- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, WuJin Hospital Affiliated with Jiangsu University, WuJin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China
- 2Rehabilitation Department, WuJin Hospital Affiliated with Jiangsu University, WuJin Clinical College of Xuzhou Medical University, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China
Background: Asthma is a serious respiratory disease attributed to multiple factors. The Life’s Essential 8 (LE8), introduced by the American Heart Association, aims to improve and maintain cardiovascular health. However, the correlation between LE8 components and asthma remains unclear. We hypothesized that LE8 is a protective factor against asthma.
Materials and methods: Multiple logistic regression analysis, restricted cubic spline (RCS) analysis, and subgroup analysis were used to analyze the data collected from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2001 to 2018.
Results: A total of 3,360 participants with asthma were included in the analysis. With all confounders controlled for, LE8 scores were negatively correlated with asthma prevalence (odds ratio (OR) per 10-point increment, 0.85 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.82–0.88]). Compared to low LE8 scores, moderate and high LE8 scores were associated with reduced asthma risk, with adjusted ORs (95% CIs) of 0.59 (0.51–0.68) and 0.48 (0.39–0.58), respectively. Non-linear correlations were observed between LE8 scores and asthma (p non-linear = 0.01) and between health factor scores and asthma (p non-linear = 0.01). However, a linear dose–response correlation was noted between health behavior scores and asthma (p non-linear = 0.30). Subgroup analysis showed no significant interaction effects (p > 0.05), except in the sex and drinking status subgroups (p for interaction = 0.02).
Conclusion: Asthma is associated with components of LE8, which warrants further attention and may contribute to reducing asthma prevalence.
Introduction
As one of the most rapidly growing diseases, asthma affects 300 million patients worldwide and causes approximately 2.5 million fatalities annually (1, 2). An American study reported an increase of $3,266 in annual medical costs for one patient, and the estimated cost for treatment of asthma is more than $80 billion annually (3). Moreover, severe asthma can have a serious negative impact on an individual’s life, physical activity, and work. Hence, asthma takes a tremendous burden on individuals and societies, amplifying the challenges for prevention.
The roles of environmental factors, hereditary factors, comorbidity, and social behaviors are all related to the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of asthma (4). Mounting research has indicated there is an interconnected association between cardiovascular disease (CVD) and asthma (5). The risk of CVD in asthma patients is 42% higher than that in non-asthma individuals (6). A meta-analysis study revealed that the risk of the failure of heart function, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, and diseases of coronary arteries increases in asthma patients (7, 8). There are multiple common risk factors for asthma and CVD, including obesity, smoking, environmental exposure, physical inactivity, and stress (7). Furthermore, chronic inflammation is the common pathogenesis for asthma and CVD (5, 9). Therefore, improving cardiovascular health (CVH) may be helpful in asthma prevention.
In 2022, the American Heart Association introduced Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) as a new indicator for monitoring cardiovascular health to replace Life’s Simple 7 (10). LE8 comprises four health behaviors, including diet, sleep health, physical activity, and nicotine exposure, and four health factors, including body mass index (BMI), blood lipids, blood glucose, and blood pressure (11). Although previous studies have investigated the association between asthma and some components of LE8, the overall effect on asthma is not clear. This cross-sectional study aims to explore our hypothesis that LE8 can reduce asthma incidence.
Materials and methods
Study design and participants
The study was conducted using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which is a cross-sectional survey with stratification and a multi-stage probability sampling design (12). The study was performed with approval from the National Center for Health Statistics Research Ethics Review Board, and the written informed consents were signed by all participants (13). All the databases can be accessed from the NHANES website.1
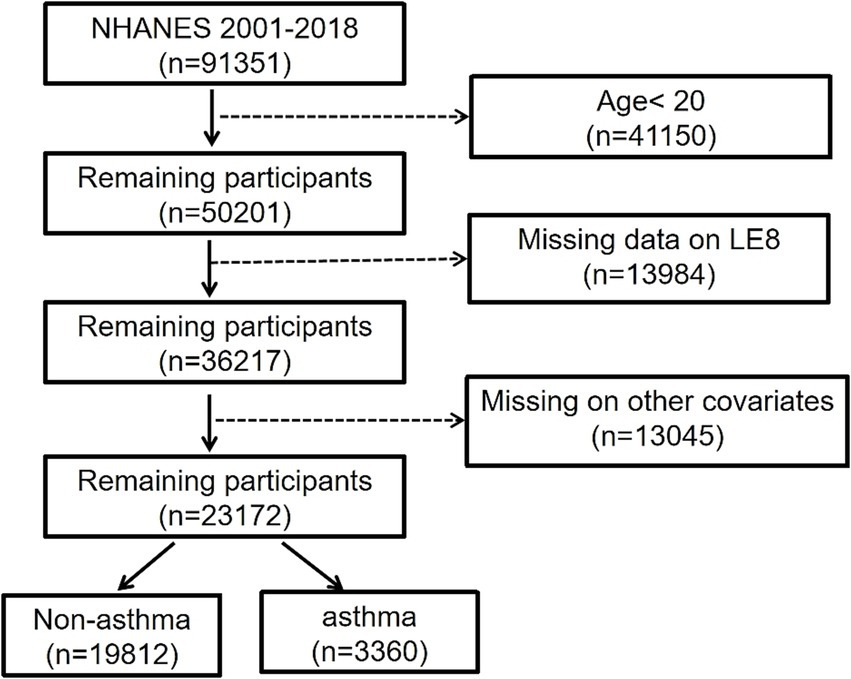
In total, 91,351 participants from the NHANES during 2001–2018 were first screened. These participants fitting the following criteria were then excluded: < 20 years of age (n = 41,150), no LE8 data (n = 13,984), and no other covariates (n = 13,045). Ultimately, 23,172 participants were enrolled, including 3,360 individuals with asthma confirmed by a certificated specialist and 19,812 individuals without asthma (Figure 1).
