- 1Gastroenterology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University/Liuzhou Worker’s Hospital, Liuzhou, China
- 2Department of General Medicine, Liuzhou People’s Hospital, Liuzhou, China
Purpose: This meta-analysis aimed to compare the diagnostic effectiveness of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET for detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancer patients.
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase databases was conducted to identify relevant articles up to June 2024. Studies were included if they evaluated the diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancer patients. Sensitivity and specificity were assessed using the DerSimonian and Laird method and were transformed using the Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation.
Results: Fifteen articles, encompassing a total of 617 patients, were included in this study. The overall sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET for diagnosing lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers was 0.82 (95% CI: 0.67–0.93), and the specificity was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.84–0.97). In comparison, the sensitivity of [18F]FDG PET was 0.51 (95% CI: 0.38–0.63), with a specificity of 0.81 (95% CI: 0.64–0.94). These results suggest that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET has a significantly higher sensitivity (P < 0.01) and similar specificity (P = 0.20) compared to [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
Conclusion: Our meta-analysis indicates that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET has higher sensitivity and similar specificity compared to [18F]FDG PET in diagnosing lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers. However, the high heterogeneity among the studies may impact the robustness of the current evidence. Therefore, future research should prioritize larger prospective studies with more diverse populations and specific cancer subtypes to draw more definitive conclusions.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024572412, Unique Identifier: CRD42024572412.
1 Introduction
Digestive system cancers are a significant health concern, impacting multiple organs and being widely prevalent (1). Gastrointestinal cancers account for over 26% of the global cancer incidence and are responsible for more than 35% of cancer-related deaths worldwide (2). In 2018, gastrointestinal tumors accounted for 4.8 million new cases and 3.4 million deaths, with Asia bearing 63% of cases and 65% of deaths. China alone contributed 38% of cases and 41% of deaths (2). Within China, four of the top five cancers leading to mortality are gastrointestinal, including liver cancer (12.85%), gastric cancer (12.48%), esophageal cancer (10.09%), and colorectal cancer (9.63%) (3). These statistics highlight the urgent need for early detection and accurate staging of gastrointestinal cancers(4). While histopathology is the gold standard, advancements in imaging technologies offer a promising non-invasive alternative (5).
Traditional imaging techniques include ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (6). Due to their cost-effectiveness and accessibility in clinical applications, these methods are widely employed for the detection of gastrointestinal malignancies. However, they possess certain limitations. For instance, ultrasound may produce artifacts due to the intestines’ complex anatomy and high gas content, reducing accuracy (7, 8). Furthermore, current endoscopic ultrasound is limited by insufficient penetration depth and difficulty in observing distant lymph nodes, making accurate assessment challenging (9). Enhanced CT and MRI may fail to accurately differentiate small nodules from atypical lesions in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (10). Furthermore, these imaging techniques may not offer adequate functional data for precise lymph node assessment. These methods frequently exhibit limitations in detecting lymph node metastases and small lesions, highlighting the urgent need for the development of enhanced diagnostic tools (11).
Positron emission tomography (PET) has been a critical tool in molecular imaging over the past decade, frequently employed in the detection of gastrointestinal cancers (12, 13). The 18F-FDG tracer, which targets abnormal glucose metabolism in tumors, is a key tool in PET imaging. It is extensively used for diagnosing malignant tumors and evaluating treatment effectiveness (14). Recent studies have identified limitations of 18F-FDG tracers in diagnosing gastrointestinal cancers, particularly in distinguishing between inflammation and malignancy (14–16). Nonspecific lymph node uptake may cause false positives and incorrect treatment decisions (17). Recent studies show that high levels of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in cancer-associated fibroblasts are linked to tumor growth, metastasis, and prognosis. As a result, FAPI has become a novel imaging agent and has been used in clinical practice since 2018 (18). Ga-labeled FAPI tracers (such as [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 and [68Ga]Ga FAPI-46) have shown rapid tumor uptake, with [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 being particularly notable (19). Its potential applications have made [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 the focus of growing research interest. [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 is being studied as a potential alternative to the well-established [18F]FDG in gastrointestinal oncologic PET imaging. Previous studies conducted by Ouyang et al. and Wang et al. indicated that [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 PET exhibit higher sensitivity than [18F]FDG PET in diagnosing primary gastrointestinal tumors or gastric cancer (20, 21). However, its diagnostic performance for detecting lymph node metastasis in gastrointestinal tumors has not been reported. Lymph node metastasis is a well-established indicator of cancer spread, and accurate N staging of the tumor is essential for developing effective treatment strategies (22).
The relative sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET compared to [18F]FDG PET in diagnosing lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers is currently under debate, given the conflicting findings in the literature. The study by Lin et al. indicates that the diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 PET is comparable to [18F]FDG PET for lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers (23); however, Gündoğan et al. found that [68Ga]Ga FAPI-04 PET has higher sensitivity than [18F]FDG PET (24). Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis, rigorously collecting and analyzing all head-to-head eligible studies to provide a more conclusive assessment.
2 Methods
This meta-analysis strictly followed the PRISMA-DTA guidelines for Diagnostic Test Accuracy (25). Additionally, the study protocol was registered with the PROSPERO network under the identifier CRD42024572412.
2.1 Search strategy
A systematic search was conducted across three major English electronic databases—PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science—from their inception through June 2024. The search strategy utilized specific terms including: (1) PET or positron emission tomography, (2) 68Ga-FAPI, FAPI-04, FAPI, fibroblast activation protein, or FAP, and (3) digestive, gastric, gastrointestinal, pancreatic, pancreas, colorectal, hepatic, hepatocellular, or liver. Detailed search terms are listed in Supplementary Table 1. In addition, the reference lists of the selected articles were manually reviewed to identify any additional relevant studies.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The selection criteria were defined according to PICOS: participants (P) were patients with digestive system tumors; the index test (I) was [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET; the comparator (C) was [18F]FDG PET; outcomes (O) were diagnostic accuracy with histopathology or follow-up imaging as reference standards; and study design (S) included both prospective and retrospective diagnostic studies published in English.
Studies were excluded based on the following criteria: (1) duplicate publications, (2) abstracts, editorial comments, letters, case reports, reviews, or meta-analyses, (3) irrelevant studies, and (4) studies lacking extractable data for true-positive (TP), false-positive (FP), true-negative (TN), and false-negative (FN) results. Additionally, studies using different radiotracers or PET without CT or MRI were excluded. In cases of potentially overlapping patient samples, the most recent publication was selected.
2.3 Quality assessment
According to the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) tool (26), two independent researchers evaluated the quality of the included studies. The QUADAS-2 tool assesses four critical domains: (1) patient selection, (2) index test, (3) reference standard, and (4) flow and timing. The risk of bias for each domain was categorized as “high risk,” “low risk,” or “unclear risk.”
2.4 Data extraction
The extracted data from the selected studies included several key elements: author, publication year, study location, type of radiotracer ([68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 or [18F]FDG), study design (prospective or retrospective), analysis type (patient-based or lesion-based), reference standard (pathology or imaging follow-up), patient demographics (mean or median age, number of patients), cancer type, interval between radiotracer tests (median and range), and diagnostic outcomes such as true-positive (TP), false-positive (FP), true-negative (TN), and false-negative (FN) results.
Two reviewers independently extracted data from each study. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion and consultation with an experienced third reviewer, ensuring consensus and accuracy in the data extraction process.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Specificity and sensitivity were evaluated using the DerSimonian and Laird method, followed by normalization of the data using the Freeman-Tukey double arcsine transformation. This transformation helps to make the data more suitable for analysis by converting proportions (which can range from 0 to 1) into values that are more evenly distributed, thereby resembling a normal distribution (27, 28). The confidence interval was calculated using the Jackson method. Heterogeneity, both within and between groups, was assessed using the Cochrane Q test and I2 statistics. Significant heterogeneity was defined as (P < 0.10 or I2 > 50%) (29). When significant heterogeneity was detected, leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was conducted by sequentially excluding individual studies and reassessing specificity or sensitivity. Additionally, meta-regression analysis was performed to identify potential sources of this heterogeneity (30).
Funnel plots and the Egger test were employed to evaluate publication bias. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05 for all analyses, except for the heterogeneity test, where a threshold of P < 0.10 was applied. All statistical analyses and figures were produced using R software (version 4.4.1).
