- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Operating Room, Hangzhou TCM Hospital Affiliated to Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
Background: Postoperative cognitive impairment is a common complication in older patients after major orthopedic surgery; however, the underlying mechanism is not completely understood.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the effects of preemptive acupuncture on cognitive dysfunction after hip replacement and explore its potential mechanisms.
Methods: Finally, 54 participants were randomized into sham acupuncture (n = 27) or acupuncture (n = 27) groups, who received acupuncture at the Sishencong (EX-HN1) and Baihui (DU20) acupoints, while participants in the sham acup group received sham acup at the target acupoints. Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) scores, the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD), and other adverse events were assessed. The levels of microRNA (miR)-124 and miR-146a and inflammatory cytokines in the peripheral blood were detected. Correlations among miR-124, miR-146a, and inflammatory cytokines were analyzed.
Results: Compared with the sham acup group, the MMSE and MoCA scores in the acup group on the first and seventh day after surgery were higher, and the incidence of POCD on the first day was lower. Acupuncture upregulated levels of miR-124 and -146a and decreased the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β to protect cognitive function. Correlation analysis indicated that upregulated miR-124 and miR-146 were associated with lower levels of inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: Acupuncture protects postoperative cognitive function in older patients undergoing hip replacement, potentially reducing the incidence of POCD by upregulating miR-124 and miR-146a to inhibit neuroinflammation.
Clinical trial registration: www.chictr.org.cn, identifier ChiCTR2200062027.
1 Introduction
With the aging world population, age-related diseases account for many medical resources. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is a common complication in older patients who undergo major surgeries such as cardiac and orthopedic surgeries (1). Clinically, POCD is characterized by impaired memory, decreased ability to handle information, and decreased attention, which contribute to a series of negative outcomes, including mood and personality changes. A recent review indicated that age and educational level were major risk factors for developing POCD (2). Data suggest that approximately 50% of older individuals experience at least one surgical intervention in their lifespan. In comparison, approximately 25% of older patients have an identifiable decline in cognition, and approximately 50% of those suffer from permanent cognitive impairment (3). With increasing age, older individuals inevitably suffer from neurological impairments caused by neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Surgery and anesthesia are regarded as the main risk factors for POCD development. For example, various analgesics contribute to impaired cognitive function. Although short-acting opioids such as remifentanil are used for anesthesia, older patients are also vulnerable to POCD (4). However, clinical studies have indicated that even short-acting anesthetics affect postoperative cognitive impairment (5). Surgical procedures are another major risk factor for persistent postoperative pain and systemic inflammation raised during surgery. For example, after orthopedic surgery, patients often experience persistent pain that contributes to microglia activation, promotes cytokine release, and impairs the normal function of neurons (6, 7). However, the specific physiological mechanism of postoperative cognitive impairment remains unclear, and optimal perioperative strategies and treatments are required to prevent POCD. There are multiple pharmacological applications in clinical practice for the postoperative prevention of cognitive dysfunction, including glucocorticoids. A recent 4-year follow-up study suggested that the administration of 0.1 mg·kg−1 dexamethasone effectively reduced the incidence of POCD after cardiac surgery (8). Pharmacological treatments may also lead to other side effects and increase hospital costs. However, non-pharmacological applications are lacking.
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese treatment or technique for anesthesia, lower back pain control, and prevention of chemotherapy-related side effects (9). Patients often experience preoperative anxiety, which is not conducive to rapid postoperative recovery. A recent meta-analysis suggested that acupuncture contributed to reducing preoperative anxiety and pain intensity (3), demonstrating the positive effects of acupuncture in patients during the preoperative period. However, further studies are needed to verify this. Surgical trauma and anesthesia-mediated neuroinflammation may be the underlying mechanisms of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Animal experiments have shown that electroacupuncture on ST25 and ST36 acupoints inhibited the release of TNF-α induced by endotoxemia, improved the survival rate of septic rats (10), and elucidated the anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture on the central circuit. The optimal effects of acupuncture were determined by optimal acupoint choice. According to the theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), acupuncture in DU20 is widely used to treat dementia, stroke, insomnia, epilepsy, and hypertension. One study suggested that electroacupuncture at DU20 helped improve cognition (11). The above evidence supports the clinical use of DU20 in cognitive protection.
Acupuncture with EX-HN1 contributes to lower glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive astrocytes in the hippocampus, inhibits oxidative stress, and improves cognitive function in perioperative neurocognitive disorders (PNDs) in rats (4). Recently, non-coding small RNA molecules, including miRNAs, have been shown to play an important role in the pathophysiology of various neurodegenerative diseases. Some have been shown to regulate neuronal function and neuroinflammation and serve as biomarkers of neuroinflammation (6). A recent study has indicated that miR-124 is a novel target for regulating microglial activation, thus mediating postoperative cognitive function (12). Upregulation miR-146a expression inhibits the release of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6), thus attenuating hippocampus-dependent learning and memory impairment in mice with POCD (13). However, it remains unclear whether acupuncture alleviates postoperative cognitive impairment by regulating these miRNAs. This study aimed to investigate the effects of acupuncture on postoperative cognitive function and neuroinflammation and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
In this study, we hypothesized that the preemptive application of acupuncture might effectively inhibit the inflammatory response by upregulating miRNA-124 and -146a, thus reducing neuroinflammation and improving cognitive function in older individuals after hip replacement.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Participant enrollment
This randomized controlled trial was conducted following the Helsinki Declaration and Good Clinical Practice Guidelines and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Hangzhou TCM Hospital, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (No. 2022KY045). The protocol used in this study was registered with the China Clinical Trial Registry (No. ChiCTR2200062027). Sixty-six participants underwent hip replacement between 20 July 2022 and 20 December 2022. All participants provided informed consent prior to the surgery. The study participants were scheduled for hip replacement under combined spinal-epidural anesthesia (CSEA). The eligibility criteria of the study are as follows: (1) aged ≥65 years old, (2) American Association of Anesthesiologists (ASA) status ≤ grade III, and (3) agreed to receive acupuncture. Exclusion criteria are as follows: (1) without full communication skills, (2) without the ability to finish the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) questionnaires or preoperative MoCA scored <26 points or MMSE <24 points, (3) with history of uncontrolled hypertension, diabetes, or other coronary system diseases, (4) target acupuncture sites were not applicable for acupuncture, (5) participants not suitable for CSEA, (6) with history of acupuncture treatment or related acupoint stimulation treatments (such as acupoint electrical stimulation, and nerve electrical stimulation), and (7) participants cannot tolerate de qi sensation.
