- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Dermatology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, National Center for Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine, Beijing, China
Background: Some patients with psoriasis experience relapses shortly after discontinuation of biologics. However, there is a lack of risk prediction tools to identify those at high risk of relapse.
Objective: To develop and validate a risk prediction model for psoriasis relapse after biologics discontinuation.
Methods: Publications from PubMed, EMBASE, Medline, and the Cochrane Library were systematically searched and meta-analyses were conducted to identify risk factors for psoriasis relapse after biologics discontinuation. Statistically significant risk factors were identified and used to create a risk assessment model weighted by the impact of each factor. The model was externally validated using a cohort of 416 Chinese psoriasis patients.
Results: Eight studies (N = 2066) were included in the meta-analysis. Body mass index (BMI), smoking, disease duration, comorbid psoriatic arthritis (PsA), remission speed and extent during treatment, history of biologic therapy, and therapy duration were identified as correlates of relapse in the meta-analysis and were incorporated into the prediction model. The median age of the 416 patients in the validation cohort was 41.5 (IQR 32, 53) years, with 63% male, and a baseline PASI score of 15.4 (IQR 10.5, 21). It was verified that the area under the curve (AUC) of the prediction model was 0.796 (95% CI, 0.753–0.839), with an optimal cut-off value of 11.25 points, sensitivity of 65.1%, and specificity of 82.2%.
Conclusion: Multivariate models using available clinical parameters can predict relapse risk in psoriasis patients after biologics discontinuation. Early individual identification of patients at risk of relapse, and screening of candidate cohorts for long-term treatment or dose reduction may benefit both patients and physicians.
1 Introduction
Psoriasis, an immune-mediated chronic systemic disease, affects approximately 2–3% of the global population, imposing a substantial disease burden and negatively impacting quality of life and systemic health (1, 2). The advent of biologics has transformed psoriasis treatment, leading to short-term reductions or clearances and effective control over inflammation and disease activity (3, 4). However, relapse post-treatment discontinuation poses a considerable therapeutic challenge, despite significant advances in treatment through the widespread use of biologics (5, 6).
Previous studies have shown that more than half of patients relapse within 6 months of discontinuation, despite achieving remission or even complete clearance with treatment (7). Psoriasis relapse has been linked to localized residual inflammation and disease memory. Research has demonstrated that genes encoding inflammatory factors and skin structural proteins in visually resolved lesions differ from those in healthy skin (8). Furthermore, tissue-resident memory T cells in these resolved lesions continue to persist, retaining their ability to produce inflammatory factors associated with psoriasis relapse, such as interleukin-22 and interleukin-17A (8, 9). The etiology and pathogenesis of relapse are not fully understood, and there is debate regarding the associated risk factors (10). For instance, while Warren et al. reported that higher body mass index (BMI) promotes psoriasis relapse (11), Topaloğlu Demir et al. (12) found no association between BMI and relapse. These conflicting findings complicate the effective clinical management of relapse.
The prediction model serves as a tool for predicting future trends, behaviors, or outcomes based on historical data or established information. It utilizes various mathematical and statistical techniques to analyze and learn from patterns within the data (13, 14). In recent years, medical prediction models have garnered increasing attention due to their substantial value in disease diagnosis and prognosis. However, there remains a deficiency of clinically useful models specifically designed for predicting psoriasis relapse.
Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to identify risk factors for psoriasis relapse following the discontinuation of biologics and developed a practical individual prediction model for relapse based on factors routinely available in clinical practice. Moreover, we established an external cohort to validate the model’s performance. This research aims to identify individuals at high risk of relapse, enabling early personalized interventions to reduce relapse rates and enhance long-term disease prognosis. Additionally, it may assist in identifying patients at low risk of relapse who could benefit from dose reduction, potentially alleviating the economic burden on the healthcare system.
2 Methods
2.1 Meta-analysis
The meta-analysis was conducted and reported following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (15). The study protocol was registered with the International Registry for Prospective Systematic Evaluation (PROSPERO) and the registration number is CRD 42024543820.
2.1.1 Search strategy
We searched electronic databases, including Pubmed, EMBASE, Medline, and the Cochrane Library, for relevant literature from the inception of database to May 1, 2024. The search formula was formulated according to the PICO criteria (Supplementary Table S1). After duplicates were removed, initial screening of the publications was conducted by assessing the titles and abstracts, followed by a full-text review to identify the final articles (Supplementary Figure S1). The literature search and screening was carried out independently by two researchers (Huang Shan and Chen Bailin), and disagreements were resolved through discussion.
2.1.2 Article selection
Articles were included in this study if they met the following criteria: (1) the study population consisted of patients with plaque psoriasis; (2) the therapeutic agent was a biologic; (3) patients achieved clinical remission during treatment with the biologic; (4) follow-up was at least 6 months after biologic discontinuation; (5) risk factors for relapse were reported, extractable odds ratios (ORs), relative risks (RRs), or hazard ratios (HRs), and 95% confidence intervals (Cls); and (6) the full text was available. The following studies were excluded: (1) conference abstracts, reviews, commentaries, author responses, meta-analyses, and case reports; (2) unclear definitions of remission or relapse; and (3) study populations with fewer than 30 patients. If multiple studies describing the same outcome in the same population were available, only the most complete one was included.
2.1.3 Data extraction and quality assessment
Data extraction and quality assessment were conducted independently by two authors (Huang Shan and Chen Bailin), and disagreements were resolved through discussion. If a study reported multiple effect values for the same factor, we selected only the estimate with the most adjusted variables and the longest follow-up time. The extracted data included authors, publication year, sample size, interventions, risk factors, effect sizes, and 95% CIs for the risk factors. The quality of the studies was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (16), which was performed independently by the two authors.
