- 1Clinical College of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 2Scientific Research Center, China-Japan Friendship Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin, China
- 3Affiliated Hospital of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Changchun, Jilin, China
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive degenerative disorder impacting bones and joints, worsened by chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation, mechanical stress, metabolic disturbances, and various other contributing factors. The complex interplay of cartilage damage, loss, and impaired repair mechanisms remains a critical and formidable aspect of OA pathogenesis. At the genetic level, multiple genes have been implicated in the modulation of chondrocyte metabolism, displaying both promotive and inhibitory roles. Recent research has increasingly focused on the influence of non-coding RNAs in the regulation of distinct cell types within bone tissue in OA. In particular, an expanding body of evidence highlights the regulatory roles of microRNAs in OA chondrocytes. This review aims to consolidate the most relevant microRNAs associated with OA chondrocytes, as identified in recent studies, and to elucidate their involvement in chondrocyte metabolic processes and ferroptosis. Furthermore, this study explores the complex regulatory interactions between long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs) in OA, with an emphasis on microRNA-mediated mechanisms. Finally, critical gaps in the current research are identified, offering strategic insights to advance the understanding of OA pathophysiology and guide therapeutic developments in this field.
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic degenerative disease that affects bones and joints, primarily in middle-aged and elderly populations. It leads to substantial pain, restricted movement, and financial burden due to joint discomfort and loss of mobility (1). The underlying causes of OA are multifactorial, potentially arising from disruptions in physiological processes such as redox homeostasis, anabolic and catabolic activities, and the balance between anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory responses (2). The pathology of OA is driven by various cellular changes, including the destabilization of cartilage metabolism, the pro-inflammatory transformation of macrophages, an imbalance between osteoblast and osteoclast activity, and impaired stem cell differentiation (3, 4). These cellular alterations underscore the importance of regulating these processes to effectively prevent and treat OA. Regulation of OA involves several critical mechanisms: maintaining chondrocyte proliferation and metabolic balance, promoting the polarization of macrophages towards anti-inflammatory states, coordinating the activities of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and influencing the differentiation and proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). MicroRNAs (miRNAs, miR), small non-coding RNAs 20 to 24 nucleotides long, play a pivotal role in these processes by binding to the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of target genes, leading to mRNA degradation or the inhibition of translation. This regulatory function allows miRNAs to influence a wide range of cellular activities (5). Several miRNAs have been implicated in the regulation of cellular processes related to OA (6, 7). Their roles are often co-regulated by long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs), with their expression being either upregulated or downregulated during the progression of OA. One specific mechanism of interest in OA pathogenesis is ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of lipid peroxidation that results in plasma membrane damage and cell death. This process has been linked to cartilage damage and the worsening of OA (8). miRNAs have been identified as potential regulators of chondrocyte ferroptosis, suggesting their involvement in OA progression. This review systematically examines the regulatory roles of miRNAs in OA, focusing on their impact on various cell types in the bones and joints. It also explored the mechanisms through which miRNAs regulate OA, with a particular emphasis on their role in ferroptosis. Furthermore, this review summarizes miRNAs that are associated with ferroptosis and investigates their relationship with chondrocyte ferroptosis. The objective is to provide a more comprehensive understanding of OA pathogenesis and offer insights that may inform future clinical treatment strategies.
2 MicroRNAs are strongly associated with osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic, irreversible disorder of the bones and joints, characterized by progressive degeneration due to sustained inflammation and multiple homeostatic imbalances, culminating in pain and reduced mobility during advanced stages. While the precise pathogenesis of OA remains elusive, key factors contributing to its progression include the loss of chondrocytes and extracellular matrix from chronic injury, cellular senescence, and the development of advanced osteochondritis dissecans. Chondrocyte damage has been attributed to various triggers, including pharmacological agents, metabolic disorders, excessive mechanical stress, immune dysfunction, and inflammatory responses, all of which disrupt metabolic homeostasis and lead to both programmed and non-programmed chondrocyte cell death. Recent research has highlighted distinct alterations in microRNAs (miRNAs) within OA chondrocytes, suggesting their potential role in modulating OA progression. Over the past few years, studies have increasingly advanced our understanding of how miRNAs regulate key processes in OA, particularly their influence on cellular dynamics within bone and joint tissues. This review synthesizes the types of cell death modulated by specific miRNAs that drive critical cellular changes in bone and joint pathology (Supplementary Table 1), alongside an overview of cartilage-associated miRNA regulation (Supplementary Table 2), based on recent findings.
Research has demonstrated (9) that several microRNAs (miR-146a-5p, miR-34a-5p, miR-127-5p, and miR-140-5p) exhibit consistent expression changes in osteoarthritis (OA). These findings highlight their significant potential for use in the diagnosis and prognosis of OA (9). Considering the consistent differential expression of these four microRNAs (miRs) in osteoarthritis (OA), this review elucidates their specific regulatory mechanisms within the context of OA. Furthermore, it underscores the potential significance of targeting these miRs for future OA prevention and treatment strategies. The primary objective is to enhance the comprehension of osteoarthritis pathomechanisms and to support the advancement of therapeutic interventions in both scientific research and clinical practice.
2.1 MiR-140
MiR-140 plays a pivotal role in regulating cartilage homeostasis and is closely linked to aging-related OA. Among its isoforms, miR-140-3p is more abundantly expressed in cartilage compared to miR-140-5p (10). Both miR-140-3p and miR-140-5p exhibit markedly reduced expression in patients with aging-related OA (11–13). MiR-140-5P has been shown to inhibit genes involved in cartilage catabolism, such as MMP13 and ADAMTS5, while promoting the expression of genes associated with cartilage anabolism, including COL2A1, ACAN, OPN, and ALP (14). Similarly, miR-140-3P enhances the expression of CyclinD1 and Bcl-2, while suppressing Bax, p21, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α (15), thus countering chondrocyte senescence, inflammation, and apoptosis and stabilizing the cartilage matrix (16). Additionally, researchers have isolated cartilage-derived progenitor cells (CPCs), which possess the capacity to differentiate into cartilage and repair damaged tissue at injury sites. This regenerative ability is vital for maintaining cartilage integrity (17). However, in patients with advanced OA, a significant decrease in the expression of surface markers (CD166) and miR-140-5Pwas observed in CPCs. This downregulation is associated with increased osteoanabolic and catabolic activity, including the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), ADAMTSs, and inflammatory markers, as well as disruptions in COL2A1 expression (17, 18). The Notch signaling pathway has been implicated in OA pathogenesis, with its components being generally upregulated in OA-affected tissues (19–21). Jagged1, a key ligand in the Notch pathway, is particularly elevated in OA chondrocytes (19). Studies using IL-1β-induced chondrocyte models and rat anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) models have revealed that miR-140-5P may negatively interact with the Jagged1/Notch pathway (21, 22), suggesting that miR-140-5P might protect chondroprogenitor cells (CPCs) in OA by mitigating the detrimental effects of Notch signaling (23). These findings underscore the potential of miR-140-5P as a therapeutic target in preserving cartilage integrity and reducing OA progression. The transcription factor YY1 has been found to exhibit elevated expression levels in OA chondroprogenitor cells (OA CPCs), where it represses miR-140-5p transcriptionally. This suppression of miR-140-5p leads to a reduction in both the quantity and activity of CPCs through the YY1/miR-140-5p/Jagged1/Notch signaling axis (24). Targeting this axis to restore CPC function holds potential as a therapeutic strategy for OA by promoting chondrocyte replenishment and cartilage repair (18). Key components in this therapeutic approach include YY1, miR-140-5p, Notch receptors, and the ligand Jagged1.
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), a member of the histone deacetylase family, interacts with Runx2 and MEF2C to regulate genes such as Col-X, COMP, and Col-II, thereby inhibiting chondrocyte hypertrophy and stabilizing the cartilage matrix (25). Under hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α induces a significant increase in miR-140-3p expression, which subsequently upregulates SOX-9, COL2, ACAN, RUNX2, and SCX mRNAs, while downregulating COL1, COL6, COMP, TNC, and FMOD. This response protects the joints and delays the progression of OA (26). miR-140-5p also directly targets HDAC4, inhibiting its activity and regulating cartilage differentiation and proliferation (25). As a critical player in OA pathogenesis, miR-140-5p has become a focus for therapeutic intervention. Recent research has demonstrated that electroacupuncture stimulation (27) effectively inhibits the methylation of miR-140-5p and miR-146a, leading to their upregulation and modulation of downstream signaling pathways. This treatment reduces the expression of DNMT family proteins, inflammation-associated NF-κB, and cartilage damage-related SMAD3, likely through the regulation of upstream microRNAs (27). Additionally, miR-140-5p has been shown to inhibit PTEN (28, 29), promoting the anti-inflammatory phenotype of M2 macrophages, which subsequently polarizes adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) and activates the PI3K/AKT (30) and AKT/mTOR/HIF-1α (31)pathways. This activation enhances the osteogenic potential of ADSCs and supports bone regeneration (32). WNT5B, a ligand of the WNT pathway (33), has also been identified as a key regulator of cartilage homeostasis and differentiation (33, 34), playing a significant role in mitigating knee OA (KOA) progression (35). MiR-140-3p targets and inhibits WNT5B (36), and its suppression by circ-PREX1 has been linked to OA progression (36). In conclusion, miR-140-5p serves as a vital regulator in reducing OA-related damage, enhancing cartilage repair, and countering senescence. Given that chondrocyte injury and loss are central to the challenges of OA treatment, upregulation of miR-140-5p in CPCs within OA contexts could promote CPC stabilization and differentiation into chondrocytes, facilitating cartilage regeneration. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate its regulatory mechanisms. MiR-140-5p is thus poised to become a promising therapeutic target for repairing and regenerating damaged cartilage in OA.
2.2 MiR-127-5p
miR-127-5P has been shown to be downregulated in OA, where it plays a pivotal role as a regulator of cartilage metabolism (37) and acts as a key factor in countering OA progression (6, 38, 39). Research indicates that miR-127-5P directly targets the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) of osteopontin (OPN), inhibiting its expression (40). Additionally, miR-127-5P suppresses the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thus curbing abnormal chondrocyte overproliferation linked to OA progression (41). The long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) MALAT1 has been found to bind to and inhibit miR-127-5P, promoting excessive chondrocyte proliferation, a process that exacerbates OA (41).
In OA, CDH11 expression is elevated (42, 43), contributing to disease progression by increasing levels of inflammatory and catabolic markers, including MMP-13, IL-6, TNF-α, and ADAMTS-5 (44–46). Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) containing miR-127-5P have been shown to target CDH11, inhibiting the Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway, thereby delaying OA development (47). DNM3OS acts as a negative regulator of miR-127-5P, promoting OA by activating the CDH11/Wnt3a/β-catenin/LEF-1 signaling axis. LEF-1’s positive correlation with DNM3OS suggests a feedback loop that worsens OA progression (48). In BMSCs, DNM3OS alleviates miR-127-5P’s suppression of GREM2, thereby hindering BMSC chondrogenic differentiation, particularly under hypoxic conditions (49). MiR-146-5P has been identified as a regulator that inhibits TLR4 (50) and LXN (51), protecting chondrocytes from apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress. The knockdown of circSCAPER and circ_0002715 amplifies this protective effect by preventing the sponging of miR-127-5P (52, 53). Additionally, miR-127-5P targets and inhibits NAMPT, offering protection to chondrocytes against inflammation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation (54, 55). Circ_0128846 directly inhibits miR-127-5P, reducing its biological activity (56). Targeting circ_0128846 to release miR-127-5P presents a potential therapeutic strategy for OA treatment and prevention. Beyond chondrocytes, miR-127-5P promotes the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by interacting with the PTEN/AKT pathway (57) and inhibiting SPHK1 through targeting PDX1 (58), further enhancing osteogenesis (59). In contrast, circ_0134944 competitively downregulates miR-127-5P expression at PDX1, inhibiting osteogenic differentiation (60). In macrophages, miR-127-3p inhibits fatty acid synthase SCD1 (61) and regulates the NF-κB pathway (62), affecting macrophage proliferation and inflammation, although this mechanism has yet to be verified in synovial macrophages. In summary, miR-127-5p regulates key processes in chondrocytes, BMSCs, and macrophages, making it a vital inhibitor of OA progression. Targeting miR-127-5p to modulate downstream signaling pathways offers a promising therapeutic approach for OA. Further exploration of the regulatory relationships between miRNAs, circRNAs, and lncRNAs could provide deeper insights into OA pathogenesis and lead to the development of innovative treatment strategies.
2.3 MiR-34a-5P
miR-34a-5P demonstrates significant differential expression between normal and osteoarthritic cartilage, showing pronounced upregulation in osteoarthritic chondrocytes compared to healthy cartilage tissue (63). This overexpression correlates with elevated levels of catabolic markers (MMP13, ADAMTS5), inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α), and markers of chondrogenic hypertrophy (COL10A1), while simultaneously downregulating anabolic markers such as COL2A1 and ACAN. Additionally, an increase in pro-apoptotic markers, including caspase-3, caspase-9, and Bax, has been observed (63). The resulting inflammation, apoptosis, and degradation of the cartilage extracellular matontribute to the progression of osteoarthritic cartilage deterioration. Studies have shown that both miR-34a-5P and miR-125b-5P target and suppress SYVN1 expression, thereby promoting chronic inflammation, apoptosis, and other mechanisms involved in OA pathogenesis (64, 65). Moreover, lncRNA SNHG7 has been found to directly bind and inhibit miR-34a-5P, thereby alleviating its suppressive effect on SYVN1 and protecting chondrocytes from inflammatory and apoptotic damage (65). This regulatory interaction between microRNAs and lncRNAs in OA introduces a promising new area of research. Research has indicated that miR-34a-5P plays a pivotal role in promoting the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) (66), primarily through the direct inhibition of HDAC1 (67), which subsequently activates estrogen receptor alpha (ER-α). This activation triggers an upregulation of osteogenic markers, including Runx2, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (68), osteocalcin (OCN), and osteopontin (OPN). Additionally, the miR-34a-5P/smad2 axis has been shown to alleviate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced suppression of osteogenic differentiation (69), while the miR-34c/SATB2 axis enhances osteoblast activity in osteoporotic mice (70), further highlighting the significant influence of miR-34a-5P on bone metabolism. lncRNA MALAT1 has emerged as a critical regulator in osteogenic differentiation and bone mineralization, acting through the negative regulation of miR-34a-5P, which in turn decreases Smad expression. This regulation impacts key osteogenic factors, such as Runx2, ALP, and OCN, thereby affecting bone mineralization processes (71). In osteoarthritic (OA) cartilage, SESN2, known to act as a leucine receptor, is significantly downregulated (72). SESN2 overexpression has been shown to inhibit mTOR pathway activity by promoting AMPK phosphorylation, thus facilitating cellular autophagy and protecting chondrocytes from senescence and extracellular matrix degradation (73). Notably, in cases of OA induced by hip dysplasia, miR-34a-5P has been identified as a suppressor of SESN2 activity, thereby impairing autophagy regulation (74). Oxidative stress and the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are key drivers of chondrocyte damage in OA, playing a central role in disease progression. Emerging evidence suggests that ROS upregulates miR-34a-5P (75), which targets the SIRT1/P53 pathway, thereby promoting chondrocyte apoptosis and exacerbating tissue damage. SIRT1, through the acetylation of NRF2, enhances antioxidant defenses (76), while P53 has been found to further upregulate miR-34a-5P, establishing a feedback loop that amplifies P53-mediated apoptosis in chondrocytes (77). These findings underscore miR-34a-5P’s role in cartilage degradation and its contribution to the pathogenesis of OA. In summary, miR-34a-5P not only regulates osteogenic differentiation but also plays a critical role in the progression of OA by inhibiting extracellular matrix synthesis and autophagy, while promoting inflammation and apoptosis. This leads to cumulative chondrocyte damage and degeneration, facilitating OA progression. Targeting miR-34a-5P inhibition offers a promising therapeutic approach, while further exploration of the interactions between miR-34a-5P and other non-coding RNAs may provide deeper insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying OA pathology.