2.2 Randomization and blinding protocol
We first numbered the participants according to the order of hospitalization, matched the above number with a random number, and divided the participants into sham acup group and acup group based on the above random numbers. Randomization was performed by an independent statistician blinded to the other trial researchers. Before surgery, an independent blinded statistician concealed the file that provided the participants with grouping information. The collected and assessed outcomes were blinded to the group information. The participants were treated separately during hospitalization to avoid mutual communication. All the participants were allowed to drop out at any time during the study period.
2.3 Intervention of acupuncture and anesthesia protocol
Before the study, the participants were well informed about the acupuncture procedure and associated adverse events. Acupuncture was performed on DU20 (located at the intersection between the midline of the head and the connecting line between the two ear tips) and EX-HN1 (composed of four acupoints, away 3.33 cm on the front, back, left, and right of DU20) according to participant grouping information in an envelope (Figure 1), which was only available to the acupuncture operator, who was not permitted to participate in data collection and analysis. Based on our experience and our previous study (14), acupuncture needles (0.25 mm, Dongbei Medical Equipment Co., Ltd., Jinan, China) were inserted at the target acupoints, with stimulation for 30 min (a distant-dense wave with a frequency of 2/10 Hz), three times a day (07:00, 13:00, and 19:00), and 3 consecutive days before surgery. De qi sensation is a landmark for the successful implementation of acupuncture (15). Acupuncture was considered successful when a de qi sensation was obtained. The needle was maintained for 30 min, connected to an acupoint stimulator (dense-disperse frequency, 2/10 Hz, 6–9 mA), and carefully protected from removal. For participants in the sham acup group, needles were inserted into the skin approximately 1 cm away from the target acupoints and connected to the acupoint stimulator; however, stimulation was not performed. Once a de qi sensation was obtained, participants were excluded from the group. The operator also protected the needles.
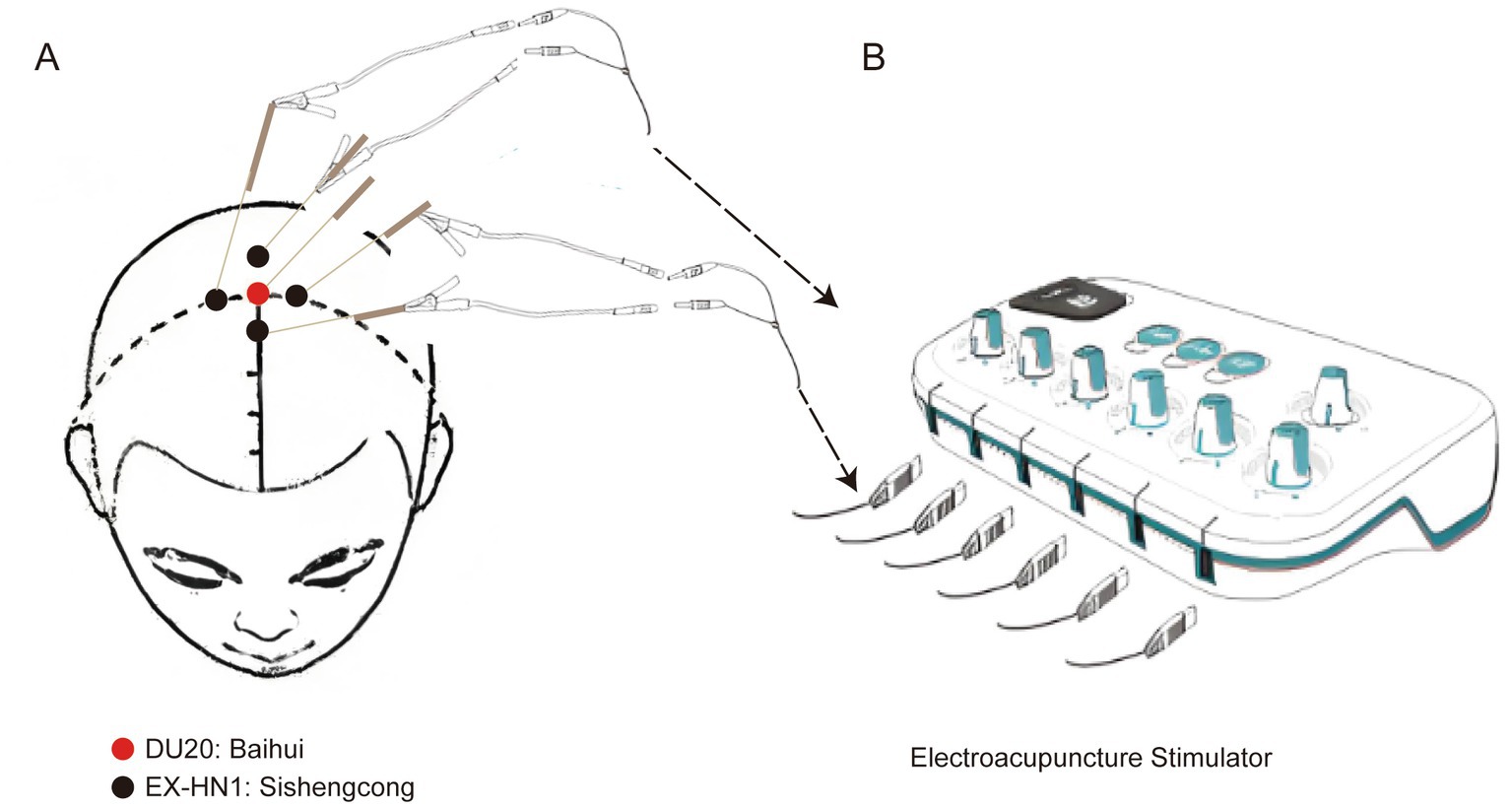
Figure 1. Acupoint diagram of target acupoints. (A) Anatomical location of DU20 and EX-HN1. (B) Electroacupuncture stimulator connects the electric needles on the target acupoints through a wire. DU20, locating at the intersection between the midline of the head and the connecting line between the two ear tips. EX-HN1, composing of four acupoints, away 3.33 cm on the front, back, left and right of DU20.
A standard CSEA protocol was used to provide anesthesia for the hip replacement. A routine intravenous cannula was inserted, and 10 mL/kg of lactated Ringer’s solution was administered. Vital signs, including invasive blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (RR), electrocardiographic monitoring (ECG), and blood oxygen saturation (SpO2), were intensively monitored throughout surgery. Before CSEA, the patient was placed on the right arm and reclined with the hands holding the knees. After skin sterilization, 5 mL of 2% lidocaine was used for local infiltration anesthesia. An 18G needle was advanced between the mid-line of the L2–3 or L3–4 intervertebral space, and a loss-of-resistance technique with saline was used to test the reattachment of the epidural space. A 27-G pencil-point needle was inserted using the needle-through-needle technique. Two volumes of 2 mL of 0.5% bupivacaine were administered in a single dose over half a minute. The epidural catheter was advanced approximately 3 cm into the epidural space, the spinal needle was removed, negative pressure was checked, and the catheter was carefully protected throughout the surgery. A single dose of 2 mL of 0.375% ropivacaine was administered to maintain anesthesia. The patients were placed in the supine position after CSEA. At the end of the surgery, 2 mg of morphine was administered for postoperative analgesia.
