- 1Department of Rheumatology and Immunology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, Guangdong, China
- 2Department of Rheumatology, Jieyang People's Hospital, Jieyang, China
- 3Department of General Family Medicine, Jieyang People's Hospital, Jieyang, China
- 4Jieyang Medical Research Center, Jieyang People's Hospital, Jieyang, China
- 5Department of Rheumatology, Shantou University Medical College, Shantou, China
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease with heterogeneous clinical manifestations, often leading to significant morbidity and mortality, particularly due to lupus nephritis (LN). The standard therapeutic approach involving mycophenolate mofetil, cyclophosphamide, and glucocorticoids has shown limitations due to cumulative toxicity and side effects. The introduction of biologic agents, especially rituximab (RTX), a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting CD20+ B cells, has revolutionized the treatment landscape. This review synthesized the current understanding of B cells’ role in SLE and LN and evaluates RTX’s therapeutic impact. B cells contribute to disease pathogenesis through autoantibody production and immune complex formation, leading to tissue damage. RTX’s mechanisms of action, including Complement-Dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and induction of apoptosis, have demonstrated efficacy in both SLE and LN treatment. Clinical studies have reported remission rates and improved renal outcomes with RTX use, although challenges such as human anti-chimeric antibody development and optimal dosing persist. The review emphasized the need for continued research to elucidate RTX’s long-term benefits and risks, and to explore personalized treatment strategies that incorporate B cell biology for better disease management in SLE and LN.
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by a recurrent-remission course and a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations (1, 2). Globally, the incidence and prevalence of SLE vary significantly by geographical location, with the highest rates observed in North America, while Africa and Australia report the lowest. Factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity play crucial roles in determining clinical outcomes and disease management. Notably, SLE is more prevalent among females; however, disease progression tends to be more severe and rapid in males, resulting in a poorer prognosis. These differences may be attributed to varying environmental factors and genomic differences (3).
To date, the pathogenesis of SLE remains unclear. It can be associated with the interplay of genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, immune system irregularities, and hormonal influences (4, 5). In pathological conditions, patients with SLE typically produce a large number of antibodies, leading to the formation of antigen–antibody complexes. These complexes deposit in the kidneys, causing renal damage, and ultimately resulting in lupus nephritis (LN) (6, 7). Consequently, LN is a severe complication and one of the most common clinical manifestations of SLE, as well as one of the leading causes of mortality among SLE patients. Approximately 60% of individuals with SLE may develop LN, and 5 ~ 20% of those with LN progress to renal failure within 10 years (8–12). Therefore, the primary goals of LN treatment are to control disease activity, prevent relapses and progression, and avert the development of end-stage renal disease.
First-line treatments for LN typically include mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) or cyclophosphamide (CYC) combined with glucocorticoids (GC). Maintenance therapy typically involves MMF or azathioprine (AZA) combined with low-dose GC. The remission rate after 1 year of LN treatment ranges from 30.4 to 66.2%, with a good renal response being associated with improved disease prognosis (13, 14). Despite the introduction of emerging immunosuppressants such as tacrolimus (TAC) and MMF, the complex pathophysiological characteristics of SLE and LN and the clinical difficulty of controlling the disease with a single drug pose significant challenges to treatment. These challenges are further compounded by the notable side effects and cumulative toxicity of immunosuppressive drugs, including ovarian failure, bone marrow suppression, gastrointestinal symptoms, teratogenicity, and an increased risk of malignancies (15). Glucocorticoids (GC) are the cornerstone of SLE and LN treatment. However, prolonged use can lead to various serious long-term adverse effects and an increased risk of infections. It is also associated with an elevated risk of early cardiovascular disease, with SLE patients experiencing a 2- to 4-fold increase in the risk of coronary artery events (16). Studies have indicated that cumulative GC doses are significantly associated with an increased risk of cataracts and osteoporosis with fractures. Additionally, prolonged GC use elevates the risk of ischemic necrosis, diabetes, and hypertension (17). Furthermore, the current treatment regimens for SLE and LN remain limited in their efficacy, with up to 28% of patients eventually progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or death (18). Therefore, additional therapeutic strategies are needed to improve the prognosis of LN patients. Given the crucial role of B cells in the development and progression of dysregulated immune responses, the use of B cell-depleting agents in the treatment of SLE and LN remains a topic of ongoing debate. Rituximab (RTX), an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb), has been extensively used in SLE and other rheumatologic disorders. Thus, we synthesized the current understanding of the role of B cells in SLE and LN, and further summarized the progress of RTX in the treatment of SLE and LN.
