- 1Department of Clinical Medicine, The Second Clinical Medical College, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Department of Emergency, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Objective: The evidence regarding the impact of underweight status on clinical outcomes in patients with sepsis are still scarce and controversial. We aimed at conducting a meta-analysis to evaluate the potential associations between underweight and the mortality rate among sepsis patients.
Methods: A comprehensive electronic search was performed in PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Web of Science databases. Odds ratios (ORs) or mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated using RevMan 5.3.
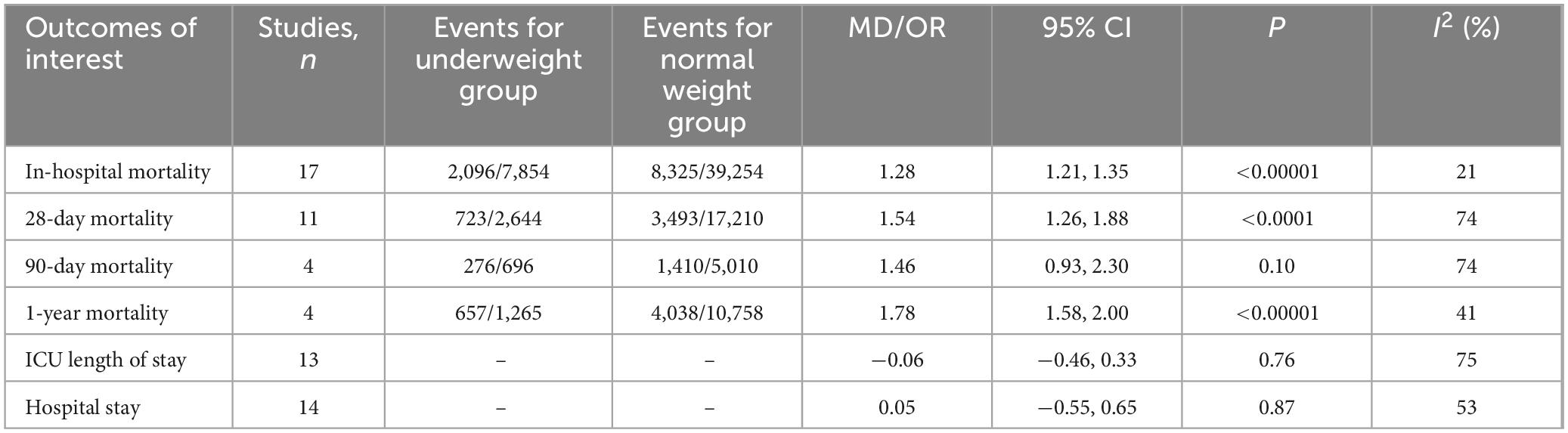
Results: A total of 58,348 patients (normal weight group: 49,084 patients; underweight group: 9,264 patients) from 23 studies were included in this meta-analysis. The results indicated that the in-hospital mortality (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.21, 1.35; heterogeneity: I2 = 21%, P = 0.21), 28-day mortality (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.26, 1.88; heterogeneity: I2 = 74%, P < 0.0001) and 1-year mortality (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.58, 2.00; heterogeneity: I2 = 41%, P = 0.17) of underweight patients were significantly higher than those of normal weight patients. However, there was no significant difference in length of hospital stay or intensive care unit length of stay between underweight patients and normal-weight patients.
Conclusion: Underweight is associated with increased mortality in patients with sepsis. Physicians should pay more attention to the management of underweight sepsis patients.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/display_record.php?RecordID=631417, identifier CRD42025631417.
1 Introduction
Sepsis is a life-threatening syndrome caused by the body’s dysfunctional immune response to a serious systemic infection, often involving multiple organs and systems (1, 2). Sepsis and septic shock are important global health problems, and sepsis is the leading cause of death in intensive care units (3). In the United States, sepsis is now more common than heart attacks and strokes (3). According to statistics, there are about 50 million cases of sepsis worldwide each year, resulting in more than 10 million deaths annually, accounting for about 20% of global deaths (1, 2). Although much progress has been made in the pathobiology and epidemiology of sepsis in recent years, the high mortality rate of the disease remains a concern for clinicians (3). Therefore, it is critical to identify prognostic factors for sepsis to help clinicians identify high-risk patients early and make more informed medical decisions.
Previous evidence suggests that body mass index (BMI) may be an important prognostic factor for death in patients with sepsis (4–6). A meta-analysis of 15 studies by Bai et al. (4) showed that overweight and obesity (BMI = 25.0–39.9 kg/m2) were associated with reduced mortality in patients with sepsis or septic shock. A recent multicenter cohort study also confirmed that obese patients had better in-hospital survival and better functional outcomes at discharge compared to non-obese patients (5). In Asian countries, fewer people are overweight and obese than in Western countries. In general, Asians have a lower BMI than Europeans (7). Therefore, it is necessary to study the effects of low BMI on patients with sepsis, especially in Asian countries. However, the relationship between underweight and the prognosis of sepsis remains controversial. A retrospective study by Li et al. (8) found that underweight significantly increased the risk of death in patients with sepsis. However, Sakr et al. (9) showed no significant difference in in-hospital mortality between patients with sepsis in the low BMI and normal BMI groups.
To overcome the current dilemma of conflicting results, we conducted a comprehensive review of published evidence and meta-analysis to determine whether being underweight increases the risk of death in patients with sepsis. These results may have important clinical implications for understanding the prognosis of patients with underweight sepsis and improving clinical decision making.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy
This study was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The study was registered in the PROSPERO database.