2.4 Measurements
POCD was diagnosed according to a previous study based on the MoCA and MMSE scale assessment (16, 17). The incidence of POCD within 7 days after surgery was documented. Peripheral levels of miR-124 and miR-146a, as well as inflammatory cytokines in the periphery, were detected.
The MMSE and MoCA scores were recorded 1 day before surgery and on the first and seventh days after surgery by a nurse anesthetist, blinded to the grouping information. When postoperative MMSE and MoCA scores were reduced by more than one standard deviation compared to baseline values, POCD was diagnosed (7, 18). A volume of 2 mL of peripheral blood was collected after surgery for detecting the levels of miR-124 and miR-146a by Quantitative real-time PCR and levels of inflammatory cytokines of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β by ELISA method (R&D system, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The sample size was calculated using a web tool1 based on our preliminary study on the incidence of POCD. In brief, a sample size of 20 participants for each group was obtained to reach a significance difference of α = 5%, with a statistical power (β-value) of 0.8. We also assumed a 20% dropout rate; therefore, the total sample size of the study was 48.
Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables or numbers and proportions for categorical variables. The ANCOVA was used to compare the differences between the two groups, and rmANOVA was used for repeated measures. Mixed linear models analyzed the correlation between miR-124, miR-146a, and inflammatory cytokines. Chi-square (and Fisher’s exact) tests were used to analyze categorical variables. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. SPSS software (version 18.0) was used to analyze the data.
3 Results
3.1 Demographic characteristics of participants
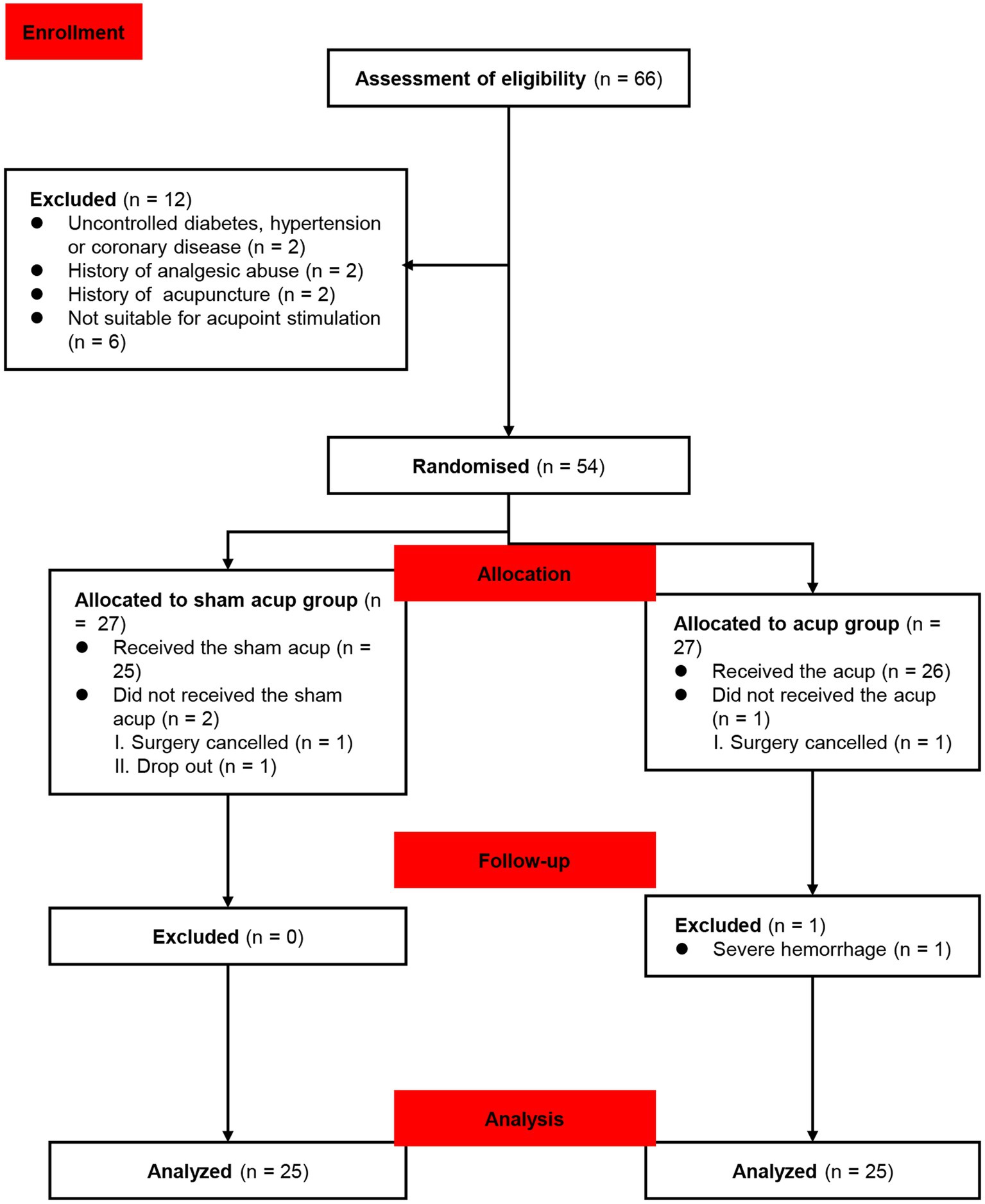
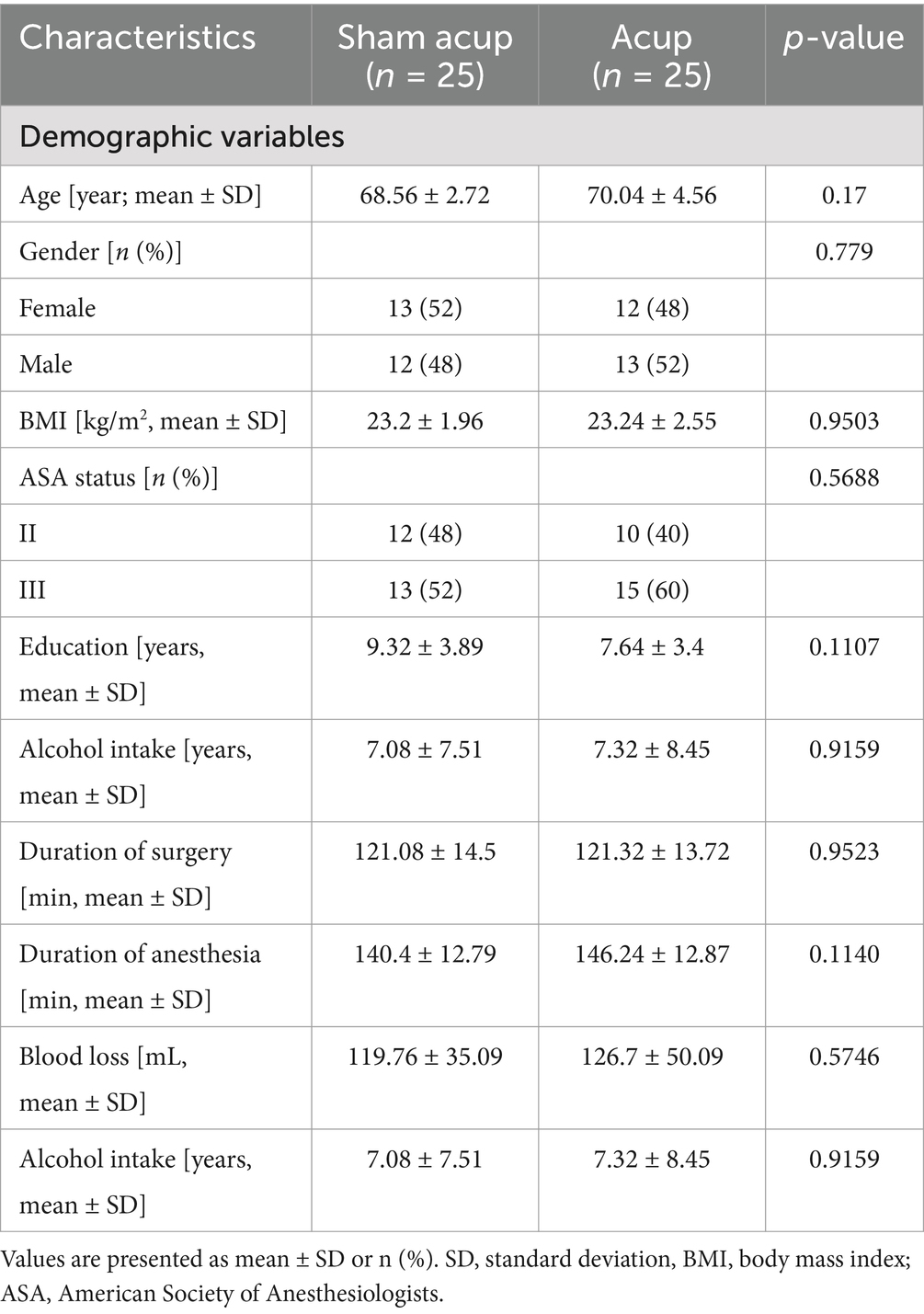
