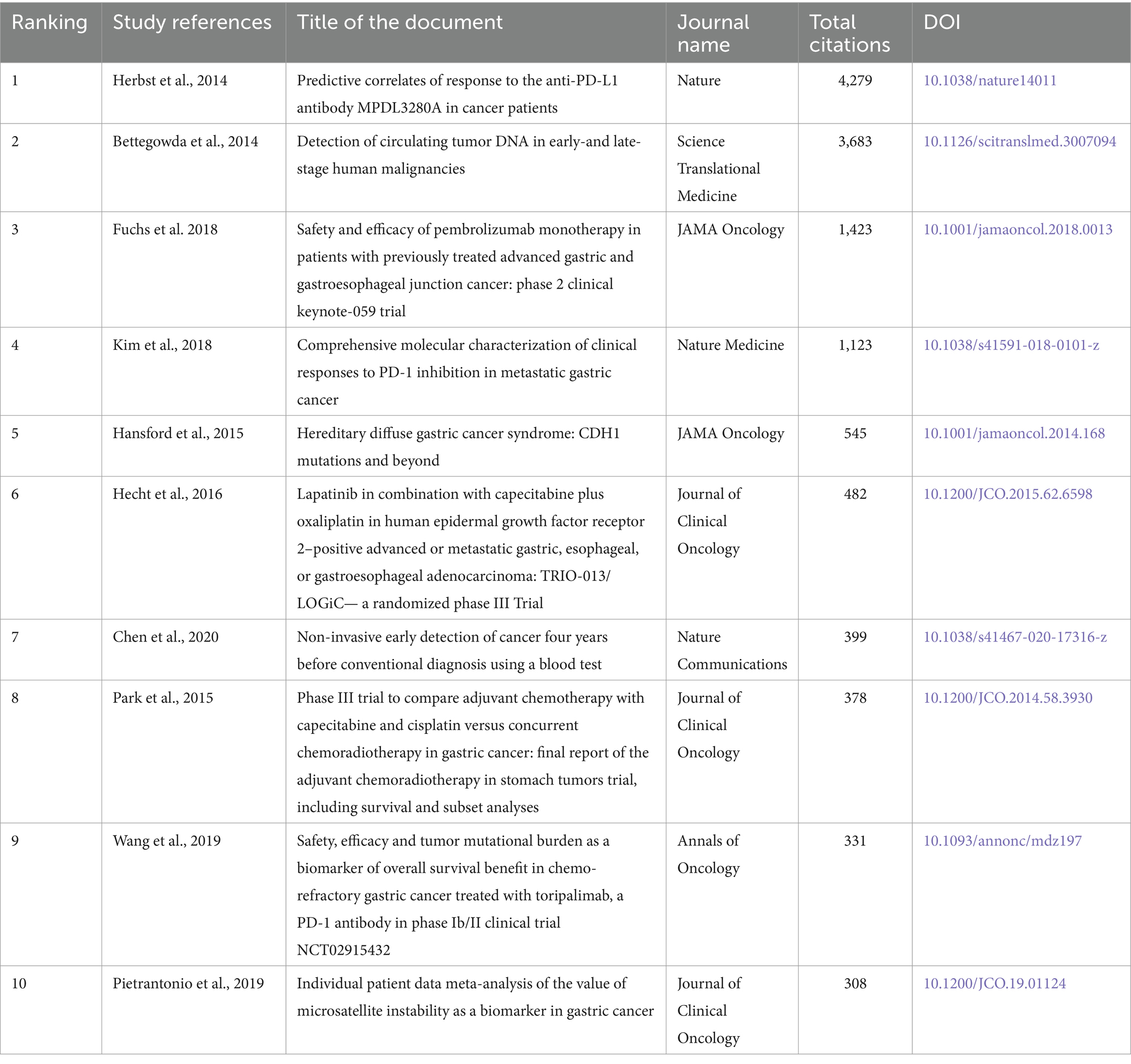
Table 3. Ranking of the 10 most cited scientific publications devoted to the study of the role of biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
Global annual citation rates of articles studying the use of biomarkers in the gastric cancer field show significant fluctuations: In 2009, 53.64 citations per article were recorded, which also confirms the high interest in the research during that period. However, starting from 2015, the citation rate began to decrease, which may indicate the completion of major studies on this topic and the lack of new publications with high scientific impact (Table 2).
The trend of average annual citations shows significant variability with periodic fluctuations from 1993 to 2017. There is a gradual decline from 2018 to 2024, with citation rates falling sharply from 14.19 citations to 0.70 citations. This may indicate a decline in interest in the field or the exhaustion of key studies that have been heavily cited over a long period of time. Notably, the highest average annual citation rate of 15.04 citations per year was observed in 2014, which dropped sharply in 2015 to 4.7 and then showed a declining trend until 2017 (Table 2).
The leader in Total Citations is the United States (12,345 citations), reflecting the strong impact of research in this country (Figure 2A). It is followed by China with 6,493 citations and Korea with 3,330 citations. The Average Article Citations is highest in Canada (277.50), indicating the high quality and impact of published papers despite their smaller number. Among Asian countries, China and Korea are the most productive, but China has a lower average citation count (32.00) compared to Korea (55.50) (Figure 2B).
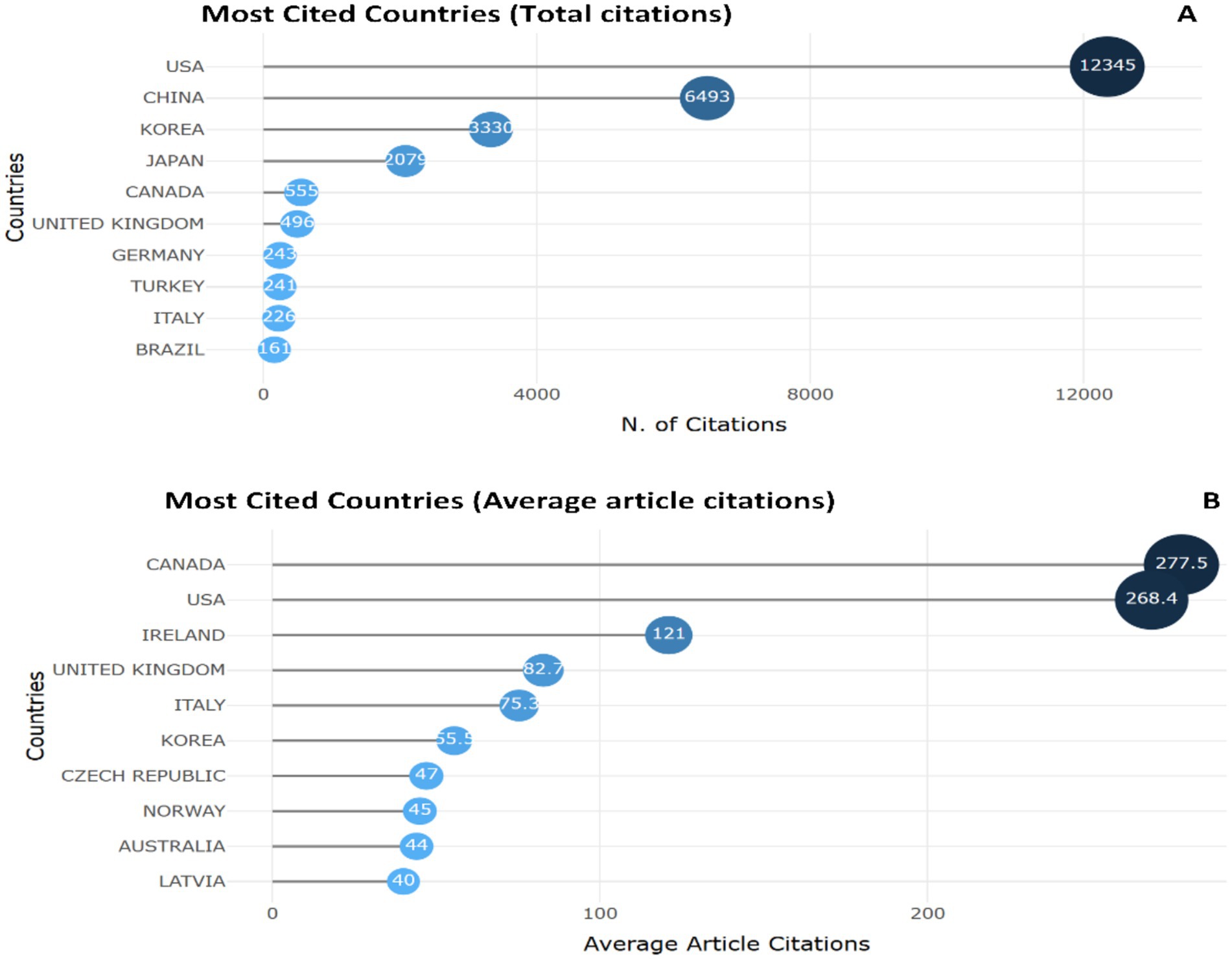
Figure 2. Top 10 most cited countries. (A) According to overall citations and (B) according to average article citations publishing papers on the use of biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
3.3 Most relevant affiliations
In the study of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients, the most productive institutions are SONGKYUNKWAN UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE and SUNYAT-SEN UNIVERSITY CANCER CENTER, which published 41 and 38 articles, respectively, on this topic (Figure 3A). These institutions have maintained interest in studying biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients for many years (Figure 3B).