Data and definitions in the NHANES
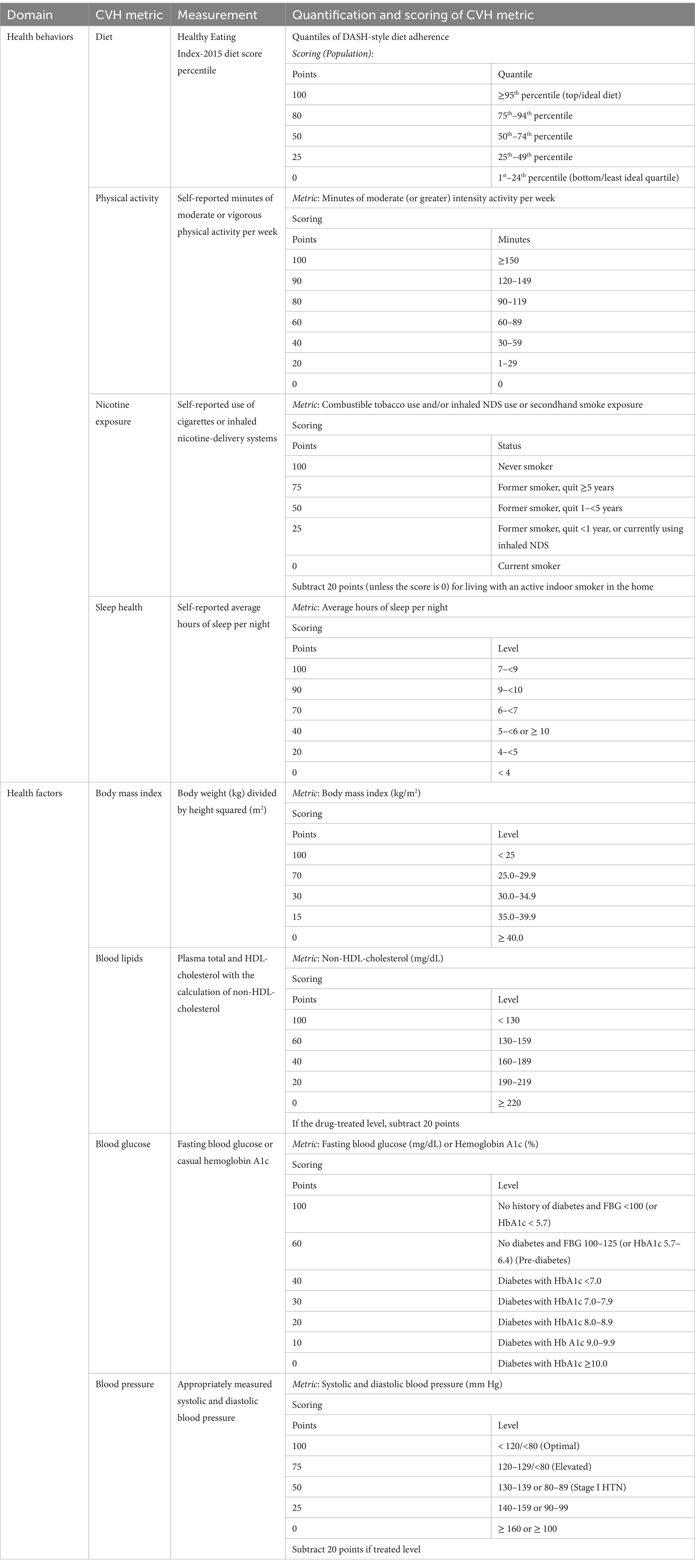
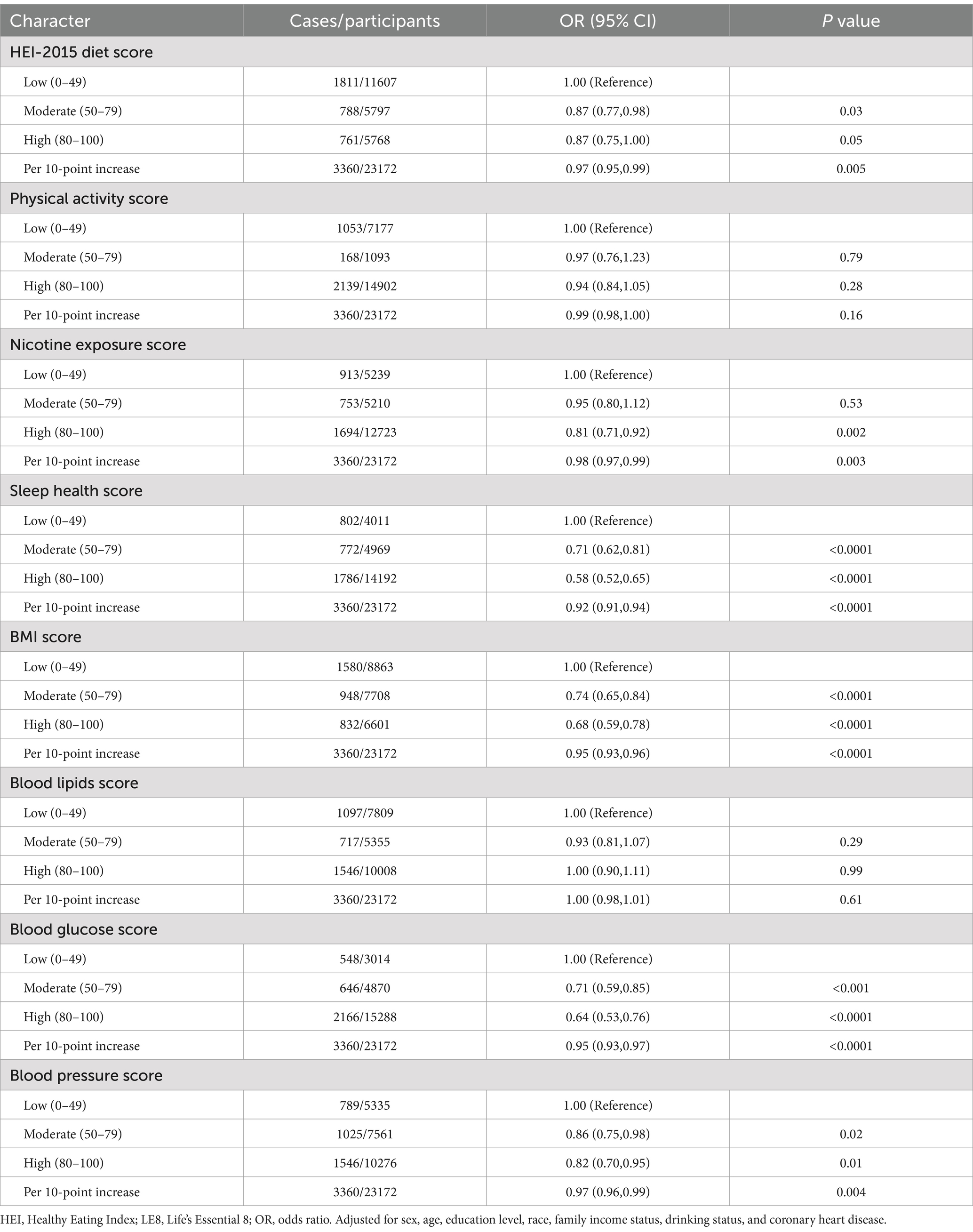
If the participant answered “Yes” to the question “Ever been told you have asthma?” in the questionnaire (MCQ010), the participant was identified as an asthma individual (14). The eight components of LE8 (11) were investigated according to a previous study (15). Dietary data were calculated using the Healthy Eating Index (HEI)-2015, with the first 24-h recall interview (16). The self-administered paper questionnaires collected the sleep duration, nicotine exposure, and physical activity. Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL) and blood glucose in fasting status were obtained from the laboratory, while blood pressure, height, and body weight were obtained from the mobile examination center. According to the presidential advisory published by the American Heart Association, each metric had an algorithm range of 0–100 points, allowing the generation of LE8 scores. As the unweighted mean of the eight components, LE8 scores were calculated from 0 to 100 points and assigned to different levels of CVH, i.e., 0–49 points too low CVH, 50–79 points to moderate CVH, and 80–100 points to high CVH (17). The detailed scoring methods of LE8 are shown in Table 1, and if all eight components of LE8 were shown as “NA,” the data was excluded. The covariates in the study, which were referred to in the previous asthmatic surveys, included sex (male/female), age (years), level of education, race, family income status, smoking status (never, former, now), drinking status (never, former, mild, moderate, heavy) and coronary heart disease status (yes or no) (18, 19). Age was grouped as 20–39, 40–59, and ≥ 60 years. Family income level was classified as low (PIR ≤ 1.3), moderate (1.3 < PIR < 3.5), and high (PIR ≥ 3.5) (20). Smoking status was classified as never smoker (< 100 cigarettes in a lifetime), former smoker (≥100 cigarettes in history but 0 currently), or current smoker (≥100 cigarettes in history and regular smoking currently) (21). There were five drinking statuses: never (<12 drinks total); former (≥12 drinks 1 year ago); mild (one drink for women and two drinks for men per day); moderate (≥2 drinks for females and ≥ 3 drinks for males per day, or 2 ≤ binge drinking <5 per month); heavy drinker (≥3 drinks for females and ≥ 4 drinks for males per day; or binge drinking ≥4 drinks for females and ≥ 5 drinks for males on the same occasion) (22, 23). BMI was classified as under/normal weight with BMI < 25, overweight with 25 ≤ BMI < 30, and obese with BMI ≥ 30 (24). Coronary heart diseases were defined when participants answered YES to “Ever told you had” of the respective conditions.