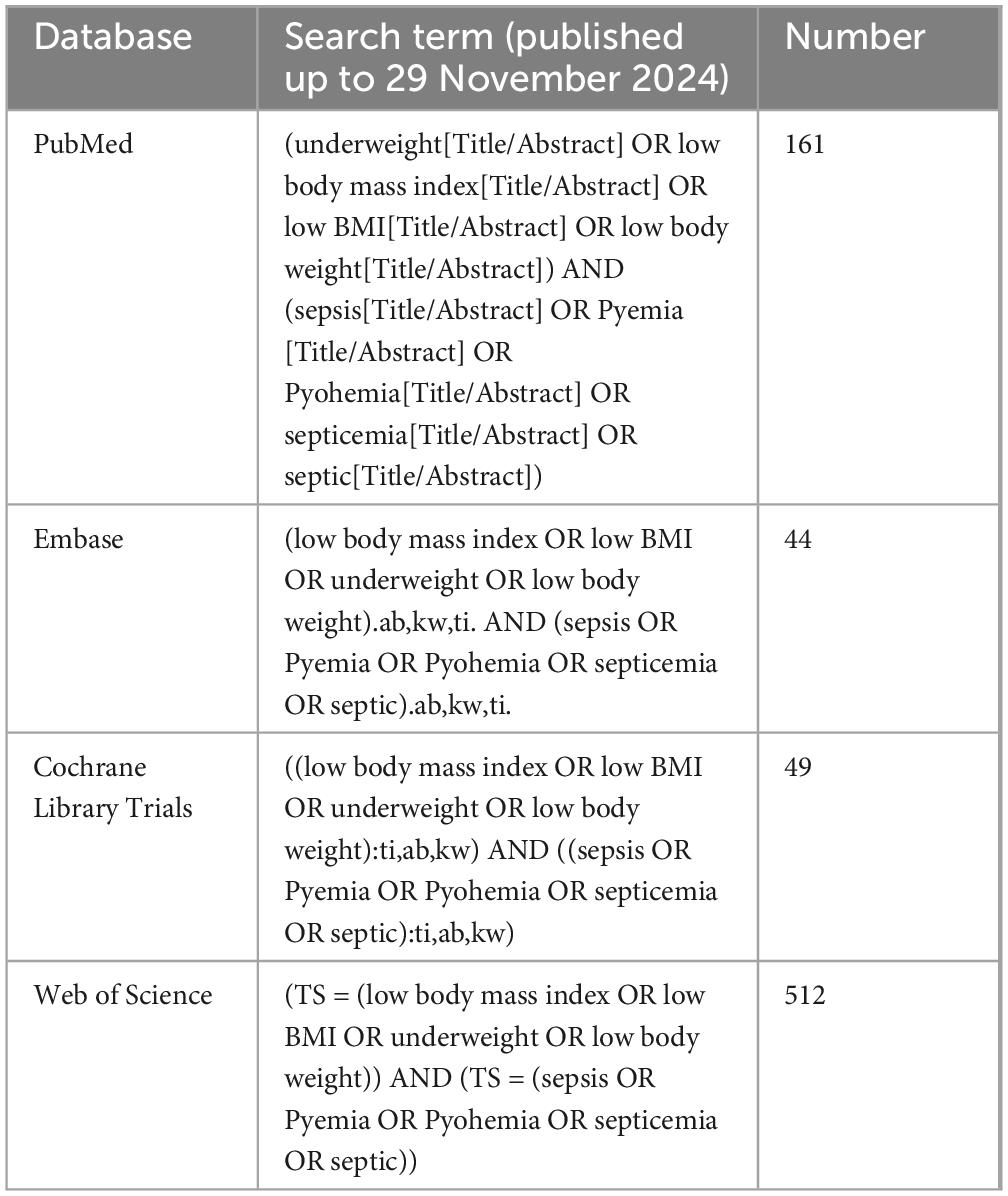
Two investigators (Jiaan Chen and Fan Zhang) independently performed a systematic literature review using the Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases to identify studies published before 29 November 2024. The detailed search strategy is presented in Table 1. In addition, we checked the reference lists of the eligible articles to identify other potential studies. No language restrictions were applied during the search process.
2.2 Study selection
Studies meeting the following criteria were analyzed: (1) Patient: patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) and treated for sepsis, severe sepsis, or septic shock; (2) Intervention: patients who are underweight (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2); (3) Comparison: patients of normal weight (BMI = 18.5–24.9 kg/m2) (according to the World Health Organization definition) (10); (4) Outcomes: the primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Secondary outcomes included 28-day mortality, 90-day mortality, 1-year mortality, ICU length of stay and hospital stay; and (5) Study type: cohort studies and case-control studies.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: case reports, duplicate literature, letters, studies available only as abstracts, unpublished manuscripts, and animal studies.
2.3 Data extraction
Two investigators (Jiaan Chen and Fan Zhang) independently extracted data, which included author name, study design, country, year of publication, period of study, study population (age, sample size, and diagnosis), and outcome information (in-hospital mortality, 28-day mortality, 90-day mortality, 1-year mortality, ICU length of stay, and hospital stay). When data of interest were unavailable, the corresponding author was contacted to obtain the missing data.
2.4 Quality assessment
The quality assessment was conducted independently by two authors (Jiaan Chen and Fan Zhang) using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), which assigns a score on a 9-point scale. A score of ≥7 indicates high quality, and scores of 5–6 indicate moderate quality. Any discrepancies were resolved by a third author (Guangjun Jin).
2.5 Statistical analysis
The meta-analysis was performed using the Review Manager software (version 5.3). Odds ratios (ORs) with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for categorical outcome variables and mean difference (MD) for continuous outcome variables. Heterogeneity among studies was assessed by using the I-squared (I2) statistic. A random-effects model was employed if I2 > 50%; otherwise, a fixed-effects model would be used (11). To explore the robustness of the outcomes, we adopted the one-study exclusion method to evaluate the impact of each study on the total effect size. The subgroup analysis was conducted based on age and the region where the study was conducted. Publication bias was assessed using Egger’s test and funnel plot when the number of studies was greater than 10. Statistical significance was established at P-value of less than 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 Literature retrieval
Our literature search identified 767 records, of which 179 were duplicates. After reviewing titles and abstracts, 553 studies were excluded, and the full texts of the remaining 35 studies were evaluated. Finally, 23 studies (1–3, 7–9, 12–28) were included in our meta-analysis (Figure 1).
3.2 Study characteristics and quality assessment
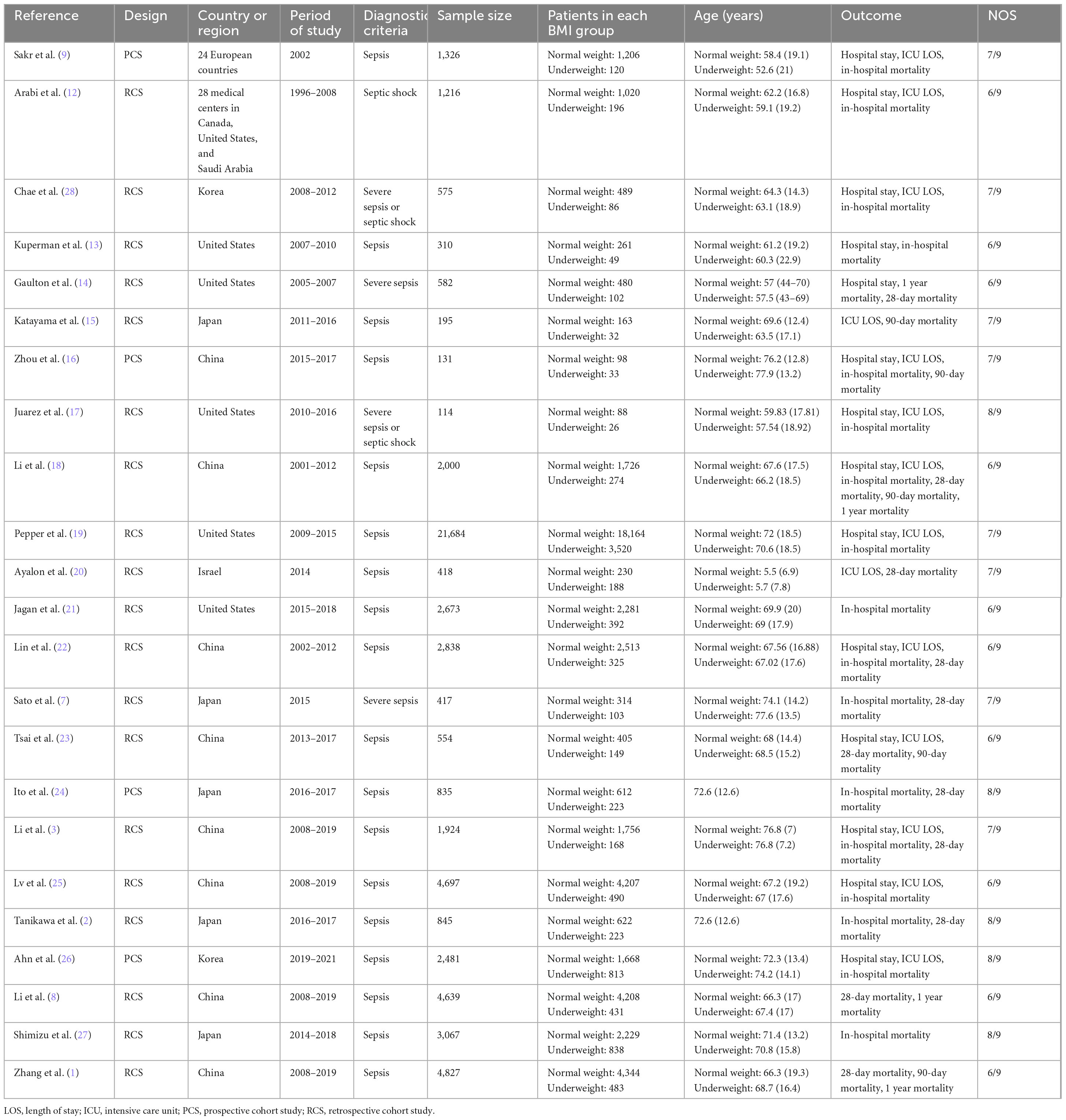
The detailed characteristics of the 23 studies (1–3, 7–9, 12–28) were described in Table 2. The studies were published between 2008 and 2024 and included 58,348 patients (normal weight group: 49,084 patients; underweight group: 9,264 patients). The sample size ranged from 114 to 21,684. Of the 23 studies we included, 4 were prospective cohort studies and 19 were retrospective studies. The included patients were mainly from the United States, Korea, China, Japan, and Israel. All studies were considered of moderate to high quality, achieving a score of ≥5 based on the NOS.