Moreover, it has been demonstrated that MiR-34a-5P can induce ferroptosis by targeting and inhibiting SIRT1 (78). However, it remains unclear whether similar regulatory mechanisms are present in osteoarthritic (OA) cartilage. Future research addressing this gap will be instrumental in expanding our understanding of MiR-mediated regulation of chondrocyte ferroptosis and its implications for OA progression. Additionally, MiR-34a-5P has been shown to be significantly upregulated in advanced OA synovial tissue (63). MiR-34-5P has been demonstrated to interact with ATF3, IL6, IL1B, and EGR1—an iron death-related gene identified in osteoarthritis (OA) synovial tissue—among others, potentially contributing to the pathogenesis of iron death (79). Notably, miR-155-5p (80, 81) may exhibit a similar function. In summary, targeting MiR-34-5P not only modulates the progression of OA in terms of inflammation, bone metabolism, and other factors, but its regulation of chondrocyte iron death also presents significant potential for targeted OA therapy.
2.4 MiR-146a-5P
The expression of miR-146a-5P in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and chondrocytes of patients with OA has been found to be significantly elevated compared to healthy controls (82). This microRNA is recognized as a key contributor to OA pathogenesis (83). Both in vivo and ex vivo studies have demonstrated that miR-146a-5P exacerbates OA through its pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic effects, as well as by destabilizing the cartilage matrix. Its mechanism likely involves enhancing P65 phosphorylation, which activates the NF-κB pathway, leading to the upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, alongside chondrolysis-associated factors like MMP13, thus promoting OA progression (83). Moreover, Prkg1, a key component of the nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP signaling pathway, has emerged as a potential therapeutic target of miR-146a-5P in OA treatment (83, 84). miR-146a-5P has also been implicated in activating the p65/NF-κB pathway by targeting TRAF6, which promotes inflammatory damage and IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis, further aggravating OA (85). In addition, resolvin D1, a mediator that supports lipid metabolism, has been shown to suppress the NF-κB-mediated pro-inflammatory pathway by inhibiting the transcription factor KLF5 (86), thereby attenuating inflammation (87, 88). However, miR-146a-5P, upregulated in OA, may hinder resolvin D1’s effects, exacerbating lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage inflammation (89). miR-146a-5P also targets NUMB, inhibiting its expression, which results in increased apoptosis and reduced autophagy in chondrocytes, contributing further to OA pathogenesis (60). Additionally, diminished POU2F1 expression in OA (90) is linked to IL-1β-induced cartilage matrix degradation, chondrocyte apoptosis, and inflammation (91), a process likely driven by the upregulation of miR-146a-5P, which suppresses POU2F1 expression (91). lncRNA FAM201A has been shown to counteract OA-associated inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis by inhibiting miR-146a-5P and interacting with the POU2F1 promoter, leading to POU2F1 upregulation. This creates a positive feedback loop, as POU2F1 also enhances lncRNA FAM201A expression (91). Despite these insights, the downstream effectors in the lncRNA FAM201A/miR-146a-5P/POU2F1 regulatory axis remain unidentified, warranting further investigation. Nonetheless, it is well established that POU2F1 regulates TWIST1 expression via transcriptional mechanisms, thereby inhibiting the WNT pathway (90, 92–94). This regulatory function may contribute to OA, though its precise role in the process remains to be fully elucidated. The downregulation of BMPR2 in OA appears to accelerate disease progression, likely due to miR-146a-5P targeting and inhibiting BMPR2, thereby disrupting BMP signaling (95, 96). Notably, overexpression of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) MINCR has been shown to counteract this mechanism, suggesting that lncRNA MINCR may alleviate OA by mitigating the suppressive effects of miR-146a-5P on BMPR2 (97). Additionally, miR-1307-3p has been identified as another microRNA capable of targeting BMPR2 (98). Furthermore, miR-146a-5P serves as a key inhibitory regulator in bone formation (99), directly targeting SMAD4 and potentially inducing osteoblast apoptosis by upregulating pro-apoptotic genes such as caspase-3 and Bax (100). Recent studies have also highlighted the role of miR-146a-5P in damaging the mitochondrial oxidative respiratory chain via inflammatory pathways, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and promoting apoptosis in MIN6 cells (101). Despite these findings, the precise regulatory mechanisms of miR-146a-5P concerning mitochondrial function in OA chondrocytes remain unclear. This underscores the need for further research into the interaction between microRNAs and mitochondrial dynamics, which may reveal novel targets for better understanding OA pathogenesis and developing more effective therapeutic strategies.
2.5 MiR-24
MiR-24 has been demonstrated to exhibit reduced expression levels in senescent or dysfunctional chondrocytes associated with osteoarthritis (OA), and it is linked to the capacity to mitigate cartilage damage and chondrocyte senescence (102). Prior research has indicated that C-myc, a gene implicated in the induction of inflammation and apoptosis in OA (103–105), can be targeted by MiR-24 to suppress its expression (106, 107). However, MiR-24 has been identified as a negative regulator of P16 and was shown early on to influence the chondrocyte senescence process (108). This underscores the significant regulatory role of MiR-24 in osteoarthritis (OA). Previous research has highlighted the substantial potential of synovial mesenchymal stem cells (SMSC) in chondrogenic differentiation (109–111). Recent investigations have demonstrated that a MiR-24/SMSC complex-associated hydrogel (MSOH) exhibits a promising therapeutic effect in the repair and differentiation of OA cartilage damage (102). MSOH effectively regulates cartilage homeostasis and facilitates the regeneration of osteoarthritic cartilage by modulating glycolytic pathways, enhancing the oxidative phosphorylation process, and mitigating chondrocyte senescence, inflammation, and ferroptosis, as evidenced by reductions in HMGB1 and p16ink4a levels. This regulatory mechanism may be attributed to the ability of MiR-24 to counteract senescence and promote chondrogenesis in synovial mesenchymal stem cells (SMSC) and chondrocytes by targeting and inhibiting the downstream effector TAOK1 (102). Additionally, it has been demonstrated that lncRNA C9ORF139 can act as a sponge for MiR-24, thereby modulating the expression of TAOK1 (112). Chondrocyte injury is a significant and persistent factor in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA). This study highlights the potential of microRNA-24 (MiR-24) in conjunction with stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells (SMSC) to facilitate the repair of damaged cartilage and mitigate chondrocyte senescence. Furthermore, it proposes a novel therapeutic direction for the management of OA. Importantly, this research represents a meaningful effort to translate the molecular insights regarding MiR-24 into clinical applications. These findings underscore the promising regulatory role of microRNAs in the context of OA and their potential for therapeutic intervention.
3 Mechanisms of action of other microRNAs associated with osteoarthritis
Damage and loss of articular cartilage are recognized as fundamental contributors to refractory osteoarthritis (OA). The etiological factors implicated in this process include inflammation, chondrocyte apoptosis, cartilage matrix degradation, and dysregulated autophagy (113, 114). This paper will examine the regulatory role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in OA chondrocytes, a topic that has gained significant attention in recent years, through these specific dimensions.
3.1 MicroRNA regulation of osteoarthritis cartilage metabolism
Previous research has indicated that miR-199a may inhibit early chondrogenesis by downregulating the expression of COMP, SOX9, and type II collagen (115). Additionally, miR-199a has been identified as a regulator of chondrogenic differentiation in stem cells via its targeting of SMAD1 (115). Moreover, miR-199a has been suggested to reduce the expression of the inflammatory marker COX-2, thereby providing protection to chondrocytes from inflammatory damage (116). Additionally, miR-199a-5p has been reported to alleviate OA symptoms by targeting MAPK4 (117). Recent studies have shown that miR-199a-5p may influence OA pathogenesis by targeting Gcnt2 and Fzd6 (118). Moreover, it has been proposed that miR-199a-5p exerts its effects by inhibiting the Indian hedgehog (Ihh) signaling pathway (119). miR-107-5p targets CASP3, protecting chondrocytes from apoptosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, thereby delaying OA progression. CircSEC24A has been identified as a negative regulator of miR-107-5p (120). Intra-articular injections of miR-81 in rats have been shown to suppress IL-16 expression, reducing MMP3 and MMP13 levels, and consequently, mitigating extracellular matrix damage and bone catabolism (121). Chondrocyte-derived exosomal miR-125 has been linked to osteogenic differentiation, influenced by sympathetic regulation, and is implicated in the pathophysiology of age-related OA (122). In contrast, miR-29b-3p negatively correlates with TGF-β1 and reduces chondrocyte numbers by inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway (123). miR-4492 has been shown to modulate IL-18 production through the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, impacting OA cartilage (124). miR-204 targets and inhibits SP1-LRP1 signaling, disrupting the neural-cartilage interface and alleviating OA-associated pain (125). miR-81 has been proposed to contribute to cartilage homeostasis and the regeneration of damaged cartilage by targeting and inhibiting Rac2, which upregulates key anabolic factors such as SOX9, COL2A1, and ACAN, facilitating the differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into cartilage and promoting bone anabolism (126). miR-362-5p has been implicated in OA by inhibiting the differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) into cartilage through the suppression of PLXNB1, reducing chondrocyte replenishment and exacerbating OA progression (127). miR-302c, by directly targeting and inhibiting TGFBR2, mitigates IL-1β-induced damage in chondrocytes (128), miR-136-5p regulates NAMPT activity, playing a role in OA progression through its modulation of this key enzyme (129).
3.2 Regulation of chondrocyte apoptosis by MicroRNAs
miR-539-3p has also been found to target and inhibit SOX9 and TGF-β1 (112), which results in a reduction in the chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) and decreased expression of COL2A1 and ACAN (130). Furthermore, miR-539-3p has been shown to inhibit Runx2, thereby reducing chondrocyte apoptosis, inflammation, and extracellular matrix degradation in pediatric OA, ultimately alleviating the disease (131). miR-214-3p, present in synovial fibroblast-derived exosomes, has been shown to protect articular cartilage from inflammatory and apoptotic damage (132). This protection is likely mediated through the inhibition of FOXM1 expression, thereby reducing chondrocyte apoptosis (133). Recent studies further suggest that miR-214 targets and inhibits Bax and TRPV4, contributing to the suppression of chondrocyte apoptosis and injury (134). Research has shown that appropriate mechanical stress can upregulate miR-214 expression in chondrocytes, contributing to the maintenance of cartilage integrity (135). Similarly, the upregulation of miR-653-5p in OA cartilage has been demonstrated to attenuate IL-6 expression and inhibit JAK1 and STAT3 phosphorylation, which helps mitigate chondrocyte senescence and delay OA progression in a destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM) rat model (136). miR-149-5p targets TRADD, reducing caspase-3, caspase-8, and TNF-α levels, which decreases chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation (137). Similarly, has-miR-4282 was found to mitigate OA by modulating cellular pyroptosis through the targeting of the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway (138). miR-506-3p, on the other hand, targets the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, promoting chondrocyte apoptosis and contributing to OA pathogenesis (139). Conversely, the long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS exhibits a negative correlation with miR-506-3p. miR-99a has been shown to inhibit FZD8, thus protecting spinal joint cells from IL-6 and TNF-α-induced apoptosis and inflammation (140). Moreover, miR-99a-5P has been found to negatively regulate TLR8, indirectly modulating the innate immune response and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in OA chondrocytes, contributing to cartilage damage (141). Additionally, miR-320c targets CREB5, inhibiting the cAMP pathway and contributing to OA development (142), while miR-320a modulates the ERK/JNK/MAPK pathways by targeting DAZAPI, potentially delaying OA progression (143). Additionally, miR-502-5p inhibits TRAF2, reducing NF-κB activity, which protects chondrocytes from apoptosis and inflammatory damage caused by TNF-α and IL-1β, while also supporting cartilage anabolism (143). miR-203a-3p protects cartilage from LPS-induced apoptosis, pyroptosis, and oxidative stress by inhibiting the MYD88/NF-κB signaling pathway (144). miR-182-5p has been shown to bind to FGF9, resulting in a reduction in its levels, which subsequently promotes chondrocyte injury and apoptosis, exacerbating OA symptoms (145). Additionally, miR-3591-5p has been shown to mitigate the progression of OA by targeting and inhibiting PRKAA2. The demethylation of the miR-3591-5p precursor by FTO impairs the maturation of miR-3591-5p, promoting OA development through the suppression of its protective effects (146). In contrast, miR-155 contributes to OA pathogenesis by targeting SMAD2 and activating the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway, leading to chondrocyte pyroptosis (147). miR-155 also disrupts the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by targeting PIK3R1, which exacerbates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix degradation (148). Exosomal miR-3960, released from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), targets PHLDA2, reducing SDC1/Wnt/β-catenin pathway activity and protecting cartilage from OA-related damage (149).
3.3 MicroRNA regulation of osteoarthritis-related inflammation
miR-199-3p has been shown to mediate autophagy and suppress OA-related inflammation by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, while also decreasing chondrocyte apoptosis through the inhibition of TCF4 and DNMT3A (150, 151). Furthermore, LINC00707, which is significantly upregulated in OA, may contribute to chondrocyte apoptosis by acting as a sponge for miR-199-3p (152). miR-26b-5p has been shown to induce cartilage damage and cellular senescence by inhibiting the TGF-β1-Smad2 signaling pathway, which occurs through the upregulation of asporin (153). Additionally, miR-26b-5p targets COL10A1 and TLR3, inhibiting the pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage phenotype and reducing inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and PTGS2. At the same time, it promotes macrophage polarization towards the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, thus mitigating OA progression by reducing synovial inflammation and preserving cartilage integrity (154). miR-4738-3p has also been shown to mitigate OA-related inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and suppressing Col1A2 expression (155). Furthermore, the upregulation of miR-877-5p has been demonstrated to reduce IL-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis in chondrocytes by inhibiting FOXM1 expression (156). miR-877-5p enhances SOX9 and collagen type II (COL II) expression, offering protective effects on the cartilage matrix (156). In osteoblasts, miR-877-5p targets and inhibits EIF4G2, facilitating osteoblast differentiation (157). Conversely, miR-350-3p has been found to promote synovial macrophage transformation into a pro-inflammatory phenotype, exacerbating inflammatory chondrocyte injury and OA pathogenesis. On the other hand, miR-350-5p, delivered via macrophage exosomes, inhibits NSD1-mediated H3K36 methylation in chondrocytes, facilitating OA progression (158). miR-515-5p protects against IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation by inhibiting TLR4 and suppressing NF-κB pathway activation, resulting in anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects (159). miR-577 reduces chondrocyte inflammation by downregulating MTF-1, while LINC01094 negatively regulates miR-577 (160). Similarly, miR-558 may exert analogous effects to miR-577 and is potentially regulated by Circ_0007482 (161). Finally, miR-98-5p has been shown to directly target and inhibit CASP3 expression, decreasing inflammatory mediators and pro-apoptotic factors such as caspase-3 and Bax, thereby offering protection to chondrocytes from inflammation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation (162). The overexpression of miR-98-5P has been demonstrated to reduce IL-1β-induced cartilage damage, offering protective effects against OA progression (162). The overexpression of miR-124-3p in OA chondrocytes has been found to inhibit the interaction between MALAT1 and KLF5, thereby reducing inflammation—marked by decreased IL-1β and IL-18 levels (163)—and preventing extracellular matrix degradation and chondrocyte pyroptosis through the suppression of CXCL11 transcription (164). This multifaceted regulatory mechanism ultimately contributes to the mitigation of OA pathogenesis (165). miR-93-5P, encapsulated in exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), has been demonstrated to inhibit ADAMTS9, leading to the activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. This activation counteracts IL-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis, providing a protective effect on chondrocytes (166). In contrast, long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) CASC2 has been identified as a negative regulator of miR-93-5P, thereby mitigating its beneficial effects in OA (167). miR-149 has been shown to play a protective role in OA by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway through targeted suppression of VCAM-1, which is associated with reduced inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis (168). Finally, miR-150-5p has been found to attenuate VCAM-1 expression by inhibiting the activity of the lncRNA XIST. This inhibition reduces monocyte recruitment and adhesion in OA synovial tissues, potentially exerting a palliative effect by decreasing inflammation and mitigating OA progression (169). The miR-150-5p/AKT axis has been identified as a key regulator in the progression of OA and is negatively regulated by the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 (170). Similarly, miR-5701 has been shown to suppress VCAM-1 activity, attenuating the inflammatory response in OA synovial tissue (171). miR-18a-3p demonstrates the ability to target and inhibit PDP1, reducing joint inflammation by downregulating IL-8, IL-6, and PGE2, as well as mitigating cartilage matrix damage through the suppression of MMP2, MMP3, and MMP9 in an OA rat model (172). Moreover, miR-224-5P alleviates synovial inflammation and OA symptoms by inhibiting PTX3, reducing P65/NF-κB activity, and promoting macrophage polarization towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype by targeting CD32 (173). Additionally, miR-212-5p, found in exosomes derived from human synovial mesenchymal stem cells, targets and inhibits ELF3, exerting both anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects (174). while adipose-derived stem cell exosomal miR-388-3P inhibits Runx2 expression, ameliorating IL-1β-induced cartilage damage (175).