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
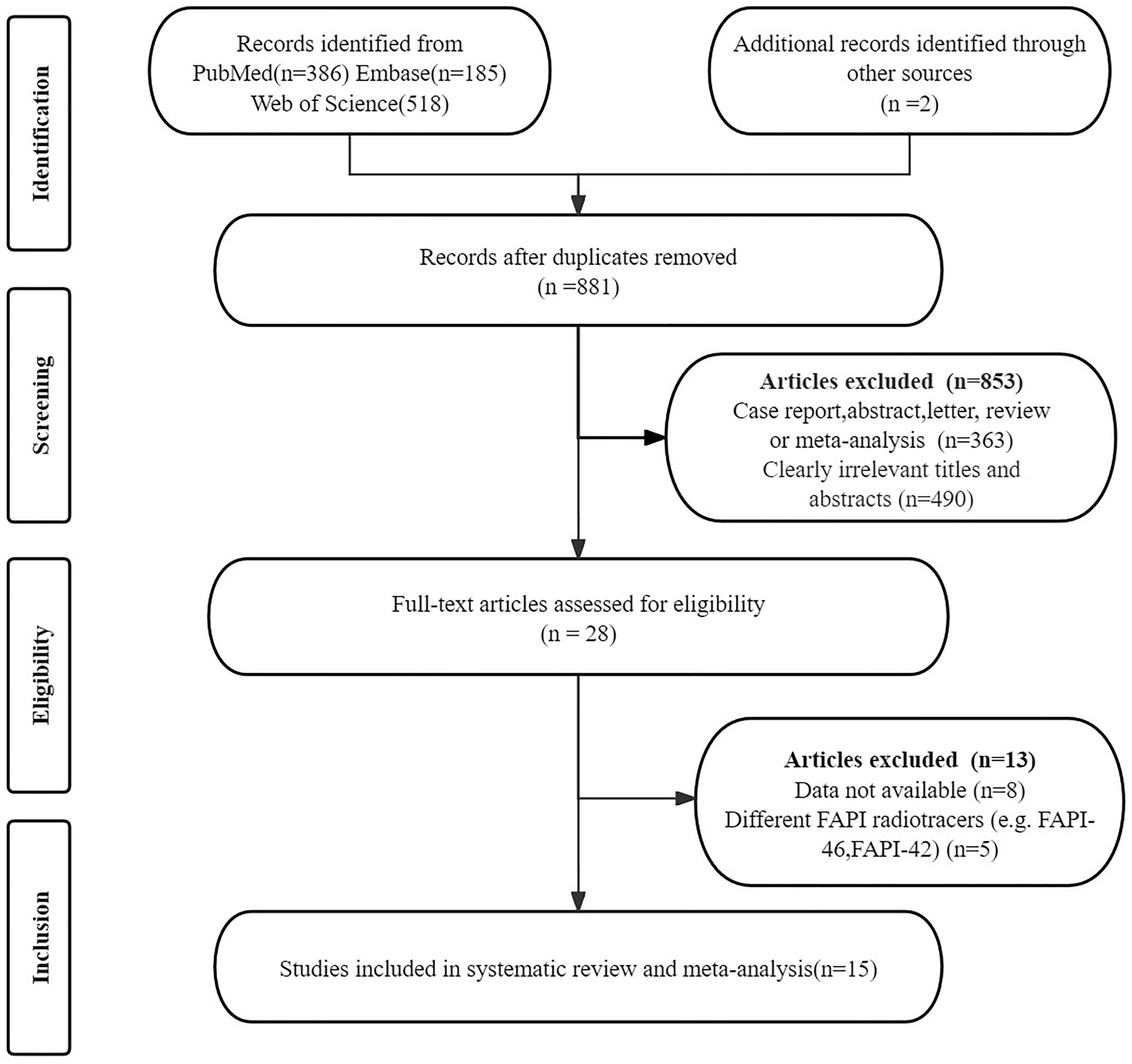
The initial search identified 1, 091 articles. After removing 210 duplicates and excluding 853 that did not meet the inclusion criteria, 28 articles remained for further consideration. Following a thorough review of the full texts, 13 articles were excluded for the following reasons: data (TP, TN, FP, and FN) not available (n = 8); articles using different FAPI radiotracers (e.g., FAPI-46, FAPI-42) (n = 5). The final analysis included 15 articles that evaluated the diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET (21, 23, 24, 31–42). Details of the article selection process are provided in Figure 1, in accordance with the PRISMA flow diagram.
3.2 Study description and quality assessment
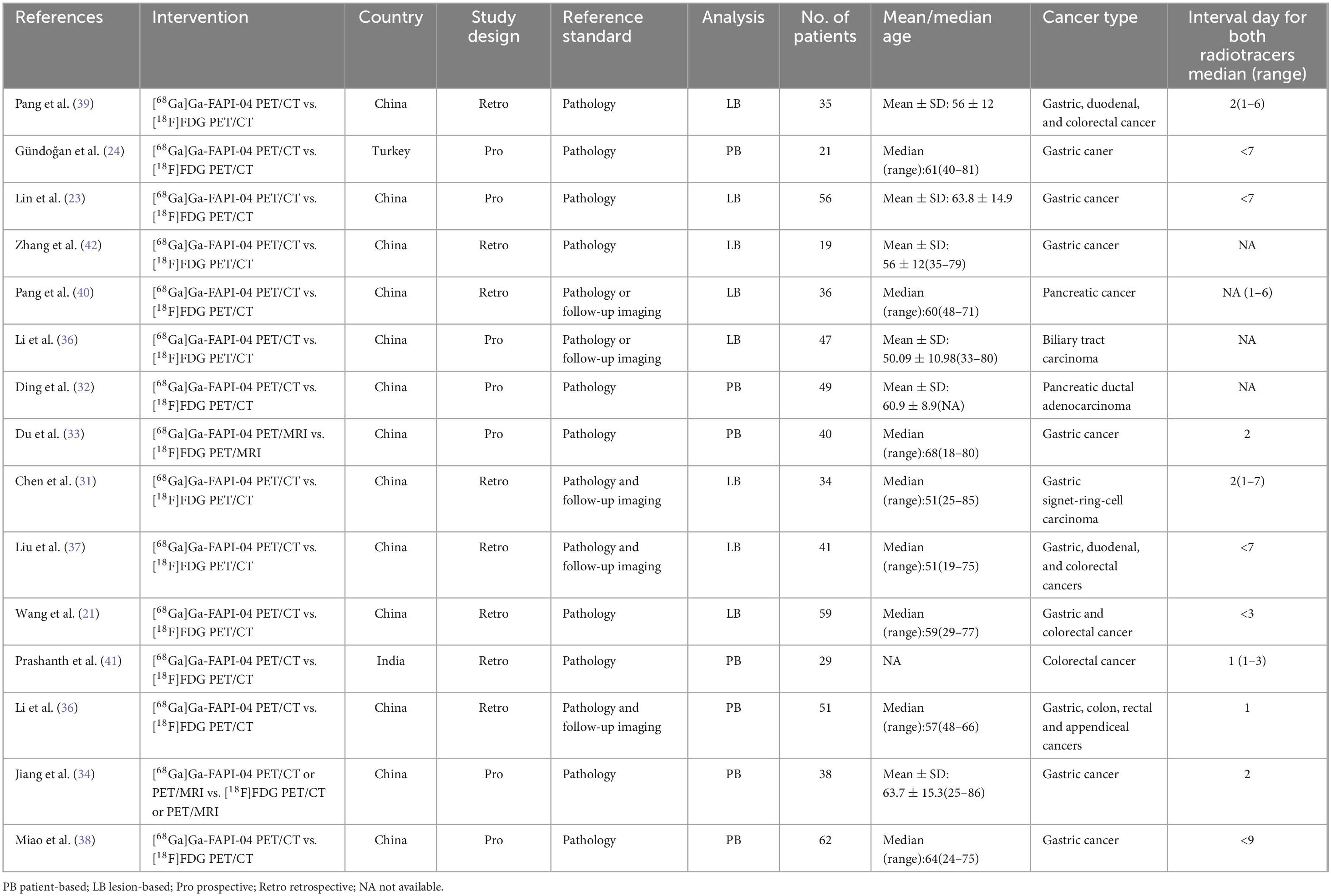
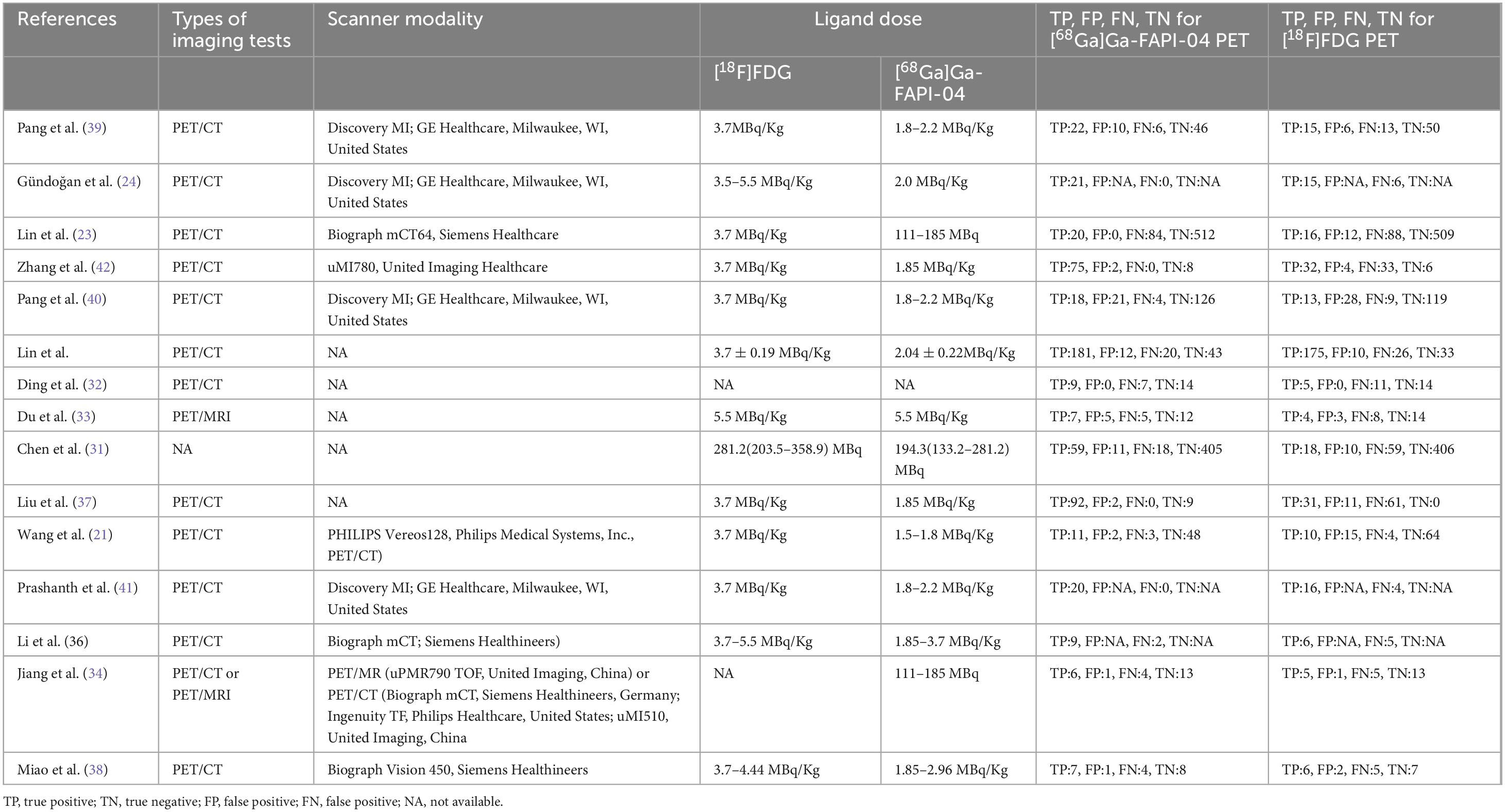
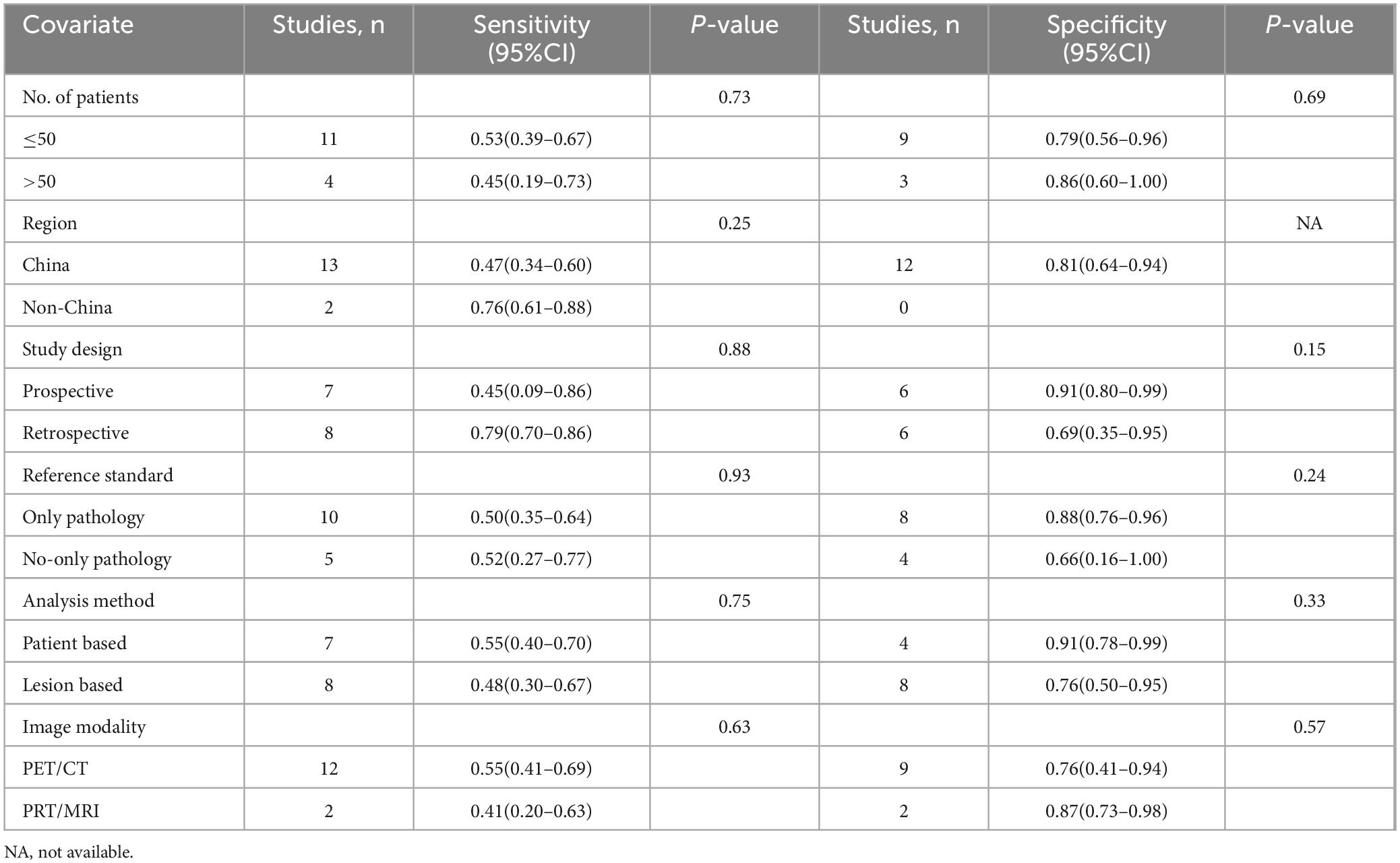
This analysis included 15 studies that met the eligibility criteria. These studies collectively involved 617 patients diagnosed with digestive system cancers (ranging from 19 to 62, with a median of 40 years). The studies were published between 2021 and 2024. Among these, the study populations for 13(86.67%) of the articles were Chinese, while 2(13.33%) articles focused on populations from other countries, specifically India and Turkey. 