- 1Department of Pharmacy, The University of Lahore, Lahore, Pakistan
- 2Riphah Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Riphah International University, Lahore, Pakistan
- 3Department of Pharmacy Practice, Faculty of Pharmacy , Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan
Introduction: Specific evidence regarding the pharmacist’s role in antifungal stewardship (AFS) is emerging. This review aims to identify pharmacist-driven AFS interventions to optimize antifungal therapy.
Methods: A systematic review was conducted using Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Data (2018–2023) were collected through Google Scholar and PubMed. The collected data were presented descriptively due to variations in interventions and outcome metrics. Conclusions were derived through a qualitative synthesis of the identified findings.
Results: A total of 232 articles were retrieved, and after applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 27 were included in the review. Among the eight studies evaluating the impact of pharmacist interventions on antifungal consumption, 6 studies reported a significant decline in defined daily dose (DDD)/1,000 patient days and days of therapy (DOT)/1,000 patient days, one reported a non-significant decrease, and one reported an increase in the utilization of echinocandins. Educational intervention was the most commonly used stewardship approach. Nineteen studies reported data on various clinical outcomes. Mortality and length of hospital stay remain non-significant, but the occurrence of ADR decreased significantly, and the quality of antifungal use improved significantly.
Conclusion: Pharmacist-led AFS has the potential to enhance the effectiveness of antifungal treatments by improving their overall quality, reduction in consumption, and adverse events. The healthcare system should encourage multidisciplinary collaboration where pharmacists play a central role in decision-making processes regarding antifungal use.
1 Introduction
Invasive fungal infections (IFIs) predominantly involving invasive candidiasis and aspergillosis represent a dynamic and growing global public health concern due to increased risk of morbidity and mortality. Patients with solid organ transplant, hematopoietic stem cell transplant, malignancy, critically ill, long-term corticosteroid and antibiotics use are at higher risk of IFIs (1). The incidence of IFIs varies based on the geographical location (2). Globally, over 800 million individuals experience IFIs, with annual mortality rates reaching 1,660,000, comparable to tuberculosis (1,700,000). In Asian countries, the prevalence of IFI is 3–15 times higher than that in the Western nations. Besides the elevated mortality rates ranging from 10 to 49%, IFIs pose significant economic challenges due to extended hospital stays and severe financial consequences (3).
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is recognized as a major deterrent to public health systems, impacting not only developing countries but also worldwide (4). Empiric use of antifungals in critically ill patients and immunocompromised patients increases the risk of antifungal resistance (AFR) (5). One of the biggest challenges in clinical practice is the resistance of Candida and Aspergillus species to azoles, followed by echinocandins (5). The resistance to antifungal agents can have various contributing factors, including host-related or drug-related factors such as inadequate dosing, inaccurate diagnosis, and patient non-compliance. Additionally, microbiological factors, such as genetic mutations in the organism, or a combination of both, may play a role in this multifactorial mechanism (6).
Drug-resistant microorganisms are becoming more prevalent, endangering the capacity to treat common infections and carry out life-saving procedures such as organ transplants and chemotherapy for cancer. Treatment for fungal infections can be challenging, in part because of interactions between drugs that are being prescribed to patients with comorbid infections, such as HIV and cancer. It is especially concerning with multidrug-resistant Candida auris, which is one of the fungal pathogens responsible for invasive fungal infections. WHO has developed a list of 19 fungal priority pathogens categorized into three priority groups, namely, critical, high, and medium priority. These fungi are responsible for invasive infections, which are difficult to treat, and there is a high risk of fungal resistance (7).
Establishing an efficient antifungal stewardship program (AFSP) is crucial for managing drug resistance. This program should integrate rapid fungal diagnostics, therapeutic drug monitoring, and clinical intervention teams. The advancement of improved diagnostic tools and strategies is imperative to enable the precise and targeted utilization of antifungals, ensuring the preservation of their effectiveness and reduction in resistance (8). Studies have shown that AFSP significantly improves the quality of antifungal use, antifungal consumption, and clinical outcomes (9). Pharmacist as a member of AFS program plays a pivotal role in promoting rational drug use and optimizing therapy. Several studies have highlighted the positive impact of pharmacist-led interventions on antimicrobial stewardship programs. Still, specific evidence regarding their role in antifungal stewardship is scarce. This systematic review aimed to explore and document the available literature on Pharmacist-led AFS and the impact of these interventions on antifungal consumption and clinical outcomes.
2 Methods
2.1 Information sources and search strategy
A comprehensive search was carried out to gather data on pharmacist interventions as a member of the antifungal stewardship team on optimizing antifungal use. The literature was searched through Google Scholar using the keywords “Antifungal stewardship and/or antimicrobial stewardship and/or pharmacist interventions and/or consumption and/or quality of antifungal use and/or clinical outcomes” which provided 130 publications; literature search through PubMed that derived 69 publications with mesh terms “Antimicrobial Stewardship” AND “Antifungal Agents” and 33 publications with mesh terms “Antimicrobial Stewardship” AND “Antifungal Agents” AND “Invasive Fungal Infections/Drug Therapy.” All the available data for the period 2018–2023 was searched in October 2023.
2.2 Study eligibility criteria
Inclusion criteria: (a) Studies that delineated an AFS program or intervention done by a pharmacist and presented data on antifungal consumption and clinical outcomes within the AFS program; (b) full access to original research articles; and (c) articles in the English language.
