
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Med., 22 January 2025
Sec. Pulmonary Medicine
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2024.1488796
 Chun Wang
Chun Wang Na Liu*
Na Liu*Objective: This study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis to assess the present state, thematic focus, and emerging developments in the research literature on the involvement of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury (PFALI), as well as other pertinent research areas.
Methods: This bibliometric study examined PFALI research published from 1 January 2004 to 24 May 2024, utilizing the Web of Science database. The analysis was conducted using CiteSpace, VOSviewer, R, and GraphPad Prism 8.0, and encompassed metadata on the countries, institutions, authors, journals, and keywords represented in the literature.
Results: This study analyzed 1,495 publications, comprising 1,194 articles and 301 reviews, to assess the publication output on PFALI. China exhibited the highest output with 964 (64.48%) articles. Central South University was the most prolific institution, contributing 54 (3.61%) publications. Zhou, Yong had the greatest individual publication record, with 15 (3.59%) articles. The journal International Immunopharmacology published the most PFALI-related articles at 76 (5.09%). The identified research frontiers for upcoming years include “iron,” “sirt1,” “repair,” and “alveolar macrophage pyroptosis.”
Conclusion: This bibliometric analysis comprehensively examined research trends and advancements related to PFALI, including the contributions of key authors, institutions, and countries.
Acute lung injury (ALI) is an acute, progressive inflammatory condition of the lungs characterized by inflammatory cell infiltration, increased permeability of the alveolar-capillary barrier, and acute diffuse alveolar edema. It is a life-threatening hypoxic respiratory disease (1). Pyroptosis is a newly discovered form of programmed cell death that depends on the cleavage of the gasdermin (GSDM) protein by caspases in the cytoplasm. The activated N-terminal domain of GSDM (GSDM-NTD) forms pores in the cell membrane, ultimately leading to cell swelling, lysis, and amplified inflammatory responses (2–4). While apoptosis is a physiological, genetically regulated form of cell death characterized by membrane blebbing, cell shrinkage, and formation of apoptotic bodies without cell rupture or inflammatory factor release (5, 6). Growing evidence suggests that pyroptosis plays a crucial role in the pulmonary inflammatory response in ALI (7–9). Inhibiting pyroptosis is a promising therapeutic approach for ALI.
Bibliometric analysis is a well-established approach to evaluate published research and identify emerging trends in scientific fields. This quantitative method utilizes mathematical and statistical techniques to investigate various aspects of academic disciplines, including collaborations among countries, institutions, authors, journals, and individual publications (10–12). In the context of ALI, there has been a substantial volume of research focused on the role of pyroptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of this condition. However, a comprehensive bibliometric assessment of the literature on pyroptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury (PFALI) is currently lacking. Such an analysis could provide valuable insights into the evolving landscape of this research domain. The present article will use bibliometric methods to provide an overview of the latest advances in the involvement of the pyroptosis mechanism in the inflammatory response of ALI, with the aim of offering new insights into the pathogenesis and treatment of ALI.
On 24 May 2024, a comprehensive literature search was conducted in the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) at The Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. The search strategy employed the following query: ((((TS = (Inflammasome OR Pyroptosis)) AND TS = (Acute Lung Injury OR Lung Injury OR ARDS OR Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome)) AND LA = (English)) AND DT = (Article OR Review)) NOT DT = (Retracted Publication OR Proceedings Paper OR Book Chapters). This search retrieved articles that referenced PFALI or its synonyms in the title, abstract, or keywords. The search was limited to English-language articles and review papers published between 1 January 2004 and 24 May 2024, excluding documents predating 1 January 2004, as well as case reports, meeting abstracts, editorial materials, and other non-article/review document types.
On 24 May 2024, a literature search was conducted in the WoSCC to retrieve comprehensive data on PFALI-related research. The bibliometric data collected included authorship details, publication titles, source information, funding acknowledgments, citation counts, abstracts, author affiliations, document types, and cited references. The data was obtained in various formats, such as txt, Excel, tab, and BibTeX, to enable further analysis. Additionally, the H-index of the top 10 most prolific authors and the 2022 impact factor and Journal Citation Report category quartile of the 10 primary PFALI-focused journals were sourced from Web of Science. This extensive data collection aimed to provide a robust foundation for the subsequent bibliometric analysis and visualization of the PFALI research landscape.
The bibliometric data was analyzed using an array of specialized software tools, including VOSviewer 1.6.19, CiteSpace 6.1R6, SCImago Graphica Beta 1.0.3, and the bibliometrix package (version 4.1.2) in R language (version 4.2.3). VOSviewer was employed to identify the top 10 keywords with the highest occurrence and to cluster the leading 46 keywords. Utilizing VOSviewer, Pajek64, and SCImago Graphica, knowledge maps were created to visualize prominent authors, contributing nations and institutions, core journals, influential publications, co-occurring keywords, and co-cited references. CiteSpace was used to evaluate the collaborative centrality among countries/regions, institutions, and authors. Furthermore, the bibliometrix package was leveraged for trend topic detection and to produce visual depictions of publication volume and collaborative relationship networks. This comprehensive suite of bibliometric analyses and visualization techniques provided a robust and multifaceted examination of the PFALI research landscape.
The comprehensive literature search of the WoSCC database yielded a total of 1,495 publications related to PFALI, covering the period from 1 January 2004 to 24 May 2024. These publications comprised 1,194 original research articles and 301 review articles, as depicted in Figure 1.
The frequency of PFALI-related publications exhibited an increasing pattern over time, meanwhile, accompanied by an overall upward trend in total citations, as shown in Figures 2A, B. Furthermore, the compiled data on total citations and annual publications by continent are presented in Figures 2C, D. Collectively, the PFALI-related publications have amassed a total of 48,158 citations, resulting in an average of 32.78 citations per article. This remarkable citation count underscores the significant impact and importance of this research field within the scientific community.
