- 1Department of Nursing, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
- 3Clinical Research Center for Neurological Diseases of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, China
- 4State Key Laboratory of Transvascular Implantation Devices, Hangzhou, China
- 5Neuroscience Intensive Care Unit, Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
- 6Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Huzhou FuYin Hospital of Huzhou University, Huzhou, China
- 7Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Background: Stroke is closely linked to inflammation, with the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) emerging as a promising inflammatory marker. This study aims to investigate the association between NLR and both morbidity and mortality in stroke patients.
Methods: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2020 were analyzed, including adults with complete neutrophil and lymphocyte count records. Multivariate logistic regression was used to examine the relationship between NLR and both stroke morbidity and all-cause mortality. Restricted cubic spline regression was employed to assess potential nonlinearity in these associations. Subgroup analyses were performed to identify influencing factors.
Results: After adjusting for confounders, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for stroke in the higher NLR quartiles, compared to the lowest quartile, were 1.28 (1.07–1.52) and 1.36 (1.12–1.65), respectively. The restricted cubic spline curve indicated a nonlinear positive association between NLR and stroke risk. Additionally, an elevated NLR was positively associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality.
Conclusion: The findings underscore the potential use of NLR in stratifying and predicting mortality risk in stroke patients, suggesting its relevance in clinical practice.
Introduction
Inflammation represents a complex host response to danger signals and is fundamental for host survival, while also being implicated in the pathogenesis of many human diseases (1). Neuroinflammatory responses play a critical role in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke, where brain ischemia-induced immunosuppression may promote concurrent infections (2, 3). Inflammatory biomarkers have been widely investigated as potential predictors of cardiovascular diseases. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), a simple ratio derived from routine complete blood count tests, reflects the relative number of neutrophils and lymphocytes in peripheral circulation and serves as a novel biomarker of baseline inflammatory response (4, 5). Previous studies have demonstrated that NLR is associated with poor functional outcomes in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage, and its relevance to stroke is increasingly recognized (5, 6).
Stroke remains the second leading cause of death globally, contributing significantly to disability, with a rising incidence among younger and middle-aged populations (7). Stroke has a complex pathophysiology, including both ischemic and hemorrhagic types, with inflammation playing a critical role in their onset, progression, and outcomes (8). Current consensus indicates that inflammation has a cumulative negative impact on stroke incidence, highlighting it as a crucial therapeutic target for stroke prevention (9). Neutrophils, a type of white blood cell involved in the initial immune response, contribute to inflammation and tissue damage during the acute phase of stroke (10, 11). Similarly, lymphocytes play a vital role in the inflammatory process and are closely associated with the detrimental effects of stroke. In mice deficient in T and B cells, the infarct size was significantly reduced following transient focal ischemia (12). Therefore, the NLR may serve as a surrogate marker for the underlying inflammatory status in patients at risk of stroke.
Research exploring the relationship between NLR and stroke has revealed several significant findings. Elevated NLR levels are associated with an increased risk of stroke, particularly ischemic stroke. This relationship is thought to result from the pro-inflammatory state indicated by a higher neutrophil count and a relatively lower lymphocyte count (5, 13). In the context of ischemic stroke, vascular occlusion leads to hypoxia and nutrient deprivation in brain tissue, exacerbating tissue damage through neutrophil-mediated inflammation (14). Thus, an elevated NLR may reflect a heightened inflammatory response, leading to a worse prognosis among stroke patients (15, 16).
NLR has been investigated as a prognostic indicator in stroke, with higher NLR being associated with poorer outcomes, including increased mortality and greater severity of neurological deficits. These findings suggest that NLR may not only help identify individuals at higher risk of stroke but also predict outcomes in patients who have already experienced a stroke. It holds potential as a simple and cost-effective tool for risk stratification and guiding therapeutic decisions in clinical settings.
Given the rise in stroke morbidity with advancing age, population growth and aging may contribute to substantial increases in global deaths and disabilities in the future (7, 17). There is an urgent need to identify prognostic parameters that are easy to measure and cost-effective to strengthen the monitoring of stroke morbidity and related mortality. The NLR shows promise as a biomarker in the context of stroke, offering insights into the inflammatory processes underlying this complex disease. Its ability to predict stroke risk and outcomes, combined with its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, makes it an attractive tool for both research and clinical practice. Further research is needed to better understand the mechanistic links between NLR and stroke and to explore its potential role in personalized approaches for stroke prevention and management. Comprehensive studies could help elucidate disease mechanisms and identify potential therapeutic targets. The aims of this study were to investigate the association of NLR with stroke morbidity and mortality and to assess the importance of inflammatory status in the development of stroke.
Materials and methods
Study population
We utilized data from the 1999–2020 cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). This survey is managed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). NHANES is a complex, multistage probability sampling survey conducted biennially to evaluate the health and nutritional status of the U.S. population, as well as disease profiles, to inform public health policy. The survey method includes face-to-face interviews, physical examinations, and laboratory testing. The study protocol received approval from the NCHS Ethics Review Board, and all participants provided written informed consent prior to participation. Detailed study design and data for NHANES can be accessed on the CDC’s official website.1
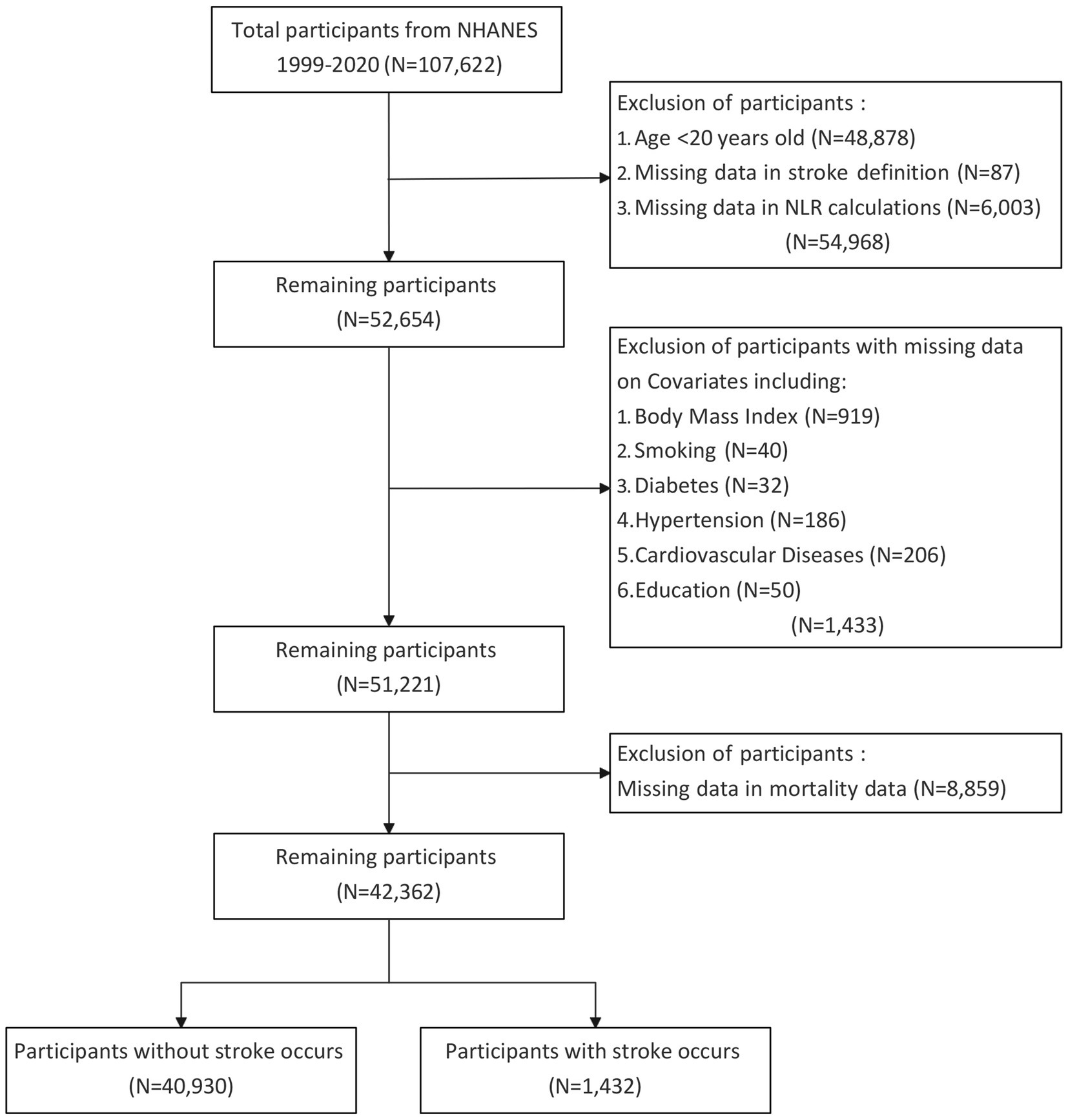
We downloaded data covering the years 1999–2020 from the NHANES website, encompassing 11 survey cycles. The data included in this study comprised demographic, examination, laboratory, and questionnaire information. The initial dataset included cross-sectional data from 107,622 participants. Exclusion criteria were applied to participants lacking complete stroke data and blood cell counts, as well as those under 20 years of age. Those lacking data on covariates were also excluded. After these exclusions, the study ultimately comprised 42,362 eligible subjects for subsequent analysis. A detailed flow chart of the participant recruitment process was shown in Figure 1.
