- 1Department of Surgery, Dow University of Health Sciences, Karachi, Pakistan
- 2Dr. Ruth K. M. Pfau, Civil Hospital Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
- 3Mahatma Gandhi Mission Medical College and Hospital, Aurangabad, India
- 4Liaquat National Medical College, Karachi, Pakistan
Introduction: Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS), also known as Naegeli Syndrome, is a rare autosomal dominant ectodermal dysplasia characterized by mutations in the KRT14 gene. These mutations disrupt ectodermal tissue development, leading to diverse clinical manifestations involving the skin, nails, teeth, and sweat glands.
Methodology: A systematic search across PubMed, Google Scholar, European PMC, and Cochrane databases was conducted up to August 2023. Only case reports, case series, and original articles reporting cases were included.
Results: This review incorporated 6 case reports, 2 case series, 3 original articles, and 1 editorials, encompassing 33 individuals diagnosed with NFJS. Key clinical features included extensive reticulate hyperpigmentation, palmoplantar keratoderma, and dental anomalies. Rarely reported findings, such as cerebellar fissures and generalized osteopenia, were noted in two cases. Treatment predominantly focused on symptomatic management using topical emollients and antioxidants.
Conclusion: NFJS remains a diagnostic challenge due to its rarity and overlap with other pigmentary disorders. This review consolidates current knowledge to aid clinicians in recognizing and managing NFJS. Further research is needed to clarify its pathogenesis and explore targeted treatments.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=447267, identifier CRD42023447267.
1 Introduction
Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS), also recognized as Naegeli Syndrome, is a distinctive autosomal dominant disorder that arises from mutations in Keratin 14 (KRT14) gene, disrupting the normal development and differentiation of ectodermal tissues. This rare genetic condition presents a range of symptoms primarily affecting the skin, nails, teeth, and sweat glands. Notably, a defining feature of NFJS is adermatoglyphia or loss of fingerprints. This absence is a cardinal diagnostic criterion, distinguishing NFJS from other conditions (1, 2).
The clinical features of NFJS present challenges and insights into genetic anomalies (3). Reticulate hyperpigmentation, marked by patterned pigmented patches on the skin, is a key characteristic. This pigmentation, appearing on the neck, chest, and abdomen during early childhood (3 months to 6 years), often fades after puberty and may resolve entirely by age 60 to 80. Localized pigmentation around the eyes and mouth is also possible (1, 4).
Individuals with NFJS often experience palmoplantar keratoderma, causing thickened skin on the palms and soles, reduced sweating, and difficulty with temperature regulation, significantly impacting their quality of life (5). Dental anomalies, such as enamel irregularities, vary in severity among patients. Additional skin symptoms, including blistering and nail dystrophy, further highlight the syndrome’s diverse clinical spectrum (1).
The genetic basis of NFJS lies in mutations affecting genes crucial for the development and function of ectodermal tissues. Among these, heterozygous nonsense or frameshift mutations in the E1/V1-encoding region of the KRT14 gene have been identified as key contributors, resulting in haploinsufficiency for KRT14, a structural protein essential for epithelial integrity. Previous studies have pinpointed the locus for NFJS on chromosome 17q, specifically between markers D17S933 and D17S1789/D17S934, with a maximum logarithm of odds score (LOD) score of 2.7 at D17S800, further corroborating the role of KRT14 mutations (1, 2, 4, 6–9). These genetic insights advance our understanding of the disorder’s complexities, offering the potential for enhanced diagnostic precision and the development of targeted therapeutic interventions in the future (1, 2, 4, 6–9).
This review systematically synthesizes data from published case reports and case series to provide an in-depth overview of NFJS. By summarizing its clinical manifestations, genetic basis, and management strategies, this study aims to enhance clinical understanding of NFJS and identify gaps in the current literature, highlighting areas for future research.
2 Methodology
This systematic review fully comply with the preferred reporting items for the systematic review and meta-analysis (PRISMA) 2020 statement (10). The protocol has been given the identification number CRD42023447267 and is recorded on the website PROSPERO.
2.1 Search and selection
Our electronic search encompassed databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, European PMC, and Cochrane, spanning from their inception to August 2023. The search strategy employed MeSH terms and relevant keywords associated with “Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome.” Specifically, the search equation employed was “Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome OR NFJ Syndrome AND case reports AND case series.” To broaden our scope, we examined the references cited within the selected original articles, and we also conducted forward citation searches via the Web of Science to identify potentially relevant articles.
All articles were imported into Rayyan, and duplicates were systematically eliminated. Two authors (FA and ZH) independently evaluated the titles and abstracts of all retrieved articles, removing those that did not meet the predefined inclusion criteria. Full texts of the remaining articles were meticulously assessed against the established eligibility criteria. In cases of conflicts or discrepancies, discussions ensued, and a resolution was achieved through consultation with a third author (HS). The inclusion criteria encompassed case reports and case series written in English, targeting the general population affected by Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome. Study designs other than case reports and case series, as well as animal studies and articles in languages other than English, were excluded from consideration.
2.2 Data extraction
Two different researchers (FA. and ZH) carried out the process of data extraction on their own, and any discrepancies that arose were resolved by discussion with a third researcher (HS). The data collected from the eligible studies encompassed various aspects, including the primary author, publication year, journal title, study design, age and gender distribution of participants, inheritance pattern, the number of affected siblings or family members, laboratory findings, radiological observations, the onset of pigmentation changes, biopsy results, and the distribution of hyperpigmented and hypopigmented areas. The study’s primary outcomes were focused on genetic alterations, skin manifestations, hair abnormalities, nail characteristics, and dental anomalies. Additionally, secondary outcomes encompassed the fading of pigmentation, intellectual functioning, and lifestyle considerations.
