
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Med. , 29 January 2025
Sec. Dermatology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1518382
Background: Afzelin, a flavonoid (kaempferol 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside) isolated from Thesium chinense, is known for its potent anti-inflammatory properties. However, its effects on the molecular aspects of inflammation and lipogenesis in SZ95 sebocytes has not been investigated.
Objective: This study aimed to (i) investigate inflammatory and sebum secretion changes when a Cutibacterium acnes-treated immortalized human sebocyte cell line (SZ95) is exposed to particulate matter (PM) and (ii) examine the effects of afzelin on these.
Methods: To investigate the effect of afzelin on PM- and C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes, we injected heat-killed C. acnes into SZ95 cells to induce acne-like status. Thereafter, the SZ95 sebocytes were treated with PM and subsequently with afzelin. The gene expression profile was determined using real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis, and protein expression was confirmed via western blotting and immunofluorescence. Intracellular lipid droplet formation was investigated using Nile Red O staining.
Results: PM treatment upregulated the mRNA and protein expression levels of inflammatory cytokine and lipogenic genes in C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes. Furthermore, intracellular lipid-droplet accumulation increased when C. acnes-stimulated SZ95 cells were exposed to PM. Interestingly, the upregulated inflammatory and lipogenic gene expression induced by C. acnes and PM was attenuated by afzelin treatment.
Conclusions: This study's findings indicate that PM potentially aggravates acne by acting on both inflammation and sebum secretion. They also reveal afzelin's ability to suppress these phenomena by not only suppressing inflammatory cytokine expression but also inhibiting sebogenesis. These findings confirm afzelin's potential therapeutic role in improving PM-exacerbated acne.
Acne, a chronic inflammatory condition of the pilosebaceous unit, is globally recognized as a highly prevalent dermatological affliction (1). Contributing factors to acne pathogenesis include augmented sebum production or changes in sebum components, follicular hyperkeratinization, colonization by Cutibacterium acnes, inflammatory responses, and an interplay between genetic and environmental influences (2, 3).
Particulate matter (PM) is a pervasive airborne pollutant, comprising a complex mixture of solid and liquid particles dispersed throughout the air. Air pollution represents a significant public health issue in numerous cities worldwide. Among the various types of air pollutants, PM is deemed one of the most detrimental (4). The skin, as the foremost barrier, is directly exposed to environmental pollutants and is susceptible to damage and a spectrum of skin diseases owing to such exposure (5, 6). PM reportedly triggers inflammatory reactions and impairs the skin barrier, potentially exacerbating conditions such as acne, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and allergic responses (2, 5, 7).
The clinical impact of PM varies with its size, with smaller particles such as PM2.5 being particularly concerning. Due to their smaller size, PM2.5 particles have a larger surface area-to-mass ratio, enabling them to carry more toxic substances and penetrate deeper into the skin. This can disrupt the skin barrier, induce oxidative stress, and promote inflammation, potentially exacerbating skin conditions like acne. In contrast, larger particles, such as PM10, tend to cause more superficial irritation. Despite the growing recognition of PM's role in dermatological disorders, further research is needed to clarify the size-dependent effects of PM on skin health.
Upon contact with the skin, PM can infiltrate the stratum corneum, hair follicles, and sweat glands, thereafter entering cells and compromising mitochondria, leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This process potentially induces oxidative stress (8, 9). The resultant ROS may cause skin inflammation by upregulating pro-inflammatory cytokine expression (10). Furthermore, exposure to PM has been linked to increased sebum production (3) and alterations in hormonal activity (11), potentially culminating in obstructed hair follicles, inflammation, and the proliferation of C. acnes (12, 13).
Afzelin (3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside) is a flavonoid extracted from Thesium chinense Turcz, a plant commonly found in Korea and China. Research has indicated that afzelin exhibits anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antibacterial activities, along with DNA-protective and antioxidant effects in ultraviolet B-exposed human skin cells (14–16). Our previous study revealed that afzelin exerts intracellular ROS-scavenging effects on PM-treated HaCaT cells and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in these cells (17). Therefore, afzelin is expected to exhibit potential in preventing PM-induced inflammatory skin diseases, including acne vulgaris.
Furthermore, previous studies have shown that exposure to PM correlates with increased visits to the clinic among adolescent and adult patients with acne (18, 19). However, literature on the association between PM exposure and acne is still emerging, and individual studies have exclusively focused on the individual effects of either PM or C. acnes on sebocytes (20–23). To date, no study has explored the effects of PM on SZ95 sebocytes in vitro following treatment with C. acnes. In a prior in vivo study, mice pre-treated with C. acnes and subsequently exposed to PM displayed increased inflammatory biomarker and sebum production (24, 25).
While the exact mechanisms underlying acne are yet to be fully elucidated, various exposome factors, such as pollutants, nutrition, medication, occupational influences, and climatic conditions, may play a role in the disease's progression, severity, and treatment effectiveness. Therefore, the present study aimed to evaluate the impact of PM on C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells and investigate the protective effects of afzelin in a PM-exposed acne cell model.
Standard reference materials (1649b) were purchased from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and dispersed in serum-free medium. C. acnes was obtained from the Korean Collection for Type Cultures (Daejeon, Korea). Afzelin was acquired from ChemFaces (Wuhan, China).
For Western blot analysis, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), RELA/NFκB p65, and SREBP-1 antibodies were procured from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). p-RELA/NFκB p65, COX-2, fatty acid synthase (FAS), IL-6, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) antibodies were secured from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA), and IL-1 beta antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Primer sequences for qRT-PCR used in this study are provided as Supplementary data.
Immortalized human SZ95 sebocytes (a patented cell line; gifted by Professor Christos C. Zouboulis, Department of Dermatology, Venereology, Allergology and Immunology, Dessau Medical Center, Theodore Fontane Medical University of Brandenburg, Germany) (26) were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12 (DMEM/F-12) in a 1:1 mixture (1×) (Welgene Inc., Daegu, Korea) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% penicillin–streptomycin (both from Gibco, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and 5 ng/mL human epidermal growth factor (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 (27). When the cultures had reached confluence, the cells were treated with 0.05% trypsin/0.53 mmol/L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Welgene Inc., Daegu, Korea) for 5–10 min at 37°C. The medium was replaced every 2–3 days.