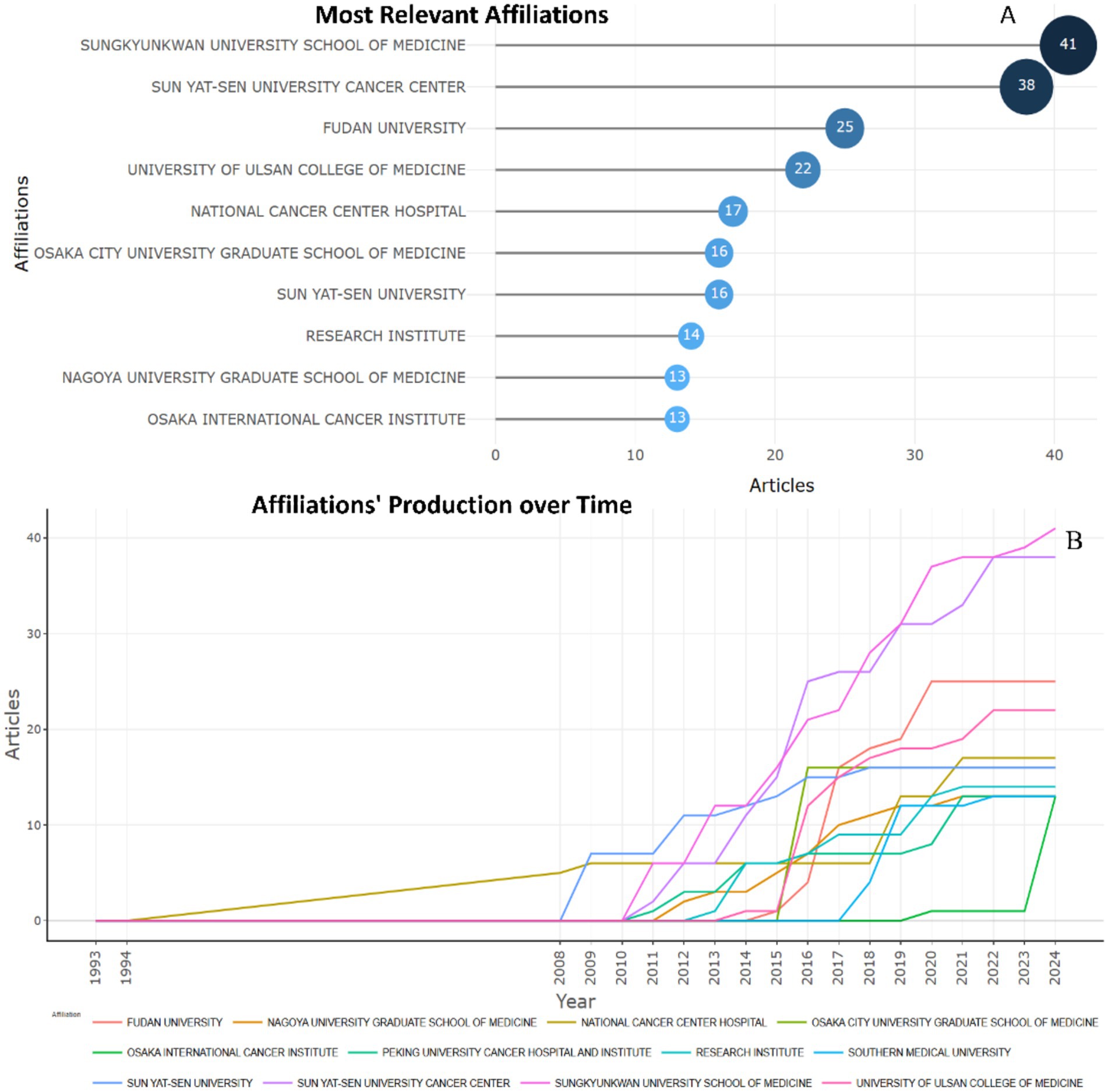
Figure 3. Most relevant affiliations of published research articles of biomarkers used in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (A) Top 10 largest organizations. (B) Top 10 affiliations’ production over time.
Among the most productive researchers in the field of studying the biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients, three leaders can be distinguished in studies: Zhang X. (21 publications), Wang Y. (18 publications), Li Y. (17 publications) (Figure 4A). Two authors: Zhang X., Wang Y. demonstrate publishing productivity over time (Figure 4B).
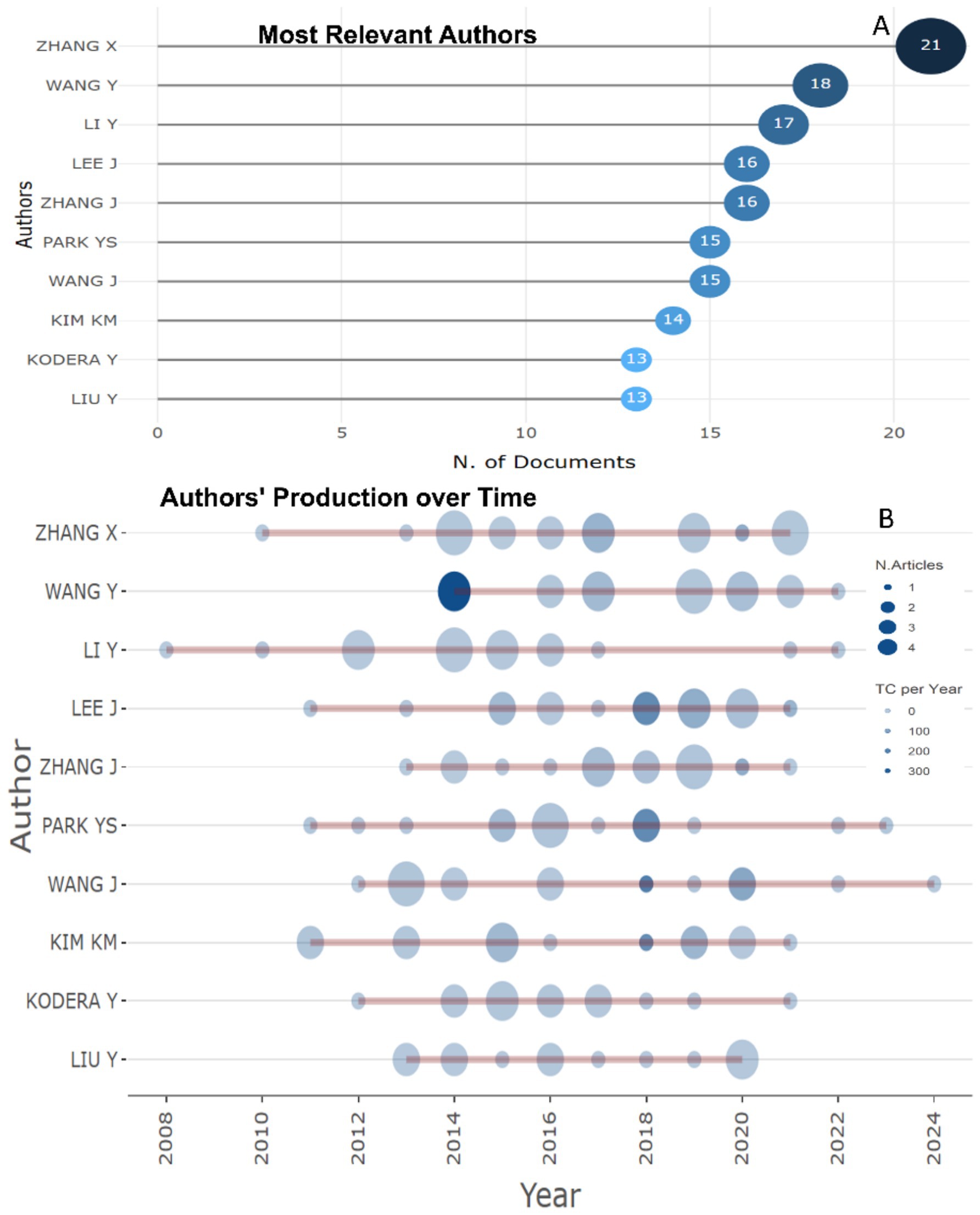
Figure 4. Most productive researchers who published research articles of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients recently. (A) Top 10 authors. (B) Top 10 prolific authors and publication activity over time (2008–2024).
China leads in scientific productivity with 743 publications, illustrating the dominance and academic influence in the field of research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. The second is the United States with 311 publications, and the third most prolific is Japan with 272 publications (Table 4). China’s productivity has also grown exponentially over the years, as illustrated in Figure 5.
