
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Med., 01 April 2025
Sec. Hematology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1544025
This article is part of the Research TopicInfectious Diseases and Hematology: Diagnosis and Management - Volume IIView all 11 articles
 Zhi Guo1,2*†
Zhi Guo1,2*† Jie Zhu2†
Jie Zhu2† Jun Wang3
Jun Wang3 Liang Wang4
Liang Wang4 Feifei Tang5
Feifei Tang5 Huiqiang Huang6
Huiqiang Huang6 Zhongjun Xia7
Zhongjun Xia7 Liqiong Liu1
Liqiong Liu1 Danyu Wang1
Danyu Wang1 Nan Zhong1
Nan Zhong1 Huanhuan Zhou1
Huanhuan Zhou1 Zhaogui Zhou1
Zhaogui Zhou1 Wei Dai1
Wei Dai1 Xiaojun Xu8
Xiaojun Xu8 Hao Zhou9
Hao Zhou9 Lijuan Deng10
Lijuan Deng10 Jingye Meng11
Jingye Meng11 Zhiqiang Sun12
Zhiqiang Sun12 Liang Shao13
Liang Shao13 Yu J. Cao14
Yu J. Cao14 Yansong Liu15
Yansong Liu15 Rong Qu16
Rong Qu16 Guowei Li17
Guowei Li17 Peng Chen18
Peng Chen18 Hongyan Zhang19
Hongyan Zhang19 Jing Liang20
Jing Liang20 Yuhua Li21,22
Yuhua Li21,22 Jiajun Liu23
Jiajun Liu23 Zishan Xu24
Zishan Xu24 Soong Sung Inda25
Soong Sung Inda25 Xiaochen Xiang2
Xiaochen Xiang2 Qingming Wu2
Qingming Wu2 Qiang Wang2* on behalf of China Collaborative Group on Research and Transformation of Infection Immunity and Microecology
Qiang Wang2* on behalf of China Collaborative Group on Research and Transformation of Infection Immunity and MicroecologyIntravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), first developed for the treatment of patients with antibody deficiencies, is now widely used in clinical practice, especially in hematological and immune system diseases, and its application in hematological oncology chemotherapy, cellular immunotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is becoming more and more common. The Chinese Collaborative Group for Infection Immunology and Microecology Research Translation Collaborative Group organized relevant experts to discuss and propose the “Chinese expert consensus on the application of intravenous immunoglobulin in hematological diseases,” which was formulated based on the progress of research on the application of IVIG in blood diseases, and provides a basis for the standardization of the use of IVIG in hematologic disorders.
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a blood product obtained from the plasma of healthy donors, consisting primarily of polyclonal immunoglobulin G (IgG). It has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, and was first introduced in the early 1980s for the treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency (1). At present, IVIG has been widely used in clinic, such as the treatment of immune system diseases (including systemic lupus erythematosus, Kawasaki disease, primary immunodeficiency, etc.), hematologic disorders (including immune thrombocytopenia, autoimmune hemolytic anemias, hemolytic disease of the newborn, etc.) and neurological disease (including Guillain-Barre syndrome, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, myasthenia gravis, polymyositis, multiple sclerosis and autoimmune encephalitis) (2–5). Its application in chemotherapy, targeted therapy, cellular immunotherapy and HSCT for malignant hematological tumors is also becoming more prevalent (6–8). In order to further improve the standardized application of IVIG in hematological diseases, the Chinese Collaborative Group for Infection Immunology and Microecology Research Translation Collaborative Group has organized a multi-disciplinary team (MDT) steering committee composed of experts from hematology (including HSCT), infectious diseases, critical care medicine, pharmacy and other specialties to discuss the issue, and to synthesize the current status of related research at home and abroad to formulate expert recommendations for the standardized application of IVIG in hematological diseases. The expert recommendation on the application of IVIG in hematological diseases was formulated based on the progress of domestic and international research on the application of IVIG in hematological diseases, which provides a basis for the standardization of the use of IVIG in hematological diseases. This expert recommendation uses the GRADE/DECISION Evidence to Decision Making Framework to determine the direction and strength of the recommendation, with the GRADE methodology assessing the quality of evidence rated as high (A), moderate (B), low (C), or very low (D). Based on the GRADE evidence the MDT panel rated the strength of the recommendation as strong and weak recommendation (for or against interest intervention), or not recommended if the overall quality of the evidence in the key endpoints was very low, and ultimately the full MDT experts voted and reached consensus. Strength of evidence recommendations and level of evidence criteria in treatment guidelines (Table 1).
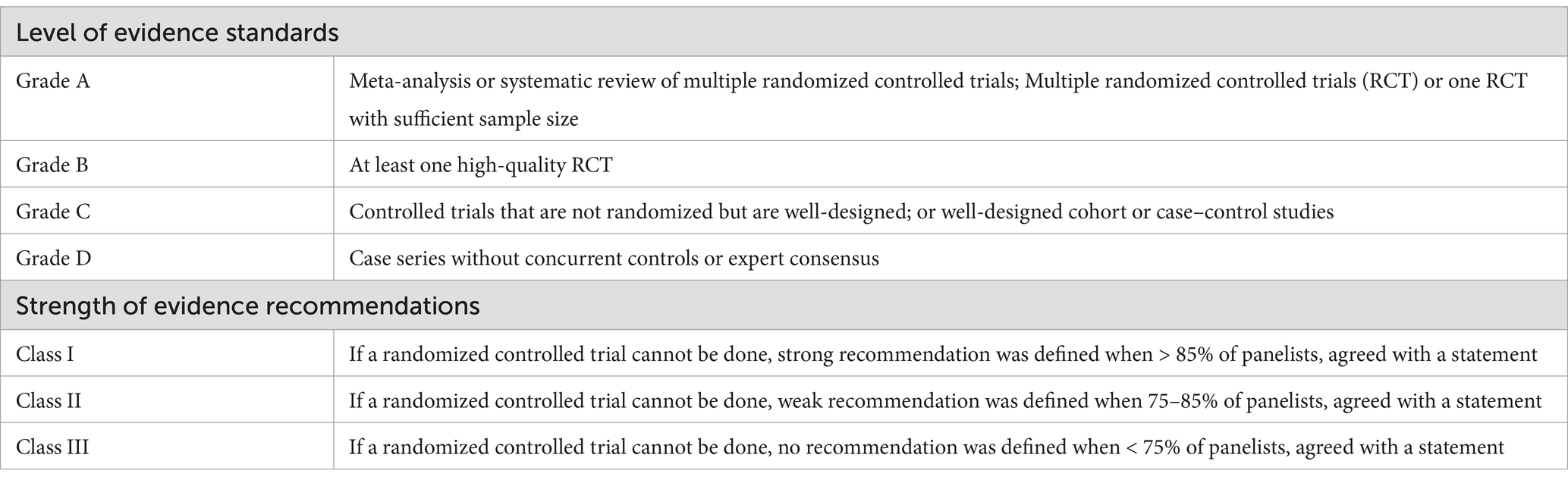
Table 1. Strength of evidence recommendations and level of evidence criteria in treatment guidelines.
