- 1Dr. Tytus Chałubiński Specialist Hospital in Radom, Radom, Poland
- 2Faculty of Medical Sciences and Health Sciences, Casimir Pulaski University of Radom, Radom, Poland
- 3Students’ Scientific Club “Biochemistry of Civilization Diseases” at the Department of Hygiene, Epidemiology and Ergonomics, Medical University of Białystok, Białystok, Poland
- 4Department of Hygiene, Epidemiology and Ergonomics, Medical University of Białystok, Białystok, Poland
Introduction: Carbamylation involves the non-enzymatic binding of isocyanic acid to the amino groups of proteins, making it associated with many pathological conditions, including inflammation, aging, arteriosclerosis, and renal failure. However, there are no data on protein carbamylation in patients with COVID-19. Our study is the first to evaluate the association between blood inflammation and protein carbamylation in patients who died from COVID-19 compared to COVID-19 survivors.
Methods: The study included 50 patients admitted to Dr. Tytus Chałubiński Specialist Hospital in Radom, Poland. Twenty-five of them were COVID-19 survivors (15 men, 10 women), and 25 were COVID-19 deceased patients (15 men, 10 women). The number of subjects was based on a pilot study assuming a significance level of 0.05 and a test power of 0.8. Plasma/serum samples were assayed for carbamyl-lysine (CBL) and inflammatory biomarkers (CRP, procalcitonin, D-dimer, IL-6, and WBC). The concentration of CBL was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney U test and Spearman rank correlation. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to assess the diagnostic utility of serum CBL.
Results: Serum CBL levels were significantly higher in patients who died from COVID-19 compared to COVID-19 survivors (p = 0.0011). There was a positive correlation of serum CBL with IL-6, D-dimer, and WBC. Serum CBL levels >101 ng/mL, with moderate sensitivity and specificity, differentiate COVID-19 deceased from recovered patients (area under the curve 0.76).
Discussion: In conclusion, COVID-19 is associated with excessive protein carbamylation. Inflammation may be a source of higher CBL production in COVID-19. A thorough understanding of the consequences of increased protein carbamylation may clarify the consequences of COVID-19 complications.
Introduction
As of December 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported more than 776.8 million cases of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and more than 7 million deaths (1). The innate immune response to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is inflammation. Upon entering cells, the virus activates the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) to detect pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) (2). Under such conditions, host immune cells produce pro-inflammatory cytokines [tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α); interleukin-1α (IL-1α); interleukin-6 (IL-6)] and chemokines [C-C motif chemokine ligand 2, (CCL2) (2) and C-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CCL8)]. A cytokine storm is an immune dysregulation characterized by systemic inflammation (hypercytokinemia) and multi-organ dysfunction. Many patients with COVID-19 have respiratory symptoms, including cough and tachypnoea, which can lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (3). Although most of the COVID-19-related deaths happened at the beginning of the pandemic, SARS-CoV-2 occurs with no apparent seasonality and causes severe acute illness and post-COVID-19 conditions (1). Therefore, a thorough understanding of the causes of COVID-19 and the development of new therapeutic approaches is still a public health concern.
Proteins undergo numerous post-translational modifications, including prolyl and lysyl residues hydroxylation, deformylation of the N-terminal methionine, or generation of disulfide bridges/protein cross-links (4, 5). The modified protein gains unique properties or loses biological activity (6). The most well-known modification of proteins is non-enzymatic glycation involving the coupling of an aldehyde/ketone group of a sugar to the free amino group of a protein, leading to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGE) (7). AGE binding to a specific receptor (RAGE) activates an inflammatory cascade, including the release of interleukins and cytokines, overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and disruption of apoptosis and autophagy (7, 8). The involvement of AGE/RAGE signaling has been proven in the course of numerous metabolic (9), cardiovascular (10), neurodegenerative (11), and cancer complications (12). Interestingly, RAGE is expressed mainly by type 2 epithelial cells in the alveolar sac, which plays a key role in COVID-19 lung inflammation and damage (13). Although the direct role of AGE in COVID-19 severity has not yet been clarified, there is a more significant correlation between AGE level and COVID-19 severity (13–15). However, little is known about other protein modifications in COVID-19. In19. In the available literature, we found no data on protein carbamylation in patients with COVID-19. Carbamylation involves the non-enzymatic binding of isocyanic acid to amino groups of proteins, especially under inflammatory conditions (16). Carbamylation alters proteins’ secondary and tertiary structure, affecting their biological activity and accelerated aging (16, 17). The main product of blood protein carbamylation is carbamyl-lysine (CBL), commonly known as homocitrulline (16). The association of protein carbamylation in patients with chronic renal failure has been demonstrated (18, 19) to date. It has also been shown that lipoprotein carbamylation catalyzed by myeloperoxidase (MPO) facilitates many atherosclerotic activities and, thus, may be a mechanism linking inflammation and coronary artery disease (20). However, little is known about the involvement of CBL in the pathogenesis of other inflammatory diseases. Given the complexity of COVID-19 and the interdependence of protein glycation and carbamylation, it is reasonable to know the role of CBL in the pathogenesis of COVID-19. Our study is the first to evaluate the association between blood inflammation and protein carbamylation in patients who died from COVID-19 compared to COVID-19 survivors.
Materials and methods
Study subjects
The study was performed according to the World Medical Association (WMA) Declaration of Helsinki. The Medical Chamber of Gdansk, Poland (KB-29/21) granted Institutional Ethics Clearance (IEC). Each person provided a signed informed consent form.
The study included 50 patients admitted to Dr. Tytus Chałubiński Specialist Hospital in Radom, Poland due to COVID-19. Twenty-five of them were COVID-19 survivors (15 men, 10 women), and 25 were COVID-19 deceased patients (15 men, 10 women). COVID-19 was confirmed by a positive test for SARS-CoV-2 genetic material in nasopharyngeal swabs by PCR assay (VIASURE SARS-CoV-2 (N1 + N2) Real-Time PCR Detection Kit for BD MAX; Becton Dickinson & Co., BD Diagnostic Systems, 7 Loveton Circle, MD, USA). Exclusion criteria in both groups were the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases such as acute and chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, multiple sclerosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, thyroiditis, psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, and cancer.
Blood samples were collected at the last blood measurement prior to discharge from the hospital in case of surviving patients or the last blood measurement before death for patients who died from COVID-19. Blood samples were collected into tubes with ethylenediaminetetraacetate tripotassium (K3-EDTA; S-Monovette<reg>(</reg> EDTA K3E, Sarstedt) and clotting activator (S-Monovette<reg>(</reg> Serum Gel CAT; Sarstedt) and centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C to separate plasma or serum. The supernatant fluid was preserved for the study and frozen at −80°C until the determinations were made.
Complete blood count (CBC), including platelets (PLT), white blood cells (WBC), and red blood cells (RBC), along with RBC parameters such as mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), hematocrit (HCT), and hemoglobin (HGB), was performed automatically using a Sysmex XN-550 (21). Sysmex XN-550 is a multiparameter hematology analyzer with the ability to target low sample volumes.