Assessment of stroke
Stroke patients were identified based on self-reported health status and medical history. Participants were classified as having had a stroke if they responded “yes” to the question, “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you had a stroke?” This question was administered by trained interviewers using a Computer-Assisted Personal Interviewing (CAPI) system, which included built-in consistency checks to reduce data entry errors and employed on-screen help tools to clarify key terms. Alerts were immediately triggered when responses were flagged as unusual, inconsistent, or unrealistic, prompting interviewers to verify or edit the initial responses. It is important to note that self-reported measures are susceptible to recall bias, which may impact data interpretation.
Measurement of NLR
Neutrophil and lymphocyte counts were determined by trained medical professionals at Mobile Examination Centers using a Beckman Coulter automated hematology analyzer. Complete blood counts were performed on blood samples and reported as ×10 (3) cells/μL. The NLR was calculated by dividing the absolute neutrophil count by the absolute lymphocyte count.
Assessment of mortality
The study endpoint was all-cause mortality. Mortality data were determined through probabilistic matching between NHANES and the National Death Index (NDI) death certificate records, using personal identifiers such as name, race, gender, date of birth, and social security number. Follow-up duration was defined as the time from the NHANES interview date to the date of death or December 31, 2021.
Covariates
Various covariates were included in our analysis to account for potential confounders. These covariates, selected based on existing literature, encompassed factors such as age, gender, race, education level, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, diabetes status, hypertension status, congestive heart failure status, and coronary heart disease status. Gender was categorized as female or male. Race/ethnicity was classified as Mexican American, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, other Hispanic, or other race/multiracial. Education level was grouped into three categories: less than high school, high school, and more than high school. Diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, and coronary heart disease were defined based on self-reported questionnaire data. Laboratory data, including white blood cell, monocyte, neutrophil, and lymphocyte counts, were obtained from the NHANES website.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented as means ± standard deviations (SD), while categorical variables were shown as frequency counts and percentages. p-values for continuous variables were calculated using a weighted logistic regression model, and p-values for categorical variables were obtained using a weighted chi-square test. NLR was divided into four quartiles, with the first quartile (Q1) designated as the reference quartile.
Kaplan–Meier (K–M) survival analysis was performed, and comparisons were made across NLR quartiles. A multivariable Cox regression model was used to assess the linear associations between NLR and both stroke morbidity and all-cause mortality. Three Cox regression models with varying levels of confounder adjustment were established: Model 1 with no covariate adjustments, Model 2 adjusted for age, gender, and race, and Model 3 adjusted for age, gender, race, education level, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, and smoking status. Additionally, a restricted cubic spline regression model was applied to explore potential relationships between NLR and both stroke morbidity and all-cause mortality. Subgroup analyses were conducted to evaluate the impact of NLR on stroke morbidity and all-cause mortality across different subgroups, stratified by age, gender, race/ethnicity, BMI, education level, smoking status, diabetes, hypertension, and coronary heart disease. All statistical tests were two-tailed, with a p-value <0.05 considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using R software version 4.3.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
Baseline characteristics
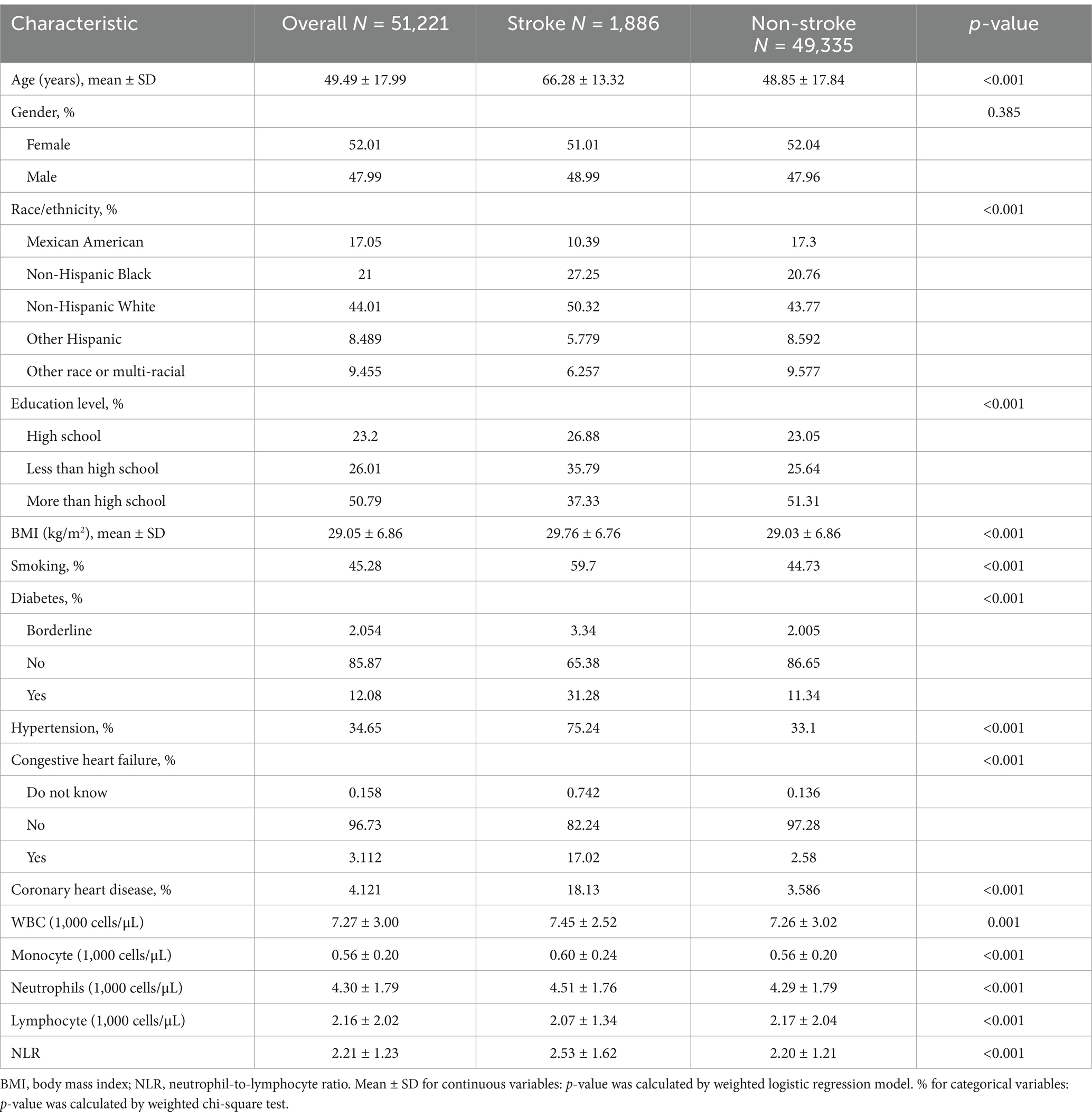
A total of 51,221 participants were included in the analysis, with a weighted mean age of 49.49 years. The overall stroke prevalence among all participants was 3.68%. Compared to individuals without stroke, stroke patients were generally older and more likely to be non-Hispanic White. They were also less educated, more likely to be smokers, and had higher prevalences of diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, and coronary heart disease. Additionally, stroke patients exhibited higher white blood cell counts, monocyte counts, neutrophil counts, and NLR, coupled with lower lymphocyte counts (all p < 0.05). Detailed baseline characteristics of all participants, grouped by stroke status, were presented in Table 1.