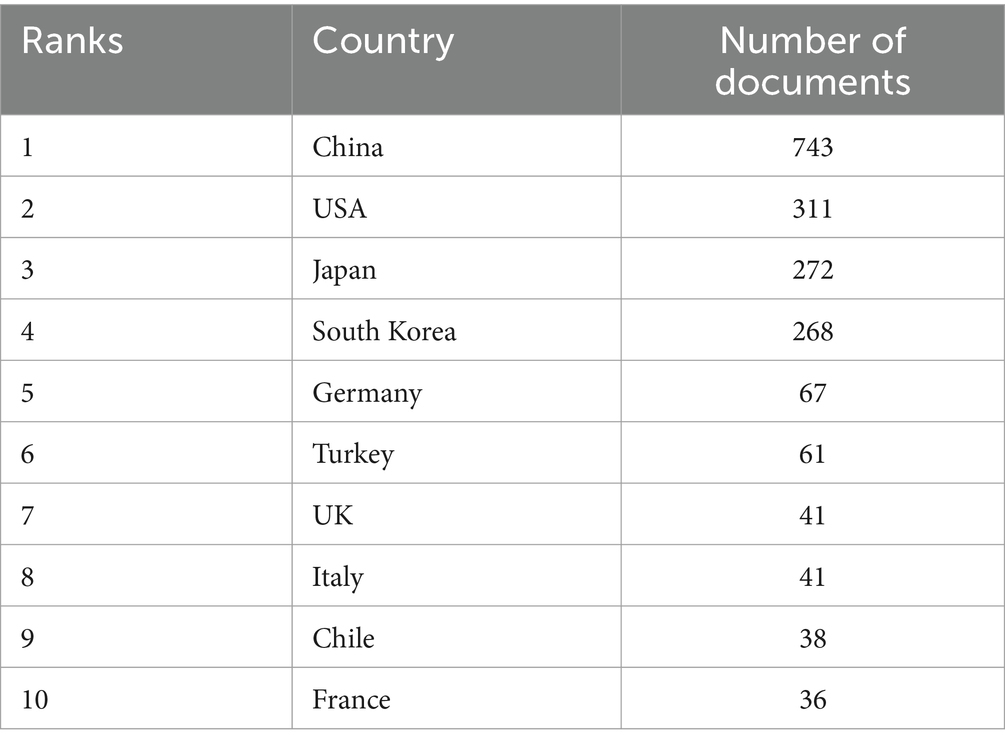
Table 4. Top 10 countries’ scientific production publishing articles of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
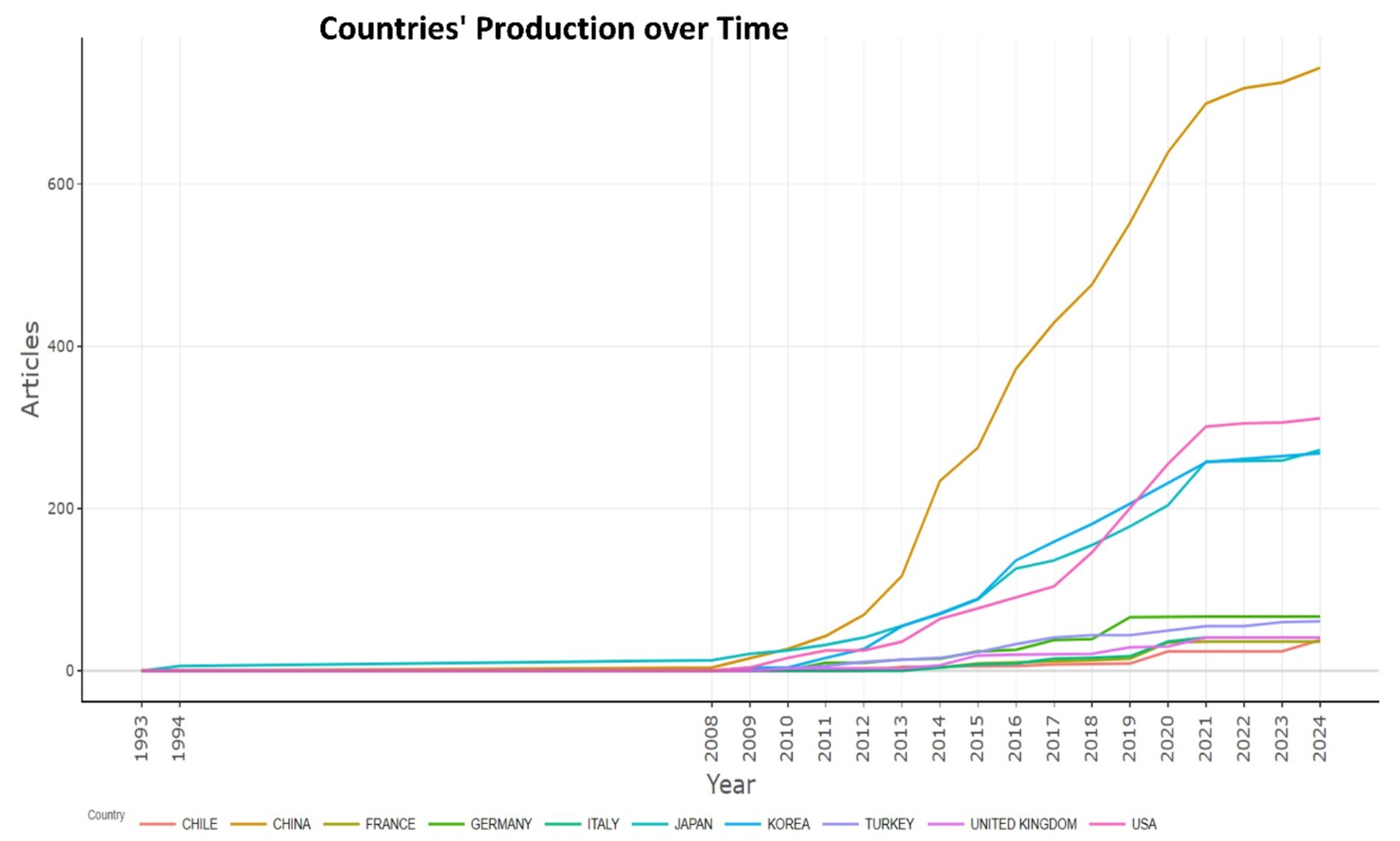
Figure 5. Countries’ production over time of biomarkers used in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
We identified the top 10 most actively publishing journals, among which the top three are: Oncotarget (24 publications), Gastric cancer (19 publications), Anticancer research (18 publications) (Figure 6A). Using the Bradford’s law, we identified 14 main sources that contain the largest number of publications of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients from 1993 to 2024 (Figure 6B).
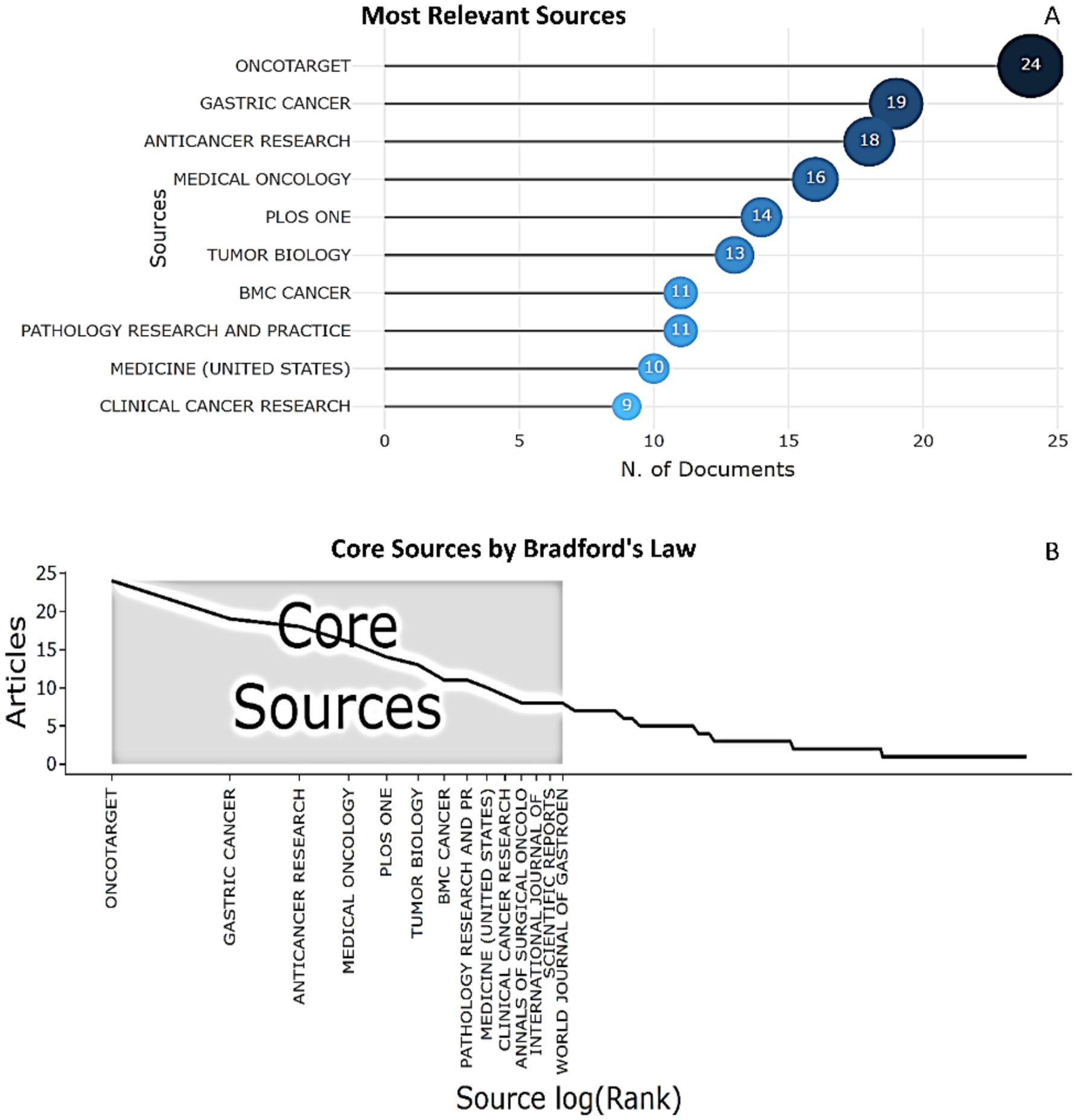
Figure 6. The top 10 most actively publishing journals that published articles regarding biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (1993–2024). (A) Top 10 productive journals. (B) Broadford’s law plot.