Exclusion criteria: (a) Review papers, editorials, abstracts, and duplicate studies were excluded; (b) Studies lacking an intervention; and (c) those not assessing the designated outcome of interest. The outcomes of interest include any stewardship interventions done by pharmacists that impact antifungal consumption and clinical measures (infectious diseases [IDs] consultation, mortality, length of hospital stay, adherence to guidelines, and adverse events).
2.3 Study selection and data extraction process
Two researchers independently screened studies by titles and abstracts initially. After screening titles and abstracts, 27 full-text articles that met the inclusion criteria were reviewed by one researcher. Microsoft Excel spreadsheet was used to document information on all of the included variables: study reference, study design, study setting and location, study period, number of patients, type of intervention, study objective, and study outcomes. A second researcher independently reviewed the extracted data. Any disagreement between collected data was resolved through discussion between all authors.
2.4 Synthesis of results
The systematic review adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist (10). The collected data were presented descriptively due to the variations in interventions and outcome metrics. Conclusions were derived through a qualitative synthesis of the identified findings. All primary studies used descriptive statistics for their evaluations, presenting findings as frequencies and percentages without employing an effect measure estimate. Therefore, the study results were organized descriptively into tables, ensuring transparent reporting of the systematic review findings.
2.5 Quality assessment
Three investigators independently assessed the risk of bias in all included studies using the Robin-I tool (11) which evaluates studies across seven domains, including confounding, participant selection, intervention classification, deviation from intended intervention, missing data, measured outcome, and selection of reported results, as shown in Figure 1. The final assessment regarding the risk of bias in all studies was made through a mutual agreement among all authors. Studies were judged as having a low risk of bias if it is comparable to randomized trials, a moderate risk of bias if it provides solid evidence for a non-randomized design, though they cannot be considered equivalent to a well-conducted randomized trial, and a serious risk of bias if it has significant issues that can impact the credibility of results (11). Studies with low or moderate risk were included.

Figure 1. Risk of bias assessment using Risk of Bias In Non-randomized Studies-of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool. Domains: D1. Bias due to confounding, D2. Bias in the selection of participants in the study, D3. Bias in the classification of interventions, D4. Bias due to deviations from intended interventions, D5. Bias due to missing data, D6. Bias in measurement of outcome, D7. Bias in the selection of the reported result. Judgment: low risk  , moderate risk
, moderate risk  , serious risk
, serious risk  .
.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
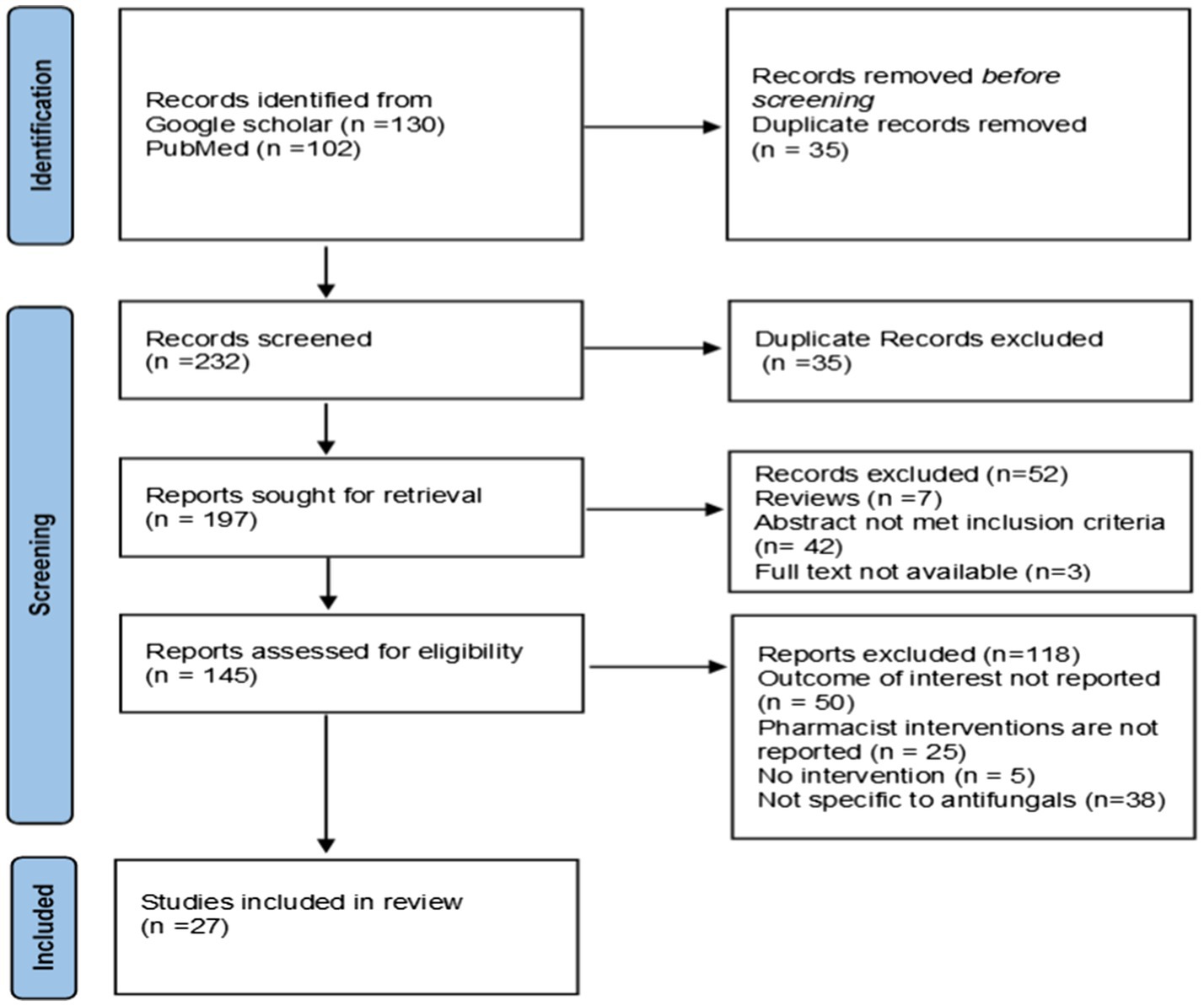
Two hundred and thirty two articles were identified using keywords and mesh terms through Google Scholar and PubMed. After removing duplicates, abstracts only, review papers, not evaluating pharmacist interventions or the outcome of interest, and not evaluating poststewardship activity impact on outcomes were excluded. After exclusion, 27 articles that met the criteria were included in the systematic review (Figure 2).
