
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Med. , 20 February 2025
Sec. Gastroenterology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1509947
Background: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, a prevalent chronic liver condition, can cause severe complications like hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. In recent years, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP - 1RA) have shown unique therapeutic advantages and may become a preferred treatment for it. This meta-analysis aims to systematically examine GLP-1RA associated adverse events, providing a basis for guiding patient clinical management.
Methods: We conducted a search for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the therapeutic effects of GLP-1RA in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease across four databases: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library. The search period extended from the inception of each database until December 2023. Information pertaining to various adverse events was collected as outcome measures. Statistical analysis of the results and assessment of bias risk were conducted utilizing Review Manager (version 5.4.1) software.
Results: An analysis of 10 studies encompassing 960 participants revealed a significantly higher overall incidence of adverse events in the GLP-1RA group compared to the control group (OR: 2.40 [1.10, 5.26], P = 0.03). Subgroup analysis based on treatment duration demonstrated a higher rate of adverse events in the GLP-1RA group during follow-ups of less than 30 weeks (P = 0.0005, OR: 3.58 [1.75, 7.32]), but no statistical difference was observed between the two groups in follow-ups exceeding 30 weeks. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in adverse events leading to discontinuation (P = 0.29, OR: 1.47 [0.72, 2.98]). However, a notable difference was observed in gastrointestinal adverse events (P < 0.00001, OR: 4.83 [3.36, 6.95]).
Conclusion: GLP-1RA exhibits an overall higher incidence of adverse events in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, particularly in the gastrointestinal domain. Short-term use of GLP-1RA may be associated with a greater occurrence of adverse events, underscoring the importance of educating patients on preventive measures and establishing tolerance. However, there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in severe adverse events and adverse events leading to discontinuation, confirming the safety profile of GLP-1RA application.
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a chronic liver disease, which is primarily characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver resulting from underlying metabolic dysfunctions. It represents a spectrum of liver diseases that are strongly associated with metabolic risk factors, such as overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. This metabolic dysfunction leads to a series of liver alterations, ranging from simple hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) to more severe forms such as MASH (Metabolic Associated Steatohepatitis), and may progress to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma over time (1–3). As the most common cause of steatotic liver disease, MASLD is witnessing a rapid global surge, affecting up to one-third of the world’s adult population, and posing a significant challenge to global public health (4, 5).
GLP-1RA, an exemplary drug in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, has garnered widespread attention in recent years for its potential application in the management of MASLD (6, 7). The interest in GLP-1RA is partly due to its established efficacy in improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss in patients with type 2 diabetes, which are also common features of MASLD. By mimicking the biological effects of glucagon-like peptide-1, GLP-1RA offers unique advantages in regulating blood glucose levels, improving insulin resistance, and mitigating hepatic fat accumulation, positioning it as an effective therapeutic approach for MASLD (8–11). However, despite demonstrating significant therapeutic efficacy in several clinical trials, the relatively high incidence of associated adverse reactions has constrained its widespread clinical utilization and may impact patients’ quality of life (12–14). These adverse reactions, which can include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, have led to concerns about patient tolerability and adherence to treatment. Therefore, gaining a thorough understanding of the safety profile of GLP-1RA in the treatment of MASLD, particularly regarding the nature and occurrence of adverse reactions, is crucial for a comprehensive assessment of its risk-benefit profile.
This meta-analysis is designed to systematically review the existing evidence on the safety of GLP-1RA in MASLD patients, with a focus on assessing the characteristics of adverse events. We aim to contribute to the optimization of treatment decisions and the prevention of adverse events as much as possible, thereby facilitating more effective and safer management of MASLD patients.
The research design, data collection, article composition, and result analysis in this study were conducted in accordance with the guidelines outlined in the PRISMA (2020 version) statement (15). As the data used in this study were derived from publicly available published articles and did not involve patients’ private information, ethical committee review and approval were deemed unnecessary.
The preliminary data collection for this meta-analysis was independently conducted by two researchers. A comprehensive search was performed on four independent databases—PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase. The search period extended from the inception of each database to March 2024. Articles included in the search were limited to those published in English. The search strategy involved two categories of keywords: Glucagon Like Peptide 1, GLP-1, GLP 1, Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, NAFLD, Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, MASLD, Steatotic Liver Disease, SLD, Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, MASH, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Fatty Liver Nonalcoholic, Fatty Livers Nonalcoholic, Liver Nonalcoholic Fatty, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver, Nonalcoholic Fatty Livers, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitides, Steatohepatitis Nonalcoholic. The two sets of keywords were combined using the ‘AND’ operator in accordance with Boolean logic principles to formulate the final data retrieval strategy.