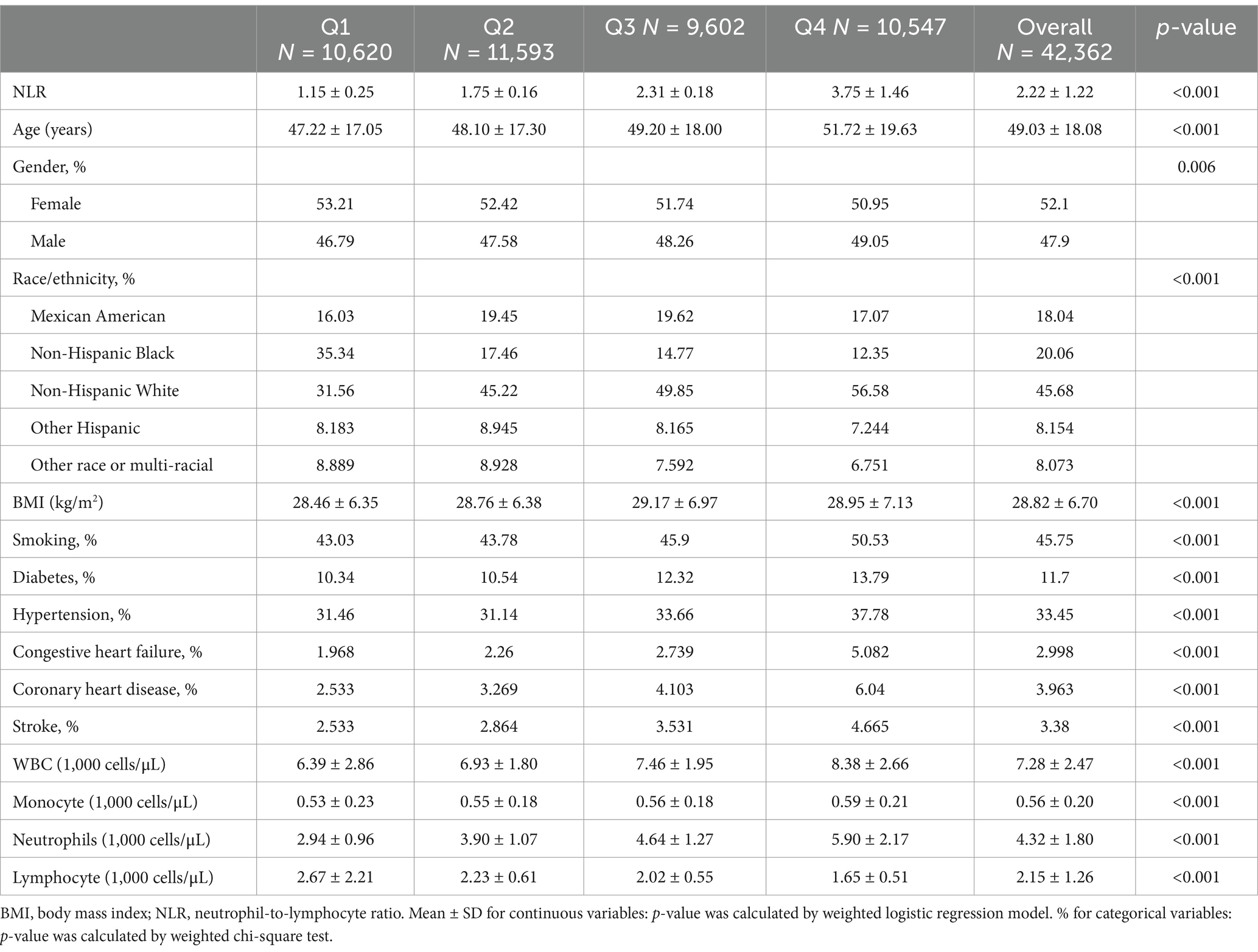
Table 2 summarized the baseline characteristics of participants stratified by NLR quartiles. The mean NLR values for quartiles Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4 were 1.15, 1.75, 2.31, and 3.75, respectively. Compared to those in the highest quartile, participants with lower NLR were more likely to be younger, female, non-Hispanic Black, have a lower BMI, be nonsmokers, and be free from diabetes, hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, and stroke.
Association between NLR and stroke morbidity
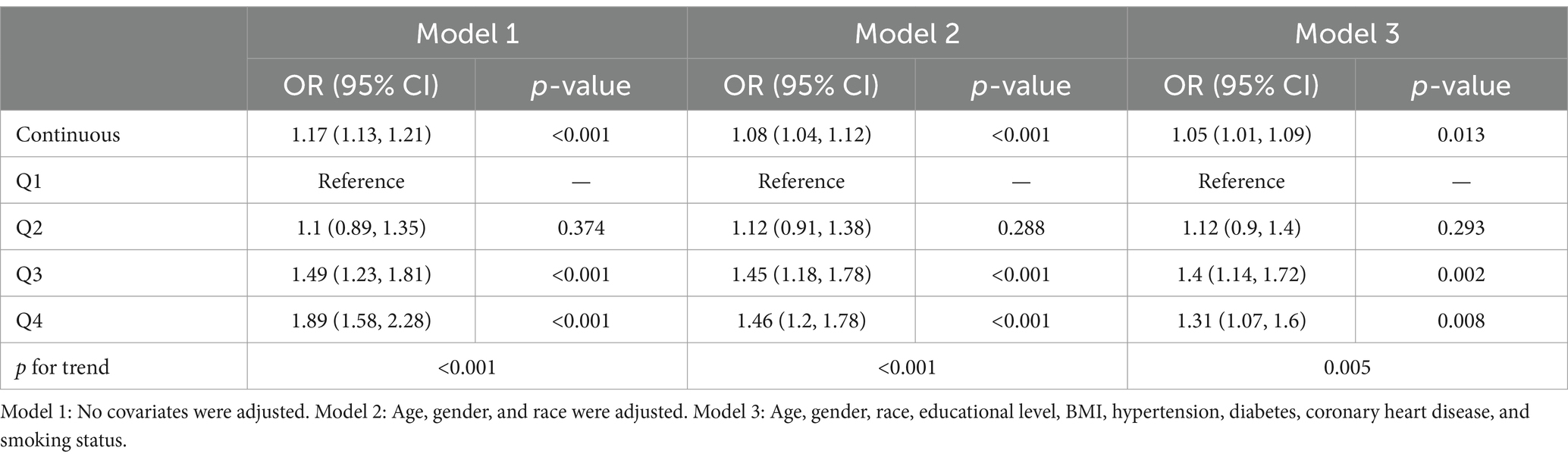
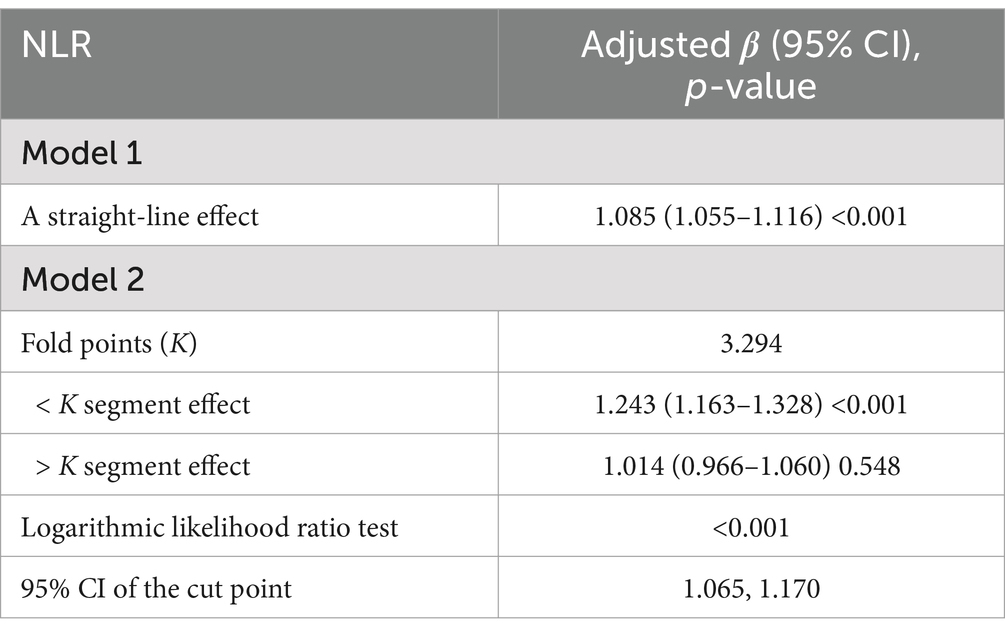
In all multivariable models adjusted for potential confounders, NLR was found to be independently and positively associated with stroke morbidity (Table 3). After fully adjusting for confounders, the adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for stroke morbidity in the higher NLR quartiles, compared to the lowest quartile, were 1.12 (0.9–1.4), 1.4 (1.14–1.72) and 1.31 (1.07, 1.6), respectively. The restricted cubic spline regression analysis further substantiated a nonlinear positive association between NLR and stroke risk (p for nonlinearity <0.001, Figure 2). Table 4 showed the threshold effect analysis of NLR on stroke morbidity.