Sixty-six participants were enrolled in the study from 20 July 2022 to 20 December 2022. Twelve patients were excluded as they were ineligible for the study. One of them had uncontrolled hypertension and diabetes (the participant had not been diagnosed); 1 of them had coronary disease, diagnosed through auxiliary examinations after admission; 2 of them had a history of abuse of analgesics, which may potentially affect cognitive function during the perioperative period; 2 of them had a history of other types of acupuncture treatment; 6 of them were found unsuitable for acupuncture, and 54 participants were randomized into the sham acup and acup groups. After allocation, two participants did not receive sham acup for cancellation of the surgery, as well as one surgical cancellation was performed in the acup group. During follow-up, one participant dropped out because of a severe hemorrhage during surgery. Fifty participants completed the study and were included in the data analysis (Figure 2). The baseline characteristics of the groups are shown in Table 1.
3.2 MMSE, MoCA assessment, the incidence of POCD, and adverse events
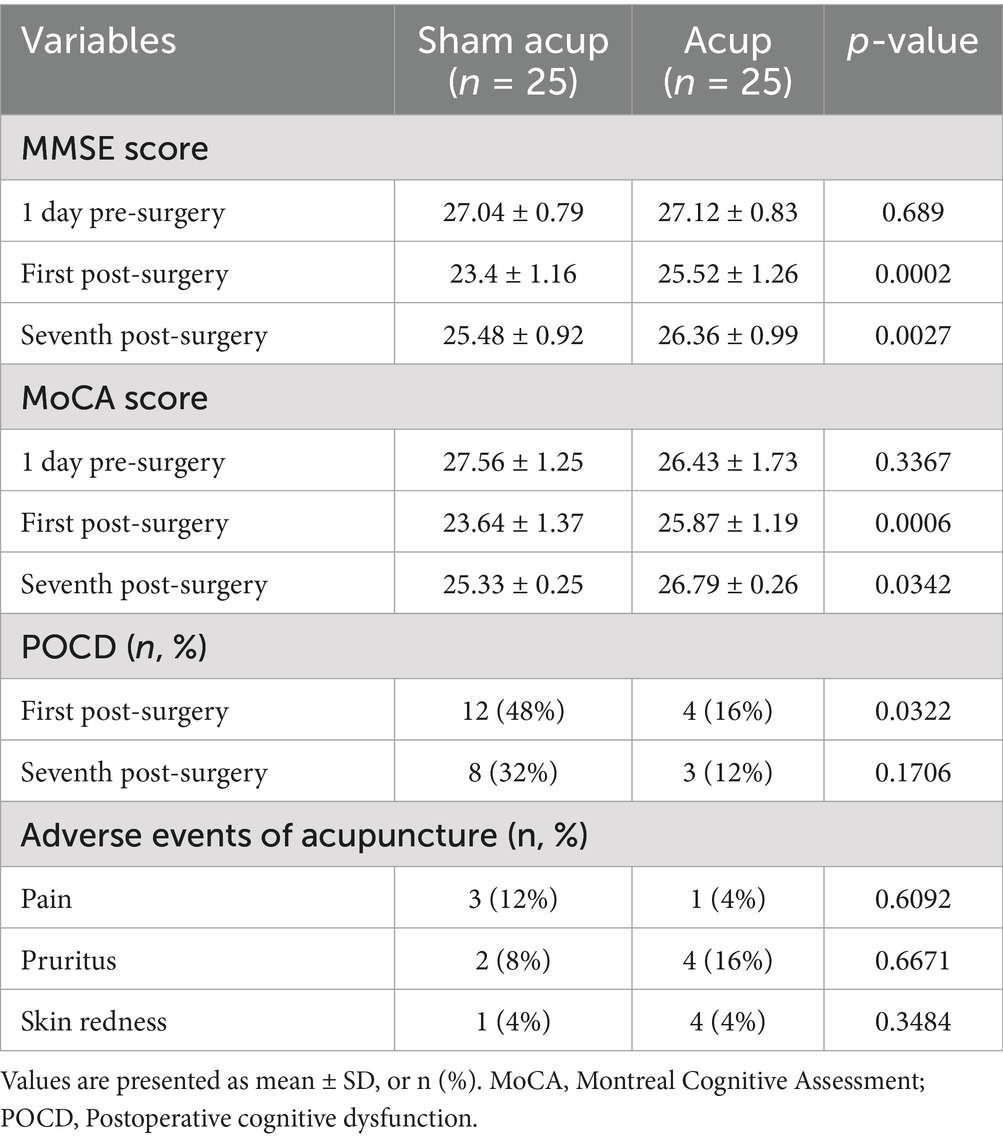
Except for the MoCA score on the seventh day, the MMSE and MoCA scores in both groups declined compared to those recorded before the surgical procedure. The MMSE scores on the first (p = 0.0002) and seventh (p = 0.0027) were higher in the acup group than in the sham acup group. In addition, the MoCA scores in the acup group were higher than those in the sham acup group on the first (p = 0.0006) and seventh (p = 0.0342) days after surgery. The incidence of POCD in the acup group was lower on the first day (p = 0.0322), but not on the seventh (p = 0.1706) day after surgery, compared with the sham acup group. We also documented the adverse effects of acupuncture at the target site. Pain, pruritus, and redness were common side effects of acupuncture; however, no significant differences were observed between the groups (Table 2).