IVIG is used as a therapeutic substitution in primary and secondary immunodeficiencies as well as an immunomodulatory agent. IVIG has many immunomodulatory effects, however the exact mechanism for of this is not completely clear. At present, the mechanisms of IVIG include: (1) the Fc fragment of IgG specifically binds to some immune effector cells, closes the monocyte macrophage Fc receptor, and inhibits antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. (2) IVIG plays an immunosubstitutive role by binding to antigens in the F(ab)2 fraction. A variety of specific antibodies in IVIG can either directly seal off the site of action of the organism’s antigens, resulting in a decrease in the titer of pathogenic antibodies, or bind to the organism’s antigens to form an antigen–antibody complex that is phagocytosed by the phagocytes. (3) IVIG has a broad spectrum of anti-normal human protein and anti-idiotypic antibody, which can accelerate the clearance and neutralization of circulating autoantibodies by seizing the action site of autoantibodies. (4) Anti-inflammatory effect: IVIG can regulate the secretion of various cytokines and inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus achieving anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, IVIG may also exert potential anti-inflammatory effects through complement inhibition, blockade of Fas ligand-mediated apoptosis, and other mechanisms, and these mechanisms are not mutually exclusive but synergistic. (5) Eliminating pathogenic microorganisms: IVIG contains a variety of anti-bacterial toxin antibodies, neutralizing superantigens contained in bacterial toxins, and can eliminate pathogenic microorganisms such as viruses and bacterial toxins that persist in the body (9–12). (6) FcγRIII regulates dendritic cell properties: IVIG enhances the production of IL-1 and inhibits the production of IL-12 by inhibiting the differentiation and maturation of DCs (13) (Figure 1).
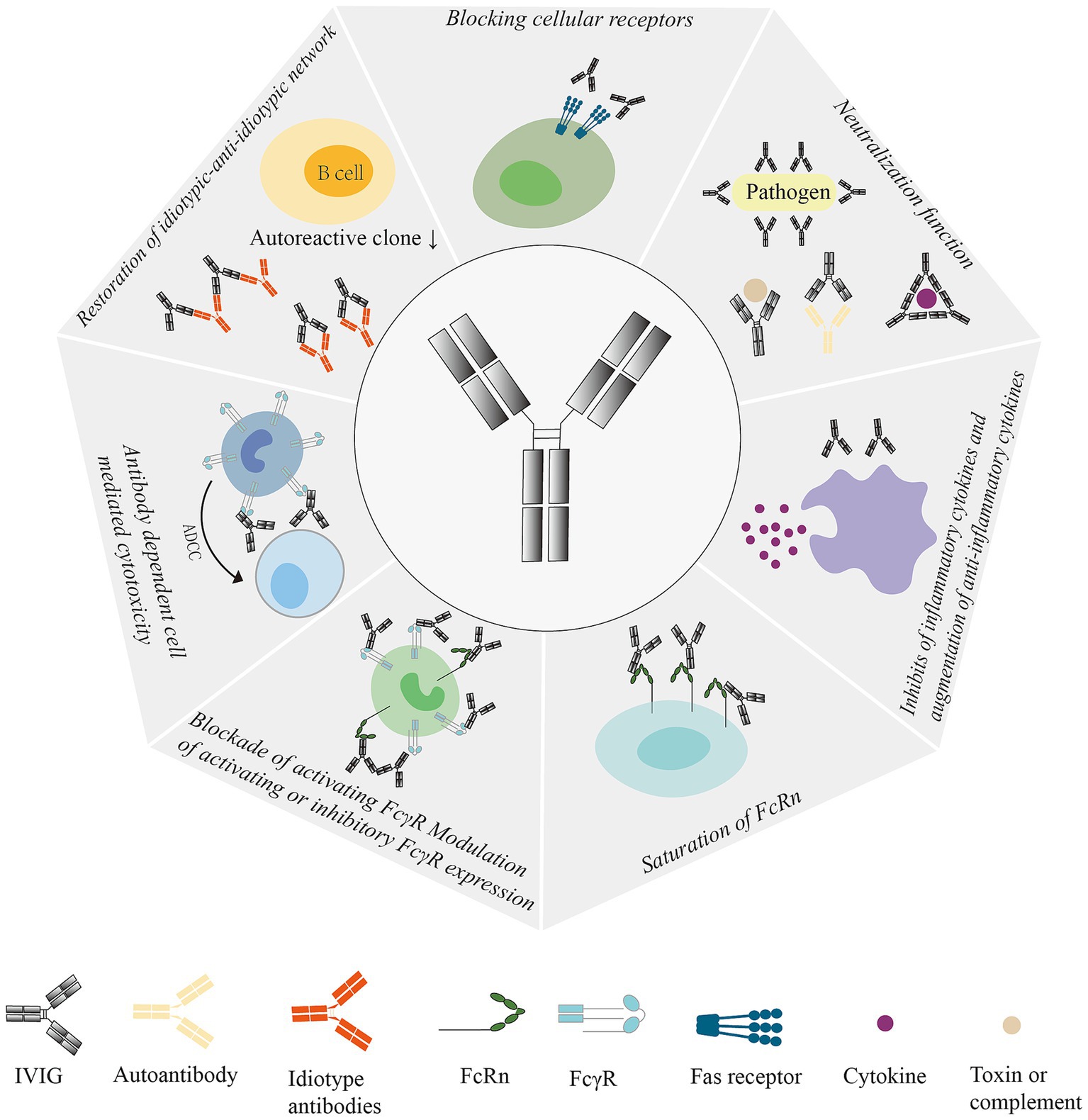
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of IVIG: Regulates Fc receptor expression and function, interferes with complement activation and regulates cytokine secretion, delivers anit-idiotype antibodies, neutralizes bacterial toxins, and regulates dendritic cell, T-cell, and B-cell activation, differentiation, and their effector functions. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; IVIG, Intravenous Immunoglobulin; Fas, Factor-related Apoptosis; FcRn, neonatal Fc receptor; FcγR, IgG Fc receptor.
The risk of infectious complications from IVIG is extremely low. The requirements for donor screening and infectious disease testing for imported plasma are very stringent. In addition, at least one step in the IVIG manufacturing process must remove the enveloped virus, while at least two complementary viral inactivation methods must be used to prevent infectious pathogens that may be present during the screening process. Recently, significant advances have been made in the way IVIG is produced, reducing the likelihood of the presence of infectious pathogens while ensuring safety and that side effects are minimized (14). However, IVIG, a blood product isolated from the combined plasma of thousands of healthy blood donors, still carries the risk of infectious agent transmission (15). There are few reports on the prospective data of IVIG-related adverse reactions. The overall incidence of IVIG infusion-related reactions is between 3 and 15%, and these reactions are usually phlogistic in nature and self-limited (16). IVIG related reactions are headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, rash, etc. Mild to moderate adverse reactions can usually be alleviated or avoided by slowing down the infusion speed of IVIG or stopping the infusion. Patients with multiple reactions are given antipyretics and antihistamines in advance. Contraindications to IVIG include individuals who are allergic to human immunoglobulin and individuals with selective IgA deficiency with anti-IgA antibodies. Serious adverse reactions are severe allergic reactions, acute renal failure, thromboembolic events, aseptic meningitis occurrences, neutropenia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia and rare events of arthritis. In view of the lack of data on the severity and incidence of their potential adverse events, this Expert Advice concludes that clinicians should limit the prescription of IVIG and use it only when there is sufficient evidence (17), and since cost is a limiting factor as well as the huge cost of IVIG.
The earliest discovery of the efficacy of high-dose IVIG was in the treatment of primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) (18). ITP is an autoimmune disorder characterized by a decrease in platelet count due to destruction of platelets by the immune system. ITP treatment guidelines mention that the first line treatment of choice is glucocorticoids and IVIG (19). ITP was the first autoimmune disease to be treated with IVIG, which is as effective as corticosteroid treatment (20, 21). In cases of active bleeding or when corticosteroids are contraindicated in patients, IVIG can induce a rapid increase in platelet count and quickly stop bleeding. The effect begins 1–3 days and the peak lasts for 2–7 days (22). Different centers use different IVIG doses and regimens. A meta-analysis showed that there were no significant differences in clinical outcomes and progression to chronic ITP with low-dose IVIG (<2 g/kg) versus high-dose IVIG (>2 g/kg), and that low-dose IVIG had fewer adverse effects and was less costly (23). The American Society of Hematology guideline panel recommends a single dose of IVIG 0.8 to 1 g/kg or a short course of glucocorticoids as first-line treatment for ITP, but both can be used in combination in order to rapidly elevate platelet levels (24). Patients with ITP treated with IVIG must have weekly complete blood counts (CBC) to assess efficacy and duration of therapy. In addition, patients should be informed that headache due to aseptic meningitis may occur after administration (25).
