- 1Faculty of Medicine, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- 2School of Nursing, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, Henan, China
Introduction: Community-based learning approaches are gaining recognition in nursing education as a means to address the needs of aging societies by fostering empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors among nursing students. These attributes are essential for enhancing the quality of care and building strong interpersonal connections with older adults. While community-based education programs offer promising benefits, there is still limited understanding of their impact on nursing students’ empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors. This scoping review aims to examine how community-based educational interventions can assist nursing students in developing these essential competencies, ultimately contributing to better outcomes in geriatric care.
Method: A scoping review was conducted following the framework of Arksey and O’Malley. The following electronic databases were searched: Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), MEDLINE, Web of Science, Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection, PubMed, and Google Scholar. Gray literature was also searched through Google Scholar and ProQuest. Studies included reports on nursing students’ emotional changes due to educational engagements with older adults.
Results: A total of 3,001 abstracts were screened, with 78 full texts reviewed, resulting in 9 studies being included in the analysis. The results demonstrate that interactions with older adults enhance nursing students’ empathy and emotional intelligence while fostering positive changes in their caring behaviors. Participants reported greater sensitivity to the feelings and physical discomforts of older adults, contributing to improved care and stronger relational dynamics.
Discussion: Community-based education programs involving older adults represent an effective strategy for enhancing nursing students’ empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors, suggesting valuable implications for nursing education methodologies.
Introduction
Community-based education serves as a pathway to address the educational needs of the community and enhance healthcare systems by training healthcare personnel in both developing and industrialized nations, aligning education with community requirements. A community-based educational program consists of an adequate amount of learning activities in a range of well-balanced educational venues. A community learning plan requires that teachers fully consider the needs of community learning and reasonably arrange curriculum content and activities in the process of curriculum planning (1). Teachers should provide students with as many opportunities as possible to participate in community learning activities, and through these activities, students can obtain real and meaningful experiences, make them feel that they are members of the community, and then cultivate their sense of responsibility and mission to society (2, 3). Community-based education programs are increasingly used in professional training for nurses to provide care and social support to various populations, particularly older adults (4). The literature has primarily focused on nursing student groups rather than community care recipients. Community-based education is a valuable method for improving clinical skills, providing technical assistance, and enabling social contact (5). This type of education has the potential to enhance empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors (6–8).
As the number of studies highlighting the potential advantages of community-based education in geriatric nurse training continues to rise, there is increased interest in exploring its benefits for improving and supporting patient care (9). While existing research suggests that community-based education can be an effective and cost-efficient method for nursing students to enhance their communication skills and social awareness, there remains a significant gap when it comes to identifying programs that support the development of empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors (5, 10, 11). Despite previous literature reviews exploring the use of social services or community-based education for improving empathy in student nurses, no studies have yet examined the role of community-based education in promoting such skills, specifically when it comes to geriatric care (12). This review thus aims to bridge that gap by offering a comprehensive examination of the evidence surrounding the efficacy of community-based education programs in promoting empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors in the context of geriatric nurse training.
In the field of nursing education, both empathy and emotional intelligence are essential aspects that encompass various dimensions including moral, cognitive, and behavioral enlightenment (13–17). Amidst the current emphasis on community nursing practice in nursing education focuses more on active learning in real situations to enhance nursing students’ social–emotional awareness of poverty and illness among individuals and families (18), community-based education emerges as a strongly recommended approach in pedagogical innovations. As society rapidly ages, projections indicate that by 2025, one in five Chinese individuals aged 60 and above may experience multiple chronic illnesses, primarily within the confines of their homes (19). This implies that nursing students will have to regularly engage with these elderly individuals within communities.
The current teaching approach is mainly based on classroom teaching, which often does not achieve the nursing students’ learning outcomes on empathy and emotional intelligence (20). Research conducted by Zhao and Kong (21) investigated the empathy level of undergraduate nursing students in Hubei Province, China found nursing students struggle to identify or respond to changes in others’ emotions, as evidenced by their low scores on the “on others’ pain” item. According to another study conducted in China, nursing students in placement had an average emotional intelligence score of 69.29 out of a possible 100 points (22).
Empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors are recognized as primary elements to improve care outcomes. After investigating 362 undergraduate nursing students, Liu (23) concluded that the empathy ability of undergraduate nursing students and the willingness to serve older adults were both at a medium level, and the two were positively correlated. In other words, improving the empathy ability of undergraduate nursing students can improve their willingness to serve older adults, which is extremely beneficial for China with its rapidly aging population. Emotional intelligence and empathy can help improve moral sensitivity and caring behaviors (24). Nursing students’ empathy is related to personality and emotional intelligence, which can be improved by cultivating their personality and emotional intelligence (25). The higher the level of emotional intelligence of nursing students, the stronger their caring ability (26). It is suggested that educating students about aging and giving them more opportunities to interact with older adults will develop empathy, eliminate negative attitudes, produce a greater willingness to care for old adults, and thereby boost their interest and motivation to provide care and service to them (26). The scoping review method is appropriate for addressing the research question/objectives because it provides a comprehensive overview of the literature on a specific topic (27). The priority is given to including a wide range of studies, not necessarily empirical, which enables a comprehensive understanding of the topic. Furthermore, scoping reviews can aid in identifying important concepts, definitions, and gaps in the available evidence, which can guide future research directions (28). Regarding this review, the objective is to map the evidence on how community-based education programs for older adults can be used to improve empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors among nursing students.