3.4 Global research collaboration
The global collaboration map shows the most productive collaborations between the US and China (22 publications), the US and Korea (18 publications), and the US and Japan (17 publications), illustrating the dominant position of the US as the country of choice for collaboration in research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (Figure 7).
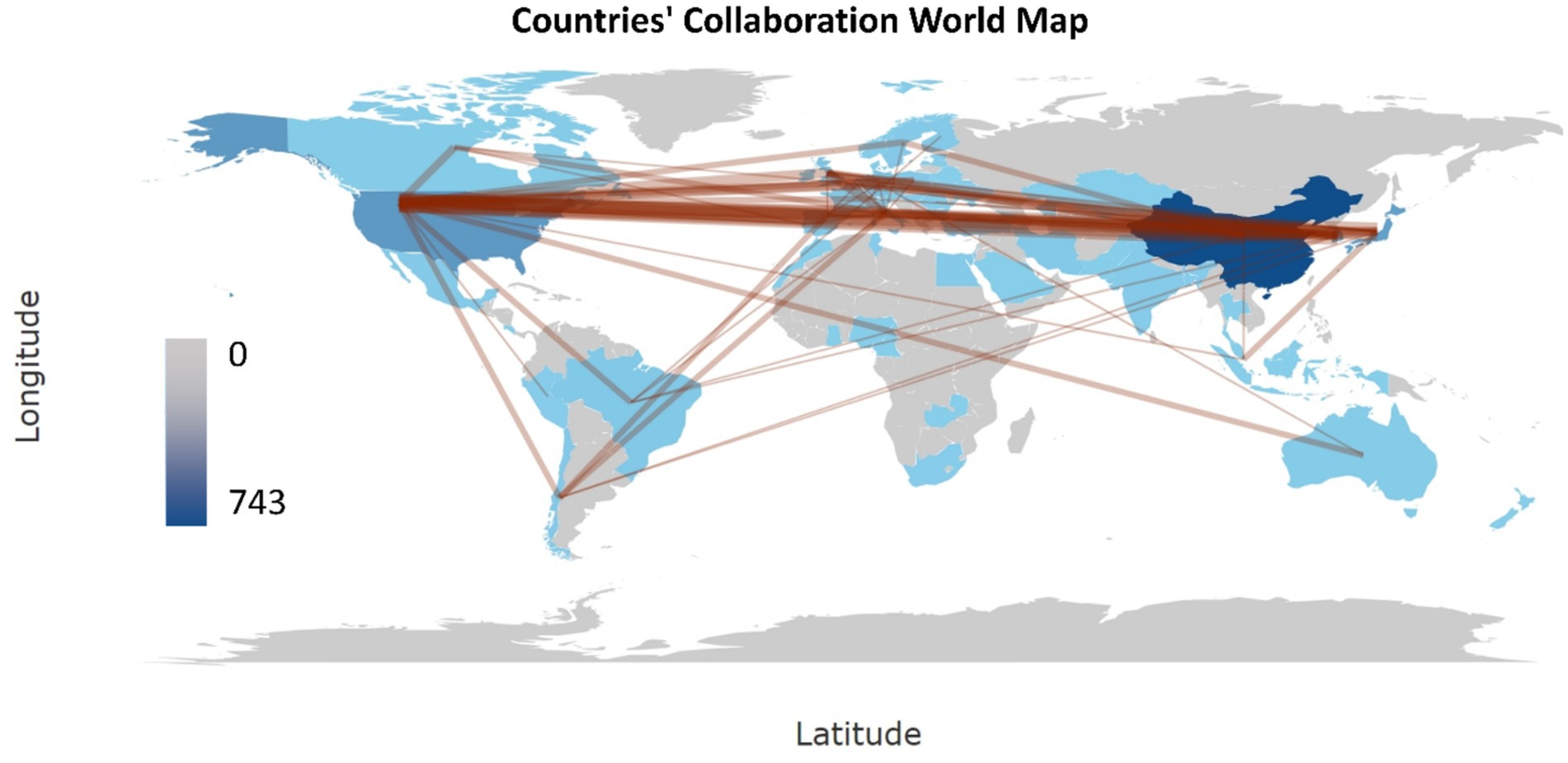
Figure 7. Map of global collaboration of biomarkers used in diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (1993–2024). The intensity of color saturation corresponds to the increasing number of articles in each country. Collaboration between countries is shown by the thickness of the connecting arrows.
A collaboration network has been established to identify central institutions, peripheral institutions and key clusters. As the collaboration network shows Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine cooperates with a large number of both local and foreign organizations (Figure 8).
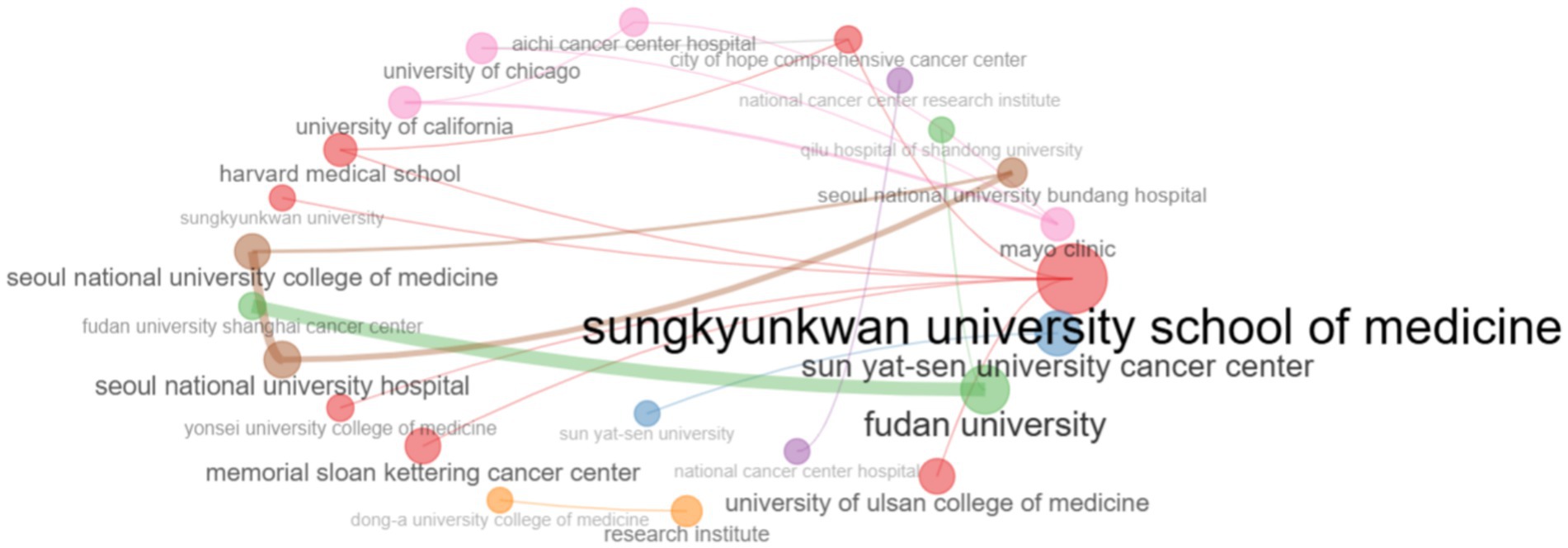
Figure 8. The institutional collaboration network identifies research centers or centers of excellence in research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
The author collaboration network illustrates the key author players, their influence and centrality. Li X. and Zhang X. are leaders who play key roles in the academic environment through whom important communications pass. Authors with lower metric values, such as Wang X., Liu Y. and Wang Z., have more specialized or less influential positions (Figure 9).