Role of B cells in the pathogenesis and progression of SLE and LN
In patients with SLE and LN, B cells play a multifaceted pathogenic role, characterized by abnormalities in their differentiation and function. B cells contribute to immune damage through multiple mechanisms, including the production of autoantibodies, which can induce immune injury via antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) or complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). Additionally, B cells play a crucial role by producing various cytokines, presenting antigens, regulating immune responses, and providing co-stimulatory signals, highlighting their significant involvement in the pathogenesis of SLE and LN (19, 20). As a B cell hyperactivity-driven, non-organ-specific autoimmune disease, SLE is characterized by several B cell abnormalities. These abnormalities primarily function to promote the production of autoantibodies (21). Autoimmune dysregulation leading to the production of autoantibodies against various cellular components is a hallmark of the disease, particularly against nuclear antigens. Over 95% of patients possess autoantibodies targeting antinuclear antigens (antinuclear antibody, ANA) (22). Autoantibodies, as the core pathological feature of the disease, include characteristic antibodies against double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), histones, and the entire nucleosome, as well as antibodies against RNA-binding proteins. These proteins notably include Sm, U1RNP, Ro (SS-A), La (SS-B), and hnRNP A2 (RA33), along with phospholipids (e.g., cardiolipin) or phospholipid-binding proteins like β-2-glycoprotein-I. Under normal circumstances, these charged antibodies tend to form immune complexes to some extent, which deposit in the glomerular basement membrane (GBM) of the kidneys, thereby progressing to LN (23). As early as 1967, dsDNA antibodies were discovered in renal tissue biopsies from LN patients, and high specificity for SLE (24, 25). Moreover, the reciprocal changes in elevated dsDNA antibodies and serum complement levels (C3 and C4) serves as markers for onset, classification, diagnosis, and disease activity assessment in SLE and LN. These levels also correlate with treatment response, making autoantibodies valuable as therapeutic diagnostic biomarkers for outcome measurement in routine clinical practice and clinical trials (26, 27). Advancements in technology have enabled more sophisticated and precise analyses of autoantibodies, providing new insights into SLE pathogenesis and positioning it at the forefront of autoimmune mechanism research.
Self-reactive B cells, a type of lymphocyte, produce autoantibodies leading to autoimmune diseases. The mechanisms behind the generation of self-reactive B cells remain unclear, but potential mechanisms include: (1) During B cell development in the bone marrow, abnormalities in the central checkpoint may lead to a vast diversity in the pre-B cell receptor repertoire. This results in the failure of apoptosis of self-reactive B cells, allowing their survival; (2) T cell-dependent B cells, upon antigen and T cell stimulation, enter the germinal center. During the process of somatic hypermutation, abnormalities in negative selection can result in the production of self-reactive B cells (28). Under normal conditions, the survival and activation of self-reactive B cells in the body are regulated by multiple checkpoints. The immune system effectively modulates self-reactive B cells through negative selection mechanisms, including clonal deletion, clonal anergy, and receptor editing, which suppress their proliferation and promote B cell immune tolerance. Consequently, the development of self-reactive B cells is effectively inhibited.
However, when central and peripheral checkpoints become dysfunctional due to factors such as abnormal levels of B lymphocyte stimulatory factors, defects in inhibitory receptors on self-reactive B cells, lowered activation thresholds for B cells, impaired clearance of apoptotic products, and genetic abnormalities, self-reactive B cells can become activated and proliferate. This breakdown in B cell self-tolerance leads to the production of autoantibodies against self-antigens, resulting in the onset of autoimmune diseases such as SLE and LN (29, 30). Yurasov et al. discovered that in patients with SLE, the number of self-reactive mature naive B cells was double that of healthy individuals. This increase was accompanied by a higher quantity of polyreactive antibodies (30). Additionally, high levels of B lymphocyte activating factor (BAFF) from the tumor necrosis factor family and type I interferons (IFNs) may enhance the survival of self-reactive B cells (31). Therefore, B cell abnormalities, particularly self-reactive B cells, play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of SLE and LN. Given the role of B cells in the development of dysregulated immune responses, B cell depletion therapy has been pioneered in patients with refractory SLE and LN.
B cell-targeted therapy
To date, targeted therapies against autoreactive B cells have become significant therapeutic strategies for systemic lupus erythematosus and various other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and autoimmune thrombocytopenia. The mechanisms of B cell-targeted therapies can be broadly categorized into the following strategies: elimination of autoreactive B cells, blockade of extracellular soluble factors or receptors, intrinsic blockade of B cell activation pathways, and receptor editing (32). Numerous emerging agents are currently under development based on these mechanisms.
In terms of eliminating autoreactive B cells, the predominant approaches involve monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T cell therapy. Monoclonal antibodies target various CD molecules expressed at different stages of B cell development and maturation. These antibodies mediate B cell elimination through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity. Examples include anti-CD19 antibodies such as inebilizumab, obexelimab, and tafasitamab; anti-CD20 antibodies like rituximab, ocrelizumab, and obinutuzumab; anti-CD22 antibody epratuzumab; and anti-CD38 antibody daratumumab. CAR-T cell therapy involves the genetic modification of T cells to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that recognize B cell surface molecules, thereby leveraging T cell-mediated cytotoxicity for effective B cell elimination (33). Examples include Anti-CD19 CAR-T cells and BCMA-CD19 compound CAR-T cells.
Regarding the blockade of extracellular soluble factors or receptors, recent research has focused on agents that inhibit BAFF (B-cell activating factor). BAFF, a member of the TNF superfamily, plays a critical role in preventing B cell apoptosis and promoting B cell differentiation (34). Relevant therapeutic agents include belimumab, tabalumab, blisibimod, and ianalumab. Telitacicept is a dual-target agent that inhibits both BAFF and APRIL, with analogous mechanism agents including atacicept and povetacicept.
The elevated expression of type I interferons is associated with both innate and adaptive immune dysfunctions in systemic lupus erythematosus (35). For instance, anifrolumab, a type I IFN receptor inhibitor. Other agents targeting this pathway include rontalizumab and sifalimumab.
Beyond BAFF and IFN-α, other cytokine-targeted therapeutics are under development, such as IL-12 and IL-23 inhibitors like ustekinumab and IL-6/sIL-6R inhibitors including sirukumab, tocilizumab, and vobarilizumab (a soluble IL-6 receptor). CD40 ligand inhibitors, such as dapirolizumab pegol, are also being explored.
