- 1Department of General Surgery, The First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical School of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 3School of Nursing, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 4Gansu Province Key Laboratory of Biological Therapy and Regenerative Medicine Transformation, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
- 5Evidence-Based Medicine Centre, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, Gansu, China
Introduction: Health education is an important part of nursing care. Verbal health education is a common practice in surgical wards, which is time-consuming and laborious. Thus, this study aims to evaluate whether multimedia health education reduces nurses’ workload without compromising patient and family satisfaction in a surgical context.
Methods: We conducted a parallel-group, prospective randomized controlled trial at the Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute of Lanzhou University’s First Hospital between July 2019 and May 2022. Eligible patients (≥18 years) with general surgical conditions and acceptable for surgery were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive a multi-media health education group or a standard health education group. Randomization was performed by an independent statistician using a computer-generated randomization list. The nurses’ workload and satisfaction were the main outcomes; the anxiety level of patients and the variables affecting nurse workload were the secondary outcomes.
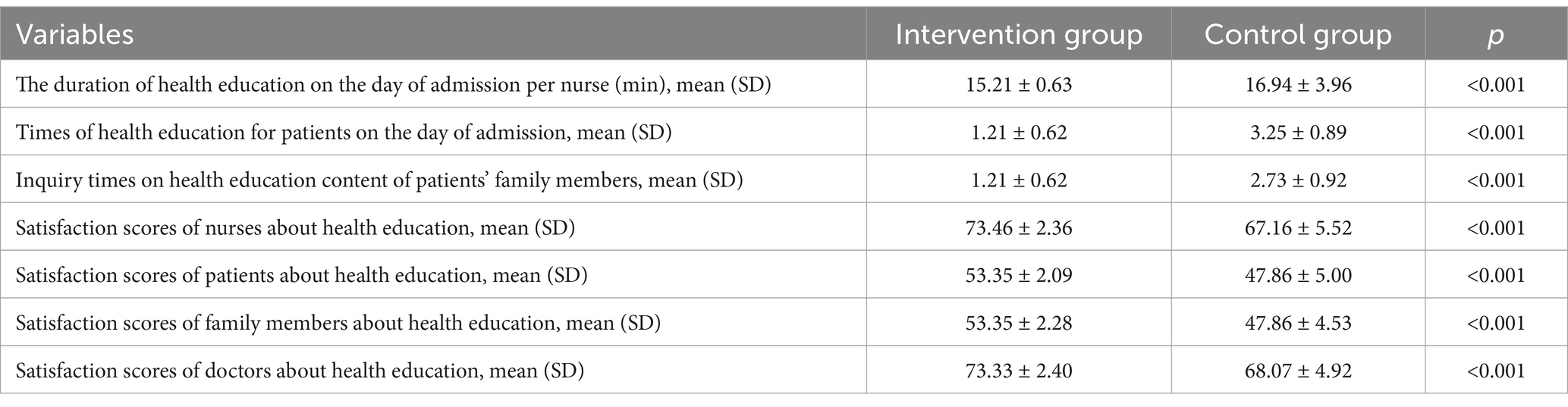
Results: A total of 184 eligible participants were randomly assigned to receive multimedia health education and standard health education. The results showed that multimedia health education can shorten the time [15.21 (0.63)vs.16.94 (3.96)] nurses spend on health education during patient admissions, the difference being statistically significant (p < 0.001), but it did not lower the satisfaction levels of nurses [73.46 (2.36) vs. 67.16 (5.52)], patients [53.35 (2.09) vs. 47.86 (5.00)], their families [53.35 (2.28) vs. 47.86 (4.53)] and doctors [73.33 (2.40) vs. 68.07 (4.92)] regarding health education (p < 0.001); in fact, it increased their satisfaction.
Conclusion: Multi-media health education could reduce nurses’ workload and enhance patient satisfaction but not increase complications.
Clinical trial registration: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/, identifier [NCT03989401].
Introduction
Health education has become one of the most important aspects of nursing care. Nurses need to possess a wealth of medical knowledge to effectively execute health education while also fostering patient cooperation for treatment and care. Various studies (1, 2) have shown that surgical procedures often cause severe physical and mental stress to patients. This is the reason why many medical experts and clinical psychologists all over the world are interested in health education for perioperative patients (3). The fear, anxiety, and pain that patients experience during surgery, as well as other complications brought on by surgical trauma, can be significantly reduced by high-quality health education (4, 5).
Additionally, a significant component of nursing work in the medical management of patients is health education (6). Health education methods that address the perioperative needs of patients can not only pique their interest in the subject but also aid them in understanding the disease and receiving training in the healing process. This is crucial for the healing and also to avoid further complications (4, 7–9).
Currently, health education is primarily delivered in the department of surgery through face-to-face verbal guidance and communication, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Studies have shown that the increase in nurse workload not only poses a potential threat to nursing quality, but is also closely related to patient mortality, rescue failure rate, and hospital stay (10). Additionally, verbal instruction is influenced by the nurse’s capacity for expression and acknowledgment (3, 6), and because patients vary in terms of age, gender, education level, emotional state, and physical conditions, their responses to the health education are different.
Multimedia health education is a health education model combined with audio-visual stimulation and patients’ participation; it uses the combination of images, words and explanations to make it simpler for patients to understand and also makes health education knowledge more systematic and complete, avoids omissions, addresses patient concerns, and makes health education work procedural, standardized and specific (4, 5, 9, 11, 12). Multimedia health education can expand the scope of information dissemination, making it easier for patients and their families to access more health information. Audio-visual materials are characterized by scientific accuracy, engaging content, timeliness, practicality, and readability, which encourage patients to watch and learn. Moreover, these materials enable patients to relate the information to their own conditions and behaviors, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of health education (4, 5, 8, 9). Some studies (4, 5, 11, 12) have shown that multimedia health education can enhance patients’ and family members’ understanding of perioperative care, promote adequate preoperative preparation, and reduce the incidence of surgical cancelations. Additionally, preoperative multimedia education contributes to positive surgical outcomes, significantly alleviates patient anxiety, improves satisfaction with medical services, and effectively reduces postoperative pain (13–15). Although there are some comparatively effective health education strategies (11–15) that are helpful for the management of perioperative patients, prevention of perioperative complications. Multimedia health education can enhance the effectiveness of verbal health education, making it easier for patients to consolidate, understand, and retain the educational content while reducing the time and frequency required for nurses to deliver education (14–17). However, whether this approach can be both easily and profoundly accepted by patients has become a topic worth exploring in the field of nursing.
