
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Med. , 13 February 2025
Sec. Gastroenterology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1509269
This article is part of the Research Topic Cholesterol, inflammation and immunity View all 4 articles
Background: Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection is one of the major global health problems resulting in multiple system disorders. The serum uric acid to high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (UHR) is a novel index of inflammation and metabolism, but its association with the development of Hp infection is still unclear.
Materials and methods: This is a cross-sectional study involving 2,666 participants, using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted in the United States. The relationship between UHR and Hp infection was evaluated by multivariate logistic regression and sensitivity analysis to enhance the stability of the results.
Results: Among all individuals, 1,165 were Hp positive (43.7%) and 1,501 were Hp negative (56.3%). After adjustment, there was a positive correlation between UHR and Hp infection (OR = 1.15; 95% CI 1.02–1.30; P = 0.020). This association is relatively stable in the subgroup analysis (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: There is a positive correlation between the UHR and the development of Hp infection in our study. This non-invasive indicator can improve the ability to monitor Hp infection and may find alternative therapeutic intervention targets.
The Gram-negative microaerophilic bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori, Hp) colonizes the human gastric mucosa and forms a chronic infection closely associated with atrophic gastritis, peptic ulcer and gastric cancer and is considered to be one of the most prevalent chronic bacterial infections worldwide (1, 2), affecting nearly half of the world’s population and 35.6% of Americans. Although H. pylori infection has decreased in recent decades, it continues to be an important burden of global health given its close association to a range of other diseases (3). Helicobacter pylori is listed as the category I carcinogen by the World Health Organization, and is a major factor in the pathogenesis of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, and noncardiac gastric cancer. Over 75% of duodenal ulcer cases and 17% of gastric ulcer cases are related to infection. In addition, it has been associated with extra-gastrointestinal diseases, including iron deficiency anemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (4), cardiovascular disease (5), endocrine dysfunction (6), and Alzheimer’s disease (7). The health burden associated with H. pylori infection extends beyond its direct clinical manifestations, affecting patients’ quality of life and imposing considerable healthcare costs due to prolonged treatment and disease management.
Previous studies have shown that H. pylori infection is often accompanied by changes in some metabolic indicators and lipid profiles in the blood, for example, a study of black urban Congolese individuals indicate that H. pylori infection leads to a significant increase in SUA (8, 9), and another study of adults from Australia and New Zealand indicate that chronic Hp infection reduces the level of HDL in plasma (2, 10). Serum uric acid (SUA) is widely recognized as a biomarker for measuring abnormal renal metabolic function (10). When the concentration of serum uric acid (SUA) increases, it often indicates the occurrence of cell damage (11), and it is closely linked to various disease states such as gout (12), dyslipidemia and cardiovascular disease (13). In contrast, normal high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) plays an important role in cardiovascular health and overall protection, by promoting reverse transport of cholesterol, as well as having significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-thrombotic capacity (14). Notably, the SUA-to-HDL ratio (UHR) has emerged as a novel biomarker reflecting both inflammatory and metabolic states. Recent studies have demonstrated that UHR is superior to individual SUA or HDL levels in predicting a wide spectrum of diseases, including diabetic nephropathy (15), non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (16), hypertension, thyroid inflammation and other diseases (17). However, its relationship with H. pylori infection remains underexplored. This study aims to investigate the association between UHR and H. pylori infection, using a large, nationally representative dataset to provide insights into its potential role as a clinical biomarker in this context.
This study is a representative study based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database 1999-2000, which is a publicly available database.1 NHANES is a nationally representative survey conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics, designed to assess the health and nutritional status of community adults and children in Central African institutions in the United States through a complex, stratified, multi-stage probability sampling framework (18). All of the study participants signed a written, informed consent form. NHANES Is an open database, so the ethical approval was waived. Of the 4,881 participants included in this survey cycle, individuals were eligible to be included if they had complete data on H. pylori serology, lipid profiles, and demographic variables. Participants with missing data or a history of diabetes or hypertension were excluded and the final study cohort was 2666. The selection process of the participants is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Flow diagram of the sample selection from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999-2000. UHR, serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; Hp, Helicobacter pylori; PIR, poverty income ratio; BMI, body mass index; HEI, health eating index; DM, diabetes mellitus; CRP, C-reactive protein; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; SCR, serum creatinine; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; SUA, serum uric acid; HDL, high-density lipoprotein.
In accordance with the NHANES protocol, serum samples were collected via venipuncture, stored at –80°C, and tested for H. pylori immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Wampole Laboratories, Cranbury, NJ). Seropositivity was defined as an optical density (OD) value ≥ 1.1, while values < 0.9 were classified as seronegative. Ambiguous results (0.9–1.1) were excluded to avoid misleading statistical results.