Study Type: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs); Study Population: Patients diagnosed with MASLD. MASLD is defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis in conjunction with at least one cardiometabolic risk factor (CMRF), in the absence of any other discernible cause (16). CMRF encompass the following:
① BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 OR waist circumference > 94 cm (male) 80 cm(female) OR ethnicity adjusted equivalent
② Fasting serum glucose ≥ 5.6 mmol/L[100 mg/dL] OR 2-h post-load glucose levels ≥7.8 mmol/L[≥140 mg/dL] OR HbA1c ≥ 5.7%[39 mmol/L] OR type 2 diabetes OR treatment for type 2 diabetes
③ Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg OR specific antihypertensive drug treatment
④ Plasma triglycerides ≥ 1.70 mmol/L[150 mg/dL] OR lipid lowering treatment
⑤ Plasma HDL-cholesterol ≤1.0 mmol/L[40 mg/dL] (male) and ≤ 1.3 mmol/L [50 mg/dL] (female) OR lipid lowering treatment.
Intervention: Experimental group received GLP-1RA, while the control group received other antidiabetic medications or a placebo; Outcome Measures: The study and statistical endpoints encompassed the occurrence of various types of adverse events, including the overall incidence of adverse events, the incidence of severe adverse events, the incidence of adverse events leading to discontinuation, and the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events.
Studies published in the form of conference abstracts, reviews, animal experiments, case reports; duplicate publications; studies lacking clear conclusions; articles where full-text information cannot be obtained; studies involving participants using GLP-1RA oral formulations; and studies of poor quality, which typically include: unreasonable study design, such as non-randomized controlled trials (RCTs), lack of control groups; incomplete or inaccurate data, with missing or erroneous key outcome indicators; statistical method errors that cannot be corrected through re-analysis; with a high risk of bias.
The inclusion and data extraction for the study were independently performed by two researchers (MH and XY). Through initial screening (searching, reading titles and abstracts) and in-depth analysis (full-text review and internal discussions), the following data were extracted from the 10 eligible studies: the first author’s name, publication year, main study country, total number of patients involved in the trials, gender ratio, treatment regimen for the control group, and the follow-up period for the study. Any discrepancies or queries during data synthesis were resolved through internal team discussions, with final decisions made by a senior physician (YZ).
This meta-analysis employed the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool to evaluate the risk of bias in the included studies. A risk of bias analysis was conducted for each study based on the various criteria outlined in the research guidelines (17).
The summary and analysis of results were conducted using Review Manager software (version 5.4.1). Regarding the choice of the study model, if the final statistical result’s P-value > 0.1 and I2 < 50%, indicating internal consistency in the pooled studies, a fixed-effects model was chosen for the analysis. Conversely, a random-effects model was employed for analysis if P-value ≤ 0.1 or I2 ≥ 50%, suggesting significant heterogeneity among the studies. As the outcome measure was the incidence of adverse events, the analysis involved calculating the Odds Ratio (OR) for binary variables from individual trials.
In cases of substantial heterogeneity, a stepwise exclusion method and sensitivity analysis were performed to identify the source of clinical heterogeneity. If significant clinical heterogeneity was observed, subgroup analysis and funnel plots were further employed to assess publication bias.
A total of 3,177 articles were initially retrieved from the databases. Among them, 982 articles were identified as duplicates. After reviewing titles, abstracts, and full texts, 2,185 articles were excluded. Finally, 10 relevant studies were included in the analysis (18–27).
A total of 10 clinical studies were included, with a combined sample size of 960 participants. Among them, 544 participants were in the intervention group, and 416 participants were in the control group. All 10 studies reported on all adverse events associated with GLP-1RA, 8 studies reported adverse events leading to treatment termination, and 6 studies reported severe adverse events related to GLP-1RA. Detailed baseline characteristics information can be found in Table 1. Overall, the included articles demonstrated a low risk of bias, indicating a high quality of evidence. Specific results are presented in Figure 1.
The meta-analysis of the 10 included studies revealed that patients undergoing GLP-1RA treatment had an overall higher incidence of adverse events compared to the control group. The results showed a statistically significant difference with an odds ratio (OR) of 2.40 [1.10, 5.26], and a P-value of 0.03 (Figure 2).
Subgroup analysis was conducted on the statistical results of all adverse events, stratifying the analysis based on whether the treatment and follow-up duration exceeded 30 weeks. The results indicated that when the treatment follow-up period was less than 30 weeks, GLP-1RA treatment was associated with a higher incidence of adverse events compared to the control group, and this difference was statistically significant (P = 0.0005, OR: 3.58 [1.75, 7.32]). However, when the treatment follow-up period exceeded 30 weeks, the incidence of adverse events with GLP-1RA did not show statistical significance compared to the control group (P = 0.35, OR: 1.74 [0.55, 5.52]) (Figure 3).