In this prospective, single-center, randomized controlled trial, we aim to evaluate whether the application of multimedia health education reduces nurses’ workload without compromising the satisfaction of surgical patients and their families in the surgical context.
Materials and methods
Ethical approval
The ethics committee of the First Hospital of Lanzhou University gave its approval to the research protocol (registry number: LDYYLL2019-203). Written informed consent was given by each patient or their legal representative. The trial was registered prior to patient enrollment at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03989401, Principal investigator: Jia Yao, Date of registration: July 3, 2019).
Study design and participants
This study, which was carried out at the Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute of Lanzhou University’s First Hospital, was a prospective randomized controlled trial with two arms (intervention group and control group), the intervention group received multimedia health education, while the control group received face-to-face oral health education. The following criteria were required for inclusion: (1) age between 18 and 75 years old; (2) general surgery diseases requiring surgical treatment; (3) education history of at least primary school level; (4) patients with clear awareness, be able to cooperate clinical data collection; (5) adequate communication ability; and (6) informed consent obtained. As exclusion criteria, we determined that patients with visual or hearing impairment, mental illness, dementia or other mental disorders, cardiac, brain or nephropathy complications, those unable to care for themselves, emergency or critically ill patients, and participants of prior studies would be excluded from the study.
Randomization
Patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to the multimedia health education intervention group or the control group (oral health education). An impartial statistician used a computer generated randomization list to perform the randomization. Office nurses used a series of sequentially numbered, sealed, and opaque envelopes to implement allocation. After the participants had finished the baseline assessment, the envelope was opened in front of them, and the patients were informed of their assignment. Satisfaction was assessed by clinical nurses who know the patient distribution.
Interventions
Multimedia health education
Except for multimedia health education, the participants in the intervention group received the same level of clinical care as those in the control group (standard general surgical nursing care). After the patient has finished the admission process, the clinical responsible nurses have brought patients and/or their family members into the ward, explained how to use the multimedia video player for health education, and turned on the television to play the video on admission. Other wards could not hear the video sound. The following topics are covered in the health education video: (1) hospital and ward environment; (2) primary clinical staff; (3) safety precautions; (4) preoperative planning; (5) visiting, ward round and leave system; (6) regular medical checkups and precautions; (7) dietary advice and precautions; (8) rehabilitation advice and precautions; (9) issues with medication knowledge and patient identification (4, 5, 9, 18–20). The health education video was filmed and produced by our research team in the research department. Nurses and doctors from the research team played the roles of doctors, nurses, and patients in the video, which has a total duration of 14 min. Additionally, the participants and their families should be advised to consult doctors or nurses if they have any doubts.
Standard health education
At the time of admission, trained clinical nurses conducted a face-to-face verbal health evaluation with the control group. The verbal health education had the same information as the video did, and the nurses also advised the participants to speak with the doctor or nurse if they had any questions.
Each participant who was placed in wards with only one bed was instructed not to share their admission health education with other patients in other wards in order to minimize the possibility of cross-contamination between the two groups of the trial. In addition, patients and their families can watch the video repeatedly.
Outcomes
The main outcomes were the workload of nurses on admission (the duration of health education per nurse, times of health education of nurse, inquiry times on health education content of patients and family members on the day of admission) and the satisfaction of patients, families, doctors and nurses with health education. Patients, family members, doctors and nurses were required to fill in the satisfaction questionnaires within 24 h after admission.
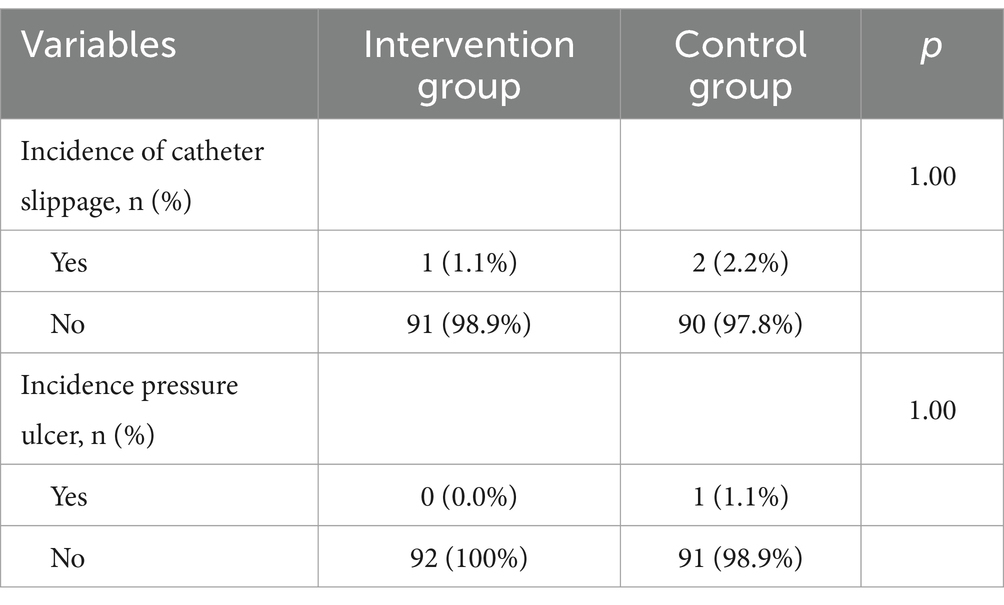
The level of patient anxiety before and after receiving health education was a secondary outcome. Additional monitored parameters include the incidence of catheter slippage and pressure ulcers.
Statistical analysis
Based on the results of the prior studies (19, 20), the satisfaction of the intervention group is 98.22 ± 1.15, while the satisfaction of the control group is 97.03 ± 2.49. Thus, 184 participants were needed using the formula for a two-sample mean comparison, with a power of 90% and a two-sided α of 0.05.
Continuous variables were expressed as mean and standard deviation, while categorical variables were expressed as numbers and percentages. Tests of paired t-test, independent t-test, ANOVA, χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test were used to compare differences between groups. The Poisson regression model was used to analyze the related factors influencing the workload of health education on admission for nurses, and the results are presented as regression coefficient (β) with a 95% confidence interval [CI]. The multivariable model evaluated variables for which the p-value in the univariate analysis was less than 0.10. All tests were two-sided, and a p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. SPSS software (SPSS version 22.0) was employed for the analysis.