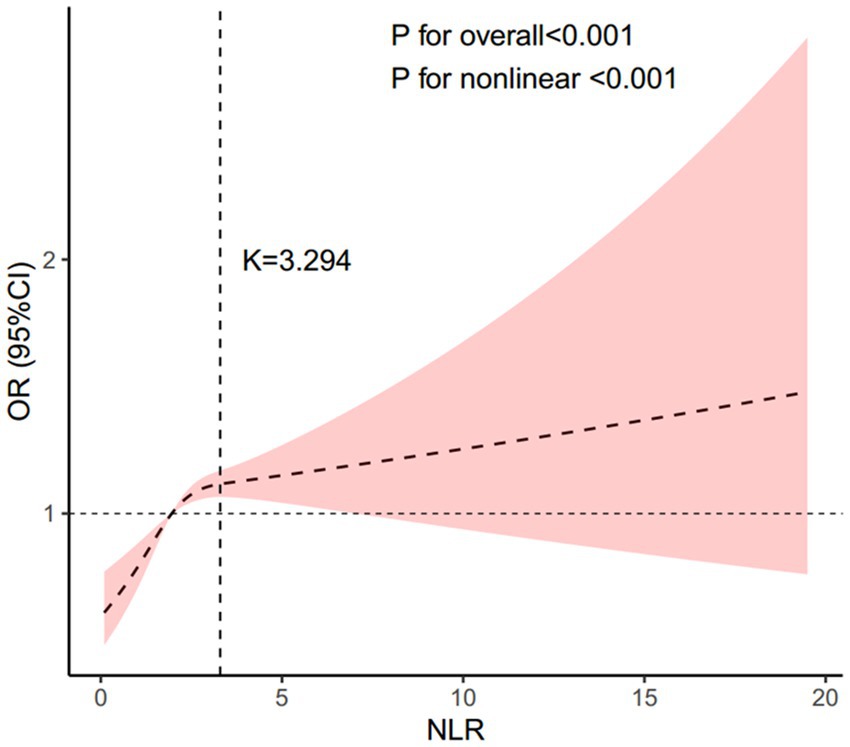
Figure 2. Association between the NLR and stroke morbidity. Adjusted for age, gender, race, educational level, BMI, hypertension, diabetes, coronary heart disease, and smoking status. The solid line and pink area represent the estimated values and their corresponding 95% CIs, respectively. NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Subgroup analyses indicated that the association between NLR and stroke morbidity remained consistent across all stratified variables, including gender, age, race/ethnicity, education level, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, hypertension, and coronary heart disease. No effect modification was observed (all interaction p-values >0.05) (Figure 3). Subgroup analyses were conducted to evaluate whether recent infections or inflammatory events modified the association between NLR and stroke morbidity. The results indicated that the association remained consistent across all infectious-associated variables (Supplementary Figure 1).
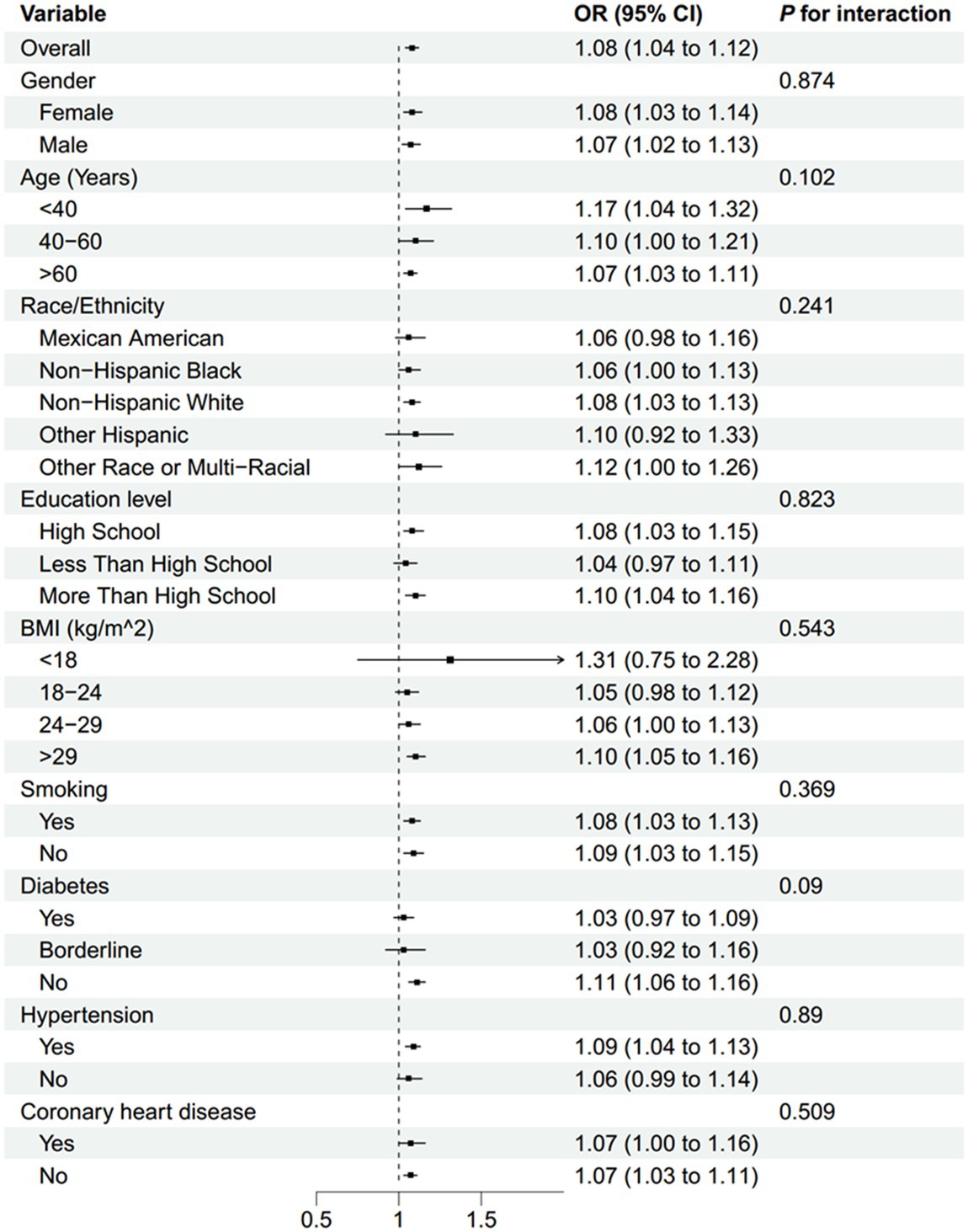
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis of the association between NLR and stroke morbidity. BMI, body mass index; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Association between NLR and all-cause mortality
Table 5 presented the three Cox regression models used to evaluate the association between NLR and all-cause mortality, as well as the Cox regression model specifically for all-cause mortality among stroke patients. A total of 7,062 deaths were observed among the 42,362 participants. Among these, 740 mortalities occurred in the 1,432 stroke patients included in this subset. After full adjustment for potential confounders, NLR was positively associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality in stroke patients. Specifically, patients in the fourth NLR quartile had a significantly higher risk of all-cause mortality compared to those in the second quartile (HR, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.2–2.02; p < 0.001).