Expert recommendation 1: For adult patients with acute ITP requiring treatment, the recommended first-line treatment is a single dose of IVIG 0.8–1.0 g/kg or 0.4 g/kg/d for 3 to 5 days, with repeated administration if necessary. For emergency treatment of patients with hemorrhage, glucocorticoids in combination with IVIG 1 g/kg/d for 2 days are recommended (Class I).
Hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS), also known as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), is a syndrome of excessive inflammatory response caused by abnormal activation and proliferation of the lymphocyte, monocyte and macrophage systems, and secretion of large amounts of inflammatory cytokines, causing a series of inflammatory reactions. Depending on the etiology, HLH is categorized as primary and secondary. Primary HLH results in defective cytotoxic function of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes. Secondary HLH can be triggered by infection, malignancy, autoimmunity, etc. It is considered to be caused by temporary acquired immunodeficiency leading to defective NK cells, and the clinical manifestations are characterized by persistent fever, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia, and hemophagocytosis found in bone marrow, liver, spleen, and lymph node tissues. The HLH-1994 regimen is suitable for all types of HLH First-line induction therapy, including etoposide and dexamethasone (26–28). The application of IVIG can inhibit the activity of macrophages and reduce the damage of tissues and cells through various anti-inflammatory mechanisms. At present, IVIG can be considered as an auxiliary treatment for HLH, especially in the early stage of infection-related HLH. Some patients show a good response to IVIG alone, and the treatment with IVIG can avoid the adverse reactions of other treatment medications. IVIG should be supplemented with treatment of infection and criteria for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in accordance with treatment guidelines (29–31).
Expert recommendation 2: IVIG 0.4 g/kg/week can be added as co-infection supportive therapy or neutropenia co-infection in patients with HLH (Class I).
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) is a severe diffuse thrombotic microangiopathy characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, consumptive reduction of platelets, and organ damage (e.g., kidneys, central nervous system, etc.) due to microthrombosis. The pathogenesis of TTP mainly involves factors such as lack of activity of von Willebrand factor (vWF) lyase (ADAMTS13), abnormal release of vascular endothelial cell vWF, abnormal activation of complement, and abnormal activation of platelets, leading to microvascular thrombosis, microvascular hemolysis, and subsequent organ ischemia, hypoxia, and dysfunction, resulting in clinical symptoms of TTP pentad syndrome, namely thrombocytopenic purpura, microvascular hemolysis, central nervous system symptoms, fever, and kidney damage. Most TTP patients have a sudden onset and dangerous condition, with a mortality rate of up to 90% if left untreated. High-dose immunoglobulin may be effective in some patients who fail plasma exchange by inhibiting platelet aggregation and splenic destruction of platelets and red blood cells (32).
Expert recommendation 3: High-dose IVIG is recommended for patients with recurrent or refractory TTP, at a dose of 1.0 g/kg/d for 2 days or 0.4 g/kg/d for 5 days. If necessary, it can be given repeatedly, but the therapeutic effect may not be as good as plasma exchange (Class II).
Acquired Hemophilia A (AHA) is an acquired hemorrhagic disease characterized by a decrease in FVIII activity (FVIII: C) due to the production of specific autoantibodies that inhibit FVIII in the body. AHA is often associated with severe life-threatening bleeding, and subcutaneous hematomas are a characteristic manifestation of AHA, in addition to muscle, joint, gastrointestinal, and vaginal bleeding. Effective hemostasis is achieved with correct diagnosis and prompt treatment. The principles of treatment include initial hemostatic therapy (bypass, and activated human or activated porcine FVII are the current standard of care) and etiologic therapy (human or porcine FVIII), which depends on the severity of the hemorrhage and the characteristics of the antibodies (33, 34).
Expert recommendation 4: In patients with AHA who do not respond to immunosuppressive regimens, the administration of IVIG 1.0 g/kg/d for 2 days or 0.4 g/kg/d for 5 days is recommendedIVIG has poor efficacy in the AHA, and therefore its use for the purpose of blocking autoantibodies to FVIII is not recommended (Class II).
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) is a type of hemolytic anemia caused by disorders in the regulation of the body’s immune function, leading to the production of autoantibodies attached to the surface of red blood cells accelerating the destruction of red blood cells through the antigen–antibody reaction, typically mediated by complement activation. The production of autoantibodies involves many links of the immune system, such as the cross reaction between endogenous red blood cells and exogenous/environmental antigens, acquired factors such as infection and malignant tumors, structural change of auto-antigens and the disorder of antigen presentation, and the dysfunction of B cells and T cells. AIHA is usually categorized based on a positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT) and the optimal temperature required for the antibody to act on the erythrocyte membrane (hot, cold, and mixed forms), with the IgG-mediated warm-antibody phenotype being the most common. First line treatment for AIHA consists of glucocorticosteroids or glucocorticosteroids in combination with rituximab. For patients who fail glucocorticoid therapy, relapse, intolerant and dependent, second-line therapy is administered and the preferred regimen is rituximab. Third-line treatment includes splenectomy and immunosuppressive agents such as cyclosporine A, sirolimus, and azathioprine. AIHA may occur secondary to diseases that may trigger autoantibody production, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia and systemic autoimmune diseases. In addition, the incidence of AIHA after HSCT is increasing (35). In common variable immunodeficiency, disease-associated warm antibody-type secondary AIHA, maybe present in some patients with this condition. In addition to the risk of infection caused by the underlying immunodeficiency itself, such patients are further prone to severe and life threatening infections especially after glucocotricoids, immunosuppressants or rituximab, and the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin is recommended to elevate the level of immunoglobulin during the course of treatment and reduce the risk of infection (36).
Expert recommendation 5: High-dose IVIG can be used for life-threatening hemolysis or hemolysis for which other treatments are ineffective, and it is recommended that high-dose corticosteroids be given in combination with IVIG 1.0 g/kg/d for 2 days or 0.4 g/kg/d for 5 days as salvage therapy only in cases of severe or rapid hemolysis (Class I).
Hypogammaglobulinemia (HG) is an immune system disorder, defined as serum IgG < 7 g/L, which results in lower antibody serum levels and an increased risk of infection due to the failure of the immune system to produce enough immunoglobulin (37). HG may be caused by various underlying primary/congenital immune system defects or secondary immune deficiency states (such as hematological malignancies, protein loss diseases, etc.). Primary humoral immune deficiencies are most commonly X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) and common variable immune deficiencies. The most common clinical features of HG are recurrent bacterial infections, malabsorption syndrome, steatorrhea, protein-losing enteropathy, etc. Primary immunodeficiencies may be associated with a variety of autoimmune diseases, such as AIHA, ITP, dermatomyositis, etc., and malignant tumors (38, 39).
Expert recommendation 6: When complications related to primary immunodeficiency, such as infection, occur in HG patients, prophylactic treatment IVIG infusion, IVIG 0.4 g/kg/dose, is used, recommended every 3 weeks typically for the remainder of the patient’s life.
