
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Med., 17 March 2025
Sec. Obstetrics and Gynecology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1552185
Objective: This meta-analysis aimed to assess the diagnostic efficacy of transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the detection of rectosigmoid deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE).
Methods: A thorough systematic review was performed by searching the PubMed and Embase databases for studies evaluating the diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in rectosigmoid DIE, up until August 12, 2024. The DerSimonian and Laird approach was utilized to calculate sensitivity and specificity, with the Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation employed for data analysis. The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) tool.
Results: The meta-analysis encompassed 10 studies involving 1,604 patients. The findings revealed that TVS had an overall sensitivity of 0.85 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92) and specificity of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.85–0.98), while MRI demonstrated a sensitivity of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.73–0.92) and specificity of 0.95 (95% CI: 0.90–0.99). Statistical analysis indicated no significant differences in sensitivity (p = 0.86) or specificity (p = 0.50) between the two imaging techniques. Additionally, the funnel plot asymmetry test did not reveal significant publication bias for any outcomes (Egger’s test: all p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The meta-analysis reveals nearly equivalent diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in detecting rectosigmoid DIE, with no statistical differences in sensitivity and specificity. However, high heterogeneity among studies highlights the need for further prospective research.
Systematic review registration: The protocol for this meta-analysis has been registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the ID: CRD42024559141, https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024559141.
Rectosigmoid deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) is a severe form of endometriosis that involves the bowel, specifically affecting the rectosigmoid colon (1). This condition is characterized by the infiltration of endometrial-like tissue into the bowel wall. It leads to significant morbidity, including chronic pelvic pain, dyschezia, and bowel obstruction (2). The prevalence of rectosigmoid DIE among women with endometriosis is reported to be approximately 5–12%, making it a relatively common manifestation of this disease (3). Therefore, early and accurate diagnosis is vital in guiding appropriate management. Timely identification enables clinicians to determine whether medical therapy or surgical intervention is required, which can significantly enhance patient outcomes and quality of life (4).
Traditionally, the diagnosis of rectosigmoid DIE has involved a combination of clinical evaluation and various imaging techniques, including computed tomography, biopsy, and rectal endoscopic sonography. However, each of these methods has significant limitations in the context of DIE. Computed tomography, while useful for general pelvic imaging, lacks the soft-tissue contrast necessary to accurately delineate endometriotic lesions, particularly those involving the bowel. This limitation reduces its sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing DIE (5). Biopsy, though definitive, is invasive and often difficult to perform on deep lesions, which can lead to sampling errors and a higher risk of complications (6). Rectal endoscopic sonography may not effectively differentiate between DIE and other forms of bowel pathology, such as malignancies or inflammatory diseases, limiting its diagnostic performance (7). These limitations highlighted the need for more effective, less invasive diagnostic tools for the early detection and management of rectosigmoid DIE.
In recent years, the comparison between magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) for the diagnostic performance of DIE has become an emerging area of researches. MRI is renowned for its superior soft-tissue contrast and multiplanar imaging capabilities, which allow detailed assessment of the pelvic anatomy and the extent of disease (8). TVS, on the other hand, is a readily available, cost-effective, and patient-friendly tool that can provide real-time imaging with high resolution (9). Despite their widespread use, there is ongoing debate regarding the diagnostic performance of MRI versus TVS in detecting rectosigmoid DIE. In addition to their diagnostic capabilities, both TVS and MRI play important roles in the follow-up examinations of patients with rectosigmoid deep infiltrating endometriosis. TVS can be utilized for regular monitoring due to its accessibility and ability to provide immediate feedback on changes in the condition (10). MRI, with its detailed imaging, is particularly useful for assessing the extent of disease progression and planning further management strategies (11). The literature presents different findings, with some studies favoring MRI for its comprehensive imaging capabilities, while others suggest that TVS may offer comparable diagnostic performance, particularly when performed by experienced operators (8, 9, 12, 13).
The purpose of this meta-analysis is to systematically compare the diagnostic performance of MRI and TVS in detecting rectosigmoid DIE, aiming to provide evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice.
This meta-analysis adhered rigorously to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses: Diagnostic Test Accuracy (PRISMA-DTA) guidelines (14), ensuring comprehensive and transparent methodological reporting of diagnostic research. The protocol for this meta-analysis has been registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under the ID CRD42024559141.
A thorough search of the PubMed and Embase databases was performed to identify relevant studies up from August 1994 to August 12, 2024. The search was based on specific key terms, including “endometriosis,” “ultrasonography,” and “magnetic resonance imaging.” The detailed search strategy can be found in Supplementary Table 1. In addition to the database search, the reference lists of the identified articles were manually reviewed to identify any additional studies that may not have been captured in the initial search. This combined approach was employed to ensure the inclusion of all potentially eligible studies.
Studies were eligible to be included: Population (P): Patients suspected of rectosigmoid DIE; Intervention (I): TVS; Comparison (C): MRI; Outcome (O): Sensitivity and specificity; Study design (S): Retrospective or prospective studies.
Studies were excluded from this analysis based on several criteria to ensure the relevance and quality of the included data. First, articles were excluded if they lacked full texts, had irrelevant titles or abstracts, or were identified as duplicates. Publications such as case reports, letters, reviews, meta-analyses, non-English articles, and editorial comments were also excluded. In addition, studies that did not provide the necessary data for calculating key diagnostic outcomes, sensitivity and specificity, were excluded. Studies that did not involve direct head-to-head comparisons of the imaging modalities were also excluded. For studies with potentially overlapping patient populations, only the most recent study was included to ensure the inclusion of the most up-to-date data.