Methods
Study design
This scoping review was based on the approach described by Arksey and O’Malley (29) and further developed by Levac, Colquhoun (30). This systematic review method is recommended by the Joanna Briggs Institute as it improves the review’s rigor and clarity (31). This procedure entails a 5-step process that includes the following steps: (1) establishing and aligning the objective(s) and questions(s); (2) developing and matching the inclusion criteria with the objective(s) and question(s); (3) outlining the planned approach from evidence searching, selecting data extracting, to presenting the evidence; (4) summarizing the evidence as to the review’s purpose, (5) drawing a conclusion, and noting any implications that the results have. This scoping review was registered on Open Science Framework, with registration DOI number https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/JK7EB. The PRISMA reporting guidelines was followed to provide guidance for the reporting of this scoping review by evaluating the effects of interventions (32). This scoping review was structured and organized according to the PRISMA checklist, ensuring that all relevant components were systematically addressed. Following these established guidelines enhances the clarity and completeness of the review, providing a robust foundation for the findings and conclusions. Adhering to PRISMA reflects a commitment to maintaining high standards in research methodology.
Identifying research question
The question “What is the existing literature on the use of community-based education programs for older adults to support empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors development among nursing students?” was acted as a starting point to provide search terms. According to the PICO framework for formulating clinical questions, the queries include four aspects: Patient-Problem (P), Intervention (I), Comparison (C) and Outcome (O). In this regard, Population, Intervention, Comparators, Outcomes, Study Design (PICOS) criteria were used for this study: population (undergraduate nursing students and medical students), intervention (community-based education and geriatric curriculum innovation) and outcome (empathy, emotional intelligence, caring behavior).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Following the PCC framework (Population, Concept, and Context) (33), studies were included if they were: (1) English language articles that were published in the past 10 years, from 2013 to 2024; (2) primary research articles about community-based education, and examined the changes in the undergraduate nursing students’ empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors (dissertations, peer-reviewed research, evidence-based practice guidelines); (3) primary research that looking into the effectiveness of the older adults’ education for improving nursing students’ capabilities or competencies; and (4) articles related to community-based medical education. The search also included gray literature, such as conference reports, graduate thesis, and so on.
The exclusion criteria were: (1) studies that did not answer the main research question or meet the main objective of this scoping review (for instance, the studies that focused on the effects on older people rather than on nursing students); (2) an inappropriate study design (for example, observational studies); (3) studies that were not published in peer-reviewed journals or in conference reports; (4) studies not published in English; and (5) outdated or insufficient information included in the document.
Search strategy: approach, evidence searching, selected data extracting
The literature search was performed using English databases including the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Web of Science, MEDLINE, Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection, PubMed, and Google Scholar. These databases were selected for their information contained on nursing education.
A three-step search strategy was implemented (33). Initially, to make sure no synonyms had been missed in the search strategy, the author and another researcher who have studied systematic reviews of literature search methods and methods of evaluating the quality of literature double-checked the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) in PubMed and keywords that showed in the results from the initial search. The keywords used for the search were “medical student* “[MeSH terms] OR “nursing student* “[MeSH terms] OR “students, health occupations” [MeSH terms]; “community-based” [Title/Abstract] OR “service learning” [Title/Abstract] OR “service education” [Title/Abstract] OR “community education” [Title/Abstract]; “Education” [MeSH terms]; “Geriatric Nursing” [MeSH terms] OR “Senior Centers” [MeSH terms] OR “Geriatric care” [MeSH terms]; OR “Elderly” [MeSH terms] OR “Older adult*” [Title/Abstract] “Gerontologic” [MeSH terms] “Curriculum” [MeSH terms] OR “Problem-Based Learning” [MeSH terms]; “Empathy” [MeSH terms]; “Emotional Intelligence” [MeSH terms]; “caring behavior*” [Title/Abstract]. The keywords were searched as individual words and in combination using the Boolean phrase such as “AND” and “OR.” Boolean operators such as “AND,” “NOT” and “OR” were employed to combine or exclude keywords. These helped to connect the keywords during the search, to either narrow or broaden the results. In addition, secondary citations from books and journals were also used.
Secondly, more keyword synonyms were included in the search phrases in the listed databases. Thirdly, eligible publications were found by manual-searching reference lists from the included research. This was followed by a Google search of gray literature. Two distinct researchers conducted the searches and then compared and evaluated the records for inclusion. Loading citations into the EndNote 20.0 reference manager program simplifies the process of removing duplicates and screening articles for complete text. The remaining studies were examined for relevance and compared to the inclusion criteria.
