- 1Graduate School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
- 2Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
Objective: This paper aims to evaluate the disparities in efficacy and safety across various oral Chinese patent medicines for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), using a frequency-based reticulated meta-analysis.
Methods: The researchers searched the following databases: Web of Science, PubMed, Excerpta Medical Database (Embase), Cochrane Library, China Knowledge Network (CNKI), China Biomedical Literature Service System (SinoMed), Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform and China Science and Technology Periodicals Database (VIP). Besides, the researchers collected all randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of oral Chinese patent medicines, as well as simple preparations and simple preparations for benign prostatic hyperplasia from the establishment of the database until July1, 2024. After two researchers independently screened literature, extracted data, and evaluated the risk of bias in the included studies, a net meta-analysis was conducted using Stata 16.0 software.
Results: Seventy-two RCTs involving 15 oral Chinese patent medicines and a total of 7,800 patients were included. Net meta-analysis manifested that “Jinkuishenqi capsule (JKSQ) + conventional western medicine (CWM)” was the most effective way in increasing total efficiency ratio. “Huange capsule (HE) + CWM” was the most effective method in decreasing prostate volume. “Qianliesutong capsule (QLST) + CWM” was the most effective approach in decreasing residure volume. “Xialiqi capsule (XLQ) + CWM” was the most effective way in increasing maximum urinary flow rate. “Longbisu capsule (LBS) + CWM” was the most effective method in decreasing international prostate symptom score (IPSS). To reduce the adverse reactions, “HE + CWM” has the best efficacy. Considering both drug efficacy and safety, “Ningmitai capsule (NMT) + CWM” would be the most ideal choice.
Conclusion: Based on NMA, JKSQ, HE, QLST, XLQ, LBS, NMT plus CWM have been proved to possess the highest probability of being the best therapy. Due to the limitations of this study, these results should be confirmed through detailed randomized controlled trials.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, Identifier, CRD42023484071.
1 Introduction
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a prevalent condition among middle-aged and elderly men, characterized by urinary frequency, urgency, and progressive dysuria, invariably associated with bladder outlet obstruction, significantly impacting the quality of the patients’ life in this demographic. For older men, the aging process and the presence of functional testes result in hormonal imbalances and altered cellular processes, causing hyperplasia of the prostate’s interstitial glandular components and prostatic hypertrophy (1). Studies have shown that the prevalence of prostatic hyperplasia in men over the age of 45 reaches 45% in the United States and 80% by the age of 70 (2, 3) and it increases with age, risk factors including diet, exercise, smoking, and inflammation (4), and that the number of people with prostatic hyperplasia has reached 205 million globally (5), with an increasing burden of diseases (6). However, the efficacy of α-blockers (e.g., doxazosin) and 5αreductase inhibitors (e.g., finasteride) has been controversial, and the use of the drugs is limited by adverse effects such as the production of upright hypotension and erectile dysfunction. Therefore, the researchers need to choose the drug with fewer side effects and a longer course of treatment due to the longer course of the treatment (7).
According to traditional Chinese medicine theory, BPH is referred to as “Jinglong” and “Longbi.” Clinical practice has shown that Chinese medicine has great advantages in the treatment of BPH, and oral Chinese patent medicines (OCPMs) have been widely used in the clinic due to their multi-targeted effects, simplicity of use, and low adverse effects. However, there are many types of OCPMs and there is a lack of cross-sectional comparisons (8). Network meta-analysis (NMA) combines the available evidence and allows for simultaneous comparisons of different therapeutic options. Therefore, this study was based on a network meta-analysis based on a frequency-based framework to compare the efficacy and safety of 15 different OCPMs to reveal the optimal OCPM for BPH treatment and to illustrate more perspectives on the choice of medicine for BPH. The graphic workflow in our research is illustrated in Figure 1.
2 Methods
2.1 Eligibility criteria
2.1.1 Types of studies
Randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies, limited to Chinese and English studies, with no restriction on the blinding method used for the trial or the publication platform.
2.1.2 Types of participants
Patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia meet the relevant criteria in the Chinese Urology and Male Diseases Diagnostic and Treatment Guidelines 2022 Edition, i.e.: ① men over 50 years old, with the following urinary symptoms: with urinary frequency, urinary urgency, increased nocturia, difficulty in urination, incontinence of urination, post urinary dribbling, etc.; ② rectal fingerprinting: increase in the size of the prostate gland, with the central sulcus becoming shallower or disappearing; ③ ultrasound: prostate gland volume > 20 mL; Urine flow rate examination: urine volume > 150 mL, maximum urine flow rate < 15 mL/s; ⑤ International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) >5 points and ≤ 19 points. BPH can be diagnosed if more than 2 of the above symptoms and auxiliary tests are met.
2.1.3 Types of interventions
The experimental group used OCPM combined with conventional CWM; the control group used CWM alone or placebo combined with CWM.CWM included α-blockers (e.g., doxazosin mesylate, terazosin hydrochloride, tamsulosin hydrochloride), 5α-reductase inhibitors (e.g., finasteride, eplerenone), M-receptor antagonists (e.g., tolterodine tartrate), and treatment regimens consisting of a combination of the above drugs, for the convenience of the performing reticulated Meta-analysis as well as to simplify the analyzed data. They were uniformly named as CWM.
2.1.4 Types of outcomes
The primary outcome was the total efficiency ratio. The secondary outcome were prostate volume, residure volume, maximum urinary flow rate and IPSS. The safety indexes were the adverse reactions occurred during the study observation. The total effective rate = (apparent effect + effective)/total number of cases × 100%.
2.2 Excluded criteria
(1) Studies that do not explicitly include patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia or exclude patients with other complications; (2) studies in which the intervention involved unlisted OCPM preparations in hospitals, combination of other TCM therapies in addition to OCPMs, or combination of both or more OCPMs; (3) studies of the type of dissertation, animal experiments, clinical trial protocols, and self-control trials; (4) studies with missing data, unavailable full text, duplicate publications, or incorrect data; (5) literature of OCPM studies with less than 2 RCTs; (6) studies with a sample size of less than 20 cases in trial groups.
2.3 Search strategy
We searched Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane Library, China Knowledge Network, Wanfang Data and Wipu databases, and the search time was from the establishment of the database until July 1, 2024, and the search languages were Chinese and English. The search was conducted by combining subject words and free words, and the search strategy was developed according to different databases. The English search terms included: benign prostatic hyperplasia, oral Chinese patent medicines, Chinese herbal drugs, International English search terms include: benign prostatic hyperplasia, oral Chinese patent medicines, Chinese herbal drugs, International Prostate Symptom Score, Postvoid Residure volume, Prostate Volume, mean maximal flow rate, randomized controlled trial, RCT, etc. Chinese search terms include: prostatic hyperplasia, Chinese patent medicine, traditional Chinese medicine, tablet, bulk, capsule, capsule, tablets, bulk, capsules, pills, granules, effective rate, IPSS, bladder residual urine volume, prostate volume size, maximal flow rate, quality of life score, randomized controlled, trial, clinical, efficacy, and so on. References to the included literature were also traced for more relevant studies. The detailed search strategies are described in Supplementary File 1.
2.4 Study selection and data extraction
The results of the literature search were uploaded to NoteExpress, and after checking the weight of the software, two researchers screened independently according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, and then, reading the full text of the literature obtained from the initial screening and rescreened, and if there was any disagreement, a third researcher took part to decide on the final inclusion of the literature. Data were extracted from the screened literature using Excel 2021, including: publication date, study title, first author, sample size, mean age, intervention, and outcome indicators.
2.5 Quality evaluation
The Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool provided by RevMan 5.4 software was used to assess the risk of bias of the included literature, which included 7 items of randomized sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of investigators and subjects, blinding of outcome assessors, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting, and other biases, and the answers were provided for each item according to the categories of “low risk,” “unclear,” “high risk,” and any disagreements were resolved through discussion and consultation with the third investigator (9).
2.6 Statistical analysis
For categorical variables, the ratio of ratios (OR) was used, and continuous variables were expressed by applying the mean difference (MD) and its 95% confidence interval (CI). Traditional Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software, and inter-study heterogeneity was assessed using chi-square test and I2 values. If there was no significant inter-study heterogeneity (p < 0.05, I2 < 50%), the analysis was performed using a fixed-effects model. Conversely, the analysis was performed using a random-effects model. If inter-study heterogeneity was excessive (p < 0.01 or I2 >50%), descriptive analysis was used.
Meta-analysis was performed based on the frequency-based framework using the network and mvmeta packages of Stata 16.0 software to visualize the network diagrams of the evidence between the outcome indicators and the interventions to calculate the surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA), and to perform a “comparison-correction” funnel plot to identify any small-sample effect or publication bias. The area under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) was calculated and ranked to compare the efficacy of the interventions in each outcome indicator, and a “comparison-correction” funnel plot was drawn to identify whether there was a small-sample effect or publication bias. When studies had closed loops, inconsistency tests were performed to assess the degree of agreement between the results of direct and indirect comparisons.
3 Results
3.1 Selection and identification of studies
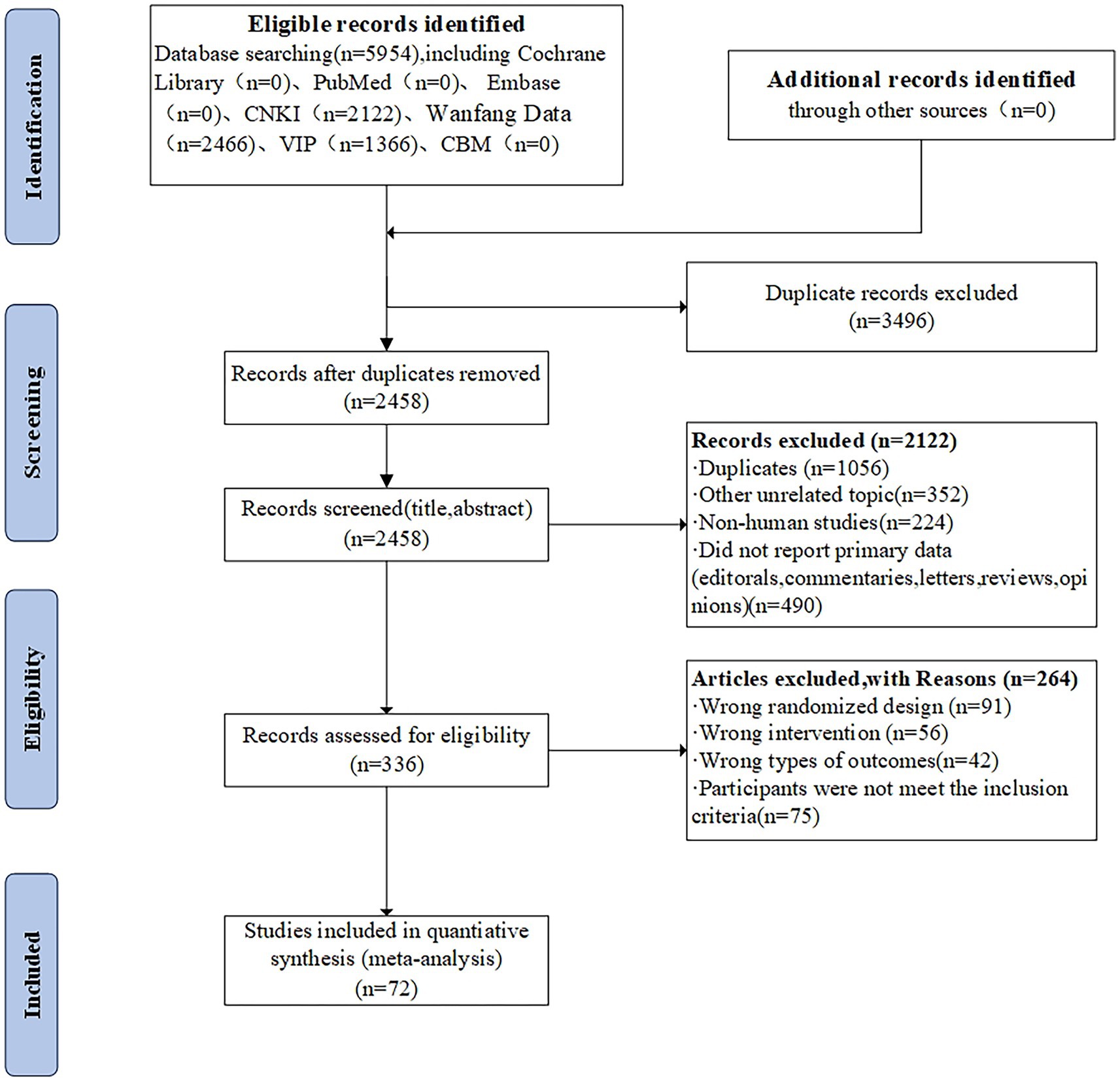
The title and abstract of 2,122 studies that did not meet the predefined inclusion criteria were excluded, resulting in 5954 citations, including 3,496 duplicate studies, and 336 full-text articles. A total of 336 full-text articles were screened and 264 were excluded due to inappropriate study designs, interventions, study objects, or outcomes. In total, 72 two-armed RCTs were included, which were conducted in China and published between 2009 and 2023. The PRISMA flow diagram is depicted in Figure 2.