3.2 Study characteristics
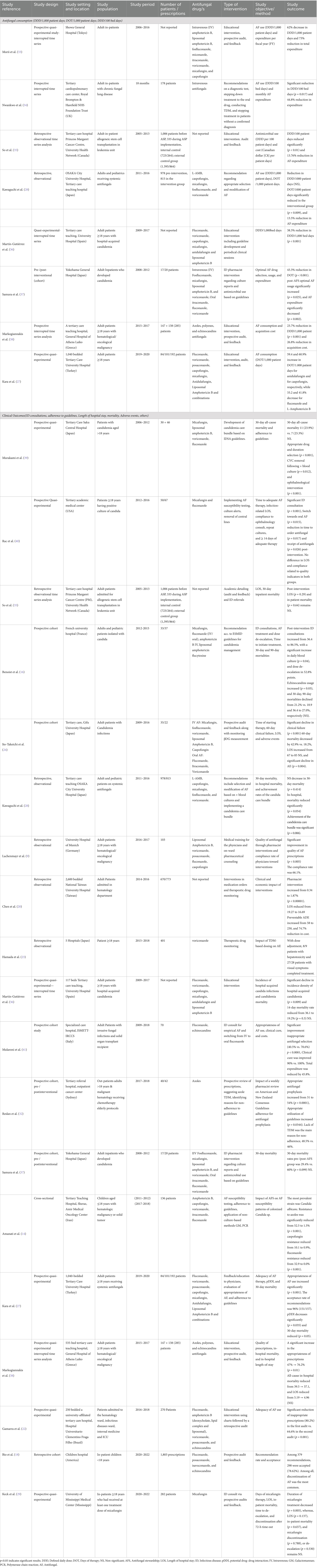
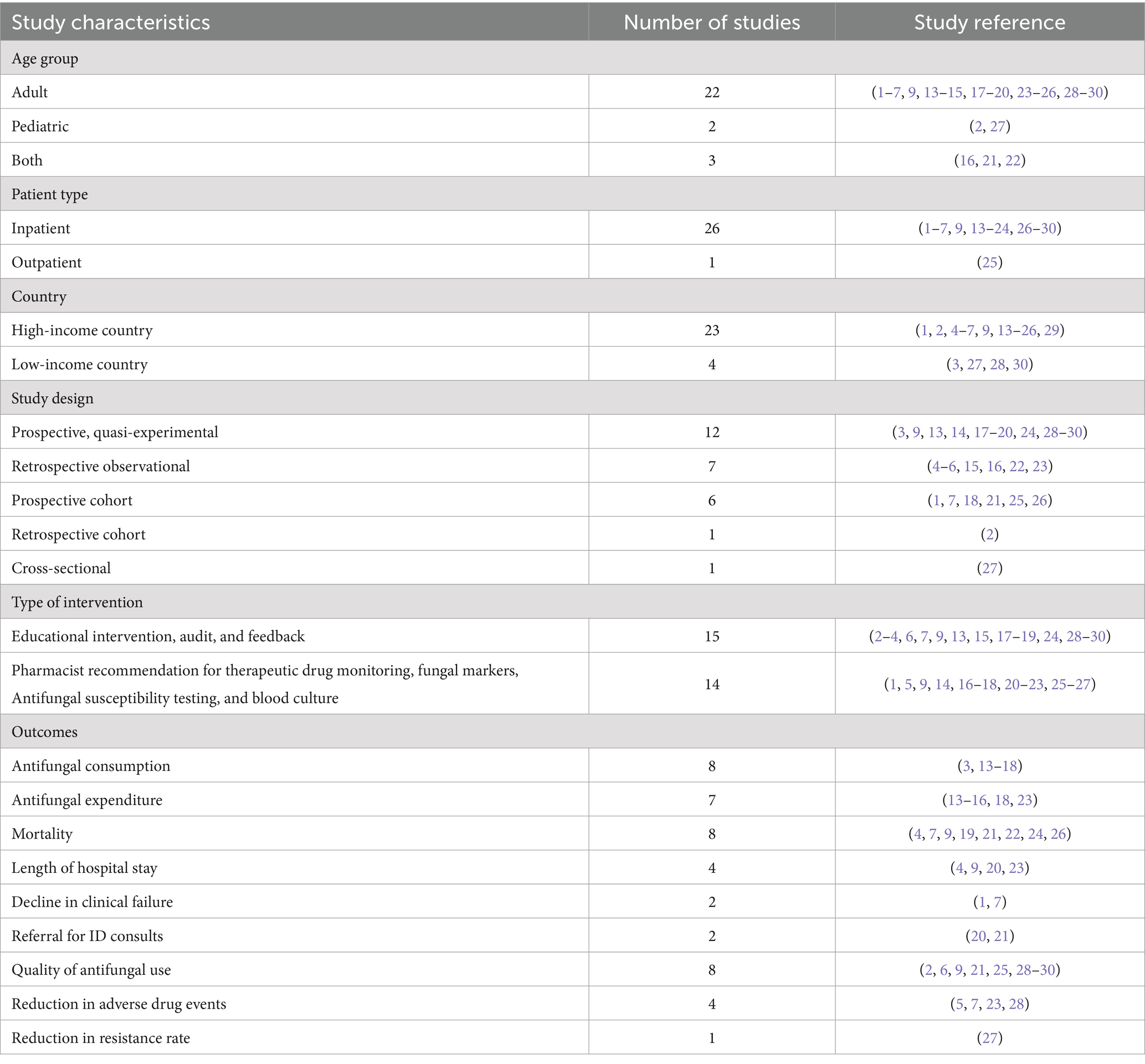
Among 27 studies that are included in the review, eight studies evaluated the impact of pharmacist interventions on antifungal consumption in terms of defined daily dose (DDD) or days of therapy (DOT) and cost reduction. DDD is the assumed average maintenance dose per day of a drug for its primary indication in adults, whereas DOT measures the number of days a patient receives a particular drug, regardless of the dose (12). The remaining 19 studies evaluated the impact of pharmacist interventions on clinical outcomes, including 30-day mortality, length of hospital stay, ID consultations, and occurrence of adverse events, as summarized in Table 1.
All studies were single-centered except one that was conducted in five different hospitals. Among all included studies evaluating antifungal consumption, four studies evaluated DDD/1,000 patient days, and three studies measured DOT/1,000 patient days. Two studies measured DDD/100 patient or bed days (3, 13–18). Five studies were prospective quasi-experimental in design and conducted time series analysis, while two studies were observational, and 1 was prospective cohort. All studies have variable duration, with a least 18 months and a maximum duration of 10 years. Pharmacist interventions include educational interventions, prospective audits and feedback, and focusing adherence to guidelines.
Among studies evaluating clinical outcomes, seven studies were prospective, quasi-experimental in design, five studies were retrospective observational, five studies were prospective cohort, one was retrospective cohort, and one was cross-sectional in design. All studies were single-centered except one that evaluated clinical outcomes of AFS in five hospitals. The majority of studies were carried out on adult patients >18 years of age, and the maximum duration of the study was 7 years, and the minimum duration was 2 years (1, 2, 4–7, 9, 19–30), as shown in Table 1.
3.3 Interventions
Pharmacist interventions vary among the included studies. In five of the eight studies evaluating the impact of the consumption of antifungals, pharmacist interventions were based on educational activities that included academic detailing inculcating prospective audits and feedback (3, 13, 15, 17, 18). Other interventions include recommendations about diagnostic tests, TDM-based dosing and stopping treatment in patients without confirmed diagnosis (14), appropriate selection and modification of therapy (16), and optimizing antifungal therapy based on culture reports and guideline recommendations (18).