13(86.67%) utilized PET CT scanners, while 2(13.33%) employed PET MRI scanners. 9 (60%) were retrospective studies, and 6 (40%) were prospective. Regarding analysis methods, 7 (46.67%) studies conducted patient-based analysis, 8(53.33%) employed lesion-based analysis. The reference standard was pathology and imaging follow-up in 5 (33.33%) articles, pathology in 10 (66.67%) articles. Table 1 summarizes the basic information and patient characteristics of the included studies, and Table 2 summarizes the technical aspects of included studies.
The risk of bias for all studies was evaluated using the QUADAS-2 tool, as illustrated in Figure 2. Regarding the index test, 5 studies (33.33%) were classified as “unclear” due to insufficient information on the use of predefined thresholds. For other aspects, including patient selection, reference standard, flow and timing, and applicability concerns related to patient selection, the index test, and the reference standard, all studies were rated as “low” risk. Overall, no significant quality issues were identified in the included studies.
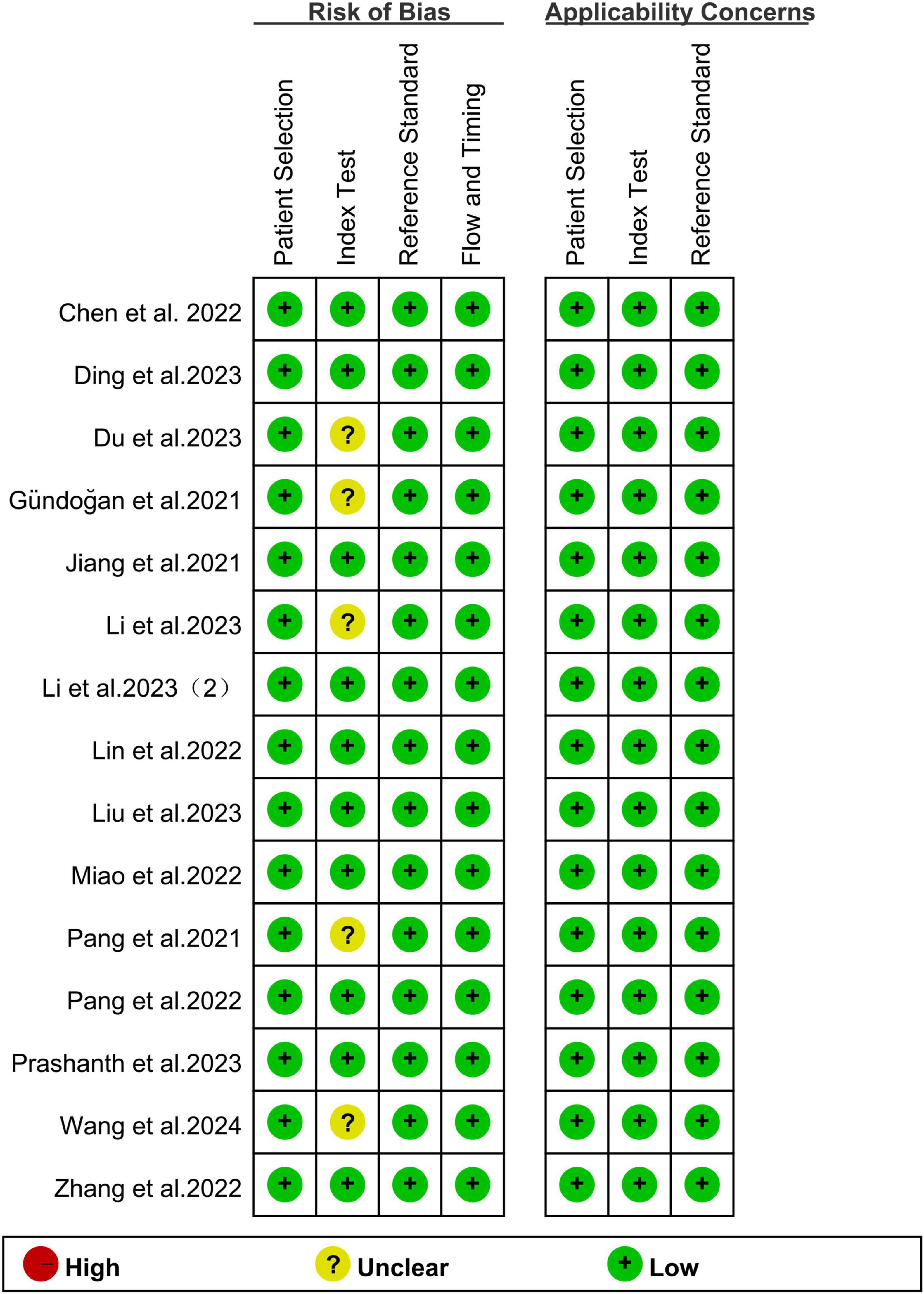
Figure 2. Summary of risk of bias and applicability concerns of all included studies according to QUADAS-2 tool.
