- 1Department of General Surgery, West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov Medical University, Aktobe, Kazakhstan
- 2Department of Surgical Diseases No. 2, West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov Medical University, Aktobe, Kazakhstan
Background: This study aims to analyzing scientific publications related to necrotizing pancreatitis and its mortality, identifying key areas and trends, and determining the leading research institutions, authors, countries, and journals actively working in this field.
Methods: The Web of Science and Scopus databases were searched for articles on NP published between January 1, 2013, and April 22, 2024. Articles published before 2013, conference abstracts, and case reports were excluded. The articles were assessed based on various metrics, including the number of citations, publication dates, countries of origin, institutions, journals, and authors.
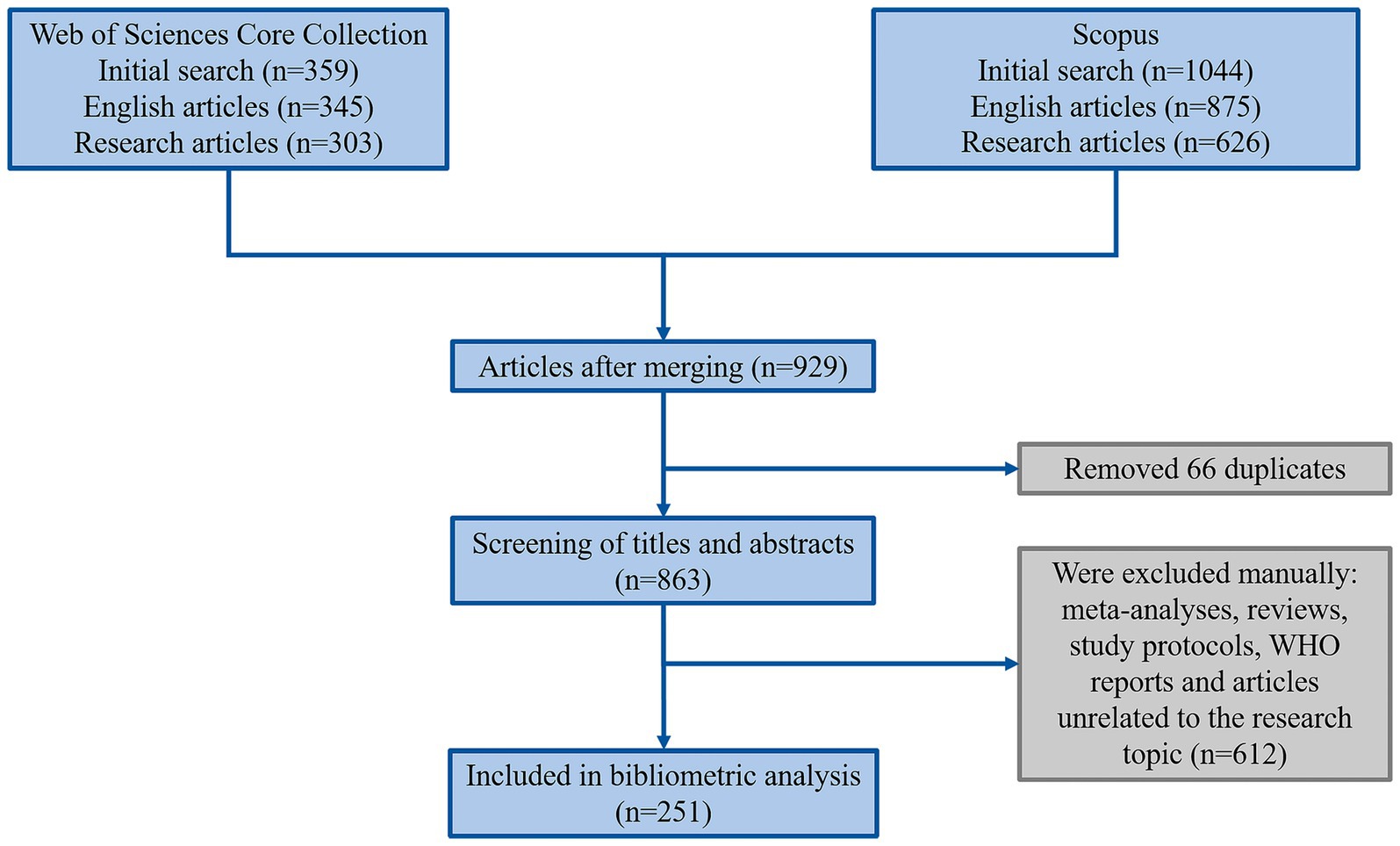
Results: A total of 929 articles were identified, of which 251 were deemed suitable for analysis after duplicates were removed. China contributed the most articles, followed by the United States and India. The most frequent publications appeared in specialized journals such as “Pancreatology” and “Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.” The primary research institutions were universities and medical centers. The highest-impact articles focused on minimally invasive treatment methods for NP. There has been a growing body of research in NP over the past decade, particularly in China and the United States.
Conclusion: Despite advancements in medical science, the mortality rate associated with pancreatic necrosis remains high. This highlights the continued challenge in effectively addressing complications of acute pancreatitis. Researchers worldwide are actively exploring alternative therapeutic approaches to mitigate these complications and improve patient outcomes.
1 Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a widespread condition affecting the pancreas and is the primary cause of hospitalization in surgical wards among gastrointestinal diseases (1). According to a systematic review and meta-analysis by Iannuzzi et al. (2) the incidence of acute pancreatitis has been increasing annually from 1961 to 2016. The overall incidence has risen by 3.07% per year. This trend has been observed in most regions worldwide, including North America, Europe, South America, and Oceania, while in Asia, the rates have remained relatively stable (2).
Zilio et al. (3) conducted a comprehensive analysis of publications to identify the etiology of acute pancreatitis (AP), including data from 46 studies involving a total of 2,341,007 patients across 36 countries. The global estimates for the distribution of etiologies were 42% (95% CI: 39–44%) for biliary, 21% (95% CI: 17–25%) for alcoholic, and 18% (95% CI: 15–22%) for idiopathic (3). Less commonly, these include tumors, trauma, hypertriglyceridemia, and the use of certain medications, such as azathioprine, furosemide, and corticosteroids (4, 5). Additionally, AP can develop as a result of iatrogenic injuries, particularly following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography or surgical procedures (6).
Approximately 80% of acute pancreatitis (AP) cases present in a mild edematous form, while around 20% progress to severe or complicated pancreatitis, which is characterized by early or delayed systemic and local complications (7). In severe cases, up to 10.5% may require surgical intervention, and up to 40% may die during hospitalization (8). Overall, mortality in severe AP can reach 50%, contrasting with an overall mortality rate of 2–5% for all forms of AP (9). This increased risk of mortality and complications is often associated with the development of pancreatic necrosis, which is frequently accompanied by infectious complications (10, 11). Mortality rates in these cases can range from 15 to 39% (12). Specifically, in North America and Europe, the mortality rates vary between 18 and 20% (13), while in China, they range from 8 to 39% (14, 15) and in Japan, the rates fluctuate between 10 and 26% (16). Pancreatic necrosis may involve the pancreatic parenchyma, the peripancreatic tissues, or both regions simultaneously (17).
Surgical intervention is usually required for the management of infected pancreatic necrosis (18), and, less frequently, for sterile necrosis when it leads to gastric, duodenal, or biliary obstruction (12, 19). For many years, open surgical necrosectomy was the standard treatment for infected necrotizing pancreatitis, despite its high complication rate and significant mortality (18). However, in the past two decades, there has been a shift toward minimally invasive techniques, such as percutaneous abscess drainage, endoscopic transgastric necrosectomy (ETN), laparoscopy, and video-assisted retroperitoneal debridement (VARD) (20). Mehta et al. (20) and van Baal et al. (21), in their study, highlight the significance of percutaneous drainage as a primary method for effectively eliminating abscesses and minimizing the need for open surgical interventions (20, 21). Similarly, Tan et al. (22) and Mathew et al. (23) explore laparoscopic necrosectomy, which offers significant advantages by minimizing tissue trauma. Additionally, Revoredo Rego et al. (24) investigate VARD a technique that ensures precise access to necrotic tissue while reducing the invasiveness of the procedure (24). Moreover, Bakker et al. (25) compare ETN with conventional surgical necrosectomy. Collectively, these studies highlight the efficacy of minimally invasive techniques in enhancing clinical outcomes, reducing hospitalization duration, and promoting faster recovery.