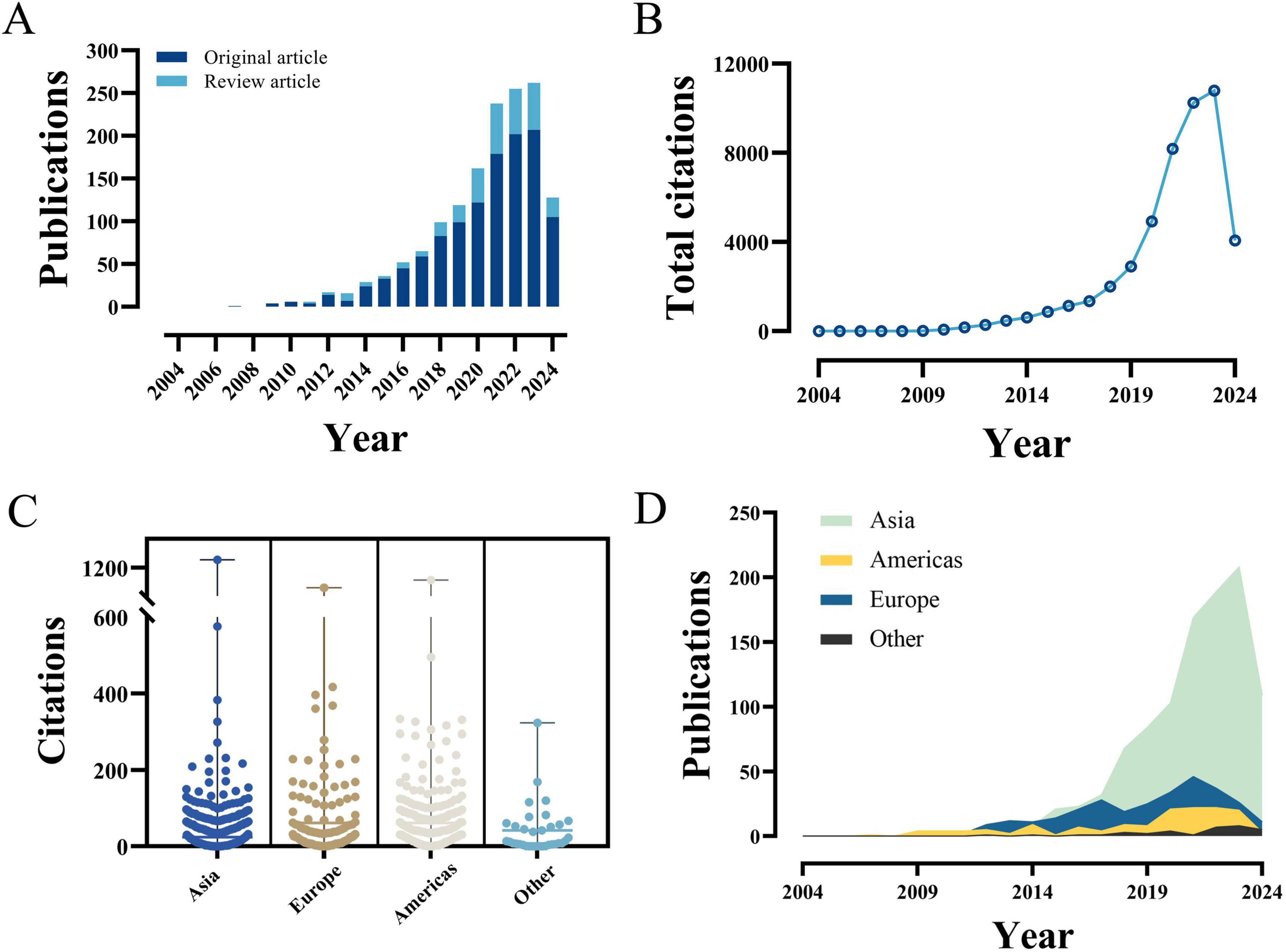
Figure 2. The yearly quantity and citations of publications pertaining to PFALI. (A) The yearly quantity. (B) The yearly citations. (C) The yearly citations to each continent. (D) The yearly quantity to each continent.
The PFALI-related publications were disseminated across 62 countries/regions spanning six continents, with notable collaboration observed among the regions of East Asia, North America, and Western Europe, as depicted in Figure 3A. The top five countries ranked by productivity in publishing PFALI articles are: China with 964 publications (64.48%), the United States with 324 publications (21.67%), Germany with 44 publications (2.94%), the United Kingdom with 43 publications (2.88%), and France with 36 publications (2.41%). Regarding citation impact, the articles originating from China have received the highest total number of citations at 21,785, while those from Germany have the highest average number of citations per article at 76.48, as shown in Table 1. The citation patterns across the contributing countries were further visualized in Figure 3B.
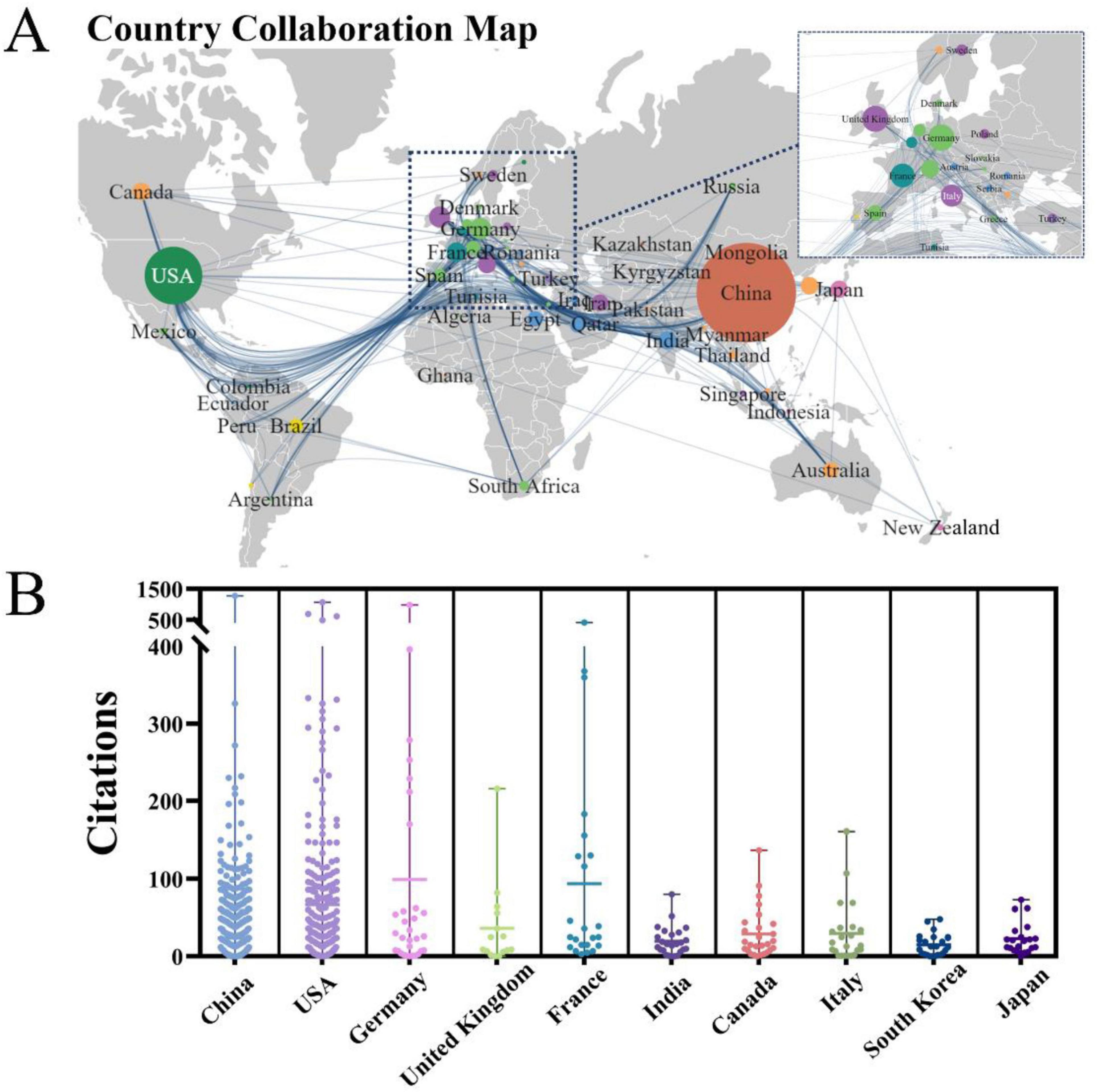
Figure 3. The collaborative map and clusters of the country. (A) Country collaboration map and documents density. (B) Visualization of publication output among major countries.
