
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Med., 26 March 2025
Sec. Geriatric Medicine
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1516853
This article is part of the Research TopicMolecular mechanisms and clinical studies of multi-organ dysfunction in sepsis associated with pathogenic microbial infectionView all 9 articles
Background: Sepsis-associated liver injury (SALI) is a frequent and lethal complication among critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). Despite its significance, there has been a notable lack of specialized tools for evaluating the in-ICU mortality risk in these patients. This study seeks to address this gap by developing a practical nomogram to predict risk factors associated with in-ICU mortality in patients suffering from SALI.
Methods: Data were extracted from the MIMIC-IV database, a Critical Care Public Medical Information Mart. The diagnostic criteria for sepsis adhered to the Sepsis 3.0 guidelines, requiring a SOFA score of ≥ 2. SALI was defined as total bilirubin (TBIL) levels > 2 mg/dL in patients with sepsis and an International Normalized Ratio (INR) > 1.5. Lasso regression analyses were conducted on the training set (n = 653) to develop a predictive nomogram model. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate model discrimination. Model calibration was assessed through calibration curves and Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit tests. Clinical decision curves were plotted to analyze the net benefit of the model and evaluate its clinical applicability.
Results: A total of 934 elderly patients with SALI were included in the study. Random seeds were allocated in a 7:3 ratio, resulting in training and validation sets comprising 653 and 281 patients, respectively. Variables were selected using lasso regression, culminating in the inclusion of six final variables within the model. The nomogram was evaluated against standard ICU scoring systems, specifically SAPS II and SOFA scores, yielding AUROC values of 0.814, 0.798, and 0.634 for the training set, respectively. Conversely, the validation set demonstrated AUROC values of 0.809, 0.791, and 0.596. The nomogram exhibited strong predictive performance for in-ICU outcomes. P-values from the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test for both training and validation sets were recorded at 0.627 and 0.486, respectively, indicating good fit quality. Decision curve analysis revealed that the nomogram consistently provides greater net benefits compared to SAPS II and SOFA scores.
Conclusion: A prediction model of in-ICU mortality in SALI elderly patients was established by screening variables through lasso regression. Nomgram was the best predictor of in-ICU mortality in SALI patients, which has a high reference value and clinical application.
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by infection and is one of the common causes of death in patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) (1). The production of endotoxins and the release of inflammatory factors in sepsis lead to an abnormal immune response that impairs the functioning of many organs, including the liver and kidneys (2). The liver plays a central role in metabolic and immune homeostasis, and liver injury is one of the common complications in patients with septic shock and one of the risk factors for death in septic patients (3, 4). Early liver damage is caused by inflammation and microcirculation disorders, which can be recovered later with treatment. The mechanism of late injury may be related to organ failure caused by sepsis (5).
Sepsis-associated liver injury (SALI) is one of the most common complications in patients with sepsis. The mechanism is that the onset of primary dysfunction is usually associated with inadequate hepatic perfusion, which leads to liver injury and further complications such as diffuse intravascular coagulation and multi-organ failure (6). Secondly, sepsis also causes dysfunction of the intestinal microcirculation, prompting leakage of intestinal toxins and bacteria into the liver through the portal vein, which can lead to hepatitis (7). There are several main types of SALI: ischemic-hypoxic liver injury, cholestatic liver injury, and hepatocellular injury (8). Ischemic-hypoxic liver injury results from hepatic hypoperfusion and hypoxemia, characterized by a significant elevation in serum aminotransferase levels, along with coagulation abnormalities and minimal jaundice (9). Cholestasis is primarily defined by hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice, which may be linked to impaired bile formation and reduced motility (10). The classification of hepatocellular injury types predominantly relies on drug-related liver injury criteria established in the literature (11). There is a lack of clarity about the mechanisms by which SALI occurs, which may be related to the following pathways, including microcirculation and endothelial damage (12), intestinal flora dysbiosis (13), inflammatory factor imbalance (7), oxidative stress (14), and mitochondrial metabolic disorders (15), among other points. Studies have shown that liver failure is an independent risk factor for multi-organ dysfunction and high mortality in patients with sepsis (16). However, there are no studies of in-ICU mortality prediction models for patients with SALI. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to explore the independent risk factors for the development of SALI.
Sepsis is most prevalent among the elderly, infants, and individuals with certain underlying conditions that compromise the immune system. As society ages, the population of elderly patients is growing, leading to an increase in the incidence of sepsis (17). Reducing the mortality and disability rates of SALI in the elderly population is one of the current issues that needs to be addressed. Nomograms are visual statistical tools that integrate various data to develop continuous scoring systems reflecting individual risk probabilities accurately (18). Therefore, it is crucial to establish an accurate dynamic nomogram, which has important implications for both individuals and society through prognostic and clinical management decisions.