In recent years, the focus of bibliometric research has shifted significantly toward the study of minimally invasive surgery, pancreatic cystic disease, and oncological interventions, which have emerged as dominant topics in scientific publications (26–28). Acute pancreatitis has also become a focus of attention among researchers. Bibliometric analyses in this field have predominantly utilized the Web of Science (WoS) database and CiteSpace software to identify trends and patterns (29, 30). To broaden the scope and ensure a more thorough evaluation, our study includes both the WoS and Scopus databases, we employed RStudio for advanced data processing and visualization. To fill the gap in the existing literature, we conducted a bibliometric analysis aimed at analyzing scientific publications related to necrotizing pancreatitis and its mortality, identifying key areas and trends, and determining the leading research institutions, authors, countries, and journals actively working in this field.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Search strategy and data collection
The literature search was conducted in two databases, Web of Science and Scopus, covering the period from January 1, 2013, to April 22, 2024. Research articles written in English were selected. Case reports, conference abstracts, and editorial materials were excluded from the analysis. A combination of keywords (“necrotizing pancreatitis” and “mortality”) and their synonyms were used, employing Boolean operators (AND, OR). Information regarding authors, titles, sources, sponsors, abstracts, document types, cited references, and keywords was retrieved in txt format for Web of Science and in BibTeX format for Scopus for further analysis. The obtained data were merged using RStudio. The result was a single file in xlsx format. The detailed search strategy is demonstrated in Figure 1.
2.2 Study selection and data extraction
The titles, abstracts, and full texts of the articles were thoroughly reviewed by two authors (GGG and MKJ) to determine their relevance to the objectives of the study. In case of disagreements, a third author was consulted to help resolve any discrepancies.
2.3 Visualization and statistical tools
Data processing and analysis were performed using the Bibliometrix package (version 3.2.11) in the RStudio environment (version 4.1.2). The Biblioshiny web interface allowed for the creation of various visualizations, bibliometric mapping, and statistical calculations.
3 Results
3.1 Summary of the papers
This bibliometric analysis includes 251 documents from 121 journals over the period from 2013 to 2024 (Figure 2). The mean age of the documents was 5.16 years, with an average citation count of 21.42 per document. Among the 2,082 authors, only 3 produced a document independently, while the mean number of co-authors per document was 11.8. A total of 1,838 keywords were identified, with 439 occurring most frequently. The analysis also revealed an annual growth rate of −8.23%.
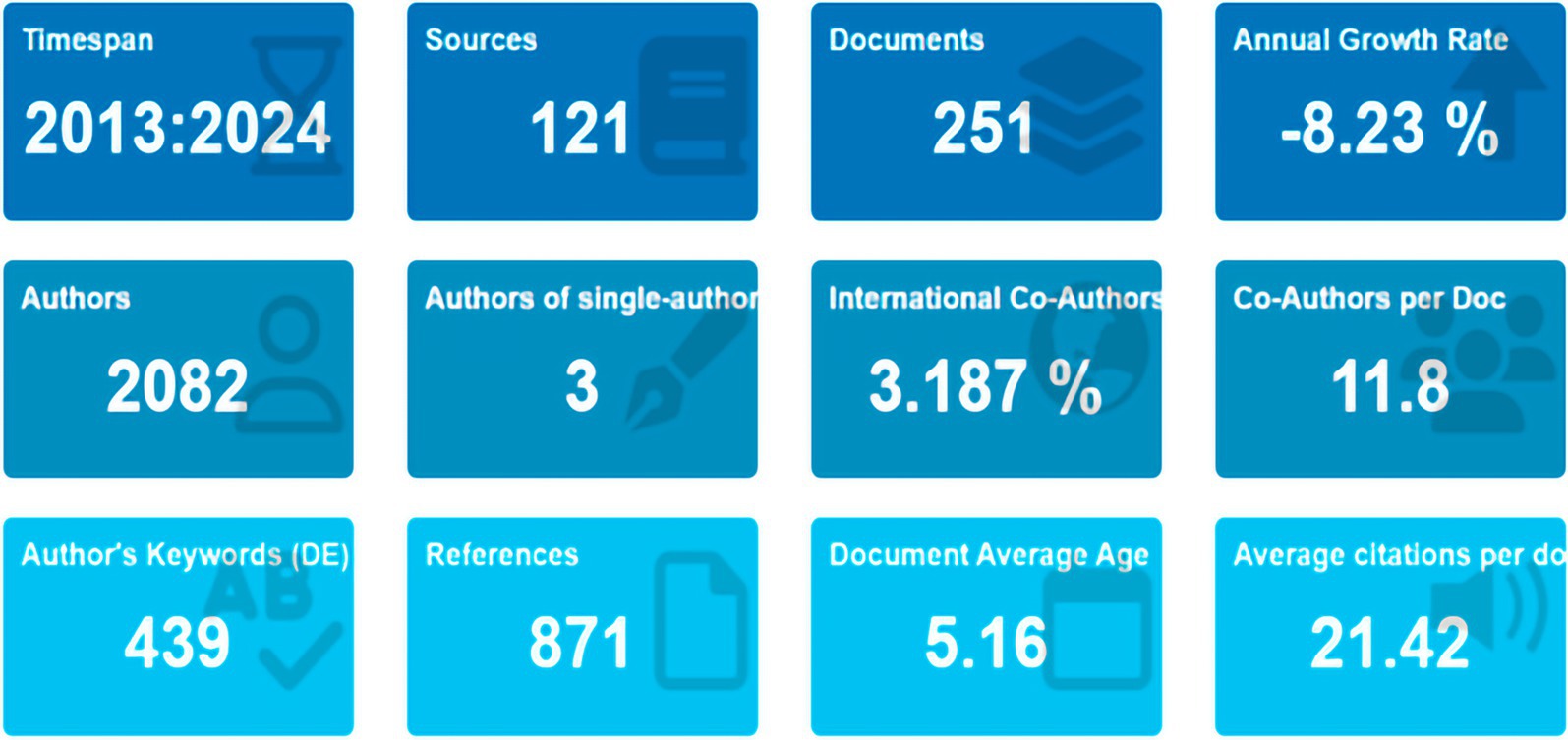
Figure 2. Main information on the bibliometric analysis of publications on necrotizing pancreatitis.