2.2 Validation cohort
We reported the validation of the prediction model following the Transparent Reporting of Multivariate Predictive Models for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD) statement (17). The study received approval from the ethics committees of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2019-159-K108) and Dongzhimen Hospital (DZMEC-KY-2019-164). Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
2.2.1 Study population
Patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis who discontinued treatment after achieving remission with biologics between October 2019 and April 2023 at China-Japan Friendship Hospital and Dongzhimen Hospital were identified. Remission was defined as a 75% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) from baseline (achievement of PASI 75). Patients’ baseline information and PASI scores during treatment were extracted from the Psoriasis Case Registry System (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: ChiCTR1900021629) or electronic medical records.
2.2.2 Endpoint event
The endpoint event of the study was relapse, defined as the deterioration of skin lesions post-discontinuation in patients who had met remission criteria, with an increase in PASI score to more than 25% of the baseline (loss of PASI 75) or the resumption of systemic therapy or phototherapy. During the 6-month follow-up, physicians recorded patients’ PASI scores and treatments through offline clinics, Internet health services, or video calls to assess for relapse.
2.3 Statistical analysis
We reported the validation of the prediction model following the Transparent Reporting of Multivariate Predictive Models Used for Individual Prognosis or Diagnosis (TRIPOD) statement (17). The study received approval from the ethics committees of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2019-159-K108) and Dongzhimen Hospital (DZMEC-KY-2019-164). Written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
2.3.1 Meta-analysis
The extracted effect values were converted into RR values, and the detailed extraction and conversion transformation strategy is described in Supplementary Tables S2, S3. RR values and 95% CIs for each risk factor were pooled separately using the corresponding meta-analysis model selected based on the heterogeneity of the studies. Cochran’s Q test and I2 statistics were utilized to test statistical heterogeneity between studies. If there was statistically significant heterogeneity (p-value <0.10 or I2 > 50%), the pooled RRs and 95% CIs were calculated using a random-effects model; otherwise, they were generated by a fixed-effects model. Sensitivity analyses were conducted by altering the effects model to assess the robustness of the results.
2.3.2 Model development
First, we examined the statistically significant risk factors from the meta-analyses mentioned above and identified the factors included in the model after removing overlapping variables with covariates. Second, we calculated the β coefficients of all risk factors in the model using the pooled RR values, which represent the multiplicative increase in an individual’s risk of developing a particular disease for each unit increase in the risk variable (18).
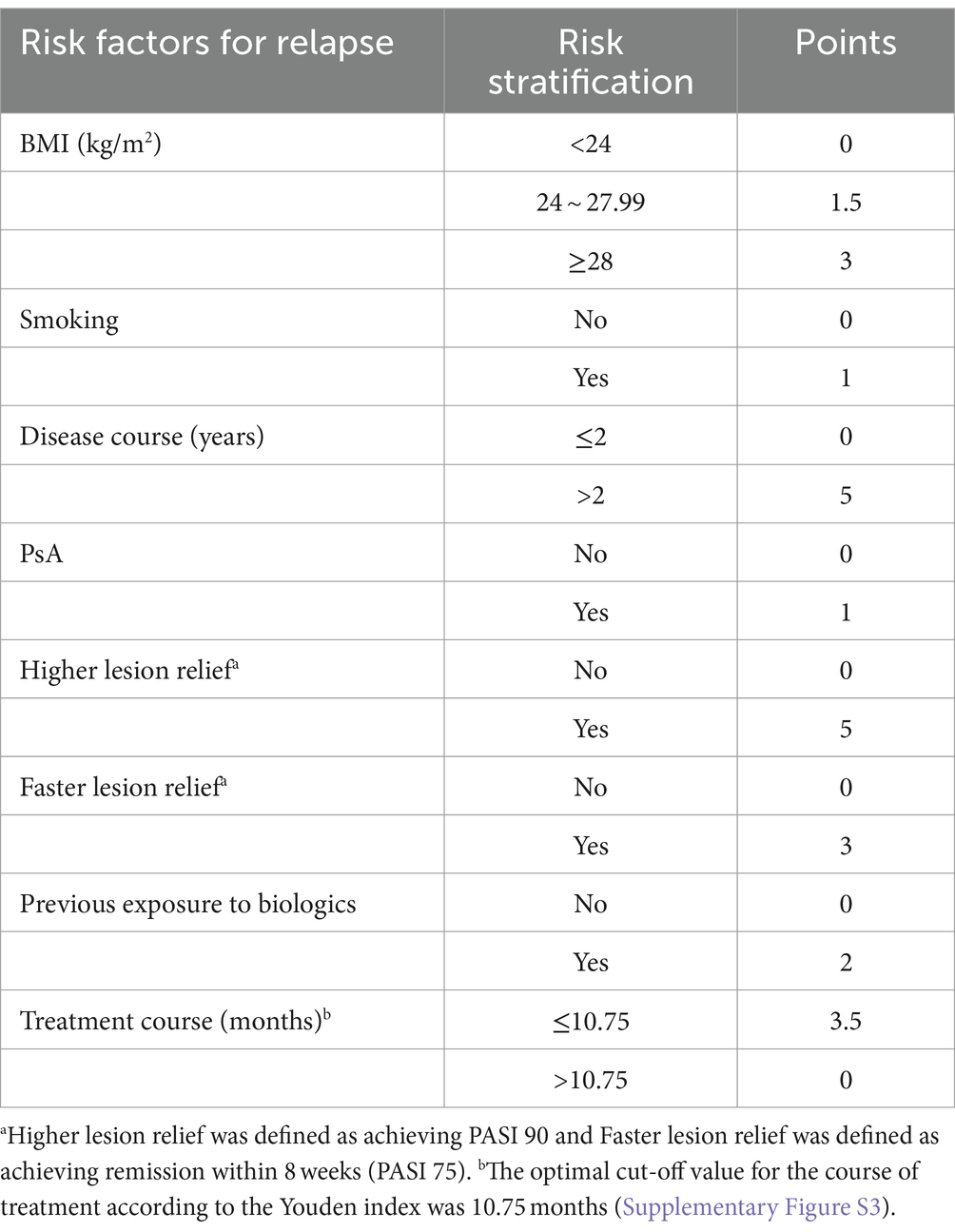
The β coefficients were then multiplied by 10 to obtain the corresponding score for each risk factor. Finally, all risk factors were stratified and evaluated to develop a risk prediction model for psoriasis relapse. The total score was calculated by summing the scores for each risk factor. For individuals, a higher cumulative score indicates a greater risk of relapse after discontinuing medication.