This study used a retrospective cohort design. Data were obtained from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC)-IV database (version 3.0), which includes patients from 2020 to 2022 in addition to those from version 2.2, access to MIMIC-IV v3.0 (physionet.org). The MIMIC database is a large, freely available database that contains de-identified health-related data for over 40,000 patients admitted to the intensive care unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts (19). The first author, Xuemei Hu, completed the “data or specimen research” training and was granted permission to use public data (ID: 13677449). As this study was conducted using an anonymous public database by the review board protocol, ethical consent was not required.
The inclusion criteria consisted of the following: (1) Meet the diagnostic criteria of sepsis 3.0 (1). (2) Patients admitted to the ICU for the first time and have been hospitalized for at least 24 h. (3) age ≥ 60 years. (4) Meet the definition of SALI: total bilirubin level > 2 mg/dL (34.2 μmol/L), international normalized ratio > 1.5 (16, 20).
The exclusion criteria encompassed: (1) does not meet the diagnostic criteria for sepsis 3.0. (2) ICU stay time less than 24 h. (3) age < 60 years. (4) did not meet the diagnostic criteria for SALI. (5) patients with previous liver disease, liver cirrhosis, and other liver disease-related diseases.
The study extracted relevant variables from the MIMIC-IV database: (1) patient general information; (2) past disease history; (3) severity scores, including Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II), Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS); (4) vital signs and biochemical indicators of patients admitted to ICU within 24 h; and (5) treatment after ICU admission. (6) outcome: death after ICU admission.
Variables with data missing rates greater than 30% were excluded. For the variables included in the analysis, we used R version 4.2.2 for data cleaning and input of missing values and processed missing values based on R’s “randomForest” package and used the RF method to handle missing values and the multiple imputation method to generate five input datasets for Lasso regression analysis. Specific details are provided in Supplementary Figure 1.
This study was analyzed and plotted through the R version 4.2.2, and the software package used is detailed in Supplementary Table 1. Categorical variables were analyzed for differences in distribution between the two groups using the chi-square test (or Fisher’s exact probability method), continuous information that conformed to a normal distribution was described in the form of (means ± standard deviation) and analyzed for differences in distribution between the two groups using the t-test, and information that did not conform to a normal distribution was described in the form of medians (percentiles) and analyzed for differences in distribution between the two groups using the rank-sum test. The results of intergroup comparisons were expressed as p-values.
A total of 70% of the patients were randomly selected as the training set, and a nomogram visualization model was developed. The predicted outcome was the patient’s risk of dying during ICU. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC), calibration curve and decision curve analysis (DCA) were constructed to further evaluate the applicability of the model.
A total of 934 elderly patients with SALI were enrolled in this study (Figure 1). They were categorized into survival group (n = 673) and non-survival group (n = 261) based on ICU mortality. Details of the specific subgroups and clinical baseline information are shown in Table 1.
Correlation matrix and correlation test were performed for all variables for 934 elderly patients and correlation heat map was drawn (Supplementary Figure 2). From the figure, there was much collinearity between various variables, which meant that all the above variables could not be directly included in the logistic regression analysis.
According to the correlation heat map, we can conclude that there is collinearity between the variables, which cannot be directly analyzed, so we performed lasso regression to screen out the most suitable variables for establishing the prognosis model of patients. Lasso regression was used to screen the predictor variables of the ML model, and cross-validated lasso fit mean square error (Figure 2A), and lasso fit coefficient trajectory plots (Figure 2B) were used. According to the calculation, when the minimum mean square error of λ is 0.029, the corresponding model predictor variables are selected in detail.
