
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Med. , 03 February 2025
Sec. Geriatric Medicine
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1525205
This article is part of the Research Topic Mechanisms and Novel Treatments of Muscle Wasting View all articles
 Yifan Lu1,2†
Yifan Lu1,2† Tiao Li3†
Tiao Li3† Yang Shu2,4
Yang Shu2,4 Chengyin Lu1,2
Chengyin Lu1,2 Zhiqiang Luo1,2
Zhiqiang Luo1,2 Jingrui Wang2,4
Jingrui Wang2,4 Hui Xiong4
Hui Xiong4 Wangyang Li1,2*
Wangyang Li1,2*Sarcopenia is an age-related condition characterized by the progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength. With the global aging population, its incidence is rapidly increasing. Lipid peroxidation is a critical biochemical process that generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to the destruction of muscle cell structure and function. It plays a pivotal role in the onset and progression of sarcopenia. This review summarizes the mechanisms by which lipid peroxidation contributes to sarcopenia, with a focus on its regulatory effects on cell membrane damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cell death. In addition, we discuss the protective role of antioxidant factors such as GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4) and antioxidant peptides like SS peptides in mitigating lipid peroxidation and delaying the progression of sarcopenia. Finally, the potential of various strategies, including natural compounds, supplements, natural extracts, and lifestyle interventions, in inhibiting lipid peroxidation and promoting muscle health is explored.
Sarcopenia is a progressive and systemic loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength associated with aging, significantly affecting the quality of life and functional independence of elderly individuals. It is also linked to adverse health outcomes, such as an increased risk of falls, fractures, hospitalization, and mortality (1). With the global aging population, sarcopenia has become an increasingly serious public health issue. Despite its substantial impact, a universally established diagnostic standard is still lacking. Current epidemiological studies indicate a global prevalence of sarcopenia ranging from 10% to 27%, with a prevalence of 8% to 36% in individuals under 60 years of age and 10% to 27% in those aged 60 and above (2). Additionally, elderly women are generally at a higher risk of developing sarcopenia than men (3), possibly due to factors such as decreased bone density (4), hormonal changes, and physiological differences (5). While sarcopenia is common among older adults, it can also occur in middle-aged and even young individuals (6), and is frequently observed in patients with chronic kidney disease, cancer, diabetes, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (7–10). The prevalence of sarcopenia varies widely, from 18% in diabetic patients to 66% in those with inoperable esophageal cancer (11). These conditions not only accelerate muscle loss but may also exacerbate muscle degeneration through mechanisms such as inflammation, metabolic disorders, and malnutrition (12, 13). Although the etiology of sarcopenia is complex, lipid peroxidation has emerged as a key factor in its onset and progression, attracting growing attention.
Lipid peroxidation involves a series of chemical reactions in which lipid molecules, particularly polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), are oxidatively attacked by free radicals or non-radical species in the cell membrane or intracellular structures. This process generates lipid radicals and peroxides, which damage the cell membrane structure and function, triggering a chain reaction that further impairs cellular function and induces apoptosis (14). Excessive lipid peroxidation is considered a central mechanism in various diseases. The resulting oxidative stress and cell death or necrosis are particularly prominent in the context of metabolic disorders, inflammation, and aging. Studies have shown that lipid peroxidation is closely associated with the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic disorders, and sarcopenia (15–17).
Lipid peroxidation is a free radical-driven oxidation of fatty acids, leading to damage of cell membranes and organelles. Cells have endogenous defense mechanisms to counteract this oxidative damage. The main defense mechanisms include antioxidant enzyme systems (such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase) and non-enzymatic antioxidants (such as glutathione, vitamin E, and vitamin C) (18–21). These mechanisms protect cells from oxidative damage by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and neutralizing lipid peroxidation products. However, under aging or chronic disease conditions, these endogenous defense mechanisms may be impaired, leading to elevated lipid peroxidation levels and exacerbating cellular damage, potentially contributing to diseases such as muscle atrophy.
In sarcopenia, lipid peroxidation may impact muscle health through several pathways. Firstly, lipid peroxidation products directly damage muscle cell membranes, leading to apoptosis and muscle loss (22). Secondly, lipid peroxidation products can induce inflammation and oxidative stress, further exacerbating muscle damage (23). Additionally, lipid peroxidation influences sarcopenia through various mechanisms, including metabolic disorders (24), ferroptosis (25), mitochondrial dysfunction (26), autophagy and apoptosis (27), extracellular matrix remodeling (28), cell signaling pathways (29), as well as lifestyle and nutritional factors (30).
This review summarizes the current research on lipid peroxidation and sarcopenia, including the molecular mechanisms by which lipid peroxidation influences muscle atrophy, protective mechanisms that reduce lipid peroxidation in slowing sarcopenia progression, and lipid peroxidation-based therapeutic strategies for sarcopenia. Finally, we will summarize recent findings and propose future research directions and potential interventions, offering new insights and approaches for the clinical treatment and prevention of sarcopenia.
Free radicals, particularly reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), are the primary inducers of lipid peroxidation. The mechanism of lipid peroxidation typically occurs in three stages: initiation, propagation, and termination (Figure 1). Initially, free radicals abstract hydrogen atoms from the fatty acid chain, forming lipid radicals and initiating the reaction. This reaction primarily occurs in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) due to their multiple double bonds, which make them more susceptible to free radical attack (31). During the propagation stage, the generated lipid radicals react with oxygen molecules to form lipid peroxides. These peroxides further attack other fatty acids, generating new lipid radicals, and continuing the chain reaction (32). This process continues until antioxidants, such as vitamin E or glutathione, intervene to terminate the reaction. In the termination stage, antioxidants stabilize lipid radicals by donating hydrogen atoms, thereby preventing further lipid peroxidation (33).