2.3 Assessment of risk of bias
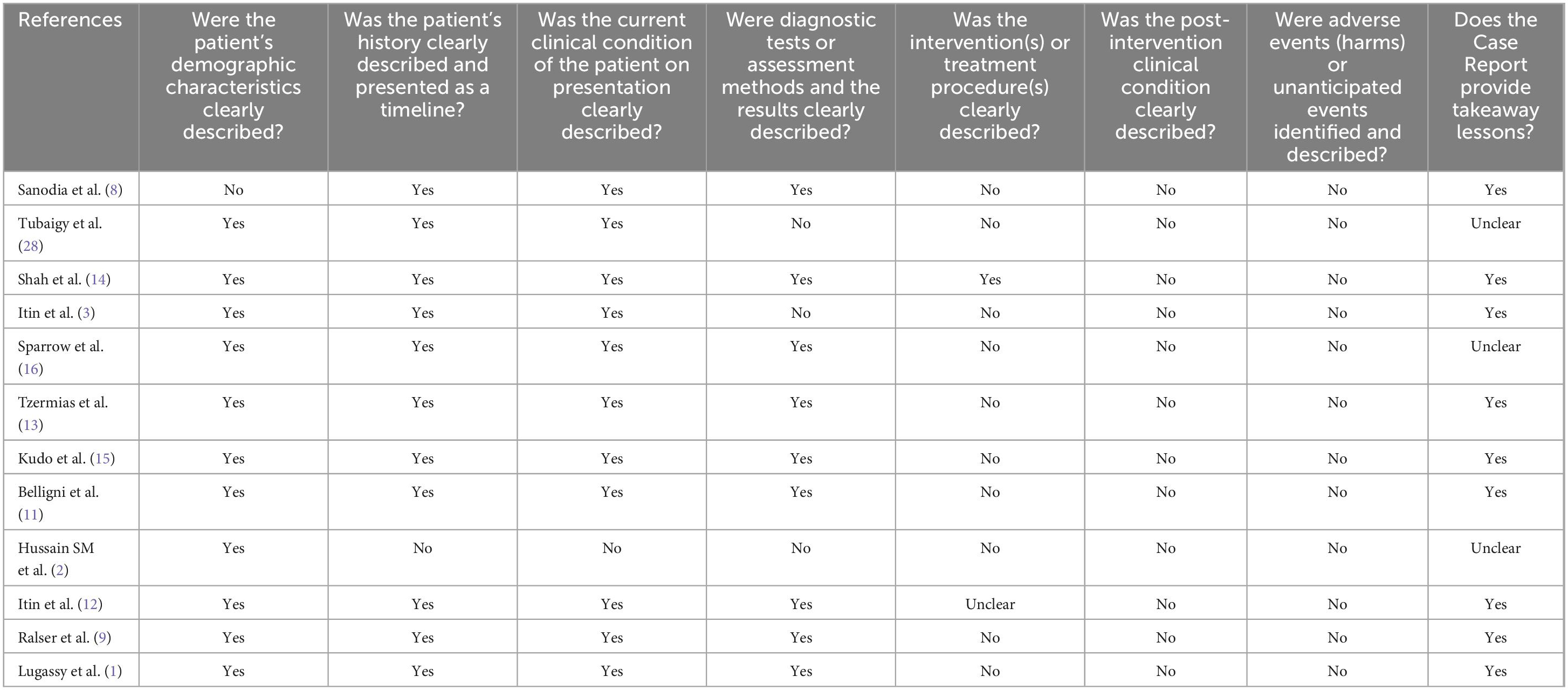
Using the JBI Checklist for Case Reports, two separate authors (FA and ZH) analyzed to determine the level of bias that existed among the studies that were included in the review. This checklist consists of eight distinct domains, each addressing specific aspects: (1) patient demographic characteristics, (2) patient history presented as a timeline, (3) current clinical condition on presentation, (4) description of diagnostic tests or assessment methods along with results, (5) clear depiction of interventions or treatment procedures, (6) description of post-intervention clinical condition, (7) identification and description of adverse events or (8) unanticipated occurrences, and provision of takeaway lessons. For each study, this tool was applied, and the presence of bias was categorized as yes, no, unclear, or not applicable, ultimately determining the level of bias risk as high, low, or with some concerns. Any inconsistencies that were discovered were discussed with a third author (HHS) to find a solution.