3.2 Annual analysis of publication
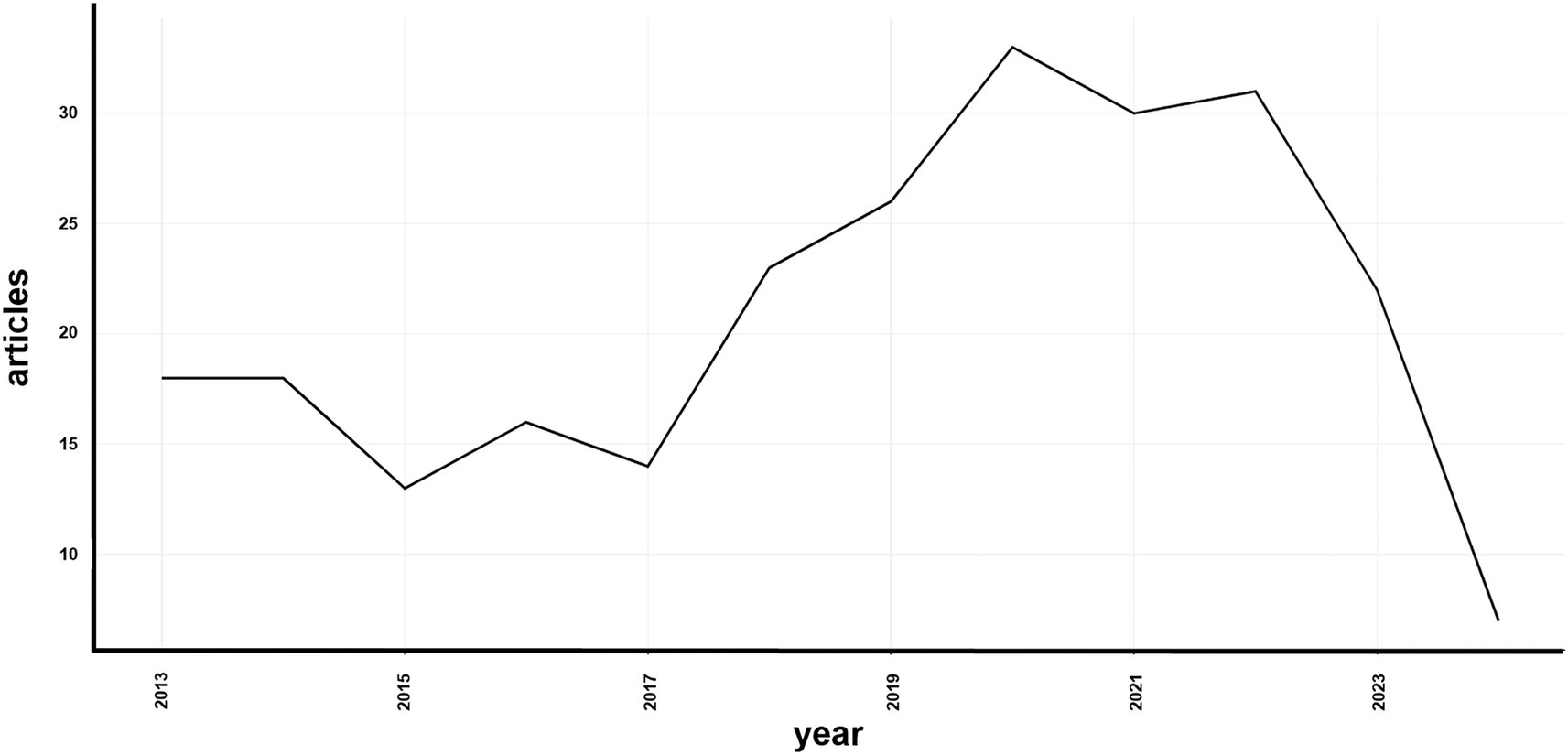
The annual scientific publication trends, shown in Figure 3, indicate fluctuations from 2013 to 2024. From 2013 to 2017, the number of publications remained relatively stable with minor variations. However, from 2018 to 2021, a noticeable increase occurred, peaking in 2020 with 33 articles. A slight decrease in publications was observed in 2023, with 23 articles published.
3.3 The most productive country
The global research landscape on necrotizing pancreatitis (NP) spans 35 countries, with the most prolific contributors being China (62 publications), the United States (45 publications), and India (27 publications). Additionally, the United States, Germany, and Spain are involved in international collaborations (Figure 4A). Notably, China and the United States have demonstrated the most substantial growth in publication output, with their contributions increasing from 3 and 1 in 2013 to 74 and 77 in 2024, respectively (Figure 4B). Other countries, such as Germany, Japan, and India, have shown steady growth, while Spain experienced a significant surge in publications from 2018, peaking in 2020. The United States and the Netherlands lead in citations with 1,522 and 1,112, respectively, followed by China and India with 800 and 285 citations, respectively (Figure 4C).
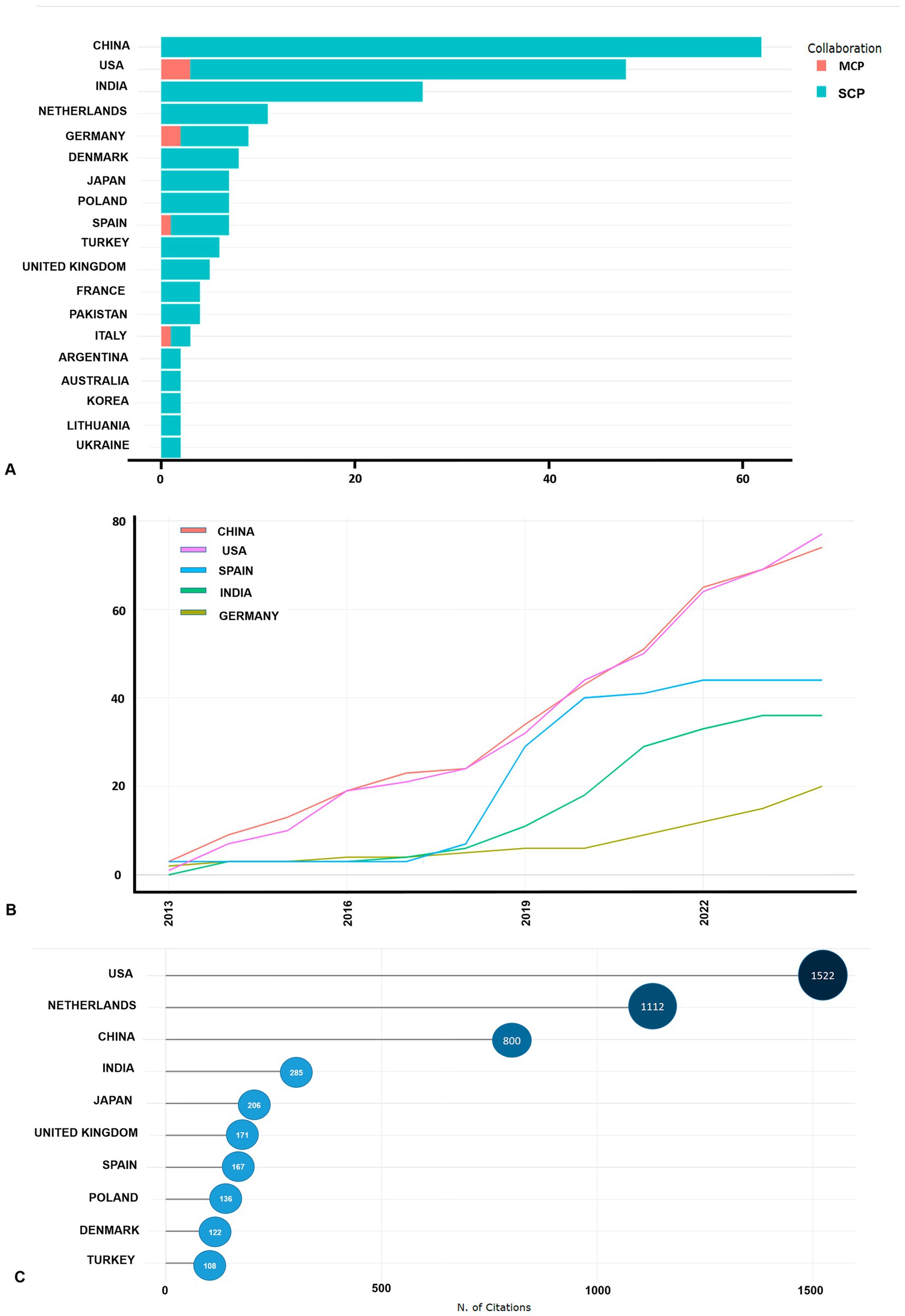
Figure 4. Scientific collaborations within countries and international scientific research projects. SCP, Single country publications; MCP, Multiple country publications (A), countries’ production over time (B), top 10 most cited countries (C).