Results
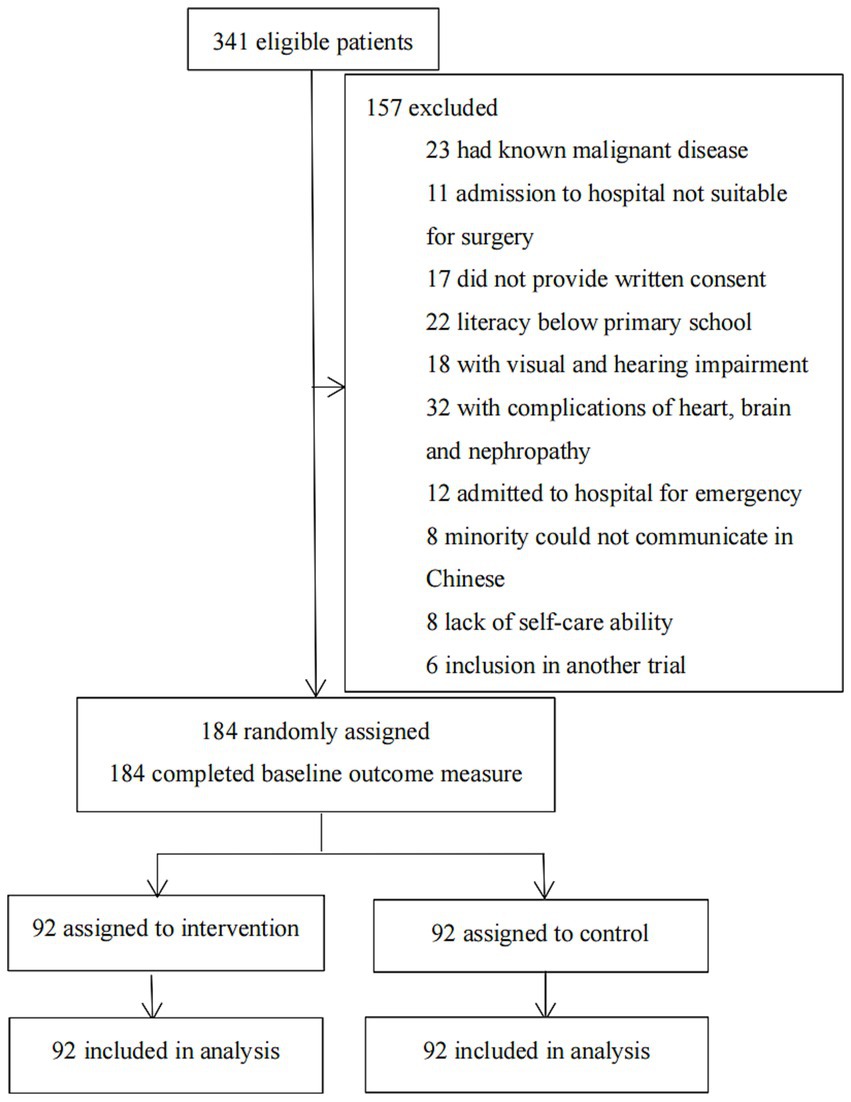
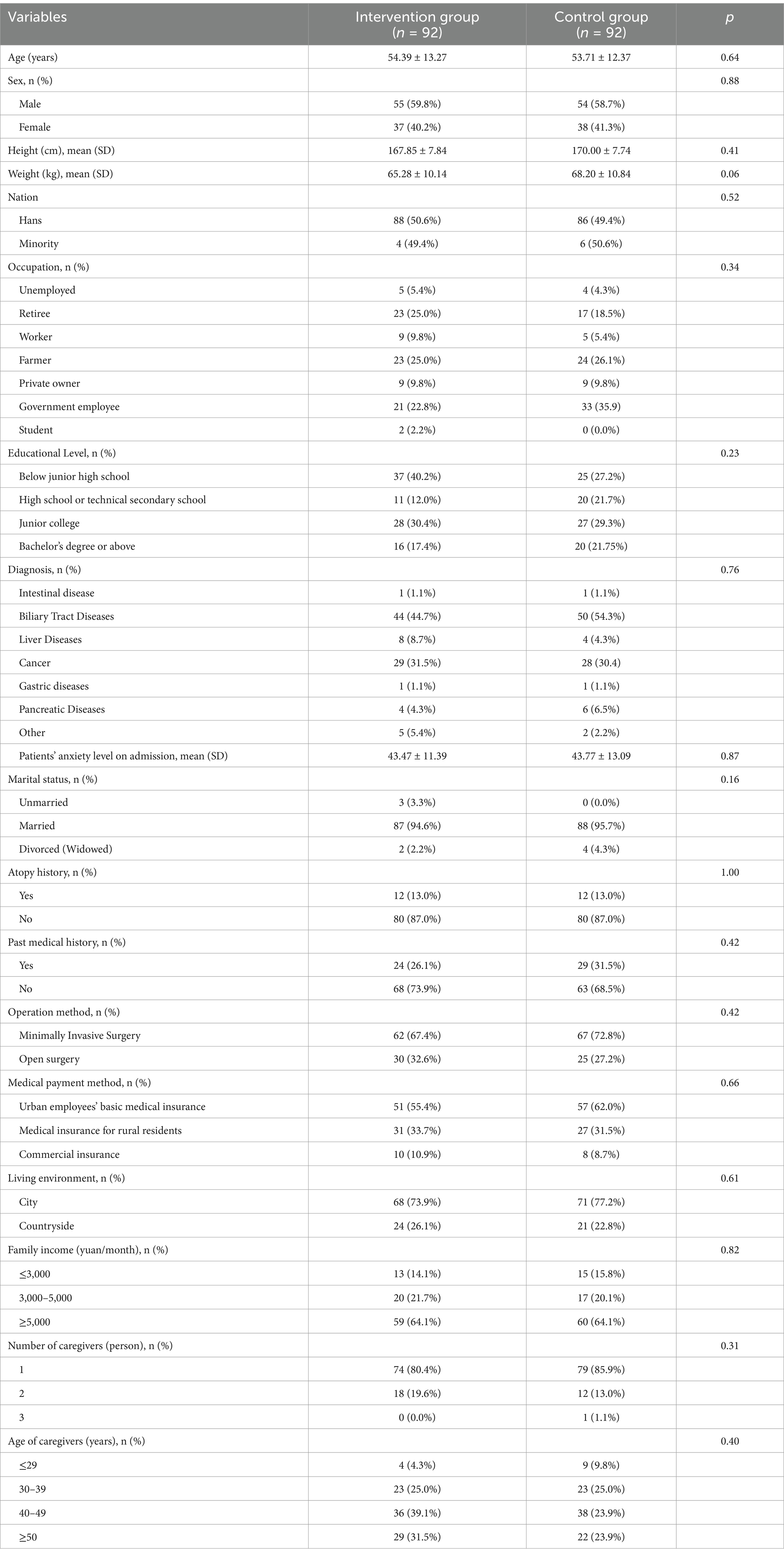
From July 29, 2019, to June 1, 2022, 341 consecutive patients who were admitted to the Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute at the First Hospital of Lanzhou University were evaluated for eligibility. Following the screening, 157 patients were disqualified (Figure 1). 184 patients who were left were split evenly (1:1) between the multimedia health education group and the standard health education group. The baseline characteristics of the two groups were similar (p > 0.05; Table 1). In the intervention group (n = 30, 32.6%) more patients underwent open surgery than in the control group (n = 25, 27.2%). Additionally, since February 2020, in order to cooperate with the national COVID-19 prevention and control policy, the one-on-one escort system has been strictly implemented in the ward, except in special cases.