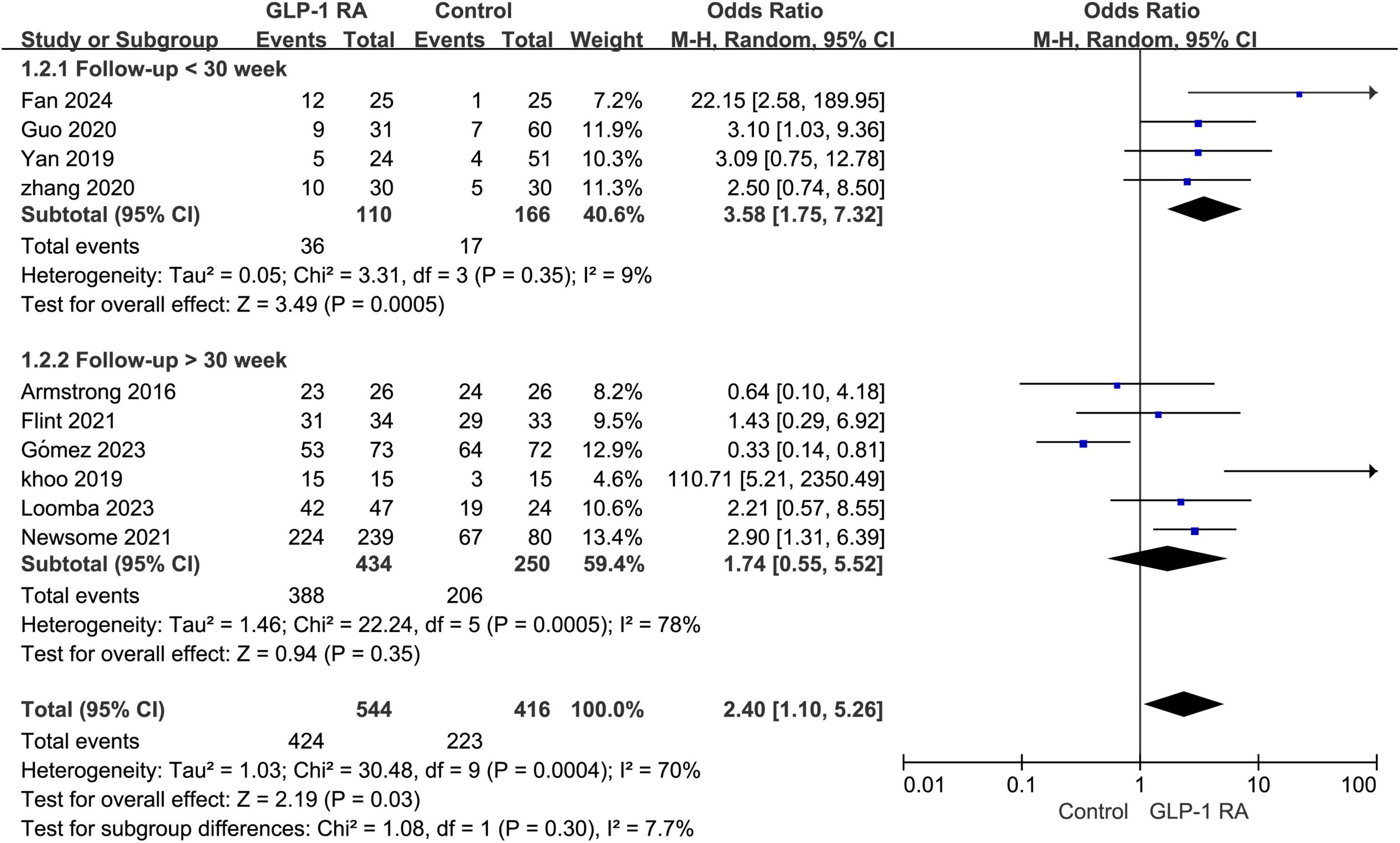
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis of GLP-1RA compared to control group with a treatment period greater than or less than 30 weeks.
Subgroup analysis was conducted on the statistical results of all adverse events, stratifying the analysis based on whether the adverse events were categorized as severe. The results indicated that there was no statistically significant difference in the severity of adverse events between the two groups (P = 0.06, combined OR: 1.33 [0.99, 1.78]) (Figure 4).