Blood inflammation
Procalcitonin (PCT) concentration was measured in vitro using the Elecsys BRAHMS PCT serum assay (22) through a three-step process. The first step involved incubation with sample antigen, biotinylated PCT-specific monoclonal antibodies, and PCT-specific monoclonal antibodies conjugated with a ruthenium complex. Next, labeled microparticles were added to streptavidin to bind the complex to the solid phase using the affinity of biotin and streptavidin. In the final step, the reaction mixture was transferred to the measuring chamber, where a magnet attracted the microparticles to the electrode surface. The unbound particles were processed using the ProCell/ProCell M method. Then, a photomultiplier was used to measure electrochemiluminescence and photon emission induced by the applied voltage. The results were quantified by reference to the calibration curve.
D-dimer’ levels were measured via photometric Dia-D-DIMER (23), an immunoturbidimetric test reinforced with latex particles. In this method, latex particles are additionally coated with antibodies directed to D-dimer. An antigen-antibody photometric reaction determines the concentration of D-dimer.
IL-6 concentration was measured in serum collected from separation gel tubes. The procedure followed the next steps: first incubation of 30 μL of a sample with a biotinylated monoclonal IL6-specific antibody. This was followed by the second incubation with IL6-specific antibodies labeled with ruthenium complex, and streptavidin-coated microparticles were added. Altogether, both antibodies form a sandwich complex with the antigen of the sample. Next, the mixture was aspirated into the measuring cell, where the microparticles were magnetically captured on the surface of the electrode. The unbound substances were then removed with Procell/ProCell M. The next step involved applying the voltage to the electrode to induce chemiluminescent emission, measured by a photomultiplier. Finally, the results were determined by an instrument-specific calibration curve and generated by a 2-point calibration and a master curve (24).
CRP concentration in serum was measured using an in vitro immunoturbidimetric assay (Tina-quant C-reactive protein IV) (25). It is a latex particle-enhanced assay that consists of TRIS buffer, bovine serum albumin (BSA), and latex particles coated with mouse anti-CRP glycine buffer and mouse immunoglobulins. The human CRP was agglutinated with latex particles coated with anti-CRP monoclonal antibodies, and the precipitate was measured by turbidimetry.
Blood carbamylation
The concentration of CBL in serum samples was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) obtained from Novatein Biosciences (catalog number BG-HUM09021; Woburn MA 01801 United States) (26). In this case, ELISA measured CBL levels by binding anti-CBL antibodies to the target protein, followed by detection using an enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody that produced a calorimetric signal, recorded by the microplate reader at 450 nm. The procedure for measuring carbamylated protein levels is presented in Figure 1. The sensitivity or minimum detectable dose (MDD) of CBL was determined to be 0.51 ng/ml. Inter-assay reproducibility is <9.6%, and intra-assay reproducibility is <7.1%.
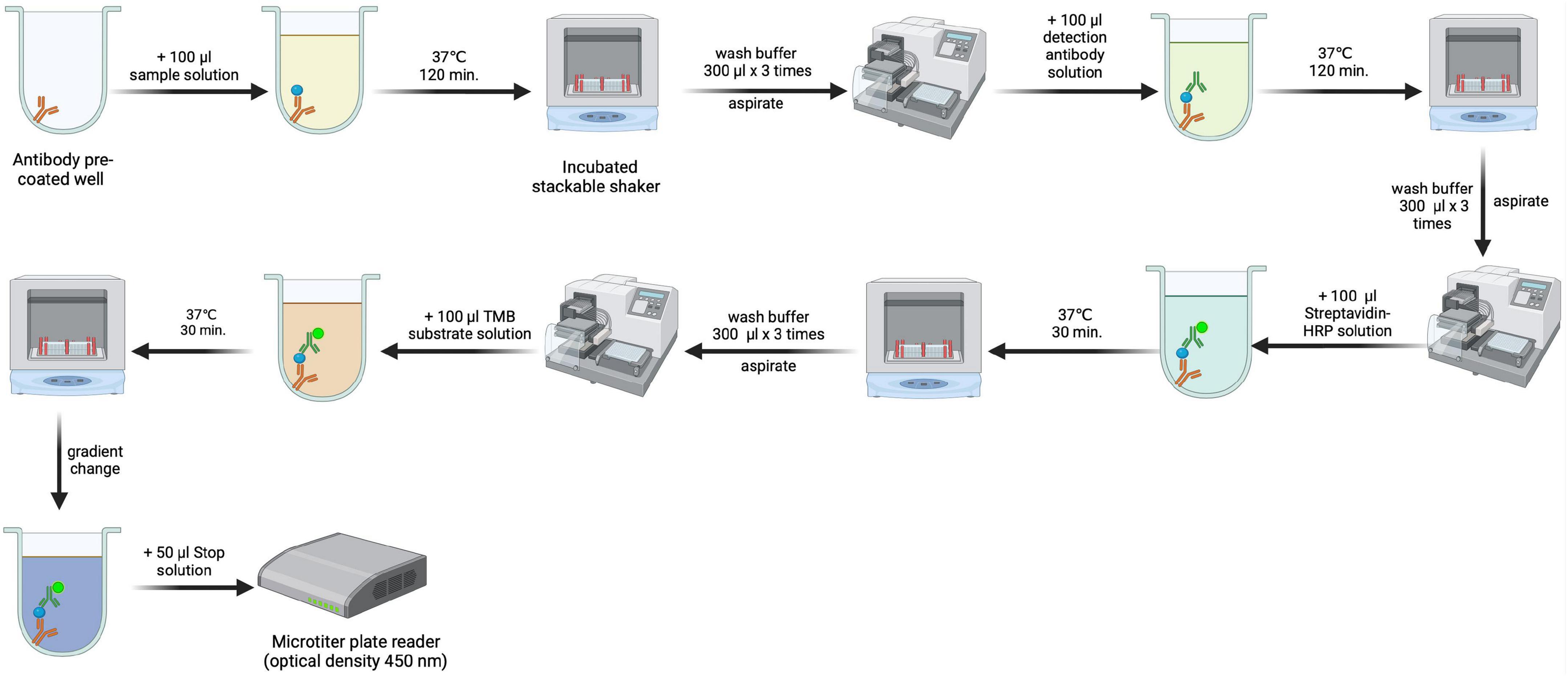
Figure 1. Methodological scheme for estimating serum carbamyl-lysine (CBL) concentration by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Created using biorender.com.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, USA), and the level of statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Normality of distribution was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test, and differences between the two independent groups were evaluated using the Mann-Whitney U test. Results are presented in box-and-whisker plots as median (minimum-maximum). The relationship between blood inflammation and protein carbamylation was assessed using Spearman rank correlation. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to assess the diagnostic utility of serum CBL. Area under the curve (AUC) and optimal cut-off values were determined, ensuring high sensitivity and specificity.
The number of subjects was based a priori on a pilot study with 12 patients (ClinCalc online software). The variables used to calculate the sample size were PCT and IL-6 concentrations. The significance level was set at 0.05, and the power of the test was set at 0.8. The minimum number of patients per group was 23; therefore, 25 survivors and 25 deceased patients were included in the study.