The findings revealed that using multimedia health education can shorten the time nurses spend on health education during patient admissions [15.21 (0.63) vs. 16.94 (3.96), p < 0.001] and reduce the number of times patients and their families spend seeking health education information [1.21 (0.62) vs. 2.73 (0.92), p < 0.001]. Additionally, the control group’s nurses had to repeatedly explain admission related information to the patients and their families [3.25 (0.89) vs. 1.21 (0.62), p < 0.001].
To create satisfaction questionnaires, previous research was consulted (18–20). A team of four experts with backgrounds in medicine, nursing, psychology and outcome measurement evaluated the questionnaires before they were used in the trial. The questionnaire of patients and their families consisted of 11 questions with a total score ranging from 11 (dissatisfaction) to 55 (high satisfaction). The Cronbach’s coefficient (α) of this questionnaire was 0.927, expert validity (scale-level content validity index) was 0.93, and Kaiser Meyer Olkin (KMO) was 0.929 (See Supplementary 1). The satisfaction questionnaire for doctors and nurses consisted of 15 questions with a total score ranging from 15 (dissatisfaction) to 75 (high satisfaction). The Cronbach’s coefficient (α) of this questionnaire was 0.915, expert validity (scale-level content validity index) was 0.95, and Kaiser Meyer Olkin (KMO) was 0.886 (See Supplementary 2). The results of satisfaction scores showed that use of multimedia health education did not lower the satisfaction levels of patients [53.35 (2.09) vs. 47.86 (5.00), p < 0.001], family members [53.35 (2.28) vs. 47.86 (4.53), p < 0.001], nurses [73.46 (2.36) vs. 67.16 (5.52), p < 0.001] and doctors [73.33 (2.40) vs. 68.07 (4.92), p < 0.001] regarding health education (Table 2).
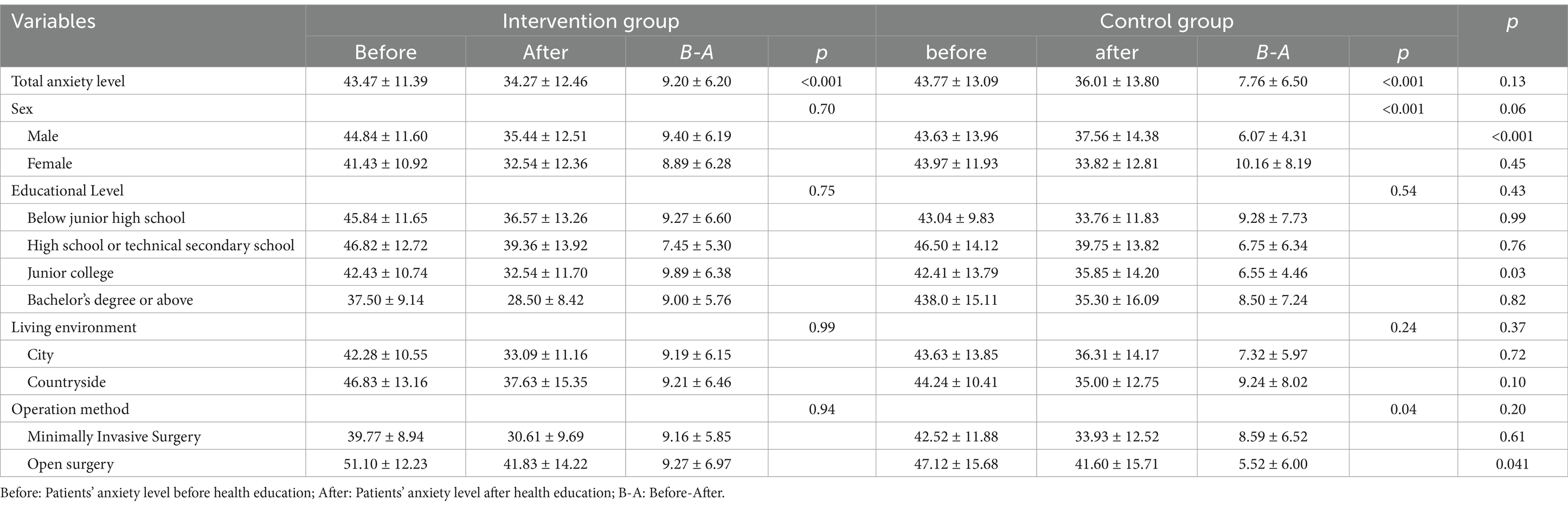
The Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) (21) was used to assess patient anxiety levels before and after receiving health education (See Supplementary 3). This scale has high internal consistency in this study sample (α = 0.92, 95% CI 0.88–0.95). At admission, there was no difference in anxiety scores between the two groups [43.47 (11.39) vs.43.77 (13.09), p = 0.87]. The anxiety scores of the two groups decreased following health education, but there was no statistically significant difference between the two groups [9.20 (6.20) vs. 7.76 (6.50), p = 0.13]. According to subgroup analysis, there was a statistically significant difference between anxiety scores of male patients before and after health education [9.40 (6.19) vs. 6.07 (4.31), p < 0.001], junior college students [9.89 (6.38) vs. 6.55 (4.46), p = 0.03], and patients having open surgery [9.27 (6.97) vs. 5.52 (6.00), p = 0.041] (Table 3).