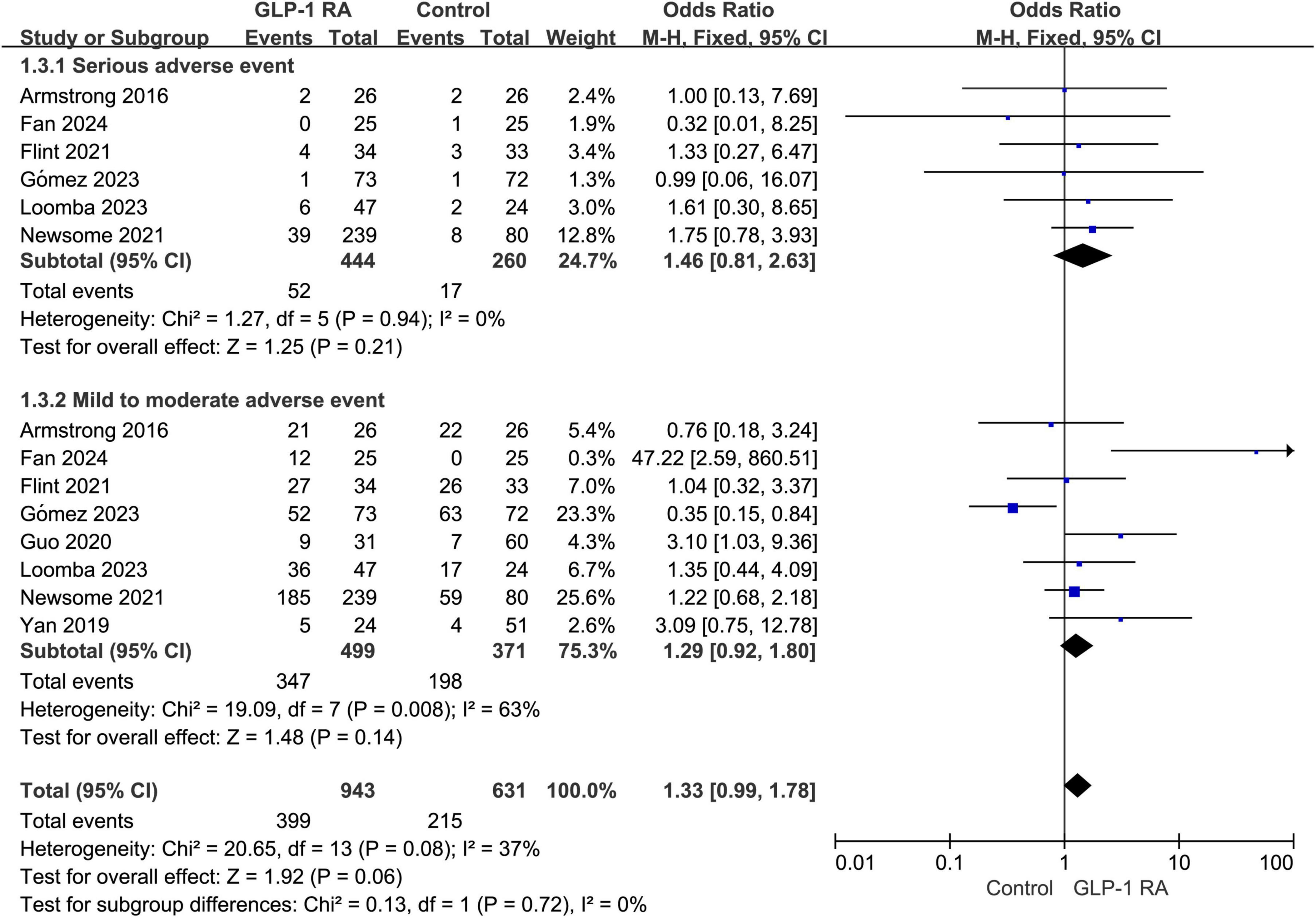
Figure 4. Subgroup analysis of GLP-1RA compared to control group with different levels of adverse events.
A total of 8 articles addressed discontinuation of treatment due to adverse events. According to the forest plot analysis, the P-value was 0.29, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.47 [0.72, 2.98]. The results indicate that there is no statistically significant difference in the rate of adverse events leading to discontinuation between the GLP-1RA group and the control group (Figure 5).
A total of 8 studies provided specific data on gastrointestinal adverse events. Upon summarizing the data for GLP-1RA and the control group, a statistically significant difference in the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events between the two groups was observed (P < 0.00001, OR: 4.83 [3.36, 6.95]). The I2 value was 40%, indicating internal consistency among the studies. The results were presented using a fixed-effects model (Figure 6).
In the treatment of MASLD with GLP-1RA, a spectrum of gastrointestinal adverse events was observed, with an overall mean incidence rate of 58.9% for these events. The specific incidence rates are detailed in Figure 7. Nausea was the most frequently reported adverse event, affecting 32.54% of patients. Diarrhea and vomiting were also common, with incidence rates of 19.99% and 16.18%, respectively. Constipation and decreased appetite were noted in 12.5% and 10.66% of patients, respectively. Abdominal pain and dyspepsia occurred in 8.27% and 5.7% of patients, respectively. Less common events, including flatulence (4.6%), bloating (3.68%), eructation (2.02%), and reflux (0.92%), were also observed.