2.3.3 Model validation
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted based on the total scores from the prediction model, and decision curve analysis (DCA) was performed. The sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) value of the model were calculated. The AUC, indicative of predictive accuracy, ranges from 0.5 to 1.0, with higher values denoting greater accuracy. The optimal cut-off point with high sensitivity and specificity was identified based on the Youden index. Patients were divided into four groups according to the optimal cut-off and interquartile range: low risk, intermediate risk, high risk, and very high risk. Kaplan–Meier curve analysis was used to assess the cumulative risk of relapse in the different groups.
Statistical analyses were performed using R version 4.3.3 and Stata 12.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, TX). All tests were considered statistically significant with a two-sided p-value of <0.05, except the heterogeneity test with a p-value of <0.1.
3 Results
3.1 Meta-analysis
3.1.1 Characteristics of included studies
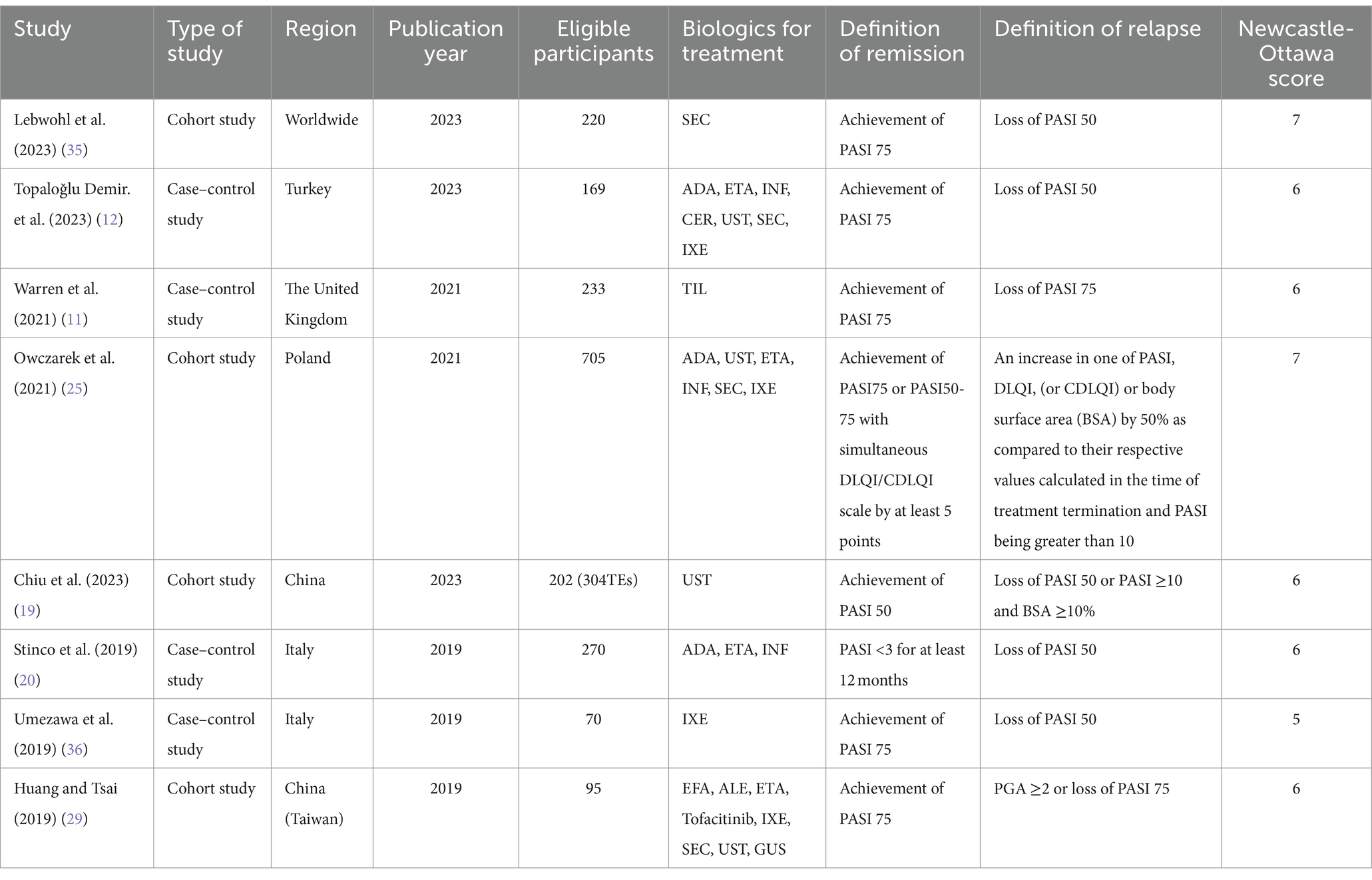
A total of 3,769 articles were retrieved from the database, and eight studies (four cohort studies and four case–control studies involving 2,066 patients) were included based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria (Table 1 and Supplementary Table S4). According to the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), the scores of the included studies ranged from 5 to 7, with 7/8 being of high quality. These studies identified 15 risk factors for relapse, including age, gender, body mass index, body weight, alcohol consumption, smoking, baseline PASI, baseline BSA, disease duration (years), disease duration (>2 years), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), speed of lesion remission, extent of lesion remission, history of treatment with biologics, and course of treatment.