The observed patterns of collaboration and citation influence shed light on the global collaborative networks and intellectual structure underpinning the PFALI research domain.
The comprehensive analysis of the PFALI research landscape identified a total of 1,495 publications authored by 8,806 individuals affiliated with 1,629 institutes across 62 countries and regions. The top five most prolific institutions contributing to this body of research are: Central South University (54 publications, 3.61%), Fudan University (50 publications, 3.34%), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (47 publications, 3.14%), Huazhong University of Science and Technology (38 publications, 2.54%), and Nanjing Medical University (36 publications, 2.41%), as shown in Table 2.
The institutional collaboration network revealed seven distinct clusters, with the cluster consisting of Central South University, Fudan University, Nanjing Medical University, and others demonstrating the highest degree of collaboration, as depicted in Figure 4A. The citation patterns for the top institutions were further visualized in Figure 4B, providing insights into the intellectual influence and impact of these leading research centers within the PFALI domain. Among the top 10 most productive authors, Zhou, Yong was the most prolific with 15 publications (3.59%), followed by Carvajal, Richard D. with 11 publications and Johnson, Douglas B. with 16 publications (1.07%). Notably, 6 of the top 10 most productive authors were affiliated with institutions in China, while the remaining 4 were from the United States. Dietrich, W. Dalton from the University of Miami in the United States exhibited the highest h-index of 93 among the top authors, underscoring his significant scholarly impact (Table 3).
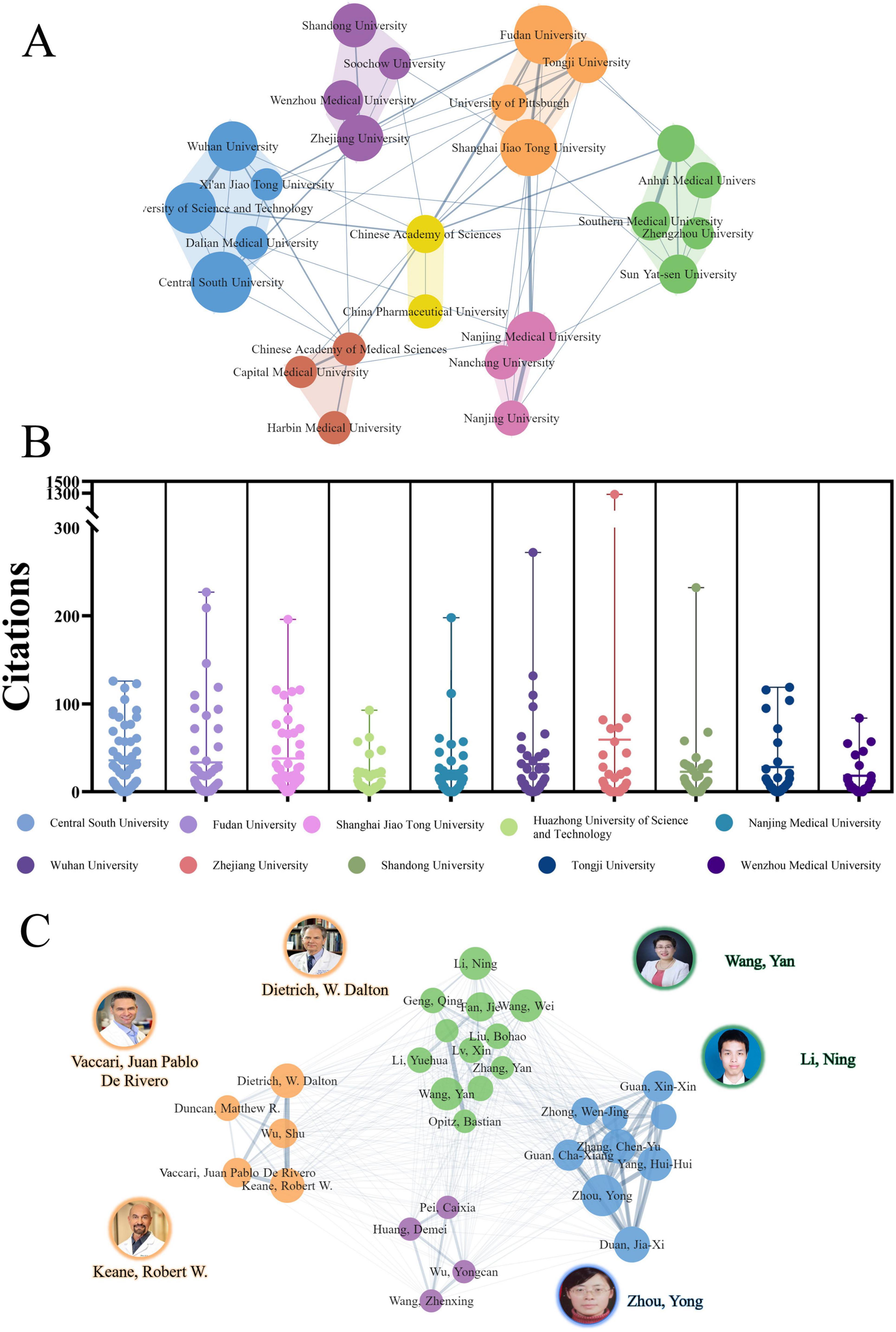
Figure 4. Collaborative clustering of institutions and authors. (A) Collaborative clustering of institutions. (B) Citations to each institute. (C) Collaborative clustering of authors.