We used C. acnes KCTC 3314, a standard reference strain from the Korean Collection for Type Cultures, known for its role in assessing inflammatory responses. Reinforced clostridial liquid and solid medium (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI, USA) was used to grow C. acnes for 3–4 days at 37°C under anaerobic conditions (5% H2, 5% CO2, and 90% N2).
Cultured C. acnes isolates were centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C and subsequently washed three times with cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Finally, the bacterial count was estimated by measuring the optical density of the suspension at 600 nm (OD600) using a spectrophotometer. As we had previously observed OD600 = 1.0 to be equivalent to 7.0 × 108 colony forming units (CFU) per 1 mL, we adjusted the number of bacterial cells to 7.0 × 108 CFU/mL using PBS. To obtain heat-killed bacteria, the C. acnes suspension (7.0 × 108 CFU/mL) was heated at 80°C for 30 min (2). The heat-killed C. acnes isolates were stored at 4°C and centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 10 min before use. Heat-killed C. acnes reportedly induces an inflammatory response similar to viable C. acnes (28).
Cell viability was evaluated using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Dojindo Laboratories), following the manufacturer's instructions. SZ95 cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 8 × 103 cells/well. After 24 h, the cells were treated with varying concentrations of particulate matter (PM) (0, 0.5, 1, 5, 10 μg/cm2) and C. acnes (0, 100, 200, 300, 500, 1,000 MOI [Multiplicity of Infection]) for 24 h. Then, 10 μL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 3 h. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm.
SZ95 cells were seeded in six-well plates (2 × 105 cells/well). After 24 h, the medium was replaced with serum-free medium. Cells were exposed to C. acnes for 18 h, followed by PM exposure for 6 h. Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent, and cDNA was synthesized using the RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit. qRT-PCR was performed using PowerUp™ SYBR® Green Master Mix, and gene expression was normalized to GAPDH.
SZ95 cells were lysed in RIPA buffer containing a protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail. Protein concentration was determined using a bicinchoninic acid assay, and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. Membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk and incubated with primary antibodies overnight, followed by HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. Protein expression was visualized using the EZ-Western Lumi Femto Kit and normalized to GAPDH.
SZ95 cells were seeded in 24-well plates (2 × 104 cells/well) and treated with C. acnes for 18 h, followed by PM for 6 h. Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, stained with Nile Red O dye, and counterstained with DAPI. Cells were visualized using a confocal fluorescence microscope (Leica® Microsystems CMS GmbH).
Cells were treated similarly as in Nile Red O staining. After fixation and permeabilization, cells were blocked with 1% BSA and incubated with primary antibodies targeting SREBP-1, COX-2, p-NFκB p65, FAS, and PPARγ overnight. Secondary antibodies (Alexa Fluor 488) were applied, and cells were visualized using a confocal microscope.