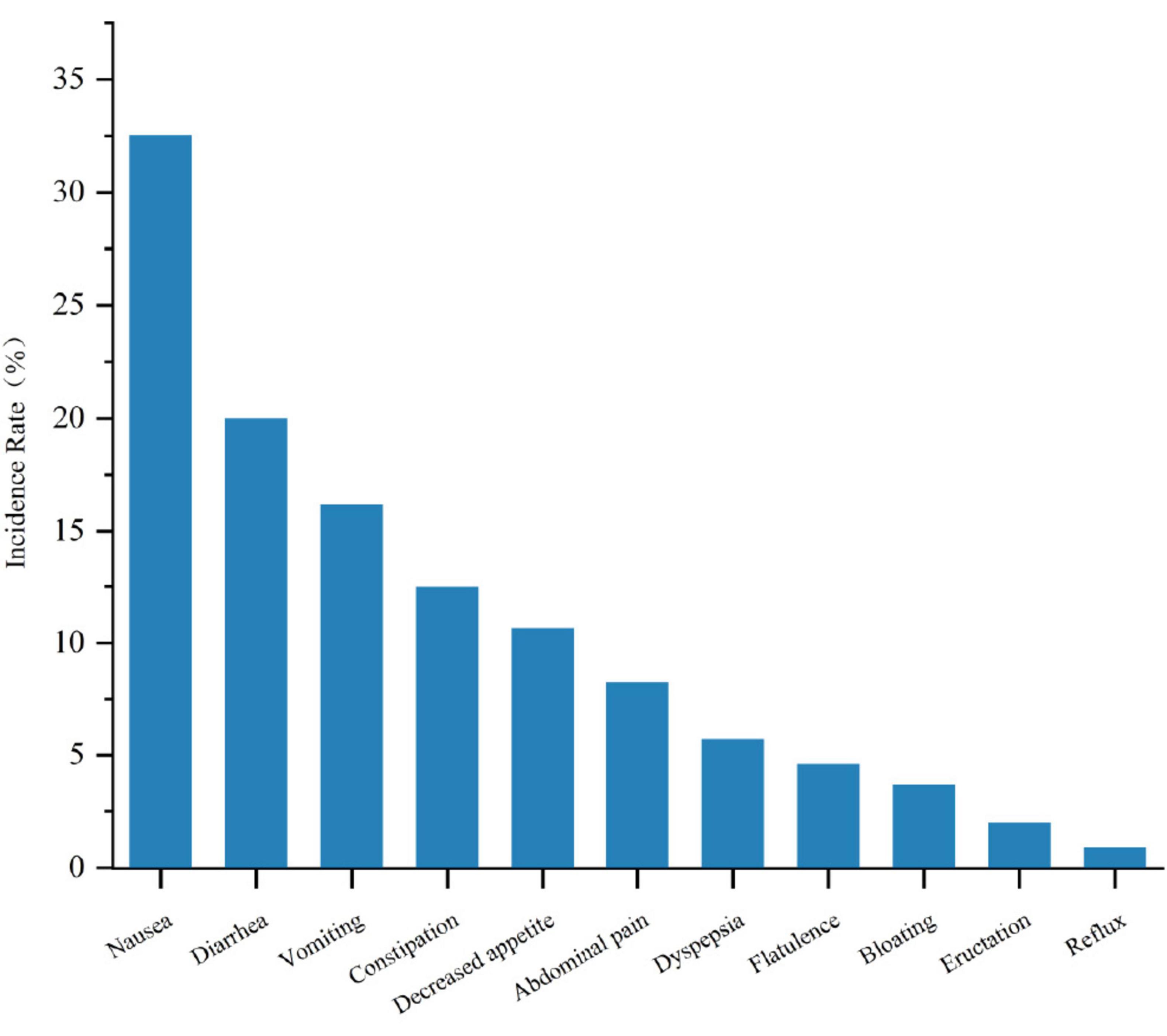
Figure 7. Comparison of the incidence rates of different gastrointestinal adverse reactions in GLP-1RA therapy for MASLD.
After consolidating data from the 10 included articles, observation of the funnel plot revealed a generally symmetrical distribution of points on both sides, indicating the absence of publication bias (Figure 8).
This study systematically reviewed the adverse events associated with GLP-1RA therapy for MASLD. Despite demonstrating significant advantages in treatment efficacy, GLP-1RA revealed a higher overall incidence of adverse events, thereby limiting its extensive clinical application. These findings are consistent with the results observed in most past clinical trials, highlighting the inherent contradiction and complexity in the risk-benefit profile of GLP-1RA therapy for MASLD (28–31).