For the intrinsic blockade of B cell activation pathways, relevant drugs include SYK inhibitors (cevidoplenib, lanraplenib), BTK inhibitors (rilzabrutinib, fenebrutinib, Evobrutinib), and proteasome inhibitors (bortezomib). In the domain of receptor editing, research is ongoing to use edited CAR-Treg cells to suppress autoreactive B cell functions. Additionally, theoretically, receptor editing of autoreactive B cells could potentially avoid autoreactive binding, though no such therapeutics have yet been developed, which might be a future exploration direction.
Mechanism of action of RTX in B cell-targeted therapy
The anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody RTX is the first to receive FDA approval for the treatment of CD20-positive B cell malignancies, such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Subsequently, its therapeutic reach has expanded to autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), SLE, and LN (36–38). The therapeutic effectiveness of rituximab is based on its impact on B cells. Consequently, the recognition that B cells play a more important part in autoimmune diseases than last believed has resulted in its growing usage for off-label reasons. The multifaceted mechanisms by which RTX treats SLE and LN include: (1) Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC): RTX effectively binds to C1q, activating complement in vitro, leading to a cascade reaction and the formation of a membrane attack complex, inducing lysis of CD20+ B cells; (2) Inhibition of Cell Proliferation and Induction of Apoptosis: RTX cross-linking by cells expressing Fc receptors induces apoptosis through the activation of the Caspase-3 signaling pathway, leading to B lymphocyte apoptosis. Additionally, RTX can directly induce cell death via Fab-mediated pathways; (3) Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC): RTX induces the aggregation of monocytes, macrophages, and natural killer cells through the binding of their Fc receptors to the Fc fragment of RTX, leading to the lysis of B lymphocytes (39). Although ADCC is identified as the primary action mechanism of RTX, complement-mediated cytotoxicity also plays a significant role; (4) Follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cells are a specific subset of regulatory T cells concentrated mostly in the germinal center (GC), which act as regulators of GC responses. They may interfere with the identification mechanism of Tfh cells and B cells, trigger Tfh death, and inhibit B cell activity. Using RTX to rebuild GC responses might also contribute to the treatment of SLE (40). Additionally, RTX can affect the function and number of T cells, further contributing to its therapeutic profile. B lymphocytes may function as antigen presentation cells (APC) for T lymphocytes, resulting in a pro-inflammatory response via generating cytokines.
Progress in RTX drug research for SLE and LN treatment
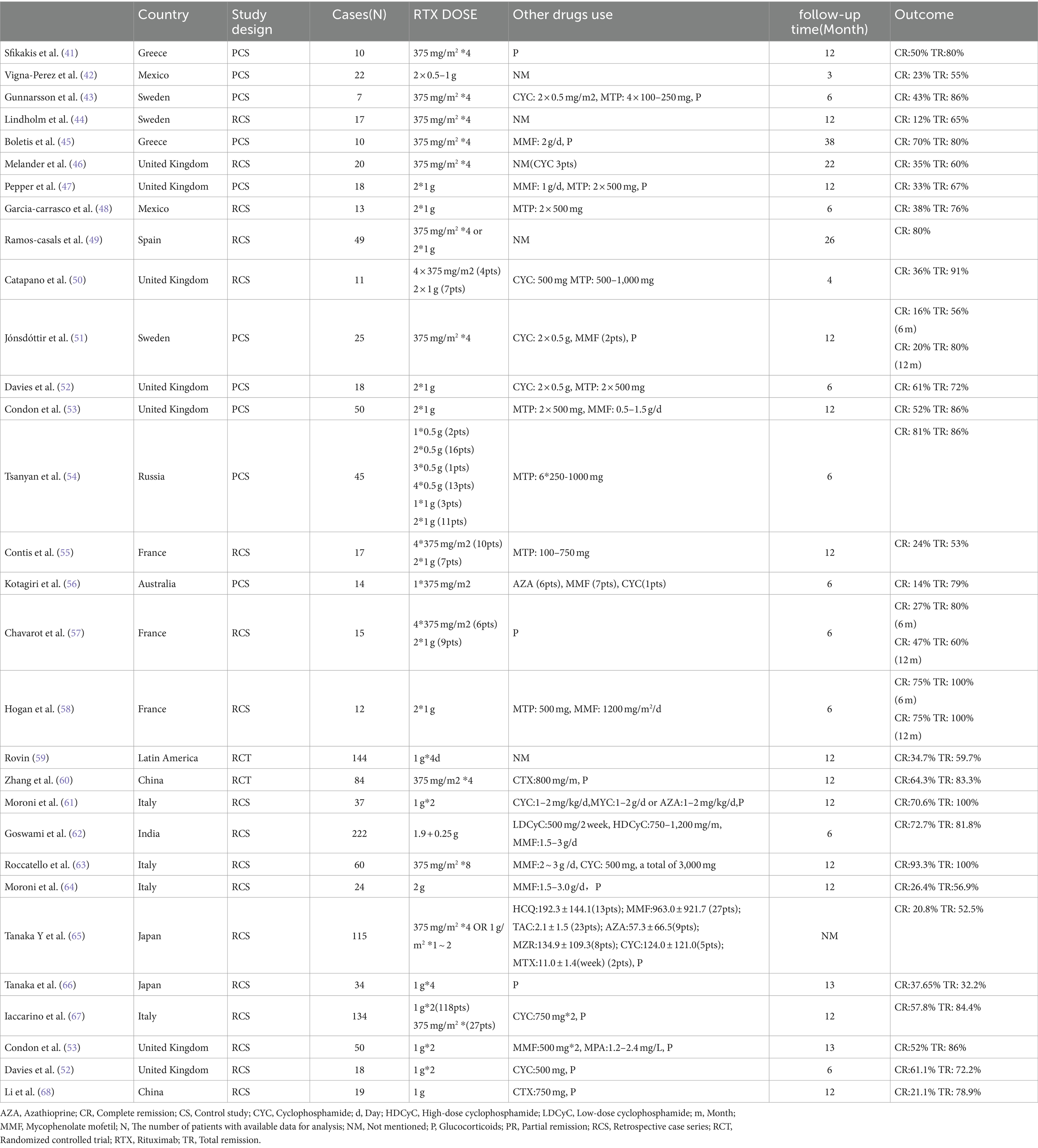
The clinical studies that have been published regarding the treatment of SLE and LN related to RTX are shown in Table 1 (41–68).