3.3 Comparing the sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis of digestive system cancers
For lymph node metastasis diagnosis in digestive system cancers, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET had a pooled sensitivity of 0.82 (95% CI: 0.67–0.93), while the overall sensitivity of [18F]FDG PET was 0.51 (95% CI: 0.38–0.63) (Figure 3). The overall sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET showed statistical difference (P < 0.01) (Figure 3).
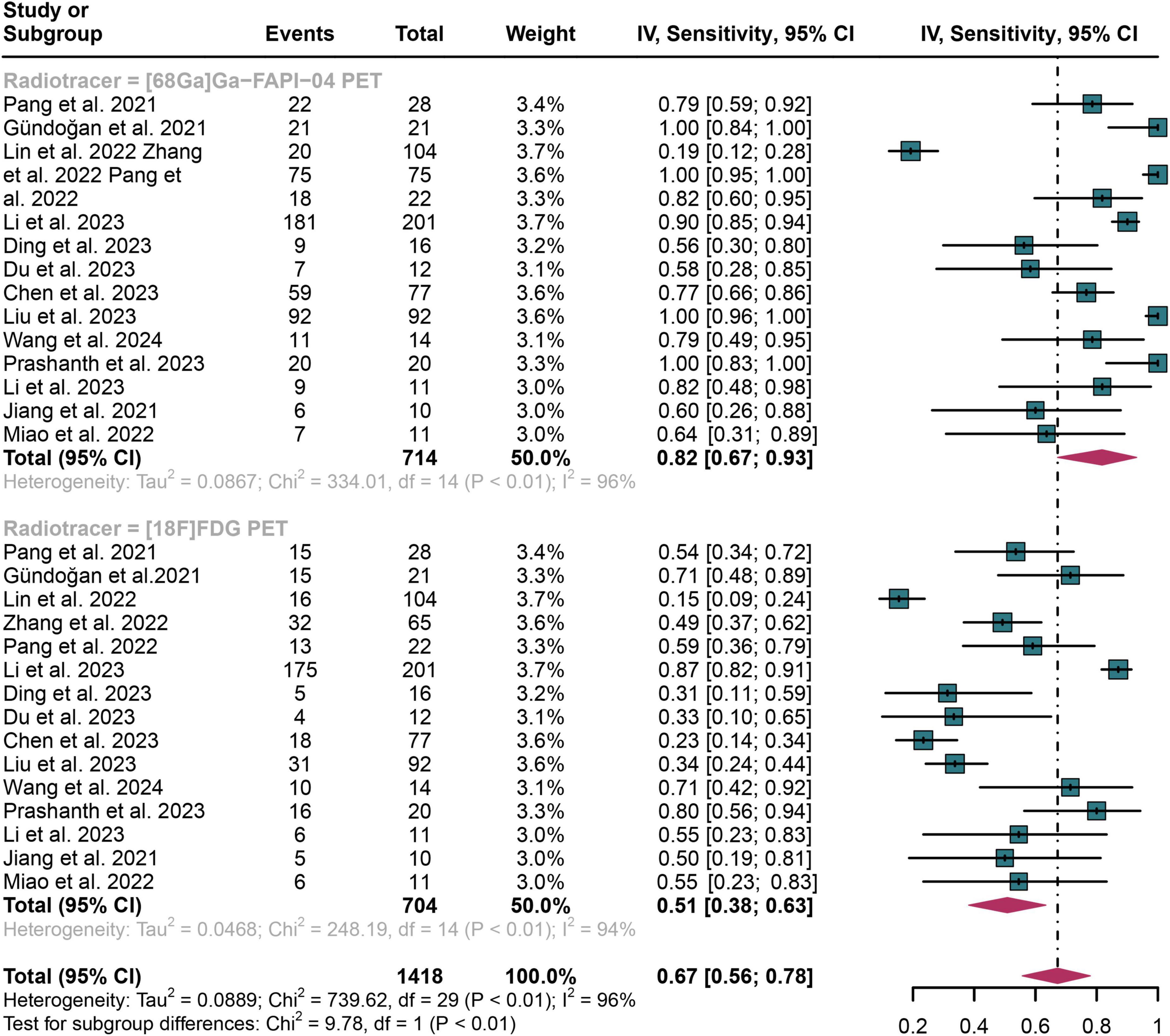
Figure 3. Forest plot shows a sensitivity analysis comparing [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
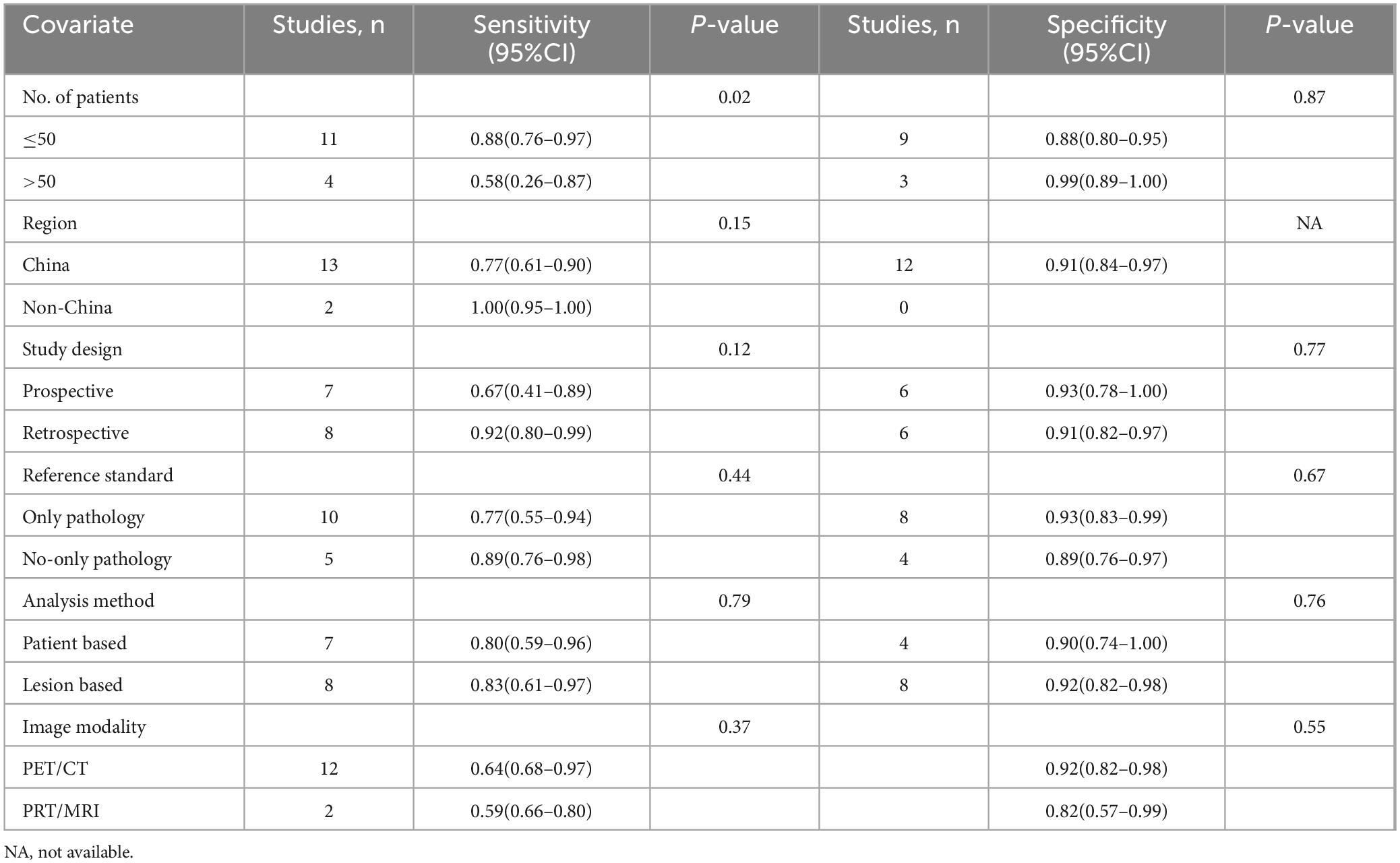
The I2 value was 96% for both [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET sensitivity. Leave-one-out analyses demonstrated result stability (range: 0.87–0.96 and 0.84–0.95, respectively; Supplementary Figures 1, 2). Meta-regression revealed patient number as a significant source of heterogeneity for [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET (P = 0.02), while no covariates significantly influenced [18F]FDG PET (Tables 3, 4).
3.4 Comparing the specificity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis of digestive system cancers
In detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET showed an overall specificity of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.84–0.97), compared to a pooled specificity of 0.81 (95% CI: 0.64–0.94) for [18F]FDG PET (Figure 4). The total specificity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET showed no statistical difference (P = 0.20) (Figure 4).