We employed the QUADAS-2 framework to systematically evaluate the methodological quality of diagnostic accuracy studies. The assessment focused on four critical domains: patient selection, indicator testing, reference criteria and process, and timing (15). To ensure methodological rigor, two independent researchers conducted comprehensive quality evaluations, with any interpretative discrepancies resolved through collaborative deliberation or third-party adjudication.
The assessment protocol involved customizing domain-specific evaluation criteria aligned with QUADAS-2 guidelines. These tailored questions were strategically designed to critically examine potential biases and assess the overall applicability of primary diagnostic studies within the systematic review. Bias risk was stratified into three hierarchical categories: “high risk,” “low risk,” and “unclear risk.”
We extracted the following data from the selected studies: the author, publication year, country of the study, study design (prospective or retrospective), reference standard (surgery, histopathology), number of observers, number of patients, mean or median age of patients, cases with rectosigmoid DIE, imaging method of MRI technique and imaging method of TVS technique.
To ensure methodological integrity, two independent researchers conducted simultaneous data extraction, implementing a robust verification mechanism. A collaborative consensus-building approach was employed to resolve potential interpretative discrepancies.
In this meta-analysis, the primary focus was on evaluating the diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in the detection of rectosigmoid DIE. The study assessed the sensitivity and specificity of both imaging technique. Sensitivity is defined as the proportion of true positives (TP) identified by the imaging method, relative to the sum of TP and false negatives (FN). This measure reflects the ability of the imaging technique to correctly identify cases of rectosigmoid DIE. On the other hand, specificity refers to the proportion of true negatives (TN) detected by the imaging technology, in relation to the total number of TN and false positives (FP). Specificity quantifies the performance of the imaging method in correctly ruling out individuals without rectosigmoid DIE.
Meta-analytical techniques were applied to quantify diagnostic performance, employing the DerSimonian and Laird statistical approach for estimating pooled specificity and sensitivity. The Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation was implemented to normalize the diagnostic performance metrics. Confidence intervals were computed utilizing the Jackson method, which provides robust interval estimation. Statistical heterogeneity was comprehensively assessed through Cochrane Q and I2 statistical measures (16). When significant inter-study heterogeneity was detected (defined by p < 0.10 or I2 > 50%), a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was implemented through sequential article exclusion and subsequent reassessment of sensitivity and specificity. Meta-regression analysis was strategically employed to explore potential sources of heterogeneity.
Publication bias was rigorously evaluated using funnel plot visualization and Egger’s statistical test (17). All statistical analysis were conducted by using R software (version 4.4.0), and the quality assessment was conducted using Revman 5.3 software.
The initial search identified 1,488 potential articles, supplemented by 2 additional articles discovered through alternative references. Preliminary screening eliminated 293 duplicate articles. Subsequent application of predefined inclusion criteria further narrowed the selection, excluding 1,175 articles, resulting in 22 articles meeting initial screening requirements.
A meticulous full-text review initiated a critical evaluation phase, leading to the exclusion of 12 additional articles based on specific methodological criteria. Exclusion rationales encompassed critical research limitations, including: incomplete diagnostic data sets (n = 10); non-English language publications (n = 1); not head-to-head comparison (n = 1). The final analytical cohort comprised 10 articles specifically focused on evaluating the diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in rectosigmoid DIE detection (18–27). The selection process adhered to PRISMA guidelines, ensuring a structured, transparent, and reproducible approach to literature curation. A detailed flow diagram (Figure 1) comprehensively illustrated the article selection process.
This meta-analysis encompassed a diverse cohort of 10 eligible studies, involving 1,604 patients (ranging from 33 to 555, with a median of 98). Among these, 5 (50%) were retrospective studies, and 5 (50%) were prospective. Regarding number of patients, 5 (50%) studies analyzed more than 100 patients and 5 (50%) studies analyzed fewer than 100 patients. For the reference standard, these studies all used surgery and histopathology as the diagnostic gold standard. Detailed patient characteristics and study-specific information, and technical aspect were comprehensively documented in Tables 1, 2.
The comprehensive methodological evaluation utilized the QUADAS-2 tool to systematically assess research quality and potential bias across the included studies. Detailed bias risk characteristics were comprehensively documented in Table 3. In the aspect of index testing, 8 (80%) studies were judged as “unclear” because it was unclear whether a pre-determined cut-off value was used. With regards to the aspect of flow and timing, 1 (10%) study was judged as “high risk” because the time interval between some diagnostic tests and the gold standard was more than 3 months. Overall, the qualities of the included studies were deemed acceptable.
The pooled sensitivity of TVS was calculated to be 0.85 (95% CI: 0.76–0.92), while for MRI, it was 0.83 (95% CI: 0.73–0.92) (Figure 2). There was no statistically significant difference between the sensitivities of TVS and MRI (p = 0.86) (Figure 2).