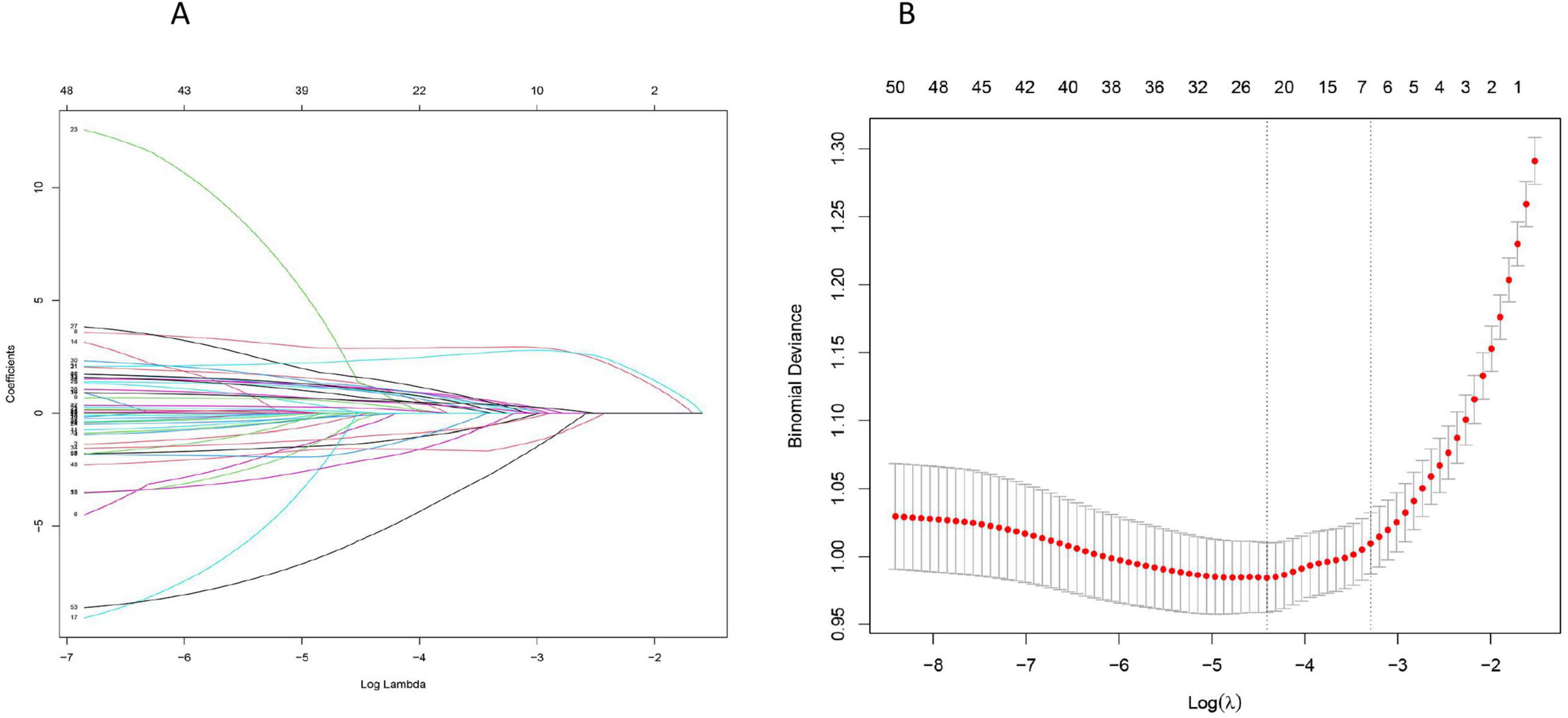
Figure 2. Lasso regression screening of prognostic model predictor variables: (A) The selection process of the most appropriate λ in the lasso model; (B) Lasso coefficient curves.
The data of senile SALI patients were imported into R4.2.2 software, and the data were randomly assigned in a ratio of about 7:3 by setting random seeds. The final number of cases in the training set and the validation set were 653 and 281, respectively (Supplementary Table 2). The variables selected by lasso regression were used to establish a model, final inclusion of albumin (ALB), Anion gap (AG), Activated partial thromboplastin time (PTT), Alanine transaminase-to-Alkaline phosphatase ratio (ALT/ALP), Aspartate transaminase-to-platelets ratio (APRI), and Mechanical ventilation were six variables. According to the “Points” in the nomogram, the individual scores of each variable of a specific individual can be obtained, and the sum of the individual scores can obtain the “Total Points” in the nomogram, and the corresponding “ICU mortality rate” is the ICU mortality probability (Figure 3). To ensure that the variables selected from the Lasso regression conform to the optimal model, we compute the values of Akaike information criterion and Bayesian information criterion, thus validating the statistical model selection and evaluation, as detailed in Supplementary Table 1.
A multifactorial logistic analysis was performed on the six potential predictors (Table 2). The results showed that ALB, AG, PTT, ALT/ALP, APRI, and mechanical ventilation were independent prognostic factors in patients with SALI. To rule out covariance between the variables, we again tested the variables for variance inflation factors, as shown in Supplementary Table 2.
The ROC curve was drawn to evaluate the discrimination of the model. The area under the curve of the training cohort was 0.814 (95% CI: 0.777–0.842), while the area under the curve of the validation cohort was 0.809 (95% CI: 0.752–0.866), which were significantly better than the SAPSII score (AUC of the training cohort: 0.794, 95% CI:0.760–0.828); AUC of the validation cohort: 0.791, 95% CI: 0.727–0.854) and SOFA score (AUC of the training cohort: 0.629, 95% CI: 0.588–0.669; AUC of the validation cohort: 0.596, 95% CI: 0.522–0.670). The specific results are shown in Figure 4.