Results
Results of search with procedures of diagram
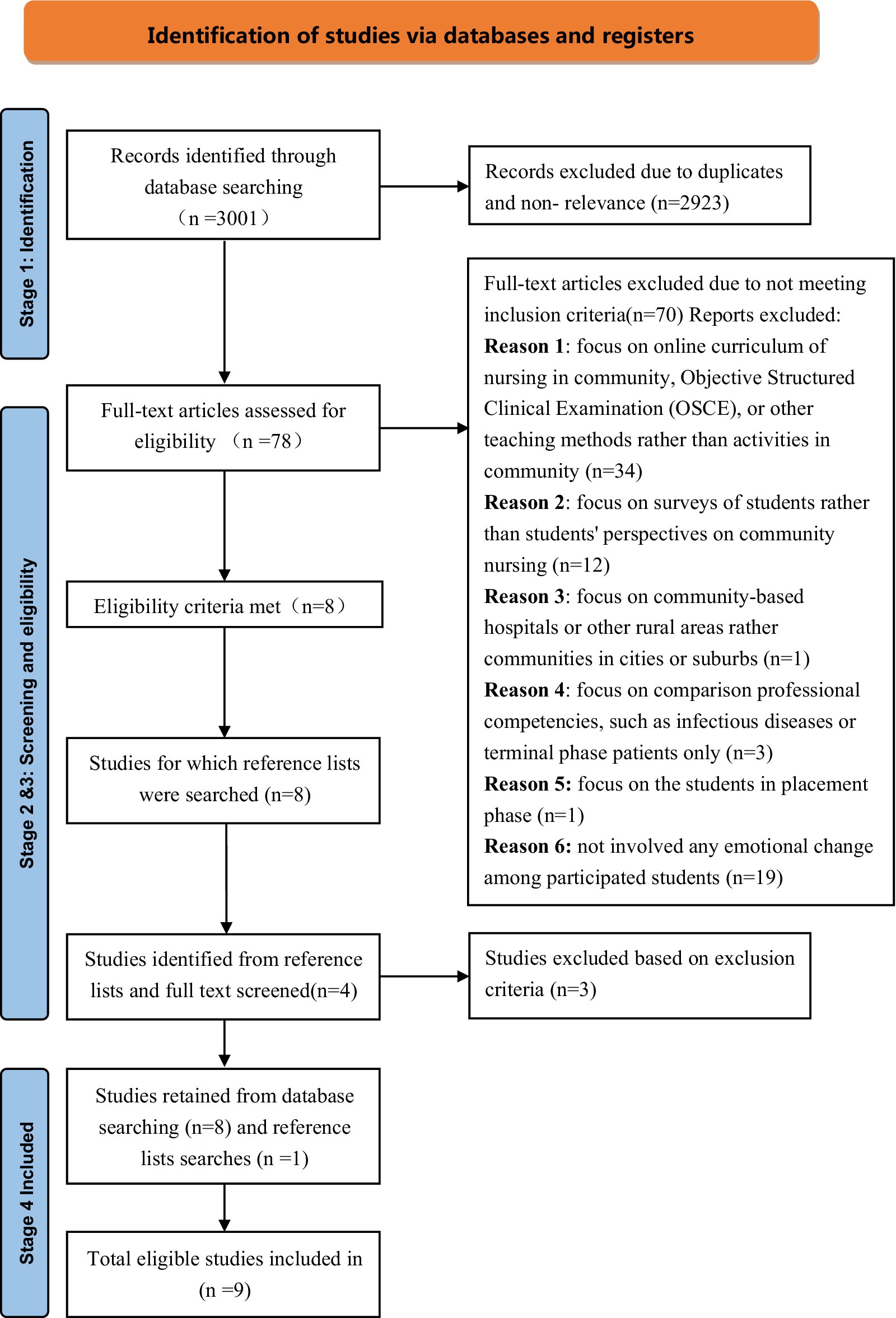
In accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR), the researcher completed the search strategy, evidence screening and selection, data extraction, and data analysis (34). Figure 1 illustrates a PRISMA flowchart that visually outlines the processes of study identification, screening, and eligibility assessment related to the specified research question. Although the review primarily focuses on literature from the past ten years (2013–2024), older seminal studies have been included where necessary to provide a comprehensive understanding of the foundational concepts and to trace the historical development of community-based education for nursing students. This approach aligns with the flexibility inherent in scoping review methodologies, as highlighted by Munn (35), which prioritize inclusivity and a broad range of evidence to address the research objectives. A total of 3,001 records were identified and retrieved from 6 electronic databases: CINAL (n = 28); PubMed (n = 86); Web of Science (n = 2,175); MEDLINE (n = 211); Psychology and Behavioral Sciences Collection (n = 412); and Google Scholar (n = 89).
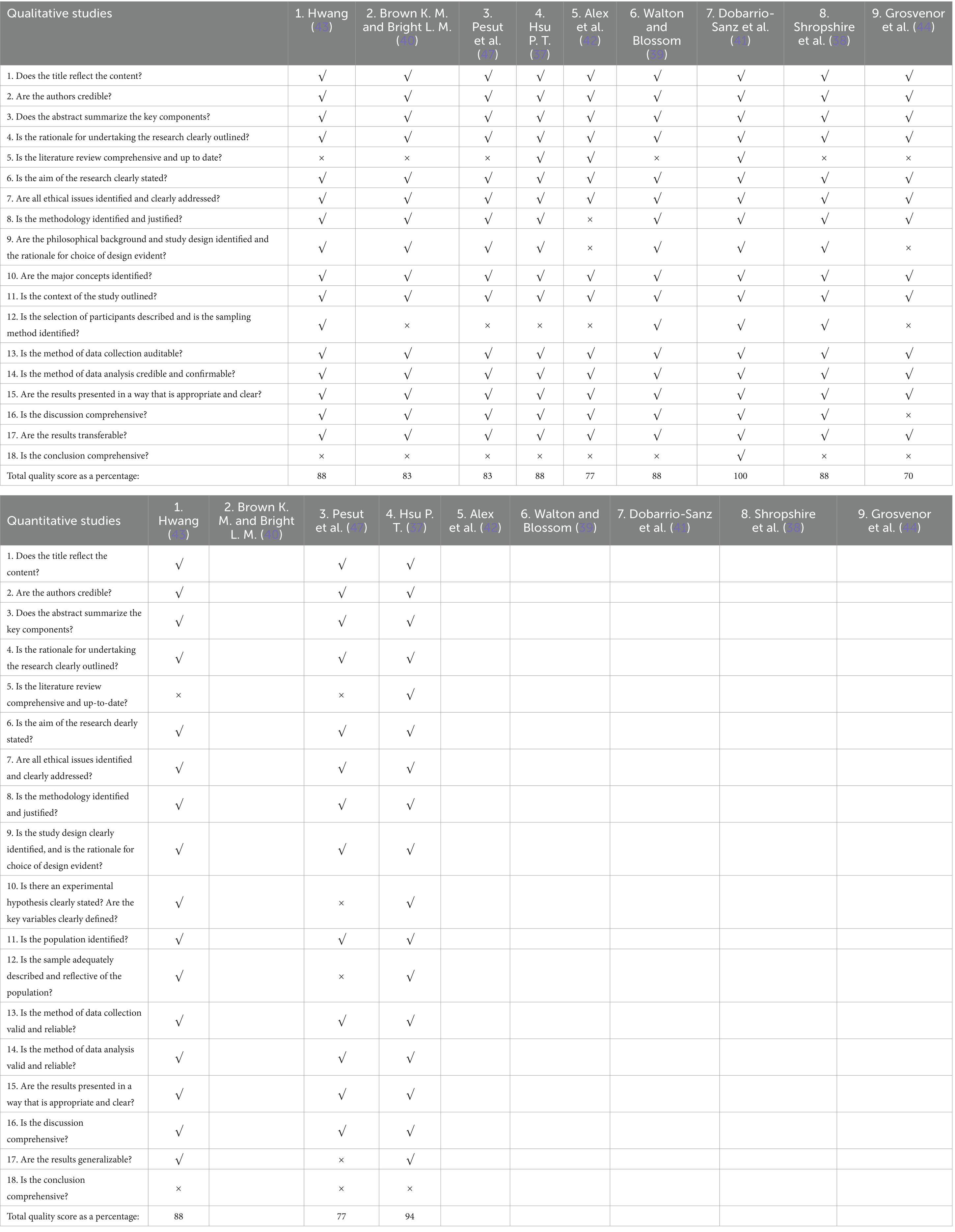