Clinical usage and dosage of RTX
In August 1997, the chimeric mouse/human monoclonal antibody (mAb) RTX, which targets the B cell CD20 receptor, was approved for use in follicular lymphoma. Edwards et al. were pioneers in demonstrating its effectiveness and safety in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (36). In a randomized, double-blind, controlled study involving patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving methotrexate (MTX) treatment, a single course of two infusions of RTX significantly improved disease symptoms at both week 24 and week 48 compared to MTX alone or in combination with cyclophosphamide (CYC) or continuous MTX therapy (37). Additionally, Leandro et al. were the first to publish an open-label study involving six female patients with refractory SLE who were resistant to standard immunosuppressive therapy. This study provided preliminary evidence for the safety and efficacy of RTX in the treatment of refractory SLE (38). To date, the clinical usage and dosing of RTX vary by condition. For lymphoma and pediatric autoimmune diseases, the standard dosage is 375 mg/m3 for 4 weeks. For conditions such as SLE and RA, the dosage often increases to 100 mg administered twice over 2 weeks. The dosing of RTX for treating SLE and LN typically falls between these two regimens (69). However, a multicenter systematic review involving 1,370 patients with systemic autoimmune diseases treated with biologics found that rituximab (RTX) treatment for refractory SLE might be more effective when using the lymphoma treatment regimen (375 mg/m3 for 4 weeks) compared to the two-week doses of two 100 mg (70). However, based solely on the aforementioned review, it is challenging to draw definitive conclusions regarding the relative efficacy of the two regimens. Catapano et al. used both RTX dosing regimens to treat refractory SLE and, although not in a formal comparative setting, did not find significant differences in B cell depletion levels, clinical outcomes, or adverse effects (50). Therefore, the two-week doses of two 100 mg might be more convenient and could become the preferred treatment regimen for patients with SLE and LN.
In clinical practice, RTX is rarely used alone; it is often combined with glucocorticoids or with both glucocorticoids and immunosuppressants. When used in combination therapy, the dose of glucocorticoids is gradually reduced as clinical symptoms improve, significantly enhancing efficacy and reducing the risks of infection, bone marrow suppression, liver function impairment, and secondary malignancies (71, 72).
Efficacy and safety of RTX
To date, extensive clinical research has been conducted on rituximab, and its efficacy is still uncertain. Both randomized controlled trials of rituximab for SLE patients, the EXPLORER and LUNAR studies, failed to meet their primary endpoints. In the EXPLORER study, 257 patients with moderate to severe non-renal SLE were randomly assigned to receive either RTX or placebo treatment. RTX was administered at a dose of 1,000 mg at weeks 0, 2, 24, and 26, against a background treatment of azathioprine (AZA), methotrexate (MTX), or mycophenolic acid (MPA). At week 52, there was no significant difference between the treatment group and the placebo group in terms of the primary endpoint (73). In the LUNAR study, 144 patients with class III or IV lupus nephritis (LN) receiving mycophenolate mofetil (MPA) treatment were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or rituximab (RTX) treatment. Similarly, in this study, RTX failed to achieve the primary endpoint, and there was no significant difference between the placebo and treatment groups in the proportion of patients achieving complete or partial renal remission (59).
However, numerous clinical trials and case reports have observed significant efficacy and reliable safety of RTX in patients with SLE and LN (74). In the study by Yi et al., patients in the RTX group had lower 24-h urinary protein and SLEDAI scores and a significantly higher complete remission rate than those in the CTX group (75). Looney et al. concluded that RTX relieved symptoms in most patients with refractory severe SLE (76). Ramos et al. found that RTX significantly improved symptoms in 91% of patients with refractory and recurrent LN (77). In addition, several systematic evaluations and network meta-analyses have analyzed the efficacy and safety of RTX in the treatment of LN (78–80), suggesting that RTX has significant clinical efficacy and good safety, making it a promising therapy for the treatment of SLE and LN, particularly for refractory severe SLE and refractory LN. Jens Vikse et al. retrospectively analyzed the clinical data of 70 patients with systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and treated with long-term rituximab (≥16 years). In their study, infections and persistent dysgammaglobulinemia were the most common adverse events, occurring in 34.3 and 25.7%, respectively. End organ damage occurred in two patients, and no opportunistic infections were observed. Three patients died of lethal infection during the observational period. They concluded that long-term rituximab treatment is relatively well tolerated, and that no cumulative side effects were observed (81). In 2012, the American College of Rheumatology recommended RTX as a second-line treatment for refractory class III and IV LN. Additionally, the Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lupus nephritis indicate that for refractory or frequently relapsing LN, RTX can be used in combination therapy (71, 72). Furthermore, the 2019 management recommendations for LN, jointly developed by the European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) and the European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association, proposed that for non-responsive and refractory LN, RTX can also be used either as monotherapy or as an adjunct to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), mycophenolic acid (MPA), or cyclophosphamide (CYC) (13).