Fasting blood samples were analyzed to measure SUA and HDL levels. SUA was quantified using the DxC800 automated chemical analyzer (Beckman Coulter) through uricase-based oxidation, while HDL was measured using enzymatic colorimetric methods. Specific descriptions of the NHANES database can be found on the website (see text footnote 1). The UHR was calculated as the ratio of SUA (mg/dL) to HDL (mg/dL) (19).
Covariates in this research included age, sex, race, marital status, education level, poverty-income ratio (PIR), BMI, alcohol consumption, smoking status, alcohol consumption, Healthy Eating Index (HEI), DM, hypertension and relative laboratory parameters, including C-reactive protein (CRP), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (SCR), total cholesterol (TC), and triglycerides (TG). Among them, ethnicity was classified as Mexican American, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, other Hispanic, or other race, while marital status was classified as individuals living with a partner, married, never married, or widowed, divorced or separated. And the education level is classified as lower than high school, high school or equivalent, or college or above. In addition, lifestyle and disease history, including smoking status (current, past, or never), alcohol consumption (current, past or never), HEI calculated by HEI-2015 criterion, DM (yes or no) and hypertension (yes or no) were further collected.
Continuous variables are represented by the median (range of quartiles) or the mean (standard deviation, SD). The UHR was divided into four groups called quintiles. We used the χ 2 test for categorical variables and the Student’s t test or Kruskal–Wallis test for continuous variables to assess the difference between each group. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) of the relationship between UHR and HP infection were determined using logistic regression models. Specifically, the unadjusted analysis model is Model 1. In addition, age, gender and race were briefly adjusted in Model 2. In model 3, we assessed age, gender, race, marital status, educational level, PIR, BMI, smoking status, drinking status, HEI score, DM, hypertension, CRP, BUN, SCR, TC and TG. Furthermore, we performed a subgroup analysis on age group, sex, BMI, DM and hypertension. All analyses were performed using Free Statistics software version 1.9 and the statistical package R.2 A two-tail test was performed, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Among all individual data, 1,165 were positive for Hp infection (43.7%), and 1,501 were negative (56.3%). Table 1 describes the weighted characteristics of the 2,666 subjects based on UHR quartiles. Substantial differences were observed between the UHR quartiles and baseline characteristics. Individuals in the higher quartiles were more likely to be male, smoke more, drink more, and have a higher incidence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus. At the same time, BMI, BUN, SUA, TG, SCR were higher, while HEI and HDL were lower. However, no significant differences were found in age, race, marital status, PIR, TC, or CRP.
Table 2 provides a multivariate regression analysis between the effects of Hp infection and UHR. In the unadjusted model, UHR was positively correlated with Hp infection (OR = 1.11; 95%CI: 1.03 ∼ 1.20; P = 0.006), after adjusting for variables, Model 2 (OR = 1.16; 95%CI: 1.05 ∼ 1.28; P = 0.002) and Model 3 (OR = 1.15; 95%CI: 1.02 ∼ 1.30; P = 0.020), the correlation between UHR and Hp infection was still positive. In addition, Hp infection rates increased by 3% (P = 0.819), 71% (P < 0.001), and 45% (P = 0.024) in the 2, 3, and 4 quantiles, respectively, compared with the lowest levels of UHR (Q1) in Model 3, and the trend test for Model 3 was P = 0.002.
Hierarchical analysis of additional variables. As shown in Figure 2, we performed a stratified analysis across several subgroups to assess the potential impact of the relationship between Hp infection and UHR. When stratified by age, sex, BMI, and hypertension, no significant interactions were found in any subgroup. Considering multiple tests, a P-value of DM interaction less than 0.05 May not be statistically significant.