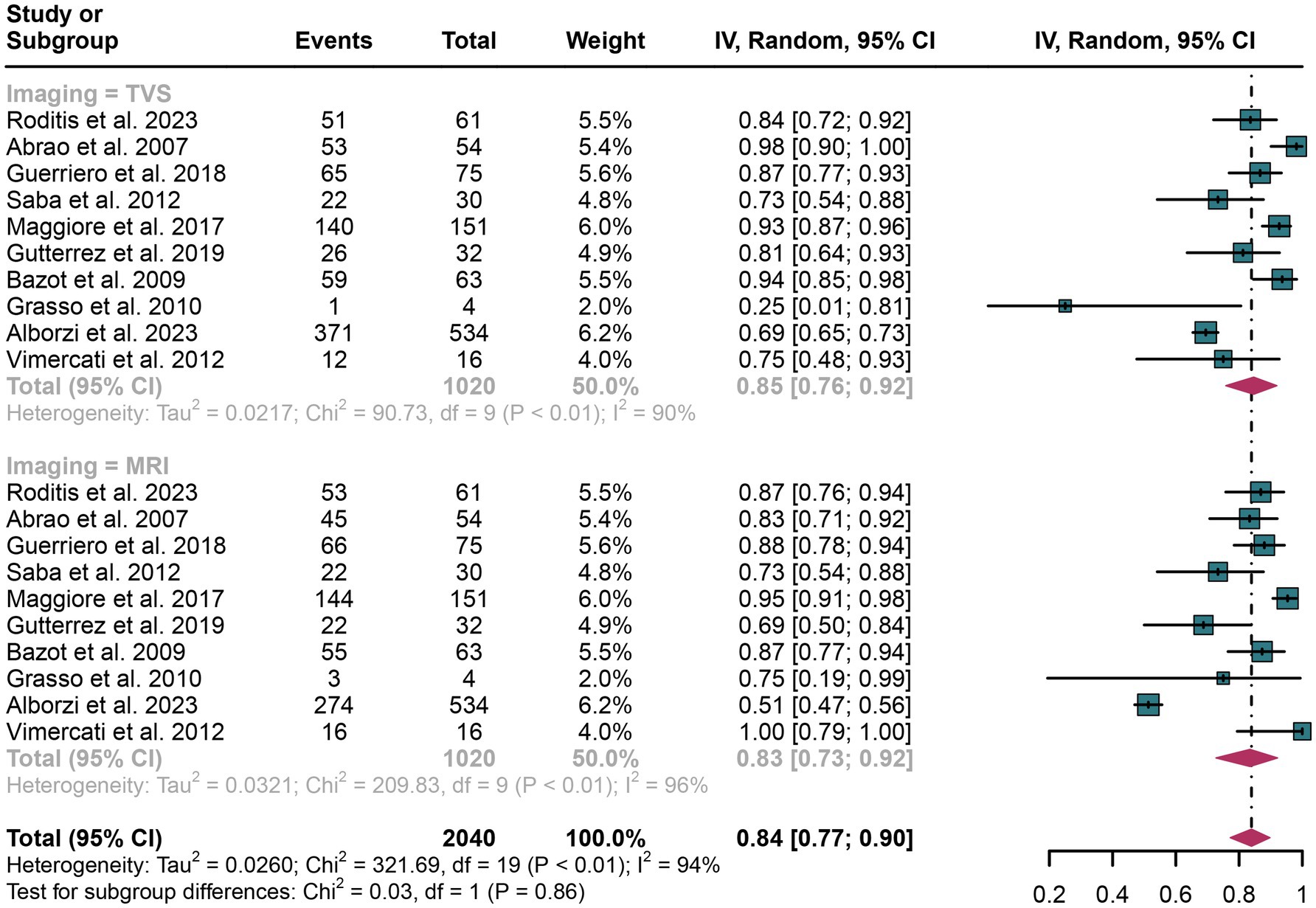
Figure 2. Forest plot showing the analysis for the sensitivity of TVS and MRI in diagnosing rectosigmoid DIE. The squares in the figure represent the estimated values of each individual study, the size of the squares indicates the relative weight of each study in this meta-analysis, the horizontal lines represent the corresponding 95% confidence intervals, and the diamonds represent the aggregated combined sensitivity estimates.
The I2 statistic for TVS sensitivity was 90%. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis did not identify the potential sources of heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure 1). Moreover, a meta-regression analysis was performed to explore possible factors contributing to heterogeneity, with results indicating that none of the three covariates—study design, patient number, or geographical region—significantly affected TVS sensitivity (Table 4).
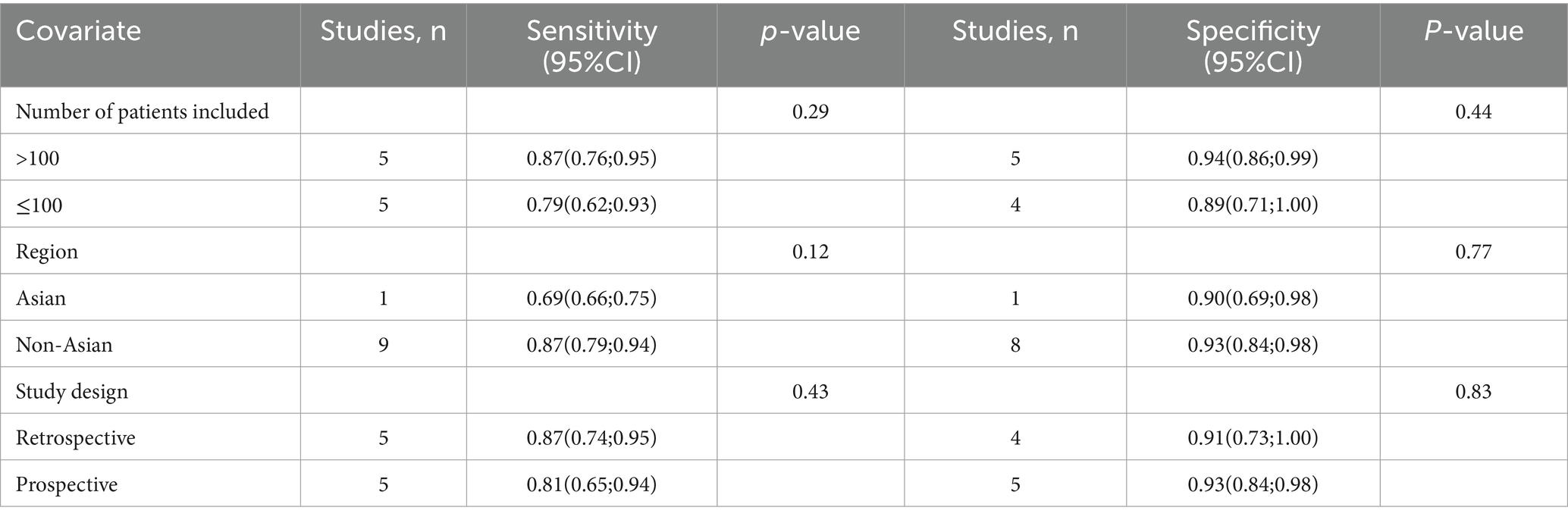
Table 4. Meta-regression analysis of factors affecting the sensitivity and specificity of transvaginal ultrasonography.