The authors exhibited a relatively elevated level of cooperation, as evidenced by the presence of seven clusters in the collaborative network visualized relatively elevated level of cooperation, as evidenced by the presence of seven clusters, as depicted in Figure 4C. This comprehensive analysis of the PFALI research landscape, encompassing the institutional, authorial, and collaborative dimensions, provides a rich and multifaceted understanding of the intellectual structure, productivity, and impact within this important field of study.
The expansive PFALI research has been disseminated across 445 academic journals, with the top 10 most productive journals presented in Table 4.
The journal exhibiting the highest level of productivity is International Immunopharmacology, which has published 76 (5.09%) PFALI-related articles, followed by Frontiers in Immunology with 62 (4.15%) articles, International Journal of Molecular Sciences with 36 (2.41%) articles, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy with 28 (1.87%) articles, and Inflammation with an additional 28 (1.87%) articles (Table 4). Applying the bibliometric principle of Bradford’s Law, which describes the distribution of scientific literature, a core set of 13 journals has been identified as the most influential in the PFALI research domain, including the aforementioned top publishing outlets as well as others (Supplementary Figure 1A). The citation patterns for these core journals were further visualized (Supplementary Figure 1B), providing insights into their relative intellectual impact within the field. Notably, the Journal of Immunology has achieved the highest average citation rate among the PFALI publications, with an average of 81.04 citations per article. The top 10 most-cited PFALI publications, as listed in Table 5, underscores the significant influence and impact of these seminal works within the research community.
Ahmed et al. (13) conducted a comprehensive review of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, its downstream targets, and its effects in animal models of inflammatory diseases. The review also addressed the crosstalk between this pathway and the NF-κB pathway, as well as the regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by Nrf2. Additionally, the current landscape of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals and other agents that modulate the Nrf2/ARE signaling axis was summarized.
The comprehensive analysis of keyword co-occurrence among the 46 most prominent keywords in the PFALI research landscape has revealed four distinct thematic clusters. The cluster comprising keywords such as “acute lung injury,” “pyroptosis,” “NLRP3,” and “inflammation” demonstrated the most frequent and robust co-occurrence, underscoring the central importance of these conceptual focal points within the PFALI research domain (Figure 5A). Furthermore, a heatmap visualization of the top 30 keywords exhibiting the most dynamic emergence over time was presented in Figure 5B.
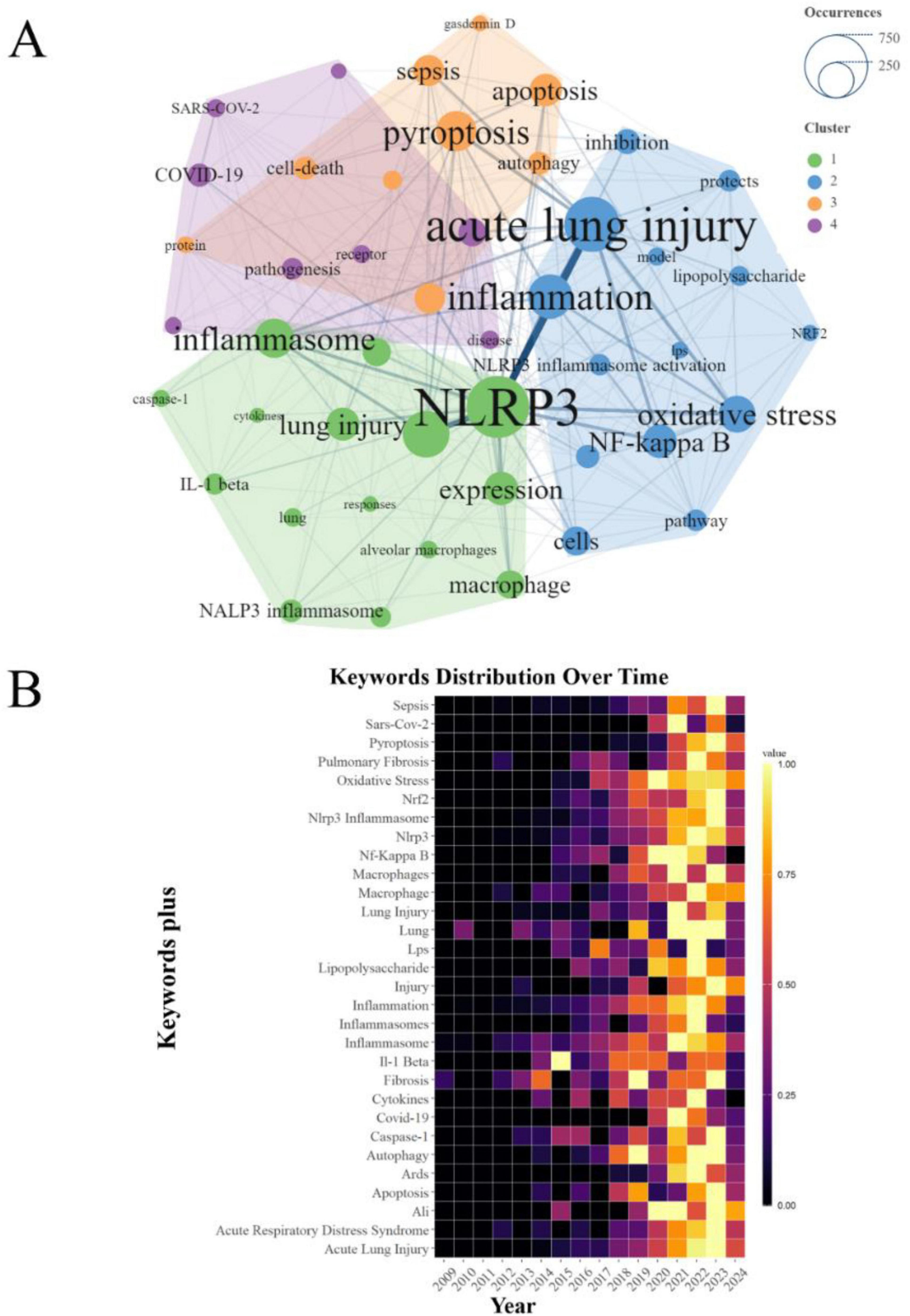
Figure 5. Analysis of keywords. (A) Clustering of the top 46 keywords with the highest number of occurrences. (B) Keywords heatmap of the top 30.
Building upon these synchronic and diachronic analyses of keyword patterns, the study also examined the broader trend topics that have gained prominence in PFALI research from 2000 to 2024. This longitudinal perspective illuminates the shifting research foci and emerging areas of scholarly interest within the field over the past two decades and into the near future. The research frontiers for the upcoming years have been identified as “iron,” “sirt1,” “repair,” and “alveolar macrophage pyroptosis” (Supplementary Figure 2), suggesting that these newly ascendant themes are poised to drive the next wave of advancements and discoveries within the dynamic and rapidly evolving PFALI research landscape.