In vitro assays were conducted at least in triplicate. The effects of PM were compared between the treatment and control groups using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's multiple-comparison post-hoc test. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-correction test algorithm. Differences between groups were considered significant at P < 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 8.0; GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Cell viability was measured using a CCK assay kit. At a PM concentration of 10 μg/cm2, cell viability was ~90% compared with that of the control after 24 h of exposure (Supplementary Figure 1A). C. acnes did not exhibit toxicity to the cells at any tested concentration (Supplementary Figure 1B).
The mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as NFκB1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and COX-2, were evaluated. The expression levels of these cytokines increased in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group compared with those in the control group (Figure 1A). Additionally, the expression of lipogenesis-related transcription factors and enzymes, such as SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, was confirmed. The expression levels of SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ were also higher in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group than in the control group (Figure 1B).
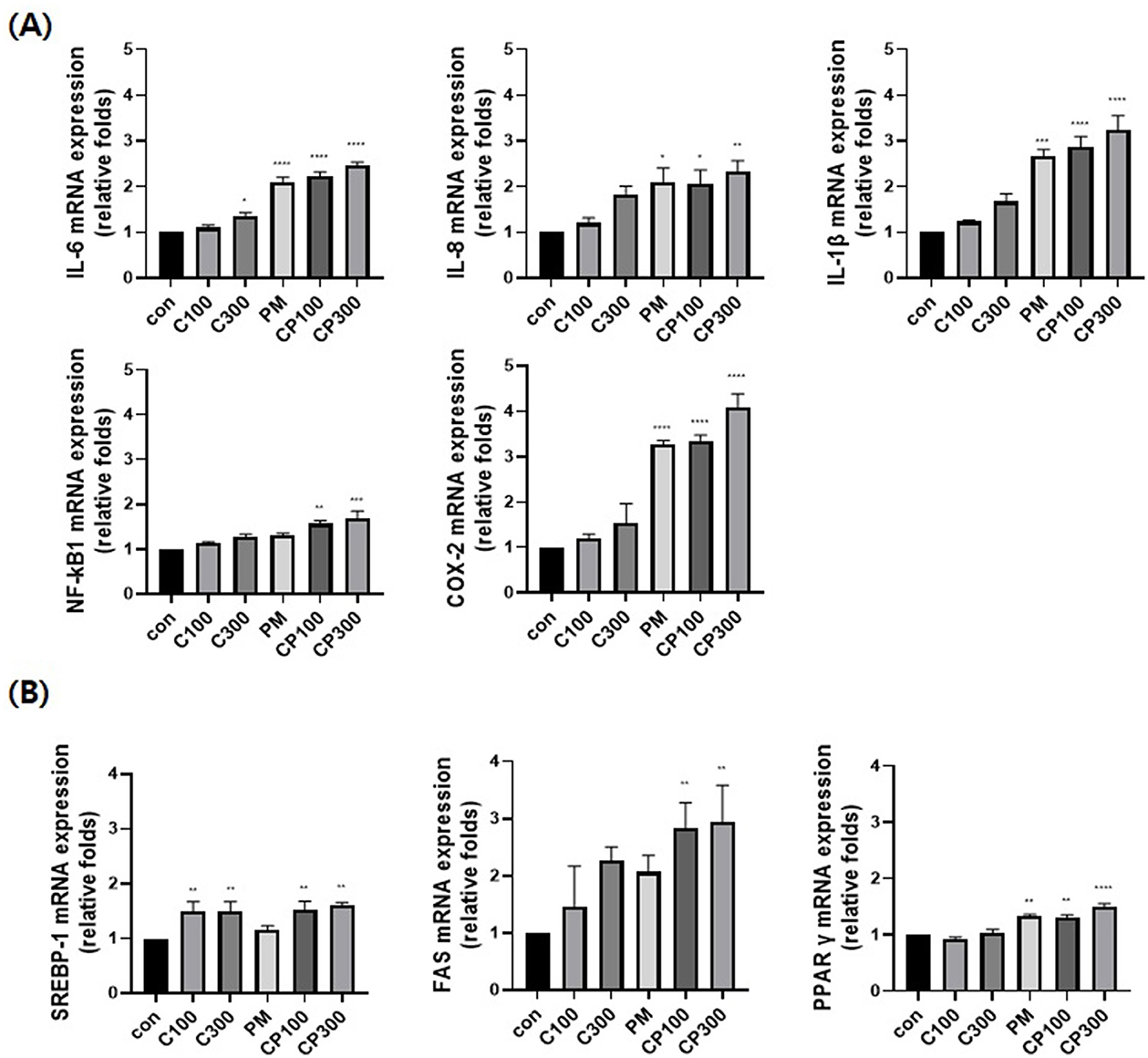
Figure 1. Effect of PM on the mRNA expression levels of inflammatory and lipogenic genes in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells. The effect of PM (10 μg/cm2) on SZ95 cells treated with C. acnes (100, 300 MOI) for 6 h was investigated; qRT-PCR was conducted to confirm the mRNA expression levels. (A) The expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β, and markers, such as NFκB1 and COX-2, were higher in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group than in the control group. (B) Lipogenic genes, such as SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, also exhibited increased expression in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group relative to those in the control group. Data are expressed as the mean + standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. control. Con, control; C100, C. acnes 100 MOI; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group.
The protein expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as NFκB1, p-NFκB1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and COX-2, were found to be elevated in the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group (Figure 2A). Similarly, the protein expression levels of lipogenic genes, including SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, increased in the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group compared with those in the control group (Figure 2B). No significance was noted, except for IL-1β and FAS.
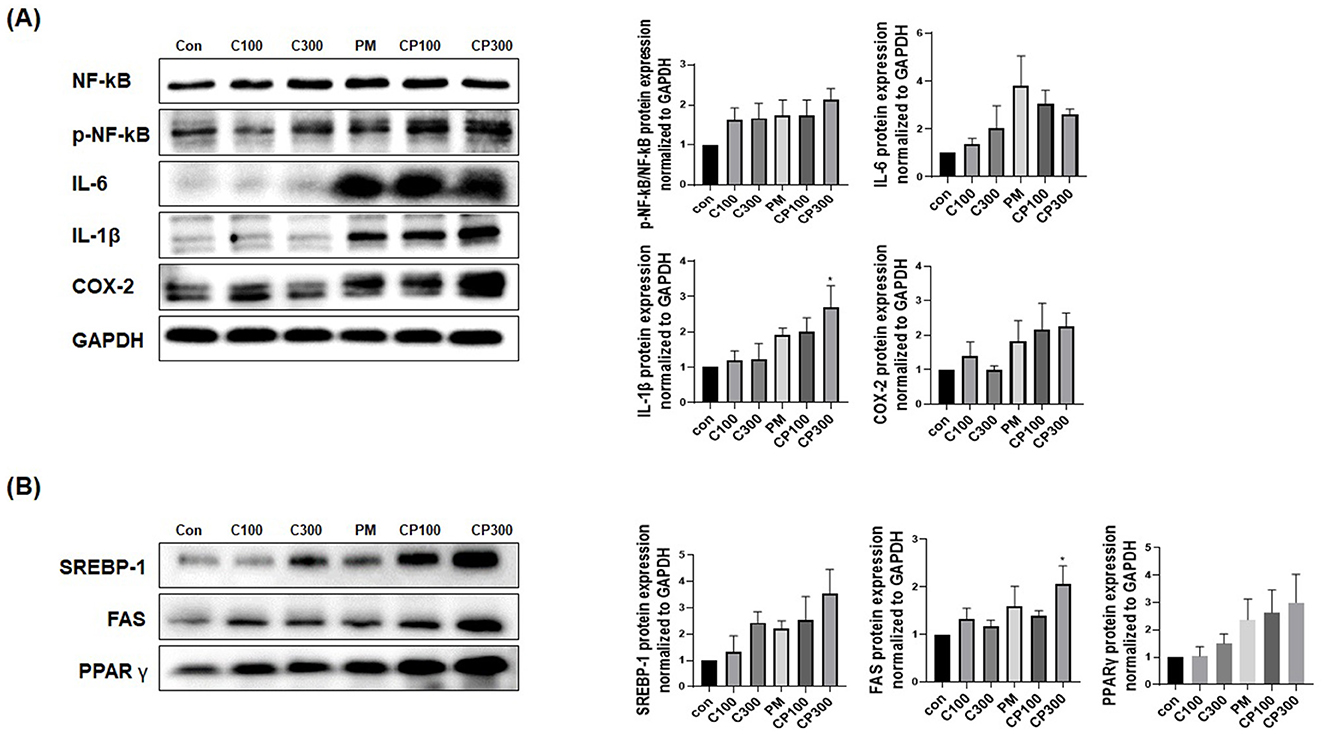
Figure 2. Effects of PM on the protein expression levels of inflammatory and lipogenic genes in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells. The expression levels of proteins involved in inflammation and lipogenesis were investigated in SZ95 cells treated with PM (10 μg/cm2) and C. acnes (100, 300 MOI). Protein levels confirmed via Western blot analysis demonstrated that (A) PM induced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as NFκB, p-NFκB, IL-6, IL-1β, and COX-2, with the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group displaying a more marked increase in inflammation. (B) PM increased the expression levels of lipogenic genes, such as SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, with the expression being significantly higher in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group. Con, control; C100, C. acnes 100 MOI; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group.