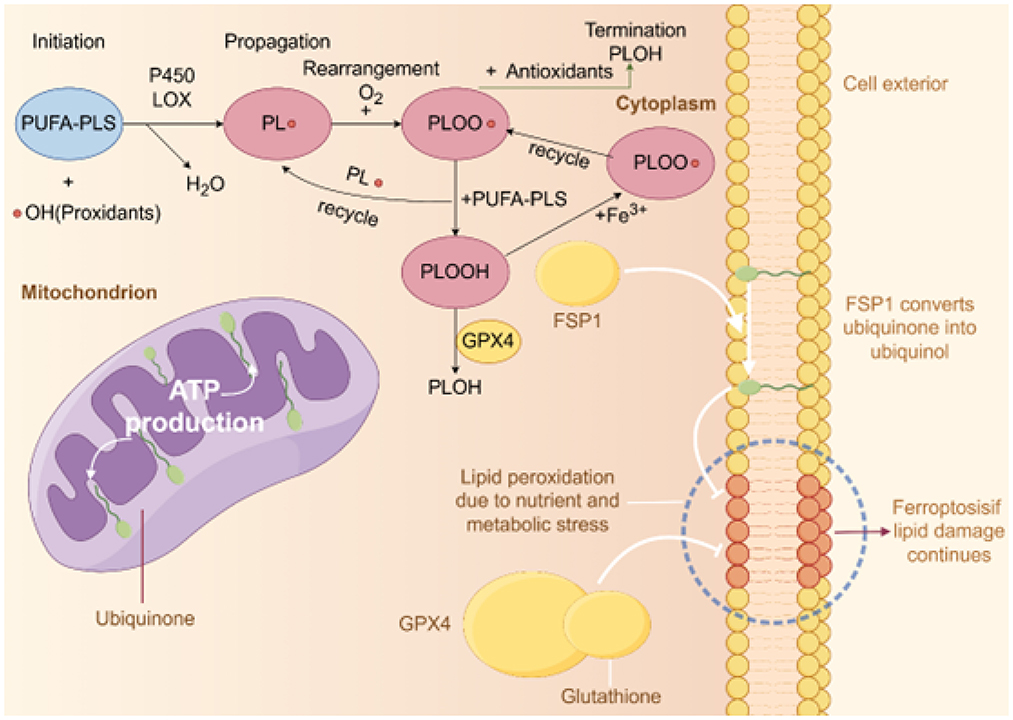
Figure 1. Diagram of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant mechanisms. This figure illustrates the three main stages of intracellular lipid peroxidation and corresponding antioxidant mechanisms: initiation, propagation, and termination. In the initiation stage, polyunsaturated phospholipids (PUFA-PLs) react with hydroxyl radicals (•OH) to form lipid radicals (PL•) under the catalysis of P450 and LOX enzymes. During propagation, PL• reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce lipid peroxyl radicals (PLOO•), which further react with other PUFA-PLs to form lipid hydroperoxides (PLOOH), a process that can be promoted by iron ions (Fe3+). In the termination stage, antioxidants such as GPX4 and glutathione reduce PLOO• to stable products (PLOH), ending the chain reaction and preventing further lipid peroxidation. Additionally, the figure shows cellular and mitochondrial structures. In mitochondria, ubiquinone is converted to ubiquinol by FSP1, which inhibits lipid damage caused by ferroptosis. Nutritional and metabolic stress can lead to increased lipid peroxidation, and if antioxidant defenses are insufficient, this may trigger ferroptosis.
Lipid peroxidation is one of the key mechanisms in muscle atrophy. The cell membrane plays a critical role in muscle cell function, particularly in muscle contraction, signal transduction, and metabolism. Lipid peroxidation not only damages the structure and function of the cell membrane but also triggers a series of secondary pathological changes, including cell death and muscle atrophy. The lipid peroxidation process mainly involves the oxidation of fatty acid double bonds, resulting in the formation of hydrogen peroxide, lipid peroxides, and their derivatives (e.g., α,β-unsaturated aldehydes). These products chemically damage membrane lipids, membrane proteins, and cholesterol, especially since membrane phospholipids are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, making them more vulnerable to free radical attack. This attack alters the membrane's conformation and fluidity, compromising its integrity (34, 35). These changes increase membrane permeability, affect membrane protein function, and lead to ion imbalance, particularly the influx of calcium ions, which in turn causes muscle fiber damage (36).
Membrane proteins, such as the sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ ATPase) and calcium ATPase (SERCA), are crucial molecules in maintaining the cell's electrochemical gradient and material transport. Lipid peroxidation alters the structure and function of these proteins, resulting in elevated intracellular calcium concentrations, promoting uncoordinated muscle contraction, and leading to cellular damage, thus exacerbating muscle atrophy (36). Additionally, lipid peroxidation products, such as 4-HNE and MDA, have immune-activating properties and can induce the recruitment and activation of immune cells, such as macrophages. The inflammatory factors (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) released by these immune cells further aggravate membrane damage and cellular destruction, creating a vicious cycle that accelerates the progression of sarcopenia (37, 38). The impact of lipid peroxidation on membrane damage is not limited to the cell membrane; mitochondrial membranes may also be affected. Therefore, membrane damage induced by lipid peroxidation is one of the key pathological mechanisms driving sarcopenia. Inhibiting lipid peroxidation or clearing its products may serve as an effective strategy for treating muscle atrophy.
Mitochondrial-associated lipid peroxidation plays a crucial role in the progression of sarcopenia. Mitochondria, as the powerhouses of the cell, are involved in ATP synthesis, metabolic regulation, and cell survival. Lipid peroxidation damages mitochondrial membranes and disrupts mitochondrial function, leading to insufficient energy supply in muscle cells, which exacerbates muscle atrophy and the onset of sarcopenia (39). The outer and inner mitochondrial membranes are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, and lipid peroxidation products, such as 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) and malondialdehyde (MDA), alter the fluidity and permeability of the membrane by binding with membrane lipids. This, in turn, induces mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT). MPT leads to intracellular calcium ion accumulation, triggering mitochondrial dysfunction. Lipid peroxidation also directly affects ATP synthase and membrane proteins, inhibiting ATP synthesis, disrupting energy metabolism, and further accelerating the decline in muscle cell function (40, 41).
Mitochondria are major sources of free radicals, and lipid peroxidation exacerbates oxidative stress by increasing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), damaging mitochondrial membranes and DNA, and weakening repair capabilities. Excessive ROS accumulation not only causes membrane damage but also induces mitochondrial DNA damage, alters gene expression, and promotes muscle atrophy. Lipid peroxidation products can also activate intrinsic apoptotic pathways within mitochondria, leading to cell death and further exacerbating sarcopenia (42, 43).
Lipid peroxidation can also inhibit mitochondrial autophagy. Damaged mitochondria are not removed in time and accumulate to form “waste” mitochondria, which release more ROS, accelerating muscle atrophy (7). Moreover, studies show that increased mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) can damage the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), leading to contraction dysfunction. In mSod2KO mice, despite an increase in muscle mass, significant reductions in contraction force were observed due to elevated mitochondrial ROS and lipid peroxidation, highlighting a new role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in maintaining muscle mass via fiber branching (44). Therefore, lipid peroxidation may disrupt mitochondrial membranes, induces oxidative stress, activates apoptotic pathways, and inhibits autophagy, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and exacerbating muscle atrophy. Improving mitochondrial function or activating mitochondrial autophagy may serve as potential therapeutic strategies to alleviate sarcopenia.
Lipid peroxidation is a byproduct of cellular responses to oxidative stress. In addition to damaging muscle cell membranes and mitochondrial function, lipid peroxidation exacerbates muscle atrophy by inducing muscle cell death. Muscle cell death mainly occurs through apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy, resulting in muscle fiber loss and promoting the progression of sarcopenia.
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death process. Lipid peroxidation increases ROS generation and damages cell membranes, activating a series of pro-apoptotic signaling molecules (e.g., caspase-3, p53), which lead to muscle cell apoptosis. Lipid peroxidation products, such as 4-HNE and MDA, activate the p53 pathway, inhibit Bcl-2 (an anti-apoptotic protein), activate Bax (a pro-apoptotic protein), increase mitochondrial membrane permeability, release cytochrome c, and initiate the caspase cascade, ultimately leading to cell death (45–47).
Moreover, lipid peroxidation is closely associated with necrotic cell death. Necrosis is an acute form of cell death caused by membrane damage, which is accompanied by cell swelling, membrane rupture, and leakage of cellular contents. Lipid peroxidation induces membrane damage, leading to uncontrolled calcium ion influx and exacerbating intracellular calcium accumulation, thereby triggering necrosis. Necrotic cells release danger signals (such as high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1), ATP, etc.), which activate inflammatory responses and aggravate oxidative stress and muscle damage (48–50).
Autophagy is a self-protective mechanism of cells, but lipid peroxidation disrupts the function of autophagy-related genes (e.g., Beclin-1, LC3), leading to autophagic decline, preventing the clearance of damaged mitochondria and protein complexes, and accelerating muscle cell death (51–53).