Results
Clinical characteristics
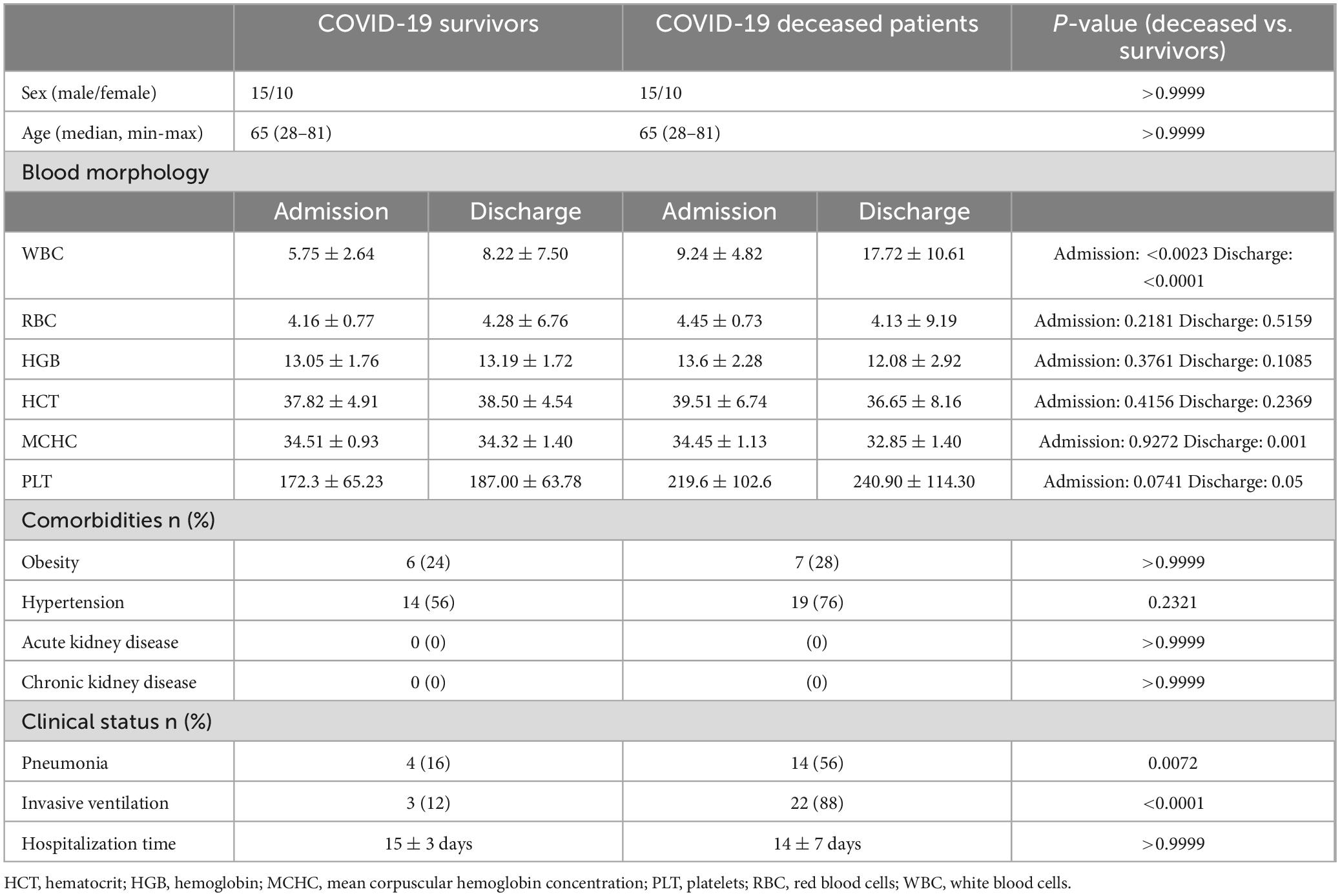
Table 1 shows the clinical characteristics of the patients. Importantly, no patients in either group had acute or chronic renal failure.
Blood inflammation
The levels of inflammatory biomarkers such as CRP (p < 0.0001), PCT (p < 0.0001), D-dimer (p = 0.0214), and IL-6 (p < 0.0001) were significantly higher in patients who died of COVID-19 compared to the recovered patients (Figure 2).
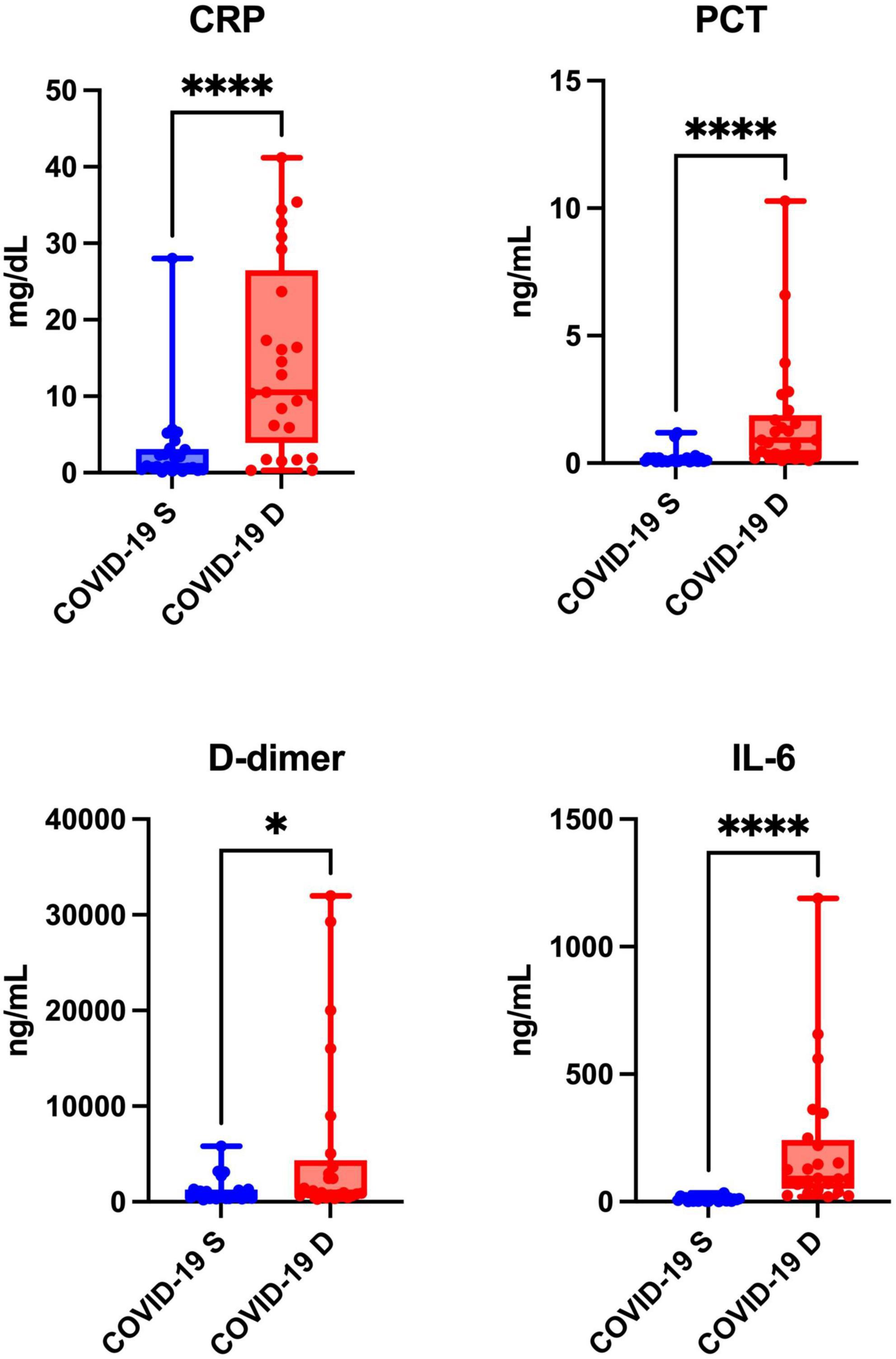
Figure 2. Blood inflammation of COVID-19 survivors (COVID-19 S) and COVID-19 deceased (COVID-19 D) patients. The results are presented in box-and-whisker plots as median (minimum-maximum) and percentiles with individual data points. w, C-reactive protein; PCT, procalcitonin; IL-6, interleukin-6. Differences statistically significant at *<0.05, ****<0.0001.