The clinical efficacy of rituximab in treating systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) demonstrates considerable variability, probably attributable to the following factors: elevated levels of BAFF (B-cell activating factor), B-cell reconstitution and the disease-specific high degree of heterogeneity in lupus. B-cell reconstitution after the infusion of rituximab is associated with increased BAFF levels. Elevated BAFF promote autoreactive B-cell proliferation and survival (82). Additionally, SLE is a highly heterogeneous disease with various pathogenic mechanisms, including autoreactive B-cells, alterations in TLR receptor function, differences in the IFN-α pathway, T-cell dysfunction, etc. (83). This heterogeneity may result in diverse patient responses to treatment, suggesting that a single therapeutic approach may not address all underlying mechanisms.
To overcome these challenges, potential strategies include combination therapy and sequential treatment. The potential of combining anti-B cell and anti-BAFF therapies should be further explored. Besides, in terms of sequential treatment, clinical studies of belimumab administration followed by RTX or RTX administration followed by belimumab are currently under investigation (84, 85).
Conclusion
As an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody B cell depleting agent, rituximab (RTX) has shown promising efficacy in several retrospective and open-label studies. Despite this, continued monitoring of RTX’s significant biological effects is necessary to evaluate long-term clinical benefits and risks. Considering the pathogenic significance of the B cell family in SLE and LN, targeting B cells and plasma cells presents a highly attractive therapeutic approach for SLE and LN. Understanding and advancing B cell biology in SLE and LN is crucial. In addition to the specific targeting of B cell surface antigens by RTX, treatment failures in SLE and LN have also been noted. This has driven interest in alternative targets for B cell activation, such as B lymphocyte stimulator (BlyS) and B cell activating factor (BAFF), which are expected to become focal points for future research. Additionally, selective targeting of B cell therapies will play a pivotal role in the personalized treatment management of SLE and LN patients. Moving forward, further work is needed to elucidate the full potential of B cell depletion strategies through drugs like RTX in the clinical setting.
Author contributions
SM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. YL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JH: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LL: Methodology, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2024A1515012910) and the Special Funds for science and technology of Guangdong Province (2021–88).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Cojocaru, M, Cojocaru, IM, Silosi, I, and Vrabie, CD. Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Maedica (Bucur). (2011) 6:330–6.
2. Tsokos, GC. Autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol. (2020) 21:605–14. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0677-6
3. Rees, F, Doherty, M, Grainge, MJ, Lanyon, P, and Zhang, W. The worldwide incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2017) 56:1945–61. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex260
4. Relle, M, Foehr, B, and Schwarting, A. Epigenetic aspects of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Ther. (2015) 2:33–46. doi: 10.1007/s40744-015-0014-y
5. Bodis, G, Toth, V, and Schwarting, A. Role of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) in autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Ther. (2018) 5:5–20. doi: 10.1007/s40744-018-0100-z
6. Tang, S, Lui, SL, and Lai, KN. Pathogenesis of lupus nephritis: an update. Nephrology (Carlton). (2005) 10:174–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00392.x
7. Wenderfer, SE, and Eldin, KW. Lupus nephritis. Pediatr Clin N Am. (2019) 66:87–99. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2018.08.007
8. Li, M, Wang, Y, Zhao, J, Wang, Q, Wang, Z, Tian, X, et al. Chinese SLE treatment and research group (CSTAR) registry 2009-2019: major clinical characteristics of Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Immunol Res. (2021) 2:43–7. doi: 10.2478/rir-2021-0001
9. Morales, E, Galindo, M, Trujillo, H, and Praga, M. Update on lupus nephritis: looking for a new vision. Nephron. (2021) 145:1–13. doi: 10.1159/000511268
10. Wang, Z, Li, M, Ye, Z, Li, C, Li, Z, Li, X, et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter cohort study from CSTAR registry. Rheumatol Immunol Res. (2021) 2:195–202. doi: 10.2478/rir-2021-0025
11. Anders, HJ, Saxena, R, Zhao, MH, Parodis, I, Salmon, JE, and Mohan, C. Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2020) 6:7. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0141-9
12. Saxena, R. Predicting kidney survival in lupus nephritis by adding clinical data to pathologic features. Kidney360. (2022) 3:5–7. doi: 10.34067/KID.0007082021
13. Fanouriakis, A, Kostopoulou, M, Cheema, K, Anders, HJ, Aringer, M, Bajema, I, et al. 2019 update of the joint European league against rheumatism and European renal association-European Dialysis and transplant association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2020) 79:713–23. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-216924
14. Cattran DC, Feehally J, Cook HT, Liu ZH, Fervenza FC, Mezzano SA, et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) glomerulonephritis work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis Kidney Int Suppl. (2012) 2:139–274. doi: 10.1038/kisup.2012.9
15. Almaani, S, Meara, A, and Rovin, BH. Update on lupus nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2017) 12:825–35. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05780616
16. Nikpour, M, Urowitz, MB, Ibanez, D, Harvey, PJ, and Gladman, DD. Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective proof-of-concept cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2011) 13:R156. doi: 10.1186/ar3473
17. Davidson, JE, Fu, Q, Rao, S, Magder, LS, and Petri, M. Quantifying the burden of steroid-related damage in SLE in the Hopkins lupus cohort. Lupus Sci Med. (2018) 5:e000237. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2017-000237