3.1.2 Risk factors for relapse
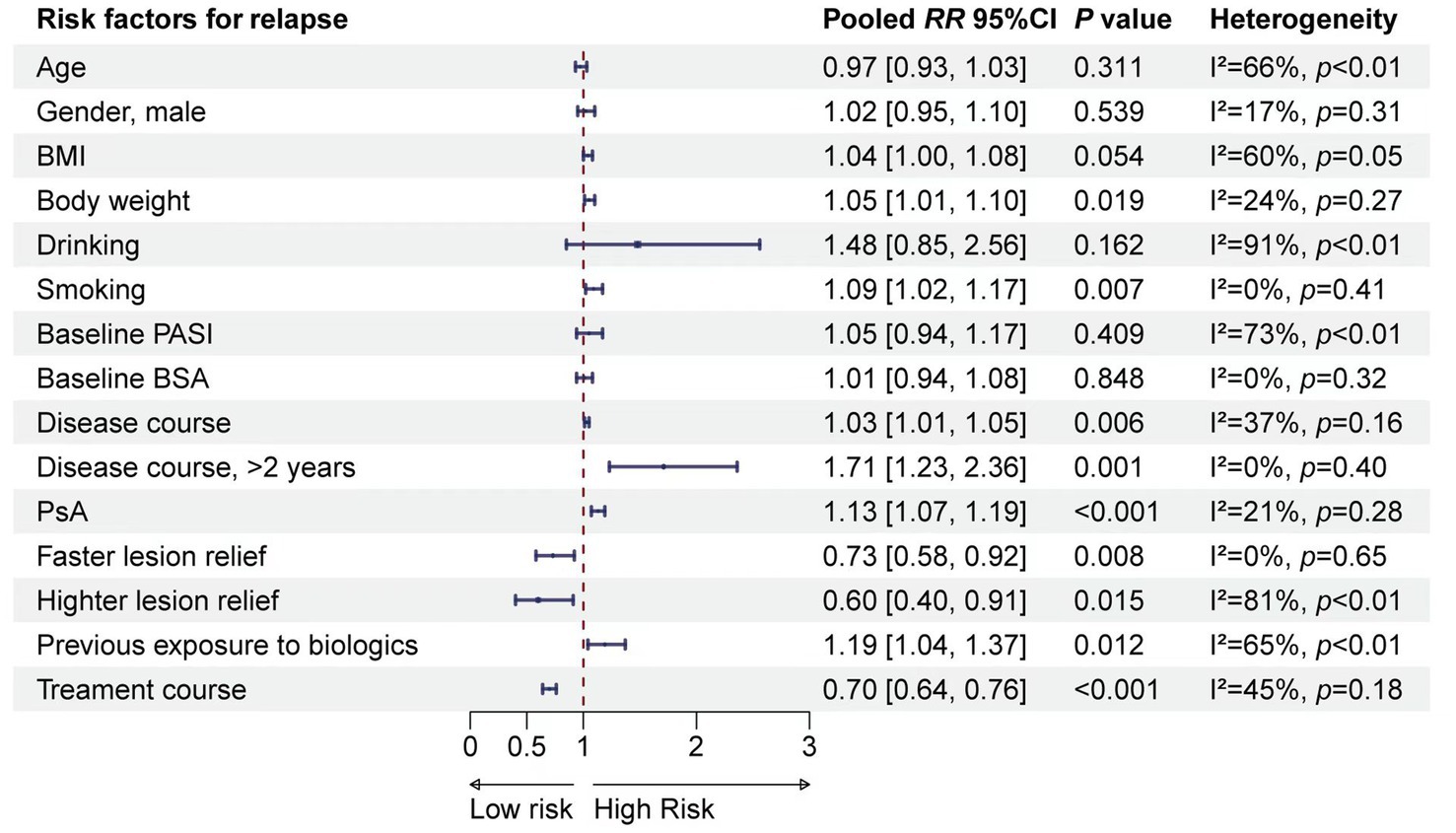
A total of 15 risk factors were included in the meta-analysis. The results suggested that BMI, weight, smoking, disease duration (years), disease duration (>2 years), PsA, speed of lesion remission, degree of lesion remission, previous exposure to biologics, and duration of therapy were associated with relapse (Figure 1). Detailed results of the meta-analyses, heterogeneity tests, and sensitivity analyses for each risk factor are provided in Supplementary Figure S2. No publication bias test was conducted due to the limited number of studies included for a valid test.
3.2 Model development
The meta-analysis identified 10 risk factors associated with psoriasis relapse. Considering multicollinearity, we selected BMI instead of weight and disease duration (>2 years) instead of disease duration (years) for inclusion in the model. The final model included eight variables: BMI (RR = 1.03, 95% CI 1.00–1.07), smoking (RR = 1.09, 95% CI 1.02–1.17), disease duration >2 years (RR = 1.71, 95% CI 1.23–2.36), PsA (RR = 1.13, 95% CI 1.07–1.19), faster lesion remission (RR = 0.73, 95% CI 0.51–0.92), higher skin lesion remission (RR = 0.60, 95% CI 0.40–0.91), previous exposure to biologics (RR = 1.19, 95% CI 1.04–1.37), and duration of therapy (RR = 0.70, 95% CI 0.64–0.76). The β coefficients of the risk factors were calculated, and a risk prediction model for psoriasis relapse after discontinuation of biologics was developed based on the grading and scoring of the risk factors (Table 2).