3.2 Study characteristics of the involved researches
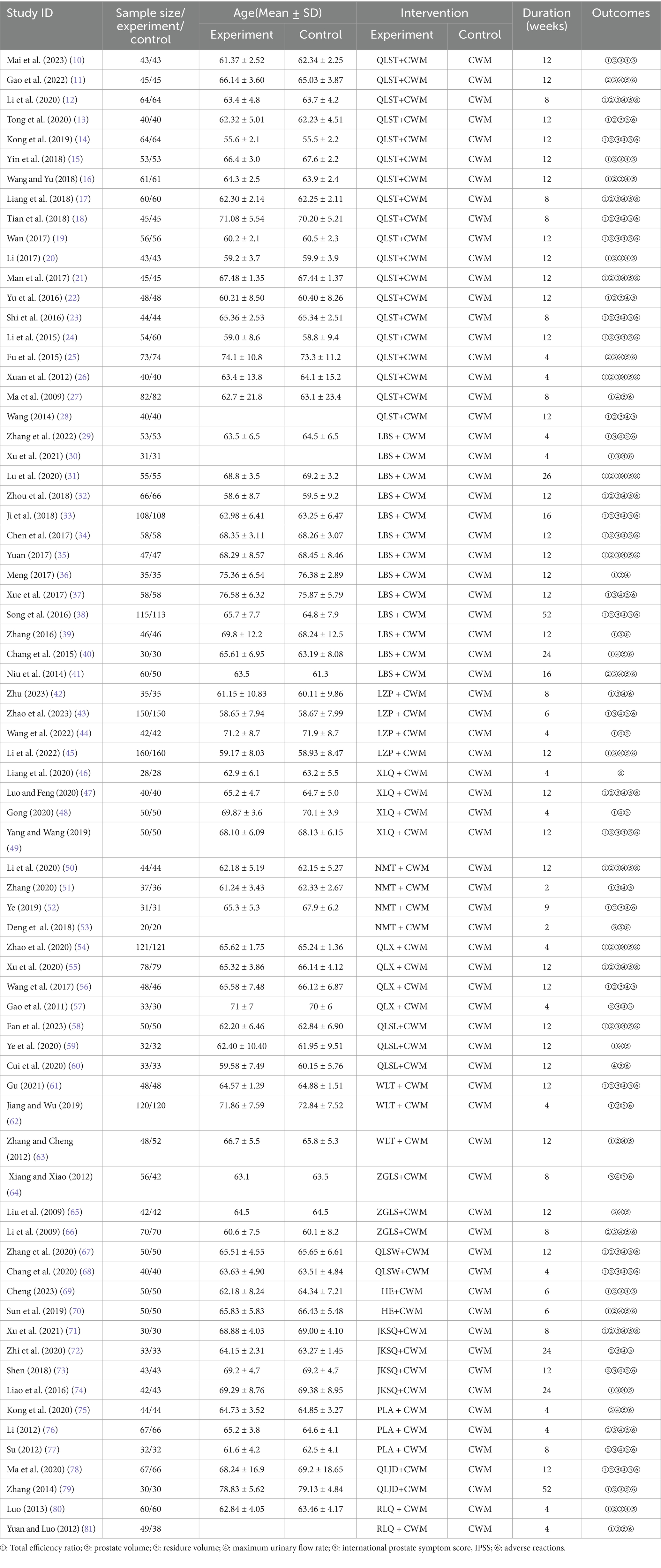
Seventy-two trials (10–81) involving 7,800 patients with BPH were included. 3,915 patients in the experimental group were treated with one of 15 proprietary Chinese medicines (Table 1) in combination with conventional western medicines, and 3,885 patients in the control group were treated with CWM alone.
Treatments ranged from 2 to 52 weeks in duration. Among these RCTs, the most frequently used were QLST (19 studies, 1,000 cases), LBS (13 studies, 762 cases), LZP (4 studies, 387 cases), XLQ (4 studies, 168 cases), NMT (4 studies, 132 cases), QLX (4 studies, 280 cases), QLSL (3 studies, 115 cases), WLT (3 studies, 216 cases), ZGLS (3 studies, 168 cases), QLSW (2 studies, 90 cases), HE (2 studies, 100 cases), JKSQ (4 studies, 148 cases), PLA (3 studies, 143 cases), QLJD (2 studies, 97 cases), RLQ (2 studies, 109 cases). Improvement of lower urinary tract symptoms, smooth muscle relaxation to relieve bladder outlet obstruction, and reduction of prostate volume were the primary therapeutic options for the treatment of all patients. The characteristics of the 72 eligible randomized controlled trials are shown in Table 1.
3.3 Methodological quality assessment
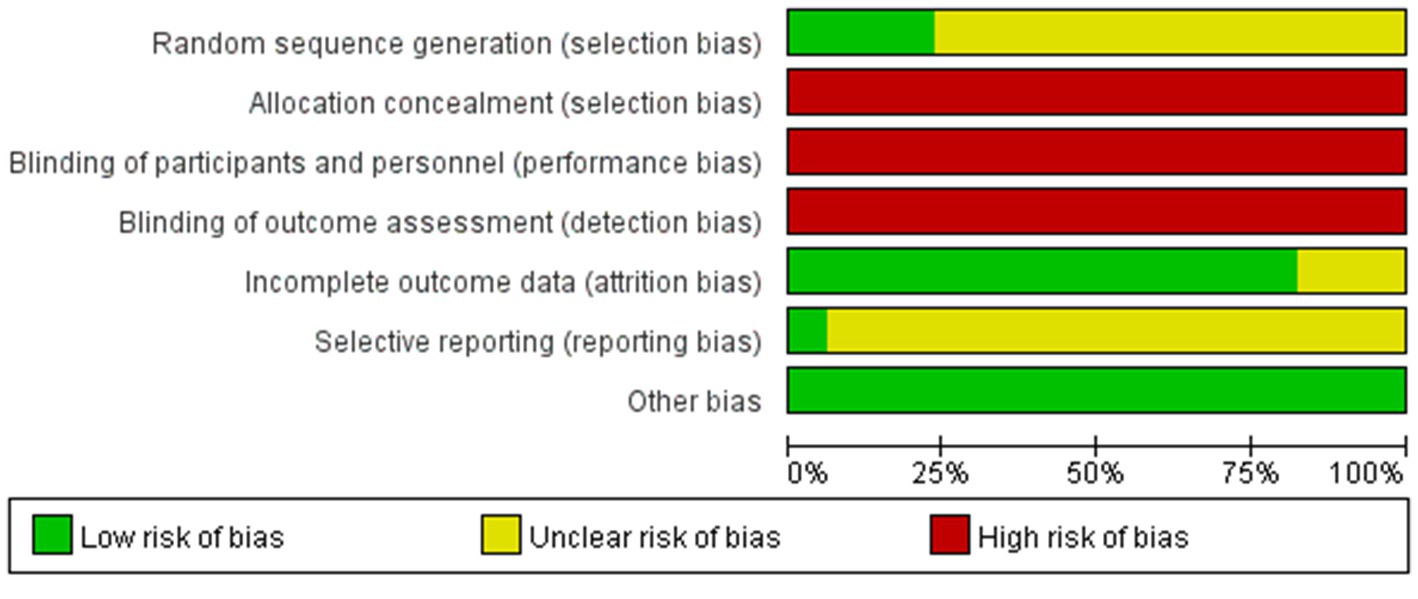
Two researchers separately evaluated the risk of bias of the included studies using the Cochrane Risk of bias tool presented in the Cochrane Handbook 5.1. The results of the assessment items were as follows: Low-risk items: (1) 15 studies in selective bias (interpretation using a random number table) and 3 studies on reporting bias (description using the shakedown method). (2) 62 studies in attrition bias (complete reporting of outcome data). (3) all studies in other bias (baseline of randomized controlled trials described). High-risk events: (1) All studies in selection bias (allocation concealment not used). (2) All studies in performance bias (blinding of participants and personnel not used). (3) All studies in detection bias (blinding of outcome assessments not reported). Risk items were unclear: (1) 57 studies in selection bias (specific randomization method not stated) and 69 studies in reporting bias (unclear selective reporting). (2) 10 studies in attrition bias (unclear selective reporting). A detailed description of the risk of bias assessment is shown in Figure 3.
3.4 Outcomes
3.4.1 Total efficiency ratio
All 56 pieces of research including 14 OCPMs and 14 interventions recorded the total efficiency ratio of BPH (Figure 4A).