18. Mahajan, A, Amelio, J, Gairy, K, Kaur, G, Levy, RA, Roth, D, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis and end-stage renal disease: a pragmatic review mapping disease severity and progression. Lupus. (2020) 29:1011–20. doi: 10.1177/0961203320932219
19. Suurmond, J, Calise, J, Malkiel, S, and Diamond, B. DNA-reactive B cells in lupus. Curr Opin Immunol. (2016) 43:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2016.07.002
20. Iwata, S, and Tanaka, Y. B-cell subsets, signaling and their roles in secretion of autoantibodies. Lupus. (2016) 25:850–6. doi: 10.1177/0961203316643172
21. Lipsky, PE. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an autoimmune disease of B cell hyperactivity. Nat Immunol. (2001) 2:764–6. doi: 10.1038/ni0901-764
22. Olsen, NJ, and Karp, DR. Autoantibodies and SLE: the threshold for disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2014) 10:181–6. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.184
23. Aringer, M, Finzel, S, and Voll, RE. Immunpathogenese des systemischen lupus erythematodes [Immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus]. Z Rheumatol. (2024) 83:68–76. doi: 10.1007/s00393-022-01214-4
24. Koffler, D, Schur, PH, Kunkel, HG, and Koffler, BD. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis OF systemic lupus erythematosus*. J Exp Med. (1967) 126:607–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607
25. Cockx, M, Van Hoovels, L, De Langhe, E, Lenaerts, J, Thevissen, K, Persy, B, et al. Laboratory evaluation of anti-dsDNA antibodies. Clin Chim Acta. (2022) 528:34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.12.029
26. Weinstein, A, Alexander, RV, and Zack, DJ. A review of complement activation in SLE. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2021) 23:16. doi: 10.1007/s11926-021-00984-1
27. Lou, H, Ling, GS, and Cao, X. Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: from immunopathology to therapeutic target. J Autoimmun. (2022) 132:102861. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102861
28. Yap, DYH, and Chan, TM. B cell abnormalities in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis-role in pathogenesis and effect of immunosuppressive treatments. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:6231. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246231
29. Giltiay, NV, Chappell, CP, and Clark, EA. B-cell selection and the development of autoantibodies. Arthritis Res Ther. (2012) 14:S1. doi: 10.1186/ar3918
30. Yurasov, S, Wardemann, H, Hammersen, J, Tsuiji, M, Meffre, E, Pascual, V, et al. Defective B cell tolerance checkpoints in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. (2005) 201:703–11. doi: 10.1084/jem.20042251
31. Batten, M, Groom, J, Cachero, TG, Qian, F, Schneider, P, Tschopp, J, et al. BAFF mediates survival of peripheral immature B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:1453–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1453
32. Parodis, I, Long, X, Karlsson, MCI, and Huang, X. B cell tolerance and targeted therapies in SLE. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:6268. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196268
33. Kansal, R, Richardson, N, Neeli, I, Khawaja, S, Chamberlain, D, Ghani, M, et al. Sustained B cell depletion by CD19-targeted CAR T cells is a highly effective treatment for murine lupus. Sci Transl Med. (2019) 11:eaav1648. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav1648
34. Möckel, T, Basta, F, Weinmann-Menke, J, and Schwarting, A. B cell activating factor (BAFF): structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implications in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Autoimmun Rev. (2021) 20:102736. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102736
35. Psarras, A, Wittmann, M, and Vital, EM. Emerging concepts of type I interferons in SLE pathogenesis and therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:575–90. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00826-z
36. Edwards, JCW, and Cambridge, G. Sustained improvement in rheumatoid arthritis following a protocol designed to deplete B lymphocytes. Rheumatology. (2001) 40:205–11. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.2.205
37. Edwards, JCW, Szczepanski, L, Szechinski, J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A, Emery, P, Close, DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. (2004) 350:2572–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032534
38. Leandro, MJ, Edwards, JC, Cambridge, G, Ehrenstein, MR, and Isenberg, DA. An open study of B lymphocyte depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2002) 46:2673–7. doi: 10.1002/art.10541
39. Boross, P, and Leusen, JH. Mechanisms of action of CD20 antibodies. Am J Cancer Res. (2012) 2:676–90.
40. Xia, X, Yang, J, and Wang, S. Follicular regulatory T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2021/9943743
41. Sfikakis, PP, Boletis, JN, Lionaki, S, Vigklis, V, Fragiadaki, KG, Iniotaki, A, et al. Remission of proliferative lupus nephritis following B cell depletion therapy is preceded by down-regulation of the T cell costimulatory molecule CD40 ligand: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2005) 52:501–13. doi: 10.1002/art.20858
42. Vigna-Perez, M, Hernández-Castro, B, Paredes-Saharopulos, O, Portales-Pérez, D, Baranda, L, Abud-Mendoza, C, et al. Clinical and immunological effects of rituximab in patients with lupus nephritis refractory to conventional therapy: a pilot study. Arthritis Res Ther. (2006) 8:R83. doi: 10.1186/ar1954
43. Gunnarsson, I, Sundelin, B, Jónsdóttir, T, Jacobson, SH, Henriksson, EW, and van Vollenhoven, RF. Histopathologic and clinical outcome of rituximab treatment in patients with cyclophosphamideresistant proliferative lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. (2007) 56:1263–72. doi: 10.1002/art.22505
44. Lindholm, C, Börjesson-Asp, K, Zendjanchi, K, Sundqvist, AC, Tarkowski, A, and Bokarewa, M. Longterm clinical and immunological effects of anti-CD20 treatment in patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. (2008) 35:826–33.