3.3 Model validation
3.3.1 Baseline characteristics of the validation cohort
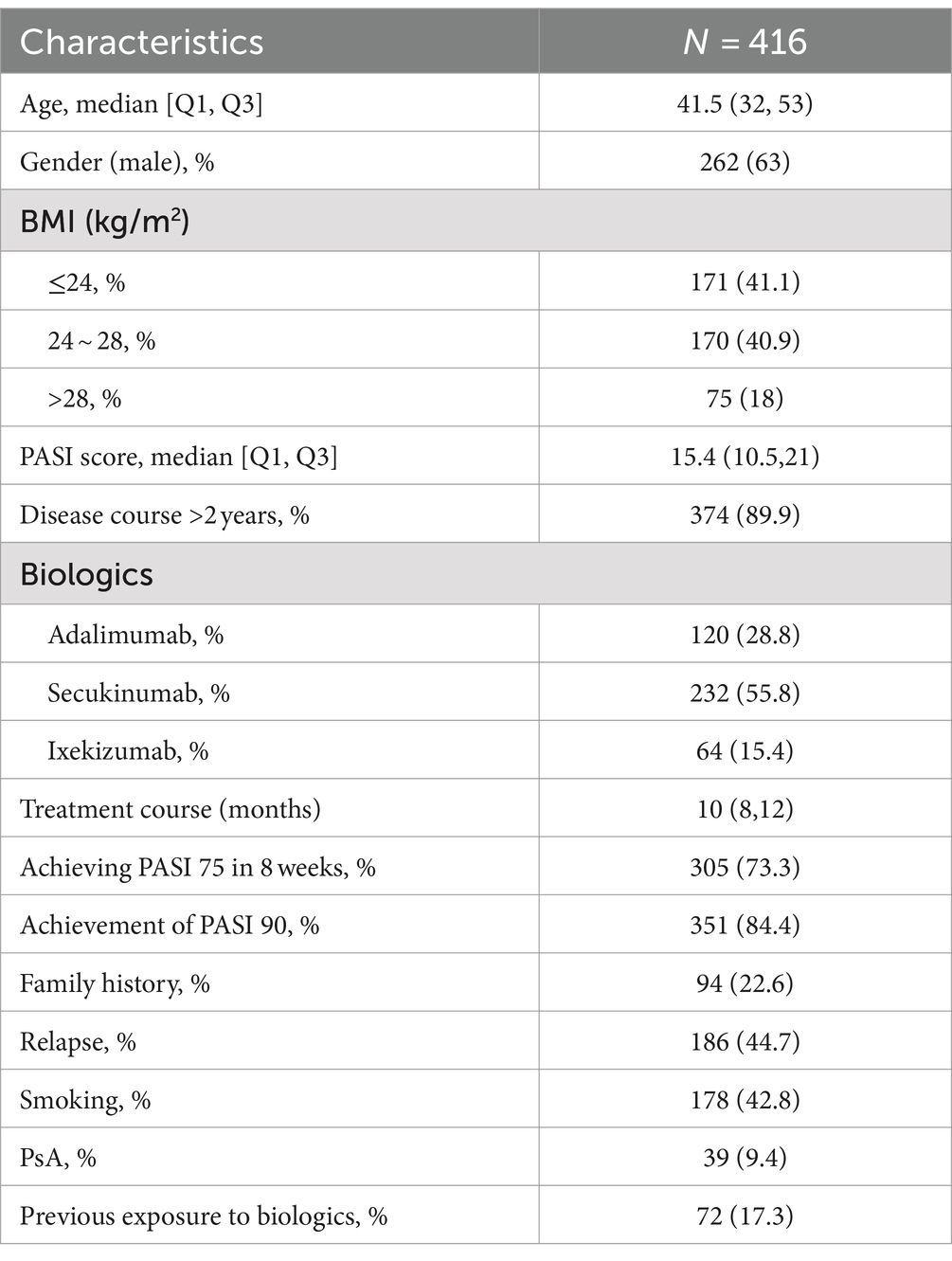
The validation cohort consisted of 416 patients with psoriasis who had achieved remission with biologic therapy and then discontinued treatment. The median age of the patients was 41.5 years, and 262 (63%) were male. Within 6 months past-discontinuation, 186 (44.7%) patients experienced a relapse. Detailed characteristics of the validation cohort are presented in Table 3.
3.3.2 Performance of the model
In the validation cohort, the AUC value of the risk prediction model was 0.796 (95% CI 0.753–0.839). The optimal cutoff value was determined to be 11.25 by the Youden index, with a sensitivity of 0.651 and a specificity of 0.822, which indicates good predictive performance of the model (Figure 2A). The 6-month relapse rate of psoriasis after discontinuation of biologics has been reported to be 25.4–59.7% in previous literature (19–21). Within this range, the decision curve lies above the none and all lines, suggesting clinical utility for the model (Figure 2B). Based on the total risk score, patients in the validation cohort were categorized into four groups: low-risk (n = 67, 0–6 points), intermediate-risk (n = 187, 6.5–11.25 points), high-risk (n = 144, 11.25–17.5 points), and very high-risk (n = 18, 18–23.5 points). Compared to the low-risk group, the intermediate-risk group (HR = 2.43, 95% CI 1.20–4.90, p < 0.001), the high-risk group (HR = 8.78, 95% CI 4.44–17.38, p < 0.001), and very high-risk group (HR = 19.54, 95% CI 8.67–44.02, p < 0.001) exhibited significantly elevated risk of relapse (Figure 2C).