Chimeric antigen receptor T-Cells (CAR-T) are genetically engineered to integrate gene fragments of single-chain variable regions and co-stimulatory molecules targeting tumor antigens into the T-cell genome and express them on T-cells, which specifically recognizes tumor antigens and initiates the downstream signaling pathway to proliferate, activate, and exert a CAR-T cell targeted tumor-killing effect, and the common targets of CAR-T cell therapy for refractory/relapsed acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia are CD19 and CD22 (40). CAR-T cell products have been used to achieve good efficacy in the treatment of relapsed refractory B-cell tumors, with CD19 as the main target, and the indications mainly include diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, condylomatous cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma (41). CAR-T cell in the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma is targeted at B cell maturation antigen (BCMA), and many other CAR-T targets such as CS1 (CS1 is a cell surface glycoprotein of the signaling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) receptor family), G protein-coupled receptor class C group 5 member D (GPRC5D), CD38 and CD138 have also entered clinical trials (42). Pretreatment chemotherapy regimens prior to infusing CAR-T cells back into the body can cause lymphocyte exhaustion (43), CAR-T cell therapy also destroys normal B cells, and the majority of patients receiving CAR-T therapy have varying degrees of hypogammaglobulinemia or B-cell deficiencies (44, 45). This along with other factors may lead to increased risk of infections after CAR-T therapy. After receiving BCMA CAR-T cell therapy, 76% of patients with multiple myeloma developed hypogammaglobulinemia, increasing the risk of infection (46). The incidence of infection within 28 days after reinfusion of CAR-T in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia was 40% (47), while in another clinical trial of BCMA CAR-T cell therapy for multiple myeloma, the incidence of infections ranged from 42 to 69% (48). The consensus among Chinese experts is that prophylactic intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is a routine adjuvant therapy for patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy. National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend that patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy should be regularly supplemented with immunoglobulin infusions. The European Society for Hematology and Bone Marrow Transplantation and the American Society for Hematology and Bone Marrow Transplantation recommend that IVIG replacement therapy after CAR-T therapy should follow the X-linked absence of gammaglobulinemia principle (48).
Expert recommendation 7: After CAR-T cell therapy, the number of B lymphocytes and immunoglobulin level should be checked regularly, and IVIG infused at least once a month, at a dose of 0.4 g/kg/dose, until immunoglobulins and B cells returned to normal range or 6 months after CAR-T cell therapy (Class I).
Expert recommendation 8: Patients with serum IgG < 4 g/L and severe or recurrent infections after CAR-T cell therapy should continue to receive IVIG infusion at least once a month at a dose of 0.4 g/kg/dose until the risk factors are eliminated. If the serum IgG level is 4–6 g/L and there is still severe or recurrent infections after treatment, IVIG infusion should be given at least once a month at a dose of 0.4 g/kg/dose. If the serum IgG is greater than 6 g/L and there are recurrent infections, it is recommended to further evaluate the levels of the types of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgM and IgE) and the number of B cells (Class I).
Intense chemotherapy is the main method for patients with acute leukemia (AL) to alleviate their illness and prolong their survival. However, AL supplemented is affected by various factors such as severe granulocyte deficiency after chemotherapy and increased risk of infection associated with the use of immunosuppressants and glucocoticoids causing significant economic burden and increased morbidity and mortality. Therefore, it is extremely important to prevent and actively control the occurrence of infection after AL chemotherapy. Although B cells are affected and immunoglobulin levels maybe decreased in AL patients receiving chemotherapy, IVIG infusion has not been widely and systematically studied for the prevention or treatment of related infections in AL patients. Most infections are due to the disease itself and/or chemotherapy-related neutropenia, and for patients who are in remission and have completed treatment, the immune deficiency may last for 6–12 months after the treatment is completed (49). When neutropenia occurs after AL chemotherapy, the inflammatory response mediated by neutrophils is not significant. Severe neutropenia most commonly occurs during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, AL initial induction chemotherapy, and high-dose chemotherapy consolidation stage. It is necessary to identify neutropenic fever early and start empirical systemic antimicrobial therapy in a timely manner to avoid sepsis and death. It is important to administer IVIG simultaneously with anti-infective therapy (50).
Expert recommendation 9: Individualized assessment of the benefits and risks of IVIG infusion in patients with AL is recommended, and after weighing the risks and costs associated with treatment, at least one IVIG infusion per month is recommended at IVIG 0.4 g/kg/dose, with a target serum IgG of 4 to 6 g/L, and in the presence of breakthrough infections, a serum IgG > 6 to 8 g/L. Serum IgG levels, specific antibody titers and infection pattern are used to guide the IVIG treatment (Class II).
AL-intense chemotherapy can also cause severe myelosuppression, and repeated transfusion therapy is required after chemotherapy. Repeated transfusions can lead to a number of adverse transfusion reactions and platelet ineffective transfusion can occur in some patients with repeated platelet transfusion, which is mainly attributed to the development of specific antibodies against human leukocyte antigens. AL can also cause a decrease in ABO blood type antigens in patients, affecting clinical blood matching, increasing the risk of hemolytic reactions due to blood type incompatibility, and even leading to patient death in severe cases. The application of IVIG can block the Fc receptors of monocytes and macrophages, reducing the destruction of tissue cells mediated by allogenic antibodies and thereby, reducing adverse reactions to blood transfusion, and improving safety.
Expert recommendation 10: For AL patients with ineffective repeated platelet transfusions and obvious adverse reactions to blood transfusion, IVIG before transfusion can be recommended at a dose of 0.2–0.4 g/kg/dose (Class II).
Infection remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) due to the cumulative effect of disease, treatment and host-related factors. Disease-related plasma cell abnormalities, the effects of antitumor therapy, older age of onset and disease-related complications (e.g., renal failure) all contribute to an increased susceptibility to infections in patients with myeloma, and therefore the prevention of infections during the treatment of MM is of utmost importance. Prevention of infection during the process is crucial, and optimal prevention strategies include antimicrobial prophylaxis, infection control measures, and IVIG infusion in some patients (51). The NCCN guidelines mention that the risk of infection in MM patients is associated with treatments such as autologous HSCT, bispecific antibodies, CAR-T cell therapy, cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs, proteasome inhibitors, anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies, glucocorticoids, etc. 75% of patients receiving bispecific antibody therapy in the MajesTEC-1 study developed hypogammaglobulinemia (52). An earlier study retrospectively analyzed 3,000 MM patients showed 10% died within 60 days, 45% of whom died of infections (53). It has also been shown that myeloma patients receiving IVIG prophylaxis had fewer cases of serious infections than patients who did not receive IVIG, and that prophylactic use of IVIG reduced the risk of serious infections by 90% in MM patients treated with bispecific antibodies to BCMA (54, 55). Therefore, 0.4 to 0.6 g/kg IVIG infusion every month for 6–12 months is beneficial to MM patients, and the dosage and time should be adjusted according to the patient’s condition to ensure full prevention of infection (56). IVIG has a major limitation: it accelerates immunoglobulin metabolism in people with high levels of myeloma protein. There are two points to note when administering IVIG: (1) Immune modulators such as thalidomide, lenalidomide, and pomalidomide increase the risk of thrombosis during treatment, and IVIG infusion can further increase the risk of thrombosis (57). (2) Some MM patients may experience renal dysfunction, and IVIG infusion may further increase the risk of renal injury. Currently, most IVIG products remove sucrose (previously used as a stabilizer), which can reduce the risk of IVIG renal injury (58).
Expert recommendation 11: For MM patients with serum IgG ≤4 g/L and severe or recurrent infections, at least one IVIG infusion of 0.4 g/kg/dose per month is recommended, and for MM patients after CAR-T cell therapy, at least one IVIG infusion of 0.4 g/kg/dose per month is recommended until 1 year after the end of CAR-T therapy (Class II).
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) is the most common malignant tumor of lymphatic system, among which B cell-derived lymphoma accounts for more than 85% of the cases (59). Chemotherapy can effectively treat lymphoma, but chemotherapy not only leads to bone marrow suppression, but also has an immunosuppressive effect. CD20 monoclonal antibody is a major breakthrough in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma. However, CD20 monoclonal antibody in combination with chemotherapy leads to a further decrease in the immune function of the patient, predisposing to a variety of infections, such as herpes zoster, lung infections and others. CD20 monoclonal antibody kills abnormal and normal B lymphocytes at the same time, which reduces the number of B lymphocytes in peripheral blood and antibody production, eventually leading to humoral immune deficiency and increasing the risk of infection in NHL patients (60). The use of targeted drugs (such as Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors), immune modulators (such as lenalidomide), immune checkpoint inhibitors, and other drugs can also increase the incidence of infection (61, 62). The guidelines of the British Hematology Standards Committee suggest that NHL patients should receive regular IVIG infusions during treatment to reduce the occurrence of infections (63), while the NCCN guidelines recommend that NHL patients receiving CD20 monoclonal antibody and CAR-T cell therapy should receive regular IVIG infusions.