45. Boletis, JN, Marinaki, S, Skalioti, C, Lionaki, SS, Iniotaki, A, and Sfikakis, PP. Rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil for relapsing proliferative lupus nephritis: a long-term prospective study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2009) 24:2157–60. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp002
46. Melander, C, Sallee, M, and Trolliet, P. Rituximab in severe lupus nephritis: early B-cell depletion affects long-term renal outcome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 4:579–87. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04030808
47. Pepper, R, Griffith, M, Kirwan, C, Levy, J, Taube, D, Pusey, C, et al. Rituximab is an effective treatment for lupus nephritis and allows a reduction in maintenance steroids. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2009) 24:3717–23. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp336
48. Garcia-Carrasco, M, Mendoza-Pinto, C, Sandoval-Cruz, M, Soto-Vega, E, Beltran-Castillo, A, Jimenez-Hernandez, M, et al. AntiCD20 therapy in patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal analysis of 52 Hispanic patients. Lupus. (2010) 19:213–9. doi: 10.1177/0961203309351541
49. Ramos-Casals, M, García-Hernández, FJ, de Ramón, E, Callejas, JL, Martínez-Berriotxoa, A, Pallarés, L, et al. Off-label use of rituximab in 196 patients with severe, refractory systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2010) 28:468–76.
50. Catapano, F, Chaudhry, AN, Jones, RB, Smith, KGC, and Jayne, DW. Long-term efficacy and safety of rituximab in refractory and relapsing systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2010) 25:3586–92. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq256
51. Jónsdóttir, T, Zickert, A, and Sundelin, B. Long-term follow-up in lupus nephritis patients treated with rituximab–clinical and histopathological response. Rheumatology. (2013) 52:847–55. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes348
52. Davies, RJ, Sangle, SR, Jordan, NP, Aslam, L, Lewis, MJ, Wedgwood, R, et al. Rituximab in the treatment of resistant lupus nephritis: therapy failure in rapidly progressive crescentic lupus nephritis. Lupus. (2013) 22:574–82. doi: 10.1177/0961203313483376
53. Condon, MB, Ashby, D, Pepper, RJ, Cook, HT, Levy, JB, Griffith, M, et al. Prospective observational single-Centre cohort study to evaluate the effectiveness of treating lupus nephritis with rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil but no oral steroids. Ann Rheum Dis. (2013) 72:1280–6. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202844
54. Tsanyan, ME, Soloviev, SK, Radenska-Lopovok, SG, Torgashina, AV, Nikolaeva, EV, Khrennikov, YB, et al. Clinical and morphological improvement of lupus nephritis treated with rituximab. Folia Med. (2014) 56:245–52. doi: 10.1515/folmed-2015-0003
55. Contis, A, Vanquaethem, H, Truchetet, M-E, Couzi, L, Rigothier, C, Richez, C, et al. Analysis of the effectiveness and safety of rituximab in patients with refractory lupus nephritis: a chart review. Clin Rheumatol. (2016) 35:517–22. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3166-9
56. Kotagiri, P, Martin, A, Hughes, P, Becker, G, and Nicholls, K. Single-dose rituximab in refractory lupus nephritis. Intern Med J. (2016) 46:899–901. doi: 10.1111/imj.13136
57. Chavarot, N, Verhelst, D, Pardon, A, Caudwell, V, Mercadal, L, Sacchi, A, et al. Rituximab alone as induction therapy for membranous lupus nephritis: a multicenter retrospective study. Medicine. (2017) 96:e7429. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007429
58. Hogan, J, Godron, A, Baudouin, V, Kwon, T, Harambat, J, Deschênes, G, et al. Combination therapy of rituximab and mycophenolate mofetil in childhood lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. (2018) 33:111–6. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3767-4
59. Rovin, BH, Furie, R, Latinis, K, Looney, RJ, Fervenza, FC, Sanchez-Guerrero, J, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active proliferative lupus nephritis: the lupus nephritis assessment with rituximab study. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64:1215–26. doi: 10.1002/art.34359
60. Zhang, J, Zhao, Z, and Hu, X. Effect of rituximab on serum levels of anti-C1q and antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies in refractory severe lupus nephritis. Cell Biochem Biophys. (2015) 72:197–201. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0437-z
61. Moroni, G, Raffiotta, F, Trezzi, B, Giglio, E, Mezzina, N, del Papa, N, et al. Rituximab vs mycophenolate and vs cyclophosphamide pulses for induction therapy of active lupus nephritis: a clinical observational study. Rheumatology. (2014) 53:1570–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket462
62. Goswami, RP, Sircar, G, Sit, H, Ghosh, A, and Ghosh, P. Cyclophosphamide versus mycophenolate versus rituximab in lupus nephritis remission induction: a historical head-to-head comparative study. J Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 25:28–35. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000760
63. Roccatello, D, Sciascia, S, Naretto, C, Alpa, M, Fenoglio, R, Ferro, M, et al. A prospective study on Long-term clinical outcomes of patients with lupus nephritis treated with an intensified B-cell depletion protocol without maintenance therapy. Kidney Int Rep. (2021) 6:1081–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.01.027
64. Moroni, G, Gallelli, B, Sinico, RA, Romano, G, Sinigaglia, L, and Messa, P. Rituximab versus oral cyclophosphamide for treatment of relapses of proliferative lupus nephritis: a clinical observational study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71:1751–2. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201442
65. Tanaka, Y, Nakayamada, S, Yamaoka, K, Ohmura, K, and Yasuda, S. Rituximab in the real-world treatment of lupus nephritis: a retrospective cohort study in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. (2023) 33:145–53. doi: 10.1093/mr/roac007
66. Tanaka, Y, Takeuchi, T, Miyasaka, N, Sumida, T, Mimori, T, Koike, T, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis who are refractory to conventional therapy. Mod Rheumatol. (2016) 26:80–6. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1060665
67. Iaccarino, L, Bartoloni, E, and Carli, L. Efficacy and safety of off-label use of rituximab in refractory lupus: data from the Italian multicentre registry. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2015) 33:449–56.