Additionally, multimedia health education does not raise the frequency of adverse events in comparison to standard health education (p > 0.05; Table 4).
The results of a univariate analysis indicated that factors influencing nurses’ workload include nation [95% CI: 0.00–0.82, p = 0.048], high school or technical secondary school education [95% CI: 0.07–0.64, p = 0.014], sequence of patients of the admission day [95% CI: 0.03–0.23, p = 0.013] and healthy education methods [95% CI: 1.12–1.68, p < 0.0001]. The results of multivariate regression analysis revealed that factors influencing nurses’ workload included healthy education method [95% CI: 1.09–1.67, p < 0.0001]. Patients who received oral health education had 1.38 more inquiries than those who received multimedia health education (Table 5).
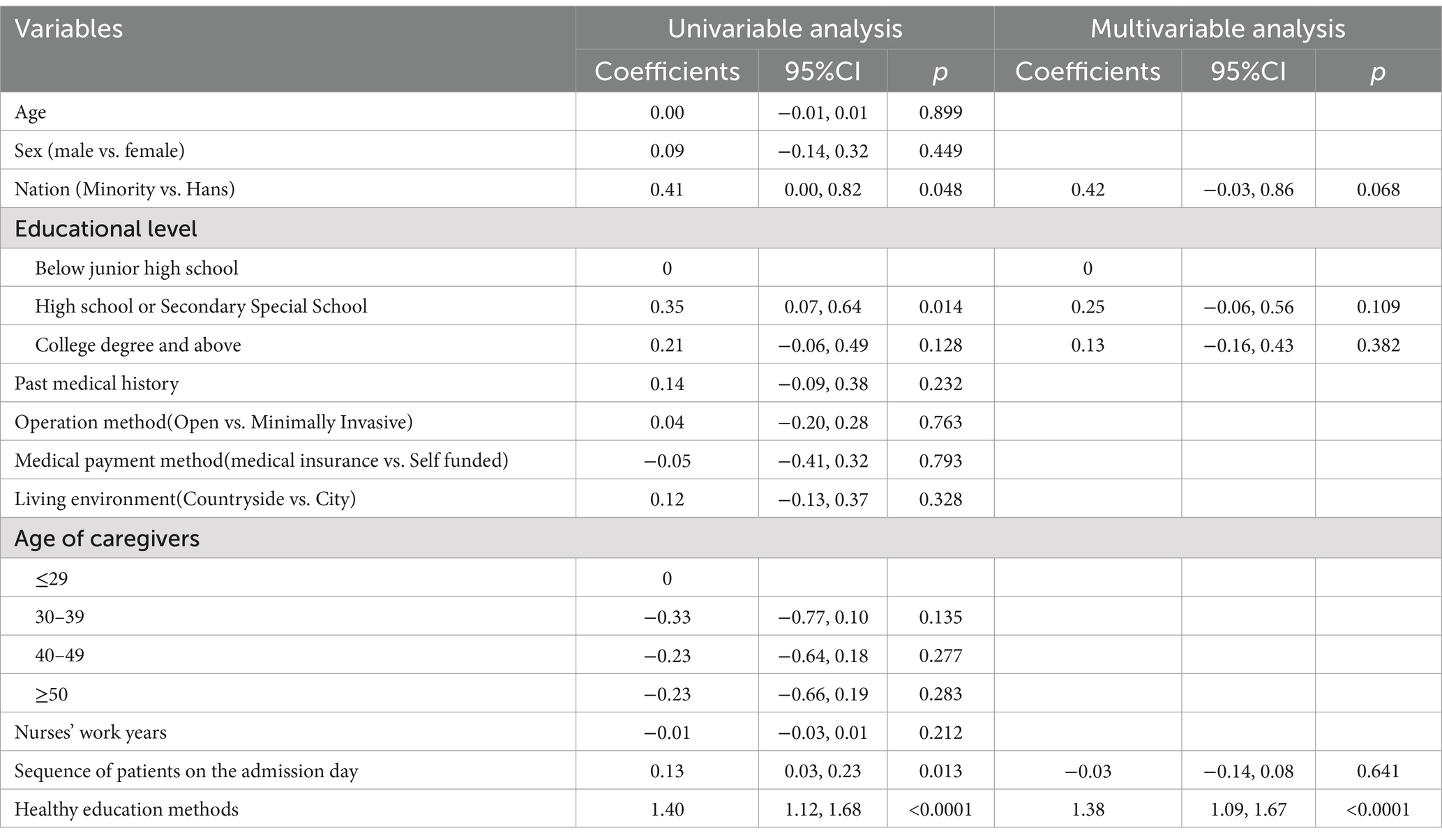
Table 5. Poisson regression analysis of the influence factors of the health education workload on admission.
In a subgroup analysis, doctors, nurses, patients and their families were found to be more satisfied with senior nurse health education (p < 0.001; Figures 2, 3). However, there was no significant difference in the duration of health education between nurses with high seniority and those with low seniority (p = 0.20). Senior nurses took less time than junior nurses to complete health education for patients and to inquire about the health education of patient family members (p < 0.001; Figure 4). The satisfaction with nurse health education was also higher among patients and their families who had been hospitalized earlier in the same shift (Figure 5).
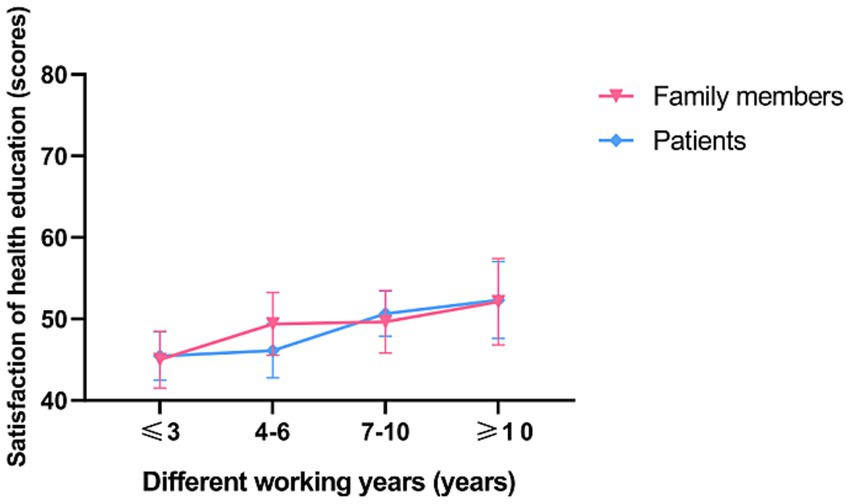
Figure 2. The satisfaction of patients and family members with the health education of nurses with different working years in the control group.