For MRI sensitivity, the I2 value was 96%, and the leave-one-out sensitivity analysis also revealed no clear source of heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure 2). However, meta-regression suggested that the geographical region (p < 0.01) could be a significant factor contributing to the heterogeneity in MRI sensitivity (Table 5).
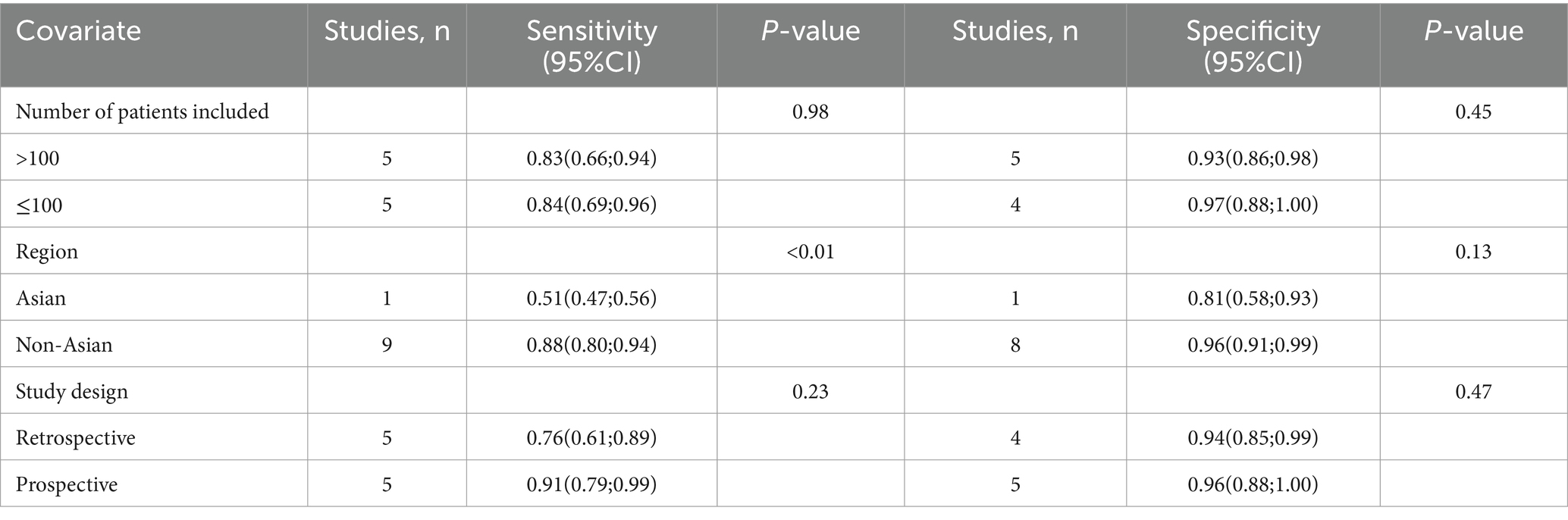
Table 5. Meta-regression analysis of factors affecting the sensitivity and specificity of magnetic resonance imaging.
In the assessment of rectosigmoid DIE, TVS demonstrated an overall specificity of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.85–0.98), whereas MRI showed a pooled specificity of 0.95 (95% CI: 0.90–0.99) (Figure 3). The difference in specificity between TVS and MRI was not statistically significant (p = 0.50) (Figure 3).