Expert recommendation 12: NHL patients need regular infusion of IVIG to enhance immunity and prevent infection during treatment, especially for NHL patients with IgG ≤ 4 g/L, recurrent or severe infection, using IVIG infusion every 3–4 weeks, IVIG 0.4 g/kg/dose (Class II).
HSCT, especially allogenetic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT), is still the only cure for many benign and malignant hematological diseases (64, 65). Meanwhile, post-transplant complications such as infection, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), thrombotic microangiopathy, and sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS), also know as Veno-occlusive Disease (VOD) are closely related to transplantation-related mortality, and these complications have hindered transplantation development (66, 67). Human immunoglobulin has synergistic anti-infection and immune regulation functions, and is often used to control infection and complications such as GVHD after transplantation. After HSCT, IVIG can effectively prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection, GVHD, bacterial infection, etc. The FDA of the United States approved IVIG as a preventive drug for patients with HSCT over 20 years old to reduce the incidence of infection complications such as pneumonia (11).
CMV infection is one of the main causes of infection and poor prognosis in patients undergoing allogeneic HSCT. CMV can lead to CMV disease, acute and chronic GVHD, opportunistic infection, bone marrow suppression and other serious adverse events, affecting the prognosis of patients undergoing HSCT. The incidence of CMV disease ranges from 10 to 40%, with CMV pneumonia being the most predominant type, with a mortality rate as high as 70%. Due to the wide application of prevention and preemptive treatment, the incidence of CMV disease has been reduced to less than 10%, with a case fatality rate of about 20 to 60% (68). The reactivation of CMV within 100 days after transplantation is accompanied by the increase of transplant-related mortality. The preemptive Treatment with antiviral drugs and the use of CMV-negative or leukocyte-depleted blood products have greatly reduced the incidence of CMV infection after transplantation (69). Early studies showed that preventive application of IVIG reduced CMV infection rate and mortality of interstitial pneumonia without CMV infection (70). IVIG combined with ganciclovir significantly changed the prognosis of patients with CMV pneumonia after transplantation. However, Schmidt et al. gave prophylactic IVIG to patients at high risk of CMV disease after allograft transplantation and showed no significant difference in the rate of CMV infection, or in the cumulative incidence of GVHD, when compared to a control group that was not given prophylactic IVIG (70). Another study evaluated the weekly preventive use of IVIG 5 g from −7 days to +98 days after transplantation. The results showed that the cumulative incidence of CMV infection was similar between the subjects treated with IVIG and the control group at +100 days after transplantation. These data showed that IVIG had no obvious advantage for CMV reactivation in transplant patients who could receive antiviral drugs. However, whether the high-risk population of CMV reactivation can benefit from these interventions has not been confirmed by research (71).
Expert recommendation 13: It is recommended that IVIG can be used prophylactically in patients with CMV high-risk activators in allo-HSCT, with 1 to 2 weekly infusions of IVIG, IVIG 5 g to 10 g/dose, up to 100 days post-transplantation (Class II).
At least 50% or more of transplant related deaths are directly or indirectly related to GVHD, and effective prevention and treatment methods for GVHD need to be sought. GVHD is often closely related to delayed immune function reconstruction in transplant patients, and promoting the formation of immune reconstruction is the fundamental way to solve complications after allo HSCT. Induced immune tolerance means that after transplantation the recipient is resistant to rejection and the graft maintains stable function for a long time (72). The research hotspots in recent years mentioned that the role of intestinal flora in the body’s anti-tumor immune response including chemotherapy and allo-HSCT has received increasing attention. The gut microbiota plays an important role in the pathological and physiological processes of GVHD (73). Changes in gut microbiota may determine the severity of GVHD. After transplantation, the composition of gut microbiota is altered, leading to dysbiosis. Gut microbiota can easily penetrate damaged intestinal mucosa, causing abnormal immune responses, activating T lymphocytes, promoting the release of inflammatory mediators, and causing damage to the gastrointestinal mucosal barrier, thereby damaging target organs such as the gastrointestinal tract (74–76). Based on the immunomodulatory effect of IVIG, a large randomized controlled study was conducted on allo-HSCT patients, comparing the weekly administration of IVIG 0.5 g/kg from −7 days to +90 days after transplantation, followed by monthly administration of IVIG 0.5 g/kg from 90 days to 360 days. Multivariate analysis showed that compared with IVIG recipients, the control group had an increased risk of acute GVHD > grade 2 (RR 1.63, p < 0.0056) (77). In another study, more than 600 subjects received 0.1 g/kg, 0.25 g/kg or 0.5 g/kg IVIG at random, once a week until the 90th day after transplantation, and then once a month until 1 year after transplantation. The study showed that the incidence of acute GVHD was the lowest in the HLA-matched unrelated donor group and the subjects who received the highest dose of IVIG (78).
Expert recommendation 14: IVIG 0.5 g/kg per week from pre-transplantation −7 days to post-transplantation day 90 and 0.5 g/kg per month from post-transplantation day 90 to 1 year post-transplantation is recommended for those at high risk for GVHD when mismatched with allo-HSCT (Class II).
HSCT patients undergo myeloablative chemotherapy. After ultra-intensive pretreatment and radiotherapy, the patients are in the ablative period of bone marrow, and the process of immune function reconstruction is longer, with longer period of severe neutrophil deficiency. In addition, the incidence of various infections such as bacteria, fungi and viruses is higher after long-term use of immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids. Regarding whether IVIG is needed to prevent bacterial infection during transplantation, the relevant guidelines of the American Society of Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation unanimously recommend that IVIG should not be routinely used to prevent bacterial infection after transplantation (79). However, when the patient is complicated with severe hypogammaglobulinemia (serum IgG < 4 g/L), it is suggested to receive preventive IVIG infusion from the beginning of pretreatment chemotherapy before transplantation to 100 days after transplantation to maintain serum IgG > 4 g/L. There is a lack of sufficient randomized controlled studies to support this recommendation, and the only objective data are based on IVIG pharmacokinetic studies showing a half-life of approximately 6 days in transplanted patients and 22 days in normal subjects, and the explanation for this discrepancy may be the increased proteolytic metabolism and reduced protein conversion and synthesis due to GVHD (80).
Expert recommendation 15: IVIG 0.5 g/kg per week is recommended for patients with serum IgG <4 g/L from 7 days pretransplant to 90 days posttransplant, and 0.5 g/kg per month from 90 days posttransplant to 1 year posttransplant, so as to prevent serious bacterial infection. Serum IgG concentration should be monitored every 2 weeks, and individualized treatment should be carried out according to serum IgG level and infection (Class II).
This consensus is based on the existing evidence both domestically and internationally, as well as the careful discussions organized by the Chinese Infection Immunology and Microecology Research Translation Collaborative Group with relevant experts. Based on the evidence grading method, 15 suggestions were proposed for the application of IVIG in the treatment of hematological diseases, hematological tumors, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Table 2). It is hoped to serve as a reference for clinicians and help standardize the dosage of IVIG used to treat hematological diseases.