3.3 Levels of microRNAs in peripheral blood
MiR-124 and miR-146a have been suggested to protect cognitive function and anti-neuroinflammation (12, 13). We detected peripheral blood levels of miR-124 and miR-146a. Compared with patients treated with sham acup, those treated with acupuncture showed higher levels of miR-124 (Figure 3A) and miR-146a (Figure 3B).
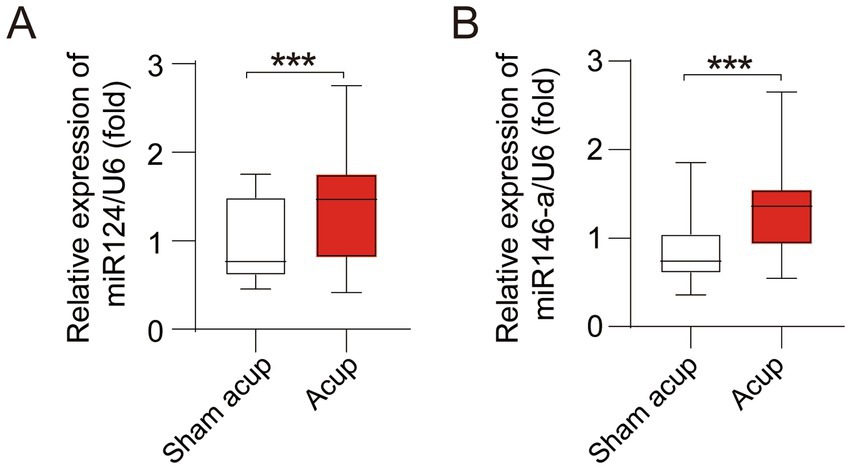
Figure 3. Levels of miRNAs in in peripheral of participants treated with sham acupuncture or acupuncture. (A) Levels of miR124 in peripheral; (B) Levels of miR146-a in peripheral. ***p < 0.001.
3.4 Levels of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood
Neuroinflammation is a major cause of perioperative cognitive impairment. Compared with the sham acup group, patients treated with acupuncture showed lower levels of TNF-α (Figure 4A), IL-6 (Figure 4B), and IL-1β (Figure 4C), suggesting that acupuncture inhibited the inflammatory response during the perioperative period, which might help reduce the neuroinflammation and thus to alleviate cognitive impairment.
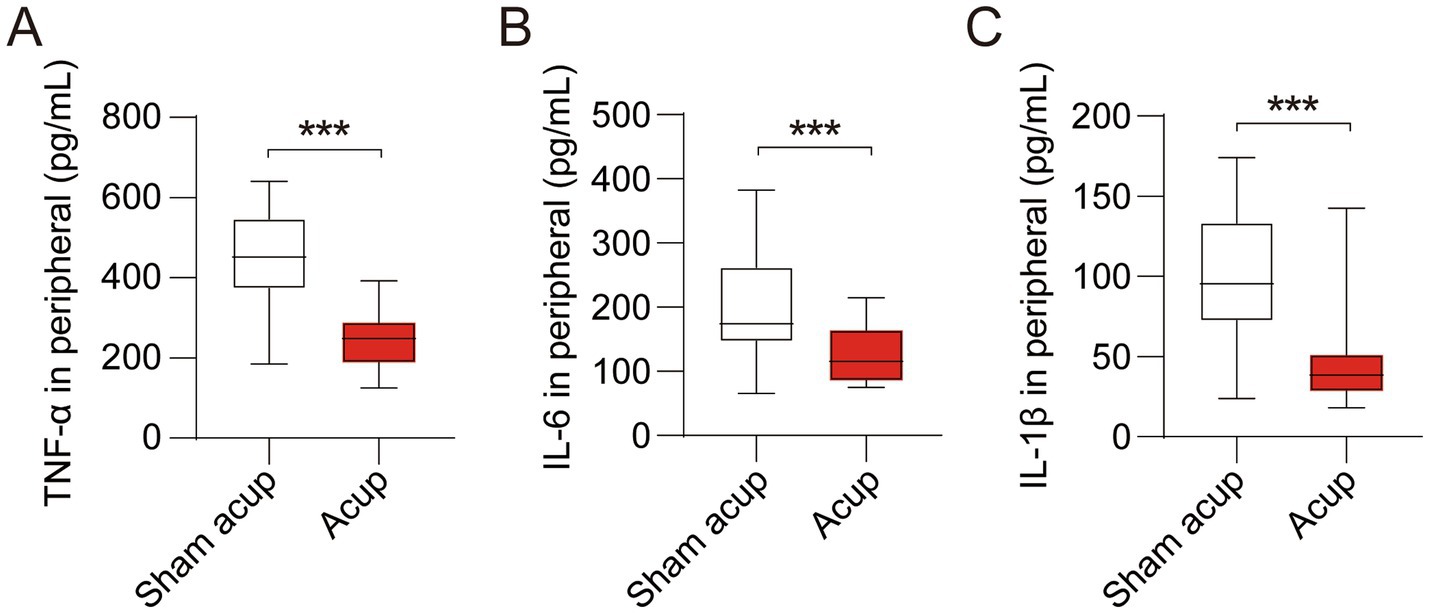
Figure 4. Levels of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral of participants treated with sham acup or acup. (A) Levels of TNF-α in peripheral; (B) Levels of IL-6 in peripheral; (C) Levels of IL-1β in peripheral. ***p < 0.001.