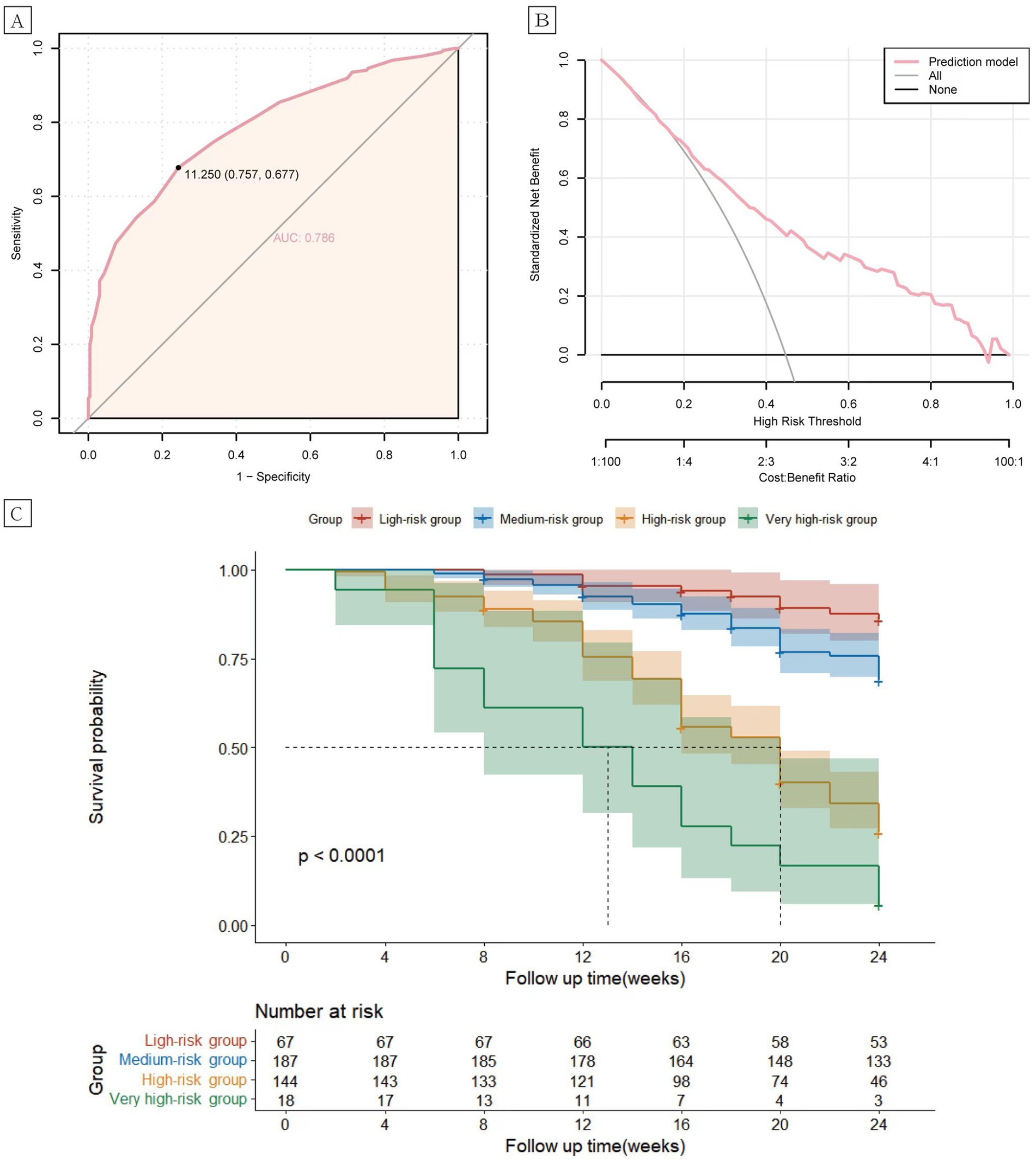
Figure 2. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (A) and clinical decision analysis (DCA) curves (B) for the psoriasis relapse prediction model. Kaplan–Meier curves (C) of the cumulative risk of relapse in patients in the low, intermediate, high, and very high-risk groups.
4 Discussion
Psoriasis remains incurable, and due to the high relapse rate after discontinuation of therapy, biologics are recommended for long-term maintenance therapy (5, 22). However, patients in remission often stop treatment due to secondary loss of efficacy, high financial burden, and concerns about long-term therapy safety (23, 24). The differences in patient outcomes after discontinuation of biologics are significant. More than half of these patients experience relapse within 6 months, while some enjoy prolonged periods of remission (7, 25). To date, no sophisticated models have been developed to predict the risk of relapse after discontinuation of biologics. Gordon et al. (26) discovered that maintenance of the PASI90 response after discontinuation of Guselkumab was associated with sustained suppression of interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22. However, cytokine levels were not predictive of psoriasis relapse, as their increase lagged behind the rise in PASI scores. Rivera et al. (27) constructed a multivariate linear regression model for psoriasis relapse, but the performance and clinical decision-making ability of the model have not been validated. Additionally, the small sample size used to develop the model may introduce potential biases.
Our study utilized meta-analysis based on eight published moderate-to-high quality clinical studies to identify 10 risk factors influencing psoriasis relapse. These include BMI, body weight, smoking, disease duration (years), disease duration (>2 years), psoriatic arthritis, rate of skin lesion resolution, extent of skin lesion resolution, history of biologic therapy, and treatment duration. The inclusion of both BMI and body weight in the predictive model could lead to overfitting and diminish the model’s performance due to their correlation. BMI was selected over body weight as it more accurately reflects an individual’s physique and metabolic state, and evidence supports its stronger association with the efficacy of biologic therapy for psoriasis compared to body weight (28). Disease duration was modeled as a binary variable (≤2 years or >2 years) to simplify the model and align with the current consensus in psoriasis relapse research that a 2-year threshold is significant for distinguishing disease chronicity (25, 29–31). In the end, 8 risk factors were incorporated into a prediction model designed to forecast the risk of psoriasis relapse after discontinuation of biologics therapy, with each factor weighted by its impact.
The prediction model exhibited robust performance (AUC = 0.796) and clinical decision-making ability, capability within the validation cohort, suggesting its practical utility in clinical settings. Furthermore, all variables integrated into the prediction model are clinically accessible non-invasively, highlighting the model ‘s practicality and ease of use. Moreover, the prediction model demonstrated excellent clinical discrimination, with significant differences in relapse rates observed among patients classified into low-risk, intermediate-risk, high-risk, and very high-risk groups based on their total scores in the validation cohort (p < 0.001).
Translating predictive outcomes into clinical decisions is imperative, particularly when guided by a comprehensive and precise stratification of relapse risk. For patients classified as high-risk and very high-risk with scores above 17.5, long-term maintenance therapy using biologics is advised, with a minimum treatment duration of 10.75 months as informed by ROC analysis. Treatments shorter in duration may not be effective in managing the inflammatory environment, even with lesion resolution. Notably, more than half of the risk factors incorporated in this model are modifiable, suggesting that weight reduction, smoking cessation, timely treatment initiation, and extended therapy duration may mitigate the incidence of psoriasis relapse following biologic discontinuation and enhance long-term prognosis.