3.4 MicroRNA regulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM)
Additionally, miR-485-3p targets NRP1, reducing IL-1β-induced cartilage matrix degradation by attenuating the PI3K/Akt pathway, thus slowing OA progression (176). In an in vivo rat model of OA induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection into the joint cavity, miR-106a was shown to alleviate OA symptoms (177). miR-21 has been linked to the activation of TLR7, exacerbating OA progression by promoting cartilage degradation (178). Finally, miR-217 suppresses SIRT1 expression, promoting inflammatory injury by elevating IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α levels, facilitating apoptosis via Bax and caspase-3 upregulation, and increasing MMP-13 and MMP-9 expression through the NF-κB and P53 acetylation pathways (179). miR-217 has been found to inhibit bone anabolism by downregulating the expression of key cartilage matrix components such as COL2A1 and ACAN, ultimately accelerating the progression of OA (179). Additionally, miR-223 directly inhibits NLRP3 and reduces the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) (180), thus protecting chondrocytes from pyroptosis and helping to stabilize the cartilage matrix in OA (181). In contrast, miR-760 has been found to target Heparin-Binding EGF-Like Growth Factor (HBEGF), promoting the degradation of the cartilage extracellular matrix and contributing to cartilage damage in OA (182). miR-322 protects the cartilage matrix from catabolic stress by targeting and inhibiting TRAF3. This inhibition leads to the upregulation of COL2A1 and ACAN, while simultaneously downregulating the expression of catabolic enzymes such as MMPs and ADAMTS5, thereby mitigating the progression of OA (183). Overexpression of miR-15a, which targets the inhibition of β1,4-GalT-I mRNA, may reduce NF-κB phosphorylation, a critical mediator of inflammation and cartilage degradation, potentially offering protection against extracellular matrix degradation and inflammatory injury in OA (184). In temporomandibular joint OA (TMJOA), miR-132-3p targets PTEN, providing protection against extracellular matrix degradation, inflammation, and chondrocyte apoptosis (185).
3.5 Regulation of chondrocyte autophagy by MicroRNAs (MiRs)
Furthermore, miR-128-3p, targeting ZEB1, has been shown to alleviate IL-1β-induced cartilage damage (186), while miR-128, by inhibiting NR1D2, may facilitate OA progression through the suppression of cartilage anabolism and extracellular matrix synthesis (187). miR-375 has been demonstrated to inhibit the autophagy gene ATG2B, thereby inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and chondrocyte injury (188). It also mitigates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation by targeting PI3R3 (189). Circ_0044235 has been identified as a regulator that inhibits miR-375, influencing these pathways (154). miR-429 has also been identified as a key regulator of cartilage protection, as it targets and inhibits FEZ2, which activates autophagy, thereby safeguarding cartilage from damage and slowing OA progression (190). miR-378, by targeting Atg2a and Sox6, inhibits autophagy and impairs the chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs, further contributing to OA pathology (191).
Collectively, these miRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of OA by interacting with various genes and signaling pathways, exerting both positive and negative regulatory effects on inflammation, apoptosis, cartilage metabolism, and stem cell differentiation. Notably, a wide range of lncRNAs and circRNAs are actively involved in modulating the regulatory functions of miRNAs in OA, either by enhancing or counteracting their effects. The intricate crosstalk among lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs holds significant potential for advancing therapeutic strategies and preventive measures in OA. Furthermore, exosomal miRNAs play a critical role in OA’s regulatory mechanisms, emphasizing the complex intercellular communication facilitated by these exosomal miRNAs. This presents new opportunities for future treatments and prevention strategies for OA. In summary, microRNAs are pivotal regulators of key processes such as extracellular matrix homeostasis, inflammation, cellular senescence, apoptosis, and non-regulated cell death in chondrocytes during the progression of OA. Additionally, miRNAs influence the balance between proliferation and differentiation in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), osteoblasts, and osteoclasts, as well as the regulation of macrophage proliferation and the phenotypic switch between pro-inflammatory (M1) and anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages. These mechanisms highlight the critical role of miRNAs in OA pathogenesis, positioning the regulation of key miRNAs as a promising target for therapeutic interventions. Future research is expected to increasingly focus on the targeted modulation of miRNAs and the interactions between various non-coding RNAs, offering new insights and strategic directions for the effective treatment of OA.
4 MicroRNA (miR) influences osteoarthritis (OA) chondrocytes through the regulation of ferroptosis
Since its proposal in 2012, iron-dependent cell death, known as ferroptosis, has been linked to a variety of metabolic diseases (192). Ferroptosis is distinguished by the accumulation of lipid peroxides in an iron-dependent manner, ultimately causing plasma membrane rupture and cell death (193). The role of ferroptosis in chondrocytes has been extensively studied in OA, where it has been identified as a significant contributor to disease progression (8, 194). As a result, targeting chondrocyte ferroptosis has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for OA management. Recently, miRNAs have gained attention as potential therapeutic targets in OA, with growing evidence highlighting their regulatory roles in ferroptosis. These processes involve complex changes in the levels of downstream effectors, and various non-coding RNAs are also involved in regulating these pathways. This study explores the mechanisms through which miRNAs regulate ferroptosis and presents a comprehensive overview of miR targets and the associated pathways that modulate ferroptosis in chondrocytes, emphasizing their broader implications for OA regulation (Figure 1 and Table 1).
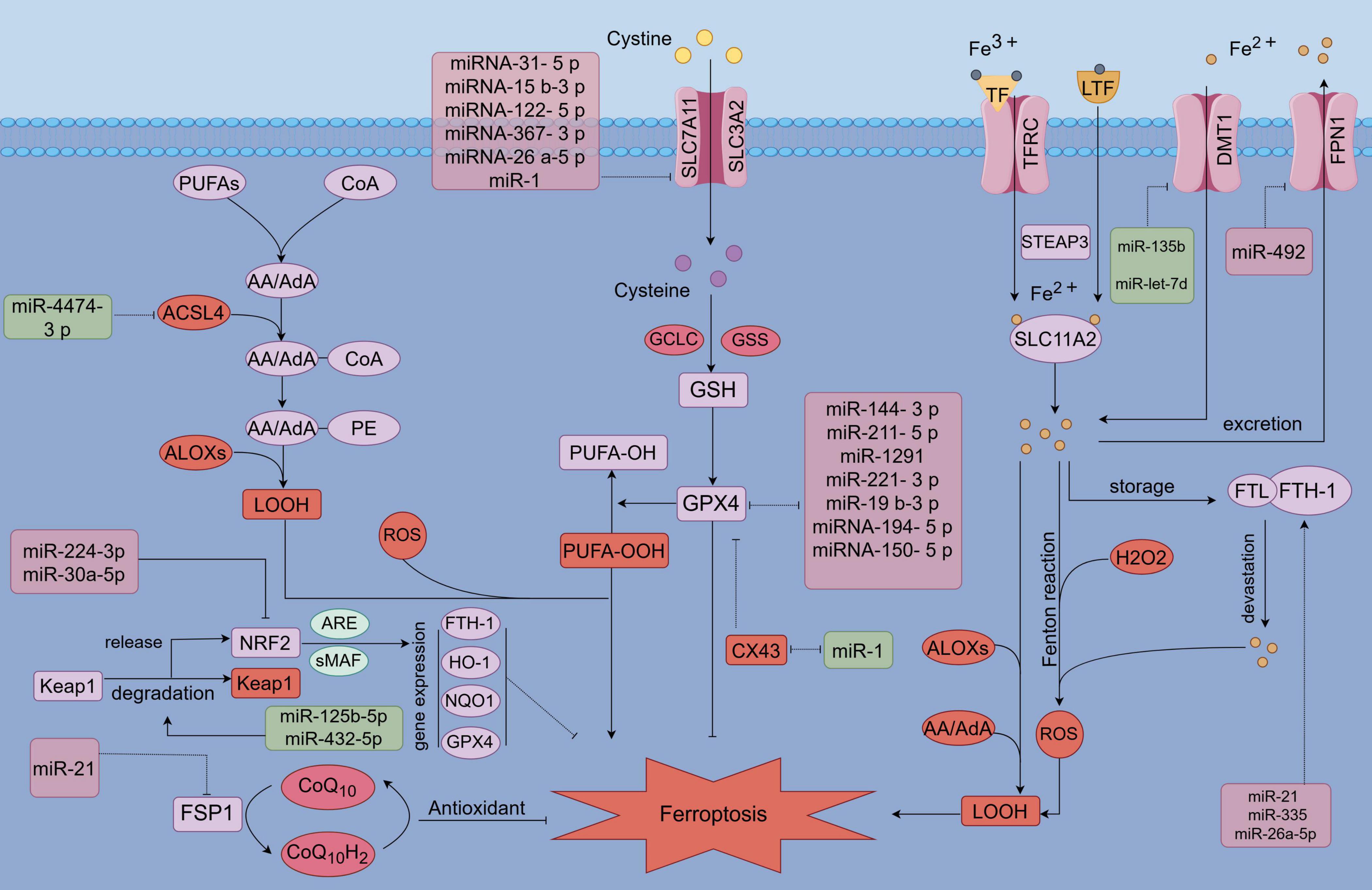
Figure 1. MicroRNA (MiR) involvement in the regulation of ferroptosis. MicroRNAs (miRs) modulate ferroptosis by targeting key components of antioxidant pathways, lipid metabolism, and iron metabolism pathways. Specifically, miRs influence antioxidant pathways, including GPX4, SLC7A11, NRF2, and FSP1, as well as iron metabolism-related factors such as FPN, DMT1, FTH1, and TFR1. Additionally, miRs target lipid metabolism-related factors, including ACSL4 and ALOXs.
4.1 MicroRNA (miR) modulates ferroptosis by influencing factors both upstream and downstream within antioxidant-related pathways
Firstly, the SLC7A11/GSH/GPX4 pathway, recognized as the most classical antioxidant mechanism, effectively counteracts the initiation of ferroptosis through its antioxidative properties (195–197). However, microRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in the regulation of ferroptosis by directly or indirectly modulating the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway. Certain microRNAs (miRs) have been identified to directly target key components of the pathway (Figure 1). In the following discussion, we examine the indirect regulation of SLC7A11/GPX4 by several notable miRs in recent years. Specifically, miR-144-3p targets and inhibits the expression of ZEB1, which in turn suppresses the expression of GPX4 (198). Additionally, miR-211-5p targets and inhibits P2RX7, leading to a downregulation of P2RX7 that subsequently activates the MAPK/ERK pathway, thereby upregulating the expression of GPX4 (199). miR-1291 targets FOXA2, leading to the down-regulation of GSH and GPX4 expression (200). Similarly, miR-221-3p targets ATF3, resulting in the down-regulation of GPX4 expression (201). Additionally, miR-129-2-3p targets and inhibits SMAD3, thereby inhibiting GPX4 expression. Furthermore, miR-19b-3p targets and inhibits RBMS1, which subsequently up-regulates GPX4 expression (202). Conversely, circIDE acts as a sponge for miR-19b-3p, thereby exerting an opposite effect on GPX4 expression (203). MicroRNA-194-5p targets and inhibits the activity of PTGS2, leading to a downregulation of GPX4 expression (204). Similarly, microRNA-150-5p targets and suppresses c-Myb expression, which results in an increase in CDO1 expression and a subsequent decrease in GPX4 levels (205). Furthermore, microRNA-31-5p inhibits the production of BAP1 by targeting and suppressing SLC7A11 expression (206). Additionally, microRNA-15b-3p targets KLF2, thereby modulating the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis (207). MicroRNA-122-5p targets TP53, resulting in the upregulation of SLC7A11 expression (208). Similarly, microRNA-367-3p inhibits EZH2 expression, which also leads to the upregulation of SLC7A11 (209). Furthermore, microRNA-26a-5p inhibits MAT2A, thereby suppressing the SIRT1/SLC7A11 signaling pathway (210). In addition to the regulation of the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway, microRNAs also indirectly regulate the FSP1/CoQ pathway, an antioxidant and ferroptosis-related pathway that operates independently of the GPX4 pathway (211, 212). MiR-21 targets the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), leading to the upregulation of FSP1 expression and the activation of the FSP1/CoQ10 pathway, thereby exerting antioxidant effects and mitigating ferroptosis (213). Similarly, miR-30a-5p inhibits the expression of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and disrupts the nuclear translocation of NRF2, resulting in the downregulation of downstream anti-ferroptotic factors such as GPX4 and FTH (214). Furthermore, miR-125b-5pand miR-432-5p promote the degradation of kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), which liberates NRF2 activity and enhances the expression of antioxidant proteins that counteract ferroptosis (215, 216). Overall, microRNAs (miRs) exert regulatory effects on ferroptosis by directly targeting or indirectly modulating antioxidant pathways, including SLC7A11/GPX4, FSP1/CoQ10, and NRF2. Although these miRNAs have not been directly linked to chondrocyte ferroptosis in OA, their differential expression and involvement in oxidative stress and ferroptosis in other tissues suggest a potential regulatory role in OA. Further research is warranted to investigate the role of these differentially expressed miRNAs in chondrocyte ferroptosis and their implications for OA progression. Validating the influence of these miRNAs on chondrocyte ferroptosis could provide valuable insights into novel therapeutic targets for OA.
4.2 MicroRNAs (miRNAs) modulate ferroptosis by influencing pathways associated with iron and lipid metabolism
Alterations in iron metabolism are crucial for the regulation of iron-induced cell death, with certain precursor proteins involved in modulating cellular iron levels and influencing sensitivity to this form of cell death. Furthermore, microRNAs (miRs) can either directly target (Figure 1) or indirectly regulate factors associated with iron metabolism, thereby influencing the process of cellular ferroptosis. Specifically, miR-492 targets and inhibits MZF-1, resulting in a reduction of ferroportin (FPN) levels (217). This results in a decreased exclusion of intracellular iron, thereby increasing susceptibility to ferroptosis through cellular iron overload. MicroRNAs miR-135b and miR-let-7d are implicated in targeting and inhibiting DMT1 expression (29, 218), which subsequently reduces intracellular iron levels and mitigates the progression of ferroptosis. Additionally, miR-30d targets the inhibition of the autophagy-related gene ATG5, which plays a role in the regulation of ferroptosis by modulating the FTH1 autophagy process associated with iron overload-induced cell death (219). Abnormalities in lipid metabolism significantly contribute to ferroptosis, and microRNAs (MiRs) play a crucial role in the regulation of this process. Specifically, miR-4474-3p has been identified as a regulator of ferroptosis through its modulation of ALOX15 expression (220). In conclusion, MiRs are implicated in the regulation of ferroptosis by directly targeting or indirectly influencing pathways associated with the antioxidant system, lipid metabolism, and iron metabolism. While the roles of certain aforementioned microRNAs (MiRs) in osteoarthritis (OA) remain inadequately defined, several have been demonstrated to exhibit differential expression in OA chondrocytes. Consequently, further investigation into the regulatory functions of MiRs in ferroptosis within chondrocytes is both necessary and holds significant promise for the future treatment of OA.