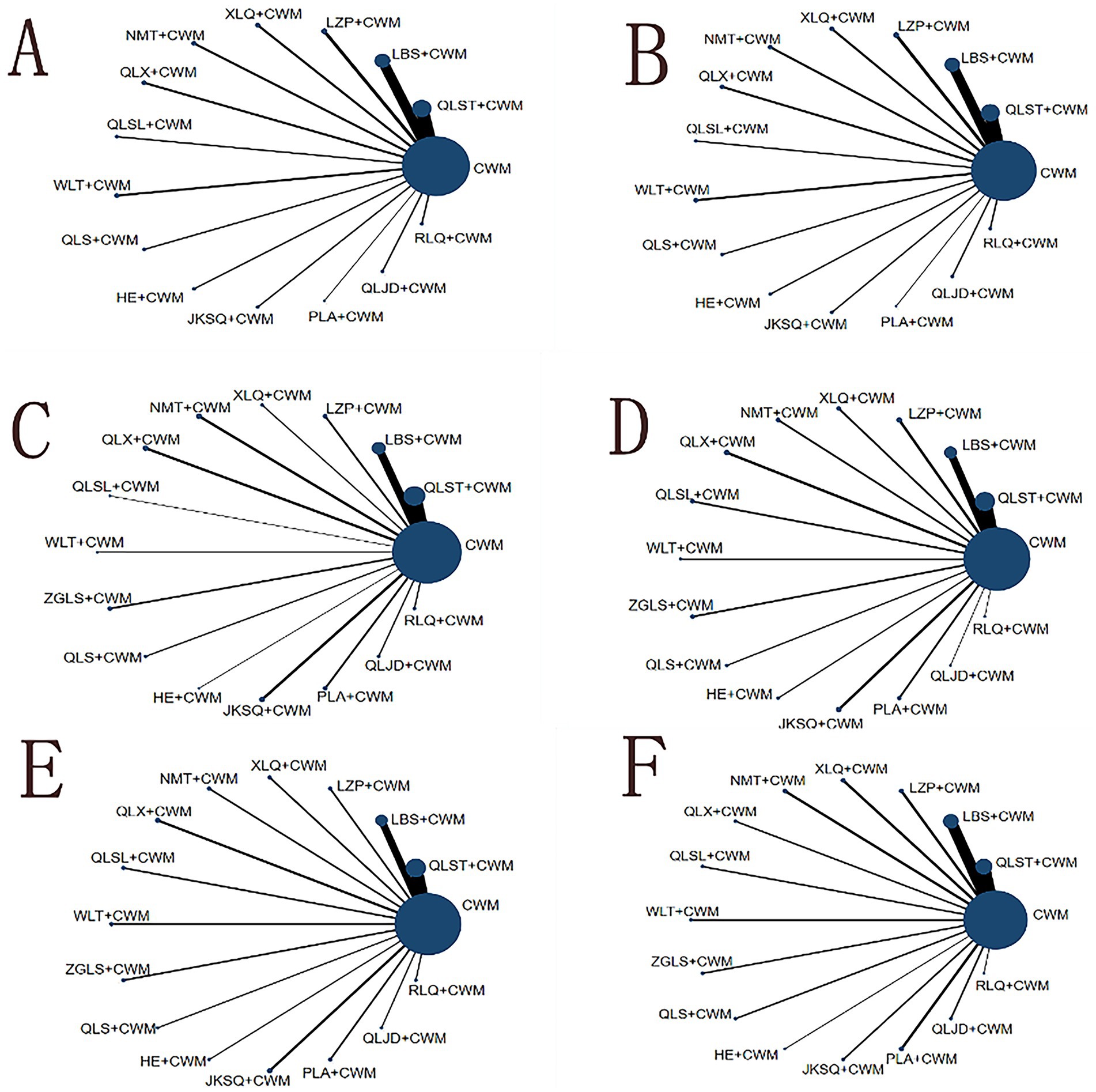
Figure 4. Network graph of outcomes. The blue nodes represent the total number of treatments. The line thickness corresponds to the number of comparison trials. (A) Total efficiency ratio; (B) prostate volume; (C) residure volume; (D) maximum urinary flow rate; (E) international prostate symptom score; (F) adverse reactions. CWM, conventional western medicine; QLST, Qianliesutong capsule; LBS, Longbisu capsule; LZP, Lingzepian tablet; XLQ, Xialiqi capsule; NMT, Ningmitai capsule; QLX, Qianliexin capsule; QLSL, Qianliesule capsule; WLT, Wenglitong capsule; ZGLS, Zeguilongsu capsule; QLS, Qianliesu capsule; HE, Huange capsule; JKSQ, Jinkuishenqi capsule; PLA, Puleai capsule, QLJD, Qianliejindan capsule; RLQ, Relinqing granules.
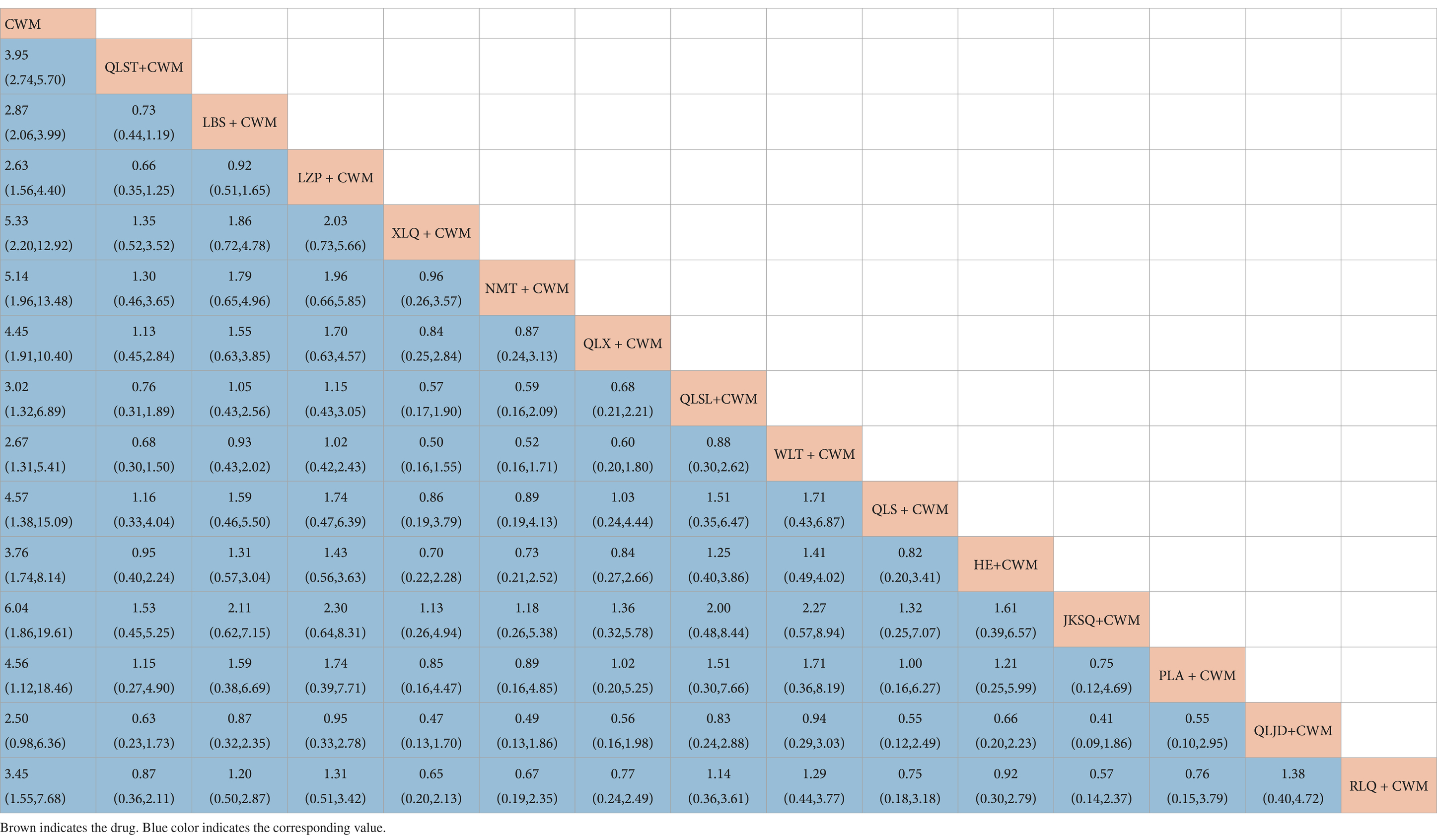
Compared with CWM alone, QLST + CWM (MD 3.95, 95% CI 2.74–5.70, low certainty), LBS + CWM (MD 2.87, 95% CI 2.06–3.99, very low certainty), LZP + CWM (MD 2.63, 95% CI 1.56–4.40, low certainty), XLQ + CWM (MD 5.33, 95% CI 2.20–12.92, very low certainty), NMT + CWM (MD 5.14, 95% CI 1.96–13.48, low certainty), QLX + CWM (MD 4.45, 95% CI 1.91–10.40, very low certainty), QLSL + CWM (MD 3.02, 95% CI 1.32–6.89, low certainty), WLT+ CWM (MD 2.67, 95% CI 1.31–5.41, very low certainty), QLS + CWM (MD 4.57, 95% CI 1.38–15.39, very low certainty), HE+ CWM (MD 3.76, 95% CI 1.74–8.14, low certainty), JKSQ+ CWM (MD 6.04, 95% CI 1.86–19.61, low certainty), PLA + CWM (MD 4.56, 95% CI 1.12–18.46, very low certainty), RLQ + CWM (MD 3.45, 95% CI 1.55–7.68, very low certainty) were beneficial to rise total efficiency ratio (Table 2). Compared with CWM alone, there was no significant difference in RLQ + CWM in the treatment of BPH (Table 2).
Based on the SUCRA values, JKSQ + CWM had the highest probability for rise total efficiency ratio (SUCRA: 76.5%), followed by XLQ + CWM (SUCRA: 74.2%), and NMT + CWM (SUCRA: 71.6%; Figure 5A; Table 3).
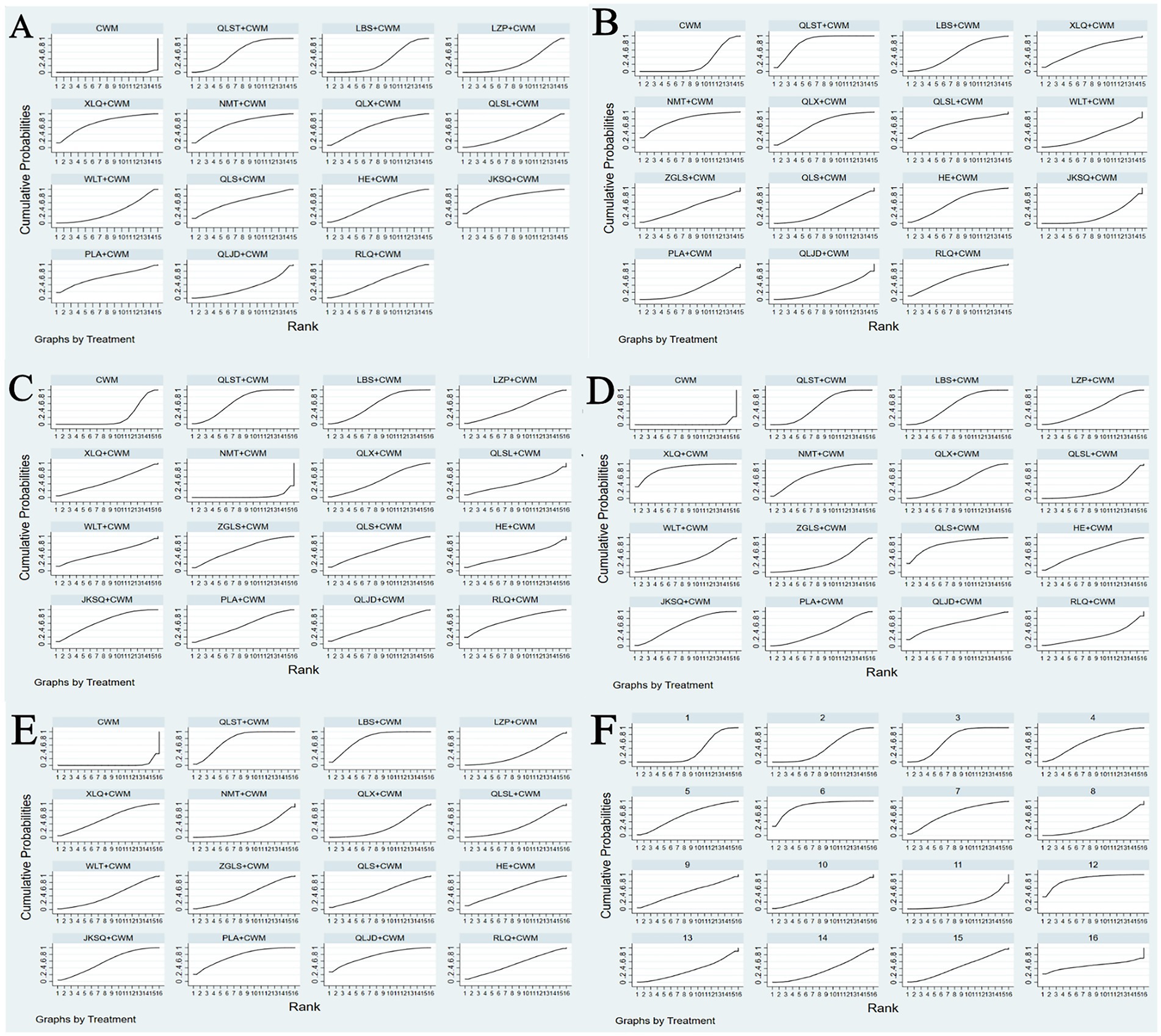
Figure 5. Plots of the surface under the cumulative ranking curves for all treatments (A) Total efficiency ratio; (B) prostate volume; (C) residure volume; (D) maximum urinary flow rate; (E) international prostate symptom score; (F) adverse reactions.