During the initial screening, 390 duplicated articles and 787 irrelevant articles were deleted, while 725 items were not retrieved. After being evaluated for eligibility, 1,021 of these records were excluded because they did not meet the inclusion criteria, specifically, that they did not investigate or assess a communication-based older people education method to support nursing students’ empathy, emotional intelligence, or caring behaviors and were mostly discussion articles. A total of 2,923 articles were excluded during this process. The full text of the remaining 78 remaining papers was then evaluated, and eight of them met the inclusion criteria. The reference lists of these eight articles were further examined for relevant studies, resulting in the identification of four additional studies. However, three of them were excluded based to the criteria. One more article was included in the reference lists. Finally, the narrative synthesis includes 9 suitable full-text articles all published between 2013 and 2024. The quality appraisal scores for the included studies ranged from 70 to 100%, based on the guidelines developed by Caldwell, Henshaw (36).
Summarizing the evidence
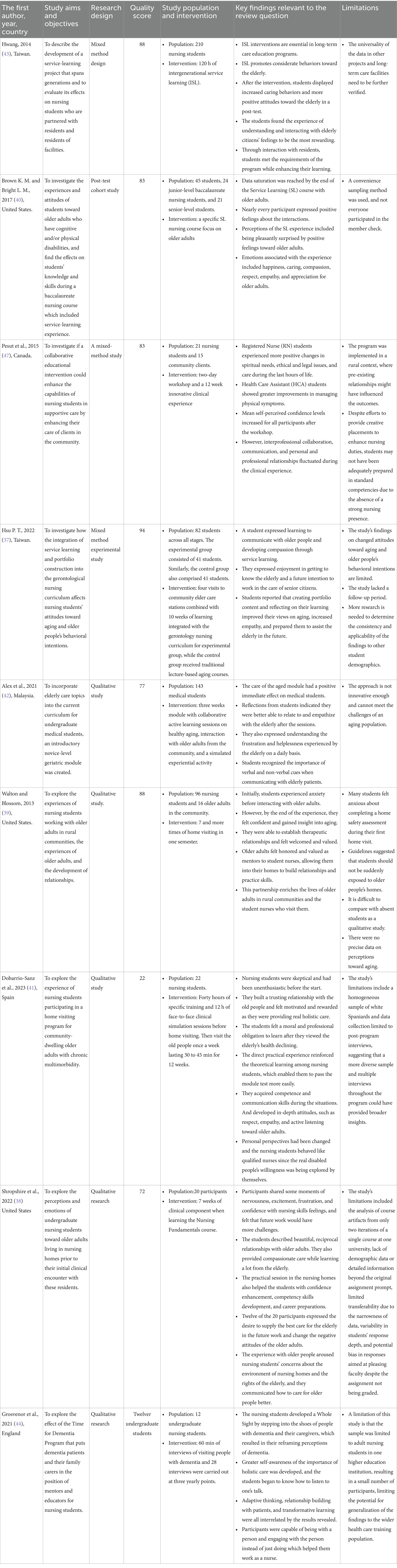
Publication dates were from 2013 until 2024, with research originating from the United States (n = 3), Canada (n = 1), Malaysia (n = 1), England (n = 1), Spain (n = 1), and Taiwan (n = 2). The total number of nursing students who participated in these nine studies was 651. Six studies were qualitative (67%), and three mixed method studies (33%).