Furthermore, it is also clinically important to identify low-risk relapse populations using a predictive model. Dose reductions are common in long-term treatment of psoriasis, yet there is ambiguity regarding the identification of individuals suitable for such reductions, and indiscriminate reductions potentially leading to premature relapses (32–34). Patients with a risk score of ≤6, identified as low risk, may be candidates for dose reduction, with the recommendation that this occurs post 10.75 months of treatment. For those with low relapse risk and cautionary factors for biologics, such as chronic infections, abnormal liver function, or a history of tumors, dose reduction or discontinuation may be considered once skin lesion control is achieved. Individualized determinations based on the prediction model can alleviate the healthcare burden, mitigate the adverse effects of long-term medication, and protect patient prognosis. By diminishing medical interventions, patients are afforded the opportunity to live without the ongoing necessity of treatment, aligning their lifestyle with that of healthy individuals, and consequently improving their quality of life.
5 Limitations
Firstly, heterogeneity between studies was unavoidable due to variations in study design, geographic region, and patient baseline characteristics, potentially impacting the reliability of the meta-analysis results. Secondly, the limited number of studies included for certain risk factors, such as alcohol consumption and baseline BSA, may have biased the results. Thirdly, the candidate variables identified through secondary data analyses did not include potential biomarkers and failed to account all potential risk factors associated with psoriasis relapse. Fourthly, while the meta-analysis included participants from various countries and regions, the validation cohort was composed solely of Chinese patients, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. Therefore, further validation of the model’s predictive performance using multicenter external cohorts is necessary.
6 Conclusion
This study found that BMI, weight, smoking, disease duration, PsA, the speed and degree of lesion remission during treatment, history of biologic therapy, and therapy duration were associated with psoriasis relapse following biologic discontinuation. A multivariate model leveraging routinely collected clinical data was developed to predict the relapse risk of psoriasis vulgaris post-biologic withdrawal, potentially aiding in individualized, long-term management of psoriasis. However, additional validation of the model’s clinical utility is necessary.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics committees of China-Japan Friendship Hospital (2019-159-K108) and Dongzhimen Hospital (DZMEC-KY-2019-164). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. BC: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. YQ: Investigation, Writing – original draft. XD: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YB: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the fund of Beijing Municipal Finance Project (2019bjwjw-01).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all patients and staff who participated in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1488096/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Griffiths, CEM, Armstrong, AW, Gudjonsson, JE, and Barker, J. Psoriasis. Lancet. (2021) 397:1301–15. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32549-6
2. Armstrong, AW, and Read, C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis a review. JAMA J Am Med Assoc. (2020) 323:1945–60. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4006
3. Boehncke, WH, and Brembilla, NC. Pathogenesis-oriented therapy of psoriasis using biologics. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (2022) 22:1463–73. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2022.2100219
4. Mahil, SK, Ezejimofor, MC, Exton, LS, Manounah, L, Burden, AD, Coates, LC, et al. Comparing the efficacy and tolerability of biologic therapies in psoriasis: an updated network Meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. (2020) 183:638–49. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19325
5. Masson Regnault, M, Konstantinou, MP, Khemis, A, Poulin, Y, Bourcier, M, Amelot, F, et al. Early relapse of psoriasis after stopping Brodalumab: a retrospective cohort study in 77 patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2017) 31:1491–6. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14387
6. Harris, KM, Smilek, DE, Byron, M, Lim, N, Barry, WT, McNamara, J, et al. Effect of costimulatory blockade with Abatacept after Ustekinumab withdrawal in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: the pause randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2021) 157:1306–15. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.3492
7. Masson Regnault, M, Shourick, J, Jendoubi, F, Tauber, M, and Paul, C. Time to relapse after discontinuing systemic treatment for psoriasis: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol. (2022) 23:433–47. doi: 10.1007/s40257-022-00679-y
8. Puig, L, Costanzo, A, Muñoz-Elías, EJ, Jazra, M, Wegner, S, Paul, CF, et al. The biological basis of disease recurrence in psoriasis: a historical perspective and current models. Br J Dermatol. (2022) 186:773–81. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20963
9. Owczarczyk Saczonek, A, Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M, Kasprowicz-Furmańczyk, M, and Placek, W. Immunological memory of psoriatic lesions. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:625. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020625
10. Kamiya, K, Kishimoto, M, Sugai, J, Komine, M, and Ohtsuki, M. Risk factors for the development of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:14. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184347
11. Warren, RB, Carrascosa, JM, Fumero, E, Schoenenberger, A, Lebwohl, MG, Szepietowski, JC, et al. Time to relapse after Tildrakizumab withdrawal in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis who were responders at week 28: post hoc analysis through 64weeks from resurface 1 trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2021) 35:919–27. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16964
12. Topaloğlu Demir, F, Polat Ekinci, A, Aytekin, S, Topkarcı, Z, Aslan Kayıran, M, Özkök Akbulut, T, et al. Clinical course of psoriasis patients that discontinued biologics during the Covid-19 pandemic. J Cosmet Dermatol. (2023) 22:722–31. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15638
13. Grant, SW, Collins, GS, and Nashef, SAM. Statistical primer: developing and validating a risk prediction model. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. (2018) 54:203–8. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezy180
14. Staffa, SJ, and Zurakowski, D. Statistical development and validation of clinical prediction models. Anesthesiology. (2021) 135:396–405. doi: 10.1097/aln.0000000000003871
15. Shamseer, L, Moher, D, Clarke, M, Ghersi, D, Liberati, A, Petticrew, M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and Meta-analysis protocols (Prisma-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. (2015) 350:g7647. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7647