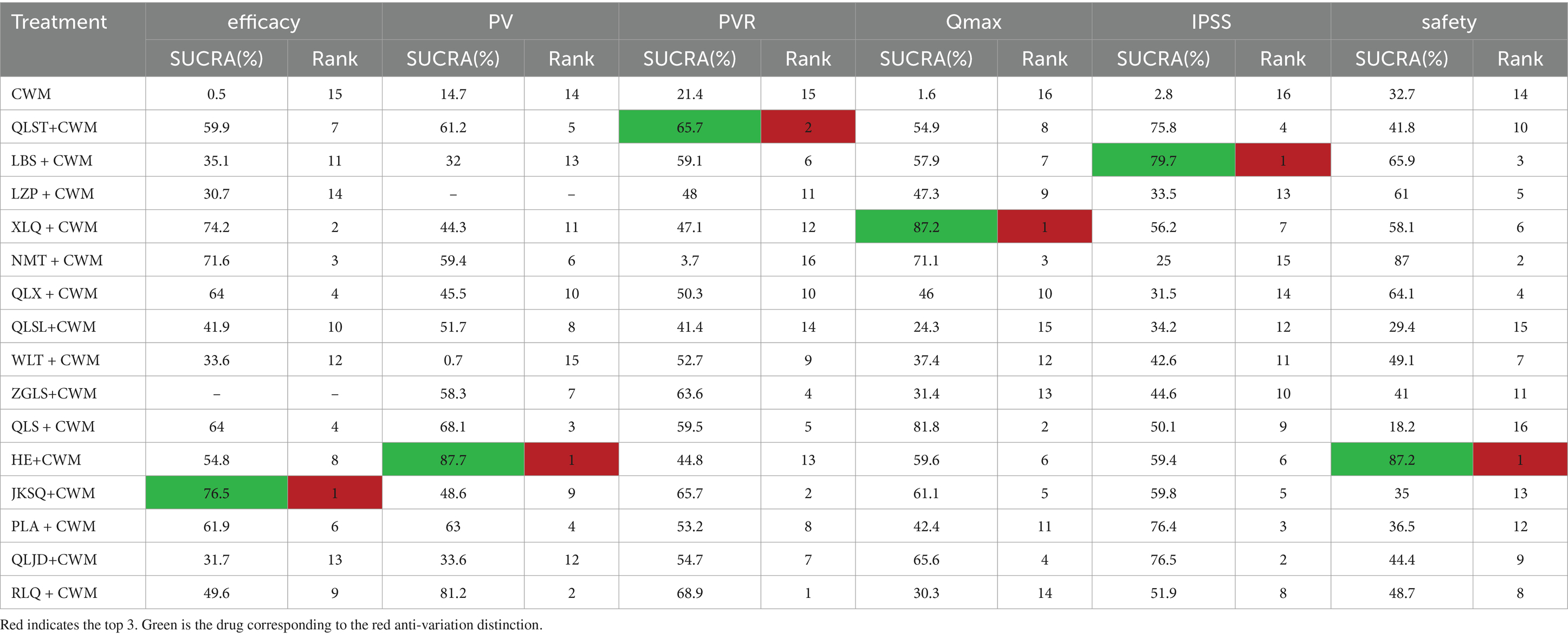
Table 3. Surface under the cumulative ranking curve and ranking probability of different Chinese patent medicines on each outcome.
3.4.2 Prostate volume
All 40 pieces of research including 14 OCPMs and 14 interventions recorded the prostate volume of BPH (Figure 4B).
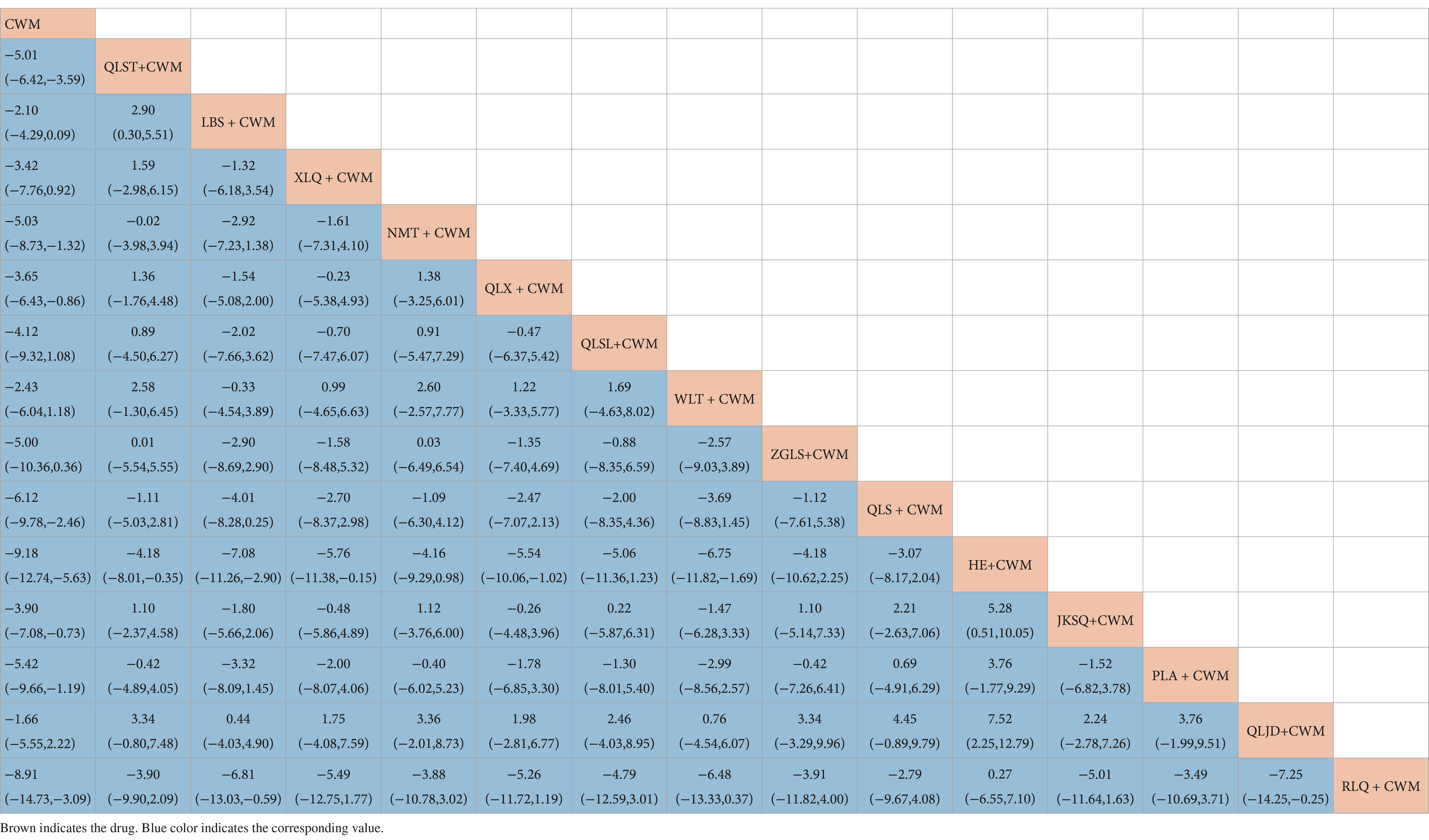
Compared with CWM alone, QLST + CWM (MD −5.01, 95% CI −6.42–−3.59, low certainty), NMT + CWM (MD −5.03, 95% CI −8.73–−1.32, low certainty), QLX + CWM (MD −3.65, 95% CI −6.43–−0.86, very low certainty), QLS + CWM (MD −6.12, 95% CI −9.78–−2.46, very low certainty), HE + CWM (MD −9.18, 95% CI −12.74–−5.63, low certainty), JKSQ + CWM (MD −3.90, 95% CI −7.08–−0.73, low certainty), PLA + CWM (MD −5.42, 95% CI −9.66–−1.19, very low certainty), RLQ + CWM (MD −8.91, 95% CI −14.73–−3.09, very low certainty) were beneficial to reduce prostate volume (Table 4). Compared with CWM alone, there were no significant differences between LBS + CWM, XLQ + CWM, QLSL + CWM, WLT + CWM, ZGLS + CWM, and QLJD + CWM in the treatment of BPH (Table 4).
Based on the SUCRA values, HE + CWM had the highest probability of reducing prostate volume. (SUCRA: 87.7%), followed by RLQ + CWM (SUCRA: 81.2%), and QLS + CWM (SUCRA: 68.1%; Figure 5B; Table 3).
3.4.3 Residure volume
All 61 pieces of research including 15 OCPMs and 15 interventions recorded the residure volume of BPH (Figure 4C).
Compared with CWM alone, QLST + CWM (MD −8.90, 95% CI −13.76–−4.05, low certainty), LBS + CWM (MD −7.72, 95% CI −14.00–−1.44, very low certainty) were beneficial to reduce residure volume (Table 5). Compared with CWM alone, there were no significant differences in others in the treatment of BPH (Table 5).
Based on the SUCRA values, QLST + CWM had the highest probability of reducing residure volume (SUCRA: 65.7%), followed by LBS+ CWM (SUCRA: 59.1%; Figure 5C; Table 3).
3.4.4 Maximum urinary flow rate
All 64 pieces of research including 15 OCPMs and 15 interventions recorded the maximum urinary flow rate of BPH (Figure 4D).
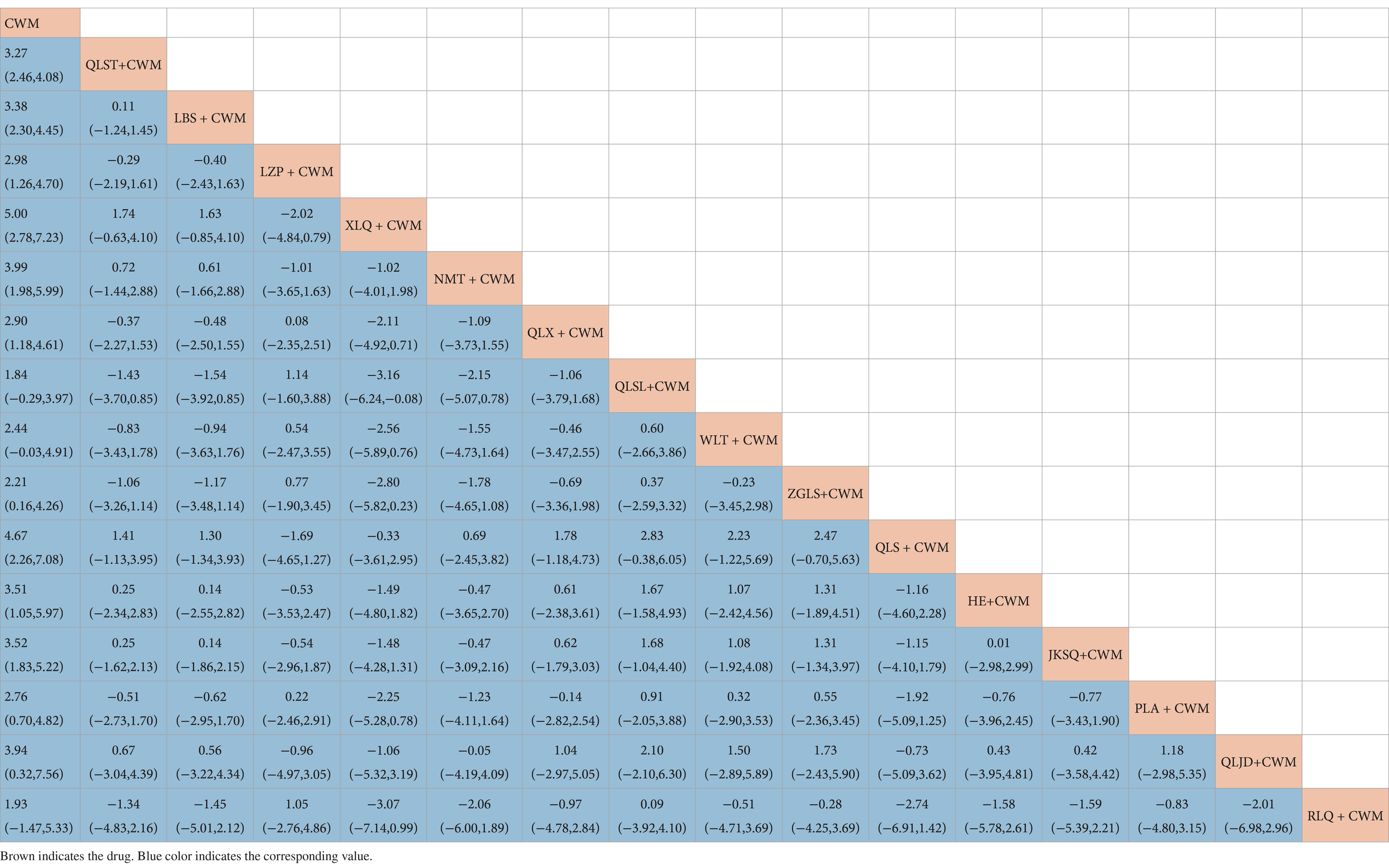
Compared with CWM alone, QLST + CWM (MD 3.27, 95% CI 2.46–4.08, low certainty), LBS + CWM (MD 3.38, 95% CI 2.30–4.45, very low certainty), LZP + CWM (MD 2.98, 95% CI 1.26–4.70, low certainty), XLQ + CWM (MD 5.00, 95% CI 2.78–7.23, very low certainty), NMT + CWM (MD 3.99, 95% CI 1.98–5.99, low certainty), QLX + CWM (MD 2.90, 95% CI 1.18–4.61, very low certainty), ZGLS+ CWM (MD 2.21, 95% CI 0.16–4.26, very low certainty), QLS + CWM (MD 4.67, 95% CI 2.26–7.08, very low certainty), HE + CWM (MD 3.51, 95% CI 1.05–5.97, low certainty), JKSQ+ CWM (MD 3.52, 95% CI 1.83–5.22, low certainty), PLA + CWM (MD 2.76, 95% CI 0.70–4.82, very low certainty), QLJD + CWM (MD 3.94, 95% CI 0.32–7.56, very low certainty) were beneficial to rise maximum urinary flow rate (Table 6). Compared with CWM alone, there were no significant differences between QLSL + CWM, WLT + CWM, RLQ + CWM in the treatment of BPH (Table 6).