Selection of studies
The study selection involved a two-step process for data extraction. Two researchers independently screened the titles and abstracts based on predetermined criteria. Afterward, the remaining articles were subjected to full-text screening. For each eligible study, two reviewers independently extracted key information using a standard data extraction form, including the first author’s name, country, year of publication, study design, study aims and objectives, study population, intervention, the key findings, and limitations. Any discrepancies were resolved by a third reviewer. To record study characteristics, a data extraction table was created, quality score and key findings relevant to the review question are included in Table 1.
Quality appraisal and evidence presentation
The critical assessment methodology proposed by Caldwell, Henshaw (36) was followed to conduct the assessment of the included literature. To analyze the advantages and disadvantages of research using qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-method designs, each paper was evaluated against 18 appraisal criteria. To determine how well each paper satisfied the quality appraisal guidelines, a percentage score was computed. The outcomes can be referred to in the quality assessment table shown in Table 2. Assessments of the risk of bias due to missing results were conducted, and each synthesis was assessed. A narrative review was employed to synthesize knowledge. Through this approach, relationships in data could be discursively explored and findings could be compared across studies using divergent methodologies.
Discussion
The effects of a community-based education program for older adults on nursing students are discussed under five subheadings: empathy improvement was observed in the literature; emotional intelligence improved during the interaction; caring behavior changes were observed after the interactions with the older adults; nursing students showed sensitivity to others’ feelings and physical discomfort, which triggered better care; a solid and relaxing relationship developed through inter-generational interactions. The results presented include both community-based education programs and service-learning programs since the themes identified across all papers did not significantly differ.
Empathy improvement was observed in the literature
Nursing students showed empathy improvement through the curriculum intervention aimed to improve the students’ “aging-related awareness,” “feeling toward older adults” and “interpersonal interactions with older adults” (37, 38). Negative emotions were observed to diminish during the interactions; students stated that their perspective had completely changed with regard to older adults (38). The dissolution of age-related stereotypes was one of the developments. Before the educational intervention, most of the nursing students held the opinion that “older adults are often frail and sick, they often have a patronizing attitude and are difficult to get along with, they are frequently disconnected from normal day-to-day life, they have poor work efficiency.” These original attitudes were also noticed in the study by Walton and Blossom (39). However, as the nursing students began to realize that the older adults were easy to get along with and well-mannered, their first impressions changed. Their attitude became more positive as they better understood and began to respect the selflessness of the older adults (40). The students reported a deeper emotional connection and a better appreciation of the challenges faced by older adults (41). Meanwhile, they realized that the older adults who were in their 80s were, nevertheless, still capable of caring for themselves, with some medical support. The interaction with older adults allowed students to learn directly from their experiences, which fostered a more compassionate and empathetic approach to care (38). Ultimately, the nursing students expressed astonishment at and appreciation for their aged charges, in contrast to their previous stereotypes (39). Other positive feelings that came about from these interactions with older people included compassion, caring, happiness, respect, empathy, appreciation of older adults, insightfulness, inspiration, gratitude for the encounter, and appreciation for the life-changing experience (42, 43).
Emotional intelligence improved during the interaction
Students recognized the value of what they were learning from older adults. They gained a closer understanding of the community resources and a closer look at the socioeconomic determinants of health. Students’ admiration for people with disabilities was sparked by their efforts to overcome limitations, such as the woman who cooked and baked with just one arm (41). During the participation in the “Time for Dementia” program, nursing students learned to better navigate their emotional responses and understand the emotions of dementia patients (44). Similar changes were also reported by Shropshire et al. (38) and Dobarrio-Sanz et al. (41), participants in the research noted a marked increase in their ability to empathize and understand the emotional states of older adults. Nursing students also gained valuable first-hand knowledge about the social determinants of health and living with chronic disease. They learned how to define the occasions to listen rather than interrupt or pose solutions for clients. When dealing with someone who is aging and growing less and less capable in his or her place, visiting older adults at home differs from institutional care in that it involves a sense of giving and being personally involved (40). In terms of older adults’ frustrating changes due to aging such as physical disability, students understood the significance of older adults advocacy using non-verbal communication and silent observation (37). During their weekly interactions, the nursing students eventually learned to trust their charges and converse empathetically with them (43). Most of the students and older adults became friends, with a sense of mutual understanding arising between them (37). Finally, the nursing students began to approach the topics of age and change with a constructive perspective, and there was a sense of achievement and a feeling of cheerfulness. They obtained the pathway to communicating with older adults with high emotional intelligence (37). Nursing students were able to address older adults’ concerns in a better way and so would likely appreciate any opportunity to encounter an older adult in the future.
Caring behavior changes were observed after the interactions with older people
The caring behaviors of the nursing students improved over the course of communicating with the older people. The mean score of the caring behaviors improved from 50.25 ± 9.30 to 55.75 ± 8.62, while the attitude improved from 101.9 ± 10.85 to 106.12 ± 11.52 (43). Nursing students realized the importance of having better caring skills with older adults as they truly believed that they needed to equip themselves well for work with the elderly, which would be more likely in the future (42). They learned how to create a comfortable therapeutic relationship while also improving their listening and communication skills. Not only talking but also feeling comfortable with silence, which also showed their willingness simply to “be with.” The nursing students observed the value of silence in therapeutic communication. Even limited encouragement and attentiveness were quite helpful (39). Moreover, the experience led to personal and professional growth, emphasizing person-centered care through practice, and students reflected that they were more confident in learning nursing knowledge, which will induce high-quality care (41). Caring holistically is essential to the maintenance of a therapeutic relationship. The nursing students often discussed life stories with the older adults and learned the value of hard work from them, which also inspired them to enhance their caring behaviors by exploring the skills to relax and comfort the older adults during their connection.