Blood carbamylation
Serum CBL levels were significantly higher in patients who died from COVID-19 compared to COVID-19 survivors (p = 0.0011) (Figure 3).
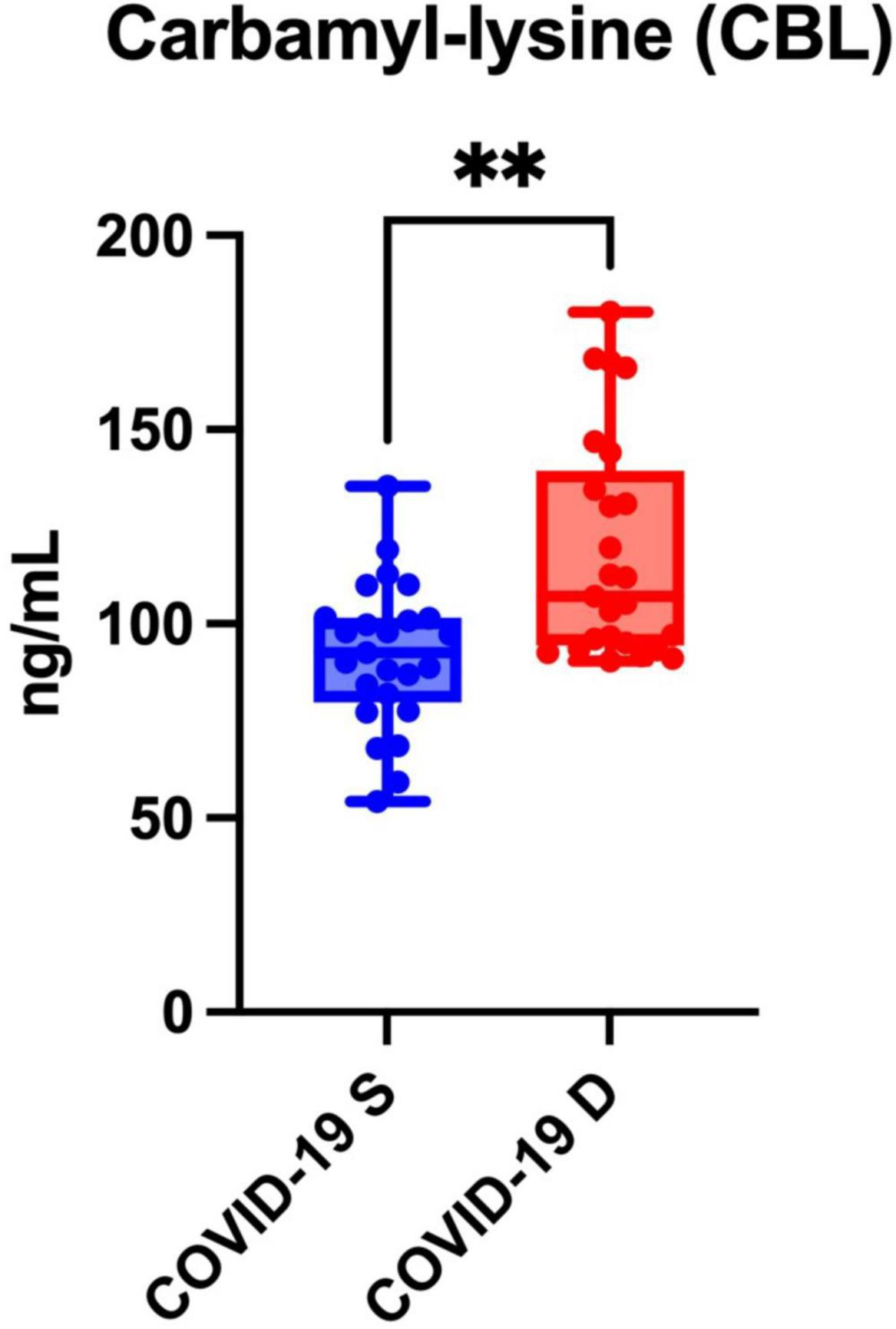
Figure 3. Serum carbamyl-lysine (CBL) of COVID-19 survivors (COVID-19 S) and COVID-19 deceased (COVID-19 D) patients. The results are presented in box-and-whisker plots as median (minimum-maximum) and percentiles with individual data points. COVID-19 S, COVID-19 survived patients; COVID-19 D, COVID-19 died patients. Differences statistically significant at **<0.01.
ROC analysis
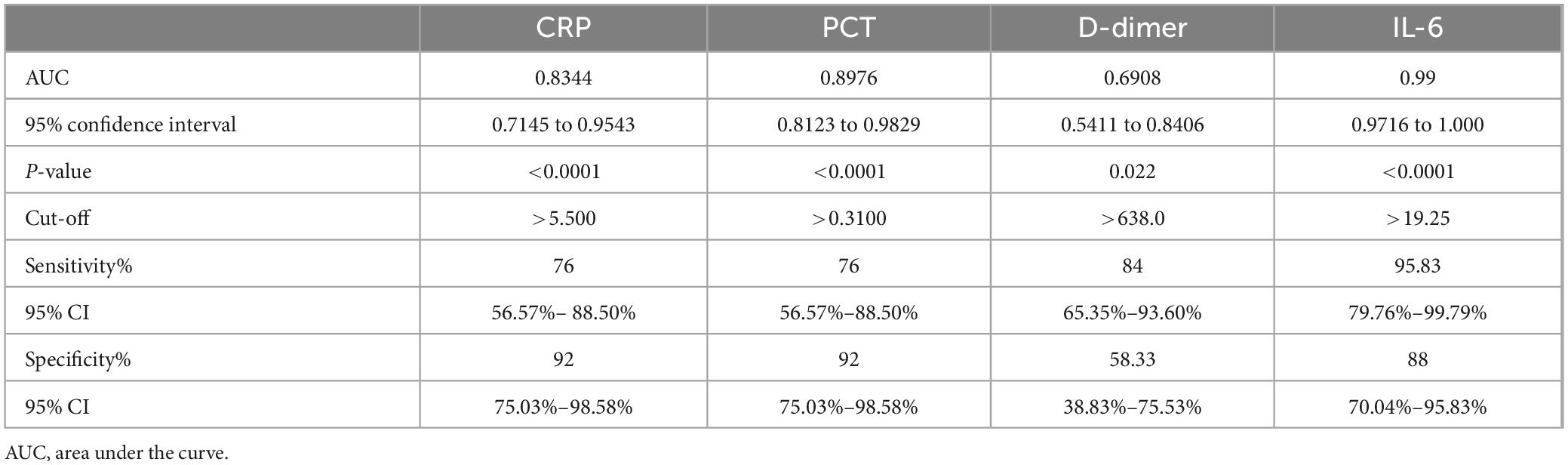
We showed that serum CBL levels >101 ng/mL, with a sensitivity of 60% (CI: 40.74 to 76.60%) and specificity of 72% (CI: 52.42 to 85.72%), differentiate COVID-19 deceased from recovered patients. The AUC was 0.76 (CI: 0.63 to 0.89) (Figure 4).