Based on the SUCRA values, XLQ + CWM had the highest probability of elevating the maximum urinary flow rate (SUCRA: 87.2%), followed by QLS + CWM (SUCRA: 81.8%), and NMT + CWM (SUCRA: 71.1%; Figure 5D; Table 3).
3.4.5 IPSS
All 67 pieces of research including 15 OCPMs and 15 interventions recorded the IPSS of BPH (Figure 4E).
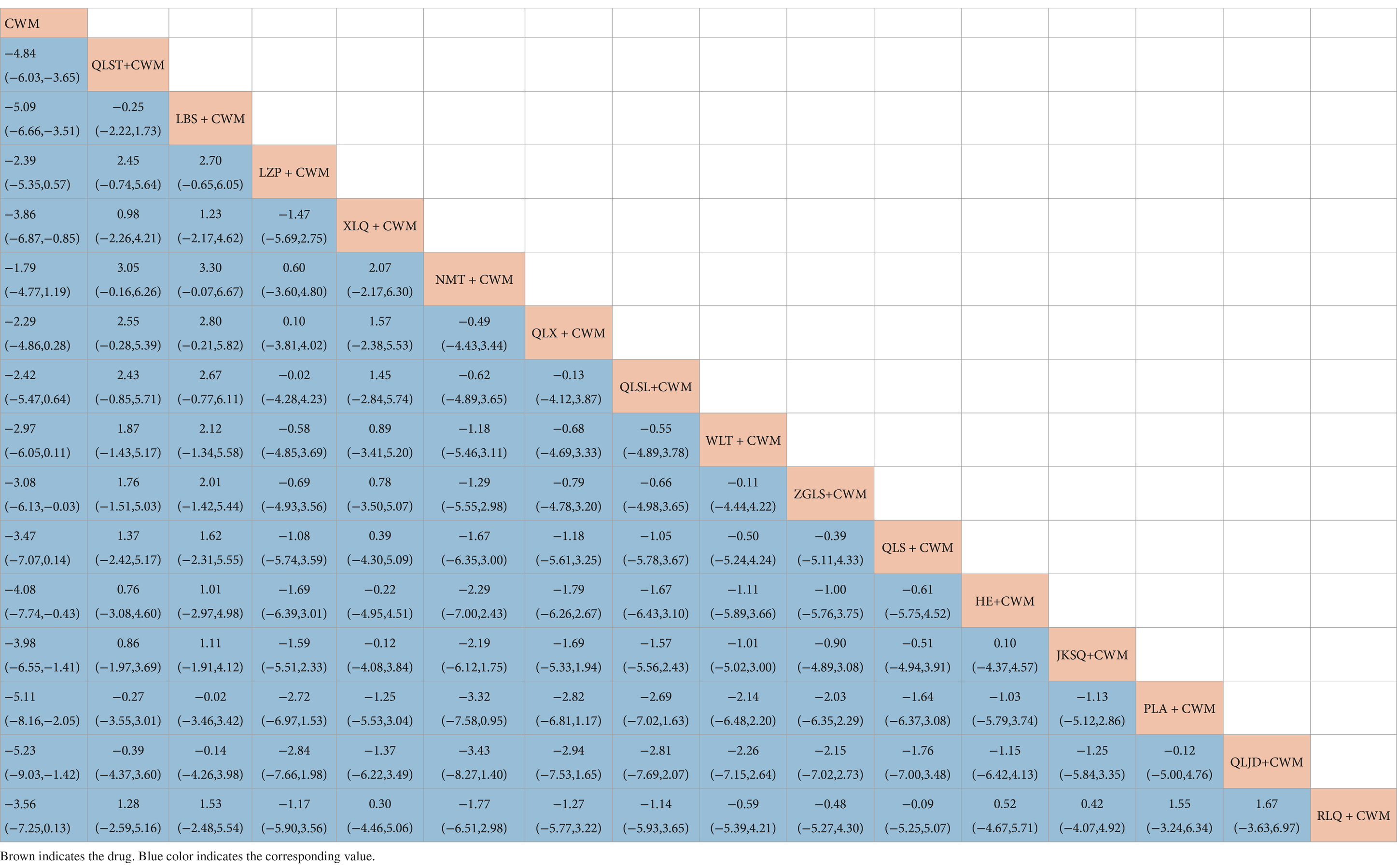
Compared with CWM alone, QLST + CWM (MD −4.84, 95% CI −6.03–−3.65, low certainty), LBS + CWM (MD −5.09, 95% CI −6.66–−3.51, very low certainty), XLQ + CWM (MD −3.86, 95% CI −6.87–−0.85, very low certainty), ZGLS + CWM (MD −3.08, 95% CI −6.05–−0.03, very low certainty), HE+ CWM (MD −4.08, 95% CI −7.74–−0.43 low certainty), JKSQ + CWM (MD −3.98, 95% CI −6.55–−1.41, low certainty), PLA + CWM (MD −5.11, 95% CI −8.16–−2.05, very low certainty), QLJD+ CWM (MD −5.23, 95% CI −9.03–−1.42, very low certainty) were beneficial to reduce IPSS (Table 7). Compared with CWM alone, there were no significant differences between LZP + CWM, NMT + CWM, QLX + CWM, QLSL+ CWM, QLS + CWM,WLT + CWM, and RLQ + CWM in the treatment of BPH (Table 7).
Based on the SUCRA values, LBS + CWM had the highest probability of reducing IPSS (SUCRA: 79.7%), followed by QLJD + CWM (SUCRA: 76.5%), and PLA+ CWM (SUCRA: 76.4%; Figure 5E; Table 3).
3.4.6 Adverse reactions
Of the 72 included studies, 53 reported the occurrence of adverse reactions. Ten studies reported no adverse reactions in both experimental and control groups, while the remaining 43 studies reported example adverse events. Adverse reactions included gastrointestinal reactions such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointestinal discomfort, dizziness, hypotension, rash, impotence, as well as mild hepatic and renal impairment. (Figure 4F; Table 8).
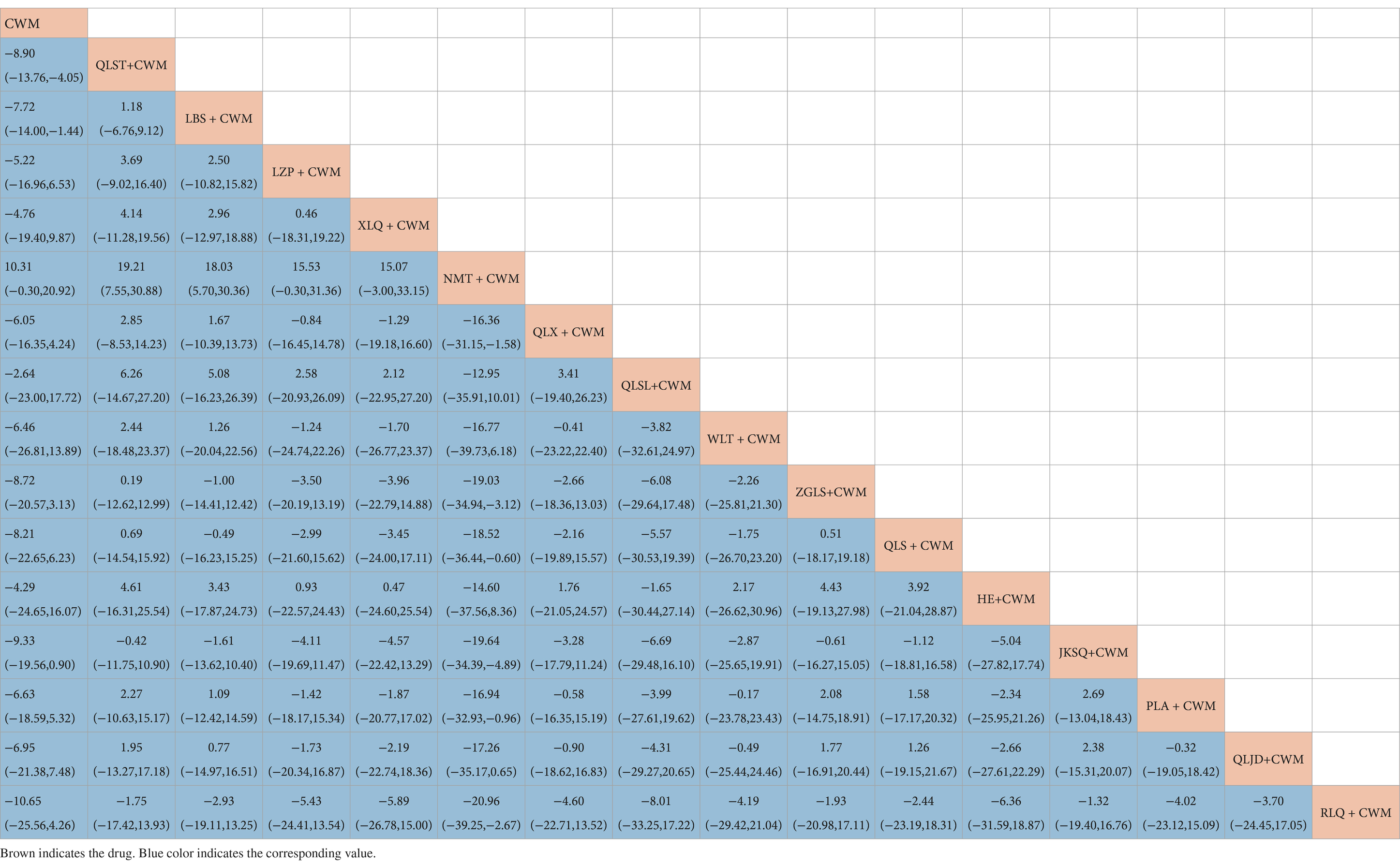
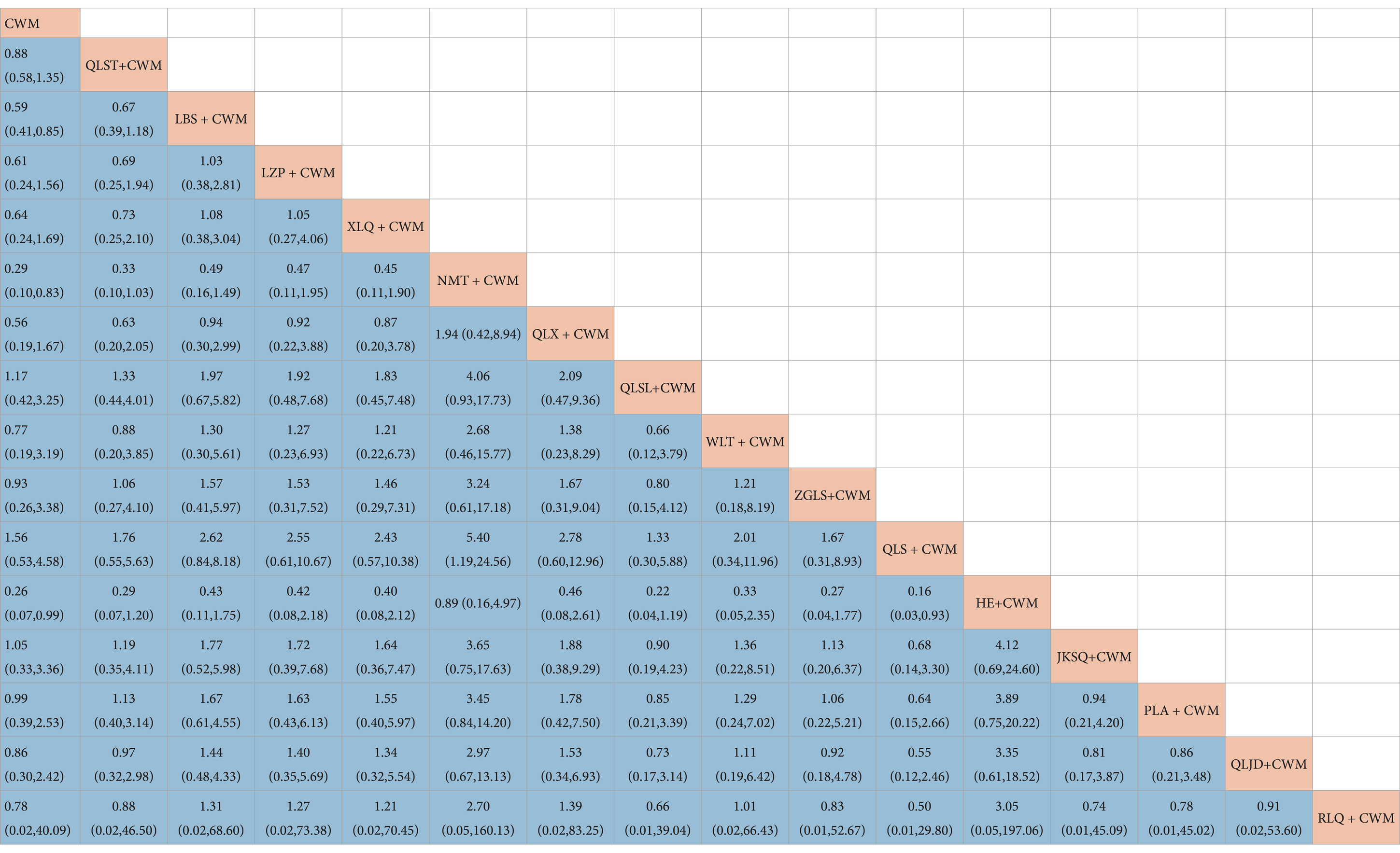