4.3 Regulatory mechanisms of microRNAs associated with iron-induced chondrocyte death
miR-138-5P serves as a positive regulator of cartilage metabolism by promoting anabolic processes, reducing catabolic activity, and exerting anti-inflammatory effects in osteoarthritic (OA) cartilage (221). In OA, the expression of miR-138-5P is diminished, likely due to the inhibitory influence of the upregulated CREB1 protein. miR-138-5P directly targets and inhibits CREB1, which in turn liberates GPX4, a critical enzyme inhibited by CREB1. This pathway provides resistance to ferroptosis and oxidative stress in chondrocytes by reducing Fe2 + levels, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and malondialdehyde (MDA) (222). However, overexpression of CREB1 can counteract the protective effects of miR-138-5P. Additionally, CircTRIM25 has been identified as a direct inhibitor of miR-138-5P, promoting ferroptosis in chondrocytes. The knockdown of CircTRIM25, via the miR-138-5P/CREB1/GPX4 axis, presents a promising therapeutic approach for mitigating chondrocyte ferroptosis and treating OA (223). Research has shown that miR-1 is downregulated in OA (224). Under normal conditions, miR-1 serves a protective function by enhancing cartilage proliferation, regulating cartilage metabolism, and preventing chondrocyte apoptosis. It accomplishes this by upregulating key osteosynthesis-related genes such as COL2A1, ACAN, and SOX9 while suppressing osteocatabolism-related genes like MMPs and ADAMTSs. Additionally, miR-1 inhibits caspase-3 and promotes BCl-2 expression, further safeguarding chondrocytes from apoptotic damage (225). CX43, however, has been found to inhibit the proliferation of SX43 and suppress the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway, thereby inducing ferroptosis (226). In the context of chondrocyte ferroptosis, miR-1 regulates this process by directly targeting and inhibiting CX43. This inhibition leads to a reduction in ferroptosis-related alterations in chondrocytes, such as increases in Fe2 + levels, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and malondialdehyde (MDA). By inhibiting CX43, miR-1 enhances the activity of GPX4 and SLC7A11, key players in reducing oxidative stress and ferroptosis. This mechanism plays a pivotal role in mitigating chondrocyte ferroptosis and, consequently, alleviating the progression of OA (225, 227).
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is highly upregulated in OA and plays a significant role as a pro-inflammatory cytokine (228). IL-6 downregulates ferroportin 1 (FPN1) and upregulates divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1), thereby increasing cellular iron uptake and reducing iron excretion (69, 229). This dysregulation results in intracellular iron overload, enhancing susceptibility to ferroptosis in chondrocytes and contributing to OA progression. The interplay between inflammation and ferroptosis in OA is further highlighted by this iron overload-induced chondrocyte death. Notably, miR-10a-5p targets and inhibits IL-6R, potentially mitigating the effects of IL-6 on chondrocyte injury and ferroptosis. This inhibition may protect cartilage by preventing IL-6-induced ferroptosis in OA (230). However, IL-6 upregulation can inhibit miR-10a-5p, enhancing IL-6R activity, which ultimately exacerbates chondrocyte ferroptosis. This mechanism may explain the observed downregulation of miR-10a-5p in osteoarthritic cartilage (230).
miR-885-5p has been identified as a direct regulator of SLC7A11, enhancing the susceptibility of C28/I2 human chondrocytes to Erastin-induced ferroptosis. The overexpression of miR-885-5p is implicated in the progression of OA by promoting ferroptosis in chondrocytes (231). Similarly, miR-181b directly targets and inhibits SLC7A11, facilitating the initiation of chondrocyte ferroptosis and advancing OA progression (232). miR-1972, miR-665, and miR-181a-2-3p have also been found to regulate the expression of GPX4 and glutathione (GSH) by modulating JUN, ATF3, and CDKN1A, which may influence chondrocyte ferroptosis (233). Furthermore, miR-19b-3P, found in synoviocyte-derived exosomes in OA, inhibits SLC7A11, exacerbating ferroptosis and oxidative stress-induced injury in chondrocytes (234). The SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway plays a critical role in protecting chondrocytes from ferroptosis by mitigating oxidative stress, and its proper function is essential for safeguarding articular cartilage from OA damage (235, 236). The role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in modulating ferroptosis has been increasingly recognized as critical to the pathogenesis of OA. Numerous miRNAs have been implicated in either promoting or resisting OA progression by targeting ferroptosis-related factors and their upstream or downstream regulators. Understanding miRNA-mediated regulation of chondrocyte ferroptosis is essential for elucidating the mechanisms underlying OA. Investigating how miRNAs influence chondrocyte iron-dependent cell death could not only improve our understanding of OA but also pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies aimed at preventing and treating the disease. This research avenue offers substantial promise for developing innovative treatments for OA in the future.
5 Novel avenues for the regulation of osteoarthritis-associated ferroptosis by microRNAs
It has been observed that lncRNA AC011511.5 competitively inhibits hsa-miR-520c-5p, hsa-miR-518d-5p, hsa-miR-518f-5p, and hsa-miR-665, among others, thereby regulating the expression of GABARAPL2, HMOX1, NOX4, STMN1, and TXNIP, as well as other genes implicated in OA iron-induced cell death (237). Similarly, the competitive inhibition of lncRNA AL358072.1 with hsa-miR-138-5p and hsa-miR-122-5p modulates the expression of AGPAT3, HERPUD1, JDP2, SLC38A, SQSTM1, and UBC (237). Through bioinformatics analysis, eight hub genes (ATF3, EGR1, FOSB, FOSL1, FOSL2, JUN, JUNB, and MYC) were identified as potential regulators of osteoarthritis (OA) iron-death-related genes. These hub genes modulate iron death genes, with ALOX15, CISD1, SAT1, and TFRC showing positive correlations, and ATP5MC3, GPX4, HSPB1, and MT1G exhibiting negative correlations. Consequently, these hub genes may play a role in regulating the OA iron death process (238–241). Previous studies have highlighted the significant role of these hub genes in OA (104, 242–246). This analysis suggests a potential interaction between the hub gene and ferroptosis-related genes. The recent study identified ACSF2 (247, 248), AURKA (249–252), EGFR (253, 254), and KLHL24 (51, 255) as biomarkers associated with iron deposition in osteoarthritis (OA). Additionally, a targeted investigation was conducted on EGFR (256). Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression was significantly diminished in osteoarthritic (OA) cartilage and iron-dead chondrocytes (66), demonstrating an inhibitory effect on chondrocyte iron-induced cell death. Importantly, EGFR was competitively regulated by three long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs: LINC00265, LINC00051, and KCTD21-AS) and four microRNAs (miRNAs: hsa-miR-6846-5p, hsa-miR-4763-3p, hsa-miR-6796-5p, and hsa-miR-6860), which collectively modulated EGFR inhibition. A recent study indicates that hsa-miR-149-3p, hsa-miR-423-5p, hsa-miR-31-5p, and hsa-miR-30b-3p may influence the progression of osteoarthritis (OA) through the regulation of CDKN1A (257, 258) and SLC39A14 (259, 260), the latter of which has been identified as a differentially expressed gene associated with ferroptosis in OA (222). In conclusion, this not only broadens the scope of scientific research but also offers a novel therapeutic direction for future exploration. The regulatory mechanisms between these genes remain poorly understood. Further investigation into the interrelationships among these genes holds significant potential for advancing our understanding of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis and improving strategies for its prevention and management. Most importantly, this insight offers novel strategies for targeting microRNAs (MiRs) to regulate the progression of osteoarthritis (OA). Specifically, the modulation of MiRs and other non-coding RNAs to control chondrocyte ferroptosis presents a promising therapeutic approach for OA management.
6 Discussions
OA is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease of unknown origin, leading to irreversible joint pain, mobility loss, and significant functional impairments. These consequences greatly reduce patients’ quality of life while also imposing substantial financial burdens. Current OA management strategies focus on pain relief and partial restoration of joint function, but a complete and effective cure remains elusive. A deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of OA is essential to developing more comprehensive and innovative therapeutic approaches. In this context, microRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs of about 20 nucleotides, have emerged as key players. miRNAs have been shown to play a pivotal role in regulating osteoarthritic chondrocytes through mechanisms such as apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, and ferroptosis—types of programmed and non-programmed cell death. These regulatory pathways are intricately connected to chondrocyte anabolic and catabolic metabolism, osteoblast redox balance, the differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes and osteoblasts, macrophage polarization, and other key processes in OA pathology. The regulation of miRNAs in OA occurs at the genetic level, making them promising targets for future OA treatments and preventive strategies. Numerous miRNAs have already been linked to OA progression, with additional upstream non-coding RNAs, such as lncRNAs and circRNAs, playing indirect roles by modulating miRNA activity. These upstream RNAs influence downstream pathways and further shape the regulatory network in OA. Targeting non-coding RNAs, including lncRNAs, circRNAs, and miRNAs, offers a promising avenue for the future treatment of OA. Mechanistically, the role of miRNAs in regulating chondrocyte ferroptosis, a form of cell death implicated in OA progression, deserves particular attention. Exploring this regulatory axis may enhance our understanding of OA and broaden therapeutic strategies. Despite extensive research on non-coding RNAs, including miRNAs, significant knowledge gaps remain. Current insights into their preventive, palliative, or therapeutic effects on OA are largely theoretical, necessitating rigorous clinical validation to confirm their safety and efficacy. Emerging studies on exosomal miRNAs and intra-articular injections of miRNA-related therapies have shown promise in experimental models of OA treatment and prevention. However, their clinical application faces challenges, and substantial work remains to ensure their efficacy in human patients. Bridging basic research with clinical practice through comprehensive trials and further investigation is essential for integrating these miRNA-based therapies into OA management. This research direction holds great promise for transforming the treatment landscape of OA, potentially paving the way for novel therapeutic interventions and even a future cure.
Author contributions
QY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YX: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. MG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. GZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing. XZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. JY: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. MH: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Software, Methodology. WY: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. YW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of the article. The research, writing and/or publication of this article were funded. This work is supported by the Discipline Layout Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (No.: 20210101205JC), Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Osteoporosis health identification and intervention technology evaluation research project, Natural Science Foundation of Science and Technology Department of Jilin Province (grant Number YDZJ202301ZYTS040).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1478153/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Buchanan W, Kean C, Kean W, Rainsford K. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology. (2024) 32:13–22. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01223-y
2. Bland J, Cooper S. Osteoarthritis: a review of the cell biology involved and evidence for reversibility. Management rationally related to known genesis and pathophysiology. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (1984) 14:106–33. doi: 10.1016/0049-017290002-7
3. Jeon O, David N, Campisi J, Elisseeff J. Senescent cells and osteoarthritis: a painful connection. J Clin Invest. (2018) 128:1229–37. doi: 10.1172/JCI95147
4. Zhou X, Cao H, Yuan Y, Wu W. Biochemical signals mediate the crosstalk between cartilage and bone in osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int (2020) 2020:5720360. doi: 10.1155/2020/5720360
5. Bartel D. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell (2004) 116:281–97. doi: 10.1016/s0092-867400045-5
6. Swingler T, Niu L, Smith P, Paddy P, Le L, Barter M, et al. The function of microRNAs in cartilage and osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2019) 37:40–7.
7. Goldring M, Marcu K. Epigenomic and microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis, and osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. (2012) 18:109–18. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.11.005
8. Yao X, Sun K, Yu S, Luo J, Guo J, Lin J, et al. Chondrocyte ferroptosis contribute to the progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. (2021) 27:33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2020.09.006
9. Felekkis K, Pieri M, Papaneophytou C. Exploring the Feasibility of Circulating miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Osteoarthritis: Challenges and Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:13144. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713144
10. Woods S, Charlton S, Cheung K, Hao Y, Soul J, Reynard L, et al. microRNA-seq of cartilage reveals an overabundance of miR-140-3p which contains functional isomiRs. RNA. (2020) 26:1575–88. doi: 10.1261/rna.075176.120
11. Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, Grogan S, Higashiyama R, Inoue A, et al. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Arthrit Rheum. (2009) 60:2723–30. doi: 10.1002/art.24745
12. Tardif G, Pelletier J, Fahmi H, Hum D, Zhang Y, Kapoor M, et al. NFAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3 regulate the expression of miR-140 in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2013) 15:R197. doi: 10.1186/ar4387
13. Ma S, Wang J, He F, Zuo D, Li F, Fan H, et al. Sodium propionate improves rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting survivin mediated proliferation of fibroblast like synoviocytes by promoting miR-140-5p. Autoimmunity. (2022) 55:378–87. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2022.2073589
14. Si H, Zeng Y, Liu S, Zhou Z, Chen Y, Cheng J, et al. Intra-articular injection of microRNA-140 (miRNA-140) alleviates osteoarthritis (OA) progression by modulating extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis in rats. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2017) 25:1698–707. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2017.06.002
15. Cheng S, Nie Z, Cao J, Peng H. Circ_0136474 promotes the progression of osteoarthritis by sponging mir-140-3p and upregulating MECP2. J Mol Histol. (2023) 54:1–12. doi: 10.1007/s10735-022-10100-x
16. Toury L, Frankel D, Airault C, Magdinier F, Roll P, Kaspi E. miR-140-5p and miR-140-3p: key actors in aging-related diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:11439. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911439
17. Rikkers M, Korpershoek J, Levato R, Malda J, Vonk L. The clinical potential of articular cartilage-derived progenitor cells: a systematic review. NPJ Regen Med. (2022) 7:2. doi: 10.1038/s41536-021-00203-6
18. Gu J, Wang B, Wang T, Zhang N, Liu H, Gui J, et al. Effects of cartilage progenitor cells, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes on cartilage repair as seed cells: an in vitro study. Drug Design Dev Therapy. (2022) 16:1217–30. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S356936
19. Hosaka Y, Saito T, Sugita S, Hikata T, Kobayashi H, Fukai A, et al. Notch signaling in chondrocytes modulates endochondral ossification and osteoarthritis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2013) 110:1875–80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207458110
20. Liu Z, Chen J, Mirando A, Wang C, Zuscik M, O’Keefe R, et al. A dual role for NOTCH signaling in joint cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis. Sci Signal. (2015) 8:ra71. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa3792
21. Lin N, Distler A, Beyer C, Philipi-Schöbinger A, Breda S, Dees C, et al. Inhibition of Notch1 promotes hedgehog signalling in a HES1-dependent manner in chondrocytes and exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:2037–44. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208420
22. Qi L, Wang M, He J, Jia B, Ren J, Zheng S. E3 ubiquitin ligase ITCH improves LPS-induced chondrocyte injury by mediating JAG1 ubiquitination in osteoarthritis. Chem Biol Interact. (2022) 360:109921. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109921
23. Chen J, Liu Z, Sun H, Liu M, Wang J, Zheng C, et al. MiR-203a-3p attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes by regulating the MYD88/NF-κB pathway to alleviate osteoarthritis progression. Aging. (2023) 15:14457–72. doi: 10.18632/aging.205373
24. Chen Y, Huang H, Zhong W, Li L, Lu Y, Si H. miR-140-5p protects cartilage progenitor/stem cells from fate changes in knee osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 114:109576. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109576
25. Yao W, Kulyar M, Ding Y, Du H, Hong J, Loon K, et al. The Effect of miR-140-5p with HDAC4 towards Growth and Differentiation Signaling of Chondrocytes in Thiram-Induced Tibial Dyschondroplasia. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:10975. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310975
26. Hu Y, Liu H, Xu D, Xue X, Xu X. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of miR-140-3p in BMSCs-Exosomes on Osteoarthritis. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. (2023) 90:267–76.