16. The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomised studies in meta-analyses. Available at: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed May 16, 2024)
17. Collins, GS, Reitsma, JB, Altman, DG, and Moons, KG. Transparent reporting of a multivariable prediction model for individual prognosis or diagnosis (Tripod): the Tripod statement. BMJ. (2015) 350:g7594. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g7594
18. Liu, X, Chen, D, Fu, H, Liu, X, Zhang, Q, Zhang, J, et al. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for early diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1128069. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1128069
19. Chiu, H-Y, Hui, RC-Y, Tsai, T-F, Chen, Y-C, Chang Liao, N-F, Chen, P-H, et al. Predictors of time to relapse following Ustekinumab withdrawal in patients with psoriasis who had responded to therapy: an 8-year multicenter study. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2023) 88:71–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.01.035
20. Stinco, G, Balato, N, Buligan, C, Campanati, A, Dastoli, S, Di Meo, N, et al. A multicenter retrospective case-control study on suspension of Tnf-inhibitors and outcomes in psoriatic patients (stop study). G Ital Dermatol Venereol. (2019) 154:392–9. doi: 10.23736/S0392-0488.18.06156-4
21. Arcese, A, Aste, N, Bettacchi, A, Camplone, G, Cantoresi, F, Caproni, M, et al. Treating psoriasis with Etanercept in Italian clinical practice: prescribing practices and duration of remission following discontinuation. Clin Drug Investig. (2010) 30:507–16. doi: 10.2165/11537470-000000000-00000
22. Kim, HJ, and Lebwohl, MG. Biologics and psoriasis: the beat Goes on. Dermatol Clin. (2019) 37:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.det.2018.07.004
23. van den Reek, J, Tummers, M, Zweegers, J, Seyger, MMB, van Lumig, PPM, Driessen, RJB, et al. Predictors of Adalimumab drug survival in psoriasis differ by reason for discontinuation: long-term results from the bio-capture registry. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2015) 29:560–5. doi: 10.1111/jdv.12636
24. Li, Y, Lu, J-J, Zhong, X-Y, Yu, Y-Y, Yu, N, Wang, Y, et al. Drug survival outcomes associated with the real-world use of Ixekizumab, Secukinumab, Guselkumab, and Adalimumab for the treatment of plaque psoriasis in China: a 52-week single-center retrospective study. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. (2022) 15:2245–52. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S387759
25. Owczarek, W, Dzik, M, Narbutt, J, Walecka, I, and Kowalczyk, M. Real-world evidence on time to relapse of plaque psoriasis after discontinuation of biologic treatment in Poland. Dermatol Ther. (2021) 34:5052. doi: 10.1111/dth.15052
26. Gordon, KB, Armstrong, AW, Foley, P, Song, M, Shen, Y-K, Li, S, et al. Guselkumab efficacy after withdrawal is associated with suppression of serum Il-23-regulated Il-17 and Il-22 in psoriasis: voyage 2 study. J Invest Dermatol. (2019) 139:2437–46.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.016
27. Rivera, R, Martorell, A, López, A, Salgado, L, Sahuquillo, A, de la Cueva, P, et al. Maintenance of response following discontinuation of Guselkumab and Secukinumab in Spanish patients who participated in the eclipse study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2021) 35:e65–7. doi: 10.1111/jdv.16809
28. Hjort, G, Schwarz, CW, Skov, L, and Loft, N. Clinical characteristics associated with response to biologics in the treatment of psoriasis: a meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. (2024) 160:830–7. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.1677
29. Huang, YW, and Tsai, TF. Remission duration and long-term outcomes in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis treated by biologics or Tofacitinib in controlled clinical trials: a 15-year single-center experience. Dermatol Ther. (2019) 9:553–69. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-0310-5
30. Eyerich, K, Weisenseel, P, Pinter, A, Schakel, K, Asadullah, K, Wegner, S, et al. Il-23 blockade with Guselkumab potentially modifies psoriasis pathogenesis: rationale and study protocol of a phase 3b, randomised, double-blind, multicentre study in participants with moderate-to-severe plaque-type psoriasis (guide). BMJ Open. (2021) 11:e049822. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049822
31. Huang, S, Duan, XW, Zhang, HC, Dai, BW, and Bai, YP. Adjunctive Chinese medicine therapy reduces relapse of psoriasis vulgaris after discontinuation of biologics: a prospective registry-based cohort study. J Dermatolog Treat. (2024) 35:2355261. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2024.2355261
32. Atalay, S, van den Reek, J, den Broeder, AA, van Vugt, LJ, Otero, ME, Njoo, MD, et al. Comparison of tightly controlled dose reduction of biologics with usual Care for Patients with psoriasis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. (2020) 156:393–400. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.4897
33. van Riel, CAM, Michielsens, CAJ, van Muijen, ME, van der Schoot, LS, van den Reek, J, and de Jong, E. Dose reduction of biologics in patients with plaque psoriasis: a review. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1369805. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1369805
34. van Bezooijen, JS, van Doorn, MBA, Schreurs, MWJ, Koch, BCP, Te Velthuis, H, Prens, EP, et al. Prolongation of biologic dosing intervals in patients with stable psoriasis: a feasibility study. Ther Drug Monit. (2017) 39:379–86. doi: 10.1097/ftd.0000000000000420
35. Lebwohl, M, Iversen, L, Eidsmo, L, Krueger, JG, Suarez-Farinas, M, Tomalin, L, et al. Investigation of plaque psoriasis relapse after Secukinumab withdrawal in patients from two phase 3 studies. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2023) 49:793–800. doi: 10.1093/ced/llad329
36. Umezawa, Y, Torisu-Itakura, H, Morisaki, Y, ElMaraghy, H, Nakajo, K, Akashi, N, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety results from an open-label phase iii study (uncover-J) in Japanese plaque psoriasis patients: impact of treatment withdrawal and retreatment of Ixekizumab. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. (2019) 33:568–76. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15292
Keywords: psoriasis, biologics, prediction model, risk factor, relapse
Citation: Huang S, Chen B, Qi Y, Duan X and Bai Y (2024) Development and external validation of a prediction model for the risk of relapse in psoriasis after discontinuation of biologics. Front. Med. 11:1488096. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1488096
Edited by:
Vito Di Lernia, Azienda USL-IRCCS di Reggio Emilia, ItalyReviewed by:
Thomas Graier, Medical University of Graz, AustriaXinling Bi, Changhai Hospital, China
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Chen, Qi, Duan and Bai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xingwu Duan, aHMxODgxMTM4NTM3N0AxNjMuY29t; Yanping Bai, MzE4MDE3OTk3QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Shan Huang
Shan Huang Bailin Chen2†
Bailin Chen2† Yanping Bai
Yanping Bai