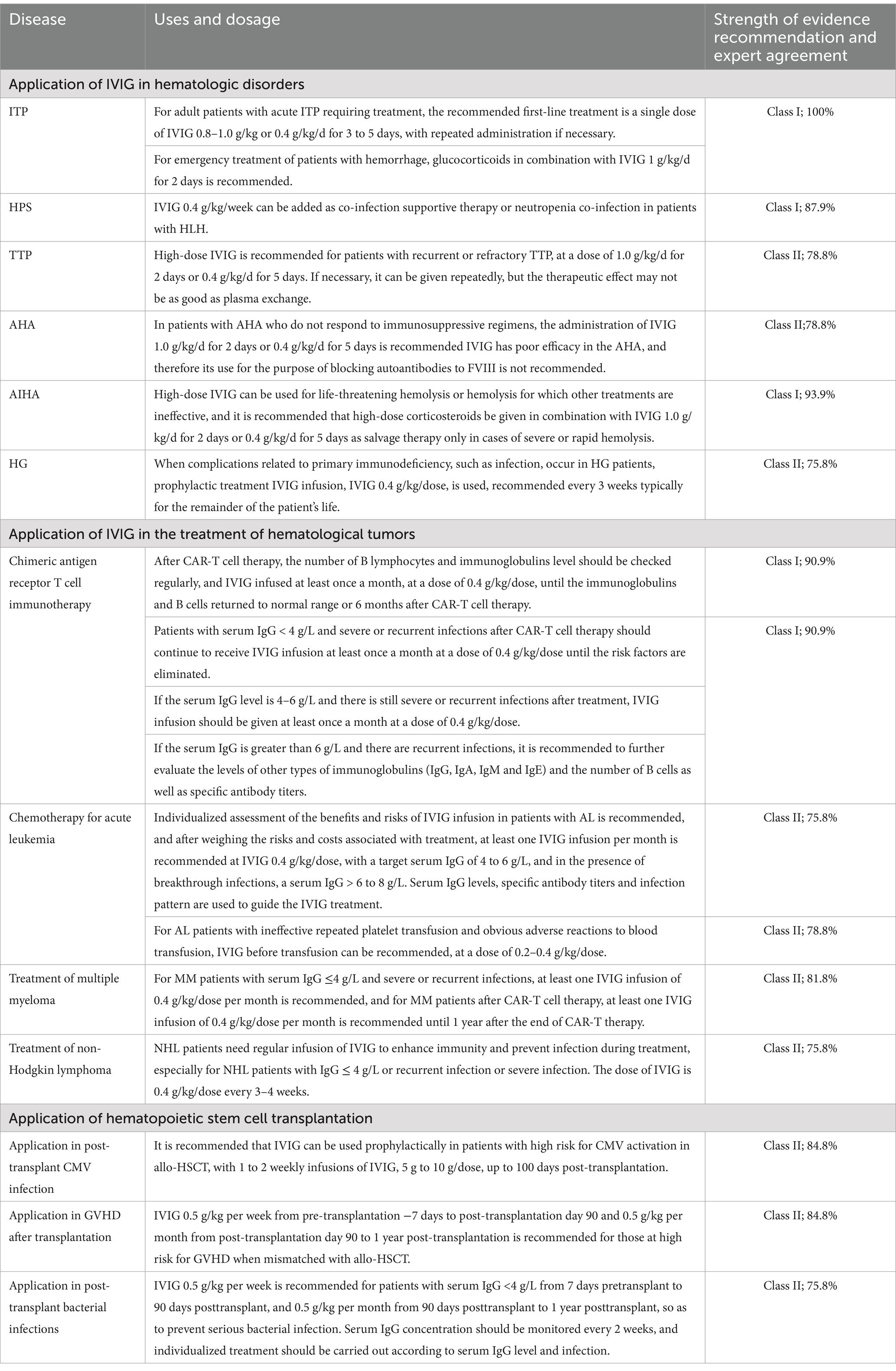
Table 2. 15 recommendations were proposed for the application of IVIG in the treatment of hematological diseases, hematological tumors, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
ZG: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Data curation, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JW: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LW: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. FT: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HH: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZhX: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DW: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. NZ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HuZ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. WD: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XJX: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HaZ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LD: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JM: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LS: Writing – review & editing. YC: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YaL: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. RQ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. GL: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. PC: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HoZ: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YuL: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JJL: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZiX: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SS: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XCX: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. QMW: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. QW: Data curation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Nanshan District medical key discipline construction financial support project, Shenzhen Nanshan.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Eibl, MM. History of immunoglobulin replacement. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am. (2008) 28:737–64. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2008.06.004
2. Pecoraro, A, Crescenzi, L, Granata, F, Genovese, A, and Spadaro, G. Immunoglobulin replacement therapy in primary and secondary antibody deficiency: the correct clinical approach. Int Immunopharmacol. (2017) 52:136–42. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.005
3. Chen, S, Dong, Y, Yin, Y, and Krucoff, MW. Intravenous immunoglobulin plus corticosteroid to prevent coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease: a meta-analysis. Heart. (2013) 99:76–82. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2012-302126
4. Beecher, G, Anderson, D, and Siddiqi, ZA. Subcutaneous immunoglobulin in myasthenia gravis exacerbation: a prospective, open-label trial. Neurology. (2017) 89:1135–41. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004365
5. Olyaeemanesh, A, Rahmani, M, and Goudarzi, R. Safety and effectiveness assessment of intravenous immunoglobulin in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Med J Islam Repub Iran. (2016) 30:336.
6. Wat, J, and Barmettler, S. Hypogammaglobulinemia after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy: characteristics, management, and future directions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2022) 10:460–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.10.037
7. Sahin, U, Toprak, SK, Atilla, PA, Atilla, E, and Demirer, T. An overview of infectious complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Infect Chemother. (2016) 22:505–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.05.006
8. Kotton, CN, Torre-Cisneros, J, and Aguado, JM. Cytomegalovirus in the transplant setting: where are we now and what happens next? A report from the international CMV symposium 2021. Transpl Infect Dis. (2022) 24:e13977. doi: 10.1111/tid.13977
9. Roschewski, M, Lionakis, MS, Sharman, JP, Roswarski, J, Goy, A, Monticelli, MA, et al. Inhibition of Bruton tyrosine kinase in patients with severe COVID-19. Sci Immunol. (2020) 5:5. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd0110
10. Rizk, JG, Kalantar-Zadeh, K, Mehra, MR, Lavie, CJ, Rizk, Y, and Forthal, DN. Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19. Drugs. (2020) 80:1267–92. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01367-z
11. Perez, EE, Orange, JS, Bonilla, F, Chinen, J, Chinn, IK, Dorsey, M, et al. Update on the use of immunoglobulin in human disease: a review of evidence. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2017) 139:S1–s46. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.023
12. Johnston, SL, and Hollingsworth, R. Immunoglobulin therapy. Clin Med (Lond). (2016) 16:576–9. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.16-6-576
13. Othy, S, Bruneval, P, Topçu, S, Dugail, I, Delers, F, Lacroix-Desmazes, S, et al. Effect of IVIg on human dendritic cell-mediated antigen uptake and presentation: role of lipid accumulation. J Autoimmun. (2012) 39:168–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2012.05.013
14. João, C, Negi, VS, Kazatchkine, MD, Bayry, J, and Kaveri, SV. Passive serum therapy to immunomodulation by IVIG: a fascinating journey of antibodies. J Immunol. (2018) 200:1957–63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701271
15. Guo, Y, Tian, X, Wang, X, and Xiao, Z. Adverse effects of immunoglobulin therapy. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01299
16. Stiehm, ER. Adverse effects of human immunoglobulin therapy. Transfus Med Rev. (2013) 27:171–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2013.05.004
17. Orbach, H, Katz, U, Sherer, Y, and Shoenfeld, Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin: adverse effects and safe administration. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2005) 29:173–84. doi: 10.1385/CRIAI:29:3:173
18. Imbach, P, Barandun, S, d’Apuzzo, V, Baumgartner, C, Hirt, A, Morell, A, et al. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet. (1981) 1:1228–31. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(81)92400-4
19. Provan, D, Arnold, DM, Bussel, JB, Chong, BH, Cooper, N, Gernsheimer, T, et al. Updated international consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood Adv. (2019) 3:3780–817. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000812
20. Cooper, N, and Ghanima, W. Immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:945–55. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1810479
21. Zufferey, A, Kapur, R, and Semple, JW. Pathogenesis and therapeutic mechanisms in immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). J Clin Med. (2017) 6:6. doi: 10.3390/jcm6020016
22. Rodeghiero, F, Stasi, R, Gernsheimer, T, Michel, M, Provan, D, Arnold, DM, et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood. (2009) 113:2386–93. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-162503
23. Qin, YH, Zhou, TB, Su, LN, Lei, FY, Zhao, YJ, and Huang, WF. The efficacy of different dose intravenous immunoglobulin in treating acute idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a meta-analysis of 13 randomized controlled trials. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. (2010) 21:713–21. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0b013e3283401490
24. Neunert, CE, and Cooper, N. Evidence-based management of immune thrombocytopenia: ASH guideline update. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. (2018) 2018:568–75. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.568
25. Mingot-Castellano, ME, Canaro Hirnyk, M, Sánchez-González, B, Álvarez-Román, M, Bárez-García, A, Bernardo-Gutiérrez, Á, et al. Recommendations for the clinical approach to immune thrombocytopenia: Spanish ITP working group (GEPTI). J Clin Med. (2023) 12:12. doi: 10.3390/jcm12206422
26. Jordan, MB, Allen, CE, Greenberg, J, Henry, M, Hermiston, ML, Kumar, A, et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: recommendations from the North American consortium for Histiocytosis (NACHO). Pediatr Blood Cancer. (2019) 66:e27929. doi: 10.1002/pbc.27929