The results demonstrated an elevation in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as p-NFκB and COX-2, in the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group compared with that in the control group (Figure 3A). Similarly, the expression of lipogenic genes, including SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, was higher in the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group than in the control group (Figure 3B).
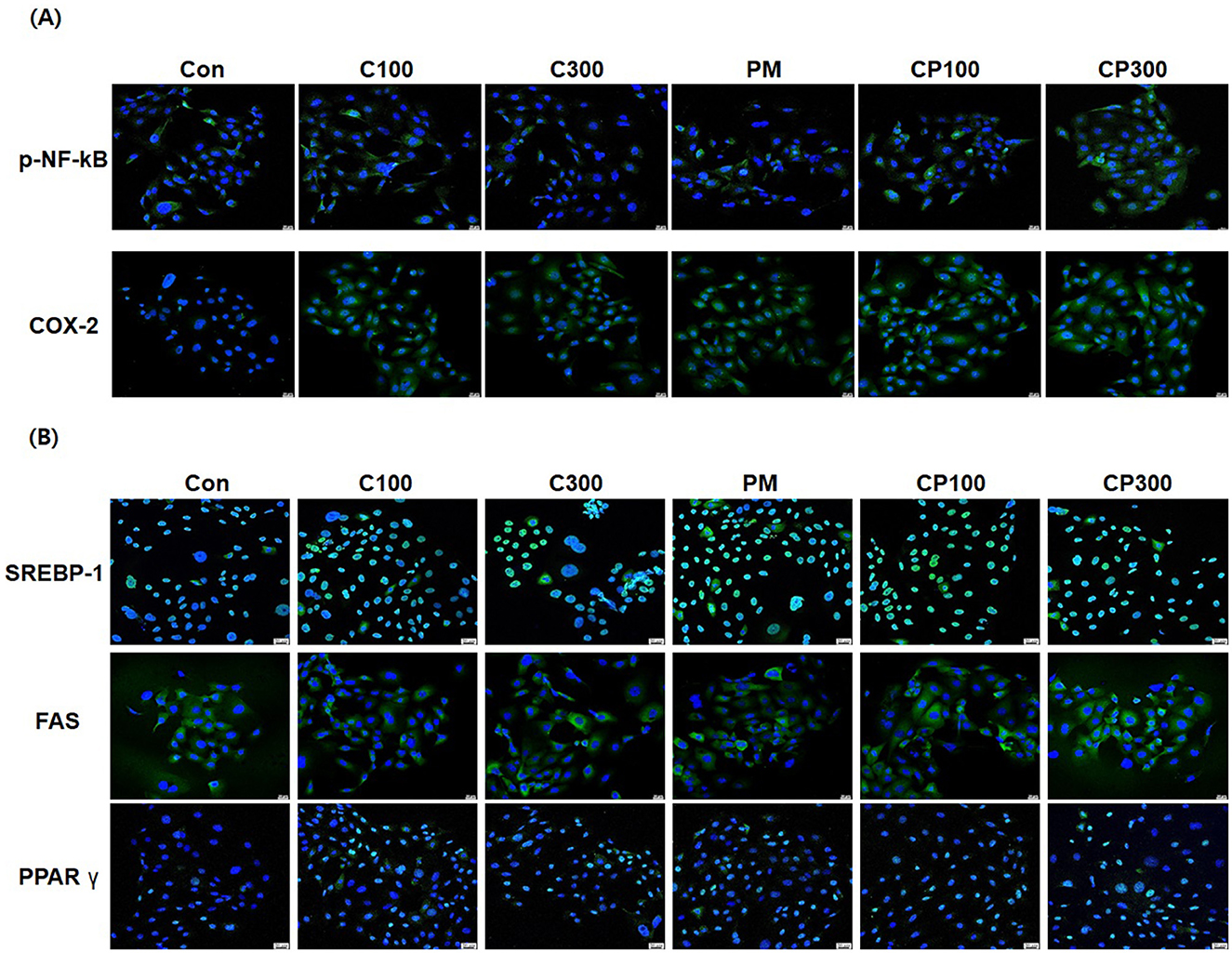
Figure 3. Immunofluorescence staining to confirm the effects of PM and C. acnes on inflammatory cytokines and lipogenic genes in SZ95 cells (×400 magnification). SZ95 cells were treated with C. acnes (100, 300 MOI) for 18 h, followed by treatment with PM at a concentration of 10 μg/cm2 for 6 h. (A) p-NFκB and COX-2 expression was increased by PM treatment, with a significant increase observed in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group compared with that in the control group. (B) PM induced the nuclear translocation of SREBP-1 and PPARγ and increased the expression of FAS. Expression levels were more elevated in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group (scale bar = 20 μm). Con, control; C100, C. acnes 100 MOI; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group.
As shown in Figure 4A, afzelin significantly downregulated the mRNA expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, including IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and COX-2, in C. acnes-treated, PM-exposed SZ95 sebocytes. Additionally, afzelin suppressed the increased expression of lipogenic genes, including SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, in the afzelin-treatment group compared with that in the respective C. acnes- and PM-treatment groups (Figure 4B). These results suggest that afzelin suppressed inflammation and lipogenesis in C. acnes-treated, PM-exposed SZ95 sebocytes.