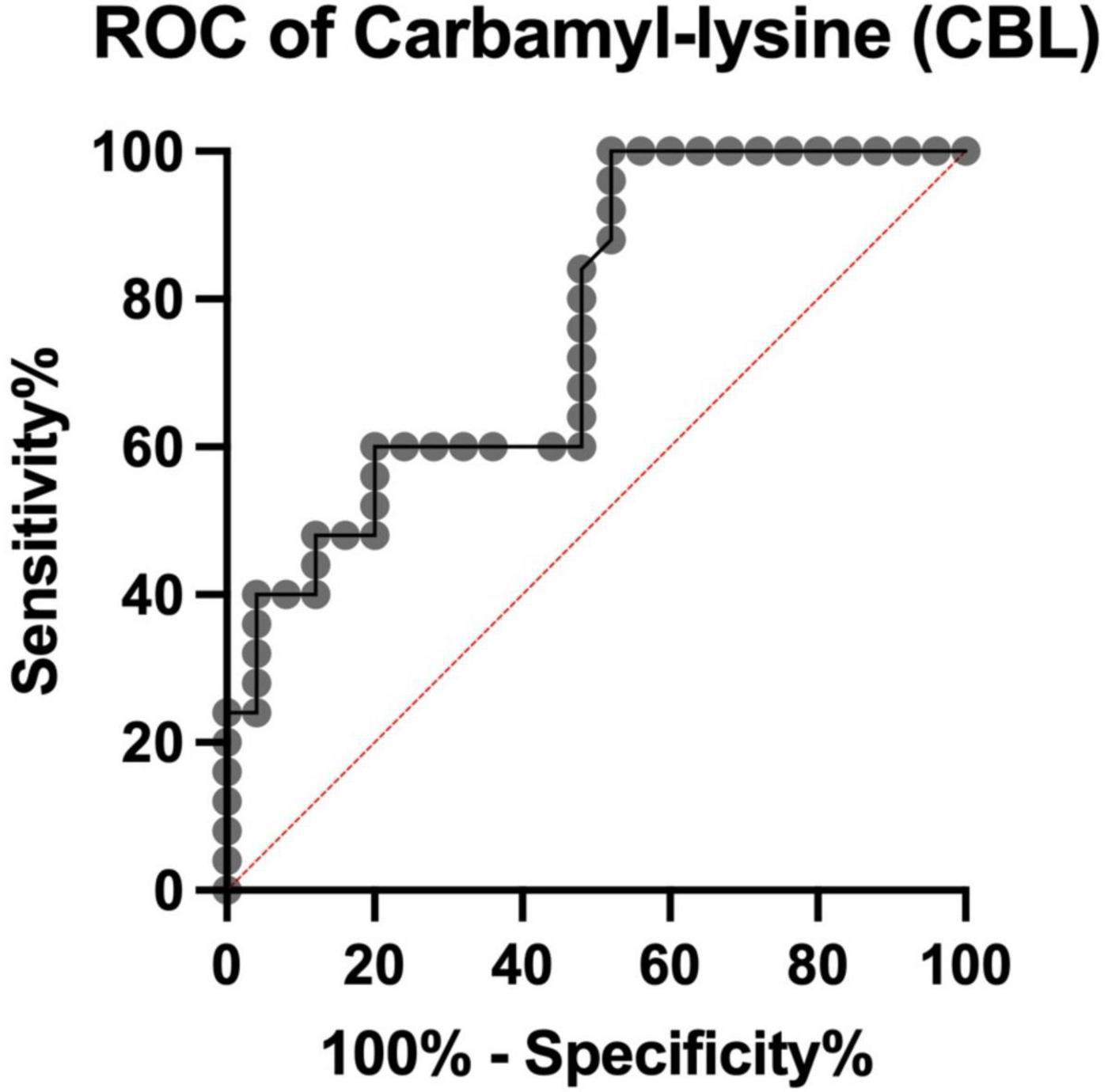
Figure 4. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve for serum carbamyl-lysine (CBL) of COVID-19 survivors and COVID-19 deceased patients. ROC, Receiver Operating Characteristic analysis.
The results of the ROC analysis for inflammatory biomarkers are shown in Table 2.
Correlations
Serum CBL levels were correlated with inflammatory biomarkers such as D-dimer (r = 0.38, p = 0.008), WBC (r = 0.31, p = 0.031) and IL-6 (r = 0.38, p = 0.008) (Figure 5).
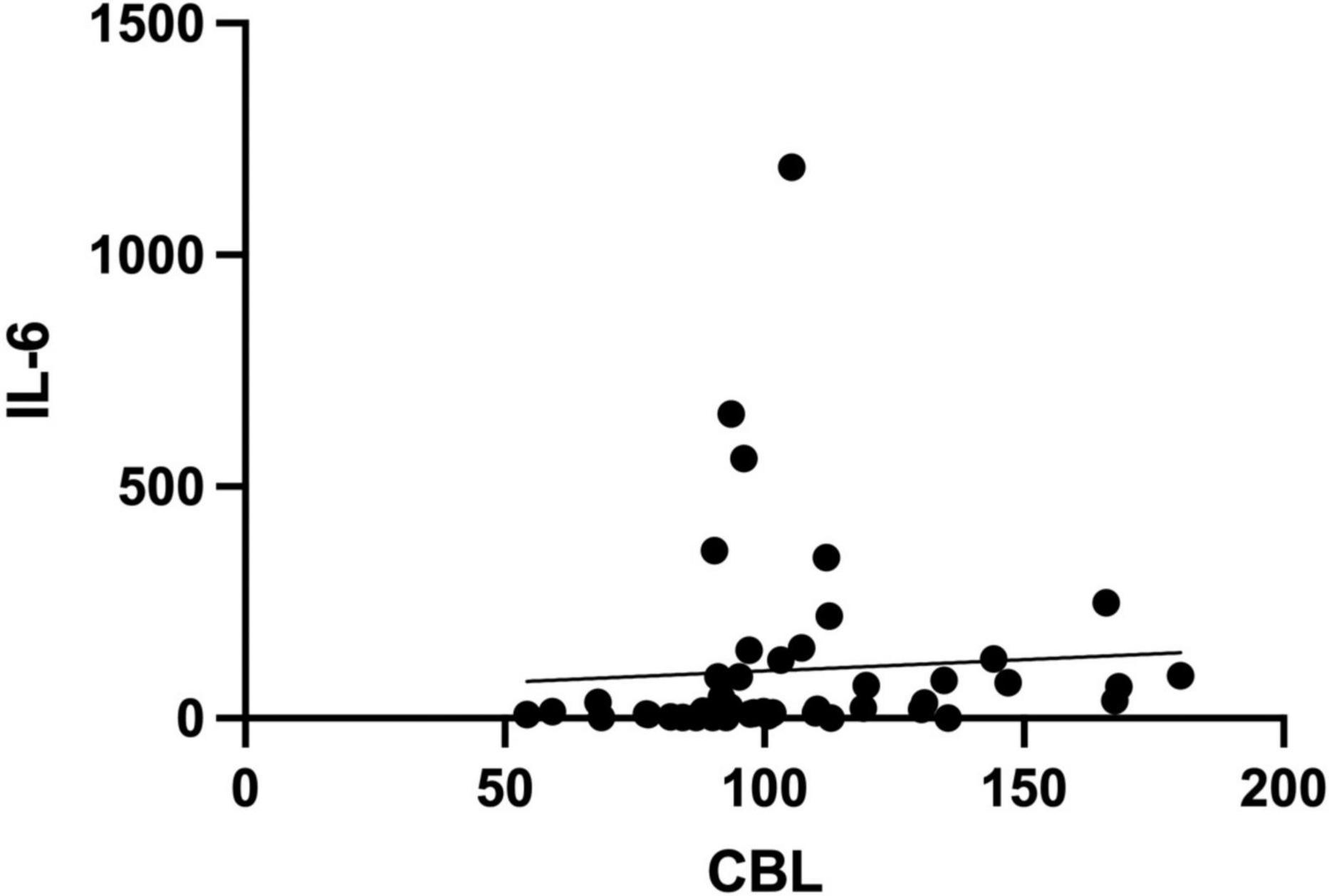
Figure 5. Spearman rank correlation of serum carbamyl-lysine (CBL) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in COVID-19 survivors and COVID-19 deceased patients.