3.5 Upregulation of miR-124 and miR-146a associated with the low level of inflammatory response
These results indicated that acupuncture upregulated the levels of miR-124 and miR-146a and inhibited the inflammatory response in older patients after hip replacement. Animal experiments have shown that miRNAs regulate inflammatory responses in some disease models (12, 13). To reveal the potential mechanisms, we conducted a correlation analysis between the levels of miR-124 and miR-146a and the levels of inflammatory cytokines. The results suggested that upregulated miR-124 (Figures 5A–C) and miR-146a (Figures 5D–F) are associated with lower levels of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. These results suggested that acupuncture inhibited the inflammatory response by upregulating the expression of miR-124 and miR-146a.
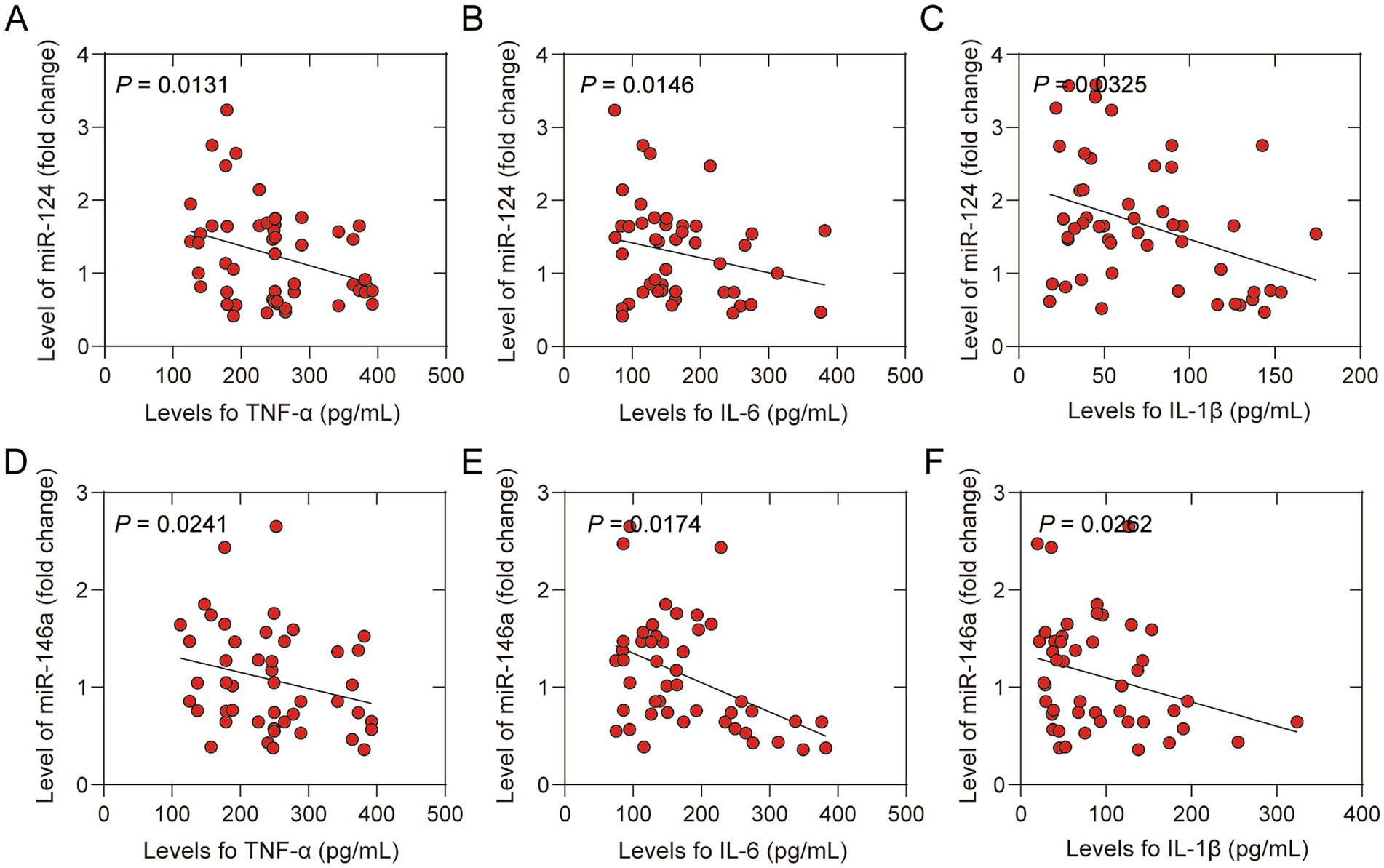
Figure 5. Correlation between levels of inflammatory cytokines in peripheral and microRNAs of participants treated with sham acup or acup. (A) Correlation between levels of TNF-α and miR-124 in peripheral; (B) Correlation between levels of IL-6 and miR-124 in peripheral; (C) Correlation between levels of IL-1β and miR-124 in peripheral; (D) Correlation between levels of TNF-α and miR-146a in peripheral; (E) Correlation between levels of IL-6 and miR-146a in peripheral in peripheral; (F) Correlation between levels of IL-1β and miR-146a in peripheral.
4 Discussion
The results of the present study suggested that acupuncture decreased the incidence of POCD in the early postoperative period after hip replacement. Mechanistically, acupuncture alleviated the postoperative inflammatory response by upregulating miR-124 and miR-146a levels. Correlation analysis indicated that the upregulation of miR-124 and miR-146a, associated with a decreased release of inflammatory cytokines, might help reduce neuroinflammation, thus alleviating cognitive impairment. These results suggest potential mechanisms by which acupuncture inhibits the inflammatory response, contributing to cognitive protection during the perioperative period.
However, pathophysiological mechanisms underlying POCD remain unclear. The risk factors include age, educational level, and mental health. For patients undergoing surgical procedures, anesthesia and surgery may further deteriorate postoperative cognitive function. A recent study suggested that approximately 50% of older patients experienced cognitive decline on the first day after a total hip arthroplasty (19). Early prevention and management of POCD are crucial for its prognosis. However, the medical treatment is often delayed. Therefore, the application of preventive measures before surgery may be beneficial. Recent evidence has shown that acupuncture contributes to the alleviation of POCD by inhibiting inflammatory responses and oxidative stress (20). In this study, we selected DU20 and EX-HN1 as the target acupoints.