3.3 Meta-analysis
3.3.1 In-hospital mortality
Seventeen studies (2, 3, 7, 9, 12, 13, 16–19, 21, 22, 24–28) reported data on in-hospital mortality. The combined results of the 17 studies showed that in-hospital mortality was significantly higher in the underweight group than in the normal weight group (OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.21, 1.35; heterogeneity: I2 = 21%, P = 0.21) (Figure 2 and Table 3).
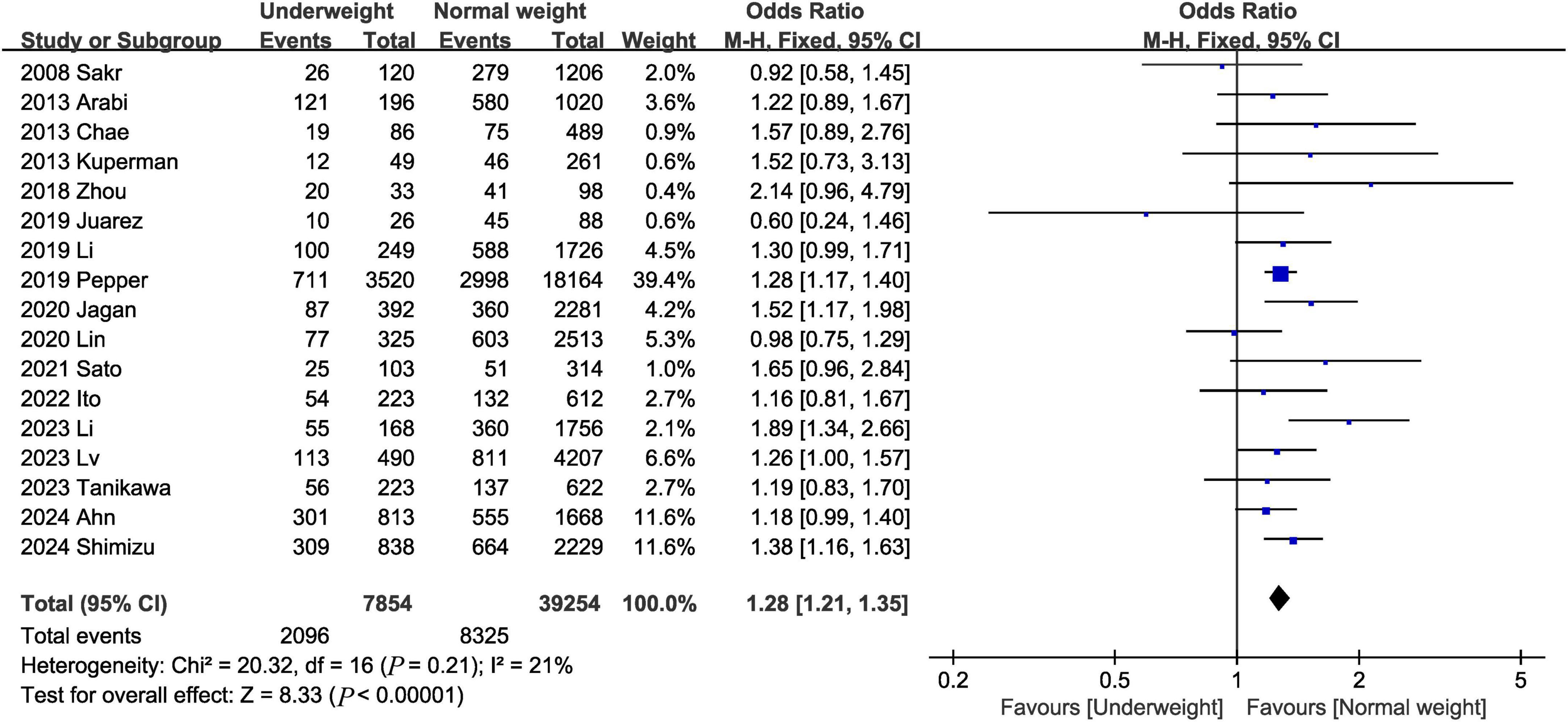
Figure 2. Meta-analysis of in-hospital mortality between underweight and normal weight septic patients.
3.3.2 28-Day mortality
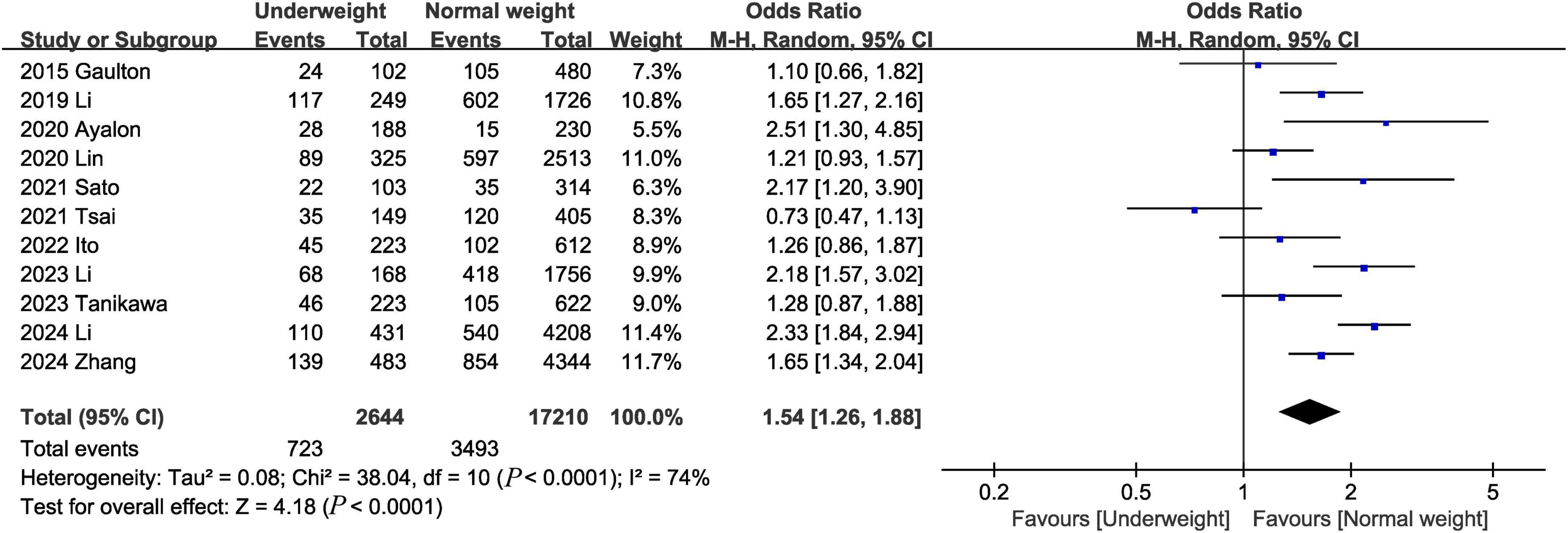
Eleven studies (1–3, 7, 8, 14, 18, 20, 22–24) assessed 28-day mortality. The pooled results showed that being underweight was associated with an increased risk of the 28-day mortality (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.26, 1.88; heterogeneity: I2 = 74%, P < 0.0001) (Figure 3).