27. Chinnici, A, Beneforti, L, Pegoraro, F, Trambusti, I, Tondo, A, Favre, C, et al. Approaching hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1210041. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210041
28. Townsend, JL, Shanbhag, S, Hancock, J, Bowman, K, and Nijhawan, AE. Histoplasmosis-induced Hemophagocytic syndrome: a case series and review of the literature. Open forum. Infect Dis Ther. (2015) 2:ofv055. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofv055
29. Argyraki, CK, Gabeta, S, Zachou, K, Boulbou, M, Polyzos, A, and Dalekos, GN. Favourable outcome of life-threatening infectious-related haemophagocytic syndrome after combination treatment with corticosteroids and intravenous immunoglobulin infusions. Eur J Intern Med. (2011) 22:e155–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2011.07.010
30. Rajajee, S, Ashok, I, Manwani, N, Rajkumar, J, Gowrishankar, K, and Subbiah, E. Profile of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Indian J Pediatr. (2014) 81:1337–41. doi: 10.1007/s12098-014-1461-0
31. Hines, MR, von Bahr, GT, and Beutel, G. Consensus-based guidelines for the recognition, diagnosis, and Management of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill children and adults. Crit Care Med. (2022) 50:860–72. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005361
32. Zheng, XL, Vesely, SK, Cataland, SR, Coppo, P, Geldziler, B, Iorio, A, et al. ISTH guidelines for the diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Thromb Haemost. (2020) 18:2486–95. doi: 10.1111/jth.15006
33. Pai, M. Acquired hemophilia a. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. (2021) 35:1131–42. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2021.07.007
34. Knoebl, P, Thaler, J, Jilma, P, Quehenberger, P, Gleixner, K, and Sperr, WR. Emicizumab for the treatment of acquired hemophilia a. Blood. (2021) 137:410–9. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006315
35. Fattizzo, B, Giannotta, JA, Serpenti, F, and Barcellini, W. Difficult cases of autoimmune hemolytic Anemia: a challenge for the internal medicine specialist. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:9. doi: 10.3390/jcm9123858
36. Barcellini, W, and Fattizzo, B. How I treat warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Blood. (2021) 137:1283–94. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003808
37. Caballero-Ávila, M, Álvarez-Velasco, R, Moga, E, Rojas-Garcia, R, Turon-Sans, J, Querol, L, et al. Rituximab in myasthenia gravis: efficacy, associated infections and risk of induced hypogammaglobulinemia. Neuromuscul Disord. (2022) 32:664–71. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2022.06.006
38. Cardenas-Morales, M, and Hernandez-Trujillo, VP. Agammaglobulinemia: from X-linked to autosomal forms of disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2022) 63:22–35. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08870-5
39. Viallard, JF. Management of hypogammaglobulinemia. Rev Med Interne. (2023) 44:133–8. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2023.01.010
40. Lin, H, Cheng, J, Mu, W, Zhou, J, and Zhu, L. Advances in universal CAR-T cell therapy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:744823. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.744823
41. Lee, YG, Guruprasad, P, Ghilardi, G, Pajarillo, R, Sauter, CT, Patel, R, et al. Modulation of BCL-2 in both T cells and tumor cells to enhance chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy against Cancer. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:2372–91. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1026
42. Yang, J, Zhou, W, Li, D, Niu, T, and Wang, W. BCMA-targeting chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. Cancer Lett. (2023) 553:215949. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215949
43. Wang, S, Wang, X, Ye, C, Cheng, H, Shi, M, Chen, W, et al. Humanized CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells for relapsed/refractory pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. (2021) 96:E162–e65. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26123
44. Dai, H, Wu, Z, Jia, H, Tong, C, Guo, Y, Ti, D, et al. Bispecific CAR-T cells targeting both CD19 and CD22 for therapy of adults with relapsed or refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13:30. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00856-8
45. Li, P, Liu, Y, Liang, Y, Bo, J, Gao, S, Hu, Y, et al. 2022 Chinese expert consensus and guidelines on clinical management of toxicity in anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Biol Med. (2023) 20:129–46. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2022.0585
46. Kambhampati, S, Sheng, Y, Huang, CY, Bylsma, S, Lo, M, Kennedy, V, et al. Infectious complications in patients with relapsed refractory multiple myeloma after BCMA CAR T-cell therapy. Blood Adv. (2022) 6:2045–54. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020004079
47. Vora, SB, Waghmare, A, Englund, JA, Qu, P, Gardner, RA, and Hill, JA. Infectious complications following CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for children, adolescents, and Young adults. Open forum. Infect Dis Ther. (2020) 7:ofaa121. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa121
48. Mohan, M, Chakraborty, R, Bal, S, Nellore, A, Baljevic, M, D’Souza, A, et al. Recommendations on prevention of infections during chimeric antigen receptor T-cell and bispecific antibody therapy in multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. (2023) 203:736–46. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18909
49. Ueda, M, Berger, M, Gale, RP, and Lazarus, HM. Immunoglobulin therapy in hematologic neoplasms and after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood Rev. (2018) 32:106–15. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.09.003
50. Wang, J, Liang, J, He, M, Xie, Q, Wu, Q, Shen, G, et al. Chinese expert consensus on intestinal microecology and management of digestive tract complications related to tumor treatment (version 2022). J Cancer Res Ther. (2022) 18:1835–44. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1444_22
51. Raje, NS, Anaissie, E, Kumar, SK, Lonial, S, Martin, T, Gertz, MA, et al. Consensus guidelines and recommendations for infection prevention in multiple myeloma: a report from the international myeloma working group. Lancet Haematol. (2022) 9:e143–61. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00283-0
52. Moreau, P, Garfall, AL, and van de Donk, N. Teclistamab in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. (2022) 387:495–505. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2203478
53. Augustson, BM, Begum, G, Dunn, JA, Barth, NJ, Davies, F, Morgan, G, et al. Early mortality after diagnosis of multiple myeloma: analysis of patients entered onto the United Kingdom Medical Research Council trials between 1980 and 2002--Medical Research Council adult Leukaemia working party. J Clin Oncol. (2005) 23:9219–26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.03.2086
54. Garfall, AL, and Stadtmauer, EA. Understanding infection risk with anti-BCMA bispecific antibodies. Blood Cancer Discov. (2023) 4:427–9. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0157
55. Lancman, G, Parsa, K, Kotlarz, K, Avery, L, Lurie, A, Lieberman-Cribbin, A, et al. IVIg use associated with ten-fold reduction of serious infections in multiple myeloma patients treated with anti-BCMA bispecific antibodies. Blood Cancer Discov. (2023) 4:440–51. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0049
56. Lucas, M, Lee, M, Lortan, J, Lopez-Granados, E, Misbah, S, and Chapel, H. Infection outcomes in patients with common variable immunodeficiency disorders: relationship to immunoglobulin therapy over 22 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2010) 125:1354–60.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.02.040
57. Li, A, Wu, Q, Warnick, G, Li, S, Libby, EN, Garcia, DA, et al. The incidence of thromboembolism for lenalidomide versus thalidomide in older patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol. (2020) 99:121–6. doi: 10.1007/s00277-019-03860-2