3.4 Core journals and references
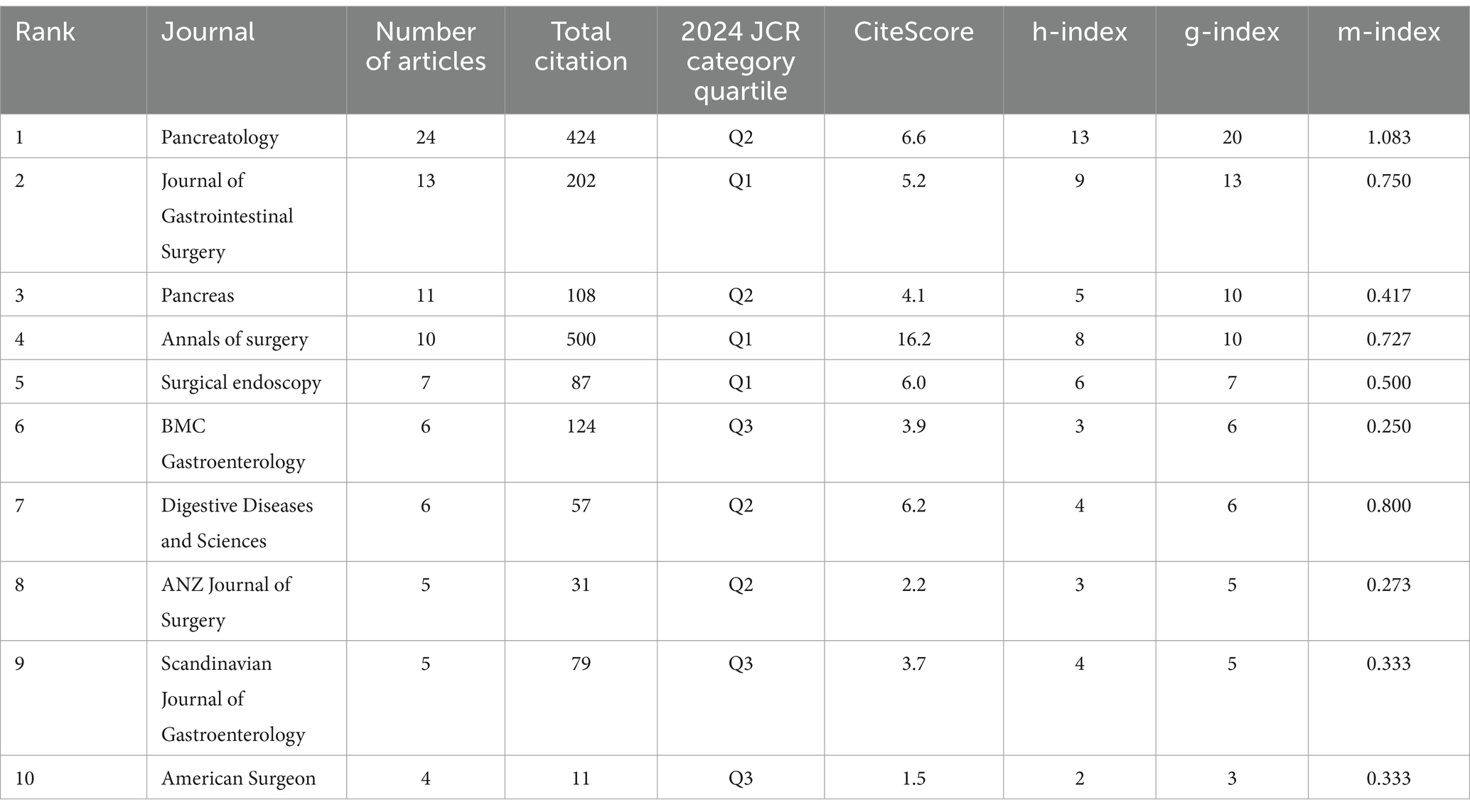
The largest number of articles on necrotizing pancreatitis was published in Pancreatology (24 articles), followed by the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery (13 articles) and Pancreas (11 articles) (Table 1). The journal with the highest total citation count was Annals of Surgery, with 500 citations, a CiteScore of 16.2, and classification in the Q1 JCR category. Pancreatology ranked second in total citations (424), with a CiteScore of 6.6, and is categorized in Q2. The Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery and Pancreas are also positioned in the first and second quartiles, respectively, and demonstrate high citation rates and impact indexes. Conversely, journals such as the American Surgeon and the ANZ Journal of Surgery have lower citation metrics and are classified in Q3.
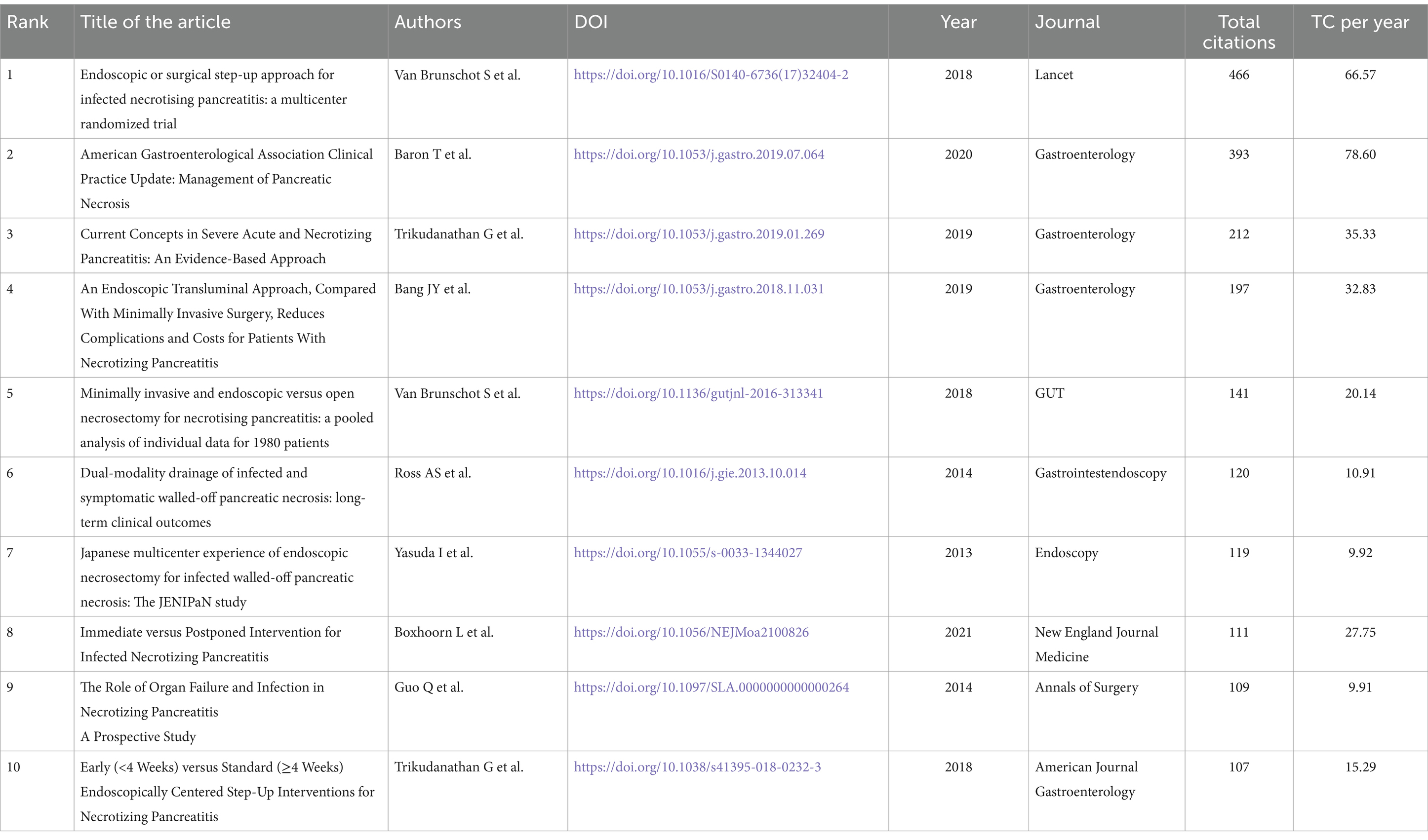
Table 2 highlights 10 notable scientific articles published across various journals, detailing their DOI, total citations, average citations per year, and normalized citation counts. The article by Van Brunschot et al. (31) in Lancet recorded the highest total citations (466) and a normalized citation count of 10.35. Additionally, the article by Baron et al. (32) in Gastroenterology achieved the highest average citations per year (78.60) and a normalized citation count of 15.93. Other significant contributions include works by Trikudanathan et al. (45, 46), which also demonstrated high citation rates.
3.5 The most productive institutions and authors
Table 3 highlights the 10 most productive institutions contributing to research on necrotizing pancreatitis. Topping the list is the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in India, with 25 publications (9.96%), followed by the University of Amsterdam in the Netherlands (23 publications, 9.16%) and Central South University in China (19 publications, 7.57%). Notably, five of these institutions are located in the Netherlands, while three are based in China.