3.3.3 90-Day mortality
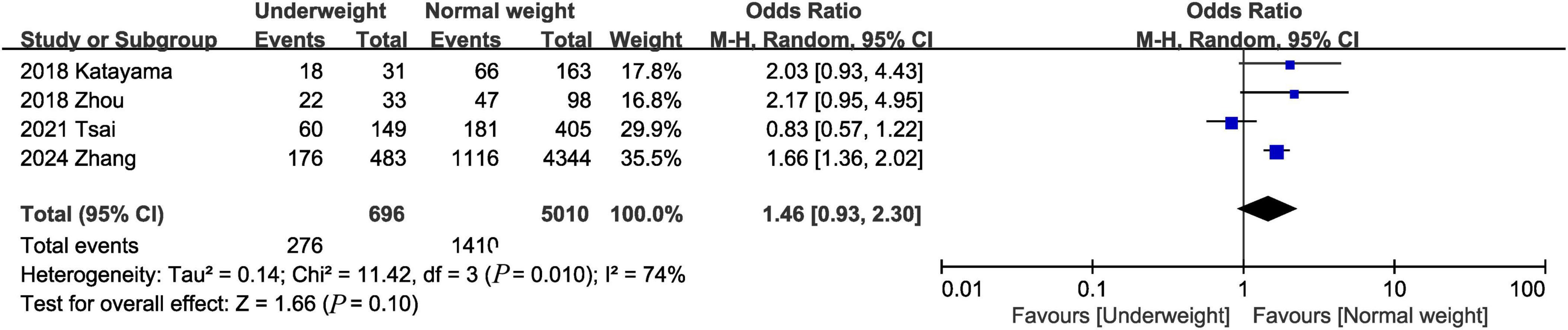
Data from 4 studies (1, 15, 16, 23) of 5,706 patients did not reveal any difference between the underweight and normal weight groups (OR, 1.46; 95% CI, 0.93, 2.30; heterogeneity: I2 = 74%, P = 0.010) (Figure 4) in terms of 90-day mortality.
3.3.4 1-Year mortality
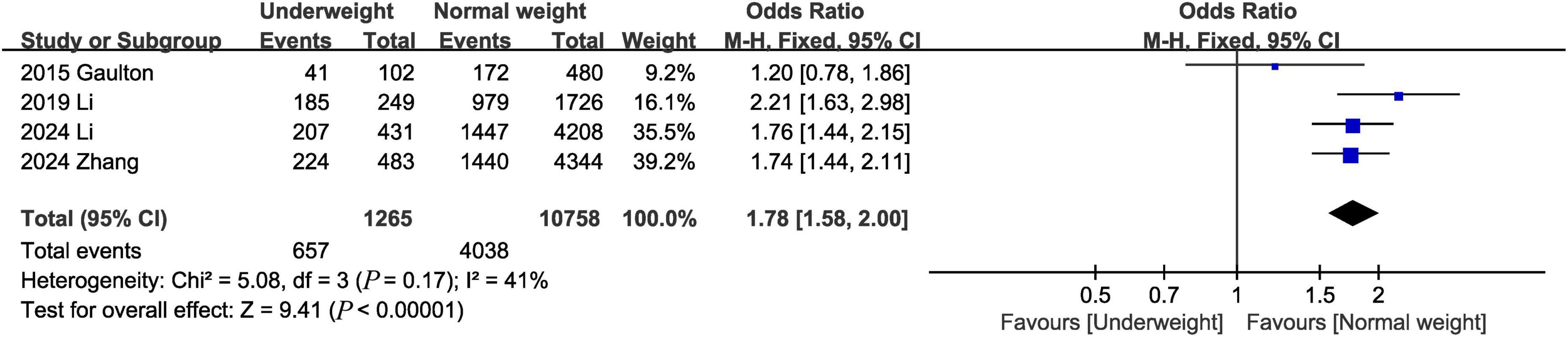
One-year mortality was evaluated in 4 studies (1, 8, 14, 18), and the pooled results showed that the 1-year mortality was higher in the underweight group than in the normal weight group (OR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.58, 2.00; P < 0.00001) (Figure 5).
3.3.5 ICU length of stay
Thirteen studies (3, 9, 12, 16–20, 22, 23, 25, 26, 28) provided information on ICU length of stay. The combined results showed that the underweight group had similar ICU length of stay as the normal weight group (MD, −0.06 days; 95% CI, −0.46, 0.33, P = 0.76; I2 = 75%) (Figure 6).
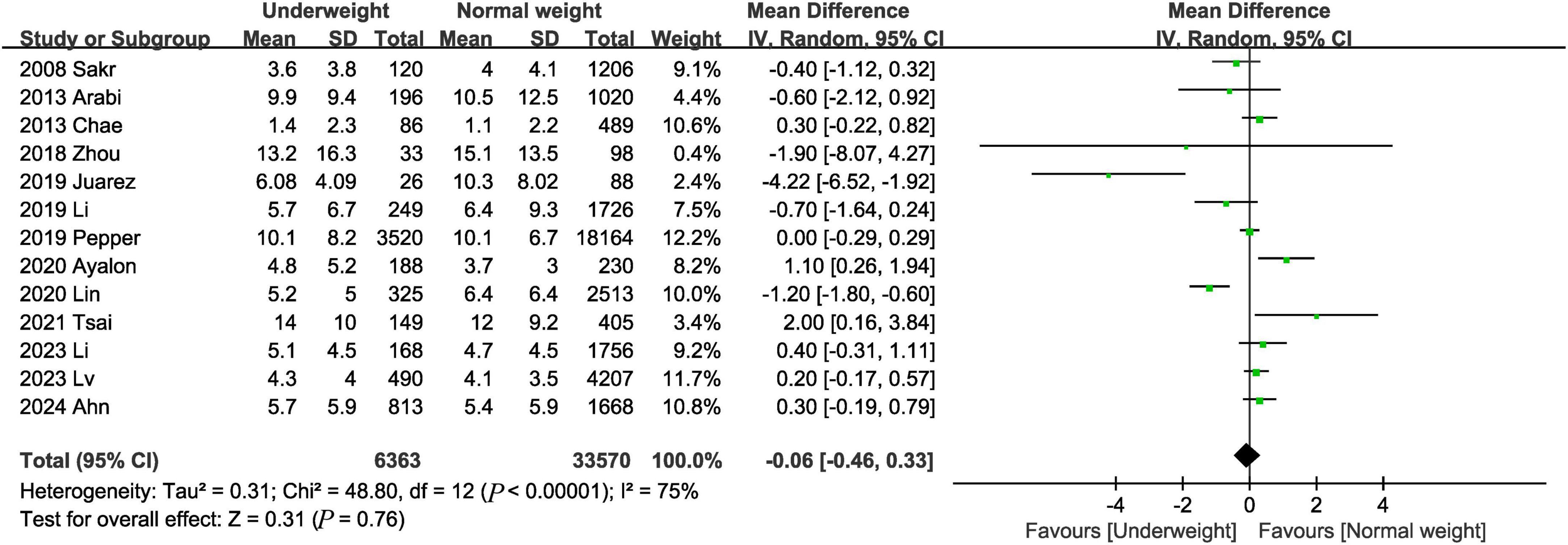
Figure 6. Meta-analysis of ICU length of stay between underweight and normal weight septic patients.