27. Luobin D, Huajun W, Yao L, Jia L, Ling L, Yangping G, et al. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p. J Tradit Chin Med. (2023) 43:983–90. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2023.05.004
28. Worby C, Dixon J. PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. (2014) 83:641–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-082411-113907
29. Zhang C, Yu H, Bai X, Zhou X, Feng Z, Li Y, et al. MiR-15b-3p weakens bicalutamide sensitivity in prostate cancer via targeting KLF2 to suppress ferroptosis. J Cancer. (2024) 15:2306–17. doi: 10.7150/jca.92379
30. Xia T, Dong S, Tian J. miR-29b promotes the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue via the PTEN/AKT/β−catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. (2020) 46:709–17. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4615
31. Yang C, You D, Huang J, Yang B, Huang X, Ni J. Effects of AURKA-mediated degradation of SOD2 on mitochondrial dysfunction and cartilage homeostasis in osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:17727–38. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28398
32. Zhang G, Song S, Chen Z, Liu X, Zheng J, Wang Y, et al. Inhibition of PTEN promotes osteointegration of titanium implants in type 2 diabetes by enhancing anti-inflammation and osteogenic capacity of adipose-derived stem cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2024) 12:1358802. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1358802
33. Huang J, Chen C, Liang C, Luo P, Xia G, Zhang L, et al. Dysregulation of the Wnt Signaling Pathway and Synovial Stem Cell Dysfunction in Osteoarthritis Development. Stem Cells Dev. (2020) 29:401–13. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0260
34. Sisson B, Dale R, Mui S, Topczewska J, Topczewski J. A role of glypican4 and wnt5b in chondrocyte stacking underlying craniofacial cartilage morphogenesis. Mech Dev. (2015) 138:279–90. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2015.10.001
35. Tao S, Yuan T, Zhang Y, Yin W, Guo S, Zhang C. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. (2017) 7:180–95. doi: 10.7150/thno.17133
36. Wu L, Tang R, Xiong W, Song S, Guo Q, Zhang Q. Paeoniflorin shows chondroprotective effects under IL-1β stress by regulating circ-PREX1/miR-140-3p/WNT5B axis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:766. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04238-x
37. Park S, Cheon E, Lee M, Kim H. MicroRNA-127-5p regulates matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression and interleukin-1β-induced catabolic effects in human chondrocytes. Arthrit Rheum. (2013) 65:3141–52. doi: 10.1002/art.38188
38. Shukla G, Singh J, Barik S. MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. (2011) 3:83–92.
39. Yu Y, Zhao J. Modulated autophagy by MicroRNAs in osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:1484152. doi: 10.1155/2019/1484152
40. Tu M, Li Y, Zeng C, Deng Z, Gao S, Xiao W, et al. MicroRNA-127-5p regulates osteopontin expression and osteopontin-mediated proliferation of human chondrocytes. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:25032. doi: 10.1038/srep25032
41. Liang J, Xu L, Zhou F, Liu A, Ge H, Chen Y, et al. MALAT1/miR-127-5p Regulates Osteopontin (OPN)-Mediated Proliferation of Human Chondrocytes Through PI3K/Akt Pathway. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:431–9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26200
42. Lee D, Kiener H, Agarwal S, Noss E, Watts G, Chisaka O, et al. Cadherin-11 in synovial lining formation and pathology in arthritis. Science. (2007) 315:1006–10. doi: 10.1126/science.1137306
43. Bowler M, Bersi M, Ryzhova L, Jerrell R, Parekh A, Merryman W. Cadherin-11 as a regulator of valve myofibroblast mechanobiology. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2018) 315:H1614–26. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00277.2018
44. Chang S, Noss E, Chen M, Gu Z, Townsend K, Grenha R, et al. Cadherin-11 regulates fibroblast inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2011) 108:8402–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019437108
45. Wang T, He C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2018) 44:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2018.10.002
46. Matsumura T, Saito Y, Suzuki T, Teramoto A, Ozasa Y, Yamashita T, et al. Phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor receptor-positive cells with anti-apoptotic properties accumulate in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:241. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00241
47. Dong J, Li L, Fang X, Zang M. Exosome-Encapsulated microRNA-127-3p released from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviates osteoarthritis through regulating CDH11-Mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Pain Res. (2021) 14:297–310. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S291472
48. Wang J, Li X, Guo X, Wang C, Liu Z, Liu X, et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p promotes the progression of osteoarthritis secondary to developmental dysplasia of the hip by restraining SESN2-induced autophagy. J Orthop Res. (2024) 42:66–77. doi: 10.1002/jor.25639
49. Zhou X, Xu W, Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Li C, et al. LncRNA DNM3OS regulates GREM2 via miR-127-5p to suppress early chondrogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxic conditions. Cell Mol Biol Lett. (2021) 26:22. doi: 10.1186/s11658-021-00269-6
50. Zhang L, Zhang Y, Miao M, Hu S, Wang X, Zhao L, et al. Erxian herbal pair enhances bone formation in infected bone nonunion models and attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoblastinhibition by regulating miRNA-34a-5p. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:14339–56. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2085388
51. Liu H, Zhao H, Huang Y, Lei M. Circ_0002715 promotes the development of osteoarthritis through regulating LXN by sponging miR-127-5p. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:230. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03638-3
52. Zhang Y, Zhao P, Li S, Mu X, Wang H. CircSCAPER knockdown attenuates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury by miR-127-5p/TLR4 axis in osteoarthritis. Autoimmunity. (2022) 55:577–86. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2022.2103798
53. Liu W, Jiang T, Zheng W, Zhang J, Li A, Lu C, et al. FTO-mediated m6A demethylation of pri-miR-3591 alleviates osteoarthritis progression. Arthritis Res Ther. (2023) 25:53. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03035-5
54. Laiguillon M, Houard X, Bougault C, Gosset M, Nourissat G, Sautet A, et al. Expression and function of visfatin (Nampt), an adipokine-enzyme involved in inflammatory pathways of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16:R38. doi: 10.1186/ar4467
55. Yang S, Ryu J, Oh H, Jeon J, Kwak J, Kim J, et al. NAMPT (visfatin), a direct target of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, is an essential catabolic regulator of osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum Dis. (2015) 74:595–602. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204355
56. Liu C, Cheng P, Liang J, Zhao X, Du W. Circular RNA circ_0128846 promotes the progression of osteoarthritis by regulating miR-127-5p/NAMPT axis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2021) 16:307. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02428-z
57. Kuang M, Xing F, Wang D, Sun L, Ma J, Ma X. CircUSP45 inhibited osteogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by sponging miR-127-5p through PTEN/AKT signal pathway: Experimental studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2019) 509:255–61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.116
58. Zhang D, Chen T, Li J, Wang H, Huang Z, Lv H. Circ_0134944 inhibits osteogenesis through miR-127-5p/PDX1/SPHK1 pathway. Regen Ther. (2021) 18:391–400. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2021.09.004
59. Wang A, Ren M, Song Y, Wang X, Wang Q, Yang Q, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head associated with osteogenesis. Med Sci Monit. (2018) 24:1813–25. doi: 10.12659/msm.909655
60. Zhang H, Zheng W, Li D, Zheng J. miR-146a-5p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and inhibits autophagy of osteoarthritis by targeting NUMB. Cartilage. (2021) 13:1467S–77S. doi: 10.1177/19476035211023550
61. Cheng X, Xi Q, Wei S, Wu D, Ye R, Chen T, et al. Critical role of miR-125b in lipogenesis by targeting stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD-1). J Anim Sci. (2016) 94:65–76. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9456
62. Gusar V, Timofeeva A, Chagovets V, Vysokikh M, Kan N, Manukhova L, et al. Interrelation between miRNAs expression associated with redox state fluctuations, immune and inflammatory response activation, and neonatal outcomes in complicated pregnancy, accompanied by placental insufficiency. Antioxidants. (2022) 12:6. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010006
63. Endisha H, Datta P, Sharma A, Nakamura S, Rossomacha E, Younan C, et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p Promotes Joint Destruction During Osteoarthritis. Arthrit Rheumatol. (2021) 73:426–39. doi: 10.1002/art.41552
64. Ge F, Li H, Yin X. Upregulation of microRNA-125b-5p is involved in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by downregulating SYVN1. Oncol Rep. (2017) 37:2490–6. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5475
65. Tian F, Wang J, Zhang Z, Yang J. LncRNA SNHG7/miR-34a-5p/SYVN1 axis plays a vital role in proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Biol Res. (2020) 53:9. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00275-6
66. Sun H, Peng G, Chen K, Xiong Z, Zhuang Y, Liu M, et al. Identification of EGFR as an essential regulator in chondrocytes ferroptosis of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics, in vivo, and in vitro study. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e19975. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19975
67. Yu Y, Oh S, Kim H, Choi J, Jo S, Jo I. Valproic Acid-Induced CCN1 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation by Increasing CCN1 Protein Stability through HDAC1 Inhibition in Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. (2022) 11:534. doi: 10.3390/cells11030534
68. Fu L, Li N, Ye Y, Ye X, Xiao T, Wu X, et al. MicroRNA Hsa-Let-7b Regulates the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells by Targeting CTHRC1. Stem Cells Int. (2021) 2021:5791181. doi: 10.1155/2021/5791181
69. Zhang Z, Tang J, Song J, Xie M, Liu Y, Dong Z, et al. Elabela alleviates ferroptosis, myocardial remodeling, fibrosis and heart dysfunction in hypertensive mice by modulating the IL-6/STAT3/GPX4 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. (2022) 181:130–42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.020
70. Yang C, Liu X, Zhao K, Zhu Y, Hu B, Zhou Y, et al. miRNA-21 promotes osteogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and enhances bone regeneration in critical size defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. (2019) 10:65. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1168-2
71. Miao M, Li M, Sheng Y, Tong P, Zhang Y, Shou D. Epimedium-Curculigo herb pair enhances bone repair with infected bone defects and regulates osteoblasts through LncRNA MALAT1/miR-34a-5p/SMAD2 axis. J Cell Mol Med. (2024) 28:e18527. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18527
72. Shen T, Alvarez-Garcia O, Li Y, Olmer M, Lotz M. Suppression of Sestrins in aging and osteoarthritic cartilage: dysfunction of an important stress defense mechanism. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2017) 25:287–96. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2016.09.017
73. Jiang Y. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: biology. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2022) 30:207–15. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.11.009
74. Wang L, Li M, Liu B, Zheng R, Zhang X, Yu S. miR-30a-5p mediates ferroptosis of hippocampal neurons in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced cognitive dysfunction by modulating the SIRT1/NRF2 pathway. Brain Res Bull. (2024) 212:110953. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110953
75. Zhou M, Liu B, Ye H, Hou J, Huang Y, Zhang P, et al. ROS-induced imbalance of the miR-34a-5p/SIRT1/p53 axis triggers chronic chondrocyte injury and inflammation. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e31654. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31654
76. Lepetsos P, Papavassiliou A. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2016) 1862:576–91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.01.003
77. Srivastava S, Saksena A, Khattri S, Kumar S, Dagur R. Curcuma longa extract reduces inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers in osteoarthritis of knee: a four-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Inflammopharmacology. (2016) 24:377–88. doi: 10.1007/s10787-016-0289-9
78. Hao R, Ge J, Song X, Li F, Sun-Waterhouse D, Li D. Cadmium induces ferroptosis and apoptosis by modulating miR-34a-5p/Sirt1axis in PC12 cells. Environ Toxicol. (2022) 37:41–51. doi: 10.1002/tox.23376
79. Xia L, Gong N. Identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis. Front Mol Biosci. (2022) 9:992044. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.992044
80. Soyocak A, Kurt H, Ozgen M, Turgut Cosan D, Colak E, Gunes H. miRNA-146a, miRNA-155 and JNK expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells according to grade of knee osteoarthritis. Gene. (2017) 627:207–11. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.027
81. Li G, Cui L, Wang G. miR-155-5p regulates macrophage M1 polarization and apoptosis in the synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. (2021) 21:68. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9500
82. Liu J, Lu S, Fu C. MiR-146a expression profiles in osteoarthritis in different tissue sources: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:148. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-02989-7
83. Qin H, Wang C, He Y, Lu A, Li T, Zhang B, et al. Silencing miR-146a-5p Protects against Injury-Induced Osteoarthritis in Mice. Biomolecules. (2023) 13:123. doi: 10.3390/biom13010123
84. Kleppisch T, Pfeifer A, Klatt P, Ruth P, Montkowski A, Fässler R, et al. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region of mice lacking cGMP-dependent kinases is normal and susceptible to inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. J Neurosci. (1999) 19:48–55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-01-00048.1999
85. Shao J, Ding Z, Peng J, Zhou R, Li L, Qian Q, et al. MiR-146a-5p promotes IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis through the TRAF6-mediated NF-kB pathway. Inflamm Res. (2020) 69:619–30. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01346-w
86. Sur I, Undén A, Toftgård R. Human Krüppel-like factor5/KLF5: synergy with NF-kappaB/Rel factors and expression in human skin and hair follicles. Eur J Cell Biol. (2002) 81:323–34. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00257
87. Aizawa K, Suzuki T, Kada N, Ishihara A, Kawai-Kowase K, Matsumura T, et al. Regulation of platelet-derived growth factor-A chain by Krüppel-like factor 5: new pathway of cooperative activation with nuclear factor-kappaB. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:70–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306621200
88. Fujiu K, Manabe I, Nagai R. Renal collecting duct epithelial cells regulate inflammation in tubulointerstitial damage in mice. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:3425–41. doi: 10.1172/JCI57582
89. Amin Mohedin J, Rezaiemanesh A, Asadi S, Haddadi M, Abdul Ahmed B, Gorgin Karaji A, et al. Resolvin D1 (Rvd1) Attenuates In Vitro LPS-Stimulated Inflammation Through Downregulation of miR-155, miR -146, miR -148 and Krupple Like Factor 5. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. (2024) 12:566–74. doi: 10.61186/rbmb.12.4.566
90. Tian H. Detection of differentially expressed genes involved in osteoarthritis pathology. J Orthop Surg Res. (2018) 13:49. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0734-0
91. Gan K, Wu W, Li J, Xu D, Liu Y, Bi M, et al. Positive feedback loop of lncRNA FAM201A/miR-146a-5p/POU2F1 regulates IL-1β−induced chondrocyte injury in vitro. Mol Med Rep. (2022) 25:20. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12536
92. Guzzo R, Alaee F, Paglia D, Gibson J, Spicer D, Drissi H. Aberrant expression of Twist1 in diseased articular cartilage and a potential role in the modulation of osteoarthritis severity. Genes Dis. (2016) 3:88–99. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2015.12.005
93. Tu J, Huang W, Zhang W, Mei J, Yu Z, Zhu C. TWIST1-MicroRNA-10a-MAP3K7 Axis Ameliorates Synovitis of Osteoarthritis in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2020) 22:1107–20. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.020
94. Ye C, Ye J, Wu H, Zhang F, Liu Y. Evidence of TWIST1 and transforming growth factor-B1 aberrant expressions as novel therapeutic targets in modulating the severity of osteoarthritis with focus on biologic agents. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2020) 71:6. doi: 10.26402/jpp.2020.6.06
95. Reddi A. Interplay between bone morphogenetic proteins and cognate binding proteins in bone and cartilage development: noggin, chordin and DAN. Arthrit Res. (2001) 3:1–5. doi: 10.1186/ar133