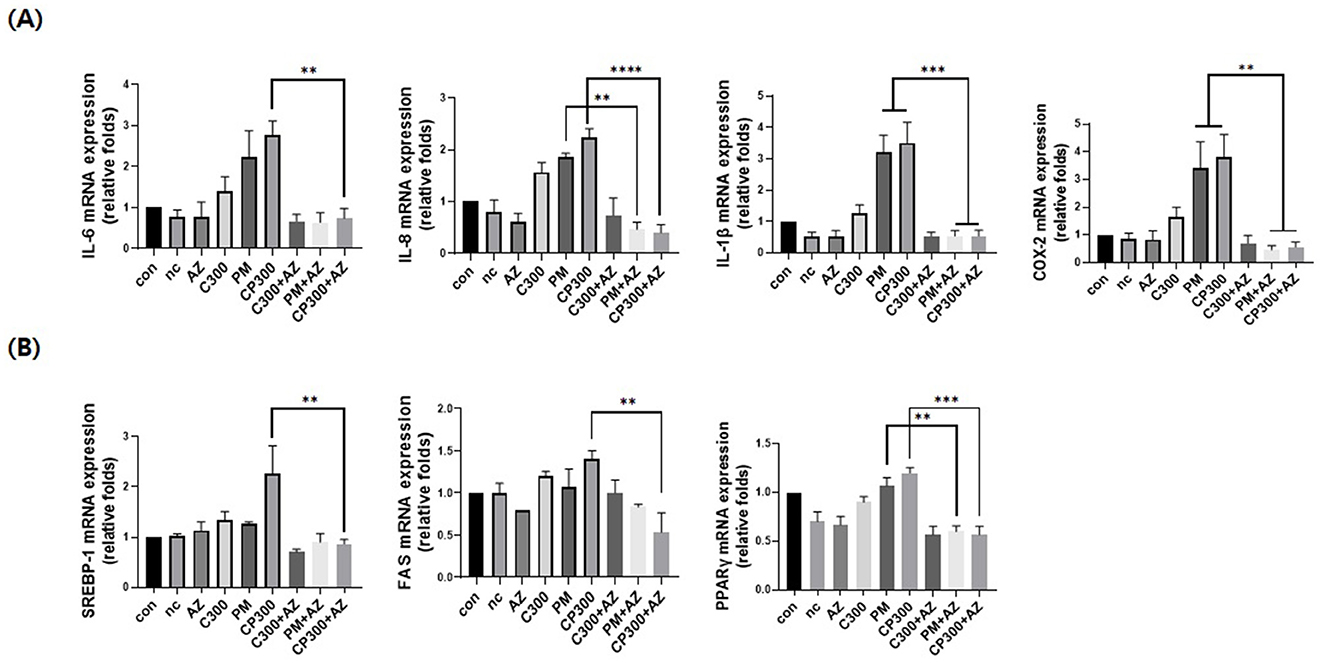
Figure 4. Afzelin suppressed inflammation and lipogenesis in PM-treated SZ95 sebocytes. Afzelin (500 μM) was administered to C. acnes-treated, PM-exposed SZ95 sebocytes for 6 h. (A) Relative mRNA expression levels of IL-6, IL-8, IL-1b, and COX-2 in SZ95 cells following 6-h treatment with PM (10 μg/cm2) and afzelin (500 μM). (B) Relative mRNA levels of SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ after 6-h treatment with afzelin. Expression was normalized to GAPDH. Data are expressed as the mean + standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 vs. PM or/and CP300. Con, control; nc, negative control; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group; AZ, afzelin.
Our results revealed that afzelin downregulated the protein expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, including IL-6, IL-1β, and COX-2, induced by C. acnes and PM (Figure 5A). Moreover, afzelin diminished the protein expression levels of lipogenic genes, such as SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, compared with the respective C. acnes and PM treatments (Figure 5B). No significance was observed, except for IL-6 and SREBP-1. Our findings demonstrate that afzelin can attenuate the inflammatory and lipogenic responses in PM-exposed SZ95 sebocytes.
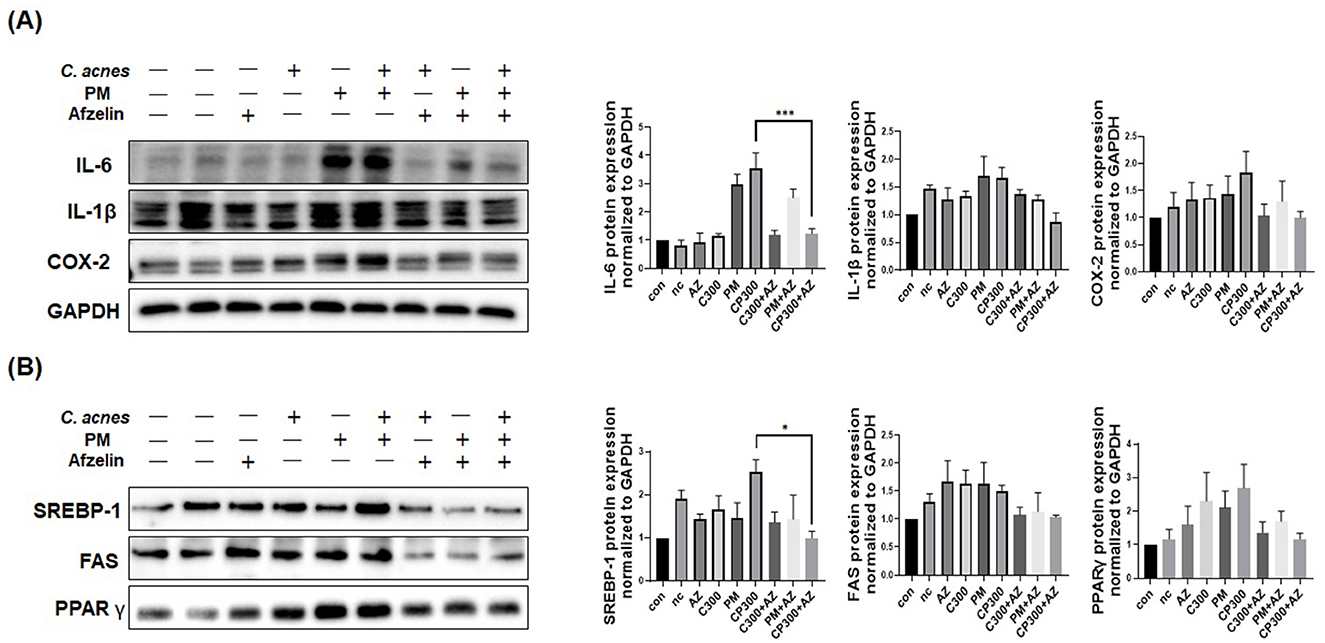
Figure 5. Effects of afzelin on the expression of PM-induced inflammatory and lipogenic genes in C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes. Afzelin (500 μM) was administered to C. acnes-treated, PM-exposed SZ95 sebocytes for 6 h. (A) The protein expression levels of IL-6, IL-1b, and COX-2 in SZ95 cells following 6-h treatment with PM (10 μg/cm2) and afzelin (500 μM). (B) Protein expression levels of SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ after 6-h treatment with afzelin. Expression was normalized to GAPDH. Data are expressed as the mean + standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. CP 300. Con, control; nc, negative control; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group; AZ, afzelin.