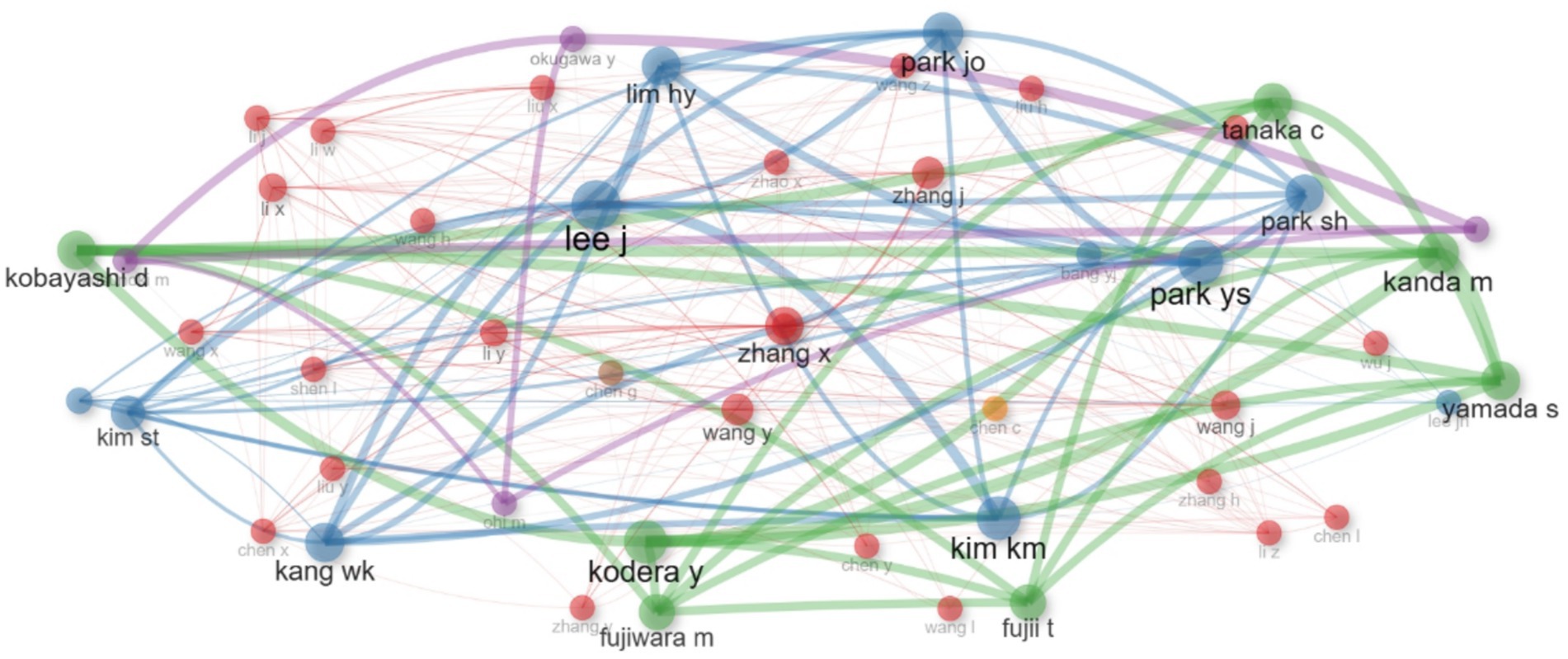
Figure 9. Authors’ collaboration network in research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
3.5 Trending keywords
To identify research trends, main topics and directions in scientific literature, keyword analysis was conducted. The thematic map of the 10 most popular keywords reveals significant insights into research focus and trends in the field of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (Figure 10A). This map provides valuable insights into the research focus and trends in gastric cancer. Dominant topic “Gastric cancer” (201/43%) is the main focus, highlighting the key link position. The second placed topic “Prognosis” (101/22%) indicates a strong focus on research conducted to better understand the outcomes, complications and progression of gastric cancer, finding prognostic biomarkers, which are crucial for diagnosis, patient management and therapeutic approaches. The third most rated topic “Immunohistochemistry” (38/8%) indicates the widespread use of this diagnostic method to detect specific markers. The relatively frequent mention of the topics “biomarker” and “biomarkers” under different spellings (30/6% and 12/3%, respectively) highlights the importance of molecular and genetic markers in the diagnosis of gastric cancer in young patients, prognosis and targeted therapy.
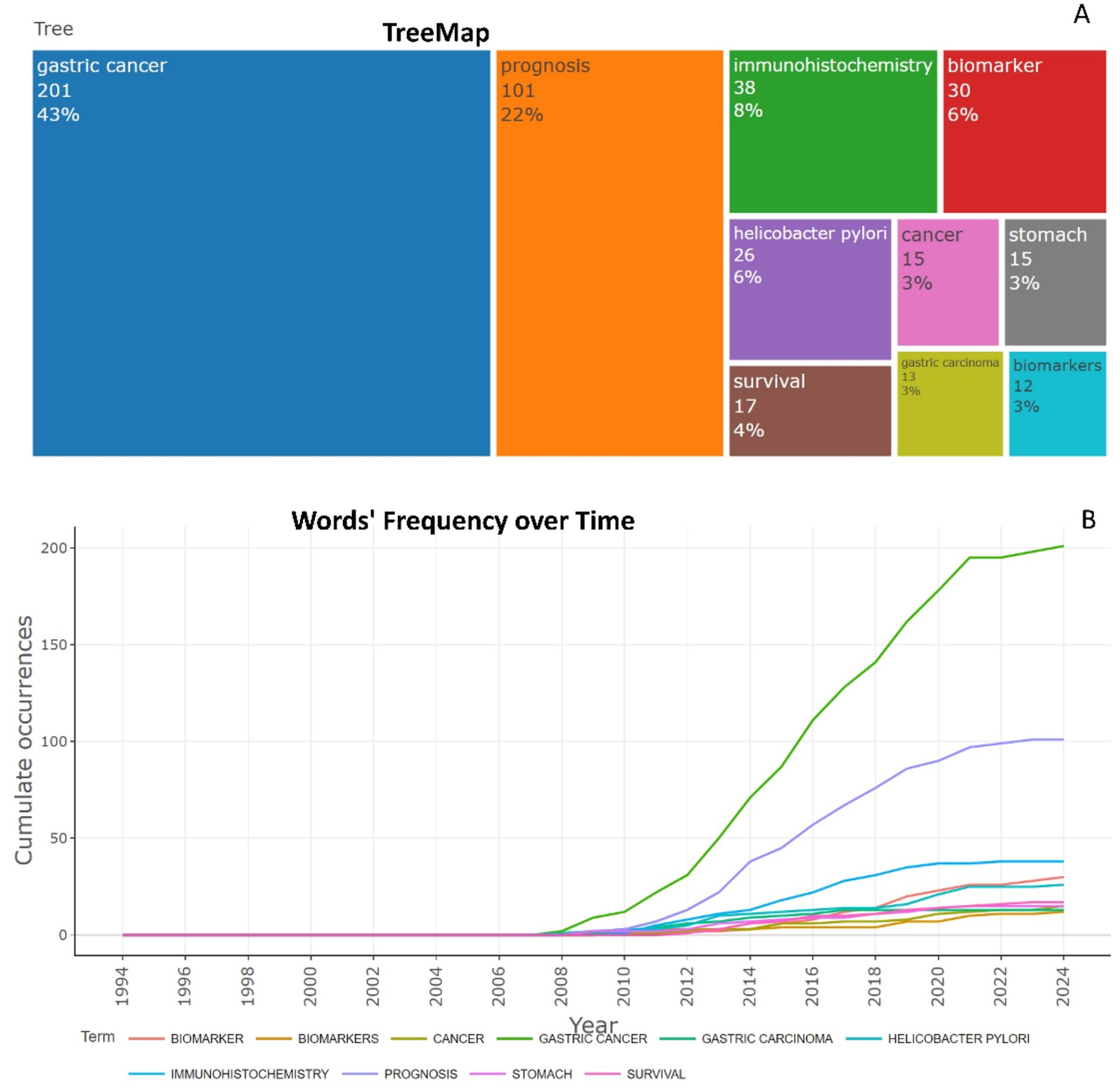
Figure 10. The 10 most popular author’s keywords in studies of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients from 1993 to 2024. (A) Tree map and (B) scatterplot-Words’ Frequency over Time.
Analysis of word frequency over time in the dataset reflects the evolving research interest in various keywords related to biomarkers used to diagnose and predict prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (Figure 10B).