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
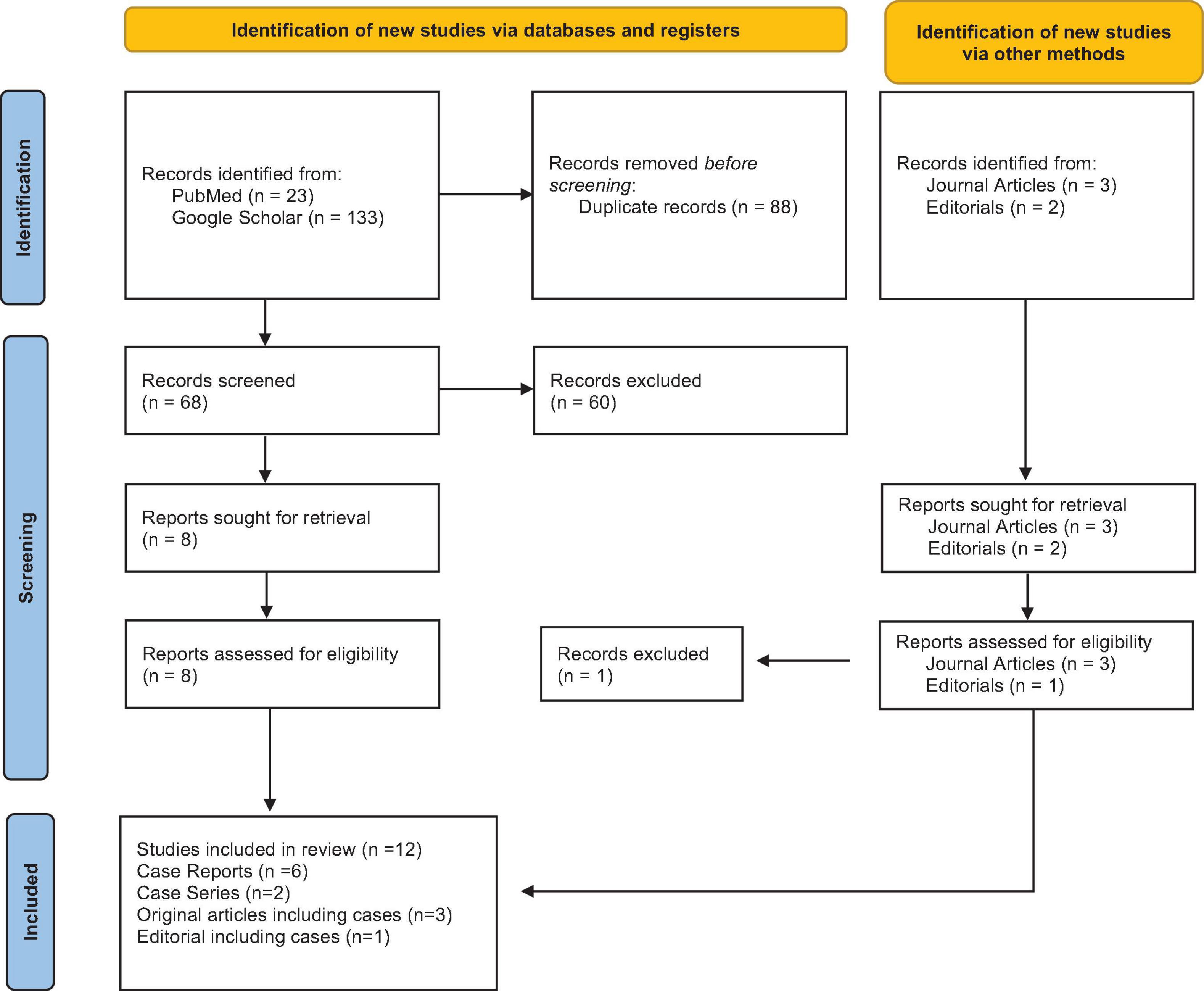
In our systematic review, the search method yielded 156 records, of which only 68 were retrieved after deleting 88 duplicate articles. After screening the title and abstract, we eliminated 61 records, leaving us with 8 for the full-text screening. Furthermore, 5 items were retrieved, including 3 journal articles and 2 editorials reporting on cases, and were thus included. Finally, the systematic review contained 13 papers, of which 6 were recognized as case reports, 2 as case series, 3 as original pieces reporting cases, and 1 as editorials reporting cases (Figure 1).
3.2 Patient characteristics
The features of the studies that were considered in this review can be seen in Table 1. The research consisted of a total of 33 individuals who had been diagnosed with NFJ syndrome. The review contained a total of 6 case reports, 2 case series, 3 original articles reporting cases, and 1 editorial reporting cases. A total of 33 patients were reviewed, including 18 females (54.5%) and 15 males (45.5%). The age of diagnosis ranged from 2 to 66 years. Most cases 90.0% (n = 30) exhibited autosomal dominant inheritance, while 3% (n = 1) showed autosomal recessive inheritance, and 6.9% (n = 2) had unspecified inheritance patterns. The age of NFJ syndrome diagnosis exhibited a broad range, spanning from the early onset at 2 years of age to a relatively late presentation at 66 years of age.
Onset of Pigmentation was primarily noted at around 2 years of age, although cases were documented with earlier onset as early as 18 months (11) and later onset as late as 65 years of age (12) in two individuals.
3.3 Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation of the NFJ syndrome prominently featured extensive reticulate hyperpigmentation affecting various regions of the body. 90.9% (n = 30) cases displayed pronounced hyperpigmentation notably around the neck, upper trunk, chest, flexural areas such as axillae, cruro-inguinal, antecubital, and popliteal regions, as well as the proximal extremities, and the groin.