Compared with CWM alone, LBS + CWM (MD 0.59, 95% CI 0.41–0.85, very low certainty), NMT + CWM (MD 0.29, 95% CI 0.10–0.83, low certainty), HE + CWM (MD 3.76, 95% CI 1.74–8.14, low certainty) were beneficial to reduce adverse reactions (Table 9). Compared with CWM alone, there were no significant differences in others in the treatment of BPH (Table 9).
Based on the SUCRA values, HE + CWM had the highest probability of reducing adverse reactions (SUCRA: 87.2%), followed by NMT + CWM (SUCRA: 87%), and LBS + CWM (SUCRA: 65.9%; Figure 5F; Table 3).
3.5 Cluster analysis
The impact of intervention measures on two different outcomes was comprehensively compared through cluster analysis. The study conducted two cluster analyses, including the clinical efficacy and therapeutic effect of BPH. The results are shown in Figure 6. Through comprehensive analysis of cluster analysis, JKSQ + WM has better efficacy and HE + WM has higher in safety. Considering the combination of effectiveness and safety, NMT + CWM might possess good therapeutic results and high safety.
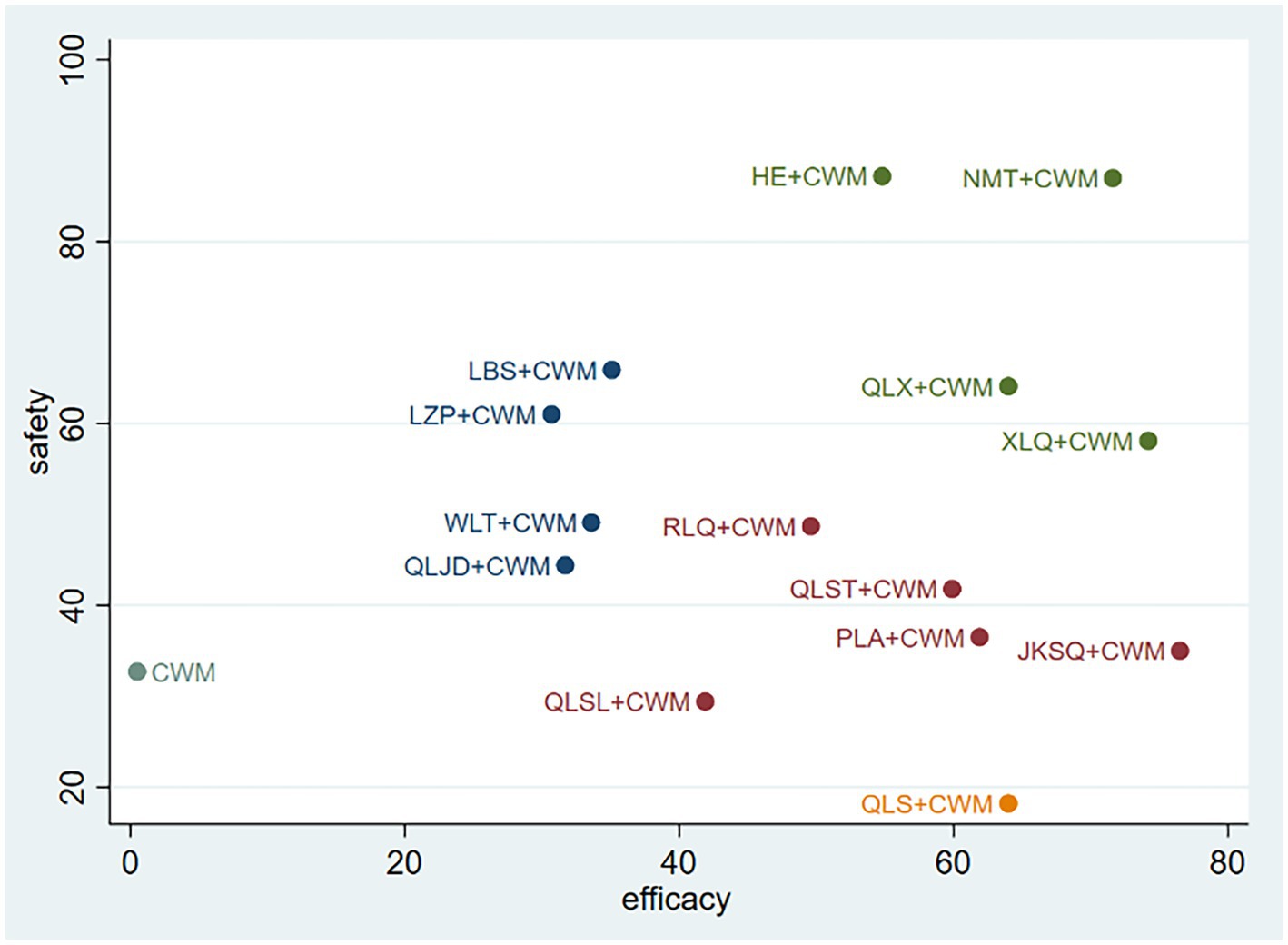
Figure 6. Cluster analysis plots. Interventions located in the upper right corner indicate optimal combination therapy for two different outcomes.
3.6 Inconsistency test
There is a lack of direct comparison among various intervention measures, and no closed loop has been found in NMA. We are unable to conduct inconsistency testing. Therefore, a consistency model for further analysis is used.
3.7 Publication bias
Figure 7 shows a funnel plot of six main results to assess publication bias. All funnel plots are not completely symmetrical visually, and each adjusted auxiliary line is not perpendicular to the centerline. Therefore, there may be significant publishing deviations.
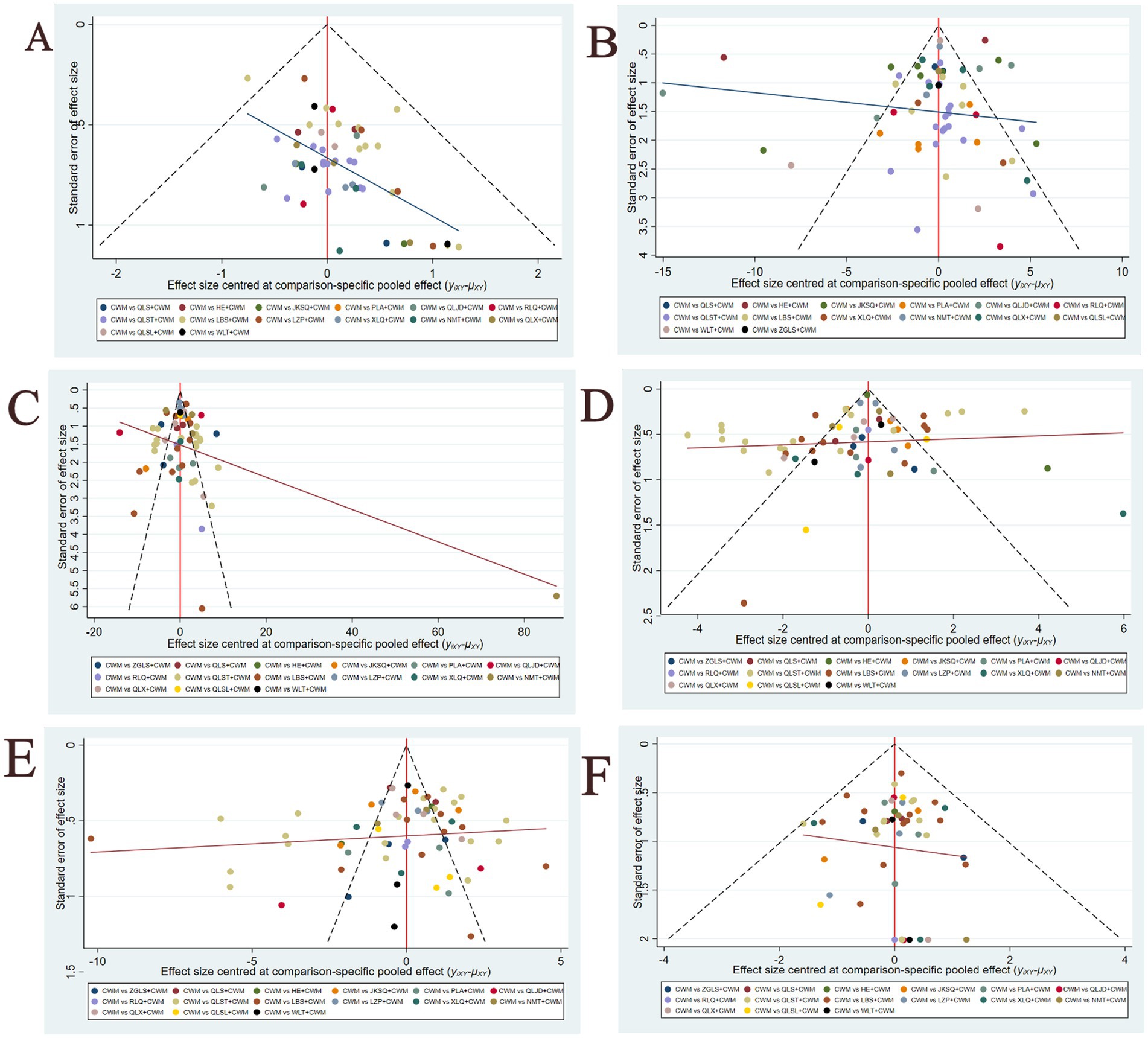
Figure 7. Funnel plots(A) Total efficiency ratio; (B) prostate volume; (C) residure volume; (D) maximum urinary flow rate; (E) international prostate symptom score; (F) adverse reactions.