Lipid peroxidation also exacerbates muscle atrophy by activating muscle protein degradation pathways (e.g., the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, calcium-dependent pathways). Elevated ROS stimulate protein degradation pathways, resulting in reduced protein synthesis and increased degradation, thus accelerating muscle fiber loss. Furthermore, lipid peroxidation products promote inflammation through cytokines (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α), further exacerbating metabolic dysregulation and muscle atrophy (54, 55).
Additionally, lipid peroxidation products play distinct roles under specific pathological conditions. For example, cholesterol oxidation derivatives, such as 7β-hydroxycholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol, are significantly elevated in sarcopenia patients and exert cytotoxic effects on myoblasts and myotubes (56). These oxidized sterols exacerbate muscle atrophy by inducing inflammation and cell death. Antioxidants, such as α-tocopherol and pistachio oil, effectively reduce oxidized sterol-induced cytotoxicity and decrease the release of inflammatory factors, suggesting that antioxidant therapy may help slow the progression of sarcopenia. In conclusion, lipid peroxidation-induced muscle cell death and atrophy are key factors in the development of sarcopenia. Regulating lipid peroxidation may become an important strategy for the future treatment of sarcopenia.
Lipid peroxidation drives the pathological progression of sarcopenia through free radical reactions in conditions such as aging, disuse atrophy, denervation, and chronic diseases. The accumulation of lipid peroxidation products is closely associated with multiple factors, including genetic variation, denervation, immobilization and remobilization, chronic diseases, nutritional deficiencies, iron overload, alcoholic myopathy, and others. This section explores these aggravating factors, their effects in specific pathological environments, and potential intervention strategies (Table 1).
Genetic variation can significantly influence the accumulation of lipid peroxidation products. For example, the ALDH2 gene mutation (rs671, ALDH2*2) leads to the accumulation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE) in muscles, disrupting metabolic balance and causing muscle atrophy. Supplementation with the antioxidant vitamin E significantly lowers 4-HNE levels and alleviates muscle atrophy, highlighting the role of lipid peroxidation in genetically susceptible sarcopenia (57).
Denervation is another major cause of lipid peroxidation accumulation. In denervation-induced muscle atrophy models, increased activity of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) leads to high levels of lipid peroxidation products, such as lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH), aggravating muscle atrophy. Inhibition of cPLA2 reduces LOOH production, mitigates atrophy, and maintains muscle fiber size. This finding has been validated in several age-related muscle atrophy models (58, 59).
Both immobilization and subsequent remobilization are closely associated with changes in lipid peroxidation. During immobilization, lipid peroxidation in both muscles and blood increases significantly, peaking during the initial stage of immobilization and again during remobilization. The elevated lipid peroxidation during immobilization, coupled with reduced glutathione levels, indicates persistent oxidative stress, which further exacerbates muscle damage and atrophy (60).
Chronic Diseases and Lipid Peroxidation Chronic diseases, such as heart failure, are also associated with the accumulation of lipid peroxidation products. In heart failure mouse models, lipid peroxidation products like 4-HNE and acrolein significantly increase, while pathways for detoxifying these toxic aldehydes decrease, leading to further accumulation and exacerbation of muscle atrophy (61).
Nutritional Deficiencies and Lipid Peroxidation Nutritional deficiencies, particularly vitamin D deficiency, exacerbate sarcopenia by increasing lipid peroxidation and negatively impacting skeletal muscle function. In smoking mouse models, vitamin D deficiency initially does not affect muscle mass but, over time, leads to elevated lipid peroxidation, which, in combination with smoking, accelerates muscle loss and atrophy (62). Furthermore, protein malnutrition is closely linked to increased lipid peroxidation. In a rat model of liver cirrhosis induced by carbon tetrachloride, a low-protein diet exacerbates type IIa fiber atrophy, which is associated with increased iron content in muscles (63).
Moderate iron load can induce lipid peroxidation and impair skeletal muscle function. Research shows that moderate iron load significantly increases non-heme iron levels in skeletal muscles. Although body weight and muscle mass remain unchanged, specific force (tension) decreases, indicating impaired contractile function. This damage is likely caused by oxidative stress, increased protein degradation, and abnormal calcium release mechanisms within muscles (64).
Alcoholic Myopathy and Lipid Peroxidation Alcoholic myopathy is the result of both lipid peroxidation and protein malnutrition, leading to type II muscle fiber atrophy. The synergistic effect of alcohol and protein deficiency significantly increases lipid peroxidation products like malondialdehyde (MDA), which aggravates muscle atrophy. Notably, in animals with protein deficiency, the effects of iron overload and lipid peroxidation are more pronounced, suggesting that oxidative stress and iron overload are key contributors to sarcopenia in alcoholic myopathy (65).
Oxidative Stress and Muscle Damage In a hindlimb unloading model, increased oxidative stress significantly impairs the antioxidant capacity of skeletal muscles, elevating lipid peroxidation levels and making muscles more susceptible to damage and atrophy during prolonged unloading and reloading. This increase in oxidative stress, combined with weakened antioxidant defenses, exacerbates muscle damage (66). Another study confirmed this finding, showing that during hindlimb unloading and reloading, lipid peroxidation in skeletal muscles significantly increases, accompanied by dysregulation of heat shock proteins (HSPs), especially a decrease in Hsp70 and Hsp25 expression, which further aggravates muscle damage and atrophy (67).
Some drugs, such as dexmedetomidine, may have adverse effects on muscles through lipid peroxidation. Dexmedetomidine increases lipid peroxidation levels in the diaphragm of mechanically ventilated rats. Although it has some antioxidant potential, it does not alleviate ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction, indicating that oxidative stress and activation of proteolytic pathways play a central role in this process (68).
Sensitivity of Muscle Fiber Types to Oxidative Stress Different muscle fiber types exhibit varying sensitivities to oxidative stress. In a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model, lipid peroxidation levels in fast-twitch fibers (such as the extensor digitorum longus) were significantly increased and closely associated with atrophy. In contrast, slow-twitch fibers, like those in the soleus muscle, are more adaptable to oxidative stress and have higher antioxidant enzyme activity, although both fiber types ultimately undergo atrophy. This suggests that fast-twitch fibers are more susceptible to damage induced by oxidative stress (69).
In the mechanism by which lipid peroxidation contributes to muscle atrophy and functional loss, various protective mechanisms play a crucial role. By reducing lipid peroxidation, maintaining cellular redox balance, or modulating specific signaling pathways, these mechanisms can effectively slow the progression of sarcopenia. Table 2 summarizes these important protective mechanisms, including GPx4, ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and LPCAT3, which mitigate the negative effects of lipid peroxidation through different pathways. In the following sections, we will discuss each mechanism in detail, along with its potential clinical applications.
GPX4 (glutathione peroxidase 4) is an essential member of the antioxidant enzyme family, playing a key role in preventing cellular damage caused by lipid peroxidation. Lipid peroxidation leads to damage to cell membranes and mitochondria, which in turn results in cellular dysfunction and muscle atrophy. As a direct scavenger of lipid peroxides, GPX4 effectively removes harmful lipid peroxides and prevents the propagation of lipid peroxidation chain reactions through reduction processes, thereby maintaining cellular redox balance (70). The protective role of GPX4 becomes particularly important during aging and muscle atrophy. As aging progresses, the accumulation of lipid peroxides increases, causing instability in cell membranes, particularly in muscle cells. During this process, GPX4 expression or activity often decreases, leading to reduced cellular responses to oxidative damage and accelerating muscle degeneration. Studies have shown that enhancing GPX4 activity or overexpression can effectively reduce muscle damage caused by lipid peroxidation and delay the progression of muscle atrophy (71).