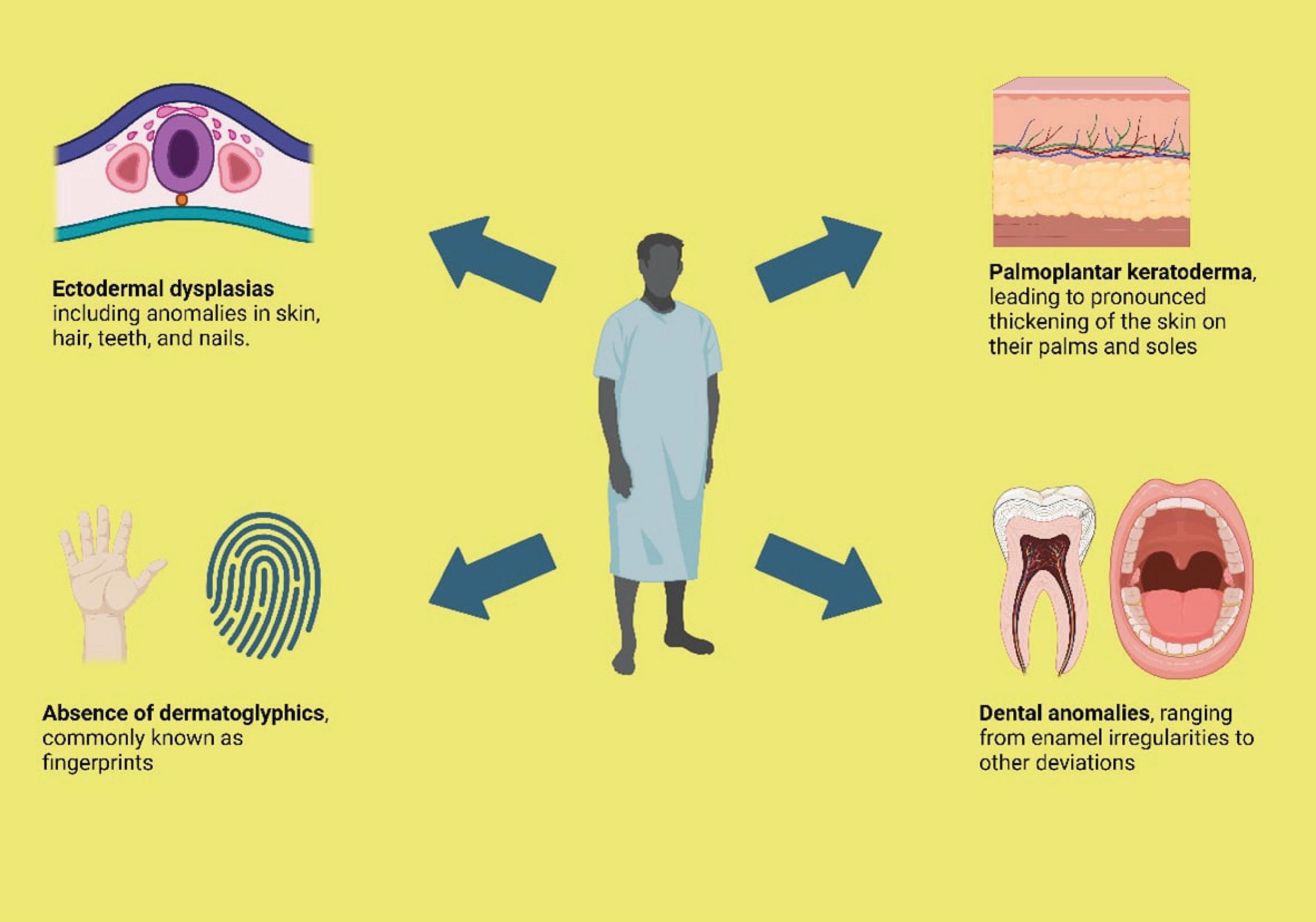
Additionally, reticulate hyperpigmentation was sporadically observed in the waist, lateral abdominal area in 12.1% patients (n = 4), and the dorsal aspect of the tongue (8) in 3% cases (n = 1). Moreover, the palmar and plantar surfaces, including periungual areas of fingers and toes, also exhibited this hyperpigmentation along with palmoplantar keratoderma. In one particular case (n = 1), the patient also manifested reticulate hyperpigmentation on the forehead, nose, and cheeks (11). Furthermore, a rare occurrence of hypopigmented macules was noted in one case (n = 1), primarily around the hyperpigmented lesions in the abdominal and flexural regions in one particular case (13). Figure 2 Illustrates the common clinical features of NFJ syndrome.
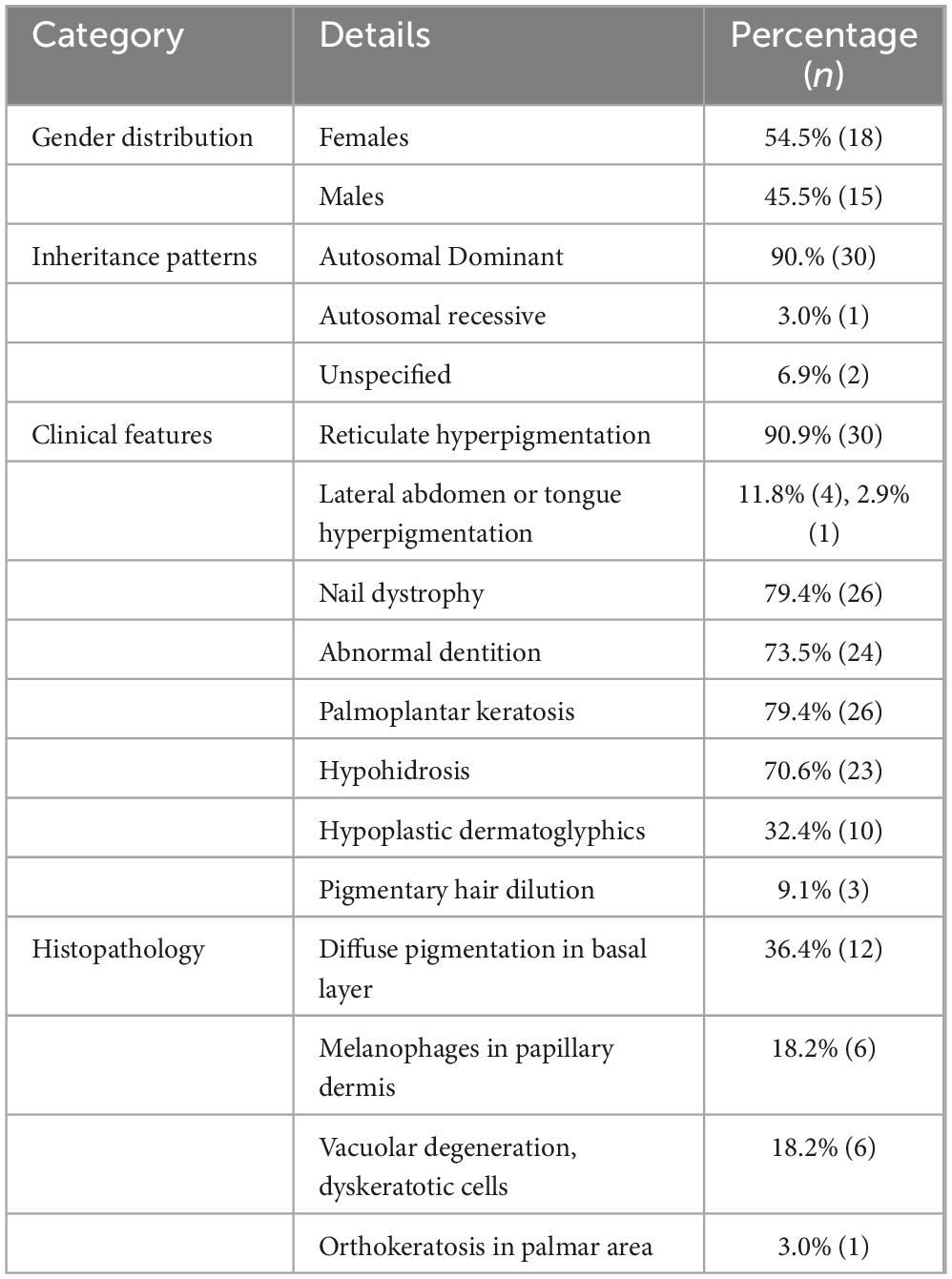
Teeth, nail and hair changes were also observed in the patients. Dystrophy, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis with slight yellowish hue of the nails was a prevalent clinical finding that affected patients (n = 27, 81.8%). Abnormal dentition including yellowish discoloration, abnormal dentition, and enamel defects were seen in patients (n = 25, 75.8%). Two cases reported poor anterior teeth representing bottle caries as well as impressive enamel defects requiring total prostheses at a young age (11, 12). Hair changes included mild pigmentary dilution with patchy brown discoloration (1, 3, 8, 11, 14). One of the cases in a case series reported sparse, thin hair which had turned silvery blond (11).