Nineteen studies that evaluated the impact on clinical outcomes, namely, pharmacist interventions included the development of candidemia care bundle based on Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines (19, 22), implementing antifungal (AF) susceptibility testing, culture alerts, initiation of echinocandins, removal of central lines (20), academic detailing (audit and feedback) regarding appropriate empiric regimen, tailoring and reassessment (2, 4, 29, 30), therapeutic drug monitoring (4, 5, 23, 25), and infectious disease referrals (1, 4) along with β-d-glucan (βDG) measurement (7, 9), recommendation according to European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESMID) guidelines for candidemia management (21), medical training for the physicians, pocket card summarizing recommendations for antifungal use and on-ward pharmaceutical counselling (6), stopping empirical antifungal after 72 h, automated alert and ID consult for empirical antifungals and switching from intravenous (IV) to oral fluconazole (1), ID pharmacist intervention regarding culture reports (26, 27), adherence to guidelines, application of non-culture based methods Galactomannan, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (27), feedback/education to physician (28) are shown in Table 1.
3.4 Antifungal consumption
Eight studies evaluated the impact of pharmacist interventions on antifungal consumption. Consumption metrics used were variable, and few studies involved more than one metric. Three studies measured DDD/1,000 patient days (3, 16, 18), One study measured DDD/100 bed days (14), one measured DDD/100 patients (15), three measured DOT/1,000 patient days (3, 16, 18), and one measured DDD/1,000 bed days (17). Due to the variability in measuring units, a quantitative estimation was not possible; however, DDD/1,000 patient days significantly declined (62%; p = 0.009; p < 0.001); a significant reduction in DDD/100 bed days (p < 0.017); a significant decrease in DDD/100 patients (p < 0.01); DOT/1,000 patient days remained insignificant in one study and a significant decrease in one study (p < 0.001) was evident; and one study showed an increase in DOT/1000 patients for anidulafungin and caspofungin while declining in fluconazole and L-amphotericin B as a result of pharmacist interventions (Table 1).