58. Ahsan, N, Wiegand, LA, Abendroth, CS, and Manning, EC. Acute renal failure following immunoglobulin therapy. Am J Nephrol. (1996) 16:532–6. doi: 10.1159/000169055
59. Salles, G, Barrett, M, Foà, R, Maurer, J, O’Brien, S, Valente, N, et al. Rituximab in B-cell hematologic malignancies: a review of 20 years of clinical experience. Adv Ther. (2017) 34:2232–73. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0612-x
60. Reboursiere, E, Fouques, H, Maigne, G, Johnson, H, Chantepie, S, Gac, AC, et al. Rituximab salvage therapy in adults with immune thrombocytopenia: retrospective study on efficacy and safety profiles. Int J Hematol. (2016) 104:85–91. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-1992-4
61. Byrd, JC, Furman, RR, Coutre, SE, Burger, JA, Blum, KA, Coleman, M, et al. Three-year follow-up of treatment-naïve and previously treated patients with CLL and SLL receiving single-agent ibrutinib. Blood. (2015) 125:2497–506. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-606038
62. Wei, LY, Xie, J, Wang, YQ, Liu, XY, Chen, X, Zhang, YH, et al. The efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors in the maintenance treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a single-center retrospective analysis. J Cancer Res Ther. (2022) 18:525–31. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_255_22
63. Oscier, D, Dearden, C, Eren, E, Fegan, C, Follows, G, Hillmen, P, et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis, investigation and management of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. (2012) 159:541–64. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12067
64. Saad, A, de Lima, M, Anand, S, Bhatt, VR, Bookout, R, Chen, G, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation, version 2.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. (2020) 18:599–634. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2020.0021
65. Tarlock, K, Sulis, ML, Chewning, JH, Pollard, JA, Cooper, T, Gamis, A, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation in the treatment of pediatric acute myelogenous leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation and cellular therapy. Transplant Cell Ther. (2022) 28:530–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.06.005
66. Lehrnbecher, T, Fisher, BT, Phillips, B, Beauchemin, M, Carlesse, F, Castagnola, E, et al. Clinical practice guideline for systemic antifungal prophylaxis in pediatric patients with Cancer and hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation recipients. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38:3205–16. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00158
67. Maertens, JA, Girmenia, C, Brüggemann, RJ, Duarte, RF, Kibbler, CC, Ljungman, P, et al. European guidelines for primary antifungal prophylaxis in adult haematology patients: summary of the updated recommendations from the European conference on infections in Leukaemia. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2018) 73:3221–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky286
68. Ljungman, P, de la Camara, R, Robin, C, Crocchiolo, R, Einsele, H, Hill, JA, et al. Guidelines for the management of cytomegalovirus infection in patients with haematological malignancies and after stem cell transplantation from the 2017 European conference on infections in Leukaemia (ECIL 7). Lancet Infect Dis. (2019) 19:e260–72. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30107-0
69. Teira, P, Battiwalla, M, Ramanathan, M, Barrett, AJ, Ahn, KW, Chen, M, et al. Early cytomegalovirus reactivation remains associated with increased transplant-related mortality in the current era: a CIBMTR analysis. Blood. (2016) 127:2427–38. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-679639
70. Bass, EB, Powe, NR, Goodman, SN, Graziano, SL, Griffiths, RI, Kickler, TS, et al. Efficacy of immune globulin in preventing complications of bone marrow transplantation: a meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. (1993) 12:273–82.
71. Ichihara, H, Nakamae, H, Hirose, A, Nakane, T, Koh, H, Hayashi, Y, et al. Immunoglobulin prophylaxis against cytomegalovirus infection in patients at high risk of infection following allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. (2011) 43:3927–32. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2011.08.104
72. Guo, Z, Gao, HY, Zhang, TY, Liu, XD, Yang, K, Lou, JX, et al. Analysis of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with high-dose cyclophosphamide-induced immune tolerance for severe aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol. (2016) 104:720–8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2106-z
73. Storb, R, Prentice, RL, Buckner, CD, Clift, RA, Appelbaum, F, Deeg, J, et al. Graft-versus-host disease and survival in patients with aplastic anemia treated by marrow grafts from HLA-identical siblings. Beneficial effect of a protective environment. N Engl J Med. (1983) 308:302–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302103080602
74. Paratore, M, Santopaolo, F, Cammarota, G, Pompili, M, Gasbarrini, A, and Ponziani, FR. Fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with HBV infection or other chronic liver diseases: update on current knowledge and future perspectives. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:10. doi: 10.3390/jcm10122605
75. Biliński, J, Jasiński, M, and Basak, GW. The role of fecal microbiota transplantation in the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Biomedicine. (2022) 10:10. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040837
76. Wang, Q, Lei, Y, Wang, J, Xu, X, Wang, L, Zhou, H, et al. Expert consensus on the relevance of intestinal microecology and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Transpl. (2024) 38:e15186. doi: 10.1111/ctr.15186
77. Sullivan, KM, Kopecky, KJ, Jocom, J, Fisher, L, Buckner, CD, Meyers, JD, et al. Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin in bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. (1990) 323:705–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009133231103
78. Cordonnier, C, Chevret, S, Legrand, M, Rafi, H, Dhdin, N, Lehmann, B, et al. Should immunoglobulin therapy be used in allogeneic stem-cell transplantation? A randomized, double-blind, dose effect, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Ann Intern Med. (2003) 139:8–18. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-1-200307010-00007
79. Tomblyn, M, Chiller, T, Einsele, H, Gress, R, Sepkowitz, K, Storek, J, et al. Guidelines for preventing infectious complications among hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients: a global perspective. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. (2009) 15:1143–238. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.06.019
Keywords: IVIG, clinical application, hematologic disorders, chimeric antigen receptor T-Cell, hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT), expert consensus
Citation: Guo Z, Zhu J, Wang J, Wang L, Tang F, Huang H, Xia Z, Liu L, Wang D, Zhong N, Zhou H, Zhou Z, Dai W, Xu X, Zhou H, Deng L, Meng J, Sun Z, Shao L, Cao YJ, Liu Y, Qu R, Li G, Chen P, Zhang H, Liang J, Li Y, Liu J, Xu Z, Sung Inda S, Xiang X, Wu Q and Wang Q (2025) Chinese expert consensus on the application of intravenous immunoglobulin in hematological diseases. Front. Med. 12:1544025. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1544025
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 10 March 2025;
Published: 01 April 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Perrella, Hospital of the Hills, ItalyReviewed by:
Terry Harville, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Guo, Zhu, Wang, Wang, Tang, Huang, Xia, Liu, Wang, Zhong, Zhou, Zhou, Dai, Xu, Zhou, Deng, Meng, Sun, Shao, Cao, Liu, Qu, Li, Chen, Zhang, Liang, Li, Liu, Xu, Sung Inda, Xiang, Wu and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhi Guo, Z3VvemhpNzdAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Qiang Wang, d2FuZ3FpYW5nQHd1c3QuZWR1LmNu
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.