Research indicates that GPX4 plays a critical regulatory role in reducing the accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides during denervation-induced oxidative stress. In CuZn superoxide dismutase gene knockout mice, overexpression of GPX4 significantly improves mitochondrial respiratory function, restores contraction strength and membrane excitability in fast-twitch muscle fibers. Additionally, GPX4 enhances the activity of muscle/ER Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA), maintaining calcium homeostasis and excitation-contraction coupling, thereby alleviating sarcopenia progression (72). Apart from reducing lipid hydroperoxide levels, GPX4 also regulates the formation of oxidized phospholipids. By decreasing age-related lipid peroxidation and oxidative damage, overexpression of GPX4 offers a promising preventive and therapeutic approach for age-related sarcopenia by maintaining cell membrane integrity and reducing oxidative stress (71).
In a hindlimb suspension model of muscle atrophy, oxidative stress increases, and antioxidant enzyme imbalance is a key factor. Studies have shown that regulating oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme expression, such as enhancing manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and GPx activity, can effectively slow the progression of muscle atrophy, providing a new approach to sarcopenia prevention (73).
The accumulation of lipid peroxides is the foundation for lipid peroxides' role in sarcopenia. As aging and disuse atrophy progress, lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) in muscle tissue significantly increase, promoting muscle atrophy through carbonyl stress. Research indicates that the accumulation of LOOH is associated with insufficient activity of key antioxidant enzyme GPX4. When GPX4 activity decreases, LOOH levels rise, initiating lysosome-dependent and proteasome-independent pathways of atrophy (74). Genetic and pharmacological interventions that neutralize LOOH and its reaction products can effectively prevent muscle atrophy and weakness induced by aging and disuse.
In addition to GPX4, ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) possess significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, particularly in mitigating cachexia induced by hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Transgenic mice with elevated levels of n-3 PUFAs show reduced inflammatory responses and lipid peroxidation after injury, along with improved hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function, suggesting that n-3 PUFAs play a protective role in alleviating metabolic imbalances associated with cachexia (75).
Moreover, inhibiting the Lands cycle by modulating the activity of lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3 (LPCAT3) in skeletal muscle effectively reduces lipid peroxidation and alleviates muscle atrophy and weakness. In skeletal muscle-specific LPCAT3 knockout mice, lipid hydroperoxide levels were significantly reduced, indicating that suppressing the Lands cycle may be an effective strategy for alleviating sarcopenia (76).
Kynurenine (KYN), a tryptophan metabolite that increases with age, activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and increases ROS levels, which are associated with decreased protein synthesis and increased lipid peroxidation. Inhibition of KYN production improves muscle fiber size and strength in aged mice, suggesting that KYN is a key mediator of sarcopenia. Interestingly, KYN's effects on oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation occur independently of direct activation of AhR, making KYN metabolic inhibition a potential preventive approach for sarcopenia (77).
Sarcopenia also occurs in patients with asthma, closely linked to reduced SERCA (sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase) activity. Asthma patients exhibit decreased SERCA activity, increased oxidative stress, and lipid peroxidation, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy. Enhancing SERCA activity may provide a potential strategy for improving sarcopenia associated with asthma (78).
Iron accumulation in aged skeletal muscle is another factor that leads to increased lipid peroxidation and impaired regenerative capacity. In aged mice after ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury, iron levels rise significantly and are associated with lipid peroxidation. While deferiprone (DFP) treatment can reduce iron levels in muscle, it does not significantly improve muscle regeneration, underscoring the importance of iron homeostasis regulation for muscle health and regeneration (79).
Mitochondrial dysfunction plays a crucial role in the occurrence and progression of sarcopenia. Increased expression of mitochondrial autophagy-related proteins is closely associated with age-related mitochondrial dysfunction. However, overexpression of PGC-1α reduces autophagy marker levels, improves mitochondrial metabolic function and antioxidant capacity, thereby alleviating muscle atrophy, offering a potential approach to age-related sarcopenia (80). During cancer cachexia, mitochondrial dysfunction also plays a role in muscle atrophy. Although no significant lipid peroxidation is observed in cancer-associated muscle atrophy, increased mitochondrial protein carbonylation impairs mitochondrial function, suggesting that regulating mitochondrial phospholipid biosynthesis pathways may be an effective therapeutic target for cancer-associated muscle wasting (81).
Overexpression of the mitochondrial T3 receptor (p43) has also been shown to induce lipid peroxidation and lead to muscle atrophy. In p43-overexpressing mice, mitochondrial mass initially increases, but mitochondrial DNA content declines over time, impairing mitochondrial function. This overexpression triggers significant oxidative stress, increasing lipid and protein oxidation levels, and ultimately exacerbates atrophy through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, likely stimulated by muscle-specific E3 ligases Atrogin-1/MAFbx and MuRF1. This suggests that dysregulation of the direct T3 mitochondrial pathway may be an important driver of sarcopenia, emphasizing the need for precise control of p43 expression (82).
Moreover, mitochondrial dysfunction significantly affects muscle function recovery after disuse atrophy. In the hindlimb unloading-induced atrophy model, reduced mitochondrial respiration, calcium retention capacity, and increased oxidative stress are closely associated with muscle function decline, suggesting that maintaining mitochondrial function is critical for muscle recovery (83).
Under both normal and low-temperature conditions, apoptotic factors such as caspase-3 are activated during hindlimb unloading-induced atrophy, accompanied by DNA fragmentation and lipid peroxidation. Modulating the apoptosis pathway may play an important role in preventing disuse muscle atrophy (84).
In the treatment strategies for muscle atrophy related to lipid peroxidation, in addition to natural compounds, various interventions such as supplements, natural extracts, and lifestyle modifications are also included. These strategies work through different mechanisms to slow down or reverse muscle damage caused by lipid peroxidation. Table 3 summarizes these therapeutic strategies, including natural compounds, supplements, natural extracts, and other intervention methods, along with their mechanisms of action. Next, we will discuss each of these strategies in detail, exploring their specific effects, mechanisms, and potential clinical applications.
Among various interventions targeting oxidative stress and muscle atrophy, natural compounds play a central role. For instance, astaxanthin (AX), a carotenoid with strong antioxidant properties, can reduce mitochondrial ROS production, enhance mitochondrial respiration, inhibit mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, and effectively prevent muscle atrophy (85).
Fucoxanthin (Fx) also reduces muscle mass loss and oxidative stress induced by glucocorticoids in a dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy model, highlighting its potential in preventing glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy by inhibiting lipid peroxidation and enhancing mitochondrial function (86).
Quercetin and resveratrol have shown potential in combating disuse muscle atrophy. Quercetin reduces the expression of ubiquitin ligases and lipid peroxidation, effectively alleviating muscle atrophy in disuse suspension models while preserving muscle mass and function (87). Resveratrol significantly reduces lipid peroxidation levels, alleviates oxidative stress, and prevents muscle strength loss by enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity in disuse models, showing promise for improving redox balance (88).
Similarly, S-allyl cysteine (SAC), an organic sulfur compound derived from garlic, demonstrates broad antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects by lowering ROS levels and inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and myostatin), thus alleviating muscle atrophy (89).