4 Discussion
4.1 Summary of findings
This research systematically evaluates the efficacy of 15 frequently utilized OCPMs (QLST, LBS, LZP, XLQ, NMT, QLX, QLSL, WLT, ZGLS, QLSW, HE, JKSQ, PLA, QLJD, RLQ) in conjunction with CWMs for the treatment of BPH, based on data from 72 relevant studies employing network meta-analysis. The findings from the NMA indicate that the majority of OCPMs in conjunction with CWM outperformed CWM alone across all outcomes, with statistically significant differences observed between the groups.
Considering the statistical variability and SUCRA results, in total efficiency ratio, JKSQ + CWM was most likely to be the best treatment option; in prostate volume, HE + CWM was most likely to be the best treatment option; in residure volume, QLST + CWM was most likely to be the optimal treatment regimen; in maximum urinary flow rate, XLQ + CWM was most likely to be the optimal treatment regimen; in IPSS, LBS + CWM was most likely to be the optimal treatment regimen; in adverse reactions, HE + CWM was most likely to be the optimal treatment regimen.
Combining the two indicators of total efficiency ratio and adverse reactions, NMT + CWM is the best treatment option for BPH. Therefore, the efficacy of NMT + CWM in treating BPH is worthy of attention, but clinicians should also choose the appropriate method according to the specific conditions of clinical patients.
4.2 Research significance and importance
The precise process of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) remains unclear; it may result from the regulated destruction of epithelial and mesenchymal cell proliferation and death. Its etiology also encompasses the interplay of androgens, estrogens, growth hormones, and inflammatory cells, among other factors. In Chinese medicine, it is classified under “essence retention.” In Chinese medicine, this ailment is classified as “urinary retention” and predominantly affects elderly men with deficiencies in the spleen and kidneys, resulting in bladder failure, water-dampness, and the accumulation of damp-heat in the lower body, which contributes to the condition.
Alpha blockers can alleviate lower urinary tract symptoms and pain by relaxing the smooth muscle of the prostate and bladder, while 5α-reductase inhibitors can diminish prostate size (7). According to Chinese medicine theory, prostate hyperplasia is associated with deficiency and stasis; oral Chinese patent medicines can address spleen and kidney deficiency, enhance kidney function and blood circulation, and regulate bladder urinary storage capacity. Consequently, oral Chinese patent medicines and standard Western treatments are complementary and equally significant.
Oral Chinese patent medicines are offered in tablets, pills, capsules, granules, powders, and oral liquids, providing advantages such as convenient clinical use, ease of storage and transportation, and excellent safety, making them widely utilized in the treatment of BPH (82). Currently, a diverse array of oral Chinese patent medicines is employed for the management of BPH. Nevertheless, there is an absence of cross-sectional comparisons among the various medications. This study involved a retrospective meta-analysis utilizing a frequency-based methodology to evaluate the efficacy and safety of various OCPMs and to rank their respective advantages and disadvantages.
4.3 Limitations
The quality of the included studies was inconsistent; several studies failed to specify the randomization method, potentially introducing random error. Furthermore, the majority of studies did not detail the execution of allocation concealment and blinding, which could lead to selection bias and affect the validity of the study results.
The quantity of included studies exhibited considerable variability among OCPMs, potentially influencing the conclusions. The absence of direct comparisons among OCPMs may have affected the dependability of the results.
4.4 Prospects
We hereby present the subsequent recommendations. The study’s inclusion criteria are inadequate in rigor in identification and classification, with the application of OCPMs reliant on symptom identification guided by traditional Chinese medicine philosophy. Consequently, we recommend that clinicians select the OCPMs with optimal therapeutic efficacy aligned with the patient’s symptoms, contingent upon precise diagnosis, to enhance treatment effectiveness, decrease disease duration, and alleviate patient discomfort. Secondly, in the execution of randomized controlled trials, multicenter randomized double-blind trials must be conducted in strict compliance with pertinent rules, and meticulous attention should be given to the random number generation, allocation concealment, and blinding procedures. Finally, multicenter large-sample randomized controlled RCTs need to be conducted to compare the effects of different OCPMs to make up for the lack of research in this area. Implementing the study across various centers can enhance the control of potential confounders and selection biases, so as to augment the study’s authenticity. Furthermore, boosting the sample size can bolster the study’s reliability.
5 Conclusion
The efficacy of OCPM combined with CWM in the treatment of BPH is better than that of CWM alone, and the safety is good; various OCPMs have different therapeutic focuses, which can be individualized according to the specific symptoms of BPH patients in the clinic. Moreover, with the combined efficacy and safety, NMT + CWM is worth paying attention to in CPM. However, considering the limitations of this paper, these conclusions should be verified by multicenter, high-quality, large-sample randomized controlled trials.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YT: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation. YC: Writing – original draft. JD: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. RJ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XW: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. ZZ: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. FX: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition. ZG: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Hospital capability enhancement project of Xiyuan Hospital, CACMS (No. XYZX0201-05). Hospital capability enhancement project of Xiyuan Hospital, CACMS (No. XYZX0202-02).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1483864/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Sun, ZX, Song, CS, Xing, JP, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in combination with Chinese and Western medicine (trial version) [J]. National Journal of Andrology. (2017) 23:280–5. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2017.03.017
2. Maserejian, NN, Chen, S, Chiu, GR, et al. Incidence of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in a Population-based Study of Men and Women[J]. Urology. (2013) 82:560–4.
3. Platz, EA, Smit, E, Curhan, GC, et al. Prevalence of and racial/ethnic variation in lower urinary tract symptoms and noncancer prostate surgery in U.S. men[J]. Urology. (2002) 59:877–83.
4. He, Y, Yang, L, Wei, Q, et al. Reversible risk factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Sichuan Medical Journal. (2022) 43:99–103. doi: 10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2022.01.021
5. Xie, JP, and Peng, B. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of benign prostatic hyperplasia:an update[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Medical Science). (2021) 42:568–73. doi: 10.12289/j.issn.1008-0392.20187
6. Launer, BM, Mcvary, KT, Ricke, WA, et al. The rising worldwide impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Bju International. (2021) 127:722–8.
7. Sun, ZX, and Li, PC. Research progress of benign prostatic hyperplasia treated by traditional Chinese medicine [J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy. (2018) 33:2482–4.
8. Yu, WX. Guidelines for Integrative Multidisciplinary Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (2022 Edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Andrology. (2022) 36:96–102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0848.2022.02.017
9. Cumpston, M, Li, T, Page, MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 10:1–2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000142
10. Mai, HL, Lan, PG, Yue, ZM, et al. Analysis of the effect of prostate shutong capsule in the adjuvant treatment of stasis-type prostatic hyperplasia [J]. The Medical Forum. (2023) 27:102–4. doi: 10.19435/j.1672-1721.2023.13.032
11. Gao, W, Xue, XT, et al. Effect of Prostate Dredging Capsule Combined with Epprete on Symptom Score and Serum Tand E2 in Patients with Prostatic Hyperplasia [J]. Reflexology and Rehabilitation Medicine. (2022) 3:140–3.
12. Li, WQ, Jin, FL, et al. Clinical observation of Qianlieshutong capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in middle-aged and the elderly [J]. Journal of Community Medicine. (2020) 18:1333–5. doi: 10.19790/j.cnki.JCM.2020.19.08
13. Tong, P, Song, SH, Yang, J, et al. Effect of Qianqianshutong on clinical symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of North Pharmacy. (2020) 17:84–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2020.01.061
14. Kong, LJ, Wang, HM, and Zhao, JL. Effect of Qianlie Shutong Capsule combined with tamsulosin on urethral function in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Hainan Medical Journal. (2019) 30:2373–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2019.18.017
15. Yin, ZK, Wang, YY, and Fan, XM. Clinical efficacy of Qianlie shutong capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use. (2018) 11:91–2. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2018.27.046
16. Wang, GR, and Yu, GF. Efficacy of Qianlieshutong capsule in the adjuvant treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and its influence on serum testosterone and estradiol levels[J]. Journal of Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences. (2018) 39:570–1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7115.2018.05.032
17. Liang, JM, Zhao, GY, Luo, JL, et al. Clinical study of prostaglandin capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Chinese. Journal of Human Sexuality. (2018) 27:13–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2018.04.003
18. Tian, ZY, Feng, W, Zhu, YQ, et al. Curative effect of Qianlie shutong capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Medical Journal of West China. (2018) 30:224–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2018.02.017
19. Wan, T. Efficacy of Qianlieshtong capsule combined with tamsulosin in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and its effect on serum testosterone and estradiol levels[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. (2017) 26:2370–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2017.21.033
20. Li, WM. Observation on the efficacy of prostate Shutong capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2017) 36:76–7. doi: 10.16040/j.cnki.cn15-1101.2017.12.079
21. Man, YP, He, ZY, and Li, GH. Clinical observation of Qianlie Shutong Capsules combined with Epristeride Tablets in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Drugs &. Clinic. (2017) 32:1093–6. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2017.06.031
22. Yu, HC, Zhong, WY, and Bao, P. Randomized controlled study of Qianlie Shutong combined with Harnal in the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia[J]. China Practical Medicine, (2016) 11:1–2. doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2016.24.001
23. Shi, B, Chen, K, Zhang, ZM, et al. Clinical observation of Qianlie Shutong Capsules combined with finasteride in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drugs & Clinic. (2016) 31:500–3. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2016.04.022
24. Li, H, Mi, QH, Gao, YJ, et al. Effect of QianlieShutong capsule combined with tamsulosin on serum testosterone and estrogen in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and its efficacy[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceuticals. (2015) 35:89–91.
25. Fu, XJ, Hu, QH, Chen, JR, et al. Effect of Qianlie Shutong capsule combined with phenoxybenzamine for treating elderly patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia in 74 cases[J]. China Pharmaceuticals. (2015) 24:34–5.
26. Xuan, SQ, Wu, DF, Wei, HS, et al. Observation on the efficacy of prostate shutong capsule combined with tamsulosin in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Zhejiang. Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. (2012) 22:708–9.
27. Ma, ZF, Wang, DW, Liu, C, et al. Clinical efficacy of prostate shutong capsule combined with alpha receptor blocker in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia observed. [J].Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. (2009) 18:4107–8.
28. Wang, J. Analysis of the clinical effect of terazosin combined with Qianlieshtong capsule in the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Henan Journal of Surgery. (2014) 20:64–5. doi: 10.16193/j.cnki.hnwk.2014.01.086
29. Zhang, DX, Huang, C, Wang, SY, et al. Clinical efficacy of Longbishu tablets combined with tamsulosin hydrochloride sustained release capsules in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use. (2022) 15:111–3. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2022.15.035
30. Xu, YT, Wu, ZL, and Sun, YB. Observation on the efficacy of retention of urine in combination with tamoxifen in the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Yiyao Qianyan. (2021) 11:97–8.