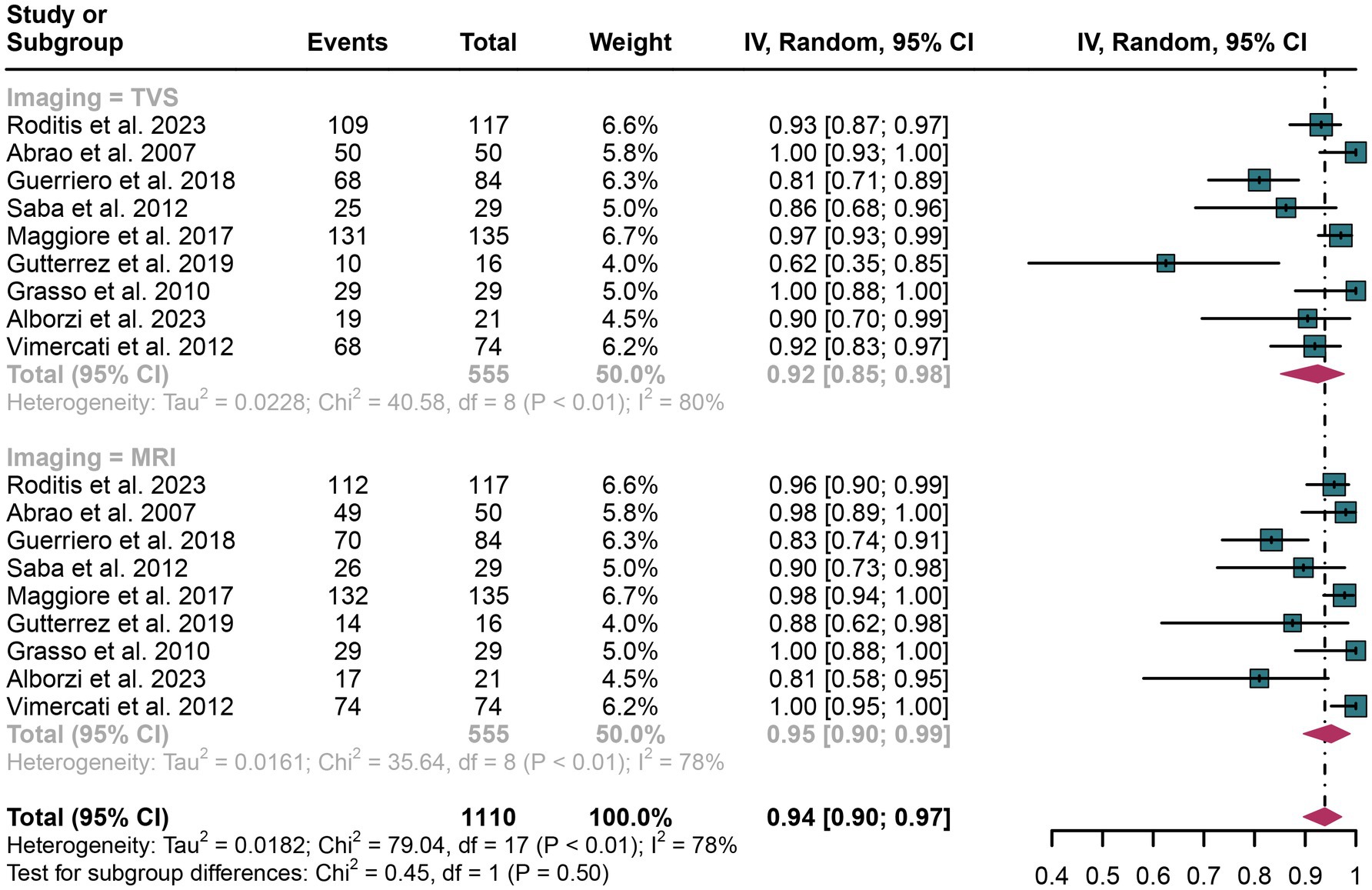
Figure 3. Forest plot showing the analysis for the specificity of TVS and MRI in diagnosing rectosigmoid DIE. The squares in the figure represent the estimated values of each individual study, the size of the squares indicates the relative weight of each study in this meta-analysis, the horizontal lines represent the corresponding 95% confidence intervals, and the diamonds represent the aggregated combined specificity estimates.
For TVS, the I2 value for specificity was 80%. A leave-one-out sensitivity analysis did not pinpoint any potential sources of heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure 3). Additionally, a meta-regression analysis examining three covariates—study design, patient count, and geographical region—revealed that none had a significant impact on the specificity of TVS (Table 4).
In the case of MRI, the I2 value for specificity was 78%. The leave-one-out sensitivity analysis similarly did not identify any sources of heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure 4). Furthermore, meta-regression analysis indicated that none of the covariates significantly influenced the specificity of MRI (Table 5).
The funnel plot asymmetry test did not reveal significant publication bias for any outcomes (Egger’s test: all p > 0.05; Supplementary Figures 5–8).
In 2014, Piessens et al. (13) found that TVS is the most commonly studied and frequently used imaging method for the preoperative diagnosis of DIE. TVS is preferred due to its accessibility, low cost, and non-invasive nature. However, in 2023, Rousset et al. (28) established that MRI remains the gold standard for imaging in patients with DIE, recommending the use of standardized MRI segmental structured reports to ensure performance. Despite these guidelines, recent studies have demonstrated inconsistent diagnostic performance between TVS and MRI for diagnosing rectosigmoid DIE. Gerges et al. suggested that TVS might offer slightly better sensitivity than MRI for detecting rectal or rectosigmoid involvement (29). Conversely, Guerriero et al. systematically evaluated the diagnostic performance of these imaging modalities in multiple anatomical regions, including the rectosigmoid region, uterosacral ligaments, and rectovaginal septum. They evaluated and compared diagnostic methods and concluded that TVS and MRI had similar diagnostic performance (30). Therefore, there remains a lack of systematic head-to-head comparisons between these two modalities, and the question of which diagnostic tool provides superior performance for rectosigmoid DIE remains unresolved.
This meta-analysis included 10 studies with a total of 1,604 patients, and the findings demonstrated that both TVS and MRI have similar diagnostic performance for detecting rectosigmoid DIE. The similar performance of TVS and MRI can be attributed to several factors. TVS, despite being a less invasive and more cost-effective technique, allows for high-resolution imaging of pelvic structures, making it highly effective in detecting endometriotic lesions, especially in the rectosigmoid region (31). TVS can screen the rectal wall up to 16 cm from the anal verge (32); however, it may not be able to detect more cranial or proximal bowel lesions. On the other hand, MRI offers superior soft tissue contrast and is particularly valuable for visualizing deeper lesions that are located further cranially in the rectum and proximal bowel (33).