Camphene also reduces ROS levels induced by starvation and hydrogen peroxide in both in vitro and in vivo models, improving muscle atrophy induced by starvation in rats. Its antioxidant activity offers significant protective effects on skeletal muscle atrophy (90). Moreover, the combined use of geranylgeraniol (GGOH) and green tea polyphenols (GTP) reduces fat accumulation, increases skeletal muscle mass, and alleviates the adverse effects of high-fat diets on skeletal muscles through modulation of the gut microbiota (91).
In rat models, oral supplementation of glutamine (GLN) increases the expression of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), balances intracellular redox status, and reduces skeletal muscle protein degradation and atrophy (92).
Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ), a natural redox cofactor, shows analgesic effects in chronic constriction injury (CCI) models. PQQ reduces pro-inflammatory mediators and lipid peroxidation products, thus alleviating muscle atrophy and pain associated with nerve damage (93).
Vitamin E, another potent antioxidant, protects against glucocorticoid-induced muscle atrophy (e.g., dexamethasone) by reducing lipid peroxidation and protein carbonylation, thereby reducing muscle atrophy (94).
Other natural compounds, such as handelin and Schisandra extracts, show significant anti-atrophy effects. Handelin, derived from chrysanthemums, protects against cachexia and age-related muscle atrophy by increasing the expression of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and inhibiting the activation of NF-κB. These effects help preserve muscle mass, improve muscle function, and maintain structural integrity by regulating inflammatory factors and reducing lipid peroxidation (95). Schisandra extract modulates genes involved in protein synthesis and degradation, inhibits lipid peroxidation, enhances endogenous antioxidant enzyme activity, reduces oxidative stress-related muscle damage, and enhances post-exercise muscle adaptation (96).
A compound in lemon peel, Eriocitrin, reduces lipid peroxidation and alleviates disuse muscle atrophy in denervated mice by inhibiting the expression of the ubiquitin ligases Atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 (97).
Long-term intake of Chlorella can restore muscle mass in mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-deficient mice and alleviate skeletal muscle atrophy associated with mitochondrial defects (98).
Exercise training is an effective strategy against muscle atrophy, particularly in heart failure (HF) patients. Exercise training improves skeletal muscle function by restoring lipid hydroperoxide and protein carbonyl levels, inhibiting excessive activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), reducing oxidative stress, and preventing skeletal muscle atrophy (99).
In vivo electrical stimulation significantly reduces lipid peroxidation levels following denervation, restores antioxidant enzyme activity, and effectively prevents oxidative damage and muscle atrophy caused by denervation (100).
In denervation-induced muscle atrophy, lipid hydroperoxides and lipid mediators are considered key driving factors. The use of lipid hydroperoxide scavenger Liproxstatin-1 significantly alleviates muscle atrophy and mitochondrial oxidative damage following denervation (101). Complete denervation of the gastrocnemius muscle increases ROS formation, leading to increased lipid peroxidation, further protein degradation, and muscle atrophy. Substances such as neurobolil and thyroxin, which stimulate tissue growth and enhance antioxidant enzyme activity, have been shown to reduce muscle atrophy (102).
In specific disease models, bioactive compounds have demonstrated unique protective properties. In Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients, He-Ne laser irradiation has been shown to alleviate oxidative stress by increasing nitric oxide (NO) levels and reducing lipid peroxidation, thereby slowing disease progression (103).
Szeto-Schiller peptides (SS peptides) are a class of engineered, mitochondria-targeted short peptides that bind to cardiolipin in the inner mitochondrial membrane, mitigating oxidative damage and improving mitochondrial function, thereby demonstrating potential protective effects in various disease models related to aging and tissue injury. SS peptides can interact with cell membranes to inhibit oxidative damage, showing potential in reducing oxidative stress and improving cellular health. Research indicates that the antioxidant properties of SS peptides make them valuable for the treatment of lipid peroxidation and sarcopenia (104, 105).
SS peptides, such as SS-31, may also enhance antioxidant defenses by modulating antioxidant enzyme systems like GPX4, helping to reduce lipid peroxidation and protect muscle cells from oxidative damage. Through this mechanism, SS peptides could improve muscle mass and delay the progression of muscle atrophy. While preliminary studies support the role of SS peptides in antioxidant and muscle protection, further clinical and animal research is needed to validate their therapeutic potential. Future studies should explore their mechanisms, especially in antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and muscle metabolism regulation, to provide new treatment options for muscle atrophy induced by aging.
Lipid peroxidation plays a crucial role in sarcopenia, acting both as a key pathological driver and a potential therapeutic target. An increasing body of research suggests that lipid peroxidation products exacerbate degenerative muscle changes by inducing oxidative stress, disrupting cell membrane structures, impairing mitochondrial function, and regulating cell death pathways. However, interventions involving antioxidants and natural bioactive compounds—particularly those that effectively inhibit lipid peroxidation—have shown significant potential in slowing the progression of sarcopenia.
Future research should focus on elucidating the mechanisms by which lipid peroxidation affects different types of muscle fibers, as well as how gene regulation and metabolic interventions can precisely control lipid peroxidation levels. Combining lipid peroxidation-targeted therapies with other interventions, such as exercise training, nutritional supplementation, and electrical stimulation, could provide more effective solutions for the comprehensive management of sarcopenia. Moreover, developing new biomarkers to monitor the dynamic changes of lipid peroxidation in muscle health will be crucial for early diagnosis and intervention.
In summary, lipid peroxidation is both a promoter of sarcopenia pathology and a unique therapeutic entry point. A deeper understanding of lipid peroxidation mechanisms holds promise for providing more precise and effective treatment strategies, ultimately improving patients' quality of life and delaying muscle degeneration.
YL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. TL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. CL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JW: Writing – review & editing. HX: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (Grant number 2023RC3167) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 82300062).