PM treatment augmented the intracellular accrual of lipid droplets, comprising neutral lipids, in the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Notably, the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group exhibited a more pronounced increase in lipid accumulation. Nonetheless, afzelin treatment significantly mitigated PM-induced lipid-droplet accumulation in C. acnes-stimulated SZ95 cells (Supplementary Figure 2).
We investigated the effects of PM on inflammation and lipid synthesis in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells. Our findings revealed that PM increases the expression of phosphorylated NF-κB and its subfactors, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, and COX-2. Additionally, PM upregulated the expression of lipogenesis-related genes, such as SREBP-1, FAS, and PPARγ, and promoted the accumulation of intracellular lipid droplets in the cytoplasm. Notably, this increase in expression was significantly greater in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group than in the groups exclusively treated with either PM or C. acnes. Based on our findings, PM can increase inflammation, lipid synthesis, and the accumulation of lipid droplets, potentially contributing to sebum composition changes (29). These results indicate that PM can aggravate acne by increasing lipid synthesis and inflammation via activation of the NF-κB pathway in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells.
Acne is a multifactorial inflammatory dermatosis with numerous contributing factors. Among these, increased sebum secretion is considered a principal factor (30), and alterations in sebum composition presumably play a significant role in acne development. Although a well-established association exists between acne severity and facial sebum secretion (31, 32), recent research has indicated that sebum production may not directly precipitate acne development but may instead influence inflammatory changes in the skin (33).
PM is known to trigger the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which has been implicated in the generation of inflammatory cytokines (2, 5, 34). The increased activity of NF-κB observed in clinical acne lesions underscores its critical role in the disorder's pathophysiology (35, 36). Upon activation, NF-κB migrates to the nucleus and initiates the upregulation of inflammatory genes, such as those encoding COX-2. Indeed, the inflammatory milieu in sebocytes, as evidenced by increased levels of cytokines, including IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β, and the lipid metabolism enzyme COX-2, is reportedly elevated in acne (37).
While numerous studies have linked the effects of PM to skin diseases, research specifically addressing the role of PM in sebaceous glands, where acne manifests, is relatively scarce. To the best of our knowledge, the impact of PM on C. acnes-treated sebocytes has not yet been reported. Based on our findings and those of previous studies (3, 38, 39), PM potentially induces inflammation in an environment conducive to the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria, thereby exacerbating acne via enhanced inflammation and alterations in lipid composition. NF-κB-induced oxidative stress may transform the pilosebaceous unit into a breeding ground for anaerobic bacteria, creating conditions favorable for the survival of acne-causing bacteria. Additionally, this potentially leads to lipid peroxidation, which may exacerbate acne severity (40).
In addition, our study investigated the preventative effects of afzelin on PM-induced inflammation and lipogenesis in C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes. The results indicate that afzelin significantly downregulates the expression of inflammation- and lipogenesis-related genes and proteins. However, the reduction in protein expression was statistically significant only for IL-6 and SREBP-1. The lack of statistical significance in IL-6 and SREBP-1 protein levels may stem from variability in cellular responses to PM and C. acnes or suboptimal experimental conditions, such as timing and stimulus concentrations. Additionally, post-translational modifications or compensatory mechanisms may attenuate changes at the protein level despite significant mRNA expression. It is also possible that afzelin's effects are more pronounced on other mediators. Further studies with larger sample sizes and optimized conditions are needed to clarify these findings.
Moreover, this study examined the effect of afzelin on lipid-droplet accumulation in SZ95 cells. PM treatment led to an increase in lipid droplets within the cytoplasm, especially around the nucleus. This accumulation was more pronounced in the C. acnes + PM co-treatment group. Notably, afzelin significantly reduced PM-induced lipid-droplet accumulation in these cells. These findings collectively suggest that afzelin exerts a protective effect against PM-induced inflammation and lipogenesis in C. acnes-treated sebocytes.
Taken together, our study confirms that PM incites inflammation and escalates the expression of lipogenic genes in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells, while afzelin holds promise as a therapeutic agent for environmental pollutant-exacerbated conditions, such as acne vulgaris, by mitigating both inflammatory responses and lipid synthesis. The findings of this study underscore the need to consider the size of particulate matter (PM) when evaluating its impact on skin conditions like acne. Smaller particles, such as PM2.5, are capable of deeper skin penetration and carry more toxic substances, which may amplify oxidative stress and inflammatory responses. This mechanism could explain why PM exposure exacerbates acne symptoms. Larger particles, while less capable of deep penetration, may still provoke localized irritation and inflammation. Understanding these size-dependent effects is essential for designing effective preventative and therapeutic interventions tailored to mitigate the dermatological impact of PM exposure. Future studies focusing on specific PM sizes will help further elucidate these mechanisms.
Notwithstanding, the interpretation of our results is subject to certain limitations. First, the upstream mechanisms of NF-κB, including oxidative stress and aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression, were not explored. Second, further investigations are warranted to elucidate specific changes in sebum composition. In acne pathogenesis, not only the increase in sebum production but also the alterations and oxidation of sebum composition are significant. For instance, the variation in lipid content, particularly squalene oxidation in individuals with acne, has been implicated in the development of lesions, bacterial toxicity, and inflammatory processes (41, 42). Third, our study was performed in vitro. To ascertain the biological significance of these findings, additional studies employing animal models and clinical trials are essential. To decode the mechanism behind our results, identifying specific biomarkers directly associated with acne and examining the link between lipid synthesis pathways and inflammatory responses are imperative. Further studies are warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and explore the clinical relevance of these findings.