Nursing students showed sensitivity to others’ feelings and physical discomfort
Students who participated in the supportive care project for older adults living with advanced chronic illness became increasingly aware of their psychological and spiritual needs, were more sensitive to ethical and legal issues, and more competent in communication. Even though they also showed concerns about old adults’ pain and other physical symptoms, they showed more subjective emotions or feelings (37, 40). By involving two senior citizens from the community in the active learning session, the nursing students realized that older people have different needs compared to the general population. They also understood how individual experience plays an integral role in managing the patient as a whole. They adapted their daily life to show their respect and did not just do everything for them. They became more confident as they better empathized and related to their elderly charges after each active session (42). The nursing students’ attitude to older adults complaining about their constant aches and pains changed from assuming they were exaggerating the discomfort to now trusting their word and empathizing with their frustration and feeling of helplessness (42).
A solid and relaxing relationship developed through inter-generational interactions
Nursing students went into the experience of the course with a lack of confidence and nervousness but came out of it with confidence and self-assurance. The older participants were referred to by the nursing students as their “health partners.” They always welcomed students and offered hospitality. They invariably greeted each other with hugs and kisses, which brought fun and mutual respect to the interaction (38). Through these enjoyable visits, a trusting bond between the students and the older adults quickly formed. A turning point was sometimes reached when a talk of a spiritual nature occurred, or some other meaningful social interaction happened, which meant a deeper understanding then developed between the two (40). Some students said they even felt a type of love grow between them, and it was a sad day when the program, and their contact, finally ended (39). This experience provided nursing students with more knowledge and background for detecting nonverbal cues. After a while, they could tell by the older person’s expression and voice whether they were happy or sad. They understood what it meant to listen and were more sensitive to the unique needs of each patient (39).
Strengths, limitations, and recommendations
This scoping review offers a comprehensive mapping of the evidence on community-based education programs for nursing students, with a particular focus on their impact on empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors in geriatric care. A key strength of this review lies in its inclusive approach, incorporating a wide range of study designs and methodologies to ensure a broad understanding of the topic. By synthesizing evidence across diverse cultural and contextual, the findings provide valuable insights into the applicability of community-based education in different settings. Additionally, the review examines how cultural background differences can influence emotional reactions during interactions, highlighting their impact on student development. These nine studies were carried out in North America, Europe (Spain, England), Southeast Asia, and East Asia, representing different cultural differences, that is, from Western and Eastern perspectives. The diversity of different regions and cultures makes this scoping review more informative. Additionally, the cultural differences between the East and the West shape nursing undergraduates’ diverse attitudes toward the elderly. This has the potential to bias the research findings. Because compared with the unadulterated attitude toward the elderly without affection from other factors in the West, the respect for older adults, kindness and feedback cultural education from a young child in the Eastern countries may bias the research results in East Asia, as the cultural influence has been deeply rooted in nursing students, which may cover up the true level of empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors.
However, limitations should also be acknowledged. First, the review primarily includes literature published in English, which may have excluded relevant studies published in other languages. Second, despite a rigorous search strategy, the lack of empirical studies specifically focused on geriatric-focused community-based education limits the ability to draw definitive conclusions. Thirdly, the potential for publication bias, as only published literature was reviewed, may have excluded unpublished but relevant studies.
To better equip future nursing professionals with essential humanistic qualities, it is crucial to promote further research on effective methods for fostering empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behavior within educational settings. Currently, nursing educators tend to prioritize the improvement of nursing procedures and the dissemination of health information. Although they acknowledge the importance of training in humanistic qualities, few have received systematic education on the methods to enhance emotional perception and sensitivity. As a result, many lack the skills necessary to explore and effectively address the development of empathy and emotional intelligence in nursing education (45). Only a limited number of papers related to empathy and emotional intelligence training, including actual teaching activities, have been published. Although caring is regarded as the basis of nursing, the education of caring behavior can only be embodied in certain scenarios and cannot be separated from situations, so at present, there is a lack of analysis and understanding of it and a dearth of related papers (46). One thing to keep in mind while planning and analyzing research on the consequences of helping older adults in the community is that if research participants are aware that the research team is watching them, the Hawthorne effects could happen. The impact of this effect on these studies is unknown, but it appears important to emphasize the research team’s independence from assessing course completion and the confidentiality of participants. A related issue in intervention design is whether and how to include nursing teachers, as this may directly influence nursing students’ attitudes and behaviors, limiting the openness with which they communicate and express their emotions toward older people. It is expected that more nursing educators will pay attention to the research of empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behavior, to offer guidance for training students on how to provide more humanized nursing.