In comparison with previous meta-analyses, our study offers several important advantages. One of the most notable comparisons is with the work of Guerriero et al. (30), who included six studies that focused on comparing the performance of TVS and MRI in diagnosing DIE. Their findings, which indicated similar sensitivity and specificity between TVS and MRI, align with our meta-analysis results. However, the limited number of studies included in their analysis restricted the robustness of their conclusions. Moreover, their analysis involved comparisons across multiple anatomical sites, while we only focus on rectosigmoid site. In clinical practice, patients may present with lesions in multiple different sites. The preferred method for detecting multiple lesions may depend on clinical context, as each modality has its unique advantages.
Similarly, when comparing our study with Gerges et al. (29), there are clear strengths in our approach. Gerges et al. focused on comparing a variety of diagnostic tools, including TVS and MRI, but they performed an indirect comparison, which lowered the level of evidence and potentially introduced bias (29). In contrast, our meta-analysis focused exclusively on head-to-head studies, which strengthens the reliability of our conclusions. These improvements in methodology and study selection make our meta-analysis more reliable evidence for assessing the diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in rectosigmoid DIE.
Both modalities have their own advantages and disadvantages. When considering the similar diagnostic performance, TVS appears to be a more cost-effective choice, given its higher availability and lower cost compared to MRI. TVS is non-invasive, widely accessible, and generally well-tolerated by patients, making it a preferred initial diagnostic tool in many settings (34). In addition to these advantages, one of the key benefits of TVS is its speed of detection. The ability to provide real-time imaging allows clinicians to quickly assess and identify lesions, which can be crucial in urgent clinical situations (35). In contrast, MRI, while offering superior soft tissue contrast and being highly effective in detecting deep-seated lesions, is more expensive, less accessible, and requires specialized equipment and expertise (36). However, the TVS is also limited by the diagnostic performance that depends on the operator’s experience. Regarding safety, both modalities are generally safe; however, MRI involves the use of strong magnetic fields, which may pose a risk for patients with certain implants, such as pacemakers (37), while TVS has minimal risk aside from the discomfort associated with the procedure. The complementary strengths of TVS and MRI should be considered, as each modality offers unique advantages in specific clinical scenarios. Despite these advantages and disadvantages, it should be noted that the high heterogeneity in the studies included in our meta-analysis, suggests that further researches focus in more specific patients are needed. It is important to note that while we compared the diagnostic performance of these two tools, each imaging technique has its own characteristics and strengths, leading to distinct diagnostic criteria. These differences are inherent and unavoidable. Furthermore, the adoption of a standardized classification system, such as #Enzian, in the evaluation of rectal endometriosis could facilitate more consistent reporting across studies (38). Its use would enhance comparability between sonographers and radiologists, ultimately improving the reliability and generalizability of diagnostic outcomes.
Beside rectosigmoid DIE, both TVS and MRI can effectively diagnose adenomyosis, with each modality presenting distinct diagnostic advantages, and with similar diagnostic performance (39). TVS offers real-time imaging and dynamic assessment capabilities, enabling clinicians to quickly evaluate uterine structures with immediate feedback. In contrast, MRI provides superior soft tissue contrast and comprehensive three-dimensional anatomical information, particularly useful for assessing the depth and extent of junctional zone alterations. However, on clinical grounds, the use of TVS would imply lower costs, faster examination times, and broader clinical accessibility, making it a preferred first-line imaging technique for initial adenomyosis screening (40). In addition, for rectosigmoid DIE, the commonly used intrasurgical laparoscopic ultrasound (IOUS) has demonstrated excellent diagnostic performance. It can be particularly advantageous during laparoscopic surgeries for real-time imaging, allowing for better visualization of endometriotic lesions and facilitating their identification and management (41). Future evaluations comparing IOUS with MRI and TVS may also be a worthwhile direction for discussion.
Several limitations of this meta-analysis should be acknowledged when interpreting the results. First, the heterogeneity observed across the included studies could have influenced the overall sensitivities and specificities of TVS and MRI. To address this, we performed meta-regression and leave-one-out sensitivity analysis to explore potential sources of heterogeneity, and our findings suggest that the region in which the studies were conducted may be a contributing factor. However, differences in healthcare infrastructure and patient situation from virous regions could have affected the diagnostic performance of both modalities. Second, approximately half of the included studies were retrospective design, which introduces the possibility of selection bias. Considering the retrospective nature of these studies, some data may not be homogeneous, leading to potential inaccuracies in the diagnoses. This limitation highlights the need for caution when interpreting the results, as the variability in data quality and collection methods across studies could impact the reliability of our findings. In terms of clinical practice, the results of this meta-analysis underscore the importance of both TVS and MRI as valuable diagnostic tools for rectosigmoid DIE. Given the similar diagnostic performance of these modalities, clinicians can consider TVS as a first-line imaging option, especially in settings where MRI may not be readily accessible due to cost or availability. Additionally, our findings suggest that future research should focus on developing standardized protocols that integrate both imaging techniques to enhance diagnostic accuracy and improve patient outcomes.