The keyword “Gastric cancer” was absent until 2008, marking the beginning of systematic research interest. Since 2008, its usage has steadily increased, with an exponential growth from 50 mentions in 2013 to 201 by 2024, highlighting the growing global recognition of gastric cancer as an important public health problem. “Prognosis,” which first appeared in 2009, has shown a steady upward trend, reaching 101 mentions by 2024. This reflects the sustained interest in predicting outcomes, complications, survival, and improving treatment strategies in gastric cancer. “Immunohistochemistry” with one mention in 2010, the frequency increased to 38 mentions by 2024. This trend highlights the increasing reliance on advanced diagnostic methods in gastric cancer research. “Biomarker” and “Biomarkers” these keywords were rarely mentioned before 2012 but experienced a noticeable surge after 2015. This trend suggests an increasing focus on molecular markers for diagnosis, therapy and prognosis. The combined frequency of “Biomarker” + “Biomarkers” reaches 42 mentions in 2024, highlighting the importance of this research method. This progression reflects the dynamic nature of research priorities and the expanding scope of biomarker research in the context of gastric cancer.
The analysis of the Topical Map of studies on biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients shows that the central theme is “Gastric cancer.” This term serves as the main focus, combining key aspects such as prognosis, biomarkers, treatments (e.g., chemotherapy) and biological processes including DNA methylation. The high frequency of mentions confirms the relevance of this topic. The leading diagnostic methods are “immunohistochemistry” and “next generation sequencing.” Their importance is emphasized by the overlap with biomarker-related topics such as HER2. The high centrality and density of the Helicobacter pylori-related cluster confirm its key role in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer, especially in the context of gastric neoplasms and adenocarcinoma. Processes such as apoptosis, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA), and tumor microenvironment show potential for identifying new therapeutic targets. The topics “neoadjuvant chemotherapy” and “overall survival” are less common, indicating the need for further analysis. Their low frequency may be due to gaps in existing data or the need for new studies. Thus, this map provides a holistic view of current research directions and potential growth points for further study of gastric cancer in young patients (Figure 11).
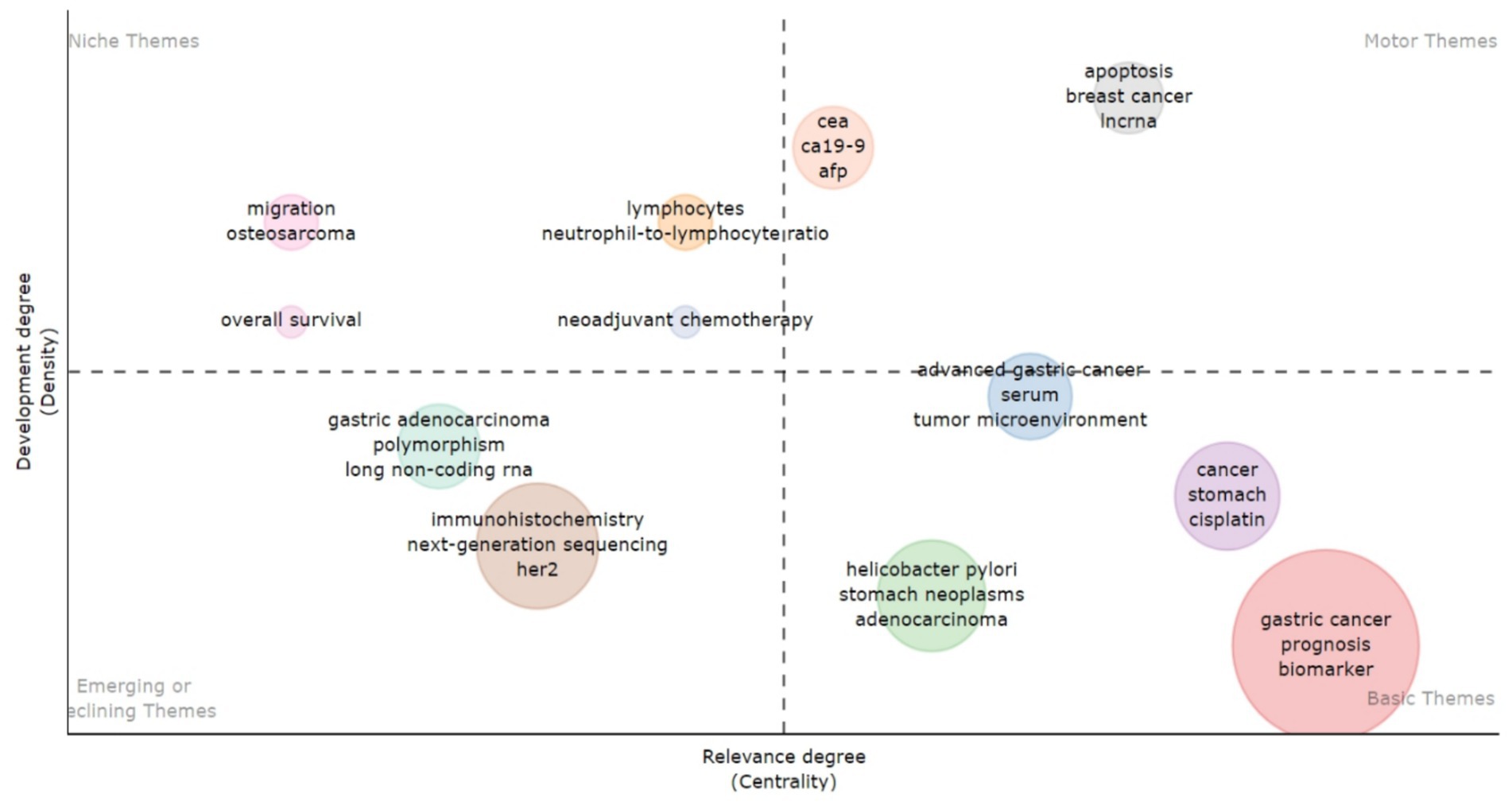
Figure 11. Visualization of thematic map based on author’s keywords frequently used in research articles demonstrates recurring terms and their thematic significance in the context of studying biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
This topic map shows the complex relationships between author keyword-based clusters in the field of biomarker research for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients.
The analysis of trending topics shows the temporal evolution and focus of research in the study of biomarkers used for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. The findings provide valuable insight into the emergence, peak activity, and stability of key themes concerning biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients (Figure 12).
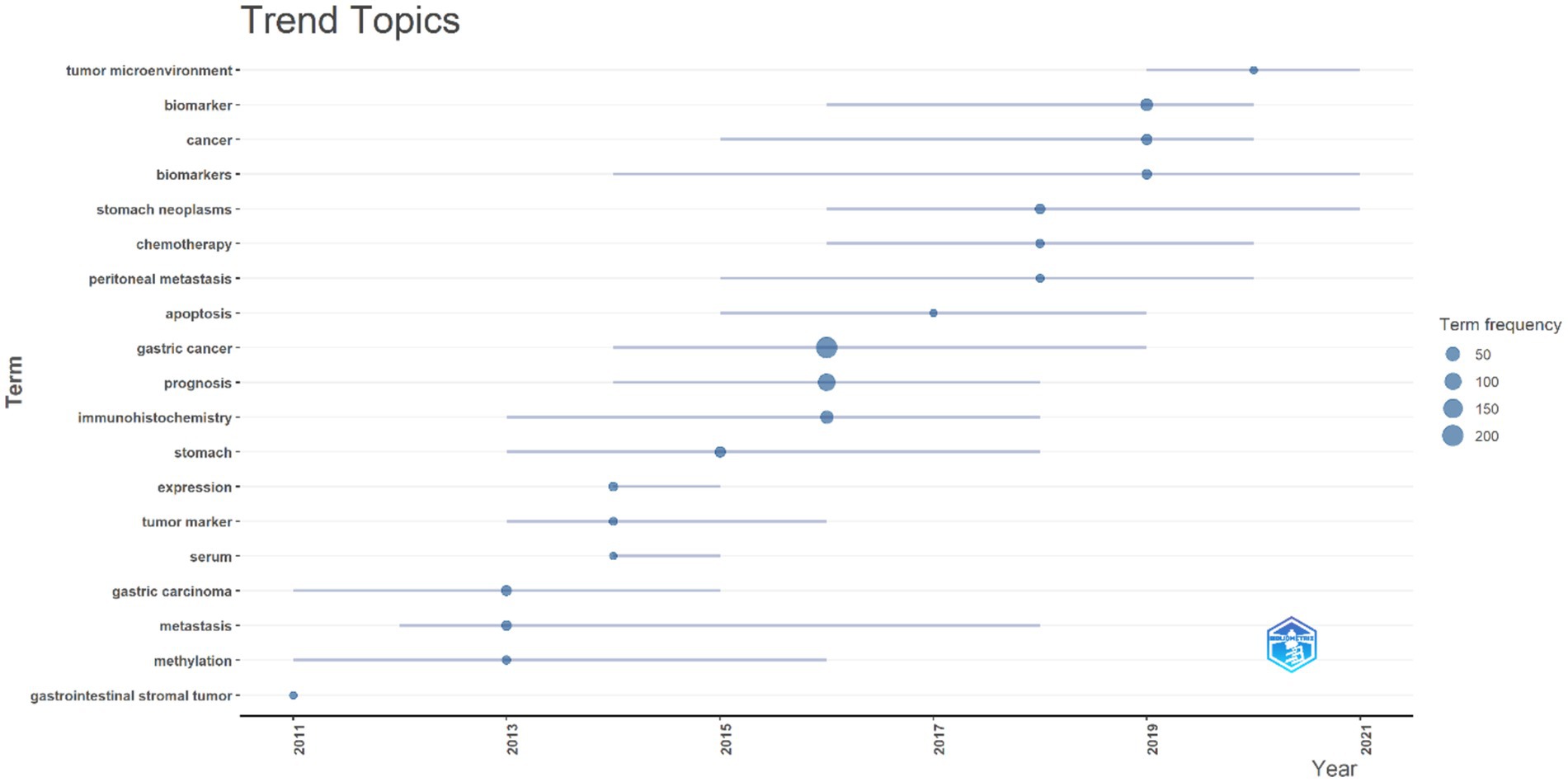
Figure 12. A visualization of the evolution of key topics over time. Each bubble represents the peak frequency of a particular topic, indicating its highest level of relevance or interest in the research community. Connecting lines trace the years during which the topic was actively discussed, illustrating its persistence and overall influence in the field.