Concurrently with reticulate hyperpigmentation, 81.8% participants displayed palmoplantar keratosis (n = 27), 72% coupled with hypo hydrosis (n = 24). 32.4% of participants exhibited a hypoplastic dermatoglyphic pattern and adermatoglyphia (n = 11). Additionally, a small group of participants also displayed Pigmentary dilution of hair with brown patches (n = 3). Figure 2 shows common clinical features of NFJ syndrome.
3.4 Management
Currently, no established treatment protocols are available with regards to the NFJ syndrome. Management primarily focuses on addressing associated conditions. Most case reports and series included in this systematic review did not provide specific treatment details. However, a single case report described the management of NFJ Syndrome in which the patient was presented with extensive reticulate hyperpigmentation. The patient was counseled to avoid vigorous physical activity, maintain proper hydration, and was administered oral antioxidants and topical emollients to support skin health (14). In one case, laboratory results revealed elevated TSH levels, leading to the prescription of thyroxine for subclinical hypothyroidism (15).
3.5 Radiological findings
The majority of case series and case reports analyzed in this systematic review did not incorporate radiological findings. Only one case series contained radiological findings. Among the two cases within case series (11), the first case exhibited a brain MRI displaying prominence of cerebellar fissures and the fourth ventricle, with an otherwise normal brain anatomy. A skeletal survey and abdominal ultrasound yielded normal results. In the second case (11), a skeletal survey revealed generalized osteopenia, delayed bone age, and tapering of distal phalanges in the hands and feet.
3.6 Histopathology
Most of the case reports and case series mentioned histopathology. (n = 15) of patients had their biopsy specimens taken from the skin in the neck, trunk, thigh, calf, and palmar surfaces or directly from the hyperpigmented macule. In most of the case reports diffuse pigmentation and pigment incontinence in the basal layer were common (n = 12, 36.4% cases). Sanodia et al also reported a basket weave pattern of basal layer with diffuse pigmentation (8). Other case reports 18.2% (n = 6) demonstrated epidermal atrophy, vacuolar degeneration, edema, dyskeratotic cells, eosinophilic degenerating cells, and basal cell apoptosis (1, 8, 11, 14–16). Additionally, melanin-containing melanophores in the upper dermis were visible as well as melanophages in the papillary dermis of intensely hyperpigmented areas (1, 13–16). One case report also observed orthokeratosis in the palmar area (13). Only one case (3%) in a case series of two cases showed no abnormal histopathology (11).
The findings and percentages of cases reported are shown in Table 2.
3.7 Genetic changes
The majority of case reports included in our review discuss the genetic changes associated with NFJS syndrome. Among these cases, the most common mutation identified in NFJS syndrome affects the KRT14 gene, primarily in the non-helical E1/V1 domains of keratin 14 (2, 8, 12, 14). In one instance, a unique mutation was uncovered through PCR amplification and direct sequencing, revealing a homozygous one-base pair deletion in exon 4, labeled as c.827delC, along with a reduction in KRT14 mRNA levels (2). In separate investigations involving two case reports and one case series, genetic analysis indicated a normal 46, XX chromosomal composition without any chromosomal abnormalities or markers (11, 13, 15). Another noteworthy mutation in the KRT14 gene involved a c.54C > A substitution, resulting in a premature stop codon at position 18, as reported by Ralser et al. (9). Additionally, Lugassy et al. demonstrated a heterozygous single-nucleotide deletion at position 29 of the complementary DNA (cDNA) nucleotide sequence (1).
3.8 Quality assessment
To carry out a comprehensive analysis of the studies’ level of quality, the critical appraisal checklist for case reports developed by the Joanna Briggs Institute was utilized (17). This systematic review includes several studies, a major portion of which lacked information regarding therapy, management, post-interventional results, and post-interventional adverse events. The quality evaluation table for the studies that we included may be seen in Table 3.
4 Discussion
Our review aims to analyze and highlight the clinical manifestations and genetic basis of NFJ syndrome, offering insights to clinicians and researchers. As far as we know, this is the first systematic review of NFJ syndrome. This work consolidates existing knowledge while addressing gaps in understanding this rare condition. NFJ syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia affecting various body parts such as the skin, sweat glands, nails, hair, and teeth. The estimated incidence is one case in two to four million population. The syndrome is allelic to dermopatia pigmentosa reticularis (DPR) (18) (MIM125595).