3.5 Clinical outcomes
Clinical outcomes that were evaluated post-AFS implementation included mortality, the length of hospital stay, the occurrence of adverse events, and the quality of antifungal use (Table 1).
3.6 Mortality
The impact of stewardship interventions was evaluated on 30-day, 60-day, and 14-day mortalities and on in-patient mortality in the included studies. Five studies reported the data of 30-day mortality, in which four showed non-significant results pre-/postintervention (19, 21, 22, 26) and one study showed a significant decline in 30-day mortality post-AFS (p = 0.05) (28). Furthermore, 60-day, 90-day, and 14-day mortalities pre-/post-AFS also remained non-significant (7, 21, 24). In-hospital/in-patient mortality was decreased significantly in one study (p = 0.054) (22) and non-significantly in two studies (9, 29).
3.7 Length of hospital stay
Five studies measured the length of hospital stay as an outcome of antifungal stewardship, and in all included studies post-AFS, there is a non-significant change in the length of hospital stay (4, 7, 9, 20, 29).
3.8 Adverse events
Four studies evaluated the role of pharmacist interventions on the occurrence of adverse drug events. One study showed that pharmacist interventions resulted in a significant decline in adverse events (p = 0.004) (7), and one study showed a significant increase in preventable adverse drug events post-AFS 58 vs. 230 (23). The results of another study evaluating TDM-based dosing identified that the drug discontinuation due to hepatotoxicity and visual symptoms was 62.5 and 26.3%, respectively (5), and one study identified that potential drug–drug interaction (pDDI) decreased significantly as a result of pharmacist interventions (p = 0.035) (28).
3.9 Quality of antifungal use
Quality of antifungal use encompasses appropriate drug selection, referrals for ID consultation, implementing culture tests, and adherence to guidelines. Fifteen studies evaluated different parameters of the quality of antifungal use post-AFS. Seven studies (1, 6, 19, 25, 28–30) evaluated appropriate drug selection, and all studies showed significant improvement in antifungal selection (p < 0.001, p < 0.005, p < 0.0001, p = 0.0001, p < 0.001, p = 0.01, and p = 0.001) respectively. The result of one study showed that repeat blood cultures were improved significantly (p = 0.012 and p = 0.04) (19, 21). One study reported a significant increase in ID consultation (p < 0.001) (20), and another study reported an increase from 36.4 to 86.5% (21). One study reported data on the resistance rate to azoles post-AFS, which was significantly declined (p < 0.001) (27), and the incidence of hospital-acquired candidemia was also decreased (p = 0.009). Three studies evaluated adherence to guidelines. One study showed significant adherence to IDSA guidelines (19); another study reported that achievement and adherence to the candidemia care bundle were significant postintervention (p = 0.006) (22); and one study showed significant adherence to clinical guidelines for antifungal prophylaxis (p = 0.0344) (25) as shown in Table 1.
3.10 Antifungal expenditure
Seven studies reported the impact of pharmacist intervention on antifungal expenditure or cost savings. Among all, the maximum reduction in antifungal expenditure was 73% (13), and the least reduction in cost was 13.5% (16). Two studies reported a significant decline in antifungal cost (p = 0.03 and p = 0.002), as shown in Table 1. An overall summary of study characteristics is shown in Table 2.
4 Discussion
This review aims to evaluate the role of AFS pharmacists in optimizing antifungal therapy and its impact on antifungal usage, consumption, and clinical outcomes globally. The majority of healthcare systems lack proper diagnostic techniques, and suboptimal levels of antifungal drugs with non-linear kinetics result in treatment failure (21). Literature has shown that pharmacist-driven AFS can enhance the appropriateness of antifungal treatments by improving the selection of drugs, dosages, and therapy durations, while also preventing potential drug interactions (27).
The stewardship approach was variable among all included studies, but the most common pharmacist intervention was academic detailing with audit and feedback followed by dose adjustments based on therapeutic drug monitoring. Prospective audits and feedback in hospital settings have been demonstrated to enhance the quality of prescription practices and are advocated as a vital component of antifungal stewardship (18). Medical training for physicians and on-ward pharmaceutical counseling regarding antifungal utilization can be crucial in securing a sustained impact of an interdisciplinary AFSP (9). Previous studies have shown that prescribers could not differentiate between fungal colonization and underlying disease, as well as the appropriate use of prophylactic vs. empirical antifungal medication (31). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) plays a crucial role in optimizing antifungal therapy, with routine recommendations for voriconazole monitoring outlined in the guidelines of the British Society for Medical Mycology and the IDSA (15). Voriconazole, being the first-line drug for invasive aspergillosis, exhibits non-linear pharmacokinetics, where both high and low serum concentrations are associated with increased risks of hepatotoxicity and therapeutic failure, respectively (25). Study results showed that with TDM-based dose adjustment, the treatment completion rate was increased (8.8%) (23). Another study reported that the major reason for non-adherence was a lack of TDM (32). Implementing TDM practices within healthcare institutions can enhance the effectiveness and safety of antifungal therapy by ensuring optimal drug exposure for each patient. Antifungal stewardship teams involving pharmacists in hospitals led to a notable decrease in the consumption and acquisition costs of antifungals (30). Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium recommended that Stewardship team core members should possess a deep understanding of fungal epidemiology and susceptibility patterns, laboratory diagnosis of IFD, the spectrum, and pharmacokinetics of antifungal drugs, strategies for optimizing dosing and duration, fungal surveillance, and the ability to anticipate, interpret, and manage drug–drug interactions and antifungal toxicities. Furthermore, proficiency in interpreting therapeutic drug monitoring is essential. Ideally, the team should include infectious diseases (ID) physician(s) and ID-trained pharmacist(s) whenever feasible (26).