Figure 1 was drawn using Figdraw (www.figdraw.com) (accessed on 30 October 2024).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Damluji AA, Alfaraidhy M, AlHajri N, Rohant NN, Kumar M, Al Malouf C, et al. Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases. Circulation. (2023) 147:1534–53. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.064071
2. Petermann-Rocha F, Balntzi V, Gray SR, Lara J, Ho FK, Pell JP, et al. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:86–99. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12783
3. Hwang J, Park S. Sex differences of sarcopenia in an elderly Asian population: the prevalence and risk factors. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:11980. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191911980
4. Walsh MC, Hunter GR, Livingstone MB. Sarcopenia in premenopausal and postmenopausal women with osteopenia, osteoporosis and normal bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int. (2006) 17:61–7. doi: 10.1007/s00198-005-1900-x
5. Kenny AM, Dawson L, Kleppinger A, Iannuzzi-Sucich M, Judge JO. Prevalence of sarcopenia and predictors of skeletal muscle mass in nonobese women who are long-term users of estrogen-replacement therapy. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2003) 58:M436–40. doi: 10.1093/gerona/58.5.M436
6. Jung HN, Jung CH, Hwang YC. Sarcopenia in youth. Metabolism. (2023) 144:155557. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155557
7. Shu X, Lin T, Wang H, Zhao Y, Jiang T, Peng X, et al. Diagnosis, prevalence, and mortality of sarcopenia in dialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:145–58. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12890
8. Fang P, Zhou J, Xiao X, Yang Y, Luan S, Liang Z, et al. The prognostic value of sarcopenia in oesophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2023) 14:3–16. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13126
9. Izzo A, Massimino E, Riccardi G, Della Pepa G, A. narrative review on sarcopenia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: prevalence and associated factors. Nutrients. (2021) 13:183. doi: 10.3390/nu13010183
10. Sepúlveda-Loyola W, Osadnik C, Phu S, Morita AA, Duque G, Probst VS. Diagnosis, prevalence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia in COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2020) 11:1164–76. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12600
11. Yuan S, Larsson SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. (2023) 144:155533. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155533
12. Eid AA, Ionescu AA, Nixon LS, Lewis-Jenkins V, Matthews SB, Griffiths TL, et al. Inflammatory response and body composition in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2001) 164:1414–8. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.8.2008109
13. Noce A, Marrone G, Ottaviani E, Guerriero C, Di Daniele F, Pietroboni Zaitseva A, et al. Uremic sarcopenia and its possible nutritional approach. Nutrients. (2021) 13:147. doi: 10.3390/nu13010147
14. Rochette L, Dogon G, Rigal E, Zeller M, Cottin Y, Vergely C. Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24:449. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010449
15. Butterfield DA. Brain lipid peroxidation and alzheimer disease: synergy between the Butterfield and Mattson laboratories. Ageing Res Rev. (2020) 64:101049. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101049
16. Gianazza E, Brioschi M, Martinez Fernandez A, Casalnuovo F, Altomare A, Aldini G, et al. Lipid peroxidation in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2021) 34:49–98. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7955
17. Shabalala SC, Johnson R, Basson AK, Ziqubu K, Hlengwa N, Mthembu S, et al. Detrimental effects of lipid peroxidation in type 2 diabetes: exploring the neutralizing influence of antioxidants. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:2071. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102071
18. Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. (2021) 31:107–25. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
19. Jomova K, Alomar SY, Alwasel SH, Nepovimova E, Kuca K, Valko M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch Toxicol. (2024) 98:1323–67. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03696-4
20. Mirończuk-Chodakowska I, Witkowska AM, Zujko ME. Endogenous non-enzymatic antioxidants in the human body. Adv Med Sci. (2018) 63:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2017.05.005
21. Sies H. Oxidative stress: oxidants and antioxidants. Exp Physiol. (1997) 82:291–5. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1997.sp004024
22. Barrera G, Pizzimenti S, Daga M, Dianzani C, Arcaro A, Cetrangolo GP, et al. Lipid peroxidation-derived aldehydes, 4-hydroxynonenal and malondialdehyde in aging-related disorders. Antioxidants (Basel). (2018) 7:102. doi: 10.3390/antiox7080102
23. Vladykovskaya E, Sithu SD, Haberzettl P, Wickramasinghe NS, Merchant ML, Hill BG, et al. Lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-trans-2-nonenal causes endothelial activation by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem. (2012) 287:11398–409. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.320416
24. Nishikawa H, Asai A, Fukunishi S, Nishiguchi S, Higuchi K. Metabolic syndrome and sarcopenia. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3519. doi: 10.3390/nu13103519
25. Huang Y, Wu B, Shen D, Chen J, Yu Z, Chen C. Ferroptosis in a sarcopenia model of senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8). Int J Biol Sci. (2021) 17:151–62. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.53126
26. Marzetti E, Calvani R, Cesari M, Buford TW, Lorenzi M, Behnke BJ, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and sarcopenia of aging: from signaling pathways to clinical trials. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2013) 45:2288–301. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.024
27. Park SS, Kwon ES, Kwon KS. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions in sarcopenia. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. (2017) 3:117–22. doi: 10.1016/j.afos.2017.08.098
28. Melouane A, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J. Extracellular matrix/mitochondria pathway: a novel potential target for sarcopenia. Mitochondrion. (2020) 50:63–70. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2019.10.007
29. Gellhaus B, Böker KO, Schilling AF, Saul D. Therapeutic consequences of targeting the IGF-1/PI3K/AKT/FOXO3 axis in sarcopenia: a narrative review. Cells. (2023) 12:2787. doi: 10.3390/cells12242787
30. Ganapathy A, Nieves JW. Nutrition and sarcopenia-what do we know. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1755. doi: 10.3390/nu12061755
31. Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2014) 2014:360438. doi: 10.1155/2014/360438
32. Yin H, Xu L, Porter NA. Free radical lipid peroxidation: mechanisms and analysis. Chem Rev. (2011) 111:5944–72. doi: 10.1021/cr200084z
33. Niki E. Lipid peroxidation: physiological levels and dual biological effects. Free Radic Biol Med. (2009) 47:469–84. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.05.032
34. Mortensen MS, Ruiz J, Watts JL. Polyunsaturated fatty acids drive lipid peroxidation during ferroptosis. Cells. (2023) 12:804. doi: 10.3390/cells12050804
35. Li Z, Lange M, Dixon SJ, Olzmann JA. Lipid quality control and ferroptosis: from concept to mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. (2024) 93:499–528. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052521-033527
36. Hirata Y, Cai R, Volchuk A, Steinberg BE, Saito Y, Matsuzawa A, et al. Lipid peroxidation increases membrane tension, Piezo1 gating, and cation permeability to execute ferroptosis. Curr Biol. (2023) 33:1282–94.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.02.060
37. Dmitriev LF, Titov VN. Lipid peroxidation in relation to ageing and the role of endogenous aldehydes in diabetes and other age-related diseases. Ageing Res Rev. (2010) 9:200–10. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2009.09.004
38. Tidball JG, Wehling-Henricks M. Macrophages promote muscle membrane repair and muscle fibre growth and regeneration during modified muscle loading in mice in vivo. J Physiol. (2007) 578:327–36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.118265
39. Miranda ER, Shahtout JL, Funai K. Chicken or egg? Mitochondrial phospholipids and oxidative stress in disuse-induced skeletal muscle atrophy. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2023) 38:338–51. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0151
40. Monroe TB, Hertzel AV, Dickey DM, Hagen T, Santibanez SV, Berdaweel IA, et al. Lipid peroxidation products induce carbonyl stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cellular senescence in human and murine cells. Aging Cell. (2024) 11:e14367. doi: 10.1111/acel.14367