Terms such as “Prognosis” and “Immunohistochemistry” reached their peak in 2016, reflecting their alignment with diagnostic and prognostic advancements driven by the development of precision medicine during this period. The terms “Expression” and “Serum” peaked in 2014 and exhibited relatively short active periods, emphasizing specific but transient areas of focus in biomarker identification and analysis.
The rising prominence of “Apoptosis,” which peaked in 2017, and “Tumor Microenvironment,” which peaked in 2020, underscores a growing emphasis on molecular processes and their implications for therapeutic strategies. This shift signifies a deeper exploration of the mechanistic foundations of gastric cancer. The terms “Chemotherapy” and “Peritoneal Metastasis,” with median activity around 2018, highlight critical clinical challenges, particularly in managing advanced stages of gastric cancer. “Biomarker” and “Biomarkers,” both with median activity in 2019, underscore the pivotal role of molecular markers in diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Their prominence aligns with the increasing adoption of advanced technologies such as next-generation sequencing, which have driven significant progress in the field. Persistent and expanding themes from 2019 to 2021 include “Gastric Neoplasms,” which, with a median activity in 2018, demonstrates both foundational and clinical research dimensions due to its high frequency of usage and extended timeline. Additionally, “Tumor Microenvironment,” although lower in frequency, reflects a recent surge in interest as a potential therapeutic target, marking it as an emerging area of importance. This analysis provides a comprehensive view of research trends, highlighting the dynamic evolution of focus areas in gastric cancer biomarker studies.
4 Discussion
As the clinical application of biomarkers improves, understanding the biology and treatment of gastric cancer becomes more complex. Biomarker-based treatment approaches provide more personalized care for gastric cancer (20). The introduction of immuno-oncology concepts has opened a new era in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of gastric cancer (21).
Modern advances in gastric cancer therapy are accompanied by active identification of new biomarkers associated with various cellular pathways and advanced diagnostic technologies. Standardization of clinical protocols and technological improvement of biomarker assessment methods are expected to facilitate a more personalized approach to treatment and further enhance the effectiveness of therapeutic outcomes (21). As of 2021, it was established that three molecular biomarkers predict response to targeted therapies in gastric and gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer: HER2 positivity for trastuzumab and trastuzumab deruxtecan, and PD-L1 expression for pembrolizumab and microsatellite instability (MSI) status (22). Chen X. et al. found that eXosomal PD-L1 (exoPD-L1) may contribute to functional immunosuppression, which negatively affects the survival of patients with gastric cancer (23). Shimura T. et al. showed that m6A regulators may become promising prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer (24).
Identifying key changes and biomarkers that can predict the efficacy of immunotherapy based on a limited number of samples is a critical task (25). Zhuo Hanet et al. in their study studied the relationship between the level of PD-L1 expression and clinical characteristics. They found that age (>60 years), tumor size (>5 cm), EBV infection (+), Her-2 expression (+), microsatellite status (MSI), and mismatch repair status (dMMR) were risk factors for positive expression of PD-L1 in gastric cancer (26). The study of the relationship between PD-L1 and HER2 and the clinicopathological features of gastric cancer and its prognostic effect revealed that TNM stage and PD-L1 expression were independent prognostic factors for survival time. PD-L1 expression has biological significance in gastric cancer and is closely related to the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis (27). The study of prognostic biomarkers of gastric cancer for a subgroup of young patients (>40) is an important direction for identification of key markers that may facilitate the development of new therapeutic approaches. This will make it possible to reduce premature morbidity and mortality associated with gastric cancer at a young age. Today there is a lack of data regarding the study of biomarkers, clinical characteristics and prognostic factors for stomach cancer in young people (6). This was also confirmed by the paucity of studies examining biomarkers used to diagnose and predict gastric cancer specifically in young patients.
This bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive overview of studies on biomarkers used for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer (GC) in young patients. Results show significant fluctuations in both publication and citation trends over a 31-year period, highlighting evolving research interests and results. A consistent 7.71% annual growth indicates sustained scientific interest in biomarkers for gastric cancer in young patients. The low rate of international co-authorship (19.4%), highlighting the need for greater global partnerships. Articles by US authors have a high average citation rate (53.56 citations per year). Publications were particularly concentrated in 2014 (59articles) and 2020 (57articles), likely due to advances in molecular biology and genomics that have stimulated interest in GC biomarkers. A steady decline in citations since 2015, suggest a saturation in foundational research and fewer high-impact publications in recent years. The 2014 article on anti-PD-L1 antibody by Herbst et al. was the most cited, emphasizing the importance of therapeutic innovations like immune agents. The study identifies Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University School of Cancer Center and Fudan University, as the most prolific institutions, highlighting the concentration of research efforts in East Asia. These institutions have been key contributors, generating much of the literature regarding biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. Central figures like Li X. and Zhang X. facilitate influential collaborations. The top three countries in terms of productivity were (1) China with 743 publications; (2) USA with 311 publications; (3) Japan with 272 publications. Their leadership in stomach cancer research reflects a combination of epidemiological burden, investment in science, and global collaboration. The analysis also emphasizes the importance of international collaboration in advancing this research, especially between institutions in East Asia, North America, and Europe.
However, a critical gap in the number of studies specifically targeting young patients with GC is evident, highlighting the need for more targeted research. Despite the progress made in molecular biomarker research, citation rates have dropped sharply from 2018 to 2024, suggesting a slowdown in this field. This decline may reflect difficulties in translating molecular discoveries into clinical applications or changing research priorities.
Co-citation analysis classified studies into distinct intellectual groups, identifying key themes and areas of focus in GC biomarker research. This structure may help identify emerging topics and guide future research. In addition, significant differences in citation rates were noted across regions, with studies from the US receiving the highest citation rates, indicating regional differences in research impact. The strongest research partnerships exist between the USA and China, followed by the USA with Korea and Japan. Central figures like Li X. and Zhang X. facilitate influential collaborations.
Analysis of key terms such as “gastric cancer,” “prognosis” and “biomarkers” indicates the dominant importance of clinical issues related to disease outcomes and the development of precision medicine. After 2020, there is a stabilization or slowdown in the frequency of mention of these terms, which may indicate maturity in certain research areas. Significant growth in interest in keywords related to diagnostics (immunohistochemistry, biomarkers) and outcomes (prognosis, survival) reflects a shift in research focus toward personalized medicine. Simultaneously, the moderate growth of terms such as “gastric carcinoma” and “gastric” indicates their secondary importance in the context of specialized research.
The present analysis demonstrates the dynamic development and major research directions of biomarkers used for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer, especially in young patients. It also suggests strategic approaches for further research, including a focus on prognostic markers, the role of the tumor microenvironment, and Helicobacter pylori-associated pathogenesis.
The thematic review emphasizes the promise of integrating diagnostic technologies and data on apoptosis processes with molecular studies to develop new treatments and improve patient survival rates. The temporal dynamics of the studies indicate a shift from more general topics such as “gastric carcinoma” and “gastric” to specialized aspects including the study of biomarkers, tumor microenvironment and methylation processes. Early work focused on identifying the underlying pathologic mechanisms, whereas current trends emphasize molecular mechanisms and therapeutic innovations.
4.1 Strengths and limitations
This study offers several notable advantages. It represents the first comprehensive bibliometric analysis systematically examining the global landscape of research of biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients over the past 31 years. We performed a thorough and consistent analysis, presenting and interpreting metadata using a widely accepted and reliable software platform. However, there are some limitations that should be considered. Our analysis is based solely on data from the Scopus database and focuses exclusively on research articles, which may lead to a potential underestimation of publications indexed in other databases. The focus on research articles means that reviews and other forms of research papers were not included in the analysis.