The subgroup results of the meta-analysis revealed that, during the treatment follow-up period of less than 30 weeks, the incidence of adverse events in the GLP-1RA group was significantly higher than that in the control group. This suggests that short-term treatment with GLP-1RA may lead to a higher occurrence of adverse events, particularly in patients who are newly exposed to such medications and have not yet developed tolerance. However, when the treatment follow-up period exceeded 30 weeks, there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between the GLP-1RA group and the control group. This implies that the long-term use of GLP-1RA is safer, and in clinical practice, it is advisable to employ extended dosing regimens whenever possible.
Subgroup analysis of adverse events of varying severity did not reveal any statistically significant differences between the GLP-1RA group and the control group, indicating that the heterogeneity between the two groups does not stem from the severity of adverse events. However, given the proximity of the results’ p-values to the significance threshold and the diverse nature of adverse events, we posit that further research with a larger sample size and more comprehensive data is needed to verify whether there is an association between the severity of adverse events and the two groups.
Despite clinical trials reporting instances of discontinuation of GLP-1RA treatment due to adverse events (32–35), the results of the meta-analysis did not reveal any statistically significant differences between the GLP-1RA group and the control group in this regard. This suggests that, although GLP-1RA may lead to certain adverse events, the occurrence of patient-initiated discontinuation in response to these events is not significant. Considering the absence of statistically significant differences in severe adverse events between the two groups, we infer that the safety profile of GLP-1RA remains relatively high. However, given the overall higher incidence of adverse events associated with GLP-1RA, we conducted a subgroup analysis focusing on the most commonly reported gastrointestinal adverse events in previous GLP-1RA studies (36, 37). The analysis revealed a significant statistical difference between the GLP-1RA treatment group and the control group, indicating that gastrointestinal adverse events are indeed a relatively prominent concern in GLP-1RA therapy. The low internal heterogeneity observed after grouping suggests that gastrointestinal adverse events may be a major contributing factor to the overall adverse event profile.
In our analysis of the included studies, we aggregated the adverse events associated with GLP-1RA treatment. Subgroup analysis of the GLP - 1RA group revealed a relatively high overall mean incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events, which was 58.9%. The incidence of discontinuation due to adverse events was 4.41%. Nausea, as the most prevalent adverse event, affected up to 32.54% of the patients. This finding highlights the necessity of in-depth investigation into the influencing factors of adverse events. Due to the limited number of included studies and the lack of comprehensive raw data, it was difficult to perform a standardized correlation analysis. However, after attempting a preliminary analysis of the combined data, we identified potential associations. After considering the sample size weights, we performed a correlation analysis on patient age, gender, BMI, glycated hemoglobin levels, drug dosage, and the incidence of various adverse events. The results showed a significant positive correlation between the incidence of gastrointestinal events and the discontinuation rate due to adverse events (P < 0.01). Additionally, a higher total incidence of adverse events was associated with a higher incidence of severe adverse events (P < 0.05). Notably, a higher proportion of female patients was also related to an increased incidence of gastrointestinal events and discontinuation due to adverse events (P < 0.05). These correlation analysis results indicate that early intervention for adverse events and high-risk populations may bring clinical benefits. For example, early intervention for patients at high risk of developing gastrointestinal adverse events, or implementing more preventive strategies for female patients, might improve patients’ treatment adherence.
Given the significant impact of gastrointestinal adverse events on patients, several strategies can be implemented to effectively manage these issues. First, gradually increasing the dose of GLP - 1RA can help patients better tolerate the treatment and reduce the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events. Second, educating patients about the potential side effects of GLP - 1RA, and informing them that adverse reactions usually subside as their body adapts, while providing them with strategies to manage these symptoms (such as dietary adjustments, adjusting eating frequency, and appropriate exercise) has been shown to alleviate gastrointestinal discomfort (38–40). Furthermore, providing supportive care measures, including antiemetics, acid suppressants, or antidiarrheals, can help control symptoms and enhance patient comfort. Additionally, regular monitoring of patients during treatment, especially during the initial treatment period, is crucial for early identification and resolution of adverse events. Early intervention can prevent symptom exacerbation and reduce the likelihood of treatment discontinuation.
For patients with persistent symptoms, temporary medication breaks or “drug holidays” may be considered to facilitate symptom resolution. In cases where adverse events are intolerable, alternative therapeutic strategies must be promptly explored. This may involve adjustments to the treatment regimen, such as switching to a different GLP - 1RA or combining it with other medications with a lower risk of gastrointestinal side effects. Numerous studies have demonstrated differences in the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events among various GLP - 1RAs (41–43). For example, tirzepatide may cause fewer such events compared to semaglutide (44), selecting a GLP - 1RA with better gastrointestinal safety for high - risk patients might be a beneficial strategy.
The strengths of this study lie in the inclusion of a substantial number of high-quality randomized controlled trials, encompassing overall adverse events, follow-up duration, severity, discontinuation rates, and specific gastrointestinal adverse events. This approach has enhanced the credibility and representativeness of the meta-analysis to a certain extent. Additionally, the utilization of various subgroup analyses, examining factors that may influence adverse events, contributes to a more comprehensive evaluation for clinical decision-making.