96. Kobayashi T, Lyons K, McMahon A, Kronenberg H. BMP signaling stimulates cellular differentiation at multiple steps during cartilage development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2005) 102:18023–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503617102
97. Li C, Li W, Pu G, Wu J, Qin F. Exosomes derived from miR-338-3p-modified adipose stem cells inhibited inflammation injury of chondrocytes via targeting RUNX2 in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:567. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03437-2
98. Yang Z, Li R, Ao J, Wa Q, Zhang Y, Chen L, et al. miR-1307-3p suppresses the chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by targeting BMPR2. Int J Mol Med. (2018) 42:3115–24. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3891
99. Zheng M, Tan J, Liu X, Jin F, Lai R, Wang X. miR-146a-5p targets Sirt1 to regulate bone mass. Bone Rep. (2021) 14:101013. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2021.101013
100. Liu L, Liao R, Wu Z, Du C, You Y, Que K, et al. Hepatic stellate cell exosome-derived circWDR25 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miRNA-4474-3P-ALOX-15 and EMT axes. Biosci Trends. (2022) 16:267–81. doi: 10.5582/bst.2022.01281
101. Krishnan P, Branco R, Weaver S, Chang G, Lee C, Syed F, et al. miR-146a-5p mediates inflammation-induced β cell mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. bioRxiv. [Preprint]. (2024): doi: 10.1101/2024.03.18.585543
102. Sun Y, You Y, Wu Q, Hu R, Dai K. Senescence-targeted MicroRNA/Organoid composite hydrogel repair cartilage defect and prevention joint degeneration via improved chondrocyte homeostasis. Bioact Mater. (2024) 39:427–42. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.05.036
103. Wu Y, Liu W, Zhang L, Liu X, Wang Y, Xue B, et al. Effects of microRNA-24 targeting C-myc on apoptosis, proliferation, and cytokine expressions in chondrocytes of rats with osteoarthritis via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. (2018) 119:7944–58. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26514
104. Zou J, Li X, Shi Z, Xue J. Effects of C-myc gene silencing on interleukin-1β-induced rat chondrocyte cell proliferation, apoptosis and cytokine expression. J Bone Miner Metab. (2018) 36:286–96. doi: 10.1007/s00774-017-0845-4
105. Li H, Li Z, Pi Y, Chen Y, Mei L, Luo Y, et al. MicroRNA-375 exacerbates knee osteoarthritis through repressing chondrocyte autophagy by targeting ATG2B. Aging. (2020) 12:7248–61. doi: 10.18632/aging.103073
106. Pan H, Zhu Y, Wei W, Shao S, Rui X. Transcription factor FoxM1 is the downstream target of c-Myc and contributes to the development of prostate cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2018) 16:59. doi: 10.1186/s12957-018-1352-3
107. Sun Y, Wang H, Li Y, Liu S, Chen J, Ying H. miR-24 and miR-122 Negatively Regulate the Transforming Growth Factor-β/Smad Signaling Pathway in Skeletal Muscle Fibrosis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2018) 11:528–37. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.04.005
108. Philipot D, Guérit D, Platano D, Chuchana P, Olivotto E, Espinoza F, et al. p16INK4a and its regulator miR-24 link senescence and chondrocyte terminal differentiation-associated matrix remodeling in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16:R58. doi: 10.1186/ar4494
109. Sharafabadi A, Abdellahi M, Kazemi A, Khandan A, Ozada N. A novel and economical route for synthesizing akermanite (CaMgSiO) nano-bioceramic. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. (2017) 71:1072–8. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.11.021
110. Wang T, Nimkingratana P, Smith C, Cheng A, Hardingham T, Kimber S. Enhanced chondrogenesis from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. (2019) 39:101497. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2019.101497
111. Wu Q, Xu S, Wang X, Jia B, Han Y, Zhuang Y, et al. Complementary and synergistic effects on osteogenic and angiogenic properties of copper-incorporated silicocarnotite bioceramic: In vitro and in vivo studies. Biomaterials. (2021) 268:120553. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120553
112. Qin F, Wang F, Wang X, Chen J, Zeng F, Sun C, et al. MiR-539-3p inhibited chondrogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells by targeting Sox9. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:168. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03053-0
113. Liu X, Zhang K, Wang L, Geng B, Liu Z, Yi Q, et al. Fluid shear stress-induced down-regulation of miR-146a-5p inhibits osteoblast apoptosis via targeting SMAD4. Physiol Res. (2022) 71:835–48. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934922
114. Zhao B, Shi X, Feng D, Han J, Hu D. MicroRNA let-7d attenuates hypertrophic scar fibrosis through modulation of iron metabolism by reducing DMT1 expression. J Mol Histol. (2023) 54:77–87. doi: 10.1007/s10735-023-10113-0
115. Lin E, Kong L, Bai X, Luan Y, Liu C. miR-199a, a bone morphogenic protein 2-responsive MicroRNA, regulates chondrogenesis via direct targeting to Smad1. J Biol Chem. (2009) 284:11326–35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807709200
116. Akhtar N, Haqqi T. MicroRNA-199a* regulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71:1073–80. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200519
117. Lu H, Yang Y, Ou S, Qi Y, Li G, He H, et al. The silencing of miR-199a-5p protects the articular cartilage through MAPK4 in osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. (2022) 10:601. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2057
118. Feng T, Zhang Q, Li S, Ping Y, Tian M, Zhou S, et al. Inhibition of miR-199b-5p reduces pathological alterations in osteoarthritis by potentially targeting Fzd6 and Gcnt2. Elife. (2024) 12:R92645. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92645
119. Huang L, Jin M, Gu R, Xiao K, Lu M, Huo X, et al. miR-199a-5p Reduces Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Attenuates Osteoarthritis Progression via the Indian Hedgehog Signal Pathway. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:1313. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041313
120. Dadihanc T, Zhang Y, Li G, Zhou H, Huang J, Zhang X, et al. CircRNA SEC24A promotes osteoarthritis through miR-107-5p/CASP3 axis. Regen Ther. (2024) 26:60–70. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.04.011
121. Luo Z, Han Q, Lu J, Ouyang X, Fan Y, Liu Y, et al. IL16 Regulates Osteoarthritis Progression as a Target Gene of Novel-miR-81. Cartilage. (2024) 15:175–83. doi: 10.1177/19476035231168387
122. Guan Z, Liu Y, Luo L, Jin X, Guan Z, Yang J, et al. Sympathetic innervation induces exosomal miR-125 transfer from osteoarthritic chondrocytes, disrupting subchondral bone homeostasis and aggravating cartilage damage in aging mice. J Adv Res. (2024) doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.03.022 [Epub ahead of print].
123. Horita M, Hsu S, Raper A, Farquharson C, Stephen L. miR-29b inhibits TGF-β1-induced cell proliferation in articular chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Rep. (2022) 29:101216. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101216
124. Lee K, Lin C, Liu S, He X, Tsai C, Ko C, et al. IL-17 promotes IL-18 production via the MEK/ERK/miR-4492 axis in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts. Aging. (2024) 16:1829–44. doi: 10.18632/aging.205462
125. Lu K, Wang Q, Hao L, Wei G, Wang T, Lu W, et al. miR-204 ameliorates osteoarthritis pain by inhibiting SP1-LRP1 signaling and blocking neuro-cartilage interaction. Bioact Mater. (2023) 26:425–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.03.010
126. Luo L, Zhang S, Guo N, Li H, He S. ACSF2-mediated ferroptosis is involved in ulcerative colitis. Life Sci. (2023) 313:121272. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121272
127. Li D, Wang X, Yi T, Zhang L, Feng L, Zhang M, et al. LncRNA MINCR attenuates osteoarthritis progression via sponging miR-146a-5p to promote BMPR2 expression. Cell Cycle. (2022) 21:2417–32. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2099191
128. Chen Y, Chen Y, Wang W, Chen J, Tang Q, Wu R, et al. The miR-302c/transforming growth factor-β receptor type-2 axis modulates interleukin-1β-induced degenerative changes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Cell Commun Signal. (2022) 16:93–102. doi: 10.1007/s12079-020-00591-2
129. Yang J, Li Q, Wang T, Lv K. Circular RNA triple functional domain promotes osteoarthritis’ development by modulating the microRNA-136-5p/Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase axis. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:6070–9. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2018095
130. Qin W, Cai X, Han W, Lu X, Chen M, Jia Z, et al. [The role and mechanism of lncRNA C9ORF139 targeting miR-24-3P/TAOK1 in regulating the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. (2022) 102:576–83. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210703-01501
131. Jin T, Zheng H, Feng X, Wu T, Yang K, Huang Y. MiR-539-3p Alleviates Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Chondrocytes of Childhood-Onset Osteoarthritis by Targeting RUNX2. Physiol Res. (2024) 73:415–26. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935291
132. Lai C, Liao B, Peng S, Fang P, Bao N, Zhang L. Synovial fibroblast-miR-214-3p-derived exosomes inhibit inflammation and degeneration of cartilage tissues of osteoarthritis rats. Mol Cell Biochem. (2023) 478:637–49. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04535-9
133. Yin Y, He Q, He J, Feng Y, Xu Y. Inhibition of LINC00958 hinders the progression of osteoarthritis through regulation of the miR-214-3p/FOXM1 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:66. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04545-x
134. He B, Liao Y, Tian M, Tang C, Tang Q, Ma F, et al. Identification and verification of a novel signature that combines cuproptosis-related genes with ferroptosis-related genes in osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation. Arthritis Res Ther. (2024) 26:100. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03328-3
135. Cao H, Zhou X, Li H, Wang M, Wu W, Zou J. Study on the Role of MicroRNA-214 in the Rehabilitation of Cartilage in Mice with Exercise-Induced Traumatic Osteoarthritis. Curr Issues Mol Biol. (2022) 44:4100–17. doi: 10.3390/cimb44090281
136. Lin R, Yin J, Huang J, Zou L, Liu L, Tang W, et al. Macrophage-derived ectosomal miR-350-3p promotes osteoarthritis progression through downregulating chondrocyte H3K36 methyltransferase NSD1. Cell Death Discov. (2024) 10:223. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01986-5
137. Xie S, Yang L, Shu T, Liu Q, Wang W. miR-149-5p mitigates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced chondrocyte apoptosis by inhibiting TRADD. Arch Med Sci. (2024) 20:602–11. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.92324
138. Chen K, Yeh C, Yadav V, Pikatan N, Fong I, Lee W, et al. Notopterol mitigates IL-1β-triggered pyroptosis by blocking NLRP3 inflammasome via the JAK2/NF-kB/hsa-miR-4282 route in osteoarthritis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e28094. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28094
139. Zhang J, Zheng K, Wu Y, Zhang S, Guo A, Sui C. The experimental study of mir-99a-5p negative regulation of TLR8 receptor mediated-mediated innate immune response in rabbit knee cartilage injury. Immun Inflamm Dis. (2024) 12:e1211. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1211
140. Wang L, Wu S, He H, Ai K, Xu R, Zhang L, et al. CircRNA-ST6GALNAC6 increases the sensitivity of bladder cancer cells to erastin-induced ferroptosis by regulating the HSPB1/P38 axis. Lab Invest. (2022) 102:1323–34. doi: 10.1038/s41374-022-00826-3
141. Zhang Y, Ding R, Zhang Y, Qi J, Cao W, Deng L, et al. Dysfunction of DMT1 and miR-135b in the gut-testis axis in high-fat diet male mice. Genes Nutr. (2024) 19:1. doi: 10.1186/s12263-024-00737-6
142. Zhou R, Zhao L, Wang Q, Cheng Y, Song M, Huang C. Plasma microRNA-320c as a Potential Biomarker for the Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis and Regulates cAMP Responsive Element Binding Protein 5 (CREB5) in Chondrocytes. Dis Markers. (2024) 2024:9936295. doi: 10.1155/2024/9936295
143. Zhou Q, Liu J, Wan L, Zhu Y, Qi Y, Hu Y. [Xinfeng Capsule alleviates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the miR-502-5p/TRAF2/NF-κB axis]. J South Med Univ. (2024) 44:108–18. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.13
144. Chen Y, Liao G, Ma T, Li L, Yang J, Shen B, et al. YY1/miR-140-5p/Jagged1/Notch axis mediates cartilage progenitor/stem cells fate reprogramming in knee osteoarthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 121:110438. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110438
145. Sun D, Chen Y, Liu X, Huang G, Cheng G, Yu C, et al. miR-34a-5p facilitates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and modulates bone metabolism by targeting HDAC1 and promoting ER-α transcription. Connect Tissue Res. (2023) 64:126–38. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2022.2108415
146. Liu W, Liu A, Li X, Sun Z, Sun Z, Liu Y, et al. Dual-engineered cartilage-targeting extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance osteoarthritis treatment via miR-223/NLRP3/pyroptosis axis: Toward a precision therapy. Bioact Mater. (2023) 30:169–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.06.012
147. Li G, Xiu L, Li X, Ma L, Zhou J. miR-155 inhibits chondrocyte pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis by targeting SMAD2 and inhibiting the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:48. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02886-5
148. Fan Z, Liu Y, Shi Z, Deng K, Zhang H, Li Q, et al. MiR-155 promotes interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and catabolic activity by targeting PIK3R1-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:8441–51. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15388
149. Ye P, Mi Z, Wei D, Gao P, Ma M, Yang H. miR-3960 from Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inactivates SDC1/Wnt/β-Catenin Axis to Relieve Chondrocyte Injury in Osteoarthritis by Targeting PHLDA2. Stem Cells Int. (2022) 2022:9455152. doi: 10.1155/2022/9455152
150. Gu W, Shi Z, Song G, Zhang H. MicroRNA-199-3p up-regulation enhances chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in knee osteoarthritis via DNMT3A repression. Inflamm Res. (2021) 70:171–82. doi: 10.1007/s00011-020-01430-1
151. Yan M, Zhang D, Yang M. Saikosaponin D alleviates inflammatory response of osteoarthritis and mediates autophagy via elevating microRNA-199-3p to target transcription Factor-4. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:151. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04607-0
152. Xu Y, Duan L, Liu S, Yang Y, Qiao Z, Shi L. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation in osteoarthritis by serving as a sponge for microRNA-199-3p. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:11137–45. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2061287
153. Liu L, Zhao C, Zhang H, Lu Y, Luo B, Yao Z, et al. Asporin regulated by miR-26b-5p mediates chondrocyte senescence and exacerbates osteoarthritis progression via TGF-β1/Smad2 pathway. Rheumatology. (2022) 61:2631–43. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab725
154. Qian W, Mei K, Zhu L, Chu Y, Lv J, Yun C. Circ_0044235 regulates the development of osteoarthritis by the modulation of miR-375/PIK3R3 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:241. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04694-z
155. Xu J, Zhou K, Gu H, Zhang Y, Wu L, Bian C, et al. Exosome miR-4738-3p-mediated regulation of COL1A2 through the NF-κB and inflammation signaling pathway alleviates osteoarthritis low-grade inflammation symptoms. Biomolec Biomed. (2024) 24:520–36. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9921
156. Zhu S, Deng Y, Gao H, Huang K, Nie Z. miR-877-5p alleviates chondrocyte dysfunction in osteoarthritis models via repressing FOXM1. J Gene Med. (2020) 22:e3246. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3246
157. Shen Y, Zhang Y, Wang Q, Jiang B, Jiang X, Luo B. MicroRNA-877-5p promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting EIF4G2 expression. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:134. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04396-y
158. Lin Y, Zhang L, Ji M, Shen S, Chen Y, Wu S, et al. MiR-653-5p drives osteoarthritis pathogenesis by modulating chondrocyte senescence. Arthritis Res Ther. (2024) 26:111. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03334-5
159. Cai D, Yang Z, Zhong C, Zhang J, Hong S. [miR-515-5p targeting Toll-like receptor 4 regulates myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88/nuclear factor-kappa B pathway to inhibit apoptosis and inflammatory response of osteoarthritis chondrocytes]. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi. (2024) 38:315–23. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202312091
160. Huang F, Su Z, Yang J, Zhao X, Xu Y. Knocking-down long non-coding RNA LINC01094 prohibits chondrocyte apoptosis via regulating microRNA-577/metal-regulatory transcription factor 1 axis. J Orthop Surg. (2024) 32:10225536241254588. doi: 10.1177/10225536241254588
161. Hou D, Lu L, Tao R. Hsa_circ_0007482 Promotes Proliferation and Differentiation of Chondrocytes in Knee Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. (2024) doi: 10.1177/19476035241250198 [Epub ahead of print].