Discussion
Our study is the first to demonstrate increased protein carbamylation in patients with COVID-19. We found that serum CBL levels were significantly higher in those who died of COVID-19 and correlated with inflammatory biomarkers.
Carbamylation is the non-enzymatic binding of a carbamoyl moiety (−CONH2) to the nucleophilic amino groups of proteins. Lysyl residues are particularly vulnerable to carbamylate due to an ε-amino group in the side chain and easy availability to carbamylating agents (16). The main compound responsible for protein carbamylation is electrophilic isocyanic acid. Isocyanic acid is produced from cyanate, formed from urea (27). Not surprisingly, increased carbamylation of proteins is observed in patients with renal failure who have accumulated uremic toxins (19, 20). However, isocyanic acid can also be formed from thiocyanate (SCN–) (16, 27). MPO catalyzes the oxidation of thiocyanate to hypothiocyanous acid (HOSCN) in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Further transformations result in the formation of cyanate and isocyanic acid (16, 27) (Figure 6). Since our study did not include patients with renal failure, it can be assumed that inflammation is the source of increased protein carbamylation in the COVID-19 deceased. It is well known that COVID-19 is associated with an excessive immune system response (28, 29). Our earlier study showed that an increase in cytokine levels in early-stage COVID-19 can be an important diagnostic factor, especially in patients with mild disease symptoms (30). Serum IL-1α, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), basic fibroblast growth factor (basic-FGF), and monokine induced by interferon-γ (MIG) have high diagnostic potential. They can be used to differentiate COVID-19 severity (30, 31). Another study indicates that increased neutrophil MPO activation and endothelial glycocalyx damage are independently associated with COVID-19 severity (32). MPO levels, activity, and soluble endothelial glycocalyx levels are significantly elevated in patients with COVID-19, increasing proportionally to disease severity. Despite clinical recovery, biomarker levels remain significantly higher. There is also a tendency to increase MPO activity in the plasma of convalescents in both severe and non-severe groups (32). Under conditions of prolonged MPO activation, there may be enhanced isocyanic acid production (33), which increases protein carbamylation. Unfortunately, in our study, we did not isolate neutrophils from whole blood, and thus did not assess MPO activity. A potential link between protein carbamylation and inflammation may be evidenced by the positive correlation of serum CBL with IL-6, D-dimer, and WBC. It is well known that IL-6 induces platelet activation, causing endothelial damage and thrombotic disorders with increased D-dimer production (34). Carbamylated proteins can also induce endothelial dysfunction through ROS overproduction and activation of lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) by uncoupling endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) (35–38) (Figure 6).
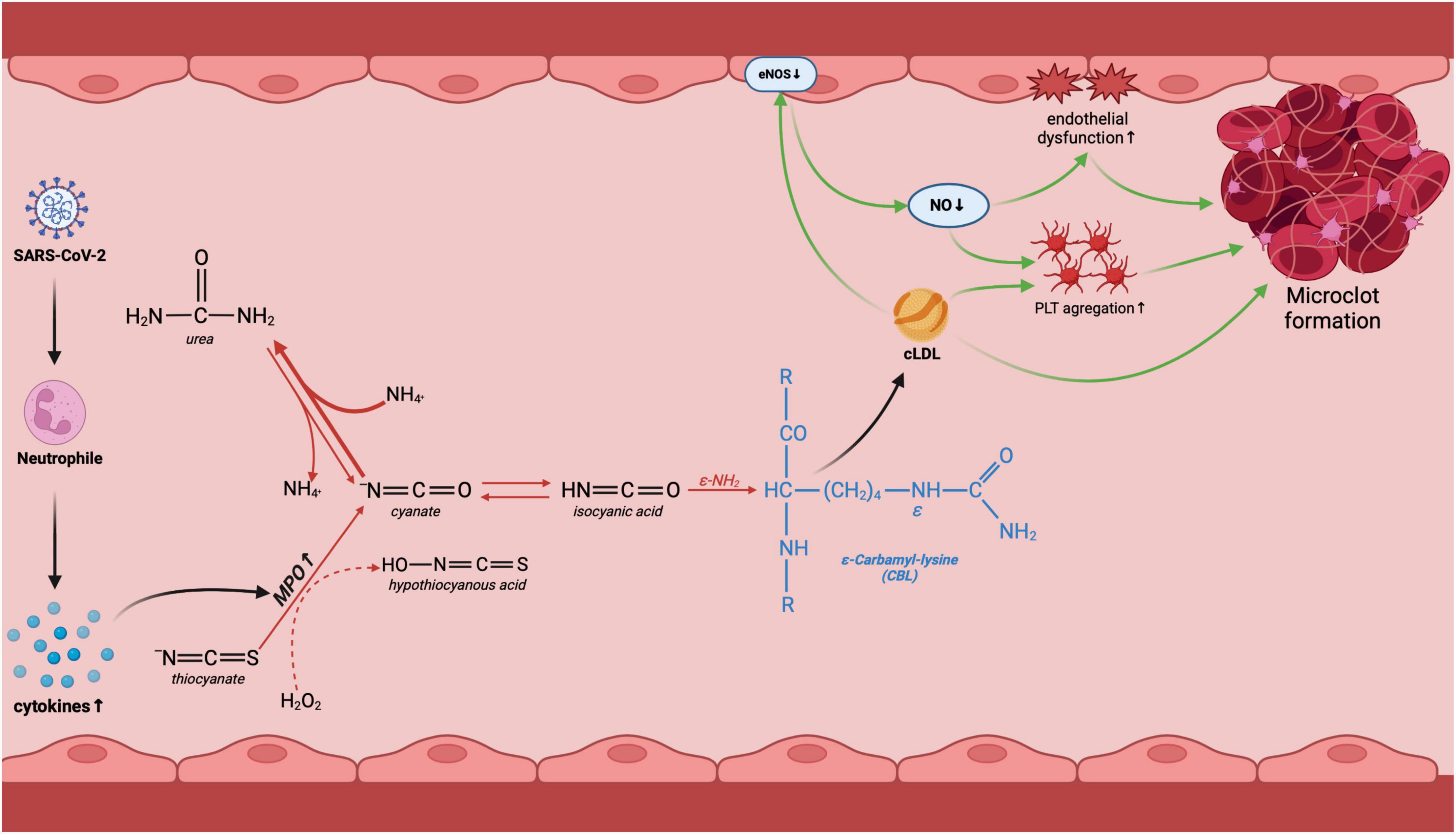
Figure 6. Potential involvement of protein carbamylation in COVID-19-related complications. Following COVID-19 infection, the organism initiates the innate immune response involving neutrophils. This triggers an increase in MPO activity, an enzyme responsible for urea-independent carbamylation. Lysine carbamylation leads to the creation of carbamyl-lysine (CBL), which in turn results in the carbamylation of LDL. Carbamylated low-density lipoproteins (LDL) decrease endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity, causing endothelial dysfunction and platelet aggregation, ultimately leading to the formation of microclots and vascular complications of COVID-19. cLDL, carbamylated low-density lipoprotein; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PLT, platelets. Created using biorender.com.