Statistical methods
Considering NHANES sampling weights, the data were analyzed by R (version 4.3.2). First, the baselines of the participants were evaluated by univariate analysis. The categorical data were expressed as percentages (%) for statistical analysis with a weighted Chi-square test, while continuous variables were analyzed by weighted t-test and shown as the mean ± errors (SE). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the associations between LE8 groups and asthma, represented by odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). There were three statistical models: the univariate model (no adjustment of covariates), Model I (with adjustment of education level, age, sex, race, and family income status), and Model II (with adjustment of all covariates). Next, whether non-linear relationships existed between LE8 and asthma was investigated by restricted cubic spline (RCS) analyses. 4 knots were selected to balance the smoothness of the curve and avoid the loss of accuracy caused by overfitting. Finally, subgroup analysis was performed to determine the interaction between the stratified factors and LE8 scores. A two-tailed p-value of <0.05 was considered the statistical significance level.
Results
Characteristics of participants
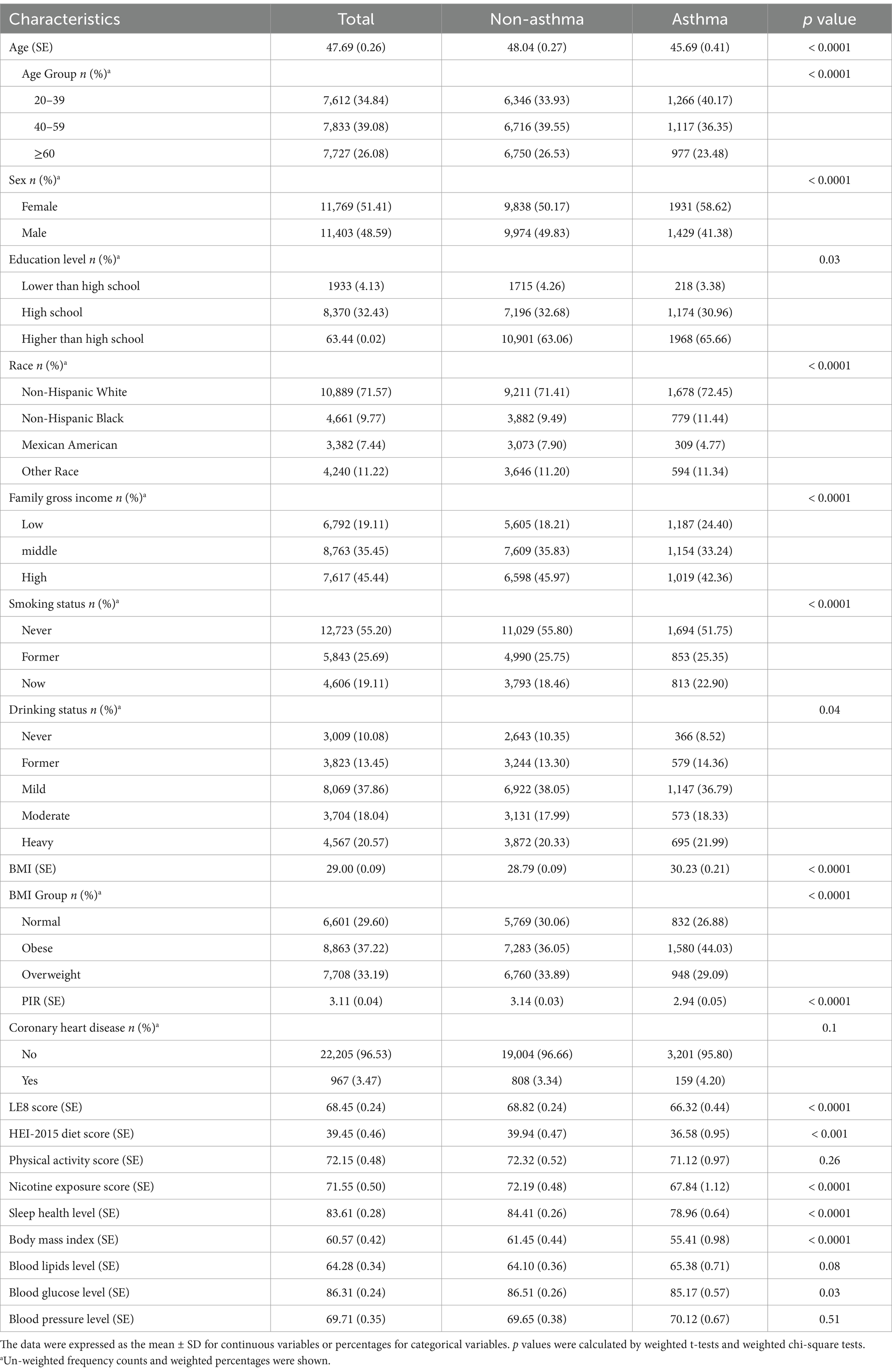
There were 23,172 participants from the NHANES during 2001–2018 who were finally enrolled in this study, including 3,360 asthma patients. The age, sex, education level, race, poverty income ratio, smoking status, drinking status, BMI, LE8 score, HEI-2015 diet, nicotine exposure condition, sleep health, body mass index, and blood glucose level in the asthma group were significantly different from the non-asthma group (p < 0.05), while coronary heart disease, physical activity level, blood lipids score and blood pressure level were not statistically different between the two groups (p > 0.05) (Table 2).