DU20 is widely used to treat dementia, stroke, insomnia, epilepsy, and hypertension. Studies have suggested that electroacupuncture at DU20 could help improve cognitive function (10, 11). These findings offer guidance for the clinical application of DU20 in enhancing cognitive function. Acupuncture with EX-HN1 has been shown to have calming effects and to improve cognitive abilities (21). Another study indicated that acupuncture of EX-HN1 contributes to reducing the GFAP GFAP-positive astrocytes in the hippocampus, mitigating oxidative stress, and enhancing the cognitive function of PNDs in rats (5). A recent meta-analysis suggested that acupuncture could successfully treat and prevent POCD (22). However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In early 1975, the MMSE emerged as the preferred tool for the clinical evaluation of cognitive function in older individuals (23). It is simple and convenient to operate, leading to its widespread use worldwide, and has become the main scale to evaluate postoperative cognitive impairment (17). The MoCA questionnaire is frequently used to evaluate postoperative cognitive function (16). In the current study, the MMSE and MoCA scores declined after surgery. However, patients who received acupuncture experienced higher MMSE and MoCA scores and a lower incidence of POCD in the early postoperative period, consistent with the findings of a previous study (18). These results suggest that perioperative acupuncture at DU20 and EX-HN1 may enhance cognitive function in older patients undergoing hip replacement.
Neuroinflammation is a significant factor in the development of POCD (24). Research involving animal models has indicated that surgical procedures increased pro-inflammation in the peripheral and central nervous systems, ultimately resulting in neuronal injury (25, 26). Another study revealed that lipopolysaccharide administration before surgery increases the incidence and severity of POCD (27). This evidence suggests that peripheral and central inflammation contribute significantly to cognitive dysfunction. A previous study demonstrated that acupuncture could effectively inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation (28), potentially mitigating neuroinflammation during surgical procedures. However, existing evidence remains insufficient. In this study, anesthesia and surgery were associated with a pronounced release of inflammatory cytokines, as evidenced by increased TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β levels. Conversely, patients who received acupuncture exhibited lower levels of inflammatory responses, indicating that acupuncture may exert anti-inflammatory effects that could help reduce cognitive impairment and the incidence of POCD.
A recent review indicated a strong association between miRNAs, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairment (29). A few miRNAs have been identified to be influential in the development of POCD (30). Furthermore, miRNAs have recently been recognized as significant bridges related to the effects of acupuncture, although their biological mechanisms remained unclear (31). MiR-124 is one of the most abundant miRNAs in the brain and regulates the function of microglia (12). MiR-146a is upregulated in neurodegenerative diseases and is involved in modulating the function of microglia (32). This indicates that miR-124 and miR-146a may influence cognitive function and possess anti-neuroinflammatory properties (12, 13). Therefore, in the present study, we examined the levels of miR-124 and miR-146a. Acupuncture triggered the expression of both miR-124 and miR-146a, and patients who received acupuncture exhibited lower inflammatory levels. Correlation analysis showed that the upregulation of miR-124 and miR-146a was associated with decreased levels of inflammatory cytokines, implying that acupuncture may mitigate the inflammatory response by upregulating miR-124 and miR-146a.
Despite favorable outcomes, the limitations of this study must be acknowledged. First, the participant cohort was drawn from a single center, indicating the need for a more diverse sample encompassing various races and nationalities to enhance the generalizability of the findings. Second, other factors, such as postoperative pain, may contribute to the triggering of inflammatory responses. Various studies have reported that acupuncture is widely used as an analgesia (27, 28). Third, POCD mainly occurs within 7 days after anesthesia and surgery (33), and we only recorded the MMSE and MoCA scores within 7 days after surgery. Given that POCD may affect the long-term prognosis of patients, including cognitive function and quality of life, further research is required to evaluate the long-term effects of acupuncture on postoperative cognitive impairment. Fourth, the implementation of acupuncture in this study may not have been optimal. We intend to refine this operational process further to decrease the associated labor costs. Correlation analysis indicated that the upregulated miR-124 and miR-146a levels were associated with reduced levels of inflammatory cytokines. However, further investigations are required to confirm this, especially through in vitro experiments. We designed an animal experiment to test this hypothesis. In this study, the acupuncturists could not be blinded to the nature of the intervention. This may have introduced a performance bias. However, the acupuncturists were not allowed to participate in the data collection and analysis. Pain, pruritus, and redness of the target acupoints were the most common complications. Therefore, we mainly included the incidence of these three complications. More potential complications or side reactions would be beneficial for a comprehensive safety assessment. During registration, we only listed the main outcomes, such as MMSE scores, levels of miR-124, and inflammatory cytokines. However, a detailed assessment of outcomes should be included in the trial registration. Using multiple methods to assess the postoperative cognitive function makes these results more convincing. Finally, the study is a single-center study, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. Therefore, more strictly designed studies, including more centers and results involving long-term effects, are needed to confirm the results of the study further.
5 Conclusion
This study indicated that the proactive application of acupuncture at the DU20 and EX-HN1 points in older patients undergoing hip replacement surgery effectively enhanced postoperative cognitive function, improved MMSE and MoCA scores, and decreased the incidence of POCD in the early postoperative period. Mechanistically, acupuncture upregulates the levels of miR-124 and miR-146a, which play roles in mitigating neuroinflammation, thereby facilitating improvements in postoperative cognitive function. However, owing to certain limitations, further rigorously designed studies are necessary to validate the findings of this study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Hangzhou TCM Hospital, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University (No. 2022KY045). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
QT: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RZ: Software, Writing – review & editing. GL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. SC: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. BQ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was financially supported by grants from the Zhejiang TCM Science and Technology Plan (No. 2022ZA105).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Wang, L, Yang, JW, Lin, LT, Huang, J, Wang, XR, Su, XT, et al. Acupuncture attenuates inflammation in microglia of vascular dementia rats by inhibiting miR-93-mediated TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:8253904–15. doi: 10.1155/2020/8253904
2. Yang, X, Huang, X, Li, M, Jiang, Y, and Zhang, H. Identification of individuals at risk for postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Ther Adv Neurol Disord. (2022) 15:17562864221114356. doi: 10.1177/17562864221114356
3. Zhuang, Y, Xing, J, Li, J, Zeng, BY, and Liang, FR. History of acupuncture research. Int Rev Neurobiol. (2013) 111:1–23. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-411545-3.00001-8
4. Liu, YC, Meguro, K, Nakamura, K, Akanuma, K, Nakatsuka, M, Seki, T, et al. Depression and dementia in old-old population: history of depression may be associated with dementia onset the tome project. Front Aging Neurosci. (2017) 9:335. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00335