In addition, the database used includes a limited number of studies related to the keywords “gastric cancer,” “biomarkers,” and “young adults.” This limitation may lead to an incomplete representation of the research landscape in this field, highlighting the need for further exploration of other data sources and research areas.
Future studies should examine a wider range of databases and include a wider range of publications to obtain a more holistic view of the research landscape.
5 Conclusion
The growth of publications, high citation rates and participation of researchers from many countries confirm the importance of research devoted to the biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients. However, despite significant progress, this bibliometric analysis demonstrates the need for more targeted research in younger patients. Identifying age-specific biomarkers will be critical to improving diagnosis, prognosis, and personalized treatment strategies for young patients with gastric cancer. The study highlights the need for global collaboration and multidisciplinary approaches to drive the next wave of breakthroughs in this field. Tumor microenvironment, molecular diagnostics, immune agents, and advanced sequencing methods present promising future directions. Greater focus on underexplored topics like neoadjuvant chemotherapy and long-term survival outcomes is needed to fill existing gaps.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
NA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. SA: Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. TN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. AK: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AR: Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AT: Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. NK: Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the committee of science of the Ministry of science and higher education of the Republic of Kazakhstan (Grant No. AP23490776).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Sung, H, Ferlay, J, Siegel, RL, Laversanne, M, Soerjomataram, I, Jemal, A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2. Wang, X, Wang, C, Han, W, Ma, C, Sun, J, Wang, T, et al. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of global research on micro RNAs in gastric cancer: from 2013 to 2023. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1374743. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1374743
3. Ge, Y, Wu, Q, Ma, G, Shao, W, Liu, H, Zhang, Q, et al. Hypermethylation of EIF4E promoter is associated with early onset of gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. (2018) 39:66–71. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx110
4. Song, M, Kang, D, Yang, JJ, Choi, JY, Sung, H, Lee, Y, et al. Age and sex interactions in gastric cancer incidence and mortality trends in Korea. Gastric Cancer. (2015) 18:580–9. doi: 10.1007/s10120-014-0411-x
5. Merchant, SJ, Kim, J, Choi, AH, Sun, V, Chao, J, and Nelson, R. A rising trend in the incidence of advanced gastric cancer in young Hispanic men. Gastric Cancer. (2017) 20:226–34. doi: 10.1007/s10120-016-0603-7
6. Zhou, L, Jiang, Z, Gu, W, and Han, S. STROBE-clinical characteristics and prognosis factors of gastric cancer in young patients aged ≤30 years. Medicine. (2021) 100:e26336. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026336
7. Herbert, A, Lyratzopoulos, G, Whelan, J, Taylor, RM, Barber, J, Gibson, F, et al. Diagnostic timeliness in adolescents and young adults with cancer: a cross-sectional analysis of the BRIGHTLIGHT cohort. Lancet Child Adolescent Health. (2018) 2:180–90. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(18)30004-X
8. Puhr, HC, Karner, A, Taghizadeh, H, Jomrich, G, Schoppmann, SF, Preusser, M, et al. Clinical characteristics and comparison of the outcome in young versus older patients with upper gastrointestinal carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2020) 146:3313–22. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03302-x
9. Etemadi, A, Safiri, S, Sepanlou, SG, Ikuta, K, Bisignano, C, Shakeri, R, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of stomach cancer in 195 countries, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:42–54. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30328-0
10. Ławniczak, M, Gawin, A, Jaroszewicz-Heigelmann, H, Rogoza-Mateja, W, Białek, A, Kulig, J, et al. Analysis of clinicopathologic characteristics of gastric cancer in patients ≤40 and ≥40 years of age. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2020) 55:62–6. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2019.1699597
11. Tavakkoli, A, Pruitt, SL, Hoang, AQ, Zhu, H, Hughes, AE, McKey, TA, et al. Ethnic disparities in early-onset gastric Cancer: a population-based study in Texas and California. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. (2022) 31:1710–9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-22-0210
12. Wang, YM, Gu, ML, and Ji, F. Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol. (2015) 21:2303–14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2303
13. Wang, Z, Xu, J, Shi, Z, Shen, X, Luo, T, Bi, J, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic of gastric cancer in young patients. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2016) 51:1043–9. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2016.1180707
14. Dong, D, Fang, MJ, Tang, L, Shan, XH, Gao, JB, Giganti, F, et al. Deep learning radiomic nomogram can predict the number of lymph node metastasis in locally advanced gastric cancer: an international multicenter study. Ann Oncol. (2020) 31:912–20. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.003
15. Lee, DH, Kim, SH, Joo, I, and Han, JK. CT Perfusion evaluation of gastric cancer: correlation with histologic type. Eur Radiol. (2018) 28:487–95. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4979-5
16. Zeng, D, Li, M, Zhou, R, Zhang, J, Sun, H, Shi, M, et al. Tumor microenvironment characterization in gastric cancer identifies prognostic and immunotherapeutically relevant gene signatures. Cancer Immunol Res. (2019) 7:737–50. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0436
17. Zeng, D, Zhou, R, Yu, Y, Luo, Y, Zhang, J, Sun, H, et al. Gene expression profiles for a prognostic immunoscore in gastric cancer. Br J Surg. (2018) 105:1338–48. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10871
18. Wang, Y, Chen, W, Li, K, Wu, G, Zhang, W, Ma, P, et al. Tissue-based metabolomics reveals metabolic signatures and major metabolic pathways of gastric cancer with help of transcriptomic data from TCGA. Biosci Rep. (2021) 41:BSR20211476. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211476
19. Li, M, Gao, N, Wang, SL, Guo, YF, and Liu, Z. Hotspots and trends of risk factors in gastric cancer: a visualization and bibliometric analysis. World J Gastrointestinal Oncol. (2024) 16:2200–18. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i5.2200
20. Smith, SM, Wachter, K, Burris, HA 3rd, Schilsky, RL, George, DJ, Peterson, DE, et al. Clinical cancer advances 2021: ASCO's report on progress against cancer. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:1165–84. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03420
21. Myer, NM, Shitara, K, Chung, HC, Lordick, F, Kelly, RJ, Szabo, Z, et al. Evolution of predictive and prognostic biomarkers in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2022) 148:2023–43. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03902-1
22. Nakamura, Y, Kawazoe, A, Lordick, F, Janjigian, YY, and Shitara, K. Biomarker-targeted therapies for advanced-stage gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction cancers: an emerging paradigm. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. (2021) 18:473–87. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00492-2
23. Chen, X, Du, Z, Huang, M, Wang, D, Fong, WP, Liang, J, et al. Circulating PD-L1 is associated with T cell infiltration and predicts prognosis in patients with CRLM following hepatic resection. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2022) 71:661–74. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-03021-3
24. Shimura, T, Kandimalla, R, Okugawa, Y, Ohi, M, Toiyama, Y, He, C, et al. Novel evidence for m6A methylation regulators as prognostic biomarkers and FTO as a potential therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. (2022) 126:228–37. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01581-w
25. Cho, YA, Lee, H, Kim, DG, Kim, H, Ha, SY, Choi, YL, et al. PD-L1 expression is significantly associated with tumor mutation burden and microsatellite instability score. Cancers. (2021) 13:4659. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184659
26. Han, Z, Wang, N, Qiao, Q, He, X, and Wang, N. Association of PD-L1 expression with Clinicopathologic characters in gastric Cancer: a comprehensive Meta-analysis. Curr Med Chem. (2024) 31:3198–216. doi: 10.2174/0109298673263784230922060257
Keywords: stomach cancer, biomarkers, adults, young, immunohistochemistry
Citation: Azbergenov NK, Akhmetova SZ, Nurulla TA, Kaliev AR, Ramankulova AB, Tulyayeva AB and Kereeva NM (2025) Biomarkers used in the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer in young patients: a scientometric analysis. Front. Med. 12:1586742. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1586742
Edited by:
Jingchao Wang, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Manjusha Roy Choudhury, Aspira Women’s Health Inc., United StatesAhmed Abduljabbar Jaloob Aljanaby, University of Kufa, Iraq
Copyright © 2025 Azbergenov, Akhmetova, Nurulla, Kaliev, Ramankulova, Tulyayeva and Kereeva. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nurbek Kozhakhmetuly Azbergenov, ZHIucGF0aG9sb2dpc3RAbWFpbC5ydQ==
†ORCID: Nurbek Kozhakhmetuly Azbergenov, https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6328-3883
Saule Zhumabaevna Akhmetova, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6508-7790
Talshyn Amirkhanovna Nurulla, https://orcid.org/0009-0001-7963-8298
Abdiraman Rsalievich Kaliev, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4192-0025
Aigul Bulatovna Ramankulova, https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0155-7663
Anarzhan Balkashevna Tulyaeva, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7149-0121
Nurgul Meirimovna Kereeva, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6205-4029
 Nurbek Kozhakhmetuly Azbergenov
Nurbek Kozhakhmetuly Azbergenov Saule Zhumabaevna Akhmetova1†
Saule Zhumabaevna Akhmetova1† Talshyn Amirkhanovna Nurulla
Talshyn Amirkhanovna Nurulla