Protein carbamylation can inhibit many biologically active enzymes or hormones (39). Carbamylated proteins aggregate and accumulate in tissues, are more resistant to proteolysis, and undergo further modification by oxidation or glycation (16, 39). Protein carbamylation is also a biomarker of molecular aging, making it associated with many pathological conditions (40). Indeed, the involvement of protein carbamylation has been described in chronic kidney disease (41), rheumatoid arthritis (42), cataracts (43), atherosclerosis (44), and neurological disorders (45). It was shown that carbamylation of proteins can be induced by neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (46). Since COVID-19 causes severe inflammatory reactions with the formation of NETs (47, 48), neutrophils may be the cause of the increased CBL levels. However, studies on the diagnostic utility of carbamylation biomarkers in COVID-19 patients are lacking. Our ROC analysis showed that the AUC for serum CBL differentiating the deceased and recovered patients on COVID-19 was 0.76. However, it should be noted that the blood samples were taken during the last blood measurement before hospital discharge for survivors or the last blood measurement before death for patients who died from COVID-19. Since no measurements were taken upon admission to the hospital, the baseline carbamylation predictive value cannot be used as a biomarker of the worst outcome. Further studies should evaluate the usefulness of CBL in monitoring disease progression. The sensitivity (60%) and specificity (72%) of CBL are moderate and lower than those of routinely used inflammatory biomarkers, which does not indicate a high diagnostic potential. Although the sample size has been statistically determined, evaluation of the diagnostic potential of CBL is also required on a larger patient population. In addition, the severity of protein carbamylation should be analyzed concerning the patient’s clinical condition [e.g., using the Modified Early Warning Score (MEWS)], lifestyle factors (e.g., diet, smoking, physical activity), concomitant diseases, and medications taken (49). Future studies should also assess other biomarkers of protein carbamylation, e.g., carbamylated hemoglobin, carbamylated albumin, and carbamylated low-density lipoproteins (LDL).
Conclusion
In conclusion, COVID-19 is associated with excessive protein carbamylation. Evaluation of serum CBL levels with moderate sensitivity and specificity differentiates COVID-19 deceased from recovered patients. Inflammation may be a source of increased protein carbamylation in COVID-19. A thorough understanding of the consequences of increased CBL production may clarify the consequences of COVID-19 complications. Therefore, our research indicates the need for further studies.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Chamber of Gdansk, Poland (KB-29/21). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. RC: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JB: Resources, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. MM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Medical University of Białystok, Poland (grant number no. B.SUB.24.250).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. World Health Organization [WHO]. COVID-19 Epidemiological Update. (2024). Available online at: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update—24-december-2024 (Accessed January 7, 2025).
2. Chung YS, Lam CY, Tan PH, Tsang HF, Wong SCC, Chung YS, et al. Comprehensive review of COVID-19: epidemiology, pathogenesis, advancement in diagnostic and detection techniques, and post-pandemic treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:8155. doi: 10.3390/IJMS25158155
3. Fajgenbaum DC, June CH. Cytokine storm. New Eng J Med. (2020) 383:2255–73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2026131
4. Schofield LC, Dialpuri JS, Murshudov GN, Agirre J. Post-translational modifications in the protein data bank. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. (2024) 80:647–60. doi: 10.1107/S2059798324007794
5. Zhong Q, Xiao X, Qiu Y, Xu Z, Chen C, Chong B, et al. Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. MedComm. (2023) 4:e261. doi: 10.1002/MCO2.261
6. Dutta H, Jain N. Post-translational modifications and their implications in cancer. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1240115. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1240115
7. Najjar JA, Calvert JW. Effects of protein glycation and protective mechanisms against glycative stress. Curr Opin Pharmacol. (2024) 76:102464. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2024.102464
8. Dorf J, Pryczynicz A, Matowicka-Karna J, Zaręba K, Żukowski P, Zalewska A, et al. Could circulating biomarkers of nitrosative stress and protein glycoxidation be useful in patients with gastric cancer? Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1213802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1213802
9. Rabbani N, Thornalley PJ. Protein glycation - biomarkers of metabolic dysfunction and early-stage decline in health in the era of precision medicine. Redox Biol. (2021) 42:101920. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101920
10. Simm A. Protein glycation during aging and in cardiovascular disease. J Proteomics. (2013) 92:248–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.05.012
11. Li J, Liu D, Sun L, Lu Y, Zhang Z. Advanced glycation end products and neurodegenerative diseases: mechanisms and perspective. J Neurol Sci. (2012) 317:1–5. doi: 10.1016/J.JNS.2012.02.018
12. Haque E, Kamil M, Hasan A, Irfan S, Sheikh S, Khatoon A, et al. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), protein aggregation and their cross talk: new insight in tumorigenesis. Glycobiology. (2019) 30:2–18. doi: 10.1093/GLYCOB/CWZ073
13. Sellegounder D, Zafari P, Rajabinejad M, Taghadosi M, Kapahi P. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and its receptor, RAGE, modulate age-dependent COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. A review and hypothesis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 98:107806. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107806
14. Wolszczak-Biedrzycka B, Dorf J, Matowicka-Karna J, Dymicka-Piekarska V, Wojewódzka-Żeleźniakowicz M, Żukowski P, et al. Redox biomarkers - an effective tool for diagnosing COVID-19 patients and convalescents. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:2589–607. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S456849
15. Wolszczak-Biedrzycka B, Dorf J, Matowicka-Karna J, Wojewódzka-Żeleźniakowicz M, Żukowski P, Zalewska A, et al. Significance of nitrosative stress and glycoxidation products in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:9198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59876-w
16. Jaisson S, Pietrement C, Gillery P. Protein carbamylation: chemistry, pathophysiological involvement, and biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem. (2018) 84:1–38. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2017.12.001
17. Maciejczyk M, Nesterowicz M, Szulimowska J, Zalewska A. Oxidation, glycation, and carbamylation of salivary biomolecules in healthy children, adults, and the elderly: can saliva be used in the assessment of aging? J Inflamm Res. (2022) 15:2051–73. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S356029
18. Kalim S, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani RI, Berg AH. Protein carbamylation in kidney disease: pathogenesis and clinical implications. Am J Kidney Dis. (2014) 64:793–803. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.04.034
19. Kalim S, Berg AH, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R, Allegretti AS, Nigwekar S, et al. Protein carbamylation and chronic kidney disease progression in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2021) 37:139–47. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfaa347
20. Wang Z, Nicholls SJ, Rodriguez ER, Kummu O, Hörkkö S, Barnard J, et al. Protein carbamylation links inflammation, smoking, uremia and atherogenesis. Nat Med. (2007) 13:1176–84. doi: 10.1038/nm1637
21. Sysmex. XN-550. Available online at: https://www.sysmex-ap.com/product/xn-550/ (Accessed January 16, 2025).
22. Roche Diagnostics. Elecsys® BRAHMS PCT. Available online at: https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/lab/elecsys-brahms-pct-cps-000496.html (Accessed January 16, 2025).