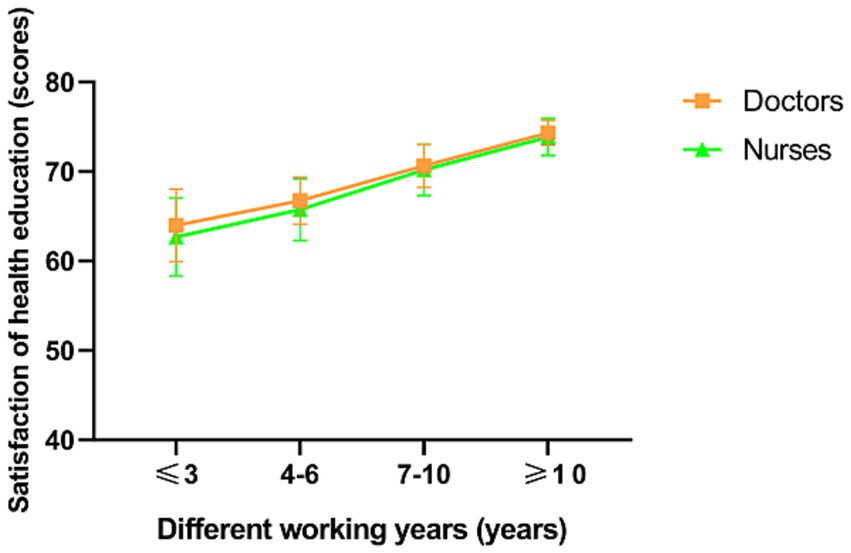
Figure 3. The satisfaction of doctors and nurses with the health education of nurses with different working years in the control group.
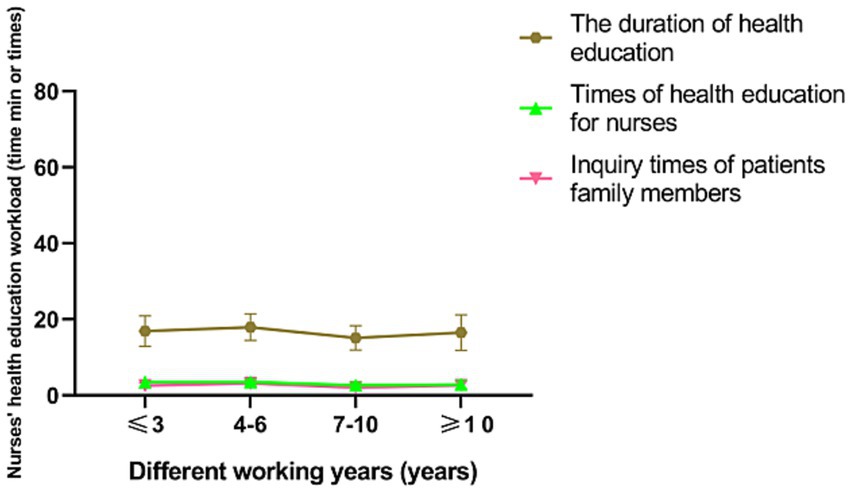
Figure 4. The workload of nurses of health education in the control group with different working year.
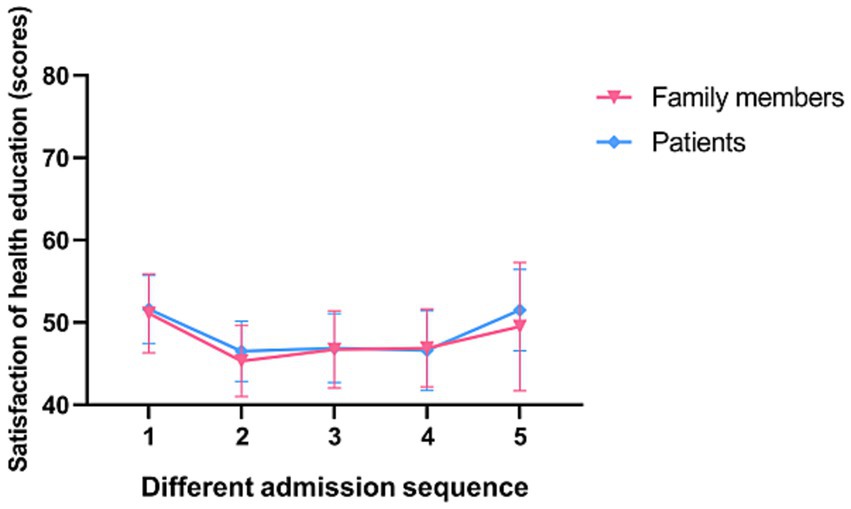
Figure 5. The satisfaction of patients and family members of different admission sequences for health education in the control group.
Discussion
Health information sharing with patients is an important component of treatment plans, which is required and obligated. This information must also be clear, impartial and appropriate. The focus of information must be on the serious risks associated with interventions, any potential alternative strategies and the effects of rejection (22).
Postoperative complications and patient anxiety levels can be decreased with good health education (4, 13, 14, 23, 24). However, whether multimedia health education can significantly reduce the workload of nurses has not been studied yet. In our study, we found that using multimedia health education can shorten the time nurses spend on health education during patient admissions and reduce the number of times patients and their families spend seeking health education information (p < 0.001). Our study’s results were consistent with the results of Chang et al.’s study (25) that fewer hours were spent by nurses on health education for the multimedia CD group in comparison with the printed material group. Furthermore, the use of multimedia health education did not lower the satisfaction levels of doctors, nurses, patients, and their families regarding health education; in fact, it increased their satisfaction (p < 0.001). Most surgical patients experience varying degrees of psychological stress during the perioperative period (26, 27); good health education can significantly reduce the perioperative patient fear and pain caused by surgical trauma and achieve disease prevention (27–29), as evidenced by high satisfaction scores of patients in the multimedia video health education group. Our study’s findings align with previous research (18, 19), indicating that alternative health education approaches tend to outperform oral health education in terms of patient satisfaction.