However, the limitations of this study should be acknowledged. We restricted our search to articles published in English, potentially introducing language bias. Moreover, despite incorporating data from 10 clinical studies, the overall sample size was relatively small, which may impact the stability and generalizability of the results. Future research efforts should consider including larger sample sizes to further validate the study findings. Additionally, within the limited scope of available studies, the inclusion of diverse control interventions has hindered a more detailed exploration of varying doses of the same treatment regimen. This limitation underscores the need for future trials to provide more robust evidence in this regard.
In summary, GLP-1RA demonstrates a relatively high level of safety in the treatment of MASLD. There is no statistically significant difference compared to the control group in terms of severe adverse events and adverse events leading to discontinuation. Further analysis reveals a higher overall incidence of adverse events associated with GLP-1RA, primarily concentrated in the early stages of treatment and related to the gastrointestinal system. Therefore, when using GLP-1RA in the treatment of MASLD patients, overall safety is favorable, but monitoring patients’ tolerance to early treatment and their gastrointestinal adverse reactions is crucial.
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
XH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. BH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YZ: Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Quanzhou Science and Technology Project (2022NS066).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Byrne C, Targher G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J Hepatol. (2015) 62:S47–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.12.012
2. Targher G, Byrne C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging driving force in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2017) 13:297–310. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.16
3. Adams L, Anstee Q, Tilg H, Targher G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut. (2017) 66:1138–53. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313884
4. Zhou J, Zhou F, Wang W, Zhang X, Ji Y, Zhang P, et al. Epidemiological features of NAFLD from 1999 to 2018 in China. Hepatology. (2020) 71:1851–64. doi: 10.1002/hep.31150
5. Targher G, Byrne C, Tilg H. NAFLD and increased risk of cardiovascular disease: Clinical associations, pathophysiological mechanisms and pharmacological implications. Gut. (2020) 69:1691–705. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320622
6. Nevola R, Epifani R, Imbriani S, Tortorella G, Aprea C, Galiero R, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current evidence and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1703. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021703
7. Sumida Y, Yoneda M. Current and future pharmacological therapies for NAFLD/NASH. J Gastroenterol. (2018) 53:362–76. doi: 10.1007/s00535-017-1415-1
8. Rong L, Zou J, Ran W, Qi X, Chen Y, Cui H, et al. Advancements in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2022) 13:1087260. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1087260
9. Kim E, Park J, Kim J, Oh J, Oh I, Choi D, et al. A GLP-1/GLP-2 receptor dual agonist to treat NASH: Targeting the gut-liver axis and microbiome. Hepatology. (2022) 75:1523–38. doi: 10.1002/hep.32235
10. Li Q, Gao H, Guo Y, Wang B, Hua R, Gao L, et al. GLP-1 and underlying beneficial actions in Alzheimer’s disease, hypertension, and NASH. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2021) 12:721198. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.721198
11. Mahapatra M, Karuppasamy M, Sahoo B. Therapeutic potential of semaglutide, a newer GLP-1 receptor agonist, in abating obesity, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and neurodegenerative diseases: A narrative review. Pharm Res. (2022) 39:1233–48. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03302-1
12. Sodhi M, Rezaeianzadeh R, Kezouh A, Etminan M. Risk of gastrointestinal adverse events associated with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for weight loss. JAMA. (2023) 330:1795–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.19574
13. Karagiannis T, Avgerinos I, Liakos A, Del Prato S, Matthews D, Tsapas A, et al. Management of type 2 diabetes with the dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia. (2022) 65:1251–61. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05715-4
14. Andrikou E, Tsioufis C, Andrikou I, Leontsinis I, Tousoulis D, Papanas N. GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiovascular outcome trials: An update. Hellenic J Cardiol. (2019) 60:347–51. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2018.11.008
15. Hutton B, Salanti G, Caldwell D, Chaimani A, Schmid C, Cameron C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
16. Rinella M, Lazarus J, Ratziu V, Francque S, Sanyal A, Kanwal F, et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:1542–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.06.003
17. Higgins J, Altman D, Gøtzsche P, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman A, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
18. Loomba R, Abdelmalek M, Armstrong M, Jara M, Kjær M, Krarup N, et al. Semaglutide 2⋅4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2023) 8:511–22. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(23)00068-7
19. Newsome P, Buchholtz K, Cusi K, Linder M, Okanoue T, Ratziu V, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of subcutaneous semaglutide in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1113–24. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2028395
20. Romero-Gómez M, Lawitz E, Shankar R, Chaudhri E, Liu J, Lam R, et al. A phase IIa active-comparator-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of efinopegdutide in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. (2023) 79:888–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.05.013