Conclusion
This scoping review is the first to map out how community-based programs for older adults can be used to support empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors among nursing students. The findings suggest that community-based education programs for older adults may have the potential to improve nursing students’ empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors. It can provide an accessible and cost-effective means of supporting emotional intelligence development and nurturing, caring behaviors among nursing students on campus whose study is usually restricted in a purely academic environment. Such innovations could be beneficial to nursing students’ communication skills, fostering responsibility for social service, and providing better care for older adults. Further research is needed in this area, as this review highlights research involving the development of humanistic care competencies in nursing students. The individual study interests, social requirements, and educational backgrounds of nursing students in different geographic areas should be considered when conducting future research in this area. Standards of care in aging societies can be improved by further research into how community-based education programs for older adults can be used to support the development of specialist geriatric nurses. Community-based education programs for older adults and how they benefit nursing students may have implications for the curriculum of nursing professionals around the world.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. TM: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Auckland, S, and Kilpatrick, S. Leadership and social capital: engaging small Australian communities in development and implementation of learning plans. Int J Lifelong Educ. (2018) 37:495–512. doi: 10.1080/02601370.2018.1513427
2. Jia, Y, and Yue, Y. Influencing factors of sense of responsibility among undergraduate nursing students: a cross-sectional study. Nurse Educ Today. (2023) 130:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105938
3. Jull, J, Giles, A, and Graham, ID. Community-based participatory research and integrated knowledge translation: advancing the co-creation of knowledge. Implement Sci. (2017) 12:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0696-3
4. Pagatpatan, CP Jr, Valdezco, JAT, and Lauron, JDC. Teaching the affective domain in community-based medical education: a scoping review. Med Teach. (2020) 42:507–14. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2019.1707175
5. Zeydani, A, Atashzadeh-Shoorideh, F, Abdi, F, Hosseini, M, Zohari-Anboohi, S, and Skerrett, V. Effect of community-based education on undergraduate nursing students’ skills: a systematic review. BMC Nurs. (2021) 20:1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12912-021-00755-4
6. Dirette, D. Compassion: importance and implications for the profession of occupational therapy. Open J Occup Ther. (2021) 9:1–6. doi: 10.15453/2168-6408.1951
7. McNulty, JP, and Politis, Y. Empathy, emotional intelligence and interprofessional skills in healthcare education. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. (2023) 54:238–46. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2023.02.014
8. Sundararajan, S, and Gopichandran, V. Emotional intelligence among medical students: a mixed methods study from Chennai, India. BMC Med Educ. (2018) 18:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1213-3
9. Yoong, SQ, Liao, AWX, Goh, SH, and Zhang, H. Educational effects of community service-learning involving older adults in nursing education: an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. (2022) 113:105376. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2022.105376
10. Lestari, E, Scherpbier, A, and Stalmeijer, R. Stimulating students’ interprofessional teamwork skills through community-based education: a mixed methods evaluation. J Multidiscip Healthc. (2020) 13:1143–55. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S267732
11. Guo-Brennan, L, Van Leeuwen, C, Mac Phee, MM, and Guo-Brennan, M. Community-based learning for international graduate students: impact and implications. Michigan J Community Serv Learn. (2020) 26:39–69. doi: 10.3998/mjcsloa.3239521.0026.203
12. Aksoy, Z, Gokdemir, O, and Şemin, İ. The role of community-based health practice on the improvement of healthcare students’ communication, empathy and perception of the elderly: a qualitative study at Izmir University of Economics. Connectist. (2021): 33–51. doi: 10.26650/CONNECTIST2021-0088
13. Bas-Sarmiento, P, Fernández-Gutiérrez, M, Baena-Baños, M, Correro-Bermejo, A, Soler-Martins, PS, and de la Torre-Moyano, S. Empathy training in health sciences: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Pract. (2020) 44:102739. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2020.102739
14. Cleary, M, Visentin, D, West, S, Lopez, V, and Kornhaber, R. Promoting emotional intelligence and resilience in undergraduate nursing students: an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. (2018) 68:112–20. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.05.018
15. Menezes, P, Guraya, SY, and Guraya, SS. A systematic review of educational interventions and their impact on empathy and compassion of undergraduate medical students. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:758377. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.758377
16. Patel, S, Pelletier-Bui, A, Smith, S, Roberts, MB, Kilgannon, H, Trzeciak, S, et al. Curricula for empathy and compassion training in medical education: a systematic review. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0221412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221412
17. Singer, T, and Klimecki, OM. Empathy and compassion. Curr Biol. (2014) 24:R875–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.06.054
18. Rodríguez-Nogueira, Ó, Moreno-Poyato, AR, Álvarez-Álvarez, MJ, and Pinto-Carral, A. Significant socio-emotional learning and improvement of empathy in physiotherapy students through service learning methodology: a mixed methods research. Nurse Educ Today. (2020) 90:104437. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104437
19. Chen, X, Giles, J, Yao, Y, Yip, W, Meng, Q, Berkman, L, et al. The path to healthy ageing in China: a Peking University–lancet commission. Lancet. (2022) 400:1967–2006. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01546-X
20. Li, J, Li, X, Gu, L, Zhang, R, Zhao, R, Cai, Q, et al. Effects of simulation-based deliberate practice on nursing students' communication, empathy, and self-efficacy. J Nurs Educ. (2019) 58:681–9. doi: 10.3928/01484834-20191120-02
21. Zhao, M, and Kong, L. Study on correlation between empathy of undergraduate nursing students and their attitude towards the elderly. Gen Nurs. (2020) 18:480–2. doi: 10.12104/j.issn.1674-4748.2020.04.025
22. Zhou, YH, Li, Q, and Zhang, W. Undergraduate nursing students' knowledge, attitudes and self-efficacy regarding palliative care in China: a descriptive correlational study. Nurs Open. (2021) 8:343–53. doi: 10.1002/nop2.635
23. Liu, X, Yan, M, Liu, X, Liu, Z, Tian, W, and Xiao, Z. The correlation between undergraduate nursing Students' willingness to engage in elderly care and their empathy level. Health Vocat Educ. (2021) 39:3.