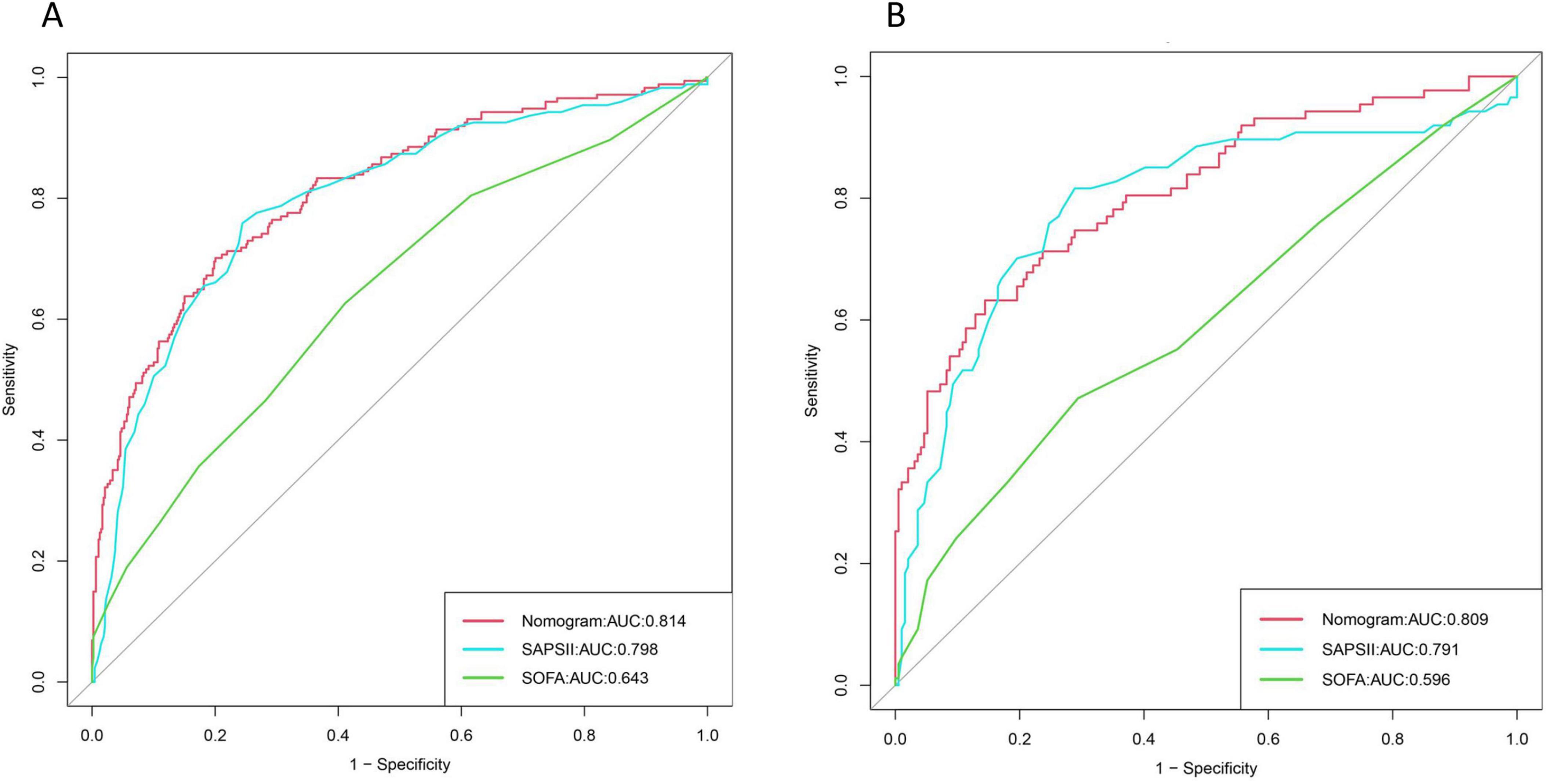
Figure 4. Area under the three curves for nomogram, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II), and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA): (A) Training set; (B) Validation set.
The calibration degree of the model was evaluated by drawing the calibration curve and Hosmer-Lemeshaw goodness of fit test. According to the calibration plot, there was good prediction accuracy between the actual probability and the predicted probability. The P-values of the training cohort and validation cohort models are 0.627 and 0.486, respectively, and the fits are good, as shown in Figure 5.
We use the clinical DCA to evaluate the clinical utility of the model. Within a certain threshold range > 0.4, there are net benefits for both validation and training sets, and the specific results are shown in Figure 6.