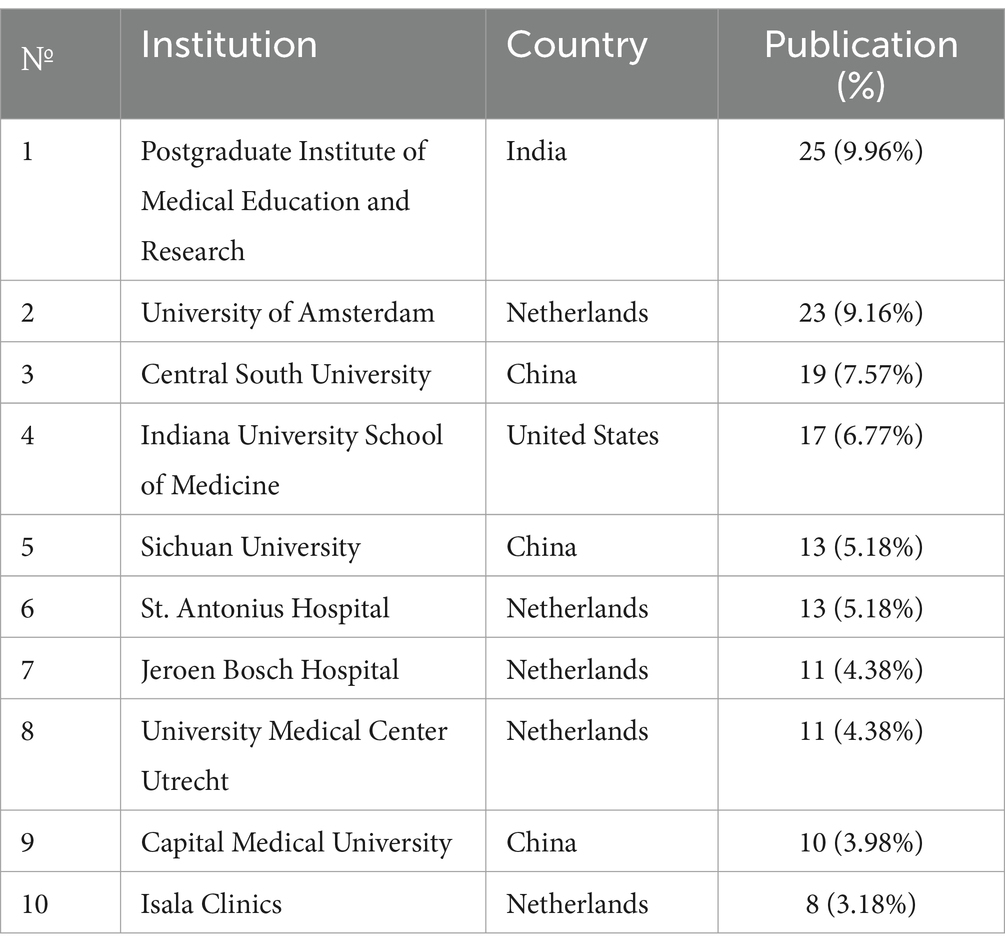
Table 3. List of universities and medical institutions by the number of publications in the field of NP research.
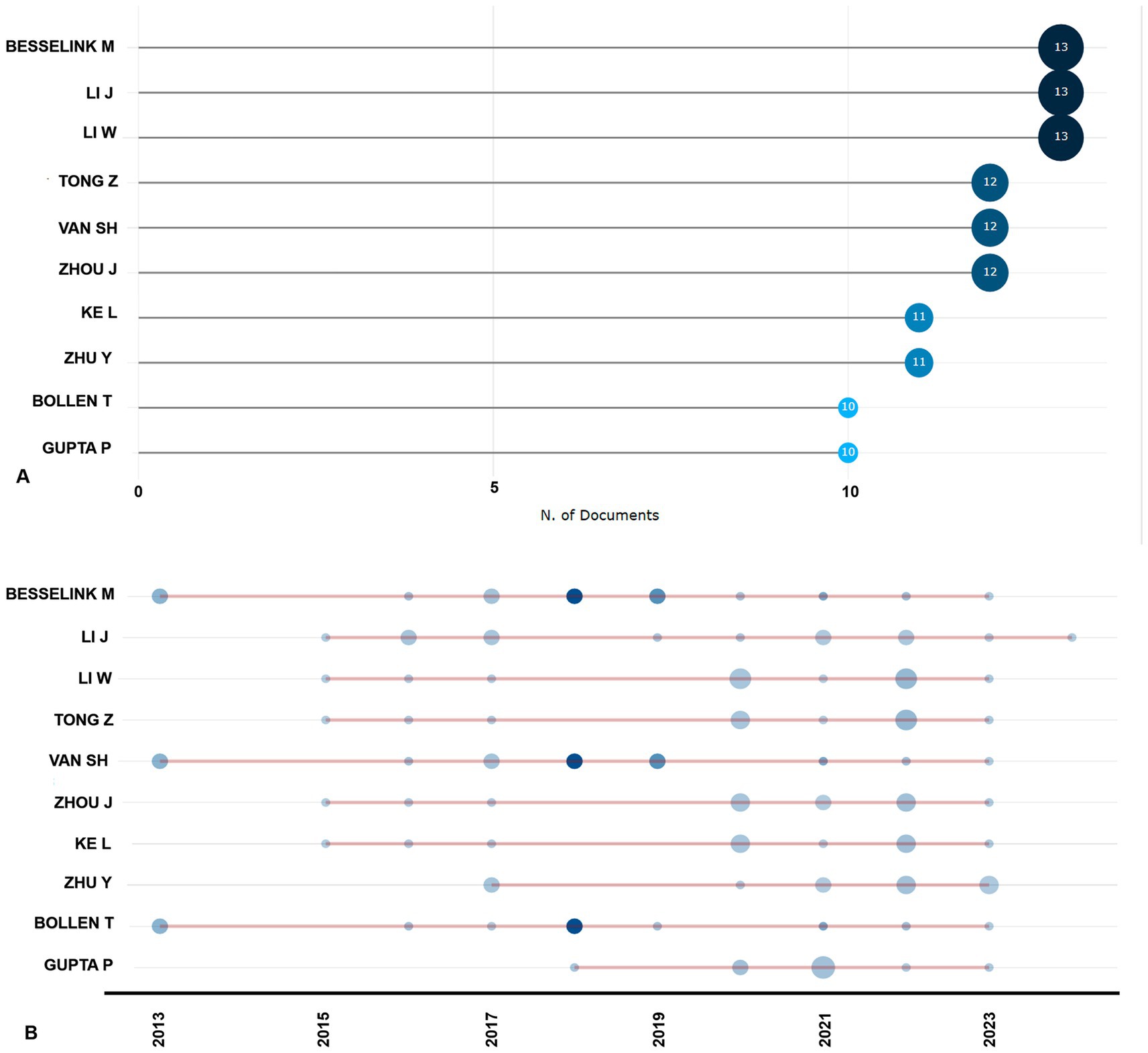
Figure 5A illustrates the most prolific authors in the field, with Besselink M., Li J., and Li W. leading with 13 publications each. They are closely followed by Tong Z., Van S.H., and Zhou J., each contributing 12 publications. Notably, Besselink M. and Bollen T. are notable for their frequent collaborations and high citation counts, particularly in 2018. Gupta P. displayed significant citation activity in 2018 and 2020 but saw a decline by 2022. Conversely, Ke L. reached a peak citation index in 2022, despite low citation counts in 2015 and 2021. Meanwhile, authors Li J., Li W., and Tong Z. exhibit varying citation patterns across years, indicating differences in the temporal impact of their work (Figure 5B).
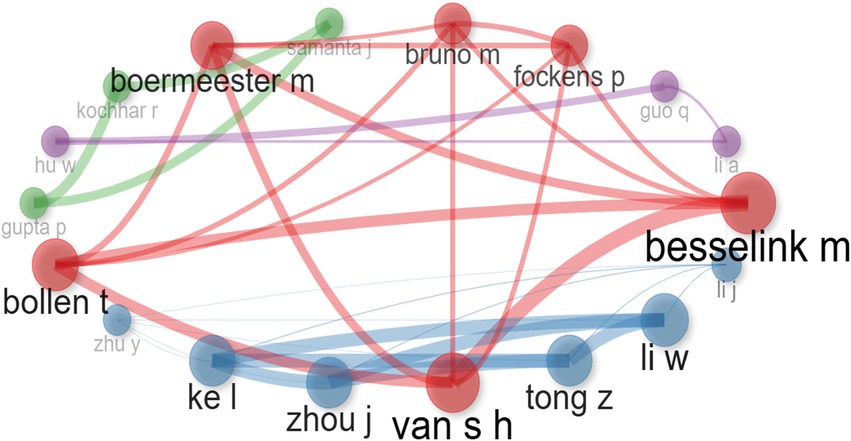
Figure 6 illustrates a co-authorship and co-citation network based on cluster analysis. The network is divided into four distinct clusters, differentiated by node color. The red cluster features authors such as Besselink M., Boermeester M., and Bollen T., who are tightly interconnected, indicating strong collaborative ties and a high degree of co-authorship within their research area. The blue cluster, dominated by authors like Ke L., Zhou J., Tong Z., and Li W., primarily from Chinese institutions, exhibits dense connections, signifying frequent and robust collaborations. This cluster demonstrates the most significant internal cohesion, as reflected by the thick lines connecting its members. The purple cluster includes authors such as Hu W. and Guo Q., who display notable connections within the group. While this cluster is smaller and less dense than the red and blue clusters, it highlights a cohesive network among its members. Finally, the green cluster consists of authors like Gupta P., Kochhar R., and Samanta, who maintain consistent connections with one another. This cluster represents a distinct group of researchers with aligned thematic interests and a moderate level of collaborative activity.