162. Lv H, Liu P, Hu H, Li X, Li P. MiR-98-5p plays suppressive effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury associated with osteoarthritis by targeting CASP3. J Orthop Surg Res. (2024) 19:239. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04628-9
163. Singh U, Singh N, Murphy E, Price R, Fayad R, Nagarkatti M, et al. Chemokine and cytokine levels in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Cytokine. (2016) 77:44–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.10.008
164. Klein K, Kabala P, Grabiec A, Gay R, Kolling C, Lin L, et al. The bromodomain protein inhibitor I-BET151 suppresses expression of inflammatory genes and matrix degrading enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. (2016) 75:422–9. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205809
165. Rozi R, Zhou Y, Rong K, Chen P. miR-124-3p sabotages lncRNA MALAT1 stability to repress chondrocyte pyroptosis and relieve cartilage injury in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:453. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03334-8
166. Li Y, Duan J, Lin W, Liu J. Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9. Open Med. (2023) 18:20230668. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0668
167. Sun Y, Kang S, Pei S, Sang C, Huang Y. MiR93-5p inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by targeting lncRNA CASC2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2020) 21:26. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-3025-y
168. Jiang M, Jike Y, Liu K, Gan F, Zhang K, Xie M, et al. Exosome-mediated miR-144-3p promotes ferroptosis to inhibit osteosarcoma proliferation, migration, and invasion through regulating ZEB1. Mol Cancer. (2023) 22:113. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01804-z
169. Wang Y, Tsai C, Liu S, Chen H, Chang J, Ko C, et al. miR-150-5p and XIST interaction controls monocyte adherence: Implications for osteoarthritis therapy. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1004334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1004334
170. Zhang Y, Wang F, Chen G, He R, Yang L. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes osteoarthritis by modulating miR-150-5p/AKT3 axis. Cell Biosci. (2019) 9:54. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0302-2
171. Wu T, Chang S, Lin C, Lai C, He X, Tsai C, et al. IL-17 Facilitates VCAM-1 Production and Monocyte Adhesion in Osteoarthritis Synovial Fibroblasts by Suppressing miR-5701 Synthesis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:6804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126804
172. Feng L, Yang Z, Li Y, Pan Q, Zhang X, Wu X, et al. MicroRNA-378 contributes to osteoarthritis by regulating chondrocyte autophagy and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2022) 28:328–41. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.03.016
173. Yin J, Zeng H, Fan K, Xie H, Shao Y, Lu Y, et al. Pentraxin 3 regulated by miR-224-5p modulates macrophage reprogramming and exacerbates osteoarthritis associated synovitis by targeting CD32. Cell Death Dis. (2022) 13:567. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04962-y
174. Zheng T, Li Y, Zhang X, Xu J, Luo M. Exosomes Derived From miR-212-5p Overexpressed Human Synovial Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Chondrocyte Degeneration and Inflammation by Targeting ELF3. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2022) 10:816209. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.816209
175. Li Q, Xu P, Zhang C, Gao Y. MiR-362-5p inhibits cartilage repair in osteoarthritis via targeting plexin B1. J Orthop Surg. (2022) 30:10225536221139887. doi: 10.1177/10225536221139887
176. Qiu M, Xie Y, Tan G, Wang X, Huang P, Hong L. Synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-485-3p relieves cartilage damage in osteoarthritis by targeting the NRP1-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway: Exosomal miR-485-3p relieves cartilage damage. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e24042. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24042
177. Cui L, Han Y, Dong Z. miR-106a mimics the nuclear factor-κB signalling pathway by targeting DR6 in rats with osteoarthritis. Arch Med Sci. (2024) 20:302–8. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.92831
178. Jaiswal A, Reddy S, Maurya M, Maurya P, Barthwal M. MicroRNA-99a mimics inhibit M1 macrophage phenotype and adipose tissue inflammation by targeting TNFα. Cell Mol Immunol. (2019) 16:495–507. doi: 10.1038/s41423-018-0038-7
179. Papageorgiou A, Roussos A, Papathanasiou I, Balis C, Karachalios T, Varitimidis S, et al. MiR-217 Regulates SIRT1 Expression and Promotes Inflammatory and Apoptotic Responses in Osteoarthritis. Genes. (2023) 14:2155. doi: 10.3390/genes14122155
180. Li Y, Fu T, Zhao Y, Yuan L, Wang B, Guan J, et al. Micro-223 Promotes Diabetic Osteoarthritis Progression by Regulating Cartilage Degeneration and Subchondral Bone Remodeling. Cartilage (2023) doi: 10.1177/19476035231210631 [Epub ahead of print].
181. Liu Y, Cui J, Zhang J, Chen Z, Song Z, Bao D, et al. Excess KLHL24 Impairs Skin Wound Healing through the Degradation of Vimentin. J Invest Dermatol. (2023) 143:1289.e–98.e. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.01.007
182. Zhu Y, Zhang C, Jiang B, Dong Q. MiR-760 targets HBEGF to control cartilage extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:186. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03664-1
183. Wang D, Fang Y, Lin L, Long W, Wang L, Yu L, et al. Upregulating miR-181b promotes ferroptosis in osteoarthritic chondrocytes by inhibiting SLC7A11. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2023) 24:862. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-07003-7
184. Wang J, Chai L, Tang Y, Wang G, Bao Y, Ma B. MicroRNA-322 Attenuates Cartilage Matrix Degradation in Osteoarthritis via Direct Suppression of TRAF3. Cartilage. (2023) doi: 10.1177/19476035231213207 [Epub ahead of print].
185. Zhou L, Chen D, Liu P, Chen L, Su Y. miR-132-3p participates in the pathological mechanism of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by targeting PTEN. Arch Oral Biol. (2022) 142:105511. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2022.105511
186. Sun Y, Bao X, Chen H, Zhou L. MicroRNA-128-3p suppresses interleukin-1β-stimulated cartilage degradation and chondrocyte apoptosis via targeting zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 in osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. (2022) 13:1736–45. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2019879
187. Ko J, Wang F, Lian W, Fang H, Kuo S. Cartilage-specific knockout of miRNA-128a expression normalizes the expression of circadian clock genes (CCGs) and mitigates the severity of osteoarthritis. Biomed J. (2024) 47:100629. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100629
188. Li T, Song L, Zhang Y, Han Y, Zhan Z, Xv Z, et al. Molecular mechanism of c-Myc and PRPS1/2 against thiopurine resistance in Burkitt’s lymphoma. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:6704–15. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15322
189. Qian Y, Chu G, Zhang L, Wu Z, Wang Q, Guo J, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-26b-5p regulates macrophage polarization and chondrocyte hypertrophy by targeting TLR3 and COL10A1 to alleviate osteoarthritis. J Nanobiotechnology. (2024) 22:72. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02336-4
190. Meng C, Na Y, Han C, Ren Y, Liu M, Ma P, et al. Exosomal miR-429 derived from adipose-derived stem cells ameliorated chondral injury in osteoarthritis via autophagy by targeting FEZ2. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110315. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110315
191. Feng X, Lu J, Wu Y, Xu H. MiR-18a-3p improves cartilage matrix remodeling and inhibits inflammation in osteoarthritis by suppressing PDP1. J Physiol Sci. (2022) 72:3. doi: 10.1186/s12576-022-00827-3
192. Dixon S, Lemberg K, Lamprecht M, Skouta R, Zaitsev E, Gleason C, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. (2012) 149:1060–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
193. Jiang H, Pang H, Wu P, Cao Z, Li Z, Yang X. LncRNA SNHG5 promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis by regulating miR-10a-5p/H3F3B axis. Connect Tissue Res. (2021) 62:605–14.
194. Tong L, Yu H, Huang X, Shen J, Xiao G, Chen L, et al. Current understanding of osteoarthritis pathogenesis and relevant new approaches. Bone Res. (2022) 10:60. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00226-9
195. Ursini F, Maiorino M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. (2020) 152:175–85. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
196. Rochette L, Dogon G, Rigal E, Zeller M, Cottin Y, Vergely C. Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 24:449. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010449
197. Liu Y, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Zhang L, Cheng W. GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. (2023) 1878:188890. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188890
198. Jiang D, Chen H, Cao J, Chen Y, Huang J, Weng Y. AURKA, as a potential prognostic biomarker, regulates autophagy and immune infiltration in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Immunobiology. (2023) 228:152314. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152314
199. Li S, Lv F, Xu W, Yin Y, Wei H, Li K, et al. lncRNA SNHG4 inhibits ferroptosis by orchestrating miR-150-5p/c-Myb axis in colorectal cancer. Int J Biol Macromol. (2024) 268:131961. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131961
200. Ma X, Xu M, Zhang X, Wang X, Su K, Xu Z, et al. Gambogenic acid inhibits proliferation and ferroptosis by targeting the miR-1291/FOXA2 and AMPKα/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis in colorectal cancer. Cell Biol Int. (2023) 47:1813–24. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12072
201. Shao C, Zhou H, Gao X, Xu C. Downregulation of miR-221-3p promotes the ferroptosis in gastric cancer cells via upregulation of ATF3 to mediate the transcription inhibition of GPX4 and HRD1. Transl Oncol. (2023) 32:101649. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101649
202. Mo G, Guo J, Zhang L, Shao Y, Hu K, Wu B, et al. miR-129-2-3p mediates LPS-induced macrophage polarization and ferroptosis by targeting the SMAD3-GPX4 axis. Gene. (2024) 894:147962. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147962
203. Zhai H, Zhong S, Wu R, Mo Z, Zheng S, Xue J, et al. Suppressing circIDE/miR-19b-3p/RBMS1 axis exhibits promoting-tumour activity through upregulating GPX4 to diminish ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Epigenetics. (2023) 18:2192438. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2023.2192438
204. Yi T, Zhang L, Huang X. Glycyrrhizic acid protects against temporal lobe epilepsy in young rats by regulating neuronal ferroptosis through the miR-194-5p/PTGS2 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. (2023) 39:154–65. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12642
205. Li X, Quan P, Si Y, Liu F, Fan Y, Ding F, et al. The microRNA-211-5p/P2RX7/ERK/GPX4 axis regulates epilepsy-associated neuronal ferroptosis and oxidative stress. J Neuroinflammation. (2024) 21:13. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-03009-z
206. Liu Y, Hu N, Ai B, Xia H, Li W. MiR-31-5p alleviates septic cardiomyopathy by targeting BAP1 to inhibit SLC7A11 deubiquitination and ferroptosis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2024) 24:286. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03954-4
207. Zhang Z, Guo R, Cai C, Guo P. Down-regulation of long noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS nullifies the impact of microRNA-506-3p on chondrocytes proliferation and apoptosis in osteoarthritis. Clinics. (2024) 79:100393. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100393
208. Zhao H, Li X, Yang L, Zhang L, Jiang X, Gao W, et al. Isorhynchophylline Relieves Ferroptosis-Induced Nerve Damage after Intracerebral Hemorrhage Via miR-122-5p/TP53/SLC7A11 Pathway. Neurochem Res. (2021) 46:1981–94. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03320-2
209. Fan J, Han Y, Sun H, Sun S, Wang Y, Guo R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-367-3p alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via inhibition of microglial ferroptosis by targeting EZH2. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 162:114593. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114593
210. Xia S, Liang Y, Shen Y, Zhong W, Ma Y. MAT2A inhibits the ferroptosis in osteosarcoma progression regulated by miR-26b-5p. J Bone Oncol. (2023) 41:100490. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2023.100490
211. Bersuker K, Hendricks J, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang P, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. (2019) 575:688–92. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1705-2
212. Gao M, Fan K, Chen Y, Zhang G, Chen J, Zhang Y. Understanding the mechanistic regulation of ferroptosis in cancer: the gene matters. J Genet Genomics. (2022) 49:913–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2022.06.002
213. Wang J, Qiu Y, Shi N, Zhao J, Wang Y, Jiang H, et al. microRNA-21 mediates the TGF-β1-induced migration of keratinocytes via targeting PTEN. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2016) 20:3748–59.