LE8 score and asthma
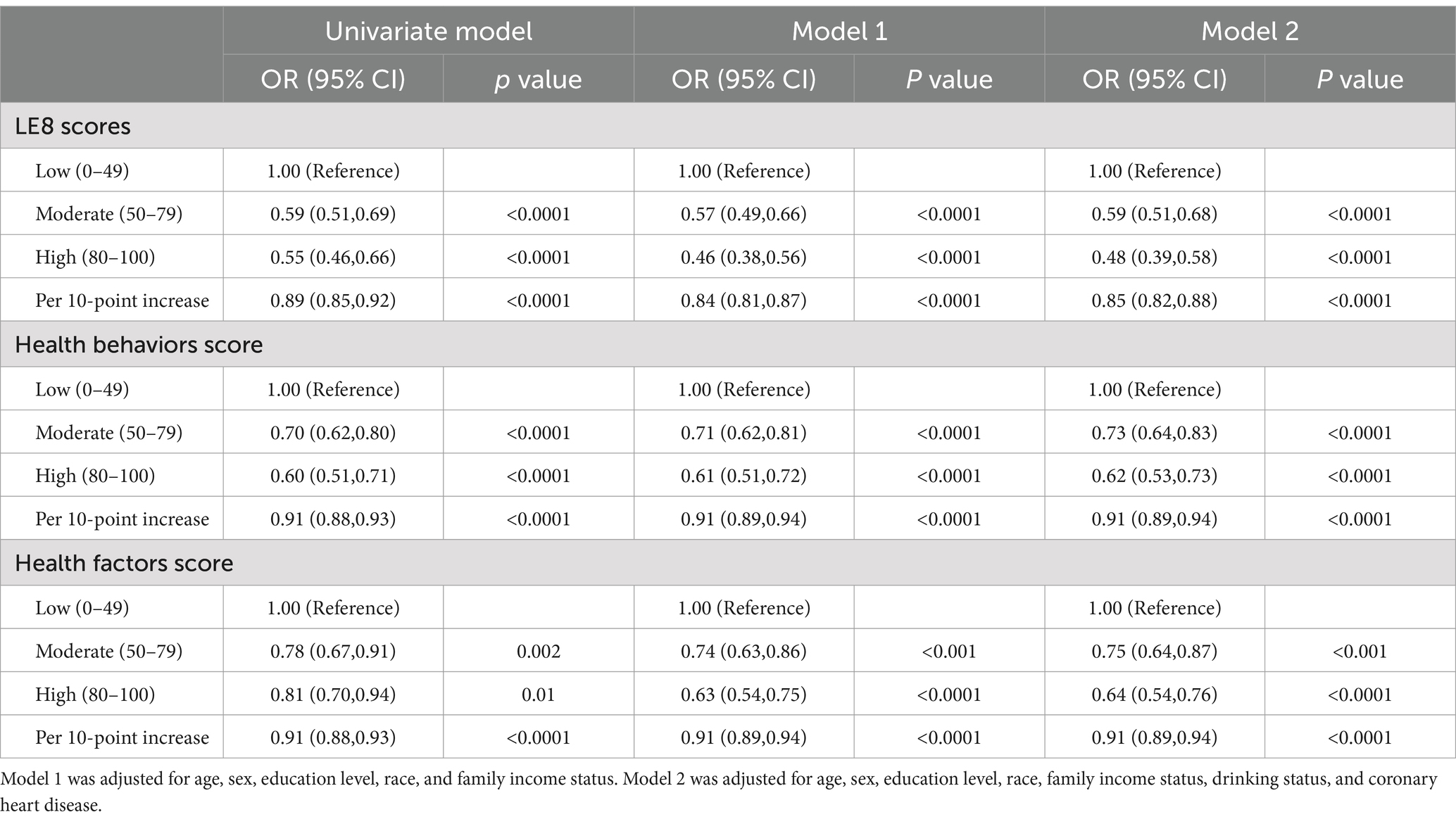
The univariate analysis model indicated that asthma is significantly correlated with the LE8 score, with ORs of 0.59 (95% CI 0.51, 0.69) for the moderate LE8 group and 0.55 (95% CI 0.46, 0.66) for the high LE8 group compared to the low LE8 group. Additionally, for each 10-point increase in the L38 score, the OR was 0.89 (95% CI 0.85, 0.92).
After adjustment using multivariate analysis model 1, the ORs for asthma were 0.57 (95% CI 0.49, 0.66) in the moderate LE8 group and 0.46 (95% CI 0.38, 0.56) in the high LE8 group compared to the low LE8 group, while the OR for each 10-point increase in the LE8 score was 0.84 (95% CI 0.81, 0.87). When all covariates were adjusted using multivariate analysis model 2, the ORs were 0.59 (95% CI 0.51, 0.68) for the moderate LE8 group and 0.48 (95% CI 0.39, 0.58) for the high LE8 group, with an OR of 0.85 (95% CI 0.82, 0.88) for each 10-point increase in the LE8 score, compared to the low LE8 group (Table 3). A non-linear association was observed between the LE8 score and asthma (p for non-linearity = 0.01, Figure 2).
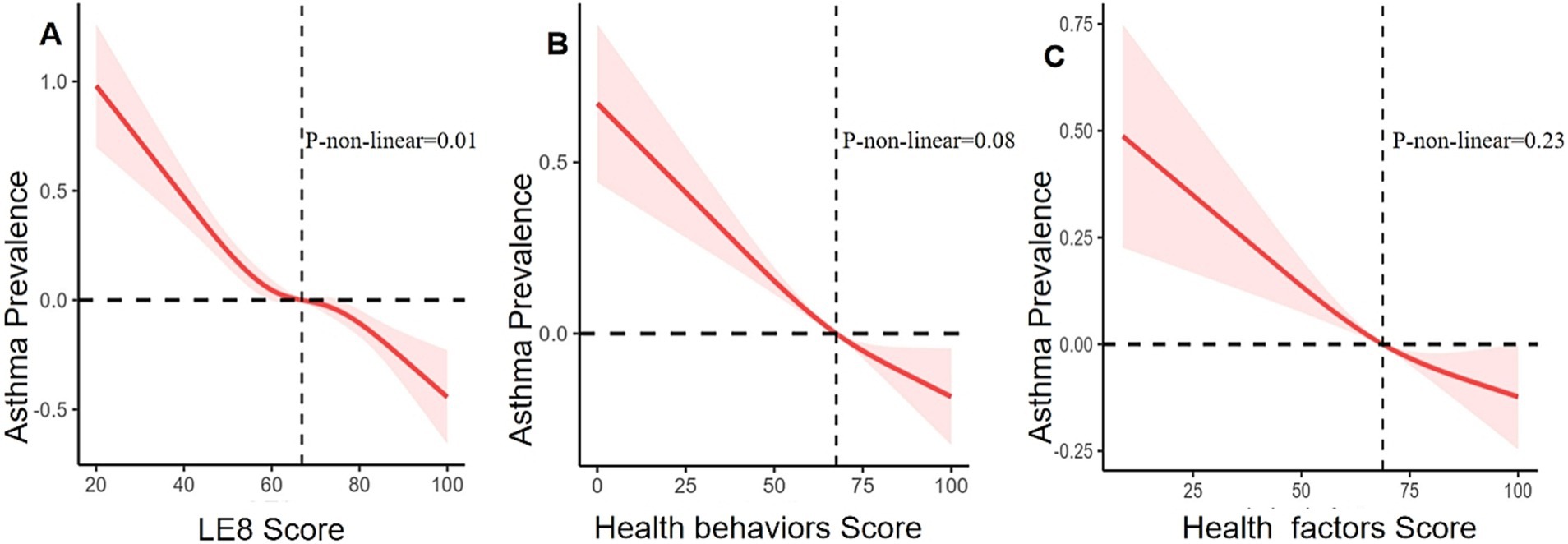
Figure 2. Relationships between asthma prevalence and LE8 score (A), health behaviors score (B), and health factors score (C). ORs (solid lines) and 95% CIs (shaded areas) were adjusted for sex, age, education level, race, family income status, drinking status, and coronary heart disease.