5. Wang, CM, Huang, HW, Wang, YM, He, X, Sun, XM, Zhou, YM, et al. Incidence and risk factors of postoperative delirium in patients admitted to the ICU after elective intracranial surgery: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. (2020) 37:14–24. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001074
6. Honig, LS, Vellas, B, Woodward, M, Boada, M, Bullock, R, Borrie, M, et al. Trial of Solanezumab for mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378:321–30. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1705971
7. Rudolph, J, Schreiber, K, Culley, D, Mcglinchey, R, Crosby, G, Levitsky, S, et al. Measurement of post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery: a systematic review. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. (2010) 54:663–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02236.x
8. Glumac, S, Kardum, G, Sodic, L, Bulat, C, Covic, I, Carev, M, et al. Longitudinal assessment of preoperative dexamethasone administration on cognitive function after cardiac surgery: a 4-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. (2021) 21:129. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01348-z
9. Acar, HV. Acupuncture and related techniques during perioperative period: a literature review. Complement Ther Med. (2016) 29:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2016.09.013
10. Li, C, Yu, T, Zhang, Y, Wei, LP, Dong, SA, Shi, J, et al. Electroacupuncture improves cognition in rats with Sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Surg Res. (2020) 256:258–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.06.056
11. Wen, T, Zhang, X, Liang, S, Li, Z, Xing, X, Liu, W, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment and spontaneous low-frequency brain activity in rats with ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. (2018) 27:2596–605. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.05.021
12. Chen, Y, Sun, JX, Chen, WK, Wu, GC, Wang, YQ, Zhu, KY, et al. miR-124/VAMP3 is a novel therapeutic target for mitigation of surgical trauma-induced microglial activation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2019) 4:27. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0061-x
13. Chen, L, Dong, R, Lu, Y, Zhou, Y, Li, K, Zhang, Z, et al. MicroRNA-146a protects against cognitive decline induced by surgical trauma by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice. Brain Behav Immun. (2019) 78:188–201. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.020
14. Que, B, Tu, Q, Shi, J, Wan, Z, Li, Y, Zhou, R, et al. Effects of transcutaneous electrical Acupoint stimulation on systemic inflammatory response syndrome of patients after percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: a randomized controlled trial. Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:5909956. doi: 10.1155/2021/5909956
15. Chae, Y, and Olausson, H. The role of touch in acupuncture treatment. Acupunct Med. (2017) 35:148–52. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2016-011178
16. Hou, R, Wang, H, Chen, L, Qiu, Y, and Li, S. POCD in patients receiving total knee replacement under deep vs light anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav. (2018) 8:e00910. doi: 10.1002/brb3.910
17. Jia, X, Wang, Z, Huang, F, Su, C, du, W, Jiang, H, et al. A comparison of the Mini-mental state examination (MMSE) with the Montreal cognitive assessment (MoCA) for mild cognitive impairment screening in Chinese middle-aged and older population: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry. (2021) 21:485. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03495-6
18. Gan, J, Tu, Q, Miao, S, Lei, T, Cui, X, Yan, J, et al. Effects of oxycodone applied for patient-controlled analgesia on postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2020) 32:329–37. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01202-w
19. Nelson, PT, Alafuzoff, I, Bigio, EH, Bouras, C, Braak, H, Cairns, NJ, et al. Correlation of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes with cognitive status: a review of the literature. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. (2012) 71:362–81. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31825018f7
20. Liu, PR, Cao, F, Zhang, Y, and Peng, S. Electroacupuncture reduces astrocyte number and oxidative stress in aged rats with surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction. J Int Med Res. (2019) 47:3860–73. doi: 10.1177/0300060519860026
21. Suh, HW, Kim, J, Kwon, O, Cho, SH, Kim, JW, Kwak, HY, et al. Neurocircuitry of acupuncture effect on cognitive improvement in patients with mild cognitive impairment using magnetic resonance imaging: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2019) 20:310. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3446-9
22. Safavynia, SA, and Goldstein, PA. The role of Neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: moving from hypothesis to treatment. Front Psych. (2019) 9:752. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00752
23. Folstein, MF, Folstein, SE, and McHugh, PR. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. (1975) 12:189–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6
24. Liu, S, Wang, ZF, Su, YS, Ray, RS, Jing, XH, Wang, YQ, et al. Somatotopic organization and intensity dependence in driving distinct NPY-expressing sympathetic pathways by Electroacupuncture. Neuron. (2020) 108:436–450.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.07.015
25. Fidalgo, AR, Cibelli, M, White, JP, Nagy, I, Maze, M, and Ma, D. Systemic inflammation enhances surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. Neurosci Lett. (2011) 498:63–6. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.04.063
26. Ho, Y, Zhao, F, Yeung, W, Wong, GT, Zhang, HQ, Chang, RC, et al. Application of acupuncture to attenuate immune responses and oxidative stress in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: what do we know so far? Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2020) 2020:9641904–21. doi: 10.1155/2020/9641904
27. Tang, Y, Wang, T, Yang, L, Zou, X, Zhou, J, Wu, J, et al. Acupuncture for post-operative cognitive dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acupunct Med. (2021) 39:423–31. doi: 10.1177/0964528420961393
28. Wang, P, Cao, J, Liu, N, Ma, L, Zhou, X, Zhang, H, et al. Protective effects of Edaravone in adult rats with surgery and lipopolysaccharide administration-induced cognitive function impairment. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0153708. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153708
29. Du, S, Wang, X, Zhu, W, Ye, Y, Yang, JW, Ma, SM, et al. Acupuncture inhibits TXNIP-associated oxidative stress and inflammation to attenuate cognitive impairment in vascular dementia rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2018) 24:39–46. doi: 10.1111/cns.12773
30. Zhong, Y, Zhang, Y, and Zhu, Z. Research progress on the association between MicroRNA and postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Minerva Anestesiol. (2024) 90:191–9. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.23.17614-0
31. Yazit, NAA, Juliana, N, Das, ST, Teng, NIMF, Fahmy, NM, Azmani, S, et al. Association of Micro RNA and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a review. Mini Rev Med Chem. (2020) 20:1781–90. doi: 10.2174/1389557520666200621182717
32. Ko, JH, and Kim, SN. MicroRNA in acupuncture studies: does small RNA shed light on the biological mechanism of acupuncture? Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2019) 2019:3051472–8. doi: 10.1155/2019/3051472
Keywords: postoperative cognitive dysfunction, orthopedic procedures, hip replacement, inflammation, microRNA
Citation: Tu Q, Zhou R, Lv G, Wan Z, Chen S and Que B (2025) Effects of preemptive acupuncture on cognitive function of older patients after hip replacement: a randomized controlled trial. Front. Med. 12:1503727. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1503727
Edited by:
Pengxu Wei, Chinese Association of Rehabilitative Medicine, ChinaReviewed by:
Sandeep Bhushan, Chengdu Second People’s Hospital, ChinaZhenfeng Zhou, Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China
Chen Jiabao, Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital, China
Copyright © 2025 Tu, Zhou, Lv, Wan, Chen and Que. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Que, cXVlYmlucXFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Qiguo Tu1
Qiguo Tu1 Bin Que
Bin Que