3.6 Authors keywords
The analysis of frequently occurring keywords reveals the primary research foci in the field of necrotizing pancreatitis. The terms “acute pancreatitis” (70 mentions), “infected pancreatic necrosis” (52 mentions), and “necrotizing pancreatitis” (38 mentions) predominate, indicating a concentrated focus on the severe forms of the disease. Additionally, keywords such as “mortality” (28 mentions) and “necrosectomy” (25 mentions) emphasize the significant role of surgical interventions in managing complications associated with necrotizing pancreatitis. Moreover, minimally invasive techniques, such as “percutaneous catheter drainage” (22 mentions), alongside the management of systemic complications, notably “organ failure” (16 mentions), are identified as critical areas of focus within both clinical applications and ongoing research efforts (Figure 7A).
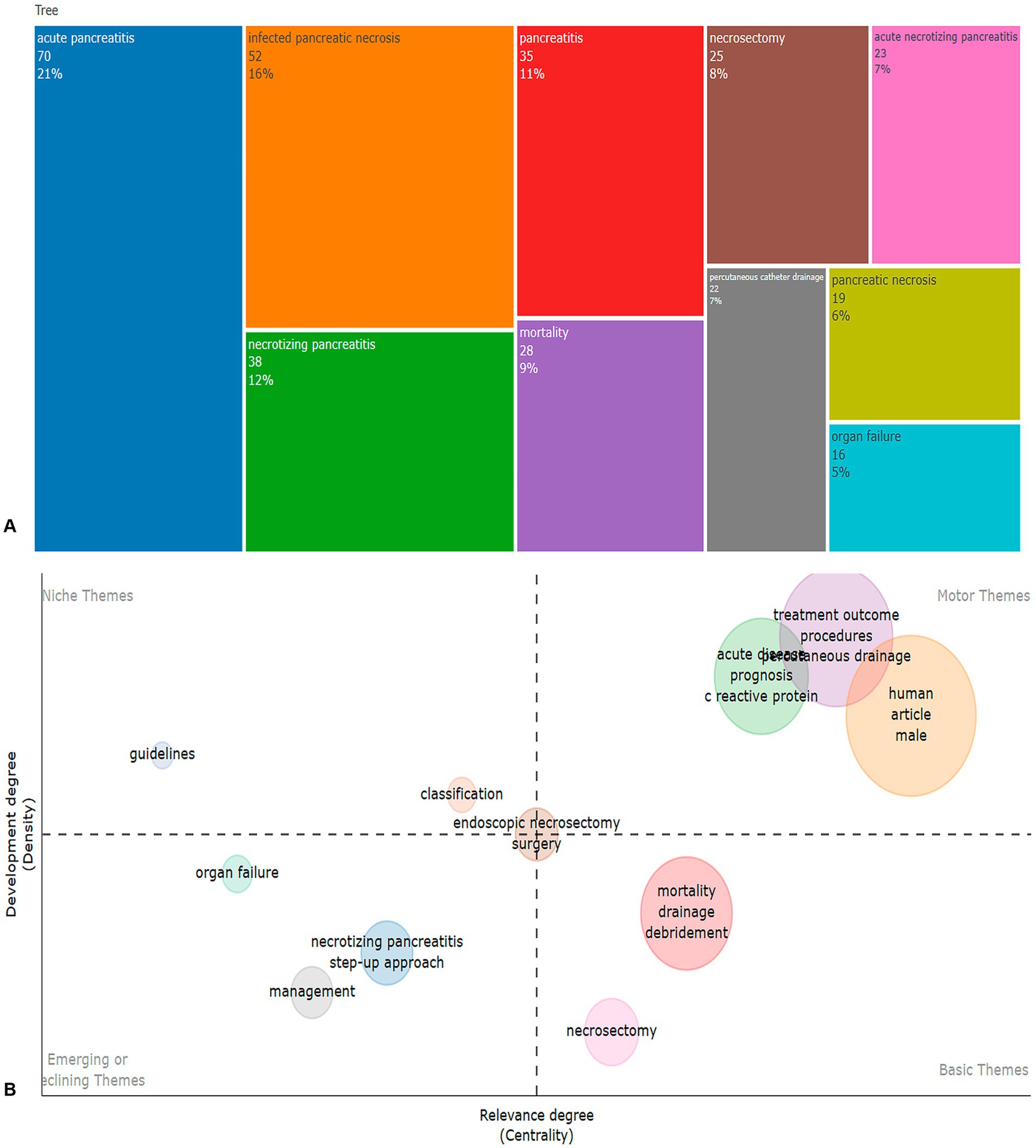
Figure 7. Tree map about frequency of mention of various terms and keywords (A), thematic keyword map (B).
Figure 7B presents a clustering of key terms related to necrotizing pancreatitis (NP), based on their relevance and level of development. In the “Emerging or Declining Themes” cluster, terms such as organ failure, necrotizing pancreatitis, and management are characterized by low relevance and development, indicating either the early stages of research or decreasing relevance. The “Niche Themes” cluster includes terms like guidelines and classification, which, despite having a high level of development, have low relevance, suggesting their specialized nature. In the “Basic Themes” cluster, terms such as mortality, drainage, and necrosectomy exhibit high relevance but require further research, indicating they are underdeveloped. The “Motor Themes” cluster, which includes terms like treatment outcomes, procedures, prognosis, and C-reactive protein, shows both high relevance and development, emphasizing their central role and well-established research foundation in NP.
4 Discussion
The findings of this bibliometric analysis highlight the growing global interest in pancreatic necrosis and associated mortality over the past decade. From 2013 to 2024, there has been a notable increase in the volume of scientific publications on this topic, with a particularly significant growth observed in the last 5 years. This trend underscores the rising recognition of pancreatic necrosis as a critical medical issue, driving extensive research efforts to improve understanding, management, and outcomes. A slight decline in publications in 2023 may be attributed to the reallocation of research funding to other areas, particularly those more directly associated with the pandemic, potentially influencing the volume of publications in subsequent years. By identifying the most productive countries, authors, and institutions, as well as high-impact journals and commonly used keywords, this analysis provides valuable insights into the global research landscape and highlights the collaborative nature of advancements in this field.
Guo Qiang et al. conducted a study revealing that patients with necrotic pancreatitis had a higher mortality rate compared to those with sterile necrosis (33). The primary predictors of mortality identified in the study included bacteremia, advanced age, persistent organ failure during the first week, and pancreatic necrosis. Therefore, a significant portion of the publications analyzed in this study focused on treatment strategies for pancreatic necrosis, with a marked emphasis on minimally invasive approaches. Sandra van Brunschot’s research highlighted that although the endoscopic step-up approach did not surpass the surgical step-up approach in reducing severe complications or mortality in patients with infected necrotizing pancreatitis, it demonstrated advantages such as a reduced incidence of pancreatic fistulas and shorter hospital stays (31). These findings suggest the potential for a paradigm shift toward the endoscopic step-up approach as the preferred treatment method. Similarly, Ji Young Bang’s study reinforced these advantages, finding no significant differences in mortality between the approaches (34). However, patients in the endoscopic group experienced fewer severe complications, no cases of enterocutaneous or pancreatic-cutaneous fistulas, better physical health and quality of life outcomes at 3 months, and significantly lower costs ($75,830 compared to $117,492 for surgical intervention). These findings align with the evidence reviewed by Todd H. Baron in the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Institute Clinical Practice Update, which emphasized the importance of individualized and evidence-based management in optimizing outcomes and reducing morbidity in pancreatic necrosis (32). The comprehensive review, commissioned and approved by the AGA Institute Clinical Practice Updates Committee and the AGA Governing Board, was based on 15 best practice recommendations developed by experts in the field. These recommendations integrate insights from key studies and the extensive clinical experience of authors, including leading endoscopists and hepatopancreatobiliary surgeons, to provide guidance for effective management of this challenging condition.