Acute lung injury and its progression to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) represent the clinical manifestations of severe acute pulmonary inflammation. Globally, the mortality rate associated with ALI/ARDS can be as high as 35%–40% (16, 23). The common etiologies of ALI include infection, trauma, pulmonary contusion, and aspiration of gastric contents. The primary pathological features of ALI are a result of the severe inflammatory response in the lungs, leading to a series of lung tissue and cellular injuries, such as diffuse infiltration of mononuclear macrophages, destruction of the alveolar epithelial structure, increased microvascular permeability, and impaired gas exchange (24–26). However, the precise pathogenic mechanisms underlying the development of ALI remain unclear. Pyroptosis is a distinct form of cell death, primarily involving the classical inflammasome-induced pathway, the non-classical inflammasome-induced pathway, and the GSDM-related pathway. Pyroptosis is characterized by cell swelling and lysis, accompanied by the release of inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) (27–29). Growing evidence suggests that pyroptosis plays a crucial role in the pulmonary inflammatory response in ALI. Inhibiting pyroptosis is a promising therapeutic approach for ALI. To better elucidate the role of PFALI, this study conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis, examining a total of 1,495 publications, including 1,194 articles and 301 reviews, to assess the publication output on PFALI. Notably, China exhibited the highest publication output with 964 (64.48%) articles. Among the institutions analyzed, Central South University was found to be the most productive with 54 (3.61%) publications. The study findings indicate that Zhou, Yong had the highest publication records. International Immunopharmacology was the most productive journal with a total of 76 (5.09%) articles published. The research frontiers for the upcoming years have been identified as “iron,” “sirt1,” “repair,” and “alveolar macrophage pyroptosis.” Recent studies have focused on repairing cell functions through various mechanisms, such as the crosstalk between pyroptosis and ferroptosis (30), the SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway (31–33), alveolar macrophage (AM) pyroptosis (34–36). Cao et al. (30) found that crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 mechanisms contributes to sepsis-induced lung injury in a mouse model. Zhang et al. (31) concluded that Apelin alleviates sepsis-induced ALI by modulating the SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway to inhibit endothelial cell (EC) pyroptosis, highlighting its clinical significance. Huang et al. (32) found that circVAPA overexpression targets miR-212-3p, negatively regulating SIRT1 and pyroptosis-related factors, which mitigates inflammatory damage in sepsis-induced ALI. Jin et al. (33) engineered VCAM-1-targeted nanostructured lipid carriers to deliver melatonin against acute lung injury via the SIRT1/NLRP3 pyroptosis signaling pathway. Zhao et al. (34) emphasized the protective role of ADAR1 in pulmonary macrophages against pyroptosis, suggesting targeting ADAR1/miR-21 signaling as a therapeutic option for sepsis-related lung injury. Liu et al. (35) demonstrated that MSC-derived exosomes effectively treat ALI by inhibiting AM pyroptosis and reducing inflammation through specific miRNAs and immunoregulatory proteins. Finally, Gong et al. (36) found that exosomal Tenascin-C, released from AECs under unresolved ER stress, exacerbates acute lung injury by intensifying sepsis-associated inflammatory responses, providing new insights into the cellular interactions involved in sepsis-induced ALI.
The research on PFALI has progressed and exhibited a global trend over time, and we have conducted a detailed bibliometric analysis of the literature. The key findings are as follows:
Pulmonary ECs line the inner wall of the lung microvasculature, forming the endothelial barrier (37). Pyroptosis of ECs and the subsequent release of IL-1β can induce injury and inflammation to the endothelial barrier, leading to the loss of endothelial integrity, increased vascular permeability, and the development of pulmonary edema in ALI (38, 39). Inflammatory caspases drive pyroptosis in acute lung injury, and the inhibition of EC pyroptosis may be an important therapeutic strategy for ALI. ECs injury and death occur at different stages of ALI, with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) inducing EC pyroptosis via the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway (40). NF-κB is a pro-inflammatory transcription factor that activates several genes, including NLRP3. Inhibiting the NF-κB-NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in ECs can reduce LPS-induced ALI (41).
Alveolar macrophages are essential for innate immunity and host defense. The release of inflammatory cytokines by AMs and the subsequent regulation of other immune cells contribute to the persistent and excessive inflammatory response, which is a key factor in the pathogenesis of ALI. AMs pyroptosis is involved in the initiation of the inflammatory response in ALI (42, 43). The NLRP3-mediated pathway of AMs pyroptosis can trigger the release of HMGB1 from AMs. As a PAMP, HMGB1 further activates NLRP3 and caspase-1, creating a positive feedback loop that amplifies AM pyroptosis and worsens ALI severity (44). Pyroptosis can lead to organ injury resulting from ischemia/reperfusion injury. HMGB1 protein can activate the production of ROS and induce oxidative stress, triggering a series of inflammatory responses that contribute to the development of ALI. Recombinant HMGB1 (rH-MGBL1) can inhibit AMs pyroptosis and improve lung ischemia-reperfusion injury through the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. This pathway suppresses the deleterious effects of pyroptosis and the associated inflammatory responses (45). Jiang et al. (46) identified the TRAF3-ULK1-NLRP3 axis as a critical regulatory pathway governing AMs pyroptosis in the context of ALI. The findings underscore the significance of this regulatory axis in ALI pathogenesis and suggest that targeting this pathway could represent an effective therapeutic strategy for ALI treatment. Liu et al. (35) reported that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) exhibited efficacy in the treatment of ALI by inhibiting AMs pyroptosis and attenuating the inflammatory response. The proposed mechanism involves pyroptosis-targeting miRNAs and immunoregulatory proteins delivered by MSC-Exo. These findings suggest that MSC-Exo may represent a promising new therapeutic option for the early management of ALI.
In the LPS-induced ARDS mouse model and in ARDS patients, the cleavage of GSDMD is upregulated in neutrophils (NEs). The cleaved N-terminal fragment of GSDMD forms pores in the neutrophil membrane, promoting the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). NETs are web-like structures composed of chromatin fibers and granule-derived antimicrobial peptides and enzymes, which can capture and kill bacteria. The GSDMD fragments cleaved in neutrophils play a critical role in the development of ARDS through their involvement in NET formation (47). Huang et al. (48) found that ficolin-A/2 exacerbates severe lung injury by promoting NET formation, a process mediated by gasdermin D-induced pyroptosis. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) are crucial in the development of sepsis-associated ALI. PMN-derived exosomes contain miR-30d-5p, which targets cytokine signaling inhibitors SOCS-1 and SIRT1, activating the NF-κB pathway. This activation upregulates NLRP3 inflammasome expression in macrophages, leading to macrophage pyroptosis and promoting M1 polarization. The interactions between PMNs and macrophages contribute to the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated ALI (49). Pyroptosis of other cell types also contributes to the development of ALI. The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediates LPS-induced pyroptosis of BEAS-2B cells through the miR-26a-5p/Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) axis, contributing to the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated ALI (50) (Figure 6).