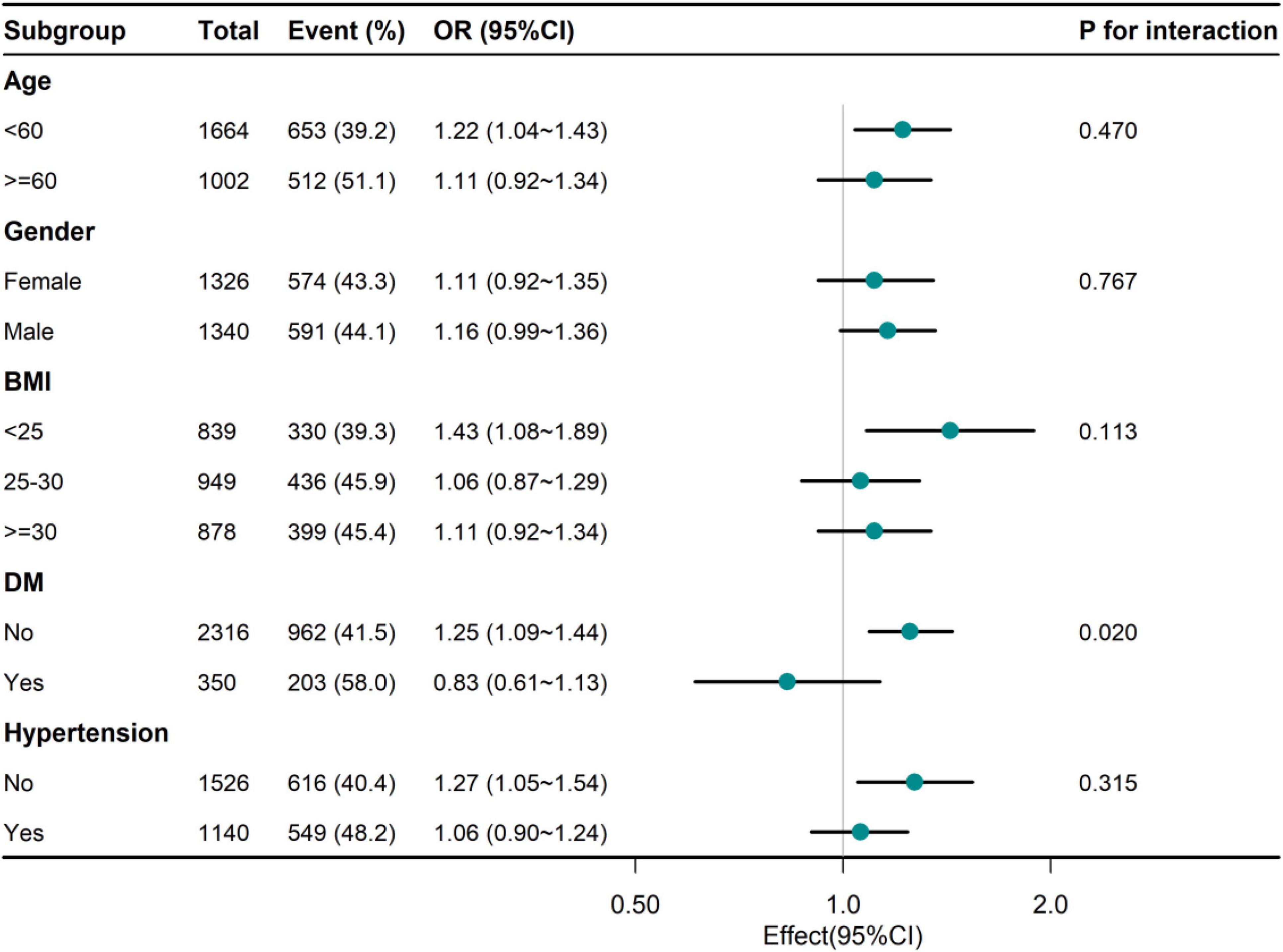
Figure 2. Association between NHHR and Hp infection of adults in different subgroups. UHR, serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio; Hp, Helicobacter pylori; BMI, body mass index; DM, diabetes mellitus.
This study is among the first to explore the association between the SUA-to-HDL ratio (UHR) and H. pylori infection, revealing a significant positive correlation that persists after adjusting for multiple demographic, metabolic, and inflammatory confounders. These findings highlight the potential of UHR as a novel biomarker reflecting the interplay between metabolic dysregulation and chronic infection. While prior research has independently linked elevated SUA and reduced HDL to inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, our results underscore the clinical utility of UHR as a composite index that integrates these factors.
The data of this study showed that the high quartile UHR individuals were more male, smokers, drinkers and hypertensive diabetic patients, and had lower HEI levels and higher TG, BUN and SCR levels, which were consistent with the results of previous studies to varying degrees (16, 20). In the association between UHR and Hp infection, we found that UHR was positively correlated with Hp infection regardless of model adjustment. After adjusting for multiple confounders, the risk of Hp infection increased by 15% for each SD increase in UHR. (21) Furthermore, subgroup analyses indicate that this relationship is robust across diverse demographic and clinical subpopulations, suggesting its generalizability and relevance to clinical practice. The marginal interaction observed in the diabetes subgroup, while intriguing, requires further investigation to clarify its biological significance.