In our study, we discovered that the anxiety level of patients included in the study was low and that there was no significant change in the anxiety score following health education (p = 0.13). The results of this study were different from the results of Wang Y et al.’s study (14), mainly because patients with serious complications were excluded from this study. However, when compared to female patients, the anxiety score of male patients improved more significantly in the multimedia group (p < 0.001). This might be the case because stress may affect male and female brains differently. Furthermore, we discovered that patients with open surgery and a junior college degree experienced a greater reduction in anxiety scores (p < 0.05), which was statistically significant as compared to the control group.
Medical management includes health education as a crucial component. The use of patient-needs-oriented health education techniques during the perioperative period can not only increase patient interest in health education but also improve their level of disease management (16, 30–34). Our study demonstrated that the incidence of complications was not increased by multimedia health education. The main reason was that the video presentation was easier to understand than the straightforward verbal presentation. Patients can learn more about the process (31) by participating in multimedia health education and by developing disease self-management abilities (32).
There may be significant differences in the content and outcomes of nurse education at various levels as a result of differences in the professional level, language expressive ability and emotional communication ability of nurses (5, 6). Additionally, because senior nurses have more clinical experience than junior nurses (6), our study found that doctors, nurses, patients and their families were more satisfied with the health education provided by senior nurses in the control group than by junior nurses.
Our study also found that with the increase of patients in the same shift, the satisfaction score of patients and their families gradually decreased, which may be related to nurse compassion fatigue and patience consumption. In addition, our study also found that the health education methods were the influencing factors of nurse health education workload. The effect of health education on other postoperative outcomes and the influencing factors of nurses’ workload are subjects suitable for future research.
The implementation of Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols in surgical wards requires patients and their families to have a profound theoretical understanding of the essence of ERAS. Multimedia video health education can enhance patients’ awareness and comprehension of ERAS, thereby improving their qualification rate of ERAS knowledge. Furthermore, this educational approach can elevate patients’ recovery speed and quality to a higher level. In addition, the scarcity of nursing human resources is a prevalent issue faced by most countries presently. Exploring how to address the shortage of nursing personnel through the utilization of information technology, without compromising patients’ healthcare experiences, constitutes a significant area of research. This study provides a reference basis for the practice of the above clinical measures.
Our study also had limitations. The main limitations of this study were as follows: (1) no multicenter study was conducted, and no information based health education was adopted for medical patients; (2) no specific health education methods were implemented for the different diseases and populations; (3) the research results of this study are not reproducible as they require consideration of specific periods in specific countries, the characteristics of the hospital’s level.
In conclusion, our randomized trial demonstrated that multi-media health education could reduce the workload of nurses and enhance patient satisfaction, but not increase complications. It is worth promoting and applying in clinical nursing work.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the First Hospital of Lanzhou University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. ZQ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. JY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HX: Investigation, Writing – original draft. JT: Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YR: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Gansu Province natural sciences foundation (21JR7RA368) and the Foundation of the First Hospital of Lanzhou University (ldyyyn-2019-15).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all those who helped them write the thesis, all professors in the nursing department of the first hospital of Lanzhou University, and Chongfei Huang for their assistance during the shooting and editing of the health education video.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1400061/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Saba, S, Faizi, F, Sepandi, M, and Nehrir, B. Effect of short-term magnesium supplementation on anxiety, depression and sleep quality in patients after open-heart surgery. Magnes Res. (2022) 35:62–70. doi: 10.1684/mrh.2022.0503
2. Fulop, A, Lakatos, L, Susztak, N, Szijarto, A, and Banky, B. The effect of trimodal prehabilitation on the physical and psychological health of patients undergoing colorectal surgery: a randomised clinical trial. Anaesthesia. (2021) 76:82–90. doi: 10.1111/anae.15215
3. Pueyo-Garrigues, M, Pardavila-Belio, MI, Canga-Armayor, A, Esandi, N, Alfaro-Díaz, C, and Canga-Armayor, N. NURSES’ knowledge, skills and personal attributes for providing competent health education practice, and its influencing factors: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Pract. (2022) 58:103277. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103277
4. Haack, M, Fischer, ND, Frey, L, Sparwasser, P, Dotzauer, R, Duwe, G, et al. Digital informed consent for urological surgery - randomized controlled study comparing multimedia-supported vs. traditional paper-based informed consent concerning satisfaction, anxiety, information gain and time efficiency. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. (2024) 27:715–9. doi: 10.1038/s41391-023-00737-4
5. Venkatraman, V, Heo, H, Kaplan, S, Parente, BA, and Lad, SP. Digital health for patients undergoing spine surgery: a systematic review. World Neurosurg. (2024) 182:70–82. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2023.11.035
6. Kim, MY, and Oh, S. Nurses’ perspectives on health education and health literacy of older patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:6455. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186455
7. Mann, J, Li, L, Kulakov, E, Bassett, P, and Birnie, A. Home viewing of educational video improves patient understanding of Mohs micrographic surgery. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2022) 47:93–7. doi: 10.1111/ced.14845
8. Navidad, L, Padial-Ruz, R, and González, MC. Nutrition, physical activity, and new technology programs on obesity prevention in primary education: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:10187. doi: 10.3390/ijerph181910187
9. Biro, M, Kim, I, Huynh, A, Fu, P, Mann, M, and Popkin, DL. The use of 3-dimensionally printed models to optimize patient education and alleviate perioperative anxiety in Mohs micrographic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2019) 81:1339–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.05.085