Leading journals that cover a broad spectrum of topics, such as surgery and gastroenterology, have contributed significantly to the research on pancreatic necrosis. Additionally, most of the journals cited in the primary sources were highly influential, falling within the top quartiles (Q1 and Q2). The choice of high-impact, peer-reviewed journals is essential for ensuring the reliability of scientific findings, thus enhancing the quality of the evidence (35). This is particularly crucial, as policymakers and healthcare providers often base their decisions on robust, high-quality evidence (36). Authors consider several factors when choosing a journal for submission, including its impact factor, JCR ranking, open access options, indexing in major databases, and the associated publication fees (37).
In our study, China emerged as the most productive country in the field of pancreatic necrosis research, which aligns with the findings of other bibliometric analyses (29). Furthermore, among the four identified clusters of collaboration networks, the strongest and most prominent was the cluster formed predominantly by Chinese authors. This prominence may be attributed to the stable incidence rate and the high mortality associated with pancreatic necrosis in China, which likely motivated a focused national response to tackle this pressing healthcare issue (2, 14, 15). The strong collaborative efforts within this cluster highlight significant investments in research infrastructure, funding, and the prioritization of healthcare-related studies in the country (38, 39). Another contributing factor is the involvement of the Chinese Acute Pancreatitis Clinical Trials Group (CAPCTG) and the Chinese Critical Care Nutrition Trials Group (CCCNTG) in international randomized controlled trials. This marks a significant step toward integrating into the global research community and enhancing international collaboration in the field (40). Furthermore, China’s leadership in pancreatic necrosis research can be attributed to its strong focus on fostering innovation and creating an enabling environment for scientific advancement. The government prioritizes increased investments in educational funds to develop innovative talent and support the growth of research organizations. Additionally, legislative reforms have been introduced to strengthen intellectual property protection and combat rights violations, ensuring the rights and interests of researchers and stakeholders are safeguarded (41).
Among all universities, Netherlands institutions have proven to be the most prominent, with the University of Amsterdam standing out as a leader. One of the studies conducted by their research group focuses on clinical symptoms and treatment approaches, specifically Indication and timing for intervention, and is published in the high-impact journal The Lancet (42). Additionally, a multicenter randomized superiority trial was carried out involving patients with infected necrotizing pancreatitis. This trial compared the effects of immediate drainage within 24 h and delayed drainage after the formation of walled-off necrosis. The findings revealed that delayed drainage offered advantages in terms of reduced complication rates and fewer invasive interventions (43). Furthermore, in collaboration with experts specializing in minimally invasive surgery from America, Europe, and Oceania, they played a crucial role in the development of the guidelines for robotic pancreatic surgery (44). Notably, researchers from this university form the largest collaboration cluster (red cluster) dedicated to addressing issues related to pancreatic necrosis and are part of the Dutch Pancreatitis Study Group.
Furthermore, а key factor in the success of the Netherlands in the field of pancreatic necrosis research is the strong national collaboration between hospitals and universities, spanning a wide range of disciplines including surgery, gastroenterology, epidemiology, biostatistics, and radiology. This collaborative framework has facilitated the country’s leadership in citation counts within this area. For instance, in the study by Olaf Bakker et al., five prominent Netherlands institutions played a pivotal role in comparing the efficacy of endoscopic and surgical necrosectomy in patients with infected necrotizing pancreatitis (25). This collaborative effort underscores the importance of national partnerships between leading healthcare institutions and academic centers in achieving exceptional clinical outcomes. Moreover, it highlights the significant impact of such interdisciplinary cooperation in advancing medical research and treatment strategies for complex conditions like pancreatic necrosis.
In the conducted analysis, the most frequent key terms were related to acute pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis, necrosectomy, and mortality. These terms highlight significant areas of research focused on the pathogenesis, treatment, and outcomes of pancreatic diseases. Although significant progress has been made in the diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis continues to pose a major challenge due to its association with a high mortality rate (9) and requires further investigation into timely diagnosis, optimization of treatment (32), and the exploration of novel interventions such as surgical and endoscopic necrosectomy (31). The high mortality rate from infected pancreatic necrosis continues to be a pressing concern, emphasizing the need for alternative treatment methods and the development of more accurate predictive models to improve clinical outcomes.
5 Conclusion
In this bibliometric analysis, we aimed to systematically review and evaluate the global literature on the topic of mortality due to pancreatic necrosis. The analysis of the publications enabled us to identify key research trends and directions in the study of this condition. Despite advancements in medical science, the mortality rate associated with pancreatic necrosis remains high. This highlights the continued challenge in effectively addressing complications of acute pancreatitis. Researchers worldwide are actively exploring alternative therapeutic approaches to mitigate these complications and improve patient outcomes. Thus, while progress has been made, there is an ongoing need for innovative treatment strategies to further reduce the morbidity and mortality linked to this severe condition.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
GG: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. MJ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources. UK: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Investigation. KT: Data curation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. BK: Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by a grant from West Kazakhstan Marat Ospanov Medical University (оrder dated May 29, 2024, grant No: 13/2).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Lee, PJ, and Papachristou, GI. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 16:479–96. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0158-2
2. Iannuzzi, JP, King, JA, Leong, JH, Quan, J, Windsor, JW, Tanyingoh, D, et al. Global incidence of acute pancreatitis is increasing over time: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. (2022) 162:122–34. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.043
3. Zilio, MB, Eyff, TF, Azeredo-Da-Silva, ALF, Bersch, VP, and Osvaldt, AB. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the aetiology of acute pancreatitis. HPB. (2019) 21:259–67. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2018.08.003
4. Kokosis, G, Perez, A, and Pappas, TN. Surgical management of necrotizing pancreatitis: an overview. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:16106–12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16106
5. Lankisch, PG, Apte, M, and Banks, PA. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. (2015) 386:85–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60649-8
6. Bostancı, Ö, Battal, M, Yazıcı, P, Demir, U, and Alkım, C. Management of iatrogenic injuries due to endoscopic sphincterotomy: surgical or conservative approaches. Turk J Surg. (2018) 34:24–7. doi: 10.5152/turkjsurg.2017.3820
7. Garg, PK, and Singh, VP. Organ failure due to systemic injury in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:2008–23. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.12.041
8. Sarri, G, Guo, Y, Iheanacho, I, and Puelles, J. Moderately severe and severe acute pancreatitis: a systematic review of the outcomes in the USA and European Union-5. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. (2019) 6:e000248. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2018-000248
9. Gliem, N, Ammer-Herrmenau, C, Ellenrieder, V, and Neesse, A. Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis: an update. Digestion. (2021) 102:503–7. doi: 10.1159/000506830
10. Rashid, MU, Hussain, I, Jehanzeb, S, Ullah, W, Ali, S, Jain, AG, et al. Pancreatic necrosis: complications and changing trend of treatment. World J Gastrointest Surg. (2019) 11:198–217. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i4.198
11. Wolbrink, DRJ, Kolwijck, E, Ten Oever, J, Horvath, KD, Bouwense, SAW, and Schouten, JA. Management of infected pancreatic necrosis in the intensive care unit: a narrative review. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2020) 26:18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.017
12. Bugiantella, W, Rondelli, F, Boni, M, Stella, P, Polistena, A, Sanguinetti, A, et al. Necrotizing pancreatitis: a review of the interventions. Int J Surg. (2016) 28:S163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.12.038
13. Dellinger, EP, Tellado, JM, Soto, NE, Ashley, SW, Barie, PS, Dugernier, T, et al. Early antibiotic treatment for severe acute necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Surg. (2007) 245:674–83. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000250414.09255.84
14. Xiao, J, Quan, X, Liu, F, and Li, W. Comparison of different surgical methods for necrotizing pancreatitis: a Meta-analysis. Front Surg. (2021) 8:723605. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.723605
15. Yu, L, Xie, F, Luo, L, Lei, Y, Huang, X, Yang, X, et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of organ failure and death in necrotizing pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:19. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02651-4
16. Hamada, S, Masamune, A, Kikuta, K, Hirota, M, Tsuji, I, and Shimosegawa, T. Nationwide epidemiological survey of acute pancreatitis in Japan. Pancreas. (2014) 43:1244–8. doi: 10.1097/mpa.0000000000000200
17. Türkvatan, A, Erden, A, Türkoğlu, MA, Seçil, M, and Yüce, G. Imaging of acute pancreatitis and its complications. Part 2: complications of acute pancreatitis. Diagnostic and interventional. Imaging. (2015) 96:161–9. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2013.12.018
18. Zerem, E. Treatment of severe acute pancreatitis and its complications. World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:13879–92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13879
19. Freeman, M, Werner, J, Santvoort, H, Baron, T, Besselink, M, Windsor, J, et al. Interventions for necrotizing pancreatitis summary of a multidisciplinary consensus conference. Pancreas. (2012) 41:1176–94. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318269c660
20. Mehta, V, Kumar, R, Parkash, S, Singla, S, Singh, A, Chaudhary, J, et al. Role of percutaneous catheter drainage as primary treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2019) 30:184–7. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.17542
21. van Baal, MC, van Santvoort, HC, Bollen, TL, Bakker, OJ, Besselink, MG, and Gooszen, HG. Systematic review of percutaneous catheter drainage as primary treatment for necrotizing pancreatitis. Br J Surg. (2011) 98:18–27. doi: 10.1002/bjs.7304
22. Tan, J, Tan, H, Hu, B, Ke, C, Ding, X, Chen, F, et al. Short-term outcomes from a multicenter retrospective study in China comparing laparoscopic and open surgery for the treatment of infected pancreatic necrosis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. (2012) 22:27–33. doi: 10.1089/lap.2011.0248
23. Mathew, MJ, Parmar, AK, Sahu, D, and Reddy, PK. Laparoscopic necrosectomy in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: our experience. J Minim Access Surg. (2014) 10:126–31. doi: 10.4103/0972-9941.134875
24. Revoredo Rego, F, Reaño Paredes, G, De Vinatea De Árdenas, J, Kometter Barrios, F, Alfaro Ita, S, and Vereau, RJ. Infected necrotizing pancreatitis. Video-assisted retroperitoneal debridement. Medicina (B Aires). (2021) 81:115–8.