The first description of the syndrome dates back to 1927 when Naegeli described a Swiss family consisting of a father and two daughters. Later on, in 1954, Franceschetti and Jadassohn reexamined the family, while Itin et al. (3) expanded the pedigree to include six generations with 14 affected individuals. Similarly, Sparrow et al. conducted a case series of seven patients with suspected NFJS syndrome and found that the findings were closely related to dyskeratosis congenita (DKC) which is commonly inherited as an X-linked recessive disorder, thus making it different from NFJS (14, 16).
NFJ syndrome shares overlapping features with other reticulate pigmentary disorders, such as DPR and DKC. However, NFJ is distinct in its fading pigmentation, absence of leukoplakia, and associated dental anomalies (19). According to Lugassy et al., both NFJ syndrome and DPR are allelic diseases resulting from dominant mutations in the KRT14 gene, located on chromosome 17q11.2–q21, which encodes keratin 14 (5). This gene is essential for the production of keratin 14, a protein that plays a critical role in the structure and function of the skin, hair, and sweat glands. Studies have identified heterozygous nonsense or frameshift mutations in KRT14 that segregate with the disease in affected families. These mutations are located in the non-helical head (E1/V1) domain of the keratin 14 protein, as opposed to mutations in the central α-helical rod domain, which are associated with epidermolysis bullosa simplex. NFJ syndrome and DPR are linked to mutations in the non-helical E1/V1 domains of KRT14 (5, 18). While both disorders share a common genetic origin, they present with distinct clinical manifestations. NFJ syndrome is characterized by epidermal hyperkeratosis and pigmentation changes, while DPR shows greater emphasis on diffuse keratoderma and palmoplantar abnormalities, with less involvement of the epidermal features seen in NFJ syndrome (5, 18). Furthermore, a deficiency in keratin 14 increases the likelihood of epidermal cells undergoing apoptosis. This loss of cells disrupts the normal development and structure of ectodermal tissues, leading to the skin and nail abnormalities that are hallmark features of NFJS/DPR (20, 21).
Our findings confirm that NFJ syndrome is linked to mutations in the KRT14 gene, particularly within the E1/V1-encoding region, generating a premature termination codon (PTC) close to the KRT14 translation initiation site (5). Those mutations result in a Keratin 14 haploinsufficiency, leading to increased epidermal cell susceptibility to tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-a) mediated apoptosis resulting in developmental anomalies such as enamel defects and early caries in teeth. The same mechanisms likely contribute to potential bone involvement, although further research is needed to elucidate this aspect fully (22). The pigmentation has a brown or gray-brown reticulate pattern, starting at about 2 years of age without a preceding inflammatory stage. It may fade after puberty and often disappears by about the age of 60. Pigmentation occurs primarily on the abdomen and around the eyes and mouth, with the neck, trunk, axillae, groins, and proximal extremities and flexures more variably involved. Some patients develop bullae on the feet during the newborn period (3).
Affected individuals may also display palmoplantar hyperkeratosis, brittle fingernails, and in some cases misalignment of the great toenails (23). Among the most distinctive characteristics of this syndrome is the complete absence of the patterned ridges on the skin of the hands and feet, called dermatoglyphics that are the basis for each person’s unique fingerprints (24, 25).
A significant difference between DPR and NFJS is that reticulate pigmentation lasts until adulthood, and there is alopecia and no dental abnormalities. Although these conditions have similar skin changes to DKC and Poikiloderma Clericuzio, differential diagnosis can be made based on factors such as leukoplakia and bone marrow dysfunction in DKC and features such as telangiectasias, generalized hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles, and nail pachyonychia in Poikiloderma Clericuzio type (11). Compared to reticulate hyperpigmentation, which may fade, hypohidrosis and palmoplantar keratoderma are enduring characteristics of NFJ syndrome. DKC can also have similarities with NFJS but encompasses additional features such as alopecia, mucosal leukoplakia, poikiloderma, and blood dyscrasias (14). Table 4 shows the Pigmentation patterns and clinical manifestations of Inherited Reticulate Pigmentary Disorders.