21. Armstrong M, Gaunt P, Aithal G, Barton D, Hull D, Parker R, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet. (2016) 387:679–90. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00803-X
22. Flint A, Andersen G, Hockings P, Johansson L, Morsing A, Sundby Palle M, et al. Randomised clinical trial: Semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 54:1150–61. doi: 10.1111/apt.16608
23. Yan J, Yao B, Kuang H, Yang X, Huang Q, Hong T, et al. Liraglutide, Sitagliptin, and Insulin Glargine Added to Metformin: The Effect on Body Weight and Intrahepatic Lipid in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology. (2019) 69:2414–26. doi: 10.1002/hep.30320
24. Khoo J, Hsiang J, Taneja R, Koo S, Soon G, Kam C, et al. Randomized trial comparing effects of weight loss by liraglutide with lifestyle modification in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. (2019) 39:941–9. doi: 10.1111/liv.14065
25. Zhang L, Qu X, Sun Z, Zhang Y. Effect of liraglutide therapy on serum fetuin A in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2020) 44:674–80. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2020.01.007
26. Guo W, Tian W, Lin L, Xu X. Liraglutide or insulin glargine treatments improves hepatic fat in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in twenty-six weeks: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. (2020) 170:108487. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108487
27. Fan Y, Xia M, Yan H, Li X, Chang X. Efficacy of beinaglutide in the treatment of hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2024) 26:772–6. doi: 10.1111/dom.15359
28. Ussher J, Drucker D. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: Cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2023) 20:463–74. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00849-3
29. Marso S, Daniels G, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann J, Nauck M, et al. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2016) 375:311–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603827
30. Tamborlane W, Barrientos-Pérez M, Fainberg U, Frimer-Larsen H, Hafez M, Hale P, et al. Liraglutide in children and adolescents with Type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2019) 381:637–46. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903822
31. Consoli A, Formoso G. Potential side effects to GLP-1 agonists: Understanding their safety and tolerability. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2015) 14:207–18. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2015.987122
32. Rosenstock J, Wysham C, Frías J, Kaneko S, Lee C, Fernández Landó L, et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2021) 398:143–55. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01324-6
33. Moore P, Malone K, VanValkenburg D, Rando L, Williams B, Matejowsky H, et al. GLP-1 agonists for weight loss: Pharmacology and clinical implications. Adv Ther. (2023) 40:723–42. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02394-w
34. Ma H, Lin Y, Dai L, Lin C, Huang Y, Liu S. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists versus SGLT-2 inhibitors in overweight/obese patients with or without diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e061807. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-061807
35. Lincoff A, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun H, Deanfield J, Emerson S, Esbjerg S, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity without diabetes. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389:2221–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2307563
36. Palmer S, Tendal B, Mustafa R, Vandvik P, Li S, Hao Q, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. (2021) 372:m4573. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m4573
37. Marathe C, Rayner C, Jones K, Horowitz M. Effects of GLP-1 and incretin-based therapies on gastrointestinal motor function. Exp Diabetes Res. (2011) 2011:279530. doi: 10.1155/2011/279530
38. Lis D. Exit gluten-free and enter low FODMAPs: A novel dietary strategy to reduce gastrointestinal symptoms in athletes. Sports Med. (2019) 49:87–97. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-01034-0
39. Zhi S, Zhang L, Cheng W, Jin Y, Long Z, Gu W, et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and Hyperemesis gravidarum. Nutrients. (2024) 16:2618. doi: 10.3390/nu16162618
40. Grgic J, Pedisic Z, Saunders B, Artioli G, Schoenfeld B, McKenna M, et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Sodium bicarbonate and exercise performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. (2021) 18:61. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00458-w
41. Yao H, Zhang A, Li D, Wu Y, Wang C, Wan J, et al. Comparative effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists on glycaemic control, body weight, and lipid profile for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. (2024) 384:e076410. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-076410
42. Drucker D. Efficacy and safety of GLP-1 medicines for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetes Care. (2024) 47:1873–88. doi: 10.2337/dci24-0003
43. Zhang Z, Zhang Q, Tan Y, Wu Y, Wang C, Wan J, et al. GLP-1RAs caused gastrointestinal adverse reactions of drug withdrawal: A system review and network meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2023) 14:1149328. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1149328
Keywords: MASLD, GLP-1RA, adverse event, gastrointestinal reactions, meta-analysis
Citation: Huang X, Wu M, Huang B and Zhang Y (2025) Gastrointestinal adverse events associated with GLP-1 receptor agonists in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1509947. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1509947
Received: 18 November 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 20 February 2025.
Edited by:
Iain Brownlee, Northumbria University, United KingdomReviewed by:
Anna Cantalupo, Mount Sinai Hospital, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Huang, Wu, Huang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Zhang, emhheWlzbkAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.