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis demonstrated significant differences in all-cause mortality across the four NLR quartiles during follow-up, with the highest mortality rate observed in the fourth quartile (log-rank p < 0.001) (Figure 4).
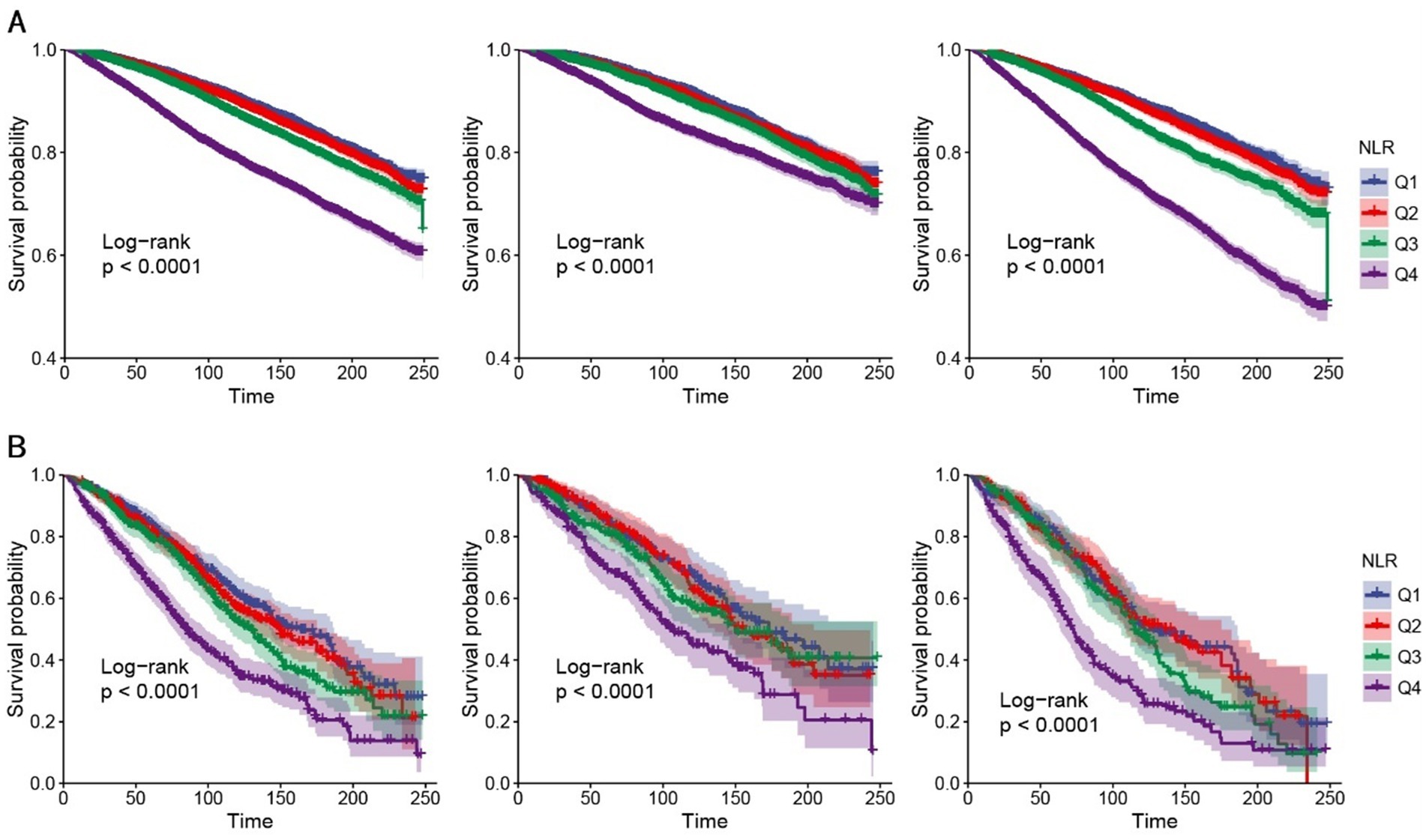
Figure 4. K–M analyses for all-cause mortality among the four groups. (A) K–M analyses for all-cause mortality in all people (left), female (middle), and male (right). (B) K–M analyses for all-cause mortality in people with stroke (left), female (middle), and male (right). NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, Q1–Q4, quartiles 1–4.
The restricted cubic spline regression analysis further indicated a nonlinear positive association between NLR and all-cause mortality in the overall population (p for nonlinearity = 0.007, Figure 5A) and a linear positive association between NLR and all-cause mortality among stroke patients (p for nonlinearity = 0.685, Figure 5B).
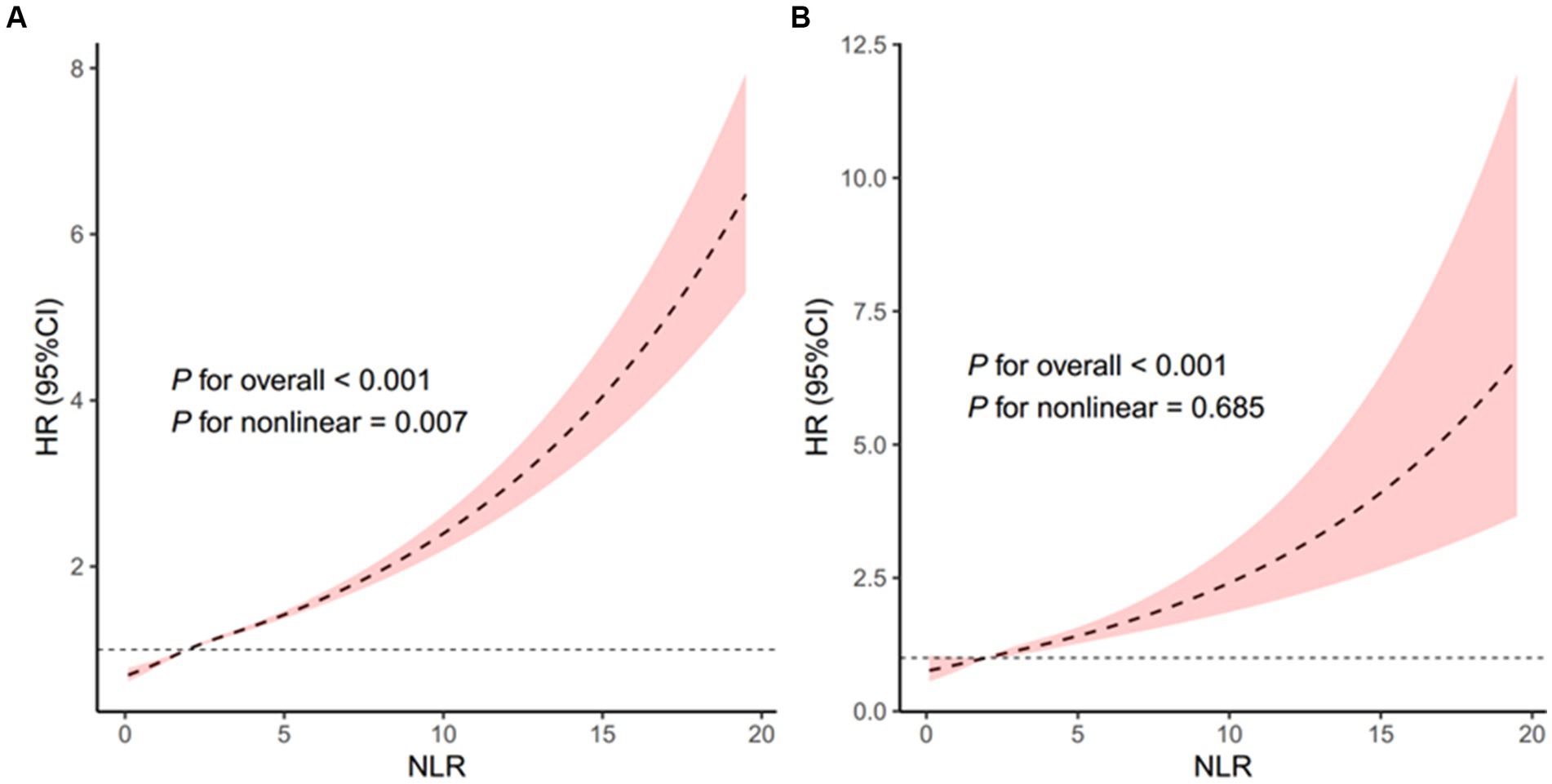
Figure 5. Association of the NLR with all-cause mortality in all people (A) and patients with stroke (B). Adjusted for age, sex, and race. The solid line and pink area represent the estimated values and their corresponding 95% CIs, respectively. NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Subgroup analyses, presented in Figures 6, 7, demonstrated that the relationship between NLR and mortality was consistent across various subgroups in both the overall population and among stroke patients. No significant interactions were observed between NLR and the stratified variables, as indicated by all interaction p-values being greater than 0.05. Supplementary Table 1 provided detailed information on the time intervals between NLR examination, stroke and mortality.