3.3.6 Hospital stay
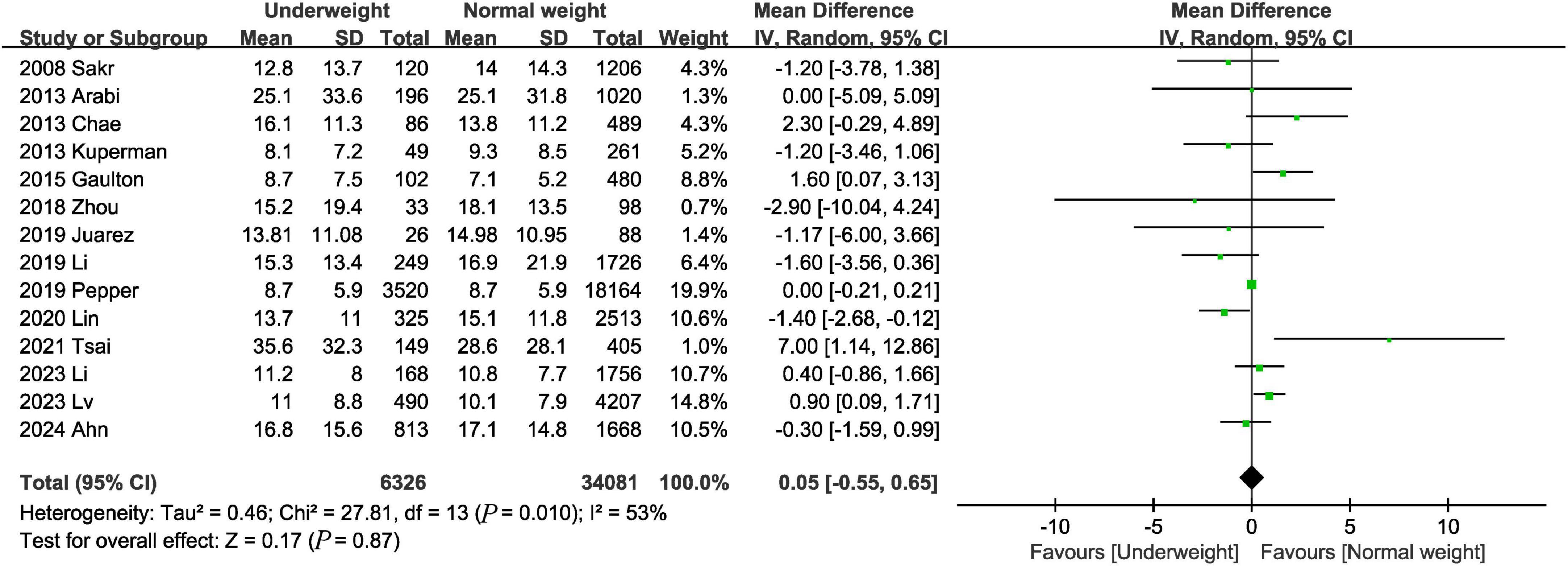
The hospital stay was reported in 14 trials (3, 9, 12–14, 16–19, 22, 23, 25, 26, 28). The combined results showed that there was no significant difference in length of hospital stay between the underweight group and the normal weight group (MD, 0.05 days; 95% CI, −0.55, 0.65, P = 0.87) (Figure 7).
3.4 Subgroup analysis
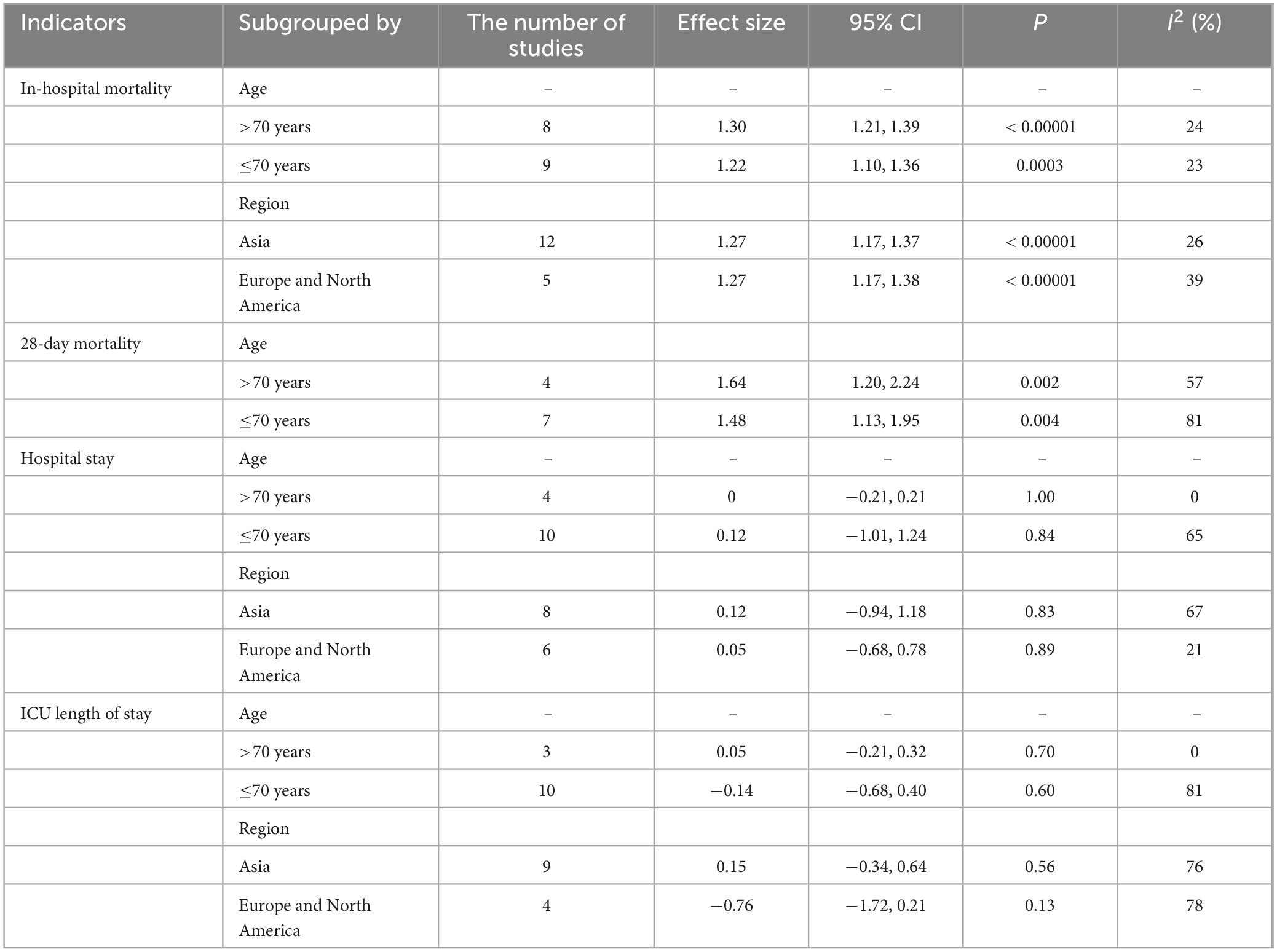
The subgroup analyses were performed based on age and the region where the study was conducted (Table 4). Underweight was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital mortality and 28-day mortality in both the age >70 and ≤70 subgroups. In addition, ICU length of stay and length of stay were not significantly different between the underweight and normal weight groups. When subgroups were analyzed by region, underweight significantly increased in-hospital mortality in both Asian subgroups, European and North American subgroups.