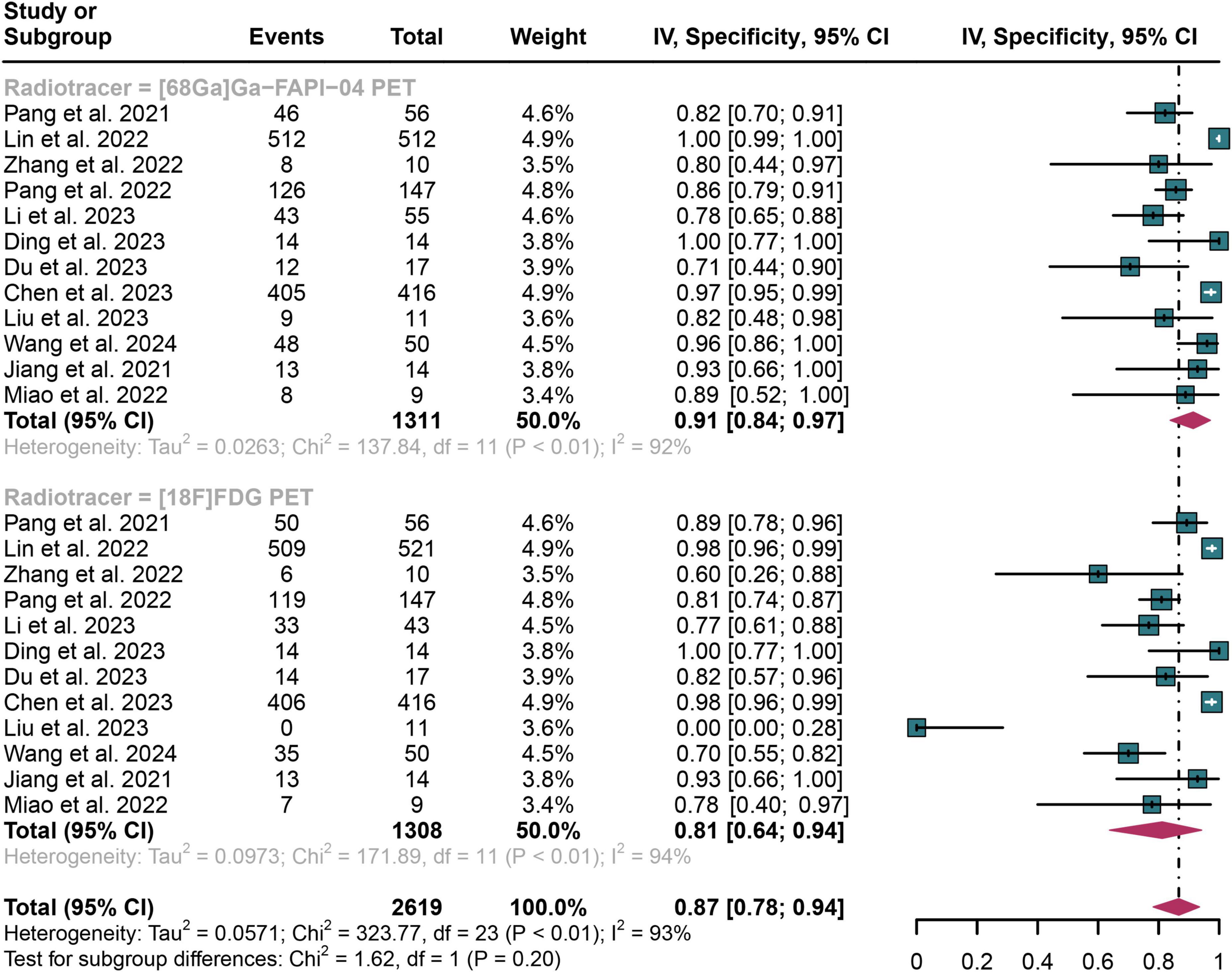
Figure 4. Forest plot shows a specificity analysis comparing [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
The I2 value was 92% for [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET specificity and 94% for [18F]FDG PET. Leave-one-out analyses demonstrated result stability (range: 0.83–0.93 and 0.91–0.94, respectively; Supplementary Figures 3, 4). Meta-regression showed no significant impact of study design, patient number, reference standard, or analysis type on either tracer’s specificity (Tables 3, 4).
3.5 Comparing the sensitivity and specificity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis of specific digestive system cancers
For gastric cancer (for sensitivity, 7 studies with 610 patients were included; for specificity, 6 studies with 1, 965 patients were included), the pooled sensitivity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET was 0.74 (95% CI: 0.45–0.95), significantly higher than the 0.40 (95% CI: 0.24–0.57) observed for [18F]FDG PET (P = 0.04). The specificity of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET was 0.93 (95% CI: 0.80–1.00), while that of [18F]FDG PET was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.77–0.99), showing no significant difference (P = 0.73).
For pancreatic cancer (For sensitivity, 2 studies and 76 patients were included; for specificity, 2 studies with 322 patients were included), [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET had a sensitivity of 0.71 (95% CI: 0.43–0.92), compared to 0.46 (95% CI: 0.20–0.73) for [18F]FDG PET, with the difference not reaching statistical significance (P = 0.21). The specificities were similar, with [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET at 0.93 (95% CI: 0.75–1.00) and [18F]FDG PET at 0.92 (95% CI: 0.66–1.00) (P = 0.90).
For biliary tract carcinoma (for sensitivity, 1 study and 402 patients were included; for specificity, 1 studies with 98 patients were included), [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET achieved a sensitivity of 0.90 (95% CI: 0.87–0.91), slightly higher than the 0.87 (95% CI: 0.82–0.91) observed with [18F]FDG PET, although this difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.35). The specificity was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.65–0.88) for [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and 0.77 (95% CI: 0.61–0.88) for [18F]FDG PET, with no significant difference (P = 0.86).
For colorectal cancer (for sensitivity, 1 study and 40 patients were included, no data for specificity), only sensitivity data were available. [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET exhibited a sensitivity of 1.00 (95% CI: 0.83–1.00), significantly higher than the 0.80 (95% CI: 0.56–0.94) recorded for [18F]FDG PET (P = 0.02). Detailed results can be found in Table 5.
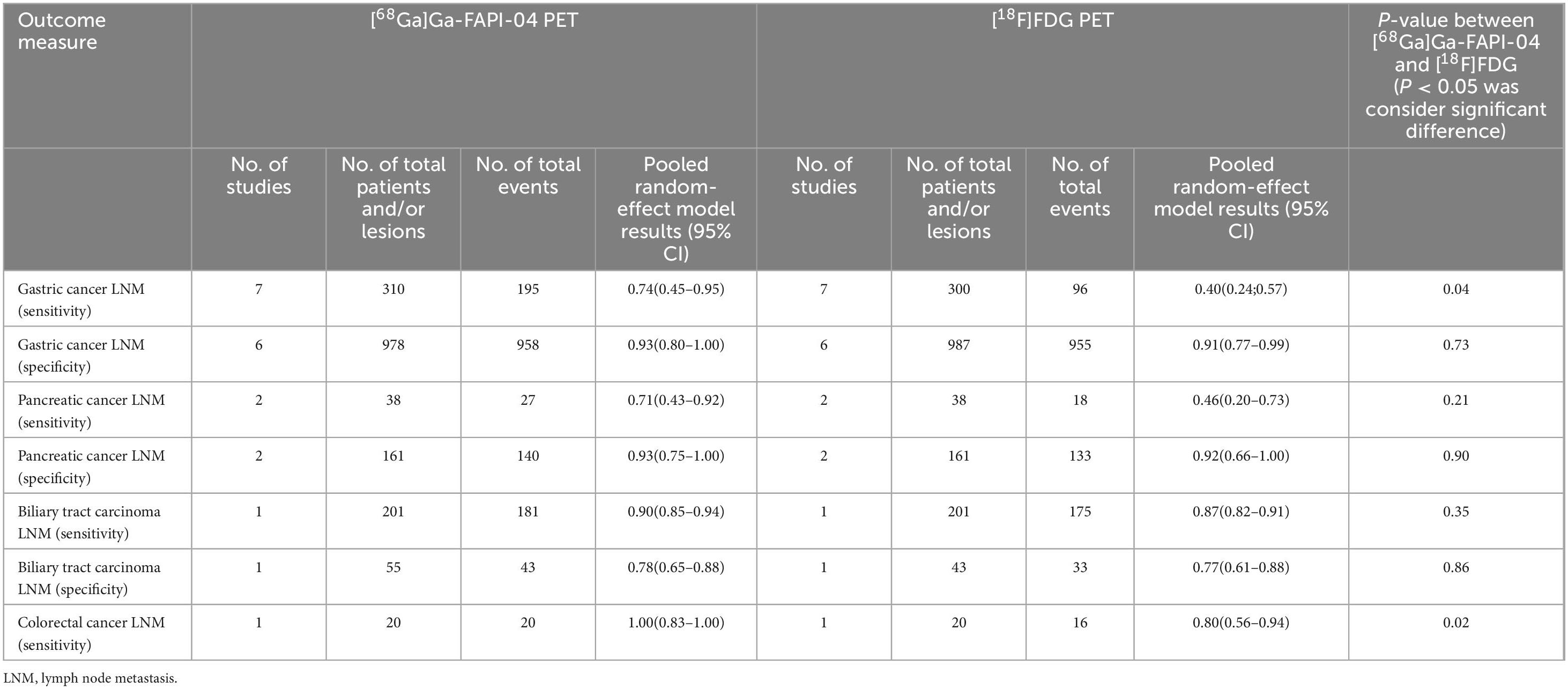
Table 5. Diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET vs. [18F]FDG PET in lymph node metastasis of specific digestive cancers.