Health behavior scores and asthma
The univariate analysis model indicated that asthma is significantly correlated with the health behavior score, with ORs of 0.70 (95% CI 0.62, 0.80) in the moderate health behavior group and 0.60 (95% CI 0.51, 0.71) in the high health behavior group, compared to the low health behavior group. Additionally, for each 10-point increase in the health behavior score, the OR was 0.91 (95% CI 0.88, 0.93).
After adjustment using multivariate analysis model 1, the ORs for asthma were 0.71 (95% CI 0.62, 0.81) in the moderate health behavior group and 0.61 (95% CI 0.51, 0.72) in the high health behavior group, compared to the low health behavior group. For each 10-point increase in the health behavior score, the OR was 0.91 (95% CI 0.89, 0.94).
In multivariate analysis model 2, the ORs for asthma were 0.73 (95% CI 0.64, 0.83) in the moderate behavior group and 0.62 (95% CI 0.53, 0.73) in the high health behavior group, compared to the low health behavior group. The OR for each 10-point increase in the health behavior score was 0.91 (95% CI 0.89, 0.94) (Table 3). However, health behavior scores and asthma did not show a non-linear association (p = 0.08, Figure 2).
Health factors scores and asthma
The univariate analysis model indicated that asthma is significantly correlated with the health factor score, with ORs of 0.78 (95% CI 0.67, 0.91) in the moderate health factor group and 0.81 (95% CI 0.70, 0.94) in the high health factor group, compared to the low health factor group. Additionally, for each 10-point increase in the health factor score, the OR was 0.91 (95% CI 0.88, 0.93).
After adjustment using multivariate analysis model 1, the ORs for asthma were 0.74 (95% CI 0.63, 0.86) in the group with moderate health factor and 0.63 (95% CI 0.54, 0.75) in the group with high health factor, compared to the low health factor group. For each 10-point increase in the health score, the OR was 0.91 (95% CI 0.89, 0.94).
After full adjustment with multivariate analysis model 2, the ORs for asthma were 0.75 (95% CI 0.64, 0.87) in the group with moderate health factors and 0.64 (95% CI 0.54, 0.76) in the group with high health factors, while the OR for each 10-point increase in health factor scores was 0.91 (95% CI 0.89, 0.94), compared to the group with low health factors (Table 3). There was no linear association between health factor scores and asthma (non-linear p = 0.23, Figure 2).
Components of LE8 and asthma
In a fully adjusted model, asthma showed significantly negative associations with sleep health levels and blood glucose levels (Table 4). The risk of asthma was significantly lower in the group with moderate sleep health level (6–7 average hours of sleep per night) and the group with high sleep health level (7–10 average hours of sleep per night) when compared with the group with low sleep health level (<6 or ≥ 10 average hours of sleep per night). The OR for asthma in a per-10-point increase of sleep health level was 0.92 (95% CI, 0.91–0.94). Additionally, the risk of asthma was significantly lower in the group with moderate blood glucose levels (no diabetes, fasting blood glucose 100–125 [or glycosylated hemoglobin 5.7–6.4]) and the group with high blood glucose levels (no history of diabetes, fasting blood glucose <100 [or glycosylated hemoglobin <5.7]), compared with the group with low blood glucose levels (people with diabetes). The OR for asthma in a 10-point increase of blood glucose level was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.93–0.97).
Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analysis with stratification of sex, age, education level, race, family gross income, drinking status, and coronary heart disease was performed. Complications such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), which were shown in Table 1, have been included in LE8 components and assumed as parts of variables. Hence, we did not explore their interaction effects on LE8 components. The negative association between LE8 scores and asthma remained consistent in different categories, including age group, race, education level, family gross income, and coronary heart disease, but without significant interaction (p for interaction >0.05). However, LE8 scores and sex and drinking status with asthma demonstrated significant interactions (p for interaction = 0.02) (Figure 3).
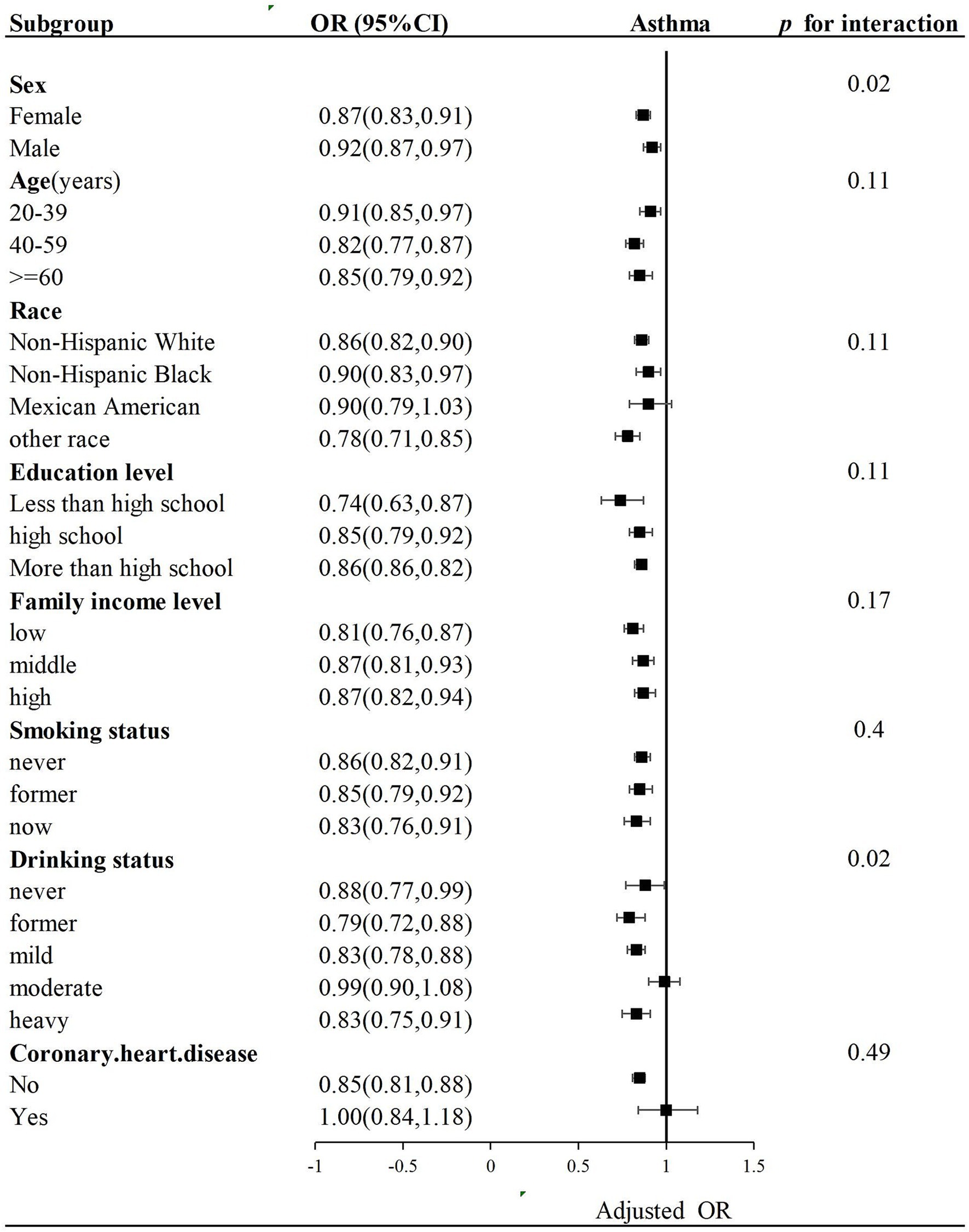
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis of the association of LE8 scores and asthma. OR was calculated as per a 10-point increase in LE8 score. Each stratification was adjusted for sex, age, education level, race, family income status, drinking status, and coronary heart disease.