Figure 6. Nomogram, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II (SAPS II), and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) clinical decision curves: (A) Training set; (B) Validation set.
The Delong test showed a significant difference in AUROC between our model and the three previous models (p < 0.05), indicating that our model performed significantly better than these previous models in predicting ICU mortality in SALI patients. In addition, the results of net reclassification index (NRI) and integrated discrimination index (IDI) showed better reclassification performance of our model. Thus, these results indicate that the predictive accuracy of our model is significantly improved over previous models, as shown in Supplementary Table 3.
Sepsis continues to be a critical concern in modern medicine, demanding urgent attention. If left unchecked, it can escalate into MODS, significantly increasing patient morbidity and mortality (21). Liver failure is an important aspect of septic MODS and usually portends a poor prognosis (22, 23). Despite advances in treatment, mortality rates continue to rise progressively, a problem further exacerbated by the significant aging of today’s population (24). Therefore, it is essential to assess the mortality of elderly SALI patients admitted to the ICU.
This study primarily utilized the MIMIC database to evaluate the incidence and progression of mortality in SALI patients following their admission to the ICU. Lasso regression analysis was employed to identify independent risk factors associated with ICU mortality in these patients. Ultimately, six clinical variables of ALB, AG, PTT, ALT/ALP, APRI and mechanical ventilation were determined by the construction of the model.
Albumin has binding, translocation, and detoxification of endogenous and exogenous molecules, killing effects, antioxidant activity, and modulation of immune and inflammatory responses (25, 26). The mechanisms of SALI are unknown, and previous studies have shown that cytokine-induced inflammation and mitochondrial oxidative stress are key factors contributing to SALI (27). Previous studies have shown that ALB reduces the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria by inhibiting the leakage of the cysteine protease histone B from lysosomes while reducing the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, concluding that ALB not only protects hepatocytes from the cytotoxic effects of the cytokine TNFα but also prevents inflammatory mediators from further damaging tissues (28). Evidence-based indications for albumin administration in clinical guidelines are primarily liver disease (29). In patients with sepsis or septic shock who remain hemodynamically unstable after resuscitation with 30 ml/kg crystalloid, albumin infusion may be considered clinically for further treatment. It can be added to a large crystalloid infusion rather than used alone for crystalloid therapy (30, 31). In conclusion, when the concentration of ALB in the patient’s body decreases, the mortality rate of the patient will increase, and our modeling further validates that ALB has a strong ability for the prognosis of the patients, and further by strengthening the management of the patient in terms of ALB.
Anion gap is a comprehensive outcome indicator determined by the measured anion and cation concentrations (32). However, AG is also significantly affected by ALB levels (33). In the setting of severe sepsis, the development of hyperlactatemia can trigger a high AG metabolic acidosis. Previous studies have shown that AG in early ICU admission is one of the risk factors for the outcome of sepsis patients (34). In this study, AG variables were included through lasso review to predict the mortality of patients admitted to the ICU, and the effect of ALB on AG was considered, so after screening ALB was also used as a part of the model, which complemented the previous study and thus predicted in several ways.
Alanine transaminase and ALP are sensitive indicators of liver damage, and liver injury can cause elevated serum levels of ALT and ALP (35). ALT is a specific marker of hepatocellular injury, whereas bilirubin and PT-INR represent liver function (36). ALP is an enzyme found primarily in the hepatobiliary tract and is elevated in the cholestatic form of liver injury (37). However, mild to moderate elevations of ALP are common in all types of hepatitis are common, even in hepatocellular injury (36). The ALT/ALP ratio, which combines both ALT and ALP, is more closely related to the pathologic features of liver injury and changes in disease (38). PLT is involved in sepsis combined with multiorgan dysfunction by regulating inflammation, tissue integrity, and defense against infection (39). Studies have shown that APRI is a good predictor of SALI in children that platelets accumulate in the liver when the body is attacked by inflammatory cytokines, leading to liver injury and a decrease in platelet counts in the peripheral blood, and that platelets can influence the regeneration of damaged liver tissue (40). Previous studies have shown that two novel indicators, ALT/ALP and APRI, can be good predictors of SALI, but in the modeling developed in this study, both accounted for a small proportion of the modeling, which may be related to the fact that we did not include enough sample sizes of the elderly. Secondly, ALT and ALP may increase simultaneously in liver injury, resulting in no significant difference in their ratios, and the P-value of APRI tends to be close to 0.05 when predicting SALI alone at the beginning of the modeling, which means that it does not have a significant meaning when predicting alone. Therefore, the weighting of the scores in the modeling was not high, which means that we need to include more cases in the future to explore the predictive value of APRI for SALI.