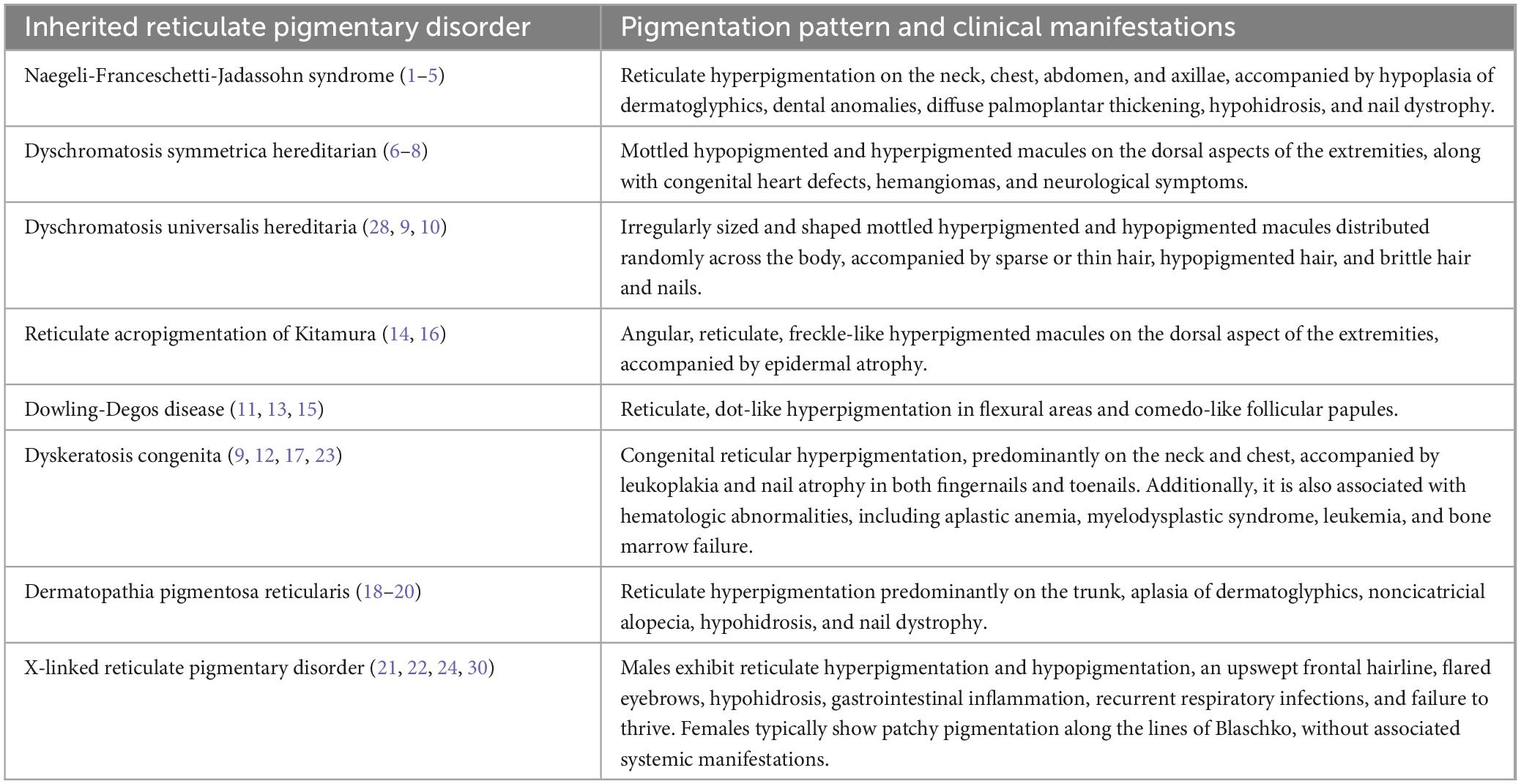
Table 4. Pigmentation patterns and clinical manifestations of Inherited Reticulate Pigmentary Disorders.
Currently, no established treatment protocols are available for the NFJ syndrome. Management primarily focuses on addressing associated conditions. Most case reports and series included in this systematic review did not provide specific treatment details. Oral health maintenance is essential to prevent premature dental caries. Notably, doxycycline has demonstrated potential in vitro by interfering with TNF-a–mediated signaling and apoptosis, potentially holding promise for future therapeutic applications (1). Individuals afflicted with NFJ syndrome are encouraged to avoid strenuous physical activities, given that hypohidrosis represents the most debilitating aspect and can culminate in post-exertional collapse (14).
It is imperative to explore other treatment options. For other reticulate pigmentary disorders such as reticulate acropigmentation of Kitamura and DDD, it was observed that 20% azelaic acid ointment showed improvement in one patient following treatment after several weeks. For DSH, surgical therapy with transplantation of thin split-thickness skin autografts has been tried, whereas the keratoderma associated to DPR has been successfully treated with etretinate (26).
The current lack of pharmaceutical interventions and clinical trials in this domain underscores the existence of a significant research gap, underscoring the potential for future investigative studies. Although NFJS is a rare autosomal dominant ailment with an estimated incidence of one case in two to four million individuals, and currently shows no racial predilection (3, 14), it is crucial to recognize the significant impact on the quality of life of patients affected by this condition, primarily due to the noticeable dermatological manifestations and the associated challenges. In this context, serious consideration should be given to genetic testing and genetic counseling regarding NFJ Syndrome and a precise clinical diagnosis must be reached between the various types of reticular pigmentary disorders, especially for those families with an intense desire for future pregnancies.
5 Conclusion
NFJ Syndrome is a rare diagnosis that affects the skin, nails, teeth, and sweat glands. Our paper aims to provide insights into the clinical features, genetic mutations, and management of this condition. The information presented in this review could be useful for physicians in clinical practice to understand the clinical presentation and features of NFJ Syndrome.
6 Limitations and strengths
Our study presents the first systematic review summarizing the available clinical literature on NFJ Syndrome through case reports and case series. We have provided a comprehensive overview of published data, with a robust quality appraisal of the included studies. However, this systematic review has its limitations. Due to the limited literature on NFJ Syndrome, only case reports and case series were included, which may have introduced potential bias. Additionally, the absence of follow-up data in most cases hindered the evaluation of primary and secondary outcomes, limiting our ability to assess long-term clinical progression and management effectiveness.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Methodology. TH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RQ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. FA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RW: Writing – review and editing. MH: Writing – review and editing. MZ: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lugassy J, McGrath J, Itin P, Shemer R, Verbov J, Murphy H, et al. KRT14 haploinsufficiency results in increased susceptibility of keratinocytes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis and causes Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome. J Invest Dermatol. (2008) 128:1517–24. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5701187
2. Hussain S, Ahmed S. Identity dilemma: Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome. J Rawalpindi Med Coll. (2012) 16:200–1.