The observed association between UHR and H. pylori infection may reflect underlying pathophysiological mechanisms shared by metabolic and inflammatory processes (22). Elevated SUA, a byproduct of purine metabolism, is known to promote oxidative stress and low-grade systemic inflammation, both of which can facilitate (23–25). H. pylori colonization and persistence in the gastric mucosa (26). Moreover, reduced HDL levels impair cholesterol transport and endothelial protection, which may compromise the host’s immune defense against bacterial infection (27–29). Together, these metabolic alterations may create a permissive environment for H. pylori to establish chronic infection, contributing to the observed association. Besides, for the interaction observed in the diabetes subgroup, we hypothesized that this may be due to increased levels of inflammation and metabolic disorders in diabetic patients themselves, which in turn disrupt the normal metabolic pathways of SUA and HDL in humans (30), thus reducing the negative effect of UHR. (23, 31)
The implications of these findings extend beyond H. pylori infection, given the established role of UHR in predicting cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. The overlap between metabolic and infectious pathways emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to disease prevention and management. For instance, targeting UHR through dietary and pharmacological interventions may not only improve metabolic health but also mitigate the risk of chronic infections, including H. pylori. This hypothesis warrants exploration in future interventional studies.
The study has several limitations. First, this cross-sectional study was unable to establish a causal relationship between serum UHR levels and Hp infection, and the absence of follow-up data limits understanding of how UHR changes with Hp treatment or progression. Besides, our study does not explore the biological mechanisms underlying the association between UHR and Hp infection, which needs further investigation. Moreover, despite adjustments, residual confounding factors, such as dietary habits, physical activity, or genetic predisposition, may influence the results. Finally, because the NHANES database represents only the U.S. population, the results may have some limitations worldwide. To further confirm our conclusions, a prospective cohort study with a larger sample size is needed.
In conclusion, our study identifies UHR as a promising biomarker for H. pylori infection, reflecting its potential role at the intersection of metabolic dysfunction and chronic inflammation. Future research should focus on elucidating the mechanistic underpinnings of this relationship, exploring its clinical utility in risk stratification and targeted interventions, and validating these findings in diverse populations. By integrating metabolic and infectious pathways, UHR offers a novel perspective on the complex interplay between chronic diseases, advancing our understanding of their shared pathophysiology.
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Centers for disease Control and Prevention. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
ZQ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YF: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – original draft. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Science and Technology Program of the Joint Fund of Scientific Research for the Public Hospitals of Inner Mongolia Academy of Medical Sciences (No. 2024GLLH1036 and No. 2024GLLH1037), and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University (No. 2023NYFYSYS003).
We are grateful to Dr. Jie Liu and Dr. Siru Wu for their contribution to the comments regarding the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Sidebotham R, Baron J. Hypothesis: Helicobacter pylori, urease, mucus, and gastric ulcer. Lancet. (1990) 335(8683):193–5. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90279-e
2. Malfertheiner P, Camargo M, El-Omar E, Liou J, Peek R, Schulz C, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9(1):19.
3. Gatta L, Vakil N, Vaira D, Scarpignato C. Global eradication rates for Helicobacter pylori infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis of sequential therapy. Bmj. (2013) 347:f4587. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f4587
4. Robinson K, Atherton J. The spectrum of Helicobacter-mediated diseases. Annu Rev Pathol. (2021) 16:123–44.
5. Li W, Zhang J, Ma J, Li Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y, et al. Effects of Helicobacter pylori treatment and vitamin and garlic supplementation on gastric cancer incidence and mortality: Follow-up of a randomized intervention trial. Bmj. (2019) 366:l5016. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l5016
6. McCracken K, Catá E, Crawford C, Sinagoga K, Schumacher M, Rockich B, et al. Modelling human development and disease in pluripotent stem-cell-derived gastric organoids. Nature. (2014) 516(7531):400–4.
7. Xie J, Cools L, Van Imbschoot G, Van Wonterghem E, Pauwels M, Vlaeminck I, et al. Helicobacter pylori-derived outer membrane vesicles contribute to Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis via C3-C3aR signalling. J Extracell Vesicles. (2023) 12(2):e12306. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12306
8. Feig D, Kang D, Johnson R. Uric acid and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med. (2008) 359(17):1811–21.
9. Longo-Mbenza B, Nsenga J, Mokondjimobe E, Gombet T, Assori I, Ibara J, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is identified as a cardiovascular risk factor in Central Africans. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2012) 6:455–61. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S28680
10. Badve S, Pascoe E, Tiku A, Boudville N, Brown F, Cass A, et al. Effects of allopurinol on the progression of chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. (2020) 382(26):2504–13.