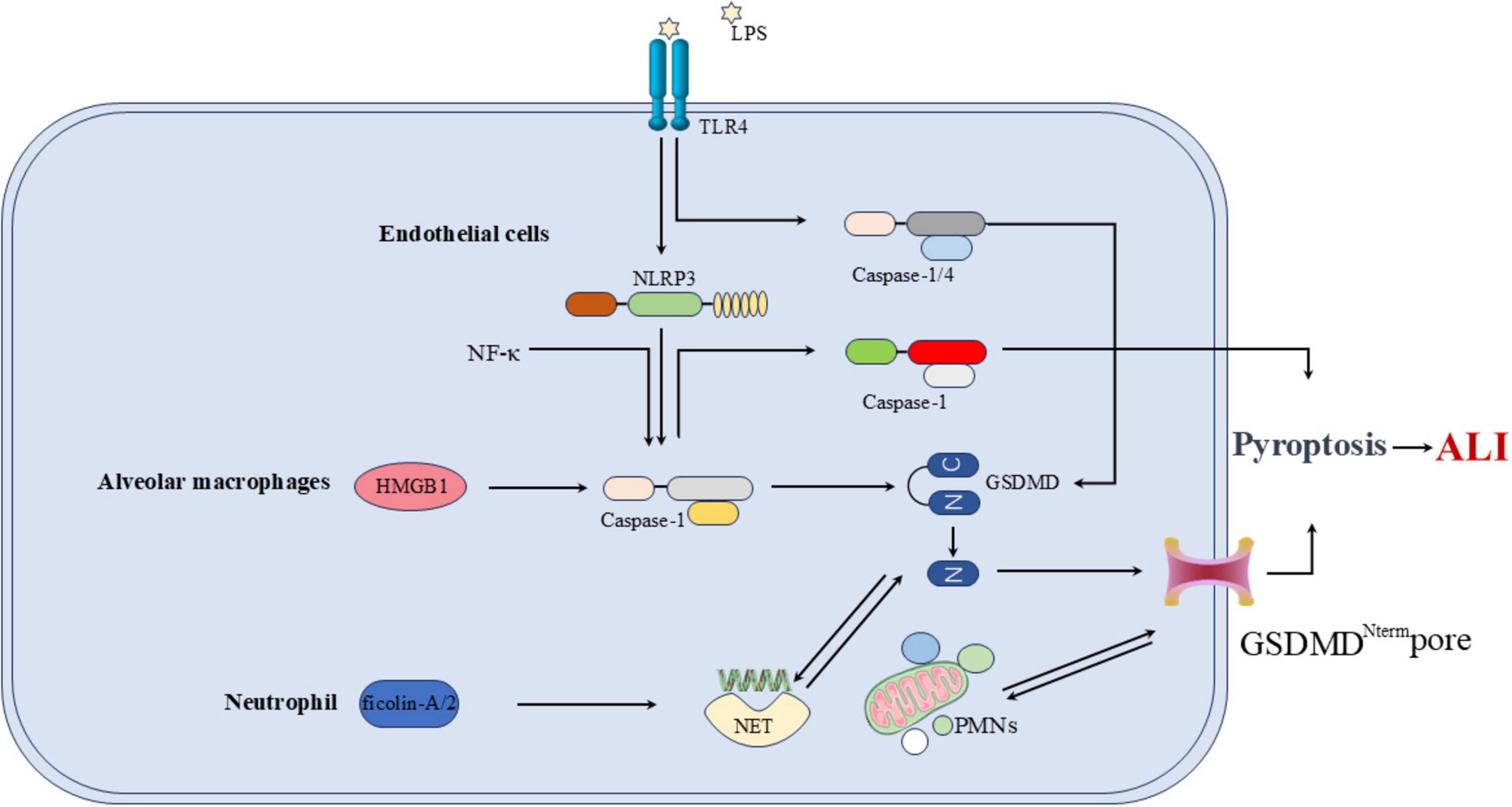
Figure 6. Overall mechanism of pyroptosis in relation to ALI. In ECs, ECs injury and death occur at different stages of ALI, with LPS inducing EC pyroptosis via the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway. NF-κB is a pro-inflammatory transcription factor that activates several genes, including NLRP3. In AMs, the NLRP3-mediated pathway of AMs pyroptosis can trigger the release of HMGB1 from AMs. As a PAMP, HMGB1 further activates NLRP3 and caspase-1, creating a positive feedback loop that amplifies AM pyroptosis and worsens ALI severity. In NE, ficolin-A/2 exacerbates severe lung injury by promoting NET formation, polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) are crucial in the development of sepsis-associated ALI.
CircEXOC5 is a significantly upregulated circular RNA in ALI. It can suppress the Nrf2 transcription factor in LPS-stimulated mouse pulmonary microvascular ECs, thereby promoting cellular pyroptosis and attenuating LPS-associated ALI (51). Han et al. (52) revealed that irisin attenuates ALI by inhibiting the HSP90/NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD axis, reversing macrophage polarization, and reducing macrophage pyroptosis. These findings elucidate the mechanistic role of irisin in the treatment of ALI and ARDS. LL-37, also known as murine CRAMP, is a human antimicrobial peptide that plays a critical role in innate immune defense against sepsis through multiple mechanisms (53). Wang et al. (54) demonstrated that the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 protects against septic lung injury by modulating the expression of key pyroptotic mediators, including NLRP3, caspase-1, and GSDMD, as well as downstream inflammatory factors, in alveolar epithelial cells. 4-Hydroxynonenal (HNE) is a major endogenous product of lipid peroxidation. It can suppress the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in AMs, thereby reducing pyroptosis-related ALI in a sepsis mouse model (55). Shan et al. (56) showed that dynasore, a pharmacological agent, could alleviate LPS-induced ALI by regulating macrophage pyroptosis, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy for ALI and ARDS. Natural products that inhibit cellular pyroptosis pathways can alleviate ALI. Emodin, a natural compound, can suppress NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis of AMs, thereby mitigating ALI (57). Citrulline provides protective effects against ALI by inhibiting ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent cellular pyroptosis (58). Zhang et al. (59) demonstrated that syringaresinol mitigates IgG immune complex-induced ALI by activating PPARγ and suppressing pyroptosis.