The impact of stewardship intervention was evaluated on the consumption of antifungals. All included studies utilize variable matrices DDD/100 patient days, DOT/1,000 patient days, or DDD/1,000 bed days. However, overall, antifungal consumption decreases (3, 13–18) and results in a cost reduction of up to 74.7 (23), with another reporting 73% (13). In a systematic review conducted in 2017 on AFS interventions and performance measures, it was noted that antifungal consumption exhibited a decrease ranging from 11.8 to 71% and a reduction in expenditure of 50% (17). AFS programs aim to strike a balance between effective treatment and prudent use of antifungal agents, decreasing overall antifungal consumption. Pharmacist interventions are crucial in reducing antifungal consumption by optimizing therapy, implementing evidence-based guidelines, utilizing therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), providing education and training, and transitioning patients from intravenous to oral antifungals when appropriate. These strategies help ensure the judicious use of antifungal agents, ultimately reducing both consumption and associated healthcare costs (9). Antifungal drugs are expensive; their judicious use promotes better resource allocation, reduces healthcare costs, and improves patient outcomes. Optimization of antifungal therapy by ensuring appropriate selection, dosing, and treatment duration, not only curbs unnecessary spending but also lowers the risk of antifungal resistance, ultimately enhancing the quality of care for patients with fungal infections (13).
Another parameter evaluated in this review was clinical outcomes including mortality, the length of hospital stay, the occurrence of adverse events, and the quality of antifungal prescribing or use. Major interventions of pharmacists include academic detailing, tailoring drug therapy based on culture reports, and conducting therapeutic drug monitoring. In-hospital/patient mortality decreased significantly in one study (22), and one study showed a significant decline in 30-day mortality post-AFS (28), while all other included studies reported a non-significant decline in mortality and length of hospital stay. Although it was non-significant, overall, AFS decreases mortality and length of hospital stay. However, the exact estimate is not possible as the underlying disease may be associated with early mortality. More studies are required to further strengthen this evidence. Moreover, heterogeneity of patient population, diverse clinical presentation and variable treatment response contribute to the difficulty in providing precise estimates for mortality and LOS in immunocompromised patients with systemic fungal infections. Four studies identifying the impact of adverse events reported a significant decline in adverse event occurrence and potential drug–drug interactions (5, 7, 23, 28). AFS programs involve regular monitoring of patients on antifungal therapy. This surveillance helps promptly identify and address adverse events, contributing to improved patient safety (27).
Quality of antifungal use evaluated post-AFS in 15 studies includes appropriate prescribing, culture-based drug tailoring, and adherence to guidelines for fungal infection management. All included studies reported significant improvement in antifungal prescribing, culture evaluation for targeting therapy, and adherence to guidelines. Diagnostic precision and optimized dosing overall improve the quality of antifungal use (19).
5 Conclusion
Pharmacist-led AFS has the potential to enhance the effectiveness of antifungal treatments by improving their overall quality and reduction in antifungal consumption, adverse events, and antifungal expenditure. Moreover, novel fungal diagnostic techniques, TDM, and antifungal susceptibility testing must be integrated with AFS in hospitals to rationalize antifungal use and decrease the emerging threat of antifungal resistance.
5.1 Strength and limitation
Systematic reviews focusing on pharmacist-driven antifungal stewardship interventions after 2018 are scarce. Thus, we collected literature from PubMed and Google Scholar databases to present and evaluate the published evidence in the last 5 years (2018–2023). Due to limited institutional access to other resources such as Embase and Scopus, data collection was restricted only to two databases. The major limitation is variation in interventions and outcome metrics; hence, an integrative review approach was utilized. Variations in healthcare settings may limit the generalizability of the findings. All primary studies used descriptive statistics for their evaluations, presenting findings as frequencies and percentages without employing an effect measure estimate; therefore, results were presented descriptively.