11. Iracheta-Vellve A, Petrasek J, Satishchandran A, Gyongyosi B, Saha B, Kodys K, et al. Inhibition of sterile danger signals, uric acid and ATP, prevents inflammasome activation and protects from alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J Hepatol. (2015) 63(5):1147–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.06.013
13. Mackenzie I, Ford I, Nuki G, Hallas J, Hawkey C, Webster J, et al. Long-term cardiovascular safety of febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with gout (FAST): A multicentre, prospective, randomised, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. (2020) 396(10264):1745–57. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32234-0
14. Magnussen C, Ojeda F, Leong D, Alegre-Diaz J, Amouyel P, Aviles-Santa L, et al. Global effect of modifiable risk factors on cardiovascular disease and mortality. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389(14):1273–85.
15. Aktas G, Yilmaz S, Kantarci D, Duman T, Bilgin S, Balci S, et al. Is serum uric acid-to-HDL cholesterol ratio elevation associated with diabetic kidney injury? Postgrad Med. (2023) 135(5):519–23. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2023.2214058
16. Xie Y, Huang K, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wu Y, Chu J, et al. Association of serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in American adults: A population-based analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2023) 10:1164096. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1164096
17. Li Z, Liu Q, Yao Z. The serum uric acid-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a predictor for all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality: A cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1417485.
18. Curtin L, Mohadjer L, Dohrmann S, Kruszon-Moran D, Mirel L, Carroll M, et al. National health and nutrition examination survey: Sample design, 2007-2010. Vital Health Stat. (2013) 160:1–23.
19. Chen Z, Cheang I, Qu Q, Zhu X, Fu Y, Gao R, et al. Associations of serum uric acid-to-high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio with age-related diseases and mortality among older population in the United States. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. (2024) 130:105707. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2024.105707
20. Huang X, Hu L, Tao S, Xue T, Hou C, Li J. Relationship between uric acid to high-density cholesterol ratio (UHR) and circulating α-klotho: Evidence from NHANES 2007-2016. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02234-6
21. Danesh J, Peto R. Risk factors for coronary heart disease and infection with Helicobacter pylori: Meta-analysis of 18 studies. Bmj. (1998) 316(7138):1130–2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7138.1130
22. Kocak M, Aktas G, Erkus E, Sincer I, Atak B, Duman T. Serum uric acid to HDL-cholesterol ratio is a strong predictor of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). (2019) 65(1):9–15. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.1.9
23. Du L, Zong Y, Li H, Wang Q, Xie L, Yang B, et al. Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y
24. Kisker C, Schindelin H, Baas D, Rétey J, Meckenstock R, Kroneck PMA. structural comparison of molybdenum cofactor-containing enzymes. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (1998) 22(5):503–21.
25. Crawley W, Jungels C, Stenmark K, Fini MAU-. shaped association of uric acid to overall-cause mortality and its impact on clinical management of hyperuricemia. Redox Biol. (2022) 51:102271. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102271
26. Kusters J, van Vliet A, Kuipers E. Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2006) 19(3):449–90.
27. Riwanto M, Rohrer L, von Eckardstein A, Landmesser U. Dysfunctional HDL: From structure-function-relationships to biomarkers. Handb Exp Pharmacol. (2015) 224:337–66.
28. Vitali C, Wellington C, Calabresi L. HDL and cholesterol handling in the brain. Cardiovasc Res. (2014) 103(3):405–13.
29. Poliakova T, Wellington C. Roles of peripheral lipoproteins and cholesteryl ester transfer protein in the vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia. Mol Neurodegener. (2023) 18(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00671-y
30. Ishibashi T, Kaneko H, Matsuoka S, Suzuki Y, Ueno K, Ohno R, et al. HDL cholesterol and clinical outcomes in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2023) 30(8):646–53.
Keywords: Hp, Hp infection, serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, serum uric acid, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, adults
Citation: Qin Z, Fang Y, Liu Y, Zhang L, Zhang R and Zhang S (2025) Association between Hp infection and serum uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in adults. Front. Med. 12:1509269. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1509269
Received: 10 October 2024; Accepted: 06 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Giuseppe Castaldo, University of Naples Federico II, ItalyReviewed by:
Gulali Aktas, Bolu Abant Ýzzet Baysal University, TürkiyeCopyright © 2025 Qin, Fang, Liu, Zhang, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruoyi Zhang, MTM5NDgxNjgxMTFAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Shutian Zhang, emhhbmdzdHl5QDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.