Discussion
Asthma is a major non-communicable respiratory disease that affected 262 million people and killed 455,000 patients in 2019 (25). This disease imposes a tremendous burden on individuals, public health systems, society, and the economy. Therefore, early prevention and effective management of asthma are critical and important tasks. The results of the present study suggest that LE8 is a comprehensive and easy-to-use tool to evaluate the risk of asthma, demonstrating that higher LE8 scores are associated with a lower incidence of asthma. Our study also proposes that maintaining optimal CVH could help reduce the onset of asthma and should be promoted as a strategy for the timely identification and management of asthma. In addition, LE8 scores could facilitate interdisciplinary cooperation, enabling a comprehensive assessment and optimal interventions for patients.
There has been an increase in the incidence of asthma over the past few decades, especially in developed Western countries (26). More and more studies have demonstrated that many lifestyles and factors may be related to asthma, and changing these factors could reduce asthma attacks. A high-fiber diet could decrease asthma prevalence, especially for women and specific racial groups (27). The offspring of women taking pregnant vitamin D have 40–50% less wheezing than babies without vitamin D during pregnancy (28, 29). In the Chinese population, short night sleep duration is reported to increase the number of asthma incidents (30). Very short sleep (<6 h) is found to be associated with more persistent asthma (31). Approximately 50% of adults having asthma are current or former smokers, and they have a 25-fold asthma incidence compared to non-smokers (32).
Furthermore, smoking is found to be associated with worse clinical outcomes of asthma (33). Physical activity is proposed to improve asthma control and health-related life quality and reduce incident asthma (34, 35). Obesity and asthma often coexist in the same person. Individuals who are obese have a 50% incidence of asthma (36). In addition, obesity can increase the prevalence of asthma and/or make asthma control difficult. Some comorbidities of obesity, i.e., type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, breathing disorder related to sleeping, or hypertension, can deteriorate asthma (37). A positive association is proved between asthma and type 1 diabetes (OR, 1.15; 95%CI, 1.06–1.25), and children with asthma tend to have higher triglyceride levels and higher insulin resistance (38, 39). Abnormal lipid metabolism is present in asthma, which is correlated with the severity and IgE levels (40). These studies indicated that asthma is a kind of disease attributed to multiple factors, including diet, sleep duration, smoking, physical activity, obesity, diabetes, dyslipidemia, et al., which can contribute to the susceptibility of asthma. However, the combined effect of all the factors in LE8 on asthma has not been comprehensively investigated.
The former CVH assessment tool Life’s Simple 7 has been applied in assessing non-communicable chronic diseases (NCDs). Based on health factors and health behaviors, the new CVH indicator LE8 reflects self-rated health and health-related quality of life. A high LE8 score shows a beneficial impact on chronic disorders, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, atherosclerotic CVD, chronic kidney disease, stroke, and dementia (41–46). In the UK Biobank, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease accounts for 40.0% of the top 10 NCDs in low-moderate CVH (<80 points) (47). A prospective cohort study suggested that low asthma-PRS (polygenic risk score) and high CVH have a minimal risk of adult-onset asthma (0.28, 95% CI: 0.23, 0.34) (48). Using NHANES data from the U.S., we investigated the dose–response association between LE8 and asthma, and the results indicated that higher LE8 scores, health behavior scores, and health factor scores demonstrated a significant association with a lower risk of asthma.
Meanwhile, higher sleep health scores and blood glucose levels demonstrated a significant association with a lower risk of asthma. These results indicated that addressing sleep difficulties and controlling glucose may benefit asthma patients. Blood lipids include triglycerides, phospholipids, glycolipids, sterols, and steroids, essential substances for living cells’ basic metabolism. While blood lipids in LE8 only include non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), this contradicts previous research. Compared to healthy patients, asthma patients spend less time doing moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and do very few daily steps (49). Participating in physical activity will increase the fear of provoking asthma symptoms, and those with serious asthma are prone to avoiding exercise (50, 51). In our study, only 13% (437) of 3,360 asthma patients had moderate and high physical activity scores, demonstrating that asthma patients lack enough physical activity. Besides, there are only a few limited forms of physical activity and greater heterogeneity in NHANES, such as daily, leisure time, and sedentary activities. At last, the physical activity score came from the physical activity questionnaire present with recall bias. There are sex-related differences in asthma (52). The prevalence of female asthma is 20% higher compared with male asthma. Moreover, asthma symptom attacks are more frequent and more common in women than in men (53–55).
In our previous study, a higher OBS had a stronger antioxidant exposure. OBS was negatively associated with female asthma, which meant reducing pro-oxidant factors simultaneously, such as smoking, drinking, and obesity, could reduce the prevalence of female asthma (18). Improving the LE8 score would likely significantly reduce the incidence of female asthma. A nonfunctional ALDH2 was found in 50% of Asians. Approximately half of Japanese asthma patients had asthma exacerbation after drinking alcohol, which was referred to as alcohol-induced asthma resulting from the increase of histamine plasma concentrations. Shimoda et al. investigated 55% of asthma patients, reduced 20% of forced expiratory volume in 1 s, and increased blood acetaldehyde and plasma histamine levels (55). However, in non-Asians, alcohol has also been proven to have a therapeutic effect on asthma. Alcohol may reduce the sensitivity of the airways, and chronic alcohol consumption may inhibit asthmatic immunity over time (56). Hence, the relationship between LE8 and asthma will be affected by alcohol for its effect on asthma attacks and alleviation of asthmatic symptoms. Overall, LE8 scores and asthma demonstrated stronger negative associations in middle-aged, other races, and no coronary heart disease populations.
The present study used a cross-sectional method to investigate the association between LE8 and asthma with representative data of American adults from the NHANES. We believe that LE8 is a risk for asthma onset, and improving LE8 scores would be good for asthma. However, some limitations in the present study should be pointed out. First, causal relationships cannot be identified in this cross-sectional study. The second limitation is that the definitions of most LE8 components are based on questionnaires, which would have a certain extent of recall bias. Another limitation was that the results were from the American asthma population, and there may be population and regional differences.