The insights from our study may be instrumental in deciphering the relationship between air pollution and acne development, including its underlying mechanisms. Modulating the expression of inflammatory markers, cytokines, and lipogenic genes may help identify potential therapeutic targets for mitigating the PM-induced exacerbation of acne in the future.
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because some datasets may prohibit redistribution, requiring users to direct others to the original source rather than sharing the dataset themselves. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to a3lreUBjYXVocy5vci5rcg==.
JH: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. YR: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. M-KL: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. KP: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Chung-Ang University Research Grants in 2024. This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: H12300860).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1518382/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary File 1 | Primer sequences for qRT-PCR used in this study.
Supplementary Figure 1 | Effects of PM and C. acnes on SZ95 cell viability. The cytotoxicity of PM and heat-killed C. acnes to SZ95 cells was measured using the CCK-8 assay. (A) SZ95 cells were treated with various PM concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 μg/cm2) for 6–24 h. (B) SZ95 cells were treated with various heat-killed C. acnes concentrations (100, 200, 300, 500, and 1,000 MOI) for 6–24 h. Data are expressed as the mean + standard error of the mean. **P < 0.01. Conc, concentration.
Supplemental Figure 2 | Effect of afzelin on PM-induced lipid-droplet increase in C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes (×400 magnification). SZ95 cells were treated with C. acnes (300 MOI) for 18 h, followed by PM (10 μg/cm2) treatment for 6 h. Nile Red O staining and subsequent fluorescence microscopy were used to observe lipid-droplet changes in SZ95 cells. PM and C. acnes increased the number of lipid droplets in SZ95 cells, and this increase was more pronounced in the PM + C. acnes co-treatment group. Notably, afzelin treatment significantly inhibited the PM-induced formation of lipid droplets in C. acnes-treated SZ95 cells (scale bar = 20 μm). Con, control; C300, C. acnes 300 MOI; CP, C. acnes + PM co-treatment group; AZ, afzelin.
1. Tuchayi SM, Makrantonaki E, Ganceviciene R, Dessinioti C, Feldman SR, Zouboulis CC. Acne vulgaris. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:15029. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.29
2. Noh HH, Shin SH, Roh YJ, Moon NJ, Seo SJ, Park KY. Particulate matter increases Cutibacterium acnes-induced inflammation in human epidermal keratinocytes via the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. PLoS ONE. (2022) 17:e0268595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268595
3. Krutmann J, Moyal D, Liu W, Kandahari S, Lee GS, Nopadon N, et al. Pollution and acne: is there a link? Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. (2017) 10:199–204. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S131323
4. Arias-Perez RD, Taborda NA, Gomez DM, Narvaez JF, Porras J, Hernandez JC. Inflammatory effects of particulate matter air pollution. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2020) 27:42390–404. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10574-w
5. Kim KE, Cho D, Park HJ. Air pollution and skin diseases: adverse effects of airborne particulate matter on various skin diseases. Life Sci. (2016) 152:126–34. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.03.039
6. English JS, Dawe RS, Ferguson J. Environmental effects and skin disease. Br Med Bull. (2003) 68:129–42. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldg026
7. Kim M, Kim JH, Jeong GJ, Park KY, Lee MK, Seo SJ. Particulate matter induces pro-inflammatory cytokines via phosphorylation of p38 MAPK possibly leading to dermal inflammaging. Exp Dermatol. (2019) 28:809–15. doi: 10.1111/exd.13943
8. Jin SP, Li Z, Choi EK, Lee S, Kim YK, Seo EY, et al. Urban particulate matter in air pollution penetrates into the barrier-disrupted skin and produces ROS-dependent cutaneous inflammatory response in vivo. J Dermatol Sci. (2018). doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.04.015
9. Traboulsi H, Guerrina N, Iu M, Maysinger D, Ariya P, Baglole CJ. Inhaled pollutants: The molecular scene behind respiratory and systemic diseases associated with ultrafine particulate matter. Int J Mol Sci. (2017) 18:243. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020243
10. Li Q, Kang Z, Jiang S, Zhao J, Yan S, Xu F, et al. Effects of ambient fine particles PM(2.5) on human HaCaT cells. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2017) 14:72. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14010072
11. Wenger D, Gerecke AC, Heeb NV, Schmid P, Hueglin C, Naegeli H, et al. In vitro estrogenicity of ambient particulate matter: contribution of hydroxylated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Appl Toxicol. (2009) 29:223–32. doi: 10.1002/jat.1400
12. Makrantonaki E, Ganceviciene R, Zouboulis C. An update on the role of the sebaceous gland in the pathogenesis of acne. Dermatoendocrinol. (2011) 3:41–9. doi: 10.4161/derm.3.1.13900
13. Li X, Zhou LX, Yang LL, Huang XL, Wang N, Hu YG, et al. The relationship between short-term PM(2.5) exposure and outpatient visits for acne vulgaris in Chongqing China: A time-series study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2022) 29:61502–11. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20236-8
14. Kim SK, Kim HJ, Choi SE, Park KH, Choi HK, Lee MW. Anti-oxidative and inhibitory activities on nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (COX-2) production of flavonoids from seeds of Prunus tomentosa. Thunberg Arch Pharm Res. (2008) 31:424–8. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-1174-9
15. Lee SY, So YJ, Shin MS, Cho JY, Lee J. Antibacterial effects of afzelin isolated from Cornus macrophylla on Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a leading cause of illness in immunocompromised individuals. Molecules. (2014) 19:3173–80. doi: 10.3390/molecules19033173
16. Shin SW, Jung E, Kim S, Kim JH, Kim EG, Lee J, et al. Antagonizing effects and mechanisms of afzelin against UVB-induced cell damage. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e61971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061971
17. Kim JH, Kim M, Kim JM, Lee MK, Seo SJ, Park KY. Afzelin suppresses proinflammatory responses in particulate matter-exposed human keratinocytes. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 43:2516–22. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4162