Common complications at the onset of severe sepsis include coagulation abnormalities and liver injury. Overall coagulation indices such as PTT and prothrombin time are generally used in the clinical setting, and a single index may reflect only part of the coagulation system (41). DCIs that occur when there is decreased production of coagulation factors associated with hepatocellular injury or sepsis-associated coagulation abnormalities can exacerbate the depletion. Studies have shown that a longer PTT may reflect the most severe sepsis due to coagulation factor depletion or high-dose heparin therapy and that a prolonged PTT is associated with higher mortality (42), and PTT prolongation is also an important marker of severe hyperfibrinolysis (43). This is consistent with our study. As the PTT value prolongs, the percentage of PTT increases, leading to a gradual rise in patient mortality rates. The occurrence of SALI further impacts the consumption of coagulation factors, resulting in sepsis-related coagulation abnormalities. In severe cases, DIC develops, accelerating patient mortality. These two conditions exacerbate each other, so it is crucial to clinically monitor changes in coagulation function when SALI occurs.
The last variable incorporated in our model is mechanical ventilation. When a patient is in a critical situation, such as respiratory failure, respiratory arrest, or oxygen desaturation, clinical work is mostly done with a ventilator. Mechanical ventilation is widely used in the management of septic patients but is prone to complications. Ventilator-associated pneumonia, a lung infection during mechanical ventilation, is the most common nosocomial lung infection in intensive care patients. Whereas sepsis itself, as a severe systemic inflammatory disease, its combination with ventilator-associated pneumonia may lead to deterioration of the patient’s condition and increase the risk of death (44, 45).
Simplified Acute Physiology Score II and SOFA scores are commonly used to evaluate the prognosis of patients in clinical practice (5, 46), so the two variables are not included in the model construction. In this study, SOFA and SAPS2 scores were used to compare their performance with that of predictive models. We found that nomogram performed the best. In addition, the DCA curve supports this finding. Through the above comparison, it is further shown that the efficiency of the constructed model is better.
Intensive care unit mortality in elderly SALI patients was the endpoint of this study. Independent risk factors were screened by lasso regression, and a risk prediction model was successfully constructed based on these factors. Lasso regression analysis can solve the problem of multicollinearity among variables and is superior to univariate analysis. The nomogram constructed based on the Lasso regression model has a certain reference value for medical workers to visually analyze individual prognosis. As a visual scoring tool suitable for clinical research, the nomogram can synthesize various influencing factors and present their results intuitively. Decision makers can formulate individualized treatment plans to prolong survival based on the predicted risk of death. Through the predictive model, doctors can find out in advance whether a patient is likely to have a poor prognosis and take appropriate measures to reduce the risk of mortality, thus improving treatment outcomes, lowering healthcare costs, and enhancing patients’ quality of life.
By establishing a robust predictive model, clinicians can proactively identify health issues at an early stage, thereby improving both treatment efficacy and the overall quality of life for patients. However, it is crucial to recognize the limitations inherent in this study. Firstly, it relies on a single-center retrospective analysis, and the findings require validation through prospective cohort studies. Secondly, despite the approach of randomly dividing the data into training and validation sets, and the highly reliable models produced during the development process, the generalizability of the models is still limited by the lack of external validation of the centralized dataset. This limitation emphasizes the need for further evaluation of its stability and applicability. Lastly, while this analysis focused on 934 elderly patients, future research would benefit from multi-center approaches and larger-scale validations to enhance both stability and performance.
We successfully constructed a model of in-ICU mortality of SALI elderly patients. The nomogram created based on the above factors assessed the risk of death in patients, which is of great informative value and clinical applicability.
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethical approval was not required for the studies involving humans because the datasets presented in the current study are avaliable in the MIMIC IV 3 database. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements because the datasets presented in the current study are avaliable in the MIMIC IV 3 database.