Conclusion
LE8 scores and health factors demonstrated a negative, non-linear correlation with the prevalence of asthma, whereas health behavior scores were negatively and linearly associated with asthma. Notably, the investigation highlighted the importance of optimal sleep duration and normal glucose levels. These findings suggest that LE8, as a practical and comprehensive health indicator, may be useful for the early identification of asthma risk and for minimizing the burden of asthma. However, the causal relationship between LE8 and asthma requires further investigation, and the precise mechanisms linking LE8 to asthma remain to be clarified.
Future directions
Overall, LE8 may be a simple and comprehensive tool for preventing asthma. The eight components of LE8, including diet, sleep health, physical activity, nicotine exposure, BMI, blood lipids, blood glucose, and blood pressure, can be obtained from clinical practice and simple questionnaires. More large-scale prospective clinical programs and randomized controlled studies can be conducted to comprehensively address the interactions between LE8 and asthma.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the National Center for Health Statistics Research Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JX: Writing – original draft. JT: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Medical Science and Laboratory Medicine Open Project (No. JSKLM-Y-2024-006).
Acknowledgments
We thank NHANES participants and staff.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BMI, Body mass index; CVD, Cardiovascular disease; CVH, Cardiovascular health; CI, Confidence intervals; HEI, Healthy Eating Index; LE8, Life’s Essential 8; NCDs, Non-communicable chronic diseases; OR, Odds ratio; PIR, Poverty income ratio.
Footnotes
References
1. Papi, A, Brightling, C, Pedersen, SE, and Reddel, HK. Asthma. Lancet. (2018) 391:783–800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33311-1
2. Collaborators, GCRD. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. (2017) 5:691–706. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30293-X
3. Nurmagambetov, T, Kuwahara, R, and Garbe, P. The economic burden of asthma in the United States, 2008-2013. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2018) 15:348–56. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201703-259OC
4. Stern, J, Pier, J, and Litonjua, AA. Asthma epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Immunopathol. (2020) 42:5–15. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00785-1
5. Adrish, M, and Hanania, NA. Asthma and cardiovascular disease: a bidirectional association? Respirology. (2023) 28:217–9. doi: 10.1111/resp.14468
6. Hekking, PP, Amelink, M, Wener, RR, Bouvy, ML, and Bel, EH. Comorbidities in difficult-to-control asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2018) 6:108–13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.06.008
7. Hua, ML, Li, L, and Diao, LL. Bronchial asthma, and risk of 4 specific cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular mortality: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2022) 26:5081–91. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202207_29294
8. Liu, H, Fu, Y, and Wang, K. Asthma and risk of coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of cohort studies. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. (2017) 118:689–95. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.03.012
9. Tattersall, MC, Guo, M, Korcarz, CE, Gepner, AD, Kaufman, JD, Liu, KJ, et al. Asthma predicts cardiovascular disease events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:1520–5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.305452
10. Lloyd-Jones, DM, Allen, NB, Anderson, C, Black, T, Brewer, LC, Foraker, RE, et al. Life's essential 8: updating and enhancing the American Heart Association's construct of cardiovascular health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 146:e18–43. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078
11. Herraiz-Adillo, Á, Ahlqvist, VH, Daka, B, Wångdahl, J, Wennberg, P, Carlsson, J, et al. Life’s essential 8 in relation to self-rated health and health-related quality of life in a large population-based sample: the SCAPIS project. Qual Life Res. (2024) 33:1003–14. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03580-1
12. Christensen, K, Gleason, CE, and Mares, JA. Dietary carotenoids and cognitive function among US adults, NHANES 2011–2014. Nutr Neurosci. (2018) 23:554–62. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2018.1533199
13. Du, YZ, Guo, B, Hu, HJ, Dong, QX, Li, YH, Zhang, J, et al. Association between kidney stones and life's essential 8: a population-based study. World J Urol. (2024) 42:274. doi: 10.1007/s00345-024-04994-3
14. Odebeatu, CC, Taylor, T, Fleming, LE, and Osborne, N. Phthalates and asthma in children and adults: US NHANES 2007-2012. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2019) 26:28256–69. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06003-2
15. Ren, Y, Cai, Z, Guo, C, Zhang, Y, Xu, H, Liu, L, et al. Associations between Life’s essential 8 and chronic kidney disease. J Am Heart Assoc. (2023) 12:e030564. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.030564
16. Krebs-Smith, SM, Pannucci, TE, Subar, AF, Kirkpatrick, SI, Lerman, JL, Tooze, JA, et al. Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2015. J Acad Nutr Diet. (2018) 118:1591–602. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2018.05.021
17. Lloyd-Jones, DM, Ning, H, Labarthe, D, Brewer, L, Sharma, G, Rosamond, W, et al. Status of cardiovascular health in US adults and children using the American Heart Association's new "Life's essential 8" metrics: prevalence estimates from the National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES), 2013 through 2018. Circulation. (2022) 146:822–35. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060911
18. Qi, X, Zhou, T, and Tang, J. Correlations between oxidative balance score and female asthma among U.S. adults. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:22451. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73533-2
19. Cheng, W, Bu, X, Xu, C, Wen, G, Kong, F, Pan, H, et al. Higher systemic immune-inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index levels are associated with stroke prevalence in the asthmatic population: a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 1999-2018. Front. Immunol. (2023) 14:1191130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1191130
20. Liu, Q, Han, X, Chen, Y, Gao, Y, Yang, W, and Huang, L. Asthma prevalence is increased in patients with high metabolism scores for visceral fat: study reports from the US. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:14. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1162158
21. McClave, AK, Dube, SR, Strine, TW, and Mokdad, AH. Associations between health-related quality of life and smoking status among a large sample of U.S. adults. Prev Med. (2009) 48:173–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2008.11.012
22. Hicks, CW, Wang, D, Matsushita, K, Windham, BG, and Selvin, E. Peripheral neuropathy and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in U.S. Adults Annals Internal Med. (2021) 174:167–74. doi: 10.7326/m20-1340
23. Rattan, P, Penrice, DD, Ahn, JC, Ferrer, A, Patnaik, M, Shah, VH, et al. Inverse association of telomere length with liver disease and mortality in the US population. Hepatol Commun. (2021) 6:399–410. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1803
24. Caballero, B. Humans against Obesity: Who Will Win? Adv Nutr. (2019) 10:S4–9. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy055
25. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396:1204–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9
26. Holgate, ST, Wenzel, S, Postma, DS, Weiss, ST, Renz, H, and Sly, PD. Asthma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:15025. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.25
27. Saeed, MA, Gribben, KC, Alam, M, Lyden, ER, Hanson, CK, and LeVan, TD. Association of dietary fiber on asthma, respiratory symptoms, and inflammation in the adult national health and nutrition examination survey population. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2020) 17:1062–8. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201910-776OC