10. Moghadam, KN, Chehrzad, MM, Masouleh, SR, Mardani, A, Maleki, M, Akhlaghi, E, et al. Nursing workload in intensive care units and the influence of patient and nurse characteristics. Nurs Crit Care. (2021) 26:425–31. doi: 10.1111/nicc.12548
11. Adam, M, McMahon, SA, Prober, C, and Bärnighausen, T. Human-centered Design of Video-Based Health Education: an iterative, collaborative, community-based approach. J Med Internet Res. (2019) 21:e12128. doi: 10.2196/12128
12. Lattuca, B, Barber-Chamoux, N, Alos, B, Sfaxi, A, Mulliez, A, Miton, N, et al. Impact of video on the understanding and satisfaction of patients receiving informed consent before elective inpatient coronary angiography: a randomized trial. Am Heart J. (2018) 200:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2018.03.006
13. Bozkul, G, Karakul, A, Düzkaya, DS, and Dilşen, Ş. Effect of short film video and video-based education on fear, pain, and satisfaction of children undergoing day surgery. J Pediatr Nurs. (2024) 75:49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.pedn.2023.11.029
14. Wang, Y, Huang, X, and Liu, Z. The effect of preoperative health education, delivered as animation videos, on postoperative anxiety and pain in femoral fractures. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:881799. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.881799
15. Chuang, TY, Cheng, W, Chiu, YC, Fan, YH, Chi, CC, Chang, CC, et al. Free interactive counselling program in a mobile communication application for improving health education on indwelling ureteric stents after ureterorenoscopic lithotripsy: an observational study. Digit Health. (2022) 8:205520762211177. doi: 10.1177/20552076221117754
16. Liu, J, Zheng, X, Chai, S, Lei, M, Feng, Z, Zhang, X, et al. Effects of using WeChat-assisted perioperative care instructions for parents of pediatric patients undergoing day surgery for herniorrhaphy. Patient Educ Couns. (2018) 101:1433–8. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2018.02.010
17. Abuzaid, M, Alshahrani, MS, Ahmed, AM, Moafa, MN, Alomar, O, O’Mahony, A, et al. Effectiveness of preoperative multimedia educational sessions on the levels of anxiety and satisfaction among women undergoing cesarean: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Women Health. (2024) 64:416–26. doi: 10.1080/03630242.2024.2349560
18. Zhou, Y, Li, X, Zhang, M, Lv, G, Duan, B, and Tang, Z. Effect of multimedia health education on psychological burden, quality of life ability, and self-efficacy of congenital Microtia. Comput Math Methods Med. (2022) 2022:1482865–8. doi: 10.1155/2022/1482865
19. Xiao, H, Wu, W, Xu, N, and Cheng, Y. Application of multimedia collective education model in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Nurs J Chin PLA. (2017) 34:50–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9993.2017.07.014
20. Cheng, F, Yan, C, Li, N, and Cheng, F. Application of health knowledge assessment in health education for patients with hypertension. Nurs J Chin PLA. (2008) 4:27–9.
21. Liu, Z, Qiao, D, Xu, Y, Zhao, W, Yang, Y, Wen, D, et al. The efficacy of computerized cognitive behavioral therapy for depressive and anxiety symptoms in patients with COVID-19: randomized controlled trial. J Med Internet Res. (2021) 23:e26883:e26883. doi: 10.2196/26883
22. Ng, SX, Wang, W, Shen, Q, Toh, ZA, and He, HG. The effectiveness of preoperative education interventions on improving perioperative outcomes of adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. (2022) 21:521–36. doi: 10.1093/eurjcn/zvab123
23. Mavrogiorgou, P, Zogas, H, Zogas, G, Juckel, G, and Heuer, JF. Perioperative ängste und die angst vor dem Tod. Anaesthesiologie. (2023) 72:266–72. doi: 10.1007/s00101-023-01267-3
24. Medina Aguerrebere, P, Medina, E, and Gonzalez, PT. Promoting health education through Mobile apps: a quantitative analysis of American hospitals. Healthcare (Basel). (2022) 10:2231. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10112231
25. Chang, SF, Hung, CH, Hsu, YY, Liu, Y, and Wang, TN. The effectiveness of health education on maternal anxiety, circumcision knowledge, and nursing hours: a quasi-experimental study. J Nurs Res. (2017) 25:296–303. doi: 10.1097/JNR.0000000000000177
26. Sorel, JC, Veltman, ES, Honig, A, and Poolman, RW. The influence of preoperative psychological distress on pain and function after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. (2019) 101-B:7–14. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.101B1.BJJ-2018-0672.R1
27. Turkdogan, S, Roy, CF, Chartier, G, Payne, R, Mlynarek, A, Forest, VI, et al. Effect of perioperative patient education via animated videos in patients undergoing head and neck surgery: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2022) 148:173–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.3765
28. Kim, S, Ju, MK, Son, S, Jun, S, Lee, SY, and Han, CS. Development of video-based educational materials for kidney-transplant patients. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0236750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236750
29. Delcambre, M, Haynes, D, Hajar, T, Golden, S, Bar, A, Latour, E, et al. Using a multimedia tool for informed consent in Mohs surgery: a randomized trial measuring effects on patient anxiety, knowledge, and satisfaction. Dermatologic Surg. (2020) 46:591–8. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000002213
30. Patel, P, Malik, K, and Khachemoune, A. Patient education in Mohs surgery: a review and critical evaluation of techniques. Arch Dermatol Res. (2021) 313:217–24. doi: 10.1007/s00403-020-02119-5
31. Ahmet, A, Gamze, K, Rustem, M, and Sezen, KA. Is video-based education an effective method in surgical education? A systematic review. Curr Surg. (2018) 75:1150–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2018.01.014
32. Hawkins, SD, Koch, SB, Williford, PM, Feldman, SR, and Pearce, DJ. Web app- and text message-based patient education in Mohs micrographic surgery-a randomized controlled trial. Dermatologic Surg. (2018) 44:924–32. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001489
33. Ergen, WF, Pasricha, T, Hubbard, FJ, Higginbotham, T, Givens, T, Slaughter, JC, et al. Providing hospitalized patients with an educational booklet increases the quality of colonoscopy bowel preparation. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2016) 14:858–64. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.015
Keywords: multi-media health education, surgical patients, workload of nurses, patient’s satisfaction, anxiety level
Citation: Yang L, Qin Z, Yao J, Xu H, Tian J, Ren Y, Wang H and Meng W (2025) Enhancing patient satisfaction and reducing nurse workload: the impact of multimedia health education in a prospective single-center randomized controlled trial. Front. Med. 12:1400061. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1400061
Edited by:
Mansoor Malik, Johns Hopkins Medicine, United StatesReviewed by:
Yaritza Perez-Soto, Physicians Regional Medical Group, United StatesThirimon Moe-Byrne, University of York, United Kingdom
Luis Miguel Ferreira, Escola Superior de Enfermagem do Porto, Portugal
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Qin, Yao, Xu, Tian, Ren, Wang and Meng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jia Yao, bGR5eV95YW9qQGx6dS5lZHUuY24=; Wenbo Meng, bWVuZ3diQGx6dS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Liping Yang
Liping Yang Zilan Qin1,2,3†
Zilan Qin1,2,3† Jinhui Tian
Jinhui Tian Haiping Wang
Haiping Wang Wenbo Meng
Wenbo Meng