XH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AX: Methodology, Software, Writing – review and editing. XJ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. TH: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. MY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82072134), the Research Fund of Anhui Institute of translational medicine (Nos. 2023zhyx-C64 and 2022zhyx-C76), the Basic and Clinical Enhancement Project of Anhui Medical University (No. 2023xkjT042), Anhui Province Key Research and Development Plan High-tech Special Project (No. 202304a05020071), and An-hui University Excellent Young Talents Support Plan (No. gxyqZD2018026).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1516853/full#supplementary-material
1. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
2. Yan J, Li S, Li S. The role of the liver in sepsis. Int Rev Immunol. (2014) 33:498–510. doi: 10.3109/08830185.2014.889129
3. Dai JM, Guo WN, Tan YZ, Niu KW, Zhang JJ, Liu CL, et al. Wogonin alleviates liver injury in sepsis through Nrf2-mediated NF-κB signalling suppression. J Cell Mol Med. (2021) 25:5782–98. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16604
4. Wang J, Zhu Q, Li R, Zhang J, Ye X, Li X. YAP1 protects against septic liver injury via ferroptosis resistance. Cell Biosci. (2022) 12:163. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00902-7
5. Hu T, Lv H, Jiang Y. The association between four scoring systems and 30-day mortality among intensive care patients with sepsis: A cohort study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:11214. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90806-2
6. Dhainaut JF, Marin N, Mignon A, Vinsonneau C. Hepatic response to sepsis: Interaction between coagulation and inflammatory processes. Crit Care Med. (2001) 29:S42–7. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200107001-00016
7. Sun J, Zhang J, Wang X, Ji F, Ronco C, Tian J, et al. Gut-liver crosstalk in sepsis-induced liver injury. Crit Care. (2020) 24:614. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03327-1
8. Kobashi H, Toshimori J, Yamamoto K. Sepsis-associated liver injury: Incidence, classification and the clinical significance. Hepatol Res. (2013) 43:255–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2012.01069.x
9. Henrion J, Schapira M, Luwaert R, Colin L, Delannoy A, Heller FR. Hypoxic hepatitis: Clinical and hemodynamic study in 142 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). (2003) 82:392–406. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000101573.54295.bd
10. Bhogal HK, Sanyal AJ. The molecular pathogenesis of cholestasis in sepsis. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). (2013) 5:87–96. doi: 10.2741/e598
11. Fontana RJ, Seeff LB, Andrade RJ, Björnsson E, Day CP, Serrano J, et al. Standardization of nomenclature and causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury: Summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology. (2010) 52:730–42. doi: 10.1002/hep.23696
12. Zhang W, Jiang H, Wu G, Huang P, Wang H, An H, et al. The pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets in sepsis. MedComm (2020). (2023) 4:e418. doi: 10.1002/mco2.418
13. Ji Y, Yin Y, Li Z, Zhang W. Gut microbiota-derived components and metabolites in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Nutrients. (2019) 11:1712. doi: 10.3390/nu11081712
14. Lv M, Wang C, Li F, Peng J, Wen B, Gong Q, et al. Structural insights into the recognition of phosphorylated FUNDC1 by LC3B in mitophagy. Protein Cell. (2017) 8:25–38. doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0328-8
15. Vanhorebeek I, Gunst J, Derde S, Derese I, Boussemaere M, D’Hoore A, et al. Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and biogenesis in prolonged critically ill patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 97:E59–64. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-1760
16. Woźnica EA, Inglot M, Woźnica RK, Łysenko L. Liver dysfunction in sepsis. Adv Clin Exp Med. (2018) 27:547–51. doi: 10.17219/acem/68363
17. Iwashyna TJ, Cooke CR, Wunsch H, Kahn JM. Population burden of long-term survivorship after severe sepsis in older Americans. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2012) 60:1070–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.03989.x
18. Jalali A, Alvarez-Iglesias A, Roshan D, Newell J. Visualising statistical models using dynamic nomograms. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0225253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225253
19. Johnson AEW, Bulgarelli L, Shen L, Gayles A, Shammout A, Horng S, et al. MIMIC-IV, a freely accessible electronic health record dataset. Sci Data. (2023) 10:1. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01899-x
20. Pruinelli L, Westra BL, Yadav P, Hoff A, Steinbach M, Kumar V, et al. Delay within the 3-hour surviving sepsis campaign guideline on mortality for patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. (2018) 46:500–5. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000002949
21. Hotchkiss RS, Moldawer LL, Opal SM, Reinhart K, Turnbull IR, Vincent JL. Sepsis and septic shock. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:16045. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.45
22. Beyer D, Hoff J, Sommerfeld O, Zipprich A, Gaßler N, Press AT. The liver in sepsis: Molecular mechanism of liver failure and their potential for clinical translation. Mol Med. (2022) 28:84. doi: 10.1186/s10020-022-00510-8
23. Tanaka S, De Tymowski C, Stern J, Bouzid D, Zappella N, Snauwaert A, et al. Relationship between liver dysfunction, lipoprotein concentration and mortality during sepsis. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0272352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272352