41. Ye T, Yang W, Gao T, Yu X, Chen T, Yang Y, et al. Trastuzumab-induced cardiomyopathy via ferroptosis-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 206:143–61. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.06.019
42. Al-Menhali AS, Banu S, Angelova PR, Barcaru A, Horvatovich P, Abramov AY, et al. Lipid peroxidation is involved in calcium dependent upregulation of mitochondrial metabolism in skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. (2020) 1864:129487. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.129487
43. Kujoth GC, Hiona A, Pugh TD, Someya S, Panzer K, Wohlgemuth SE, et al. Mitochondrial DNA mutations, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in mammalian aging. Science. (2005) 309:481–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1112125
44. Ahn B, Ranjit R, Premkumar P, Pharaoh G, Piekarz KM, Matsuzaki S, et al. Mitochondrial oxidative stress impairs contractile function but paradoxically increases muscle mass via fibre branching. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2019) 10:411–28. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12375
45. Wang B, Wang Y, Zhang J, Hu C, Jiang J, Li Y, et al. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch Toxicol. (2023) 97:1439–51. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03476-6
46. Vaseva AV, Marchenko ND Ji K, Tsirka SE, Holzmann S. Moll UM p53 opens the mitochondrial permeability transition pore to trigger necrosis. Cell. (2012) 149:1536–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.014
47. Vladimirov YA, Proskurnina EV, Alekseev AV. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis structure of cytochrome c-cardiolipin complex. Biochemistry (Mosc). (2013) 78:1086–97. doi: 10.1134/S0006297913100027
48. Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature. (2002) 418:191–5. doi: 10.1038/nature00858
49. Yu Y, Tang D, Kang R. Oxidative stress-mediated HMGB1 biology. Front Physiol. (2015) 6:93. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00093
50. Careccia G, Saclier M, Tirone M, Ruggieri E, Principi E, Raffaghello L, et al. Rebalancing expression of HMGB1 redox isoforms to counteract muscular dystrophy. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13:eaay8416. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay8416
51. Luo C, Li Y, Wang H, Feng Z, Li Y, Long J, et al. Mitochondrial accumulation under oxidative stress is due to defects in autophagy. J Cell Biochem. (2013) 114:212–9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24356
52. Troncoso R, Paredes F, Parra V, Gatica D, Vásquez-Trincado C, Quiroga C, et al. Dexamethasone-induced autophagy mediates muscle atrophy through mitochondrial clearance. Cell Cycle. (2014) 13:2281–95. doi: 10.4161/cc.29272
53. Li W, Luo LX, Zhou QQ, Gong HB, Fu YY, Yan CY, et al. Phospholipid peroxidation inhibits autophagy via stimulating the delipidation of oxidized LC3-PE. Redox Biol. (2022) 55:102421. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102421
54. Pang X, Zhang P, Chen X, Liu W. Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in skeletal muscle atrophy. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1289537. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1289537
55. Jang YC, Rodriguez K, Lustgarten MS, Muller FL, Bhattacharya A, Pierce A, et al. Superoxide-mediated oxidative stress accelerates skeletal muscle atrophy by synchronous activation of proteolytic systems. Geroscience. (2020) 42:1579–91. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00200-5
56. Ghzaiel I, Zarrouk A, Pires V, de Barros JP, Hammami S, Ksila M, et al. 7β-Hydroxycholesterol and 7-ketocholesterol: New oxidative stress biomarkers of sarcopenia inducing cytotoxic effects on myoblasts and myotubes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2023) 232:106345. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2023.106345
57. Kobayashi H, Nakamura S, Sato Y, Kobayashi T, Miyamoto K, Oya A, et al. ALDH2 mutation promotes skeletal muscle atrophy in mice via accumulation of oxidative stress. Bone. (2021) 142:115739. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115739
58. Pharaoh G, Brown JL, Sataranatarajan K, Kneis P, Bian J, Ranjit R, et al. Targeting cPLA(2) derived lipid hydroperoxides as a potential intervention for sarcopenia. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:13968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70792-7
59. Bhattacharya A, Muller FL, Liu Y, Sabia M, Liang H, Song W, et al. Denervation induces cytosolic phospholipase A2-mediated fatty acid hydroperoxide generation by muscle mitochondria. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:46–55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806311200
60. Liu MJ, Li JX, Lee KM, Qin L, Chan KM. Oxidative stress after muscle damage from immobilization and remobilization occurs locally and systemically. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2005) 434:246–50. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000150464.29883.ca
61. Chaudhari M, Zelko I, Lorkiewicz P, Hoetker D, Nong Y, Doelling B, et al. Metabolic pathways for removing reactive aldehydes are diminished in the skeletal muscle during heart failure. Skelet Muscle. (2024) 14:24. doi: 10.1186/s13395-024-00354-2
62. Cielen N, Heulens N, Maes K, Carmeliet G, Mathieu C, Janssens W, et al. Vitamin D deficiency impairs skeletal muscle function in a smoking mouse model. J Endocrinol. (2016) 229:97–108. doi: 10.1530/JOE-15-0491
63. López-Lirola A, González-Reimers E, Martín Olivera R, Santolaria-Fernández F, Galindo-Martín L, Abreu-González P, et al. Protein deficiency and muscle damage in carbon tetrachloride induced liver cirrhosis. Food Chem Toxicol. (2003) 41:1789–97. doi: 10.1016/S0278-6915(03)00218-7
64. Liang C, Mickey MC, Receno CN, Atalay M, DeRuisseau KC. Functional and biochemical responses of skeletal muscle following a moderate degree of systemic iron loading in mice. J Appl Physiol. (2019) 126:799–809. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00237.2018
65. Durán Castellón MC, González-Reimers E, López-Lirola A, Martín Olivera R, Santolaria-Fernández F, Galindo-Martín L, et al. Alcoholic myopathy: lack of effect of zinc supplementation. Food Chem Toxicol. (2005) 43:1333–43. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2005.03.006
66. Lawler JM, Song W, Demaree SR. Hindlimb unloading increases oxidative stress and disrupts antioxidant capacity in skeletal muscle. Free Radic Biol Med. (2003) 35:9–16. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00186-2
67. Lawler JM, Song W, Kwak HB. Differential response of heat shock proteins to hindlimb unloading and reloading in the soleus. Muscle Nerve. (2006) 33:200–7. doi: 10.1002/mus.20454
68. Breuer T, Bleilevens C, Rossaint R, Marx G, Gehrenkemper J, Dierksen H, et al. Dexmedetomidine impairs diaphragm function and increases oxidative stress but does not aggravate diaphragmatic atrophy in mechanically ventilated rats. Anesthesiology. (2018) 128:784–95. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000002081
69. Nonaka K, Une S, Tatsuta N, Ito K, Akiyama J. Changes in antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation in extensor digitorum longus muscles of streptozotocin-diabetic rats may contribute to muscle atrophy. Acta Physiol Hung. (2014) 101:421–8. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.101.2014.007
70. Xie Y, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D. GPX4 in cell death, autophagy, and disease. Autophagy. (2023) 19:2621–38. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2218764
71. Czyżowska A, Brown J, Xu H, Sataranatarajan K, Kinter M, Tyrell VJ, et al. Elevated phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (GPX4) expression modulates oxylipin formation and inhibits age-related skeletal muscle atrophy and weakness. Redox Biol. (2023) 64:102761. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102761
72. Xu H, Czyżowska A, Van Remmen H, Brown JL. Modulation of sarcopenia phenotypes by glutathione peroxidase 4 overexpression in mice. J Physiol. (2023) 601:5277–93. doi: 10.1113/JP285259
73. Nuoc TN, Kim S, Ahn SH, Lee JS, Park BJ, Lee TH. The analysis of antioxidant expression during muscle atrophy induced by hindlimb suspension in mice. J Physiol Sci. (2017) 67:121–9. doi: 10.1007/s12576-016-0444-5
74. Eshima H, Shahtout JL, Siripoksup P, Pearson MJ, Mahmassani ZS, Ferrara PJ, et al. Lipid hydroperoxides promote sarcopenia through carbonyl stress. Elife. (2023) 12:e85289. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85289
75. Zhang Y, Lu W, Li X, Wang Y, Li L, Dai Y, et al. Mfat-1 ameliorates cachexia after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in mice by protecting the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Life Sci. (2023) 333:122172. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122172