23. Diagon. Dia-D-Dimer. Available online at: http://www.diagon.com/en/ddi/diaddinagy (Accessed January 16, 2025).
24. Tomasiuk R, Dabrowski J, Smykiewicz J, Wiacek M. Predictors of COVID-19 hospital treatment outcome. Int J Gen Med. (2021) 14:10247–56. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S334544
25. Roche Diagnostics. CRP4 Diagnostics. Available online at: https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/lab/crp4-cps-000847.html (Accessed January 16, 2025).
26. Novateinbio. Anti-Carp ELISA. Available online at: https://novateinbio.com/human-elisa-kits/1156325-human-anti-carbamylated- protein-antibody-elisa-kit.html?srsltid=AfmBOorGAMecY38kXa7IIRF6oscaRNN748 MS3Qm399CiJE2ykLmZuIuw (Accessed January 16, 2025).
27. Badar A, Arif Z, Alam K. Role of carbamylated biomolecules in human diseases. IUBMB Life. (2018) 70:267–75. doi: 10.1002/iub.1732
28. Tan LY, Komarasamy TV, Rmt Balasubramaniam V. Hyperinflammatory immune response and COVID-19: a double edged sword. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:742941. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.742941
29. Sher EK, Ćosović A, Džidić-Krivić A, Farhat EK, Pinjić E, Sher F. Covid-19 a triggering factor of autoimmune and multi-inflammatory diseases. Life Sci. (2023) 319:121531. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121531
30. Wolszczak-Biedrzycka B, Dorf J, Wojewódzka-Żelezniakowicz M, Żendzian-Piotrowska M, Dymicka-Piekarska VJ, Matowicka-Karna J, et al. Unveiling COVID-19 secrets: harnessing cytokines as powerful biomarkers for diagnosis and predicting severity. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:6055–70. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S439217
31. Wolszczak-Biedrzycka B, Dorf J, Wojewódzka-Żelezniakowicz M, Żendzian-Piotrowska M, Dymicka-Piekarska V, Matowicka-Karna J, et al. Changes in chemokine and growth factor levels may be useful biomarkers for monitoring disease severity in COVID-19 patients; a pilot study. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1320362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1320362
32. Teo A, Chan LLY, Cheung C, Chia PY, Ong SWX, Fong SW, et al. Myeloperoxidase inhibition may protect against endothelial glycocalyx shedding induced by COVID-19 plasma. Commun Med. (2023) 3:62. doi: 10.1038/s43856-023-00293-x
33. Kisic B, Miric D, Dragojevic I, Rasic J, Popovic L. Role of myeloperoxidase in patients with chronic kidney disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:1069743. doi: 10.1155/2016/1069743
34. Wolf A, Khimani F, Yoon B, Gerhart C, Endsley D, Ray AK, et al. The mechanistic basis linking cytokine storm to thrombosis in COVID-19. Thromb Update. (2022) 8:100110. doi: 10.1016/j.tru.2022.100110
35. Apostolov EO, Shah SV, Ray D, Basnakian AG. Scavenger receptors of endothelial cells mediate the uptake and cellular proatherogenic effects of carbamylated LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2009) 29:1622–30. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.189795
36. Verbrugge FH, Tang WHW, Hazen SL. Protein carbamylation and cardiovascular disease. Kidney Int. (2015) 88:474–8. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.166
37. Speer T, Owala FO, Holy EW, Zewinger S, Frenzel FL, Stähli BE, et al. Carbamylated low-density lipoprotein induces endothelial dysfunction. Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:3021–32. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu111
38. Stankova T, Delcheva G, Maneva A, Vladeva S. Serum levels of carbamylated LDL and soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 are associated with coronary artery disease in patients with metabolic syndrome. Medicina. (2019) 55:493. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080493
39. Tang M, Kalim S. Avenues for post-translational protein modification prevention and therapy. Mol Aspects Med. (2022) 86:101083. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101083
40. Carracedo J, Ramírez-Carracedo R, Martínez de Toda I, Vida C, Alique M, De la Fuente M. Protein carbamylation: a marker reflecting increased age-related cell oxidation. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:1495. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051495
41. Awwad A, Rhee EP, Grams M, Choles HR, Sondheimer J, He J, et al. Comparative CKD risk prediction using homocitrulline and carbamylated albumin: two circulating markers of protein carbamylation. BMC Nephrol. (2024) 25:185. doi: 10.1186/S12882-024-03619-6
42. Pruijn GJM. Citrullination and carbamylation in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2015) 6:192. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00192
43. Harding JJ, Rixon KC. Carbamylation of lens proteins: a possible factor in cataractogenesis in some tropical countries. Exp Eye Res. (1980) 31:567–71. doi: 10.1016/S0014-4835(80)80015-7
44. Saar-Kovrov V, Pawlowska A, Hermann J, Gijbels MJ, Sluimer J, Jankowski V, et al. Protein carbamylation associates with collagen in atherosclerotic plaque and impacts macrophage functions. Atherosclerosis. (2022) 355:27. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.06.310
45. Guru KrishnaKumar V, Baweja L, Ralhan K, Gupta S. Carbamylation promotes amyloidogenesis and induces structural changes in Tau-core hexapeptide fibrils. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. (2018) 1862:2590–604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.07.030
46. O’Neil LJ, Oliveira CB, Wang X, Navarrete M, Barrera-Vargas A, Merayo-Chalico J, et al. Neutrophil extracellular trap-associated carbamylation and histones trigger osteoclast formation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:630–8. doi: 10.1136/ARD-2022-223568
47. Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI, Al-hussaniy HA, Al-Harcan NAH, Alexiou A, Batiha GES. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and Covid-19: a new frontiers for therapeutic modality. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 104:108516. doi: 10.1016/J.INTIMP.2021.108516
48. Ackermann M, Anders HJ, Bilyy R, Bowlin GL, Daniel C, De Lorenzo R, et al. Patients with COVID-19: in the dark-NETs of neutrophils. Cell Death Differ. (2021) 28:3125. doi: 10.1038/S41418-021-00805-Z
Keywords: protein carbamylation, carbamyl-lysine, COVID-19, biomarkers, CBL
Citation: Smykiewicz J, Tomasiuk R, Cemaga R, Buczkowski J and Maciejczyk M (2025) Association of inflammation and protein carbamylation in patients with COVID-19. Front. Med. 12:1561670. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1561670
Received: 17 January 2025; Accepted: 18 March 2025;
Published: 02 April 2025.
Edited by:
Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, National Institute of Respiratory Diseases-Mexico (INER), MexicoReviewed by:
Ernesto Satoshi Nakayasu, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesJoshna Gadhavi, Emory University, United States
Aya Awwad, Mass General Brigham, United States
Copyright © 2025 Smykiewicz, Tomasiuk, Cemaga, Buczkowski and Maciejczyk. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mateusz Maciejczyk, bWF0Lm1hY2llamN6eWtAZ21haWwuY29t
 Jolanta Smykiewicz1
Jolanta Smykiewicz1