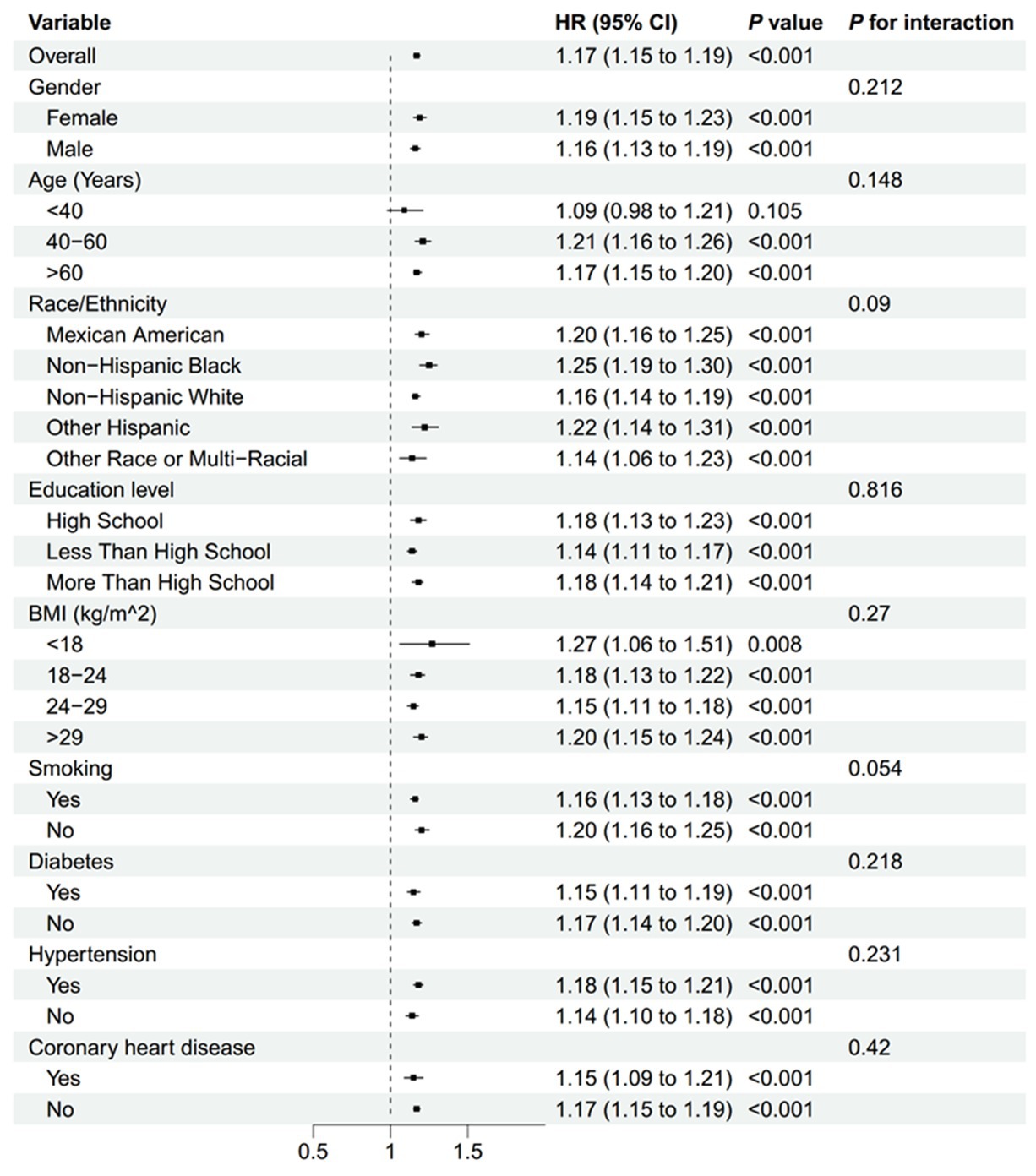
Figure 6. Subgroup analyses of the association between the NLR and all-cause mortality in all people. BMI, body mass index; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
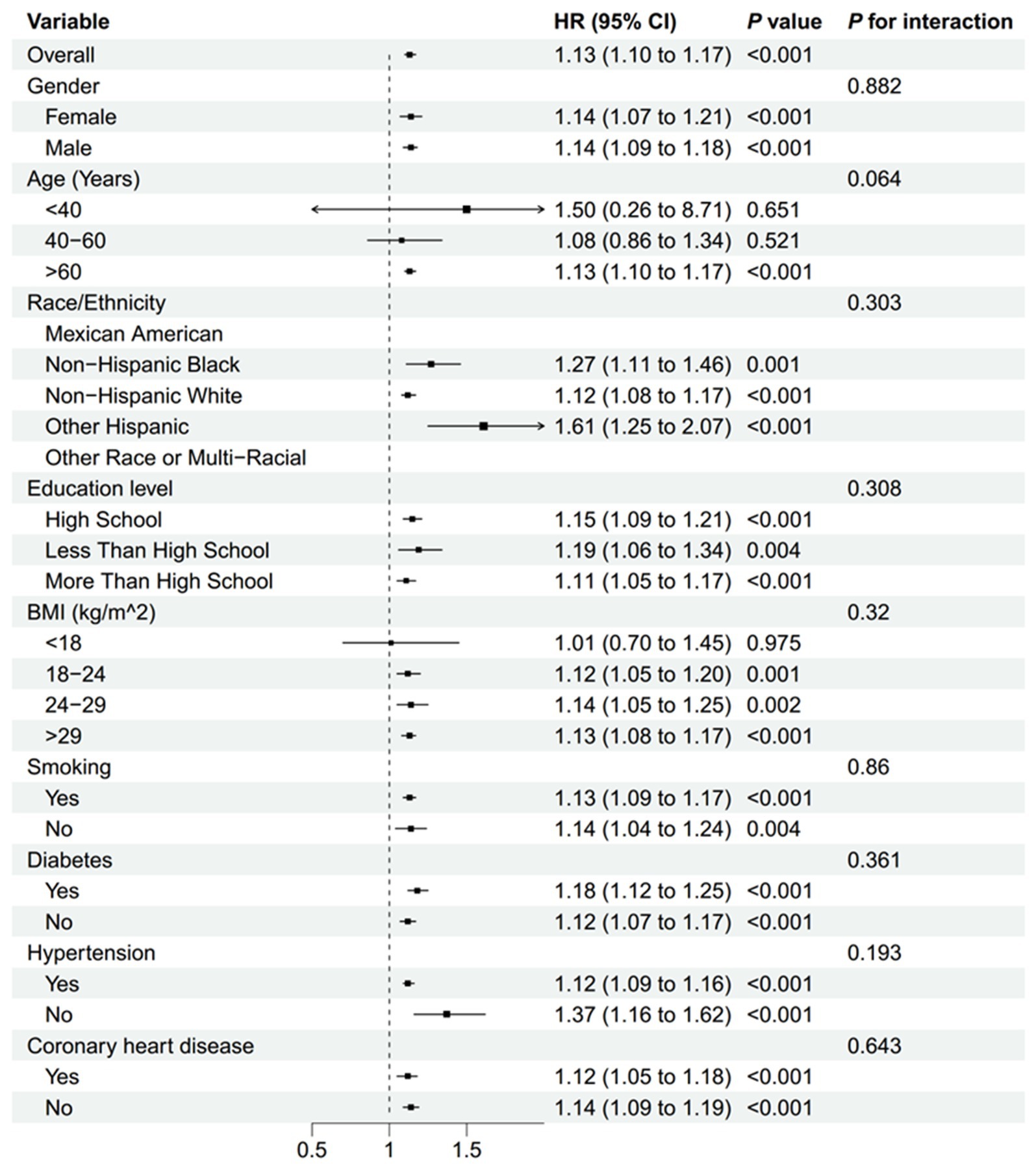
Figure 7. Subgroup analyses of the association between the NLR and all-cause mortality in patients with stroke. BMI, body mass index; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
Discussion
In this study, we found a positive correlation between NLR and stroke prevalence. Additionally, NLR was positively associated with all-cause mortality both in the general population and among stroke patients. Subgroup analyses further demonstrated similar trends across different demographic and clinical groups.