18. Liu W, Pan X, Vierkotter A, Guo Q, Wang X, Wang Q, et al. A time-series study of the effect of air pollution on outpatient visits for acne vulgaris in Beijing. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. (2018) 31:107–13. doi: 10.1159/000484482
19. Li X, Cao Y, An SJ, Xiang Y, Huang HX, Xu B, et al. The association between short-term ambient air pollution and acne vulgaris outpatient visits: a hospital-based time-series analysis in Xi'an. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2022) 29:14624–33. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-16607-2
20. Nguyen CT, Sah SK, Zouboulis CC, Kim TY. Inhibitory effects of superoxide dismutase 3 on Propionibacterium acnes-induced skin inflammation. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:4024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31453-y
21. Huang YC, Yang CH, Li TT, Zouboulis CC, Hsu HC. Cell-free extracts of Propionibacterium acnes stimulate cytokine production through activation of p38 MAPK and toll-like receptor in SZ95 sebocytes. Life Sci. (2015) 139:123–31. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.07.028
22. Liu Q, Wu J, Song J, Liang P, Zheng K, Xiao G, et al. Particulate matter 2.5 regulates lipid synthesis and inflammatory cytokine production in human SZ95 sebocytes. Int J Mol Med. (2017) 40:1029–36. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3109
23. Cao K, Chen G, Chen W, Hou X, Hu T, Lu L, et al. Formalin-killed Propionibacterium acnes activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and modifies differentiation of SZ95 sebocytes in vitro. Eur J Dermatol. (2021) 31:32–40. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2021.3964
24. Kwack MH, Ha NG, Lee WJ. Dieckol inhibits the effects of particulate matter 10 on sebocytes, outer root sheath cells, and Cutibacterium acnes-pretreated mice. Ann Dermatol. (2022) 34:182–90. doi: 10.5021/ad.2022.34.3.182
25. Kwack MH, Ha DL, Lee WJ. Preventative effects of antioxidants on changes in sebocytes, outer root sheath cells, and Cutibacterium acnes-pretreated mice by particulate matter: No significant difference among antioxidants. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. (2022) 36:3946320221112433. doi: 10.1177/03946320221112433
26. Zouboulis CC, Seltmann H, Neitzel H, Orfanos CE. Establishment and characterization of an immortalized human sebaceous gland cell line (SZ95). J Invest Dermatol. (1999) 113:1011–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00771.x
27. Xia L, Zouboulis CC, Ju Q. Culture of human sebocytes in vitro. Dermatoendocrinol. (2009) 1:92–5. doi: 10.4161/derm.1.2.8736
28. Lyte P, Sur R, Nigam A, Southall MD. Heat-killed Propionibacterium acnes is capable of inducing inflammatory responses in skin. Exp Dermatol. (2009) 18:1070–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.00891.x
29. Ottaviani M, Camera E, Picardo M. Lipid mediators in acne. Mediators Inflamm. (2010) 2010:858176. doi: 10.1155/2010/858176
30. Li X, He C, Chen Z, Zhou C, Gan Y, Jia Y. A review of the role of sebum in the mechanism of acne pathogenesis. J Cosmet Dermatol. (2017) 16:168–73. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12345
31. Harris HH, Downing DT, Stewart ME, Strauss JS. Sustainable rates of sebum secretion in acne patients and matched normal control subjects. J Am Acad Dermatol. (1983) 8:200–3. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(83)70023-X
32. Pierard-Franchimont C, Pierard GE, Saint-Leger D, Leveque JL, Kligman AM. Comparison of the kinetics of sebum secretion in young women with and without acne. Dermatologica. (1991) 183:120–2. doi: 10.1159/000247650
33. Youn SW, Park ES, Lee DH, Huh CH, Park KC. Does facial sebum excretion really affect the development of acne? Br J Dermatol. (2005) 153:919–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06794.x
34. Dijkhoff IM, Drasler B, Karakocak BB, Petri-Fink A, Valacchi G, Eeman M, et al. Impact of airborne particulate matter on skin: a systematic review from epidemiology to in vitro studies. Part Fibre Toxicol. (2020) 17:35. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00366-y
35. Yoon JY, Kwon HH, Min SU, Thiboutot DM, Suh DH. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves acne in humans by modulating intracellular molecular targets and inhibiting P. acnes. J Invest Dermatol. (2013) 133:429–40. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.292
36. Kang S, Cho S, Chung JH, Hammerberg C, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ. Inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation mediated by activated transcription factors nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1 in inflammatory acne lesions in vivo. Am J Pathol. (2005) 166:1691–9. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62479-0
37. Alestas T, Ganceviciene R, Fimmel S, Muller-Decker K, Zouboulis CC. Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of leukotriene B4 and prostaglandin E2 are active in sebaceous glands. J Mol Med (Berl). (2006) 84:75–87. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0715-8
38. Roberts W. Air pollution and skin disorders. Int J Womens Dermatol. (2021) 7:91–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2020.11.001
39. El Haddad C, Gerbaka NE, Hallit S, Tabet C. Association between exposure to ambient air pollution and occurrence of inflammatory acne in the adult population. BMC Public Health. (2021) 21:1664. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11738-0
40. Bowe WP, Logan AC. Clinical implications of lipid peroxidation in acne vulgaris: old wine in new bottles. Lipids Health Dis. (2010) 9:141. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-141
41. Cao K, Liu Y, Liang N, Shen X, Li R, Yin H, et al. Fatty acid profiling in facial sebum and erythrocytes from adult patients with moderate acne. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:921866. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.921866
Keywords: C. acnes, inflammation, afzelin, particulate matter, sebocyte, acne vulgaris
Citation: Hong JY, Choi YH, Roh YJ, Lee M-K, Zouboulis CC and Park KY (2025) Effect of afzelin on inflammation and lipogenesis in particulate matter-stimulated C. acnes-treated SZ95 sebocytes. Front. Med. 12:1518382. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1518382
Received: 28 October 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Jolanta Idkowiak-Baldys, L'Oreal, United StatesReviewed by:
Jongkon Saising, Mae Fah Luang University, ThailandCopyright © 2025 Hong, Choi, Roh, Lee, Zouboulis and Park. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kui Young Park, a3lreUBjYXVocy5vci5rcg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.