The meta-analysis reveals nearly equivalent diagnostic performance of TVS and MRI in detecting rectosigmoid DIE, with no statistical differences in sensitivity and specificity. However, high heterogeneity among studies highlights the need for further prospective research. Optimal diagnostic strategy for DIE requires comprehensive evaluation of imaging modalities’ distinctive characteristics. Clinicians must critically analyze the nuanced strengths and inherent limitations of each diagnostic technique to ensure patient-centered imaging selection.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
ZX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YinW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YitW: Conceptualization, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Shanghai 2020 “Science and Technology Innovation Action Plan” Medical Innovation Research Project (No. 20Z21900400), the Future Plan of Shanghai Medical Innovation and Development Foundation (No. WL-HBMS-2022006 K), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82205156), the Training Program for High-Caliber Talents of Clinical Research at Affiliated Hospitals of SHUTCM (2023LCRC19), and the Shanghai Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine Study Abroad Program (No. RCYS40042023041).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1552185/full#supplementary-material
1. Hur, C, and Falcone, T. Robotic treatment of bowel endometriosis. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. (2021) 71:129–43. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2020.05.012
2. Abrão, MS, Petraglia, F, Falcone, T, Keckstein, J, Osuga, Y, and Chapron, C. Deep endometriosis infiltrating the recto-sigmoid: critical factors to consider before management. Hum Reprod Update. (2015) 21:329–39. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmv003
3. Weed, JC, and Ray, JE. Endometriosis of the bowel. Obstet Gynecol. (1987) 69:727–30. Epub 1987/05/01.
4. Halis, G, Mechsner, S, and Ebert, AD. The diagnosis and treatment of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int. (2010) 107:446–55; quiz 456; quiz 56. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0446
5. Collin, M, Barat, M, Oudjit, A, Terris, B, Dohan, A, Rousset, P, et al. Comparison between CT-enterography and MR-enterography for the diagnosis of right-sided deep infiltrating endometriosis of the bowel. Eur J Radiol. (2023) 161:110730. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.110730
6. Kazanegra, R, Zaritsky, E, Lathi, RB, Clopton, P, and Nezhat, C. Diagnosis of stage I endometriosis: comparing visual inspection to histologic biopsy specimen. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. (2008) 15:176–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2007.10.005
7. Bazot, M, Malzy, P, Cortez, A, Roseau, G, Amouyal, P, and Daraï, E. Accuracy of transvaginal sonography and rectal endoscopic sonography in the diagnosis of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2007) 30:994–1001. doi: 10.1002/uog.4070
8. Medeiros, LR, Rosa, MI, Silva, BR, Reis, ME, Simon, CS, Dondossola, ER, et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance in deeply infiltrating endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. (2015) 291:611–21. doi: 10.1007/s00404-014-3470-7
9. Guerriero, S, Ajossa, S, Pagliuca, M, Borzacchelli, A, Deiala, F, Springer, S, et al. Advances in imaging for assessing pelvic endometriosis. Diagnostics. (2022) 12. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12122960
10. Keckstein, S, Dippon, J, Hudelist, G, Koninckx, P, Condous, G, Schroeder, L, et al. Sonomorphologic changes in colorectal deep endometriosis: the long-term impact of age and hormonal treatment. Ultraschall Med. (2024) 45:285–92. doi: 10.1055/a-2209-5653
11. Knez, J, Bean, E, Nijjar, S, Tellum, T, Chaggar, P, and Jurkovic, D. Natural progression of deep pelvic endometriosis in women who opt for expectant management. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2023) 102:1298–305. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14491
12. Gerges, B, Li, W, Leonardi, M, Mol, BW, and Condous, G. Meta-analysis and systematic review to determine the optimal imaging modality for the detection of uterosacral ligaments/torus uterinus, rectovaginal septum and vaginal deep endometriosis. Hum Reprod Open. (2021) 2021:1–17. doi: 10.1093/hropen/hoab041
13. Piessens, S, Healey, M, Maher, P, Tsaltas, J, and Rombauts, L. Can anyone screen for deep infiltrating endometriosis with transvaginal ultrasound? Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. (2014) 54:462–8. doi: 10.1111/ajo.12242
14. McInnes, MDF, Moher, D, Thombs, BD, McGrath, TA, Bossuyt, PM, Clifford, T, et al. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and Meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies: the PRISMA-DTA statement. JAMA. (2018) 319:388–96. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.19163
15. Yang, B, Mallett, S, Takwoingi, Y, Davenport, CF, Hyde, CJ, Whiting, PF, et al. QUADAS-C: a tool for assessing risk of Bias in comparative diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. (2021) 174:1592–9. doi: 10.7326/m21-2234
16. Higgins, JP, Thompson, SG, Deeks, JJ, and Altman, DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
17. Egger, M, Davey Smith, G, Schneider, M, and Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
18. Vimercati, A, Achilarre, MT, Scardapane, A, Lorusso, F, Ceci, O, Mangiatordi, G, et al. Accuracy of transvaginal sonography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance-colonography for the presurgical staging of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2012) 40:592–603. doi: 10.1002/uog.11179
19. Saba, L, Guerriero, S, Sulcis, R, Pilloni, M, Ajossa, S, Melis, G, et al. MRI and "tenderness guided" transvaginal ultrasonography in the diagnosis of recto-sigmoid endometriosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. (2012) 35:352–60. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22832
20. Roditis, A, Florin, M, Rousset, P, Touboul, C, Bendifallah, S, Bazot, M, et al. Accuracy of combined physical examination, transvaginal ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose deep endometriosis. Fertil Steril. (2023) 119:634–43. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2022.12.025