31. Lu, HZ, Li, XY, and Liu, JS. Clinical study on Longbishu capsules combined with doxazosin for benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of New Chinese Medicine. (2020) 52:48–50. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2020.21.015
32. Zhou, Q, Li, HX, Wang, L, et al. Clinical effects of Longbishu Capsules in the adjuvant treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia patients due to kidney deficiency and blood stasis pattern[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. (2018) 40:2399–403. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2018.11.008
33. Ji, DL, Xue, C, Li, T, et al. Efficacy of Longbishu capsule combined with epristeride tablets in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Guizhou Medical Journal. (2018) 42:989–90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2018.08.032
34. Chen, XS, Ou, TW, and Zhang, J. Efficacy of Longbishu Capsule combined with western medicine in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and its influence on TCM syndrome score and QOL score[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. (2017) 26:4072–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2017.36.027
35. Yuan, MD. Effect of Longbishu Capsule on serum IL-10 and TNF-α in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2017) 19:147–50. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2017.08.042
36. Meng, F. Effect of Long Bi Shu capsule combined with finasteride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Chinese Community Doctors, (2017) 33:81+83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2017.18.48
37. Xue, P, Ren, B, Zhang, XY, et al. The efficacy and safety of Longbishu joint Haroldin treating elderly patients with prostatic hyperplasi[J].Chinese. Journal of Human Sexuality. (2017) 26:30–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1993.2017.05.009
38. Song, CS, Zhao, JY, Guo, J, et al. Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Longbishu Capsule Combined Doxazosin Mesylate Tablet[J].Chinese. Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. (2016) 36:1465–9. doi: 10.7661/CJIM.2016.12.1465
39. Zhang, YJ. Efficacy observation of 46 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia treated with the combined medication of Longbishu capsules and tamsulosin[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. (2016) 11:101–3. doi: 10.13935/j.cnki.sjzx.160130
40. Chang, DG, Li, GS, Peng, CH, et al. Longbishu capsule combined with mesylate doxazosin: An efficacious therapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. National Journal of Andrology. (2015) 21:165–9. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2015.02.014
41. Niu, M, Chen, TF, Chen, SJ, et al. Observation on the efficacy of Longbishu capsule combined with epristeride tablets in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (60 cases)[J]. China Practical Medicine. (2014) 9:140–1. doi: 10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2014.28.307
42. Zhu, JH. Lingze Pill Combined with Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Sustained Release Capsules in the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Medicine Modern Distance Education of China. (2023) 21:132–5.
43. Zhao, MJ, Sha, KF, and Wang, Y. Clinical observation of Lingze Tablets combined with epristeride in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia [J].Drugs & Clinic, (2023) 38:1203–1207. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2023.05.030
44. Wang, CL, Wang, YG, Zhang, J, et al. Clinical Study on Lingze Tablets Combined with Tamsulosin Hydrochloride for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia of Kidney Deficiency and Blood Stasis Type [J]. New Chinese Medicine. (2022) 54:80–3. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2022.04.022
45. Li, HQ, Sun, YF, and Liu, SM. Clinical effects of Lingze tablets combined with tamsulosin hydrochloride in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Chinese. Journal of Andrology. (2022) 36:85–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0848.2022.01.012
46. Liang, XH, Yang, XQ, He, SX, et al. Clinical observation on the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with Xialiqi capsule combined with tamsulosin hydrochloride extended-release capsule [J].Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Medicine, (2020) 36:1155.
47. Luo, QY, and Feng, P. Clinical efficacy and safety evaluation of Xia Li Qi capsule combined with tamsulosin hydrochloride sustained-release capsules in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Modern Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. (2020) 29:1311–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2020.12.013
48. Gong, YC. Effect of Xialiqi capsule combined with tamsulosin sustained-release capsule in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Practical Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2020) 36:482–3.
49. Yang, Z, and Wang, Y. Clinical study on Xialiqi Capsules combined with finasteride in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drugs & Clinic. (2019) 34:3071–5. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2019.10.040
50. Li, YQ, Li, QZ, Li, Y, et al. Clinical study on Ningmitai Capsules combined with tamsulosin in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J].Drugs &. Clinic. (2020) 35:1808–11. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.09.016
51. Zhang, F. Therapeutic effect of ningtuotai capsule combined with tamsulosin hydrochloride extended-release capsule on benign prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Henan Medical Research. (2020) 29:1465–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2020.08.063
52. Ye, M. Clinical study on the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with ningguotai capsule combined with terazosin [J]. Chinese and Foreign Medical Research. (2019) 17:43–5. doi: 10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2019.19.019
53. Deng, ZX, Ji, LX, Zhang, YR, et al. Ningmitai Capsules relieve lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia:A short-term clinical observation [J].National Journal of Andrology, (2018) 24:72–77. doi: 10.13263/j.cnki.nja.2018.01.014
54. Zhao, XS, Du, J, Chen, HL, et al. Clinical study on the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia with Prostexin capsule combined with terazosin [J].Drugs & Clinic, (2020) 35:2216–2219. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.11.021
55. Xu, MK, Hao, YL, and Liu, H. Curative effect of Qianliexin combined with doxazosin tablets on benign prostatic hyperplasia in the elderly[J]. Hainan Medical Journal. (2020) 31:851–4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2020.07.011
56. Wang, CX, Gong, XY, Zhang, SY, et al. Efficacy Observation of Qianliexin Combined with Tamsulosin Hydrochloride and Finasteride in the Treatment of Elderly Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia[J]. China Pharmacy. (2017) 28:1108–11. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2017.08.28
57. Gao, Z, Lun, LJ, Shao, KQ, et al. Clinical observation on Qian Lie Xin capsule plus tamsulosin hydrochloride sustained release capsules in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with Shi Re Yu Zu syndrome [J]. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine. (2011) 31:17–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2011.10.006.017.04
58. Fan, YX, Wang, YH, Cai, JH, et al. Clinical study on Qianlie Shule Granules combined with finasteride in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia [J].Drugs & Clinic, (2023) 38:2568–2572. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2023.10.032
59. Ye, X, Yang, WT, Li, QS, et al. Efficacy of Qianlie Shule Granules combined with Tamsulosin Hydrochloride Sustained-Release Capsules for treating benign prostatic hyperplasia complicated with chronic prostatitis [J]. Guangxi Medical Journal. (2020) 42:3058–60. doi: 10.11675/j.issn.0253-4304.2020.23.13
60. Cui, G, Zhou, SH, Guo, J, et al. Qianlie shule Granules for benign prostatic hyperplasia:A randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Andrology, (2020) 34:42–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0848.2020.04.008
61. Gu, DL. Clinical study on Wenglitong Capsules combined with tansulosin in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drugs & Clinic. (2021) 36:577–81. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2021.03.033
62. Jiang, F, and Wu, PF. Effect of doxazosin mesylate combined with Wenglitong on benign prostatic hyperplasia and its effect on matrix metalloproteinase-9 and S100 calcium-binding protein P levels. [J].Hainan Medical Journal. (2019) 30:562–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2019.05.006
63. Zhang, XS, and Cheng, HS. Wenglitong Capsule and western medicine in treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. (2012) 18:325–7. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2012.23.100
64. Xiang, Y, and Xiao, D. Clinical observation of terazosin combined with Zeguilongshuang in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Chinese Community Doctors (Medicine Edition). (2012) 14:219–20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2012.10.211
65. Liu, JT, Zhang, CL, and Yi, YH. Evaluation of the efficacy of Zegui Urinary Capsules combined with alpha-blockers in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia [J]. Acta Academiae Medicinae Weifang. (2009) 31:401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3101.2009.05.031
66. Li, Z, Wang, Y, Wang, WH, et al. Effect of Zeguilongshuang combined with naftopidil in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition). (2009) 35:936–9. doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587x.2009.05.041
67. Zhang, TB, Deng, YJ, Zheng, T, et al. Clinical study on Qianqianshu Pills combined with doxazosin in treatment of prostatic hyperplasia[J].Drugs &. Clinic. (2020) 35:243–6. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.02.010
68. Chang, JK, Hou, JQ, Zhu, CY, et al. Clinical study on Qianlieshu Pills combined with silodosin in treatment of prostatic hyperplasia[J].Drugs &. Clinic. (2020) 35:1671–4. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.08.037
69. Cheng, W. Clinical Study on Huang’e Capsules Combined with Western Medicine for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia [J]. New Chinese Medicine. (2023) 55:66–70. doi: 10.13457/j.cnki.jncm.2023.18.014
70. Sun, J, Li, M, Zhang, J, et al. Clinical Observation on Huang’e Capsules Combined with Finasteride in the Treatment of Senile Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia[J].China Pharmaceuticals, (2019) 28:87–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2019.11.027
71. Xu, ZC, Zhang, MJ, Su, MY, et al. Clinical controlled research of Jinkui Shenqi Pill in the treatment of patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia of Yang deficiency[J]. China Medicine and Pharmacy, (2021) 11:47–49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0616.2021.13.013
72. Zhi, QM, Huang, ZM, Zhu, HB, et al. Clinical observation of Jingui Shenqi tablet combined with finasteride tablet in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (kidney-yang deficiency syndrome) [J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2020) 39:84–5. doi: 10.16040/j.cnki.cn15-1101.2020.04.051
73. Shen, XX. Clinical study of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2018) 36:114–6.
74. Liao, QX, Hou, BN, Luo, XG, et al. Clinical effect of Jinguishengqi pill in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in the elderly[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica. (2016) 32:96–8. doi: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2016.05.025
75. Kong, XH, Jing, X, and Dong, JJ. Clinical observation of Pulean tablets combined with napidil in treatment of prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drugs & Clinic. (2020) 35:765–8. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.04.035
76. Li, ZS. Proan tablets combined with Tamsulosin in the treatment of 67 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. ChinaPharmaceuticals. (2012) 21:69–70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2012.06.040
77. Su, M. Clinical observation of terazosin combined with propranolol in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal. (2012) 24:174–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2012.11.098
78. Ma, JH, Wei, HB, Li, XL, et al. Clinical observation of Qianlie Jindan Tablets combined with doxazosin in treatiment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Drugs & Clinic. (2020) 35:980–3. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-5515.2020.05.034
79. Zhang, GX. Clinical observation Of Tamsulosin united Qian lie jin dan tablets for the treatment of elderly damp heat stasis benign prostatic hyperplasia[D]. Shandong University of Chinese Medicine, (2014).
80. Luo, Q. N.60 cases of benign prostatic hyperplasia were treated with finasteride tablets combined with Relinqing granules[J]. China Pharmaceuticals. (2013) 22:124–5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2013.08.080
81. Yuan, CY, and Luo, YD. Curative effect of Relinqing granule combined with finasteride tablets in thetreatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. (2012) 31:1–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0979.2012.23.001
Keywords: network meta-analysis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, oral Chinese patent medicines, efficacy, safety
Citation: Tang Y, Cai Y, Ding J, Ji R, Wang X, Zhang Z, Xu F and Gao Z (2024) Efficacy and safety of oral Chinese patent medicine for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Med. 11:1483864. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1483864
Edited by:
Vivek P. Chavda, L M College of Pharmacy, IndiaReviewed by:
Johid Malik, University of Nebraska Medical Center, United StatesHimanshu Sharma, Teerthanker Mahaveer University, India
Copyright © 2024 Tang, Cai, Ding, Ji, Wang, Zhang, Xu and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Xu, eHVmZW5nMTgwMEAxNjMuY29t; Zhan Gao, Z2Fvemhhbm1kQHZpcC4xNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yiwen Tang
Yiwen Tang Yuyang Cai
Yuyang Cai Jiasen Ding2
Jiasen Ding2 Xiong Wang
Xiong Wang