24. Eshghi F, Tahmasebi S, Alimohammadi M, Soudi S, Khaligh SG, Khosrojerdi A, et al. Study of immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in a mouse model of LPS induced systemic inflammation. Life Sci. (2022) 310:120938. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120938
25. Fanali G, di Masi A, Trezza V, Marino M, Fasano M, Ascenzi P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol Aspects Med. (2012) 33:209–90. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2011.12.002
26. Casulleras M, Flores-Costa R, Duran-Güell M, Alcaraz-Quiles J, Sanz S, Titos E, et al. Albumin internalizes and inhibits endosomal TLR signaling in leukocytes from patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12:aax5135. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax5135
27. Duran-Güell M, Garrabou G, Flores-Costa R, Casulleras M, López-Vicario C, Zhang IW, et al. Essential role for albumin in preserving liver cells from TNFα-induced mitochondrial injury. Faseb J. (2023) 37:e22817. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201526R
28. Duran-Güell M, Flores-Costa R, Casulleras M, López-Vicario C, Titos E, Díaz A, et al. Albumin protects the liver from tumor necrosis factor α-induced immunopathology. Faseb J. (2021) 35:e21365. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001615RRR
29. Abedi F, Zarei B, Elyasi S. Albumin: A comprehensive review and practical guideline for clinical use. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2024) 80:1151–69. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03664-y
30. Yu SH, Ma YT, Li X. [The correlation between coagulation function and prognosis in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by extrapulmonary sepsis or pulmonary infection]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. (2021) 60:650–5. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20201217-01017
31. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. (2021) 49:e1063–143. doi: 10.1097/ccm.0000000000005337
32. Oh MS, Carroll HJ. The anion gap. N Engl J Med. (1977) 297:814–7. doi: 10.1056/nejm197710132971507
33. Nanji AA, Campbell DJ, Pudek MR. Decreased anion gap associated with hypoalbuminemia and polyclonal gammopathy. JAMA. (1981) 246:859–60.
34. Lou Z, Zeng F, Huang W, Xiao L, Zou K, Zhou H. Association between the anion-gap and 28-day mortality in critically ill adult patients with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e39029. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000039029
35. Meng YJ, Yu HL, Yang S. Clinical significance of GLDH, GGT, ALT and ALP combined detection in the diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury. Lab Med Clinic. (2019) 16:1735–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2019.12.032
36. Kwo PY, Cohen SM, Lim JK. ACG clinical guideline: Evaluation of abnormal liver chemistries. Am J Gastroenterol. (2017) 112:18–35. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.517
37. Kalas MA, Chavez L, Leon M, Taweesedt PT, Surani S. Abnormal liver enzymes: A review for clinicians. World J Hepatol. (2021) 13:1688–98. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1688
38. Chunyang H, Zhang XD, Huang YL, Han Y, Li WJ, et al. Serum ALT/ALP ratio changes and histopathological features of patients with drug-induced liver injury acute hepatocellular type. J Pract Hepatol. (2021) 24:379–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2021.03.019
39. Graham SM, Liles WC. Platelets in sepsis: Beyond hemostasis. Blood. (2016) 127:2947–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-706168
40. Dou J, Zhou Y, Cui Y, Chen M, Wang C, Zhang Y. AST-to-platelet ratio index as potential early-warning biomarker for sepsis-associated liver injury in children: A database study. Front Pediatr. (2019) 7:331. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00331
41. Mohapatra P, Kumar A, Singh RK, Gupta R, Hussain M, Singh S, et al. The effect of sepsis and septic shock on the viscoelastic properties of clot quality and mass using thromboelastometry: A prospective observational study. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2023) 27:625–34. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24539
42. Niederwanger C, Bachler M, Hell T, Linhart C, Entenmann A, Balog A, et al. Inflammatory and coagulatory parameters linked to survival in critically ill children with sepsis. Ann Intensive Care. (2018) 8:111. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0457-8
43. Martin-Loeches I. Current concepts in community and ventilator associated lower respiratory tract infections in ICU patients. Antibiotics (Basel). (2020) 9:380. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9070380
44. Gopalakrishnan R, Vashisht R. Sepsis and ECMO. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2021) 37:267–74. doi: 10.1007/s12055-020-00944-x
45. Lambden S, Laterre PF, Levy MM, Francois B. The SOFA score-development, utility and challenges of accurate assessment in clinical trials. Crit Care. (2019) 23:374. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2663-7
Keywords: sepsis-associated liver injury, in-ICU mortality, nomogram, lasso regression, MIMIC-III database, model
Citation: Hu X, Wang J, Cao S, Xia A, Jiang X, Hua T and Yang M (2025) Development of a nomogram to predict in-ICU mortality of elderly patients with sepsis-associated liver injury: an analysis of the MIMIC-IV database. Front. Med. 12:1516853. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1516853
Received: 28 October 2024; Accepted: 07 March 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Marios Kyriazis, National Gerontology Centre, CyprusReviewed by:
Hongsheng Wu, Southern Medical University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Hu, Wang, Cao, Xia, Jiang, Hua and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Yang, eWFuZ21pbkBhaG11LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.