21. Maggiore, ULR, Biscaldi, E, Vellone, VG, Venturini, PL, and Ferrero, S. Magnetic resonance enema vs rectal water-contrast transvaginal sonography in diagnosis of rectosigmoid endometriosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2017) 49:524–32. doi: 10.1002/uog.15934
22. Gutiérrez, AH, Spagnolo, E, Hidalgo, P, López, A, Zapardiel, I, and Rodriguez, R. Magnetic resonance imaging versus transvaginal ultrasound for complete survey of the pelvic compartments among patients with deep infiltrating endometriosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. (2019) 146:380–5. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12894
23. Guerriero, S, Alcázar, JL, Pascual, MA, Ajossa, S, Perniciano, M, Piras, A, et al. Deep infiltrating endometriosis: comparison between 2-dimensional ultrasonography (US), 3-dimensional US, and magnetic resonance imaging. J Ultrasound Med. (2018) 37:1511–21. doi: 10.1002/jum.14496
24. Grasso, RF, Di Giacomo, V, Sedati, P, Sizzi, O, Florio, G, Faiella, E, et al. Diagnosis of deep infiltrating endometriosis: accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and transvaginal 3D ultrasonography. Abdom Imaging. (2010) 35:716–25. doi: 10.1007/s00261-009-9587-7
25. Bazot, M, Lafont, C, Rouzier, R, Roseau, G, Thomassin-Naggara, I, and Daraï, E. Diagnostic accuracy of physical examination, transvaginal sonography, rectal endoscopic sonography, and magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose deep infiltrating endometriosis. Fertil Steril. (2009) 92:1825–33. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.09.005
26. Alborzi, S, Poordast, T, Askary, E, Javedanmehr, M, Shahraki, MH, Alborzi, S, et al. Evaluation and comparison of the accuracy of transvaginal ultrasound and MRI for the diagnosis of deep rectal endometriosis: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gynecol Obstet. (2023) 161:586–93. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14554
27. Abrao, MS, Gonçalves, MO, Dias, JA Jr, Podgaec, S, Chamie, LP, and Blasbalg, R. Comparison between clinical examination, transvaginal sonography and magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of deep endometriosis. Hum Reprod. (2007) 22:3092–7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dem187
28. Rousset, P, Florin, M, Bharwani, N, Touboul, C, Monroc, M, Golfier, F, et al. Deep pelvic infiltrating endometriosis: MRI consensus lexicon and compartment-based approach from the ENDOVALIRM group. Diagn Interv Imaging. (2023) 104:95–112. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2022.09.004
29. Gerges, B, Li, W, Leonardi, M, Mol, BW, and Condous, G. Optimal imaging modality for detection of rectosigmoid deep endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2021) 58:190–200. doi: 10.1002/uog.23148
30. Guerriero, S, Saba, L, Pascual, MA, Ajossa, S, Rodriguez, I, Mais, V, et al. Transvaginal ultrasound vs magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing deep infiltrating endometriosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2018) 51:586–95. doi: 10.1002/uog.18961
31. Collins, BG, Ankola, A, Gola, S, and McGillen, KL. Transvaginal US of endometriosis: looking beyond the Endometrioma with a dedicated protocol. Radiographics. (2019) 39:1549–68. doi: 10.1148/rg.2019190045
32. Ren, Y, Ye, J, Wang, Y, Xiong, W, Xu, J, He, Y, et al. The optimal application of Transrectal ultrasound in staging of rectal Cancer following neoadjuvant therapy: a pragmatic study for accuracy investigation. J Cancer. (2018) 9:784–91. doi: 10.7150/jca.22661
33. Bianek-Bodzak, A, Szurowska, E, Sawicki, S, and Liro, M. The importance and perspective of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of endometriosis. Biomed Res Int. (2013) 2013:436589. doi: 10.1155/2013/436589
34. Arezzo, F, Cormio, G, La Forgia, D, Kawosha, AA, Mongelli, M, Putino, C, et al. The application of Sonovaginography for implementing ultrasound assessment of endometriosis and other Gynaecological diseases. Diagnostics. (2022) 12. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040820
35. Hussain, S, Mubeen, I, Ullah, N, Shah, S, Khan, BA, Zahoor, M, et al. Modern diagnostic imaging technique applications and risk factors in the medical field: a review. Biomed Res Int. (2022) 2022:5164970. doi: 10.1155/2022/5164970
36. Marcal, L, Nothaft, MA, Coelho, F, and Choi, H. Deep pelvic endometriosis: MR imaging. Abdom Imaging. (2010) 35:708–15. doi: 10.1007/s00261-010-9611-y
37. Yang, E, Suzuki, M, Nazarian, S, and Halperin, HR. Magnetic resonance imaging safety in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices. Trends Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 32:440–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2021.08.001
38. Keckstein, J, Saridogan, E, Ulrich, UA, Sillem, M, Oppelt, P, Schweppe, KW, et al. The #Enzian classification: a comprehensive non-invasive and surgical description system for endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2021) 100:1165–75. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14099
39. Alcázar, JL, Vara, J, Usandizaga, C, Ajossa, S, Pascual, M, and Guerriero, S. Transvaginal ultrasound versus magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing adenomyosis: a systematic review and head-to-head meta-analysis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. (2023) 161:397–405. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.14609
40. Harmsen, MJ, Trommelen, LM, de Leeuw, RA, Tellum, T, Juffermans, LJM, Griffioen, AW, et al. Uterine junctional zone and adenomyosis: comparison of MRI, transvaginal ultrasound and histology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2023) 62:42–60. doi: 10.1002/uog.26117
Keywords: ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, rectosigmoid, endometriosis, meta-analysis
Citation: Xu Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Wan Y and Chen J (2025) Transvaginal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in detecting rectosigmoid deep infiltrating endometriosis: a comparative meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1552185. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1552185
Received: 27 December 2024; Accepted: 03 March 2025;
Published: 17 March 2025.
Edited by:
Ali Çetin, University of Health Sciences, TürkiyeReviewed by:
Ferdinando Antonio Gulino, University of Messina, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Xu, Li, Wang, Wan and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Chen, Y2oxMjc1QDEyNi5jb20=; Yiting Wan, MTA5NDk0MzUxQHFxLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.