25. Bakker, OJ, van Santvoort, HC, van Brunschot, S, Geskus, RB, Besselink, MG, Bollen, TL, et al. Endoscopic transgastric vs surgical necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized trial. JAMA. (2012) 307:1053–61. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.276
26. Xia, C, Yin, H, Zhang, K, Wang, Z, Yang, X, and Huang, H. The global research status and trends of the application of endoscopic ultrasonography in pancreatic tumors over the last decades: a bibliometric study. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:980415. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980415
27. Wu, K, Liu, Y, Liu, L, Peng, Y, Pang, H, Sun, X, et al. Emerging trends and research foci in tumor microenvironment of pancreatic cancer: a bibliometric and visualized study. Front Oncol. (2022) 12:810774. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.810774
28. Cui, M, Hu, Y, You, L, Liu, Q, Lita, A, Wu, W, et al. A bibliometric study on pancreatic cystic disease research. J Pancreatol. (2019) 2:43–7. doi: 10.1097/JP9.0000000000000015
29. Luo, X, Zhong, R, Wang, X, Yang, G, Jiang, X, Peng, Y, et al. Twenty-year span of global acute pancreatitis trends: a bibliometric analysis. Pancreatology. (2022) 22:356–66. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2022.01.009
30. Sun, W, Huang, P, Song, H, and Feng, D. Bibliometric analysis of acute pancreatitis in web of science database based on CiteSpace software. Medicine (Baltimore). (2020) 99:e23208. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000023208
31. van Brunschot, S, van Grinsven, J, van Santvoort, HC, Bakker, OJ, Besselink, MG, Boermeester, MA, et al. Endoscopic or surgical step-up approach for infected necrotising pancreatitis: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. (2018) 391:51–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32404-2
32. Baron, TH, DiMaio, CJ, Wang, AY, and Morgan, KA. American Gastroenterological Association clinical practice update: management of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:67–75.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.064
33. Guo, Q, Li, A, Xia, Q, Liu, X, Tian, B, Mai, G, et al. The role of organ failure and infection in necrotizing pancreatitis: a prospective study. Ann Surg. (2014) 259:1201–7. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000264
34. Bang, JY, Arnoletti, JP, Holt, BA, Sutton, B, Hasan, MK, Navaneethan, U, et al. An endoscopic transluminal approach, compared with minimally invasive surgery, reduces complications and costs for patients with necrotizing pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:1027–40.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.031
35. Lunny, C, Neelakant, T, Chen, A, Shinger, G, Stevens, A, Tasnim, S, et al. Bibliometric study of 'overviews of systematic reviews' of health interventions: evaluation of prevalence, citation and journal impact factor. Res Synth Methods. (2022) 13:109–20. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1530
36. Tunis, SR, Stryer, DB, and Clancy, CM. Practical clinical trials: increasing the value of clinical research for decision making in clinical and health policy. JAMA. (2003) 290:1624–32. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.12.1624
37. Wenaas, L. Choices of immediate open access and the relationship to journal ranking and publish-and-read deals. Front Res Metr Anal. (2022) 7:943932. doi: 10.3389/frma.2022.943932
38. Mao, W, Li, K, Zhou, J, Chen, M, Ye, B, Li, G, et al. Prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis in acute necrotizing pancreatitis by the modified pancreatitis activity scoring system. United European Gastroenterol J. (2023) 11:69–78. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12353
39. Ke, L, Zhou, J, Mao, W, Chen, T, Zhu, Y, Pan, X, et al. Immune enhancement in patients with predicted severe acute necrotising pancreatitis: a multicentre double-blind randomised controlled trial. Intensive Care Med. (2022) 48:899–909. doi: 10.1007/s00134-022-06745-7
40. Chinese Acute Pancreatitis Clinical Trials Group and the Chinese Critical Care Nutrition Trials Group. Bid farewell to the old year and usher in the new. (2024). Available at: https://capctg.medbit.cn/en/2024/02/08/bid-farewell-to-the-old-year-and-usher-in-the-new/.
41. Liu, L, Zhang, Y, Zhang, J, and Zhang, S. Coupling coordination degree of government support, financial support and innovation and its impact on economic development. IEEE Access. (2020) 8:104039–51. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2999501
42. Boxhoorn, L, Voermans, RP, Bouwense, SA, Bruno, MJ, Verdonk, RC, Boermeester, MA, et al. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet. (2020) 396:726–34. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31310-6
43. Boxhoorn, L, van Dijk, SM, van Grinsven, J, Verdonk, RC, Boermeester, MA, Bollen, TL, et al. Immediate versus postponed intervention for infected necrotizing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 385:1372–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2100826
44. Liu, R, Abu Hilal, M, Besselink, MG, Hackert, T, Palanivelu, C, Zhao, Y, et al. International consensus guidelines on robotic pancreatic surgery in 2023. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2024) 13:89–104. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-132
45. Trikudanathan, G, Tawfik, P, Amateau, SK, Munigala, S, Arain, M, Attam, R, et al. Early (<4 Weeks) Versus Standard (≥4 Weeks) Endoscopically Centered Step-Up Interventions for Necrotizing Pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. (2018) 113:1550–8. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0232-3
Keywords: acute pancreatitis, necrotizing pancreatitis, pancreatic necrosis, mortality, bibliometric analysis
Citation: Gainollina GG, Jakanov MK, Zhakiev BS, Karsakbayev UG, Taishibayev KR and Kurmanbayev BA (2025) Global research trends in necrotizing pancreatitis: a bibliometric analysis from 2013 to 2024. Front. Med. 12:1515418. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1515418
Edited by:
Feng Shi, ShanghaiTech University, ChinaReviewed by:
Preeti Sahay, University of Alabama at Birmingham, United StatesJing Li, Second Military Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Gainollina, Jakanov, Zhakiev, Karsakbayev, Taishibayev and Kurmanbayev. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gulnur G. Gainollina, Z3VsbnVyLjExOTJAbWFpbC5ydQ==
 Gulnur G. Gainollina
Gulnur G. Gainollina Murat K. Jakanov1
Murat K. Jakanov1