3.5 Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
According to the Egger tests and funnel plots, none of the outcomes (in-hospital mortality, 28-day mortality, ICU length of stay, and hospital stay) demonstrated significant publication bias (Figure 8). Sensitivity analysis showed that no single study affected the overall effect size of the in-hospital mortality, 28-day mortality, 90-day mortality, 1-year mortality, ICU length of stay, and hospital stay.
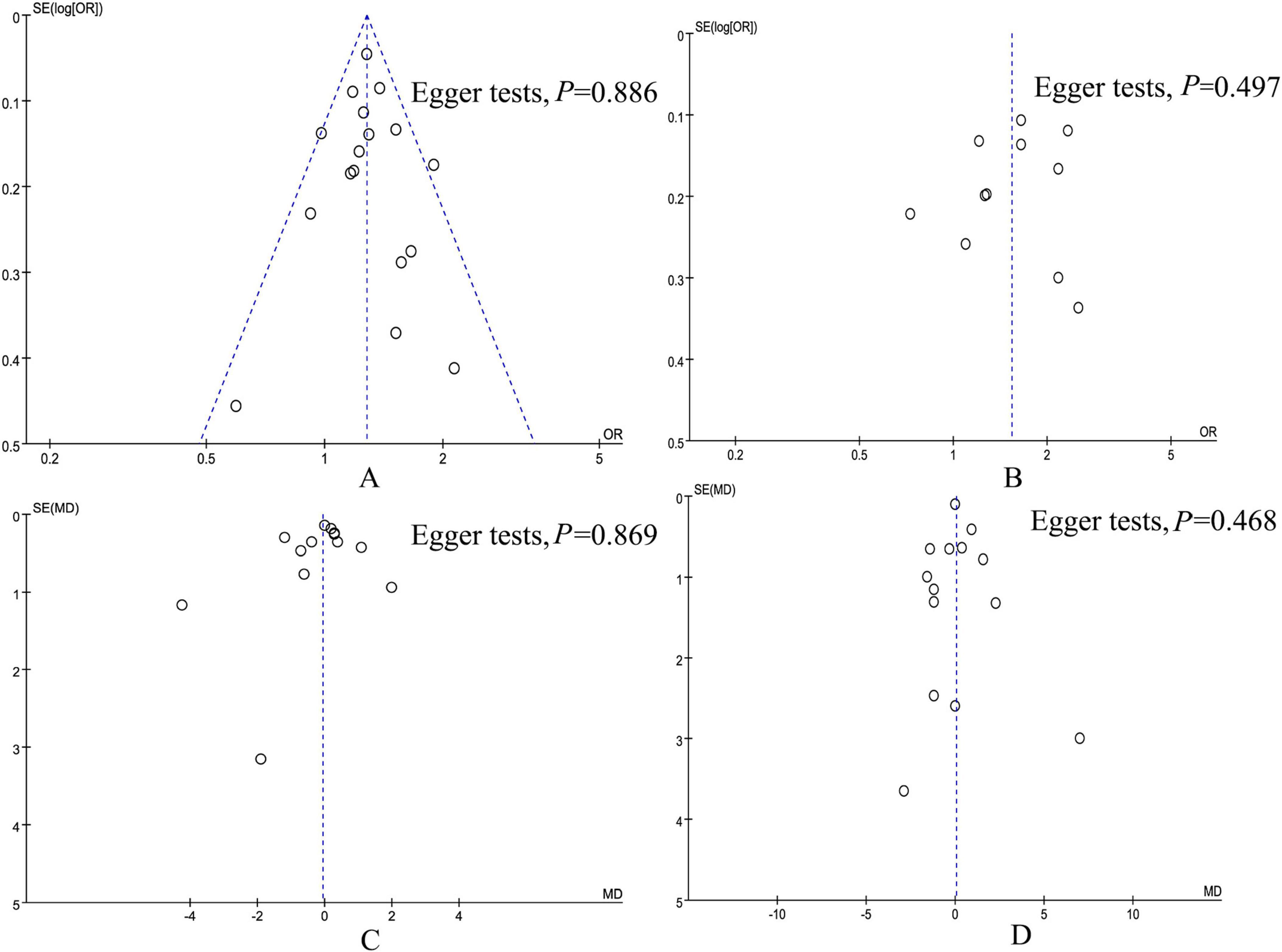
Figure 8. Funnel plot of underweight versus normal weight. (A) In-hospital mortality, (B) 28-day mortality, (C) ICU length of stay, and (D) hospital stay.
4 Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest meta-analysis to evaluate the association between underweight and mortality in patients with sepsis. Data from 23 studies with 58,348 patients showed that while being underweight did not increase length of hospital stay or ICU stay, being underweight was associated with an increased risk of in-hospital mortality, 28-day mortality, and 1-year mortality. Our study has important clinical value as we provide evidence through meta-analysis that underweight is a risk factor for mortality, which may help clinicians detect and intervene early in underweight patients to reduce mortality.