3. Itin P, Lautenschlager S, Meyer R, Mevorah B, Rufli T. Natural history of the Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome and further delineation of its clinical manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. (1993) 28:942–50. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70135-g
4. Sprecher E, Itin P, Whittock N, McGrath J, Meyer R, DiGiovanna J, et al. Refined mapping of Naegeli-Franceschetti- Jadassohn syndrome to a 6 cM interval on chromosome 17q11.2-q21 and investigation of candidate genes. J Invest Dermatol. (2002) 119:692–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.01855.x
5. Lugassy J, Itin P, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Holland K, Huson S, Geiger D, et al. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome and dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis: Two allelic ectodermal dysplasias caused by dominant mutations in KRT14. Am J Hum Genet. (2006) 79:724–30. doi: 10.1086/507792
6. Itin P, Fistarol S. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. (2004) 131C:45–51. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30033
7. Zhang J, Li M, Yao Z. Updated review of genetic reticulate pigmentary disorders. Br J Dermatol. (2017) 177:945–59. doi: 10.1111/bjd.15575
8. Sanodia G, Hulmani M, Kumar V. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome: A rare reticulate pigmentary disorder. Indian J Dermatol. (2019) 64:235–8. doi: 10.4103/ijd.IJD_653_16
9. Ralser D, Kumar S, Borisov O, Sarig O, Richard G, Wolf S, et al. Identification of a founder mutation in KRT14 associated with Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome. Br J Dermatol. (2020) 183:756–7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19123
10. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. (2021) 88:105906.
11. Belligni E, Dokal I, Hennekam R. Prenatal and postnatal growth retardation, microcephaly, developmental delay, and pigmentation abnormalities: Naegeli syndrome, dyskeratosis congenita, poikiloderma Clericuzio type, or separate entity? Eur J Med Genet. (2011) 54:231–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2011.01.001
12. Itin P, Burger B. Spontaneous fading of reticular pigmentation in Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome. Dermatology. (2010) 221:135–6. doi: 10.1159/000314693
13. Tzermias C, Zioga A, Hatzis I. Reticular pigmented genodermatosis with milia–a special form of Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome or a new entity? Clin Exp Dermatol. (1995) 20:331–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1995.tb01336.x
14. Shah B, Jagati A, Gupta N, Dhamale S. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome: A rare case. Indian Dermatol Online J. (2015) 6:403–6. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.169712
15. Kudo Y, Fujiwara S, Takayasu S, Ooki H, Ogawa A. Reticulate pigmentary dermatosis associated with hypohydrosis and short stature: A variant of Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome? Int J Dermatol. (1995) 34:30–1. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1995.tb04373.x
16. Sparrow G, Samman P, Wells R. Hyperpigmentation and hypohidrosis. (The Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome): Report of a family and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. (1976) 1:127–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1976.tb01408.x
17. Gagnier J, Kienle G, Altman D, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D, et al. The CARE guidelines: Consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. Headache J Head Face Pain. (2013) 53:1541–7.
18. Itin P, Lautenschlager S. Genodermatosis with reticulate, patchy and mottled pigmentation of the neck–A clue to rare dermatologic disorders. Dermatology. (1998) 197:281–90. doi: 10.1159/000018015
19. Schnur R, Heymann W. Reticulate hyperpigmentation. Semin Cutan Med Surg. (1997) 16:72–80. doi: 10.1016/s1085-5629(97)80038-7
20. Hesse M, Zimek A, Weber K, Magin T. Comprehensive analysis of keratin gene clusters in humans and rodents. Eur J Cell Biol. (2004) 83:19–26. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00354
21. Irvine A. Inherited defects in keratins. Clin Dermatol. (2005) 23:6–14. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2004.09.014
22. Chang M. Disorders of hyperpigmentation. 3rd ed. In: J Bolognia, J Jorizzo, J Schaffer eds Dermatology. Atlanta: Elsever Saunders (2012). 1066.
23. Whittock N, Coleman C, Mclean W, Ashton G, Acland K, Eady R, et al. The gene for Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome maps to 17q21. J Invest Dermatol. (2000) 115:694–8.
24. Babler W. Embryologic development of epidermal ridges and their configurations. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. (1991) 27:95–112.
25. Baird H. Kindred showing congenital absence of the dermal ridges (fingerprints) and associated anomalies. J Pediatr. (1964) 64:621–31. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80610-7
26. Sardana K, Goel K, Chugh S. Reticulate pigmentary disorders. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. (2013) 79:17–29. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.104665
27. Tubaigy S, Hassan H. Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome in a Saudi Arabian family. J Forensic Sci. (2014) 59:555–8. doi: 10.1111/1556-4029.12316
Keywords: Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome, NFJS, dermatological disorders, clinical presentation, systematic review
Citation: Shah HH, Hussain T, Subash A, Qadir RA, Meshram YR, Shahzad M, Sultan W, Hadi Z, Ashfaque F, Anas Z, Rauf SA, Waseem R, Hussain MS and Zuberi MAW (2025) Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome: a systematic review of case studies. Front. Med. 12:1453172. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1453172
Received: 22 June 2024; Accepted: 31 January 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Robert Gniadecki, University of Alberta, CanadaReviewed by:
Maurizio Romagnuolo, IRCCS Ca’ Granda Foundation Maggiore Policlinico Hospital, ItalyHiram Almeida Jr, Federal University of Pelotas, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Shah, Hussain, Subash, Qadir, Meshram, Shahzad, Sultan, Hadi, Ashfaque, Anas, Rauf, Waseem, Hussain and Zuberi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sameer Abdul Rauf, c2FtZWVycmF1ZjgwQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Hussain Haider Shah, orcid.org/0000-0002-8032-7462; Maryam Shahzad, orcid.org/0009-0002-3565-8358; Sameer Abdul Rauf, orcid.org/0009-0009-4776-9064
 Hussain Haider Shah
Hussain Haider Shah Tooba Hussain1
Tooba Hussain1 Arun Subash
Arun Subash Maryam Shahzad
Maryam Shahzad Sameer Abdul Rauf
Sameer Abdul Rauf Radeyah Waseem
Radeyah Waseem Muhammad Sheheryar Hussain
Muhammad Sheheryar Hussain Muhammad Abdul Wasay Zuberi
Muhammad Abdul Wasay Zuberi