68. Li, EK, Tam, LS, Zhu, TY, Li, M, Kwok, CL, Li, TK, et al. Is combination rituximab with cyclophosphamide better than rituximab alone in the treatment of lupus nephritis? Rheumatology. (2009) 48:892–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep124
69. Reddy, V, Jayne, D, Close, D, and Isenberg, D. B-cell depletion in SLE: clinical and trial experience with rituximab and ocrelizumab and implications for study design. Arthritis Res Ther. (2013) 15:S2. doi: 10.1186/ar3910
70. Ramos-Casals, M, Brito-Zerón, P, Muñoz, S, and Soto, MJBIOGEAS STUDY Group. A systematic review of the off-label use of biological therapies in systemic autoimmune diseases. Medicine (Baltimore). (2008) 87:345–64. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e318190f170
71. Hahn, BH, McMahon, MA, Wilkinson, A, Wallace, WD, Daikh, DI, Fitzgerald, JD, et al. American College of Rheumatology guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res. (2012) 64:797–808. doi: 10.1002/acr.21664
72. Guidelines Writing Group for Lupus Nephritis in China. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lupus nephritis in China. Chin Med J. (2019) 99:3441–55.
73. Merrill, JT, Neuwelt, CM, Wallace, DJ, Shanahan, JC, Latinis, KM, Oates, JC, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: the randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62:222–33. doi: 10.1002/art.27233
74. Parodis, I, Stockfelt, M, and Sjöwall, C. B cell therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: from rationale to clinical practice. Front Med (Lausanne). (2020) 7:316. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00316
75. Yi, L, Luo, FZ, and Deng, CP. The clinical study of rituximab in the treatment of severe lupus nephritis. Acta Universities Medicinalis Nanjing (Natural Sci). (2014) 8:1102–4.
76. Looney, RJ, Srinivasan, R, and Calabrese, LH. The effects of rituximab on immunocompetency in patients with autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. (2008) 58:5–14. doi: 10.1002/art.23171
77. Ramos-Casals, M, Soto, MJ, Cuadrado, MJ, and Khamashta, MA. Rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of off-label use in 188 cases. Lupus. (2009) 18:767–76. doi: 10.1177/0961203309106174
78. Li, K, Yu, Y, Gao, Y, Zhao, F, Liang, Z, and Gao, J. Comparative effectiveness of rituximab and common induction therapies for lupus nephritis: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:859380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859380
79. Yuan, Z, Xie, Q, Wu, X, Tan, B, and Zhang, X. Rituximab treatment for lupus nephritis: a systematic review. Clin Invest Med. (2020) 43:E47–54. doi: 10.25011/cim.v43i2.33864
80. Zhong, Z, Li, H, Zhong, H, and Zhou, T. Clinical efficacy and safety of rituximab in lupus nephritis. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2019) 13:845–56. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S195113
81. Vikse, J, Jonsdottir, K, Kvaløy, JT, Wildhagen, K, and Omdal, R. Tolerability and safety of long-term rituximab treatment in systemic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Rheumatol Int. (2019) 39:1083–90. doi: 10.1007/s00296-019-04272-1
82. Ehrenstein, MR, and Wing, C. The BAFFling effects of rituximab in lupus: danger ahead? Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:367–72. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.18
83. Tsai, YG, Liao, PF, Hsiao, KH, Wu, HM, Lin, CY, and Yang, KD. Pathogenesis and novel therapeutics of regulatory T cell subsets and interleukin-2 therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1230264. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1230264
84. Shipa, M, Embleton-Thirsk, A, Parvaz, M, Santos, LR, Muller, P, Chowdhury, K, et al. Effectiveness of Belimumab after rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. (2021) 174:1647–57. doi: 10.7326/M21-2078
Keywords: rituximab, systemic lupus erythematosus, lupus nephritis, B cells, treatment
Citation: Mo S, Li Y, He J and Lin L (2024) Progress of rituximab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Front. Med. 11:1472019. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1472019
Edited by:
Zhiming Lin, Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Xinxiang Huang, People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, ChinaShui Lian Yu, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
Zetao Liao, Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, China
Copyright © 2024 Mo, Li, He and Lin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ling Lin, bGxpbmNAMTYzLm5ldA==; Junbing He, anVuYmluZ2dAZ2RtdS5lZHUuY24=
 Shouqi Mo
Shouqi Mo Yilan Li3
Yilan Li3 Junbing He
Junbing He Ling Lin
Ling Lin