5.2 Future perspective
Future research should investigate the influence of pharmacist-led stewardship in outpatient clinics and community settings. In addition, further studies are also warranted on the pediatric population using the DOT methodology to provide a more comprehensive and standardized assessment of pharmacist interventions on consumption as well as clinical outcomes. Detailed subgroup analyses based on specific healthcare settings and intervention types are also required to elucidate how differences in healthcare settings and types of interventions impact clinical outcomes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZA: Data curation, Writing – original draft. MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Jenks, JD, Cornely, OA, Chen, SCA, Thompson Iii, GR, and Hoenigl, M. Breakthrough invasive fungal infections: who is at risk? Mycoses. (2020) 63:1021–32. doi: 10.1111/myc.13148
2. Kmeid, J, Jabbour, J-F, and Kanj, SS. Epidemiology and burden of invasive fungal infections in the countries of the Arab league. J Infect Public Health. (2020) 13:2080–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2019.05.007
3. Borjian Boroujeni, Z, Shamsaei, S, Yarahmadi, M, Getso, MI, Salimi Khorashad, A, Haghighi, L, et al. Distribution of invasive fungal infections: molecular epidemiology, etiology, clinical conditions, diagnosis and risk factors: a 3-year experience with 490 patients under intensive care. Microb Pathog. (2021) 152:104616. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104616
4. Dadgostar, P. Antimicrobial resistance: implications and costs. Infect Drug Resist. (2019) 12:3903–10. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S234610
5. Hendrickson, JA, Hu, C, Aitken, SL, and Beyda, N. Antifungal resistance: a concerning trend for the present and future. Curr Infect Dis Rep. (2019) 21:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11908-019-0702-9
6. Gupta, AK, Venkataraman, M, Renaud, HJ, Summerbell, R, Shear, NH, and Piguet, V. The increasing problem of treatment-resistant fungal infections: a call for antifungal stewardship programs. Int J Dermatol. (2021) 60:e474–9. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15495
7. Fisher, MC, and Denning, DW. The who fungal priority pathogens list as a game-changer. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2023) 21:211–2. doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00861-x
8. Perlin, DS, Rautemaa-Richardson, R, and Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. The global problem of antifungal resistance: prevalence, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Infect Dis. (2017) 17:e383–92. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30316-X
9. Lachenmayr, SJ, Strobach, D, Berking, S, Horns, H, Berger, K, and Ostermann, H. Improving quality of antifungal use through antifungal stewardship interventions. Infection. (2019) 47:603–10. doi: 10.1007/s15010-019-01288-4
10. Page, MJ, Mckenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. The Prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
11. Sterne, JA, Hernán, MA, Reeves, BC, Savović, J, Berkman, ND, Viswanathan, M, et al. Robins-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. (2016) 355. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4919
12. Vallès, J, Fernández, S, Cortés, E, Morón, A, Fondevilla, E, Oliva, JC, et al. Comparison of the defined daily dose and days of treatment methods for evaluating the consumption of antibiotics and antifungals in the intensive care unit. Med Intensiva. (2020) 44:294–300. doi: 10.1016/j.medin.2019.06.008
13. Alsalman, J, Althaqafi, A, Alsaeed, A, Subhi, A, Mady, AF, Alhejazi, A, et al. Middle Eastern expert opinion: strategies for successful antifungal stewardship program implementation in invasive fungal infections. Cureus. (2024) 16:e61127. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61127
14. Amanati, A, Badiee, P, Jafarian, H, Ghasemi, F, Nematolahi, S, Haghpanah, S, et al. Impact of antifungal stewardship interventions on the susceptibility of colonized Candida species in pediatric patients with malignancy. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:14099. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93421-3
15. Ashok, A, Mangalore, RP, and Morrissey, CO. Azole therapeutic drug monitoring and its use in the Management of Invasive Fungal Disease. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. (2022) 16:55–69. doi: 10.1007/s12281-022-00430-4
16. Benoist, H, Rodier, S, De La Blanchardière, A, Bonhomme, J, Cormier, H, Thibon, P, et al. Appropriate use of antifungals: impact of an antifungal stewardship program on the clinical outcome of candidaemia in a French university hospital. Infection. (2019) 47:435–40. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-01264-4
17. Bienvenu, AL, Argaud, L, Aubrun, F, Fellahi, JL, Guerin, C, Javouhey, E, et al. A systematic review of interventions and performance measures for antifungal stewardship programmes. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2018) 73:297–305. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx388
18. Bio, LL, Weng, Y, and Schwenk, HT. Antifungal stewardship in practice: insights from a prospective audit and feedback program. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. (2023) 44:2017–21. doi: 10.1017/ice.2023.129
19. Chakrabarti, A, Mohamed, N, Capparella, MR, Townsend, A, Sung, AH, Yura, R, et al. The role of diagnostics-driven antifungal stewardship in the Management of Invasive Fungal Infections: a systematic literature review. Open Forum Infect Dis. (2022) 9:ofac234. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofac234
20. Chen, P-Z, Wu, C-C, and Huang, C-F. Clinical and economic impact of clinical pharmacist intervention in a hematology unit. J Oncol Pharm Pract. (2020) 26:866–72. doi: 10.1177/1078155219875806
21. Fisher, MC, Alastruey-Izquierdo, A, Berman, J, Bicanic, T, Bignell, EM, Bowyer, P, et al. Tackling the emerging threat of antifungal resistance to human health. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2022) 20:557–71. doi: 10.1038/s41579-022-00720-1