214. Wang J, Yang Z, He X, Wang Y, Luo D, Xu W, et al. DNM3OS/miR-127-5p/CDH11, activates Wnt3a/β-catenin/LEF-1 pathway to form a positive feedback and aggravate spine facet joint osteoarthritis. Noncoding RNA Res. (2024) 9:294–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.008
215. Geng W, Yan S, Li X, Liu Q, Zhang X, Gu X, et al. miR-432-5p Inhibits the Ferroptosis in Cardiomyocytes Induced by Hypoxia/Reoxygenation via Activating Nrf2/SLC7A11 Axis by Degrading Keap1. Anal Cell Pathol. (2023) 2023:1293200. doi: 10.1155/2023/1293200
216. Yu Y, MohamedAl-Sharani H, Zhang B. EZH2-mediated SLC7A11 upregulation via miR-125b-5p represses ferroptosis of TSCC. Oral Dis. (2023) 29:880–91. doi: 10.1111/odi.14040
217. Chen Y, Zhang Z, Yang K, Du J, Xu Y, Liu S. Myeloid zinc-finger 1 (MZF-1) suppresses prostate tumor growth through enforcing ferroportin-conducted iron egress. Oncogene. (2015) 34:3839–47. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.310
218. Zhao K, Ruan J, Nie L, Ye X, Li J. Effects of synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1164137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1164137
219. Tang S, Wang Y, Ma T, Lu S, Huang K, Li Q, et al. MiR-30d inhibits cardiomyocytes autophagy promoting ferroptosis after myocardial infarction. Panminerva Med. (2024) 66:249–55. doi: 10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03979-8
220. Liu Y, Zhang Z, Li T, Xu H, Zhang H. Senescence in osteoarthritis: from mechanism to potential treatment. Arthritis Res Ther. (2022) 24:174. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02859-x
221. Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X, Kang R, Tang D. CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protection against mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2016) 478:838–44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.034
222. He C, Zeng Z, Yang Y, Ye S, Wu Q, Liu X, et al. Silencing of CircTRIM25/miR-138-5p/CREB1 axis promotes chondrogenesis in osteoarthritis. Autoimmunity. (2024) 57:2361749. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2361749
223. He J, Zuo J, Fan X, Li Z. Electro-acupuncture modulated miR-214 expression to prevent chondrocyte apoptosis and reduce pain by targeting BAX and TRPV4 in osteoarthritis rats. Brazilian J Med Biol Res. (2024) 57:e13238. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2024e13238
224. Che X, Chen T, Wei L, Gu X, Gao Y, Liang S, et al. MicroRNA-1 regulates the development of osteoarthritis in a Col2a1-Cre-ERT2/GFPfl/fl-RFP-miR-1 mouse model of osteoarthritis through the downregulation of Indian hedgehog expression. Int J Mol Med. (2020) 46:360–70. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4601
225. Zhou M, Zhai C, Shen K, Liu G, Liu L, He J, et al. miR-1 Inhibits the Ferroptosis of Chondrocyte by Targeting CX43 and Alleviates Osteoarthritis Progression. J Immunol Res. (2023) 2023:2061071. doi: 10.1155/2023/2061071
226. Yu M, Lin Z, Tian X, Chen S, Liang X, Qin M, et al. Downregulation of Cx43 reduces cisplatin-induced acute renal injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. (2021) 158:112672. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112672
227. Miao Y, Chen Y, Xue F, Liu K, Zhu B, Gao J, et al. Contribution of ferroptosis and GPX4’s dual functions to osteoarthritis progression. EBioMedicine. (2022) 76:103847. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103847
228. Pacifici M. Osteoarthritis and chronic pain: Interleukin-6 as a common denominator and therapeutic target. Sci Signal. (2022) 15:eadd3702. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.add3702
229. Sterling J, Kam T, Guttha S, Park H, Baumann B, Mehrabani-Tabari A, et al. Interleukin-6 triggers toxic neuronal iron sequestration in response to pathological α-synuclein. Cell Rep. (2022) 38:110358. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110358
230. Bin S, Xin L, Lin Z, Jinhua Z, Rui G, Xiang Z. Targeting miR-10a-5p/IL-6R axis for reducing IL-6-induced cartilage cell ferroptosis. Exp Mol Pathol. (2021) 118:104570. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104570
231. Zhu C, Chen B, He X, Li W, Wang S, Zhu X, et al. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses erastin-induced ferroptosis of chondrocytes via regulating miR-885-5p/SLC7A11 axis. Mol Biol Rep. (2024) 51:139. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09095-9
232. Wang H, Wang W, Wang J, Zhang L, Luo Y, Tang X. MicroRNA-15a/β1,4-GalT-I axis contributes to cartilage degeneration via NF-κB signaling in osteoarthritis. Clinics. (2023) 78:100254. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2023.100254
233. Ma J, Yu P, Ma S, Li J, Wang Z, Hu K, et al. Bioinformatics and Integrative Experimental Method to Identifying and Validating Co-Expressed Ferroptosis-Related Genes in OA Articular Cartilage and Synovium. J Inflamm Res. (2024) 17:957–80. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S434226
234. Kong R, Ji L, Pang Y, Zhao D, Gao J. Exosomes from osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes promote cartilage ferroptosis and damage via delivering microRNA-19b-3p to target SLC7A11 in osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1181156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181156
235. Xiao J, Luo C, Li A, Cai F, Wang Y, Pan X, et al. Icariin inhibits chondrocyte ferroptosis and alleviates osteoarthritis by enhancing the SLC7A11/GPX4 signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 133:112010. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112010
236. Zeng L, Liu Y, Wang Q, Wan H, Meng X, Tu P, et al. Botulinum toxin A attenuates osteoarthritis development via inhibiting chondrocyte ferroptosis through SLC7Al1/GPX4 axis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2024) 1870:167215. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167215
237. Yang T, Yang G, Wang G, Jia D, Xiong B, Lu X, et al. Bioinformatics identification and integrative analysis of ferroptosis-related key lncRNAs in patients with osteoarthritis. Biosci Rep. (2023) 43:BSR20230255. doi: 10.1042/BSR20230255
238. Yuan Y, Zhang G, Chai W, Ni M, Xu C, Chen J. Silencing of microRNA-138-5p promotes IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation in human chondrocytes by targeting FOXC1: miR-138 promotes cartilage degradation. Bone Joint Res. (2016) 5:523–30. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.510.BJR-2016-0074.R2
239. Dai Y, Hu L. HSPB1 overexpression improves hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by attenuating ferroptosis in rats through promoting G6PD expression. J Neurophysiol. (2022) 128:1507–17. doi: 10.1152/jn.00306.2022
240. Wang Y, Zheng X, Luo D, Xu W, Zhou X. MiR-99a alleviates apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in experimentally induced spine osteoarthritis by targeting FZD8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23:872. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05822-8
241. Xu W, Wang X, Liu D, Lin X, Wang B, Xi C, et al. Identification and validation of hub genes and potential drugs involved in osteoarthritis through bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet. (2023) 14:1117713. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1117713
242. Chan C, Macdonald C, Litherland G, Wilkinson D, Skelton A, Europe-Finner G, et al. Cytokine-induced MMP13 Expression in Human Chondrocytes Is Dependent on Activating Transcription Factor 3 (ATF3) Regulation. J Biol Chem. (2017) 292:1625–36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756601
243. Huber R, Kirsten H, Näkki A, Pohlers D, Thude H, Eidner T, et al. Association of Human FOS Promoter Variants with the Occurrence of Knee-Osteoarthritis in a Case Control Association Study. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1382. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061382
244. Sun X, Huang H, Pan X, Li S, Xie Z, Ma Y, et al. EGR1 promotes the cartilage degeneration and hypertrophy by activating the Krüppel-like factor 5 and β-catenin signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. (2019) 1865:2490–503. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.06.010
245. Ansari M, Ahmad N, Voleti S, Wase S, Novak K, Haqqi T. Mitochondrial dysfunction triggers a catabolic response in chondrocytes via ROS-mediated activation of the JNK/AP1 pathway. J Cell Sci. (2020) 133:jcs247353. doi: 10.1242/jcs.247353
246. Lin Z, Miao J, Zhang T, He M, Wang Z, Feng X, et al. JUNB-FBXO21-ERK axis promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting autophagy. Aging Cell. (2021) 20:e13306. doi: 10.1111/acel.13306
247. Luo Z, Xie J, Ye H, Zhang J, Liu Y, Ma C, et al. Novel-miR-81 Promotes the Chondrocytes Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Inhibiting Rac2 Expression. Cartilage. (2023) doi: 10.1177/19476035231207778
248. Shi H, Qi H, Xie D, Zhuang J, Qi H, Dai Y, et al. Inhibition of ACSF2 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via mediating mitophagy in proximal tubular cells. Free Radic Biol Med. (2023) 198:68–82. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.02.003
249. Yang X, Yang J, Lei P, Wen T. LncRNA MALAT1 shuttled by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells-secreted exosomes alleviates osteoporosis through mediating microRNA-34c/SATB2 axis. Aging. (2019) 11:8777–91. doi: 10.18632/aging.102264
250. Jung P, Horst D, Kirchner T, Klauschen F, Neumann J. AURKA is a prognostic biomarker for good overall survival in stage II colorectal cancer patients. Pathol Res Pract. (2022) 235:153936. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153936
251. Jiang Y, Zhang L, Tian H. MicroRNA-149 improves osteoarthritis via repression of VCAM-1 and inactivation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Gerontol. (2023) 174:112103. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112103
252. Richard F, De Schepper M, Maetens M, Leduc S, Isnaldi E, Geukens T, et al. Comparison of the genomic alterations present in tumor samples from patients with metastatic inflammatory versus non-inflammatory breast cancer reveals AURKA as a potential treatment target. Breast. (2023) 69:476–80. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2023.01.010
253. Linder M, Hecking M, Glitzner E, Zwerina K, Holcmann M, Bakiri L, et al. EGFR controls bone development by negatively regulating mTOR-signaling during osteoblast differentiation. Cell Death Differ. (2018) 25:1094–106. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0054-7
254. Qin L, Beier F. EGFR Signaling: Friend or Foe for Cartilage. JBMR Plus. (2019) 3:e10177. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10177
255. Cui J, Zhao Q, Song Z, Chen Z, Zeng X, Wang C, et al. KLHL24-Mediated Hair Follicle Stem Cells Structural Disruption Causes Alopecia. J Invest Dermatol. (2022) 142:2079.e–87.e. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2022.01.007
256. Sun Y, Su S, Li M, Deng A. Inhibition of miR-182-5p Targets FGF9 to Alleviate Osteoarthritis. Anal Cell Pathol. (2023) 2023:5911546. doi: 10.1155/2023/5911546
257. Bertram K, Narendran N, Tailor P, Jablonski C, Leonard C, Irvine E, et al. 17-DMAG regulates p21 expression to induce chondrogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Dis Model Mech. (2018) 11:dmm033662. doi: 10.1242/dmm.033662
258. Faust H, Zhang H, Han J, Wolf M, Jeon O, Sadtler K, et al. IL-17 and immunologically induced senescence regulate response to injury in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:5493–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI134091
259. Pinilla-Tenas J, Sparkman B, Shawki A, Illing A, Mitchell C, Zhao N, et al. Zip14 is a complex broad-scope metal-ion transporter whose functional properties support roles in the cellular uptake of zinc and nontransferrin-bound iron. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2011) 301:C862–71. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00479.2010
260. Aydemir T, Cousins R. The Multiple Faces of the Metal Transporter ZIP14 (SLC39A14). J Nutr. (2018) 148:174–84. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxx041
261. Wang J, Zhao X, Wang X, Liu M, Wan W. Low expression of miR-1 promotes osteogenic repair of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting TLR1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:3492–500.
262. Cong L, Jiang P, Wang H, Huang L, Wu G, Che X, et al. MiR-1 is a critical regulator of chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophy by inhibiting Indian hedgehog pathway during postnatal endochondral ossification in miR-1 overexpression transgenic mice. Bone. (2022) 165:116566.
263. Gu H, Shi S, Xiao F, Huang Z, Xu J, Chen G, et al. MiR-1-3p regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to prevent osteoporosis by targeting secreted frizzled-related protein 1. Bone. (2020) 137:115444.
264. Chen T, Che X, Han P, Lu J, Wang C, Liang B, et al. MicroRNA-1 promotes cartilage matrix synthesis and regulates chondrocyte differentiation via post-transcriptional suppression of Ihh expression. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:2404–14.
265. Yang Y, Wang Y, Jia H, Li B, Xing D, Li J. MicroRNA-1 Modulates Chondrocyte Phenotype by Regulating FZD7 of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Cartilage. (2021) 13:1019S–29S.
266. Bhattacharyya S, Kumar P, Tsuchiya M, Bhattacharyya A, Biswas R. Regulation of miR-155 biogenesis in cystic fibrosis lung epithelial cells: antagonistic role of two mRNA-destabilizing proteins, KSRP and TTP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2013) 433:484–8.
267. Yuan X, Guo Y, Chen D, Luo Y, Chen D, Miao J, et al. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 functions as miR-1 sponge to regulate Connexin 43-mediated ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Bone. (2019) 127:305–14.
268. Georgantas R, Streicher K, Greenberg S, Greenlees L, Zhu W, Brohawn P, et al. Inhibition of myogenic microRNAs 1, 133, and 206 by inflammatory cytokines links inflammation and muscle degeneration in adult inflammatory myopathies. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:1022–33.
269. Tian M, Zhou Y, Jia H, Zhu X, Cui Y. The Clinical Significance of Changes in the Expression Levels of MicroRNA-1 and Inflammatory Factors in the Peripheral Blood of Children with Acute-Stage Asthma. Biomed Res Int. (2018) 2018:7632487.
270. Mohammadi A, Karami A, Mashtani V, Sahraei T, Tarashoki Z, Khattavian E, et al. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Expression of MicroRNA-208a and MicroRNA-1 in Cardiovascular Patients. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. (2021) 10:183–96.
271. Yan W, Zhang W, Sun L, Liu Y, You G, Wang Y, et al. Identification of MMP-9 specific microRNA expression profile as potential targets of anti-invasion therapy in glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Res. (2011) 1411:108–15.
272. Pan W, Hu Y, Wang L, Li J. Circ_0003611 acts as a miR-885-5p sponge to aggravate the amyloid-β-induced neuronal injury in Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis. (2022) 37:961–71.
273. Tu G, Ma J, Li J, Su Y, Luo J, Hao G, et al. Exosome-Derived From Sepsis Patients’, Blood Promoted Pyroptosis of Cardiomyocytes by Regulating miR-885-5p/HMBOX1. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2022) 9:774193.
274. Chunlei H, Chang Z, Sheng L, Yanchun Z, Lulin L, Daozhang C. Down-regulation of MiR-138-5p Protects Chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1 β-induced Inflammation Via Up-regulating SOX9. Curr Pharm Des. (2020) 25:4613–21.
275. Shi J, Cao F, Chang Y, Xin C, Jiang X, Xu J, et al. Long non-coding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 protects chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1β-induced inflammation via regulating miR-138-5p/SIRT1. Bioengineered. (2021) 12:1445–56.
276. Hu X, Ma R, Cao J, Du X, Cai X, Fan Y. CircSAMD4A aggravates H/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammatory response by sponging miR-138-5p. J Cell Mol Med. (2022) 26:1776–84.
277. Feng X, Zhan F, Luo D, Hu J, Wei G, Hua F, et al. LncRNA 4344 promotes NLRP3-related neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment by targeting miR-138-5p. Brain Behav Immun. (2021) 98:283–98.
278. Saenz-Pipaon G, Jover E, Bent M, Orbe J, Rodriguez J, Fernández-Celis A, et al. Role of LCN2 in a murine model of hindlimb ischemia and in peripheral artery disease patients, and its potential regulation by miR-138-5P. Atherosclerosis. (2023) 385:117343.
279. Chen Z, Huai Y, Chen G, Liu S, Zhang Y, Li D, et al. MiR-138-5p Targets MACF1 to Aggravate Aging-related Bone Loss. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:4837–52.
280. Liu D, Tang W, Tang D, Yan H, Jiao F. Ocu-miR-10a-5p promotes the chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit BMSCs by targeting BTRC-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. (2024) 60:343–53.
281. Jiang X, Stockwell B, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. (2021) 22:266–82. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
282. Hong Y, Sun Y, Rong X, Li D, Lu Y, Ji Y. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate UVB-induced apoptosis. ROS, and the Ca(2+) level in HLEC cells. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 396:112321.
283. Zhang Y, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Ren F, Chen L, Lan Z. miR-10a-5p inhibits osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:135–44.
284. Hussain N, Zhu W, Jiang C, Xu J, Wu X, Geng M, et al. Down-regulation of miR-10a-5p in synoviocytes contributes to TBX5-controlled joint inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:241–50.
285. Vaher H, Runnel T, Urgard E, Aab A, Badosa G, Maslovskaja J, et al. miR-10a-5p is increased in atopic dermatitis and has capacity to inhibit keratinocyte proliferation. Allergy. (2019) 74:2146–56.
286. Shen Z, Letra A, Silva R. MicroRNAs Markedly Expressed in Apical Periodontitis Cooperatively Regulate Cytokines and Growth Factors Promoting an Anti-inflammatory Response. J Endod. (2023) 49:286–93.
287. Guo F, Tang C, Li Y, Liu Y, Lv P, Wang W, et al. The interplay of LncRNA ANRIL and miR-181b on the inflammation-relevant coronary artery disease through mediating NF-κB signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2018) 22:5062–75.
288. Xie B, Qiao M, Xuan J. lncRNA MEG3 Downregulation Relieves Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in an miR-181b-Dependent Manner. Med Sci Monit. (2021) 27:e929435.
289. Hutchison E, Kawamoto E, Taub D, Lal A, Abdelmohsen K, Zhang Y, et al. Evidence for miR-181 involvement in neuroinflammatory responses of astrocytes. Glia. (2013) 61:1018–28.
290. Yan X, Kang D, Lin Y, Qi S, Jiang C. CBX4-dependent regulation of HDAC3 nuclear translocation reduces Bmp2-induced osteoblastic differentiation and calcification in adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. Cell Commun Signal. (2022) 20:3.
291. Xiaoling G, Shuaibin L, Kailu L. MicroRNA-19b-3p promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by interacting with lncRNA H19. BMC Med Genet. (2020) 21:11. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-0948-y
292. Duan L, Duan D, Wei W, Sun Z, Xu H, Guo L, et al. MiR-19b-3p attenuates IL-1β induced extracellular matrix degradation and inflammatory injury in chondrocytes by targeting GRK6. Mol Cell Biochem. (2019) 459(1–2): 205–14.
Keywords: osteoarthritis, ferroptosis, chondrocytes, circRNAs, lncRNAs, MicroRNAs, macrophages
Citation: Yu Q, Xiao Y, Guan M, Zhou G, Zhang X, Yu J, Han M, Yang W, Wang Y and Li Z (2024) Regulation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis and osteoarthritic chondrocytes by typical MicroRNAs in chondrocytes. Front. Med. 11:1478153. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1478153
Received: 09 August 2024; Accepted: 01 October 2024;
Published: 05 November 2024.
Edited by:
Federico Castro-Muñozledo, Center for Research and Advanced Studies, National Polytechnic Institute of Mexico (CINVESTAV), MexicoReviewed by:
Yanyang Cao, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesXiaolei Li, University of Pennsylvania, United States
Hong Sun, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, China
Copyright © 2024 Yu, Xiao, Guan, Zhou, Zhang, Yu, Han, Yang, Wang, and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenghua Li, TGl6aGVuaHVhMTk3MkAxNjMuY29t
 Qingyuan Yu
Qingyuan Yu Yanan Xiao1
Yanan Xiao1 Xianshuai Zhang
Xianshuai Zhang Jianan Yu
Jianan Yu Wei Yang
Wei Yang Zhenhua Li
Zhenhua Li