24. Suazo, I, Pérez-Fuentes, MDC, Molero Jurado, MDM, Martos Martínez, Á, Simón Márquez, MDM, Barragán Martín, AB, et al. Moral sensitivity, empathy and prosocial behavior: implications for humanization of nursing care. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:8914. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17238914
25. Xiang, J, and Ji, C. Research progress on concept of nursing empathy and its assessment tools. Nurs J Chin Peoples Lib Army. (2016) 33:5.
26. Wang, Y, Zhang, Y, Liu, M, Zhou, L, Zhang, J, Tao, H, et al. Research on the formation of humanistic care ability in nursing students: a structural equation approach. Nurse Educ Today. (2020) 86:104315. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2019.104315
27. Pollock, D, Davies, EL, Peters, MD, Tricco, AC, Alexander, L, McInerney, P, et al. Undertaking a scoping review: a practical guide for nursing and midwifery students, clinicians, researchers, and academics. J Adv Nurs. (2021) 77:2102–13. doi: 10.1111/jan.14743
28. Peters, MD, Marnie, C, Tricco, AC, Pollock, D, Munn, Z, Alexander, L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. (2020) 18:2119–26. doi: 10.11124/JBIES-20-00167
29. Arksey, H, and O'Malley, L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. (2005) 8:19–32. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616
30. Levac, D, Colquhoun, H, and O'Brien, KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. (2010) 5:1–9. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
31. Peters, M, Godfrey, C, McInerney, P, Soares, C, Khalil, H, and Parker, D. The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers' manual 2015: methodology for JBI scoping reviews, (2015) (accessed April, 2019); 29.
32. PRISMA. PRISMA 2020 statement (2020). Available at: https://www.prisma-statement.org/ (Accessed November 06, 2023).
33. Peters, MD, Godfrey, CM, Khalil, H, McInerney, P, Parker, D, and Soares, CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Based Healthc. (2015) 13:141–6. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050
34. Tricco, AC, Lillie, E, Zarin, W, O'Brien, KK, Colquhoun, H, Levac, D, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. (2018) 169:467–73. doi: 10.7326/M18-0850
35. Munn, Z, Peters, MDJ, Stern, C, Tufanaru, C, McArthur, A, and Aromataris, E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2018) 18:143. doi: 10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
36. Caldwell, K, Henshaw, L, and Taylor, G. Developing a framework for critiquing health research: an early evaluation. Nurse Educ Today. (2011) 31:e1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2010.11.025
37. Hsu, PT, Ho, YF, and Chen, JJ. The effect of integrating service-learning and learning portfolio construction into the curriculum of Gerontological nursing. Healthcare (Basel). (2022) 10:652. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10040652
38. Shropshire, M, Hovey, S, Ford, C, and Wendler, MC. Older adults “Have so much to teach Us”: a qualitative study of BSN student perceptions when anticipating clinical in the nursing home. Int J Older People Nursing. (2022) 17:e12438. doi: 10.1111/opn.12438
39. Walton, J, and Blossom, H. The experience of nursing students visiting older adults living in rural communities. J Prof Nurs. (2013) 29:240–51. doi: 10.1016/j.profnurs.2012.05.010
40. Brown, KM, and Bright, LM. Teaching caring and competence: student transformation during an older adult focused service-learning course. Nurse Educ Pract. (2017) 27:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2017.08.013
41. Dobarrio-Sanz, I, Chica-Pérez, A, Fernández-Sola, C, Ruiz-Fernández, MD, Del Mar, J-LM, and Hernández-Padilla, JM. Nursing students' experiences of a home visiting programme for older adults with multimorbidity (VISITAME project): a phenomenological study. Nurse Educ Today. (2023) 128:105881. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105881
42. Alex, D, Kumari, Y, and Kadirvelu, A. An experiential aged care module for first-year undergraduate medical students. Educ Sci. (2021) 11:565. doi: 10.3390/educsci11100565
43. Hwang, HL, Wang, HH, Tu, CT, Chen, S, and Chang, SH. Reciprocity of service learning among students and paired residents in long-term care facilities. Nurse Educ Today. (2014) 34:854–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2012.04.001
44. Grosvenor, W, Gallagher, A, and Banerjee, S. Reframing dementia: nursing students' relational learning with rather than about people with dementia. A constructivist grounded theory study. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. (2021) 36:558–65. doi: 10.1002/gps.5452
45. Oliveira, S, Roberto, MS, Pereira, NS, Marques-Pinto, A, and Veiga-Simão, AM. Impacts of social and emotional learning interventions for teachers on teachers' outcomes: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:677217. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.677217
46. Koukourikos, K, Tsaloglidou, A, Kourkouta, L, Papathanasiou, IV, Iliadis, C, Fratzana, A, et al. Simulation in clinical nursing education. Acta Inform Med. (2021) 29:15–20. doi: 10.5455/aim.2021.29.15-20
Keywords: nursing students, empathy, emotional intelligence, caring behavior, community-based education
Citation: Jing M, Chui P, Chong MC and Maoting T (2024) The effects of community-based education programs on empathy, emotional intelligence, and caring behaviors among nursing students: a scoping review. Front. Med. 11:1479466. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1479466
Edited by:
Colette Joy Browning, Federation University Australia, AustraliaReviewed by:
Shane Andrew Thomas, Federation University Australia, AustraliaSanrong Lan, Fujian Provincial Hospital, China
Copyright © 2024 Jing, Chui, Chong and Maoting. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pinglei Chui, Y2h1aXBpbmdsZWlAdW0uZWR1Lm15
 Ma Jing
Ma Jing Pinglei Chui1*
Pinglei Chui1* Mei Chan Chong
Mei Chan Chong Tang Maoting
Tang Maoting