This bibliometric study offers a comprehensive assessment of the PFALI research landscape. The analysis evaluates the field’s overall progress, emerging trends, and influential references. The findings provide valuable guidance for researchers to prioritize the most impactful and recent literature. However, the study acknowledges certain limitations, including potential exclusion of recently published articles and the data source being constrained to the WoSCC. Additionally, inherent subjectivity in data interpretation is recognized. Nonetheless, this work serves as a representative snapshot of the current state and general trajectory of PFALI research, offering insights beneficial for researchers, clinicians, and policymakers in the domain.
Cellular pyroptosis, a programmed cell death pathway associated with inflammation, plays a role in the inflammatory process of ALI. Our bibliometric analysis revealed that China has the highest publication output, with Central South University being the most prolific institution, and Zhou, Yong having the most publications. The journal International Immunopharmacology was the most productive. Key research frontiers for the coming years include “iron,” “sirt1,” “repair,” and “alveolar macrophage pyroptosis.” Targeting key factors in pyroptosis pathways, such as inflammatory caspases, offers new insights for reducing inflammation in ALI. Additionally, natural compounds that target this pathway show promising anti-inflammatory effects. However, the inflammatory response in ALI is influenced by various interconnected pathways, and the mechanisms of typical and atypical pyroptosis in lung tissue, along with targeted applications, require further study.
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
CW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NL: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1488796/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure 1 | Analysis of core journals. (A) Bibliometric coupling within journals. (B) Citations to each journal.
Supplementary Figure 2 | Trend topics from 2000 to 2024.
ALI, acute lung injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; AM, alveolar macrophage; EC, endothelial cell; GSDM, gasdermin; IL-1 β, interleukin-1 β; IL-18, interleukin-18; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NE, neutrophil; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; PFALI, pyroptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil; WoSCC, Web of Science Core Collection.
1. Mokrá D. Acute lung injury - from pathophysiology to treatment. Physiol Res. (2020) 69(Suppl. 3):S353–66.
2. Elias EE, Lyons B, Muruve DA. Gasdermins and pyroptosis in the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2023) 19:337–50.
3. Anderson MJ, den Hartigh AB, Fink SL. Molecular mechanisms of pyroptosis. Methods Mol Biol. (2023) 2641:1–16.
4. Liang X, Qin Y, Wu D, Wang Q, Wu H. Pyroptosis: A double-edged sword in lung cancer and other respiratory diseases. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:40.
5. Dejas L, Santoni K, Meunier E, Lamkanfi M. Regulated cell death in neutrophils: From apoptosis to NETosis and pyroptosis. Semin Immunol. (2023) 70:101849.
6. Rodríguez-González J, Gutiérrez-Kobeh L. Apoptosis and its pathways as targets for intracellular pathogens to persist in cells. Parasitol Res. (2023) 123:60.
7. Liu B, Wang Z, He R, Xiong R, Li G, Zhang L, et al. Buformin alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis through an AMPK-dependent pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). (2022) 136:273–89. doi: 10.1042/CS20211156
8. Liu B, Li Y, Xiang J, Li Y, Zhou M, Ren Y, et al. Significance of pyroptosis in immunoregulation and prognosis of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: Evidence from RNA-Seq of alveolar macrophages. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:3547–62. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S422585
9. Hu X, Zou M, Zheng W, Zhu M, Hou Q, Gao H, et al. Bhlhe40 deficiency attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury through preventing macrophage pyroptosis. Respir Res. (2024) 25:100. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02740-2
10. Wang Y, Sun Y, Hu Y, Xiao Z. Bibliometric analysis of anesthetic drugs’ effects on immune function- current knowledge, hotspots and future perspectives. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2023) 17:3219–30. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S433629
11. Hu Y, Yang R, Liu S, Wang H. Bibliometric analysis of interspinous device in treatment of lumbar degenerative diseases. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e37351. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037351
12. Hu YX, Yang R, Liu SM, Wang H. Bibliometric analysis of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spine surgery. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 28:907–23.
13. Ahmed SM, Luo L, Namani A, Wang XJ, Tang X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2017) 1863:585–97.
16. Butt Y, Kurdowska A, Allen TC. Acute lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. (2016) 140(4):345–50.
17. Mueller AL, McNamara MS, Sinclair DA. Why does COVID-19 disproportionately affect older people? Aging (Albany NY). (2020) 12:9959–81.
18. Soy M, Keser G, Atagündüz P, Tabak F, Atagündüz I, Kayhan S. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: Pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment. Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 39:2085–94.
19. Dolinay T, Kim YS, Howrylak J, Hunninghake GM, An CH, Fredenburgh L, et al. Inflammasome-regulated cytokines are critical mediators of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2012) 185:1225–34. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201201-0003OC
20. Gasse P, Mary C, Guenon I, Noulin N, Charron S, Schnyder-Candrian S, et al. IL-1R1/MyD88 signaling and the inflammasome are essential in pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest. (2007) 117:3786–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI32285
21. Babelova A, Moreth K, Tsalastra-Greul W, Zeng-Brouwers J, Eickelberg O, Young MF, et al. Biglycan, a danger signal that activates the NLRP3 inflammasome via toll-like and P2X receptors. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:24035–48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014266
22. Nieto-Torres JL, DeDiego ML, Verdiá-Báguena C, Jimenez-Guardeño JM, Regla-Nava JA, Fernandez-Delgado R, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein ion channel activity promotes virus fitness and pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. (2014) 10:e1004077. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004077
23. Wang Y, Zhao Z, Xiao Z. The emerging roles of ferroptosis in pathophysiology and treatment of acute lung injury. J Inflamm Res. (2023) 16:4073–85. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S420676
24. Long ME, Mallampalli RK, Horowitz JC. Pathogenesis of pneumonia and acute lung injury. Clin Sci (Lond). (2022) 136:747–69.
25. Millar MW, Fazal F, Rahman A. Therapeutic targeting of NF-κB in acute lung injury: A double-edged sword. Cells. (2022) 11:3317.
26. Zhang J, Guo Y, Mak M, Tao Z. Translational medicine for acute lung injury. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:25.
27. Rao Z, Zhu Y, Yang P, Chen Z, Xia Y, Qiao C, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Theranostics. (2022) 12:4310–29.
28. Dai Z, Liu WC, Chen XY, Wang X, Li JL, Zhang X. Gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis: Mechanisms, diseases, and inhibitors. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1178662. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1178662
29. Zhou J, Qiu J, Song Y, Liang T, Liu S, Ren C, et al. Pyroptosis and degenerative diseases of the elderly. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:94.