3.6 Comparing the false positive rates (FPR) and false negative rates (FNR) of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis of digestive system cancers
For lymph node metastasis diagnosis in digestive system cancers, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET had a pooled FPR of 0.09 (95% CI: 0.03–0.16), while the overall FPR of [18F]FDG PET was 0.19 (95% CI: 0.06–0.36) (Figure 5). The overall FPR of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET showed no statistical difference (P = 0.20) (Figure 5).
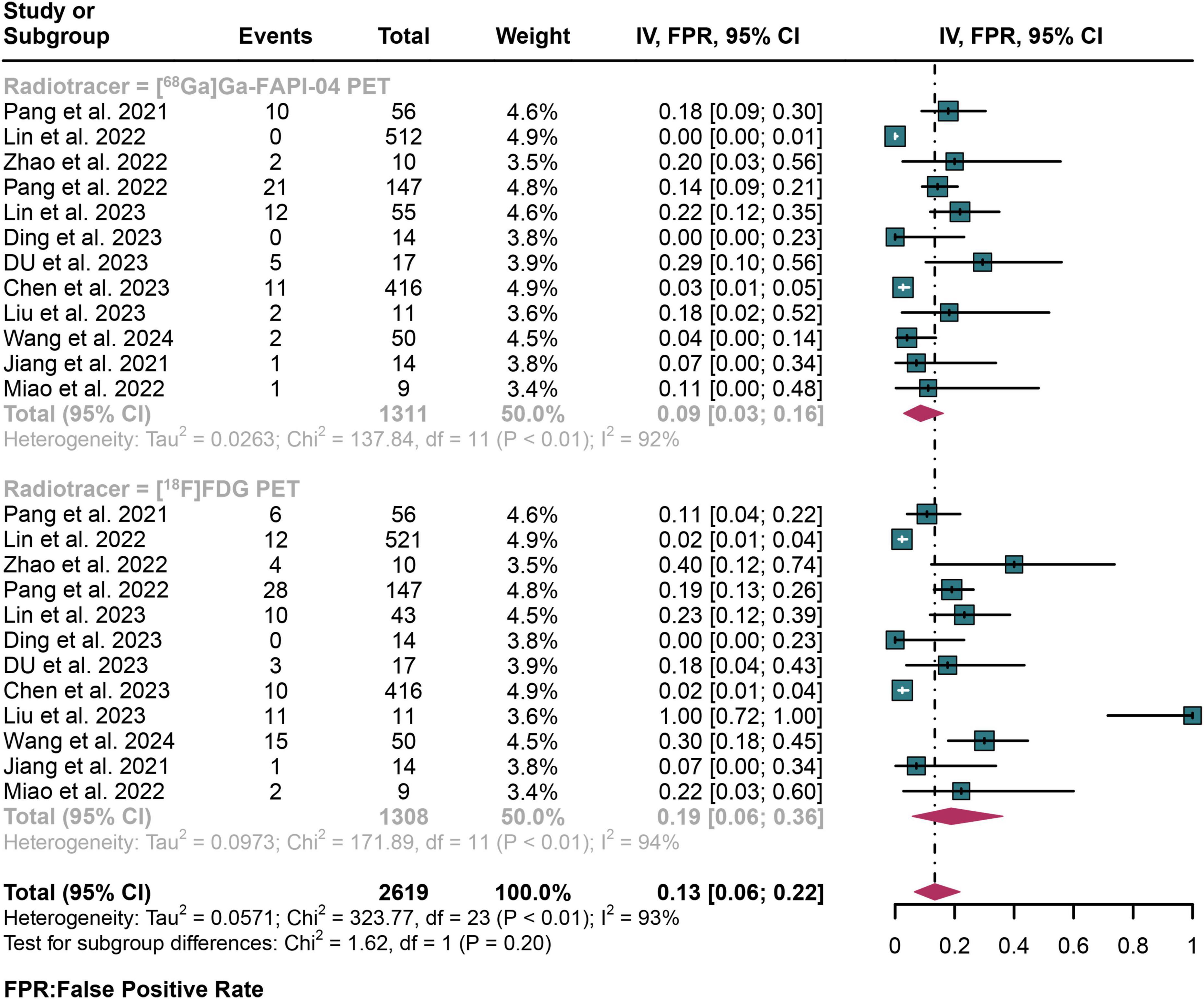
Figure 5. Forest plot shows a false positive rate (FPR) analysis comparing [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancer.
For lymph node metastasis diagnosis in digestive system cancers, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET had a pooled FNR of 0.18 (95% CI: 0.07–0.33), while the overall FNR of [18F]FDG PET was 0.49 (95% CI: 0.37–0.62) (Figure 6). The overall FNR of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET showed statistical difference (P < 0.01) (Figure 6).
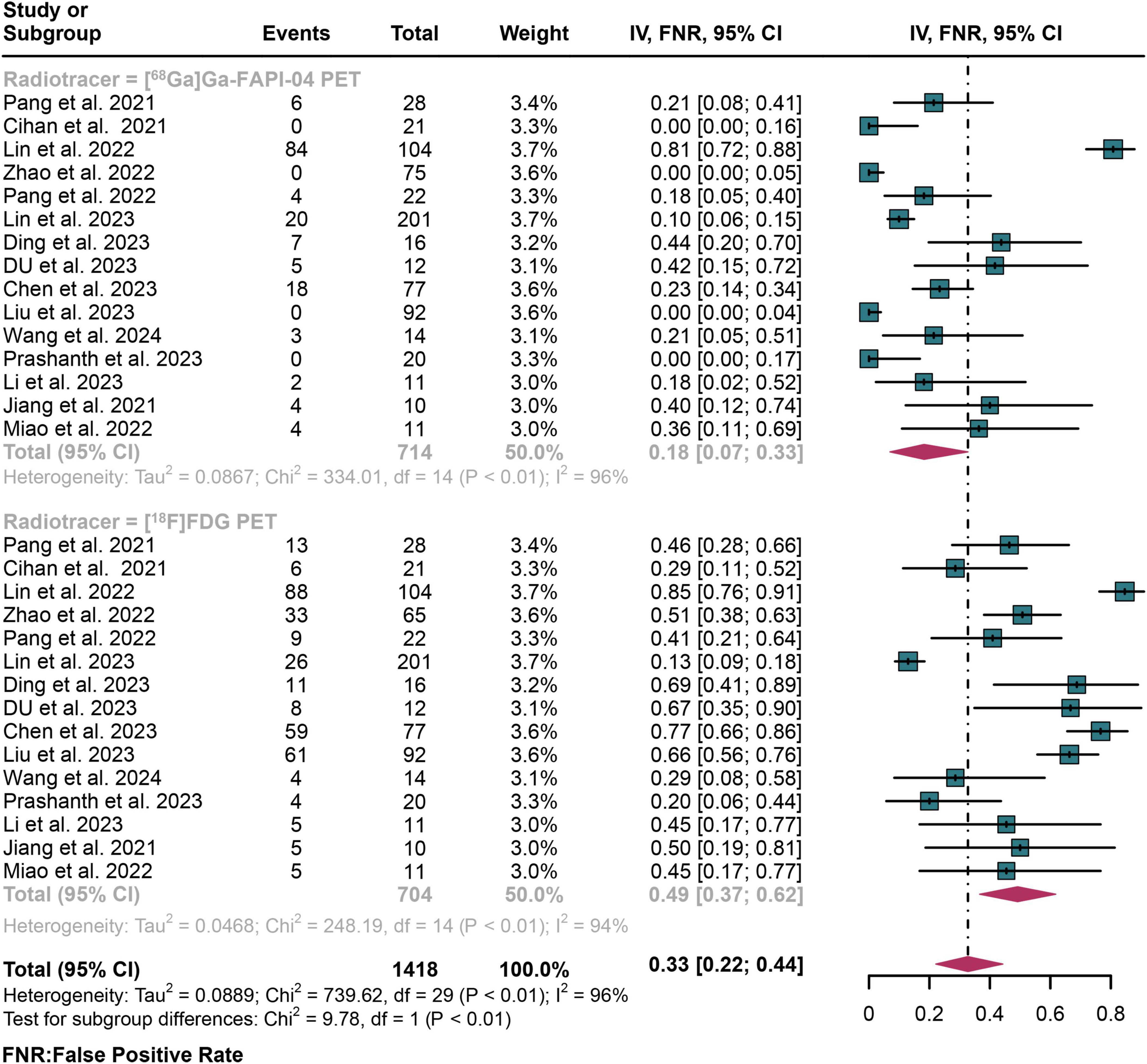
Figure 6. Forest plot shows a false negative rate (FNR) analysis comparing [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
3.7 Publication bias
The funnel plot asymmetry test and Egger’s test were conducted to assess potential publication bias in sensitivity estimates. The results indicated no significant publication bias for [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET (Egger’s test: P = 0.76) or [18F]FDG PET (Egger’s test: P = 0.64) (Supplementary Figures 5, 6). In contrast, these tests revealed significant publication bias in the specificity estimates for both [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET (Egger’s test: P = 0.02) and [18F]FDG PET (Egger’s test: P = 0.01, Supplementary Figures 7, 8).