Previous studies have reported associations between NLR and various diseases, including cardiovascular disease (18), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (19, 20), acute intracerebral hemorrhage (21), and subarachnoid hemorrhage (22), using diverse epidemiological approaches and target populations. It is widely recognized that components of the immune system are closely linked to the onset and progression of ischemic brain injury, particularly ischemic stroke, which is largely attributed to a chronic inflammatory state. This inflammation, triggered by infectious or non-infectious factors, leads to systemic and vascular inflammation, resulting in oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, vascular wall injury, platelet activation and aggregation, and ultimately, intravascular thrombosis (14, 23). Peripheral immune markers have been shown to correlate with changes in multiple cortical and subcortical regions and white matter tracts, supporting the hypothesis that neuroinflammation is a significant contributor to the etiology of various brain diseases (24).
NLR is a potential novel biomarker of the baseline inflammatory response and has been shown to be an important predictor of morbidity and mortality in acute ischemic stroke (25). Furthermore, NLR has been studied as a predictive marker for stroke-associated pneumonia in stroke patients (6, 26). Our study identified a positive association between NLR and both stroke morbidity and all-cause mortality in stroke patients. Consistent with our findings, a study of 4,854 participants revealed that those in the higher NLR quartiles had an increased risk of incident stroke compared to those in the lowest quartile. For patients with minor ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA), high neutrophil counts and ratios were linked to increased risks of recurrent stroke, composite events, and ischemic stroke (5).
A retrospective study also found that stroke patients with poorer outcomes at discharge and 3 months were more likely to have elevated NLR both at discharge and 3 months post-stroke (27). In a study evaluating the outcomes of patients with large vessel occlusion treated with mechanical thrombectomy, each unit increase in NLR was independently associated with increased odds of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage and 3-month mortality. This suggests that NLR may help identify target groups for testing adjunctive anti-inflammatory therapies (15). Another study of 1,069 patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis found that NLR was associated with early neurological deterioration after thrombolysis (28). Collectively, these findings suggest an association between NLR and the risk of stroke and all-cause mortality in stroke patients. This study also identified the clinical value of NLR in assessing these risks.
The potential mechanisms linking NLR with stroke morbidity include interactions with endothelial cells and platelets, as well as excessive activation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (29). Neutrophils can release tissue factors that induce vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation, thereby promoting thrombosis (30–32). Some reports suggest that brain-infiltrating neutrophils play a detrimental role in ischemic tissue injury, causing brain damage through the release of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory mediators (33). Increased neutrophil concentration may lead to enhanced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9, a protein associated with blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption and brain injury (34, 35). Disruption of the BBB occurs in the early stages of stroke and facilitates the infiltration of peripheral leukocytes into the injured brain (36). Guided by inflammatory cytokines and chemokines released by ischemic tissue, these peripheral leukocytes may also affect ischemic regions (9). Lymphocytes, on the other hand, play a key role in inflammation, with certain lymphocytes exhibiting neuroprotective effects (37). Although further investigation is needed to fully understand the inflammatory mechanisms involved in stroke, NLR measurement is cost-effective, rapid, and widely available, making it a practical tool for low-cost monitoring systems. NLR could potentially enhance our ability to stratify risk in minor ischemic stroke or TIA, providing valuable guidance for prevention and treatment.
The primary strength of this study is the use of 11 cycles of NHANES data, which represents a multiethnic and gender-diverse adult population in the United States, making our findings more generalizable to the broader population. The large dataset enabled subgroup analyses, and extensive adjustments were made to account for potential confounders. The results of this study corroborated the importance of inflammation in stroke development and emphasized the value of inflammatory responses for treating and preventing stroke. The findings suggest NLR as a simple, cost-effective biomarker for predicting both stroke risk and all-cause mortality, particularly in clinical settings. This positions NLR as a potentially valuable tool for early stroke identification, risk stratification, and outcome prediction. However, several key limitations should be acknowledged. First, the use of self-reported methods to assess disease presence is susceptible to recall bias, which may impact data interpretation. Second, the NHANES database does not differentiate between the two main types of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic) or stroke subtypes, and the heterogeneous etiologies may affect the potential association between NLR and stroke. Third, although we adjusted for several potential confounders in the multivariable models, NLR may still be influenced by other factors. Finally, the cross-sectional design of the study precludes the establishment of causality, and further validation is required in large-scale prospective studies to confirm these findings.
Conclusion
This study, by investigating the association of NLR with stroke morbidity and mortality, has identified the potential clinical value of NLR in assessing the risk and severity of stroke. The findings supported the critical role of inflammation status in stroke.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies were reviewed and approved by the NCHS Ethics Review Board. No additional ethical review consent was needed.