22. Gamarra, F, Nucci, M, and Nouér, SA. Evaluation of a stewardship program of antifungal use at a Brazilian tertiary care hospital. Braz J Infect Dis. (2022) 26:102333. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2022.102333
23. Hamada, Y, Ueda, T, Miyazaki, Y, Nakajima, K, Fukunaga, K, Miyazaki, T, et al. Effects of antifungal stewardship using therapeutic drug monitoring in voriconazole therapy on the prevention and control of hepatotoxicity and visual symptoms: a multicentre study conducted in Japan. Mycoses. (2020) 63:779–86. doi: 10.1111/myc.13129
24. Ito-Takeichi, S, Niwa, T, Fujibayashi, A, Suzuki, K, Ohta, H, Niwa, A, et al. The impact of implementing an antifungal stewardship with monitoring of 1-3, β-D-glucan values on antifungal consumption and clinical outcomes. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2019) 44:454–62. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12809
25. Job, KM, Olson, J, Stockmann, C, Constance, JE, Enioutina, EY, Rower, JE, et al. Pharmacodynamic studies of voriconazole: informing the clinical management of invasive fungal infections. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther. (2016) 14:731–46. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2016.1207526
26. Johnson, MD, Lewis, RE, Dodds Ashley, ES, Ostrosky-Zeichner, L, Zaoutis, T, Andes, DR, et al. Core recommendations for antifungal stewardship: a statement of the mycoses study group education and research consortium. J Infect Dis. (2020) 222:S175–98. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa394
27. Kara, E, Metan, G, Bayraktar-Ekincioglu, A, Gulmez, D, Arikan-Akdagli, S, Demirkazik, F, et al. Implementation of pharmacist-driven antifungal stewardship program in a tertiary care hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2021) 65:e0062921. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00629-21
28. Kawaguchi, H, Yamada, K, Imoto, W, Yamairi, K, Shibata, W, Namikawa, H, et al. The effects of antifungal stewardship programs at a tertiary-care teaching hospital in Japan. J Infect Chemother. (2019) 25:458–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.01.015
29. Keck, JM, Cretella, DA, Stover, KR, Wagner, JL, Barber, KE, Jhaveri, TA, et al. Evaluation of an antifungal stewardship initiative targeting micafungin at an Academic Medical Center. Antibiotics. (2023) 12:193. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12020193
30. Khanina, A, Cairns, KA, Kong, DC, Thursky, KA, Slavin, MA, and Roberts, JA. The impact of pharmacist-led antifungal stewardship interventions in the hospital setting: a systematic review. J Pharm Pract Res. (2021) 51:90–105. doi: 10.1002/jppr.1721
31. Valerio, M, Vena, A, Bouza, E, Reiter, N, Viale, P, Hochreiter, M, et al. How much European prescribing physicians know about invasive fungal infections management? BMC Infect Dis. (2015) 15:80. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-0809-z
32. Reslan, Z, Lindsay, J, Kerridge, I, and Gellatly, R. Pharmacist review of high-risk haematology outpatients to improve appropriateness of antifungal prophylaxis. Int J Clin Pharm. (2020) 42:1412–8. doi: 10.1007/s11096-020-01090-5
33. Morii, D, Ichinose, N, Yokozawa, T, and Oda, T. Impact of an infectious disease specialist on antifungal use: an interrupted time-series analysis in a tertiary hospital in Tokyo. J Hosp Infect. (2018) 99:133–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2018.01.003
34. Nwankwo, L, Periselneris, J, Cheong, J, Thompson, K, Darby, P, Leaver, N, et al. Impact of an antifungal stewardship programme in a tertiary respiratory medicine setting: A prospective real-world study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2018) 62:e00402-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00402-18
35. So, M, Mamdani, M, Morris, A, Lau, T, Broady, R, Deotare, U, et al. Effect of an antimicrobial stewardship programme on antimicrobial utilisation and costs in patients with leukaemia: a retrospective controlled study. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2018) 24:882–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2017.11.009
36. Martín-Gutiérrez, G, Peñalva, G, De Pipaón, MR-P, Aguilar, M, Gil-Navarro, MV, Pérez-Blanco, JL, et al. Efficacy and safety of a comprehensive educational antimicrobial stewardship program focused on antifungal use. J Infect. (2020) 80:342–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.01.002
37. Samura, M, Hirose, N, Kurata, T, Ishii, J, Nagumo, F, Takada, K, et al. Support for fungal infection treatment mediated by pharmacist-led antifungal stewardship activities. J Infect Chemother. (2020) 26:272–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2019.09.016
38. Markogiannakis, A, Korantanis, K, Gamaletsou, MN, Samarkos, M, Psichogiou, M, Daikos, G, et al. Impact of a non-compulsory antifungal stewardship program on overuse and misuse of antifungal agents in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2021) 57:106255. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106255
39. Murakami, M, Komatsu, H, Sugiyama, M, Ichikawa, Y, Ide, K, Tsuchiya, R, et al. Antimicrobial stewardship without infectious disease physician for patients with candidemia: a before and after study. J Gen Fam Med. (2018) 19:82–9. doi: 10.1002/jgf2.159
40. Rac, H, Wagner, JL, King, ST, Barber, KE, and Stover, KR. Impact of an antifungal stewardship intervention on optimization of candidemia management. Ther Adv Infect Dis. (2018) 5:3–10. doi: 10.1177/2049936117745267
Keywords: antifungal, stewardship, pharmacist, consumption, clinical, interventions
Citation: Akbar Z, Aamir M and Saleem Z (2024) Optimizing antifungal therapy: a systematic review of pharmacist interventions, stewardship approaches, and outcomes. Front. Med. 11:1489109. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1489109
Edited by:
L Gayani Tillekeratne, Duke University, United StatesReviewed by:
Josh Clement, Mount Sinai Hospital, United StatesAna Afonso, NOVA University of Lisbon, Portugal
Copyright © 2024 Akbar, Aamir and Saleem. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zunaira Akbar, enVuYWlyYS5ha2JhckBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Zunaira Akbar
Zunaira Akbar Muhammad Aamir1
Muhammad Aamir1 Zikria Saleem
Zikria Saleem