76. Shahtout JL, Eshima H, Ferrara PJ, Maschek JA, Cox JE, Drummond MJ, et al. Inhibition of the skeletal muscle Lands cycle ameliorates weakness induced by physical inactivity. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:319–30. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13406
77. Kaiser H, Yu K, Pandya C, Mendhe B, Isales CM, McGee-Lawrence ME, et al. Kynurenine, a tryptophan metabolite that increases with age, induces muscle atrophy and lipid peroxidation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2019) 2019:9894238. doi: 10.1155/2019/9894238
78. Qaisar R, Qayum M, Muhammad T. Reduced sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase activity underlies skeletal muscle wasting in asthma. Life Sci. (2021) 273:119296. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119296
79. Alves FM, Kysenius K, Caldow MK, Hardee JP, Crouch PJ, Ayton S, et al. Iron accumulation in skeletal muscles of old mice is associated with impaired regeneration after ischaemia-reperfusion damage. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2021) 12:476–92. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12685
80. Yeo D, Kang C, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Vina J, Ji LL. Intensified mitophagy in skeletal muscle with aging is downregulated by PGC-1alpha overexpression in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 130:361–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.456
81. Antunes D, Padrão AI, Maciel E, Santinha D, Oliveira P, Vitorino R, et al. Molecular insights into mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer-related muscle wasting. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2014) 1841:896–905. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.03.004
82. Casas F, Pessemesse L, Grandemange S, Seyer P, Baris O, Gueguen N, et al. Overexpression of the mitochondrial T3 receptor induces skeletal muscle atrophy during aging. PLoS One. (2009) 4:e5631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005631
83. Trevino MB, Zhang X, Standley RA, Wang M, Han X, Reis F, et al. Loss of mitochondrial energetics is associated with poor recovery of muscle function but not mass following disuse atrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2019) 317:E899–899E910. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00161.2019
84. Nagano K, Suzaki E, Nagano Y, Kataoka K, Ozawa K. The activation of apoptosis factor in hindlimb unloading-induced muscle atrophy under normal and low-temperature environmental conditions. Acta Histochem. (2008) 110:505–18. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2007.12.009
85. Sun L, Miyaji N, Yang M, Mills EM, Taniyama S, Uchida T, et al. Astaxanthin prevents atrophy in slow muscle fibers by inhibiting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species via a mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway. Nutrients. (2021) 13:379. doi: 10.3390/nu13020379
86. Yoshikawa M, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K, Nishino H, Hashimoto T. Effects of fucoxanthin on the inhibition of dexamethasone-induced skeletal muscle loss in mice. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1079. doi: 10.3390/nu13041079
87. Mukai R, Nakao R, Yamamoto H, Nikawa T, Takeda E, Terao J. Quercetin prevents unloading-derived disused muscle atrophy by attenuating the induction of ubiquitin ligases in tail-suspension mice. J Nat Prod. (2010) 73:1708–10. doi: 10.1021/np100240y
88. Jackson JR, Ryan MJ, Hao Y, Alway SE. Mediation of endogenous antioxidant enzymes and apoptotic signaling by resveratrol following muscle disuse in the gastrocnemius muscles of young and old rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2010) 299:R1572–81. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00489.2010
89. Gupta P, Dutt V, Kaur N, Kalra P, Gupta S, Dua A, et al. S-allyl cysteine: a potential compound against skeletal muscle atrophy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. (2020) 1864:129676. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129676
90. Baek S, Kim J, Moon BS, Park SM, Jung DE, Kang SY, et al. Camphene attenuates skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in rats. Nutrients. (2020) 12:3731. doi: 10.3390/nu12123731
91. Shen CL, Elmassry MM, Grue K, Joiner HE, Jacobo AU, Hamood A, et al. Geranylgeraniol and green tea polyphenols mitigate negative effects of a high-fat diet on skeletal muscle and the gut microbiome in male C57BL/6J mice. Metabolites. (2022) 12:913. doi: 10.3390/metabo12100913
92. Petry ÉR, Dresch DF, Carvalho C, Medeiros PC, Rosa TG, de Oliveira CM, et al. Oral glutamine supplementation attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress-mediated skeletal muscle protein content degradation in immobilized rats: role of 70 kDa heat shock protein. Free Radic Biol Med. (2019) 145:87–102. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.08.033
93. Gong D, Geng C, Jiang L, Aoki Y, Nakano M, Zhong L. Effect of pyrroloquinoline quinone on neuropathic pain following chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. (2012) 697:53–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.09.052
94. Ohtsuka A, Kojima H, Ohtani T, Hayashi K. Vitamin E reduces glucocorticoid-induced oxidative stress in rat skeletal muscle. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol. (1998) 44:779–86. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.44.779
95. Zhang HJ, Wang BH, Wang X, Huang CP, Xu SM, Wang JL, et al. Handelin alleviates cachexia- and aging-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by improving protein homeostasis and inhibiting inflammation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2024) 15:173–88. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13381
96. Kim KY, Ku SK, Lee KW, Song CH, An WG. Muscle-protective effects of Schisandrae Fructus extracts in old mice after chronic forced exercise. J Ethnopharmacol. (2018) 212:175–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.022
97. Takase T, Ikeuchi S, Inoue T, Mukai R. Eriocitrin contained in lemon peel ameliorates disuse muscle atrophy by suppressing the expression of atrogin-1 and MuRF-1 in denervated mice. J Nat Prod. (2021) 84:2048–52. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00271
98. Nakashima Y, Ohsawa I, Nishimaki K, Kumamoto S, Maruyama I, Suzuki Y, et al. Preventive effects of Chlorella on skeletal muscle atrophy in muscle-specific mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 activity-deficient mice. BMC Compl Altern Med. (2014) 14:390. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-390
99. Cunha TF, Bacurau AV, Moreira JB, Paixão NA, Campos JC, Ferreira JC, et al. Exercise training prevents oxidative stress and ubiquitin-proteasome system overactivity and reverse skeletal muscle atrophy in heart failure. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e41701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041701
100. Sendhilvadivu M. Impact of in vivo electrical stimulation during denervation dis-use muscle atrophy. Indian J Exp Biol. (2009) 47:839–42.
101. Brown JL, Peelor FF 3rd, Georgescu C, Wren JD, Kinter M, Tyrrell VJ, et al. Lipid hydroperoxides and oxylipins are mediators of denervation induced muscle atrophy. Redox Biol. (2022) 57:102518. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102518
102. Brazaluk AZ. Possible mechanism of metabolic disturbance in gastrocnemius muscle after denervation. Ukr Biokhim Zh. (1997) 69:91–103.
103. Abdel SE, Abdel-Meguid I, Korraa S. Markers of oxidative stress and aging in Duchene muscular dystrophy patients and the possible ameliorating effect of He:Ne laser. Acta Myol. (2007) 26:14–21.
104. Rocha M, Hernandez-Mijares A, Garcia-Malpartida K, Bañuls C, Bellod L, Victor VM. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant peptides. Curr Pharm Des. (2010) 16:3124–31. doi: 10.2174/138161210793292519
Keywords: sarcopenia, lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, antioxidants, therapeutic strategies
Citation: Lu Y, Li T, Shu Y, Lu C, Luo Z, Wang J, Xiong H and Li W (2025) Lipid peroxidation and sarcopenia: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches. Front. Med. 12:1525205. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1525205
Received: 09 November 2024; Accepted: 02 January 2025;
Published: 03 February 2025.
Edited by:
Young Hoon Son, Emory University, United StatesReviewed by:
Seung-Min Lee, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Republic of KoreaCopyright © 2025 Lu, Li, Shu, Lu, Luo, Wang, Xiong and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wangyang Li, d295b2xlZUBobnVjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.