4 Discussion
[18F]FDG PET is utilized for both the initial staging and subsequent restaging of lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers, ensuring precise assessment and supporting the optimization of therapeutic strategies (43). Recent studies show that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 outperforms [18F]FDG PET in diagnosing primary digestive system tumors. However, there is ongoing debate about their relative effectiveness in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers. This is the first systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the detection performance of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET for identifying lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
A significant difference in sensitivity was found between [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET (P < 0.01), although no difference in specificity was observed (P = 0.20), consistent with previous studies (37, 39). The diagnostic performance of [18F]FDG PET is limited due to the variable physiological uptake of [18F]FDG in the gastrointestinal tract, which can interfere with the detection of lesions (44). Additionally, [18F]FDG shows reduced uptake in certain histological subtypes, such as adenocarcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma, further affecting its diagnostic sensitivity (45, 46). In contrast, FAP, which is highly expressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and minimally in normal tissues, leads to a lower uptake of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI in healthy tissue (47). This results in a higher tumor-to-background ratio (TBR), thereby enhancing tumor visualization, particularly in regions with high glucose metabolism (48, 49). The comparable high specificity of both imaging agents in detecting lymph node metastasis may be due to the fact that both modalities provide functional information. When evaluating specific tumor subgroups-pancreatic cancer (2 studies), cholangiocarcinoma (1 study), and colorectal cancer (1 study)-no significant differences in sensitivity or specificity were found between [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET. However, in a systematic review by Zhuang et al. (included 3 studies), [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET demonstrated a higher positive detection rate for lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer compared to [18F]FDG PET, although sensitivity and specificity were not reported (50). The discrepancies between the findings for specific tumor subgroups and the overall results from the systematic review may be due to the small number of studies and patient samples in our analysis. Additionally, not all lymph node metastases were confirmed by pathological biopsy, with some relying on imaging follow-up as the standard. These factors could contribute to the variability and instability of the results.
Ouyang et al. found that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET was more effective than [18F]FDG PET in diagnosing primary cancers of the digestive system, particularly gastric, liver, biliary tract, and pancreatic cancers, with pooled sensitivity and specificity of 0.98 and 0.81, respectively (20). Multiple studies further confirmed the superior accuracy of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET in these contexts. However, it is important to note that Ouyang et al. did not assess its efficacy in diagnosing lymph node metastasis. To address this research gap, we conducted the first analysis of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET for diagnosing lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers. Our findings revealed that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET has a higher sensitivity of 0.82, compared to 0.51 for [18F]FDG PET. This underscores the superior diagnostic capability of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET in this specific application.
[18F]FDG PET offers advantages such as broad availability, established clinical validation, and valuable metabolic information for tumor assessment. However, it has limitations, including physiological uptake in normal tissues, which complicates lesion detection, and susceptibility to variations in tissue glucose metabolism. In contrast, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET provides high selectivity for tumor detection, potential for early diagnosis, and theragnostic applications. Our investigation of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET reveals statistically significant improvements in diagnostic sensitivity (P = 0.04) among gastric cancer patients. By precisely targeting fibrotic and tumor microenvironmental markers, this imaging technique demonstrates enhanced staging capabilities. Preliminary findings suggest potential advancements in early diagnostic strategies for specific patient populations. Nonetheless, its limited availability, the need for broader clinical validation, and concerns about radiation exposure are significant drawbacks. The half-life of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 is determined by the 68Ga radioisotope, with a half-life of 68 min, which poses certain challenges for its preparation and transportation. In contrast, [18F]FDG has a longer half-life (109.8 min), potentially offering advantages in transportation and application (51). [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 synthesis is characterized by extreme sensitivity to reaction conditions, requiring precise technical parameters. The synthesis process demands meticulous control, including temperature regulation precisely at 100°C, specialized reagents like 4-(2-hydroxyethyl) piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid, and professional radioisotope synthesis equipment such as cassette-based automated synthesizers (52). Multiple parameters necessitate precise optimization, resulting in a complex synthesis protocol (52). These multifaceted technical complexities may significantly constrain its widespread adoption in clinical practice. The safety assessments in the included studies indicated that no adverse reactions were reported during or after the use of either tracer, suggesting that both are safe for diagnostic purposes. Our findings indicate that [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET offers higher sensitivity and similar specificity compared to [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers. This improved sensitivity could enhance cancer staging accuracy and reduce the need for additional tests or treatments. FAPI-based radiotracers may significantly advance the diagnosis and treatment of digestive system cancers, particularly gastric cancer, leading to more personalized patient care and improved survival outcomes. Molecular imaging with [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 demonstrates heightened diagnostic precision in lesion identification, potentially mitigating false-negative occurrences and reducing unnecessary subsequent radiological assessments (53, 54). Notwithstanding these initial promising indicators, rigorous comparative analyses remain imperative to comprehensively evaluate the tracer’s clinical effectiveness and economic rationalization.
Several limitations should be noted. First, study heterogeneity may have affected the sensitivity and specificity results, with meta-regression suggesting that sample size (>50, <50) could be a contributing factor. Second, our results indicate significant publication bias in the specificity estimates for both [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET and [18F]FDG PET. This bias may primarily stem from the substantial overrepresentation of Chinese populations in the literature, with the majority of included studies originating from Chinese research centers. Third, due to technical and ethical constraints, not all positive lesions were confirmed by histopathology, necessitating the use of morphological criteria and follow-up imaging as reference standards. Fourth, the limited number of head-to-head studies has hindered our ability to compare the diagnostic performance of tools for specific gastrointestinal tumors, such as liver, duodenal, and appendiceal cancers. To address this gap, future research should prioritize head-to-head studies on these specific tumors. Additionally, to validate the current findings, further research involving diverse populations and well-designed prospective studies is required.
5 Conclusion
[68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET showed higher sensitivity but comparable specificity to [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis of digestive system cancers, particularly in gastric cancer. Both tracers performed similarly in biliary tract, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers. However, due to the limited sample sizes and notable heterogeneity observed in the current studies, there is a pressing need for larger prospective multicenter studies. Such research should focus on underrepresented populations outside of China and specific cancer subtypes, such as liver and duodenal cancers, to enhance the generalizability of findings and validate the efficacy of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET in diverse clinical settings.
Key points
Question: Is [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET more effective than [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in patients with digestive system cancers?
Pertinent findings: In a meta-analysis of 15 studies including 617 patients, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET showed significantly higher sensitivity (0.82 vs. 0.51) and similar specificity (0.91 vs. 0.81) compared to [18F]FDG PET for detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers.
Implications for patient care: [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET may provide more accurate lymph node staging in patients with digestive system cancers, potentially leading to better treatment planning and patient outcomes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JQ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. SH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SQ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. ZC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. RO: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1541461/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Washington M, Goldberg R, Chang G, Limburg P, Lam A, Salto-Tellez M, et al. Diagnosis of digestive system tumours. Int J Cancer. (2021) 148:1040–50. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33210
2. Arnold M, Abnet C, Neale R, Vignat J, Giovannucci E, McGlynn K, et al. Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology. (2020) 159: 335–49.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.068
3. Xia C, Dong X, Li H, Cao M, Sun D, He S, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin Med J (Engl). (2022) 135:584–90. doi: 10.1097/cm9.0000000000002108
4. Fitzgerald R, Antoniou A, Fruk L, Rosenfeld N. The future of early cancer detection. Nat Med. (2022) 28:666–77. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01746-x
5. Ramzan A, Tafti D. Nuclear medicine PET/CT gastrointestinal assessment, protocols, and interpretation. StatPearls, Ramzan A, Gao X, Tafti D, editors (Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing LLC), (2024).