30. Cao Z, Qin H, Huang Y, Zhao Y, Chen Z, Hu J, et al. Crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-related mechanisms in sepsis-induced lung injury in a mouse model. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:4810–20. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2033381
31. Zhang M, Ning J, Lu Y. Apelin alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury in part by modulating the SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway to inhibit endothelial cell pyroptosis. Tissue Cell. (2023) 85:102251. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102251
32. Huang Y, Lin J, Wu Z, Li Y. Circular RNA circVAPA modulates macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-induced acute lung injury through targeting miR-212-3p/Sirt1/Nrf2/NLRP3 axis. Int J Exp Pathol. (2024) 105:21–32. doi: 10.1111/iep.12497
33. Jin JB, Li J, Wang HB, Hu JB, Yang CL. Engineering of VCAM-1-targeted nanostructured lipid carriers for delivery of melatonin against acute lung injury through SIRT1/NLRP3 mediated pyroptosis signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 266(Pt. 1):130637. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130637
34. Zhao X, Xie J, Duan C, Wang L, Si Y, Liu S, et al. ADAR1 protects pulmonary macrophages from sepsis-induced pyroptosis and lung injury through miR-21/A20 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. (2024) 20:464–85. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.86424
35. Liu P, Yang S, Shao X, Li C, Wang Z, Dai H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate acute lung injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage pyroptosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2024) 13:371–86. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szad094
36. Gong T, Zhang X, Liu X, Ye Y, Tian Z, Yin S, et al. Exosomal Tenascin-C primes macrophage pyroptosis amplifying aberrant inflammation during sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Transl Res. (2024) 270:66–80. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2024.04.001
37. Kolesnichenko OA, Whitsett JA, Kalin TV, Kalinichenko VV. Therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cells in pulmonary diseases. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2021) 65:473–88.
38. Niethamer TK, Stabler CT, Leach JP, Zepp JA, Morley MP, Babu A, et al. Defining the role of pulmonary endothelial cell heterogeneity in the response to acute lung injury. Elife. (2020) 9:e53072.
39. Li Y, Liu Y, Yao X, Zhu L, Yang L, Zhan Q. MLKL protects pulmonary endothelial cells in acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2024) 70:295–307.
40. Yang J, Zhao Y, Zhang P, Li Y, Yang Y, Yang Y, et al. Hemorrhagic shock primes for lung vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis: Role in pulmonary inflammation following LPS. Cell Death Dis. (2016) 7:e2363. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.274
41. Zhang Y, Zhang H, Li S, Huang K, Jiang L, Wang Y. Metformin alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the SIRT1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and inhibiting endothelial cell pyroptosis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:801337. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.801337
42. Fan EKY, Fan J. Regulation of alveolar macrophage death in acute lung inflammation. Respir Res. (2018) 19:50.
43. Kojima M, Gimenes-Junior JA, Chan TW, Eliceiri BP, Baird A, Costantini TW, et al. Exosomes in postshock mesenteric lymph are key mediators of acute lung injury triggering the macrophage activation via Toll-like receptor 4. FASEB J. (2018) 32:97–110. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700488R
44. Hou L, Yang Z, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Yang H, et al. NLRP3/ASC-mediated alveolar macrophage pyroptosis enhances HMGB1 secretion in acute lung injury induced by cardiopulmonary bypass. Lab Invest. (2018) 98:1052–64. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0073-0
45. Fei L, Jingyuan X, Fangte L, Huijun D, Liu Y, Ren J, et al. Preconditioning with rHMGB1 ameliorates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophage pyroptosis via the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Transl Med. (2020) 18:301. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02467-w
46. Jiang L, Ye C, Huang Y, Hu Z, Wei G. Targeting the TRAF3-ULK1-NLRP3 regulatory axis to control alveolar macrophage pyroptosis in acute lung injury. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). (2024) 56:789–804. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024035
47. Xie J, Zhu CL, Wan XJ, Zhao ZZ, Meng Y, Li P, et al. GSDMD-mediated NETosis promotes the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur J Immunol. (2023) 53:e2250011. doi: 10.1002/eji.202250011
48. Huang L, Tan X, Xuan W, Luo Q, Xie L, Xi Y, et al. Ficolin-A/2 aggravates severe lung injury through neutrophil extracellular traps mediated by gasdermin D-induced pyroptosis. Am J Pathol. (2024) 194:989–1006. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.02.011
49. Jiao Y, Zhang T, Zhang C, Ji H, Tong X, Xia R, et al. Exosomal miR-30d-5p of neutrophils induces M1 macrophage polarization and primes macrophage pyroptosis in sepsis-related acute lung injury. Crit Care. (2021) 25:356. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03775-3
50. Fan XY, Ma ZX, Tang LB, Shen HZ, Qi F, Xia JW. lncRNA NEAT1 mediates LPS-induced pyroptosis of BEAS-2B cells via targeting miR-26a-5p/ROCK1 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2023) 39:665–74. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12681
51. Wang W, Xiong Y, Zhao H, Xu R. CircEXOC5 facilitates cell pyroptosis via epigenetic suppression of Nrf2 in septic acute lung injury. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:743–54. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04521-1
52. Han Z, Ma J, Han Y, Yuan G, Jiao R, Meng A. Irisin attenuates acute lung injury by suppressing the pyroptosis of alveolar macrophages. Int J Mol Med. (2023) 51:32. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5235
53. Nagaoka I, Tamura H, Reich J. Therapeutic potential of cathelicidin Peptide LL-37, an antimicrobial agent, in a murine sepsis model. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5973. doi: 10.3390/ijms21175973
54. Wang Q, Wen W, Zhou L, Liu F, Ren X, Yu L, et al. LL-37 improves sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing pyroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 129:111580. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111580
55. Hsu CG, Chávez CL, Zhang C, Sowden M, Yan C, Berk BC. The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and macrophage pyroptosis. Cell Death Differ. (2022) 29:1790–803. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-00966-5
56. Shan M, Wan H, Ran L, Ye J, Xie W, Lu J, et al. Dynasore alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2024) 18:1369–84. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S444408
57. Wu X, Yao J, Hu Q, Kang H, Miao Y, Zhu L, et al. Emodin ameliorates acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury through inhibiting the alveolar macrophages pyroptosis. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:873053. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.873053
58. Xue Y, Zhang Y, Chen L, Wang Y, Lv Z, Yang LQ, et al. Citrulline protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting ROS/NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis and apoptosis via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. (2022) 24:632. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11569
Keywords: acute lung injury, pyroptosis, inflammasome, Nrf2 signaling pathway, targeted therapy
Citation: Wang C and Liu N (2025) Bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis in pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury. Front. Med. 11:1488796. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1488796
Received: 30 August 2024; Accepted: 31 December 2024;
Published: 22 January 2025.
Edited by:
Qinghe Meng, Upstate Medical University, United StatesReviewed by:
Sumit Ghosh, The Research Institute at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Wang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Na Liu, MTg2NDA5NjQ0NjlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.