Several previous studies have reported that underweight is associated with poorer clinical outcomes for a variety of diseases (29–31). A retrospective study (29) of 21,019 participants showed that underweight subjects (BMI < 18.5 kg/m2) were 1.6 times more likely to be hospitalized within a year than those with a BMI > 18.5 kg/m2. In addition, emergency room visits and mortality rates are increased in underweight patients. A meta-analysis by Zhao et al. (30) showed that underweight significantly increased postoperative complications in patients with gastric cancer. In addition, several studies have reported that underweight is associated with increased mortality (31, 32). Wier et al. (33) found that underweight orthopedic surgery patients had 1.2 times and 1.5 times higher rates of in-hospital complications and in-hospital mortality than normal-weight patients, respectively. Studies by Haga et al. (32) have shown that being underweight is a risk factor for death in psychopaths. In 2016, Pepper et al. (34) conducted a meta-analysis of data from three studies and found that being underweight increased the risk of death in patients with sepsis, but the difference was not significant (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.79, 1.95). This may be due to the limited number of studies included. A subsequent updated meta-analysis by Bai et al. (4) included more data (12 studies) and showed that underweight was associated with increased mortality (OR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.11, 1.54). The association between underweight and mortality was also confirmed by our study. Our results suggest that being underweight not only increases the risk of in-hospital mortality, but also increases the risk of 28-day mortality and 1-year mortality. Similarly, several retrospective studies (35, 36) have shown that underweight is associated with an increased risk of death in patients with sepsis. Danninger et al. (35) showed that underweight significantly increased ICU mortality. Lebovitz et al. (36) found that patients with low BMI (BMI ≤ 19 kg/m2) had higher mortality and longer hospital stays compared to patients with sepsis with higher BMI. The mechanism by which underweight is associated with an increased risk of death is unclear and may be related to the following factors. On the one hand, fat tissue has an immune function, and underweight patients have less fat tissue. Therefore, underweight sepsis patients may have weakened immunity (36). On the other hand, patients with sepsis have increased catabolism. In early sepsis, glycolysis is the primary source of energy. As the disease progresses, fat and protein become the main sources of energy. Underweight patients have poor energy reserves and are unable to withstand the effects of catabolism (1, 3, 37). Nutritional therapy is beneficial to the rehabilitation and functional state recovery of patients, and is an important strategy that affects the prognosis of patients. A meta-analysis of 25 studies showed that immunonutritional support reduced mortality in patients with sepsis and reduced length of hospital stay compared to controls (38). In addition, early enteral nutritional support in critically ill patients may provide similar protection as high BMI (36). Given that underweight is associated with a poorer prognosis in patients with sepsis, nutritional support for such patients is warranted to improve outcomes in patients with sepsis.
Some studies suggest that the association between underweight and mortality may vary by age (25, 31, 39). Age is the biggest risk factor for hospitalization (29). Aging results in a redistribution of body composition, including weight loss and decreased bone density (8). Ting et al. (40) found that patients’ risk of malnutrition increased with age. In addition, muscle mass tends to decrease with age (41). As a result, there is a higher proportion of underweight in older patients (31). Previous studies have suggested that weight loss associated with muscle tissue loss (sarcopenia) may be associated with worsening prognosis in sepsis (34). Myostatin is a negative regulator of muscle mass and has been reported to be upregulated in diseases associated with muscle atrophy (42). Kobayashi et al. (43) found that reducing myostatin levels in mice reduced sepsis induced liver dysfunction, acute kidney injury, and neutrophil infiltration into the liver and kidney. Therefore, the effect of underweight on mortality may be influenced by age, which is consistent with our results. The results of our subgroup analysis suggest that the OR values of underweight and mortality are higher in the older subgroup than in the younger subgroup. Similarly, Zhang et al. (1) found that the protective effect of obesity on patients with sepsis becomes more pronounced with age. Given the rising prevalence of sepsis in the elderly population and the potential impact of underweight on patient outcomes, clinicians need to pay more attention to the management of this vulnerable population.
Underweight is more common in Asian populations. Considering that the distribution of BMI in different regions may vary, we conducted a subgroup analysis based on region. The results of subgroup analyses showed that underweight was associated with increased mortality in Asia, Europe, and the Americas. This suggests that the association between underweight and mortality can be generalized to other parts of the world.
Our research has several strengths. First, we conducted a comprehensive search, which helped to enhance the reliability of the study results. In addition, we strictly defined underweight and normal weight according to WHO standards, which helps to ensure the homogeneity between studies and enhance the reliability of this study. Finally, we further confirmed the robustness of the results of this study by sensitivity analysis.
This study has the following limitations. First, most of the studies we included were retrospective studies and were affected by the inherent limitations of retrospective studies. Secondly, the heterogeneity of some outcomes (28-day mortality, ICU length of stay, and hospital stay) was high, and although we performed subgroup analysis by age and region, the source of heterogeneity was still not found. Finally, some results (90-day mortality and 1-year mortality) are based on data pooled from a small number of studies, and more studies are needed to validate these results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this meta-analysis, based on currently available and updated evidence, suggests that underweight is associated with increased mortality in patients with sepsis. Considering the impact of underweight on the prognosis of sepsis, it is necessary to design and implement appropriate nutritional support programs to improve the prognosis of underweight patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XP: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by Zhejiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project (2023ZL448).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; I2, I-squared; ICU, intensive care unit; MD, mean difference; NOS, Newcastle-Ottawa Scale; OR, odds ratios; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
References
1. Zhang T, Li X, Meng Z, Fang W, Lian G, Ma W, et al. Obesity and septic patient outcomes: Shaping the puzzle through age and sex perspectives. Clin Nutr. (2024) 43(4):1013–20. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2024.03.009
2. Tanikawa A, Kudo D, Ohbe H, Kushimoto S. Association of body mass index and hypoglycemia with mortality rates among sepsis patients: A retrospective sub-analysis of the FORECAST study. Acute Med Surg. (2023) 10(1):e00864. doi: 10.1002/ams2.864
3. Li N, Tian L, Zhou Q, Miao Y, Ma H. The association between body mass index and mortality in septic older adults. Geriatr Nurs. (2023) 54:199–204. doi: 10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.10.003
4. Bai L, Huang J, Wang D, Zhu D, Zhao Q, Li T, et al. Association of body mass index with mortality of sepsis or septic shock: An updated meta-analysis. J Intensive Care. (2023) 11(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40560-023-00677-0
5. Yeo H, Kim T, Jang J, Jeon K, Oh D, Park M, et al. Obesity paradox and functional outcomes in sepsis: A multicenter prospective study. Crit Care Med. (2023) 51(6):742–52. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000005801
6. Yeo H, Kim H, So M, Park J, Kim D, Cho W. Obesity paradox of sepsis in long-term outcome: The differential effect of body composition. Intensive Crit Care Nurs. (2024) 87:103893. doi: 10.1016/j.iccn.2024.103893
7. Sato T, Kudo D, Kushimoto S, Hasegawa M, Ito F, Yamanouchi S, et al. Associations between low body mass index and mortality in patients with sepsis: A retrospective analysis of a cohort study in Japan. PLoS One. (2021) 16(6):e0252955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252955
8. Li C, Huang H, Xia Q, Zhang L. Correlation between body mass index and gender-specific 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1462637. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1462637
9. Sakr Y, Madl C, Filipescu D, Moreno R, Groeneveld J, Artigas A, et al. Obesity is associated with increased morbidity but not mortality in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. (2008) 34(11):1999–2009. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1243-0
10. Yang S, Ni H, Zhang A, Zhang J, Liang H, Li X, et al. Body mass index is a risk factor for postoperative morbidity after laparoscopic hepatectomy of hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2024) 150(10):445. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05979-w
11. Higgins J, Thompson S. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21(11):1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
12. Arabi Y, Dara S, Tamim H, Rishu A, Bouchama A, Khedr M, et al. Clinical characteristics, sepsis interventions and outcomes in the obese patients with septic shock: An international multicenter cohort study. Crit Care (London, England). (2013) 17(2):R72. doi: 10.1186/cc12680
13. Kuperman E, Showalter J, Lehman E, Leib A, Kraschnewski J. The impact of obesity on sepsis mortality: A retrospective review. BMC Infect Dis. (2013) 13:377. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-377
14. Gaulton T, Marshall MacNabb C, Mikkelsen ME, Agarwal AK, Cham Sante S, Shah CV, et al. A retrospective cohort study examining the association between body mass index and mortality in severe sepsis. Intern Emerg Med. (2015) 10(4):471–9. doi: 10.1007/s11739-015-1200-1
15. Katayama S, Koyama K, Goto Y, Koinuma T, Tonai K, Shima J, et al. Body weight definitions for evaluating a urinary diagnosis of acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis. BMC Nephrol. (2018) 19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0895-4
16. Zhou Q, Wang M, Li S, Zhang J, Ma Q, Ding Y, et al. Impact of body mass index on survival of medical patients with sepsis: A prospective cohort study in a university hospital in China. BMJ Open. (2018) 8(9):e021979. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021979
17. Juarez E, Edriss H, Lear M, Sanchez A, Yang S, Nugent K. The association between body mass index and outcomes in patient with sepsis and acute respiratory failure. Southwest Respiratory Crit Care Chronicles. (2019) 7(31):13–23.