6. Bisschops R, East J, Hassan C, Hazewinkel Y, Kamiński M, Neumann H, et al. Advanced imaging for detection and differentiation of colorectal neoplasia: European society of gastrointestinal endoscopy (ESGE) guideline - Update 2019. Endoscopy. (2019) 51:1155–79. doi: 10.1055/a-1031-7657
7. Atkinson N, Bryant R, Dong Y, Maaser C, Kucharzik T, Maconi G, et al. How to perform gastrointestinal ultrasound: Anatomy and normal findings. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23:6931–41. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.6931
8. Zhou J, Chen L, Chen L, Zhang Y, Yuan Y. Emerging role of nanoparticles in the diagnostic imaging of gastrointestinal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. (2022) 86:580–94. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.04.009
9. Impellizzeri G, Donato G, De Angelis C, Pagano N. Diagnostic endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) of the luminal gastrointestinal tract. Diagnostics (Basel). (2024) 14:996. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14100996
10. Mokrane F, Lu L, Vavasseur A, Otal P, Peron J, Luk L, et al. Radiomics machine-learning signature for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients with indeterminate liver nodules. Eur Radiol. (2020) 30:558–70. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06347-w
11. Haubner R, Weber W, Beer A, Vabuliene E, Reim D, Sarbia M, et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated alphavbeta3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. (2005) 2:e70. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020070
12. Koppula B, Fine G, Salem A, Covington M, Wiggins R, Hoffman J, et al. PET-CT in clinical adult oncology: III. Gastrointestinal malignancies. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:2668. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112668
13. Lin M, Wong K, Ng W, Shon I, Morgan M. Positron emission tomography and colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2011) 77:30–47. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.04.011
14. Annunziata S, Treglia G, Caldarella C, Galiandro F. The role of 18F-FDG-PET and PET/CT in patients with colorectal liver metastases undergoing selective internal radiation therapy with yttrium-90: A first evidence-based review. ScientificWorldJournal. (2014) 2014:879469. doi: 10.1155/2014/879469
15. Arçay Öztürk A, Flamen P. FAP-targeted PET imaging in gastrointestinal malignancies: A comprehensive review. Cancer Imaging. (2023) 23:79. doi: 10.1186/s40644-023-00598-z
16. Yun M, Bang S, Kim J, Park J, Kim K, Lee J. The importance of acetyl coenzyme A synthetase for 11C-acetate uptake and cell survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nucl Med. (2009) 50:1222–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.062703
17. Brunette L, Bonyadlou S, Ji L, Groshen S, Shuster D, Mehta A, et al. Predictive value of FDG PET/CT to detect lymph node metastases in cervical cancer. Clin Nucl Med. (2018) 43:793–801. doi: 10.1097/rlu.0000000000002252
18. Kobayashi H, Enomoto A, Woods S, Burt A, Takahashi M, Worthley D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in gastrointestinal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:282–95. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0115-0
19. Loktev A, Lindner T, Burger E, Altmann A, Giesel F, Kratochwil C, et al. Development of fibroblast activation protein-targeted radiotracers with improved tumor retention. J Nucl Med. (2019) 60:1421–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.224469
20. Ouyang J, Ding P, Zhang R, Lu Y. Head-to-head comparison of (68)Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the evaluation of primary digestive system cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1202505. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1202505
21. Wang B, Zhao X, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Chen X, Jing F, et al. Comparison of 68 Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT with 18 F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosis and staging of gastric and colorectal cancer. Nucl Med Commun. (2024) 45:612–21. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000001845
22. Reticker-Flynn NE, Zhang W, Belk JA, Basto PA, Escalante NK, Pilarowski GOW. Lymph node metastasis induces immune tolerance and distant metastasis. Cancer Discov. (2022) 12:1610. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-rw2022-092
23. Lin R, Lin Z, Chen Z, Zheng S, Zhang J, Zang J, et al. [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of gastric cancer: Comparison with [(18)F]FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 49:2960–71. doi: 10.1007/s00259-022-05799-5
24. Gündoğan C, Kömek H, Can C, Yildirim ÖA, Kaplan İ, Erdur E, et al. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the staging and restaging of gastric adenocarcinoma. Nucl Med Commun. (2022) 43:64–72. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000001489
25. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman D. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ. (2009) 339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535
26. Schueler S, Schuetz G, Dewey M. The revised QUADAS-2 tool. Ann Intern Med. (2012) 156:323. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-156-4-201202210-00018
27. DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. (1986) 7:177–88. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
28. Negeri Z, Shaikh M, Beyene J. Bivariate random-effects meta-analysis models for diagnostic test accuracy studies using arcsine-based transformations. Biom J. (2018) 60:827–44. doi: 10.1002/bimj.201700101
29. Hoaglin D. Assessment of heterogeneity in meta-analyses. JAMA. (2014) 312:2286–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.14346
30. Lo K, Stephenson M, Lockwood C. Analysis of heterogeneity in a systematic review using meta-regression technique. Int J Evid Based Healthc. (2019) 17:131–42. doi: 10.1097/xeb.0000000000000163
31. Chen H, Pang Y, Li J, Kang F, Xu W, Meng T, et al. Comparison of [(68)Ga]Ga-FAPI and [(18)F]FDG uptake in patients with gastric signet-ring-cell carcinoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:1329–41. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09084-9
32. Ding J, Qiu J, Hao Z, Huang H, Liu Q, Liu W, et al. Comparing the clinical value of baseline [(68) Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and [(18)F]F-FDG PET/CT in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Additional prognostic value of the distal pancreatitis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:4036–50. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06297-y
33. Du T, Zhang S, Cui X, Hu R, Wang H, Jiang J, et al. Comparison of [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [(18)F]FDG PET/MRI in the preoperative diagnosis of gastric cancer. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 2023:6351330. doi: 10.1155/2023/6351330
34. Jiang D, Chen X, You Z, Wang H, Zhang X, Li X, et al. Comparison of [(68) Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 and [(18)F]-FDG for the detection of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with gastric cancer: A bicentric retrospective study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 49:732–42. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05441-w
35. Jinghua L, Kui X, Deliang G, Bo L, Qian Z, Haitao W, et al. Clinical prospective study of Gallium 68 ((68)Ga)-labeled fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor PET/CT in the diagnosis of biliary tract carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2023) 50:2152–66. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06137-z
36. Li C, Tian Y, Chen J, Jiang Y, Xue Z, Xing D, et al. Usefulness of [(68)Ga]FAPI-04 and [(18)F]FDG PET/CT for the detection of primary tumour and metastatic lesions in gastrointestinal carcinoma: A comparative study. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:2779–91. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09251-y
37. Liu H, Yang X, Liu L, Qu G, Chen Y. Comparison of 18 F-FDG and 68 Ga-FAPI-04 uptake in postoperative re-evaluation of gastric, duodenal, and colorectal cancers. Clin Nucl Med. (2023) 48:304–8. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000004604
38. Miao Y, Feng R, Guo R, Huang X, Hai W, Li J, et al. Utility of [(68)Ga]FAPI-04 and [(18)F]FDG dual-tracer PET/CT in the initial evaluation of gastric cancer. Eur Radiol. (2023) 33:4355–66. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09321-1
39. Pang Y, Zhao L, Luo Z, Hao B, Wu H, Lin Q, et al. Comparison of (68)Ga-FAPI and (18)F-FDG uptake in gastric, duodenal, and colorectal cancers. Radiology. (2021) 298:393–402. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020203275
40. Pang Y, Zhao L, Shang Q, Meng T, Zhao L, Feng L, et al. Positron emission tomography and computed tomography with [(68)Ga]Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitors improves tumor detection and staging in patients with pancreatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 49:1322–37. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05576-w
41. Prashanth A, Kumar Ravichander S, Eswaran P, Kalyan S, Maheswari Babu S. Diagnostic performance of Ga-68 FAPI 04 PET/CT in colorectal malignancies. Nucl Med Commun. (2023) 44:276–83. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0000000000001661
42. Zhang S, Wang W, Xu T, Ding H, Li Y, Liu H, et al. Comparison of Diagnostic Efficacy of [(68)Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 and [(18)F]FDG PET/CT for staging and restaging of gastric cancer. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:925100. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925100
43. Veziant J, Bouche O, Aparicio T, Barret M, El Hajbi F, Lepilliez V, et al. Esophageal cancer - French intergroup clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatments and follow-up (TNCD, SNFGE, FFCD, GERCOR, UNICANCER, SFCD, SFED, SFRO, ACHBT, SFP, RENAPE, SNFCP, AFEF, SFR). Dig Liver Dis. (2023) 55:1583–601. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2023.07.015
44. Tasdemir B, Güzel Y, Komek H, Can C. Evaluation of dual time-point fluorodeoxyglucose PET/computed tomography imaging in gastric cancer. Nucl Med Commun. (2020) 41:1322–7. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000001290
45. Dondi F, Albano D, Giubbini R, Bertagna F. 18F-FDG PET and PET/CT for the evaluation of gastric signet ring cell carcinoma: A systematic review. Nucl Med Commun. (2021) 42:1293–300. doi: 10.1097/mnm.0000000000001481
46. Kuten J, Levine C, Shamni O, Pelles S, Wolf I, Lahat G, et al. Head-to-head comparison of [(68)Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 and [(18)F]-FDG PET/CT in evaluating the extent of disease in gastric adenocarcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2022) 49:743–50. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05494-x
47. Garin-Chesa P, Old L, Rettig W. Cell surface glycoprotein of reactive stromal fibroblasts as a potential antibody target in human epithelial cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (1990) 87:7235–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7235
48. Giesel F, Kratochwil C, Lindner T, Marschalek M, Loktev A, Lehnert W, et al. (68)Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Biodistribution and preliminary dosimetry estimate of 2 DOTA-containing FAP-targeting agents in patients with various cancers. J Nucl Med. (2019) 60:386–92. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.118.215913
49. Hirmas N, Hamacher R, Sraieb M, Ingenwerth M, Kessler L, Pabst K, et al. Fibroblast-activation protein PET and histopathology in a single-center database of 324 patients and 21 tumor entities. J Nucl Med. (2023) 64:711–6. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264689
50. Zhuang Z, Zhang Y, Yang X, Deng X, Wang Z. Head-to-head comparison of the diagnostic performance between (68)Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT and (18)F-FDG PET/CT in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2024) 49:3166–74. doi: 10.1007/s00261-024-04266-z
51. Giesel F, Adeberg S, Syed M, Lindner T, Jiménez-Franco L, Mavriopoulou E, et al. FAPI-74 PET/CT using either (18)F-AlF or Cold-Kit (68)Ga labeling: Biodistribution, radiation dosimetry, and tumor delineation in lung cancer patients. J Nucl Med. (2021) 62:201–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.120.245084
52. Kang W. Development of a synthetic method for [68 Ga] Ga-FAPI-04 using a cassette-based synthesizer. Korean J Clin Lab Sci. (2024) 56:43–51.
53. Shu Q, He X, Chen X, Liu M, Chen Y, Cai L. Head-to-head comparison of 18 F-FDG and 68 Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT for radiological evaluation of cervical cancer. Clin Nucl Med. (2023) 48:928–32. doi: 10.1097/rlu.0000000000004833
Keywords: digestive system cancers, [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET, [18F]FDG PET, lymph node metastasis, meta-analysis
Citation: Li H, Li Z, Qin J, Huang S, Qin S, Chen Z and Ouyang R (2025) Diagnostic performance of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET vs. [18F]FDG PET in detecting lymph node metastasis in digestive system cancers: a head-to-head comparative meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1541461. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1541461
Received: 07 December 2024; Accepted: 05 March 2025;
Published: 21 March 2025.
Edited by:
Hao Wang, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Edel Noriega-Álvarez, University Hospital of Guadalajara, SpainGhanshyam Ratilal Parmar, Sumandeep Vidyapeeth University, India
Copyright © 2025 Li, Li, Qin, Huang, Qin, Chen and Ouyang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rong Ouyang, b3V5YW5nLWd4bXVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Huo Li1†
Huo Li1† Zhixin Chen
Zhixin Chen Rong Ouyang
Rong Ouyang