Author contributions
XX: Data curation, Writing – original draft. GZ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. FL: Data curation, Writing – original draft. JZ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SH: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XS: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WW: Validation, Writing – review & editing. LX: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82301454), the Medical Health Science and Technology Project of Zhejiang Provincial Health Commission (2022RC168), and the Seed Fund for Young Researchers of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine (ZZ94692022).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all participants in NHANES for providing us with study data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1570630/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Netea, MG, Balkwill, F, Chonchol, M, Cominelli, F, Donath, MY, Giamarellos-Bourboulis, EJ, et al. A guiding map for inflammation. Nat Immunol. (2017) 18:826–31. doi: 10.1038/ni.3790
2. Meisel, C, Schwab, JM, Prass, K, Meisel, A, and Dirnagl, U. Central nervous system injury-induced immune deficiency syndrome. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2005) 6:775–86. doi: 10.1038/nrn1765
3. Urra, X, Cervera, A, Villamor, N, Planas, AM, and Chamorro, Á. Harms and benefits of lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with acute stroke. Neuroscience. (2009) 158:1174–83. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.014
4. Tokgoz, S, Kayrak, M, Akpinar, Z, Seyithanoğlu, A, Güney, F, and Yürüten, B. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2013) 22:1169–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.01.011
5. Zhu, B, Pan, Y, Jing, J, Meng, X, Zhao, X, Liu, L, et al. Neutrophil counts, neutrophil ratio, and new stroke in minor ischemic stroke or TIA. Neurology. (2018) 90:e1870–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000005554
6. Xu, M, Wang, J, Zhan, C, Zhou, Y, Luo, Z, Yang, Y, et al. Association of follow-up neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and systemic inflammation response index with stroke-associated pneumonia and functional outcomes in cerebral hemorrhage patients: a case-controlled study. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:4014–22. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001329
7. Feigin, VL, and Owolabi, MOWorld Stroke Organization–Lancet Neurology Commission Stroke Collaboration Group. Pragmatic solutions to reduce the global burden of stroke: a World Stroke Organization-Lancet Neurology Commission. Lancet Neurol. (2023) 22:1160–206. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(23)00277-6
9. Macrez, R, Ali, C, Toutirais, O, Le Mauff, B, Defer, G, Dirnagl, U, et al. Stroke and the immune system: from pathophysiology to new therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. (2011) 10:471–80. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(11)70066-7
10. Herz, J, Sabellek, P, Lane, TE, Gunzer, M, Hermann, DM, and Doeppner, TR. Role of neutrophils in exacerbation of brain injury after focal cerebral ischemia in hyperlipidemic mice. Stroke. (2015) 46:2916–25. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.115.010620
11. Ruhnau, J, Schulze, J, Dressel, A, and Vogelgesang, A. Thrombosis, neuroinflammation, and poststroke infection: the multifaceted role of neutrophils in stroke. J Immunol Res. (2017) 2017:5140679. doi: 10.1155/2017/5140679
12. Hurn, PD, Subramanian, S, Parker, SM, Afentoulis, ME, Kaler, LJ, Vandenbark, AA, et al. T- and B-cell-deficient mice with experimental stroke have reduced lesion size and inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2007) 27:1798–805. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600482
13. Shi, K, Tian, DC, Li, ZG, Ducruet, AF, Lawton, MT, and Shi, FD. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:1058–66. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30078-X
14. Esenwa, CC, and Elkind, MS. Inflammatory risk factors, biomarkers and associated therapy in ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Neurol. (2016) 12:594–604. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.125
15. Goyal, N, Tsivgoulis, G, Chang, JJ, Malhotra, K, Pandhi, A, Ishfaq, MF, et al. Admission neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker of outcomes in large vessel occlusion strokes. Stroke. (2018) 49:1985–7. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.021477
16. Guo, Z, Yu, S, Xiao, L, Chen, X, Ye, R, Zheng, P, et al. Dynamic change of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolysis in stroke. J Neuroinflammation. (2016) 13:199. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0680-x
17. Wu, S, Wu, B, Liu, M, Chen, Z, Wang, W, Anderson, CS, et al. Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol. (2019) 18:394–405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30500-3
18. Bagyura, Z, Kiss, L, Lux, Á, Csobay-Novák, C, Jermendy, ÁL, Polgár, L, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an independent risk factor for coronary artery disease in central obesity. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:7397. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087397
19. Lan, CC, Su, WL, Yang, MC, Chen, SY, and Wu, YK. Predictive role of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratios for mortality in patients with COPD: evidence from NHANES 2011–2018. Respirology. (2023) 28:1136–46. doi: 10.1111/resp.14589
20. Zinellu, A, Zinellu, E, Mangoni, AA, Pau, MC, Carru, C, Pirina, P, et al. Clinical significance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in acute exacerbations of COPD: present and future. Eur Respir Rev. (2022) 31:220095. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0095-2022
21. Lattanzi, S, Cagnetti, C, Provinciali, L, and Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts the outcome of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. (2016) 47:1654–7. doi: 10.1161/strokeaha.116.013627
22. Tao, C, Wang, J, Hu, X, Ma, J, Li, H, and You, C. Clinical value of neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratio after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. (2017) 26:393–401. doi: 10.1007/s12028-016-0332-0
23. Iadecola, C, and Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med. (2011) 17:796–808. doi: 10.1038/nm.2399
24. Zhong, X, Qiang, Y, Wang, L, Zhang, Y, Li, J, Feng, J, et al. Peripheral immunity and risk of incident brain disorders: a prospective cohort study of 161,968 participants. Transl Psychiatry. (2023) 13:382. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02683-0
25. Brooks, SD, Spears, C, Cummings, C, VanGilder, R, Stinehart, KR, Gutmann, L, et al. Admission neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts 90 day outcome after endovascular stroke therapy. J Neurointerv Surg. (2014) 6:578–83. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010780
26. Wang, RH, Wen, WX, Jiang, ZP, Du, ZP, Ma, ZH, Lu, AL, et al. The clinical value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) for predicting the occurrence and severity of pneumonia in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1115031. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1115031
27. Liu, YL, Wu, ZQ, Qu, JF, Qiu, DH, Luo, GP, Yin, HP, et al. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a predictor of poor short-term outcome in patients with mild acute ischemic stroke receiving intravenous thrombolysis. Brain Behav. (2020) 10:e01857. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1857
28. Gong, P, Liu, Y, Gong, Y, Chen, G, Zhang, X, Wang, S, et al. The association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte to monocyte ratio with post-thrombolysis early neurological outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroinflammation. (2021) 18:51. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02090-6
29. Borissoff, JI, and ten Cate, H. From neutrophil extracellular traps release to thrombosis: an overshooting host-defense mechanism? J Thromb Haemost. (2011) 9:1791–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04425.x
30. Darbousset, R, Thomas, GM, Mezouar, S, Frère, C, Bonier, R, Mackman, N, et al. Tissue factor-positive neutrophils bind to injured endothelial wall and initiate thrombus formation. Blood. (2012) 120:2133–43. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-437772
31. Frangogiannis, NG, Smith, CW, and Entman, ML. The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2002) 53:31–47. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(01)00434-5
32. Ott, I, Neumann, FJ, Gawaz, M, Schmitt, M, and Schömig, A. Increased neutrophil-platelet adhesion in patients with unstable angina. Circulation. (1996) 94:1239–46. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.6.1239
33. Ceulemans, AG, Zgavc, T, Kooijman, R, Hachimi-Idrissi, S, Sarre, S, and Michotte, Y. The dual role of the neuroinflammatory response after ischemic stroke: modulatory effects of hypothermia. J Neuroinflammation. (2010) 7:74. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-74
34. Jickling, GC, Liu, D, Stamova, B, Ander, BP, Zhan, X, Lu, A, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation after ischemic stroke in animals and humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2014) 34:185–99. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.203
35. Justicia, C, Panés, J, Solé, S, Cervera, A, Deulofeu, R, Chamorro, A, et al. Neutrophil infiltration increases matrix metalloproteinase-9 in the ischemic brain after occlusion/reperfusion of the middle cerebral artery in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. (2003) 23:1430–40. doi: 10.1097/01.Wcb.0000090680.07515
36. Giraud, M, Cho, TH, Nighoghossian, N, Maucort-Boulch, D, Deiana, G, Østergaard, L, et al. Early blood brain barrier changes in acute ischemic stroke: a sequential MRI study. J Neuroimaging. (2015) 25:959–63. doi: 10.1111/jon.12225
Keywords: cross-sectional study, stroke, NHANES, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, predictor
Citation: Xu X, Zhang G, Liu F, Zheng J, Jiang Z, Hu S, Shi X, Wang W, Xu L and Wang Z (2025) Association of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with stroke morbidity and mortality: evidence from the NHANES 1999–2020. Front. Med. 12:1570630. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1570630
Edited by:
Md. Mohaimenul Islam, The Ohio State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Rizaldy Taslim Pinzon, Duta Wacana Christian University, IndonesiaMedha Sharath, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, India
Dhrumil Shah, Super Metro Specialized Medical Center, Kuwait
Luis E. Fernández-Garza, Mexican Institute of Social Security, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhang, Liu, Zheng, Jiang, Hu, Shi, Wang, Xu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liang Xu, drliangxu@zju.edu.cn; Zixin Wang, zixinwang@zju.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xin Xu1†
Xin Xu1†