18. Li S, Hu X, Xu J, Huang F, Guo Z, Tong L, et al. Increased body mass index linked to greater short- and long-term survival in sepsis patients: A retrospective analysis of a large clinical database. Int J Infect Dis. (2019) 87:109–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.07.018
19. Pepper D, Demirkale C, Sun J, Rhee C, Fram D, Eichacker P, et al. Does obesity protect against death in sepsis? A retrospective cohort study of 55,038 adult patients. Crit Care Med. (2019) 47(5):643–50. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000003692
20. Ayalon I, Woo J, Basu R, Kaddourah A, Goldstein S, Kaplan J. Weight as a risk factor for mortality in critically Ill patients. Pediatrics (2020) 146(2):e20200703. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2829
21. Jagan N, Morrow L, Walters R, Plambeck R, Wallen T, Patel T, et al. Sepsis and the obesity paradox: Size matters in more than one way. Crit Care Med. (2020) 48(9):e776–82. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000004459
22. Lin S, Ge S, He W, Zeng M. Association between body mass index and short-term clinical outcomes in critically Ill patients with sepsis: A real-world study. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:5781913. doi: 10.1155/2020/5781913
23. Tsai Y, Lin C, Chen Y, Chang Y, Hung K, Chang Y, et al. Impact of Body Mass Index on the Survival of Patients with Sepsis with Different Modified NUTRIC Scores. Nutrients. (2021) 13(6):1873. doi: 10.3390/nu13061873
24. Ito Y, Kudo D, Kushimoto S. Association between low body temperature on admission and in-hospital mortality according to body mass index categories of patients with sepsis. Medicine. (2022) 101(44):e31657. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000031657
25. Lv X, Yue Y, Jia B, Weng Y, Lu Y, Yang Z. Bilirubin influences the predictive effect of body mass index on hospital mortality in critically Ill patients. Heliyon. (2024) 10(11):e32089. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32089
26. Ahn Y, Yoon S, Lee J, Lee S, Oh D, Lee S, et al. Early sepsis-associated acute kidney injury and obesity. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7(2):e2354923. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54923
27. Shimizu R, Nakanishi N, Ishihara M, Oto J, Kotani J. Utility of lean body mass equations and body mass index for predicting outcomes in critically Ill adults with sepsis: A retrospective study. Diseases (Basel, Switzerland). (2024) 12(2):30. doi: 10.3390/diseases12020030
28. Chae M, Choi D, Shin T, Jeon K, Suh G, Sim M, et al. Body mass index and outcomes in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Acute Crit Care. (2013) 28(4):266–71.
29. Takahashi P, Sauver J, Olson T, Huber J, Cha S, Ebbert J. Association between underweight and hospitalization, emergency room visits, and mortality among patients in community medical homes. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. (2013) 6:1–6. doi: 10.2147/rmhp.S39976
30. Zhao B, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zou S, Luo R, Xu H, et al. The impact of preoperative underweight status on postoperative complication and survival outcome of gastric cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Cancer. (2018) 70(8):1254–63. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2018.1559937
31. Roh L, Braun J, Chiolero A, Bopp M, Rohrmann S, Faeh D. Mortality risk associated with underweight: A census-linked cohort of 31,578 individuals with up to 32 years of follow-up. BMC Public Health. (2014) 14:371. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-371
32. Haga T, Ito K, Ono M, Maruyama J, Iguchi M, Suzuki H, et al. Underweight and hypoalbuminemia as risk indicators for mortality among psychiatric patients with medical comorbidities. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. (2017) 71(12):807–12. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12553
33. Wier J, Firoozabadi R, Duong A, Patterson J. Underweight patients experience higher inpatient complication and mortality rates following acetabular fracture. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. (2024) 34(7):3543–51. doi: 10.1007/s00590-023-03739-z
34. Pepper D, Sun J, Welsh J, Cui X, Suffredini A, Eichacker P. Increased body mass index and adjusted mortality in ICU patients with sepsis or septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. (2016) 20(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1360-z
35. Danninger T, Rezar R, Mamandipoor B, Dankl D, Koköfer A, Jung C, et al. Underweight but not overweight is associated with excess mortality in septic ICU patients. Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2022) 134(3–4):139–47. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01912-0
36. Lebovitz S, Rozen G, Abu Ghosh Z, Korem M, Elinav H, Zayyad H, et al. The relationship between body mass index and in-hospital mortality in bacteremic sepsis. J Clin Med. (2023) 12(11):3848. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113848
37. Wang S, Liu X, Chen Q, Liu C, Huang C, Fang X. The role of increased body mass index in outcomes of sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. (2017) 17(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0405-4
38. Wang H, Su S, Wang C, Hu J, Dan W, Peng X. Effects of fish oil-containing nutrition supplementation in adult sepsis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Burns Trauma (2022) 10:tkac012. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkac012
39. Lee J, Kim H, Kim C, Park K, Ahn S, Kang D, et al. Underweight and mortality. Public Health Nutr. (2016) 19(10):1751–6. doi: 10.1017/s136898001500302x
40. Ting T, Lo T, Lo W, Ding Q, Yuk D, Hui E, et al. Inadequate energy and protein intake, underweight and malnutrition are associated with in-hospital mortality among COVID-19 rehabilitation patients during the omicron outbreak in Hong Kong. Aging Med (Milton). (2022) 5(3):204–10. doi: 10.1002/agm2.12220
41. Laukkanen J, Kunutsor S, Hernesniemi J, Immonen J, Eskola M, Zaccardi F, et al. Underweight and obesity are related to higher mortality in patients undergoing coronary angiography: The KARDIO invasive cardiology register study. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. (2022) 100(7):1242–51. doi: 10.1002/ccd.30463
42. Lee S, Gharbi A, Shin J, Jung I, Park Y. Myostatin inhibitor YK11 as a preventative health supplement for bacterial sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 543:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.030
Keywords: 1-year mortality, in-hospital mortality, meta-analysis, sepsis, underweight
Citation: Chen J, Zhang F, Liang L, Pan X, Zhang J and Jin G (2025) Impact of underweight status on mortality in sepsis patients: a meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1549709. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1549709
Received: 21 December 2024; Accepted: 21 January 2025;
Published: 06 February 2025.
Edited by:
Georgia Damoraki, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, GreeceReviewed by:
Marcos Edgar Herkenhoff, University of São Paulo, BrazilSpyros Foutadakis, Biomedical Research Foundation of the Academy of Athens (BRFAA), Greece
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhang, Liang, Pan, Zhang and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiancheng Zhang, emhhbmdqaWFuY2hlbjIwMTVAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Guangjun Jin, amluZ3VhbmdqdW4xOTczQDE2My5jb20=
 Jiaan Chen1
Jiaan Chen1 Guangjun Jin
Guangjun Jin