28. Devereux, G, Litonjua, AA, Turner, SW, Craig, LC, McNeill, G, Martindale, S, et al. Maternal vitamin D intake during pregnancy and early childhood wheezing. Am J Clin Nutr. (2007) 85:853–9. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/85.3.853
29. Camargo, CA Jr, Rifas-Shiman, SL, Litonjua, AA, Rich-Edwards, JW, Weiss, ST, Gold, DR, et al. Maternal intake of vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of recurrent wheeze in children at 3 y of age. Am J Clin Nutr. (2007) 85:788–95. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/85.3.788
30. Hu, Z, Tian, Y, Song, X, Hu, K, and Yang, A. Associations between incident asthma with comorbidity profiles, night sleep duration, and napping duration trajectories: a 7-year prospective study. Int J Public Health. (2022) 67:1604939. doi: 10.3389/ijph.2022.1604939
31. Teodorescu, M, Polomis, DA, Gangnon, RE, Consens, FB, Chervin, RD, and Teodorescu, MC. Sleep duration, asthma and obesity. J Asthma. (2013) 50:945–53. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2013.831871
32. Aanerud, M, Carsin, A-E, Sunyer, J, Dratva, J, Gislason, T, Jarvis, D, et al. Interaction between asthma and smoking increases the risk of adult airway obstruction. Eur Respir J. (2015) 45:635–43. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00055514
33. Thomson, NC. Asthma and smoking-induced airway disease without spirometric COPD. Eur Respir J. (2017) 49:1602061. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02061-2016
34. McLoughlin, RF, Clark, VL, Urroz, PD, Gibson, PG, and McDonald, VM. Increasing physical activity in severe asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. (2022) 60:2200546. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00546-2022
35. Fisher, JE, Loft, S, Ulrik, CS, Raaschou-Nielsen, O, Hertel, O, Tjønneland, A, et al. Physical activity, air pollution, and the risk of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 194:855–65. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201510-2036OC
36. Beuther, DA, and Sutherland, ER. Overweight, obesity, and incident asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2007) 175:661–6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200611-1717OC
37. Shore, SA. Obesity and asthma: possible mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2008) 121:1087–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.03.004
38. Zeng, R, Wang, Z, Zhang, J, Liang, Z, Xu, C, Wang, J, et al. Type 1 diabetes and asthma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Endocrine. (2022) 75:709–17. doi: 10.1007/s12020-021-02973-x
39. Perez, MK, and Piedimonte, G. Metabolic asthma: is there a link between obesity, diabetes, and asthma? Immunol Allergy Clin N Am. (2014) 34:777–84. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2014.07.002
40. Jiang, T, Dai, L, Li, P, Zhao, J, Wang, X, An, L, et al. Lipid metabolism and identification of biomarkers in asthma by lipidomic analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. (2021) 1866:158853. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158853
41. Zhang, N, Wei, Z, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Q, Chen, Z, Tse, G, et al. Association of Life's essential 8 with incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in cancer patients: the Kailuan prospective cohort study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. (2023) 30:e78–80. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwad256
42. Zhang, J, Chen, G, Xia, H, Wang, X, Wang, C, Cai, M, et al. Associations of Life's essential 8 and fine particulate matter pollution with the incidence of atrial fibrillation. J Hazard Mater. (2023) 459:132114. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132114
43. Wu, S, Wu, Z, Yu, D, Chen, S, Wang, A, Wang, A, et al. Life's essential 8 and risk of stroke: a prospective community based study. Stroke. (2023) 54:2369–79. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.123.042525
44. Isiozor, NM, Laukkanen, JA, Voutilainen, A, Bensenor, IM, and Kunutsor, SK. Life's essential 8 is associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease but not venous thromboembolism in men: a prospective cohort study. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2233894. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2233894
45. Petermann-Rocha, F, Deo, S, Lyall, D, Orkaby, AR, Quinn, TJ, Sattar, N, et al. Association between the AHA Life's essential 8 score and incident all-cause dementia: a prospective cohort study from UK biobank. Curr Probl Cardiol. (2023) 48:101934. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101934
46. Tang, R, Wang, X, Li, X, Ma, H, Liang, Z, Heianza, Y, et al. Adherence to life's essential 8 and incident chronic kidney disease: a prospective study of 147, 988 UK biobank participants. Am J Clin Nutr. (2023) 118:804–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.08.007
47. Yu, Y, Sun, Y, Yu, Y, Wang, Y, Chen, C, Tan, X, et al. Life's essential 8 and risk of non-communicable chronic diseases: outcome-wide analyses. Chin Med J. (2023) 137:1553–62. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002830
48. Zhang, H, Chang, Q, Yang, H, Yu, H, Chen, L, Zhao, Y, et al. Life's essential 8, genetic predisposition, and risk of incident adult-onset asthma: a prospective cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. (2024) 119:100–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.11.009
49. Cordova-Rivera, L, Gibson, PG, Gardiner, PA, Powell, H, and McDonald, VM. Physical activity and exercise capacity in severe asthma: key clinical associations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 6:814–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2017.09.022
50. Aggarwal, B, Mulgirigama, A, and Berend, N. Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction: prevalence, pathophysiology, patient impact, diagnosis and management. NPJ Prim Care Respir Med. (2018) 28:31. doi: 10.1038/s41533-018-0098-2
51. Parsons, JP, Craig, TJ, Stoloff, SW, Hayden, ML, Ostrom, NK, Eid, NS, et al. Impact of exercise-related respiratory symptoms in adults with asthma: exercise-induced bronchospasm landmark National Survey. Allergy Asthma Proc. (2011) 32:431–7. doi: 10.2500/aap.2011.32.3501
52. Jenkins, CR, Boulet, LP, Lavoie, KL, Raherison-Semjen, C, and Singh, D. Personalized treatment of asthma: the importance of sex and gender differences. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2022) 10:963–971.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.02.002
53. Leynaert, B, Sunyer, J, Garcia-Esteban, R, Svanes, C, Jarvis, D, Cerveri, I, et al. Gender differences in prevalence, diagnosis and incidence of allergic and non-allergic asthma: a population-based cohort. Thorax. (2012) 67:625–31. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201249
54. Borges, RC, Alith, MB, Nascimento, OA, and Jardim, JR. Gender differences in the perception of asthma respiratory symptoms in five Latin American countries. J Asthma. (2022) 59:1030–40. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2021.1922914
55. Shimoda, T, Obase, Y, Matsuse, H, Asai, S, and Iwanaga, T. The pathogenesis of alcohol-induced airflow limitation in acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2-deficient mice. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. (2016) 171:276–84. doi: 10.1159/000452709
Keywords: Life’s Essential 8, asthma, health behaviors score, health factors score, odd ratios
Citation: Xu J and Tang J (2025) Associations between asthma and Life’s Essential 8: a cross-sectional study. Front. Med. 12:1446900. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1446900
Edited by:
Dawei Yang, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Alexandru Corlateanu, Nicolae Testemiţanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy, MoldovaYuquan Chen, Monash University, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Xu and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianlei Tang, dGFuZ2ppYW5sZWlAd2pybXl5LmNu
 Jiao Xu1
Jiao Xu1 Jianlei Tang
Jianlei Tang